Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- My Account Login
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Review Article
- Open access
- Published: 11 January 2023

The effectiveness of collaborative problem solving in promoting students’ critical thinking: A meta-analysis based on empirical literature
- Enwei Xu ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-6424-8169 1 ,
- Wei Wang 1 &
- Qingxia Wang 1
Humanities and Social Sciences Communications volume 10 , Article number: 16 ( 2023 ) Cite this article
22k Accesses
26 Citations
3 Altmetric
Metrics details
- Science, technology and society
Collaborative problem-solving has been widely embraced in the classroom instruction of critical thinking, which is regarded as the core of curriculum reform based on key competencies in the field of education as well as a key competence for learners in the 21st century. However, the effectiveness of collaborative problem-solving in promoting students’ critical thinking remains uncertain. This current research presents the major findings of a meta-analysis of 36 pieces of the literature revealed in worldwide educational periodicals during the 21st century to identify the effectiveness of collaborative problem-solving in promoting students’ critical thinking and to determine, based on evidence, whether and to what extent collaborative problem solving can result in a rise or decrease in critical thinking. The findings show that (1) collaborative problem solving is an effective teaching approach to foster students’ critical thinking, with a significant overall effect size (ES = 0.82, z = 12.78, P < 0.01, 95% CI [0.69, 0.95]); (2) in respect to the dimensions of critical thinking, collaborative problem solving can significantly and successfully enhance students’ attitudinal tendencies (ES = 1.17, z = 7.62, P < 0.01, 95% CI[0.87, 1.47]); nevertheless, it falls short in terms of improving students’ cognitive skills, having only an upper-middle impact (ES = 0.70, z = 11.55, P < 0.01, 95% CI[0.58, 0.82]); and (3) the teaching type (chi 2 = 7.20, P < 0.05), intervention duration (chi 2 = 12.18, P < 0.01), subject area (chi 2 = 13.36, P < 0.05), group size (chi 2 = 8.77, P < 0.05), and learning scaffold (chi 2 = 9.03, P < 0.01) all have an impact on critical thinking, and they can be viewed as important moderating factors that affect how critical thinking develops. On the basis of these results, recommendations are made for further study and instruction to better support students’ critical thinking in the context of collaborative problem-solving.
Similar content being viewed by others
A meta-analysis of the effects of design thinking on student learning
Fostering twenty-first century skills among primary school students through math project-based learning
A meta-analysis to gauge the impact of pedagogies employed in mixed-ability high school biology classrooms
Introduction.
Although critical thinking has a long history in research, the concept of critical thinking, which is regarded as an essential competence for learners in the 21st century, has recently attracted more attention from researchers and teaching practitioners (National Research Council, 2012 ). Critical thinking should be the core of curriculum reform based on key competencies in the field of education (Peng and Deng, 2017 ) because students with critical thinking can not only understand the meaning of knowledge but also effectively solve practical problems in real life even after knowledge is forgotten (Kek and Huijser, 2011 ). The definition of critical thinking is not universal (Ennis, 1989 ; Castle, 2009 ; Niu et al., 2013 ). In general, the definition of critical thinking is a self-aware and self-regulated thought process (Facione, 1990 ; Niu et al., 2013 ). It refers to the cognitive skills needed to interpret, analyze, synthesize, reason, and evaluate information as well as the attitudinal tendency to apply these abilities (Halpern, 2001 ). The view that critical thinking can be taught and learned through curriculum teaching has been widely supported by many researchers (e.g., Kuncel, 2011 ; Leng and Lu, 2020 ), leading to educators’ efforts to foster it among students. In the field of teaching practice, there are three types of courses for teaching critical thinking (Ennis, 1989 ). The first is an independent curriculum in which critical thinking is taught and cultivated without involving the knowledge of specific disciplines; the second is an integrated curriculum in which critical thinking is integrated into the teaching of other disciplines as a clear teaching goal; and the third is a mixed curriculum in which critical thinking is taught in parallel to the teaching of other disciplines for mixed teaching training. Furthermore, numerous measuring tools have been developed by researchers and educators to measure critical thinking in the context of teaching practice. These include standardized measurement tools, such as WGCTA, CCTST, CCTT, and CCTDI, which have been verified by repeated experiments and are considered effective and reliable by international scholars (Facione and Facione, 1992 ). In short, descriptions of critical thinking, including its two dimensions of attitudinal tendency and cognitive skills, different types of teaching courses, and standardized measurement tools provide a complex normative framework for understanding, teaching, and evaluating critical thinking.
Cultivating critical thinking in curriculum teaching can start with a problem, and one of the most popular critical thinking instructional approaches is problem-based learning (Liu et al., 2020 ). Duch et al. ( 2001 ) noted that problem-based learning in group collaboration is progressive active learning, which can improve students’ critical thinking and problem-solving skills. Collaborative problem-solving is the organic integration of collaborative learning and problem-based learning, which takes learners as the center of the learning process and uses problems with poor structure in real-world situations as the starting point for the learning process (Liang et al., 2017 ). Students learn the knowledge needed to solve problems in a collaborative group, reach a consensus on problems in the field, and form solutions through social cooperation methods, such as dialogue, interpretation, questioning, debate, negotiation, and reflection, thus promoting the development of learners’ domain knowledge and critical thinking (Cindy, 2004 ; Liang et al., 2017 ).
Collaborative problem-solving has been widely used in the teaching practice of critical thinking, and several studies have attempted to conduct a systematic review and meta-analysis of the empirical literature on critical thinking from various perspectives. However, little attention has been paid to the impact of collaborative problem-solving on critical thinking. Therefore, the best approach for developing and enhancing critical thinking throughout collaborative problem-solving is to examine how to implement critical thinking instruction; however, this issue is still unexplored, which means that many teachers are incapable of better instructing critical thinking (Leng and Lu, 2020 ; Niu et al., 2013 ). For example, Huber ( 2016 ) provided the meta-analysis findings of 71 publications on gaining critical thinking over various time frames in college with the aim of determining whether critical thinking was truly teachable. These authors found that learners significantly improve their critical thinking while in college and that critical thinking differs with factors such as teaching strategies, intervention duration, subject area, and teaching type. The usefulness of collaborative problem-solving in fostering students’ critical thinking, however, was not determined by this study, nor did it reveal whether there existed significant variations among the different elements. A meta-analysis of 31 pieces of educational literature was conducted by Liu et al. ( 2020 ) to assess the impact of problem-solving on college students’ critical thinking. These authors found that problem-solving could promote the development of critical thinking among college students and proposed establishing a reasonable group structure for problem-solving in a follow-up study to improve students’ critical thinking. Additionally, previous empirical studies have reached inconclusive and even contradictory conclusions about whether and to what extent collaborative problem-solving increases or decreases critical thinking levels. As an illustration, Yang et al. ( 2008 ) carried out an experiment on the integrated curriculum teaching of college students based on a web bulletin board with the goal of fostering participants’ critical thinking in the context of collaborative problem-solving. These authors’ research revealed that through sharing, debating, examining, and reflecting on various experiences and ideas, collaborative problem-solving can considerably enhance students’ critical thinking in real-life problem situations. In contrast, collaborative problem-solving had a positive impact on learners’ interaction and could improve learning interest and motivation but could not significantly improve students’ critical thinking when compared to traditional classroom teaching, according to research by Naber and Wyatt ( 2014 ) and Sendag and Odabasi ( 2009 ) on undergraduate and high school students, respectively.
The above studies show that there is inconsistency regarding the effectiveness of collaborative problem-solving in promoting students’ critical thinking. Therefore, it is essential to conduct a thorough and trustworthy review to detect and decide whether and to what degree collaborative problem-solving can result in a rise or decrease in critical thinking. Meta-analysis is a quantitative analysis approach that is utilized to examine quantitative data from various separate studies that are all focused on the same research topic. This approach characterizes the effectiveness of its impact by averaging the effect sizes of numerous qualitative studies in an effort to reduce the uncertainty brought on by independent research and produce more conclusive findings (Lipsey and Wilson, 2001 ).
This paper used a meta-analytic approach and carried out a meta-analysis to examine the effectiveness of collaborative problem-solving in promoting students’ critical thinking in order to make a contribution to both research and practice. The following research questions were addressed by this meta-analysis:
What is the overall effect size of collaborative problem-solving in promoting students’ critical thinking and its impact on the two dimensions of critical thinking (i.e., attitudinal tendency and cognitive skills)?
How are the disparities between the study conclusions impacted by various moderating variables if the impacts of various experimental designs in the included studies are heterogeneous?
This research followed the strict procedures (e.g., database searching, identification, screening, eligibility, merging, duplicate removal, and analysis of included studies) of Cooper’s ( 2010 ) proposed meta-analysis approach for examining quantitative data from various separate studies that are all focused on the same research topic. The relevant empirical research that appeared in worldwide educational periodicals within the 21st century was subjected to this meta-analysis using Rev-Man 5.4. The consistency of the data extracted separately by two researchers was tested using Cohen’s kappa coefficient, and a publication bias test and a heterogeneity test were run on the sample data to ascertain the quality of this meta-analysis.
Data sources and search strategies
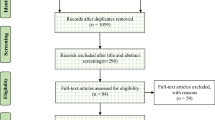
There were three stages to the data collection process for this meta-analysis, as shown in Fig. 1 , which shows the number of articles included and eliminated during the selection process based on the statement and study eligibility criteria.
