- CBSE Class 10

CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter Wise Important Case Study Questions
Chapter wise important case study questions cbse class 10 science: cbse class 10 science board exam 2024 is just around the corner and students are working hard to score maximum marks. check these case study questions from class 10 science to ace your examination this year also download the solutions from the pdf attached towards the end. .

CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter Wise Important Case Study Questions: While the CBSE Board exam for Class 10 students are ongoing, the CBSE Class 10 Science board exam 2024 is to be held on March 2, 2024. With the exams just a few days away, CBSE Class 10th Board exam candidates are rushing to prepare the remaining syllabus, practising their weak portions, trying to revise the important questions from the past year papers, practise questions, etc.
Why are CBSE Class 10 Science Case Study Questions Important?
- Section A : 20 Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) carrying 1 mark each.
- Section B : 6 Very Short Answer type questions carrying 2 marks each. Answers to these questions should be in the range of 30 to 50 words.
- Section C : 7 Short Answer type questions carrying 3 marks each. Answers to these questions should be in the range of 50 to 80 words.
- Section D : 3 Long Answer type questions carrying 5 marks each. Answers to these questions should be in the range of 80 to 120 words.
- Section E : 3 Case Based/ Source Based units of assessment (4 marks each) with sub-parts.
How to solve case study questions in CBSE Class 10 Science?
- Read the case given and the associated questions carefully.
- Read the questions attentively and analyse what they are asking.
- Apply your subject knowledge and theories in the given case to decide what the correct answers should be.
1.A chemical reaction is a representation of chemical change in terms of symbols and formulae of reactants and products. There are various types of chemical reactions like combination, decomposition, displacement, double displacement, oxidation and reduction reactions. Reactions in which heat is released along with the formation of products are called exothermic chemical reactions. All combustion reactions are exothermic reactions.
(i) The massive force that pushes the rocket forward through space is generated due to the
(a) combination reaction
(b) decomposition reaction
(c) displacement reaction
(d) double displacement reaction
(ii) A white salt on heating decomposes to give brown fumes and yellow residue is left behind. The yellow residue left is of
(a) lead nitrate
(b) nitrogen oxide
(c) lead oxide
(d) oxygen gas
(iii) Which of the following reactions represents a combination reaction?
(a) CaO (s) + H2O (l) → Ca (OH)2 (aq)
(b) CaCO3 (s) → CaO (s) + CO2(g)
(c) Zn(s) + CuSO4 (aq) → ZnSO4 (aq) + Cu(s)
(d) 2FeSO4(s) → Fe2O3 (s) +SO2(g) + SO3(g)
(iv) Complete the following statements by choosing correct type of reaction for X and Y.
Statement 1: The heating of lead nitrate is an example of ‘X’ reaction.
Statement 2: The burning of magnesium is an example of ‘Y’ reaction.
(a)X-Combination,Y-Decomposition
(b)X-Decomposition,Y-Combination
(c)X-Combination,Y-Displacement
(d) X- Displacement, Y-Decomposition
2.The earlier concept of oxidation and reduction is based on the addition or removal of oxygen or hydrogen elements so, in terms of oxygen and hydrogen, oxidation is addition of oxygen to a substance and removal of hydrogen from a substance. On the other hand, reduction is addition of hydrogen to a substance and removal of oxygen from a substance. The substance which gives oxygen to another substance or removes hydrogen from another substance in an oxidation reaction is known as oxidising agent, while the substance which gives hydrogen to another substance or removes oxygen from another substance in a reduction reaction is known as reducing agent. For example,
(i) A redox reaction is one in which
(a) both the substances are reduced
(b) both the substances are oxidised
(c) an acid is neutralised by the base
(d) one substance is oxidised while the other is reduced.
(ii) In the reaction, H2S+Cl2⟶S+2HCl
(a) H2S is the reducing agent.
(b) HCl is the oxidising agent.
(c) H2S is the oxidising agent.
(d) Cl2 is the reducing agent.
(iii) Which of the following processes does not involve either oxidation or reduction?
(a) Formation of slaked lime from quicklime.
(b) Heating mercuric oxide.
(c) Formation of manganese chloride from manganese oxide (MnO2).
(d) Formation of zinc from zinc blende.
(iv) Mg+CuO⟶MgO+Cu
Which of the following is wrong relating to the above reaction?
(a) CuO gets reduced
(b) Mg gets oxidised.
(c) CuO gets oxidised.
(d) It is a redox reaction.
3.A copper vessel gets tarnished due to formation of an oxide layer on its surface. On rubbing lemon on the vessel, the surface is cleaned, and the vessel begins to shine again. This is due to the fact that which reacts with the acid present in lemon to form a salt which is washed away with water. As a result, the layer of copper oxide is removed from the surface of the vessel and the shining surface is exposed.
1.Which of the following acids is present in lemon?
(a) Formic acid
(b) Acetic acid
(c) Citric acid
(d) Hydrochloric acid
2.The nature of copper oxide is
d) amphoteric
3.Name the salt formed in the above reaction
a) copper carbonate
b) copper chloride
c)copper citrate
d) copper citrate
4.The phenomenon of copper getting tarnished is
a) corrosion
b) rancidity
c) displacement
d)none of these
4.Metals as we know, are very useful in all fields, industries in particular. Non-metals are no less in any way. Oxygen present in air is essential for breathing as well as for combustion. Non-metals form a large number of compounds which are extremely useful, e.g., ammonia, nitric acid, sulphuric acid, etc. Non-metals are found to exist in three states of matter. Only solid non-metals are expected to be hard however, they have low density and are brittle. They usually have low melting and boiling points and are poor conductors of electricity.
i.____________ is a non-metal but is lustrous
A.Phosphorus
ii.Which of the following is known as 'King of chemicals'?
C. Sulphuric acid
D. Nitric acid
iii.Which of the following non-metals is a liquid?
iv.Hydrogen is used
A.for the synthesis of ammonia
B. for the synthesis of methyl alcohol
C.nitrogenous fertilizers
D. all of these
5.Nisha observed that the bottoms of cooking utensils were turning black in colour while the flame of her stove was yellow in colour. Her daughter suggested cleaning the air holes of the stove to get a clean, blue flame. She also told her mother that this would prevent the fuel from getting wasted.
a) Identify the reasons behind the sooty flame arising from the stove.
b) Can you distinguish between saturated and unsaturated compounds by burning them? Justify your answer.
c) Why do you think the colour of the flame turns blue once the air holes of the stove are cleaned?
6.Blood transport food, Oxygen and waste materials in our bodies. It consists of plasma as a fluid medium. A pumping organ [heart] is required to push the blood around the body. The blood flows through the chambers of the heart in a specific manner and direction. While flowing throughout the body, blood exerts a pressure against the wall or a vessel.
- Pulmonary artery
- Pulmonary vein
- Very narrow and have high resistance
- Much wide and have low resistance
- Very narrow and have low resistance
- Much wide and have high resistance
- It is a hollow muscular organ
- It is four chambered having three auricles and one ventricle.
- It has different chambers to prevent O2 rich blood from mixing with the blood containing CO2
- Both A & C
- Blood = Plasma + RBC + WBC + Platelets
- Plasma = Blood – RBC
- Lymph = Plasma + RBC
- Serum = Plasma + RBC + WBC
7.A brain is displayed at the Allen Institute for Brain Science. The human brain is a 3-pound (1.4-kilogram) mass of jelly-like fats and tissues—yet it's the most complex of all known living structures The human brain is more complex than any other known structure in the universe. Weighing in at three pounds, on average, this spongy mass of fat and protein is made up of two overarching types of cells—called glia and neurons— and it contains many billions of each. Neurons are notable for their branch-like projections called axons and dendrites, which gather and transmit electrochemical signals. Different types of glial cells provide physical protection to neurons and help keep them, and the brain, healthy. Together, this complex network of cells gives rise to every aspect of our shared humanity. We could not breathe, play, love, or remember without the brain.
1)Animals such as elephants, dolphins, and whales actually have larger brains, but humans have the most developed cerebrum. It's packed to capacity inside our skulls and is highly folded. Why our brain is highly folded?
- b) Learning
3)Which among these protects our brain?
a)Neurotransmitter
b) Cerebrospinal fluid
d) Grey matter
4.Ram was studying in his room. Suddenly he smells something burning and sees smoke in the room. He rushes out of the room immediately. Was Ram’s action voluntary or involuntary? Why?
8.Preeti is very fond of gardening. She has different flowering plants in her garden. One day a few naughty children entered her garden and plucked many leaves of Bryophyllum plant and threw them here and there in the garden. After few days, Preeti observed that new Bryophyllum plants were coming out from the leaves which fell on the ground.
1.What does the incident sited in the paragraph indicate?
(a). Bryophyllum leaves have special buds that germinate to give rise to new plant.
(b). Bryophyllum can propagate vegetatively through leaves.
(c). Bryophyllum is a flowering plant that reproduces only asexually
(d). Both (a) and (b).
2.Which of the following plants can propagate vegetatively through leaves like Bryophyllum?
