
Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Chapter 5: The Literature Review

5.4 The Five ‘C’s of Writing a Literature Review
To help you frame and write your literature review, think about these five C’s (Callahan, 2014):
- Cite the material you have referred to and used to help you define the research problem that you will study.
- Compare the various arguments, theories, methods, and findings expressed in the literature.For example, describe where the various researchers agree and where they disagree. Describe the similarities and dissimilarities in approaches to studying related research problems.
- Contrast the various arguments, themes, methods, approaches, and controversies apparent and/or described in the literature. For example, describe what major areas are contested, controversial and/or still in debate.
- Critique the literature. Describe which arguments you find more persuasive and explain why. Explain which approaches, findings, and methods seem most reliable, valid, appropriate, and/or most popular and why. Pay attention to the verbs you use to describe what previous researchers have stated (e.g., asserts, demonstrates, argues, clarifies, etc.).
- Connect the various research studies you reviewed. Describe how your work utilizes, draws upon, departs from, synthesizes, adds to or extends previous research studies.
Research Methods for the Social Sciences: An Introduction Copyright © 2020 by Valerie Sheppard is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
- Study Documents
- Learning Tools
Writing Guides
- Citation Generator
- Flash Card Generator
- Homework Help
- Essay Examples
- Essay Title Generator
- Essay Topic Generator
- Essay Outline Generator
- Flashcard Generator
- Plagiarism Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Conclusion Generator
- Thesis Statement Generator
- Introduction Generator
- Literature Review Generator
- Hypothesis Generator
- Human Editing Service
- Essay Hook Generator
Writing Guides / How to Write a Literature Review with Examples
How to Write a Literature Review with Examples

Introduction
Writing a literature review is a necessary and important step in academic research. You’ll likely write a lit review for your Master’s Thesis and most definitely for your Doctoral Dissertation. It’s something that lets you show your knowledge of the topic. It’s also a way to show off yourself as an expert in the area. The literature review establishes the fact that you’ve done your due diligence.
For your reader, it is a good way to communicate just what is out there in terms of existing knowledge about your research topic. The lit review allows you to summarize and assess the current state of research, by bringing together and synthesizing available studies on the matter.
Ultimately, the literature review lets you present a summary of the body of knowledge and use that to identify research gaps that you can then try to fill. It is incredibly helpful in setting up a theoretical framework and justification for your own study.
This guide will help you understand what is a literature review so that you’ll know its value and importance, as well as how to write one effectively.
What is a Literature Review?
A literature review is a synthesis and critical analysis of research relevant to a specific topic or research question that you have raised for study. It is more than a summary of sources; it is a critical evaluation that weaves together current and past literature to reveal patterns, theoretical insights, research directions, and research gaps.
The main point of a literature review is to show a well-rounded understanding of the state of the topic with regard to existing studies. It helps researchers position their work in the context of what is already known, how it fits, why it is necessary, or how it extends the current understanding.
It also serves to build a solid foundation for further research, by acting as a backdrop against which new research contributions can be made.
Importance of a Literature Review in Academic Research
A literature review is necessary as it will serve several purposes for your research:
- Understanding the Field : First, the literature review provides an overview of the existing body of knowledge, which helps researchers understand the scope of previous studies and what has already been uncovered in the field.
- Identifying Gaps : Second, when they look at existing literature, researchers can more easily identify where research is lacking or where questions remain unanswered. These gaps form the justification for new investigations.
- Critical Analysis : Third, a literature review allows the researcher to critically analyze how previous studies have been conducted, what methodologies were used, what evidence was uncovered, whether they sufficiently addressed the research problem, or what areas of research are still needed.
- Theoretical Framework : Fourth, the literature review acts as support for the development of a theoretical framework with which the research can be conducted and interpreted, as it grounds the study in ideas based existing data.
Types of Literature Reviews
There are different types of literature reviews for different purposes. Knowing when to use each type will help you shape your own review.
Narrative Review
A narrative review gives an overview of the topic by focusing on the development of theories and concepts over time. It is often descriptive and used when only a brief review is possible. Its weakness is that it lacks the systematic methodology of more structured reviews. However, narrative reviews are useful for obtaining a quick understanding of the topic and where research has focused in the past.
Systematic Review
A systematic review is more rigorous than a narrative review. It has a very methodical approach to searching for and reviewing existing literature. This type of review is characterized by its well-defined research question and a detailed, reproducible methodology that allows for the collection, critical appraisal, and synthesis of all relevant evidence. Inclusion and exclusion criteria are stated. Due to their structured and transparent nature, systematic reviews are particularly prevalent in fields like healthcare and social sciences, where evidence-based conclusions are needed for guiding practice and policy decisions.
The methodology of a systematic review begins with the precise formulation of a research question, which serves as the foundation for the entire review process.
Next, a fully detailed search strategy is developed so that all relevant studies are identified. The researcher will usually require access to multiple databases and literature types (white and grey papers, etc.). The inclusion and exclusion criteria must be explicitly defined to show which studies will be considered and which will be excluded, based on predetermined factors like study design, population, year published, language, and relevance to the research question.
Finally, the data extraction and analysis phase involves systematically gathering data from the selected studies and conducting a detailed analysis, which may include quantitative synthesis (like meta-analysis) or a qualitative assessment of the evidence. This approach allows the researcher to make sure the findings are robust, reliable, and can be replicated in future research.
Theoretical Review
A theoretical review looks at theories relevant to a particular area of study. It focuses on conceptual frameworks that have been developed to explain phenomena, analyze theories’ strengths and limitations, and propose new theoretical approaches if necessary. These reviews are helpful when the research is going to explore or challenge existing theoretical assumptions.
Integrative Review
An integrative review synthesizes existing research to generate new perspectives or frameworks. Unlike systematic reviews, integrative reviews will use both qualitative and quantitative studies and offer a broader analysis of the literature. This type is helpful for researchers who want to develop new and deeper insights and more holistic theories by integrating a wider array of research findings.
Steps to Writing a Literature Review
Writing a literature review can seem like a lot to take on. However, it is a very manageable process when you break it down into simple steps. Here’s our step-by-step guide on how to write a literature review.
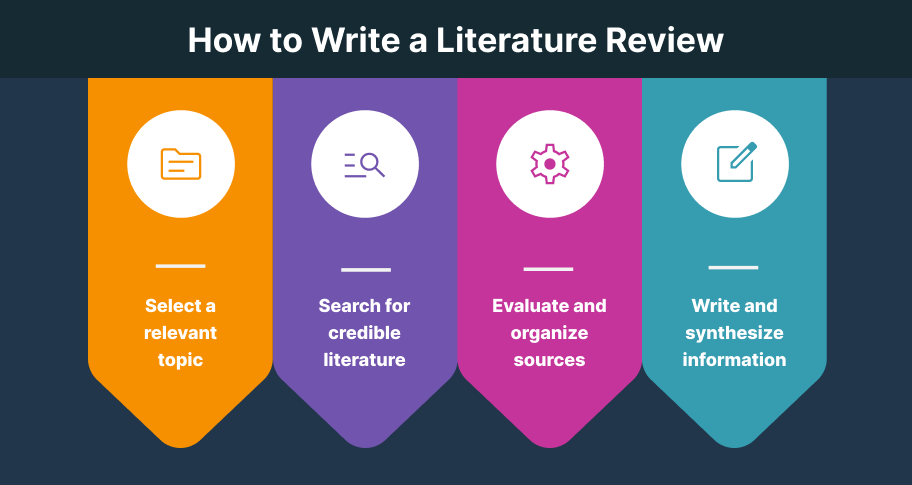
Step 1: Select a Topic
The first step in writing a literature review is to choose a topic that is relevant and interesting to your research field. It should align with your research objectives. It should be specific and focused. Don’t make it too broad—but also don’t make it so narrow that you can’t find any research on it at all. You want there to be ample literature available to review. Your research will build on that.
Tip : Focus on a specific research question that your literature review will address. Try using field relevant keywords when you search ideas in literature databases.
Step 2: Search for Relevant Literature
Once your topic is chosen, conduct a thorough search for academic sources. Use databases like PubMed, JSTOR, or Google Scholar to find peer-reviewed articles, books, and conference papers.
- Use keywords related to your topic.
- Apply filters like publication date and research area.
- Search in libraries, academic journals, and trusted repositories.
Step 3: Evaluate and Analyze the Sources
Not all sources are created equal. Critically evaluate the quality and relevance of the literature. Consider the credibility of the author, the validity of the research methods, and the significance of the findings.
Criteria for Evaluation
- Author’s credentials and publication source
- Research design and methodology
- The study’s contribution to the field
Step 4: Organize the Literature
Organize your sources based on common themes, methodologies, findings, or the chronological development of ideas. A well-structured literature review outline can help. For example, you may categorize studies based on:
- Theoretical concepts
- Methodological approaches
- Historical progression
Organization Tips
- Use thematic or chronological order to maintain a coherent review.
- Identify major trends and seminal works in the field.
Step 5: Write the Literature Review
When writing, strive for a balanced discussion. Do not just summarize; synthesize and analyze. Critique the sources. Discuss the findings in a way that brings information in from multiple studies. Point out agreements, contradictions, and unanswered questions among the various sources.
Writing Tips
- Start each section with a strong topic sentence.
- Use clear and concise language.
- Maintain an objective tone, and do not inject personal opinions.
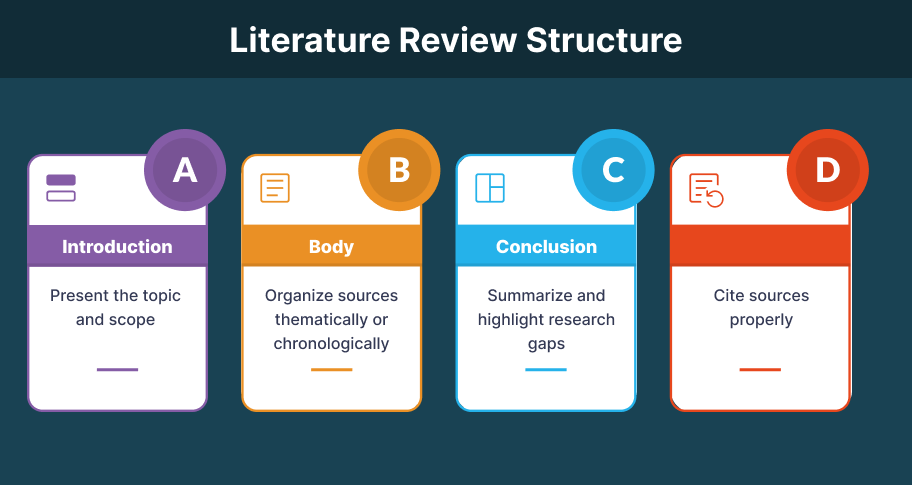
Literature Review Format
- Introduction: Present your research question and explain the purpose of the review.
- Body: Discuss studies in a structured manner.
- Conclusion: Summarize key findings and suggest future research directions.
Structure of a Literature Review
A literature review typically follows a standard structure.
Introduce your topic and explain the review’s purpose. Clearly define the scope and outline the organization of the review.
The body is where you organize your sources. This can be done thematically (grouping similar studies together) or chronologically (presenting research in order of publication). Integrate studies by discussing their contributions and limitations.
Important Reminders
- Use transition words to maintain a logical flow.
- Highlight influential works and major shifts in the research.
Summarize the insights gained from your review. Highlight research gaps and suggest directions for future study. This section also emphasizes the significance of your research within the broader academic context.
Literature Review Example
The Impact of Social Media on Adolescent Mental Health
Here is our literature review example to show you how yours can look.
Social media usage among adolescents has sparked concern among mental health professionals (Uhls et al., 2017). Given that young people today are among the most active social media users, it is important to know how these platforms impact their psychological well-being. Adolescents are at a developmental stage where identity and role confusion represent the major conflict of their age according to Erikson’s psychosocial model. Social media platforms provide a space for this dramatic conflict to play out in ways that researchers are still trying to understand (Best et al., 2014).
Numerous studies have explored the relationship between social media engagement and various mental health outcomes (Maktelow & Taylor, 2014; Przybylski et al., 2013; Uhls et al., 2017). However, the findings are often mixed, and show both beneficial and harmful effects. This literature review focuses on the positive aspects of social media, such as peer support, the negative outcomes like heightened anxiety and depression, and the limitations inherent in the methodologies used by these studies.
Positive Impacts of Social Media: Peer Support and Connection
Research on the positive implications of social media for adolescent mental health indicates that these platforms have a lot to do with how social connections are established and the extent to which peer support is obtained (Best et al., 2014). Social media can promote a sense of belonging and provide adolescents with emotional support from their peers (Best et al., 2014). These online interactions can be beneficial for adolescents who experience social isolation or struggle with face-to-face interactions (Uhls et al., 2017). The ability to connect with peers who share similar experiences or interests can give a level of emotional affirmation that traditional offline interactions sometimes lack.
Uhls et al. (2017) described the importance of online communities in providing adolescents with opportunities for social engagement and self-expression, suggesting that these platforms allow teens to seek advice, share personal experiences, and receive encouragement, which can contribute positively to their self-esteem. Adolescents experiencing challenges such as bullying or family issues often turn to social media communities for support and validation, where they feel understood and less alone. In this way, the social connectivity afforded by platforms like Facebook, Instagram, and Snapchat can enhance adolescents’ overall well-being and promote resilience.