This flowchart shows the number of records identified, included and excluded in the article.
First, the databases used to systematically search for relevant articles were the journal papers of the Web of Science Core Collection and the Chinese Core source journal, as well as the Chinese Social Science Citation Index (CSSCI) source journal papers included in CNKI. These databases were selected because they are credible platforms that are sources of scholarly and peer-reviewed information with advanced search tools and contain literature relevant to the subject of our topic from reliable researchers and experts. The search string with the Boolean operator used in the Web of Science was “TS = (((“critical thinking” or “ct” and “pretest” or “posttest”) or (“critical thinking” or “ct” and “control group” or “quasi experiment” or “experiment”)) and (“collaboration” or “collaborative learning” or “CSCL”) and (“problem solving” or “problem-based learning” or “PBL”))”. The research area was “Education Educational Research”, and the search period was “January 1, 2000, to December 30, 2021”. A total of 412 papers were obtained. The search string with the Boolean operator used in the CNKI was “SU = (‘critical thinking’*‘collaboration’ + ‘critical thinking’*‘collaborative learning’ + ‘critical thinking’*‘CSCL’ + ‘critical thinking’*‘problem solving’ + ‘critical thinking’*‘problem-based learning’ + ‘critical thinking’*‘PBL’ + ‘critical thinking’*‘problem oriented’) AND FT = (‘experiment’ + ‘quasi experiment’ + ‘pretest’ + ‘posttest’ + ‘empirical study’)” (translated into Chinese when searching). A total of 56 studies were found throughout the search period of “January 2000 to December 2021”. From the databases, all duplicates and retractions were eliminated before exporting the references into Endnote, a program for managing bibliographic references. In all, 466 studies were found.
Second, the studies that matched the inclusion and exclusion criteria for the meta-analysis were chosen by two researchers after they had reviewed the abstracts and titles of the gathered articles, yielding a total of 126 studies.
Third, two researchers thoroughly reviewed each included article’s whole text in accordance with the inclusion and exclusion criteria. Meanwhile, a snowball search was performed using the references and citations of the included articles to ensure complete coverage of the articles. Ultimately, 36 articles were kept.
Two researchers worked together to carry out this entire process, and a consensus rate of almost 94.7% was reached after discussion and negotiation to clarify any emerging differences.
Eligibility criteria
Since not all the retrieved studies matched the criteria for this meta-analysis, eligibility criteria for both inclusion and exclusion were developed as follows:
The publication language of the included studies was limited to English and Chinese, and the full text could be obtained. Articles that did not meet the publication language and articles not published between 2000 and 2021 were excluded.
The research design of the included studies must be empirical and quantitative studies that can assess the effect of collaborative problem-solving on the development of critical thinking. Articles that could not identify the causal mechanisms by which collaborative problem-solving affects critical thinking, such as review articles and theoretical articles, were excluded.
The research method of the included studies must feature a randomized control experiment or a quasi-experiment, or a natural experiment, which have a higher degree of internal validity with strong experimental designs and can all plausibly provide evidence that critical thinking and collaborative problem-solving are causally related. Articles with non-experimental research methods, such as purely correlational or observational studies, were excluded.
The participants of the included studies were only students in school, including K-12 students and college students. Articles in which the participants were non-school students, such as social workers or adult learners, were excluded.
The research results of the included studies must mention definite signs that may be utilized to gauge critical thinking’s impact (e.g., sample size, mean value, or standard deviation). Articles that lacked specific measurement indicators for critical thinking and could not calculate the effect size were excluded.
Data coding design
In order to perform a meta-analysis, it is necessary to collect the most important information from the articles, codify that information’s properties, and convert descriptive data into quantitative data. Therefore, this study designed a data coding template (see Table 1 ). Ultimately, 16 coding fields were retained.
The designed data-coding template consisted of three pieces of information. Basic information about the papers was included in the descriptive information: the publishing year, author, serial number, and title of the paper.
The variable information for the experimental design had three variables: the independent variable (instruction method), the dependent variable (critical thinking), and the moderating variable (learning stage, teaching type, intervention duration, learning scaffold, group size, measuring tool, and subject area). Depending on the topic of this study, the intervention strategy, as the independent variable, was coded into collaborative and non-collaborative problem-solving. The dependent variable, critical thinking, was coded as a cognitive skill and an attitudinal tendency. And seven moderating variables were created by grouping and combining the experimental design variables discovered within the 36 studies (see Table 1 ), where learning stages were encoded as higher education, high school, middle school, and primary school or lower; teaching types were encoded as mixed courses, integrated courses, and independent courses; intervention durations were encoded as 0–1 weeks, 1–4 weeks, 4–12 weeks, and more than 12 weeks; group sizes were encoded as 2–3 persons, 4–6 persons, 7–10 persons, and more than 10 persons; learning scaffolds were encoded as teacher-supported learning scaffold, technique-supported learning scaffold, and resource-supported learning scaffold; measuring tools were encoded as standardized measurement tools (e.g., WGCTA, CCTT, CCTST, and CCTDI) and self-adapting measurement tools (e.g., modified or made by researchers); and subject areas were encoded according to the specific subjects used in the 36 included studies.
The data information contained three metrics for measuring critical thinking: sample size, average value, and standard deviation. It is vital to remember that studies with various experimental designs frequently adopt various formulas to determine the effect size. And this paper used Morris’ proposed standardized mean difference (SMD) calculation formula ( 2008 , p. 369; see Supplementary Table S3 ).
Procedure for extracting and coding data
According to the data coding template (see Table 1 ), the 36 papers’ information was retrieved by two researchers, who then entered them into Excel (see Supplementary Table S1 ). The results of each study were extracted separately in the data extraction procedure if an article contained numerous studies on critical thinking, or if a study assessed different critical thinking dimensions. For instance, Tiwari et al. ( 2010 ) used four time points, which were viewed as numerous different studies, to examine the outcomes of critical thinking, and Chen ( 2013 ) included the two outcome variables of attitudinal tendency and cognitive skills, which were regarded as two studies. After discussion and negotiation during data extraction, the two researchers’ consistency test coefficients were roughly 93.27%. Supplementary Table S2 details the key characteristics of the 36 included articles with 79 effect quantities, including descriptive information (e.g., the publishing year, author, serial number, and title of the paper), variable information (e.g., independent variables, dependent variables, and moderating variables), and data information (e.g., mean values, standard deviations, and sample size). Following that, testing for publication bias and heterogeneity was done on the sample data using the Rev-Man 5.4 software, and then the test results were used to conduct a meta-analysis.
Publication bias test
When the sample of studies included in a meta-analysis does not accurately reflect the general status of research on the relevant subject, publication bias is said to be exhibited in this research. The reliability and accuracy of the meta-analysis may be impacted by publication bias. Due to this, the meta-analysis needs to check the sample data for publication bias (Stewart et al., 2006 ). A popular method to check for publication bias is the funnel plot; and it is unlikely that there will be publishing bias when the data are equally dispersed on either side of the average effect size and targeted within the higher region. The data are equally dispersed within the higher portion of the efficient zone, consistent with the funnel plot connected with this analysis (see Fig. 2 ), indicating that publication bias is unlikely in this situation.
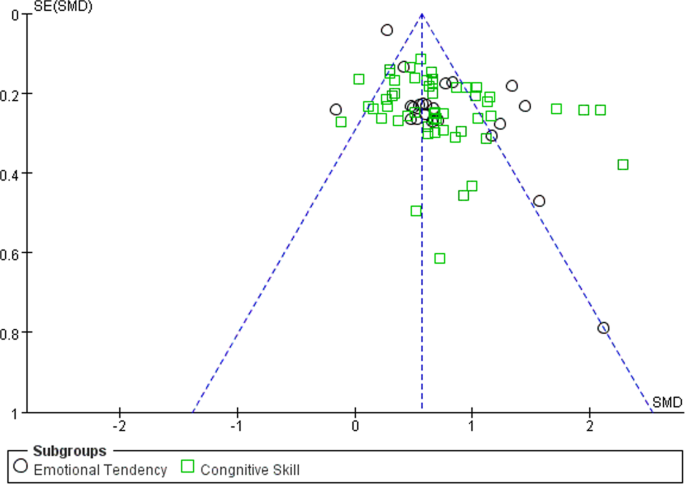
This funnel plot shows the result of publication bias of 79 effect quantities across 36 studies.
Heterogeneity test
To select the appropriate effect models for the meta-analysis, one might use the results of a heterogeneity test on the data effect sizes. In a meta-analysis, it is common practice to gauge the degree of data heterogeneity using the I 2 value, and I 2 ≥ 50% is typically understood to denote medium-high heterogeneity, which calls for the adoption of a random effect model; if not, a fixed effect model ought to be applied (Lipsey and Wilson, 2001 ). The findings of the heterogeneity test in this paper (see Table 2 ) revealed that I 2 was 86% and displayed significant heterogeneity ( P < 0.01). To ensure accuracy and reliability, the overall effect size ought to be calculated utilizing the random effect model.
The analysis of the overall effect size
This meta-analysis utilized a random effect model to examine 79 effect quantities from 36 studies after eliminating heterogeneity. In accordance with Cohen’s criterion (Cohen, 1992 ), it is abundantly clear from the analysis results, which are shown in the forest plot of the overall effect (see Fig. 3 ), that the cumulative impact size of cooperative problem-solving is 0.82, which is statistically significant ( z = 12.78, P < 0.01, 95% CI [0.69, 0.95]), and can encourage learners to practice critical thinking.
