- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
Social Mettle

Manuscript Speech: Definition, Examples, and Presentation Tips
A manuscript speech implies reading a pre-written speech word by word. Go through this SocialMettle write-up to find out its meaning, some examples, along with useful tips on how to present a manuscript speech.

Tip! While preparing the manuscript, consider who your audience is, so as to make it effectual.
Making a speech comes to us as a ‘task’ sometimes. Be it in school, for a meeting, or at a function; unless you are at ease with public speaking, speeches may not be everyone’s cup of tea. A flawless and well-structured delivery is always welcome though. Memories of delivering and listening to a variety of speeches are refreshed when confronted with preparing for one.
Being the most effective way of communication, a speech is also a powerful medium of addressing controversial issues in a peaceful manner. There are four types of speeches: impromptu, extemporaneous, manuscript, and memorized. Each has its purpose, style, and utility. We have definitely heard all of them, but may not be able to easily differentiate between them. Let’s understand what the manuscript type is actually like.
Definition of Manuscript Speech
This is when a speaker reads a pre-written speech word by word to an audience.
It is when an already prepared script is read verbatim. The speaker makes the entire speech by referring to the printed document, or as seen on the teleprompter. It is basically an easy method of oral communication.
Manuscript speaking is generally employed during official meetings, conferences, and in instances where the subject matter of the speech needs to be recorded. It is used especially when there is time constraint, and the content of the talk is of prime importance. Conveying precise and succinct messages is the inherent purpose of this speech. Public officials speaking at conferences, and their speech being telecast, is a pertinent example.
There can be various occasions where this style of speech is used. It depends on the context of the address, the purpose of communication, the target audience, and the intended impact of the speech. Even if it is understood to be a verbatim, manuscript speaking requires immense effort on the part of the speaker. Precision in the delivery comes not just with exact reading of the text, but with a complete understanding of the content, and the aim of the talk. We have witnessed this through many examples of eloquence, like the ones listed below.
- A speech given by a Congressman on a legislative bill under consideration.
- A report read out by a Chief Engineer at an Annual General Meeting.
- A President’s or Prime Minister’s address to the Parliament of a foreign nation.
- A televised news report (given using a teleprompter) seen on television.
- A speech given at a wedding by a best man, or during a funeral.
- A religious proclamation issued by any religious leader.
- A speech in honor of a well-known and revered person.
- Oral report of a given chapter in American history, presented as a high school assignment.
Advantages and Disadvantages
✔ Precision in the text or the speech helps catch the focus of the audience.
✔ It proves very effective when you have to put forth an important point in less time.
✔ Concise and accurate information is conveyed, especially when talking about contentious issues.
✘ If you are not clear in your speech and cannot read out well, it may not attract any attention of the audience.
✘ As compared to a direct speech, in a manuscript that is read, the natural flow of the speaker is lost. So is the relaxed, enthusiastic, interactive, and expressive tone of the speech lost.
✘ A manuscript speech can become boring if read out plainly, without any effort of non-verbal communication with the audience.
Tips for an Appealing Manuscript Speech
❶ Use a light pastel paper in place of white paper to lessen the glare from lights.
❷ Make sure that the printed or written speech is in a bigger font size than normal, so that you can comfortably see what you are reading, which would naturally keep you calm.
❸ Mark the pauses in your speech with a slash, and highlight the important points.
❹ You can even increase the spacing between words for easier reading (by double or triple spacing the text).
❺ Highlight in bold the first word of a new section or first sentence of a paragraph to help you find the correct line faster.
❻ Don’t try to memorize the text, highlights, or the pauses. Let it come in the flow of things.
❼ Practice reading it out aloud several times, or as many times as you can.
❽ Try keeping a smile on your face while reading.
❾ Keep in mind that a manuscript speech does not mean ‘mere reading out’. Maintaining frequent eye contact with the audience helps involving them into the subject matter.
Like it? Share it!
Get Updates Right to Your Inbox
Further insights.

Privacy Overview
- Home →
- Speech Crafting →
How to Write an Effective Manuscript Speech in 5 Steps

If your public speaking course requires you to give a manuscript speech, you might be feeling a little overwhelmed. How do you put together a speech that’s effective and engaging? Not to worry – with a few simple steps, you’ll be prepared to pull off a manuscript speech that’s both impactful and polished. In this post, we’ll walk through the 5 steps you need to follow to craft an effective manuscript speech that’ll leave your audience impressed. So let’s get started!
Quick Overview of Key Question
A manuscript speech involves writing down your entire speech word-for-word and memorizing it before delivering it. To begin, start by writing down your introduction , main points, and conclusion. Once you have written your speech, practice reading it out loud to get used to the phrasing and memorize each part .
Preparing a Manuscript Speech
When preparing for your manuscript speech, it is essential to consider both the content of your speech and the format in which you will deliver the speech. It is important to identify any key points or topics that you would like to cover in order to ensure that your manuscript is properly organized and succinct. Additionally, when selecting the style of delivery, be sure to choose one that best fits with your specific message and goals . One style of delivery includes utilizing a conversational tone in order to engage with your audience and help foster an interactive environment . When using this delivery style, be sure to use clear and concise language as well as humor and anecdotes throughout your speech . In addition, select a pacing that allows for flexibility with audience responses without detracting from the overall structure or flow of your text. Alternatively, another style of delivery involves reading directly from the manuscript without deviating from the text. This method works best when coupled with visual aids or props that support the information being relayed. Additionally, it is important to remember to practice reading the manuscript aloud several times prior to its delivery in order to ensure quality content and an acceptable rate of speed. No matter which delivery style you decide upon, careful preparation and rehearsal are essential components of delivering an effective manuscript speech. After deciding on a style of delivery and organizing the content of your speech accordingly, you can move on to formatting your document correctly in order to ensure a professional presentation during its delivery.
Document Format and Outline Structure
Before you dive into the content research and development stages of crafting your manuscript speech, it is important to consider the structure that your specific delivery will take. The format of your document can be varied depending on preferences and requirements, but always remember to keep it consistent throughout. When formatting your document, choose a universal style such as APA or MLA that may be easily recognisable to readers and familiar to most academics. Not only should this ensure your work meets some basic standards, but it will also make sure any information sources are appropriately cited for future reference. Additionally, you should provide visibility for headings to break up topics when needed, whilst keeping the language succinct and easy to understand. Creating an outline is integral in effectively structuring both a written piece of work and delivering a speech from paper. Use a hierarchical system of divisional points starting with a central concept, followed by additional details divided into sub sections where necessary and ending with a conclusion. This overview will act as a roadmap during the writing process—keeping track of ideas, identifying gaps in the presentation structure, and helping ensure clarity when presenting your points live on stage. It may be best practice to include a few statements or questions at the end of each key point to challenge thought in your audience and keep them engaged in the conversation. This could prompt new ideas or encourage defined discussion or debate amongst viewers. Depending on the topic itself, introducing two sides of an argument can allow an all-encompassing view point from which all members of an audience can draw their conclusions from majority opinion. Once you’ve established a full document format and outlined its corresponding structure for delivery, you’re ready for the next step: carefully developing comprehensive content along with appropriate ideas behind each sentence, word choice , and syntax used in every phrase. With these vital pieces in place, you are one step closer to creating an effective manuscript speech!
Content, Ideas and Language
The content, ideas, and language you use in your manuscript speech should be tailored to the audience you are addressing. It is important to consider the scope of the audience’s knowledge, level of interest in the topic and any special needs or cultural sensitivities. The most obvious way of doing this is by understanding who will be listening to the speech. You can also research the subject matter thoroughly to ensure you have a well-rounded perspective on the issue and that your opinion is well-informed.
While incorporating facts and personal experiences can help make any point stronger, ensure all ideas included in the speech have a relevancy to the main argument. Finally, avoid using difficult words or jargons as they may detract from any points being made. In terms of language, it’s recommended to use an active voice and write plainly while maintaining interesting visuals. This will help keep listeners engaged and make it easy for them to understand what’s being said. Additionally, focus on using appropriate vocabulary that will sound classy and create a good impression on your audience. Use simpler terms instead of long-winded ones, as regularly as possible, so that your message integrates easier with listeners. Now that you’ve considered content ideas and language for your manuscript speech, it’s time to go forward with writing and practicing it.
Writing and Practicing a Manuscript Speech
When writing a manuscript speech, it’s important to choose a central topic and clearly define the message you want to convey. Start by doing some research to ensure that your facts are accurate and up-to-date. Take notes and begin to organize your points into a logical flow. Once the first draft of your speech is complete, read it over multiple times, checking for grammar and typos. Also consider ways to effectively utilize visuals, such as photos or diagrams, as props within your speech if they will add value to your content. It is essential to practice delivering your speech using the manuscript long before you stand in front of an audience. Time yourself during practice sessions so that you can get comfortable staying within the parameters provided for the speech. Achieving a perfect blend of speaking out loud and reading word-by-word from the script is a vague area that speakers must strike a balance between in order to engage their audience without appearing overly rehearsed or overly off-the-cuff. Finally, look for opportunities to get feedback on your manuscript speech as you progress through writing and practicing it. Ask family members or friends who are familiar with public speaking for their input, or join an organization like Toastmasters International – an organization dedicated to improving public speaking skills – for more constructive criticism from experienced professionals. Crafting a powerful story should be the next step in preparing for an effective manuscript speech. Rather than delivering cold data points, use storytelling techniques to illustrate your point: Describe how others felt when faced with a challenge, what strategies they used to overcome it, and how their lives changed as a result. Telling stories makes data memorable, entertaining and inspiring – all qualities which should be considered when writing an engaging manuscript speech.
Crafting a Powerful Story
A powerful story is one of the most important elements of a successful manuscript speech. It is the main ingredient to make your speech memorable to the audience and help it stand out from all the other speeches. When crafting a story, there are a few things you should consider: 1) Choose an Appropriate Topic: The topic of your story should be appropriate for the type of speech you will be giving. If you are giving a motivational speech , for example, ensure your story has an uplifting message or theme that listeners can take away from it. Additionally, avoid topics that are too controversial so as not to offend any members of the audience. 2) Relay Your Experience: You could also use your own experience to create powerful stories in your manuscript speech. This gives listeners an authentic perspective of the topic and makes them feel connected to you and your message. Besides personal experiences, you may also draw stories from current events and movies/books which listeners can relate to depending on their age group. 3) Be Animated: As you deliver your story, be sure to convey emotions with proper tone and gestures in order to keep the audience engaged and increase its resonance. Using props and visual aids can also complement the delivery of your story by making it more experiential for listeners. Finally, before moving on to writing the rest of the manuscript speech, ensure that you have developed a powerful story that captures the hearts of those who hear it. With a great story to start off with, listeners will become more invested in what is about to come next in this speech – some tips for delivery!
Key Points to Remember
Writing a powerful story is essential to creating a successful manuscript speech. When selecting topics and stories, it’s important to consider the type of speech, the message, and making sure it’s appropriate and isn’t offensive. Drawing from personal experience and current events can enhance the audience’s connection with the topic, while being animated with tone and gestures will make it more engaging. Visual aids and props can complement this as well. Introducing a great story will draw people to your speech and help them get invested in what comes next.
Tips for Delivery of a Manuscript Speech
Delivering a manuscript speech effectively is essential for making sure your message gets across to your audience. While it may seem daunting, by following a few simple tips, you can ensure that you present your speech in the most professional manner possible. Before you start delivering your speech, be sure to practice it several times in advance. This will help you become comfortable with your words so that they don’t come out stilted while presenting. It is also important to emphasize vocal variety by changing the tone and intensity of your voice to keep the audience’s focus; boring monotone voices are often difficult to listen to. Remember to slow down or speed up depending on the importance of what you’re saying; never read word-for-word from your script – instead, aim for an engaging, conversational delivery. When delivering a manuscript speech, hand gestures can prove particularly useful for emphasizing key points. You can use arm movements and body language to convey the emotions behind your words without them feeling forced or unnatural. Again, practice helps here as well; make yourself aware of your posture and make subtle adjustments throughout until you feel comfortable speaking while moving around confidently on stage. Eye contact is another key element of effective presentation . Make sure to look into the eyes of every member of your audience at least once during your presentation – this will help them feel like they are interacting with you directly and make them more receptive to your ideas. Feel free to break away from traditional powerpoint slides if they aren’t necessary – take advantage of the natural lighting in the room and navigate through the visible space instead. Finally, remember that how you conclude the speech is just as important as how you began it, so aim for a powerful ending that leaves those listening with a lasting impression of what was discussed and learned throughout your presentation. With these tips for delivery in mind, you’re almost ready to leave a lasting impression on your audience – something we’ll discuss further in the next section!
Making a Lasting Impression with Your Audience
When you first create your manuscript speech, it is of utmost importance to consider your audience. Each part of the speech must be tailored to the people who will be listening. If a speaker can connect with an audience and make an emotional impact, the work that went into crafting the document will pay off. Using a conversational tone, humor, storytelling, and analogies can help keep the audience engaged during your speech. These techniques give the listener something to connect with and remember after the presentation is over. However, be sure to balance any humorous anecdotes or stories with a professional demeanor as not to lose credibility with your audience. Considering each part of the message and its potential impression on the listeners can also help guide you in tailoring a manuscript speech. When introducing yourself, try to use language that connects with the background of your peers; focus on wanting to help others with what you have learned or experienced so they feel like you are truly talking directly to them. Conclude by summing up important points in an inspirational way and leave listeners motivated and determined to apply the advice given in their own lives. Through this manner of “closing out” an effective speech, the audience can carry away meaningful information that will stay with them long after you finish speaking. Now that you understand how essential it is for speakers to make a lasting impression on their audiences, let us move onto learning how to confidently handle questions from your listeners as part of your presentation.
How to Handle Questions from Your Audience
When writing a manuscript speech, there are certain things you should consider when handling questions from your audience. This is an essential part of giving a successful talk to a group of people. The best way to handle questions is to take notes and make sure you can answer them directly after the speech is completed. It is important to be prepared with responses to any potential questions that may arise during your presentation. This will show your audience that you have taken the time and effort towards understanding their concerns and addressing them accordingly.
Additionally, it is also beneficial to anticipate possible areas of criticism or disagreement among members of your audience, as this allows you to provide evidence or offer an alternate route for them to consider when questioning the points made in your presentation. It is also important to remain courteous and professional when answering questions , even if someone challenges your views or speaks unkindly about your topic. It is always best practice to remain composed and ensure everyone in the room feels respected. Furthermore, having an open discussion with your audience following a well-prepared manuscript speech can add value by expanding on topics outlined. It also presents an opportunity for further clarifications and understanding beyond just getting out the message. This can be done by asking the participants what they thought of the presentation, what points they found most interesting, and other general feedback they might offer. If handled correctly, these moments can be used as learning opportunities for both yourself and others. Ultimately, handling questions from your audience confidently and gracefully is an important component of delivering a successful manuscript speech. By taking the time to prepare a response tailored towards each inquiry, even if it involves debate, you show respect towards those who took their time out of their day to attend your talk.
Additionally, it presents an opportunity to expand on topics covered while allowing meaningful dialogue between participants. With that said, it’s now time turn our focus onto crafting an effective conclusion for our manuscripts speeches – one which can bring our ideas full circle and leave our audience with memorable words!
Conclusion and Overall Manuscript Speech Strategy
The conclusion of any speech is an important part of the process and should not be taken lightly. Regardless of the structure or content of the speech, the conclusion can help drive home the points you have made throughout your speech. It also serves to leave a lasting impression on the listener. The conclusion should not be too long or drawn-out, but it should be meaningful and relevant to your topic and overall message. When writing your conclusion, consider recapping some of the key points made in the body of your speech. This will help to reinforce those ideas that you want to stick with the listener most. Additionally, make sure to emphasize how what has been addressed in your speech translates into real-world solutions or recommendations. This can help ensure that you have conveyed an actionable and tangible impact with your speech. One way to approach crafting an effective manuscript for a speech is to take note of the overall theme or objective that you wish to convey. From there, think about how best to organize your information into manageable sections, ensuring that each one accurately reflects your main points from both a visual and verbal standpoint. Consider what visuals or other tools could be used to further illustrate or clarify any complex concepts brought up in the main body of your speech. Finally, be sure to craft an appropriate conclusion that brings together all of these points into a cohesive whole, leaving your listeners with powerful words that underscore the importance and significance of what you have said. Overall, successful manuscript speeches depend on clear and deliberate preparation. Spending time outlining, writing, and editing your speech will ensure that you are able to effectively communicate its message within a set timeframe and leave a lasting impact on those who heard it. By following this process carefully, you can craft manuscripts that will inform and inspire audiences while driving home key talking points effectively every time.
Frequently Asked Questions and Their Answers
What are the benefits of giving a manuscript speech.
Giving a manuscript speech has many benefits. First, it allows the speaker to deliver a well-researched and thought-out message that is generally consistent each time. Since the speaker has prepared their speech in advance, they can use rehearsals to perfect their delivery and make sure their message is clear and concise.
Additionally, having a manuscript allows the speaker the freedom to focus on engaging the audience instead of trying to remember what to say next. Having a written script also helps remove the fear of forgetting important points or getting sidetracked on tangents during the presentation. Finally, with a manuscript, it’s possible to easily modify content from performance to performance as needed. This can help ensure that every version of the speech remains as relevant, meaningful, and effective as possible for each audience.
How does one prepare a manuscript speech?
Preparing a manuscript speech requires careful planning and attention to detail. Here are the five steps to help you write a successful manuscript speech: 1. Research: Take the time to do your research and gather all the facts you need. This should be done well in advance so that you can prepare your speech carefully. 2. Outline: Lay out an outline of the major points you want to make in your speech and make sure each point builds logically on the one preceding it. 3. Draft: Once you have an outline, begin to flesh it out into a first draft of your manuscript speech. Be sure to include transitions between key points as well as fleshing out any examples or anecdotes that may help illustrate your points. 4. Edit: Once you have a first draft, edit it down multiple times. This isn’t where detailed editing comes in; this is more about making sure all the big picture elements work logically together, ensuring smooth transitions between ideas, and ensuring your words are chosen precisely to best convey their meaning. 5. Practice: The last step is perhaps the most important – practice! Rehearse your manuscript speech until you know it like the back of your hand, so that when it’s time for delivery, you can be confident of success.
What are some tips for delivering a successful manuscript speech?
1. Prepare in advance: Draft a script and practice it several times before delivering it. This will allow you to be comfortable with your material and avoid any awkward pauses when you are presenting your speech. 2. Speak clearly: Make sure that you speak loudly and clearly enough for everyone in the room to hear you. It is also important to enunciate your words properly so that your message can easily be understood by your audience. 3. Engage with the audience: Use eye contact when addressing your audience, ask questions and wait for responses, and pause to allow people time to mull over your points. These techniques help to ensure that everyone is engaged and interested in what you are saying. 4. Create visual aids: Create slides or other visuals that augment the material in your manuscript speech. This can help to keep the audience focused on what they are hearing as well as providing a reference point for them after your speech is finished. 5. Rehearse: Rehearse the delivery of your manuscript speech at least once prior to giving it so that you feel confident about how it will sound when presented in front of an audience. Identify any areas where improvements may be needed and focus on perfecting them before delivering the speech.
Mastering Manuscript Speech Tips and Techniques for Effective Delivery
Delivering a manuscript style speech can be a daunting task. It’s not just about reciting written words. It’s about making them come alive. Understanding what a speech manuscript involves is the first step. How you present it makes all the difference. Your audience must feel engaged, not bored. This requires finesse and a deep connection with your material.
So, what is a manuscript speech, exactly? In simple terms, it’s a speech read word-for-word from a written text. But it goes beyond mere reading. It’s about conveying emotion and intention through each sentence. Effective manuscript speech delivery requires practice and attention to detail. A strong command over the material is crucial. Only then can you inject life into it.
The format of a speech manuscript is another critical aspect. It should be easy to follow, with clear cues for emphasis. A manuscript speech should serve as a guide, not a crutch. Speaking naturally while referring to your script can be challenging. However, with the right techniques, you can ensure your presentation feels organic and dynamic. Define manuscript speech parameters clearly in your mind. This will aid in delivering it with confidence.
Avoid monotony. Break the rhythm with varied speech patterns. What is manuscript speech delivery if not a performance? It’s a fine balance between sticking to your script and engaging your audience. Think of it as a conversation, albeit a structured one. Each word has a purpose. Each pause, a significance. This is the essence of a well-delivered speech manuscript.
In conclusion, mastering the art of presenting a manuscript speech can transform your communication skills. It’s about more than definitions and formats. It’s about connecting with your audience. It’s about delivering your message with clarity and passion. With practice, anyone can excel at this. Your journey starts here.
What is a speech manuscript?
Understanding what a speech manuscript entails is crucial. It refers to the practice of delivering a speech while reading from a written document. This approach is common in situations requiring precision and accuracy. However, it’s more than just reading words off a page. The process involves a strategic blend of preparation, performance, and engagement.
- A speech manuscript should be clear and concise.
- It must capture the essence of your message.
- Use a format that enhances readability.
- Ensure the content flows naturally.
A well-crafted manuscript can be your best ally. It provides structure and keeps you on track. You can focus on delivery without worrying about memory lapses. However, it’s important to maintain a conversational tone. You must avoid sounding monotonous or robotic. This balance is achieved through practice and familiarity with the content.
- Start by understanding the manuscript speech meaning.
- Define your key points clearly.
- Practice reading aloud to gauge pacing.
- Incorporate pauses effectively to enhance impact.
- Engage with your audience through eye contact and expressions.
With a speech manuscript, your goal is to bring the words to life. Infuse emotion and emphasis where necessary. Your voice should rise and fall naturally, reflecting the nuances of your message. This level of delivery ensures your audience remains captivated and engaged. Remember, a speech manuscript is a tool, not a crutch. Use it wisely to elevate your presentation skills to new heights.
Understanding the Fundamentals
Grasping the essentials of a speech manuscript is crucial for aspiring speakers. It’s not just about reading words from a page. It’s about translating those words into a captivating verbal experience. A manuscript style speech demands precision and clarity. When delivering such speeches, you must ensure each word hits its mark. They require skill in maintaining a natural flow while sticking to the written script.
So, what is manuscript speech ? Essentially, it involves reading a pre-written text to an audience. This approach is common in formal settings, such as political addresses or academic presentations. A manuscript speech should be meticulously prepared, leaving little room for improvisation. The speaker’s task is to present the material as though they are speaking effortlessly, despite the reliance on written text.
Understanding manuscript speech meaning also includes knowing its advantages. This method ensures consistency and accuracy. Messages are delivered precisely as intended by the author. However, it’s not without challenges. Engaging an audience while reading requires practice and a deep familiarity with your content. You might find it difficult to establish a natural connection with your listeners.
Consider the manuscript speech format . It should be organized and easy to follow. Break it into clear sections. Include transitions and cues. Your document should guide your speech delivery seamlessly. It’s also beneficial to practice proper enunciation and vocal variety. This keeps your audience interested and attentive.
Finally, let’s define manuscript speech in practical terms. It’s a strategic approach to delivering formal presentations. Whether you’re addressing a large group or a small meeting, your delivery should appear confident and spontaneous. This balance between preparation and presentation is achieved through repetition and rehearsal. Remember, your ultimate goal is to communicate your message effectively while engaging your audience fully.

