

The Ultimate Guide to Qualitative Research - Part 1: The Basics

- Introduction and overview
- What is qualitative research?
- What is qualitative data?
- Examples of qualitative data
- Qualitative vs. quantitative research
- Mixed methods
- Qualitative research preparation
- Theoretical perspective
- Theoretical framework
- Literature reviews
Research question
- Conceptual framework
- Conceptual vs. theoretical framework
Data collection
- Qualitative research methods
- Focus groups
- Observational research
What is a case study?
Applications for case study research, what is a good case study, process of case study design, benefits and limitations of case studies.
- Ethnographical research
- Ethical considerations
- Confidentiality and privacy
- Power dynamics
- Reflexivity
Case studies
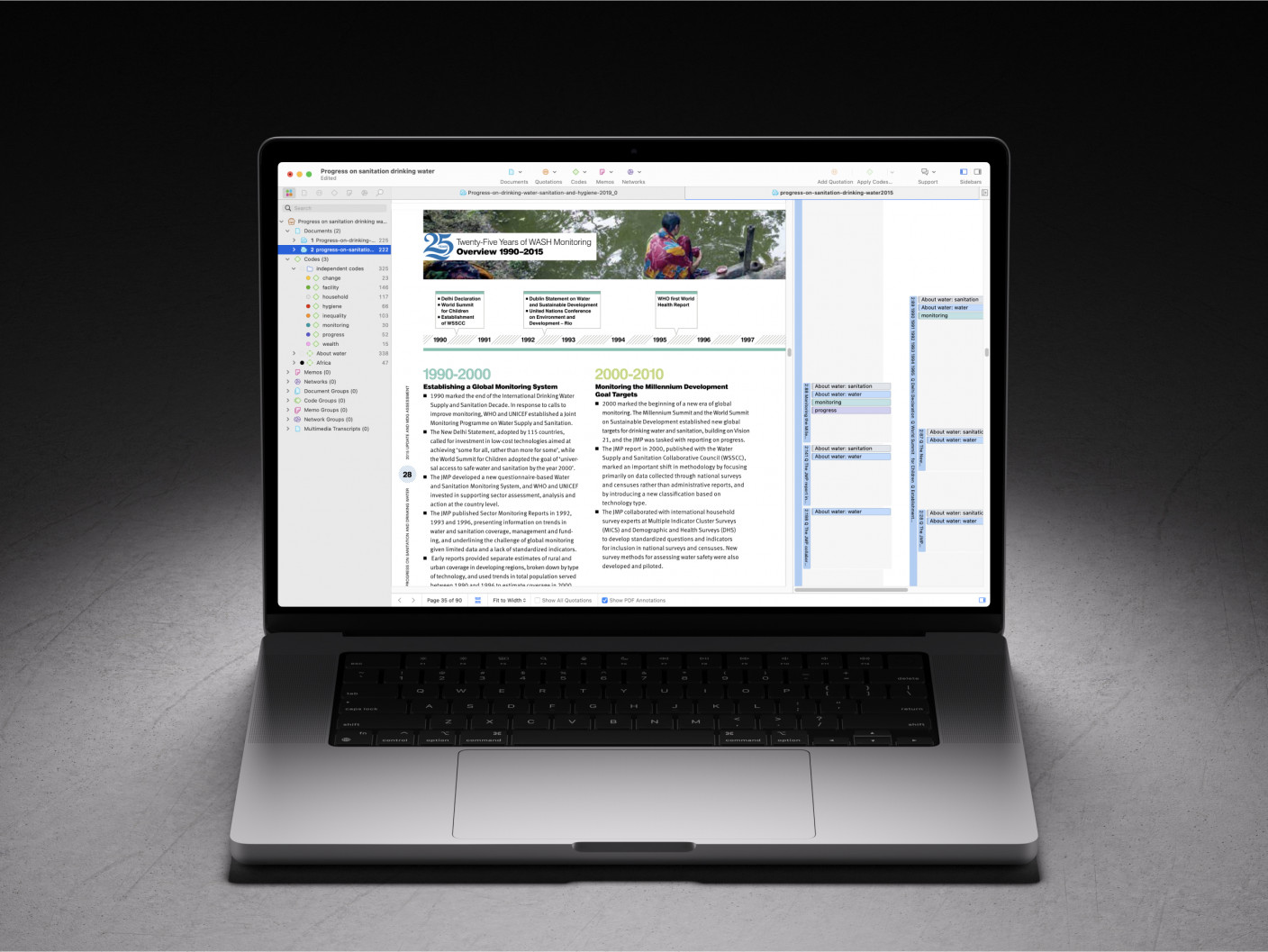
Case studies are essential to qualitative research , offering a lens through which researchers can investigate complex phenomena within their real-life contexts. This chapter explores the concept, purpose, applications, examples, and types of case studies and provides guidance on how to conduct case study research effectively.

Whereas quantitative methods look at phenomena at scale, case study research looks at a concept or phenomenon in considerable detail. While analyzing a single case can help understand one perspective regarding the object of research inquiry, analyzing multiple cases can help obtain a more holistic sense of the topic or issue. Let's provide a basic definition of a case study, then explore its characteristics and role in the qualitative research process.
Definition of a case study
A case study in qualitative research is a strategy of inquiry that involves an in-depth investigation of a phenomenon within its real-world context. It provides researchers with the opportunity to acquire an in-depth understanding of intricate details that might not be as apparent or accessible through other methods of research. The specific case or cases being studied can be a single person, group, or organization – demarcating what constitutes a relevant case worth studying depends on the researcher and their research question .
Among qualitative research methods , a case study relies on multiple sources of evidence, such as documents, artifacts, interviews , or observations , to present a complete and nuanced understanding of the phenomenon under investigation. The objective is to illuminate the readers' understanding of the phenomenon beyond its abstract statistical or theoretical explanations.
Characteristics of case studies
Case studies typically possess a number of distinct characteristics that set them apart from other research methods. These characteristics include a focus on holistic description and explanation, flexibility in the design and data collection methods, reliance on multiple sources of evidence, and emphasis on the context in which the phenomenon occurs.
Furthermore, case studies can often involve a longitudinal examination of the case, meaning they study the case over a period of time. These characteristics allow case studies to yield comprehensive, in-depth, and richly contextualized insights about the phenomenon of interest.
The role of case studies in research
Case studies hold a unique position in the broader landscape of research methods aimed at theory development. They are instrumental when the primary research interest is to gain an intensive, detailed understanding of a phenomenon in its real-life context.
In addition, case studies can serve different purposes within research - they can be used for exploratory, descriptive, or explanatory purposes, depending on the research question and objectives. This flexibility and depth make case studies a valuable tool in the toolkit of qualitative researchers.
Remember, a well-conducted case study can offer a rich, insightful contribution to both academic and practical knowledge through theory development or theory verification, thus enhancing our understanding of complex phenomena in their real-world contexts.
What is the purpose of a case study?
Case study research aims for a more comprehensive understanding of phenomena, requiring various research methods to gather information for qualitative analysis . Ultimately, a case study can allow the researcher to gain insight into a particular object of inquiry and develop a theoretical framework relevant to the research inquiry.
Why use case studies in qualitative research?
Using case studies as a research strategy depends mainly on the nature of the research question and the researcher's access to the data.
Conducting case study research provides a level of detail and contextual richness that other research methods might not offer. They are beneficial when there's a need to understand complex social phenomena within their natural contexts.
The explanatory, exploratory, and descriptive roles of case studies
Case studies can take on various roles depending on the research objectives. They can be exploratory when the research aims to discover new phenomena or define new research questions; they are descriptive when the objective is to depict a phenomenon within its context in a detailed manner; and they can be explanatory if the goal is to understand specific relationships within the studied context. Thus, the versatility of case studies allows researchers to approach their topic from different angles, offering multiple ways to uncover and interpret the data .
The impact of case studies on knowledge development
Case studies play a significant role in knowledge development across various disciplines. Analysis of cases provides an avenue for researchers to explore phenomena within their context based on the collected data.

This can result in the production of rich, practical insights that can be instrumental in both theory-building and practice. Case studies allow researchers to delve into the intricacies and complexities of real-life situations, uncovering insights that might otherwise remain hidden.
Types of case studies
In qualitative research , a case study is not a one-size-fits-all approach. Depending on the nature of the research question and the specific objectives of the study, researchers might choose to use different types of case studies. These types differ in their focus, methodology, and the level of detail they provide about the phenomenon under investigation.
Understanding these types is crucial for selecting the most appropriate approach for your research project and effectively achieving your research goals. Let's briefly look at the main types of case studies.
Exploratory case studies
Exploratory case studies are typically conducted to develop a theory or framework around an understudied phenomenon. They can also serve as a precursor to a larger-scale research project. Exploratory case studies are useful when a researcher wants to identify the key issues or questions which can spur more extensive study or be used to develop propositions for further research. These case studies are characterized by flexibility, allowing researchers to explore various aspects of a phenomenon as they emerge, which can also form the foundation for subsequent studies.
Descriptive case studies
Descriptive case studies aim to provide a complete and accurate representation of a phenomenon or event within its context. These case studies are often based on an established theoretical framework, which guides how data is collected and analyzed. The researcher is concerned with describing the phenomenon in detail, as it occurs naturally, without trying to influence or manipulate it.
Explanatory case studies
Explanatory case studies are focused on explanation - they seek to clarify how or why certain phenomena occur. Often used in complex, real-life situations, they can be particularly valuable in clarifying causal relationships among concepts and understanding the interplay between different factors within a specific context.

Intrinsic, instrumental, and collective case studies
These three categories of case studies focus on the nature and purpose of the study. An intrinsic case study is conducted when a researcher has an inherent interest in the case itself. Instrumental case studies are employed when the case is used to provide insight into a particular issue or phenomenon. A collective case study, on the other hand, involves studying multiple cases simultaneously to investigate some general phenomena.
Each type of case study serves a different purpose and has its own strengths and challenges. The selection of the type should be guided by the research question and objectives, as well as the context and constraints of the research.
The flexibility, depth, and contextual richness offered by case studies make this approach an excellent research method for various fields of study. They enable researchers to investigate real-world phenomena within their specific contexts, capturing nuances that other research methods might miss. Across numerous fields, case studies provide valuable insights into complex issues.
Critical information systems research
Case studies provide a detailed understanding of the role and impact of information systems in different contexts. They offer a platform to explore how information systems are designed, implemented, and used and how they interact with various social, economic, and political factors. Case studies in this field often focus on examining the intricate relationship between technology, organizational processes, and user behavior, helping to uncover insights that can inform better system design and implementation.
Health research
Health research is another field where case studies are highly valuable. They offer a way to explore patient experiences, healthcare delivery processes, and the impact of various interventions in a real-world context.

Case studies can provide a deep understanding of a patient's journey, giving insights into the intricacies of disease progression, treatment effects, and the psychosocial aspects of health and illness.
Asthma research studies
Specifically within medical research, studies on asthma often employ case studies to explore the individual and environmental factors that influence asthma development, management, and outcomes. A case study can provide rich, detailed data about individual patients' experiences, from the triggers and symptoms they experience to the effectiveness of various management strategies. This can be crucial for developing patient-centered asthma care approaches.
Other fields
Apart from the fields mentioned, case studies are also extensively used in business and management research, education research, and political sciences, among many others. They provide an opportunity to delve into the intricacies of real-world situations, allowing for a comprehensive understanding of various phenomena.
Case studies, with their depth and contextual focus, offer unique insights across these varied fields. They allow researchers to illuminate the complexities of real-life situations, contributing to both theory and practice.
Whatever field you're in, ATLAS.ti puts your data to work for you
Download a free trial of ATLAS.ti to turn your data into insights.
Understanding the key elements of case study design is crucial for conducting rigorous and impactful case study research. A well-structured design guides the researcher through the process, ensuring that the study is methodologically sound and its findings are reliable and valid. The main elements of case study design include the research question , propositions, units of analysis, and the logic linking the data to the propositions.
The research question is the foundation of any research study. A good research question guides the direction of the study and informs the selection of the case, the methods of collecting data, and the analysis techniques. A well-formulated research question in case study research is typically clear, focused, and complex enough to merit further detailed examination of the relevant case(s).
Propositions
Propositions, though not necessary in every case study, provide a direction by stating what we might expect to find in the data collected. They guide how data is collected and analyzed by helping researchers focus on specific aspects of the case. They are particularly important in explanatory case studies, which seek to understand the relationships among concepts within the studied phenomenon.
Units of analysis
The unit of analysis refers to the case, or the main entity or entities that are being analyzed in the study. In case study research, the unit of analysis can be an individual, a group, an organization, a decision, an event, or even a time period. It's crucial to clearly define the unit of analysis, as it shapes the qualitative data analysis process by allowing the researcher to analyze a particular case and synthesize analysis across multiple case studies to draw conclusions.
Argumentation
This refers to the inferential model that allows researchers to draw conclusions from the data. The researcher needs to ensure that there is a clear link between the data, the propositions (if any), and the conclusions drawn. This argumentation is what enables the researcher to make valid and credible inferences about the phenomenon under study.
Understanding and carefully considering these elements in the design phase of a case study can significantly enhance the quality of the research. It can help ensure that the study is methodologically sound and its findings contribute meaningful insights about the case.
Ready to jumpstart your research with ATLAS.ti?
Conceptualize your research project with our intuitive data analysis interface. Download a free trial today.
Conducting a case study involves several steps, from defining the research question and selecting the case to collecting and analyzing data . This section outlines these key stages, providing a practical guide on how to conduct case study research.
Defining the research question
The first step in case study research is defining a clear, focused research question. This question should guide the entire research process, from case selection to analysis. It's crucial to ensure that the research question is suitable for a case study approach. Typically, such questions are exploratory or descriptive in nature and focus on understanding a phenomenon within its real-life context.
Selecting and defining the case
The selection of the case should be based on the research question and the objectives of the study. It involves choosing a unique example or a set of examples that provide rich, in-depth data about the phenomenon under investigation. After selecting the case, it's crucial to define it clearly, setting the boundaries of the case, including the time period and the specific context.
Previous research can help guide the case study design. When considering a case study, an example of a case could be taken from previous case study research and used to define cases in a new research inquiry. Considering recently published examples can help understand how to select and define cases effectively.
Developing a detailed case study protocol
A case study protocol outlines the procedures and general rules to be followed during the case study. This includes the data collection methods to be used, the sources of data, and the procedures for analysis. Having a detailed case study protocol ensures consistency and reliability in the study.
The protocol should also consider how to work with the people involved in the research context to grant the research team access to collecting data. As mentioned in previous sections of this guide, establishing rapport is an essential component of qualitative research as it shapes the overall potential for collecting and analyzing data.
Collecting data
Gathering data in case study research often involves multiple sources of evidence, including documents, archival records, interviews, observations, and physical artifacts. This allows for a comprehensive understanding of the case. The process for gathering data should be systematic and carefully documented to ensure the reliability and validity of the study.
Analyzing and interpreting data
The next step is analyzing the data. This involves organizing the data , categorizing it into themes or patterns , and interpreting these patterns to answer the research question. The analysis might also involve comparing the findings with prior research or theoretical propositions.
Writing the case study report
The final step is writing the case study report . This should provide a detailed description of the case, the data, the analysis process, and the findings. The report should be clear, organized, and carefully written to ensure that the reader can understand the case and the conclusions drawn from it.
Each of these steps is crucial in ensuring that the case study research is rigorous, reliable, and provides valuable insights about the case.
The type, depth, and quality of data in your study can significantly influence the validity and utility of the study. In case study research, data is usually collected from multiple sources to provide a comprehensive and nuanced understanding of the case. This section will outline the various methods of collecting data used in case study research and discuss considerations for ensuring the quality of the data.
Interviews are a common method of gathering data in case study research. They can provide rich, in-depth data about the perspectives, experiences, and interpretations of the individuals involved in the case. Interviews can be structured , semi-structured , or unstructured , depending on the research question and the degree of flexibility needed.
Observations
Observations involve the researcher observing the case in its natural setting, providing first-hand information about the case and its context. Observations can provide data that might not be revealed in interviews or documents, such as non-verbal cues or contextual information.
Documents and artifacts
Documents and archival records provide a valuable source of data in case study research. They can include reports, letters, memos, meeting minutes, email correspondence, and various public and private documents related to the case.

These records can provide historical context, corroborate evidence from other sources, and offer insights into the case that might not be apparent from interviews or observations.
Physical artifacts refer to any physical evidence related to the case, such as tools, products, or physical environments. These artifacts can provide tangible insights into the case, complementing the data gathered from other sources.
Ensuring the quality of data collection
Determining the quality of data in case study research requires careful planning and execution. It's crucial to ensure that the data is reliable, accurate, and relevant to the research question. This involves selecting appropriate methods of collecting data, properly training interviewers or observers, and systematically recording and storing the data. It also includes considering ethical issues related to collecting and handling data, such as obtaining informed consent and ensuring the privacy and confidentiality of the participants.
Data analysis
Analyzing case study research involves making sense of the rich, detailed data to answer the research question. This process can be challenging due to the volume and complexity of case study data. However, a systematic and rigorous approach to analysis can ensure that the findings are credible and meaningful. This section outlines the main steps and considerations in analyzing data in case study research.
Organizing the data
The first step in the analysis is organizing the data. This involves sorting the data into manageable sections, often according to the data source or the theme. This step can also involve transcribing interviews, digitizing physical artifacts, or organizing observational data.
Categorizing and coding the data
Once the data is organized, the next step is to categorize or code the data. This involves identifying common themes, patterns, or concepts in the data and assigning codes to relevant data segments. Coding can be done manually or with the help of software tools, and in either case, qualitative analysis software can greatly facilitate the entire coding process. Coding helps to reduce the data to a set of themes or categories that can be more easily analyzed.
Identifying patterns and themes
After coding the data, the researcher looks for patterns or themes in the coded data. This involves comparing and contrasting the codes and looking for relationships or patterns among them. The identified patterns and themes should help answer the research question.
Interpreting the data
Once patterns and themes have been identified, the next step is to interpret these findings. This involves explaining what the patterns or themes mean in the context of the research question and the case. This interpretation should be grounded in the data, but it can also involve drawing on theoretical concepts or prior research.
Verification of the data
The last step in the analysis is verification. This involves checking the accuracy and consistency of the analysis process and confirming that the findings are supported by the data. This can involve re-checking the original data, checking the consistency of codes, or seeking feedback from research participants or peers.
Like any research method , case study research has its strengths and limitations. Researchers must be aware of these, as they can influence the design, conduct, and interpretation of the study.
Understanding the strengths and limitations of case study research can also guide researchers in deciding whether this approach is suitable for their research question . This section outlines some of the key strengths and limitations of case study research.
Benefits include the following:
- Rich, detailed data: One of the main strengths of case study research is that it can generate rich, detailed data about the case. This can provide a deep understanding of the case and its context, which can be valuable in exploring complex phenomena.
- Flexibility: Case study research is flexible in terms of design , data collection , and analysis . A sufficient degree of flexibility allows the researcher to adapt the study according to the case and the emerging findings.
- Real-world context: Case study research involves studying the case in its real-world context, which can provide valuable insights into the interplay between the case and its context.
- Multiple sources of evidence: Case study research often involves collecting data from multiple sources , which can enhance the robustness and validity of the findings.
On the other hand, researchers should consider the following limitations:
- Generalizability: A common criticism of case study research is that its findings might not be generalizable to other cases due to the specificity and uniqueness of each case.
- Time and resource intensive: Case study research can be time and resource intensive due to the depth of the investigation and the amount of collected data.
- Complexity of analysis: The rich, detailed data generated in case study research can make analyzing the data challenging.
- Subjectivity: Given the nature of case study research, there may be a higher degree of subjectivity in interpreting the data , so researchers need to reflect on this and transparently convey to audiences how the research was conducted.
Being aware of these strengths and limitations can help researchers design and conduct case study research effectively and interpret and report the findings appropriately.