Negative Consequences of Social Media: Anxiety, Depression, and Self-Esteem Issues
Even though social media can offer emotional benefits, extensive evidence also points to its potential to harm adolescent mental health. One of the most frequently documented adverse outcomes is increased anxiety and depression linked to excessive social media use (Twenge & Campbell, 2018). Twenge and Campbell (2018) conducted a large-scale study that revealed a correlation between high levels of social media engagement and rising rates of depressive symptoms among teenagers. The researchers argued that the constant exposure to curated and often idealized representations of others’ lives led to feelings of inadequacy, poor self-image, and heightened anxiety. Adolescents may feel pressured to project a perfect image of themselves online, which can be exhausting and detrimental to their self-esteem.
Moreover, the concept of “fear of missing out” (FOMO) has emerged as a significant factor contributing to adolescent anxiety. FOMO refers to the pervasive apprehension that others are having rewarding experiences from which one is absent (Przybylski et al., 2013). Adolescents who experience FOMO are more likely to engage in compulsive social media checking, which disrupts their daily routines, sleep patterns, and academic performance (Przybylski et al., 2013). This behavior creates a cycle of anxiety and stress, as constant comparison and the need to remain connected exacerbate feelings of inadequacy.
Another area of concern is the impact of cyberbullying, which has become increasingly common with the advent of social media. Patchin and Hinduja (2015) found that victims of online harassment are more likely to experience severe psychological distress, like suicidal ideation and self-harm. Unlike traditional bullying, cyberbullying can occur at any time and is often anonymous, making it particularly relentless and damaging. The permanence of online interactions means that harmful content can be shared and viewed repeatedly, amplifying the psychological toll on victims. As a result, the mental health repercussions of cyberbullying can be profound and long-lasting.
Methodological Limitations in Existing Research
Despite the wealth of research on the relationship between social media and adolescent mental health, several methodological limitations complicate the interpretation of findings. One significant challenge is the reliance on self-reported data, which can be subject to bias. Adolescents may not accurately recall or may choose to underreport the extent of their social media use or the severity of their psychological symptoms (Keles et al., 2020). Reliance on self-reported measures makes it difficult to establish causal relationships between social media use and mental health outcomes.
Furthermore, many studies use cross-sectional designs, which cannot determine the directionality of the relationship between social media use and mental health (Patchin & Hinduja, 2015). It remains unclear whether increased social media use leads to poorer mental health or if adolescents struggling with mental health issues are more likely to seek out social media as a coping mechanism. Longitudinal research is needed to better understand the temporal dynamics of this relationship. The heterogeneity of social media platforms also complicates research, as different platforms may have unique features that affect users differently.. For example, visual platforms like Instagram may have a different psychological impact than text-based platforms like Twitter, and few if any studies have accounted for these nuances.
Another limitation involves the cultural context of social media use. Much of the research is conducted in Western countries, primarily the United States and Europe, which may not fully capture the full experience of adolescent social media engagement. Cultural differences in social norms, values, and access to technology can influence how adolescents use social media and how it affects their well-being. Thus, a culturally diverse research approach may be necessary to draw the most applicable conclusions.
The impact of social media on adolescent mental health has positive and negative dimensions. Social media platforms offer adolescents opportunities to seek peer support and partake of social engagement. At the same time there is the risk of excessive use and negative experiences, such as cyberbullying and FOMO, which are linked to increased anxiety, depression, and self-esteem issues. Existing research reveals methodological limitations such as self-reported data, cross-sectional designs, and a lack of cultural diversity in studies. Future research should focus on longitudinal studies and culturally sensitive approaches for a fuller understanding of how social media influences adolescent mental health. Moreover, intervention strategies that teach adolescents healthy social media habits and provide resources for coping with online stressors may be needed.
Best, P., Manktelow, R., & Taylor, B. (2014). Online communication, social media and adolescent wellbeing: A systematic narrative review. Children and Youth Services Review , 41, 27-36.
Keles, B., McCrae, N., & Grealish, A. (2020). A systematic review: The influence of social media on depression, anxiety, and psychological distress in adolescents. International Journal of Adolescence and Youth , 25(1), 79-93.
Patchin, J. W., & Hinduja, S. (2015). Measuring cyberbullying: Implications for research. Aggression and Violent Behavior , 23, 69-74.
Przybylski, A. K., Murayama, K., DeHaan, C. R., & Gladwell, V. (2013). Motivational, emotional, and behavioral correlates of fear of missing out. Computers in Human Behavior , 29(4), 1841-1848.
Twenge, J. M., & Campbell, W. K. (2018). Associations between screen time and lower psychological well-being among children and adolescents: Evidence from a population-based study. Preventive Medicine Reports , 12, 271-283.
Uhls, Y. T., Ellison, N. B., & Subrahmanyam, K. (2017). Benefits and costs of social media in adolescence. Pediatrics , 140(Supplement 2), S67-S70.
APA Literature Review Format
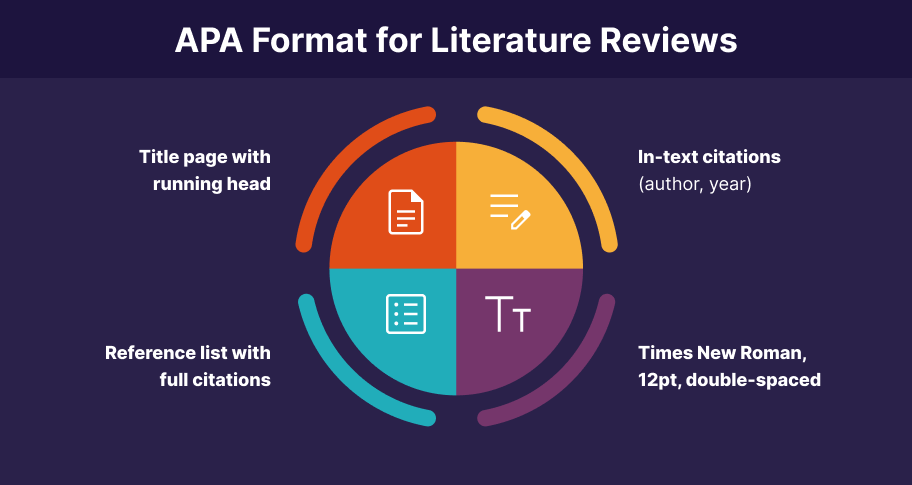
When writing in APA style, an APA literature review must follow specific guidelines for citation and formatting.
APA Formatting Guidelines
- Title Page : Include the title, author’s name, and institutional affiliation.
- Abstract : A brief summary of your review (usually 150-250 words).
- In-text Citations : Use the author-date citation method (e.g., Smith, 2020).
- Reference List : Provide full citations for all referenced works in alphabetical order.
Tips : Always adhere to the latest APA manual for formatting rules.
Literature Review Templates
A literature review template can simplify the process of organizing your review. You can find templates for APA, MLA, or Harvard formats at Purdue OWL . These templates provide a ready-to-use framework, so that your review is well-structured.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Writing a Literature Review
Even experienced researchers can fall into common pitfalls. Here’s what to avoid:
- Lack of Focus : Make sure your review addresses a clear research question.
- Poor Organization : Avoid a scattered presentation. Use an outline to maintain structure.
- Failure to Synthesize : Do not just list sources. Instead, integrate and compare studies to show meaningful conclusions.
- Outdated Sources : Always use recent and relevant research unless discussing foundational theories.