Identifying Target Audience
Recognizing the audience you are addressing is crucial. Without this understanding, even the most meticulously crafted script can miss its mark. Every group is unique. They have different interests, knowledge levels, and expectations. Tailoring the speech to these specifics can significantly enhance receptivity.
When you define manuscript speech for a specific audience, consider their background. Are they experts in the topic, or are they laypeople? This affects how in-depth you should go. For instance, a manuscript speech meaning for industry professionals would differ greatly from one aimed at high school students. Customization is key.
Understanding what is a manuscript speech involves more than just writing. It’s about delivering content that resonates. Think about the demographic details. Age, education, cultural background – all these factors influence how a speech is received. A younger audience might appreciate humor, while a more senior crowd may favor formal tones.
A manuscript speech should engage its listeners. If the audience finds the content relatable, they’re more likely to stay attentive. Utilize anecdotes and relevant examples. Ask rhetorical questions to keep them thinking. Interactive elements can work wonders in a manuscript style speech.
Remember, the process of crafting a speech includes considering how it will be delivered. Visualize the listeners. Their facial expressions, their reactions. Adjustments based on this visualization can make your speech more impactful. Aligning with the audience’s expectations ensures your message hits home.
Ultimately, what is manuscript speech without an audience? It’s half the equation, the other half being those who listen, understand, and react. Balancing content with the audience’s characteristics makes the speech not just heard, but felt and remembered.
Crafting a Compelling Script
Creating a compelling script is crucial for an impactful speech. Many ask, “What is a manuscript speech?” In essence, it involves reading a pre-written text to ensure accuracy and eloquence. Your script forms the backbone of the address, guiding both structure and content. To engage your audience, every word must count. Crafting it demands precision, creativity, and purpose. You must aim for clarity without sacrificing depth.
A well-crafted script begins with understanding what you want to convey. Consider the “manuscript definition speech” and the context in which you’re presenting. Are you explaining a complex concept, arguing a point, or simply narrating a story? Each goal will shape the “manuscript speech format” and influence its tone.
When you define manuscript speech, it becomes clear that it serves specific needs: accuracy, coherence, and polished delivery. A “speech manuscript” isn’t just about writing; it’s about foreseeing how it will be perceived. A strong introduction sets the stage. It should grab attention and hint at what’s to come. Use anecdotes or startling facts. Ensure your main points are clearly outlined.
“Manuscript speech meaning” revolves around delivering a message with precision. Every section should resonate with the audience. Break your script into digestible parts to maintain focus and interest. Your transitions should be smooth but noticeable, keeping listeners on track. Diversify your sentence length. This technique adds rhythm and keeps your audience engaged.
“A manuscript speech should” be practiced aloud. This helps in identifying potential stumbling blocks. Reading your script multiple times can improve fluency and confidence. Vary your tone and pace to emphasize key points, making the “manuscript style speech” dynamic and lively. Pauses can be powerful, giving your audience time to absorb information.
Finally, remember that a “manuscript speech definition” includes the written document and its oral delivery. Practice blending the two seamlessly. Your goal is not merely to read but to communicate genuinely. Understand your script deeply. This enables you to deliver it naturally and convincingly.
Let’s break down key elements in a table for better comprehension:
| Element | Description | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Introduction | Grabs attention and introduces main points | Engage listeners from the start |
| Main Body | Detailed discussion of key themes | Deliver the core message |
| Transitions | Smooth shifts between sections | Maintain cohesion and flow |
| Conclusion | Summarize and reinforce the main points | Leave a strong final impression |
| Practice | Rehearse the script multiple times aloud | Enhance delivery and confidence |
Engagement Techniques
In delivering a manuscript speech, keeping the audience engaged is crucial. It goes beyond merely reading word-for-word. Instead, it demands fully capturing your listeners’ attention.
Eye contact is key. Even with a speech manuscript, look up regularly. Connect visually. This makes the audience feel acknowledged. They are more likely to stay interested.
Next is vocal variety. A manuscript speech should not sound monotonous. Use changes in pitch, tone, and volume. It makes the speech lively. An animated voice maintains attention.
Body language also speaks volumes. Gestures can enhance your message. Don’t remain static. Move around, but purposefully. This keeps the energy high.
Interactivity is another powerful tool. Ask rhetorical questions or include actual pauses for reflection. Sometimes, a well-placed question keeps the audience curious. It’s a tactic that keeps them thinking about what is coming next in your speech manuscript.
Personal anecdotes and stories work wonders. They make your content relatable. When people see themselves in your stories, they become emotionally invested. This engagement is priceless.
Use visuals if possible. Visual aids can complement a manuscript style speech beautifully. They provide visual stimulation and serve as another layer of engagement. A picture says a thousand words, after all.
Lastly, practice is paramount. The more familiar you are with your manuscript speech format, the more naturally you can deliver it. This familiarity allows you to focus on engaging your audience rather than just reading. Remember, an engaged audience is an attentive audience. They take away more from your presentation, making your message more impactful.
Using Vocal Variety
Delivering a speech from a manuscript can feel restrictive. However, incorporating vocal variety can transform your delivery. A manuscript speech should not mean a monotonous recital. Think of it as a tool to enhance communication. Use your voice as an expressive instrument.
Vocal variety involves changes in pitch, pace, and volume. These elements can make your message more engaging. They breathe life into your words. Even with a prepared text, you can captivate your audience. Change your tone to reflect your message’s emotions.
Imagine a scene while reading aloud. This practice makes the speech manuscript more dynamic. Emphasize key points with a higher pitch or softer volume. Slow down to give weight to critical information. Speed up during lighter, less critical sections. This oscillation keeps the audience attentive.
Remember, a speech delivery isn’t just about words. It’s also about how those words are presented. The manuscript speech format provides structure. Yet, the vocal variety adds the necessary flair. Combine these elements for a compelling narrative.
Each part of your speech should have its own character. Define each section with a unique vocal style. This technique ensures clarity and maintains interest. A well-delivered manuscript, rich with vocal variety, becomes memorable. It moves beyond the manuscript definition speech to a broader communication experience.
Your voice is your most powerful tool. Even in a speech manuscript format, it holds immense potential. Use it to its fullest. Create contrasts, invoke emotions, and engage your listeners. With practice, your manuscript speech delivery will shine.
Public Speaking Without Notes | Training by Jim Kwik
Post navigation
Previous post.