Ready to analyze your data with ATLAS.ti?
See how our intuitive software can draw key insights from your data with a free trial today.
How many participants do I need for qualitative research?
- Participant recruitment
- Qualitative research
6 min read David Renwick

For those new to the qualitative research space, there’s one question that’s usually pretty tough to figure out, and that’s the question of how many participants to include in a study. Regardless of whether it’s research as part of the discovery phase for a new product, or perhaps an in-depth canvas of the users of an existing service, researchers can often find it difficult to agree on the numbers. So is there an easy answer? Let’s find out.
Here, we’ll look into the right number of participants for qualitative research studies. If you want to know about participants for quantitative research, read Nielsen Norman Group’s article .
Getting the numbers right
So you need to run a series of user interviews or usability tests and aren’t sure exactly how many people you should reach out to. It can be a tricky situation – especially for those without much experience. Do you test a small selection of 1 or 2 people to make the recruitment process easier? Or, do you go big and test with a series of 10 people over the course of a month? The answer lies somewhere in between.
It’s often a good idea (for qualitative research methods like interviews and usability tests) to start with 5 participants and then scale up by a further 5 based on how complicated the subject matter is. You may also find it helpful to add additional participants if you’re new to user research or you’re working in a new area.
What you’re actually looking for here is what’s known as saturation.
Understanding saturation
Whether it’s qualitative research as part of a master’s thesis or as research for a new online dating app, saturation is the best metric you can use to identify when you’ve hit the right number of participants.
In a nutshell, saturation is when you’ve reached the point where adding further participants doesn’t give you any further insights. It’s true that you may still pick up on the occasional interesting detail, but all of your big revelations and learnings have come and gone. A good measure is to sit down after each session with a participant and analyze the number of new insights you’ve noted down.
Interestingly, in a paper titled How Many Interviews Are Enough? , authors Greg Guest, Arwen Bunce and Laura Johnson noted that saturation usually occurs with around 12 participants in homogeneous groups (meaning people in the same role at an organization, for example). However, carrying out ethnographic research on a larger domain with a diverse set of participants will almost certainly require a larger sample.
Ensuring you’ve hit the right number of participants
How do you know when you’ve reached saturation point? You have to keep conducting interviews or usability tests until you’re no longer uncovering new insights or concepts.
While this may seem to run counter to the idea of just gathering as much data from as many people as possible, there’s a strong case for focusing on a smaller group of participants. In The logic of small samples in interview-based , authors Mira Crouch and Heather McKenzie note that using fewer than 20 participants during a qualitative research study will result in better data. Why? With a smaller group, it’s easier for you (the researcher) to build strong close relationships with your participants, which in turn leads to more natural conversations and better data.
There’s also a school of thought that you should interview 5 or so people per persona. For example, if you’re working in a company that has well-defined personas, you might want to use those as a basis for your study, and then you would interview 5 people based on each persona. This maybe worth considering or particularly important when you have a product that has very distinct user groups (e.g. students and staff, teachers and parents etc).
How your domain affects sample size
The scope of the topic you’re researching will change the amount of information you’ll need to gather before you’ve hit the saturation point. Your topic is also commonly referred to as the domain.
If you’re working in quite a confined domain, for example, a single screen of a mobile app or a very specific scenario, you’ll likely find interviews with 5 participants to be perfectly fine. Moving into more complicated domains, like the entire checkout process for an online shopping app, will push up your sample size.
As Mitchel Seaman notes : “Exploring a big issue like young peoples’ opinions about healthcare coverage, a broad emotional issue like postmarital sexuality, or a poorly-understood domain for your team like mobile device use in another country can drastically increase the number of interviews you’ll want to conduct.”
In-person or remote
Does the location of your participants change the number you need for qualitative user research? Well, not really – but there are other factors to consider.
- Budget: If you choose to conduct remote interviews/usability tests, you’ll likely find you’ve got lower costs as you won’t need to travel to your participants or have them travel to you. This also affects…
- Participant access: Remote qualitative research can be a lifesaver when it comes to participant access. No longer are you confined to the people you have physical access to — instead you can reach out to anyone you’d like.
- Quality: On the other hand, remote research does have its downsides. For one, you’ll likely find you’re not able to build the same kinds of relationships over the internet or phone as those in person, which in turn means you never quite get the same level of insights.
Is there value in outsourcing recruitment?
Recruitment is understandably an intensive logistical exercise with many moving parts. If you’ve ever had to recruit people for a study before, you’ll understand the need for long lead times (to ensure you have enough participants for the project) and the countless long email chains as you discuss suitable times.
Outsourcing your participant recruitment is just one way to lighten the logistical load during your research. Instead of having to go out and look for participants, you have them essentially delivered to you in the right number and with the right attributes.
We’ve got one such service at Optimal Workshop, which means it’s the perfect accompaniment if you’re also using our platform of UX tools. Read more about that here .
So that’s really most of what there is to know about participant recruitment in a qualitative research context. As we said at the start, while it can appear quite tricky to figure out exactly how many people you need to recruit, it’s actually not all that difficult in reality.
Overall, the number of participants you need for your qualitative research can depend on your project among other factors. It’s important to keep saturation in mind, as well as the locale of participants. You also need to get the most you can out of what’s available to you. Remember: Some research is better than none!
Capture, analyze and visualize your qualitative data.
Try our qualitative research tool for usability testing, interviewing and note-taking. Reframer by Optimal Workshop.

Published on August 8, 2019

David Renwick
David is Optimal Workshop's Content Strategist and Editor of CRUX. You can usually find him alongside one of the office dogs 🐕 (Bella, Bowie, Frida, Tana or Steezy). Connect with him on LinkedIn.
Recommended for you

UX research is a team effort
What’s better than a UX team doing awesome research? A whole organization backing investment in UX research. What’s that look like in practice? Collaboration and support from stakeholders across the organization throughout the research process from set up, doing studies, sharing insights, and digesting, understanding, and actioning recommendations based on the amazing insights you generate.... View Article

Remote research opens the door for richer, higher-fidelity insights
Remote research opens up a huge number of ways to empower participants and to give yourself a better chance to have a valid understanding of what’s going on.
How can we reach internal users and get them excited about participating in user research?
Internal users are more often than not a unique breed of research participant. Here's how to enlist their help.
Try Optimal Workshop tools for free
What are you looking for.
Explore all tags
Discover more from Optimal Workshop
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Methodology
- Case Study | Definition, Examples & Methods
Case Study | Definition, Examples & Methods
Published on 5 May 2022 by Shona McCombes . Revised on 30 January 2023.
A case study is a detailed study of a specific subject, such as a person, group, place, event, organisation, or phenomenon. Case studies are commonly used in social, educational, clinical, and business research.
A case study research design usually involves qualitative methods , but quantitative methods are sometimes also used. Case studies are good for describing , comparing, evaluating, and understanding different aspects of a research problem .
Table of contents
When to do a case study, step 1: select a case, step 2: build a theoretical framework, step 3: collect your data, step 4: describe and analyse the case.
A case study is an appropriate research design when you want to gain concrete, contextual, in-depth knowledge about a specific real-world subject. It allows you to explore the key characteristics, meanings, and implications of the case.
Case studies are often a good choice in a thesis or dissertation . They keep your project focused and manageable when you don’t have the time or resources to do large-scale research.
You might use just one complex case study where you explore a single subject in depth, or conduct multiple case studies to compare and illuminate different aspects of your research problem.
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Once you have developed your problem statement and research questions , you should be ready to choose the specific case that you want to focus on. A good case study should have the potential to:
- Provide new or unexpected insights into the subject
- Challenge or complicate existing assumptions and theories
- Propose practical courses of action to resolve a problem
- Open up new directions for future research
Unlike quantitative or experimental research, a strong case study does not require a random or representative sample. In fact, case studies often deliberately focus on unusual, neglected, or outlying cases which may shed new light on the research problem.
If you find yourself aiming to simultaneously investigate and solve an issue, consider conducting action research . As its name suggests, action research conducts research and takes action at the same time, and is highly iterative and flexible.
However, you can also choose a more common or representative case to exemplify a particular category, experience, or phenomenon.
While case studies focus more on concrete details than general theories, they should usually have some connection with theory in the field. This way the case study is not just an isolated description, but is integrated into existing knowledge about the topic. It might aim to:
- Exemplify a theory by showing how it explains the case under investigation
- Expand on a theory by uncovering new concepts and ideas that need to be incorporated
- Challenge a theory by exploring an outlier case that doesn’t fit with established assumptions
To ensure that your analysis of the case has a solid academic grounding, you should conduct a literature review of sources related to the topic and develop a theoretical framework . This means identifying key concepts and theories to guide your analysis and interpretation.
There are many different research methods you can use to collect data on your subject. Case studies tend to focus on qualitative data using methods such as interviews, observations, and analysis of primary and secondary sources (e.g., newspaper articles, photographs, official records). Sometimes a case study will also collect quantitative data .
The aim is to gain as thorough an understanding as possible of the case and its context.
In writing up the case study, you need to bring together all the relevant aspects to give as complete a picture as possible of the subject.
How you report your findings depends on the type of research you are doing. Some case studies are structured like a standard scientific paper or thesis, with separate sections or chapters for the methods , results , and discussion .
Others are written in a more narrative style, aiming to explore the case from various angles and analyse its meanings and implications (for example, by using textual analysis or discourse analysis ).
In all cases, though, make sure to give contextual details about the case, connect it back to the literature and theory, and discuss how it fits into wider patterns or debates.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, January 30). Case Study | Definition, Examples & Methods. Scribbr. Retrieved 14 May 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/research-methods/case-studies/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, correlational research | guide, design & examples, a quick guide to experimental design | 5 steps & examples, descriptive research design | definition, methods & examples.
Case Studies
This guide examines case studies, a form of qualitative descriptive research that is used to look at individuals, a small group of participants, or a group as a whole. Researchers collect data about participants using participant and direct observations, interviews, protocols, tests, examinations of records, and collections of writing samples. Starting with a definition of the case study, the guide moves to a brief history of this research method. Using several well documented case studies, the guide then looks at applications and methods including data collection and analysis. A discussion of ways to handle validity, reliability, and generalizability follows, with special attention to case studies as they are applied to composition studies. Finally, this guide examines the strengths and weaknesses of case studies.
Definition and Overview
Case study refers to the collection and presentation of detailed information about a particular participant or small group, frequently including the accounts of subjects themselves. A form of qualitative descriptive research, the case study looks intensely at an individual or small participant pool, drawing conclusions only about that participant or group and only in that specific context. Researchers do not focus on the discovery of a universal, generalizable truth, nor do they typically look for cause-effect relationships; instead, emphasis is placed on exploration and description.
Case studies typically examine the interplay of all variables in order to provide as complete an understanding of an event or situation as possible. This type of comprehensive understanding is arrived at through a process known as thick description, which involves an in-depth description of the entity being evaluated, the circumstances under which it is used, the characteristics of the people involved in it, and the nature of the community in which it is located. Thick description also involves interpreting the meaning of demographic and descriptive data such as cultural norms and mores, community values, ingrained attitudes, and motives.
Unlike quantitative methods of research, like the survey, which focus on the questions of who, what, where, how much, and how many, and archival analysis, which often situates the participant in some form of historical context, case studies are the preferred strategy when how or why questions are asked. Likewise, they are the preferred method when the researcher has little control over the events, and when there is a contemporary focus within a real life context. In addition, unlike more specifically directed experiments, case studies require a problem that seeks a holistic understanding of the event or situation in question using inductive logic--reasoning from specific to more general terms.
In scholarly circles, case studies are frequently discussed within the context of qualitative research and naturalistic inquiry. Case studies are often referred to interchangeably with ethnography, field study, and participant observation. The underlying philosophical assumptions in the case are similar to these types of qualitative research because each takes place in a natural setting (such as a classroom, neighborhood, or private home), and strives for a more holistic interpretation of the event or situation under study.
Unlike more statistically-based studies which search for quantifiable data, the goal of a case study is to offer new variables and questions for further research. F.H. Giddings, a sociologist in the early part of the century, compares statistical methods to the case study on the basis that the former are concerned with the distribution of a particular trait, or a small number of traits, in a population, whereas the case study is concerned with the whole variety of traits to be found in a particular instance" (Hammersley 95).
Case studies are not a new form of research; naturalistic inquiry was the primary research tool until the development of the scientific method. The fields of sociology and anthropology are credited with the primary shaping of the concept as we know it today. However, case study research has drawn from a number of other areas as well: the clinical methods of doctors; the casework technique being developed by social workers; the methods of historians and anthropologists, plus the qualitative descriptions provided by quantitative researchers like LePlay; and, in the case of Robert Park, the techniques of newspaper reporters and novelists.
Park was an ex-newspaper reporter and editor who became very influential in developing sociological case studies at the University of Chicago in the 1920s. As a newspaper professional he coined the term "scientific" or "depth" reporting: the description of local events in a way that pointed to major social trends. Park viewed the sociologist as "merely a more accurate, responsible, and scientific reporter." Park stressed the variety and value of human experience. He believed that sociology sought to arrive at natural, but fluid, laws and generalizations in regard to human nature and society. These laws weren't static laws of the kind sought by many positivists and natural law theorists, but rather, they were laws of becoming--with a constant possibility of change. Park encouraged students to get out of the library, to quit looking at papers and books, and to view the constant experiment of human experience. He writes, "Go and sit in the lounges of the luxury hotels and on the doorsteps of the flophouses; sit on the Gold Coast settees and on the slum shakedowns; sit in the Orchestra Hall and in the Star and Garter Burlesque. In short, gentlemen [sic], go get the seats of your pants dirty in real research."
But over the years, case studies have drawn their share of criticism. In fact, the method had its detractors from the start. In the 1920s, the debate between pro-qualitative and pro-quantitative became quite heated. Case studies, when compared to statistics, were considered by many to be unscientific. From the 1930's on, the rise of positivism had a growing influence on quantitative methods in sociology. People wanted static, generalizable laws in science. The sociological positivists were looking for stable laws of social phenomena. They criticized case study research because it failed to provide evidence of inter subjective agreement. Also, they condemned it because of the few number of cases studied and that the under-standardized character of their descriptions made generalization impossible. By the 1950s, quantitative methods, in the form of survey research, had become the dominant sociological approach and case study had become a minority practice.
Educational Applications
The 1950's marked the dawning of a new era in case study research, namely that of the utilization of the case study as a teaching method. "Instituted at Harvard Business School in the 1950s as a primary method of teaching, cases have since been used in classrooms and lecture halls alike, either as part of a course of study or as the main focus of the course to which other teaching material is added" (Armisted 1984). The basic purpose of instituting the case method as a teaching strategy was "to transfer much of the responsibility for learning from the teacher on to the student, whose role, as a result, shifts away from passive absorption toward active construction" (Boehrer 1990). Through careful examination and discussion of various cases, "students learn to identify actual problems, to recognize key players and their agendas, and to become aware of those aspects of the situation that contribute to the problem" (Merseth 1991). In addition, students are encouraged to "generate their own analysis of the problems under consideration, to develop their own solutions, and to practically apply their own knowledge of theory to these problems" (Boyce 1993). Along the way, students also develop "the power to analyze and to master a tangled circumstance by identifying and delineating important factors; the ability to utilize ideas, to test them against facts, and to throw them into fresh combinations" (Merseth 1991).
In addition to the practical application and testing of scholarly knowledge, case discussions can also help students prepare for real-world problems, situations and crises by providing an approximation of various professional environments (i.e. classroom, board room, courtroom, or hospital). Thus, through the examination of specific cases, students are given the opportunity to work out their own professional issues through the trials, tribulations, experiences, and research findings of others. An obvious advantage to this mode of instruction is that it allows students the exposure to settings and contexts that they might not otherwise experience. For example, a student interested in studying the effects of poverty on minority secondary student's grade point averages and S.A.T. scores could access and analyze information from schools as geographically diverse as Los Angeles, New York City, Miami, and New Mexico without ever having to leave the classroom.
The case study method also incorporates the idea that students can learn from one another "by engaging with each other and with each other's ideas, by asserting something and then having it questioned, challenged and thrown back at them so that they can reflect on what they hear, and then refine what they say" (Boehrer 1990). In summary, students can direct their own learning by formulating questions and taking responsibility for the study.
Types and Design Concerns
Researchers use multiple methods and approaches to conduct case studies.
Types of Case Studies
Under the more generalized category of case study exist several subdivisions, each of which is custom selected for use depending upon the goals and/or objectives of the investigator. These types of case study include the following:
Illustrative Case Studies These are primarily descriptive studies. They typically utilize one or two instances of an event to show what a situation is like. Illustrative case studies serve primarily to make the unfamiliar familiar and to give readers a common language about the topic in question.
Exploratory (or pilot) Case Studies These are condensed case studies performed before implementing a large scale investigation. Their basic function is to help identify questions and select types of measurement prior to the main investigation. The primary pitfall of this type of study is that initial findings may seem convincing enough to be released prematurely as conclusions.
Cumulative Case Studies These serve to aggregate information from several sites collected at different times. The idea behind these studies is the collection of past studies will allow for greater generalization without additional cost or time being expended on new, possibly repetitive studies.
Critical Instance Case Studies These examine one or more sites for either the purpose of examining a situation of unique interest with little to no interest in generalizability, or to call into question or challenge a highly generalized or universal assertion. This method is useful for answering cause and effect questions.
Identifying a Theoretical Perspective
Much of the case study's design is inherently determined for researchers, depending on the field from which they are working. In composition studies, researchers are typically working from a qualitative, descriptive standpoint. In contrast, physicists will approach their research from a more quantitative perspective. Still, in designing the study, researchers need to make explicit the questions to be explored and the theoretical perspective from which they will approach the case. The three most commonly adopted theories are listed below:
Individual Theories These focus primarily on the individual development, cognitive behavior, personality, learning and disability, and interpersonal interactions of a particular subject.
Organizational Theories These focus on bureaucracies, institutions, organizational structure and functions, or excellence in organizational performance.
Social Theories These focus on urban development, group behavior, cultural institutions, or marketplace functions.
Two examples of case studies are used consistently throughout this chapter. The first, a study produced by Berkenkotter, Huckin, and Ackerman (1988), looks at a first year graduate student's initiation into an academic writing program. The study uses participant-observer and linguistic data collecting techniques to assess the student's knowledge of appropriate discourse conventions. Using the pseudonym Nate to refer to the subject, the study sought to illuminate the particular experience rather than to generalize about the experience of fledgling academic writers collectively.
For example, in Berkenkotter, Huckin, and Ackerman's (1988) study we are told that the researchers are interested in disciplinary communities. In the first paragraph, they ask what constitutes membership in a disciplinary community and how achieving membership might affect a writer's understanding and production of texts. In the third paragraph they state that researchers must negotiate their claims "within the context of his sub specialty's accepted knowledge and methodology." In the next paragraph they ask, "How is literacy acquired? What is the process through which novices gain community membership? And what factors either aid or hinder students learning the requisite linguistic behaviors?" This introductory section ends with a paragraph in which the study's authors claim that during the course of the study, the subject, Nate, successfully makes the transition from "skilled novice" to become an initiated member of the academic discourse community and that his texts exhibit linguistic changes which indicate this transition. In the next section the authors make explicit the sociolinguistic theoretical and methodological assumptions on which the study is based (1988). Thus the reader has a good understanding of the authors' theoretical background and purpose in conducting the study even before it is explicitly stated on the fourth page of the study. "Our purpose was to examine the effects of the educational context on one graduate student's production of texts as he wrote in different courses and for different faculty members over the academic year 1984-85." The goal of the study then, was to explore the idea that writers must be initiated into a writing community, and that this initiation will change the way one writes.
The second example is Janet Emig's (1971) study of the composing process of a group of twelfth graders. In this study, Emig seeks to answer the question of what happens to the self as a result educational stimuli in terms of academic writing. The case study used methods such as protocol analysis, tape-recorded interviews, and discourse analysis.
In the case of Janet Emig's (1971) study of the composing process of eight twelfth graders, four specific hypotheses were made:
- Twelfth grade writers engage in two modes of composing: reflexive and extensive.
- These differences can be ascertained and characterized through having the writers compose aloud their composition process.
- A set of implied stylistic principles governs the writing process.
- For twelfth grade writers, extensive writing occurs chiefly as a school-sponsored activity, or reflexive, as a self-sponsored activity.
In this study, the chief distinction is between the two dominant modes of composing among older, secondary school students. The distinctions are:
- The reflexive mode, which focuses on the writer's thoughts and feelings.
- The extensive mode, which focuses on conveying a message.
Emig also outlines the specific questions which guided the research in the opening pages of her Review of Literature , preceding the report.
Designing a Case Study
After considering the different sub categories of case study and identifying a theoretical perspective, researchers can begin to design their study. Research design is the string of logic that ultimately links the data to be collected and the conclusions to be drawn to the initial questions of the study. Typically, research designs deal with at least four problems:
- What questions to study
- What data are relevant
- What data to collect
- How to analyze that data
In other words, a research design is basically a blueprint for getting from the beginning to the end of a study. The beginning is an initial set of questions to be answered, and the end is some set of conclusions about those questions.
Because case studies are conducted on topics as diverse as Anglo-Saxon Literature (Thrane 1986) and AIDS prevention (Van Vugt 1994), it is virtually impossible to outline any strict or universal method or design for conducting the case study. However, Robert K. Yin (1993) does offer five basic components of a research design:
- A study's questions.
- A study's propositions (if any).
- A study's units of analysis.
- The logic that links the data to the propositions.
- The criteria for interpreting the findings.
In addition to these five basic components, Yin also stresses the importance of clearly articulating one's theoretical perspective, determining the goals of the study, selecting one's subject(s), selecting the appropriate method(s) of collecting data, and providing some considerations to the composition of the final report.
Conducting Case Studies
To obtain as complete a picture of the participant as possible, case study researchers can employ a variety of approaches and methods. These approaches, methods, and related issues are discussed in depth in this section.

