Hard skills vs. Soft skills
After reading this guide, you will be able to clearly define the hard and soft skills needed for your open positions, resume, and CV.
Ivan Andreev
Demand Generation & Capture Strategist, Valamis
November 27, 2021 · updated October 15, 2024
9 minute read
Julia Kuzmina contributed
When seeking new recruits or considering internal promotions, it’s crucial to identify the specific skills required for each role. Some of these skills are innate, while others may require formal training.
For L&D and HR professionals, it’s essential to outline hard skills in the role specification, detailing the necessary technical competencies.
Equally important are the soft skills, which include interpersonal and emotional intelligence, to be included in the person specification.
Employees can also benefit greatly from this guide. By reading it, you will learn how to clearly distinguish between hard and soft skills. This knowledge will be invaluable for enhancing your resumes and effectively showcasing your top skills.

What are hard skills?
What are soft skills, what’s the difference between hard skills and soft skills, list of hard and soft skills, how to develop hard and soft skills.
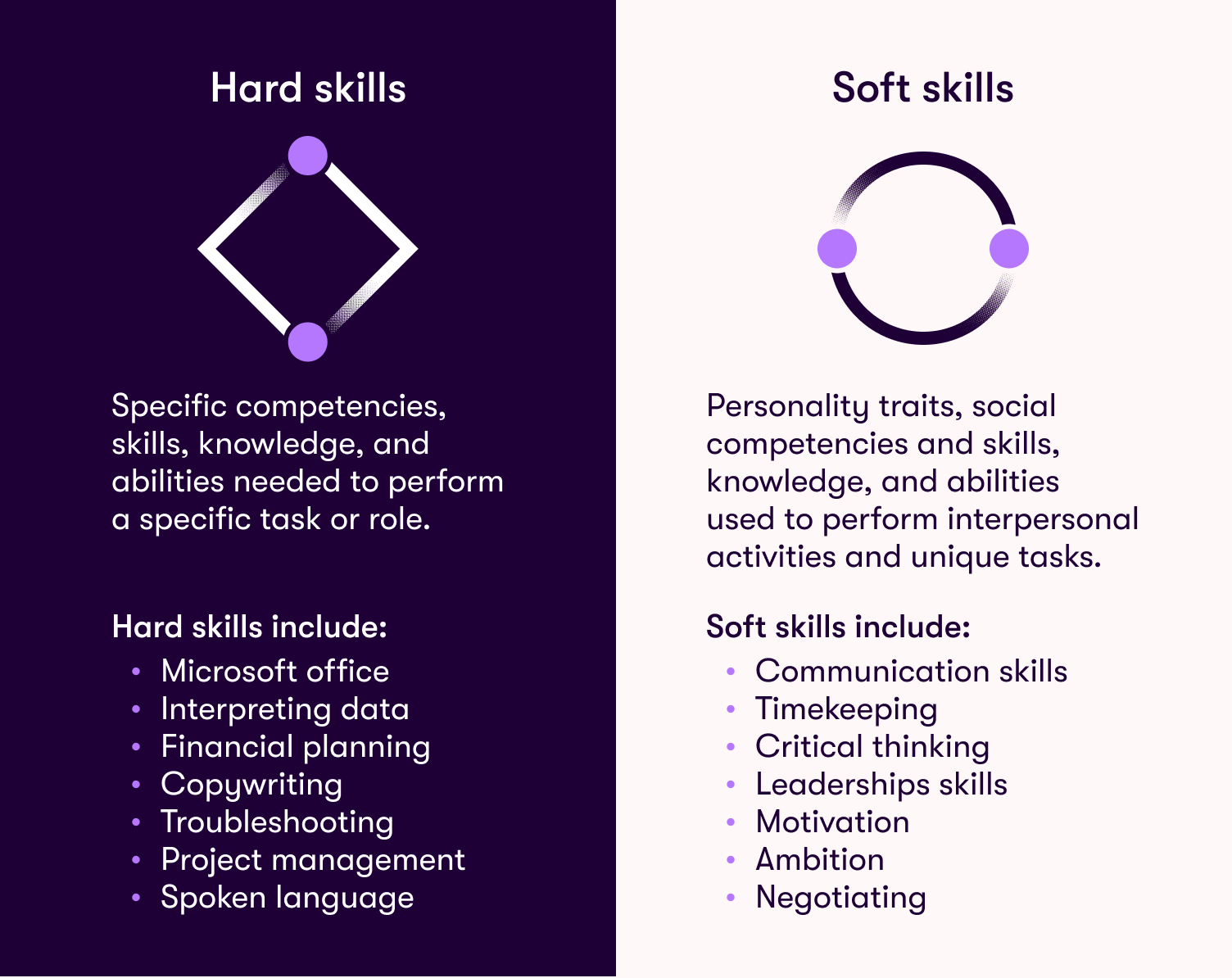
Hard skills are the specific competencies, knowledge, and abilities required to perform particular tasks or roles. These skills can be acquired through education, training, and professional development. Hard skills are typically technical in nature (though not always) and are easily measurable and objectively assessed.
Evidence of hard skills can be found in educational certificates or demonstrated through practical applications.
For instance, software development necessitates proficiency in programming languages, which is essential for writing computer programs.
The level of expertise in this area is quantifiable through various metrics and assessments.
Similarly, consider the design field. Whether it’s interior design or web design, each specialty requires a unique skill set tailored to specific tasks. Mastery of design principles and tools is crucial and can be distinctly evaluated.
Another example is proficiency in the Microsoft Office Suite. Skills in using tools like Microsoft Word and Excel are often indispensable for many job functions and can be demonstrated through both certification and practical usage.
Thus, each role demands a unique combination of hard skills essential for effective performance. Understanding and developing these skills are fundamental to achieving success in any professional setting.