3.Do you think any other vegetative part of Bryophyllum can help in propagation? If yes, then which part?
(c) Flowers
4.Which of the following plant is artificially propagated (vegetatively) by stem cuttings in horticultural practices?
(b)Snakeplant
(d)Water hyacinth
9.The growing size of the human population is a cause of concern for all people. The rate of birth and death in a given population will determine its size. Reproduction is the process by which organisms increase their population. The process of sexual maturation for reproduction is gradual and takes place while general body growth is still going on. Some degree of sexual maturation does not necessarily mean that the mind or body is ready for sexual acts or for having and bringing up children. Various contraceptive devices are being used by human beings to control the size of the population.
1) What are common signs of sexual maturation in boys?
a) Broadening of shoulders
b) Development of mammary glands
c) Broadening of waist
d) High pitch of voice
2) Common sign of sexual maturation in girls is
a) Low pitch voice
b) Appearance of moustache and beard
c) Development of mammary glands
d) Broadening of shoulders
3) Which contraceptive method changes the hormonal balance of the body?
b) Diaphragms
c) Oral pills
d) Both a) and b)
4) What should be maintained for healthy society?
a) Rate of birth and death rate
b) Male and female sex ratio
c) Child sex ratio
d) None of these
10.Pea plants can have smooth seeds or wrinkled seeds. One of the phenotypes is completely dominant over the other. A farmer decides to pollinate one flower of a plant with smooth seeds using pollen from a plant with wrinkled seeds. The resulting pea pod has all smooth seeds.
i) Which of the following conclusions can be drawn?
(1) The allele for smooth seeds is dominated over that of wrinkled seeds.
(2) The plant with smooth seeds is heterozygous.
(3) The plant with wrinkled seeds is homozygous.
(b) 1 and 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
ii) Which of the following crosses will give smooth and wrinkled seeds in same proportion?
(a) RR X rr
(b) Rr X rr
(d) rr X rr
iii) Which of the following cross can be used to determine the genotype of a plant with dominant phenotype?
(a) RR X RR
(b) Rr X Rr
(c) Rr X RR
(d) RR X rr
iv) On crossing of two heterozygous smooth seeded plants (Rr), a total of 1000 plants were obtained in F1 generation. What will be the respective number of smooth and wrinkled seeds obtained in F1 generation?
(a) 750, 250
(b) 500, 500
(C) 800, 200
(d) 950, 50
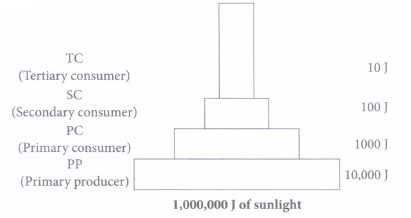
11.Food chains are very important for the survival of most species.When only one element is removed from the food chain it can result in extinction of a species in some cases.The foundation of the food chain consists of primary producers.Primary producers or autotrophs,can use either solar energy or chemical energy to create complex organic compounds,whereas species at higher trophic levels cannot and so must consume producers or other life that itself consumes producers. Because the sun’s light is necessary for photosynthesis,most life could not exist if the sun disappeared.Even so,it has recently been discovered that there are some forms of life,chemotrophs,that appear to gain all their metabolic energy from chemosynthesis driven by hydrothermal vents,thus showing that some life may not require solar energy to thrive.
1.If 10,000 J solar energy falls on green plants in a terrestrial ecosystem,what percentage of solar energy will be converted into food energy?
(d)It will depend on the type of the terrestrial plant
2.Matter and energy are two fundamental inputs of an ecosystem. Movement of
(a)Energy is by directional and matter is repeatedly circulating
(b)Energy is repeatedly circulating and matter is unidirectional
(c)Energy is unidirectional and matter is repeatedly circulating
(d)Energy is multidirectional and matter is bidirectional
3.Raj is eating curd/yoghurt. For this food intake in a food chain he should be considered as occupying
(a)First trophic level
(b)Second trophic level
(c)Third trophic level
(d)Fourth trophic level
4.Which of the following, limits the number of trophic levels in a food chain
(a)Decrease in energy at higher trophic levels
(b)Less availability of food
(c)Polluted air
5.The decomposers are not included in the food chain. The correct reason for the same is because decomposers
(a) Act at every trophic level at the food chain
(b) Do not breakdown organic compounds
(c) Convert organic material to inorganic forms
(d) Release enzymes outside their body to convert organic material to inorganic forms
12.Shyam participated in a group discussion in his inter school competition on the practical application of light and was very happy to win an award for his school. That very evening his father gave treat to celebrate Shyam’s win. Shyam while sitting saw an image of a person sitting at his backside in his curved plate and could see that person’s mobile drop in the flower bed. Person was not aware until Shyam went and informed him. He thanked Shyam for his clever move.
a)From which side of his plate Shyam observed the incident –
i)outward curved
ii)inward curved
iii)plane surface
b)Part of plate from which Shyam observed the incident acted like a-
i)concave mirror
ii)convex mirror
iii)plane mirror
c)The nature of the size of the image formed in above situation is –
i)real, inverted and magnified
ii)same size , laterally inverted
iii)virtual, erect and diminished
iv)real , inverted and diminished
d)Magnification of the image formed by convex mirror is –
more than 1
iii)equal to 1
iv)less than 1
- The location of image formed by a convex lens when the object is placed at infinity is
(a) at focus
(c) at optical center
- When the object is placed at the focus of concave lens, the image formed is
(a)real and smaller
(b) virtual and smaller
(c) virtual and inverted
- The size of image formed by a convex lens when the object is placed at the focus ofconvex lens is
(a) highly magnified
(b) point in size
- When the object is placed at 2F in front of convex lens, the location of image is
(b) between F and optical center
(c) at infinity
(d) none of the above
14.One of the wires in domestic circuits supply, usually with a red insulation cover, is called live wire. with black insulation is called neutral wire. The earth wire, which has insulation of green colour, is usually connected to a metal plate deep in the earth near the house appliances that has a metallic body. Overloading contact, in such a situation the current in the circuit abruptly increases. circuit prevents damage to the appliances and the circuit due to overloading.
1 When do we say that an electrical appliance
2 Mention the function of earth wire in electrical line
3 How is an electric fuse connected in a domestic circuit?
4 When overloading and short circuiting are said to occur?
5 What is a live wire?
15.Light of all the colours travel at the same speed in vacuum for all wavelengths. But in any transparent medium(glass or water), the light of different colours travels at different speeds for different wavelengths, which means that the refractive index of a particular medium is different for different wavelengths. As there is a difference in their speeds, the light of different colours bend through different angles. The speed of violet colour is maximum and the speed of red colour is minimum in glass so, the red light deviates least and violet colour deviates most. Hence, higher the wavelength of a colour of light, smaller the refractive index and less is the bending of light.
(i)Which of the following statements is correct regarding the propagation of Light of different colours of white light in air?
(a) Red light moves fastest.
(b) Blue light moves faster than green light.
(c) All the colours of the white light move with the same speed.
(d) Yellow light moves with the mean speed as that of the red and the violet light.
(ii)Which of the following is the correct order of wavelength?
(a) Red> Green> Yellow
(b) Red> Violet> Green
(c) Yellow> Green> Violet
(d) Red> Yellow> Orange
(iii)Which of the following is the correct order of speed of light in glass?
(a) Red> Green> Blue
(b) Blue> Green> Red
(c) Violet> Red> Green
(d) Green> Red> Blue
(iv)Which colour has maximum frequency?
16.The region around a magnet where magnetism acts is represented by the magnetic field.The force of magnetism is due to moving charge or some magnetic material. Like stationary charges produce an electric field proportional to the magnitude of charge, moving charges produce magnetic fields proportional to the current. In other words, a current carrying conductor produces a magnetic field around it. The subatomic particles in the conductor, like the electrons moving in atomic orbitals, are responsible for the production of magnetic fields. The magnetic field lines around a straight conductor (straight wire) carrying current are concentric circles whose centres lie on the wire.
1)The magnetic field associated with a current carrying straight conductor is in anti- clockwise direction. If the conductor was held horizontally along east west direction,what is the direction of current through it?
2)Name and state the rule applied to determine the direction of magnetic field in a straight current carrying conductor.
3)Ramus performs an experiment to study the magnetic effect of current around a current carrying straight conductor with the help of a magnetic compass. He reports that
a)The degree of deflection of magnetic compass increases when the compass is moved away from the conductor.
b)The degree of deflection of the magnetic compass increases when the current through the conductor is increased.
Which of the above observations of the student appears to be wrong and why?
Case Study Questions Class 10 Science CBSE Chapter Wise PDF
Related resources to prepare for cbse 10th science board exam 2024.
- CBSE class 10 Science syllabus 2024
- NCERT Book for Class 10th Science 2023-2024 (PDF)
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science