Method: Single or Multi-modal?
To obtain as complete a picture of the participant as possible, case study researchers can employ a variety of methods. Some common methods include interviews , protocol analyses, field studies, and participant-observations. Emig (1971) chose to use several methods of data collection. Her sources included conversations with the students, protocol analysis, discrete observations of actual composition, writing samples from each student, and school records (Lauer and Asher 1988).
Berkenkotter, Huckin, and Ackerman (1988) collected data by observing classrooms, conducting faculty and student interviews, collecting self reports from the subject, and by looking at the subject's written work.
A study that was criticized for using a single method model was done by Flower and Hayes (1984). In this study that explores the ways in which writers use different forms of knowing to create space, the authors used only protocol analysis to gather data. The study came under heavy fire because of their decision to use only one method.
Participant Selection
Case studies can use one participant, or a small group of participants. However, it is important that the participant pool remain relatively small. The participants can represent a diverse cross section of society, but this isn't necessary.
For example, the Berkenkotter, Huckin, and Ackerman (1988) study looked at just one participant, Nate. By contrast, in Janet Emig's (1971) study of the composition process of twelfth graders, eight participants were selected representing a diverse cross section of the community, with volunteers from an all-white upper-middle-class suburban school, an all-black inner-city school, a racially mixed lower-middle-class school, an economically and racially mixed school, and a university school.
Often, a brief "case history" is done on the participants of the study in order to provide researchers with a clearer understanding of their participants, as well as some insight as to how their own personal histories might affect the outcome of the study. For instance, in Emig's study, the investigator had access to the school records of five of the participants, and to standardized test scores for the remaining three. Also made available to the researcher was the information that three of the eight students were selected as NCTE Achievement Award winners. These personal histories can be useful in later stages of the study when data are being analyzed and conclusions drawn.
Data Collection
There are six types of data collected in case studies:
- Archival records.
- Interviews.
- Direct observation.
- Participant observation.
In the field of composition research, these six sources might be:
- A writer's drafts.
- School records of student writers.
- Transcripts of interviews with a writer.
- Transcripts of conversations between writers (and protocols).
- Videotapes and notes from direct field observations.
- Hard copies of a writer's work on computer.
Depending on whether researchers have chosen to use a single or multi-modal approach for the case study, they may choose to collect data from one or any combination of these sources.
Protocols, that is, transcriptions of participants talking aloud about what they are doing as they do it, have been particularly common in composition case studies. For example, in Emig's (1971) study, the students were asked, in four different sessions, to give oral autobiographies of their writing experiences and to compose aloud three themes in the presence of a tape recorder and the investigator.
In some studies, only one method of data collection is conducted. For example, the Flower and Hayes (1981) report on the cognitive process theory of writing depends on protocol analysis alone. However, using multiple sources of evidence to increase the reliability and validity of the data can be advantageous.
Case studies are likely to be much more convincing and accurate if they are based on several different sources of information, following a corroborating mode. This conclusion is echoed among many composition researchers. For example, in her study of predrafting processes of high and low-apprehensive writers, Cynthia Selfe (1985) argues that because "methods of indirect observation provide only an incomplete reflection of the complex set of processes involved in composing, a combination of several such methods should be used to gather data in any one study." Thus, in this study, Selfe collected her data from protocols, observations of students role playing their writing processes, audio taped interviews with the students, and videotaped observations of the students in the process of composing.
It can be said then, that cross checking data from multiple sources can help provide a multidimensional profile of composing activities in a particular setting. Sharan Merriam (1985) suggests "checking, verifying, testing, probing, and confirming collected data as you go, arguing that this process will follow in a funnel-like design resulting in less data gathering in later phases of the study along with a congruent increase in analysis checking, verifying, and confirming."
It is important to note that in case studies, as in any qualitative descriptive research, while researchers begin their studies with one or several questions driving the inquiry (which influence the key factors the researcher will be looking for during data collection), a researcher may find new key factors emerging during data collection. These might be unexpected patterns or linguistic features which become evident only during the course of the research. While not bearing directly on the researcher's guiding questions, these variables may become the basis for new questions asked at the end of the report, thus linking to the possibility of further research.
Data Analysis
As the information is collected, researchers strive to make sense of their data. Generally, researchers interpret their data in one of two ways: holistically or through coding. Holistic analysis does not attempt to break the evidence into parts, but rather to draw conclusions based on the text as a whole. Flower and Hayes (1981), for example, make inferences from entire sections of their students' protocols, rather than searching through the transcripts to look for isolatable characteristics.
However, composition researchers commonly interpret their data by coding, that is by systematically searching data to identify and/or categorize specific observable actions or characteristics. These observable actions then become the key variables in the study. Sharan Merriam (1988) suggests seven analytic frameworks for the organization and presentation of data:
- The role of participants.
- The network analysis of formal and informal exchanges among groups.
- Historical.
- Thematical.
- Ritual and symbolism.
- Critical incidents that challenge or reinforce fundamental beliefs, practices, and values.
There are two purposes of these frameworks: to look for patterns among the data and to look for patterns that give meaning to the case study.
As stated above, while most researchers begin their case studies expecting to look for particular observable characteristics, it is not unusual for key variables to emerge during data collection. Typical variables coded in case studies of writers include pauses writers make in the production of a text, the use of specific linguistic units (such as nouns or verbs), and writing processes (planning, drafting, revising, and editing). In the Berkenkotter, Huckin, and Ackerman (1988) study, for example, researchers coded the participant's texts for use of connectives, discourse demonstratives, average sentence length, off-register words, use of the first person pronoun, and the ratio of definite articles to indefinite articles.
Since coding is inherently subjective, more than one coder is usually employed. In the Berkenkotter, Huckin, and Ackerman (1988) study, for example, three rhetoricians were employed to code the participant's texts for off-register phrases. The researchers established the agreement among the coders before concluding that the participant used fewer off-register words as the graduate program progressed.
Composing the Case Study Report
In the many forms it can take, "a case study is generically a story; it presents the concrete narrative detail of actual, or at least realistic events, it has a plot, exposition, characters, and sometimes even dialogue" (Boehrer 1990). Generally, case study reports are extensively descriptive, with "the most problematic issue often referred to as being the determination of the right combination of description and analysis" (1990). Typically, authors address each step of the research process, and attempt to give the reader as much context as possible for the decisions made in the research design and for the conclusions drawn.
This contextualization usually includes a detailed explanation of the researchers' theoretical positions, of how those theories drove the inquiry or led to the guiding research questions, of the participants' backgrounds, of the processes of data collection, of the training and limitations of the coders, along with a strong attempt to make connections between the data and the conclusions evident.
Although the Berkenkotter, Huckin, and Ackerman (1988) study does not, case study reports often include the reactions of the participants to the study or to the researchers' conclusions. Because case studies tend to be exploratory, most end with implications for further study. Here researchers may identify significant variables that emerged during the research and suggest studies related to these, or the authors may suggest further general questions that their case study generated.
For example, Emig's (1971) study concludes with a section dedicated solely to the topic of implications for further research, in which she suggests several means by which this particular study could have been improved, as well as questions and ideas raised by this study which other researchers might like to address, such as: is there a correlation between a certain personality and a certain composing process profile (e.g. is there a positive correlation between ego strength and persistence in revising)?
Also included in Emig's study is a section dedicated to implications for teaching, which outlines the pedagogical ramifications of the study's findings for teachers currently involved in high school writing programs.
Sharan Merriam (1985) also offers several suggestions for alternative presentations of data:
- Prepare specialized condensations for appropriate groups.
- Replace narrative sections with a series of answers to open-ended questions.
- Present "skimmer's" summaries at beginning of each section.
- Incorporate headlines that encapsulate information from text.
- Prepare analytic summaries with supporting data appendixes.
- Present data in colorful and/or unique graphic representations.
Issues of Validity and Reliability
Once key variables have been identified, they can be analyzed. Reliability becomes a key concern at this stage, and many case study researchers go to great lengths to ensure that their interpretations of the data will be both reliable and valid. Because issues of validity and reliability are an important part of any study in the social sciences, it is important to identify some ways of dealing with results.
Multi-modal case study researchers often balance the results of their coding with data from interviews or writer's reflections upon their own work. Consequently, the researchers' conclusions become highly contextualized. For example, in a case study which looked at the time spent in different stages of the writing process, Berkenkotter concluded that her participant, Donald Murray, spent more time planning his essays than in other writing stages. The report of this case study is followed by Murray's reply, wherein he agrees with some of Berkenkotter's conclusions and disagrees with others.
As is the case with other research methodologies, issues of external validity, construct validity, and reliability need to be carefully considered.
Commentary on Case Studies
Researchers often debate the relative merits of particular methods, among them case study. In this section, we comment on two key issues. To read the commentaries, choose any of the items below:
Strengths and Weaknesses of Case Studies
Most case study advocates point out that case studies produce much more detailed information than what is available through a statistical analysis. Advocates will also hold that while statistical methods might be able to deal with situations where behavior is homogeneous and routine, case studies are needed to deal with creativity, innovation, and context. Detractors argue that case studies are difficult to generalize because of inherent subjectivity and because they are based on qualitative subjective data, generalizable only to a particular context.
Flexibility
The case study approach is a comparatively flexible method of scientific research. Because its project designs seem to emphasize exploration rather than prescription or prediction, researchers are comparatively freer to discover and address issues as they arise in their experiments. In addition, the looser format of case studies allows researchers to begin with broad questions and narrow their focus as their experiment progresses rather than attempt to predict every possible outcome before the experiment is conducted.
Emphasis on Context
By seeking to understand as much as possible about a single subject or small group of subjects, case studies specialize in "deep data," or "thick description"--information based on particular contexts that can give research results a more human face. This emphasis can help bridge the gap between abstract research and concrete practice by allowing researchers to compare their firsthand observations with the quantitative results obtained through other methods of research.
Inherent Subjectivity
"The case study has long been stereotyped as the weak sibling among social science methods," and is often criticized as being too subjective and even pseudo-scientific. Likewise, "investigators who do case studies are often regarded as having deviated from their academic disciplines, and their investigations as having insufficient precision (that is, quantification), objectivity and rigor" (Yin 1989). Opponents cite opportunities for subjectivity in the implementation, presentation, and evaluation of case study research. The approach relies on personal interpretation of data and inferences. Results may not be generalizable, are difficult to test for validity, and rarely offer a problem-solving prescription. Simply put, relying on one or a few subjects as a basis for cognitive extrapolations runs the risk of inferring too much from what might be circumstance.
High Investment
Case studies can involve learning more about the subjects being tested than most researchers would care to know--their educational background, emotional background, perceptions of themselves and their surroundings, their likes, dislikes, and so on. Because of its emphasis on "deep data," the case study is out of reach for many large-scale research projects which look at a subject pool in the tens of thousands. A budget request of $10,000 to examine 200 subjects sounds more efficient than a similar request to examine four subjects.
Ethical Considerations
Researchers conducting case studies should consider certain ethical issues. For example, many educational case studies are often financed by people who have, either directly or indirectly, power over both those being studied and those conducting the investigation (1985). This conflict of interests can hinder the credibility of the study.
The personal integrity, sensitivity, and possible prejudices and/or biases of the investigators need to be taken into consideration as well. Personal biases can creep into how the research is conducted, alternative research methods used, and the preparation of surveys and questionnaires.
A common complaint in case study research is that investigators change direction during the course of the study unaware that their original research design was inadequate for the revised investigation. Thus, the researchers leave unknown gaps and biases in the study. To avoid this, researchers should report preliminary findings so that the likelihood of bias will be reduced.
Concerns about Reliability, Validity, and Generalizability
Merriam (1985) offers several suggestions for how case study researchers might actively combat the popular attacks on the validity, reliability, and generalizability of case studies:
- Prolong the Processes of Data Gathering on Site: This will help to insure the accuracy of the findings by providing the researcher with more concrete information upon which to formulate interpretations.
- Employ the Process of "Triangulation": Use a variety of data sources as opposed to relying solely upon one avenue of observation. One example of such a data check would be what McClintock, Brannon, and Maynard (1985) refer to as a "case cluster method," that is, when a single unit within a larger case is randomly sampled, and that data treated quantitatively." For instance, in Emig's (1971) study, the case cluster method was employed, singling out the productivity of a single student named Lynn. This cluster profile included an advanced case history of the subject, specific examination and analysis of individual compositions and protocols, and extensive interview sessions. The seven remaining students were then compared with the case of Lynn, to ascertain if there are any shared, or unique dimensions to the composing process engaged in by these eight students.
- Conduct Member Checks: Initiate and maintain an active corroboration on the interpretation of data between the researcher and those who provided the data. In other words, talk to your subjects.
- Collect Referential Materials: Complement the file of materials from the actual site with additional document support. For example, Emig (1971) supports her initial propositions with historical accounts by writers such as T.S. Eliot, James Joyce, and D.H. Lawrence. Emig also cites examples of theoretical research done with regards to the creative process, as well as examples of empirical research dealing with the writing of adolescents. Specific attention is then given to the four stages description of the composing process delineated by Helmoltz, Wallas, and Cowley, as it serves as the focal point in this study.
- Engage in Peer Consultation: Prior to composing the final draft of the report, researchers should consult with colleagues in order to establish validity through pooled judgment.
Although little can be done to combat challenges concerning the generalizability of case studies, "most writers suggest that qualitative research should be judged as credible and confirmable as opposed to valid and reliable" (Merriam 1985). Likewise, it has been argued that "rather than transplanting statistical, quantitative notions of generalizability and thus finding qualitative research inadequate, it makes more sense to develop an understanding of generalization that is congruent with the basic characteristics of qualitative inquiry" (1985). After all, criticizing the case study method for being ungeneralizable is comparable to criticizing a washing machine for not being able to tell the correct time. In other words, it is unjust to criticize a method for not being able to do something which it was never originally designed to do in the first place.
Annotated Bibliography
Armisted, C. (1984). How Useful are Case Studies. Training and Development Journal, 38 (2), 75-77.
This article looks at eight types of case studies, offers pros and cons of using case studies in the classroom, and gives suggestions for successfully writing and using case studies.
Bardovi-Harlig, K. (1997). Beyond Methods: Components of Second Language Teacher Education . New York: McGraw-Hill.
A compilation of various research essays which address issues of language teacher education. Essays included are: "Non-native reading research and theory" by Lee, "The case for Psycholinguistics" by VanPatten, and "Assessment and Second Language Teaching" by Gradman and Reed.
Bartlett, L. (1989). A Question of Good Judgment; Interpretation Theory and Qualitative Enquiry Address. 70th Annual Meeting of the American Educational Research Association. San Francisco.
Bartlett selected "quasi-historical" methodology, which focuses on the "truth" found in case records, as one that will provide "good judgments" in educational inquiry. He argues that although the method is not comprehensive, it can try to connect theory with practice.
Baydere, S. et. al. (1993). Multimedia conferencing as a tool for collaborative writing: a case study in Computer Supported Collaborative Writing. New York: Springer-Verlag.
The case study by Baydere et. al. is just one of the many essays in this book found in the series "Computer Supported Cooperative Work." Denley, Witefield and May explore similar issues in their essay, "A case study in task analysis for the design of a collaborative document production system."
Berkenkotter, C., Huckin, T., N., & Ackerman J. (1988). Conventions, Conversations, and the Writer: Case Study of a Student in a Rhetoric Ph.D. Program. Research in the Teaching of English, 22, 9-44.
The authors focused on how the writing of their subject, Nate or Ackerman, changed as he became more acquainted or familiar with his field's discourse community.
Berninger, V., W., and Gans, B., M. (1986). Language Profiles in Nonspeaking Individuals of Normal Intelligence with Severe Cerebral Palsy. Augmentative and Alternative Communication, 2, 45-50.
Argues that generalizations about language abilities in patients with severe cerebral palsy (CP) should be avoided. Standardized tests of different levels of processing oral language, of processing written language, and of producing written language were administered to 3 male participants (aged 9, 16, and 40 yrs).
Bockman, J., R., and Couture, B. (1984). The Case Method in Technical Communication: Theory and Models. Texas: Association of Teachers of Technical Writing.
Examines the study and teaching of technical writing, communication of technical information, and the case method in terms of those applications.
Boehrer, J. (1990). Teaching With Cases: Learning to Question. New Directions for Teaching and Learning, 42 41-57.
This article discusses the origins of the case method, looks at the question of what is a case, gives ideas about learning in case teaching, the purposes it can serve in the classroom, the ground rules for the case discussion, including the role of the question, and new directions for case teaching.
Bowman, W. R. (1993). Evaluating JTPA Programs for Economically Disadvantaged Adults: A Case Study of Utah and General Findings . Washington: National Commission for Employment Policy.
"To encourage state-level evaluations of JTPA, the Commission and the State of Utah co-sponsored this report on the effectiveness of JTPA Title II programs for adults in Utah. The technique used is non-experimental and the comparison group was selected from registrants with Utah's Employment Security. In a step-by-step approach, the report documents how non-experimental techniques can be applied and several specific technical issues can be addressed."
Boyce, A. (1993) The Case Study Approach for Pedagogists. Annual Meeting of the American Alliance for Health, Physical Education, Recreation and Dance. (Address). Washington DC.
This paper addresses how case studies 1) bridge the gap between teaching theory and application, 2) enable students to analyze problems and develop solutions for situations that will be encountered in the real world of teaching, and 3) helps students to evaluate the feasibility of alternatives and to understand the ramifications of a particular course of action.
Carson, J. (1993) The Case Study: Ideal Home of WAC Quantitative and Qualitative Data. Annual Meeting of the Conference on College Composition and Communication. (Address). San Diego.
"Increasingly, one of the most pressing questions for WAC advocates is how to keep [WAC] programs going in the face of numerous difficulties. Case histories offer the best chance for fashioning rhetorical arguments to keep WAC programs going because they offer the opportunity to provide a coherent narrative that contextualizes all documents and data, including what is generally considered scientific data. A case study of the WAC program, . . . at Robert Morris College in Pittsburgh demonstrates the advantages of this research method. Such studies are ideal homes for both naturalistic and positivistic data as well as both quantitative and qualitative information."
---. (1991). A Cognitive Process Theory of Writing. College Composition and Communication. 32. 365-87.
No abstract available.
Cromer, R. (1994) A Case Study of Dissociations Between Language and Cognition. Constraints on Language Acquisition: Studies of Atypical Children . Hillsdale: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, 141-153.
Crossley, M. (1983) Case Study in Comparative and International Education: An Approach to Bridging the Theory-Practice Gap. Proceedings of the 11th Annual Conference of the Australian Comparative and International Education Society. Hamilton, NZ.
Case study research, as presented here, helps bridge the theory-practice gap in comparative and international research studies of education because it focuses on the practical, day-to-day context rather than on the national arena. The paper asserts that the case study method can be valuable at all levels of research, formation, and verification of theories in education.
Daillak, R., H., and Alkin, M., C. (1982). Qualitative Studies in Context: Reflections on the CSE Studies of Evaluation Use . California: EDRS
The report shows how the Center of the Study of Evaluation (CSE) applied qualitative techniques to a study of evaluation information use in local, Los Angeles schools. It critiques the effectiveness and the limitations of using case study, evaluation, field study, and user interview survey methodologies.
Davey, L. (1991). The Application of Case Study Evaluations. ERIC/TM Digest.
This article examines six types of case studies, the type of evaluation questions that can be answered, the functions served, some design features, and some pitfalls of the method.
Deutch, C. E. (1996). A course in research ethics for graduate students. College Teaching, 44, 2, 56-60.
This article describes a one-credit discussion course in research ethics for graduate students in biology. Case studies are focused on within the four parts of the course: 1) major issues, 2 )practical issues in scholarly work, 3) ownership of research results, and 4) training and personal decisions.
DeVoss, G. (1981). Ethics in Fieldwork Research. RIE 27p. (ERIC)
This article examines four of the ethical problems that can happen when conducting case study research: acquiring permission to do research, knowing when to stop digging, the pitfalls of doing collaborative research, and preserving the integrity of the participants.
Driscoll, A. (1985). Case Study of a Research Intervention: the University of Utah’s Collaborative Approach . San Francisco: Far West Library for Educational Research Development.
Paper presented at the annual meeting of the American Association of Colleges of Teacher Education, Denver, CO, March 1985. Offers information of in-service training, specifically case studies application.
Ellram, L. M. (1996). The Use of the Case Study Method in Logistics Research. Journal of Business Logistics, 17, 2, 93.
This article discusses the increased use of case study in business research, and the lack of understanding of when and how to use case study methodology in business.
Emig, J. (1971) The Composing Processes of Twelfth Graders . Urbana: NTCE.
This case study uses observation, tape recordings, writing samples, and school records to show that writing in reflexive and extensive situations caused different lengths of discourse and different clusterings of the components of the writing process.
Feagin, J. R. (1991). A Case For the Case Study . Chapel Hill: The University of North Carolina Press.
This book discusses the nature, characteristics, and basic methodological issues of the case study as a research method.
Feldman, H., Holland, A., & Keefe, K. (1989) Language Abilities after Left Hemisphere Brain Injury: A Case Study of Twins. Topics in Early Childhood Special Education, 9, 32-47.
"Describes the language abilities of 2 twin pairs in which 1 twin (the experimental) suffered brain injury to the left cerebral hemisphere around the time of birth and1 twin (the control) did not. One pair of twins was initially assessed at age 23 mo. and the other at about 30 mo.; they were subsequently evaluated in their homes 3 times at about 6-mo intervals."
Fidel, R. (1984). The Case Study Method: A Case Study. Library and Information Science Research, 6.
The article describes the use of case study methodology to systematically develop a model of online searching behavior in which study design is flexible, subject manner determines data gathering and analyses, and procedures adapt to the study's progressive change.
Flower, L., & Hayes, J. R. (1984). Images, Plans and Prose: The Representation of Meaning in Writing. Written Communication, 1, 120-160.
Explores the ways in which writers actually use different forms of knowing to create prose.
Frey, L. R. (1992). Interpreting Communication Research: A Case Study Approach Englewood Cliffs, N.J.: Prentice Hall.
The book discusses research methodologies in the Communication field. It focuses on how case studies bridge the gap between communication research, theory, and practice.
Gilbert, V. K. (1981). The Case Study as a Research Methodology: Difficulties and Advantages of Integrating the Positivistic, Phenomenological and Grounded Theory Approaches . The Annual Meeting of the Canadian Association for the Study of Educational Administration. (Address) Halifax, NS, Can.
This study on an innovative secondary school in England shows how a "low-profile" participant-observer case study was crucial to the initial observation, the testing of hypotheses, the interpretive approach, and the grounded theory.
Gilgun, J. F. (1994). A Case for Case Studies in Social Work Research. Social Work, 39, 4, 371-381.
This article defines case study research, presents guidelines for evaluation of case studies, and shows the relevance of case studies to social work research. It also looks at issues such as evaluation and interpretations of case studies.
Glennan, S. L., Sharp-Bittner, M. A. & Tullos, D. C. (1991). Augmentative and Alternative Communication Training with a Nonspeaking Adult: Lessons from MH. Augmentative and Alternative Communication, 7, 240-7.
"A response-guided case study documented changes in a nonspeaking 36-yr-old man's ability to communicate using 3 trained augmentative communication modes. . . . Data were collected in videotaped interaction sessions between the nonspeaking adult and a series of adult speaking."
Graves, D. (1981). An Examination of the Writing Processes of Seven Year Old Children. Research in the Teaching of English, 15, 113-134.
Hamel, J. (1993). Case Study Methods . Newbury Park: Sage. .
"In a most economical fashion, Hamel provides a practical guide for producing theoretically sharp and empirically sound sociological case studies. A central idea put forth by Hamel is that case studies must "locate the global in the local" thus making the careful selection of the research site the most critical decision in the analytic process."
Karthigesu, R. (1986, July). Television as a Tool for Nation-Building in the Third World: A Post-Colonial Pattern, Using Malaysia as a Case-Study. International Television Studies Conference. (Address). London, 10-12.
"The extent to which Television Malaysia, as a national mass media organization, has been able to play a role in nation building in the post-colonial period is . . . studied in two parts: how the choice of a model of nation building determines the character of the organization; and how the character of the organization influences the output of the organization."
Kenny, R. (1984). Making the Case for the Case Study. Journal of Curriculum Studies, 16, (1), 37-51.
The article looks at how and why the case study is justified as a viable and valuable approach to educational research and program evaluation.
Knirk, F. (1991). Case Materials: Research and Practice. Performance Improvement Quarterly, 4 (1 ), 73-81.
The article addresses the effectiveness of case studies, subject areas where case studies are commonly used, recent examples of their use, and case study design considerations.
Klos, D. (1976). Students as Case Writers. Teaching of Psychology, 3.2, 63-66.
This article reviews a course in which students gather data for an original case study of another person. The task requires the students to design the study, collect the data, write the narrative, and interpret the findings.
Leftwich, A. (1981). The Politics of Case Study: Problems of Innovation in University Education. Higher Education Review, 13.2, 38-64.
The article discusses the use of case studies as a teaching method. Emphasis is on the instructional materials, interdisciplinarity, and the complex relationships within the university that help or hinder the method.
Mabrito, M. (1991, Oct.). Electronic Mail as a Vehicle for Peer Response: Conversations of High and Low Apprehensive Writers. Written Communication, 509-32.
McCarthy, S., J. (1955). The Influence of Classroom Discourse on Student Texts: The Case of Ella . East Lansing: Institute for Research on Teaching.
A look at how students of color become marginalized within traditional classroom discourse. The essay follows the struggles of one black student: Ella.
Matsuhashi, A., ed. (1987). Writing in Real Time: Modeling Production Processes Norwood, NJ: Ablex Publishing Corporation.
Investigates how writers plan to produce discourse for different purposes to report, to generalize, and to persuade, as well as how writers plan for sentence level units of language. To learn about planning, an observational measure of pause time was used" (ERIC).
Merriam, S. B. (1985). The Case Study in Educational Research: A Review of Selected Literature. Journal of Educational Thought, 19.3, 204-17.
The article examines the characteristics of, philosophical assumptions underlying the case study, the mechanics of conducting a case study, and the concerns about the reliability, validity, and generalizability of the method.
---. (1988). Case Study Research in Education: A Qualitative Approach San Francisco: Jossey Bass.
Merry, S. E., & Milner, N. eds. (1993). The Possibility of Popular Justice: A Case Study of Community Mediation in the United States . Ann Arbor: U of Michigan.
". . . this volume presents a case study of one experiment in popular justice, the San Francisco Community Boards. This program has made an explicit claim to create an alternative justice, or new justice, in the midst of a society ordered by state law. The contributors to this volume explore the history and experience of the program and compare it to other versions of popular justice in the United States, Europe, and the Third World."
Merseth, K. K. (1991). The Case for Cases in Teacher Education. RIE. 42p. (ERIC).
This monograph argues that the case method of instruction offers unique potential for revitalizing the field of teacher education.
Michaels, S. (1987). Text and Context: A New Approach to the Study of Classroom Writing. Discourse Processes, 10, 321-346.
"This paper argues for and illustrates an approach to the study of writing that integrates ethnographic analysis of classroom interaction with linguistic analysis of written texts and teacher/student conversational exchanges. The approach is illustrated through a case study of writing in a single sixth grade classroom during a single writing assignment."
Milburn, G. (1995). Deciphering a Code or Unraveling a Riddle: A Case Study in the Application of a Humanistic Metaphor to the Reporting of Social Studies Teaching. Theory and Research in Education, 13.
This citation serves as an example of how case studies document learning procedures in a senior-level economics course.
Milley, J. E. (1979). An Investigation of Case Study as an Approach to Program Evaluation. 19th Annual Forum of the Association for Institutional Research. (Address). San Diego.
The case study method merged a narrative report focusing on the evaluator as participant-observer with document review, interview, content analysis, attitude questionnaire survey, and sociogram analysis. Milley argues that case study program evaluation has great potential for widespread use.
Minnis, J. R. (1985, Sept.). Ethnography, Case Study, Grounded Theory, and Distance Education Research. Distance Education, 6.2.
This article describes and defines the strengths and weaknesses of ethnography, case study, and grounded theory.
Nunan, D. (1992). Collaborative language learning and teaching . New York: Cambridge University Press.
Included in this series of essays is Peter Sturman’s "Team Teaching: a case study from Japan" and David Nunan’s own "Toward a collaborative approach to curriculum development: a case study."
Nystrand, M., ed. (1982). What Writers Know: The Language, Process, and Structure of Written Discourse . New York: Academic Press.
Owenby, P. H. (1992). Making Case Studies Come Alive. Training, 29, (1), 43-46. (ERIC)
This article provides tips for writing more effective case studies.
---. (1981). Pausing and Planning: The Tempo of Writer Discourse Production. Research in the Teaching of English, 15 (2),113-34.
Perl, S. (1979). The Composing Processes of Unskilled College Writers. Research in the Teaching of English, 13, 317-336.
"Summarizes a study of five unskilled college writers, focusing especially on one of the five, and discusses the findings in light of current pedagogical practice and research design."
Pilcher J. and A. Coffey. eds. (1996). Gender and Qualitative Research . Brookfield: Aldershot, Hants, England.
This book provides a series of essays which look at gender identity research, qualitative research and applications of case study to questions of gendered pedagogy.
Pirie, B. S. (1993). The Case of Morty: A Four Year Study. Gifted Education International, 9 (2), 105-109.
This case study describes a boy from kindergarten through third grade with above average intelligence but difficulty in learning to read, write, and spell.
Popkewitz, T. (1993). Changing Patterns of Power: Social Regulation and Teacher Education Reform. Albany: SUNY Press.
Popkewitz edits this series of essays that address case studies on educational change and the training of teachers. The essays vary in terms of discipline and scope. Also, several authors include case studies of educational practices in countries other than the United States.
---. (1984). The Predrafting Processes of Four High- and Four Low Apprehensive Writers. Research in the Teaching of English, 18, (1), 45-64.
Rasmussen, P. (1985, March) A Case Study on the Evaluation of Research at the Technical University of Denmark. International Journal of Institutional Management in Higher Education, 9 (1).
This is an example of a case study methodology used to evaluate the chemistry and chemical engineering departments at the University of Denmark.
Roth, K. J. (1986). Curriculum Materials, Teacher Talk, and Student Learning: Case Studies in Fifth-Grade Science Teaching . East Lansing: Institute for Research on Teaching.
Roth offers case studies on elementary teachers, elementary school teaching, science studies and teaching, and verbal learning.
Selfe, C. L. (1985). An Apprehensive Writer Composes. When a Writer Can't Write: Studies in Writer's Block and Other Composing-Process Problems . (pp. 83-95). Ed. Mike Rose. NMY: Guilford.
Smith-Lewis, M., R. and Ford, A. (1987). A User's Perspective on Augmentative Communication. Augmentative and Alternative Communication, 3, 12-7.
"During a series of in-depth interviews, a 25-yr-old woman with cerebral palsy who utilized augmentative communication reflected on the effectiveness of the devices designed for her during her school career."
St. Pierre, R., G. (1980, April). Follow Through: A Case Study in Metaevaluation Research . 64th Annual Meeting of the American Educational Research Association. (Address).
The three approaches to metaevaluation are evaluation of primary evaluations, integrative meta-analysis with combined primary evaluation results, and re-analysis of the raw data from a primary evaluation.
Stahler, T., M. (1996, Feb.) Early Field Experiences: A Model That Worked. ERIC.
"This case study of a field and theory class examines a model designed to provide meaningful field experiences for preservice teachers while remaining consistent with the instructor's beliefs about the role of teacher education in preparing teachers for the classroom."
Stake, R. E. (1995). The Art of Case Study Research. Thousand Oaks: Sage Publications.
This book examines case study research in education and case study methodology.
Stiegelbauer, S. (1984) Community, Context, and Co-curriculum: Situational Factors Influencing School Improvements in a Study of High Schools. Presented at the annual meeting of the American Educational Research Association, New Orleans, LA.
Discussion of several case studies: one looking at high school environments, another examining educational innovations.
Stolovitch, H. (1990). Case Study Method. Performance And Instruction, 29, (9), 35-37.
This article describes the case study method as a form of simulation and presents guidelines for their use in professional training situations.
Thaller, E. (1994). Bibliography for the Case Method: Using Case Studies in Teacher Education. RIE. 37 p.
This bibliography presents approximately 450 citations on the use of case studies in teacher education from 1921-1993.
Thrane, T. (1986). On Delimiting the Senses of Near-Synonyms in Historical Semantics: A Case Study of Adjectives of 'Moral Sufficiency' in the Old English Andreas. Linguistics Across Historical and Geographical Boundaries: In Honor of Jacek Fisiak on the Occasion of his Fiftieth Birthday . Berlin: Mouton de Gruyter.
United Nations. (1975). Food and Agriculture Organization. Report on the FAO/UNFPA Seminar on Methodology, Research and Country: Case Studies on Population, Employment and Productivity . Rome: United Nations.
This example case study shows how the methodology can be used in a demographic and psychographic evaluation. At the same time, it discusses the formation and instigation of the case study methodology itself.
Van Vugt, J. P., ed. (1994). Aids Prevention and Services: Community Based Research . Westport: Bergin and Garvey.
"This volume has been five years in the making. In the process, some of the policy applications called for have met with limited success, such as free needle exchange programs in a limited number of American cities, providing condoms to prison inmates, and advertisements that depict same-sex couples. Rather than dating our chapters that deal with such subjects, such policy applications are verifications of the type of research demonstrated here. Furthermore, they indicate the critical need to continue community based research in the various communities threatened by acquired immuno-deficiency syndrome (AIDS) . . . "