How to conduct a skills gap analysis and what to do next
Start building your foundation for strategic workforce development.
Soft skills are personality traits, social competencies, and abilities essential for performing interpersonal activities and unique tasks. Sometimes referred to as human skills, they are vital for effective interaction and collaboration.
Often rooted in inherent personality traits and social abilities, soft skills can also be refined through practice and professional development.
Unlike hard skills, measuring soft skills can be challenging, particularly during the hiring process, due to limited observable information. Personal interactions are key to truly understanding a person’s soft skills.
While various techniques and tests exist to assess these skills, their accuracy can be limited and may not always reflect a person’s true abilities.
Real-life situations are the ultimate test of how effectively someone applies their soft skills.
Certain soft skills are universally desirable for all team members, such as punctuality and effective collaboration. Other skills, such as leadership, communication, strategic thinking, and problem-solving, are crucial for specific roles.
Though soft skills are not accompanied by certifications, they become evident through daily interactions and work experiences.
Natural leaders instinctively take charge and guide others, while reliable team members consistently demonstrate punctuality and proactive communication.
By recognizing and nurturing soft skills, organizations can enhance team dynamics and overall performance, creating a more cohesive and productive work environment.
The primary difference lies in their nature: soft skills are closely tied to an individual’s personality and aren’t always teachable, while hard skills are learned and task-specific.
Soft skills, such as leadership and communication, can be enhanced through training, but there’s often an innate element. Some individuals naturally exhibit strong leadership qualities more than others.
In contrast, hard skills are acquired through education and training. These skills are specific to tasks and easier to teach. Employees can attend courses to learn new hard skills or improve existing ones.
As careers progress, individuals need to adapt and expand their skill sets, especially when moving into leadership roles. They require both the technical knowledge specific to their positions and the interpersonal skills to excel.
It’s important to recognize that your best employees may not excel in both soft and hard skills. While versatility is advantageous, not all roles require proficiency in both areas.
There are many hard and soft skills, so that we will list only a few.
Now that you know the difference between soft and hard skills, it’s time to analyze which ones need to be added to your organization. And what to do next?
How to develop hard skills
For HR and L&D professionals (If you are the one responsible for developing employees’ HARD skills):
- Identify skill gaps : Conduct skill gap analyses to determine the hard skills necessary for various roles within the organization. Use assessments and performance reviews to pinpoint areas for development.
- Design training programs : Develop and implement targeted training programs within your LMS and workshops tailored to the specific needs of your team. Utilize both internal and external resources.
- Encourage certifications : Promote and facilitate access to professional certification programs relevant to your industry. Support employees in obtaining these credentials.
- On-the-job training : Create opportunities for employees to gain practical experience through job rotations, special projects, and cross-training.
- Continuous learning culture : Foster a culture of continuous learning by providing access to educational resources, including online courses and industry conferences.
For employees (if you are the one developing your own HARD skills):