- CBSE Class 10 Science sample paper
- Previous Year Questions of CBSE Class 10 Science
- CBSE Class 10 Science Important Questions and Answers
- CBSE Class 10 Physics Chapter Wise Important Questions and Answers
- CBSE Class 10 Chemistry Chapter Wise Important Questions and Answers
- CBSE Class 10 Biology Chapter Wise Important Questions and Answers
- CBSE Class 10 Science Topper Answer Sheet
- CBSE Class 10 Science Practice Paper 2023 with Answers
- Class 10 CBSE Admit Card 2023-24
- CBSE Class 10 Date Sheet 2023
- CBSE Class 10 Syllabus 2023 - 2024
- CBSE Class 10 DELETED Syllabus 2023-24
- CBSE Class 10th Sample Paper 2022-23: Download Sample Question Papers and Marking Scheme
- CBSE Class 10 Previous Year Question Papers for 2022-23
- CBSE Class 10 Important Questions and Answers for 2023-24 of ALL Chapters
- CBSE Class 10 Practice Papers: All Subjects
- CBSE Topper Answer Sheet Class 10: Model Answer Paper Download PDF
- CBSE Class 10 Mock Tests: All Subjects
Get here latest School , CBSE and Govt Jobs notification and articles in English and Hindi for Sarkari Naukari , Sarkari Result and Exam Preparation . Download the Jagran Josh Sarkari Naukri App .
- Territorial Army Recruitment 2024
- RSMSSB Rajasthan CET Answer Key 2024
- ADRE Grade 4 Admit Card 2024
- MLSU Result 2024
- RSMSSB CET Admit Card 2024
- RSMSSB CET Exam Analysis 2024
- Rajasthan CET Question Paper 2024
- OSSC CGL Admit Card 2024
- RSMSSB Exam Calendar 2024
- Star Sighting Time Today
- CBSE Class 10 QnA
Latest Education News
ITBP Telecommunication Recruitment 2024 Notification: Registration Begins Soon for 526 SI, HC, Constable Posts
SSC CGL Result 2024 Date: Check Expected Date and Other Details
8th Pay Commission: 18 हजार की जगह कितनी होगी मिनिमम बेसिक सैलरी और कितनी बढ़ेगी पेंशन? जानें
ट्रेन छूट जाने पर उसी टिकट पर दूसरी ट्रेन से कैसे करें यात्रा? जानें यहां
Diwali 2024 Holiday: यूपी, बिहार और राजस्थान में दिवाली की कितनी छुट्टी? यहां देखें लिस्ट
[OUT] VMOU Result 2024: यहां देखें MA, BA, BCom, BSW, MBA, MSc, BCA, BEd और अन्य सभी यूजी पीजी डिप्लोमा मार्कशीट
RSMSSB CET Question Paper 2024: Download Rajasthan 12th Level Shift 1 and 2 Unofficial Answer Key PDF
ADRE Grade 4 Admit Card 2024 Out Live Updates: Direct Link to Download Hall Ticket at slrcg4.sebaonline.org, Check Updates
CLAT 2025 Correction Window Closing Today - Check Details Here
Kerala PSC Exam Calendar 2024-25 Released at keralapsc.gov.in: Download Month Wise Schedule Here
AIBE 19 Exam Dates Revised, Check Extended Registration Schedule Here
List of all Chief Justices of India (1950-2024)
Optical Illusion IQ Test: Only 1% Sharpest Eyes Can Find the Mouse Hidden Among Mushrooms In 5 Seconds!
Who is Justice Sanjiv Khanna? The Next CJI to be appointed on November 11th!
CGPSC Recruitment 2024: Apply Online for 341 SI and Subedar Vacancies
RPSC EO RO Exam 2022 Cancel: राजस्थान की ईओ, आरओ की बड़ी भर्ती परीक्षा नकल के कारण रद्द
CBSE Date Sheet 2025 PDF: Download CBSE Class 10, 12 Exam Timetable at cbse.gov.in
You have the intelligence of Sherlock Holmes if you can spot the word “Rose” in 3 seconds!
Vande Bharat Sleeper: Route, Trains, Coach Design and Ticket Price; Check All Details
Diwali Drawing 2024: 30+ Beautiful, Easy and Simple Diwali Poster Drawings for School Students
myCBSEguide
- Case Study Questions Class...
Case Study Questions Class 10 Science
Table of Contents
myCBSEguide App
Download the app to get CBSE Sample Papers 2023-24, NCERT Solutions (Revised), Most Important Questions, Previous Year Question Bank, Mock Tests, and Detailed Notes.
Download Case study questions for CBSE class 10 Science in PDF format from the myCBSEguide App . We have the new pattern case study-based questions for free download. Class 10 Science case study questions
This article will guide you through:
What are case study questions?
- Sample Papers with Case Study questions
- Class 10 Science Case Study question examples
- How to get case-based questions for free?
- How to attempt the case-based questions in Science?
Questions based on case studies are some real-life examples. The questions are asked based on a given paragraph i.e. Case Study. Usually, 4-5 questions are asked on the basis of the given passage. In most cases, these are either MCQs or assertion & reason type questions. Let’s take an example to understand. There is one paragraph on how nitrogen is generated in the atmosphere. On the basis of this paragraph, the board asks a few objective-type questions. In other words, it is very similar to the unseen passages given in language papers. But the real cases may be different. So, read this article till the end to understand it thoroughly.
What is CBE?
CBSE stands for competency-based education. The case study questions are part of this CBE. The purpose of CBE is to demonstrate the learning outcomes and attain proficiency in particular competencies.
Questions on Real-life Situations
As discussed the case study questions are based on real-life situations. Especially for grade 10 science, it is very essential to have the practical knowledge to solve such questions. Here on the myCBSEguide app, we have given many such case study paragraphs that are directly related to real-life implications of the knowledge.
Sample Papers with Case Study Questions
Class 10 Science Sample Papers with case study questions are available in the myCBSEguide App . There are 4 such questions (Q.No.17 to 20) in the CBSE model question paper. If you analyze the format, you will find that the MCQs are very easy to answer. So, we suggest you, read the given paragraph carefully and then start answering the questions. In some cases, you will find that the question is not asked directly from the passage but is based on the concept that is discussed there. That’s why it is very much important to understand the background of the case study paragraph.
CBSE Case Study Sample Papers
You can download CBSE case study sample papers from the myCBSEguide App or Student Dashboard. Here is the direct link to access it.
Case Study Question Bank
As we mentioned that case study questions are coming in your exams for the last few years. You can get them in all previous year question papers issued by CBSE for class 1o Science. Here is the direct link to get them too.
Class 10 Science Case Study Question Examples
As you have already gone through the four questions provided in the CBSE model question paper , we are proving you with other examples of the case-based questions in the CBSE class 10 Science. If you wish to get similar questions, you can download the myCBSEguide App and access the Sample question papers with case study-type questions.
Case-based Question -1
Read the following and answer any four questions: Salt of a strong acid and strong base is neutral with a pH value of 7. NaCl common salt is formed by a combination of hydrochloride and sodium hydroxide solution. This is the salt that is used in food. Some salt is called rock salt bed of rack salt was formed when seas of bygone ages dried up. The common salt thus obtained is an important raw material for various materials of daily use, such as sodium hydroxide, baking soda, washing soda, and bleaching powder.
- Phosphoric acid
- Carbonic acid
- Hydrochloric acid
- Sulphuric acid
- Blue vitriol
- Washing soda
- Baking soda
- Bleaching powder
Case-based Question -2
- V 1 + V 2 + V 3
- V 1 – V 2 +V 2
- None of these
- same at every point of the circuit
- different at every point of the circuit
- can not be determined
- 20 3 Ω 203Ω
- 15 2 Ω 152Ω
Case-based Question -3
- pure strips
- impure copper
- refined copper
- none of these
- insoluble impurities
- soluble impurities
- impure metal
- bottom of cathode
- bottom of anode
How to Attempt the Case-Based Questions in Science?
Before answering this question, let’s read the text given in question number 17 of the CBSE Model Question Paper.
All living cells require energy for various activities. This energy is available by the breakdown of simple carbohydrates either using oxygen or without using oxygen.
See, there are only two sentences and CBSE is asking you 5 questions based on these two sentences. Now let’s check the first questions given there.
Energy in the case of higher plants and animals is obtained by a) Breathing b) Tissue respiration c) Organ respiration d) Digestion of food
Now let us know if you can relate the question to the paragraph directly. The two sentences are about energy and how it is obtained. But neither the question nor the options have any similar text in the paragraph.
So the conclusion is, in most cases, you will not get direct answers from the passage. You will get only an idea about the concept. If you know it, you can answer it but reading the paragraph even 100 times is not going to help you.
Test Generator
Create question paper PDF and online tests with your own name & logo in minutes.
Question Bank, Mock Tests, Exam Papers, NCERT Solutions, Sample Papers, Notes
Related Posts
- CBSE Practice Papers 2023
- Class 10 Science Sample Papers 2024
- Competency Based Learning in CBSE Schools
- Class 11 Physical Education Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Sociology Case Study Questions
- Class 12 Applied Mathematics Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Applied Mathematics Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Mathematics Case Study Questions
3 thoughts on “Case Study Questions Class 10 Science”
Where is the answer
Class 10 Science MCQ
Leave a Comment
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Case Study Questions Class 10 Science Chapter 2 Acids, Bases, and Salts
- Post author: studyrate
- Post published:
- Post category: class 10th
- Post comments: 0 Comments
CBSE Board Exam is on the way, so you must practice some good Case Study Questions Class 10 Science to boost your preparation to score 95+% on Boards. In this post, you will get Case Study and Passage Based Questions that will come in CBSE Class 10 Science Board Exams.
Join our Telegram Channel, there you will get various e-books for CBSE 2024 Boards exams for Class 9th, 10th, 11th, and 12th.

