

45,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today
Meet top uk universities from the comfort of your home, here’s your new year gift, one app for all your, study abroad needs, start your journey, track your progress, grow with the community and so much more.

Verification Code
An OTP has been sent to your registered mobile no. Please verify

Thanks for your comment !
Our team will review it before it's shown to our readers.

- Reported Speech /
Reported Speech for Class 10: Exercises with Answers [PDF]
- Updated on
- Oct 23, 2024

Reported speech plays an integral role in maintaining effective communication skills . It also ensures accuracy, objectivity, and clarity among the speakers. Reported Speech is an essential linguistic tool from everyday conversations to formal writing. It is important to teach reported speech to Class 10 to give them a wider scope of the English language and vocabulary . Reported Speech is effective in conveying the thoughts and ideas of others accurately and without causing any misrepresentation.
This Blog Includes:
What is reported speech in english grammar, reported speech for class 10 exercise 1 – mcqs, exercise 2 – change the sentences from direct to indirect speech, reported speech for class 10: exercises with answers [download free pdf].
Reported Speech is often called Indirect Speech, which is not the exact words spoken by the speaker and is not written inside the quotation marks. It is the representation of the words spoken by the speaker in the past by another person. Reported Speech involves transforming verb tenses, pronouns, and sometimes other elements. The changes are important to accurately represent the reported information while integrating it into the speaker’s sentence structure.
Must Read! Reported Speech: Definition, Rules, Usage with Examples
Here are the MCQs on reported speech for class 10th students. Students have to select the correct option from the given options according to the statement asked based on Reported Speech.
- Which sentence is in the reported speech?
a. She said, “I will be there soon.”
b. She says, “I will be there soon.”
c. She said, “She will be there soon.”
d. She says, “She will be there soon.”
- What is the correct reported speech for: “I am studying for exams.”?
a. He said that he was studying for exams.
b. He says that he is studying for exams.
c. He says that he was studying for exams.
d. He said that he is studying for exams.
- Which pronoun change is correct in reported speech?
a. “I” changes to “he.”
b. “They” changes to “we.”
c. “You” changes to “she.”
d. “He” changes to “it.”
- What is the reported speech for: “Did you finish your homework?”?
a. She asked if she finished her homework.
b. She asked if I finished my homework.
c. She asked if I had finished my homework.
d. She asked if she had finished her homework.
- Which tense change is required in reported speech?
a. Present simple changes to past simple.
b. Past simple changes to present continuous.
c. Present continuous changes to future perfect.
d. Future simple changes to past perfect.
- Which sentence is correctly reported?
a. Sarah told me that she is leaving tomorrow.
b. Sarah told me that she was leaving tomorrow.
c. Sarah tells me that she will leave tomorrow.
d. Sarah told me that she leaves tomorrow.
- What is the reported speech for: “I will call you later.”?
a. She said that she would call me later.
b. She said that she would call me later.
c. She says that she will call me later.
d. She says that she will call me later.
- Which of the following is a reported speech question?
a. He said, “I am going to the store.”
b. She asked, “Have you seen my keys?”
c. They said, “We will arrive soon.”
d. She told me, “Don’t be late.”
- What is the correct reported speech for: “Can you help me with this?”?
a. He asked if he could help me with that.
b. He asked if I can help him with this.
c. He asks if he can help me with this.
d. He asks if I could help him with that.
- Which sentence represents reported speech?
a. “Stop!” she shouted.
b. She shouts, “Stop!”
c. She shouted to stop.
d. She shouted, “Stop!”
Also Read: Useful Idioms for IELTS Exams That Will Boost Your Score
Check Your Answers
Match your answers with the right answers given below:
1. c. She said, “She will be there soon.”
2. a. He said that he was studying for exams.
3. a. “I” changes to “he.”
4. c. She asked if I had finished my homework.
5. a. Present simple changes to past simple.
6. b. Sarah told me that she was leaving tomorrow.
7. b. She said that she would call me later.
8. b. She asked, “Have you seen my keys?”
9. a. He asked if he could help me with that.
10. c. She shouted to stop.
Also Read: 50 Examples of Direct and Indirect Speech Interrogative Sentences
As candidates are well versed with the concept of reported speech it is time for the candidates to solve this exercise based on converting direct speech to indirect speech.
- “I am reading a book,” she said.
- “We will go to the beach tomorrow,” he announced.
- “Can you help me with my homework?” she asked.
- “I have already seen that movie,” he claimed.
- “Please turn off the lights,” she requested.
- “They are cooking dinner,” he mentioned.
- “Why did you arrive late?” she inquired.
- “I cannot solve this math problem,” he admitted.
- “I will call you later,” she promised.
- “Let’s meet at the park,” he suggested.
- “She has been working all day,” he observed.
- “Do you like chocolate ice cream?” she wondered.
- “The concert starts at 8 PM,” he informed.
- “We won the championship,” she exclaimed.
- “I need more time to finish the project,” he confessed.
- “The train departs in 15 minutes,” she reminded.
- “Did you visit the museum?” he asked.
- “I’m going to visit my grandparents next weekend,” she said.
- “We should plant more trees,” he advised.
- “Don’t forget to buy milk,” she reminded.
Must Read: Subject-Verb Agreement: Definition, 12 Rules & Examples
Answers
- She said that she was reading a book.
- He announced that they would go to the beach the next day.
- She asked if I could help her with her homework.
- He claimed that he had already seen that movie.
- She requested to turn off the lights.
- He mentioned that they were cooking dinner.
- She inquired why I had arrived late.
- He admitted that he couldn’t solve that math problem.
- She promised that she would call later.
- He suggested meeting at the park.
- He observed that she had been working all day.
- She wondered if I liked chocolate ice cream.
- He informed me that the concert started at 8 PM.
- She exclaimed that they had won the championship.
- He confessed that he needed more time to finish the project.
- She reminded me that the train departed in 15 minutes.
- He asked if I had visited the museum.
- She said she was going to visit her grandparents the following weekend.
- He advised that they should plant more trees.
- She reminded me not to forget to buy milk.
You can download Reported Speech for Class 10 worksheet PDF from below:
More Reads on Reported Speech for Class 10
The four types of reported speech are assertive, interrogative, imperative, and exclamatory.
The two main types of reported speech are direct and indirect speech.
Reported Speech is effective in conveying the thoughts and ideas of others accurately and without causing any misrepresentation.
This was all about the Reported Speech Exercises for Class 10 Students with Answers. Hope you understand the concept and where it’s used. Keep an eye on Leverage Edu for more exciting and informative blogs.
Amanpreet Kaur
📚✨ From Classroom Chats Entered Into The Wordy World ….. Yes , If you all Remember that teacher who kept you on your toes with pop quizzes and endless homework? YEP! THAT WAS Me ! 🌟 But with the blessings of almighty and the key motivation of my husband who came across the spark of writing in me has insisted me to pave my way away from chalk dust to creative burst!💫 Being in this new world of writing I can compose pun-tastic content, poetry full of emotions and humorous articles that can even make Shakespeare envious of me 📝🎭.Yippee! from teaching young minds to educating worldwide readers it's an epic career switch. From teaching grammar lessons to grammatically flawless copy, I'm todays' wordsmith on a mission! Let me spin literary magic all around and conquer my exact destination of proving myself as The Best Writer in The World.🚀🏆 My promise is to provide you with valuable insights, solutions to your questions, and a momentary escape from the routine. I believe in the power of words to create connections, provoke thought, and foster growth. Woods are lovely dark and deep But I have promises to keep and Miles to go before I sleep ……..🌳✨🌌
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Contact no. *

Leaving already?
8 Universities with higher ROI than IITs and IIMs
Grab this one-time opportunity to download this ebook
Connect With Us
45,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. take the first step today..

Resend OTP in

Need help with?
Study abroad.
UK, Canada, US & More
IELTS, GRE, GMAT & More
Scholarship, Loans & Forex
Country Preference
New Zealand
Which English test are you planning to take?
Which academic test are you planning to take.
Not Sure yet
When are you planning to take the exam?
Already booked my exam slot
Within 2 Months
Want to learn about the test
Which Degree do you wish to pursue?
When do you want to start studying abroad.
January 2025
September 2025
What is your budget to study abroad?

How would you describe this article ?
Please rate this article
We would like to hear more.
Have something on your mind?
CBSE Class 10 English Grammar – Direct And Indirect Speech
CBSE Class 10 Science CBSE Class 10 Social Science CBSE Class 10 Maths
(Statements, Commands, Requests, and Questions) The words spoken by a person can be reported in two ways—Direct and Indirect. When we quote the exact words spoken by a person, we call it Direct Speech.
- Sohan said to Mohan, “I am going to school.”
The exact words spoken by Sohan are put within inverted commas. But when we give the substance of what Sohan said, it is called the Indirect Speech.
Direct and Indirect Speech
- Sohan told to Mohan that he (Sohan) was going to school.
1. Reporting Clause and Reported Speech: Sohan told Mohan that he was going to school. The words which generally come before the inverted commas are called the reporting clause, i.e. Sohan said to Mohan and the verb ‘said’, is called the reporting verb. The words spoken by Sohan and put within inverted commas are called the reported speech, i.e. “I am going to school.”
2. Rules for Changing Direct Speech into Indirect Speech:
- In the Indirect speech, no inverted commas are used.
- The conjunctions that, if, whether, are generally used after the reporting verb.
- The first word of the reported speech begins with a capital letter.
- The tense of the reporting verb is never changed.
- The reporting verb changes according to sense: it may be told, asked, inquired
3. Rules for the Change of Pronouns:
- The first person pronouns (I, me, my, we, us, our) in the reported speech change according to the subject of the reporting verb.
- The pronouns of the second person (you, your, yourself) in the reported speech change according to the object of the reporting verb.
- The pronouns of the third person do not change.
For example:
- He said, “I like the book.” He said that he liked the book.
- He said to me, “Do you like the book?” He asked me if I liked the book.
- He said, “He likes the book.”a He said that he liked the book.

- If the reporting verb is in the present or the future tense, the tense of the reported speech is not changed: Satish says, “I am flying a kite.” Satish says that he is flying a kite. Satish will say, “I want a glass of milk.” Satish will say that he wants a glass of milk.