Effective Strategies for Citing Sources in Your Speech

Top 10 Best Man Speech Examples to Inspire Your Perfect Toast

Unforgettable Father of the Bride Speech That Wow the Crowd

How to Craft the Perfect Bar Mitzvah Speech

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
36 Speaking from a Manuscript: How to Read Without Looking Like You Are Reading

How to Write and Use Manuscripts
There will be times when reading from a manuscript is helpful. When giving a eulogy and you are likely to experience strong emotions, having your words written out and in front of you will be very helpful. Politicians often speak from manuscripts because there will be people weighing the meaning of each word. They often have speech writers who take their ideas and make them sound professional, and they likely have several people look it over for any offensive words or questionable phrases.
The advantage to speaking with a manuscript is you have your speech in front of you. This gives you an opportunity to plan interesting wordplays and to use advanced language techniques. By managing the exact wording, you can better control the emotional tone. Another advantage to using a manuscript is you can share your speech with others both for proofing and for reference. For example, many people like to have written copies of the toast given to them at a special occasion or a copy of the eulogy to the loved one. Politically speaking, a manuscript can be helpful to help keep you on track and to help you say only the things that you mean to say.
The disadvantage to a manuscript is if not done properly, your speech may feel like an “essay with legs.” Speaking from a manuscript is a skill; I would argue that it is one of the most difficult of all types because your goal is to read without appearing to read. It can be so tempting to lock eyes on the page where it is safe and then never look up at the audience. Finally, it is very difficult for most people to gesture when reading a manuscript. Many people run their hands down the page to keep their place while others clutch the podium and never let go. These disadvantages can be overcome with practice. You can be dynamic and engaging while using a manuscript, but it does take work.
Keys to Using a Manuscript
- Always write a manuscript in manuscript format and never in essay format. (It should look like poetry).
- Practice your speech at a podium so you can figure out how to change pages smoothly.
- Learn the art of eye fixations.
- Practice with a friend so you can master eye contact.
- If you struggle with gestures, make a note on your manuscript to remind you to gesture.
- Practice, practice, practice–you should actually practice more than in a typical speech since it is a harder delivery method.
Formatting a Manuscript
- Do not start a sentence on one page and then finish it on another.
- Do not fold the manuscript–it won’t lay flat on the podium.
- Do not print on both sides of the page.
- Do not staple the manuscript
- Number your pages.
- Use a large font and then make it one size larger than you think you need.
- It should look like poetry.
- Have extra spaces between every main idea.
- Bold the first word of every main section.
- Use /// or …. to indicate pauses in your speech.
- Emphasize a word with a larger font or by making it bold.
- If you have a parallel construction where you repeat the same word, bold or underline the repeated word.
- Use an easy-to-read font.
- Make a note (SLIDE) when you need to change your slide.
- It is OK to omit punctuation.
- Do whatever formatting works best for you.
Sample manuscripts
Notice how this student formats her manuscript by making it spread out and easy to read:
Today // it is an honor for me to stand here before you at the Freedom Banquet and pay tribute to a man
,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,, that in his lifetime …………………………………. has touched ………………….. and changed …………………………… uncountable lives across the globe
Today /// we are here to honor ……………. a president, ……………………….. a father, ……………………………… a husband ……………………………………. and a true savior in Mr. Nelson Rolihlahla Mandela
Tribute speech by Tanica van As delivered at the University of Arkansas
Manuscript From History

Winston Churchill’s Speech in Response to German’s Invasion of Britain and Finest Hour Speech
Sometimes referred to as the Psalms format or free verse format, the speech is written like it will be spoken.
How to Present with a Manuscript
To best read a manuscript, we need to borrow some items from speed reading. When you were first learning to read, you learned to read each letter–D–O–G. You would look at the letter “D,” then your eyes would look at the letter “O, ” and finally, your eyes would move over to look at the letter “G.” You would fixate (or rest) your eyes on three different places. Eventually, you got better at reading and better at seeing, so you would now look at “dog” in one eye fixation and your brain was able to take in the information–dog. Now, you no longer read one letter at a time, that would be way too slow. Now you look at all three letters and see it as a word.
Over time, you learned to see bigger words–like “communication” (13 letters). Now, consider this… the phase “The dog ran fast” contains 13 letters. Since you can see the word “communication” as one eye fixation and understand it as one thing, in theory, your eyes should be able to see “the dog ran fast” as one eye fixation and understand it too. We have been trained to look at each word individually with separate eye fixations. For example, …the … dog… ran… fast… is four different eye fixations. With a little practice, you can train your eyes to see the whole phrase with one look. Here are some sentences, practice looking at each of the sentences with one eye fixation.
I ate the red apple
My car is green
My cat is moody
You tried it didn’t you? You can only learn if you try them out. If you didn’t try it, go back and look at those sentences again and try to see the whole sentence with one look. With practice, you can look at an entire sentence as one thing (eye fixation). Your brain can understand all those words as one thought. Now, try this. Wherever you are right now, look up at the wall nearest you and then look back down. Write down all the things you can recall about what you saw–I saw a yellow wall with brown trim, two bookcases, a clock, a printer, a bird statue. Your brain is amazing; it can look up to a wall and in one eye fixation, it can take in all that it sees.
You can take in many sentences as well. You can actually see two sentences in one look. Try to look down at these next two sentences in one eye fixation. Test yourself by looking down and then looking up and saying what you remember out loud.
The boy sang a song
The girl danced along
With a little practice, most people can see chunks of five words across and three lines down. Give it a try. Once again, try to look at the three sentences as one and then look up and say them.
The happy frog leaped
off the lily pad
and into the cool water
It takes practice, but you can do it. The bonus feature of doing the practice and learning this skill is you will learn to read faster. Since a lot of college work and professional preparation relies on reading the information, it would benefit you for the rest of your life to learn this valuable skill. While researching, I came across this excellent slide presentation by Sanda Jameson on Reading for College that goes into more depth about the process. I highly recommend you review it to help you with your manuscript reading and to help you become a better reader in your college classes.
https://www.nwmissouri.edu/trio/pdf/sss/study/Reading-for-college.pdf
By now, you have figured out that using chunking and working on eye fixations is going to help you read your manuscript easier. Arranging your manuscript where you have only five to seven words on a line will make it easier to see as one fixation. Organizing your manuscript where you can see several lines of text at once, can help you put a lot of information in one eye fixation.
Now, let’s look at a eulogy written by one of my students, Sydney Stout. She wrote this eulogy to her grandpa who loved dancing and encouraged her to do the same. First, notice the manuscript format where it is written like it will be spoken. It is chunked into lines that are usually 5-7 words long. The list of names is written like a stair step showing the stair step in the voice when the names are spoken. Try reading this except out loud focusing on eye fixations. Try to see one whole line at a time and then read it again trying to see two lines at a time.
Dancing is a delicate art
An activity many people love and enjoy
but someone that loves dancing
more than anyone I know
is my grandfather.
You all know my grandfather
Maybe you know him as James
….. Jack
……… Dad
…………. Papa Jack
………………… or in my case………………. . just Papa.
Papa // you have led me through life
like any great dance partner should
And I’ve memorized the steps you’ve taught me
………………………………………. …. And they have allowed me to dance
……………………………………………………………… gracefully
………………………………………………………….. through my own life
Tribute speech by Sydney Stout delivered at the University of Arkansas
Watch this eulogy speech to Rosa Parks by Oprah Winfrey. Notice how each word is carefully chosen and how if you notice closely, you can tell that she is using a manuscript. Notice how seamlessly she turns the pages and notice how she spends most of her time looking up at the audience. Masterfully, she uses gestures to enhance the rhythmic flow o the speech and to draw the audience’s attention.
Timing Your Manuscript
Practice your manuscript at least 5 to 7 times. Trust me when I say, It is harder to speak with a manuscript than it is to give a speech with brief notes and it requires considerable more practice to get it right.
Use this chart as a general reference for the timing of your speech to the length of your manuscript.
| 390 words in a 3- minute speech |
| 650 words in a 5- minute speech |
| 1300 words in a 10- minute speech |
| For More |
A Speech Saved the President’s Life

Teddy Roosevelt’s life was saved when an assassin’s bullet was slowed down by his 50 paged speech manuscript. The doctor on sight determined that although the bullet didn’t puncture his lungs, he should still go to the hospital immediately. A determined Roosevelt balked and said, “You get me to that speech.” He delivered a 50-minute speech before going to the hospital. Doctors decided it was safer to leave the bullet in his chest and declared that his speech had indeed saved his life.
More on this story from the history channel: https://www.history.com/news/shot-in-the-chest-100-years-ago-teddy-roosevelt-kept-on-talking
Please share your feedback, suggestions, corrections, and ideas.
I want to hear from you.
Do you have an activity to include? Did you notice a typo that I should correct? Are you planning to use this as a resource and do you want me to know about it? Do you want to tell me something that really helped you?
Click here to share your feedback.
Klein, C. (2019). When Teddy Roosevelt was shot in 1912, a speech may have saved his life. https://www.history.com/news/shot-in-the-chest-100-years-ago-teddy-roosevelt-kept-on-talking
Speech in minutes. (n.d.). http://www.speechinminutes.com/
Stout, S. (n.d.). Eulogy to Papa with the theme of dancing. Delivered in Lynn Meade’s Advanced Public Speaking Class at the University of Arkansas. Used with permission.
Van As, T. (n.d.) Tribute to Nelson Mandela. Delivered in Lynn Meade’s Advanced Public Speaking Class at the University of Arkansas. Used with permission.
Winfrey, O. (2010). Eulogy to Rosa Parks. [Video] YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5cfhtfNfIPE Standard YouTube License.
Media Attributions
- Winston Churchill’s Manuscript is licensed under a CC BY-NC-ND (Attribution NonCommercial NoDerivatives) license
- Winston Churchill’s Speech in Response to German’s Invasion of Britain
- Winston Churchill Finest Hour Speech
- Teddy’s speech © Janine Eden, Eden Pictures is licensed under a CC BY (Attribution) license
Advanced Public Speaking Copyright © 2021 by Lynn Meade is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
All Subjects
study guides for every class
That actually explain what's on your next test, manuscript speech, from class:, writing for public relations.
A manuscript speech is a type of speech that is written out in its entirety and read word-for-word by the speaker during delivery. This format allows for precise wording and careful control over language, making it ideal for formal occasions where accuracy and clarity are crucial. Manuscript speeches can also help speakers avoid forgetting key points, but may limit eye contact and spontaneity with the audience.
congrats on reading the definition of manuscript speech . now let's actually learn it.
5 Must Know Facts For Your Next Test
- Manuscript speeches are commonly used in formal settings such as political speeches, news announcements, and award ceremonies where precise language is essential.
- While manuscript speeches provide the benefit of careful wording, they can create a barrier to connecting with the audience due to less eye contact and a more rigid delivery style.
- The use of technology, such as teleprompters, has become popular for delivering manuscript speeches, allowing speakers to maintain better eye contact while still reading their script.
- Writers of manuscript speeches must pay close attention to pacing and intonation to ensure effective delivery, as reading can sometimes sound flat or monotonous.
- Despite the challenges of delivery, manuscript speeches are particularly useful when conveying complex information or data that requires accuracy.
Review Questions
- A manuscript speech differs from other types of speeches primarily in its preparation and delivery style. It is fully written out and read verbatim by the speaker, which contrasts with extemporaneous speeches that are outlined or noted but not fully scripted. This meticulous preparation ensures that every word is intentional, making it suitable for occasions requiring exact wording. However, this format may result in less engagement with the audience compared to more spontaneous delivery methods.
- Using a manuscript speech at formal events offers several advantages, such as ensuring precise language, reducing the risk of forgetting key points, and maintaining a clear structure throughout the presentation. However, it also presents disadvantages like potentially limiting eye contact with the audience, which can diminish engagement and connection. The rigid nature of reading from a script may lead to a less dynamic performance compared to more conversational speaking styles.
- Technology has significantly enhanced the effectiveness of manuscript speeches in modern communication, primarily through tools like teleprompters. These devices allow speakers to read their scripts while maintaining eye contact with their audience, thereby bridging the gap between reading verbatim and engaging dynamically. This technological integration helps speakers convey their messages more effectively by balancing accuracy with audience connection. However, over-reliance on technology may also pose challenges if technical issues arise during delivery.
Related terms
A speech that is delivered with little preparation, often using notes or an outline, allowing for a more conversational style and better audience engagement.
memorized speech : A speech that is completely memorized and delivered without any written text, which can enhance delivery but may lead to issues if the speaker forgets their lines.
A speech delivered on the spur of the moment without prior preparation or notice, often requiring quick thinking and adaptability.
" Manuscript speech " also found in:
© 2024 fiveable inc. all rights reserved., ap® and sat® are trademarks registered by the college board, which is not affiliated with, and does not endorse this website..
- Games, topic printables & more
- The 4 main speech types
- Example speeches
- Commemorative
- Declamation
- Demonstration
- Informative
- Introduction
- Student Council
- Speech topics
- Poems to read aloud
- How to write a speech
- Using props/visual aids
- Acute anxiety help
- Breathing exercises
- Letting go - free e-course
- Using self-hypnosis
- Delivery overview
- 4 modes of delivery
- How to make cue cards
- How to read a speech
- 9 vocal aspects
- Vocal variety
- Diction/articulation
- Pronunciation
- Speaking rate
- How to use pauses
- Eye contact
- Body language
- Voice image
- Voice health
- Public speaking activities and games
- Blogging Aloud
- About me/contact
- Speech delivery
- 4 modes of speech delivery
4 modes of speech delivery | an overview
Which speech delivery technique is best.
By: Susan Dugdale
There are 4 modes (methods) or ways to deliver a speech: to read it from a manuscript word by word, to completely memorize it, as an impromptu, and to give it extemporaneously.