In CBSE Class 10 Science Paper, Students will have to answer some questions based on Assertion and Re a son . There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage-based as well. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then the MCQ questions based on it will be asked.
Acids, Bases, and Salts Case Study Questions With Answers
Here, we have provided case-based/passage-based questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 2 Acids, Bases, and Salts
Case Study/Passage-Based Questions
Case Study 1:
A compound, X of sodium forms a white powder. It is a constituent of baking powder and is used in some antacids. When heated it gives a compound, Y which is anhydrous and absorbs water to become a hydrated salt. When this salt is kept in the open air, it loses water molecules in a process called efflorescence. When dissolved in water it forms a strong base and a weak acid, Z.
(i) What is the compound, X?
Answer: (c) NaOH.
(ii) The compound, Y is
Answer: (c) Na2CO3.10H2O
(iii) What is the nature of the solution formed by dissolving Y in water?
Answer: (a) Alkaline
(iv) Identify the compound, Z.
Answer: (b) H2CO3
(v) Sodium carbonate is a basic compound because it is a salt of a
Answer: (c) strong acid and weak base
Case Study 2:
pH is quite useful to us in a number of ways in daily life. Some of its applications are:
Control of pH of the soil : Plants need a specific pH range for proper growth. The soil may be acidic, basic, or neutral depending upon the relative concentration of H* and OH-. The pH of any soil can be determined by using pH paper. If the soil is too acidic, it can be corrected by adding lime to it. If the soil is too basic, it can be corrected by adding organic manure which contains acidic materials.
Regaining shine of a tarnished copper vessel by use of acids : A copper vessel gets tarnished due to formation of an oxide layer on its surface. On rubbing lenion on the vessel, the surface is cleaned and the vessel begins to shine again. This is due to the fact that copper oxide is basic in nature, which reacts with the acid (citric acid) present in lemon to form a salt (copper citrate) which is washed away with water. As a result, the layer of copper oxide is removed from the surface of the vessel and the shining surface is exposed.
Self-defence by animals through chemical warfare : Stings of bees and ants contain methanoic acid. When stung, it causes lot of pain and irritation. This can be cured by rubbing the affected area with mild base like baking soda.
(i) When black copper oxide placed in a beaker is treated with dilute HCl, its color changes to ( a) white (b) dark red (c) bluish-green (d) no change.
Answer: (c) bluish green
(ii) P is an aqueous solution of acid and Q is an aqueous solution of base. When these two are diluted separately, then (a) pH of P increases while that of Q decreases till neutralization.
(b) pH of P decreases while that of Q increases till neutralization. (C) pH of both P and Q decrease. (d) pH of both P and Q increase.
Answer: (a) pH of P increases while that of Q decreases till neutralisation.
(iii) Which of the following acids is present in bee sting? (a) Formic acid (b) Acetic acid (c) Citric acid (d) Hydrochloric acid
Answer: (c) Citric acid
(iv) Sting of ant can be cured by rubbing the affected area with soap because (a) it contains oxalic acid which neutralises the effect of formic acid (b) it contains aluminium hydroxide which neutralises the effect of formic acid (c) it contains sodium hydroxide which neutralises the effect of formic acid (d) none of these
Answer: (c) it contains sodium hydroxide which neutralises the effect of formic acid
(v) The pH of soil X is 7.5 while that of soil Y is 4.5. Which of the two soils, should be treated with powdered chalk to adjust its pH? (a) X only (b) Y only (c) Both X and Y (d) none of these
Answer: (b) Y only
Case Study 3: Acids, bases, and salts are essential substances in our daily lives and play crucial roles in various chemical reactions and processes. Acids are sour-tasting substances that can donate hydrogen ions (H+) when dissolved in water. They turn blue litmus paper red and have a pH value less than 7. Bases, on the other hand, are bitter-tasting substances that can accept hydrogen ions or donate hydroxide ions (OH-) when dissolved in water. They turn red litmus paper blue and have a pH value greater than 7. Salts are formed when acids react with bases, resulting in the neutralization process. They are formed by the combination of positive ions (cations) from bases and negative ions (anions) from acids. Understanding the properties and uses of acids, bases, and salts is important in various applications, such as in the preparation of medicines, household cleaning agents, and agricultural practices.
What are acids? a) Substances that can donate hydrogen ions when dissolved in water b) Substances that can accept hydrogen ions when dissolved in water c) Substances that turn blue litmus paper red d) Substances with a pH value less than 7 Answer: a) Substances that can donate hydrogen ions when dissolved in water
How are bases characterized? a) Sour-tasting substances b) Substances that can donate hydrogen ions c) Substances that turn red litmus paper blue d) Substances with a pH value less than 7 Answer: c) Substances that turn red litmus paper blue
What are salts formed from? a) Acids and bases b) Acids and metals c) Bases and metals d) Bases and water Answer: a) Acids and bases
What is the pH value of acids? a) Less than 7 b) Equal to 7 c) Greater than 7 d) Variable Answer: a) Less than 7
In which applications are acids, bases, and salts commonly used? a) Preparation of medicines b) Household cleaning agents c) Agricultural practices d) All of the above Answer: d) All of the above
Hope the information shed above regarding Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 2 Acids, Bases, and Salts with Answers Pdf free download has been useful to an extent. If you have any other queries about CBSE Class 10 Science Acids, Bases, and Salts Case Study and Passage Based Questions with Answers, feel free to comment below so that we can revert back to us at the earliest possible. By Team Study Rate
You Might Also Like
Science olympiad for class 10 – books, syllabus, pyq, cbse class 10 english previous year question(pyq) download pdf: last year english class 10 questions.