- If the direct speech expresses a historical fact, universal truth, or a habitual fact, then the tense of the direct speech will not change: Direct: He said, “Honesty is the best policy.” Indirect: He said that honesty is the best policy. Direct: He said, “The sun rises in the east.” Indirect: He said that the sun rises in the east. Direct: Rakesh said, “I am an early riser.” Indirect : Rakesh said that he is an early riser. Direct: She said, “God is omnipresent.” Indirect: She said that God is omnipresent. Direct: The teacher said, “The First World War started in 1914.” Indirect: The teacher said that the First World War started in 1914.
6. Changing Statements into Indirect Speech:
- The reporting verb ‘said to’ is changed-to ‘told’, ‘replied’, ‘remarked’,
- The reporting verb is not followed by an object, it is not changed.
- The inverted commas are removed. The conjunction is used to connect the reporting clause with the reported speech.
The rules for the change of pronouns, tenses, etc. are followed.
- Direct: Ramu said, “I saw a lion in the forest.” Indirect: Ramu said that he had seen a lion in the forest.
- Direct: Satish said to me, “I am very happy here.” Indirect: Satish told me that he was very happy there.
- Direct: He said, “I can do this work.” Indirect: He said that he could do that work.
- Direct: Renu said to me, “I was washing the clothes.” Indirect: Renu told me that she had been washing the clothes.
- Direct: She said, “I am not well.” Indirect: She said that she was not well.
- Direct: He said to Sita, “I have passed the test.” Indirect: He told Sita that he had passed the test.
- Direct: I said to my friend, “He has been working very hard.” Indirect: I told my friend that he had been working very hard.
- Direct: My friend said to me, “I shall go to Delhi tomorrow.” Indirect: My friend told me that he would go to Delhi the next day.
- Direct: I said, “I agree to what he said.” Indirect: I said that I agreed to what he had said.
- Direct: The student said to the teacher, “I am sorry that I am late.” Indirect: The student told the teacher that he was sorry that he was late.
7. Rules for the Change of Interrogative (Questions) sentences:
The reporting verb “say’ is changed into ask, inquire,
The interrogative sentence is changed into a statement by placing the subject before the verb and the full stop is put at the end of the sentence.
If the interrogative sentence has a wh-word (who, when, where, how, why, etc) the wh-word is repeated in the sentence. It serves as conjunction.
If the interrogative sentence is a yes-no answer type sentence (with auxiliary verbs am, are, was, were, do, did, have, shall, etc), then ‘if or ‘whether’ is used as a conjunction.
The auxiliaries do, does, did in a positive question in the reported speech are dropped.
The conjunction is not used after the reporting clause.
- Direct: I said to him, “Where are you going?” Indirect: I asked him where he was going.
- Direct: He said to me, “Will you go there?” Indirect: He asked me if I would go there.
- Direct: My friend said to Deepak, “Have you ever been to Agra?” Indirect: My friend asked Deepak if he had ever been to Agra.
- Direct: I said to him, “Did you enjoy the movie?” Indirect: I asked him if he had enjoyed the movie.
- Direct: I said to her, “Do you know him?” Indirect: I asked her if she knew him.
- Direct: He said to me, “Will you listen to me?” Indirect: He asked me if I would listen to him.
- Direct: I said to him, “When will you go there?” Indirect: I asked him when he would go there.
- Direct: He said to me, “How is your father?” Indirect: He asked me how my father was.
- Direct: I said to him, “Are you happy?” Indirect: I asked him if he was happy.
- Direct: He said to her, “Do you like apples?” Indirect: He asked her if she liked apples.
8. Changing Commands and Requests into Indirect Speech:
- In imperative sentences having commands, the reporting verb is changed into command, order, tell, allow, request,etc.
- The imperative mood is changed into the infinitive mood by putting ‘to’, before the verb. In case of negative sentences, the auxiliary ‘do’ is dropped and ‘to’ is placed after ‘not’:
- Direct: She said to me, “Open the window.” Indirect: She ordered me to open the window.
- Direct: The captain said to the soldiers, “Attack the enemy.” Indirect: The captain commanded the soldiers to attack the enemy.
- Direct: I said to him, “Leave this place at once.” Indirect: I told him to leave that place at once.
- Direct: The teacher said to the students, “Listen to me attentively.” Indirect: The teacher asked the students to listen to him attentively.
- Direct: The Principal said to the peon, “Ring the bell.” Indirect: The Principal ordered the peon to ring the bell.
- Direct: The master said to the servant, “Fetch me a glass of water.” Indirect: The master ordered the servant to fetch him a glass of water.
- Direct: I said to him, “Please bring me a glass of water.” Indirect: I requested him to bring me a glass of water.
- Direct: I said to my friend, “Please lend me your book.” Indirect: I requested my friend to lend me his book.
9. Sentences with ‘Let’.
- ‘Let’ is used in various meanings.
(i) ‘Let’ is used to make a proposal.
- First change the reporting verb into ‘proposed’ or ‘suggested’.
- Use ‘should’ instead of ‘let’. Example: Direct: He said to me, “Let us go home.” Indirect: He suggested to me that we should go home.
(ii) ‘Let’ is used as ‘to allow’.
- In Indirect Speech, we change the reporting verb to ‘requested’ or ‘ordered’.
- We start Reported Speech with ‘to’. Direct: Ram said to Mohan, “Let him do it.” Indirect: Ram ordered Mohan to let him do that. Or Ram told Mohan that he might be allowed to do that.
10. Sentences with Question Tags (i) In the indirect speech the question-tag is usually left. (ii) In indirect speech these words are removed and the word ‘respectfully’ is used in the reporting clause. Direct: Mahesh said, “Sir, may I go home?” Indirect: Mahesh respectfully asked his sir if he might go home.
11. Sentences with ‘Yes’ or ‘No’ Direct : He said, “Can you dance?” And I said, “No.” Indirect: He asked me if I could dance and I replied that I couldn’t. Direct : My mother said, “Will you come home on time?” And I said, “Yes.” Indirect: My mother asked me if I would come home on time and I replied that I would.
Note : ‘Yes’ of ‘No’ hides a complete sentence. Therefore, change yes/no into a short answer.
Direct : She said to me, “You didn’t break the window, did you?” Indirect: She asked me if/whether I had broken the window. Direct : He said to Geeta, “You are going to the station, aren’t you?” Indirect: He asked Geeta if/ whether she was going to the station.
12. Sentences with ‘have to’ or ‘had to’ (i) Change ‘have to’ according to the rules. (ii) But change ‘had to’ into ‘had had to’ in the indirect speech. Direct : Hari said, “I have to work a lot.” Indirect: Hari said that he had to work a lot. Direct : Hari said, “I had to work a lot.” Indirect: Hari said that he had had to work a lot.
13. Sentences with ‘Sir’, ‘Madam’ or ‘Your Honour’ etc.
- Generally such words are used to show respect to the person concerned.
You can master in English Grammar of various classes by our articles like Tenses, Clauses, Prepositions, Story writing, Unseen Passage, Notice Writing etc.
14. Exclamations and Wishes Sometimes Exclamatory sentences contain exclamations like Hurrah!, Alas!, Oh!, Heavens!, Bravo, etc. Such exclamatory words are removed in the indirect speech and we use ‘exclaimed with sorrow’, exclaimed with joy, exclaimed with surprise, etc. instead of ‘said’. Examples:
- Direct : Rohan said, “Hurrah! We won the match.” Indirect: Rohan exclaimed with joy that they had won the match.
- Direct : Reema said, “Alas! Karina’s mother is suffering from cancer.” Indirect: Reema exclaimed with sorrow that Karina’s mother was suffering from cancer.
- Direct : The captain said to Kapil, “Bravo! You scored 89 runs.” Indirect: The captain exclaimed with praise that he (Kapil) had scored 89 runs.
(a) Look at these sentences.
- Direct : My mother said, “May God bless you!” Indirect: My mother prayed to God for my well being.
- Direct : She said, “May God save the country!” Indirect: She prayed to God to save the country.
- Direct : They said to the king, “Long live!” Indirect: They blessed the king for his long life.
(b) Look at these sentences.
- Direct : Mohan said, “What a pity!” Indirect: Mohan exclaimed that it was a great pity.
- Direct : I said, “How stupid he is!” Indirect: I exclaimed that it was a very stupid of him.
- Direct : “What a terrible sight it is!” said the traveller. Indirect: The traveller exclaimed that it was a very terrible sight. All the sentences in inverted commas are exclamatory sentences.
(i) Use ‘exclaimed’ in place of ‘said’ in the reporting verb in the indirect speech. (ii) In Indirect sentences, we use exclamatory sentences as statements. (iii) Indirect speech begins with that and full stop (•) is used instead of the exclamation mark (!). Exercise (Solved)
Change the following sentences into Indirect Speech:
(i) He said, “I will do it now.” Answer: He said that he would do it then.
(ii) He says, “Honesty is the best policy.” Answer: He says that honesty is the best policy.
(iii) Ramesh says, “I have written a letter.” Answer: Ramesh says that he has written a letter.
(iv) She said, “Mahesh will be reading a book.” Answer: She said that Mahesh would be reading a book.
(v) She said, “Where is your father?” Answer: She inquired where his father was.
(vi) He said to me, “Please take your book.” Answer: He requested me to take my book.
(vii) The Principal said to the peon, “Let this boy go out.” Answer: The Principal ordered the peon to let that boy go out.
(viii) He said to me, “May you live long!” Answer: He prayed that I might live long.
(ix) She said, “Goodbye friends!” Answer: She bade goodbye to her friends.
(ix) The student said, “Alas! I wasted my time last year.” Answer: The student regretted that he had wasted his time the previous year. Exercise (Unsolved)
- The captain said, “Bravo! well done, my boys.”
- He said to her, “Why do you read this book?”
- He said to her, “Does your cow not kick?”
- He said to his brother, “Shailesh has broken my glass.”
- Our teacher said, “The earth revolves around the sun.”
- He said to me, “Why have you come here?”
- Usha said, “Father, you are very kind to me.”
- The teacher said to the boys, “Do not make a noise.”
- He said to his friend, “May you prosper in business!”
- The officer said to the peon, “Let the visitor come into my office.”
When we want to tell somebody else what another person said, we can use either direct speech and reported speech. When we use direct speech, we use the same words but use quotation marks, For example: Scott said, “I am coming to work. I will be late because there is a lot of traffic now.”
When we use reported speech, we usually change the verbs, specific times, and pronouns. For example: Scott said that he was coming to work. He said that he would be late because there was a lot of traffic at that time.
Reported Speech Exercises for Class 10 CBSE With Answers
This grammar section explains English Grammar in a clear and simple way. There are example sentences to show how the language is used. NCERT Solutions for Class 10 English will help you to write better answers in your Class 10 exams. Because the Solutions are solved by subject matter experts.
Rules for Reported Speech While changing direct speech into reported speech or vice-versa the following changes occur:
1. Changes In Reporting Verb Affirmative sentences: said, told (object), asserted, replied, assured, informed, responded, whispered, alleged, believed, assumed, thought Interrogative sentences: asked, enquired, wanted to know Imperative sentences: ordered, begged, pleaded, implored, advised, demanded
2. Change Of Pronouns Direct Speech: Johnny said, ‘I am playing.’ Indirect Speech: Johnny said that he was playing. First-person generally changes to third person {depending upon the subject of the reporting verb).
3. Change Of Tenses
In general, present tense becomes past tense; past tense and present perfect become past perfect.
4. Change of situations Example: Nagesh said, ‘I read this book last week. (direct speech) Nagesh said that he had read that book the previous week, (indirect speech)
- ‘this’ becomes ‘that’
- ‘last week’ becomes ‘the previous week’
- here – there
- today – that day
- yesterday – the day before/the previous day
- tomorrow – the next day/the coming day
- last week – the week before/the previous week
- next month – the next month/the coming month
5. In case of questions and answers Examples:
- Nagesh asked, ‘Have you read this book?’ (direct speech)
- Nagesh asked if’ whether I had read that book, (indirect speech)
- Nagesh asked, ‘Where is the book?’ (direct speech)
- Nagesh asked where the book was. (indirect speech)
(a) For yes/no questions – use if/whether (b) For wh- questions – use the wh-word
Word Order:
- Nagesh asked, ‘What’s the matter?’
- Nagesh asked what the matter was. (what + the matter + was)
- Nagesh asked what was the matter, (what + was + the matter)
- The word order can be either:
- who/which/what + complement + be or ‘
- who/which/what + be + complement
6. Reported Speech using present and future tenses Examples:
- Nagesh said, ‘The sun rises in the east.’ (direct speech)
- Nagesh said that the sun rises in the east, (indirect speech)
- Nagesh said, ‘I will read this book.’ (direct speech)
- Nagesh said that he will read that book, (indirect speech)
- If the original speaker’s present and future is still present and future, the tense remains unchanged.
7. In case of modal verbs can becomes could
- will – would
- shall – should
- may – might
would, should, could, might, ought to and must are unchanged. Example:
- Nagesh said, ‘I can solve this sum.’ (direct speech)
- Nagesh said that he could solve that sum. (indirect speech)
Reported Speech Solved Examples Exercises for Class 10 CBSE
Read the dialogue given below and then complete the passage that follows.
Question 1. Read the dialogue and complete the passage given below.
Interviewer: So, why do you want to be a computer programmer? Ravi: Well, I have always been interested in computers. Interviewer: I see. Do you have any experience? Ravi: No, but I’m a fast learner. Interviewer: What kind of a computer do you use? Ravi: Computer? Uhm, let me see. I can use a Mac. I also used Windows 10 once. Interviewer: That’s good.
Ravi recently attended an interview for the selection of a computer programmer. At the interview, he was asked (a) ……………………….. To this question he replied that he wanted to change his job because (b) ……………………….. When the interviewer asked him (e) ………………………. he replied that he (d) ……………………….. Finally, the interviewer wanted to know (e) ………………………. . Ravi replied that he could use a Mac and had also used Windows 10 once in the,.past. The interviewer seemed to be pleased with his answers. Answer: (a) why he wanted to be a computer programmer (b) he had always been interested in computers (c) whether he had any experience (d) didn’t but that he was a fast learner (e) the kind of computer he used
Question 2. Manu: Where are you going to? Annu: I am going to the market. Do you want anything?
Manu asked Annu (a) …………………… Annu replied (b) …………………… Annu replied (b) …………………… and she further asked (C) …………………… Answer: (a) where she was going. (b) that she was going to the market (c) if/whether she wanted anything.
Question 3. Sunita: Tomorrow is your birthday, what do you want as a gift? Neetu: That is a lovely thought but I don’t want anything.
Sunita asked Neetu since the next day was her birthday, (a) …………………… Neetu replied that (b) …………………… but (C) ………………….. . Answer: (a) what she wanted as a gift (b) that was a lovely thought (c) she did not want anything.
Question 4. Gardener: Did you water the plant today? Dev: No, but I will, today. Gardener: Then tomorrow I will get a sapling of sunflower.
The Gardener asked Dev (a) …………………… Dev replied negatively but (b) …………………… Then the gardener said that (c) ………………….. . Answer: (a) if/whether he had watered the plant that day. (b) said he would that day. (c) he would get a sapling of a sunflower the next day.
Question 5. Mr. Harish: Can you polish my shoes? Cobbler: Yes sir. But I will take 10 for each shoe.
Mr. Harish: I will not mind as long as it is done. Mr. Harish asked the cobbler (a) …………………… The cobbler replied affirmatively but (b) …………………… Mr. Harish said that (C) ……………………. Answer: (a) if/whether he could polish his shoes. (b) said that he would take 10 for each shoe (c) he would not mind as long as it was done.
Question 6. Electrician: When did your electricity go? Mohan: It is not working since evening. Electrician: Sorry sir, in this case, I will have to check the fuse now.
The electrician asked Mohan (a) …………………… Mohan replied that (b) …………………… The electrician apologetically said that in that case (c) …………………… Answer: (a) when his electricity had gone. (b) it was not working since evening. (c) he would have to check the fuse then.
Question 7. Teacher : Children, let us all pledge to save trees. Children : Yes, mam, we all pledge to save our trees as the trees are the lungs of the city. Teacher : Let us start today by planting a sapling.
The teacher asked all the children to pledge to save trees. The children replied affirmatively (a) …………………… as the (b) …………………… Then the teacher said that (c) ………………….. . Answer: (a) saying that they all pledged to save trees (b) trees are the lungs of the city. (c) they should start by planting a sapling that day.
Question 8. Buddha : Honesty is the best policy. Disciple : Does honesty always pay? Buddha : It may or may not, but at least you will never feel guilty.
Buddha in his preaching said that (a) …………………… the best policy. A disciple asked him if (b) …………………… always pays, Buddha replied (c) …………………… but at least he would never feel guilty. Answer: (a) Honesty is (b) honesty (c) that it might or might not
Question 9. Doctor : You should take this medicine every day. Patient : Should I take it before dinner or after dinner? Doctor : No, you should take it after breakfast.
The Doctor advised the patient that (a) …………………… The patient further asked (b) …………………… The doctor replied negatively and then said (c) ………………….. . Answer: (a) he should take that medicine every day. (b) if/whether he should take it before dinner or after dinner. (c) that he should take it after breakfast
Question 10. Reena : Do you know how to swim? Surbhi : Yes I know. I have learnt it during this summer vacation.
Reena asked Surbhi (a) …………………… Then Surbhi replied (b) …………………… and also added that (c) ………………….. . Answer: (a) if/whether she knew how to swim (b) in affirmative (c) she had learnt it during the summer vacation.
- English Grammar
- Grammar Exercises
- Reported Speech Exercises For Class 10
Reported Speech Exercises with Answers for Class 10
One of the English grammar concepts that almost all of us would have studied in our junior classes is reported speech . Having a clear understanding of reported speech helps students use sentences correctly. This article provides reported speech exercises for class 10 students.