How do you know which mode will be most effective?
The answer depends on how much time you have available, the type of speech you’re giving and, your audience.
Let’s briefly outline each method and their advantages and disadvantages.
What's on this page
An overview of the 4 modes of speech delivery, the pros (advantages) and cons (disadvantages) of each, plus links to examples and further resources.
- extemporaneous
1. Manuscript
One of the most common ways to deliver a speech is to use a manuscript: a word by word document of everything you plan to say from beginning to end. This ensures, when you read it out loud, what you say is exactly what you intend, without deviation.
What is the best way to write a manuscript speech?
As with any type of speech, the best way to start is not with the words but with considering your topic, your audience, how much time you have to speak and the purpose of your speech.
Once you have those clear, then you are ready to begin planning a speech outline: an overview of all the material you want to cover.
When the outline is completed you’ll use that to write your manuscript.
Click the link for more about the process of preparing a speech outline , with examples. (The page also has a free printable blank speech outline for you to download and use)
And for more about writing a speech, in particular writing oral language, words to be spoken aloud, please see how to write a speech . You’ll find a useful guide covering the principal characteristics of spoken speech. (It is very different from writing an essay!)
Who regularly delivers a manuscript speech?
Newsreaders, TV personalities, politicians, business leaders and the President! Anybody whose speech is going to be closely scrutinized will use either a manuscript or its electronic equivalent, a teleprompter. These are speeches where the content is significant, perhaps life changing, where facts and figures must be 100% accurate, and where the tone of the language used is important.
What distinguishes a good delivery of a manuscript speech from a poor one, is practice. Some of the greatest public speakers in the world ‘read’ their speeches with so much skill they sound as if they are making up what they’re saying on the spot. The speech comes across as being completely spontaneous and is delivered flawlessly.
Great public speakers who 'read' their speeches
A famous example is the Prime Minister of the United Kingdom, Sir Winston Churchill. Throughout World War Two (1939-1945) his extraordinary speeches inspired the people he led to persevere in their fight to keep the Nazis out of England in spite of the odds being stacked against them.

To find out more read Winston Churchill's Way With Words - an excellent NPR article, with audio, on how he crafted his speeches.
And another more recent example is America’s ex-President Barack Obama.
American Rhetoric has audio and text (pdf) links to his speeches spanning 2002 - 2014. Four are included in a list of 49 of the most important speeches in 21st century America . These are:
- 2004 Democratic National Convention Keynote Address
- Commencement Address at Knox College (2005)
- A More Perfect Union (2008)
- Speech at the 'Together We Thrive: Tucson and America' Memorial (2011)
How to deliver a manuscript speech
Print your speech out single sided. Make sure each page is numbered clearly. Use an easily read font like Arial, black ink, and size the font and space the lines so that the text may be read at a glance.
Use a lectern adjusted for your height to put your manuscript on. As you finish reading each page turn it over face down and move it to your left. That will help stop you from getting muddled.
Aim for at least one read through aloud before you deliver it.
The more you can practice the better your delivery will be.
How to read aloud well
Reading aloud well is a skill. Some people are very good at it, and some are ghastly, largely because they’ve had no practice. (And sadly, many who regularly read their speech scripts don’t realize how bad they are to listen to because nobody has told them. Their presentations have been endured, rather than enjoyed for years!)
If you have to regularly read your speeches here’s how to read a speech effectively: 4 good ways to improve how you read aloud . It will help a great deal!

The pros (advantages) for a manuscript speech
The major advantage of using a script is that it ensures the speaker will deliver the right message, the one that’s been prepared, without errors. This is particularly important when presenting complex subject matter.
Another is that when there's not enough time to rehearse or prepare thoroughly, reading may be the only real option available. Without the safety of a script you may forget large chunks of information, or misremember important material. The script keeps you on track.
A third reason could be that the mere presence of the script is reassuring for nervous or anxious speakers. Even if they do not actually need it, because they’ve prepared well, the script is calming. If they suddenly blank out, they’ll be alright, as they have the script to refer to.
And a fourth is that you can easily back track, return to a point you made several pages earlier, if you need to.
The cons (disadvantages) of manuscript speeches
The main disadvantages of using a manuscript are:
- being anchored to one place . If you are using a full script you need to remain in front of the lectern, or teleprompter in order to read it. You can not move freely as you deliver your speech.
- lack of eye contact with your audience because you need to keep your eyes on your words. When there is very little or no eye contact between a speaker and their audience, the audience switches off because they feel ignored, shut out. The ability to look at the audience while using notes or a teleprompter helps your audience to listen better, retain more of what they hear, and feel as if they’ve gained more value from your speech. Click the link for more about the importance of using eye contact [including 5 fun activities to teach students how to use eye contact well]
- Using language that doesn’t flow easily when you say it aloud . There are major differences between writing intended for oral language - something to be spoken aloud, and writing something that is intended to be read, like a newspaper article or an essay. For more please see how to write a speech . You’ll find an infographic on the characteristics of spoken language. Whenever possible, always read your manuscript aloud before you deliver it. It’s much nicer to find typos, missing words, vital information omissions and other glitches (such as words you are not sure how to pronounce correctly), by yourself rather than in public. Another useful thing to do is to run your manuscript through a grammar checker . It may pick up errors you've overlooked.
2. Memorized speech
A memorized speech is one delivered completely from memory. That means: no notes at all. There is just you: the speaker, the speech you recall, word for word, and your audience.
Why choose to memorize a speech?
There are three likely reasons.
- You want the illusion of a ‘natural’ conversation between yourself and your audience. The presence of a lectern with your manuscript on it, a teleprompter, or a set of cue cards in your hand makes that impossible.
- You want to be able to ‘play’ freely with your delivery: to be able to move, to gesture, as you see fit rather than be tethered to notes.
- You want to make completely sure the words you have written are faithfully delivered to the audience, without any changes at all. That can be vital in comedy.
What type of speech is enhanced through memorization?
A personal speech, for example one sharing childhood stories, a very carefully scripted humorous speech where you absolutely must get the words in the right order for them to work, or an inspirational one prepared especially to move and motivate a particular audience. All of these can be more effective delivered without notes.
There are also declamation speeches . These are in a special category of their own. They are memorized recitations of known speeches: a task set by teachers to have their pupil's fully experience the power of carefully crafted, well delivered oratorical language.
What type of speeches are NOT suited to memorization?
- Any presentation or speech covering critical information that people will use to make important, and often life-altering, decisions. For instance, a detailed weather report cannot be inaccurate. The information outlining the state government’s strategy for combating poverty, declining employment rates, and climate change needs to be presented in a way the audience can easily follow and be factually correct. Missing bits out or getting them wrong creates confusion.
- Presentations which include large amounts of data : for example, a roundup of a company’s annual performance figures would be very difficult to accurately memorize, as well as being very difficult for an audience to listen to and retain.
- Lengthy presentations - speeches running over 10 or more minutes in time.
How to memorize a speech
If you decide to memorize your entire speech, the very first thing you’ll need is lots of time to practice. This is critical. Do not be tempted to minimize how much is required.
To safely commit it to memory you have to go over and over your speech until you can easily say it out loud without hesitation, deviation or repetition. This can take weeks of regular daily practice, particularly if you’ve not done it before. If you haven’t got that time available to you, opt for an extemporized delivery. (See the notes on extemporaneous speeches below.)
Review your speech outline
Having made the decision to memorize, the next thing you need to do is carefully review your speech outline.
These are questions you’ll want to consider:
- Are the major points in the right order? Do you have supporting examples for each of them? Are the transitions between each of the points clear? Is there a memorable conclusion? Does the opening or introduction work as a hook to pull the audience in?
- Does the speech have a clear purpose? Does it meet it? Has it been tailored for its intended audience?
(Click the link for more about preparing a useful speech outline . You’ll find step by step guidelines, examples, and a free printable blank outline template to use.)
Repeat your speech out loud, a lot!
Once you are satisfied with your outline, it’s time to begin the process of committing it to memory.
This starts with saying your speech out loud multiple times while using your outline. As you do you’ll be listening for bits you need to change in some way. Perhaps the words you’re using aren’t quite right for your audience. Maybe it doesn’t flow as well as you thought it did and you’ll want to swap pieces around. Or it’s too long and needs pruning.
It’s a repetitive process: make a change. Try it out. If it’s good, keep it and move on to the next section. Repeat until you’ve worked through the entire speech.
An additional tip is for every significant change you make, make a new document, (eg. myspeech v1, myspeech v2, myspeech v3…) or at least track the changes. That way if you decide you want to revert to an earlier version you can. I’ve got at least 10 versions of some of the speeches I’ve written!
The next step is to begin working without the outline.
The 'see, walk, and talk' method
The method I use is the same one I use as an actor to learn play lines.
I call it ‘see, walk and talk’. It's a 3 part approach. Each is essential.
The seeing part is visualization: seeing the words on the page. Seeing the order they come in, and anything else that distinguishes them from the rest. Is it a heading? Is it a number? Is it highlighted?
The second part is walking. Walking helps a great deal and is an ancient technique for memorizing now backed by science. *
If it’s fine, I walk outside and as I walk, I talk (the third part), repeating out loud the section I'm trying to recall over and over until I get it right.
If the weather is bad, then I walk inside, around and around a room, or on a treadmill which works just as well.
* Schmidt-Kassow M, Zink N, Mock J, et al. Treadmill walking during vocabulary encoding improves verbal long-term memory. Behav Brain Funct. 2014;10:24. Published 2014 Jul 12. doi:10.1186/1744-9081-10-24 )
'See, walk, talk' in action
Start with the body of your speech, the main points. Your goal is to remember each one, in their correct order.
There are three steps in this process.
- Look at your outline. If it helps highlight the main points, and number them. Take a mental photograph of it.
- Put the outline behind your back. Walk and say out loud as many of the main points you can in their correct order.
- When you find yourself struggling to recall, stop. Look at your outline. Take another mental photo. Put the outline behind your back, and start over again. Walk and talk.
Repeat until you can run through the entire sequence of main points, and the transitions between them, without hesitation.
Add the subpoints to the main points
The next step is to add the fine points - the subpoints (additional material) and examples to your main points.
Go back to the first main point. Take a mental snapshot of the subpoints and examples. Note carefully the order they come in, and any specialist vocabulary or phrase you wanted to use.
Now walk and talk. Repeat the sequence until you have it as you want it. Then go back to the beginning and repeat the first main point, its supporting material and then the subsequent main points.
Your next part to memorize is the second main point's supporting material. Once you have that down, you go back to the beginning to run the first main point, its sub points, then the second point and its sub points. Then you are ready to do the third main point in exactly the same way.
Add the conclusion and the beginning
Once you have completed memorizing the body of your speech, add the conclusion and the beginning.
The pattern is simple. You add a piece, then go back and repeat it all through from the beginning. Each repetition etches it more deeply into your memory.
Please note : you are not working on delivery as you say it out loud. This is purely routine repetition. There is no need for pausing, emphasis, or changes in volume and pace. Think of it as a vanilla performance - plain. At this stage the bulk of your energy needs to go into remembering, not expression.