Welch, W., ed. (1981, May). Case Study Methodology in Educational Evaluation. Proceedings of the Minnesota Evaluation Conference. Minnesota. (Address).
The four papers in these proceedings provide a comprehensive picture of the rationale, methodology, strengths, and limitations of case studies.
Williams, G. (1987). The Case Method: An Approach to Teaching and Learning in Educational Administration. RIE, 31p.
This paper examines the viability of the case method as a teaching and learning strategy in instructional systems geared toward the training of personnel of the administration of various aspects of educational systems.
Yin, R. K. (1993). Advancing Rigorous Methodologies: A Review of 'Towards Rigor in Reviews of Multivocal Literatures.' Review of Educational Research, 61, (3).
"R. T. Ogawa and B. Malen's article does not meet its own recommended standards for rigorous testing and presentation of its own conclusions. Use of the exploratory case study to analyze multivocal literatures is not supported, and the claim of grounded theory to analyze multivocal literatures may be stronger."
---. (1989). Case Study Research: Design and Methods. London: Sage Publications Inc.
This book discusses in great detail, the entire design process of the case study, including entire chapters on collecting evidence, analyzing evidence, composing the case study report, and designing single and multiple case studies.
Related Links
Consider the following list of related Web sites for more information on the topic of case study research. Note: although many of the links cover the general category of qualitative research, all have sections that address issues of case studies.
- Sage Publications on Qualitative Methodology: Search here for a comprehensive list of new books being published about "Qualitative Methodology" http://www.sagepub.co.uk/
- The International Journal of Qualitative Studies in Education: An on-line journal "to enhance the theory and practice of qualitative research in education." On-line submissions are welcome. http://www.tandf.co.uk/journals/tf/09518398.html
- Qualitative Research Resources on the Internet: From syllabi to home pages to bibliographies. All links relate somehow to qualitative research. http://www.nova.edu/ssss/QR/qualres.html
Citation Information
Bronwyn Becker, Patrick Dawson, Karen Devine, Carla Hannum, Steve Hill, Jon Leydens, Debbie Matuskevich, Carol Traver, and Mike Palmquist. (1994-2024). Case Studies. The WAC Clearinghouse. Colorado State University. Available at https://wac.colostate.edu/repository/writing/guides/.
Copyright Information
Copyright © 1994-2024 Colorado State University and/or this site's authors, developers, and contributors . Some material displayed on this site is used with permission.
Chapter 11 Case Research
Case research, also called case study, is a method of intensively studying a phenomenon over time within its natural setting in one or a few sites. Multiple methods of data collection, such as interviews, observations, prerecorded documents, and secondary data, may be employed and inferences about the phenomenon of interest tend to be rich, detailed, and contextualized. Case research can be employed in a positivist manner for the purpose of theory testing or in an interpretive manner for theory building. This method is more popular in business research than in other social science disciplines.
Case research has several unique strengths over competing research methods such as experiments and survey research. First, case research can be used for either theory building or theory testing, while positivist methods can be used for theory testing only. In interpretive case research, the constructs of interest need not be known in advance, but may emerge from the data as the research progresses. Second, the research questions can be modified during the research process if the original questions are found to be less relevant or salient. This is not possible in any positivist method after the data is collected. Third, case research can help derive richer, more contextualized, and more authentic interpretation of the phenomenon of interest than most other research methods by virtue of its ability to capture a rich array of contextual data. Fourth, the phenomenon of interest can be studied from the perspectives of multiple participants and using multiple levels of analysis (e.g., individual and organizational).
At the same time, case research also has some inherent weaknesses. Because it involves no experimental control, internal validity of inferences remain weak. Of course, this is a common problem for all research methods except experiments. However, as described later, the problem of controls may be addressed in case research using “natural controls”. Second, the quality of inferences derived from case research depends heavily on the integrative powers of the researcher. An experienced researcher may see concepts and patterns in case data that a novice researcher may miss. Hence, the findings are sometimes criticized as being subjective. Finally, because the inferences are heavily contextualized, it may be difficult to generalize inferences from case research to other contexts or other organizations.
It is important to recognize that case research is different from case descriptions such as Harvard case studies discussed in business classes. While case descriptions typically describe an organizational problem in rich detail with the goal of stimulating classroom discussion and critical thinking among students, or analyzing how well an organization handled a specific problem, case research is a formal research technique that involves a scientific method to derive explanations of organizational phenomena.
Case research is a difficult research method that requires advanced research skills on the part of the researcher, and is therefore, often prone to error. Benbasat et al. (1987) [8] describe five problems frequently encountered in case research studies. First, many case research studies start without specific research questions, and therefore end up without having any specific answers or insightful inferences. Second, case sites are often chosen based on access and convenience, rather than based on the fit with the research questions, and are therefore cannot adequately address the research questions of interest. Third, researchers often do not validate or triangulate data collected using multiple means, which may lead to biased interpretation based on responses from biased interviewees. Fourth, many studies provide very little details on how data was collected (e.g., what interview questions were used, which documents were examined, what are the organizational positions of each interviewee, etc.) or analyzed, which may raise doubts about the reliability of the inferences. Finally, despite its strength as a longitudinal research method, many case research studies do not follow through a phenomenon in a longitudinal manner, and hence present only a cross-sectional and limited view of organizational processes and phenomena that are temporal in nature.
Key Decisions in Case Research
Several key decisions must be made by a researcher when considering a case research method. First, is this the right method for the research questions being studied? The case research method is particularly appropriate for exploratory studies for discovering relevant constructs in areas where theory building at the formative stages, for studies where the experiences of participants and context of actions are critical, and for studies aimed at understanding complex, temporal processes (why and how of a phenomenon) rather than factors or causes (what). This method is well-suited for studying complex organizational processes that involve multiple participants and interacting sequences of events, such as organizational change and large-scale technology implementation projects.
Second, what is the appropriate unit of analysis for a case research study? Since case research can simultaneously examine multiple units of analyses, the researcher must decide whether she wishes to study a phenomenon at the individual, group, and organizational level or at multiple levels. For instance, a study of group decision making or group work may combine individual-level constructs such as individual participation in group activities with group-level constructs, such as group cohesion and group leadership, to derive richer understanding than that can be achieved from a single level of analysis.
Third, should the researcher employ a single-case or multiple-case design? The single case design is more appropriate at the outset of theory generation, if the situation is unique or extreme, if it is revelatory (i.e., the situation was previously inaccessible for scientific investigation), or if it represents a critical or contrary case for testing a well-formulated theory. The multiple case design is more appropriate for theory testing, for establishing generalizability of inferences, and for developing richer and more nuanced interpretations of a phenomenon. Yin (1984) [9] recommends the use of multiple case sites with replication logic, viewing each case site as similar to one experimental study, and following rules of scientific rigor similar to that used in positivist research.
Fourth, what sites should be chosen for case research? Given the contextualized nature of inferences derived from case research, site selection is a particularly critical issue because selecting the wrong site may lead to the wrong inferences. If the goal of the research is to test theories or examine generalizability of inferences, then dissimilar case sites should be selected to increase variance in observations. For instance, if the goal of the research is to understand the process of technology implementation in firms, a mix of large, mid-sized, and small firms should be selected to examine whether the technology implementation process differs with firm size. Site selection should not be opportunistic or based on convenience, but rather based on the fit with research questions through a process called “theoretical sampling.”
Fifth, what techniques of data collection should be used in case research? Although interview (either open-ended/unstructured or focused/structured) is by far the most popular data collection technique for case research, interview data can be supplemented or corroborated with other techniques such as direct observation (e.g., attending executive meetings, briefings, and planning sessions), documentation (e.g., internal reports, presentations, and memoranda, as well as external accounts such as newspaper reports), archival records (e.g., organization charts, financial records, etc.), and physical artifacts (e.g., devices, outputs, tools). Furthermore, the researcher should triangulate or validate observed data by comparing responses between interviewees.
Conducting Case Research
Most case research studies tend to be interpretive in nature. Interpretive case research is an inductive technique where evidence collected from one or more case sites is systematically analyzed and synthesized to allow concepts and patterns to emerge for the purpose of building new theories or expanding existing ones. Eisenhardt (1989) [10] propose a “roadmap” for building theories from case research, a slightly modified version of which is described below. For positivist case research, some of the following stages may need to be rearranged or modified; however sampling, data collection, and data analytic techniques should generally remain the same.
Define research questions. Like any other scientific research, case research must also start with defining research questions that are theoretically and practically interesting, and identifying some intuitive expectations about possible answers to those research questions or preliminary constructs to guide initial case design. In positivist case research, the preliminary constructs are based on theory, while no such theory or hypotheses should be considered ex ante in interpretive research. These research questions and constructs may be changed in interpretive case research later on, if needed, but not in positivist case research.
Select case sites. The researcher should use a process of “theoretical sampling” (not random sampling) to identify case sites. In this approach, case sites are chosen based on theoretical, rather than statistical, considerations, for instance, to replicate previous cases, to extend preliminary theories, or to fill theoretical categories or polar types. Care should be taken to ensure that the selected sites fit the nature of research questions, minimize extraneous variance or noise due to firm size, industry effects, and so forth, and maximize variance in the dependent variables of interest. For instance, if the goal of the research is to examine how some firms innovate better than others, the researcher should select firms of similar size within the same industry to reduce industry or size effects, and select some more innovative and some less innovative firms to increase variation in firm innovation. Instead of cold-calling or writing to a potential site, it is better to contact someone at executive level inside each firm who has the authority to approve the project or someone who can identify a person of authority. During initial conversations, the researcher should describe the nature and purpose of the project, any potential benefits to the case site, how the collected data will be used, the people involved in data collection (other researchers, research assistants, etc.), desired interviewees, and the amount of time, effort, and expense required of the sponsoring organization. The researcher must also assure confidentiality, privacy, and anonymity of both the firm and the individual respondents.
Create instruments and protocols. Since the primary mode of data collection in case research is interviews, an interview protocol should be designed to guide the interview process. This is essentially a list of questions to be asked. Questions may be open-ended (unstructured) or closed-ended (structured) or a combination of both. The interview protocol must be strictly followed, and the interviewer must not change the order of questions or skip any question during the interview process, although some deviations are allowed to probe further into respondent’s comments that are ambiguous or interesting. The interviewer must maintain a neutral tone, not lead respondents in any specific direction, say by agreeing or disagreeing with any response. More detailed interviewing techniques are discussed in the chapter on surveys. In addition, additional sources of data, such as internal documents and memorandums, annual reports, financial statements, newspaper articles, and direct observations should be sought to supplement and validate interview data.
Select respondents. Select interview respondents at different organizational levels, departments, and positions to obtain divergent perspectives on the phenomenon of interest. A random sampling of interviewees is most preferable; however a snowball sample is acceptable, as long as a diversity of perspectives is represented in the sample. Interviewees must be selected based on their personal involvement with the phenomenon under investigation and their ability and willingness to answer the researcher’s questions accurately and adequately, and not based on convenience or access.
Start data collection . It is usually a good idea to electronically record interviews for future reference. However, such recording must only be done with the interviewee’s consent. Even when interviews are being recorded, the interviewer should take notes to capture important comments or critical observations, behavioral responses (e.g., respondent’s body language), and the researcher’s personal impressions about the respondent and his/her comments. After each interview is completed, the entire interview should be transcribed verbatim into a text document for analysis.
Conduct within-case data analysis. Data analysis may follow or overlap with data collection. Overlapping data collection and analysis has the advantage of adjusting the data collection process based on themes emerging from data analysis, or to further probe into these themes. Data analysis is done in two stages. In the first stage (within-case analysis), the researcher should examine emergent concepts separately at each case site and patterns between these concepts to generate an initial theory of the problem of interest. The researcher can interview data subjectively to “make sense” of the research problem in conjunction with using her personal observations or experience at the case site. Alternatively, a coding strategy such as Glasser and Strauss’ (1967) grounded theory approach, using techniques such as open coding, axial coding, and selective coding, may be used to derive a chain of evidence and inferences. These techniques are discussed in detail in a later chapter. Homegrown techniques, such as graphical representation of data (e.g., network diagram) or sequence analysis (for longitudinal data) may also be used. Note that there is no predefined way of analyzing the various types of case data, and the data analytic techniques can be modified to fit the nature of the research project.
Conduct cross-case analysis. Multi-site case research requires cross-case analysis as the second stage of data analysis. In such analysis, the researcher should look for similar concepts and patterns between different case sites, ignoring contextual differences that may lead to idiosyncratic conclusions. Such patterns may be used for validating the initial theory, or for refining it (by adding or dropping concepts and relationships) to develop a more inclusive and generalizable theory. This analysis may take several forms. For instance, the researcher may select categories (e.g., firm size, industry, etc.) and look for within-group similarities and between-group differences (e.g., high versus low performers, innovators versus laggards). Alternatively, she can compare firms in a pair-wise manner listing similarities and differences across pairs of firms.
Build and test hypotheses. Based on emergent concepts and themes that are generalizable across case sites, tentative hypotheses are constructed. These hypotheses should be compared iteratively with observed evidence to see if they fit the observed data, and if not, the constructs or relationships should be refined. Also the researcher should compare the emergent constructs and hypotheses with those reported in the prior literature to make a case for their internal validity and generalizability. Conflicting findings must not be rejected, but rather reconciled using creative thinking to generate greater insight into the emergent theory. When further iterations between theory and data yield no new insights or changes in the existing theory, “theoretical saturation” is reached and the theory building process is complete.
Write case research report. In writing the report, the researcher should describe very clearly the detailed process used for sampling, data collection, data analysis, and hypotheses development, so that readers can independently assess the reasonableness, strength, and consistency of the reported inferences. A high level of clarity in research methods is needed to ensure that the findings are not biased by the researcher’s preconceptions.
Interpretive Case Research Exemplar
Perhaps the best way to learn about interpretive case research is to examine an illustrative example. One such example is Eisenhardt’s (1989) [11] study of how executives make decisions in high-velocity environments (HVE). Readers are advised to read the original paper published in Academy of Management Journal before reading the synopsis in this chapter. In this study, Eisenhardt examined how executive teams in some HVE firms make fast decisions, while those in other firms cannot, and whether faster decisions improve or worsen firm performance in such environments. HVE was defined as one where demand, competition, and technology changes so rapidly and discontinuously that the information available is often inaccurate, unavailable or obsolete. The implicit assumptions were that (1) it is hard to make fast decisions with inadequate information in HVE, and (2) fast decisions may not be efficient and may result in poor firm performance.
Reviewing the prior literature on executive decision -making, Eisenhardt found several patterns, although none of these patterns were specific to high-velocity environments. The literature suggested that in the interest of expediency, firms that make faster decisions obtain input from fewer sources, consider fewer alternatives, make limited analysis, restrict user participation in decision-making, centralize decision-making authority, and has limited internal conflicts. However, Eisenhardt contended that these views may not necessarily explain how decision makers make decisions in high-velocity environments, where decisions must be made quickly and with incomplete information, while maintaining high decision quality.
To examine this phenomenon, Eisenhardt conducted an inductive study of eight firms in the personal computing industry. The personal computing industry was undergoing dramatic changes in technology with the introduction of the UNIX operating system, RISC architecture, and 64KB random access memory in the 1980’s, increased competition with the entry of IBM into the personal computing business, and growing customer demand with double-digit demand growth, and therefore fit the profile of the high-velocity environment. This was a multiple case design with replication logic, where each case was expected to confirm or disconfirm inferences from other cases. Case sites were selected based on their access and proximity to the researcher; however, all of these firms operated in the high-velocity personal computing industry in California’s Silicon Valley area. The collocation of firms in the same industry and the same area ruled out any “noise” or variance in dependent variables (decision speed or performance) attributable to industry or geographic differences.
The study employed an embedded design with multiple levels of analysis: decision (comparing multiple strategic decisions within each firm), executive teams (comparing different teams responsible for strategic decisions), and the firm (overall firm performance). Data was collected from five sources:
- Initial interviews with Chief Executive Officers: CEOs were asked questions about their firm’s competitive strategy, distinctive competencies, major competitors, performance, and recent/ongoing major strategic decisions. Based on these interviews, several strategic decisions were selected in each firm for further investigation. Four criteria were used to select decisions: (1) the decisions involved the firm’s strategic positioning,
(2) the decisions had high stakes, (3) the decisions involved multiple functions, and (4) the decisions were representative of strategic decision-making process in that firm.
- Interviews with divisional heads: Each divisional head was asked sixteen open-ended questions, ranging from their firm’s competitive strategy, functional strategy, top management team members, frequency and nature of interaction with team, typical decision making processes, how each of the previously identified decision was made, and how long it took them to make those decisions. Interviews lasted between 1.5 and 2 hours, and sometimes extended to 4 hours. To focus on facts and actual events rather than respondents’ perceptions or interpretations, a “courtroom” style questioning was employed, such as when did this happen, what did you do, etc. Interviews were conducted by two people, and the data was validated by cross-checking facts and impressions made by the interviewer and note-taker. All interview data was recorded, however notes were also taken during each interview, which ended with the interviewer’s overall impressions. Using a “24-hour rule”, detailed field notes were completed within 24 hours of the interview, so that some data or impressions were not lost to recall.
- Questionnaires: Executive team members at each firm were completed a survey questionnaire that captured quantitative data on the extent of conflict and power distribution in their firm.
- Secondary data: Industry reports and internal documents such as demographics of the executive teams (responsible for strategic decisions), financial performance of firms, and so forth, were examined.
- Personal observation: Lastly, the researcher attended a 1-day strategy session and a weekly executive meeting at two firms in her sample.
Data analysis involved a combination of quantitative and qualitative techniques. Quantitative data on conflict and power were analyzed for patterns across firms/decisions. Qualitative interview data was combined into decision climate profiles, using profile traits (e.g., impatience) mentioned by more than one executive. For within-case analysis, decision stories were created for each strategic decision by combining executive accounts of the key decision events into a timeline. For cross-case analysis, pairs of firms were compared for similarities and differences, categorized along variables of interest such as decision speed and firm performance. Based on these analyses, tentative constructs and propositions were derived inductively from each decision story within firm categories. Each decision case was revisited to confirm the proposed relationships. The inferred propositions were compared with findings from the existing literature to reconcile examine differences with the extant literature and to generate new insights from the case findings. Finally, the validated propositions were synthesized into an inductive theory of strategic decision-making by firms in high-velocity environments.
Inferences derived from this multiple case research contradicted several decision-making patterns expected from the existing literature. First, fast decision makers in high-velocity environments used more information, and not less information as suggested by the previous literature. However, these decision makers used more real-time information (an insight not available from prior research), which helped them identify and respond to problems, opportunities, and changing circumstances faster. Second, fast decision makers examined more (not fewer) alternatives. However, they considered these multiple alternatives in a simultaneous manner, while slower decision makers examined fewer alternatives in a sequential manner. Third, fast decision makers did not centralize decision making or restrict inputs from others, as the literature suggested. Rather, these firms used a two-tiered decision process in which experienced counselors were asked for inputs in the first stage, following by a rapid comparison and decision selection in the second stage. Fourth, fast decision makers did not have less conflict, as expected from the literature, but employed better conflict resolution techniques to reduce conflict and improve decision-making speed. Finally, fast decision makers exhibited superior firm performance by virtue of their built-in cognitive, emotional, and political processes that led to rapid closure of major decisions.
Positivist Case Research Exemplar
Case research can also be used in a positivist manner to test theories or hypotheses. Such studies are rare, but Markus (1983) [12] provides an exemplary illustration in her study of technology implementation at the Golden Triangle Company (a pseudonym). The goal of this study was to understand why a newly implemented financial information system (FIS), intended to improve the productivity and performance of accountants at GTC was supported by accountants at GTC’s corporate headquarters but resisted by divisional accountants at GTC branches. Given the uniqueness of the phenomenon of interest, this was a single-case research study.
To explore the reasons behind user resistance of FIS, Markus posited three alternative explanations: (1) system-determined theory: resistance was caused by factors related to an inadequate system, such as its technical deficiencies, poor ergonomic design, or lack of user friendliness, (2) people-determined theory: resistance was caused by factors internal to users, such as the accountants’ cognitive styles or personality traits that were incompatible with using the system, and (3) interaction theory: resistance was not caused not by factors intrinsic to the system or the people, but by the interaction between the two set of factors. Specifically, interaction theory suggested that the FIS engendered a redistribution of intra-organizational power, and accountants who lost organizational status, relevance, or power as a result of FIS implementation resisted the system while those gaining power favored it.
In order to test the three theories, Markus predicted alternative outcomes expected from each theoretical explanation and analyzed the extent to which those predictions matched with her observations at GTC. For instance, the system-determined theory suggested that since user resistance was caused by an inadequate system, fixing the technical problems of the system would eliminate resistance. The computer running the FIS system was subsequently upgraded with a more powerful operating system, online processing (from initial batch processing, which delayed immediate processing of accounting information), and a simplified software for new account creation by managers. One year after these changes were made, the resistant users were still resisting the system and felt that it should be replaced. Hence, the system-determined theory was rejected.
The people-determined theory predicted that replacing individual resistors or co-opting them with less resistant users would reduce their resistance toward the FIS. Subsequently, GTC started a job rotation and mobility policy, moving accountants in and out of the resistant divisions, but resistance not only persisted, but in some cases increased! In one specific instance, one accountant, who was one of the system’s designers and advocates when he worked for corporate accounting, started resisting the system after he was moved to the divisional controller’s office. Failure to realize the predictions of the people-determined theory led to the rejection of this theory.
Finally, the interaction theory predicted that neither changing the system or the people (i.e., user education or job rotation policies) will reduce resistance as long as the power imbalance and redistribution from the pre-implementation phase were not addressed. Before FIS implementation, divisional accountants at GTC felt that they owned all accounting data related to their divisional operations. They maintained this data in thick, manual ledger books, controlled others’ access to the data, and could reconcile unusual accounting events before releasing those reports. Corporate accountants relied heavily on divisional accountants for access to the divisional data for corporate reporting and consolidation. Because the FIS system automatically collected all data at source and consolidated them into a single corporate database, it obviated the need for divisional accountants, loosened their control and autonomy over their division’s accounting data, and making their job somewhat irrelevant. Corporate accountants could now query the database and access divisional data directly without going through the divisional accountants, analyze and compare the performance of individual divisions, and report unusual patterns and activities to the executive committee, resulting in further erosion of the divisions’ power. Though Markus did not empirically test this theory, her observations about the redistribution of organizational power, coupled with the rejection of the two alternative theories, led to the justification of interaction theory.
Comparisons with Traditional Research
Positivist case research, aimed at hypotheses testing, is often criticized by natural science researchers as lacking in controlled observations, controlled deductions, replicability, and generalizability of findings – the traditional principles of positivist research. However, these criticisms can be overcome through appropriate case research designs. For instance, the problem of controlled observations refers to the difficulty of obtaining experimental or statistical control in case research. However, case researchers can compensate for such lack of controls by employing “natural controls.” This natural control in Markus’ (1983) study was the corporate accountant who was one of the system advocates initially, but started resisting it once he moved to controlling division. In this instance, the change in his behavior may be attributed to his new divisional position. However, such natural controls cannot be anticipated in advance, and case researchers may overlook then unless they are proactively looking for such controls. Incidentally, natural controls are also used in natural science disciplines such as astronomy, geology, and human biology, such as wait for comets to pass close enough to the earth in order to make inferences about comets and their composition.
The problem of controlled deduction refers to the lack of adequate quantitative evidence to support inferences, given the mostly qualitative nature of case research data. Despite the lack of quantitative data for hypotheses testing (e.g., t-tests), controlled deductions can still be obtained in case research by generating behavioral predictions based on theoretical considerations and testing those predictions over time. Markus employed this strategy in her study by generating three alternative theoretical hypotheses for user resistance, and rejecting two of those predictions when they did not match with actual observed behavior. In this case, the hypotheses were tested using logical propositions rather than using mathematical tests, which are just as valid as statistical inferences since mathematics is a subset of logic.
Third, the problem of replicability refers to the difficulty of observing the same phenomenon given the uniqueness and idiosyncrasy of a given case site. However, using Markus’ three theories as an illustration, a different researcher can test the same theories at a different case site, where three different predictions may emerge based on the idiosyncratic nature of the new case site, and the three resulting predictions may be tested accordingly. In other words, it is possible to replicate the inferences of case research, even if the case research site or context may not be replicable.
Fourth, case research tends to examine unique and non-replicable phenomena that may not be generalized to other settings. Generalizability in natural sciences is established through additional studies. Likewise, additional case studies conducted in different contexts with different predictions can establish generalizability of findings if such findings are observed to be consistent across studies.
Lastly, British philosopher Karl Popper described four requirements of scientific theories: (1) theories should be falsifiable, (2) they should be logically consistent, (3) they should have adequate predictive ability, and (4) they should provide better explanation than rival theories. In case research, the first three requirements can be increased by increasing the degrees of freedom of observed findings, such as by increasing the number of case sites, the number of alternative predictions, and the number of levels of analysis examined. This was accomplished in Markus’ study by examining the behavior of multiple groups (divisional accountants and corporate accountants) and providing multiple (three) rival explanations.
Popper’s fourth condition was accomplished in this study when one hypothesis was found to match observed evidence better than the two rival hypotheses.
[8] Benbasat, I., Goldstein, D. K., and Mead, M. (1987). “The Case Research Strategy in Studies of Information Systems,” MIS Quarterly (11:3), 369-386.
[9] Yin, R. K. (2002), Case Study Research: Design and Methods . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications.
[10] Eisenhardt, K. M. (1989). “Building Theories from Case Research,” Academy of Management Review
(14:4), 532-550.
[11] Eisenhardt, K. M. (1989). “Making Fast Strategic Decisions in High-Velocity Environments,” Academy of Management Journal (32:3), 543-576.
[12] Markus, M. L. (1983). “Power, Politics, and MIS Implementation,” Communications of the ACM (26:6), 430-444.
- Social Science Research: Principles, Methods, and Practices. Authored by : Anol Bhattacherjee. Provided by : University of South Florida. Located at : http://scholarcommons.usf.edu/oa_textbooks/3/ . License : CC BY-NC-SA: Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike
Case Study vs. Survey
What's the difference.
Case studies and surveys are both research methods used in various fields to gather information and insights. However, they differ in their approach and purpose. A case study involves an in-depth analysis of a specific individual, group, or situation, aiming to understand the complexities and unique aspects of the subject. It often involves collecting qualitative data through interviews, observations, and document analysis. On the other hand, a survey is a structured data collection method that involves gathering information from a larger sample size through standardized questionnaires. Surveys are typically used to collect quantitative data and provide a broader perspective on a particular topic or population. While case studies provide rich and detailed information, surveys offer a more generalizable and statistical overview.
Further Detail
Introduction.
When conducting research, there are various methods available to gather data and analyze it. Two commonly used methods are case study and survey. Both approaches have their own unique attributes and can be valuable in different research contexts. In this article, we will explore the characteristics of case study and survey, highlighting their strengths and limitations.
A case study is an in-depth investigation of a particular individual, group, or phenomenon. It involves collecting detailed information about the subject of study through various sources such as interviews, observations, and document analysis. Case studies are often used in social sciences, psychology, and business research to gain a deep understanding of complex issues.
One of the key attributes of a case study is its ability to provide rich and detailed data. Researchers can gather extensive information about the subject, including their background, experiences, and perspectives. This depth of data allows for a comprehensive analysis and interpretation of the case, providing valuable insights into the phenomenon under investigation.
Furthermore, case studies are particularly useful when studying rare or unique cases. Since case studies focus on specific individuals or groups, they can shed light on situations that are not easily replicated or observed in larger populations. This makes case studies valuable in exploring complex and nuanced phenomena that may not be easily captured through other research methods.
However, it is important to note that case studies have certain limitations. Due to their in-depth nature, case studies are often time-consuming and resource-intensive. Researchers need to invest significant effort in data collection, analysis, and interpretation. Additionally, the findings of a case study may not be easily generalized to larger populations, as the focus is on a specific case rather than a representative sample.
Despite these limitations, case studies offer a unique opportunity to explore complex issues in real-life contexts. They provide a detailed understanding of individual experiences and can generate hypotheses for further research.
A survey is a research method that involves collecting data from a sample of individuals through a structured questionnaire or interview. Surveys are widely used in social sciences, market research, and public opinion studies to gather information about a larger population. They aim to provide a snapshot of people's opinions, attitudes, behaviors, or characteristics.
One of the main advantages of surveys is their ability to collect data from a large number of respondents. By reaching out to a representative sample, researchers can generalize the findings to a larger population. Surveys also allow for efficient data collection, as questionnaires can be distributed electronically or in person, making it easier to gather a wide range of responses in a relatively short period.
Moreover, surveys offer a structured approach to data collection, ensuring consistency in the questions asked and the response options provided. This allows for easy comparison and analysis of the data, making surveys suitable for quantitative research. Surveys can also be conducted anonymously, which can encourage respondents to provide honest and unbiased answers, particularly when sensitive topics are being explored.
However, surveys also have their limitations. One of the challenges is the potential for response bias. Respondents may provide inaccurate or socially desirable answers, leading to biased results. Additionally, surveys often rely on self-reported data, which may be subject to memory recall errors or misinterpretation of questions. Researchers need to carefully design the survey instrument and consider potential biases to ensure the validity and reliability of the data collected.
Furthermore, surveys may not capture the complexity and depth of individual experiences. They provide a snapshot of people's opinions or behaviors at a specific point in time, but may not uncover the underlying reasons or motivations behind those responses. Surveys also rely on predetermined response options, limiting the range of possible answers and potentially overlooking important nuances.
Case studies and surveys are both valuable research methods, each with its own strengths and limitations. Case studies offer in-depth insights into specific cases, providing rich and detailed data. They are particularly useful for exploring complex and unique phenomena. On the other hand, surveys allow for efficient data collection from a large number of respondents, enabling generalization to larger populations. They provide structured and quantifiable data, making them suitable for statistical analysis.
Ultimately, the choice between case study and survey depends on the research objectives, the nature of the research question, and the available resources. Researchers need to carefully consider the attributes of each method and select the most appropriate approach to gather and analyze data effectively.
Comparisons may contain inaccurate information about people, places, or facts. Please report any issues.
Research Design Review
A discussion of qualitative & quantitative research design, qualitative research “participants” are not “respondents” (& other misplaced concepts from quantitative research).