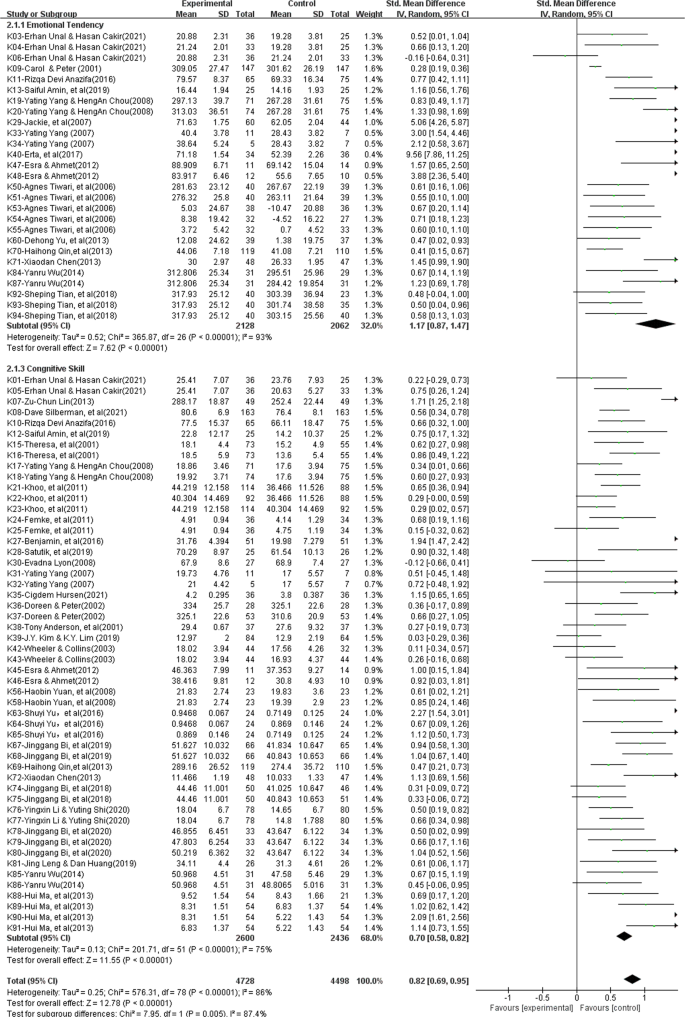
This forest plot shows the analysis result of the overall effect size across 36 studies.
In addition, this study examined two distinct dimensions of critical thinking to better understand the precise contributions that collaborative problem-solving makes to the growth of critical thinking. The findings (see Table 3 ) indicate that collaborative problem-solving improves cognitive skills (ES = 0.70) and attitudinal tendency (ES = 1.17), with significant intergroup differences (chi 2 = 7.95, P < 0.01). Although collaborative problem-solving improves both dimensions of critical thinking, it is essential to point out that the improvements in students’ attitudinal tendency are much more pronounced and have a significant comprehensive effect (ES = 1.17, z = 7.62, P < 0.01, 95% CI [0.87, 1.47]), whereas gains in learners’ cognitive skill are slightly improved and are just above average. (ES = 0.70, z = 11.55, P < 0.01, 95% CI [0.58, 0.82]).
The analysis of moderator effect size
The whole forest plot’s 79 effect quantities underwent a two-tailed test, which revealed significant heterogeneity ( I 2 = 86%, z = 12.78, P < 0.01), indicating differences between various effect sizes that may have been influenced by moderating factors other than sampling error. Therefore, exploring possible moderating factors that might produce considerable heterogeneity was done using subgroup analysis, such as the learning stage, learning scaffold, teaching type, group size, duration of the intervention, measuring tool, and the subject area included in the 36 experimental designs, in order to further explore the key factors that influence critical thinking. The findings (see Table 4 ) indicate that various moderating factors have advantageous effects on critical thinking. In this situation, the subject area (chi 2 = 13.36, P < 0.05), group size (chi 2 = 8.77, P < 0.05), intervention duration (chi 2 = 12.18, P < 0.01), learning scaffold (chi 2 = 9.03, P < 0.01), and teaching type (chi 2 = 7.20, P < 0.05) are all significant moderators that can be applied to support the cultivation of critical thinking. However, since the learning stage and the measuring tools did not significantly differ among intergroup (chi 2 = 3.15, P = 0.21 > 0.05, and chi 2 = 0.08, P = 0.78 > 0.05), we are unable to explain why these two factors are crucial in supporting the cultivation of critical thinking in the context of collaborative problem-solving. These are the precise outcomes, as follows:
Various learning stages influenced critical thinking positively, without significant intergroup differences (chi 2 = 3.15, P = 0.21 > 0.05). High school was first on the list of effect sizes (ES = 1.36, P < 0.01), then higher education (ES = 0.78, P < 0.01), and middle school (ES = 0.73, P < 0.01). These results show that, despite the learning stage’s beneficial influence on cultivating learners’ critical thinking, we are unable to explain why it is essential for cultivating critical thinking in the context of collaborative problem-solving.
Different teaching types had varying degrees of positive impact on critical thinking, with significant intergroup differences (chi 2 = 7.20, P < 0.05). The effect size was ranked as follows: mixed courses (ES = 1.34, P < 0.01), integrated courses (ES = 0.81, P < 0.01), and independent courses (ES = 0.27, P < 0.01). These results indicate that the most effective approach to cultivate critical thinking utilizing collaborative problem solving is through the teaching type of mixed courses.
Various intervention durations significantly improved critical thinking, and there were significant intergroup differences (chi 2 = 12.18, P < 0.01). The effect sizes related to this variable showed a tendency to increase with longer intervention durations. The improvement in critical thinking reached a significant level (ES = 0.85, P < 0.01) after more than 12 weeks of training. These findings indicate that the intervention duration and critical thinking’s impact are positively correlated, with a longer intervention duration having a greater effect.
Different learning scaffolds influenced critical thinking positively, with significant intergroup differences (chi 2 = 9.03, P < 0.01). The resource-supported learning scaffold (ES = 0.69, P < 0.01) acquired a medium-to-higher level of impact, the technique-supported learning scaffold (ES = 0.63, P < 0.01) also attained a medium-to-higher level of impact, and the teacher-supported learning scaffold (ES = 0.92, P < 0.01) displayed a high level of significant impact. These results show that the learning scaffold with teacher support has the greatest impact on cultivating critical thinking.
Various group sizes influenced critical thinking positively, and the intergroup differences were statistically significant (chi 2 = 8.77, P < 0.05). Critical thinking showed a general declining trend with increasing group size. The overall effect size of 2–3 people in this situation was the biggest (ES = 0.99, P < 0.01), and when the group size was greater than 7 people, the improvement in critical thinking was at the lower-middle level (ES < 0.5, P < 0.01). These results show that the impact on critical thinking is positively connected with group size, and as group size grows, so does the overall impact.
Various measuring tools influenced critical thinking positively, with significant intergroup differences (chi 2 = 0.08, P = 0.78 > 0.05). In this situation, the self-adapting measurement tools obtained an upper-medium level of effect (ES = 0.78), whereas the complete effect size of the standardized measurement tools was the largest, achieving a significant level of effect (ES = 0.84, P < 0.01). These results show that, despite the beneficial influence of the measuring tool on cultivating critical thinking, we are unable to explain why it is crucial in fostering the growth of critical thinking by utilizing the approach of collaborative problem-solving.
Different subject areas had a greater impact on critical thinking, and the intergroup differences were statistically significant (chi 2 = 13.36, P < 0.05). Mathematics had the greatest overall impact, achieving a significant level of effect (ES = 1.68, P < 0.01), followed by science (ES = 1.25, P < 0.01) and medical science (ES = 0.87, P < 0.01), both of which also achieved a significant level of effect. Programming technology was the least effective (ES = 0.39, P < 0.01), only having a medium-low degree of effect compared to education (ES = 0.72, P < 0.01) and other fields (such as language, art, and social sciences) (ES = 0.58, P < 0.01). These results suggest that scientific fields (e.g., mathematics, science) may be the most effective subject areas for cultivating critical thinking utilizing the approach of collaborative problem-solving.
The effectiveness of collaborative problem solving with regard to teaching critical thinking
According to this meta-analysis, using collaborative problem-solving as an intervention strategy in critical thinking teaching has a considerable amount of impact on cultivating learners’ critical thinking as a whole and has a favorable promotional effect on the two dimensions of critical thinking. According to certain studies, collaborative problem solving, the most frequently used critical thinking teaching strategy in curriculum instruction can considerably enhance students’ critical thinking (e.g., Liang et al., 2017 ; Liu et al., 2020 ; Cindy, 2004 ). This meta-analysis provides convergent data support for the above research views. Thus, the findings of this meta-analysis not only effectively address the first research query regarding the overall effect of cultivating critical thinking and its impact on the two dimensions of critical thinking (i.e., attitudinal tendency and cognitive skills) utilizing the approach of collaborative problem-solving, but also enhance our confidence in cultivating critical thinking by using collaborative problem-solving intervention approach in the context of classroom teaching.