Reported Speech Exercises for Class 10 with Answers
Here is an exercise on the transformation of direct speech to indirect speech. Go through the following sentences, work them out and then check your answers to assess how far you have understood their usage.
Change as directed
Read the following sentences and change them into reported speech.
- Mimi said, “I have been writing this letter.”
- I said, “Sam’s driving the car.”
- My uncle said, “I am cooking lunch.”
- My brother said, “I had already eaten.”
- The old lady said to the girl, “Where do you come from?”
- Jon said, “I like to play rugby.”
- My mother said, “I get up early every morning.”
- The maths teacher said, “Three divided by three is one.”
- Mohit said, “Switzerland is a very beautiful country.”
- Ruben said, “It is very cold outside.”
- The teacher said, “The French Revolution took place in 1789.”
- Uma said, “I saw a Royal Bengal Tiger in the zoo.”
- Luke said, “I can do this homework.”
- Aswini said to her mother, “I have passed the test”.
- Daphne said to Antony, “I will go to London tomorrow.”
- The boy said, “My father is sleeping.”
- The traffic police said to us, “Where are you going?”
- The man shouted, “Let me go.”
- Shivina said, “Alas! I am lost.”
- “I know her contact number,” said Helena.
- Stefen said, “My granny is making pasta.”
- Raj said to Simran, “Have you ever been to the National Museum?”
- Anish said to Sid, “Please lend me the book.”
- The teacher said to the parents, “Shelly is working very hard.”
- Joshua said, “I have completed my assignment.”
- I said to Alka, “How long will you stay here?”
- The child told his dad, “I want an ice cream.”
- Meera said, “I am not feeling well.”
- The teacher said to Vivek, “Draw the diagram of the plant’s parts.”
- Irin said, “I am playing the piano.”
- My mother said to me, “Help me carry this bag.”
- Rahul said, “My sister is very helpful.”
- The news reporter said, “The flight will be delayed by a few hours due to heavy rains.”
- Urmi said to her mother, “I want a slice of pizza.”
- I said to Daniel, “Are you reading this book?”
- Mimi said that she had been writing that letter.
- I said that Sam was driving the car.
- My uncle said that he was cooking lunch.
- My brother said that he had already eaten.
- The old lady asked the girl where she came from.
- Jon said that he likes to play rugby.
- My mother said that she gets up early every morning.
- The maths teacher said that three divided by three is one.
- Mohit said that Switzerland was a very beautiful country.
- Ruben said that it was very cold outside.
- The teacher said that the French Revolution took place in 1789.
- Uma said that she saw a Royal Bengal Tiger in the zoo.
- Luke said that he could do that homework.
- Aswini told her mother that she had passed the test.
- Daphne informed Antony that she would go to London the next day.
- The boy said that his father was sleeping.
- The traffic police asked us where we were going.
- The man shouted to them to let him go.
- Shivina exclaimed sadly that she was lost.
- Helena said that she knew her contact number.
- Stefen said that his granny was making pasta.
- Raj asked Simran if she had ever been to the National Museum.
- Anish requested Sid to lend him the book.
- The teacher told the parents that Shelly was working very hard.
- Joshua said that he had completed his assignment.
- I asked Alka how long she would stay there.
- The child told his dad that he wants an ice cream.
- Meera said that she was not feeling well.
- The teacher instructed Vivek to draw the diagram of the plant’s parts.
- Irin said that she was playing the piano.
- My mother asked me to help her carry the bag.
- Rahul said that his sister was very helpful.
- The news reporter said that the flight would be delayed by a few hours due to heavy rains.
- Urmi said to her mother that she wanted a slice of pizza.
- I asked Daniel if he was reading that book.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is direct narration.
When the actual words/sentences spoken by the speaker are quoted in a speech, it is known as direct speech/narration.
Is knowing reported speech necessary for Class 10?
Having a basic understanding of reported speech is necessary for students of any class or age. Solving exercises on direct and indirect speech will help them understand thoroughly and use them correctly.
What is indirect speech?
When the quoted speech is reported in the form of a narrative without changing the meaning of the actual quotation/words by the speaker, it is called indirect speech. Indirect speech is also known as reported speech.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.
Reported Speech
Perfect english grammar.

Reported Statements
Here's how it works:
We use a 'reporting verb' like 'say' or 'tell'. ( Click here for more about using 'say' and 'tell' .) If this verb is in the present tense, it's easy. We just put 'she says' and then the sentence:
- Direct speech: I like ice cream.
- Reported speech: She says (that) she likes ice cream.
We don't need to change the tense, though probably we do need to change the 'person' from 'I' to 'she', for example. We also may need to change words like 'my' and 'your'. (As I'm sure you know, often, we can choose if we want to use 'that' or not in English. I've put it in brackets () to show that it's optional. It's exactly the same if you use 'that' or if you don't use 'that'.)
But , if the reporting verb is in the past tense, then usually we change the tenses in the reported speech:
- Reported speech: She said (that) she liked ice cream.
* doesn't change.
- Direct speech: The sky is blue.
- Reported speech: She said (that) the sky is/was blue.
Click here for a mixed tense exercise about practise reported statements. Click here for a list of all the reported speech exercises.
Reported Questions
So now you have no problem with making reported speech from positive and negative sentences. But how about questions?
- Direct speech: Where do you live?
- Reported speech: She asked me where I lived.
- Direct speech: Where is Julie?
- Reported speech: She asked me where Julie was.
- Direct speech: Do you like chocolate?
- Reported speech: She asked me if I liked chocolate.
Click here to practise reported 'wh' questions. Click here to practise reported 'yes / no' questions. Reported Requests
There's more! What if someone asks you to do something (in a polite way)? For example:
- Direct speech: Close the window, please
- Or: Could you close the window please?
- Or: Would you mind closing the window please?
- Reported speech: She asked me to close the window.
- Direct speech: Please don't be late.
- Reported speech: She asked us not to be late.
Reported Orders
- Direct speech: Sit down!
- Reported speech: She told me to sit down.
- Click here for an exercise to practise reported requests and orders.
- Click here for an exercise about using 'say' and 'tell'.
- Click here for a list of all the reported speech exercises.

Hello! I'm Seonaid! I'm here to help you understand grammar and speak correct, fluent English.


Reported Speech: Rules, Examples, Exceptions

👉 Quiz 1 / Quiz 2
Advanced Grammar Course
What is reported speech?
“Reported speech” is when we talk about what somebody else said – for example:
- Direct Speech: “I’ve been to London three times.”
- Reported Speech: She said she’d been to London three times.
There are a lot of tricky little details to remember, but don’t worry, I’ll explain them and we’ll see lots of examples. The lesson will have three parts – we’ll start by looking at statements in reported speech, and then we’ll learn about some exceptions to the rules, and finally we’ll cover reported questions, requests, and commands.

So much of English grammar – like this topic, reported speech – can be confusing, hard to understand, and even harder to use correctly. I can help you learn grammar easily and use it confidently inside my Advanced English Grammar Course.
In this course, I will make even the most difficult parts of English grammar clear to you – and there are lots of opportunities for you to practice!

Backshift of Verb Tenses in Reported Speech
When we use reported speech, we often change the verb tense backwards in time. This can be called “backshift.”
Here are some examples in different verb tenses:
Reported Speech (Part 1) Quiz
Exceptions to backshift in reported speech.
Now that you know some of the reported speech rules about backshift, let’s learn some exceptions.
There are two situations in which we do NOT need to change the verb tense.
No backshift needed when the situation is still true
For example, if someone says “I have three children” (direct speech) then we would say “He said he has three children” because the situation continues to be true.
If I tell you “I live in the United States” (direct speech) then you could tell someone else “She said she lives in the United States” (that’s reported speech) because it is still true.
When the situation is still true, then we don’t need to backshift the verb.