Sort out and memorize the delivery

Delivery is how you say your speech, not what you say.
Once you have the content (what you are saying) reliably remembered, you are free to work on your vocal delivery: how you are going to say it.
Which parts need to be said more slowly? Which parts need to be highlighted through strategic pausing? What can be spoken quickly? Are there bits that need to be treated as asides? Are there ‘voices’ to take on? Perhaps an angry voice? Or a wheedling, whining voice?
How you say your speech directly affects how your audience receives it. If you deliver it like a monotone robot - one speed, one tone, one pitch, one volume, people’s ears will switch off even if the content is interesting to them. Delivery can make all the difference between listening and not listening.
To be effective, your delivery needs to fit both the content and the audience’s needs.
As with memorizing the content, getting the delivery how you want it requires experimentation and then repetition to ensure you’ve got it safely embedded.
Working with a recorder is useful to actually hear what your voice is doing, rather what you think it’s doing. There’s often a very big difference. You’ll hear if you’re going too quickly, pausing too long, not pausing long enough, mispronouncing words, gabbling, or using the same inflection pattern over and over again.
Find out more about the vocal aspects of speech delivery .
Use a mirror, a video and a test audience
It’s also useful to either work in front of a mirror or video yourself. That will show you where you need to modify your body language. Do you stand straight? Do you gesture appropriately?
Rinse, and repeat until you feel happy with what you’re doing. And then practice in front of a select test audience, whom you know will give you honest useful feedback. Incorporate what you want from the suggestions you’re given and practice again. And now you should be ready to deliver your speech!
Pros of memorizing your speech
A memorized speech is generally more engaging. If delivered well it creates the illusion of having a conversation with your audience because you are speaking directly to them and you are able to make eye contact freely, as well as move how, and where you want. This creates a more intimate and personal connection.
Cons of memorizing your speech
There are three major disadvantages to memorizing a speech. The biggest is the risk of forgetting something, especially with a longer speech. This can lead to panic which leads to scrabbling around trying to pick up the threads to start again. That can rapidly become a downward spiral which compromises the whole presentation.
Secondly, using a memorized speech can constrain or limit the ideas you express because everything is prepared in advance. It leaves little room for spontaneity: content adjustments and additions made in response to a particular audience’s needs.
And thirdly, a memorized speech can be incredibly boring if the speaker has not worked on delivery. It has a canned quality, lacking immediacy and vitality. It sounds like a switch got flicked on and out it comes: blah, blah, blah … irrespective of the audience.
3. Impromptu
An impromptu speech is, as its name suggests, a speech made without prior planning, organization or rehearsal.
Although it may be based on a brief outline or written prompt, the speaker will often have little or no opportunity for detailed or extensive preparation.
While making an impromptu speech involves little immediate preparation it require significant amounts of prior practice to give one well.
An effective impromptu speech is structured, (beginning, middle, end), and meets the needs of those listening to it. To give a good one requires versatility and flexibility: the ability to adapt and respond easily and appropriately to the unexpected.
The speaker needs to understand how to quickly choose the best format, how to decide on the main points to cover, how to order them, and how to open and close the speech.
And lastly, impromptu speaking requires confidence, and trust in oneself.
When should an impromptu speech be delivered?
There are many social or work settings where making an impromptu speech is expected, and if done well, very much appreciated.
At a family get together the person who is asked to say a few words to welcome everyone, or make the toast is giving an impromptu speech. At a meeting to discuss current work issues, a sales manager may be asked to outline areas of challenge without prior warning. The response they give is an impromptu speech.
The ability to summon up succinct, structured remarks is highly valued in all areas of life.
How do you prepare for an impromptu speech?
The essential preparation for impromptu speaking begins out of the spotlight, long before being asked to speak.
For comprehensive step by step guidelines covering how to gain the necessary skills please see: strategies and templates to succeed at impromptu speaking .
You’ll find tips to get you started, 7 different structural templates to use, suggestions for keeping any nervousness under control, and links to 100s of impromptu speaking topics to use for practice.
Pros of impromptu speeches
The advantages definitely outweigh any disadvantages.
Although some people have a natural gift for being able to talk freely and spontaneously, it can be learned. It’s a skill, like riding a bike. (But better!) When you’re beginning you fall off a few times, and graze your knees. If you get back on and keep pedaling eventually you stay upright.
Get better at impromptu speaking and you’ll find it will open many doors, leading to a richer and fuller life.
Don’t settle for silence when you can learn to speak up for yourself, and others.
If you're reluctant to attempt it and put yourself out there, please read this article: Speaking in business may be your most important skill .
The cons of impromptu speaking
In some contexts and on some subjects it would be unwise to attempt delivering an impromptu speech.
For instance, when asked for an evaluation of business risks associated with Covid-19, or to comment on possible correlations between socio-economic status and educational achievement in the USA, speaking without consulting a broad cross-section of informed specialists would be ill-advised.
Each situation needs careful consideration. Are you able to talk knowledgeably on the topic you’ve been given? Are you entitled to talk about it?
If you can not speak on the subject being asked of you, say so politely. You can offer to come back with a full response at a later date. Or you can hand the question on to someone who can answer it. Knowing your limits is very useful for maintaining credibility!
Another possible downside is succumbing to fear. It could be fear of finding yourself with nothing to say, of drying up under pressure, or of muddling material in some way. The only really useful antidote to nervousness/fear is practice. Lots, and lots of it. It does get better!
4. Extemporaneous speaking
An extemporaneous speech is one where the speaker combines the use of notes or cue cards with improvisation. It’s a mix of carefully scripted and sequenced material and impromptu speaking.
How do you deliver an extemporaneous speech?
An extemporaneous delivery is naturally flowing and conversational. The points to be made will have been carefully outlined. They will be in the correct order, along with their supporting ideas and examples but the exact wording is made up as you go along.
If you give the same speech to different audiences, the words you use may change because every audience responds differently. The result is a speech that is fresh each time it is delivered, because while you are speaking, you are in the moment, speaking off-the-cuff and from the heart. The text is neither memorized, or being read word for word.
Like the first three modes of delivery, this too needs practice, in order to become good at it.
You’ll need to practice:
- speaking to time to avoid either going on too long or being too brief
- making effective transitions - finding the bridging words to link one main point to the next, or to link one segment of your speech to the following one. For instance the introduction to the body of the speech, or the body of the speech to the conclusion.
- openings and conclusions.
For more information here's a very useful 'how to' article from The Dept. of Communication at the University of Pittsburgh on oral discourse and extemporaneous delivery .
The advantages of extemporaneous speeches
An extemporaneous speech is more spontaneous and therefore natural compared to either a manuscript or memorized speech. The speaker is free to tailor the presentation to the audience, rather than sticking to a set speech. That could include responding to any questions or objections he receives.
Disadvantages of extemporaneous speeches
There are three main drawbacks to extemporaneous speaking.
The first is becoming stranded; tongue tied and silent because you don't know how to get from one point on your outline or cue cards to the next. When that happens, the delivery becomes stilted, a stop-start presentation, which in turn can make the speaker feel anxious, which makes recovering the flow more difficult.
A second drawback is misreading the audience, and delivering the speech using either language, (word choices), or humor they find hard to understand or accept.
As an example, a speech littered with ‘corporate speak’ is not going to win me over. I don’t want to hear about ‘core competencies’, ‘going forwards’ , ‘ducks in a row’ or anything ‘scalable’ at all!
And a third is exceeding the time allowance you’d been given. Because you are fleshing it out from your cue cards or outline as you go along it is easy to lose track of time. The cumulative effect of an additional example or two and further comments, quickly soaks it up, leaving you scrambling to finish properly.
If you are a first time presenter, probably the safer option is to learn how to read a manuscript speech well and gradually build the skills required to give an extemporaneous speech.
speaking out loud
Subscribe for FREE weekly alerts about what's new For more see speaking out loud

Top 10 popular pages
- Welcome speech
- Demonstration speech topics
- Impromptu speech topic cards
- Thank you quotes
- Impromptu public speaking topics
- Farewell speeches
- Phrases for welcome speeches
- Student council speeches
- Free sample eulogies
From fear to fun in 28 ways
A complete one stop resource to scuttle fear in the best of all possible ways - with laughter.