Furthermore, the associated improvements in attitudinal tendency are much stronger, but the corresponding improvements in cognitive skill are only marginally better. According to certain studies, cognitive skill differs from the attitudinal tendency in classroom instruction; the cultivation and development of the former as a key ability is a process of gradual accumulation, while the latter as an attitude is affected by the context of the teaching situation (e.g., a novel and exciting teaching approach, challenging and rewarding tasks) (Halpern, 2001 ; Wei and Hong, 2022 ). Collaborative problem-solving as a teaching approach is exciting and interesting, as well as rewarding and challenging; because it takes the learners as the focus and examines problems with poor structure in real situations, and it can inspire students to fully realize their potential for problem-solving, which will significantly improve their attitudinal tendency toward solving problems (Liu et al., 2020 ). Similar to how collaborative problem-solving influences attitudinal tendency, attitudinal tendency impacts cognitive skill when attempting to solve a problem (Liu et al., 2020 ; Zhang et al., 2022 ), and stronger attitudinal tendencies are associated with improved learning achievement and cognitive ability in students (Sison, 2008 ; Zhang et al., 2022 ). It can be seen that the two specific dimensions of critical thinking as well as critical thinking as a whole are affected by collaborative problem-solving, and this study illuminates the nuanced links between cognitive skills and attitudinal tendencies with regard to these two dimensions of critical thinking. To fully develop students’ capacity for critical thinking, future empirical research should pay closer attention to cognitive skills.
The moderating effects of collaborative problem solving with regard to teaching critical thinking
In order to further explore the key factors that influence critical thinking, exploring possible moderating effects that might produce considerable heterogeneity was done using subgroup analysis. The findings show that the moderating factors, such as the teaching type, learning stage, group size, learning scaffold, duration of the intervention, measuring tool, and the subject area included in the 36 experimental designs, could all support the cultivation of collaborative problem-solving in critical thinking. Among them, the effect size differences between the learning stage and measuring tool are not significant, which does not explain why these two factors are crucial in supporting the cultivation of critical thinking utilizing the approach of collaborative problem-solving.
In terms of the learning stage, various learning stages influenced critical thinking positively without significant intergroup differences, indicating that we are unable to explain why it is crucial in fostering the growth of critical thinking.
Although high education accounts for 70.89% of all empirical studies performed by researchers, high school may be the appropriate learning stage to foster students’ critical thinking by utilizing the approach of collaborative problem-solving since it has the largest overall effect size. This phenomenon may be related to student’s cognitive development, which needs to be further studied in follow-up research.
With regard to teaching type, mixed course teaching may be the best teaching method to cultivate students’ critical thinking. Relevant studies have shown that in the actual teaching process if students are trained in thinking methods alone, the methods they learn are isolated and divorced from subject knowledge, which is not conducive to their transfer of thinking methods; therefore, if students’ thinking is trained only in subject teaching without systematic method training, it is challenging to apply to real-world circumstances (Ruggiero, 2012 ; Hu and Liu, 2015 ). Teaching critical thinking as mixed course teaching in parallel to other subject teachings can achieve the best effect on learners’ critical thinking, and explicit critical thinking instruction is more effective than less explicit critical thinking instruction (Bensley and Spero, 2014 ).
In terms of the intervention duration, with longer intervention times, the overall effect size shows an upward tendency. Thus, the intervention duration and critical thinking’s impact are positively correlated. Critical thinking, as a key competency for students in the 21st century, is difficult to get a meaningful improvement in a brief intervention duration. Instead, it could be developed over a lengthy period of time through consistent teaching and the progressive accumulation of knowledge (Halpern, 2001 ; Hu and Liu, 2015 ). Therefore, future empirical studies ought to take these restrictions into account throughout a longer period of critical thinking instruction.
With regard to group size, a group size of 2–3 persons has the highest effect size, and the comprehensive effect size decreases with increasing group size in general. This outcome is in line with some research findings; as an example, a group composed of two to four members is most appropriate for collaborative learning (Schellens and Valcke, 2006 ). However, the meta-analysis results also indicate that once the group size exceeds 7 people, small groups cannot produce better interaction and performance than large groups. This may be because the learning scaffolds of technique support, resource support, and teacher support improve the frequency and effectiveness of interaction among group members, and a collaborative group with more members may increase the diversity of views, which is helpful to cultivate critical thinking utilizing the approach of collaborative problem-solving.
With regard to the learning scaffold, the three different kinds of learning scaffolds can all enhance critical thinking. Among them, the teacher-supported learning scaffold has the largest overall effect size, demonstrating the interdependence of effective learning scaffolds and collaborative problem-solving. This outcome is in line with some research findings; as an example, a successful strategy is to encourage learners to collaborate, come up with solutions, and develop critical thinking skills by using learning scaffolds (Reiser, 2004 ; Xu et al., 2022 ); learning scaffolds can lower task complexity and unpleasant feelings while also enticing students to engage in learning activities (Wood et al., 2006 ); learning scaffolds are designed to assist students in using learning approaches more successfully to adapt the collaborative problem-solving process, and the teacher-supported learning scaffolds have the greatest influence on critical thinking in this process because they are more targeted, informative, and timely (Xu et al., 2022 ).
With respect to the measuring tool, despite the fact that standardized measurement tools (such as the WGCTA, CCTT, and CCTST) have been acknowledged as trustworthy and effective by worldwide experts, only 54.43% of the research included in this meta-analysis adopted them for assessment, and the results indicated no intergroup differences. These results suggest that not all teaching circumstances are appropriate for measuring critical thinking using standardized measurement tools. “The measuring tools for measuring thinking ability have limits in assessing learners in educational situations and should be adapted appropriately to accurately assess the changes in learners’ critical thinking.”, according to Simpson and Courtney ( 2002 , p. 91). As a result, in order to more fully and precisely gauge how learners’ critical thinking has evolved, we must properly modify standardized measuring tools based on collaborative problem-solving learning contexts.
With regard to the subject area, the comprehensive effect size of science departments (e.g., mathematics, science, medical science) is larger than that of language arts and social sciences. Some recent international education reforms have noted that critical thinking is a basic part of scientific literacy. Students with scientific literacy can prove the rationality of their judgment according to accurate evidence and reasonable standards when they face challenges or poorly structured problems (Kyndt et al., 2013 ), which makes critical thinking crucial for developing scientific understanding and applying this understanding to practical problem solving for problems related to science, technology, and society (Yore et al., 2007 ).
Suggestions for critical thinking teaching
Other than those stated in the discussion above, the following suggestions are offered for critical thinking instruction utilizing the approach of collaborative problem-solving.
First, teachers should put a special emphasis on the two core elements, which are collaboration and problem-solving, to design real problems based on collaborative situations. This meta-analysis provides evidence to support the view that collaborative problem-solving has a strong synergistic effect on promoting students’ critical thinking. Asking questions about real situations and allowing learners to take part in critical discussions on real problems during class instruction are key ways to teach critical thinking rather than simply reading speculative articles without practice (Mulnix, 2012 ). Furthermore, the improvement of students’ critical thinking is realized through cognitive conflict with other learners in the problem situation (Yang et al., 2008 ). Consequently, it is essential for teachers to put a special emphasis on the two core elements, which are collaboration and problem-solving, and design real problems and encourage students to discuss, negotiate, and argue based on collaborative problem-solving situations.
Second, teachers should design and implement mixed courses to cultivate learners’ critical thinking, utilizing the approach of collaborative problem-solving. Critical thinking can be taught through curriculum instruction (Kuncel, 2011 ; Leng and Lu, 2020 ), with the goal of cultivating learners’ critical thinking for flexible transfer and application in real problem-solving situations. This meta-analysis shows that mixed course teaching has a highly substantial impact on the cultivation and promotion of learners’ critical thinking. Therefore, teachers should design and implement mixed course teaching with real collaborative problem-solving situations in combination with the knowledge content of specific disciplines in conventional teaching, teach methods and strategies of critical thinking based on poorly structured problems to help students master critical thinking, and provide practical activities in which students can interact with each other to develop knowledge construction and critical thinking utilizing the approach of collaborative problem-solving.
Third, teachers should be more trained in critical thinking, particularly preservice teachers, and they also should be conscious of the ways in which teachers’ support for learning scaffolds can promote critical thinking. The learning scaffold supported by teachers had the greatest impact on learners’ critical thinking, in addition to being more directive, targeted, and timely (Wood et al., 2006 ). Critical thinking can only be effectively taught when teachers recognize the significance of critical thinking for students’ growth and use the proper approaches while designing instructional activities (Forawi, 2016 ). Therefore, with the intention of enabling teachers to create learning scaffolds to cultivate learners’ critical thinking utilizing the approach of collaborative problem solving, it is essential to concentrate on the teacher-supported learning scaffolds and enhance the instruction for teaching critical thinking to teachers, especially preservice teachers.
Implications and limitations
There are certain limitations in this meta-analysis, but future research can correct them. First, the search languages were restricted to English and Chinese, so it is possible that pertinent studies that were written in other languages were overlooked, resulting in an inadequate number of articles for review. Second, these data provided by the included studies are partially missing, such as whether teachers were trained in the theory and practice of critical thinking, the average age and gender of learners, and the differences in critical thinking among learners of various ages and genders. Third, as is typical for review articles, more studies were released while this meta-analysis was being done; therefore, it had a time limit. With the development of relevant research, future studies focusing on these issues are highly relevant and needed.