But to assume that there is a direct relationship between qualitative and quantitative research would be a grave mistake. As discussed in an article posted in 2013 – “10 Distinctive Qualities of Qualitative Research” – the design, implementation, analysis, and interpretation of qualitative research make it unique and uniquely suited to go beyond survey research to study the complexities and meaning of the human experience.
And yet, researchers – both qualitative and quantitative – regularly overextend the applicability of quantitative ideas to qualitative research design. Although survey research informs the researcher of the basic elements of “good research” – and draws the researcher’s attention to core criteria dealing with sampling, error, bias, and so on – many quantitative concepts and techniques cannot and should not be considered in qualitative research. Here are just three examples:
Generalization. It may seem obvious to most researchers that the limited and highly variable nature of qualitative research makes it a poor predictor of things to come; however, many researchers have advocated the “generalizability” of qualitative data. Whether to further a budding theory or make assertions about an entire population segment, the concept of generalization in the context of qualitative research comes up often. In referring to the case study method, for instance, Earl Babbie, in his seventh edition of The Basics of Social Research (2016), laments “the limited generalizability of what is observed in a single instance of some phenomenon,” stating further that “this risk is reduced, however, when more than one case is studied in depth” (p. 312).
Qualitative research does not need generalization to be valuable but it does need transferability – i.e., the ability to transfer the qualitative design and/or outcomes to other highly specific contexts. Transferability is discussed in several Research Design Review articles, including this one posted in 2013 .
Percentages & data graphs. Qualitative researchers have been known to use percentages to report various aspects of their findings (Smith, 2011). There is also a tendency to use graphs or charts of some sort to display the data. Illustrations can be useful to help visualize qualitative data but there is no reason why the researcher needs to fall back on bar graphs or pie charts. Even when no percentages are used – e.g., the histograms of tagged content made available by online discussion platforms – the appearance of a quantitative-like data display not only hints that the researcher believes the qualitative data are quantifiable but also serves to ignore the whole point of qualitative research – i.e., the analysis of context and personal meaning – by reducing the data to a graphical configuration.
“Respondent.” The survey respondent is appropriately referred to as a “respondent” because that is exactly the role they play in the research process. They are responding to the researcher’s questions which are typically structured and closed-ended in format. Similarly, the qualitative research participant is suitably labeled “participant” because their role goes beyond simply replying to a series of questions to encompass participation in the research on many levels. The participant elaborates on the interviewer’s/moderator’s questions, changes the topic if need be to convey an idea, takes part in a social relationship with the interviewer/moderator, engages with other participants in a focus group discussion, is willingly observed in an ethnographic study, and, in some instances, is asked to aid in the analysis. For all of these reasons (and more), it is research participants that provide qualitative data not respondents.
Babbie, E. R. (2016). The basics of social research (7th ed.). Cengage learning.
Smith, K. (2011). Anxiety, Knowledge and Help: A Model for How Black and White College Students Search for HIV/AIDS Information on the Internet. The Qualitative Report , 16 (1), 103-125. Retrieved from https://nsuworks.nova.edu/tqr/vol16/iss1/6
Share this:
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Tumblr (Opens in new window)
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window)
- Click to print (Opens in new window)
- Pingback: Qualitative Research: A Collection of Articles from 2016 | Research Design Review
Good write up
Neither qualitative nor quantitative participants should be called respondents! They are people.
I find the use of graphs and percentages can provide a mixed method contribution, which Bridges the two approaches along a continuum rather than perceiving them as black and white. I do appreciate many of the points you have raised and have shared your article with my network. Worthy of discourse for sure.
Agreed, that is the beauty of the social sciences!
Leave a comment Cancel reply
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .

- Already have a WordPress.com account? Log in now.
- Subscribe Subscribed
- Copy shortlink
- Report this content
- View post in Reader
- Manage subscriptions
- Collapse this bar
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
- QuestionPro

- Solutions Industries Gaming Automotive Sports and events Education Government Travel & Hospitality Financial Services Healthcare Cannabis Technology Use Case NPS+ Communities Audience Contactless surveys Mobile LivePolls Member Experience GDPR Positive People Science 360 Feedback Surveys
- Resources Blog eBooks Survey Templates Case Studies Training Help center
Home Market Research Case Studies
What is a Case Study, and how to conduct it? + Free Questionnaire

Do you know what a case study is and what advantages it holds for your business? As a marketing strategy, it’s highly effective to rely on your customers and their positive testimonials to convert other prospects.
Writing a case study is one of the best ways to do so. More comprehensive than a simple testimonial, it explains in detail how your company managed to find solutions to a specific client’s problems, thereby demonstrating its commitment and generating trust.
Let’s learn more about the characteristics of a case study and what you should consider when creating one.
What is a case study?
A case study is a detailed examination of a specific subject. Case studies are commonly used in social, educational, clinical, and business research .
The research design of a case study often involves qualitative methods , but sometimes quantitative methods are also utilized.
Case studies serve to describe, compare, evaluate, and understand different aspects of a research problem .
Steps to conduct a case study
A case study is an appropriate research design when you aim to obtain concrete, contextual, and in-depth knowledge about a specific subject. It allows you to explore the key characteristics, meanings, and implications of the case.
Case studies keep your project focused and manageable when you lack time or resources for large-scale research.
You can use a single complex case study to delve deep into a single topic or conduct multiple case studies to compare and shed light on different aspects of your research problem.
Now that we know what a case study is, let’s explore the steps to conduct one:
Step 1: Select a case
Once you have developed the problem statement and research questions, you should choose the specific case to focus on. A good case study should have the potential to:
Provide new or unexpected information about the subject. Propose practical measures to solve a problem. Open up new avenues for research . If you are conducting a case study on your customers, check with the relevant department, whether it’s customer service or customer success, to identify potential customers with whom you could work to obtain their testimonials.
Step 2: Gather the data
There are various research methods you can employ to collect data for your case study.
Case studies tend to focus on qualitative data using methods such as interviews, observations, and analysis of primary and secondary sources (e.g., press articles, photographs, and official records).
Sometimes, a case study also collects quantitative data , for example, through online surveys where you can incorporate open-ended questions to obtain the qualitative insights you require.
LEARN ABOUT: Testimonial Questions
Case study questionnaire sample
Here is an example of a survey that can be useful in gathering data for your case study:
- Contact Information:
How did you hear about QuestionPro?
- By recommendation from a friend or colleague
- From a co-worker
- Through a Google search
- Through social media
- From a website unrelated to QuestionPro
- I met them at an event
- Other (Please specify)
What tool or process did you use before QuestionPro? Check all that apply
- Pen and paper or other traditional tools
- Another survey software
- A different software (not for surveys)
- Secondary information
What limitations did you face with the tool(s) or process(es) you used before?
How has QuestionPro helped you overcome your challenges?
How has QuestionPro impacted your objectives and those of your company?
What do you consider the most successful project you have done with QuestionPro?
What results did you achieve, and what did you do with them?
What is your favorite part about using QuestionPro, and why?
On a scale of 1 to 10, how likely are you to recommend QuestionPro to others in your industry? 1 Very unlikely to 10 Very likely Very unlikely 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Very likely
How can we improve?
Step 3: Write a summary
Always keep in mind that internet users are busy people: not everyone will have the time to read your entire case study (or at least not right away). An executive summary is essential to give everyone a vague idea of what your case study is about and, more importantly, the results.
You can even create downloadable material where there is more information that can be consulted.
Step 4: Introduce the client
While the case study is intended to serve your company, you should not steal the spotlight from the client whose story you are telling. Present the client in the best possible way, even if it’s just to thank them for agreeing to contribute to your content.
Step 5: Show the challenges to overcome
This step is crucial: It’s about describing, in 2 or 3 paragraphs, the context in which the client was placed and the reasons why they turned to you. Ideally, this section should give the floor to the main stakeholder, who can directly explain the problems they encountered before resorting to your services or products.
This is also an opportunity to mention the objectives the client wanted to achieve (e.g., increase sales by 10%, increase blog traffic, etc.).
This is one of the main reasons to understand what a case study is and implement it as reference content for your other prospects or clients.
Step 6: Showcase the provided solutions
Now is the time to talk about what you actually did to help your client. This is precisely the most important part: knowing how you have solved a problem that others may have. This is an opportunity to present, with evidence, the advantages of your products or services and how they solved the client’s problem.
Explain how you implemented your solution and overcame challenges and limitations.
Step 7: Share the obtained results
Now that you have explained your approach and highlighted the qualities of your solution, you need to demonstrate that it really works: This is where you can truly showcase your expertise. List all the positive effects your products or services have had on your clients, with testimonials from them that support your claims.
And most importantly, evaluate how well you have met or exceeded expectations by achieving even better results. It is essential to demonstrate your ability to fulfill the objectives you have set.
Step 8: Create a great conclusion
You can take advantage of the conclusion of your case study to thank the client who kindly agreed to participate but also to review the main points of the study and your accomplishments.
Even better, invite your readers to contact you if they find themselves in a similar situation to the client you have written about.
QuestionPro’s Case Studies
Now that you know what a case study is and the advantages of obtaining feedback from your clients, start by making a list of clients with whom you have a good relationship and gathering relevant aspects that will help provide a comprehensive view of your relationship.
I would like to share some of QuestionPro’s Case Studies . In our cases, we gather information from our clients through a survey and conduct small interviews with the help of our customer success team. After collecting the information, we create the content, which is then reviewed and validated by our clients before being published on our website.
This type of content is very useful for building trust with new prospects. It’s a tool that provides assurance to new clients and helps us demonstrate the solutions we have available.
Make the decision to start a relationship that will contribute to the growth of your business. We are confident that we have the solution you are looking for.
Start by creating a free account or request a demonstration of our survey software. We will address all your questions about using our platform and the services we offer.
MORE LIKE THIS
Data Information vs Insight: Essential differences
May 14, 2024

Pricing Analytics Software: Optimize Your Pricing Strategy
May 13, 2024

Relationship Marketing: What It Is, Examples & Top 7 Benefits
May 8, 2024

The Best Email Survey Tool to Boost Your Feedback Game
May 7, 2024
Other categories
- Academic Research
- Artificial Intelligence
- Assessments
- Brand Awareness
- Case Studies
- Communities
- Consumer Insights
- Customer effort score
- Customer Engagement
- Customer Experience
- Customer Loyalty
- Customer Research
- Customer Satisfaction
- Employee Benefits
- Employee Engagement
- Employee Retention
- Friday Five
- General Data Protection Regulation
- Insights Hub
- Life@QuestionPro
- Market Research
- Mobile diaries
- Mobile Surveys
- New Features
- Online Communities
- Question Types
- Questionnaire
- QuestionPro Products
- Release Notes
- Research Tools and Apps
- Revenue at Risk
- Survey Templates
- Training Tips
- Uncategorized
- Video Learning Series
- What’s Coming Up
- Workforce Intelligence
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- BMC Med Res Methodol