Literature Review FAQ
How long should a literature review be?
The length depends on the purpose and scope of your study. A literature review for a dissertation is typically longer than one for a research paper.
Can I include non-academic sources in a literature review?
Generally, it’s best to prioritize peer-reviewed and scholarly sources. However, in some cases, reputable non-academic sources may be used to provide additional context.
How do I structure a literature review for a dissertation?
Follow a detailed outline that includes an introduction, a well-organized body (thematic or chronological), and a concise conclusion. Discuss theories, methodologies, and identify research gaps.
Writing a literature review may seem like a tremendous challenge, but don’t give up! Use our tips and idea, maintain focus, and take it step by step. You’ll find that with a structured approach, even an inexperienced researcher can quickly gain a feel for how to write a literature review! Remember, a well-organized review can help you identify gaps that your own research can fill. Don’t skip on your lit review—dive in and use it to make your research thesis or dissertation even better.
Still need assistance with your literature review? View or download our free literature review worksheet to help get you started.
Take the first step to becoming a better academic writer.
Writing tools.
- How to write a research proposal 2021 guide
- Guide to citing in MLA
- Guide to citing in APA format
- Chicago style citation guide
- Harvard referencing and citing guide
- How to complete an informative essay outline

How to Choose the Best Essay Topics

AI Text Detection Services

Unlock Your Writing Potential with Our AI Essay Writing Assistant

The Negative Impacts of Artificial Intelligence on Tactile Learning

What is a Literature Review? How to Write It (with Examples)

A literature review is a critical analysis and synthesis of existing research on a particular topic. It provides an overview of the current state of knowledge, identifies gaps, and highlights key findings in the literature. 1 The purpose of a literature review is to situate your own research within the context of existing scholarship, demonstrating your understanding of the topic and showing how your work contributes to the ongoing conversation in the field. Learning how to write a literature review is a critical tool for successful research. Your ability to summarize and synthesize prior research pertaining to a certain topic demonstrates your grasp on the topic of study, and assists in the learning process.
Table of Contents
What is the purpose of literature review , a. habitat loss and species extinction: , b. range shifts and phenological changes: , c. ocean acidification and coral reefs: , d. adaptive strategies and conservation efforts: .
- Choose a Topic and Define the Research Question:
- Decide on the Scope of Your Review:
- Select Databases for Searches:
- Conduct Searches and Keep Track:
- Review the Literature:
- Organize and Write Your Literature Review:
- How to write a literature review faster with Paperpal?
Frequently asked questions
What is a literature review .
A well-conducted literature review demonstrates the researcher’s familiarity with the existing literature, establishes the context for their own research, and contributes to scholarly conversations on the topic. One of the purposes of a literature review is also to help researchers avoid duplicating previous work and ensure that their research is informed by and builds upon the existing body of knowledge.

A literature review serves several important purposes within academic and research contexts. Here are some key objectives and functions of a literature review: 2
1. Contextualizing the Research Problem: The literature review provides a background and context for the research problem under investigation. It helps to situate the study within the existing body of knowledge.
2. Identifying Gaps in Knowledge: By identifying gaps, contradictions, or areas requiring further research, the researcher can shape the research question and justify the significance of the study. This is crucial for ensuring that the new research contributes something novel to the field.
Find academic papers related to your research topic faster. Try Research on Paperpal
3. Understanding Theoretical and Conceptual Frameworks: Literature reviews help researchers gain an understanding of the theoretical and conceptual frameworks used in previous studies. This aids in the development of a theoretical framework for the current research.
4. Providing Methodological Insights: Another purpose of literature reviews is that it allows researchers to learn about the methodologies employed in previous studies. This can help in choosing appropriate research methods for the current study and avoiding pitfalls that others may have encountered.
5. Establishing Credibility: A well-conducted literature review demonstrates the researcher’s familiarity with existing scholarship, establishing their credibility and expertise in the field. It also helps in building a solid foundation for the new research.
6. Informing Hypotheses or Research Questions: The literature review guides the formulation of hypotheses or research questions by highlighting relevant findings and areas of uncertainty in existing literature.
Literature review example
Let’s delve deeper with a literature review example: Let’s say your literature review is about the impact of climate change on biodiversity. You might format your literature review into sections such as the effects of climate change on habitat loss and species extinction, phenological changes, and marine biodiversity. Each section would then summarize and analyze relevant studies in those areas, highlighting key findings and identifying gaps in the research. The review would conclude by emphasizing the need for further research on specific aspects of the relationship between climate change and biodiversity. The following literature review template provides a glimpse into the recommended literature review structure and content, demonstrating how research findings are organized around specific themes within a broader topic.
Literature Review on Climate Change Impacts on Biodiversity:
Climate change is a global phenomenon with far-reaching consequences, including significant impacts on biodiversity. This literature review synthesizes key findings from various studies:
Climate change-induced alterations in temperature and precipitation patterns contribute to habitat loss, affecting numerous species (Thomas et al., 2004). The review discusses how these changes increase the risk of extinction, particularly for species with specific habitat requirements.
Observations of range shifts and changes in the timing of biological events (phenology) are documented in response to changing climatic conditions (Parmesan & Yohe, 2003). These shifts affect ecosystems and may lead to mismatches between species and their resources.
The review explores the impact of climate change on marine biodiversity, emphasizing ocean acidification’s threat to coral reefs (Hoegh-Guldberg et al., 2007). Changes in pH levels negatively affect coral calcification, disrupting the delicate balance of marine ecosystems.
Recognizing the urgency of the situation, the literature review discusses various adaptive strategies adopted by species and conservation efforts aimed at mitigating the impacts of climate change on biodiversity (Hannah et al., 2007). It emphasizes the importance of interdisciplinary approaches for effective conservation planning.
Strengthen your literature review with factual insights. Try Research on Paperpal for free!
How to write a good literature review
Writing a literature review involves summarizing and synthesizing existing research on a particular topic. A good literature review format should include the following elements.
Introduction: The introduction sets the stage for your literature review, providing context and introducing the main focus of your review.
- Opening Statement: Begin with a general statement about the broader topic and its significance in the field.
- Scope and Purpose: Clearly define the scope of your literature review. Explain the specific research question or objective you aim to address.
- Organizational Framework: Briefly outline the structure of your literature review, indicating how you will categorize and discuss the existing research.
- Significance of the Study: Highlight why your literature review is important and how it contributes to the understanding of the chosen topic.
- Thesis Statement: Conclude the introduction with a concise thesis statement that outlines the main argument or perspective you will develop in the body of the literature review.
Body: The body of the literature review is where you provide a comprehensive analysis of existing literature, grouping studies based on themes, methodologies, or other relevant criteria.
- Organize by Theme or Concept: Group studies that share common themes, concepts, or methodologies. Discuss each theme or concept in detail, summarizing key findings and identifying gaps or areas of disagreement.
- Critical Analysis: Evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of each study. Discuss the methodologies used, the quality of evidence, and the overall contribution of each work to the understanding of the topic.
- Synthesis of Findings: Synthesize the information from different studies to highlight trends, patterns, or areas of consensus in the literature.
- Identification of Gaps: Discuss any gaps or limitations in the existing research and explain how your review contributes to filling these gaps.
- Transition between Sections: Provide smooth transitions between different themes or concepts to maintain the flow of your literature review.
Write and Cite as yo u go with Paperpal Research. Start now for free!
Conclusion: The conclusion of your literature review should summarize the main findings, highlight the contributions of the review, and suggest avenues for future research.
- Summary of Key Findings: Recap the main findings from the literature and restate how they contribute to your research question or objective.
- Contributions to the Field: Discuss the overall contribution of your literature review to the existing knowledge in the field.
- Implications and Applications: Explore the practical implications of the findings and suggest how they might impact future research or practice.
- Recommendations for Future Research: Identify areas that require further investigation and propose potential directions for future research in the field.
- Final Thoughts: Conclude with a final reflection on the importance of your literature review and its relevance to the broader academic community.