CBSE Class 10 Science Light – Reflection & Refraction MCQ Quiz with Answers
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- New QB365-SLMS
- 12th Standard Materials
- 11th Standard Materials
- 10th Standard Materials
- 9th Standard Materials
- 8th Standard Materials
- 7th Standard Materials
- 6th Standard Materials
- 12th Standard CBSE Materials
- 11th Standard CBSE Materials
- 10th Standard CBSE Materials
- 9th Standard CBSE Materials
- 8th Standard CBSE Materials
- 7th Standard CBSE Materials
- 6th Standard CBSE Materials
- Tamilnadu Stateboard
- Scholarship Exams
- Scholarships
CBSE 10th Standard Science Subject Case Study Questions
By QB365 on 21 May, 2021
QB365 Provides the updated CASE Study Questions for Class 10 , and also provide the detail solution for each and every case study questions . Case study questions are latest updated question pattern from NCERT, QB365 will helps to get more marks in Exams
QB365 - Question Bank Software
10th Standard CBSE
Final Semester - June 2015
Redox reactions are those reactions in which oxidation and reduction occur Simultaneously. A redox reaction is made up of two half reactions. In the first half reaction, oxidation takes place and in second half reaction, reduction occurs. Oxidation is a process in which a substance loses electrons and in reduction, a substance gains electrons. The substance which gains electrons is reduced and acts as an oxidising agent. On the other hand, a substance which loses electrons is oxidised and acts as a reducing agent. (i) Which of the following is a redox reaction?
(ii) Identify the reaction in which H2 02 is acting as a reducing agent.
(iii) For the following reactions, identify the one in which H 2 S acts as a reducing agent.
(iv) For the following reaction, identify the correct statement. \(\mathrm{ZnO}+\mathrm{CO} \longrightarrow \mathrm{Zn}+\mathrm{CO}_{2}\)
(v) In the following reaction, which substance is reduced? \(\mathrm{PbS}+4 \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{2} \longrightarrow \mathrm{PbSO}_{4}+4 \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}\)
(ii) If the pH of a solution is 8, then its [H + ] ion is
(iii) In terms of acidic strength, which one of the following is in the correct increasing order?
(iv) Which of the following compounds does not give H + ions in aqueous solution?
(v) Four solutions labelled as P, Q, Rand Shave pH values 1, 9, 3 and 13 respectively. Which of the following statements about the given solutions is incorrect?
Baking powder produces carbon dioxide on heating, so it is used in cooking to make the batter spongy. Although, baking soda also produces CO 2 on heating, but it is not used in cooking because on heating, baking soda produces sodium carbonate along with carbon dioxide. Sodium carbonate, thus, produced, makes the taste bitter. Baking powder is the mixture of baking soda and a mild edible acid. Generally, tartaric acid is mixed with baking soda to make baking powder. When baking powder is heated, NaHCO 3 decomposes to give CO 2 which makes bread and cake fluffy. Tartaric acid helps to remove bitter taste due to formation of sodium tartrate. \(2 \mathrm{NaHCO}_{3}+ \ \ \mathrm{C}_{4} \mathrm{H}_{6} \mathrm{O}_{6} \quad \longrightarrow \quad 2 \mathrm{CO}_{2}+2 \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}+\mathrm{Na}_{2} \mathrm{C}_{4} \mathrm{H}_{4} \mathrm{O}_{6}\) Baking soda Tartaric acid Carbon dioxide Sodium tartrate (i) On passing excess CO 2 gas in aqueous solution of sodium carbonate, the substance obtained is
(ii) When sodium hydrogen carbonate is added to acetic acid, it evolves a gas. Which of the following statements are true about the gas evolved? (I) It turns lime water milky (II) It extinguishes a burning splinter (III) It dissolves in a solution of sodium hydroxide (IV) It has a pungent odour
(iii) Select the correct statement regarding sodium hydrogen carbonate.
(iv) Acetic acid was added to a solid X kept in a test tube. A colourless and odourless gas was evolved. The gas was passed through lime water which turned milky. It was concluded that
(v) Which of the following statements are correct regarding baking soda? (I) Baking soda is sodium hydrogen carbonate (II) On heating, baking soda gives sodium carbonate (III) It is used for manufacture of soap (IV) It is an ingredient of baking powder
The chemical reactivity of an element depends upon its electronic configuration. All elements having less than eight electrons in the outermost shell show chemical reactivity. During chemical reactions, atoms of all elements tend to achieve a completely filled valence shell. Metals are electropositive in nature. They have tendency to lose one or more electrons present in the valence shell of their atoms to form cations and achieve nearest noble gas configuration. The compounds formed by the transfer of electrons from one element to other are known as ionic or electrovalent compounds. (i) The electronic configurations of three elements X, Y and Z are: X : 2 Y: 2, 8, 7 Z : 2, 8, 2 Which of the following is correct regarding these elements?
(ii) Element X reacts with element Y to form a compound Z. During the formation of compound Z, atoms of X lose one electron each whereas atoms of Y gain one electron each. Which of the following properties is not shown by compound Z?
(iii) Which of the following is correct representation of formation of magnesium chloride?
(iv) The electronic configuration of sodium ion is
(v)Which of the following represents an electropositive element?
A hydrocarbon (P) has the molecular formula C 10 H 22 .A hydrocarbon (Q) has two carbon atoms less than (P) and belong to the same homologous series. A hydrocarbon (R) has two carbon atoms more than (P) and belong to the same homologous series. (i) What is the molecular formula of (Q) ?
(ii) To which homologous series do the compound (P), (Q) and (R) belong?
(iii) What is the molecular formula of (R) ?
(iv) Identify the correct statement about compounds (P), (Q) and (R) .
(v) Compounds (P), (Q) and (R) are
The recurrence of properties of the elements after a certain regular intervals, when they are arranged in the increasing order of their atomic numbers, is called periodicity. There are a number of physical properties such as atomic size, metallic and non -metallic character, etc. which show periodic variation. In periodic table, various properties vary differently from moving left to right in a period and going down in a group. In a period, properties vary because from moving left to right in a period, number of shells remain same but valence electron increases by one number hence nuclear charge increases. In a group, on going down, number of valence shells increases while number of valence electrons remains same. (i) From top to bottom in a group of the periodic table, the electropositive character of the element
(ii) Which element has the largest size in the second period?
(iii) Which of the following elements has three valence electrons?
(iv) In the periodic table, the metallic character of elements (a) decreases from left to right and decreases down the group (b) decreases from left to right and increases down the group (c) increases from left to right and increases down the group (d) increases from left to right and decreases down the group (v) Which of the following increases along the period?
The small intestine is the longest part of the alimentary canal. It is a narrow tube of about 6 metres which lies coiled in the abdomen. The length of small intestine varies in different animals depending on the type of food they eat. (i) Humans are not able to digest cellulose whereas they are able to digest starch due to
(iii) Butter cannot be digested in the stomach as lipase and bile are(a) released in small intestine
(iv) Which of the following is a correct statement? (a) Herbivores have shorter small intestine as they eat grasses (b) Carnivores have larger small intestine as they eat meat (c) Herbivores have larger small intestine as they eat grasses (d) None of these (v) Various types of movements are generated by the ______ layer of the small intestine.
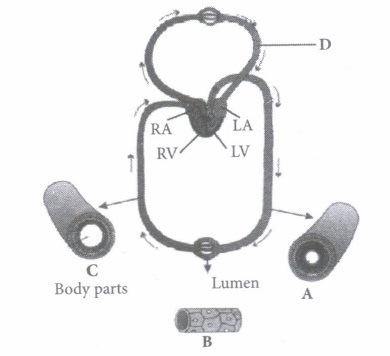
(iii) Which of the following animals shows double circulatory pathway?
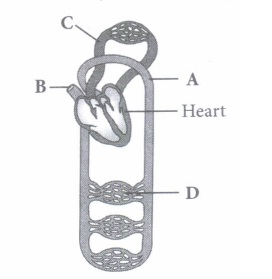
(v) Select the option which properly represents pulmonary circulation in humans. \(\text { (a) Left auricle } \frac{\text { Deoxygenated }}{\text { blood }}{\longrightarrow} \text { Lungs } \frac{\text { Oxygenated }}{\text { blood }} \text { Right ventricle }\) \(\text { (b) Left auricle } \frac{\text { Oxygenated }}{\text { blood }}{\longrightarrow} \text { Lungs } \frac{\text { Deoxygenated }}{\text { blood }}{\longrightarrow} \text { Right ventricle }\) \(\text { (c) Right ventricle } \frac{\text { Deoxygenated }}{\text { blood }}{\longrightarrow} \text { Lungs } \frac{\text { Oxygenated }}{\text { blood }} \rightarrow \text { Left auricle }\) \(\text { (d) Right ventricle } \frac{\text { Oxygenated }}{\text { blood }}>\text { Lungs } \frac{\text { Deoxygenated }}{\text { blood }} \gg \text { Left auricle }\)
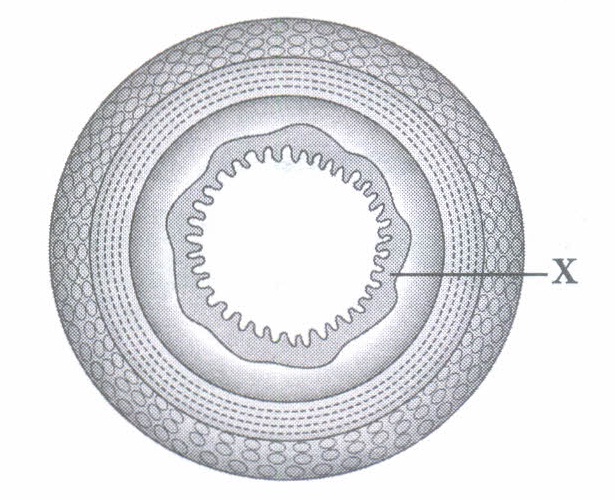
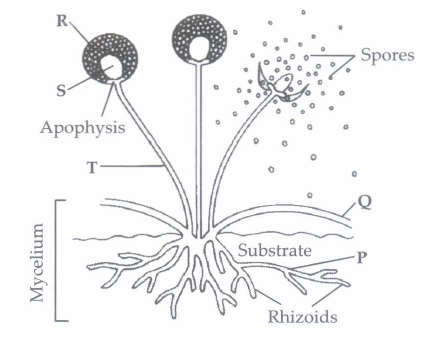
Spore formation, method of asexual reproduction is used by unicellular as well as multicellular organisms.Spores are microscopic units which could be air borne or are present in soil, etc. (i) A slice of bread kept in open for sometime shows growing white cottony mass which later turns black. This happens because (a) bacterial spores present in air germinate on the surface of bread slice (b) fungal spores present in air germinate on the surface of bread slice (c) protozoan microbes start feeding on bread slice (d) none ef these. (ii) Spore formation can be seen in
(iii) Bulb like structure at top of erect hyphae where spores are produced is
Gregor Mendel conducted hybridisation experiments on garden peas for seven years and proposed the laws of inheritance in living organisms. He investigated characters in the garden pea plant that were manifested as two opposing traits, e.g., tall or dwarf plants, yellow and green seeds, etc. (i) Among the seven pairs of contrasting traits in pea plant as studied by Mendel, the number of traits related to flower, pod and seed respectively were
(ii) The colour based contrasting traits in seven contrasting pairs, studied by Mendel in pea plant were
(iii) Refer to the given table of contrasting traits in pea plants studied by Mendel.
Which of the given traits is correctly placed? (a) (i), (ii) and (iii) only (b) (ii), (iii) and (iv) only (c) (ii) and (iii) only (d) (i), (ii), (iii) and (iv) (iv) Some of the dominant traits studied by Mendel were (a) round seed shape, green seed colour and axial flower position (b) terminal flower position, green pod colour and inflated pod shape (c) violet flower colour, green pod colour and round seed shape (d) wrinkled seed shape, yellow pod colour and axial flower position. (v) Which of the following characters was not chosen by Mendel?
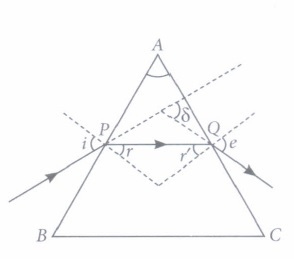
(ii) The angle between the incident ray and the emergent ray is called
(iii) When a ray is refracted through a prism, then
(iv) The angle of deviation depends on
(v) The rectangular surfaces of a prism are known as
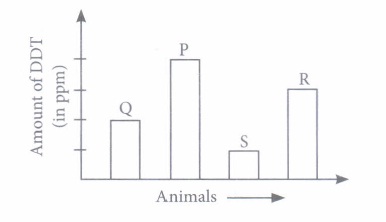
Some harmful non-biodegradable chemicals, i.e., pesticides (e.g., DDT) and heavy metals (e.g., mercury, arsenic cadmium, etc.) enter the bodies of organism through the food chain and go on concentrating at each trophic level. This phenomenon is called bio-magnification or biological magnification. (i) Refer to the given food chain Phytoplankton \(\longrightarrow\) Zooplankton \(\longrightarrow\) Small fish \(\longrightarrow\) Large fish \(\longrightarrow\) Fish eating birds If concentration of DDT in small fish is estimated to be 0.5 ppm, then amount of DDT in zooplankton and large fish would respectively be
(ii) Refer to the given table.
According to the given data. The correct order in a food chain will be
(iv) Higher amount of DDT disturb calcium metabolism of birds. This results in
(v) When animals are sprayed with poisons, they may die immediately, but their bodies still contain the poison. The poison in their bodies will then be passed on to the animals which eat them. What would be the consequence of a mass poisoning of the rabbit population in a grazing food chain and why? (a) Plants would die quickly as they are eaten by rabbits (b) Grasshopper would die quickly as all the animals in the food web would be affected (c) Western rattlesnakes would quickly become poisoned as they eat rabbits (d) Hawk would become poisoned as they feed on rabbits