But when the situation is NOT still true, then we DO need to backshift the verb.
Imagine your friend says, “I have a headache.”
- If you immediately go and talk to another friend, you could say, “She said she has a headache,” because the situation is still true
- If you’re talking about that conversation a month after it happened, then you would say, “She said she had a headache,” because it’s no longer true.
No backshift needed when the situation is still in the future
We also don’t need to backshift to the verb when somebody said something about the future, and the event is still in the future.
Here’s an example:
- On Monday, my friend said, “I ‘ll call you on Friday .”
- “She said she ‘ll call me on Friday”, because Friday is still in the future from now.
- It is also possible to say, “She said she ‘d (she would) call me on Friday.”
- Both of them are correct, so the backshift in this case is optional.
Let’s look at a different situation:
- On Monday, my friend said, “I ‘ll call you on Tuesday .”
- “She said she ‘d call me on Tuesday.” I must backshift because the event is NOT still in the future.

Review: Reported Speech, Backshift, & Exceptions
Quick review:
- Normally in reported speech we backshift the verb, we put it in a verb tense that’s a little bit further in the past.
- when the situation is still true
- when the situation is still in the future
Reported Requests, Orders, and Questions
Those were the rules for reported statements, just regular sentences.
What about reported speech for questions, requests, and orders?
For reported requests, we use “asked (someone) to do something”:
- “Please make a copy of this report.” (direct speech)
- She asked me to make a copy of the report. (reported speech)
For reported orders, we use “told (someone) to do something:”
- “Go to the bank.” (direct speech)
- “He told me to go to the bank.” (reported speech)
The main verb stays in the infinitive with “to”:
- She asked me to make a copy of the report. She asked me make a copy of the report.
- He told me to go to the bank. He told me go to the bank.
For yes/no questions, we use “asked if” and “wanted to know if” in reported speech.
- “Are you coming to the party?” (direct)
- He asked if I was coming to the party. (reported)
- “Did you turn off the TV?” (direct)
- She wanted to know if I had turned off the TV.” (reported)
The main verb changes and back shifts according to the rules and exceptions we learned earlier.
Notice that we don’t use do/does/did in the reported question:
- She wanted to know did I turn off the TV.
- She wanted to know if I had turned off the TV.
For other questions that are not yes/no questions, we use asked/wanted to know (without “if”):
- “When was the company founded?” (direct)
- She asked when the company was founded.” (reported)
- “What kind of car do you drive?” (direct)
- He wanted to know what kind of car I drive. (reported)
Again, notice that we don’t use do/does/did in reported questions:
- “Where does he work?”
- She wanted to know where does he work.
- She wanted to know where he works.
Also, in questions with the verb “to be,” the word order changes in the reported question:
- “Where were you born?” ([to be] + subject)
- He asked where I was born. (subject + [to be])
- He asked where was I born.

Reported Speech (Part 2) Quiz
Learn more about reported speech:
- Reported speech: Perfect English Grammar
- Reported speech: BJYU’s
If you want to take your English grammar to the next level, then my Advanced English Grammar Course is for you! It will help you master the details of the English language, with clear explanations of essential grammar topics, and lots of practice. I hope to see you inside!
I’ve got one last little exercise for you, and that is to write sentences using reported speech. Think about a conversation you’ve had in the past, and write about it – let’s see you put this into practice right away.
Master the details of English grammar:

You might also like...

British vs. American English Spelling

100 Superlatives: List & Examples

24 Examples of Adjective + Preposition Combinations

Hi, I’m Shayna. I create courses helping English as a Second Language learners become more fluent in just a few minutes a day – so they can speak English naturally and confidently in work and daily life.

Reported Speech
- Home
- NCERT Options
- 10th Class
- English Grammar
- cbse-ncert-10th-class-Chapter-13-Reported-Speech
Chapters
- cbse-ncert-10th-class-Chapter-1-Determiners
- cbse-ncert-10th-class-Chapter-2-Tenses
- cbse-ncert-10th-class-Chapter-3-Subject-Verb
- cbse-ncert-10th-class-Chapter-4-Non-Finites-Infinitives
- cbse-ncert-10th-class-Chapter-6-Connectors
- cbse-ncert-10th-class-Chapter-7-Conditionals
- cbse-ncert-10th-class-Chapter-8-Comparison
- cbse-ncert-10th-class-Chapter-9-Avoiding-Repetition
- cbse-ncert-10th-class-Chapter-10-Nominalisation
- cbse-ncert-10th-class-Chapter-11-Modals-Expressing-Attitudes
- cbse-ncert-10th-class-Chapter-12-Active-and-Passive
Share
- Text Book Solutions
Important Question
Question Papers / Notes Download
CBSE Class 10 English Workbook Solutions Unit 13 Reported Speech
Questiona.1. read and enjoy the following article.
The Road to English (Adapted from an article by Arishban Bagchi (Hindu college) [The Hindustan Times, 4 October 1996]
- The great question, after you have failed to put yourself in an engineering or medical college in contemporary Indian society, is whether youll ever find a job
- "Oh ! He showed such promise during his early days," says the sister of the neighbour of your aunt in Timbuctoo. "Now look at my Bittoo," she goes on. "In spite of being so brilliant and all, he could only barely manage a grade A+ at MIT, and then he only just managed a well-paid job. How difficult getting jobs must be."
- The next line reads, "I wonder how your son will find a job, being a non-engineer, and that too in India."
- Your fathers friend, a prosperous doctor, decides to come visiting. Quite predictably, his first question on seeing you is the inevitable, "Why in heavens name did you not qualify in the pre-medical test ? Followed by the equally inevitable, "Now what are you going to do
- He raves on about his nephew who has just gone to the UK for his FRCS, and his daughter who has just completed her MBBS from AIIMS with top results, and what exciting prospects they have
- Your father into whose eyes you havent dared to look for quite some time, speaks up. "I have lost all hope for him. However, educating him is my duty and I wont shirk from it."
- Someone speaks up. "Let him go to college to study Physics or Chemistry." Everyone sits in silence. You cannot help feeling a little proud. At length, someone plucks up the courage: "Its quite impossible to educate him any further. Youngsters these days never seem to listen to what we have to say."
- "I will study English Literature," you say, dropping a bombshell, fearless of the consequences. Amazingly, it works. The crowd hurries to disperse. You are so relieved to see their backs that you dont care. Thankfully, your parents voice no objection, remembering, perhaps, that you did manage to score highly in English in your Board exams
- So you finally take English literature as your subject of study
QuestionA. 2. Work in pairs and list the speakers in the passage you have just read?
- The author (Arishban Bagchi)
- Bittoos mother
- Bittoos father
- Still working in pairs, answer the following
- Is "Now look at my Bittoo", said by the same person as the extract in 1 above ? (Yes/No) How do you know
- In paragraph 4, who says "Now what are you going to do ?" What words help you to know
- ln paragraph 5, who is the speaker ? ____________ Discues and work out what must have been his exact words. Then write them below. (To be discussed as desired)
- Underline the verb which tells you how the person must have said this. [Hint: Try to work out the meaning of this verb.]
- How many of the nine paragraphs in the passage are reporting what someone has said
- How many paragraphs include the exact words of the various speakers (direct speech)
- How many paragraphs have reported themindirectly (indirect speech)
- What is your conclusion about how writers report what someone says or has said in a newspaper article such as this
- Yes . It has been put ininverted commas
- Yes .she goes on indicates it
- Fathers friend, a prosperous doctor. "Look at my nephew who has just gone to the UK for his FRCS, and my daughter who has just completed her MBBS from AIIMS with top results. What exciting results they have !"
- The verb to be underlined is -raves Meaning = talks furiously and wildly
- In a newspaper article, the writers report some very important words in direct speech ie, as they are spoken. They report some in indirect speech adding the words from their own side to exactly report the underlining emotions, feelings, moods or manners
B. Reporting Verbs
Questionb. 1. a reporting verb is used in both direct and indirect (reported) speech. the reporting verb usually adds to the meaning of each sentence for instance, it may show the speakers mood (e.g. agreed), purpose (e.g. asked), manner of speaker (e.g. shouted). an example is : the tourist complained that the hotel was hot and noisy. in this sentence, the reporting wordcomplained shows that the tourist was clearly unhappy about the arrangements. now work in groups of four. read the following sentences carefully, and circle the reporting verbs. then discuss and write the ways in which each reporting verb adds to the meaning of its arrangement.
- "When I was in school, I used to skip a few classes, especially Moral Science because of the bookish manner in which it was treated," confessed the retired IAS Officer
- Sauravs friends protested that he should have been included in the school badminton team, on the basis of his fine performance in the inter-house matches
- "Make a circle, make a circle !" Mira shouted, firmly pulling and pushing the children till a kind of vague circle was formed
- The music teacher warned the children against getting carried away and getting out of tune
- "Father, you must tell me what you meant exactly when you said that I was the same as every other teenager," Varun insisted
- "Oh God ! She is coming again," the children whispered to each other, when they saw Mrs Sharma striding towards their classroom for the third time that day
- Confessed to be circled is the reporting verb used in the sentence. It reveals the mood of the speaker as he admits his weakness of skipping the class which was contrary to rules
- protested is to be circled in the reporting verb used in the sentence. The verb shows Sauravs friends mood
- shouted is to be circled in the reporting verb in the sentence. Shouted shows Miras mood ie, irritable manner
- warned is to be circled in the reporting verb in the sentence
- insisted is to be circled in the reporting verb in the sentence
- whispered is to be circled in the reporting verb in the sentence. This verb shows childrens tone and manner i.e. afraid and disliking
QuestionB. 2. The exact words of the Prime Minister : "I shall lead this great country on the path of peace and prosperity. Not only that, but I assure you that I will lower taxes and do everything in my power to reduce inflation." [Situation : A newsreader reports the words of the Prime Minister on the radio.] "The new prime Minister said that he would lead the country on the path of peace and prosperity. He also promised to lower taxes and reduce inflation." Working in pairs, note the changes the newsreader made while reporting the PMs speech?
Now do the same with this situation. The following is a conversation that took place between Neeta and Shobhna (in the presence of Shohhnas mother) last week