Useful pages
- Search this site
- About me & Contact
- Free e-course
- Privacy policy
©Copyright 2006-24 www.write-out-loud.com
Designed and built by Clickstream Designs
Please wait while your request is being verified...
First Time Authors-Here's The Key To Getting Published
Free tips and resources for first time authors looking for publishing deals.
Subscribe via Email
How To Write A Manuscript For A Speech
Public speaking can fill one with a sense of dread, but knowing how to write a manuscript for a speech can make the difference between a successful speaking engagement and one that is not. Many factors should be considered when preparing a speech.
Preparing an outline is always helpful; make headings that clearly make key points and fill in the facts that are to be presented under each heading. Consider the phrasing of the headlines as they can be directly used as the introductory sentences to your points.
Knowing the key target audience is the most important factor in writing the manuscript. Avoid speaking over them; a group of highschool kids will need to be addressed in a different way than a roomful of adults. Keep the tone of the speech inline with the target audience. Lightheartedness may not be an appropriate tone for all occassions, but this approach is perfect for a younger audience.
Knowing how to write a manuscript for a speech sounds like an overwhelming task, but backing up the outline with well researched information keeps the manuscript interesting. When doing fact based research, try to find a new angle for the information. A speech on the deadly effects of carbon monoxide in and of itself, for instance, could be boring to listeners who already know that this is a deadly exposure. Liven the speech up with unusual facts as well, such as that in the 1800’s through the 1900’s carbon monoxide released through gas lamps accounted for sightings of ghosts and other hallucinations, and that Edgar Allen Poe is thought to have been suffering the effects of chronic carbon monoxide poisoning while writing his works. These facts would be a pertinent, entertaining and unusual way to grab audience attention. Be sure any facts offered are well researched and accurate, but do not drag the audience attention down with citing continued fact references. Terms such as “research shows” or “it has been found that” are often a better lead up to your facts and continue to keep audience attention.
Remember when writing the speech that the amount of time taken to prepare it is often far short of the amount of time it will take to deliver it. It is better to prepare the manuscript to be longer and pare it down than to consider it finished and have to add material. Using the method of paring down rather than adding on allows the ideas to flow freely, whereas adding material can often result in a speech that sounds choppy.
Once the manuscript is written, preparing to deliver it can be done at first in front of a mirror and then in front of family and friends. These practice sessions do more than boost confidence, they allow the speaker to practice inflection and emphasis. Some ideas can be changed at this point since some things sound better in writing than they do spoken aloud.
my tribute speech on barack obama? so for my english class we have to do a tribute speech on someone we look up to and first i chose my mom then i changed it to my dad then i changed it to obama can anyone help me write my tribute speech? or help me with some ideas this is what it has to have…
Step 1 (Investigate/Decide) – 250 words; due Thursday, January 8 Yes, you have to do this step, so stop whining. Reflect on a significant personality who has had an impact on our world, or who has personally influenced you. oWhy do you look up to this person? What do you consider worthy of tribute about him/her? oList his/her admirable traits oCreate a list of 5 to 10 interview questions that you would ask this person if given the opportunity to interview him or her. Consider using words and phrases such as: justify, explain, evaluate, “to what extent”, classify, describe, determine, implement, defend, etc. (See list of possible words to use in formulating a question) oIf you had an opportunity to thank this person, what would you thank him/her for?
Step Two: (Investigate/Research continues) – due with step 3 Now that you’ve chosen your subject, investigate and record on paper the answers to the following bulleted questions/statements
oBiography –origins (background, family life, education, etc) oTimeline – highlight accomplishments oRelevancy- just what is it that makes your subject worthy of this tribute speech? oUse library and Internet as needed (you must have at least 6 sources for this speech. If your speech is about a famous person, you must make sure they are accurate…keep track of them on work-cited page. If your speech is about a person who is not famous, then you must use interviews, old local newspaper articles, old family albums, etc.)
Step Three: Plan and Decide (Create Outline of Speech) – due Thursday, January 15 Decide which information you will use from your research. Plan the best way to organize your information into an effective speech.
Create an outline of your speech (please put details on the outline) Example of how you might organize speech: oQuote or eye-opening fact; statistic; etc…hook oBiography of Individual oAccomplishments oWhy tribute to this individual?
**Step Four: Create Full Written Draft of Speech – Due Tuesday, January 20 Create your manuscript with an introduction, body, and conclusion. Include the stylistic devices listed for objective #5. Cite sources within your manuscript as appropriate using MLA format. You will need a Work Cited page as well. Peer Edit and Revision
Step Five •Rehearse—create note cards and time yourself. •Did you remember to cite sources and create your work cited page?
Step Six: Presentation of Speeches with Peer Evaluation/Turn in Manuscript. All Speeches due Tuesday, January 20 whether it is your day to present or not! Keep a copy for yourself! Present and Evaluate Speeches (4 to 6 minutes)
and this is what i have so far:
January 21, 2009 English 10
Barack Obama was born August 4, 1961. Honolulu , Hawaii , USA . His full name is Barack Hussein Obama Jr.; which means “Blessed by God”, in Arabic He was born to a white American mother, Ann Dunham. And a black father, Barack Obama, Sr. they both were students at the University of Hawaii . His father left to Harvard while his wife and son stayed behind. His father went back to Kenya where he worked as an economist. Barack’s mother remarried an Indonesian. He worked as an oil manager. His father would write to him, but due to his business, he visited his son only once, and that was when Barack was ten. Barack managed to go to one of Hawaii ’s top prep academy, which is Punahou School . Then later on Barack attended Columbia University . He became a community organizer for a small Chicago church for three years. He helped poor south side people deal with a wave of plant closing. Then he attended Harvard Law School . In 1990 he became the first African-American editor of the Harvard Law Review. Then in Chicago he practiced civil-rights law. In 2004 Barack Obama was elected to the U.S senate as a Demarcate representing Illinois . Then in November, 2008 he ran for president as a democrat and won! And now he is the 44th president of the United States and the first African- American running for president. Barack Obama’s greatest accomplishment is his family, His two daughters and wife. He is worthy of my tribute speech because he is the very brave and he is the first African- American president. And because he is Step One- investigate/design I look up to this person because he has done many good things.
It’s good. Maybe find a way to replace pathos a couple times (them) towards the beginning of your essay. On the part where you say “if the paper were to be written on…” you should take out “than” after the comma. When you list the reasons why Golding might be better, I would say “he” instead of just Golding. Change “It is understandable that some people may think that Golding is more effective in his paper than Clark. Golding is older, Golding has more education, and Golding more experience in college, than Clark does. Many people may argue that Golding has the better paper, due to the previously listed reasons, and those reasons are understandable” to “Understandably, people will argue that Golding is superior to Clark when it comes to writing effectively. They will stress that Golding has experience on his side due to age and more college education.” Change “Something that may be agreeable though, is that Golding may have the better paper when it comes to following the rules of writing, and his organization style; but that Clark’s paper is actually better because he is in college, and that this paper is directed mainly towards current college students.” To “Something that may be agreeable, though, is that Golding has the better paper when it comes to the formalities of writing and organization, yet Clark’s paper is actually more meaningful due to the fact that he can relate to his target audience – he is in college, too.”
Sorry, but I’m too tired to continue. I didn’t study your essay much, so I’m not sure how well my edits would flow, but I tried. Also, there a couple of words that you should use a thesaurus on – I advise if it appears 3 or more times to do it.
It was a great essay and you can always go back to your original if you don’t like mine (but there were a few comma, etc. problems).
GOOD LUCK!!!
ENGLISH PAPER PART 2 PLEASE PROVIDE INPUT AND HELP? How many people want to be deprived of freedoms? One could assume that the majority of the United States citizens support freedom, so one could see how this idea may anger people. Pathos is a very effective way to get people to understand a view, and Clark does a great job of using it. In Golding’s article, he still uses Pathos, but to a much lesser extent. He uses pathos in some of his examples, and it is effective when it is used. Although he uses pathos a little bit in his article, for the most part he seems to simply argue and discuss the topics. By doing this he makes the reader less willing to read on, thus making his article less effective overall. Clark also is at an advantage because he is a college student, and these writings are more directed at college students than anyone else. Golding cannot control the fact that he is a professor, but it does put him at a disadvantage. Clark was a college student when he wrote this, so he knew how students his age interpreted things, Golding was from a different generation than the intended audience, and the ways of thinking among college student changed since Golding was in college. When Clark wrote this essay, one may assume that he talked to his college aged friends about this topic, and asked them what they think; Assuming that Clark did this, it helped him to be more successful in his paper than Golding. If the paper were to be written solely on free speech among college professors, than Golding would probably have the advantage of better understanding the intended audience better. It is understandable that some people may think that Golding is more effective in his paper than Clark. Golding is older, Golding has more education, and Golding more experience in college, than Clark does. Many people may argue that Golding has the better paper, due to the previously listed reasons, and those reasons are understandable. Something that may be agreeable though, is that Golding may have the better paper when it comes to following the rules of writing, and his organization style; but that Clark’s paper is actually better because he is in college, and that this paper is directed mainly towards current college students. It is also understandable that the ways of teaching how to write papers has changed, and how students are educated has changed, so due to these reasons Clark’s paper may actually be more current and apply more to it’s intended audience than Golding’s. Clark’s paper is a well written paper, and due to his use of straightforwardness, pathos, simplicity in his writing, and his advantage due to his age, he may still have the better piece of writing, even if Golding is more educated and more intelligent.
Sources Golding, M. P. (2000). Campus Speech Issues. Manuscript in preparation. Clark, Q. Speech Codes: An Insult to Education and a Threat to Our Future.
First of all, “Sir” Isaac Newton never served in Parliament. He served in 1698 and in 1701-02, but he wasn’t knighted until 1705. If the knighthood gave him the wherewithal to hire an assistant, that helper could not have written a Parliamentary speech with him. Second, Newton never argued before the House of Lords: he represented his university, Cambridge, in the House of Commons. Third, Newton’s only recorded words in Parliament were a point of order, a request to close a drafty window. He never made a “maiden speech”, nor argued for any bill. To top it all off, his service and knighthood had nothing to do with his scientific work. James II tried to turn the universities into Catholic institutions; Newton (and Cambridge itself) staunchly opposed the idea. Newton simply voted that way at every opportunity. The Queen so appreciated his efforts in support of this and other of her political causes that she knighted him.
After explaining the problems to the embarrassed vendor, Nora bought the document for £13, just as a reminder that she doesn’t know it all. She eventually got it identified: a portion of an unfinished play by a minor author, circa 1870.
She Turned Me Into a Newton!? After identifying a suspicious fellow Yankee at the local pub, Nora Shekrie decided to take a holiday at the market in Blyth. She was escorted by her not-too-distant relatives, Sir Loine of Boef and Lady Rose Boef. Nora wanted to take home some memento of her visit, something more than the prepaid travel vouchers Sir Harold had supplied. After a morning of making nice with the locals, receiving thanks, admiration, and not a few jibes about being from “the Colonies”, Nora was quite enjoying herself. The morning tea and late lunch were taking up a serene position in her abdomen, the sun was shining, and the studied quaintness of the market enchanted her more with each passing hour. She politely examined each stall of wares, commented astutely on some aspect of almost every shop, and generally impressed the vendors as something rather better than the stereotypical American tourist. Finally, at half-past two o’clock, she found the item to take home. An youngish gentleman selling out-of-print books had an item that intrigued her.
“It’s the manuscript of an early draft of the speech,” he explained as she bent over to examine the fine penmanship. “One of my ancestors was an assistant to Sir Isaac Newton. He served in Parliament, you know.” Nora nodded. “Dodgy times, what with the Glorious Revolution and all, but my many-greats grandfather found a stable position with Sir Isaac, right after the knighthood gave him enough money to hire someone permanent-like. Sir Isaac asked G-g-g-grandfather, Thomas Hanscomb was his name, to write some for his first speech in the House of Lords. Oh, Newton supplied the ideas sure enough, but Hanscomb did the first bit of writing, not what many could write back then. “Newton took Hanscomb’s draft, did it up his own way, no surprise to either of them I warrant, and gave back the first. That’s it, there in the frame and protective glass and all, and I keep it out of the sun like you see here.” The three of them noted the shade over the one item, giving it further protection from the light. “Sir Isaac made his grand speech, both houses passed whatever bill, and Thomas Hanscomb stuffed this copy into his things. It come down to me after all this time.” Nora nodded, seeming to have reached some decision. “And it’s certainly dear enough,” she held up a hand to stop him, “but fairly, given its history. Across the pond, a representative’s first speech in Congress is considered a great event.” She considered her bank balance, held a mental argument with herself, and pulled out her billfold. “I take traveler’s cheques, VISA, and cash,” he smiled. Nora smiled in return, pulling out a small plastic card. She felt a polite tug at her sleeve: Rose. ” For a purchase this significant, I usually like to get my mind well settled before I sign the papers, just to be sure. Shall we have a cuppa, and you talk to me about this?” There was a note in Rose’s voice; Nora had learned to respect that tone over her ten days with the family. She turned to the stall-keeper. “Would a fiver hold it for an hour?” “M’lady, at this price, a scone would hold it for the day.” Nora grinned. “A scone, it is. With jam?” He nodded. They had a deal.
They chose their table and allowed Harold to seat them with their food. He trundled back to the stalls with the extra scone, leaving his wife and guest to discuss the matter. “Rose, it sounds like I got off cheaply. You certainly know your business. Care to let me in on the secret? I’m usually the one who spots these things.”
How did Rose know that Nora shouldn’t buy the manuscript?
Is this paper good? What could I do to improve it? Part 2? How many people want to be deprived of freedoms? One could assume that the majority of the United States citizens support freedom, so one could see how this idea may anger people. Pathos is a very effective way to get people to understand a view, and Clark does a great job of using it. In Golding’s article, he still uses Pathos, but to a much lesser extent. He uses pathos in some of his examples, and it is effective when it is used. Although he uses pathos a little bit in his article, for the most part he seems to simply argue and discuss the topics. By doing this he makes the reader less willing to read on, thus making his article less effective overall. Clark also is at an advantage because he is a college student, and these writings are more directed at college students than anyone else. Golding cannot control the fact that he is a professor, but it does put him at a disadvantage. Clark was a college student when he wrote this, so he knew how students his age interpreted things, Golding was from a different generation than the intended audience, and the ways of thinking among college student changed since Golding was in college. When Clark wrote this essay, one may assume that he talked to his college aged friends about this topic, and asked them what they think; Assuming that Clark did this, it helped him to be more successful in his paper than Golding. If the paper were to be written solely on free speech among college professors, than Golding would probably have the advantage of better understanding the intended audience better. It is understandable that some people may think that Golding is more effective in his paper than Clark. Golding is older, Golding has more education, and Golding more experience in college, than Clark does. Many people may argue that Golding has the better paper, due to the previously listed reasons, and those reasons are understandable. Something that may be agreeable though, is that Golding may have the better paper when it comes to following the rules of writing, and his organization style; but that Clark’s paper is actually better because he is in college, and that this paper is directed mainly towards current college students. It is also understandable that the ways of teaching how to write papers has changed, and how students are educated has changed, so due to these reasons Clark’s paper may actually be more current and apply more to it’s intended audience than Golding’s. Clark’s paper is a well written paper, and due to his use of straightforwardness, pathos, simplicity in his writing, and his advantage due to his age, he may still have the better piece of writing, even if Golding is more educated and more intelligent.
Leave a Reply
Name (required)
Mail (will not be published) (required)
XHTML: You can use these tags: <a href="" title=""> <abbr title=""> <acronym title=""> <b> <blockquote cite=""> <cite> <code> <del datetime=""> <em> <i> <q cite=""> <s> <strike> <strong>
About my blog
Glad you stopped by! Don't forget to sign up on the email list so you can get a free writing guide!
Recent Posts
- Effective Tips On Discovering the Best Book Publishing Companies In Chicago
- Literary Agents In Michigan
- Literary Agents In Minnesota
- Literary Agents In Missouri
- Literary Agents Mystery Fiction
- Young Adult Literary Agents Uk
- Literary Agents Los Angeles Nonfiction
Recent Comments
- Uncategorized
- September 2016
- February 2012
- January 2012
- December 2011
- November 2011
- October 2011
- September 2011
- August 2011
- February 2011
- January 2011
- December 2010
- November 2010
- October 2010
- February 2010
- January 2010
Powered by Flexibility 3

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Chapter 32: Methods of Speech Delivery
Learning Objectives
By the end of this chapter, you should be able to:
- Distinguish between four methods of speech delivery: the impromptu speech, the manuscript speech, the memorized speech, and the extemporaneous speech
- List the advantages and disadvantages of the four types of speeches
- Explain why an extemporaneous is the preferred delivery style when using rhetorical theory
Key Terms and Concepts
- extemporaneous
We have established that presentations involve much more than the transfer of information. Sure, you could treat a presentation as an opportunity to simply read a report you’ve written out loud to a group, but you would fail to both engage your audience and make a connection with them. In other words, you would leave them wondering exactly why they had to listen to your presentation instead of reading it at their leisure.
The Four Methods of Speech Delivery
One of the ways to ensure that you engage your audience effectively is by carefully considering how best to deliver your speech. Each of you has sat in a class, presentation, or meeting where you didn’t feel interested in the information the presenter was sharing. Part of the reason for your disengagement likely originated in the presenter’s method of speech delivery .
For our purposes, there are four different methods—or types—of speech delivery used in technical communication:
- Extemporaneous
Exercise #1: The Four Methods of Speech Delivery
What comes to mind when you think about the four methods of speech delivery? How do you think they are different from one another? Have you given a speech using any of these methods before?
Watch the video below for a brief overview of each one. After you are finished, answer the questions below:
- Which method are you most comfortable with? Why?
- Which method are you the least comfortable with? Why?
- Which method do you think is the best for connecting with your audience? Why?
The public speaking section of this course will require you to deliver a speech using an extemporaneous style, but let’s take a look at how all four differ in approach:
Impromptu Speeches
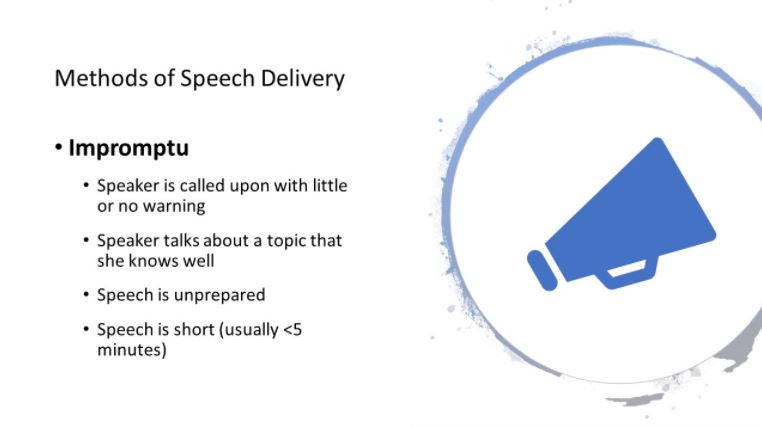
Impromptu speaking is the presentation of a short message without advanced preparation. You have probably done impromptu speaking many times in informal, conversational settings. Self-introductions in group settings are examples of impromptu speaking: “ Hi, my name is Shawnda, and I’m a student at the University of Saskatchewan .”
Another example of impromptu speaking occurs when you answer a question such as, “What did you think of the movie?” Your response has not been pre-planned, and you are constructing your arguments and points as you speak. Even worse, you might find yourself going into a meeting when your boss announces to you, “I want you to talk about the last stage of the project” with no warning.
The advantage of this kind of speaking is that it’s spontaneous and responsive in an animated group context. The disadvantage is that the speaker is giv en little or no time to contemplate the central theme of their message. As a result, the message may be disorganized and difficult for listeners to follow.
Here is a step-by-step guide that may be useful if you are called upon to give an impromptu speech in public:
- Take a moment to collect your thoughts and plan the main point that you want to make (like a mini thesis statement).
- Thank the person for inviting you to speak. Do not make comments about being unprepared, called upon at the last moment, on the spot, or uneasy. In other words, try to avoid being self-deprecating!
- Deliver your message, making your main point as briefly as you can while still covering it adequately and at a pace your listeners can follow.
- If you can use a structure, use numbers if possible: “Two main reasons. . .” or “Three parts of our plan. . .” or “Two side effects of this drug. . .” Past, present, and future or East Coast, Midwest, and West Coast are pre-fab structures.
- Thank the person again for the opportunity to speak.
- Stop talking. It is easy to “ramble on” when you don’t have something prepared. If in front of an audience, don’t keep talking as you move back to your seat.
Impromptu speeches are generally most successful when they are brief and focus on a single point.
We recommend practicing your impromptu speaking regularly. Do you want to work on reducing your vocalized pauses in a formal setting? Great! You can begin that process by being conscious of your vocalized fillers during informal conversations and settings.
Exercise #2: Impromptu Speech Example
Below are two examples of an impromptu speech. In the first video, a teacher is demonstrating an impromptu speech to his students on the topic of strawberries. He quickly jots down some notes before presenting.
What works in his speech? What could be improved?
Link to Original Video: tinyurl.com/impromptuteacher
In the above example, the teacher did an okay job, considering how little time he had to prepare.
In this next example, you will see just how badly an impromptu speech can go. It is a video of a best man speech at a wedding. Keep in mind that the speaker is the groom’s brother.
Is there anything that he does well? What are some problems with his speech?
Link to Original Video: tinyurl.com/badimpromptubestman
Manuscript Speeches