Conclusions
The subject of the magnitude of collaborative problem-solving’s impact on fostering students’ critical thinking, which received scant attention from other studies, was successfully addressed by this study. The question of the effectiveness of collaborative problem-solving in promoting students’ critical thinking was addressed in this study, which addressed a topic that had gotten little attention in earlier research. The following conclusions can be made:
Regarding the results obtained, collaborative problem solving is an effective teaching approach to foster learners’ critical thinking, with a significant overall effect size (ES = 0.82, z = 12.78, P < 0.01, 95% CI [0.69, 0.95]). With respect to the dimensions of critical thinking, collaborative problem-solving can significantly and effectively improve students’ attitudinal tendency, and the comprehensive effect is significant (ES = 1.17, z = 7.62, P < 0.01, 95% CI [0.87, 1.47]); nevertheless, it falls short in terms of improving students’ cognitive skills, having only an upper-middle impact (ES = 0.70, z = 11.55, P < 0.01, 95% CI [0.58, 0.82]).
As demonstrated by both the results and the discussion, there are varying degrees of beneficial effects on students’ critical thinking from all seven moderating factors, which were found across 36 studies. In this context, the teaching type (chi 2 = 7.20, P < 0.05), intervention duration (chi 2 = 12.18, P < 0.01), subject area (chi 2 = 13.36, P < 0.05), group size (chi 2 = 8.77, P < 0.05), and learning scaffold (chi 2 = 9.03, P < 0.01) all have a positive impact on critical thinking, and they can be viewed as important moderating factors that affect how critical thinking develops. Since the learning stage (chi 2 = 3.15, P = 0.21 > 0.05) and measuring tools (chi 2 = 0.08, P = 0.78 > 0.05) did not demonstrate any significant intergroup differences, we are unable to explain why these two factors are crucial in supporting the cultivation of critical thinking in the context of collaborative problem-solving.
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included within the article and its supplementary information files, and the supplementary information files are available in the Dataverse repository: https://doi.org/10.7910/DVN/IPFJO6 .
Bensley DA, Spero RA (2014) Improving critical thinking skills and meta-cognitive monitoring through direct infusion. Think Skills Creat 12:55–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsc.2014.02.001
Article Google Scholar
Castle A (2009) Defining and assessing critical thinking skills for student radiographers. Radiography 15(1):70–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radi.2007.10.007
Chen XD (2013) An empirical study on the influence of PBL teaching model on critical thinking ability of non-English majors. J PLA Foreign Lang College 36 (04):68–72
Google Scholar
Cohen A (1992) Antecedents of organizational commitment across occupational groups: a meta-analysis. J Organ Behav. https://doi.org/10.1002/job.4030130602
Cooper H (2010) Research synthesis and meta-analysis: a step-by-step approach, 4th edn. Sage, London, England
Cindy HS (2004) Problem-based learning: what and how do students learn? Educ Psychol Rev 51(1):31–39
Duch BJ, Gron SD, Allen DE (2001) The power of problem-based learning: a practical “how to” for teaching undergraduate courses in any discipline. Stylus Educ Sci 2:190–198
Ennis RH (1989) Critical thinking and subject specificity: clarification and needed research. Educ Res 18(3):4–10. https://doi.org/10.3102/0013189x018003004
Facione PA (1990) Critical thinking: a statement of expert consensus for purposes of educational assessment and instruction. Research findings and recommendations. Eric document reproduction service. https://eric.ed.gov/?id=ed315423
Facione PA, Facione NC (1992) The California Critical Thinking Dispositions Inventory (CCTDI) and the CCTDI test manual. California Academic Press, Millbrae, CA
Forawi SA (2016) Standard-based science education and critical thinking. Think Skills Creat 20:52–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsc.2016.02.005
Halpern DF (2001) Assessing the effectiveness of critical thinking instruction. J Gen Educ 50(4):270–286. https://doi.org/10.2307/27797889
Hu WP, Liu J (2015) Cultivation of pupils’ thinking ability: a five-year follow-up study. Psychol Behav Res 13(05):648–654. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1672-0628.2015.05.010
Huber K (2016) Does college teach critical thinking? A meta-analysis. Rev Educ Res 86(2):431–468. https://doi.org/10.3102/0034654315605917
Kek MYCA, Huijser H (2011) The power of problem-based learning in developing critical thinking skills: preparing students for tomorrow’s digital futures in today’s classrooms. High Educ Res Dev 30(3):329–341. https://doi.org/10.1080/07294360.2010.501074
Kuncel NR (2011) Measurement and meaning of critical thinking (Research report for the NRC 21st Century Skills Workshop). National Research Council, Washington, DC
Kyndt E, Raes E, Lismont B, Timmers F, Cascallar E, Dochy F (2013) A meta-analysis of the effects of face-to-face cooperative learning. Do recent studies falsify or verify earlier findings? Educ Res Rev 10(2):133–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.edurev.2013.02.002
Leng J, Lu XX (2020) Is critical thinking really teachable?—A meta-analysis based on 79 experimental or quasi experimental studies. Open Educ Res 26(06):110–118. https://doi.org/10.13966/j.cnki.kfjyyj.2020.06.011
Liang YZ, Zhu K, Zhao CL (2017) An empirical study on the depth of interaction promoted by collaborative problem solving learning activities. J E-educ Res 38(10):87–92. https://doi.org/10.13811/j.cnki.eer.2017.10.014
Lipsey M, Wilson D (2001) Practical meta-analysis. International Educational and Professional, London, pp. 92–160
Liu Z, Wu W, Jiang Q (2020) A study on the influence of problem based learning on college students’ critical thinking-based on a meta-analysis of 31 studies. Explor High Educ 03:43–49
Morris SB (2008) Estimating effect sizes from pretest-posttest-control group designs. Organ Res Methods 11(2):364–386. https://doi.org/10.1177/1094428106291059
Article ADS Google Scholar
Mulnix JW (2012) Thinking critically about critical thinking. Educ Philos Theory 44(5):464–479. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-5812.2010.00673.x
Naber J, Wyatt TH (2014) The effect of reflective writing interventions on the critical thinking skills and dispositions of baccalaureate nursing students. Nurse Educ Today 34(1):67–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nedt.2013.04.002
National Research Council (2012) Education for life and work: developing transferable knowledge and skills in the 21st century. The National Academies Press, Washington, DC
Niu L, Behar HLS, Garvan CW (2013) Do instructional interventions influence college students’ critical thinking skills? A meta-analysis. Educ Res Rev 9(12):114–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.edurev.2012.12.002
Peng ZM, Deng L (2017) Towards the core of education reform: cultivating critical thinking skills as the core of skills in the 21st century. Res Educ Dev 24:57–63. https://doi.org/10.14121/j.cnki.1008-3855.2017.24.011
Reiser BJ (2004) Scaffolding complex learning: the mechanisms of structuring and problematizing student work. J Learn Sci 13(3):273–304. https://doi.org/10.1207/s15327809jls1303_2
Ruggiero VR (2012) The art of thinking: a guide to critical and creative thought, 4th edn. Harper Collins College Publishers, New York
Schellens T, Valcke M (2006) Fostering knowledge construction in university students through asynchronous discussion groups. Comput Educ 46(4):349–370. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2004.07.010
Sendag S, Odabasi HF (2009) Effects of an online problem based learning course on content knowledge acquisition and critical thinking skills. Comput Educ 53(1):132–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2009.01.008
Sison R (2008) Investigating Pair Programming in a Software Engineering Course in an Asian Setting. 2008 15th Asia-Pacific Software Engineering Conference, pp. 325–331. https://doi.org/10.1109/APSEC.2008.61
Simpson E, Courtney M (2002) Critical thinking in nursing education: literature review. Mary Courtney 8(2):89–98
Stewart L, Tierney J, Burdett S (2006) Do systematic reviews based on individual patient data offer a means of circumventing biases associated with trial publications? Publication bias in meta-analysis. John Wiley and Sons Inc, New York, pp. 261–286
Tiwari A, Lai P, So M, Yuen K (2010) A comparison of the effects of problem-based learning and lecturing on the development of students’ critical thinking. Med Educ 40(6):547–554. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2929.2006.02481.x
Wood D, Bruner JS, Ross G (2006) The role of tutoring in problem solving. J Child Psychol Psychiatry 17(2):89–100. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-7610.1976.tb00381.x
Wei T, Hong S (2022) The meaning and realization of teachable critical thinking. Educ Theory Practice 10:51–57
Xu EW, Wang W, Wang QX (2022) A meta-analysis of the effectiveness of programming teaching in promoting K-12 students’ computational thinking. Educ Inf Technol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-022-11445-2
Yang YC, Newby T, Bill R (2008) Facilitating interactions through structured web-based bulletin boards: a quasi-experimental study on promoting learners’ critical thinking skills. Comput Educ 50(4):1572–1585. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2007.04.006
Yore LD, Pimm D, Tuan HL (2007) The literacy component of mathematical and scientific literacy. Int J Sci Math Educ 5(4):559–589. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10763-007-9089-4
Zhang T, Zhang S, Gao QQ, Wang JH (2022) Research on the development of learners’ critical thinking in online peer review. Audio Visual Educ Res 6:53–60. https://doi.org/10.13811/j.cnki.eer.2022.06.08
Download references
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the graduate scientific research and innovation project of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region named “Research on in-depth learning of high school information technology courses for the cultivation of computing thinking” (No. XJ2022G190) and the independent innovation fund project for doctoral students of the College of Educational Science of Xinjiang Normal University named “Research on project-based teaching of high school information technology courses from the perspective of discipline core literacy” (No. XJNUJKYA2003).