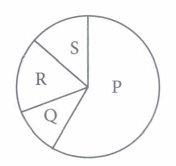
(v) Greenhouse effect is due to
Energy flow is the key function of an ecosystem. It is determined by the two basic laws of thermodynamics. Flow of energy in our ecosystem is unidirectional. Green plants capture approximately about 1% of the solar energy incident on the earth to carry out the process of photosynthesis. In an ecosystem, transfer of energy follows 10 percent law, i.e., only 10% energy is transferred from one trophic level to another and remaining 90% of energy is lost in respiration. (i) Read the given statements and select the incorrect one(s). I. At each trophic level organisms utilise energy in respiration. II. Only 10 percent of the solar radiations that fall on earth is used by green plants. III. Green plants are the ultimate source of entire energy as most of the food chain begin with them. IV. A food chain usually consist of 3-4 trophic levels.
(ii) Refer to the given flow chart. Plants \(\rightarrow\) Rat \(\rightarrow\) Snake 20 units 2 units 0.2 unit The given flow chart states that (a) flow of energy in an ecosystem is unidirectional (b) as we move along in a food chain the number of individuals at each trophic level decreases (c) only 10% of the total energy becomes available to next trophic level (d) both (a) and (c). (iii) Nearly 90% of the energy is wasted while moving from one trophic level to other. This energy is used in
(v) Which of the following correctly states the processes involved in energy transfer between the trophic levels?
*****************************************
Cbse 10th standard science subject case study questions answer keys.
(I) (b) : H 2 is oxidised to HCI while Cl 2 is reduced to HCl. (ii) (c) \((iii) (c): 2 \mathrm{Fe} \mathrm{Cl}_{3}+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{~S} \longrightarrow 2 \mathrm{FeCl}_{2}+2 \mathrm{HCl}+\mathrm{s}\) H 2 Sitself gets oxidised to Sand reduces FeCl 3 to FeCI 2 (iv) (a ): ZnO is reduced to Zn and CO is oxidised to CO 2 (v) (b) : H 2 O 2 is reduced to water by removal of oxygen.
(i) (c): As the pH value increases from 7 to 14, it represents decrease in H+ ion concentration in the solution. (ii) (c) : pH = -log l0 [H + ] = 8 log l0 [H + ] =-8 [H + ] = 10 - 8 mol/L (iii) (a) (iv) (b): C 2 H 5 OH is not an ionic compound, it is a covalent compound and hence does not give H + ions in aqueous solution. (v) (c) : (a) Lower the pH of the solution, more acidic is the solution and higher is the [H + ] ions Thus, solution P (pH = 1) has higher [H + ] ions than solution R (pH = 3). (b) Higher the pH of the solution, more basic is the solution and higher is the [OH - ] ions Thus, solution Q (pH = 9) has lower [OH - ] ions than solution S (pH = l3). (c) Solution P (pH = 1) is acidic which turns blue litmus solution red whereas solution Q (pH = 9) is basic which turns red litmus solution blue. (d) Solution P (pH = 1) is highly acidic while solution S (pH = l3) is highly basic and solution Q (pH = 9) is weakly basic.
\({ (i) }(\mathrm{b}): \mathrm{Na}_{2} \mathrm{CO}_{3}+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}+\mathrm{CO}_{2} \longrightarrow 2 \mathrm{NaHCO}_{3}\) (ii) (b) : \(\mathrm{NaHCO}_{3}+\mathrm{CH}_{3} \mathrm{COOH} \longrightarrow \mathrm{CH}_{3} \mathrm{COONa}\) \(+\mathrm{CO}_{2} \uparrow+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}\) Carbon dioxide gas is evolved which turns limewater milky. It extinguishes a burning splinter since it is not a supporter of combustion. It dissolves in sodium hydroxide solution and it is an odourless gas. \({ (iii) }(\mathrm{c}): 2 \mathrm{NaHCO}_{3} \stackrel{\text { Heat }}{\longrightarrow} \mathrm{Na}_{2} \mathrm{CO}_{3}+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}+\mathrm{CO}_{2}\) NaHCO 3 is soluble in water. \({ (iv) }(\mathbf{b}): \mathrm{NaHCO}_{3}+\mathrm{CH}_{3} \mathrm{COOH} \longrightarrow\) \(\mathrm{CH}_{3} \mathrm{COONa}+\mathrm{CO}_{2}+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}\) (v) (c): It is not used in manufacture of soap .
(i) (d) (Ii) (b): '2' is an ionic compound \({ (iii) }(\mathrm{a}): \mathrm{Mg} \longrightarrow \mathrm{Mg}^{2+}+2 e^{-}\) \(\mathrm{Cl}+e^{-} \longrightarrow \mathrm{Cl}^{-}\) \(\mathrm{Mg}^{2+}+2 \mathrm{Cl}^{-} \longrightarrow \mathrm{MgCl}_{2}\) 2,8,2 2,8 2,8,7 2,8,8 \((\text { iv })(\mathrm{d}): \mathrm{Na} \longrightarrow \mathrm{Na}^{+}+e^{-}\) 2,8,1 2,8 (v) (c): (a) and (d) represent electronegative elements and (b) represents a noble gas.
(i) (c) : Molecular formula of (Q) is CSH1Sas it has two carbon atoms less than (P). (ii) (c): Compounds (P), (Q) and (R) are alkanes having general formula C n H 2n+2 . (iii) (a): Molecular formula of (R) is C 12 H 26 as it has two carbon atoms more than (P) (iv) (b): Compound (P), (Q) and (R) belong to same homologous series so they have different physical properties but similar chemical properties. They have same general formula C n H 2n+2 .They . differ by 2 carbon atoms and 4 hydrogen atoms. (v) (a)
(i) (a): As the size of the atom increases down the group, electropositive character increases. (ii) (c): Li is the first element of the second period. As the size decreases in the period from left to right, therefore, Li is the largest atom in the period. (iii) (c): Al (Z = 13) : 2, 8, 3 (iv) (b): Metallic character of elements decreases from left to right and increases down the group. (v) (a): As we move from left to right along a period, the number of valence electrons increases from 1 to 8.
(i) (a): In human, cellulose is indigestible as it cannot be broken into smaller molecules due to absence of cellulase enzyme. (ii) (b): Finger-like projections that come out from mucosa of intestine form villi. Cells lining the villi produce numerous microscopic projections called microvilli giving a brush border appearance which increase the surface area for absorption enormously. Villi has a good supply of capillaries and a large lymph vessel for absorption of nutrients. If the inner lining of the small intestine will be smooth, the surface for absorption will be reduced. (iii) (a) (iv) (c) (v) (b)
(i) (c): A- Artery: Carries blood from heart to different body parts. It is thick-walled and elastic. It acts as a "pressure reservoir" for maintaining the blood flow. B - Capillary : Nutrients, hormones, gases, etc. can diffuse into tissue cells through capillaries and vice versa. It is thin-walled, and only one cell layer thick resting on basement membrane. C - Vein: Brings blood from different body parts to the heart. It is thin-walled and act as low-resistance conduct for blood flow. D - Pulmonary vein: Two pulmonary veins from each lung transport the oxygenated blood to the left atrium. (ii) (d): In amphibians, the left atrium receives oxygenated blood from the gills/lungs/skin and the right atrium gets the deoxygenated blood from other body parts. However, they get mixed up in the single ventricle which pumps out mixed blood i.e., incomplete double circulation (iii) (d): Whale is a mammal and in mammals, two separate circulatory pathways are found - systemic circulation and pulmonary circulation. Oxygenated and deoxygenated bloods received by the left and right atria respectively pass on to the left and right ventricles. Thus, oxygenated and deoxygenated bloods are not mixed. This is referred to as double circulation. (iv) (a) (v) (c): Pulmonary circulation is the movement of blood between heart and lungs. During this pathway deoxygenated blood entering the right atrium, moves into the right ventricle. From here it moves through the pulmonary arch into the lungs for oxygenation. Then from lungs the oxygenated blood moves into the left atrium through pulmonary veins.
(i) (b): The tiny spores of bread mould (Rhizopus) are always present in air. On coming in contact with moist surface of bread slice they settle on it and germinate to form new fungal hyphae which first look like white cottony mass and later turns black. (ii) (a): Mucor (fungus) reproduces asexually through spore formation. (iii) (d) (iv) (c) : Bacteria produce endospore which is a dormant and tough structure that enables bacteria to remain dormant for extended periods under unfavorable conditions. (v) (d)
(i) (a) : Characters studied by Mendel are as follows:
(i) (a): The angle between the two refracting surfaces of a prism is called angle of prism. (ii) (b): The angle between the incident ray and the emergent ray is called angle of deviation. (iii) (d): As the ray of light enters from rarer medium (air) to denser medium (glass), the angle of incidence is more than angle of refraction. (iv) (c): More be the refractive index, more be the angle of deviation and it also depends on the refractive index of prism. (v) (c): The refraction of light takes place through rectangular surfaces.
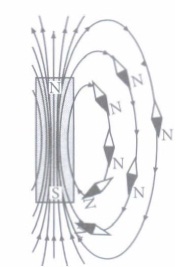
(i) (c): No two magnetic field lines are found to cross each other. If two field lines crossed each other, it would mean that at the point of intersection, the compass needle would point in two directions at the same time, which is not possible. (ii) (d): The magnetic field and hence the magnetic line of force exist in all the planes all around the magnet. (iii) (d): The relative strength of the magnetic field is shown by the degree of closeness of the field lines and the direction of the magnetic field is obtained by tangent to the field lines at the point of intersect. (iv) (d): The magnetic field lines due to a bar magnet are closed continuous curves directed from N to S outside the magnet and directed from S to N inside the magnet. Hence option (d) is correct. v) (d): Inside a bar magnet, the direction of field lines is from south pole to north pole
(i) (a): Due to bio-magnification, the concentration of DDT will always be less in zooplanktons than large fish (ii) (c) (iii) (b) : Due to bio-magnification the non bio-degradable chemicals such as DDT accumulate and go on concentrating at each trophic level. (iv) (d) : Higher amounts of DDT disturb calcium metabolism of birds resulting in thinning of egg shells and their premature breaking that kills the embryos. (v) (d)
( i) (b) : In the given pie chart, gases P, Q, Rand S respectively are CO 2 , CH 4 , CFCs and N 2 O. Methane is produced by incomplete combustion of biomass. (ii) (c): Methane (gas Q) is produced by incomplete biomass combustion and incomplete decomposition mostly by anaerobic methanogens. Flooded paddy fields, marshes and cattles are the major source of this gas. (iii) (c) : CO 2 is the principal greenhouse gas that helps to keep the earth warm. (iv) (d) (v) (c)
(i) (b): 1% of solar radiation is captured by plants. Sun is the ultimate source of all energy. (ii) (d) (iii) (d) (iv) (d): The given pyramid is pyramid of energy that shows the two basic laws of thermodynamics. (v) (c): Light energy from the sun is converted to chemical energy in producers via photosynthesis. This chemical energy is then transferred to primary consumer, then subsequently to secondary consumer via feeding.
Related 10th Standard CBSE Science Materials
10th standard cbse syllabus & materials, cbse 10th maths probability chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths statistics chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths surface areas and volumes chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths areas related to circles chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths circles chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths some applications of trigonometry chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths introduction to trigonometry chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths coordinate geometry chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths triangles chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths arithmetic progressions chapter case study questions with answers, cbse 10th maths quadratic equations chapter case study questions with answers, cbse 10th social science the making of a global world chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th social science nationalism in india chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th social science the rise of nationalism in europe chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths pair of linear equation in two variables chapter case study question with answers.