Case study research and causal inference
Judith green.
1 Wellcome Centre for Cultures & Environments of Health, University of Exeter, Exeter, UK
Benjamin Hanckel
2 Institute for Culture and Society, Western Sydney University, Sydney, Australia
Mark Petticrew
3 Department of Public Health, Environments & Society, London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine, London, UK
Sara Paparini
4 Wolfson Institute of Population Health, Queen Mary University of London, London, UK
5 Nuffield Department of Primary Care Health Sciences, University of Oxford, Oxford, UK
Associated Data
Not applicable; no new data generated in this study.
For the purpose of open access, the author has applied a ‘Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) licence to any Author Accepted Manuscript version arising.
Case study methodology is widely used in health research, but has had a marginal role in evaluative studies, given it is often assumed that case studies offer little for making causal inferences. We undertook a narrative review of examples of case study research from public health and health services evaluations, with a focus on interventions addressing health inequalities. We identified five types of contribution these case studies made to evidence for causal relationships. These contributions relate to: (1) evidence about system actors’ own theories of causality; (2) demonstrative examples of causal relationships; (3) evidence about causal mechanisms; (4) evidence about the conditions under which causal mechanisms operate; and (5) inference about causality in complex systems. Case studies can and do contribute to understanding causal relationships. More transparency in the reporting of case studies would enhance their discoverability, and aid the development of a robust and pluralistic evidence base for public health and health services interventions. To strengthen the contribution that case studies make to that evidence base, researchers could: draw on wider methods from the political and social sciences, in particular on methods for robust analysis; carefully consider what population their case is a case ‘of’; and explicate the rationale used for making causal inferences.
Case study research is widely used in studies of context in public health and health services research to make sense of implementation and service delivery as enacted across complex systems. A recent meta-narrative review identified four broad, overlapping traditions in this body of work: developing and testing complex interventions; analysing change in organisations; undertaking realist evaluations; and studying complex change naturalistically [ 1 ]. Case studies can provide essential thick description of interventions, context and systems; qualitative understanding of the mechanisms of interventions; and evidence of how interventions are adapted in the ‘real’ world [ 2 , 3 ].
However, in evaluative health research, case study designs remain relegated to a minor, supporting role [ 4 , 5 ], typically at the bottom of evidence hierarchies. This relegation is largely due to assumptions that they offer little for making the kinds of causal claims that are essential to evaluating the effects of interventions. The strengths of deep, thick studies of specific cases are conventionally set against the benefits of ‘variable-based’ designs, with the former positioned as descriptive, exploratory or illustrative, and the latter as providing the strongest evidence for making causal claims about the links between interventions and outcomes. In conventional hierarchies of evidence, the primary evidence for making causal claims comes from randomised controlled trials (RCTs), in which the linear relationship between a change in one phenomenon and a later change in another can be delineated from other causal factors. The classic account of causality drawn on in epidemiology requires identifying that the relationship between two phenomena is characterised by co-variation; time order; a plausible relationship; and a lack of competing explanations [ 6 ]. The theoretical and pragmatic limitations of RCT designs for robust and generalizable evaluation of interventions in complex systems are now well-rehearsed [ 2 , 7 – 10 ]. In theory, though, random selection from a population to intervention exposure maximises ability to make causal claims: randomisation minimises risks of confounding, and enables both an unbiased estimate of the effect size of the intervention and extrapolation to the larger population [ 6 ]. Guidance for evaluations in which the intervention cannot be manipulated, such as in natural experiments, therefore typically focuses on methods for addressing threats to validity from non-random allocation in order to strengthen the credibility of probabilistic causal effect estimates [ 4 , 11 ].
This is, however, not the only kind of causal logic. Case study research typically draws on other logics for understanding causation and making causal inferences. We illustrate some of the contributions made by case studies, drawing on a narrative review of research relating to one particularly enduring and complex problem: inequalities in health. The causal chains linking interventions to equity outcomes are long and complex, with recognised limitations in the evidence base for ‘what works’ [ 12 ]. Case study research, we argue, has a critical role to play in making claims about whether, how and why interventions reduce, mitigate, or exacerbate inequalities. Our examples are drawn from a broader review of case study research [ 1 ] and supporting literature reviews [ 5 ], from which we focused on cases which had an explanatory aim, and which shed light on how interventions in public health or health services might reduce, create or sustain inequality. In this paper, we: i) outline some different kinds of evidence relevant to causal relationships that can be derived from case study research; ii) outline what is needed for case study research to contribute to explanatory, as well as exploratory claims; and iii) advocate for greater clarity in reporting case study research to foster discoverability.
Cases and causes
There are considerable challenges in defining case study designs or approaches in ways that adequately delineate them from other research designs. Yin [ 13 ], for instance, one of the most highly cited source texts on case studies in health research [ 1 ], resists providing a definition, instead suggesting case study research is more a strategy for doing empirical research. Gerring [ 14 ] defines case study research as: “ an intensive study of a single unit for the purpose of understanding a larger class of (similar) units ” (p342, emphasis in original). This definition is useful in suggesting the basis for the inferences drawn from cases, and the need to consider the relationships between the ‘case’ (and phenomena observed within it) and the population from which it is drawn. Gerring notes that studies of single cases may have a greater “affinity” for descriptive aims, but that they can furnish “evidence for causal propositions” ( [ 14 ], p347). Case studies are, he suggests, more likely to be useful in elucidating deterministic causes: those conditions that are necessary and/or sufficient for an outcome, whereas variable based designs have advantages for demonstrating probabilistic causation, where the aim is to estimate the likelihood of two phenomena being causally related. Case studies provide evidence for the mechanisms of causal relationships (e.g. through process tracing, through observing two variables interacting in the real world) and corroboration of causal relationships (for instance, through pattern matching).
Gerring’s argument, drawing on political science examples, is that there is nothing epistemologically distinct about research using the case study: rather, it has particular affinities with certain styles of causal modelling. We take this as a point of departure to consider not whether case studies can furnish evidence to help with causal inference in health research, but rather how they have done this. From our examples on case study research on inequalities in health, we identify the kinds of claims that relate to causality that were made. We note that some relate to (1) Actors’ accounts of causality : that is, the theories of those studied about if, how and why interventions work. Other types of claim use various kinds of comparative analytic logic to elucidate evidence of causal relationships between phenomena. These claims include: (2) Demonstrations of causal relationships – in which evidence from one case is sufficient for identifying a plausible causal relationship; (3) Mechanisms – evidence of the mechanisms through which causal relationships work; (4) Conditions —evidence of the conditions under which such mechanisms operate; and (5) Complex causality —evidence for outcomes that arise from complex causality within a system. This list is neither mutually exclusive, nor exhaustive: many case studies aim to do several of these (and some more). It is also a pragmatic rather than theoretical list, focusing on the kinds of evidence claimed by researchers rather than the formal methodological underpinnings of causal claims (for a discussion of the latter, see Rohlfing [ 15 ]).
What kinds of causal evidence do case studies provide?
Actors’ accounts of causality.
This is perhaps the most common kind of evidence provided by case study research. Case studies, through in-depth research on the actors within systems, can generate evidence about how those actors themselves account for causal relationships between interventions and outcomes. This is an overt aim of many realist evaluation studies, which focus on real forces or processes that exist in the world that can provide insight into causal mechanisms for change.
Ford and colleagues [ 16 ], for example, used a series of five case studies of local health systems to explore socio-economic inequalities in unplanned hospital admission. Cases were selected on the basis of either narrowing or widening inequalities in admission, with a realist evaluation focused on delineating the context-mechanisms-outcome (CMO) configurations in each setting, to develop a broader theory of change for addressing inequalities. The case study approach used a mix of methods, including drawing on documentary data to assess the credibility of mechanisms proposed by health providers. The authors identified 17 distinct CMO configurations; and five factors that were related to trends for inequalities in emergency admissions, including health service factors (primary care workforce challenges, case finding and proactive case management) and those external to the health service (e.g., financial constraints on public services, residential gentrification). Ford and colleagues noted that none of the CMO configurations were clearly associated with improved or worsening trends in inequalities in admission.
Clearly, actors’ accounts of causality are not in themselves evidence of causality. Ford and colleagues noted that they interrogated accounts for plausibility (e.g. that interventions mentioned were prior to effects claimed) and triangulated these accounts with other sources of data, but that inability to empirically corroborate the hypothesized CMO links limited their ability to make claims about causal inference. This is crucial: actors in a system may be aware of the forces and processes shaping change but unaware of counterfactuals, and they are unlikely to have any privileged insight into whether factors are causal or simply co-occurring (see, for instance, Milton et. al. [ 17 ] on how commonly cited ‘barriers’ in accounts of not doing evaluations are also evident in actors’ accounts of doing successful evaluations). Over-interpretation of qualitative accounts of insiders’ claims about causal relationships as if they provide conclusive evidence of causal relationships is poor methodology.
This does not mean that actors’ accounts are not of value. First, in realist evaluation, as in Ford and colleagues’ study [ 16 ], these accounts provide the initial theories of change for thinking about the potential causal pathways in logic models of interventions. Second, insiders’ accounts of causality are part of the system that is being explained. An example comes from Mead and colleagues [ 18 ], who used a case study drawing largely on qualitative interviews to explore “how local actors from public health, and the wider workforce, make sense of and work on social inequalities in health” ( [ 18 ] p168). This used a case study of a partnership in northwest England to address an enduring challenge in inequalities policy: the tendency for policies that address upstream health determinants to transform, in practice, to focus more on behavioural and individual level factors . Local public health actors in the partnership recognised the structural causes of unequal health outcomes, yet discourses of policy action tended to focus only on the downstream, more individualising levels of health, and on personal choice and agency as targets for intervention. Professionals conceptualised action on inequality as relating only to the health of the poorest, rather than as a problem of a gradient in health outcomes across society. There was a geographical localism in their approach, which framed particular places as constellations of health and social problems. Drawing on theory from figurational sociology, Mead and colleagues note that actors’ own accounts are the starting point of an analysis, which then puts those accounts into play with theory about how such discourses are reproduced. The researchers suggest that partnership working itself exacerbated the individualising frameworks used to orient action, as it became a hegemonic framing, reducing the possibilities for partnerships to transform health inequalities. Here, then, a case study approach is used to shed light on the causes of a common failure in policies addressing inequalities. The authors take seriously the divergence of actors’ own accounts of causality and those of other sources, and analyse these as part of the system.
Finally, insider accounts should be taken seriously as contributing to evidence about causal inference through shedding light on the complex looping effects of theoretical models of causality and public accounts. For instance, Smith and Anderson [ 19 ], drawing on a meta-ethnographic literature review of ‘lay theorising’ about health inequalities, note that, counter to common assumptions, public understanding of the structural causes of health inequalities is sophisticated: but that it may be disavowed to avoid stigma and shame and to reassert some agency. This is an important finding for informing knowledge exchange, suggesting that further ‘awareness raising’ may be unnecessary for policy change, and counter-productive in needlessly increasing stigma and shame.
Demonstrations of causal relationships
When strategically sampled, and rooted in a sound theoretical framework, studies of single cases can provide evidence for generalizable causal inferences. The strongest examples are perhaps those that operate as ‘black swans’ for deterministic claims, in that one case may be all that is needed to show that a commonly held assumption is not generalizable. That is, a case study can demonstrate unequivocally that one phenomenon is not inevitably related to another. These can come from cases sampled because they are extreme or unusual. Prior’s [ 20 ] study of a single man in a psychiatric institution in Northern Ireland, for instance, showed that, counter to Goffman’s [ 21 ] original theory of how ‘total institutions’ lead to stigmatisation and depersonalisation, the effects of institutionalisation depended on context—in this case, how the institution related to the local community and the availability of alternative sources of self-worth available to residents.
Strategically sampled typical cases can also provide demonstrative evidence of causal relationships. To take the enduring health services challenge of inequalities in self-referral to emergency care, Hudgins and Rising’s [ 22 ] case study of a single patient is used to debunk a common assumption that high use of emergency care is related to inappropriate care-seeking by low-income patients. They look in detail at the case of “a 51-year-old low-income, recently insured, African American man in Philadelphia (USA) who had two recent ED [emergency department] visits for evaluation of frequent headaches and described fear of being at risk for a stroke.” ( [ 22 ] p50). Drawing on theories of structural violence and patient subjectivity, they use this single case to shed light on why emergency department use may appear inappropriate to providers. They analyse the interplay of gender roles, employment, and insurance status in generating competing drivers of health seeking, and point to the ways in which current policies deterring self-referral do not align well with micro- and macro-level determinants of service use. The study authors also note that because their methods generate data on ‘why’ as well ‘what’ people do, they can “lay the groundwork” ( [ 22 ], p54] for developing future interventions. Here, again, a single case is sufficient. In understanding the causal pathways that led to this patient’s use of emergency care, it is clear why policies addressing inequalities through deterring low-income users would be unlikely to work.
Mechanisms: how causal relationships operate
A strength of case study approaches compared with variable-based designs is furnishing evidence of how causal relationships operate, deriving from both direct observations of causal processes and from analysis of comparisons within and between cases. All cases contain multiple observations; variations can be observed over time and space, across or within cases [ 14 ]. Observing regularities, co-variation and deviant or surprising findings, and then using processes of analytic induction [ 23 ] or abductive logic [ 24 ] to derive, develop and test causal theories using observations from the case, can build a picture of causal pathways.
Process tracing is one formal qualitative methodology for doing this. Widely used in political and policy studies, but less in health evaluations [ 25 ], process tracing links outcomes with their causes, focusing on the mechanisms that link events on causal pathways, and on the strength of evidence for making connections on that causal chain. This requires sound theoretical knowledge (such that credible hypotheses can be developed), well described cases (ideally at different time points), observed causal processes (the activities that transfer causes to effects), and careful assessment of evidence against tests of varying strength for the necessity and sufficiency for accepting or rejecting a candidate hypothesis [ 26 , 27 ]. In health policy, process tracing methods have been combined to good effect with quantitative measures to examine casual processes leading to outcomes of interest. Campbell et. al. [ 28 ], for instance, used process tracing to look at four case studies of countries that had made progress towards universal health coverage (measured through routine data on maternal and neonatal health indicators), to identify key causal factors related to health care workforce.
An example of the use of process tracing in evaluation comes from Lohmann and colleagues’ [ 25 ] case study of a single country, Burkina Faso, to examine why performance based financing (PBF) fails to improve equity. PBF, coupled with interventions to improve health care take up among the poor, aims to improve health equity in low and middle-income countries, yet impact evaluations suggest that these benefits are typically not realised. This case study drew on data from the quantitative impact assessment; programme documentation; the intervention process evaluation; and primary qualitative research for the process tracing, in the light of the theory of change of the intervention. Lohmann and colleagues [ 25 ] identified that a number of conditions that would have been necessary for the intervention to work had not been met (such as eligible patients not receiving the card needed to access health care or providers not receiving timely reimbursement). A key finding was that although implementation challenges were a partial cause of policy failure, other causal conditions were external to the intervention, such as lack of attention to the non-health care costs incurred by the poorest to access care. Again, a single case, if there are good grounds for extrapolating to similar contexts (i.e., those in which transport is required to access health care), is enough to demonstrate a necessary part of the causal pathway between PBF and intended equity outcomes.
Conditions under which causal mechanisms operate
The example of ‘transport access’ as a necessary condition for PBF interventions to ‘work’ also illustrates a fourth type of causal evidence: that relating to the transferability of interventions. Transferable causal claims are essential for useful evidence: “(f)or policy and practice we do not need to know ‘it works somewhere’. We need evidence for ‘it-will-work-for-us’ claims: the treatment will produce the desired outcome in our situation as implemented there” ( [ 8 ] p1401). Some causal mechanisms operate widely (using a parachute will reduce injury from jumping from a plane; taking aspirin will relieve pain); others less so. In the context of health services and public health research, few interventions are likely to be widely generalizable, as the mechanisms will operate differently across contexts [ 7 ]. This context dependency is at the heart of realist evaluations, with the assumption that underlying causal mechanisms require particular contexts in order to operate, hence the focus on ‘how, where, and for whom’ interventions work [ 29 ]. Making useful claims therefore requires other kinds of evidence, relating to what Cartwright and Munro [ 30 ] call the ‘capacities’ of the intervention: what power it has to work reliably, what stops it working, what other conditions are needed for it to work. This evidence is critical for assessing whether an intervention is likely to work in a given context and to assess the intended and unintended consequences of intervention adoption and implementation. Cartwright and Munro’s recommendation is therefore to study causal powers rather than causes. That is, as well as interrogating whether the intervention ‘causes’ a particular outcome, it is also necessary to address the potential for and stability of that causal effect. To do that entails addressing a broader range of questions about the causal relationship, such as how the intervention operates in order to bring about changes in outcomes; what other conditions need to be present; what might constrain this effect; what other factors within the system also promote or constrain those effects; and what happens when different capacities interact? [ 30 ]. Case study research can be vital in providing this kind of evidence on the capacities of interventions [ 31 ].
One example is from Gibson and colleagues [ 32 ], who use within-case comparisons to shed light on why a ‘social prescribing’ intervention may have different effects across socioeconomic classes. These interventions, typically entailing link workers who connect people with complex health care needs to local services and resources, are often framed as a way to address enduring health inequalities. Drawing on sociological theory on how social class is reproduced through socially structured and unequal distribution of resources (‘capitals’), and through how these shape people’s practices and dispositions, Gibson and colleagues [ 32 ] explicate how capitals and dispositions shaped encounters with the intervention. Their analysis of similarities and differences within their case (of different clients) in the context of theory enables them to abstract inferences from the case. Drawing out the ways in which more advantaged clients mobilised capital in their pursuit of health, with dispositions more closely aligned to the intervention, they unravel classed differences in ability to benefit from the intervention, with less advantaged clients inevitably having ‘shorter horizons’ focused on day to day challenges: “This challenges the claim that social prescribing can reduce inequalities, instead suggesting it has the potential to exacerbate existing inequalities” ( [ 32 ], p6).
Case studies can shed light on the capacities of interventions to improve or exacerbate inequalities, including identifying unforeseen consequences. Hanckel and colleagues [ 33 , 34 ], for example, used a case study approach to explore implementation of a physical health intervention involving whole classes of children running for 15 min each day in the playground in schools in south London, UK. This documented considerable adaption of the intervention at the level of school, class and pupil, and identified different pathways through which the intervention might impact on inequalities. In terms of access, the intervention appeared to be equitable, in that there was no evidence of disproportionate roll out to schools with more affluent pupils or to those with fewer minority ethnic pupils [ 33 ]. However, identifying the ‘capacities’ of the intervention also identified other pathways through which it could have negative equity effects. The authors found that in practice, the intervention emphasised body weight rather than physical activity, and intervention roll-out reinforced class and ethnicity-based stigmatising discourses about lower income neighbourhoods [ 34 ].
Complex causality
There is increasing recognition that the systems that reproduce unequal health outcomes are complex: that is, that they consist of multiple interacting components that cannot be studied in isolation, and that change is likely to be non-linear, characterised by, for instance, phase shifts or feedback loops [ 35 ]. This has two rather different implications. First, case study designs can be particularly beneficial for taking a system perspective on interventions. Case studies enable a focus on aspects that are not well explicated through other designs, such as how context interacts with interventions within systems [ 7 ], or on how multiple conditional pathways might link interventions and outcomes [ 36 ]. Second, when causation is not linear, but ‘emergent’, in that it is not reducible to the accumulated changes at lower levels, evaluation designs focused on only one outcome at one level (such as weight loss in individuals) may fail to identify important effects. Case studies have an invaluable role here in unpacking and surfacing these effects at different levels within the systems within which interventions and services are delivered. One example is transport systems, which have been the focus of considerable public health interest to encourage more ‘active’ modes, in which more of the population walk or cycle, and fewer drive. However, more simplistic evaluations looking at one part of a causal chain (such as that between traffic calming interventions and local mode shift) may fail to appreciate how systems are dynamic, and that causation might be emergent. This is evident in a case study of transport policy impacts from Sheller [ 37 ], who takes the case of Philadelphia, USA, to reveal how this post-car trend has racialized effects that can exacerbate inequality. Weaving in data from participant observations, historical documentary sources and statistical evidence of declining car use, Sheller documents the racialized impacts of transport policies which may have reduced car use and encouraged active modes overall, but which have largely prioritised ‘young white’ mobility in the context of local gentrification and neglect of public transit.
One approach to synthesising evidence from multiple case studies to make claims about complex causation is Qualitative Comparative Analysis (QCA), which combines quantitative methods (based on Boolean algebra) with detailed qualitative understanding of a small to medium N sample of cases. This has strengths for identifying multiple pathways to outcomes, asymmetrical sets of conditions which lead to success or failure, or ‘conjunctural causation’, whereby some conditions are only causally linked to outcomes in relation to others [ 38 ]. There is growing interest in using these approaches in evaluative health studies [ 39 ]. One example relating to the effectiveness of interventions addressing inequalities in health comes from Blackman and colleagues [ 36 ], who explored configurations of conditions which did or did not lead to narrowing inequalities in teenage conception rates across a series of local areas as cases. This identified some surprising findings, including that ‘basic’ rather than good or exemplary standards of commissioning were associated with narrowing the equity gap, and that the proportion of minority ethnic people in the population was a key condition.
Not all case study research aims to contribute to causal inference, and neither should it [ 1 , 5 , 40 ]. However, it can. We have identified five ways in which case study evidence has contributed to causal explanations in relation to a particularly intractable challenge: inequalities in health. It is therefore time to stop claiming that case study designs have only a supporting role to play in evaluative health research. To develop a theoretical evidence base on ‘what works’, and how, in health services and public health, particularly around complex issues such as addressing unequal health outcomes, we need to draw on a greater range of evidential resources for informing decisions than is currently used. Best explanations are unlikely to be made from single studies based on one kind of causality, but instead will demand some kind of evidential pluralism [ 41 ]. That is, one single study, of any design, is unlikely to generate evidence for all links in complex causal chains between an intervention and health outcomes. We need a bricolage of evidence from a diverse range of designs [ 42 ] to make robust and credible cases for what will improve health and health equity. This will include evidence from case studies, both from single and small N studies, and from syntheses of findings from multiple cases.
Our focus on case studies that shed light on interventions for health inequalities identified the critical role that case studies can play in theorising, illuminating and making sense of: system actors’ own causal reasoning; whether there are causal links between intervention and outcome; what mechanism(s) might link them; when, where and for whom these causal relationships operate; and how unequal outcomes can be generated from the operation of complex systems. These examples draw on a range of different theoretical and methodological approaches, often from the wider political and social sciences. The approaches illustrated are rooted in very different, even incompatible, philosophical traditions: what researchers understand by ‘causality’ is diverse [ 43 ]. However, there are two commonalities across this diversity that suggest some conditions for producing good case studies that can generate evidence to support causal inferences. The first is the need for theoretically informed and comparative analysis. As Gerring [ 14 ] notes, causal inferences rely on comparisons – across units or time within a case, or between cases. It is comparison that drives the ability to make claims about the potential of interventions to produce change in outcomes of interest, and under what conditions. There are a range of approaches to qualitative data analysis, and choice of method has to be appropriate for the kinds of causal logics being explicated, and the availability of data on particular phenomena within the case. Typically, though, this will require analysis that goes beyond descriptive thematic analysis [ 31 ]. Approaches such as process tracing or analytic induction require both fine-grained and rigorous comparative analysis, and a sound theoretical underpinning that provides a framework for making credible inferences about the relationships between phenomena within the case and to the wider population from which the case is selected.
This leads to the second commonality: the need to clarify what the case is a case ‘of’, and how it relates to other candidate cases. What constitutes a ‘case’ is inevitably study specific. The examples we have drawn on include: PBF in a country [ 25 ], transport systems in a city [ 37 ], and a social prescribing intervention in primary care [ 32 ]. Clearly, in other contexts, each of these ‘cases’ could be sampling units within variable based studies (of financing systems, or countries; of infrastructures systems, or cities in a state; of particular kinds of service intervention, or primary care systems). Conversely, these cases could be populations within which lower level phenomena (districts, neighbourhoods, patients) are studied. What leads to appropriate generalisations about causal claims is a sound theorisation of the similarities and particularities of the case compared with other candidate cases: how Burkina Faso has commonalities with, or differences from, other settings in which PBF has failed to improve equity; or the contexts of gentrification and residential churn that make Philadelphia similar to other cities in the US; or the ways in which class-based dispositions and practices intersect with similar types of service provisions.
A critical question remains: How can well-conducted case study evidence be better integrated into the evidence base? Calls for greater recognition for case study designs within health research are hardly new: Flyvberg’s advocacy for a greater role for case studies in the social sciences [ 44 ] has now been cited around 20,000 times, and calls for methodological pluralism in health research go back decades [ 42 , 45 , 46 ]. Yet, case studies remain somewhat neglected, with ongoing misconceptions about their limited role, despite calls for evidence based medicine to incorporate evidence for mechanisms as complementary to evidence of correlation, rather than as inferior [ 47 ]. Even where the value of case studies for contributing to causal inference is recognised, searching for good evidence is not straightforward. Case studies are neither consistently defined nor necessarily well reported. Some of the examples in this paper do not use the term ‘case study’ in the title or abstract, although they meet our definition. Conversely, many small scale qualitative studies describe themselves as ‘case studies’, but focus on thick description rather than generalisability, and are not aiming to contribute to evaluative evidence. It is therefore challenging, currently, to undertake a more systematic review of empirical material. Forthcoming guidance on reporting case studies of context in complex systems aims to aid discoverability and transparency of reporting (Shaw S, et al: TRIPLE C Reporting Principles for Case study evaluations of the role of Context in Complex interventions, under review). This recommends including ‘case study’ in the title, clarifying how terms are used, and explicating the philosophical base of the study. To further advance the usefulness of case study evidence, we suggest that where an aim is to contribute to causal explanations, researchers should, in addition, specify their rationales for making causal inferences, and identify what broader class of phenomena their case is a case ‘of’.
Conclusions
Case study research can and does contribute to evidence for causal inferences. On challenging issues such as addressing health inequalities, we have shown how case studies provide more than detailed description of context or process. Contributions include: describing actors’ accounts of causal relationships; demonstrating theoretically plausible causal relationships; identifying mechanisms which link cause and effect; identifying the conditions under which causal relationships hold; and researching complex causation.
Acknowledgements
The research underpinning this paper was conducted as part of the Triple C study. We gratefully acknowledge the input of the wider study team, and that of the participants at a workshop held to discuss forthcoming guidance on reporting case study research.
Abbreviations
Authors’ contributions.
BH, JG and MP drafted the first version of the paper, which was revised with theoretical input from SS and SP. All authors contributed to the paper and have reviewed and approved the final manuscript.
The research was funded by the Medical Research Council (MR/S014632/1). JG is supported with funding from the Wellcome Trust (WT203109/Z/16/Z). Additional funding for SP and SS salaries over the course of the study was provided by the UK National Institute for Health Research Oxford Biomedical Research Centre (BRC-1215–20008), Wellcome Trust (WT104830MA; 221457/Z/20/Z) and the University of Oxford's Higher Education Innovation Fund.
The views and opinions expressed herein are those of the authors. Funding bodies had no input to the design of the study and collection, analysis, and interpretation of data or preparation of this paper.
Availability of data and materials
Declarations.
Not applicable.
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Participant Selection and Access in Case Study Research
- First Online: 05 January 2019
Cite this chapter