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
College of Educational Science, Xinjiang Normal University, 830017, Urumqi, Xinjiang, China
Enwei Xu, Wei Wang & Qingxia Wang
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding authors
Correspondence to Enwei Xu or Wei Wang .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.

Informed consent
Additional information.
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supplementary tables, rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Xu, E., Wang, W. & Wang, Q. The effectiveness of collaborative problem solving in promoting students’ critical thinking: A meta-analysis based on empirical literature. Humanit Soc Sci Commun 10 , 16 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1057/s41599-023-01508-1
Download citation
Received : 07 August 2022
Accepted : 04 January 2023
Published : 11 January 2023
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1057/s41599-023-01508-1
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
This article is cited by
Impacts of online collaborative learning on students’ intercultural communication apprehension and intercultural communicative competence.
- Hoa Thi Hoang Chau
- Hung Phu Bui
- Quynh Thi Huong Dinh
Education and Information Technologies (2024)
Exploring the effects of digital technology on deep learning: a meta-analysis
The influence of scaffolding for computational thinking on cognitive load and problem-solving skills in collaborative programming.
- Yoonhee Shin
- Jaewon Jung
- Bokmoon Jung
The impacts of computer-supported collaborative learning on students’ critical thinking: a meta-analysis
- Yoseph Gebrehiwot Tedla
- Hsiu-Ling Chen
Sustainable electricity generation and farm-grid utilization from photovoltaic aquaculture: a bibliometric analysis
- A. A. Amusa
- M. Alhassan
International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology (2024)
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
- Community and Engagement
- Honors and Awards
This is How Students Can Learn Problem-Solving Skills in Social Studies

A new study led by a researcher from North Carolina State University offers lessons on how social studies teachers could use computational thinking and computer-based resources to analyze primary source data, such as economic information, maps or historical documents. The findings suggest that these approaches advance not only computational thinking, but also student understanding of social studies concepts.
In the journal Theory & Research in Social Education , researchers reported findings from a case study of a high school social studies class called “Measuring the Past” that was offered in a private school. In the project-centered class, students used statistical software to analyze historical and economic data and identify trends. Researchers found students were able to learn problem-solving skills through the series of structured computer analysis projects.
“The purpose of social studies is to enhance student’s ability to participate in a democratic society,” said Meghan Manfra , associate professor of education at NC State. “Our research indicates computational thinking is a fruitful way to engage students in interdisciplinary investigation and develop the skills and habits they need to be successful.”
There is a growing effort to incorporate computational thinking across subjects in K-12 education, Manfra said, to help prepare students for a technology-driven world. Computers have made new techniques possible for historians and social scientists to analyze and interpret digital data, maps and images. Teachers face a potential “firehose” of primary source data they could bring into the classroom, such as the National Archives’ collection of historical letters, speeches, and maps important to American history .
“There are more efforts to integrate computer science across grade levels and subject areas,” Manfra said. “We take the definition of ‘computational thinking’ to be less computer science specific, and much more about a habit of mind. We see it as a structured problem-solving approach.”
In the high school class under study, researchers offered a phrase for the class to use as a guide for how to think about and structure the class projects: analyze the data, look for patterns, and then develop rules or models based on their analysis to solve a problem. They shortened that phrase to “data-patterns-rules.” The projects were also structured as a series, with each students gaining more independence with each project.
“The teacher had a lot of autonomy to develop a curriculum, and the projects were unique,” Manfra said. “Another important aspect of the structure was the students did three rounds of analyzing data, presenting their findings, and developing a model based on what they found. Each time, the teacher got more general in what he was giving the students so they had to flex more of their own thinking.”
In the first project, students analyzed Dollar Street , a website by GapMinder that has a database of photographs of items in homes around the world. Students posed and answered their own questions about the data. For example, one group analyzed whether the number of books in a home related to a family’s income.
In the second project, students tracked prices of labor or products like wool, grain and livestock in England to understand the bubonic plague’s impact on the economy during the Middle Ages.
In the last project, students found their own data to compare social or economic trends during two American wars, such as the War of 1812 and World War I. For example, one group of students compared numbers of draftees and volunteers in two conflicts and related that to the outcome of the war.
From the students’ work, the researchers saw that students were able to learn problem-solving and apply data analysis skills while looking at differences across cultures, the economic effects of historical events and to how political trends can help shape conflicts.
“Based on what we found, this approach not only enhances students’ computational thinking for STEM fields, but it also improves their social studies understanding and knowledge,” Manfra said. “It’s a fruitful approach to teaching and learning.”
From student essays about computational thinking, the researchers saw many students came away with a stronger understanding of the concept. Some students defined it as thinking “based on computer-generated statistics,” while others defined it as analyzing data so a computer can display it, and others said it meant analyzing information in a “computer-like” logical way. In addition, they also saw that students learned skills important in an age of misinformation – they were able to think deeply about potential limitations of the data and the source it came from.
“We found that students were developing data literacy,” Manfra said “They understood databases as a construction, designed to tell a story. We thought that was pretty sophisticated, and that thinking emerged because of what they were experiencing through this project.”
This story originally appeared on the NC State News site.
- Research and Impact
- faculty publications
- Meghan Manfra
- social studies education
More From College of Education News
Why gifts matter: transformational scholarship program creates opportunity for camilla torres to teach in duplin county, ofelia garcía shares importance of translanguaging pedagogies during linguistic diversity speaker series organized by goodnight distinguished professor maria coady, professor of special education and mathematics education jessica hunt to partner with black disabled high school students to improve mathematics education learning and teaching through grant-funded project.

- Solving Problems with Twenty Questions
- Social Education
- Social Education November/December 2021
William D. Edgington
Journal Issue:
How many times have we teachers thrown up our arms in exasperation and wanted to inquire of a student or a group of students, “What were you thinking?” How many times a day do we advise our students to “make good choices” and then cringe when they don’t?
All too often, students don’t, or can’t, simply because they don’t know how. Although we know that our students are constantly involved in a thinking process, we tend to take that process for granted, rationalizing that thinking is simply something that everybody does. The term thinking skills is itself broad and ambiguous. Turner refers to the “mental processes that individuals use to obtain, make sense of, and retain information, as well as how they process and use that information as a basis for solving problems.” 1 In social studies, we want to foster active citizens who have the ability to process information rationally to solve problems.
Yet many teachers are uncertain of how these skills are acquired. Too often, the idea of teaching thinking skills is synonymous with having students answer questions at the end of a chapter or recite material. My preservice methods students are often surprised that they will be responsible for teaching thinking skills in social studies instruction. Some students assume such an endeavor will be complicated and demanding; others believe that the questions written in blue ink in the margin of the teacher’s edition of textbooks will serve the purpose of “getting” children to think. But with planning and foresight, thinking skills strategies can be valuable tools in helping make the curriculum relevant, realistic, and stimulating to students. When teaching thinking skills through social studies instructions, teachers must not give these skills token attention or teach them in isolation, but must integrate them meaningfully into the curriculum.
An integral part of social studies instruction—and a key thinking skil#151;is problem solving. As defined by Hoge, problem solving is “finding the means to a distinctly conceived end or goal,” 2 and involves various formal strategies to reach that goal. As with the teaching of any thinking skill in social studies, problem solving skills need to be taught systematically, and this is next to impossible if teachers rely on the textbook for questions. As students become familiar with the process, they may need less time for actual instruction, practice, and feedback.
Steps in Problem Solving
The problem solving model, also referred to as discovery learning or inquiry , is a version of the scientific method and focuses on examining content. As applied to social studies instruction, the steps include the following:
• Define or perceive the problem. (The students are presented with a problem or question for which there is no immediate solution.)
• Formulate the hypothesis. (The students guess the causes of a problem.)
• Gather the data. (Information, either provided by the teacher or gathered by the students, is collected.)
• Evaluate or analyze the data. (The students examine and reflect on the information.)
• Use the data to confirm or reject the hypothesis. (The students use their reflections to help them consider whether their initial explanations are accurate.)
• Explain or reach a conclusion. (The students formulate and state their explanation for the original problem.)
Often, teachers see the practicality of such an approach in science but not in social studies. This misperception is ironic because social studies is filled with asking “why” and “how,” and most students are naturally curious about people and experiences, past and present.
Twenty Questions
Perhaps the simplest example of inquiry thinking is the game of Twenty Questions. By asking questions that the teacher answers with yes or no responses, students attempt to solve a problem put before them before they ask their twentieth question. Usually it is a whole-group activity, but it may be played in small groups or individually. Questions may be asked in a variety of formats: The students may take turns asking questions or each student may ask a series of questions in a row. Students may also work in pairs to formulate questions.
When first exposed to the game, the students’ questions are often random and haphazard, but with practice and the aid of the teacher, the students learn that they are working their way through the steps of inquiry as they play the game, and their questioning strategies become more sophisticated. Gathering data by asking questions, students use the answers to analyze and confirm or reject their hypotheses. For example, students can discover what led to the death of Sir Thomas More (see Box A), why Dalmatians have traditionally been the mascots of fire fighters, or why civilizations generally began near water. Applying Twenty Questions to social studies instruction involves the following steps.