Class VI to XII
Tn state board / cbse, 3000+ q&a's per subject, score high marks.

10th Standard CBSE Study Materials

10th Standard CBSE Subjects

- Book Solutions
- State Boards
Case Study Questions Class 10 Science Control and Coordination
Case study questions class 10 science chapter 7 control and coordination.

CBSE Class 10 Case Study Questions Science Control and Coordination. Important Case Study Questions for Class 10 Board Exam Students. Here we have arranged some Important Case Base Questions for students who are searching for Paragraph Based Questions Control and Coordination.
At Case Study Questions there will given a Paragraph. In where some Important Questions will made on that respective Case Based Study. There will various types of marks will given 1 marks, 2 marks, 3 marks, 4 marks.
CBSE Case Based Questions Class 10 Science Biology Chapter 7
Case study : 1.
If the body design in the squirrel relied only on electrical impulses via nerve cells, the range of tissues instructed to prepare for the coming activity would be limited. On the other hand, if a chemical signal were to be sent as well, it would reach all cells of the body and provide the wideranging changes needed. This is done in many animals, including human beings, using a hormone called adrenaline that is secreted from the adrenal glands.
i) which is the target organ for the adrenaline hormone?
Ans: Heart is the target organ for the adrenaline hormone which increases the heartbeat rate.
ii) Which hormone is released by thyroid gland?
Ans: Thyroxine is released by thyroid gland.
iii) What is the function of thyroxine hormone?
Ans: It regulates carbohydrate, protein and fat metabolism in the body and promote the best balance for growth.
iv) Name the hormone released by ovary?
Ans: Estrogen and progesterone
V) Name the three hormonal glands located in the brain?
Ans: Pineal, pituitary and hypothalamus
CASE STUDY : 2
Some plants like the pea plant climb up other plants or fences by means of tendrils. These tendrils are sensitive to touch. When they come in contact with any support, the part of the tendril in contact with the object does not grow as rapidly as the part of the tendril away from the object. This causes the tendril to circle around the object and thus cling to it. More commonly, plants respond to stimuli slowly by growing in a particular direction. Because this growth is directional, it appears as if the plant is moving.
i) How many type of tropism are shown by plants? Name them.
Ans: Generally there are 6 type of tropism namely phototropism, gravitropism, chemotropism, thigmotropism, thermotropism and hydrotropism.
ii) The touch me not plant is an example of which tropism?
Ans: it is an example of thigmotropism.
iii) give one example of chemotropism?
Ans: growth of pollen tubes to wheels is one example of chemotropism.
iv) Name the plants hormone which promotes cell division?
Ans: Cytokinins promotes cell division in plants.
v) Name the plant hormone which inhibits growth?
Ans: Abscisic acid

CASE STUDY : 3
We also think about our actions. Writing, talking, moving a chair, clapping at the end of a programme are examples of voluntary actions which are based on deciding what to do next. So, the brain also has to send messages to muscles. This is the second way in which the nervous system communicates with the muscles. The communication between the central nervous system and the other parts of the body is facilitated by the peripheral nervous system consisting of cranial nerves arising from the brain and spinal nerves arising from the spinal cord. The brain thus allows us to think and take actions based on that thinking.
i) what are the three major parts of the brain?
Ans: Forebrain, Midbrain and hindbrain.
ii) what are the function of medulla?
Ans: It controls all the involuntary action such as blood pressure, salivation, vomiting, etc.
iii) Which fluid is present in our brain?
Ans: Cerebrospinal fluid.
iv) What is the function of hypothalamus?
Ans: It regulates homeostasis, releases hormones.
v) What is the function of mid brain?
Ans: The mid brain connects the forebrain and hindbrain.
CASE STUDY : 4
Body consists of dense networks of intricately arranged neurons. It sits in the forward end of the skull, and receives signals from all over the body which it thinks about before responding to them. Obviously, in order to receive these signals, this thinking part of the brain in the skull must be connected to nerves coming from various parts of the body.
i) What is reflex?
Ans: It is the sudden action done in response to something in the environment.
ii) How does the nervous tissue cause action?
Ans: When a nerve impulse reaches the muscles, the muscles fibres move by changing their shape and their arrangements in the cell.
iii) What is the function of the motor neuron?
Ans: It transmits the impulses from spinal cord to skeletal muscles.
iv) What is reflex arc?
Ans: It is the neural pathway that controls reflex starting from a sensory neuron and end at effector.
v) What is the role of sensory neuron?
Ans: It carry signals from outer part of body to central nervous system.
CASE STUDY : 5
In animals, such control and coordination are provided by nervous and muscular tissues. Touching a hot object is an urgent and dangerous situation for us. We need to detect it, and respond to it. How do we detect that we are touching a hot object? All information from our environment is detected by the specialised tips of some nerve cells. These receptors are usually located in our sense organs, such as the inner ear, the nose, the tongue, and so on. So gustatory receptors will detect taste while olfactory receptors will detect smell.
i) What are the parts of neuron?
Ans: Dendrite, nucleus, axon, nerve ending and a cell body.
ii) Which part of neuron receive the information first?
Ans: Dendritic tip receive the information first.
iii) At which place the electrical impulse get converted to a chemical impulse?
Ans: At synapse or a gap between nerve ending and a dendritic tip.
iv) What is neuromuscular junction?
Ans: The neuromuscular is made up of two words neuron & muscles, so it is the place where neuron and muscle fibre meet.
v) Draw the picture of neuron?
For more update follow net explanations page
Thnx for more confidence
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
We have a strong team of experienced Teachers who are here to solve all your exam preparation doubts
Odisha board class 6 geography chapter 3 মানচিত্র অধ্যয়ন, odisha board class 6 geography chapter 2 ভূগোলক-অক্ষাংশ ও দ্রাঘিমা, chhattisgarh state class 9 math chapter 14 solution, the value of work class 6 extra questions.
Sign in to your account
Username or Email Address
Remember Me

- Andhra Pradesh
- Chhattisgarh
- West Bengal
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Jammu & Kashmir
- NCERT Books 2022-23
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Notes
- NCERT Exemplar Books
- NCERT Exemplar Solution
- States UT Book
- School Kits & Lab Manual
- NCERT Books 2021-22
- NCERT Books 2020-21
- NCERT Book 2019-2020
- NCERT Book 2015-2016
- RD Sharma Solution
- TS Grewal Solution
- TR Jain Solution
- Selina Solution
- Frank Solution
- Lakhmir Singh and Manjit Kaur Solution
- I.E.Irodov solutions
- ICSE - Goyal Brothers Park
- ICSE - Dorothy M. Noronhe
- Micheal Vaz Solution
- S.S. Krotov Solution
- Evergreen Science
- KC Sinha Solution
- ICSE - ISC Jayanti Sengupta, Oxford
- ICSE Focus on History
- ICSE GeoGraphy Voyage
- ICSE Hindi Solution
- ICSE Treasure Trove Solution
- Thomas & Finney Solution
- SL Loney Solution
- SB Mathur Solution
- P Bahadur Solution
- Narendra Awasthi Solution
- MS Chauhan Solution
- LA Sena Solution
- Integral Calculus Amit Agarwal Solution
- IA Maron Solution
- Hall & Knight Solution
- Errorless Solution
- Pradeep's KL Gogia Solution
- OP Tandon Solutions
- Sample Papers
- Previous Year Question Paper
- Important Question
- Value Based Questions
- CBSE Syllabus
- CBSE MCQs PDF
- Assertion & Reason
- New Revision Notes
- Revision Notes
- Question Bank
- Marks Wise Question
- Toppers Answer Sheets
- Exam Paper Aalysis
- Concept Map
- CBSE Text Book
- Additional Practice Questions
- Vocational Book
- CBSE - Concept
- KVS NCERT CBSE Worksheets
- Formula Class Wise
- Formula Chapter Wise
- Toppers Notes
- Most Repeated Question
- Diagram Based Question
- Study Planner
- JEE Previous Year Paper
- JEE Mock Test
- JEE Crash Course
- JEE Sample Papers
- JEE Toppers Notes
- JEE Formula
- JEE Important Question
- JEE Mind Map
- JEE Integer-Numerical Type Question
- JEE Study Planner
- Important Info
- SRM-JEEE Previous Year Paper
- SRM-JEEE Mock Test
- VITEEE Previous Year Paper
- VITEEE Mock Test
- BITSAT Previous Year Paper
- BITSAT Mock Test
- Manipal Previous Year Paper
- Manipal Engineering Mock Test
- AP EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- AP EAMCET Mock Test
- COMEDK Previous Year Paper
- COMEDK Mock Test
- GUJCET Previous Year Paper
- GUJCET Mock Test
- KCET Previous Year Paper
- KCET Mock Test
- KEAM Previous Year Paper
- KEAM Mock Test
- MHT CET Previous Year Paper
- MHT CET Mock Test
- TS EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- TS EAMCET Mock Test
- WBJEE Previous Year Paper
- WBJEE Mock Test
- AMU Previous Year Paper
- AMU Mock Test
- CUSAT Previous Year Paper
- CUSAT Mock Test
- AEEE Previous Year Paper
- AEEE Mock Test
- UPSEE Previous Year Paper
- UPSEE Mock Test
- CGPET Previous Year Paper
- BCECE Previous Year Paper
- JCECE Previous Year Paper
- Crash Course
- Previous Year Paper
- NCERT Based Short Notes
- NCERT Based Tests
- NEET Sample Paper
- Previous Year Papers
- Quantitative Aptitude
- Numerical Aptitude Data Interpretation
- General Knowledge
- Mathematics
- Agriculture
- Accountancy
- Business Studies
- Political science
- Enviromental Studies
- Mass Media Communication
- Teaching Aptitude
- Verbal Ability & Reading Comprehension
- Logical Reasoning & Data Interpretation
- CAT Mock Test
- CAT Important Question
- CAT Vocabulary
- CAT English Grammar
- MBA General Knowledge
- CAT Mind Map
- CAT Study Planner
- CMAT Mock Test
- SRCC GBO Mock Test
- SRCC GBO PYQs
- XAT Mock Test
- SNAP Mock Test
- IIFT Mock Test
- MAT Mock Test
- CUET PG Mock Test
- CUET PG PYQs
- MAH CET Mock Test
- MAH CET PYQs
- NAVODAYA VIDYALAYA
- SAINIK SCHOOL (AISSEE)
- Mechanical Engineering
- Electrical Engineering
- Electronics & Communication Engineering
- Civil Engineering
- Computer Science Engineering
- CBSE Board News
- Scholarship Olympiad
- School Admissions
- Entrance Exams
- All Board Updates
- Miscellaneous
- State Wise Books
- Engineering Exam
- STATE WISE BOOKS
- ENGINEERING EXAM
- SCHOLARSHIP OLYMPIAD
- STATE BOOKS
CBSE Class 10 Science Case Based MCQ Questions
CBSE Term 1 exam is not so far and surely you have begun the preparation for the board exam. Therefore we have dedicated this page to help you out in your preparation. This year for the first time the board has introduced the Case based Questions which will be asked in the Term 1 exam that is likely to be held in November-December.
Therefore, we have brought you the CBSE Class 10 Science Case Based MCQ on this page. The questions are given in objective types. Such types of questions are solved by reading the given scenario in the paragraph.
All these science case study questions are developed as per the new CBSE Pattern. The team of subject matter experts have crafted the given MCQs. The Case Based Questions that we are providing here are worthy to solve and practice because class 10th syllabus has been taken into consideration while preparing the problems.
CBSE Class 10 Science Case Study, Assertion & Reasoning, MCQ
The Class tenth CBSE Science Case Study, Assertion & Reasoning, MCQs are very helpful in practicing and getting a deep understanding in the topics of science. However, a comprehensible knowledge of NCERT Science Book is a must to be able to solve these types of problems.
The PDF that is available here to download contains the problems in three different variants; One is general objective types of questions that is MCQ (Multiple Choice Questions), second one is Assertion and Reasoning and the last one is Case-Based Questions.
If you Download PDF CBSE Class 10 Science Case Study from the given links, then you will be able to get the quick revision for each chapter that will help you to recall your learnings and give you information about some important Chemicals Formulas and reactions.
What are Assertion & Reasoning Questions?
Assertion & Reasoning questions are basically a type of multiple-choice question that is solved by reading the given statement and the reason. The question typically consists of one statement followed by its reason. Students' duty is to verify both statements and reason whether they are correct or not and if they are correct then it is time to look at whether the given statement truly satisfies the reason or not.
These questions should not be difficult to solve but you have to have rigorous and extensive practice. The Assertion & Reasoning questions along with the solutions are given in the CBSE Class 10 Science case study 2021-2022 PDF that is available here.
Class 10th has very basic and important chapters that are necessary to solve. A few chapters that are available in the beginning of the science books are Chemical Reactions and Equations, Acids, Bases and Salts, Metals and Non-metals, Carbon and Its Compounds, Periodic Classification of Elements, Life Processes, etc.
Since you are here to find out the CBSE Class 10 Science MCQ Based Questions, the possibilities are you need CBSE Class 10 Maths Case Study Questions too.
FAQs on CBSE Class 10th Science Case Study Questions