Conducting a literature review
Conducting a literature review is an essential step in research that involves reviewing and analyzing existing literature on a specific topic. It’s important to know how to do a literature review effectively, so here are the steps to follow: 1
Choose a Topic and Define the Research Question:
- Select a topic that is relevant to your field of study.
- Clearly define your research question or objective. Determine what specific aspect of the topic do you want to explore?
Decide on the Scope of Your Review:
- Determine the timeframe for your literature review. Are you focusing on recent developments, or do you want a historical overview?
- Consider the geographical scope. Is your review global, or are you focusing on a specific region?
- Define the inclusion and exclusion criteria. What types of sources will you include? Are there specific types of studies or publications you will exclude?
Select Databases for Searches:
- Identify relevant databases for your field. Examples include PubMed, IEEE Xplore, Scopus, Web of Science, and Google Scholar.
- Consider searching in library catalogs, institutional repositories, and specialized databases related to your topic.
Conduct Searches and Keep Track:
- Develop a systematic search strategy using keywords, Boolean operators (AND, OR, NOT), and other search techniques.
- Record and document your search strategy for transparency and replicability.
- Keep track of the articles, including publication details, abstracts, and links. Use citation management tools like EndNote, Zotero, or Mendeley to organize your references.
Review the Literature:
- Evaluate the relevance and quality of each source. Consider the methodology, sample size, and results of studies.
- Organize the literature by themes or key concepts. Identify patterns, trends, and gaps in the existing research.
- Summarize key findings and arguments from each source. Compare and contrast different perspectives.
- Identify areas where there is a consensus in the literature and where there are conflicting opinions.
- Provide critical analysis and synthesis of the literature. What are the strengths and weaknesses of existing research?
Organize and Write Your Literature Review:
- Literature review outline should be based on themes, chronological order, or methodological approaches.
- Write a clear and coherent narrative that synthesizes the information gathered.
- Use proper citations for each source and ensure consistency in your citation style (APA, MLA, Chicago, etc.).
- Conclude your literature review by summarizing key findings, identifying gaps, and suggesting areas for future research.
Whether you’re exploring a new research field or finding new angles to develop an existing topic, sifting through hundreds of papers can take more time than you have to spare. But what if you could find science-backed insights with verified citations in seconds? That’s the power of Paperpal’s new Research feature!
How to write a literature review faster with Paperpal?
Paperpal, an AI writing assistant, integrates powerful academic search capabilities within its writing platform. With the Research | Cite feature, you get 100% factual insights, with citations backed by 250M+ verified research articles, directly within your writing interface. It also allows you auto-cite references in 10,000+ styles and save relevant references in your Citation Library. By eliminating the need to switch tabs to find answers to all your research questions, Paperpal saves time and helps you stay focused on your writing.
Here’s how to use the Research feature:
- Ask a question: Get started with a new document on paperpal.com. Click on the “Research | Cite” feature and type your question in plain English. Paperpal will scour over 250 million research articles, including conference papers and preprints, to provide you with accurate insights and citations.

- Review and Save: Paperpal summarizes the information, while citing sources and listing relevant reads. You can quickly scan the results to identify relevant references and save these directly to your built-in citations library for later access.
- Cite with Confidence: Paperpal makes it easy to incorporate relevant citations and references in 10,000+ styles into your writing, ensuring your arguments are well-supported by credible sources. This translates to a polished, well-researched literature review.

The literature review sample and detailed advice on writing and conducting a review will help you produce a well-structured report. But remember that a good literature review is an ongoing process, and it may be necessary to revisit and update it as your research progresses. By combining effortless research with an easy citation process, Paperpal Research streamlines the literature review process and empowers you to write faster and with more confidence. Try Paperpal Research now and see for yourself.
A literature review is a critical and comprehensive analysis of existing literature (published and unpublished works) on a specific topic or research question and provides a synthesis of the current state of knowledge in a particular field. A well-conducted literature review is crucial for researchers to build upon existing knowledge, avoid duplication of efforts, and contribute to the advancement of their field. It also helps researchers situate their work within a broader context and facilitates the development of a sound theoretical and conceptual framework for their studies.
Literature review is a crucial component of research writing, providing a solid background for a research paper’s investigation. The aim is to keep professionals up to date by providing an understanding of ongoing developments within a specific field, including research methods, and experimental techniques used in that field, and present that knowledge in the form of a written report. Also, the depth and breadth of the literature review emphasizes the credibility of the scholar in his or her field.
Before writing a literature review, it’s essential to undertake several preparatory steps to ensure that your review is well-researched, organized, and focused. This includes choosing a topic of general interest to you and doing exploratory research on that topic, writing an annotated bibliography, and noting major points, especially those that relate to the position you have taken on the topic.
Literature reviews and academic research papers are essential components of scholarly work but serve different purposes within the academic realm. 3 A literature review aims to provide a foundation for understanding the current state of research on a particular topic, identify gaps or controversies, and lay the groundwork for future research. Therefore, it draws heavily from existing academic sources, including books, journal articles, and other scholarly publications. In contrast, an academic research paper aims to present new knowledge, contribute to the academic discourse, and advance the understanding of a specific research question. Therefore, it involves a mix of existing literature (in the introduction and literature review sections) and original data or findings obtained through research methods.
Literature reviews are essential components of academic and research papers, and various strategies can be employed to conduct them effectively. If you want to know how to write a literature review for a research paper, here are four common approaches that are often used by researchers. Chronological Review: This strategy involves organizing the literature based on the chronological order of publication. It helps to trace the development of a topic over time, showing how ideas, theories, and research have evolved. Thematic Review: Thematic reviews focus on identifying and analyzing themes or topics that cut across different studies. Instead of organizing the literature chronologically, it is grouped by key themes or concepts, allowing for a comprehensive exploration of various aspects of the topic. Methodological Review: This strategy involves organizing the literature based on the research methods employed in different studies. It helps to highlight the strengths and weaknesses of various methodologies and allows the reader to evaluate the reliability and validity of the research findings. Theoretical Review: A theoretical review examines the literature based on the theoretical frameworks used in different studies. This approach helps to identify the key theories that have been applied to the topic and assess their contributions to the understanding of the subject. It’s important to note that these strategies are not mutually exclusive, and a literature review may combine elements of more than one approach. The choice of strategy depends on the research question, the nature of the literature available, and the goals of the review. Additionally, other strategies, such as integrative reviews or systematic reviews, may be employed depending on the specific requirements of the research.
The literature review format can vary depending on the specific publication guidelines. However, there are some common elements and structures that are often followed. Here is a general guideline for the format of a literature review: Introduction: Provide an overview of the topic. Define the scope and purpose of the literature review. State the research question or objective. Body: Organize the literature by themes, concepts, or chronology. Critically analyze and evaluate each source. Discuss the strengths and weaknesses of the studies. Highlight any methodological limitations or biases. Identify patterns, connections, or contradictions in the existing research. Conclusion: Summarize the key points discussed in the literature review. Highlight the research gap. Address the research question or objective stated in the introduction. Highlight the contributions of the review and suggest directions for future research.
Both annotated bibliographies and literature reviews involve the examination of scholarly sources. While annotated bibliographies focus on individual sources with brief annotations, literature reviews provide a more in-depth, integrated, and comprehensive analysis of existing literature on a specific topic. The key differences are as follows:
References
- Denney, A. S., & Tewksbury, R. (2013). How to write a literature review. Journal of criminal justice education , 24 (2), 218-234.
- Pan, M. L. (2016). Preparing literature reviews: Qualitative and quantitative approaches . Taylor & Francis.
- Cantero, C. (2019). How to write a literature review. San José State University Writing Center .
Paperpal is a comprehensive AI writing toolkit that helps students and researchers achieve 2x the writing in half the time. It leverages 22+ years of STM experience and insights from millions of research articles to provide in-depth academic writing, language editing, and submission readiness support to help you write better, faster.
Get accurate academic translations, rewriting support, grammar checks, vocabulary suggestions, and generative AI assistance that delivers human precision at machine speed. Try for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime starting at US$19 a month to access premium features, including consistency, plagiarism, and 30+ submission readiness checks to help you succeed.
Experience the future of academic writing – Sign up to Paperpal and start writing for free!
Related Reads:
- Empirical Research: A Comprehensive Guide for Academics
- How to Write a Scientific Paper in 10 Steps
- How Long Should a Chapter Be?
- How to Use Paperpal to Generate Emails & Cover Letters?
6 Tips for Post-Doc Researchers to Take Their Career to the Next Level
Self-plagiarism in research: what it is and how to avoid it, you may also like, what is the purpose of an abstract why..., research process steps: research procedure and examples, what are citation styles which citation style to..., what are the types of literature reviews , what are research skills definition, importance, and examples , what is phd dissertation defense and how to..., abstract vs introduction: what is the difference , mla format: guidelines, template and examples , machine translation vs human translation: which is reliable..., what is academic integrity, and why is it....