Answer: Situation. Mrs Bhattacharya reports this to her husband. Now report Mrs Bhattacharyas words. Remember : You can decide whether to use direct or indirect speech forms
Answer: When two boys were making a loud noise, (Mrs Bhattacharya) I asked them where they lived. I advised them not to make such a noise. Then I warned them to be careful as if they did it again, I would have to complain to the police. Work with your partner. Read the following. Decide on a likely situation in which what was said has been repeated. Then use your imagination and recreate the original ("direct") speech. Everyone at the hospital looked after me very well. As soon as I arrived, a nurse asked me how I felt. Then she asked me where I lived and whether she could contact my parents. I explained that you were out today, so she couldnt contact you. After that she asked me how that accident had happened and I said I didnt know
Answer: Situation. A boy telling his parents about an accident he had met that day, and how he was treated in the hospital. Direct speech (in dialogue form)
- Nurse : How do you feel
- Boy : i am feeling nervous
- Nurse : Where do you live ? Can I contact your parents
- Boy : i live in Model Town. You cant contact my parents because they are out today
- Nurse : Do you know how this accident happened
- Boy : i dont know anything about it
C. Practising Reported Speech
Questionc.1. statements : rewrite the following in reported speech .
- Sheela to Rashmi: "You can come and stay at my place if youre ever in Delhi"
- Anand to Renu : "I dont know what Gayathri is doing these days. She hasnt visited us for ages"
- Teacher to Students : "We shall go on a field trip to study water pollution"
- Sheela told Rashmi that she could come and stay at her place if she was ever in Delhi
- Anand told Renu that he didnt know what Gayathri was doing those days as she had not visited them for ages
- The teacher informed the students that they would go on a field trip to study water pollution
QuestionC.2. Questions in indirect speech?
- He said, "Who has moved into the neighbouring house
- He said, "What have you bought for Deepawali
- He said to me, "Why didnt you wear your new dress for the party
- "Is anyone there ?" he asked
- "Shall I wait for the doctor or come again tomorrow ?" she asked the receptionist
- He asked who had moved into the neighbouring house
- He asked her what she had bought for Deepawali
- He asked me why I had not worn my new dress for the party
- He enquired if anyone was there
- She asked the receptionist if she would wait for the doctor or come again the following day
Points to Remember
- If the direct question begins with a question word (when, where, who, how, why, what etc), the question word is repeated
- Tenses, pronouns, possessive adjectives and adverbs of time and place change as in statements
- The interrogative form of the verb changes to the affirmative form. The question mark (?) is therefore replaced by a full stop
- He said, "Where does she live
- He asked where she lived.
- If the introductory verb issay, it must be changed to a verb of inquiry, e.g. ask, inquire, wonder, want to know etc
- If the direct question does not have a question word,if orwhether must be used.
QuestionC.3. Commands, requests and advice in indirect speech : Rewrite the following in indirect speech ?
- The General said," Move the tanks to the battlefield immediately."
- "Dont drive too fast", the instructor said to me
- "If I were you, Id buy that property immediately", the agent said to Anwar
- "Why dont you change into something more comfortable ?" he said to his guest
- "Go on, taste it", said the cook to the guest
- You will notice that direct commands, requests and advice are usually expressed by a suitable reporting verb in indirect speech (Refer Section B)
- The General ordered to move the tanks to the battlefield immediately
- The instructor warned me not to drive too fast
- The agent told Anwar that if he were him, he would buy that property immediately
- He asked his guest why he didnt change into something more comfortable
- The cook urged the guest to taste it (the dish)
QuestionC.4. Lets, let him etc?
- He said, "Lets have our lunch before starting the journey". He suggested that they should have their lunch before starting the journey
QuestionC.6. Change the following into indirect speech. Change tense and time expressions only when necessary. You may use a variety of reporting verbs from the box below?

- "Human nature changes," sighed the old man
- "Well win the match next week." said Vasu optimistically, (reporting just after he said it)
- "I saw him with Akanksha yesterday," she whispered
- "Sanjay, Im sorry we didnt visit you in Bombay (now Mumbai) last week," Arun said (reporting immediately after he said it)
- "This rice tastes awful," he muttered
- "Would you like to come to the party with us tomorrow, Gopa ?" Sushila asked, (reporting later in the week.)
- "Please, Ma, please," they begged. "Well play on the veranda and porch. We wont take a step off the veranda." (reporting immediately after)
- "Dont be a fool," Raghu said roughly, pushing him aside. Even Mira said, "Stop howling, Ravi. If you want to play, you can stand at the end of the line," and she put him there very firmly. (reporting immediately after)
- The old man exclaimed that human nature changes
- Vasu assured that they would win the match next week
- She confided that she had seen him with Akanksha the previous day or the day before
- Arun apologised to Sanjay saying that they hadnt visited him in Bombay last week
- He complained that that rice tasted awful
- Sushila asked Gopa if she would like to go to the party with them the next day
- They pleaded their mother to let them play on the veranda and porch assuring her that they wont take a step off the veranda
- Pushing him aside, Raghu warned Ravi not to be a fool. Even Mira scolded him to stop howling and putting him there very firmly she advised him to stand at the end of the line if he wanted to play
QuestionC.7. Correct the errors in the following sentences. Write out the correct sentence in the space provided?
- The nurse enquired how I am
- He said he live in Connaught Circus
- They asked when I have arrived
- The taxi driver asked where I want to go
- I warn Sanjay to be careful while crossing the road
- Rohit couldnt understand where all the children are gone
- The nurse enquired how I was.
- He said that he lived at Connaught (Place) Circus
- They asked when I had arrived.
- The taxi driver asked where I wanted to go.
- I warned Sanjay to be careful while crossing the road
- Rohit couldnt understand where all the children were gone
QuestionC.8. You said that .... Look at the horoscope page from a newspaper. Find your zodiac sign. Imagine that you have come to the end of the week and nothing has happened, according to the horoscope. Write a letter of complaint to Madam Kiran. Report what Madam Kiran said would happen and then describe what actually happened. You may wish to write something similar to the letter in the example below. Dear Madam Kiran, I am writing to complain about your horoscope prediction for Virgo last week. Firstly, you said that my relationships would be successful. In fact I had terrible squabbles with my mother and with no fewer than three different friends. You assured me that there would be a new admirer in my life who would make me feel confident about my future. Well, I have a new admirer but he is making my life a misery for me ...?
Answer: I requested for his help in a friendly manner. But, he took it otherwise. This has added to my worry. Now I am in a fix what to do. Secondly, you said that I would enjoy a new closeness or affinity with my husband. But he is still his old self. He is still indifferent and detached. I saw some silver lining in your prediction. But alas ! this has proved all wrong. Thirdly, your prediction about the money matters proved totally wrong. On the contrary, I have been given an increment in my salary. Also, my husband has been promoted with a big raise in his salary. I regret that your horoscope predictions for Virgo proved wrong in my case. Yours Pragya Verma

D. Reported Speech - Summary
Questiond.1. read the following extract from oliver twist, a novel by charles dickens. "where is my little brother " cried nancy, when she reached the police station. "there are no little boys here, madam," answered an officer. "where is he, then " she persisted, and began describing what oliver looked like the officer informed her that he had been driven to the home of a gentleman in pentonville. when fagin heard the news, he exploded, "the boy must be found, even if we have to kidnap him.".
- Working in pairs, note down the reporting verbs used in the above passage. Then
- describe in a few words the mood or purpose of the speakers
Reporting Verbs
Mood/purpose/manner.
- worried, anxious, upset
- polite, responsible
- curious, emphatic, demanding
- anxious, demanding
- conscious of duty, responsible
- angry, emphatic, worried, restless
QuestionD.2. Below are some common remarks made by youngsters, their parents and guardians. They show the differences of opinions on modern music and film between the three groups. First read them carefully On the basis of the above comments, write an article for your school magazine, entitled : "Yesterday, Today and Tomorrow. " Here are some tips?
- Make your article interesting and readable by reporting the feeling in the above speech bubbles
- Use bothdirect andindirect ways of reporting
- Use a variety of reporting verbs to suit the mood, purpose, and manner of the speakers above. You may wish to use some of the reporting verbs listed below
- You may like to read the article "The Road to English" (A1) again, for some ideas
Answers: Yesterday, Today and Tomorrow (By: Prerna XA) Modern music and films have undergone a drastic change for the last two decades. New electronic instruments have brought a sea-change in rhyme, rhythm and pitch in the songs. But my fathers friend has declared that it is not music. It is simply an ear¬splitting noise which almost maddens a man. My father said, "It is no music at all" because of fast beats. I tried to assert that it was lively. I asked if they could imagine a party with the sort of music that they had about 20 years ago. And films, the elderly people dont like modern films. My aunt protested, "The films today are so cheap that no one can see them with ones family." At this my friend contended, "The actors and actresses today are so natural." Another friend of mine added that he couldnt stand the theatrical andsing-song way in which actors delivered their lines in old films. Modern day films are more and convincing realistic. Another uncle of mine announced that the films in their time had meaningful stories. The argument came to an end with a concluding remark of my grandfather. He said, "Everyone thinks their time was the best." On the whole, trends change with the changing times.Change is the Law of Nature.
QuestionD. 3. Read the following excerpt from a newspaper report. Tiger numbers up, but habitat a worry New Delhi : Indias tiger population has gone up. On Monday, environment minister Jairam ramesh will announce an increase of over 100 tigers across the country at a three-day international conference of experts on tigers. But can India keep this rising numbers intact ? According to the governments own study on tiger reserves, India cannot hold more than 1000 to 1200 tigers, with its forests having witnessed a degradation in the last two decades. "Where is the habitat to keep so many tigers safe ?" asked Vivek Menon, chief executive officer of the Wildlife Trust of India. "Constant habitat destruction and illegal mining is causing wildlife stress," said Dharmendra Kandhal, a wildlife biologist?
Hindustan times-march 28, 2011.
- Where do you find sentences in direct speech in the above excerpt
- Why has the reporter used the exact words of Mr. Menon and Mr. Kandhal
- Change the sentences in direct speech to indirect speech and then read the excerpt. Does it sound better or worse ? Why
- Sentences in direct speech are in the last para of the text. "Where is the habitat to keep so many tigers safe ?" asked Vivek Menon, chief executive officer of the Wildlife Trust of India
- The reporter has used the exact words of Mr Menon and Mr Kandhal as they are very important words. It is to emphasise their viewpoints
- Vivek Menon, chief executive officer of the Wildlife Trust of India asked where the habitat to keep so many tigers was safe. Dharmendra Kandhal, a wildlife biologist said that constant habitat destruction and illegal mining were causing wildlife stress
- It sounds worse in Indirect speech because the meaning has changed due to past form of verbs
- Saturday-sinking ofprivate mother ship- 400 nautical miles west of Lakshadweep Islands
- 16 pirates captured- 12 Iranian and 4 Pakistani sailors held as hostages rescued- 120 pirates captured in last two months- In earlier three operations 104 pirates captured- facing trial in Mumbai courts
- Saturday operation- began 10 am-naval patrol aircraft spottedMorteza- Iranian traveler used asmother vessel by brigands- offshore patrol vessel INS Suvarna and coast Guard Ship Sangram sent to intercept Morteza- Pirates given warning- ordered to stop- but they fired- Suvarna returned limited fire- disabled Morteza- people seen abandoning ship- according to an official
- Later 16 pirates and 16 sailors picked up from the waters
- All being taken to Mumbai; will be handed over to police for investigation said official. You may write this report in 3-4 paragraphs
Indian navy sinks ship, nabs 16 pirates
Question 1. given below are instructions for opening a bank account. use these to complete the paragraph that follows.
- obtain form from the bank
- fill in the form with all the relevant details
- ask an account-holder to countersign your form
- submit two passport-size photographs
- deposit the minimum amount required
- First a form must be __________ All relevant details
- __________. The form must then
- __________. Two passport- size photographs along with proof of residence
- __________. Finally the minimum amount required
- obtained from the bank
- must be filled in the form
- be countersigned by an account holder
- must be submitted
- must be deposited
Question 2. Given below are a few news headlines. Using information from the same, complete the sentences that follow?
- India Allows Airspace to Pak In the first public move to diffuse tension between the two countries, India _________ through Indian airspace
- Research Work at AIIMS Stalled for Want of Animals More than 50 research projects at the prestigious All India Institute of Medical Sciences _________ to conduct experiments on
- After making Toilets, MCD Looks for Users About 250 toilet complexes constructed by the Municipal Corporation of Delhi with Japanese aid have turned into liabilities as apparently _________
- Selling Kidneys to make a Living Starving Tribals of Idduki district _________ to make a living
- Kidneys Donated without Medical Inspection Most of the kidney donation procedures _________ the required medical examination in Indian hospitals
- has allowed Pak to fly
- have been stalled for want of animals
- MCD is looking for users
- have to sell kidneys/are selling kidneys
- are done without
Question 3. The following passage has not been edited. There is one error in each of the lines. Write the incorrect word and the correction in the space provided?