- Zhongyan Wan 4
1550 Accesses
2 Citations
Case study research requires researchers to purposefully select information-rich cases, as they will allow researchers an in-depth understanding of relevant and critical issues under investigation (Patton in Qualitative evaluation and research methods. Sage, Newbury Park, 1990 , Qual Soc Work 1(3):261–283, 2002 ). To gain such insights, purposive sampling is generally believed to contribute to the richness in the range of data collected and help increase the possibilities of uncovering multiple realities (Guba and Lincoln in Handb Qual Res 2(163–194):105, 1994 ). However, dealing with research participants in the case study approach also poses great challenges for novice researchers, as humans can be a difficult factor to control among the variables in research.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Alinejad, D. (2011). Mapping homelands through virtual spaces: Transnational embodiment and Iranian diaspora bloggers. Global Networks, 11 (1), 43–62.
Google Scholar
Arcury, T., & Quandt, S. (1999). Participant recruitment for qualitative research: A site-based approach to community research in complex societies. Human Organization, 58 (2), 128–133.
Article Google Scholar
Barbour, R. (2014). Introducing qualitative research: A student’s guide . London: Sage.
Decrop, A. (1999). Qualitative research methods for the study of tourist behaviour. In A. Pizam & Y. Mansfeld. (Eds.), Consumer Behaviour in Travel and Tourism . New York: The Haworth Hospitality Press
Duff, P. (2008). Case study research in applied linguistics . New York: Taylor & Francis.
Feldman, M. S., Bell, J., & Berger, M. T. (2003). Gaining access: A practical and theoretical guide for qualitative researchers . Walnut Creek, CA: Altamira Press.
Gall, M. D., Gall, J. P., & Borg, W. T. (2003). Educational research (7th ed.). White Plains, NY: Pearson Education.
Gerring, J. (2004). What is a case study and what is it good for? American Political Science Review, 98 (02), 341–354.
Guba, E. G., & Lincoln, Y. S. (1994). Competing paradigms in qualitative research. Handbook of Qualitative Research, 2 (163–194), 105.
Gummesson, E. (2000). Qualitative methods in management research . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Hamilton, R. J., & Bowers, B. J. (2006). Internet recruitment and e-mail interviews in qualitative studies. Qualitative Health Research, 16 (6), 821–835.
Hancock, D. R., & Algozzine, B. (2015). Doing case study research: A practical guide for beginning researchers . New York: Teachers College Press.
Hewson, C. (2014). Qualitative approaches in Internet-mediated research: Opportunities, issues, possibilities. The Oxford Handbook of Qualitative Research , 423–452.
Johl, S. K., & Renganathan, S. (2010). Strategies for gaining access in doing fieldwork: Reflection of two researchers. The Electronic Journal of Business Research Methods, 8 (1), 42–50.
Kothari, C. R. (2004). Research methodology: Methods and techniques . India: New Age International.
Lee, R. (1993). Doing research on sensitive topics . London: Sage.
Merriam, S. (2009). Case study research in education: A qualitative approach . San Francisco: Jossey-Bass.
Mikecz, R. (2012). Interviewing elites addressing methodological issues. Qualitative Inquiry, 18 (6), 482–493.
Miles, M. B., & Huberman, A. M. (1994). Qualitative data analysis: An expanded sourcebook . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Noy, C. (2008). Sampling knowledge: The hermeneutics of snowball sampling in qualitative research. International Journal of Social Research Methodology, 11 (4), 327–344.
Okumus, F., Altinay, L., & Roper, A. (2007). Gaining access for research: Reflections from experience. Annals of Tourism Research, 34 (1), 7–26.
Patton, M. Q. (1990). Qualitative evaluation and research methods (2nd ed.). Newbury Park, CA: Sage.
Patton, M. Q. (2002). Two decades of developments in qualitative inquiry a personal, experiential perspective. Qualitative Social Work, 1 (3), 261–283.
Punch, K. F. (1998). Introduction to social research . London: Sage.
Seawright, J., & Gerring, J. (2008). Case selection techniques in case study research a menu of qualitative and quantitative options. Political Research Quarterly, 61 (2), 294–308.
Silverman, D. (Ed.). (2016). Qualitative research . London: Sage.
Thomas, G. (2015). How to do your case study . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Wan, Z. Y. (2016). College teacher beliefs and practices in computer-assisted language learning classrooms in China . Shanghai: Shanghai Jiaotong University Press.
Willis, J. W., Jost, M., & Nilakanta, R. (2007). Foundations of qualitative research: Interpretive and critical approaches . London: Sage.
Book Google Scholar
Wilmot, A. (2005). Designing sampling strategies for qualitative social research: With particular reference to the Office for National Statistics’ Qualitative Respondent Register. Survey Methodology Bulletin-office for National Statistics, 56, 53.
Yin, R. K. (2009). Case study research: Design and methods (4th ed.). Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Yin, R. K. (2013). Case study research: Design and methods (5th ed.). London: Sage publications.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Foreign Language Department, China Pharmaceutical University, Nanjing, China
Zhongyan Wan
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Zhongyan Wan .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Faculty of Education, Beijing Normal University, Beijing, China
Kwok Kuen Tsang
Faculty of Social Sciences, University of Stavanger, Stavanger, Norway
School of Humanities, Southeast University, Nanjing, Jiangsu, China
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
Wan, Z. (2019). Participant Selection and Access in Case Study Research. In: Tsang, K., Liu, D., Hong, Y. (eds) Challenges and Opportunities in Qualitative Research. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-5811-1_5
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-5811-1_5
Published : 05 January 2019
Publisher Name : Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN : 978-981-13-5810-4
Online ISBN : 978-981-13-5811-1
eBook Packages : Social Sciences Social Sciences (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
Qualitative study design: Sampling
- Qualitative study design
- Phenomenology
- Grounded theory
- Ethnography
- Narrative inquiry
- Action research
- Case Studies
- Field research
- Focus groups
- Observation
- Surveys & questionnaires
- Study Designs Home
As part of your research, you will need to identify "who" you need to recruit or work with to answer your research question/s. Often this population will be quite large (such as nurses or doctors across Victoria), or they may be difficult to access (such as people with mental health conditions). Sampling is a way that you can choose a smaller group of your population to research and then generalize the results of this across the larger population.
There are several ways that you can sample. Time, money, and difficulty or ease in reaching your target population will shape your sampling decisions. While there are no hard and fast rules around how many people you should involve in your research, some researchers estimate between 10 and 50 participants as being sufficient depending on your type of research and research question (Creswell & Creswell, 2018). Other study designs may require you to continue gathering data until you are no longer discovering new information ("theoretical saturation") or your data is sufficient to answer your question ("data saturation").
Why is it important to think about sampling?
It is important to match your sample as far as possible to the broader population that you wish to generalise to. The extent to which your findings can be applied to settings or people outside of who you have researched ("generalisability") can be influenced by your sample and sampling approach. For example, if you have interviewed homeless people in hospital with mental health conditions, you may not be able to generalise the results of this to every person in Australia with a mental health condition, or every person who is homeless, or every person who is in hospital. Your sampling approach will vary depending on what you are researching, but you might use a non-probability or probability (or randomised) approach.
Non-Probability sampling approaches
Non-Probability sampling is not randomised, meaning that some members of your population will have a higher chance of being included in your study than others. If you wanted to interview homeless people with mental health conditions in hospital and chose only homeless people with mental health conditions at your local hospital, this would be an example of convenience sampling; you have recruited participants who are close to hand. Other times, you may ask your participants if they can recommend other people who may be interested in the study: this is an example of snowball sampling. Lastly, you might want to ask Chief Executive Officers at rural hospitals how they support their staff mental health; this is an example of purposive sampling.
Examples of non-probability sampling include:
- Purposive (judgemental)
- Convenience
Probability (Randomised) sampling
Probability sampling methods are also called randomised sampling. They are generally preferred in research as this approach means that every person in a population has a chance of being selected for research. Truly randomised sampling is very complex; even a simple random sample requires the use of a random number generator to be used to select participants from a list of sampling frame of the accessible population. For example, if you were to do a probability sample of homeless people in hospital with a mental health condition, you would need to develop a table of all people matching this criteria; allocate each person a number; and then use a random number generator to find your sample pool. For this reason, while probability sampling is preferred, it may not be feasible to draw out a probability sample.
Things to remember:
- Sampling involves selecting a small subsection of your population to generalise back to a larger population
- Your sampling approach (probability or non-probability) will reflect how you will recruit your participants, and how generalisable your results are to the wider population
- How many participants you include in your study will vary based on your research design, research question, and sampling approach
Further reading:
Babbie, E. (2008). The basics of social research (4th ed). Belmont: Thomson Wadsworth
Creswell, J.W. & Creswell, J.D. (2018). Research design: Qualitative, quantitative and mixed methods approaches (5th ed). Thousand Oaks: SAGE
Salkind, N.J. (2010) Encyclopedia of research design. Thousand Oaks: SAGE Publications
Vasileiou, K., Barnett, J., Thorpe, S., & Young, T. (2018). Characterising and justifying sample size sufficiency in interview-based studies: systematic analysis of qualitative health research over a 15-year period. BMC Medical Research Methodology, 18(148)
- << Previous: Interviews
- Next: Appraisal >>
- Last Updated: Apr 8, 2024 11:12 AM
- URL: https://deakin.libguides.com/qualitative-study-designs
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Study Suggests Genetics as a Cause, Not Just a Risk, for Some Alzheimer’s
People with two copies of the gene variant APOE4 are almost certain to get Alzheimer’s, say researchers, who proposed a framework under which such patients could be diagnosed years before symptoms.

By Pam Belluck
Scientists are proposing a new way of understanding the genetics of Alzheimer’s that would mean that up to a fifth of patients would be considered to have a genetically caused form of the disease.
Currently, the vast majority of Alzheimer’s cases do not have a clearly identified cause. The new designation, proposed in a study published Monday, could broaden the scope of efforts to develop treatments, including gene therapy, and affect the design of clinical trials.
It could also mean that hundreds of thousands of people in the United States alone could, if they chose, receive a diagnosis of Alzheimer’s before developing any symptoms of cognitive decline, although there currently are no treatments for people at that stage.
The new classification would make this type of Alzheimer’s one of the most common genetic disorders in the world, medical experts said.
“This reconceptualization that we’re proposing affects not a small minority of people,” said Dr. Juan Fortea, an author of the study and the director of the Sant Pau Memory Unit in Barcelona, Spain. “Sometimes we say that we don’t know the cause of Alzheimer’s disease,” but, he said, this would mean that about 15 to 20 percent of cases “can be tracked back to a cause, and the cause is in the genes.”
The idea involves a gene variant called APOE4. Scientists have long known that inheriting one copy of the variant increases the risk of developing Alzheimer’s, and that people with two copies, inherited from each parent, have vastly increased risk.
The new study , published in the journal Nature Medicine, analyzed data from over 500 people with two copies of APOE4, a significantly larger pool than in previous studies. The researchers found that almost all of those patients developed the biological pathology of Alzheimer’s, and the authors say that two copies of APOE4 should now be considered a cause of Alzheimer’s — not simply a risk factor.
The patients also developed Alzheimer’s pathology relatively young, the study found. By age 55, over 95 percent had biological markers associated with the disease. By 65, almost all had abnormal levels of a protein called amyloid that forms plaques in the brain, a hallmark of Alzheimer’s. And many started developing symptoms of cognitive decline at age 65, younger than most people without the APOE4 variant.
“The critical thing is that these individuals are often symptomatic 10 years earlier than other forms of Alzheimer’s disease,” said Dr. Reisa Sperling, a neurologist at Mass General Brigham in Boston and an author of the study.
She added, “By the time they are picked up and clinically diagnosed, because they’re often younger, they have more pathology.”
People with two copies, known as APOE4 homozygotes, make up 2 to 3 percent of the general population, but are an estimated 15 to 20 percent of people with Alzheimer’s dementia, experts said. People with one copy make up about 15 to 25 percent of the general population, and about 50 percent of Alzheimer’s dementia patients.
The most common variant is called APOE3, which seems to have a neutral effect on Alzheimer’s risk. About 75 percent of the general population has one copy of APOE3, and more than half of the general population has two copies.
Alzheimer’s experts not involved in the study said classifying the two-copy condition as genetically determined Alzheimer’s could have significant implications, including encouraging drug development beyond the field’s recent major focus on treatments that target and reduce amyloid.
Dr. Samuel Gandy, an Alzheimer’s researcher at Mount Sinai in New York, who was not involved in the study, said that patients with two copies of APOE4 faced much higher safety risks from anti-amyloid drugs.
When the Food and Drug Administration approved the anti-amyloid drug Leqembi last year, it required a black-box warning on the label saying that the medication can cause “serious and life-threatening events” such as swelling and bleeding in the brain, especially for people with two copies of APOE4. Some treatment centers decided not to offer Leqembi, an intravenous infusion, to such patients.
Dr. Gandy and other experts said that classifying these patients as having a distinct genetic form of Alzheimer’s would galvanize interest in developing drugs that are safe and effective for them and add urgency to current efforts to prevent cognitive decline in people who do not yet have symptoms.
“Rather than say we have nothing for you, let’s look for a trial,” Dr. Gandy said, adding that such patients should be included in trials at younger ages, given how early their pathology starts.
Besides trying to develop drugs, some researchers are exploring gene editing to transform APOE4 into a variant called APOE2, which appears to protect against Alzheimer’s. Another gene-therapy approach being studied involves injecting APOE2 into patients’ brains.
The new study had some limitations, including a lack of diversity that might make the findings less generalizable. Most patients in the study had European ancestry. While two copies of APOE4 also greatly increase Alzheimer’s risk in other ethnicities, the risk levels differ, said Dr. Michael Greicius, a neurologist at Stanford University School of Medicine who was not involved in the research.
“One important argument against their interpretation is that the risk of Alzheimer’s disease in APOE4 homozygotes varies substantially across different genetic ancestries,” said Dr. Greicius, who cowrote a study that found that white people with two copies of APOE4 had 13 times the risk of white people with two copies of APOE3, while Black people with two copies of APOE4 had 6.5 times the risk of Black people with two copies of APOE3.
“This has critical implications when counseling patients about their ancestry-informed genetic risk for Alzheimer’s disease,” he said, “and it also speaks to some yet-to-be-discovered genetics and biology that presumably drive this massive difference in risk.”
Under the current genetic understanding of Alzheimer’s, less than 2 percent of cases are considered genetically caused. Some of those patients inherited a mutation in one of three genes and can develop symptoms as early as their 30s or 40s. Others are people with Down syndrome, who have three copies of a chromosome containing a protein that often leads to what is called Down syndrome-associated Alzheimer’s disease .
Dr. Sperling said the genetic alterations in those cases are believed to fuel buildup of amyloid, while APOE4 is believed to interfere with clearing amyloid buildup.
Under the researchers’ proposal, having one copy of APOE4 would continue to be considered a risk factor, not enough to cause Alzheimer’s, Dr. Fortea said. It is unusual for diseases to follow that genetic pattern, called “semidominance,” with two copies of a variant causing the disease, but one copy only increasing risk, experts said.
The new recommendation will prompt questions about whether people should get tested to determine if they have the APOE4 variant.
Dr. Greicius said that until there were treatments for people with two copies of APOE4 or trials of therapies to prevent them from developing dementia, “My recommendation is if you don’t have symptoms, you should definitely not figure out your APOE status.”
He added, “It will only cause grief at this point.”
Finding ways to help these patients cannot come soon enough, Dr. Sperling said, adding, “These individuals are desperate, they’ve seen it in both of their parents often and really need therapies.”
Pam Belluck is a health and science reporter, covering a range of subjects, including reproductive health, long Covid, brain science, neurological disorders, mental health and genetics. More about Pam Belluck
The Fight Against Alzheimer’s Disease
Alzheimer’s is the most common form of dementia, but much remains unknown about this daunting disease..
How is Alzheimer’s diagnosed? What causes Alzheimer’s? We answered some common questions .
A study suggests that genetics can be a cause of Alzheimer’s , not just a risk, raising the prospect of diagnosis years before symptoms appear.
Determining whether someone has Alzheimer’s usually requires an extended diagnostic process . But new criteria could lead to a diagnosis on the basis of a simple blood test .
The F.D.A. has given full approval to the Alzheimer’s drug Leqembi. Here is what to know about i t.
Alzheimer’s can make communicating difficult. We asked experts for tips on how to talk to someone with the disease .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Case studies play a significant role in knowledge development across various disciplines. Analysis of cases provides an avenue for researchers to explore phenomena within their context based on the collected data. Analysis of qualitative data from case study research can contribute to knowledge development.
Usually between 10- 20 participants. Most cases I have seen were 15. CS are difficult to do if you are conducting a focus group and trying to triangulate. Some people conduct three forms of data ...
The answer lies somewhere in between. It's often a good idea (for qualitative research methods like interviews and usability tests) to start with 5 participants and then scale up by a further 5 based on how complicated the subject matter is. You may also find it helpful to add additional participants if you're new to user research or you ...
Revised on November 20, 2023. A case study is a detailed study of a specific subject, such as a person, group, place, event, organization, or phenomenon. Case studies are commonly used in social, educational, clinical, and business research. A case study research design usually involves qualitative methods, but quantitative methods are ...
Although case studies have been discussed extensively in the literature, little has been written about the specific steps one may use to conduct case study research effectively (Gagnon, 2010; Hancock & Algozzine, 2016).Baskarada (2014) also emphasized the need to have a succinct guideline that can be practically followed as it is actually tough to execute a case study well in practice.
A case study is one of the most commonly used methodologies of social research. This article attempts to look into the various dimensions of a case study research strategy, the different epistemological strands which determine the particular case study type and approach adopted in the field, discusses the factors which can enhance the effectiveness of a case study research, and the debate ...
Case studies tend to focus on qualitative data using methods such as interviews, observations, and analysis of primary and secondary sources (e.g., newspaper articles, photographs, official records). Sometimes a case study will also collect quantitative data. Example: Mixed methods case study. For a case study of a wind farm development in a ...
This article describes a one-credit discussion course in research ethics for graduate students in biology. Case studies are focused on within the four parts of the course: 1) major issues, 2 )practical issues in scholarly work, 3) ownership of research results, and 4) training and personal decisions. DeVoss, G. (1981).
This means you have 75 min. for asking questions, and if you have four questions, this allows a total of 18 min. of speaking time for each question. If all eight respondents participate in the discussion, this boils down to about two minutes of speaking time per respondent per question.
Case study research is one method of conducting qualitative research. The case is defined as an individual, an organization, or an entity and is bounded by time and space. The researcher is the primary instrument in case study methods; therefore researcher bias should be recognized and minimized as much as possible.
Chapter 11 Case Research. Case research, also called case study, is a method of intensively studying a phenomenon over time within its natural setting in one or a few sites. Multiple methods of data collection, such as interviews, observations, prerecorded documents, and secondary data, may be employed and inferences about the phenomenon of ...
As Patton (2002) notes, "purposeful sampling is one of the core distinguishing elements of qualitative inquiry." (p. 272). Two challenges exist for novice qualitative researchers. First, they may have to dislodge the idea that randomness and representativeness are universally important to all sampling strategies.
A case study is a research approach that is used to generate an in-depth, multi-faceted understanding of a complex issue in its real-life context. It is an established research design that is used extensively in a wide variety of disciplines, particularly in the social sciences. A case study can be defined in a variety of ways (Table.
A case study involves an in-depth analysis of a specific individual, group, or situation, aiming to understand the complexities and unique aspects of the subject. It often involves collecting qualitative data through interviews, observations, and document analysis. On the other hand, a survey is a structured data collection method that involves ...
In referring to the case study method, for instance, Earl Babbie, in his seventh edition of The Basics of Social Research ... For all of these reasons (and more), it is research participants that provide qualitative data not respondents. Babbie, E. R. (2016). The basics of social research (7th ed.). Cengage learning.
The purpose of case study research is twofold: (1) to provide descriptive information and (2) to suggest theoretical relevance. Rich description enables an in-depth or sharpened understanding of the case. It is unique given one characteristic: case studies draw from more than one data source. Case studies are inherently multimodal or mixed ...
A case study is a detailed examination of a specific subject. Case studies are commonly used in social, educational, clinical, and business research. The research design of a case study often involves qualitative methods, but sometimes quantitative methods are also utilized. Case studies serve to describe, compare, evaluate, and understand ...
Case study research can and does contribute to evidence for causal inferences. On challenging issues such as addressing health inequalities, we have shown how case studies provide more than detailed description of context or process. Contributions include: describing actors' accounts of causal relationships; demonstrating theoretically ...
A notable example of an explanatory case study is the Allison & Zelikow study of the 1962 Cuban missile crisis[2], demonstrating how a "single case study can be the basis for significant explanations and generalisations" [48, p. 6]. Stake differentiates between intrinsic, instrumental, and collective case studies[40 ]. Intrinsic
This paper, drawing on the researcher's previous experience of 2 research projects which involve case study approach (her 2007-2012 Ph.D. project on 4 language teachers and a small-scaled project on 12 international students in China), tries to answer the above 3 questions by describing how the practical criteria and strategies have been developed and applied in case selection and access.
You have personal contact with respondents, so you know exactly who will be included in the sample in advance. ... The type of design you're using (e.g., a survey, experiment, or case study) Your sampling methods or criteria for selecting subjects; Your data collection methods (e.g., questionnaires, observations)
Sampling involves selecting a small subsection of your population to generalise back to a larger population. Your sampling approach (probability or non-probability) will reflect how you will recruit your participants, and how generalisable your results are to the wider population. How many participants you include in your study will vary based ...
A few respondents, handpicked for the study, can serve the purpose because they are sure to have adequate knowledge around the concerned area of research. In most cases, 10-12 participants may cut it for the panel discussion. For an interview, the researchers may rely on 5-10 experts. However, as a thumb-rule, the greater, the better.
Access the portal of NASS, the official source of agricultural data and statistics in the US, and explore various reports and products.
May 6, 2024. Scientists are proposing a new way of understanding the genetics of Alzheimer's that would mean that up to a fifth of patients would be considered to have a genetically caused form ...
The trial, which has been ongoing since mid-April, has included multiple witnesses tying Trump to the hush money scheme, with Cohen directly testifying that Trump approved the Daniels payment and ...