- Teesside University Student & Library Services
- Subject LibGuides
Business Research Methods
- Literature Review
- Studying for your Project
- Project Outline
- Project Management
- Report Writing
- How to Reference
- Reading Lists Online
What is a literature review
“A literature review is a description of the literature relevant to a particular field or topic. It gives an overview of what has been said, who the key writers are, what are the prevailing theories and hypotheses, what questions are being asked, and what methods and methodologies are appropriate and useful" (Emerald Insight).
A literature review is not just a summary of everything you have read on the topic. It is a critical analysis of the existing research relevant to your topic, and you should show how the literature relates to your topic and identify any gaps in the area of research. Our Learning Hub has lots of useful guidance for carrying out a Literature Review .
How is it different?
It's on a much larger scale from your research for previous modules.
You may need to devise new ways of searching and managing your results.
Think about:
- Using RefWorks to manage your references
- Setting up alerts to retrieve new results for your searches
How to carry out a review
- Devise a search strategy
- Search systematically
- Read critically – i.e. deconstruct the material
- Put it all back together – reconstruct

1. Devise a search strategy
Think about the sort of research that would help your project.
1. What subject areas does you topic fall into?
2. What possible sources could you use? Think broadly, for example:
- Company reports
- Industry profiles
- Market research
- Financial reports
- Newspaper articles
- Journal articles
3. What don't you want? What are the limits? For example, geographical restrictions or time periods.
2. Search systematically
- Plan your search first, thinking about your keywords
- Use the pages on this LibGuide to identify quality resources
- Use the tutorials and advice on those pages to improve your searches
- Use the Inter Library Loans service to borrow books or to obtain copies of papers which aren't in the library
- Speak to the Business Librarians for help with your searches, or to recommend new items for library stock
- Look at the programme of Succeed @ Tees workshops , and attend any which are relevant.
3. Read critically - i.e. deconstruct your results
Read critically, argument: .
- What is the main argument?
- Is the main argument clear and logical?
- What is the evidence?
- Is the evidence valid?
- Does the evidence support the conclusions?
4. Put it all back together – reconstruct
- Group your topic areas – develop themes
- Briefly summarise key findings
- See Phrasebank for suggestions of how to phrase your sentences.
- Use the academic papers as examples of the style of academic writing as well as for their content
- Check your referencing
Succeed@Tees Workshops: Writing a Literature Review
The following workshop will help you to develop your skills in writing a literature review :
Writing a literature review
- << Previous: Project Outline
- Next: Project Management >>
- Last Updated: Nov 12, 2024 11:39 AM
- URL: https://libguides.tees.ac.uk/business_research

The Literature Review: 5. Organizing the Literature Review
- 1. Introduction
- 2. Why Do a Literature Review?
- 3. Methods for Searching the Literature
- 4. Analysing the Literature
- 5. Organizing the Literature Review
- 6. Writing the Review
1. Organizing Principles
A literature review is a piece of discursive prose, not a list describing or summarizing one piece of literature after another. It should have a single organizing principle:
- Thematic - organize around a topic or issue
- Chronological - sections for each vital time period
- Methodological - focus on the methods used by the researchers/writers
4. Selected Online Resources
- Literature Review in Education & Behavioral Sciences This is an interactive tutorial from Adelphi University Libraries on how to conduct a literature review in education and the behavioural sciences using library databases
- Writing Literature Reviews This tutorial is from the Writing section of Monash University's Language and Learning Online site
- The Literature Review: A Few Tips on Conducting It This guide is from the Health Services Writing Centre at the University of Toronto
- Learn How to Write a Review of the Literature This guide is part of the Writer's Handbook provided by the Writing Center at the University of Wisconsin-Madison
2. Structure of the Literature Review
Although your literature review will rely heavily on the sources you read for its information, you should dictate the structure of the review. It is important that the concepts are presented in an order that makes sense of the context of your research project.
There may be clear divisions on the sets of ideas you want to discuss, in which case your structure may be fairly clear. This is an ideal situation. In most cases, there will be several different possible structures for your review.
Similarly to the structure of the research report itself, the literature review consists of:
- Introduction
Introduction - profile of the study
- Define or identify the general topic to provide the context for reviewing the literature
- Outline why the topic is important
- Identify overall trends in what has been published about the topic
- Identify conflicts in theory, methodology, evidence, and conclusions
- Identify gaps in research and scholarlship
- Explain the criteria to be used in analysing and comparing the literature
- Describe the organization of the review (the sequence)
- If necessary, state why certain literature is or is not included (scope)
Body - summative, comparative, and evaluative discussion of literature reviewed
For a thematic review:
- organize the review into paragraphs that present themes and identify trends relevant to your topic
- each paragraph should deal with a different theme - you need to synthesize several of your readings into each paragraph in such a way that there is a clear connection between the sources
- don't try to list all the materials you have identified in your literature search
From each of the section summaries:
- summarize the main agreements and disagreements in the literature
- summarize the general conclusions that have been drawn
- establish where your own research fits in the context of the existing literature
5. A Final Checklist
- Have you indicated the purpose of the review?
- Have you emphasized recent developments?
- Is there a logic to the way you organized the material?
- Does the amount of detail included on an issue relate to its importance?
- Have you been sufficiently critical of design and methodological issues?
- Have you indicated when results were conflicting or inconclusive and discussed possible reasons?
- Has your summary of the current literature contributed to the reader's understanding of the problems?
3. Tips on Structure
A common error in literature reviews is for writers to present material from one author, followed by information from another, then another.... The way in which you group authors and link ideas will help avoid this problem. To group authors who draw similar conclusions, you can use linking words such as:
- additionally
When authors disagree, linking words that indicate contrast will show how you have analysed their work. Words such as:
- on the other hand
- nonetheless
will indicate to your reader how you have analysed the material. At other times, you may want to qualify an author's work (using such words as specifically, usually, or generally ) or use an example ( thus, namely, to illustrate ). In this way you ensure that you are synthesizing the material, not just describing the work already carried out in your field.
Another major problem is that literature reviews are often written as if they stand alone, without links to the rest of the paper. There needs to be a clear relationship between the literature review and the methodology to follow.
- << Previous: 4. Analysing the Literature
- Next: 6. Writing the Review >>
- Last Updated: May 9, 2024 10:36 AM
- URL: https://libguides.uwi.edu/litreviewsoe

- University of Texas Libraries
Literature Reviews
Steps in the literature review process.
- What is a literature review?
- Define your research question
- Determine inclusion and exclusion criteria
- Choose databases and search
- Review Results
- Synthesize Results
- Analyze Results
- Librarian Support
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) Tools
- You may need to some exploratory searching of the literature to get a sense of scope, to determine whether you need to narrow or broaden your focus
- Identify databases that provide the most relevant sources, and identify relevant terms (controlled vocabularies) to add to your search strategy
- Finalize your research question
- Think about relevant dates, geographies (and languages), methods, and conflicting points of view
- Conduct searches in the published literature via the identified databases
- Check to see if this topic has been covered in other discipline's databases
- Examine the citations of on-point articles for keywords, authors, and previous research (via references) and cited reference searching.
- Save your search results in a citation management tool (such as Zotero, Mendeley or EndNote)
- De-duplicate your search results
- Make sure that you've found the seminal pieces -- they have been cited many times, and their work is considered foundational
- Check with your professor or a librarian to make sure your search has been comprehensive
- Evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of individual sources and evaluate for bias, methodologies, and thoroughness
- Group your results in to an organizational structure that will support why your research needs to be done, or that provides the answer to your research question
- Develop your conclusions
- Are there gaps in the literature?
- Where has significant research taken place, and who has done it?
- Is there consensus or debate on this topic?
- Which methodological approaches work best?
- For example: Background, Current Practices, Critics and Proponents, Where/How this study will fit in
- Organize your citations and focus on your research question and pertinent studies
- Compile your bibliography
Note: The first four steps are the best points at which to contact a librarian. Your librarian can help you determine the best databases to use for your topic, assess scope, and formulate a search strategy.
Videos Tutorials about Literature Reviews
This 4.5 minute video from Academic Education Materials has a Creative Commons License and a British narrator.
Recommended Reading
- Last Updated: Oct 23, 2024 11:46 AM
- URL: https://guides.lib.utexas.edu/literaturereviews

Reviewing systematic literature reviews: ten key questions and criteria for reviewers
- Open access
- Published: 12 July 2021
- Volume 71 , pages 519–524, ( 2021 )
Cite this article
You have full access to this open access article