Question 4. Complete the following paragraph on one of the earlier voyages of Columbus by choosing the correct options?
- Christopher Columbus, __________ born in 1451 AD. Unlike the people of his time,
- __________ In order to prove his belief he said
- __________ three ships. Unfortunately, one of the ships was wrecked. Columbus returned to Spain
- __________ colony
- a skilled sailor and an explorer, was
- was skilled sailor and an explorer
- being a skilled sailor and an explorer was
- a skilled sailor and an explorer is
- but Columbus believed that the Earth was round
- Columbus had believed that the Earth was round
- but Columbus believed that the Earth is round
- Columbus believed that the Earth was round
- if he sails west from Europe
- if he is sailing west of Europe
- if he sailed west from Europe
- if he sailed west to Europe
- with a crew of ninety men on
- having a crew of ninety men in
- with a crew of ninety men having
- going with a crew of ninety men on
- left behind forty men in the island of Hispaniola
- leaving behind forty men on the island of Hispaniola
- has left forty men on the island of Hispaniola
- is leaving forty men on the island of Hispaniola
Question 5. Complete the following passage by choosing the correct options from those given below.?
- Electronic commerce, it seems, still has __________ limits, even in the Silicon Valley. For all the feverish excitement
- __________ the tripling of electronic shopping last holiday season, the total money
- __________ by American consumers online still
- __________ to only about one percent of its total sales-barely a tenth
- __________ the revenues from
- __________ method of distance selling that has been
- __________ for a century; the catalogue. This may be because electronic shopping
- __________ on quite a narrow range of goods, mainly books, toys and music. Worse, there
- __________ many stories of failed and late deliveries. And, more recently, a string of hackers attacks
- __________ temporarily disabled some of the best-known e-commerce websites
- being spent
- concentrated
- is concentrating
- was concentrated
- had concentrated
Question 6. In the passage given below, one word has been omitted in each line. Write the missing word along with the word that comes before and the word that comes after it in your answer sheet against the correct blank number. Ensure that the word that forms your answer is underlined?


Reported Speech: Important Grammar Rules and Examples
Reported speech is a very common aspect of the English language. You use it nearly every day, both in conversations and in writing. This reference covers key sections about reported speech, including what it is, examples, rules, and verb tense changes. You’ll also learn about modal verbs, changes in time and place, and different reporting verbs.
Reported Speech

What Is Reported Speech?
Reported speech is simply when you tell somebody what someone else said. You can do this in your writing, or in speech. Reported speech is very different from direct speech , which is when you show what somebody said in the exact way that they said it . In reported speech though, you do not need to quote somebody directly.
Instead, you use a reporting verb, such as ‘say’ or ‘ask’. These reporting verbs are used to report the speech to someone else. There are many different reporting verbs that can be used.
In short, reported speech is the linguistic technique that you use to tell somebody what someone else’s direct speech was. In reported speech though, you may need to make certain changes to the grammar to make the sentence make sense. Some examples below highlight what needs to be changed.
Reported Speech Examples
When using reported speech, you are usually talking about the past. The verbs, therefore, usually have to be in the past too.
For example :
- Direct speech: I’ve lost my umbrella .
- Reported speech: He said (that) he had lost his umbrella.
Another example :
- Direct speech: She is doing her homework .
- Reported speech: He said (that) she was doing her homework.
Table of Changes :
Reported Speech Rules
Verb tense changes in reported speech.
When the reporting verb is in the present tense, only small changes are needed.
- Direct speech: I like dogs.
- Reported speech: She says she likes dogs.
When the reporting verb is in the past tense, you need to change the tense of both the reporting verb and the main verb.
- Reported speech: She said she liked dogs.
The tenses generally move backward as follows:
For sentences about the future, you also need to change the future verbs.
- Direct speech: I shall leave in a moment.
- Reported speech: She said that she would leave in a moment.
Here are the changes for future tenses:
Modal Verbs and Reported Speech
Modal verbs also change when used in reported speech.
- Direct speech: Will I see you later?
- Reported speech: He asked if he would see me later.
Some modal verbs do not need to change tense because they fit naturally.
- Direct speech: I should go to the park.
- Reported speech: He told me he should go to the park.
Here are both correct and incorrect examples of reported speech for clarity:
- Reported speech: He told me he should go to the park.
- Reported speech: He said he should go to the park.
- Incorrect reported speech: He told he should go to the park.
- Incorrect reported speech: He said me he should go to the park.
To correct these:
- Add ‘me’: He told me he should go to the park.
- Remove ‘me’ or add ‘to’: He said he should go to the park or He said to me he should go to the park.
Direct and Indirect Speech
Changes in time and place in reported speech.
References to time and place often need to change when you use indirect speech. Here is a useful guide to these changes:
No Change in Verb Tenses in Reported Speech
In some cases, verb tenses do not change when you report speech indirectly. Here are the key instances:
- When the introductory verb is in the present , present perfect , or future .
- When the reported sentence deals with a fact or general truth .
- When the reported sentence contains a time clause .
- If the verb of the sentence is in the unreal past (the second or the third conditional ).
- The subjunctive stays unchanged in the subordinate clause .
- Had better , could , would , used to , should , might , ought to , and mustn’t remain unchanged.
- If the speaker reports something immediately or soon after it was said .
Reporting Verbs in Indirect Speech
Reporting verbs are crucial in indirect speech. Here is a list categorized by their usage:
- Basic Verbs : Tell, say, ask
- Verb + that + clause : Complain, deny, explain, exclaim, remark, promise, boast, inform somebody, claim, agree, suggest
- Verb + to + infinitive : Agree, offer, refuse, demand, threaten, promise, claim
- Verb + indirect object + to + infinitive : Advise, allow, beg, command, encourage, forbid, invite, want, instruct, permit, urge, order, remind, warn
- Verb + “ing” form : Admit (to), accuse somebody of, apologize for, boast about/of, complain to somebody of, deny, insist on, suggest
- Verb + how : Explain to somebody
Reported Questions
When converting questions from direct to indirect speech, you follow rules similar to those for statements. Verbs used include inquire, wonder, want to know, ask.
Reported Commands and Requests
Commands and requests in Indirect Speech are formed using the to-infinitive and not to-infinitive . Common reporting verbs include order, shout, demand, warn, beg, command, tell, insist, beseech , threaten, implore, ask, propose, forbid.
Pronoun and tense changes are needed when shifting from direct to indirect speech.
Reported Speech Video
- Latest Posts
- Active vs. Passive Voice Exercises – Active vs. Passive Voice Worksheet - December 25, 2023
- Phrase Exercises – Phrase Worksheet - December 23, 2023
- Sentence Exercises – Sentence Worksheet - December 23, 2023
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
Direct and Indirect Speech Class 10 CBSE English
- English Grammar
- Direct Indirect Speech