Manuscript speaking is the word-for-word iteration of a written message. In a manuscript speech, the speaker maintains their attention on the printed page except when using presentation aids.
The advantage to reading from a manuscript is the exact repetition of original words. This can be extremely important in some circumstances. For example, reading a statement about your organization’s legal responsibilities to customers may require that the original words be exact. In reading one word at a time, in order, the only errors would typically be the mispronunciation of a word or stumbling over complex sentence structure. A manuscript speech may also be appropriate at a more formal affair (like a funeral), when your speech must be said exactly as written in order to convey the proper emotion the situation deserves.
However, there are costs involved in manuscript speaking. First, it’s typically an uninteresting way to present. Unless the speaker has rehearsed the reading as a complete performance animated with vocal expression and gestures (well-known authors often do this for book readings), the presentation tends to be dull. Keeping one’s eyes glued to the script prevents eye contact with the audience.
For this kind of “straight” manuscript speech to hold audience attention, the audience must be already interested in the message and speaker before the delivery begins. Finally, because the full notes are required, speakers often require a lectern to place their notes, restricting movement and the ability to engage with the audience. Without something to place the notes on, speakers have to manage full-page speaking notes, and that can be distracting.
It is worth noting that professional speakers, actors, news reporters, and politicians often read from an autocue device such as a teleprompter. This device is especially common when these people appear on television where eye contact with the camera is crucial. With practice, a speaker can achieve a conversational tone and give the impression of speaking extemporaneously and maintaining eye contact while using an autocue device.
However, success in this medium depends on two factors:
- the speaker is already an accomplished public speaker who has learned to use a conversational tone while delivering a prepared script, and
- the speech is written in a style that sounds conversational.
Exercise #3: Manuscript Speech Example
Below is a video that shows an example of a manuscript speech. In the video, US Presidential Historian, Doris Kearns Goodwin, gives a speech about different US presidents.
What works in her speech? What could be improved?
Link to Original Video: tinyurl.com/goodwindepauw
Here’s a video that shows the dangers of relying on a manuscript for your speech:
Michael Bay heavily relied on his manuscript , so when he suddenly lost access to it, he was left feeling embarrassed and had to hastily leave the stage. As a result, he experienced face loss .
Link to original video: https://tinyurl.com/MBayManuscript
Memorized Speeches

Memorized speaking is reciting a written message that the speaker has committed to memory. Actors, of course, recite from memory whenever they perform from a script in a stage play, television program, or movie. When it comes to speeches, memorization can be useful when the message needs to be exact and the speaker doesn’t want to be confined by notes.
The advantage to memorization is that it enables the speaker to maintain eye contact with the audience throughout the speech. Being free of notes means that you can move freely around the stage and use your hands to make gestures. If your speech uses presentation aids, this freedom is even more of an advantage.
Memorization, however, can be tricky. First, if you lose your place and start trying to ad lib, the contrast in your style of delivery will alert your audience that something is wrong. If you go completely blank during the presentation, it will be extremely difficult to find your place and keep going. Obviously, memorizing a typical seven-minute classroom speech takes a great deal of time and effort, and if you aren’t used to memorizing, it is very difficult to pull off.
Exercise #4: Memorized Speech Example
Below is a video that shows an example of a memorized speech. In the video, former Louisiana governor, Bobby Jindal, responds to Barack Obama’s State of the Union address back in 2009.
Extemporaneous Speeches

Extemporaneous speaking is the presentation of a carefully planned and rehearsed speech, spoken in a conversational manner using brief notes.
Speaking extemporaneously has some advantages. It promotes the likelihood that you, the speaker, will be perceived as knowledgeable and credible since you know the speech well enough that you don’t need to read it. In addition, your audience is likely to pay better attention to the message because it is engaging both verbally and nonverbally.
By using notes rather than a full manuscript (or everything that you’re going to say), the extemporaneous speaker can establish and maintain eye contact with the audience and assess how well they are understanding the speech as it progresses. It also allows flexibility; you are working from the strong foundation of an outline, but if you need to delete, add, or rephrase something at the last minute or to adapt to your audience, you can do so. The outline also helps you be aware of main ideas vs. subordinate ones.

Compared to the other three types of speech delivery, an extemporaneous style is the best for engaging your audience and making yourself sound like a natural speaker.
The video below provides some tips on how to deliver a speech using this method:
Link to Original Video: tinyurl.com/deliverextempres
The slide below provides a brief overview of tips for preparing your extemporaneous presentation:
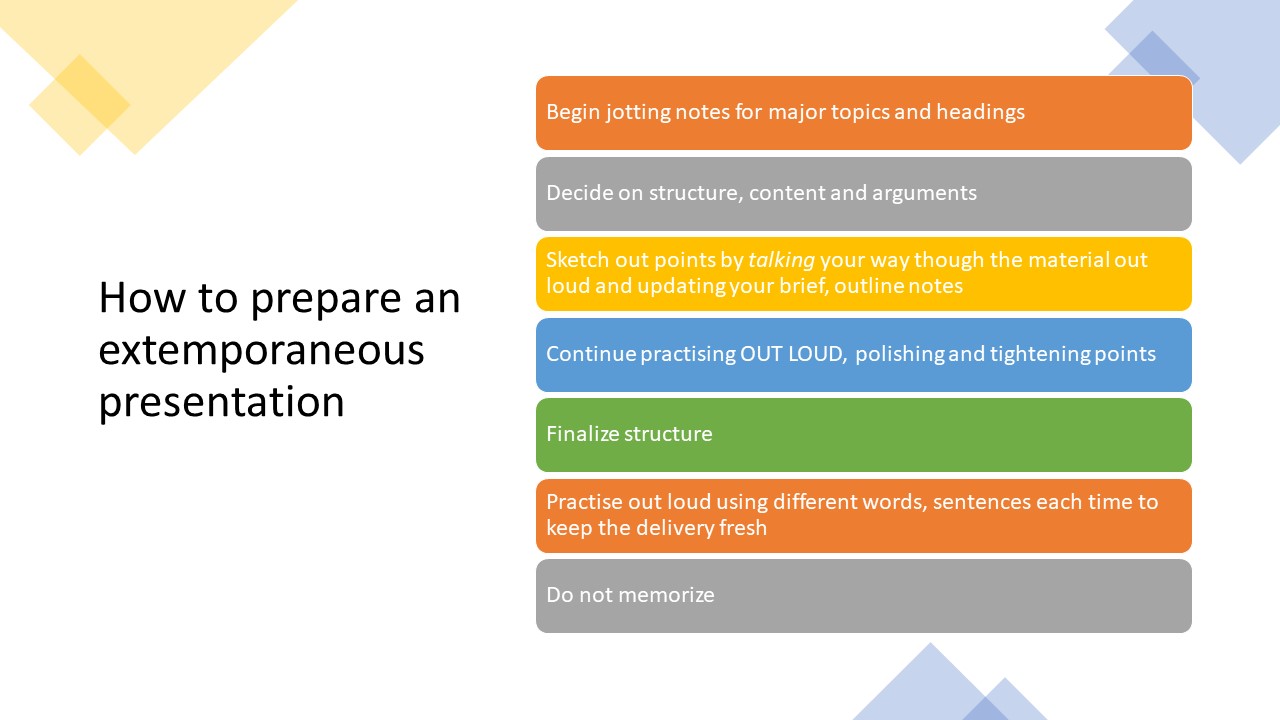
Exercise# 5: Extemporaneous Speech Example
Below is a video that shows an example of an extemporaneous speech. In the video, a former University of Saskatchewan student tries to persuade her peers to spend more solo time outside.
Link to Original Video: tinyurl.com/rcm401speech
Key Takeaways
- When designing any speech, it’s important to consider how you will deliver that speech. In technical communication, there are four different types of speech delivery, each with their advantages and disadvantages. They are: impromptu , manuscript , memorized , and extemporaneous .
- An impromptu speech can take many forms such as a toast at a wedding, being asked to give a project update at a meeting, or even simply meeting someone for the first time. While this type of speech can be spontaneous and responsive, the speaker generally has little to no warning that they will need to speak.
- A manuscript speech is completely written out and read word for word. It is often a good style when you want to nail the specific wording and do not want to make an error. However, this type of speech is not very persuasive because it does not take advantage of the immediacy of public speaking. It also completely removes audience relation from the process.
- A memorized speech is when a speaker commits an entire speech to memory. This style also harms relation with the audience because the speaker is more focused on remembering the text of the speech rather than communicating with the audience. Additionally, if you lose your place and need to ad lib, it may be obvious to your audience.
- An extemporaneous speech is done in a natural, conversational speaking style. While it is carefully planned, it is never completely written out like a manuscript. It is also not read or memorized . Instead, an outline is used to help guide the speaker. As a result, more attention can be paid to the audience, allowing the speaker to better connect with them and make adjustments as necessary. This is the style we want you to use for your presentation assignment in RCM 200.
Attributions
This chapter is adapted from “ Communication for Business Professionals ” by eCampusOntario (on Open Library ). It is licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License .
This chapter is also adapted from “ Speak Out, Call In: Public Speaking as Advocacy ” by Meggie Mapes (on Pressbooks ). It is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License .
a speech delivery method where a short message is presented without advanced preparation
a speech delivery method where a message is read word-for-word off a written page or autocue device
a speech delivery method where a message is presented after being committed to memory by the speaker
a speech delivery method where the presentation is carefully planned and rehearsed, but spoken in a conversational manner using brief notes
the experience of feeling judged, or feeling that people do not recognize us as we perceive ourselves to be
Effective Professional Communication: A Rhetorical Approach Copyright © 2021 by Rebekah Bennetch; Corey Owen; and Zachary Keesey is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

- 1-on-1 Consulting
- Online Courses

5 Manuscript Speech Tips

We like presentations that are delivered without fear, and without a script. But, if you find yourself in a public speaking circumstance where you need to read from a prepared manuscript, here are five tips to help guarantee smooth delivery.
1) Large Type . Print out your speech in type that is large enough to be read easily from a lectern. Place sheets in sheet protectors and place them in an unobtrusive thin white three-ring binder. Arrange the pages so that there are always two full pages facing you, which minimizes page-turning. That means some sheet protectors will have two pages in them, back-to-back. Here’s a short video showing what that looks like.
2) Practice Reading Aloud. Practice reading out loud and turning the pages. Try to look up from the pages as much as possible so that when you deliver the speech, you will be able to make eye contact with your audience. Use intonation when reading so that you don’t sound monotone or like you are reading it for the first time. Read in a conversational tone. Make sure you are pronouncing all the words you are using correctly.
3) Focus on your vocal variety . Remember that pausing can be powerful. Pause before and after an important point. If you are a natural fast-talker, slow down when you make important points. Practice your pace. Find the right speed. Your goal for your conclusion should be that everyone will know that you are done without you have to say “thank you.” You accomplish that by adjusting your pace and pause, and, to a lesser extent, your pitch and power.
4) Research. Before you speak, find out if the lectern will be lit well enough for you to read. Don’t forget to bring reading glasses if you need them. Also, find out if you will be speaking with a microphone and practice accordingly. If the speech is supposed to be a particular length, practice with a timer. By aware that some people read faster at a live event because of adrenaline.
5) Practice, practice, practice. Always read out loud. Practice reading it in front of friends or family. Record yourself.
By following these tips, you can turn a manuscript speech into a well-delivered presentation.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
Keep informed
- Sign up to keep informed on our upcoming events and promotions.
- Name * First Last
- Email This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
All rights reserved – Phoenix Public Speaking.
My Speech Class
Public Speaking Tips & Speech Topics
Speech Delivery

Jim Peterson has over 20 years experience on speech writing. He wrote over 300 free speech topic ideas and how-to guides for any kind of public speaking and speech writing assignments at My Speech Class.
In this article:
Types of Speech Delivery
Aspects of physical delivery.
There are four primary types of speech delivery: Manuscript, Memorized, Impromptu, and Extemporaneous.

Memorized , like it sounds, involves committing your entire speech to memory. Once again, this sounds great. But, practically speaking, who has time to memorize even a short speech? And like a manuscript speech, you can’t adapt to feedback from the audience.
An Impromptu speech is one that you are asked to deliver with little or no preparation. Chances are, that if you’re on this site, impromptu speeches aren’t what you are expected to deliver.
Finally, the Extemporaneous speech is a speech delivered with some prepared structure, such as notes or an outline, but is otherwise delivered off-the-cuff. In most cases, this is going to be your best choice. The notes allow you to structure your speech, without handcuffing you in the event that your audience needs you to adapt. Also, you will sound more natural and conversational, and this will help hold audience attention.
There are six aspects of physical delivery that will be covered in this section: voice use, facial expressions, eye contact, gesturing, and movement.
Can We Write Your Speech?
Get your audience blown away with help from a professional speechwriter. Free proofreading and copy-editing included.
Effective voice use involves several elements. Naturally, one of the most important aspects is volume. As a speaker, you must be loud enough to be heard by everyone in the room, but not so loud that you sound unnatural or bossy. Monitor the nonverbal feedback of audience members in the back of the room, if they are leaning forward or concentrating abnormally hard, you may need to speak up. It is also necessary to vary the pitch, rate, and tone of your voice to avoid sounding monotonous. We’ve all experienced the agony of listening to a monotonous-voiced speaker. This doesn’t mean that you need to be extremely flamboyant or obnoxious. Overall, you should just strive for a casual, conversational voice.
Your audience gathers a lot of information from your facial expressions . If your facial expressions and your spoken words conflict, the audience is likely to believe your face. So make sure that your facial expressions mesh with the feelings and ideas being expressed. Basically, a good rule of thumb for facial expressions (as well as gestures) is to do what comes naturally. There is no need to be overly theatrical with your facial expressions in a speech. And remember, if it’s at all appropriate, you can’t go wrong with a smile.
The simple rule on eye contact is this: The more, the better. A good strategy for eye contact is to make brief (a beat or two) eye contact with members of the audience in one section of the audience and then move to another section. Ideally, you should be making eye contact with someone whenever words are being spoken in your speech. Beware of this trap: People naturally tend to focus their eye contact on the person that is giving them the best nonverbal feedback (smiling, nodding, etc.). If you find yourself focusing too much on this person, work on moving to others.
One of the most common questions that people have about public speaking is: What do I do with my hands? The quick and easy answer is: Whatever comes naturally (unless clutching the podium is what comes naturally). The key to good gesturing is variety, which most of us have in our everyday gestures.
The final aspect of physical delivery is movement . If you are positioned behind a podium, your movements are obviously going to be restricted. But if you are not using a podium, feel free to walk to different parts of the stage as you deliver your speech. This keeps different parts of the audience involved and adds variety. Don’t just wander in place, though. If your feet move, go somewhere.
Visual Aids
Speech Anxiety
Leave a Comment
I accept the Privacy Policy
Reach out to us for sponsorship opportunities
Vivamus integer non suscipit taciti mus etiam at primis tempor sagittis euismod libero facilisi.
© 2024 My Speech Class