- Andreas Kuckertz 1 &
- Joern Block 2
10k Accesses
45 Citations
10 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
Systematic literature review articles are important for synthesizing knowledge in management and business research. However, to date, we lack clear guidelines how to review such articles. This editorial takes the perspective of the reviewer. It presents ten key questions and criteria that reviewers should ask when reviewing systematic literature reviews.
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Owing to its focus on systematic literature reviews, meta-analyses, replications, and bibliometric studies, Management Review Quarterly (MRQ) requires submissions to meet specific criteria. Several published MRQ editorials explain those criteria, namely Block and Kuckertz ( 2018 ) for replication studies, Block and Fisch ( 2020 ) for bibliometric studies, and Fisch and Block ( 2018 ) with the extension by Clark ( 2021 ) for systematic literature reviews.
We again focus on systematic literature reviews (hereafter SLRs) in this editorial but shift the perspective. Whereas previous editorials addressed (potential) authors of MRQ submissions, this one addresses MRQ’s reviewers. Reviewers for the journal are often selected for their topical expertise and publication record, allowing them to provide the highest quality feedback to authors of SLRs. However, being an experienced researcher in a particular topical domain does not necessarily come with methodological expertise in SLRs. Hence, in this editorial, we highlight ten key questions and criteria that reviewers should consider when evaluating SLRs. Of course, knowledge of these criteria might be helpful for authors as well, as it will allow them to address issues that might arise during the review process proactively and consequently avoid them.
We consider SLRs (sometimes also called structured literature reviews) to be a variant of literature reviews, primarily aiming at increasing the transparency of the literature selection process underlying the review. Doing so helps to minimize subjectivity concerning which studies are included in the review and reducing what could be called the sampling error of unsystematic literature reviews. The term systematic thus refers in particular to a structured or systematic literature identification and selection. For reviewers of such SLRs, the following ten questions are crucial.
1. Does the SLR have an explicit and well-explained research question that is also well-justified?
Every study needs a research question, and that applies to SLRs too. That research question might be broad and topic-based (e.g., What is state-of-the-art in the respective field or literature stream? What do we know about a particular phenomenon?), but could also be more specific (e.g., What is the empirical evidence regarding a specific research question?). Opportunities to frame and justify research questions are endless, but, in all cases, authors should state a clear research question, and reviewers need to check whether the submission provides one. In addition to establishing an explicit research question, authors must justify the choice clearly and convey the potential value of their answer to the research question. It is then the task of the reviewers to assess whether they support that argumentation. In our own experience as reviewers and editors of MRQ , many initial submissions of SLRs lack sufficient justification. However, a literature review is not an end in itself. It needs to be justified like any other academic study. Possible justifications could be phenomenon-based, theory-driven, or guided by practice.
2. Does the SLR acknowledge previous literature reviews (including meta-analyses)?
Particularly in subject areas with a long history of research, it is to be expected that previous literature reviews exist. Every SLR should acknowledge these previous contributions (and in particular similar SLRs), describe their character (e.g., descriptive, bibliographic, state-of-the-art, or narrative), and explicate why another attempt to synthesize the body of knowledge is necessary. Reasons can be manifold—outdated prior literature reviews might need to be updated, including a different type of publication might potentially allow for new or more complete perspectives (e.g., gray literature vs. journal publications), or perhaps researchers are attempting to answer a hitherto unanswered research question. Reviewers should also check whether the SLR acknowledges published meta-analyses as these share many of the goals of an SLR.
3. Is the research question correctly translated into a (relevant) set of search terms?
An SLR refers to databases to identify relevant studies and queries them with an appropriate set of search terms. Reviewers must check whether the SLR states its search term transparently, accurately, and ascertain if the search term can guarantee to return the relevant literature to answer the research question. Formulating search terms is essentially the operationalization of the research question, and the success of any SLR stands or falls on it. Denyer and Tranfield ( 2009 ) suggest translating a research question with the help of the context-interventions-mechanisms-outcome (CIMO) framework into a set of search terms. Adopting a CIMO framework or a similar alternative also helps to devise the research questions that an SLR could reasonably be expected to answer. The set of search terms should be carefully thought out and not be so narrow that it misses relevant studies but also not so broad that the identified studies do not match the research questions. Reviewers should also check whether the researchers followed an iterative process where the search terms are adapted based on the search process results.
4. Is the database selection explained and based on a clear rationale?
Different databases of academic literature return different results. Therefore, it is good practice to employ more than one database in the literature search. Triangulation helps compensate for particular disadvantages that naturally limit the output of each individual database. At a minimum, a paper can address triangulation simply by adding more databases (e.g., the more databases, the better); an exemplary SLR will provide tangible reasons for including (or excluding) particular databases. Gusenbauer ( 2019 ) and Gusenbauer and Haddaway ( 2020 ) evaluate numerous available databases and provide a good starting point for justifying database selection.
5. Is the literature selection up-to-date?
Authors often submit outdated SLRs to MRQ . Updating a review before the submission is essential, and not something authors should postpone until the later rounds of the review process. Submitting an outdated literature review is usually a reason for a desk rejection, but reviewers should also check that an SLR is not outdated and remains topical throughout the process of revising and resubmitting.
6. Does the SLR clearly express its inclusion and exclusion criteria?
Quite often, a simple database query returns hundreds (or perhaps thousands) of studies with the potential for inclusion in the review. An SLR will usually report the search funnel and the authors’ inclusion and exclusion criteria applied to narrow down a search. Reviewers must check whether those criteria are expressly stated in the paper and examine whether they serve their purpose. The selected inclusion and exclusion criteria depend on the aims and research questions of the SLR: They might be justified in terms of content, method, or publication quality. We recommend using a flow chart to graphically illustrate the selection process. That flow chart should include the initial number of identified studies and the number of studies eliminated at each stage of the literature search process. Further guidance on how to ensure the selection of a final sample is transparent can be found in "Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA)" (Liberati , 2009 ; Moher, 2009 ).
7. Does the SLR include one or more overview tables characterizing each study in the sample?
Another good practice is to include a table summarizing each study from the sample. The table may be incorporated within the paper or, in the case of larger samples, presented as an (online) appendix. Such tables help readers quickly orient themselves in a particular research stream and understand the individual contribution of particular studies they might be interested in. Reviewers will need to check the quality of the information presented in such tables or appendices and whether the authors summarize the right information describing a single study. Standard columns of the table should include a reference to the individual study, a literal quote (or paraphrase) of its research question, the epistemological character of the study (e.g., conceptual, qualitative, quantitative, or mixed), the specific methodological design employed in the study (in the case of empirical studies), and the main result(s), although those columns might vary to reflect the purpose of the SLR. Depending on the number of studies included in the review, splitting this table into several sub-tables based on sub-topics is recommended. It is also possible to deposit a file in a public (data) repository (for instance, that operated by the Open Science Foundation). A repository offers authors greater flexibility regarding the number of columns and lines to be included, and reviewers can point authors to appropriate repositories.
8. Does the SLR employ a particular aggregation and presentation method?
It is essential to understand that an SLR is primarily a method to arrive at a suitable sample of studies to be reviewed, but how the selected literature is then analyzed, synthesized, and presented is a decision for individual authors who can choose from among a plethora of methods (see Booth et al. ( 2012 ) for an extensive overview of options). Far too often, this is the step where authors abandon methodological considerations. Nevertheless, there are many methods available to ensure this step is conducted in a rigorous and method-led manner, and SLRs employing such methods are more convincing. Such methods might range from a thematic analysis and narrative synthesis through meta-ethnographies to bibliometric approaches (e.g., historiographic mapping). Published MRQ papers illustrate the breadth of available methods. Here, the reviewer’s task is to check whether the chosen method was correctly executed and help the authors reach for a more profound and potentially more fruitful analysis. However, the use of particular aggregation and presentation methods should be fully explained and should align with the research question(s) of the SLR.
9. Does the SLR contribute beyond merely offering an analysis of the status quo of the literature?
Synthesis builds on analysis and may come in different forms. Some authors construct integrative models, provide thematic clusters based on bibliometric analyses, or offer creative answers to the research question. Synthesis is an essential step and distinguishes a technically correct but uninformative literature review from an informative one. Literature reviews tend to be among the most often-cited of journal articles, but will only be so if they contribute something unique and provide guidance to the community on what has been done and what is yet to be done.
10. Does the SLR provide implications for (future) research and practice?
A high-quality synthesis provides a basis for assessing the status quo and can set an agenda for future research. For practitioners, an SLR offers a convenient way to understand what is known or not yet known about a particular phenomenon or problem, and hence, the SLR should make evidence-based suggestions for managerial practice. Authors should not leave this task to readers but proactively outline specific (practice) implications that might speak to consumers, employees, managers, investors, firm owners, policymakers, and any other groups interested in management research. Similarly, for a research audience, every well-executed and well-crafted SLR has the potential to set the agenda for further research. Admittedly, that demands some creativity, as the easy solution to simply point the reader to under-researched areas invites encouraging studies based on the infamous has-not-been-done-before argument. The onus is on the researcher to identify and justify important avenues for future research, and reviewers should carefully consider whether they support those choices or should highlight alternatives they consider more promising. Authors should include the part of the SLR reflecting future research opportunities in an initial submission, but be aware that the suggestions will also potentially be subject to considerable change as a result of the review process. The length and nature of the future research section also depend on the goal of the SLR. Broader, state-of-the-art SLRs should provide a broad future research agenda, whereas reviews with a narrow research question should have a more focused and precise future research section.
SLRs have an important role in the accumulation of knowledge in management and business research; however, they can only fulfill that role if they are of high quality. This editorial, through its ten questions and criteria for reviewing SLRs, aims to signpost to reviewers the key issues relevant to evaluating the quality of an SLR. We also hope that it will enhance the quality of SLRs submitted to MRQ and other outlets in management research.
Block JH, Fisch C (2020) Eight tips and questions for your bibliographic study in business and management research. Manag Rev Q 70(3):307–312. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11301-020-00188-4
Article Google Scholar
Block J, Kuckertz A (2018) Seven principles of effective replication studies: strengthening the evidence base of management research. Manag Rev Q 68(4):355–359. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11301-018-0149-3
Booth A, Papaioannou D, Sutton A (2012) Systematic Approaches to a Successful Literature Review. Sage Publications, London
Google Scholar
Clark WR et al (2021) Extending Fisch and Block’s (2018) tips for a systematic review in management and business literature. Manag Rev Q 71:215–231. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11301-020-00184-8
Denyer D, Tranfield D (2009) Producing a Systematic Review. In: Buchanan DA, Bryman A (eds) The Sage Handbook of Organizational Research Methods. Sage Publications, Thousand Oaks, CA, pp 671–689
Fisch C, Block J (2018) Six tips for your (systematic) literature review in business and management research. Manag Rev Q 68(2):103–106. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11301-018-0142-x
Gusenbauer M (2019) Google Scholar to overshadow them all? Comparing the sizes of 12 academic search engines and bibliographic databases. Scientometrics 118:177–214. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-018-2958-5
Gusenbauer M, Haddaway NR (2020) Which academic search systems are suitable for systematic reviews or meta-analyses? Evaluating retrieval qualities of Google Scholar, PubMed, and 26 other resources. Res Synth Methods 11(2):181–217. https://doi.org/10.1002/jrsm.1378
Liberati A et al (2009) The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate health care interventions: explanation and elaboration. PLoS Med. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1000100
Moher D et al (2009) Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. PLoS Med 6(7):e1000097. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1000097
Download references
Acknowledgements
We are indebted to Christian Fisch, Mirko Hirschmann, Holger Steinmetz and Rolf Wilmes for sharing their perspectives on the challenges of reviewing SLRs.
Open Access funding enabled and organized by Projekt DEAL.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Entrepreneurship Research Group, University of Hohenheim, Stuttgart, Germany
Andreas Kuckertz
University of Trier, Trier, Germany
Joern Block
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Joern Block .
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest.
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Kuckertz, A., Block, J. Reviewing systematic literature reviews: ten key questions and criteria for reviewers. Manag Rev Q 71 , 519–524 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11301-021-00228-7
Download citation
Accepted : 22 June 2021
Published : 12 July 2021
Issue Date : July 2021
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s11301-021-00228-7
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
JEL Classification
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research