Direct and Indirect Speech Exercises for Class 10 with Answers - Download Free PDF With Solutions
In English, there are mainly two ways to express the spoken words between two individuals. They are direct speech and indirect or reported speech. These two types of speeches narrate the spoken words differently. Do you know about direct and indirect speech or Reported Speech Class 10 ? Are you able to convert direct speech into indirect speech and vice versa? If not, direct and indirect speech exercises for class 10 pdf with answers will help you learn direct and indirect speeches with ease and will leave no room for doubts.
Direct and Indirect Speech Exercises for Class 10 with Answers
Direct speech.
Direct speech refers to the speech with the speaker's actual words. This type of speech has the word-to-word restatement of the speaker's speech.
Example: Rahim said, "I am going to the playground."
Indirect or Reported Speech Class 10
Indirect or reported speech refers to the speech that doesn't use the actual word-to-word statement of the speaker. Also, indirect speech follows past tense, generally.
Example: Rahim said he was going to the playground.
Benefits of Learning Reported Speech Class 10
Mastering the art of direct and indirect speech holds significant importance in the academic journey of Class 10 students. As they navigate through the intricacies of language and communication, understanding the nuances of direct and indirect speech equips them with essential skills for effective expression and comprehension. In this introduction, we unravel the benefits of learning direct and indirect speech, shedding light on its relevance and impact on the academic and linguistic development of Class 10 students. Here are some of the Benefits of Learning Direct and Indirect Speech Exercises for Class 10 with Answers:
Enhances Communication Skills: Learning direct and indirect speech enhances students' communication skills by enabling them to effectively convey messages in various contexts. It empowers them to articulate thoughts, ideas, and narratives with clarity and precision, fostering confident expression in both oral and written communication.
Improves Language Proficiency: Delving into the intricacies of direct and indirect speech enhances students' language proficiency by deepening their understanding of grammar and syntax. It familiarizes them with the rules and conventions governing Reported Speech Class 10 , enabling them to construct grammatically accurate sentences and compositions.
Facilitates Comprehension: Mastery of direct and indirect speech facilitates comprehension as students learn to decipher and interpret statements made by others accurately. It hones their ability to comprehend complex dialogues, narratives, and textual passages, thereby enhancing their reading and comprehension skills.
Enhances Critical Thinking: Engaging with direct and indirect speech prompts students to think critically as they analyze and evaluate different forms of communication. It encourages them to assess the implications of Reported Speech Class 10 , discern underlying meanings, and draw inferences, thereby fostering critical thinking and analytical skills.
Prepares for Academic Success: Proficiency in direct and indirect speech is integral to academic success, especially in subjects like English and languages. It equips Class 10 students with the requisite skills to excel in examinations, comprehension exercises, and language-based assessments, laying a strong foundation for future academic pursuits.
Basic Rules of Direct and Indirect Speech that Students of Class 10 Should Know
In the journey of language acquisition and effective communication, the mastery of direct and indirect speech stands as a pivotal skill set. For students navigating the complexities of language at the Class 10 level, understanding the fundamental rules governing direct and indirect speech is paramount. In this introduction, we delve into the significance of comprehending these rules, equipping students with the necessary knowledge to navigate the intricacies of Reported Speech Class 10 with confidence and precision.
Rules of Direct Speech for Class 10
For every character's speech, use separate lines.
Always start a speech with a capital letter.
Every speaker's speech should be in quotes ("XYZ").
We will use a reported clause (like, 'said,' 'asked,' 'replied') before the quotation.
Rules of Reported Speech Class 10
If the reporting verb of the direct speech is in the past tense, all the present tenses used in direct speech will be in the past tense in the indirect or reported speech.
Present perfect tense and present continuous tense in direct speech will be in the past perfect tense and past continuous tense in indirect or reported speech.
Simple present tense in direct speech will be in simple past in indirect or reported speech.
Simple future and future continuous tense in direct speech changes to the present conditional and conditional continuous tense in indirect speech.
Modals like must, may, and can in direct speech become would have to/ had to, might, and could respectively in indirect speech.
The First-person in direct speech becomes the subject in indirect speech.
The imperative mood becomes the infinitive in Reported Speech Class 10.
Direct to Indirect Speech Conversion
Direct Speech: I said, "I am busy."
Indirect Speech: I said I was busy.
Direct Speech: She said, "Are you okay"?
Indirect Speech: She inquired of you whether you were okay.
Direct Speech: She said, "I will leave now."
Indirect Speech: She said that she would leave then.
Important Topics for Class 10 Direct and Indirect Speech
In this chapter, you will learn:
What are direct and indirect speech?
What are the basic rules of direct and indirect speech?
How to convert direct speech into indirect speech?
Reported Speech Exercises for Class 10 with Answers
This grammar section explains English Grammar clearly and simply. There are example sentences to show how the language is used. Direct and Indirect Speech Exercises for Class 10 with Answers will help you to write better answers in your Class 10 exams. Because the Solutions are solved by subject matter experts.
Rules for Reported Speech Class 10
While changing direct speech into reported speech or vice-versa the following changes occur:
1. Changes In Reporting Verb
Affirmative sentences: said, told (object), asserted, replied, assured, informed, responded, whispered, alleged, believed, assumed, thought
Interrogative sentences: asked, enquired, wanted to know
Imperative sentences: ordered, begged, pleaded, implored, advised, demanded
2. Change Of Pronouns
Direct Speech: Johnny said, 'I am playing.'
Indirect Speech: Johnny said that he was playing.
First-person generally changes to third person {depending upon the subject of the reporting verb).
3. Change Of Tenses
In general, present tense becomes past tense; past tense and present perfect become past perfect.
4. Change of situations Example:
Nagesh said, 'I read this book last week. (direct speech)
Nagesh said that he had read that book the previous week, (indirect speech)
'this' becomes 'that'
'last week' becomes 'the previous week'
here – there
today - that day
yesterday - the day before/the previous day
tomorrow - the next day/the coming day
last week - the week before/the previous week • next month – the next month/the coming month
5. In case of questions and answers
Nagesh asked, 'Have you read this book?' (direct speech)
Nagesh asked if' whether I had read that book, (indirect speech)
Nagesh asked, 'Where is the book?' (direct speech)
Nagesh asked where the book was. (indirect speech)
(a) For yes/no questions - use if/whether
(b) For wh- questions - use the wh-word
Word Order:
Nagesh asked, 'What's the matter?'
Nagesh asked what the matter was. (what + the matter + was) Nagesh asked what was the matter, (what + was + the matter)
The word order can be either:
who/which/what + complement + be or who/which/what + be + complement
6. Reported Speech using present and future tenses Examples:
Nagesh said, "The sun rises in the east. (direct speech)
Nagesh said that the sun rises in the east, (indirect speech)
Nagesh said, 'I will read this book.' (direct speech)
Nagesh said that he will read that book, (indirect speech)
If the original speaker's present and future is still present and future, the tense remains unchanged.
7. In case of modal verbs
can becomes could
will - would
Shall - should
may - might
would, should, could, might, ought to and must are unchanged.
Nagesh said, 'I can solve this sum.' (direct speech)
Nagesh said that he could solve that sum. (indirect speech)
Reported Speech Class 10 Solved Examples Exercises for CBSE Board
Read the dialogue given below and then complete the passage that follows.
Question 1.
Read the dialogue and complete the passage given below.
Interviewer: So, why do you want to be a computer programmer?
Ravi: Well, I have always been interested in computers.
Interviewer: I see. Do you have any experience?
Ravi: No, but I'm a fast learner.
Interviewer: What kind of a computer do you use?
Ravi: Computer? Uhm, let me see. I can use a Mac. I also used Windows 10 once.
Interviewer: That's good.
Ravi recently attended an interview for the selection of a computer programmer. At the interview, he was asked (a).......... To this question he replied that he wanted to change his job because (b).
When the interviewer asked him (e) ............................... he replied that. h... (..)........................................................................................ Finally, the interviewer wanted to know. (..)...............................................................................avi. replied that he could use a Mac and had also used Windows 10 once in the,.past. The interviewer seemed to be pleased with his answers.
(a) why he wanted to be a computer programmer
(b) he had always been interested in computers
(c) whether he had any experience
(d) didn't but that he was a fast learner
(e) the kind of computer he used
Question 2.
Manu: Where are you going to?
Annu: I am going to the market. Do you want anything?
Manu asked Annu (a)..........................
(a) where she was going.
(b) that she was going to the market
(c) if/whether she wanted anything.
Question 3.
Annu replied (b).... Annu replied (b). ............ and she further asked (C)..........
Sunita: Tomorrow is your birthday, what do you want as a gift?
Neetu: That is a lovely thought but I don't want anything.
Sunita asked Neetu since the next day was her birthday, (a).....Neetu replied that (b)...but (C).....
(a) what she wanted as a gift
(b) that was a lovely thought
(c) she did not want anything.
Question 4.
Gardener: Did you water the plant today?
Dev: No, but I will, today.
Gardener: Then tomorrow I will get a sapling of sunflower.
The Gardener asked Dev (a)
Dev replied negatively but (b)
Then the gardener said that (c)
(a) if/whether he had watered the plant that day.
(b) said he would that day.
(c) he would get a sapling of a sunflower the next day.
Question 5.
Mr. Harish: Can you polish my shoes?
Cobbler: Yes sir. But I will take 10 for each shoe.
Mr. Harish: I will not mind as long as it is done. Mr. Harish asked the cobbler (a) .................. The cobbler replied affirmatively but (b).............. Mr. Harish said that (C)...
(a) if/whether he could polish his shoes.
(b) said that he would take 10 for each shoe
(c) he would not mind as long as it was done.
Question 6.
Electrician: When did your electricity go?
Mohan: It is not working since evening.
Electrician: Sorry sir, in this case, I will have to check the fuse now.
The electrician asked Mohan (a)........................................Mohan replied that(b)....................................The electrician apologetically said that in that case (c )…………………………………………….
(a) when his electricity had gone.
(b) it was not working since evening.
(c) he would have to check the fuse then.
Question 7.
Teacher Children, let us all pledge to save trees.
Children: Yes, mam, we all pledge to save our trees as the trees are the lungs of the city. Teacher: Let us start today by planting a sapling.
The teacher asked all the children to pledge to save trees. The children replied affirmatively (a)...............as the (b).......................Then the teacher said that said that (c)...........
(a) saying that they all pledged to save trees
(b) trees are the lungs of the city.
(c) they should start by planting a sapling that day.
Question 8.
Buddha: Honesty is the best policy.
Disciple: Does honesty always pay?
Buddha : It may or may not, but at least you will never feel guilty.
Buddha in his preaching said that (a).......................the best policy. A disciple asked him if (b)..................always pays, Buddha replied (C )…………………………..but at least he would never feel guilty.
(a) Honesty is
(b) honesty
(c) that it might or might not
Question 9.
Doctor: You should take this medicine every day.
Patient: Should I take it before dinner or after dinner?
Doctor: No, you should take it after breakfast.
The Doctor advised the patient that (a).....................The patient further asked (b).....................The doctor replied negatively and then said ©……………………..
(a) he should take that medicine every day.
(b) if/whether he should take it before dinner or after dinner.
(c) that he should take it after breakfast
Question 10.
Reena: Do you know how to swim?
Surbhi : Yes I know. I have learnt it during this summer vacation.
Reena asked Surbhi (a)...........Then Surbhi replied (b).................and also added that (c)....................
(a) if/whether she knew how to swim
(b) in affirmative
(c) she had learnt it during the summer vacation.
Why Should You Download Direct and Indirect Speech Exercises for Class 10 with Answers Free PDF ?
Feeling lost in the world of "said" and "that"? Does converting direct speech to indirect speech leave you scratching your head? Worry no more! Here's your chance to download a free PDF packed with Reported Speech Exercises for Class 10 with Answers specifically designed for Class 10 students. Master this essential grammar concept and boost your confidence for exams and beyond!
If you want the free direct and indirect speech exercises for Class 10 PDF, visit Vedantu’s website, find the chapter and click on the download button.
The Reported Speech Exercises for Class 10 with Answers free PDFs available at Vedantu are easy to access and are also convenient, secure and compact.
The Direct and Indirect Speech Exercises for Class 10 with Answers PDF are completely reliable to practice for exams as they have been curated by the subject matter experts based on the latest syllabus.
The Vedantu’s teachers have given all the rules and directions for converting direct to indirect speeches with many examples. Several rules for converting direct speech to indirect speech need to be practised repeatedly, and the exercises from Vedantu's end will help you with that. Download direct and indirect speech exercises for class 10 pdf with answers and practise the solved exercises to ensure firm grip of the topic and solve your exam questions with ease. You can also sign up for our online classes to improve your hold on English grammar and fetch excellent results.
FAQs on Direct and Indirect Speech Class 10 CBSE English
1. What is the alternative name for direct speech?
Direct speeches are also called quoted speeches as the speaker's statements are provided in an exact manner , word-by-word, and are always within quotation marks.
2. How many parts does a direct speech have?
A direct speech is generally made up of two parts: reporting clause (verbs like say/said, ask/asked, shout/shouted, etc.) and the reported clause (the original dialogue of the speaker).
3. What is the indirect speech form of the word 'tomorrow'?
The word 'tomorrow' in a direct speech changes to 'the following day' or 'the next day’ in the indirect or reported speech.
4. What is Direct Speech in ?
Direct speech is the exact words spoken by someone, enclosed in quotation marks. It represents the speaker's original words and is commonly used in dialogue or reporting speech directly.
5. What is Indirect Speech?
Indirect speech, also known as reported speech, is the reporting of someone's words without using their exact words. It does not require quotation marks and often involves transforming the original speaker's words into a different form.
6. Why is it important to learn direct and indirect speech exercises for class 10 pdf with answers?
Learning direct and indirect speech exercises for class 10 pdf with answers is essential in Class 10 CBSE English Grammar as it enhances students' comprehension skills, improves their writing ability, and enables them to effectively report speech in various contexts, such as narratives, essays, and dialogue-based questions in exams.
7. What are the basic rules for transforming Direct Speech into Indirect Speech?
The basic rules for transforming direct speech into indirect speech include changing verb tenses, pronouns, time and place references, and often using reporting verbs such as 'said,' 'told,' or 'asked.'
8. How can I practice Direct and Indirect Speech effectively?
Practicing direct and indirect speech involves analyzing sentences, identifying the reporting verbs, and applying the appropriate rules for transforming direct speech into indirect speech. Engaging in exercises and writing prompts, as provided in resources like the Class 10 CBSE English Grammar PDF, can enhance proficiency.
9. Is the direct and indirect speech class 10 CBSE English Grammar PDF a reliable resource for learning Direct and Indirect Speech?
Yes, the direct and indirect speech class 10 PDF is a reputable resource provided by the Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE) and is designed to align with the curriculum standards. It typically includes explanations, examples, and exercises covering various grammar topics, including direct and indirect speech.
10. Are there any tips for mastering Reported Speech Class 10 CBSE English Grammar exams?
Some tips for Reported Speech Class 10 include practicing regularly, paying attention to verb tense changes, ensuring consistency in pronoun usage, and understanding the context of reported speech. Additionally, seeking clarification from teachers or referring to supplementary study materials can aid in comprehension and application.
11. Can I find additional Reported Speech Exercises for Class 10 with Answers online?
Yes, Vedantu offers additional Reported Speech Exercises for Class 10 with Answers and explanations for direct and indirect speech. These resources can complement the Class 10 CBSE English Grammar PDF and provide further opportunities for practice and reinforcement.