1. The students understand that they must find the answer to the problem that the teacher has put before them.
2. The students guess or reason what they believe is the answer to the problem.
3. By asking questions of the teacher, the students gather data to solve the problem.
4. The students use the information to reflect on and determine whether the data are congruent with their hypothesis.
5. On the basis of the information gathered, the students determine whether their hypothesis is correct. If incorrect, they may use the information to develop a new hypothesis.
6. If the students believe that their hypothesis is correct, they may state their explanation in the form of a question (“Is it. . . ?”). If they believe that their original explanation is incorrect, they may repeat steps 3-5 until they have a new conclusion.
Because the purpose is to let the students exercise problem solving thinking skills, the activity need not be limited to only twenty questions. What is important is that the teacher walk the students through the steps as the game is played, reminding them that they are solving a problem and that their questions will help them gather data, or information, which, through reflection, will help them determine whether their original hypothesis, or explanation, was correct.
Concrete objects may aid in the inquiry. In connection with a reading lesson, a preservice teacher displayed a farming tool that was typical of those used during the era of Sarah, Plain and Tall. Working with a fourth-grade reading group, the teacher showed the students the hand-held tool (which had belonged to her family for more than one hundred years) and explained that it was similar to those on the farm in Sarah, Plain and Tall. She informed the students that through their questions, they would discover the too#146;s purpose. Their initial questions centered on what they thought it was (“Does it plow?” and “Does it cut things?”), but through the teacher’s prompting, they soon asked questions that reflected data-gathering strategies in formal problem solving (“Is it used to prepare the soil somehow?” and “Is it used after the crop or plant is picked or harvested?”). The students then tested their hypotheses. They needed to ask more than twenty questions, but eventually they concluded that the object was used to separate residue cotton fibers from the plant—an explanation that their teacher affirmed. Although growing cotton was not mentioned in Sarah, Plain and Tall, the students, living in rural Alabama, could appreciate the difficulty that harvesting cotton presented to their ancestors, and in turn they understood the hardships that farmers, such as those in the book, must have faced.
Conflicting Statements as Problem Solving Tools
Twenty Questions is a highly effective method of problem solving, but other approaches also enable middle school students to focus on complex questions. For instance, Naylor and Diem suggest examining conflicting or opposing statements from the same source; an example might be Thomas Jefferson’s public writings on equality and his private ownership of slaves. 3 Students must struggle with the contradiction between Jefferson’s words and his actions.
The question for the students to consider could be “How could Thomas Jefferson write and speak of equality for all men and yet engage in the ownership of human beings?” Because the issue is complex, the question may serve as the overriding problem to be solved, while other related questions may guide the problem solving. Progressions in inquiry might include such questions: Was Jefferson a hypocrite? Was he a racist? Did others in similar positions and circumstances reflect this contradiction? What was the social and political climate at the time? Did events make this sort of contradiction seem acceptable? Did Jefferson show any acknowledgment of this contradiction in his writings or letters? What were his views on slavery? How were his slaves treated? Was this contradiction reflected in his views and dreams for the United States? Does this contradiction make his writings and accomplishments any less important or admirable? Working in groups, pairs, or individually, students can engage in problem solving steps.
Data gathering in such an exercise works well if the students examine primary and secondary documents from a variety of sources. For example, at the Thomas Jefferson Papers at the Library of Congress (memory.loc.gov/ammem/mtjhtml/ mtjhome.html), students can view formal documents that Jefferson wrote, personal letters, letters of his contemporaries, a timeline of his life, and assorted biographies.
Teachers need to emphasize and reiterate the steps in problem solving during the assignment. A culminating discussion of, or solution to, the problem may serve as a catalyst for further exploration of another issue or contradiction. In addition to exercising their problem solving skills, students better understand Jefferson the man, eighteenth-century political and social thought, and the philosophical principles that helped found the United States. Middle school students, curious about the people and the past, are ready to discuss how the past relates to their lives and the implications for their future.
Problem Solving for Creative Thinking
Although teaching problem solving skills is a vital part of social studies instruction, teachers are too often unwilling or unsure of how to incorporate problem solving into the curriculum. Not the nebulous beast that many educators assume, problem solving skills can be a viable centerpiece for instruction if we simply take a deep breath and examine the potential that they afford. If we wish for students to be creative thinkers, we must give them opportunity to think creatively, and if we want them to make judgments and reason logically, they must have the opportunity to practice these skills regularly. Through such models as Twenty Questions and Conflicting Statements, teachers can incorporate problem solving skills into the curriculum and give these skills the attention that they, and the students, deserve.
1. Thomas N. Turner, Essentials of Elementary Social Studies (2nd ed.) (Needham Heights, MA: Allyn & Bacon, 1999), 160.
2. John Douglas Hoge, Effective Elementary Social Studies (Belmont, CA: Wadsworth, 1996), 50.
3. David T. Naylor and Richard Diem, Elementary and Middle School Social Studies (New York: Random House, 1987), 254.
William D. Edgington is an assistant professor of social science education, Sam Houston State University, P.O. Box 2119, Huntsville, Texas 77341. He may be reached at [email protected] .
Twenty Questions and the Issue of Sir Thomas More
(sixth grade).
Teacher: We’ve been talking about England under Henry VIII, and today we’re going to investigate one of the most celebrated men of the day, Sir Thomas More. More was an author who wrote about the ideal society ( Utopia ); an attorney; and even the Lord Chancellor, the second most powerful man in England. But circumstances arose that cost More not only his position in the government, but also his life. He refused to change his stance on certain issues, although he was given opportunities to do so, choosing death over a compromise of his values and beliefs. He was beheaded on July 6, 1535.
Your mission today is to figure out what cost Sir Thomas More his life—what issues did he believe in so strongly that he chose death rather than deny his principles. Remember, you may ask questions to which I can answer with “yes” or “no” as we go through the problem solving process. You may already have a hypothesis or an idea, and my answers to your questions will help you determine whether your hypothesis is correct.
Student 1: Did it have to do with Henry VIII?
Teacher: Yes.
Student 2: Did More get in a fight with Henry?
Teacher: Be more specific.
Student 2: Did he and Henry disagree on something?
Student 3: Did it have to do with war?
Teacher: No. (At this point, the teacher emphasizes that the data were either supporting or disproving the students’ hypotheses and that they might need to rethink their hypotheses as they continue their questioning.)
Student 4: Did it have to do with Henry’s religion?
Student 4: Did it have to do with Henry starting his own church?
Teacher: Partially, yes. (At this time, the students review the data.)
Student 3: Was he not in favor of it?
Student 3: Was More not in favor of Henry’s church?
Teacher: No, he wasn’t in favor of it, but there is more to it.
Student 5: Did he not think that Henry should be the head of his church?
Teacher: No, he did not. Do you want to state your hypothesis?
Student 5: More didn’t think that Henry should be head of the church.
Teacher: Good! He refused to sign the Act of Supremacy, which named the king as the Supreme Head of the Church of England. But there was another issue on which More would not budge.
Student 1: Did it have to do with all of Henry’s wives?
Student 1: Did it have to do with his divorce? His first one?
Teacher: Partially. (The teacher prompts the students as they review the circumstances surrounding the end of Henry’s marriage to Catherine of Aragon.)
Student 6: Did it have to do with his ditching Catherine of Aragon and marrying Anne Boleyn?
Teacher: Yes. Keep going.
Student 7: Did More not think that Anne Boleyn should be queen?
Teacher: That’s correct. Do you want to state your hypothesis?
Student 7: More didn’t think that Anne Boleyn should be queen.
Teacher: Right! He refused to sign the Act of Succession, which stated that Henry’s marriage to Anne Boleyn was lawful. He wouldn’t sign either the Act of Supremacy or the Act of Succession. So what issues ultimately led to Sir Thomas More’s death?
Student 8: Henry’s marriage to Anne Boleyn and Henry making himself the Head of the Church of England.
Teacher: All right, let’s discuss why More felt so strongly about these issues . . . .
For a short biography of Sir Thomas More, see Encarta Online Encyclopedia, 2000 at encarta.msn.com.
Using Problem Solving Skills in a Fifth-Grade Classroom
Alan Rock and Nicole Halbert
Like most of our classmates, we were surprised to learn that we would be expected to teach thinking skills in social studies. Before our methods course, we equated social studies with maps, states, capitals, and presidents. We were astonished to discover that we would not just be teaching facts, we would also be helping students discover concepts, make generalizations, and enhance their observation, listening, graphing, mapping, and reference skills.
One of the requirements for our social studies methods course was to incorporate thinking skills into lessons that we would teach during our practicum. When we explained to our fifth-grade students that we would be doing activities that might be a little out of the ordinary, they seemed willing to assume the position of “thinker” rather than merely that of the traditional question-answering student.