Work With Us
Private Coaching
Done-For-You
Short Courses
Client Reviews
Free Resources
How To Write An A-Grade Literature Review
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Expert Reviewed By: Dr. Eunice Rautenbach | October 2019

Q uality research is about building onto the existing work of others , “standing on the shoulders of giants”, as Newton put it. The literature review chapter of your dissertation, thesis or research project is where you synthesise this prior work and lay the theoretical foundation for your own research.
Long story short, this chapter is a pretty big deal, which is why you want to make sure you get it right . In this post, I’ll show you exactly how to write a literature review in three straightforward steps, so you can conquer this vital chapter (the smart way).
Overview: The Literature Review Process
- Understanding the “ why “
- Finding the relevant literature
- Cataloguing and synthesising the information
- Outlining & writing up your literature review
- Example of a literature review
But first, the “why”…
Before we unpack how to write the literature review chapter, we’ve got to look at the why . To put it bluntly, if you don’t understand the function and purpose of the literature review process, there’s no way you can pull it off well. So, what exactly is the purpose of the literature review?
Well, there are (at least) four core functions:
- For you to gain an understanding (and demonstrate this understanding) of where the research is at currently, what the key arguments and disagreements are.
- For you to identify the gap(s) in the literature and then use this as justification for your own research topic.
- To help you build a conceptual framework for empirical testing (if applicable to your research topic).
- To inform your methodological choices and help you source tried and tested questionnaires (for interviews ) and measurement instruments (for surveys ).
Most students understand the first point but don’t give any thought to the rest. To get the most from the literature review process, you must keep all four points front of mind as you review the literature (more on this shortly), or you’ll land up with a wonky foundation.
Okay – with the why out the way, let’s move on to the how . As mentioned above, writing your literature review is a process, which I’ll break down into three steps:
- Finding the most suitable literature
- Understanding , distilling and organising the literature
- Planning and writing up your literature review chapter
Importantly, you must complete steps one and two before you start writing up your chapter. I know it’s very tempting, but don’t try to kill two birds with one stone and write as you read. You’ll invariably end up wasting huge amounts of time re-writing and re-shaping, or you’ll just land up with a disjointed, hard-to-digest mess . Instead, you need to read first and distil the information, then plan and execute the writing.

Step 1: Find the relevant literature
Naturally, the first step in the literature review journey is to hunt down the existing research that’s relevant to your topic. While you probably already have a decent base of this from your research proposal , you need to expand on this substantially in the dissertation or thesis itself.
Essentially, you need to be looking for any existing literature that potentially helps you answer your research question (or develop it, if that’s not yet pinned down). There are numerous ways to find relevant literature, but I’ll cover my top four tactics here. I’d suggest combining all four methods to ensure that nothing slips past you:
Method 1 – Google Scholar Scrubbing
Google’s academic search engine, Google Scholar , is a great starting point as it provides a good high-level view of the relevant journal articles for whatever keyword you throw at it. Most valuably, it tells you how many times each article has been cited, which gives you an idea of how credible (or at least, popular) it is. Some articles will be free to access, while others will require an account, which brings us to the next method.
Method 2 – University Database Scrounging
Generally, universities provide students with access to an online library, which provides access to many (but not all) of the major journals.
So, if you find an article using Google Scholar that requires paid access (which is quite likely), search for that article in your university’s database – if it’s listed there, you’ll have access. Note that, generally, the search engine capabilities of these databases are poor, so make sure you search for the exact article name, or you might not find it.
Method 3 – Journal Article Snowballing
At the end of every academic journal article, you’ll find a list of references. As with any academic writing, these references are the building blocks of the article, so if the article is relevant to your topic, there’s a good chance a portion of the referenced works will be too. Do a quick scan of the titles and see what seems relevant, then search for the relevant ones in your university’s database.
Method 4 – Dissertation Scavenging
Similar to Method 3 above, you can leverage other students’ dissertations. All you have to do is skim through literature review chapters of existing dissertations related to your topic and you’ll find a gold mine of potential literature. Usually, your university will provide you with access to previous students’ dissertations, but you can also find a much larger selection in the following databases:
- Open Access Theses & Dissertations
- Stanford SearchWorks
Keep in mind that dissertations and theses are not as academically sound as published, peer-reviewed journal articles (because they’re written by students, not professionals), so be sure to check the credibility of any sources you find using this method. You can do this by assessing the citation count of any given article in Google Scholar. If you need help with assessing the credibility of any article, or with finding relevant research in general, you can chat with one of our Research Specialists .
Alright – with a good base of literature firmly under your belt, it’s time to move onto the next step.
Need a helping hand?
Step 2: Log, catalogue and synthesise
Once you’ve built a little treasure trove of articles, it’s time to get reading and start digesting the information – what does it all mean?
While I present steps one and two (hunting and digesting) as sequential, in reality, it’s more of a back-and-forth tango – you’ll read a little , then have an idea, spot a new citation, or a new potential variable, and then go back to searching for articles. This is perfectly natural – through the reading process, your thoughts will develop , new avenues might crop up, and directional adjustments might arise. This is, after all, one of the main purposes of the literature review process (i.e. to familiarise yourself with the current state of research in your field).
As you’re working through your treasure chest, it’s essential that you simultaneously start organising the information. There are three aspects to this:
- Logging reference information
- Building an organised catalogue
- Distilling and synthesising the information
I’ll discuss each of these below:
2.1 – Log the reference information
As you read each article, you should add it to your reference management software. I usually recommend Mendeley for this purpose (see the Mendeley 101 video below), but you can use whichever software you’re comfortable with. Most importantly, make sure you load EVERY article you read into your reference manager, even if it doesn’t seem very relevant at the time.
2.2 – Build an organised catalogue
In the beginning, you might feel confident that you can remember who said what, where, and what their main arguments were. Trust me, you won’t. If you do a thorough review of the relevant literature (as you must!), you’re going to read many, many articles, and it’s simply impossible to remember who said what, when, and in what context . Also, without the bird’s eye view that a catalogue provides, you’ll miss connections between various articles, and have no view of how the research developed over time. Simply put, it’s essential to build your own catalogue of the literature.
I would suggest using Excel to build your catalogue, as it allows you to run filters, colour code and sort – all very useful when your list grows large (which it will). How you lay your spreadsheet out is up to you, but I’d suggest you have the following columns (at minimum):
- Author, date, title – Start with three columns containing this core information. This will make it easy for you to search for titles with certain words, order research by date, or group by author.
- Categories or keywords – You can either create multiple columns, one for each category/theme and then tick the relevant categories, or you can have one column with keywords.
- Key arguments/points – Use this column to succinctly convey the essence of the article, the key arguments and implications thereof for your research.
- Context – Note the socioeconomic context in which the research was undertaken. For example, US-based, respondents aged 25-35, lower- income, etc. This will be useful for making an argument about gaps in the research.
- Methodology – Note which methodology was used and why. Also, note any issues you feel arise due to the methodology. Again, you can use this to make an argument about gaps in the research.
- Quotations – Note down any quoteworthy lines you feel might be useful later.
- Notes – Make notes about anything not already covered. For example, linkages to or disagreements with other theories, questions raised but unanswered, shortcomings or limitations, and so forth.
If you’d like, you can try out our free catalog template here (see screenshot below).

2.3 – Digest and synthesise
Most importantly, as you work through the literature and build your catalogue, you need to synthesise all the information in your own mind – how does it all fit together? Look for links between the various articles and try to develop a bigger picture view of the state of the research. Some important questions to ask yourself are:
- What answers does the existing research provide to my own research questions ?
- Which points do the researchers agree (and disagree) on?
- How has the research developed over time?
- Where do the gaps in the current research lie?
To help you develop a big-picture view and synthesise all the information, you might find mind mapping software such as Freemind useful. Alternatively, if you’re a fan of physical note-taking, investing in a large whiteboard might work for you.

Step 3: Outline and write it up!
Once you’re satisfied that you have digested and distilled all the relevant literature in your mind, it’s time to put pen to paper (or rather, fingers to keyboard). There are two steps here – outlining and writing:
3.1 – Draw up your outline
Having spent so much time reading, it might be tempting to just start writing up without a clear structure in mind. However, it’s critically important to decide on your structure and develop a detailed outline before you write anything. Your literature review chapter needs to present a clear, logical and an easy to follow narrative – and that requires some planning. Don’t try to wing it!
Naturally, you won’t always follow the plan to the letter, but without a detailed outline, you’re more than likely going to end up with a disjointed pile of waffle , and then you’re going to spend a far greater amount of time re-writing, hacking and patching. The adage, “measure twice, cut once” is very suitable here.
In terms of structure, the first decision you’ll have to make is whether you’ll lay out your review thematically (into themes) or chronologically (by date/period). The right choice depends on your topic, research objectives and research questions, which we discuss in this article .
Once that’s decided, you need to draw up an outline of your entire chapter in bullet point format. Try to get as detailed as possible, so that you know exactly what you’ll cover where, how each section will connect to the next, and how your entire argument will develop throughout the chapter. Also, at this stage, it’s a good idea to allocate rough word count limits for each section, so that you can identify word count problems before you’ve spent weeks or months writing!
PS – check out our free literature review chapter template…
3.2 – Get writing
With a detailed outline at your side, it’s time to start writing up (finally!). At this stage, it’s common to feel a bit of writer’s block and find yourself procrastinating under the pressure of finally having to put something on paper. To help with this, remember that the objective of the first draft is not perfection – it’s simply to get your thoughts out of your head and onto paper, after which you can refine them. The structure might change a little, the word count allocations might shift and shuffle, and you might add or remove a section – that’s all okay. Don’t worry about all this on your first draft – just get your thoughts down on paper.