- Self-assessment : Identify the hard skills required for your current role or desired career path. Use self-assessment tools and seek feedback from supervisors.
- Enroll in courses : Take advantage of courses offered by universities, community colleges, or online platforms like Valamis , Coursera, Udemy, or LinkedIn Learning to gain new skills or enhance existing ones.
- Professional training : Attend workshops and seminars to gain hands-on experience and learn from industry experts.
- Certifications : Pursue relevant certifications to validate your expertise and enhance your professional credibility.
- Practical application : Regularly practice new skills in real-world scenarios to build proficiency and confidence.
How to develop soft skills
For HR and L&D professionals (If you are the one responsible for developing employees’ SOFT skills):
- Identify key soft skills : Determine the essential soft skills required for various roles within the organization. Focus on skills such as leadership, communication, teamwork, and emotional intelligence .
- Create development programs : Design and implement development programs that include workshops, mentoring, and coaching to enhance employees’ soft skills. Download the career development plan template and use it as a starting point.
- Foster a feedback culture : Encourage a culture of continuous feedback where employees can receive constructive input on their soft skills from peers and supervisors.
- Role-playing and simulations : Incorporate role-playing exercises and simulations into training programs to allow employees to practice and refine their soft skills in a safe environment.
- Networking opportunities : Facilitate networking events and collaborative projects to help employees build and improve their interpersonal skills.
For employees (If you are the one developing your own SOFT skills):
- Self-assessment and feedback : Reflect on your current soft skills and identify areas for improvement. Seek regular feedback from peers, mentors, and supervisors to guide your development.
- Enroll in soft skills courses : Participate in courses and workshops focused on developing soft skills such as communication, leadership, and teamwork. Utilize online platforms, your company’s LMS and local training providers.
- Mentorship and coaching : Engage with a mentor or coach who can provide guidance, model effective soft skills, and offer constructive feedback.
- Practice in real scenarios : Use role-playing exercises and simulations to practice soft skills in a controlled environment, building confidence and improving techniques.
- Networking and collaboration : Actively participate in networking events and collaborative projects to enhance your interpersonal and communication skills.
- Read and learn : Read books, articles, and blogs, listen podcasts on personal development and effective interpersonal skills. Authors like Dale Carnegie and Stephen Covey offer valuable insights.
- Mindfulness and emotional intelligence : Practice mindfulness techniques to improve self-awareness and emotional regulation. Developing emotional intelligence is crucial for effective interpersonal interactions.
- Continuous improvement : Make a conscious effort to improve your soft skills by seeking feedback, reflecting on interactions, and adapting based on the input received.
By consistently working on both hard and soft skills, HR professionals can create a more capable and adaptable workforce, and employees can enhance their overall competence and career prospects.
Further reading:
- You can check our article about employee development methods , we have mentioned what methods work best for different skills sets and particular skills.
- Regarding leadership skills check our leadership development plan guide because it is a unique skill set and it requires specific training.
- One way to map, manage, and track the required skills and skill gaps of your employees is to use a skills matrix .

You might be interested in

Key areas of employee development

Learning and development fundamentals

The meaning of Learning Management System (LMS)

IMAGES
VIDEO