We used a Twenty Questions activity for a problem solving skills lesson. To preface the lesson, we explained the rules and played a practice game of Twenty Questions. The mystery object or goal that they had to identify was a paper clip. The students’ first questions were random and nonsequential: “Is it a car?” “Is it the principal?” “Is it Jeff?” They called out the first thing that popped into their heads. As the game progressed, we discussed the need for asking questions that built on previous questions and that would narrow down the search. Eventually, their questions became more focused: “Is it in the classroom?” “Is it bigger than the desk?” “Does it have moveable parts?” “Is it red?” At the close of the game, we discussed the scientific method (they were familiar with the term from science class) and applied the steps to the practice game. When they thought that they knew what the object was, they were forming a hypothesis; by asking questions, they were gathering data; our answers helped them evaluate the data and reject or confirm their hypothesis.
We then explained their problem-solving activity: They had to figure out what actually happened to Paul Revere on the night of his famous ride. Having just played the practice game helped—their questions were not nearly as off-the-wall as at first. Instead of calling out any idea that came into their heads, their questions showed thought: “Does it have anything to do with his horse?” “Does it have to do with other people?” “Does it have to do with other minutemen?” “Does it have to do with the British?” “Did the British shoot him?” We stopped the questioning periodically to think about the scientific method and to have the students talk about their hypotheses. They did solve the problem—in fewer than twenty questions. Revere was captured by a British Patrol and spent much of the night in jail.
At their own initiation, they shared ideas with one another. For example, when the class discovered that the problem had something to do with the British, one student asked whether Revere had been killed. Another student dismissed that hypothesis because Revere was famous and therefore couldn’t have been killed. Other students immediately came to the first student’s defense, naming famous people who had been killed—John F. Kennedy, Abraham Lincoln, and Martin Luther King, Jr., for example. Once they solved the problem, they had plenty of follow-up questions: “Why have we never heard that part of the story before?” “How do we know that part of the story is true?” We hadn’t planned on such questions, but we addressed the issues of reliability and resources. In retrospect, we could have had the students compare the information that they had acquired with the information in their textbook.
We used the activity as a preview to our unit on the American Revolution. But we probably learned more than the students did. As future teachers, we clearly see that social studies can advance the thinking skills that the students use each day. Social studies is too often associated with tracing and memorizing, but we know it doesn’t have to be. We now look forward to using problem solving in our lessons.
Alan Rock and Nicole Halbert are Methods Students, Sam Houston State University, Huntsville, TX
Teaching Problem-Solving Skills
Many instructors design opportunities for students to solve “problems”. But are their students solving true problems or merely participating in practice exercises? The former stresses critical thinking and decision making skills whereas the latter requires only the application of previously learned procedures.
Problem solving is often broadly defined as "the ability to understand the environment, identify complex problems, review related information to develop, evaluate strategies and implement solutions to build the desired outcome" (Fissore, C. et al, 2021). True problem solving is the process of applying a method – not known in advance – to a problem that is subject to a specific set of conditions and that the problem solver has not seen before, in order to obtain a satisfactory solution.
Below you will find some basic principles for teaching problem solving and one model to implement in your classroom teaching.
Principles for teaching problem solving
- Model a useful problem-solving method . Problem solving can be difficult and sometimes tedious. Show students how to be patient and persistent, and how to follow a structured method, such as Woods’ model described below. Articulate your method as you use it so students see the connections.
- Teach within a specific context . Teach problem-solving skills in the context in which they will be used by students (e.g., mole fraction calculations in a chemistry course). Use real-life problems in explanations, examples, and exams. Do not teach problem solving as an independent, abstract skill.
- Help students understand the problem . In order to solve problems, students need to define the end goal. This step is crucial to successful learning of problem-solving skills. If you succeed at helping students answer the questions “what?” and “why?”, finding the answer to “how?” will be easier.
- Take enough time . When planning a lecture/tutorial, budget enough time for: understanding the problem and defining the goal (both individually and as a class); dealing with questions from you and your students; making, finding, and fixing mistakes; and solving entire problems in a single session.
- Ask questions and make suggestions . Ask students to predict “what would happen if …” or explain why something happened. This will help them to develop analytical and deductive thinking skills. Also, ask questions and make suggestions about strategies to encourage students to reflect on the problem-solving strategies that they use.
- Link errors to misconceptions . Use errors as evidence of misconceptions, not carelessness or random guessing. Make an effort to isolate the misconception and correct it, then teach students to do this by themselves. We can all learn from mistakes.
Woods’ problem-solving model
Define the problem.
- The system . Have students identify the system under study (e.g., a metal bridge subject to certain forces) by interpreting the information provided in the problem statement. Drawing a diagram is a great way to do this.
- Known(s) and concepts . List what is known about the problem, and identify the knowledge needed to understand (and eventually) solve it.
- Unknown(s) . Once you have a list of knowns, identifying the unknown(s) becomes simpler. One unknown is generally the answer to the problem, but there may be other unknowns. Be sure that students understand what they are expected to find.
- Units and symbols . One key aspect in problem solving is teaching students how to select, interpret, and use units and symbols. Emphasize the use of units whenever applicable. Develop a habit of using appropriate units and symbols yourself at all times.
- Constraints . All problems have some stated or implied constraints. Teach students to look for the words "only", "must", "neglect", or "assume" to help identify the constraints.
- Criteria for success . Help students consider, from the beginning, what a logical type of answer would be. What characteristics will it possess? For example, a quantitative problem will require an answer in some form of numerical units (e.g., $/kg product, square cm, etc.) while an optimization problem requires an answer in the form of either a numerical maximum or minimum.
Think about it
- “Let it simmer”. Use this stage to ponder the problem. Ideally, students will develop a mental image of the problem at hand during this stage.
- Identify specific pieces of knowledge . Students need to determine by themselves the required background knowledge from illustrations, examples and problems covered in the course.
- Collect information . Encourage students to collect pertinent information such as conversion factors, constants, and tables needed to solve the problem.
Plan a solution
- Consider possible strategies . Often, the type of solution will be determined by the type of problem. Some common problem-solving strategies are: compute; simplify; use an equation; make a model, diagram, table, or chart; or work backwards.
- Choose the best strategy . Help students to choose the best strategy by reminding them again what they are required to find or calculate.
Carry out the plan
- Be patient . Most problems are not solved quickly or on the first attempt. In other cases, executing the solution may be the easiest step.
- Be persistent . If a plan does not work immediately, do not let students get discouraged. Encourage them to try a different strategy and keep trying.
Encourage students to reflect. Once a solution has been reached, students should ask themselves the following questions:
- Does the answer make sense?
- Does it fit with the criteria established in step 1?
- Did I answer the question(s)?
- What did I learn by doing this?
- Could I have done the problem another way?
If you would like support applying these tips to your own teaching, CTE staff members are here to help. View the CTE Support page to find the most relevant staff member to contact.
- Fissore, C., Marchisio, M., Roman, F., & Sacchet, M. (2021). Development of problem solving skills with Maple in higher education. In: Corless, R.M., Gerhard, J., Kotsireas, I.S. (eds) Maple in Mathematics Education and Research. MC 2020. Communications in Computer and Information Science, vol 1414. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-81698-8_15
- Foshay, R., & Kirkley, J. (1998). Principles for Teaching Problem Solving. TRO Learning Inc., Edina MN. (PDF) Principles for Teaching Problem Solving (researchgate.net)
- Hayes, J.R. (1989). The Complete Problem Solver. 2nd Edition. Hillsdale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
- Woods, D.R., Wright, J.D., Hoffman, T.W., Swartman, R.K., Doig, I.D. (1975). Teaching Problem solving Skills.
- Engineering Education. Vol 1, No. 1. p. 238. Washington, DC: The American Society for Engineering Education.
Catalog search
Teaching tip categories.
- Assessment and feedback
- Blended Learning and Educational Technologies
- Career Development
- Course Design
- Course Implementation
- Inclusive Teaching and Learning
- Learning activities
- Support for Student Learning
- Support for TAs
- Learning activities ,

COMMENTS
The findings show that (1) collaborative problem solving is an effective teaching approach to foster students’ critical thinking, with a significant overall effect size (ES = 0.82, z = 12.78,...
A new study led by a researcher from North Carolina State University offers lessons on how social studies teachers could use computational thinking and computer-based resources to analyze primary source data, such as economic information, maps or historical documents.
An integral part of social studies instruction—and a key thinking skil#151;is problem solving. As defined by Hoge, problem solving is “finding the means to a distinctly conceived end or goal,” 2 and involves various formal strategies to reach that goal.
In the present study he attempts to outline a problem- solving technique for teaching students how to use problem solving in presenting history to their pupils.
In order to achieve this aim, the Social Studies teachers' problem solving skills were examined according to the variables of gender, age, marital status, length of service, educational...
Problem solving can be difficult and sometimes tedious. Show students how to be patient and persistent, and how to follow a structured method, such as Woods’ model described below. Articulate your method as you use it so students see the connections. Teach within a specific context.
This study aimed to explore how the problem-based learning (PBL) approach affect the pre-service teachers’ learning experiences and what issues the instructor experienced when adopting PBL resources in her teaching.
This chapter sets forth the general theory of human problem Solving that has emerged from research in the past two decades, especially research that has employed the methods of computer simulation and analysis of thinking-aloud protocols.
Problem‐solving method in teaching the social sciences. R. Ray Scott. Pages 153-160 | Published online: 04 Nov 2009. Cite this article. https://doi.org/10.1080/01619562409534652. References.
Problem-based learning is a teaching method in which students’ learn through the complex and open ended problems. These problems are real world problems and are used to encourage students’ learning through principles and concept. PBL is both a teaching method and approach to the curriculum.