Once you’ve got a full first draft (however rough it may be), step away from it for a day or two (longer if you can) and then come back at it with fresh eyes. Pay particular attention to the flow and narrative – does it fall fit together and flow from one section to another smoothly? Now’s the time to try to improve the linkage from each section to the next, tighten up the writing to be more concise, trim down word count and sand it down into a more digestible read.
Once you’ve done that, give your writing to a friend or colleague who is not a subject matter expert and ask them if they understand the overall discussion. The best way to assess this is to ask them to explain the chapter back to you. This technique will give you a strong indication of which points were clearly communicated and which weren’t. If you’re working with Grad Coach, this is a good time to have your Research Specialist review your chapter.
Finally, tighten it up and send it off to your supervisor for comment. Some might argue that you should be sending your work to your supervisor sooner than this (indeed your university might formally require this), but in my experience, supervisors are extremely short on time (and often patience), so, the more refined your chapter is, the less time they’ll waste on addressing basic issues (which you know about already) and the more time they’ll spend on valuable feedback that will increase your mark-earning potential.
Literature Review Example
In the video below, we unpack an actual literature review so that you can see how all the core components come together in reality.
Let’s Recap
In this post, we’ve covered how to research and write up a high-quality literature review chapter. Let’s do a quick recap of the key takeaways:
- It is essential to understand the WHY of the literature review before you read or write anything. Make sure you understand the 4 core functions of the process.
- The first step is to hunt down the relevant literature . You can do this using Google Scholar, your university database, the snowballing technique and by reviewing other dissertations and theses.
- Next, you need to log all the articles in your reference manager , build your own catalogue of literature and synthesise all the research.
- Following that, you need to develop a detailed outline of your entire chapter – the more detail the better. Don’t start writing without a clear outline (on paper, not in your head!)
- Write up your first draft in rough form – don’t aim for perfection. Remember, done beats perfect.
- Refine your second draft and get a layman’s perspective on it . Then tighten it up and submit it to your supervisor.

Learn More About Lit Review:

How To Choose A Tutor For Your Dissertation
Hiring the right tutor for your dissertation or thesis can make the difference between passing and failing. Here’s what you need to consider.

5 Signs You Need A Dissertation Helper
Discover the 5 signs that suggest you need a dissertation helper to get unstuck, finish your degree and get your life back.

Writing A Literature Review: 4 Time-Saving Hacks
🎙️ PODCAST: Ace The Literature Review 4 Time-Saving Tips To Fast-Track Your Literature...

Research Question 101: Everything You Need To Know
Learn what a research question is, how it’s different from a research aim or objective, and how to write a high-quality research question.

Research Question Examples: The Perfect Starting Point
See what quality research questions look like across multiple topic areas, including psychology, business, computer science and more.
📄 FREE TEMPLATES
Research Topic Ideation
Proposal Writing
Literature Review
Methodology & Analysis
Academic Writing
Referencing & Citing
Apps, Tools & Tricks
The Grad Coach Podcast
38 Comments
Thank you very much. This page is an eye opener and easy to comprehend.
This is awesome!
I wish I come across GradCoach earlier enough.
But all the same I’ll make use of this opportunity to the fullest.
Thank you for this good job.
Keep it up!
You’re welcome, Yinka. Thank you for the kind words. All the best writing your literature review.
Thank you for a very useful literature review session. Although I am doing most of the steps…it being my first masters an Mphil is a self study and one not sure you are on the right track. I have an amazing supervisor but one also knows they are super busy. So not wanting to bother on the minutae. Thank you.
You’re most welcome, Renee. Good luck with your literature review 🙂
This has been really helpful. Will make full use of it. 🙂
Thank you Gradcoach.
Really agreed. Admirable effort
thank you for this beautiful well explained recap.
Thank you so much for your guide of video and other instructions for the dissertation writing.
It is instrumental. It encouraged me to write a dissertation now.
Thank you the video was great – from someone that knows nothing thankyou
an amazing and very constructive way of presetting a topic, very useful, thanks for the effort,
It is timely
It is very good video of guidance for writing a research proposal and a dissertation. Since I have been watching and reading instructions, I have started my research proposal to write. I appreciate to Mr Jansen hugely.
I learn a lot from your videos. Very comprehensive and detailed.
Thank you for sharing your knowledge. As a research student, you learn better with your learning tips in research
I was really stuck in reading and gathering information but after watching these things are cleared thanks, it is so helpful.
Really helpful, Thank you for the effort in showing such information
This is super helpful thank you very much.
Thank you for this whole literature writing review.You have simplified the process.
I’m so glad I found GradCoach. Excellent information, Clear explanation, and Easy to follow, Many thanks Derek!
You’re welcome, Maithe. Good luck writing your literature review 🙂
Thank you Coach, you have greatly enriched and improved my knowledge
Great piece, so enriching and it is going to help me a great lot in my project and thesis, thanks so much
This is THE BEST site for ANYONE doing a masters or doctorate! Thank you for the sound advice and templates. You rock!
Thanks, Stephanie 🙂
This is mind blowing, the detailed explanation and simplicity is perfect.
I am doing two papers on my final year thesis, and I must stay I feel very confident to face both headlong after reading this article.
thank you so much.
if anyone is to get a paper done on time and in the best way possible, GRADCOACH is certainly the go to area!
This is very good video which is well explained with detailed explanation
Thank you excellent piece of work and great mentoring
Thanks, it was useful
Thank you very much. the video and the information were very helpful.
Good morning scholar. I’m delighted coming to know you even before the commencement of my dissertation which hopefully is expected in not more than six months from now. I would love to engage my study under your guidance from the beginning to the end. I love to know how to do good job
Thank you so much Derek for such useful information on writing up a good literature review. I am at a stage where I need to start writing my one. My proposal was accepted late last year but I honestly did not know where to start
Like the name of your YouTube implies you are GRAD (great,resource person, about dissertation). In short you are smart enough in coaching research work.
This is a very well thought out webpage. Very informative and a great read.
Very timely.
I appreciate.
Very comprehensive and eye opener for me as beginner in postgraduate study. Well explained and easy to understand. Appreciate and good reference in guiding me in my research journey. Thank you
Thank you. I requested to download the free literature review template, however, your website wouldn’t allow me to complete the request or complete a download. May I request that you email me the free template? Thank you.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Submit Comment
- Print Friendly

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Critique the literature. Describe which arguments you find more persuasive and explain why. Explain which approaches, findings, and methods seem most reliable, valid, appropriate, and/or most popular and why. Pay attention to the verbs you use to describe what previous researchers have stated (e.g., asserts, demonstrates, argues, clarifies, etc.).
Examples of literature reviews. Step 1 – Search for relevant literature. Step 2 – Evaluate and select sources. Step 3 – Identify themes, debates, and gaps. Step 4 – Outline your literature review’s structure. Step 5 – Write your literature review.
A literature review is a synthesis and critical analysis of research relevant to a specific topic or research question that you have raised for study. It is more than a summary of sources; it is a critical evaluation that weaves together current and past literature to reveal patterns, theoretical insights, research directions, and research gaps.
It can also help to provide an overview of areas in which the research is disparate and interdisciplinary. In addition, a literature review is an excellent way of synthesizing research findings to show evidence on a meta-level and to uncover areas in which more research is needed, which is a critical component of creating theoretical frameworks and building conceptual models.
A literature review is a critical analysis and synthesis of existing research on a particular topic. It provides an overview of the current state of knowledge, identifies gaps, and highlights key findings in the literature. 1 The purpose of a literature review is to situate your own research within the context of existing scholarship ...
A literature review is not just a summary of everything you have read on the topic. It is a critical analysis of the existing research relevant to your topic, and you should show how the literature relates to your topic and identify any gaps in the area of research. Our Learning Hub has lots of useful guidance for carrying out a Literature Review.
Identify gaps in research and scholarlship; Explain the criteria to be used in analysing and comparing the literature; Describe the organization of the review (the sequence) If necessary, state why certain literature is or is not included (scope) Body - summative, comparative, and evaluative discussion of literature reviewed. For a thematic review:
The Literature Review by Diana Ridley The Literature Review is a step-by-step guide to conducting a literature search and writing up the literature review chapter in Masters dissertations and in Ph.D. and professional doctorate theses. The author provides strategies for reading, conducting searches, organizing information and writing the review.
Systematic literature review articles are important for synthesizing knowledge in management and business research. However, to date, we lack clear guidelines how to review such articles. This editorial takes the perspective of the reviewer. It presents ten key questions and criteria that reviewers should ask when reviewing systematic literature reviews.
As mentioned above, writing your literature review is a process, which I’ll break down into three steps: Finding the most suitable literature. Understanding, distilling and organising the literature. Planning and writing up your literature review chapter. Importantly, you must complete steps one and two before you start writing up your chapter.