Reported Speech - Class 10 PDF Download
Reported speech.
When we say things that have been said, we use two ways of expressing it. The first is direct speech when we express what the speaker said as it is and the second is indirect speech where we express what was said in our words. Examples: If you ask your friend Pradeep, ‘Did you take my book?’, the reply could be ‘Your book is with Jai.’ Now, we can report this statement in two ways:
- Pradeep told me, ‘Your book is with Jai’.
- Pradeep told me that my book is with Jai.
Rules For Reported Speech
While changing direct speech into reported speech or vice versa, the following change:
- the reporting verb
- the pronouns
- the situations
- report using present and future tenses
- modal verbs
- word order with who, which, and what
1. Changes in reporting verb
- Affirmative sentences: said, told (object), asserted, replied, assured, informed, responded, whispered, alleged, believed, assumed, though.
- Interrogative sentences: asked, inquired, wanted to know, enquired When we report.
- Imperative sentences: ordered, begged, pleaded, implored, advised, demanded.
2. Change of pronouns
- Direct speech: Surabhi said, “I am reading.”
- Indirect speech: Surabhi said that she was reading.
- A first-person and second-person generally change to a third person (depending upon the object to reporting verb).
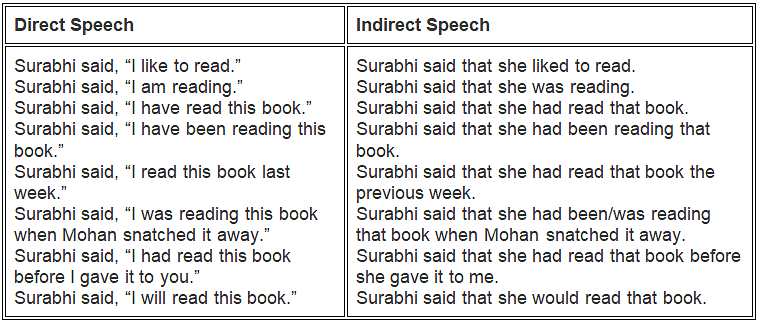
4. Change Of Situations Examples:
- Surabhi said, “I read this book last week.” (direct speech)
- Surabhi said that she had read that book the previous week, (indirect speech)
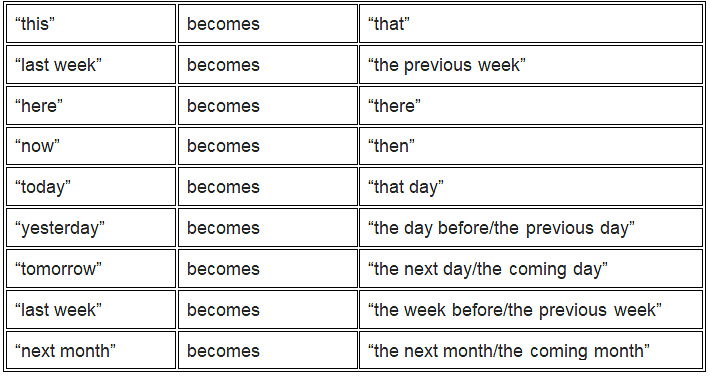
- Surabhi asked, “Have you read this book?” (Direct Speech)
- Surabhi asked if/whether I had read that book. (Indirect Speech)
- Surabhi asked, “Where is the book?” (Direct Speech)
- Surabhi asked where the book was. (Indirect Speech)
(a) yes/no questions – use if/whether (b) wh-questions – use the wh-word
- Surabhi asked, “What’s the matter?”
- Surabhi asked what the matter was. (what + the matter + was)
- Surabhi asked what was the matter, (what + was + the matter)
Can Be Either
- who/which/what + complement + be or
- who/which/what + be + complement
Reported speech using present and future tenses: Examples:
- Surabhi said, “The sun rises in the east.” (Direct Speech)
- Surabhi said that the sun rises in the east. (Indirect Speech)
- Surabhi said, “I will read this book.” (Direct Speech)
- Surabhi said that she will read that book. (Indirect Speech)
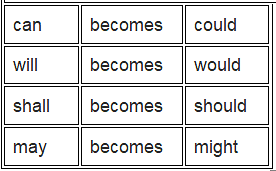
- Surabhi said, “I can solve this sum.” (Direct Speech)
- Surabhi said that she could solve that sum. (Indirect Speech)
In our daily lives, we use reported speech in many forms. We use reported speech to report statements, questions, requests, or even commands. There are certain things we need to keep in mind when we report each of them.
- When we report statements, we have to make sure what changes need to be made in the pronoun, tense or temporal-spatial expression.
- When we transform questions into reported speech, we have to check whether or not to change the tense, pronoun as well as place and time expression.
- Upon changing, we have to ensure that the question is an indirect question.
- We also have to make use of words such as where, when, how, if, whether, etc.
- In transforming requests and commands into reported speech, tenses are not relevant.
- We only have to ensure that there are changes in the pronoun and the place and time expression.
Top Courses for Class 10
Reported speech - class 10, semester notes, video lectures, study material, shortcuts and tricks, past year papers, practice quizzes, viva questions, objective type questions, sample paper, previous year questions with solutions, extra questions, mock tests for examination, important questions.

Reported Speech Free PDF Download
Importance of reported speech, reported speech notes, reported speech class 10 questions, study reported speech on the app, welcome back, create your account for free.
Forgot Password
Change country.
Reported Speech: How to Use Reported Speech | Useful Rules
One of the most common mistakes when becoming familiar with this type of grammar is not knowing the difference between direct speech and reported speech and the changes related to these types of sentences.
Reported Speech
The reported speech reproduces the words of another person by adapting certain temporal and local references of the original speech to the situation of the speaker, for example, personal pronouns, demonstratives, verb tenses, and adverbs of place or time.
It is characterized by introducing the message that is reproduced with a speaking verb followed by conjunctions that or if. The speaking verb reveals the intention of the speaker to convey what another person has said.
The most frequent speaking verbs are: say, affirm , count, explain, ask, warn, suggest, order, etc.
Direct Speech vs. Reported Speech
Both are the two different ways to transmit what someone has said.
With direct speech, the message is reproduced as we have heard it, in quotes and after a color meanwhile with reported speech the message is reproduced with our words, without commas but using that or if after the verb.
Different Types of Sentences
- Reported statements : use that before the statement and the reporting verb said or told.
- Reported questions : use reported verbs like asked, requested, or wanted to know and omit the question mark. Remember that the order in reported questions changes. In the case of yes-no questions use whether or if.
- Reported requests or commands : use to or not to before the sentence and use verbs like asked, told, ordered, urged, advised, and begged.
Changes When Using Reported Speech
Tense Changes in Reported Speech
In short, the tense changes in the reported speech are made taking into account the verb in the direct speech. The tense changes are:
- Simple present -> simple past
- Present continuous -> past continuous
- Simple past -> past perfect simple
- Past continuous -> past perfect continuous
- Past perfect simple -> past perfect simple
- Past perfect continuous -> past perfect continuous
- Present perfect -> past perfect simple
- Present perfect continuous -> past perfect continuous
- Future simple -> would
- Future perfect -> would have
- Present passive -> past passive
- Present passive continuous -> past passive continuous
- Can -> could/would be able to
- May -> might
- May -> could/ would be allowed to
- Must -> must/ had to/ would have to
- Needn’t -> didn’t have to /didn’t need to /wouldn’t have to
- Shall -> would/should
- Will -> would
Place, Demonstratives, and Time Expressions
Just as there are certain changes in the verb tenses, you have to make changes in the demonstratives, pronouns , and expressions of time and place.
- Here -> there
- There -> there
- This -> that
Time Expressions
- Today -> that day
- Tomorrow -> the next day/ the following day
- Now -> at that moment/ then
- At the present -> At the time
- Present, current -> existing current
- In one hour -> one hour later
- Next year -> the following year
- Days ago -> days before
- Tonight -> that night
- In two week’s time -> two weeks later
- Ago -> before
Pronouns and Demonstratives
- I -> he, she
- Me -> him, her
- My -> his, her, the
- Mine -> his, hers
- We -> they
- Us -> them
- Our -> their, the
- Ours -> theirs
- You -> they, them, their, the
- Yours -> theirs
- This -> that, the
- These -> those, the
- This book -> that book
Reported Speech | Infographic

Other Changes in Reported Speech

Last Updated on October 25, 2023

Leave a Comment Cancel reply

COMMENTS
RD Sharma Class 10 Solutions; 3. Rules for the Change of Pronouns: The first person pronouns (I, me, my, we, us, our) in the reported speech change according to the subject of the reporting verb. The pronouns of the second person (you, your, yourself) in the reported speech change according to the object of the reporting verb.
Reported speech is the form in which one can convey a message said by oneself or someone else, mostly in the past. It can also be said to be the third person view of what someone has said. In this form of speech, you need not use quotation marks as you are not quoting the exact words spoken by the speaker, but just conveying the message. Q2.
Reported speech, also known as indirect speech, is a way of conveying what someone else has said without quoting their exact words. Instead of using quotation marks, the speaker paraphrases or summarises the original statement.This transformation often involves changes in pronouns, tenses, and time expressions to fit the context of the reporting. . Understanding reported speech is crucial for ...
Reported Speech | Class 10 English | CBSE 2025 | Sandra Ma'am Welcome to another comprehensive English session with Sandra Ma'am! In this video, we delve int...
Reported Speech involves transforming verb tenses, pronouns, and sometimes other elements. The changes are important to accurately represent the reported information while integrating it into the speaker's sentence structure. Must Read! Reported Speech: Definition, Rules, Usage with Examples. Reported Speech for Class 10 Exercise 1 - MCQs
Reported Speech Exercises: Reporting Dialogue. Reporting Dialogue involves transforming a conversation or dialogue from direct to reported speech, focusing on accurate tense and pronoun changes. Reported Speech Exercises 1: 1. Read the dialogue and complete the following sentences in the reported speech. Shylock: I am unwell
There are example sentences to show how the language is used. NCERT Solutions for Class 10 English will help you to write better answers in your Class 10 exams. Because the Solutions are solved by subject matter experts. Rules for Reported Speech While changing direct speech into reported speech or vice-versa the following changes occur: 1.
Reported Speech Exercises for Class 10 with Answers. Here is an exercise on the transformation of direct speech to indirect speech. Go through the following sentences, work them out and then check your answers to assess how far you have understood their usage. Change as directed . Read the following sentences and change them into reported speech.
Direct speech: I like ice cream. Reported speech: She said (that) she liked ice cream. She said (that) she liked ice cream. She said (that) she was living in London. She said (that) she had bought a car OR She said (that) she bought a car. She said (that) she had been walking along the street.
Extra questions for Reported Speech - English Grammar Class 10. Worksheet questions are the type of Extra questions related to Reported Speech. These worksheet questions are designed by the experts for the preparation point of view. It is important for the students of Class 10 to go through and practice these questions.
Reported Speech Exercises for Class 10 CBSE With Answers Pdf. This grammar section explains English Grammar in a clear and simple way. There are example sentences to show how the language is used. ... Rules for Reported Speech While changing direct speech into reported speech or vice-versa the following changes occur: 1. Changes In Reporting Verb
Examples of reported speech include: 1) Santana said that she would be auditioning for the lead role in Funny Girl. 2) Blaine requested us to help him with the algebraic equations. 3) Karishma asked me if I knew where her car keys were. 4) The police ordered everyone to leave from the bus stop immediately.
Reported speech. Tips: Given dialogue is to be changed into indirect speech. Change the reporting verb. Remove commas and use conjunction. Change the pronouns and verb in the reported speech. Use a (.) at the end of every sentence. Solved exercises. 1. Read the conversation between Rama and Sita. Then report the paragraph that follows.
When we use reported speech, we often change the verb tense backwards in time. This can be called "backshift.". Here are some examples in different verb tenses: "I want to go home.". She said she wanted to go home. "I 'm reading a good book.". She said she was reading a good book. "I ate pasta for dinner last night.".
It sounds worse in Indirect speech because the meaning has changed due to past form of verbs; QuestionD.4. Given below are notes on a news report covering an operation by Indian Navy that nabbed 16 pirates. Using the notes write a newspaper report. Remember to use a combination of direct and indirect speech. Make the report interesting and ...
Reported Speech Rules Verb Tense Changes in Reported Speech. When the reporting verb is in the present tense, only small changes are needed. Example: Direct speech: I like dogs. Reported speech: She says she likes dogs. When the reporting verb is in the past tense, you need to change the tense of both the reporting verb and the main verb. Example:
Practicing direct and indirect speech involves analyzing sentences, identifying the reporting verbs, and applying the appropriate rules for transforming direct speech into indirect speech. Engaging in exercises and writing prompts, as provided in resources like the Class 10 CBSE English Grammar PDF, can enhance proficiency. 9.
Full syllabus notes, lecture and questions for Reported Speech - Class 10 - Class 10 - Plus excerises question with solution to help you revise complete syllabus - Best notes, free PDF download. ... Reported Speech - Statement - Rules. Whatever may be the tense of the Reporting Sentence, if the Reported Sentence tells a universal fact, no ...
Rules For Reported Speech. While changing direct speech into reported speech or vice versa, the following change: the reporting verb; the pronouns; ... The "Reported Speech Class 10 Questions" guide is a valuable resource for all aspiring students preparing for the Class 10 exam. It focuses on providing a wide range of practice questions to ...
2. Rules for Changing Direct Speech into Indirect Speech: In the Indirect speech, no inverted commas are used. The conjunctions that, if, whether, are generally used after the reporting verb. The first word of the reported speech begins with a capital letter. The tense of the reporting verb is never changed.
Reported questions: use reported verbs like asked, requested, or wanted to know and omit the question mark. Remember that the order in reported questions changes. In the case of yes-no questions use whether or if. Reported requests or commands: use to or not to before the sentence and use verbs like asked, told, ordered, urged, advised, and begged.