AI Generator

A manuscript is a handwritten or typed document that contains the original text of a work, such as a novel, screenplay, or script. It serves as the first version of a piece of writing before it gets edited, published, or produced. Authors and playwrights use manuscripts to draft and refine their ideas, ensuring the final product is polished and ready for an audience. Whether it’s an English essay, a gripping screenplay , or a compelling script , a manuscript is the crucial starting point for any written work.
What is Manuscript?
Manuscript format, 1.title page.
- Title : Place the title of your manuscript in the center of the page.
- Author’s Name : Add your name below the title.
- Contact Information : Include your address, phone number, and email in the upper left corner.
- Word Count : Note the word count in the upper right corner.
2. Margins and Spacing
- Margins : Use 1-inch margins on all sides of the page.
- Line Spacing : Double-space the entire manuscript for readability.
- Font : Use a readable font like Times New Roman, 12-point size.
- Page Numbers : Insert page numbers in the upper right corner.
- Author’s Last Name and Title : Include your last name and a shortened title of the manuscript in the header.
4. Body Text
- Indentation : Indent the first line of each paragraph by 0.5 inches.
- Alignment : Use left alignment and do not justify the text.
- Scene Breaks : Insert a blank line or use three asterisks (***).
5. Dialogue
- Quotation Marks : Enclose dialogue in quotation marks.
- New Paragraphs : Start a new paragraph for each new speaker.
6. Chapters
- Chapter Titles : Center the chapter title or number one-third down the page.
- Page Breaks : Begin each chapter on a new page.
7. End Matter
- Author Bio : Include a short biography at the end if requested.
- Acknowledgments : Add any acknowledgments or thank-yous.
8. Proofreading
- Grammar and Spelling : Check for and correct any grammatical or spelling errors.
- Consistency : Ensure consistency in formatting, font, and style throughout the manuscript.
Examples of Manuscript
- Medieval Religious Text : Handwritten copies of the Bible or the Quran.
- Ancient Greek Philosophical Works : Original writings of Plato or Aristotle.
- Medieval Illuminated Manuscripts : Decorative and colorful manuscripts, like the Book of Kells.
- Literary Manuscripts : Early drafts of novels by famous authors, such as “Pride and Prejudice” by Jane Austen.
- Historical Letters : Correspondence from significant historical figures, like letters written by Abraham Lincoln.
- Scientific Papers : Original manuscripts of groundbreaking scientific discoveries, such as Isaac Newton’s “Principia Mathematica.”
- Playscripts : Original scripts of plays by renowned playwrights, such as Shakespeare’s “Hamlet.”
- Poetry Collections : Handwritten collections of poems by poets like Emily Dickinson.
- Travel Diaries : Personal accounts of travels, like Marco Polo’s “The Travels of Marco Polo.”
- Historical Chronicles : Manuscripts detailing historical events, like “The Anglo-Saxon Chronicle.”
- Ancient Legal Documents : Early versions of legal codes, such as Hammurabi’s Code.
- Medical Texts : Original medical treatises, like Hippocrates’ “Corpus Hippocraticum.”
- Philosophical Essays : Handwritten essays by philosophers, such as Michel de Montaigne’s “Essays.”
- Autobiographies : Manuscripts of personal life stories, like “The Diary of Anne Frank.”
- Music Scores : Original sheet music composed by musicians like Beethoven.
- Epic Poems : Manuscripts of long narrative poems, such as Homer’s “The Iliad.”
- Art Sketchbooks : Artists’ original sketchbooks, like those of Leonardo da Vinci.
- Cookbooks : Early handwritten recipe collections, like “The Forme of Cury.”
- Scientific Journals : Personal scientific journals, such as those of Charles Darwin.
- Mythological Texts : Manuscripts of ancient myths, like the “Epic of Gilgamesh.”
Examples of Manuscript for Students
- Essay Drafts : Early versions of an essay on Shakespeare’s works.
- Science Fair Reports : Initial reports on a student’s science project.
- History Papers : Drafts of research papers on historical events.
- Creative Writing Stories : Handwritten or typed stories for a creative writing class.
- Classroom Journals : Daily entries in a student’s journal.
- Book Reports : First drafts of book summaries and analyses.
- Research Proposals : Preliminary proposals for a research project.
- Thesis Papers : Early drafts of a student’s thesis or dissertation.
- Lab Reports : Initial versions of laboratory experiment reports.
- Poetry Collections : Handwritten collections of original poems.
Examples of Manuscripts in a Sentence
- The manuscript of her novel was accepted by the publisher.
- He discovered an ancient manuscript in the library archives.
- She spent months revising her manuscript before submitting it.
- The manuscript contained detailed illustrations and maps.
- His latest research manuscript will be published next year.
- They found a medieval manuscript hidden in the monastery.
- She lost her original manuscript in a computer crash.
- The professor reviewed the manuscript for scientific accuracy.
- The manuscript was written in beautiful calligraphy.
- He donated his personal manuscript collection to the university.
Examples of Manuscripts for Research
- Thesis Drafts : Early versions of a PhD thesis.
- Research Articles : Preliminary manuscripts of journal articles.
- Grant Proposals : Initial drafts of research funding proposals.
- Literature Reviews : Manuscripts reviewing existing research.
- Case Studies : Detailed reports on specific research cases.
- Conference Papers : Drafts of papers to be presented at academic conferences.
- Field Notes : Original observations recorded during field research.
- Dissertation Proposals : Early drafts of dissertation plans.
- Experimental Reports : Manuscripts documenting research experiments.
- Annotated Bibliographies : Manuscripts compiling sources with annotations.
1. Manuscript Template Instructions

2. Manuscript Format

3. Manuscript Format Template

4. Steps to Create Manuscript

How to Write a Manuscript for Your Story
A well-written manuscript will allow readers to comprehend and understand the text written as if it was a published book. The completed manuscript will undergo a process where it will be reviewed and edited to a certain extent. The complete manuscript will have all the necessary parts of a book, this will include the cover page , references, and dedication.
Create an Outline of The Story
Begin by creating an outline that will detail the overarching plot of the story you want to write. This should follow a specific flow and should be comprised of three arcs with multiple chapters in between. The outline will act as the structure of your story, which is very important as it can help minimize and prevent writer’s block.
Write the Chapters, and Finish the Manuscript
After creating your outline, you must begin writing the chapters using the outline as the base of said chapters. Do note, this will be the longest part of the manuscript and it will take some time and effort to finish writing the manuscript.
Edit the Manuscript
When you have finished writing the manuscript, it must undergo a couple of revisions and test-read to improve the overall quality of the manuscript. Doing this will increase the chances of a publication accepting your manuscript.
Publish the Manuscript
After you have finished the editing process of the manuscript you can opt to publish your manuscript in a variety of ways. You may self-publish the manuscript, though this will be the hardest to market and sell. Alternatively, you may approach various publications to try and vet your manuscript to them.
How to Read Manuscript
- Find a Quiet Space : Choose a quiet and comfortable place where you can focus without distractions.
- Understand the Context : Research the background of the manuscript, including the author, the time period, and the purpose of the work.
- Skim the Manuscript : Quickly skim through the manuscript to get a general sense of its structure and main points.
- Read the Introduction : Carefully read the introduction to understand the main theme and objectives of the manuscript.
- Annotate as You Read : Make notes, highlight important points, and write down any questions or comments in the margins.
- Break It into Sections : Divide the manuscript into manageable sections and read each part thoroughly.
- Focus on Key Arguments : Identify and focus on the main arguments or points presented in the manuscript.
- Look Up Unfamiliar Terms : Research any unfamiliar terms or references to ensure you fully understand the content.
- Summarize Each Section : Write a brief summary of each section to reinforce your understanding and retention.
- Review and Reflect : After reading, review your notes and summaries, and reflect on the overall message and implications of the manuscript.
How Long is a Manuscript?
A manuscript typically ranges from 50,000 to 100,000 words, depending on the genre and purpose.
How to Publish a Manuscript?
Submit your manuscript to literary agents or publishers, or self-publish through platforms like Amazon Kindle Direct Publishing.
What is Another Word for Manuscript Writing?
Another term for manuscript writing is “drafting.”
What is a Manuscript vs Book?
A manuscript is the original, unpublished version of a work, while a book is the final, published version.
What Does the Word Manuscript Literally Mean?
The word “manuscript” literally means “written by hand.”
How Do I Make My Own Manuscript?
Write your content, format it according to guidelines, and revise it thoroughly before submission.
What Not to Do When Writing a Manuscript?
Avoid plagiarism, poor formatting, inconsistent style, and ignoring submission guidelines.
Is a Manuscript a Full Book?
Yes, a manuscript can be a full book, but it is in its unpublished form.
What is the Manuscript of a Paper?
The manuscript of a paper is the original version submitted for publication in an academic journal.
What to Write on the First Page of a Manuscript?
Include the title, author’s name, contact information, and word count on the first page of a manuscript.
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Definition of Manuscript Speech. This is when a speaker reads a pre-written speech word by word to an audience. It is when an already prepared script is read verbatim. The speaker makes the entire speech by referring to the printed document, or as seen on the teleprompter. It is basically an easy method of oral communication.
Preparing a manuscript speech requires careful planning and attention to detail. Here are the five steps to help you write a successful manuscript speech: 1. Research: Take the time to do your research and gather all the facts you need. This should be done well in advance so that you can prepare your speech carefully. 2.
Incorporate pauses effectively to enhance impact. Engage with your audience through eye contact and expressions. With a speech manuscript, your goal is to bring the words to life. Infuse emotion and emphasis where necessary. Your voice should rise and fall naturally, reflecting the nuances of your message.
Step 8: Practicing the Delivery. The written manuscript is only half the equation—delivery can make or break a speech. Practice is essential. Read your speech repeatedly, focusing on your intonation, pace, and breathing. Try to memorize as much as possible to reduce reliance on the manuscript during delivery.
For example, many people like to have written copies of the toast given to them at a special occasion or a copy of the eulogy to the loved one. ... Teddy Roosevelt's life was saved when an assassin's bullet was slowed down by his 50 paged speech manuscript. The doctor on sight determined that although the bullet didn't puncture his lungs ...
A manuscript speech is a type of speech that is written out in its entirety and read word-for-word by the speaker during delivery. This format allows for precise wording and careful control over language, making it ideal for formal occasions where accuracy and clarity are crucial. Manuscript speeches can also help speakers avoid forgetting key points, but may limit eye contact and spontaneity ...
The word manuscript is derived from two Latin words, "manu scriptus," that mean "to write by hand.". Before the invention of the printing press, all documents were written by hand. In today's digital age, the word manuscript has come to mean the original version of any complete text. During a manuscript speech, the speaker essentially ...
Manuscript Speaking is a written text read to an audience from a paper script or teleprompter. This method involves reading a speech verbatim and is typically used when there is a time constraint or the speech will be telecast. How can you make a manuscript presentation a success? 1. Use large print so that it will be easy to read your speech ...
Discover the art of Manuscript Speech in this engaging and informative video! Whether you're a seasoned Public Speaker or just starting out, understanding th...
An overview of the 4 modes of speech delivery, the pros (advantages) and cons (disadvantages) of each, plus links to examples and further resources. manuscript; memorized; impromptu; extemporaneous; 1. Manuscript. One of the most common ways to deliver a speech is to use a manuscript: a word by word document of everything you plan to say from ...
The manuscript speech is a presentation method where the speakers deliver the presentation with a paper or teleprompter that usually has been pre-written to give a piece of information. The entire speech has to be referred to the printed document, which means that we as the speakers don't necessarily need to read all of it, but to have a ...
Knowing the key target audience is the most important factor in writing the manuscript. Avoid speaking over them; a group of highschool kids will need to be addressed in a different way than a roomful of adults. Keep the tone of the speech inline with the target audience. Lightheartedness may not be an appropriate tone for all occassions, but ...
Manuscript Speeches. Manuscript speaking is the word-for-word iteration of a written message. In a manuscript speech, the speaker maintains their attention on the printed page except when using presentation aids. The advantage to reading from a manuscript is the exact repetition of original words. This can be extremely important in some ...
By aware that some people read faster at a live event because of adrenaline. 5) Practice, practice, practice. Always read out loud. Practice reading it in front of friends or family. Record yourself. By following these tips, you can turn a manuscript speech into a well-delivered presentation.
For example, many people like to have written copies of the toast given to them at a special occasion or a copy of the eulogy to the loved one. ... Teddy Roosevelt's life was saved when an assassin's bullet was slowed down by his 50 paged speech manuscript. The doctor on sight determined that although the bullet didn't puncture his lungs ...
Correct Manuscript Format: Full Guide [& Examples] Your manuscript format matters. We break down the process for formatting your manuscript step-by-step. Follow this guide & grab our template:
Types of Speech Delivery. There are four primary types of speech delivery: Manuscript, Memorized, Impromptu, and Extemporaneous. Manuscript speaking, like it sounds, involves reading your speech word-for-word from it's written form. The advantage to delivering a speech this way is that you can perfectly plan and control the wording of your ...
The four types of speech delivery this lesson will cover are: Extemporaneous speech. Manuscript speech. Memorized speech. Impromptu speech. Impromptu speeches are given with minimal preparation ...
Manuscript Speech Example: The Impact of Social Media on Modern Activism Introduction: Ladies and gentlemen, In the digital age, social media has become a powerful tool for shaping the world around us. Today, I'd like to discuss the profound impact of social media on modern activism, using the example of the Arab Spring. ody: . The Arab Spring:
Manuscript. A manuscript is a handwritten or typed document that contains the original text of a work, such as a novel, screenplay, or script. It serves as the first version of a piece of writing before it gets edited, published, or produced. Authors and playwrights use manuscripts to draft and refine their ideas, ensuring the final product is ...