Case Study Questions are based on the data which are given in the form of passage. These types of questions generally consist of real life examples. Usually it contains upto 4 or 5 questions.
To prepare for Class 10 Science MCQ Be thorough with the concepts, Practice the questions regularly, Attempt online tests as much as you can. To do all these things visit the Selfstudys.com. They are providing everything for free of cost.
In class 10 Science Based Questions you will be asked to answer the questions that are explained in the standard Xth Science Syllabus. However, the problems will be related to real world examples.
To find Class 10 Science Chapter wise Assertion and Reason Questions you simply need to reach at the Selfstudys website. It provides all the study resources for free of cost. You will be able to download the assertion reason with solutions as well.
No, CBSE Class 10 Science Case Based MCQ Question is not difficult, if you pay a good attention to the given paragraph. It is important to be able to find the tiny details in the passage to answer the Case Based questions.

CBSE Class 10 Science 2024-25: Chapter 10 Human Eye and Colourful World Refraction Competency-Based Questions with Answers; Download Free PDF

CBSE Board Exams 2025 : Practical Exam Schedule 2025 Released – Check Dates & Subject-Wise Marks Here

CBSE Class 10 Science 2024-25: Chapter 9 Light-Reflection and Refraction Competency-Based Questions with Answers; Download Free PDF

CBSE Class 10 Science 2024-25: Chapter 8 Heredity and Evolution Competency-Based Questions with Answers; Download Free PDF

CBSE Class 10 Science 2024-25: Chapter 7 Reproduction Competency-Based Questions with Answers; Download Free PDF

CBSE Class 10 Science 2024-25: Chapter 6 Control and Co-ordination Competency-Based Questions with Answers; Download Free PDF

- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Maths
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths
- CBSE Syllabus 2023-24
- Social Media Channels
- Login Customize Your Notification Preferences

- Second click on the toggle icon

Provide prime members with unlimited access to all study materials in PDF format.
Allow prime members to attempt MCQ tests multiple times to enhance their learning and understanding.
Provide prime users with access to exclusive PDF study materials that are not available to regular users.

CBSE Expert
Class 10 Science: Case Study Chapter 6 Life Processes PDF Download
In CBSE Class 10 Science Paper, Students will have to answer some questions based on Assertion and Reason . There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage-based as well. In that, a paragraph will be given.

Here we are providing you with Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Life Processes Case Study Questions, by practicing this Case Study and Passage Based Questions will help you in your Class 10th Board Exam.
Case Study Chapter 6 Life Processes
Here, we have provided case-based/passage-based questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Life Processes
Case Study/Passage-Based Questions
Question 1:
Transpiration is the evaporative loss of water by plants. It occurs mainly through the stoma in the leaves. Besides the loss of water vapor in transpiration, the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the leaf also occurs through pores called stomata. Normally stomata remain open in the daytime and close during the night
(i) Which of the following will not directly affect transpiration?
Answer: (d) Chlorophyll content of leaves
(ii) Water vapour comes out from the plant leaf through the stomatal opening. Through the same stomatal opening, carbon dioxide diffuses into the plant during photosynthesis. Reason out the above statements . using one of following options. (a) The above processes happen only during night time. (b) One process occurs during day time and the other at night. (c) Both processes cannot happen Simultaneously. (d) Both processes can happen together at day time.
Answer: (d) Both processes can happen together at day time.
(iii) Which of the following statements is not true for stomatal apparatus? (a) Guard cells invariably possess chloroplasts and mitochondria. (b) Guard cells are always surrounded by subsidiary cells. (c) Stomata are involved in gaseous exchange. (d) Inner wall of guard cells are thick.
Answer: (b) Guard cells are always surrounded by subsidiary cells.
(iv) Which of the following is not a purpose of transpiration? (a) Helps in absorption and transport in plants (b) Prevents loss of water (c) Maintains shape and structure of plants by keeping the cells turgid (d) Supplies water for photosynthesis
Answer: (b) Prevents loss of water
Answer: (a) P-Atmospheric temperature; Q-Atmospheric pressure
Question 2:
Heterotrophic nutrition is a mode of nutrition in which organisms obtain readymade organic food from outside sources. The organisms that depend upon outside sources for obtaining organic nutrients are called heterotrophs. Heterotrophic nutrition is of three types: saprophytic, parasitic, and holozoic nutrition.
(i) In which of the following groups of organisms food material is broken outside the body and absorbed? (a) Mushroom, green plants, Amoeba (b) Yeast, mushroom, bread mould (c) Paramecium, Amoeba, Cuscuta (d) Cuscuta, lice, tapeworm
Answer: (b) Yeast, mushroom, bread mould
(ii) Which of the following is a parasite? (a) Yeast (b) Taenia (c) Amoeba (d) Earthworm
Answer: (b) Taenia
(iii) Which of the following is an example of saprotroph? (a) Grass (b) Mushroom (c) Amoeba (d) Paramecium
Answer: (b) Mushroom
(iv) Heterotrophic nutrition involves (a) production of simple sugar from inorganic compounds (b) utilisation of chemical energy to prepare food (c) utilisation of energy obtained by plants (d) all of these.
Answer: (c) utilisation of energy obtained by plants
(v) In Paramecium, food enters the body through (a) mouth (b) pseudopodia (c) cilia (d) cytostom
Answer: (d) cytostom
You can also practice Class 10 Science MCQ Questions for Board Exams.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Download India's best Exam Preparation App Now.
Key Features
- Revision Notes
- Important Questions
- Previous Years Questions
- Case-Based Questions
- Assertion and Reason Questions
No thanks, I’m not interested!

Gurukul of Excellence
Classes for Physics, Chemistry and Mathematics by IITians
Join our Telegram Channel for Free PDF Download
Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Life Processes
- Last modified on: 3 years ago
- Reading Time: 7 Minutes
In CBSE Class 10 Science Paper, Students will have to answer some questions based on Assertion and Reason . There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage based as well. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then the MCQ questions based on it will be asked.
Here, we have provided case based/passage based questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Life Processes .
Question 1:
Read the following and answer any four questions from (i) to (v).
All living cells need nutrients, O, and other essential substances. Also, the waste and harmful substances need to be removed continuously for healthy functioning of cells. So, a well developed transport system is mandatory for living organisms. Complex organisms have special fluids within their bodies to transport such materials. Blood is the most commonly used body fluid by most of the higher organisms. Lymph also helps in the transport of certain substances.
(i) Which of the following does not exhibit phagocytic activity? (a) Monocytes (b) Neutrophils (c) Basophil (d) Macrophage
(ii) Amount of blood corpusles in changed in dengue fever. One of the common symptoms observed in people infected with dengue fever is (a) significant decrease in RBC count (b) significant decrease in WBC count (c) significant decrease in platelets count (d) significant increase in platelets count.
(iii) Why are WBCs called soldiers of the body? (a) They are capable of squeezing out of blood capillaries. (b) They are manufactured in bone marrow. (c) They fight against disease causing germs. (d) They have granular cytoplasm with lobed nucleus.
(iv) Name the blood cells, whose reduction in number can cause clotting disorder, leading to excessive loss of blood from the body. (a) Erythrocytes (b) Neutrophils (c) Leucocytes (d) Thrombocytes
(v) Which of the following is the correct feature of lymph? (a) It is similar to the plasma of blood, but is colourless and contains less proteins. (b) It is similar to the WBCs of blood, but is colourless and contain more proteins. (c) It is similar to the RBCs of blood and red in colour. (d) It contains more fats.
Question 2:
Heterotrophic nutrition is a mode of nutrition in which organisms obtain readymade organic food from outside sources. The organisms that depend upon outside sources for obtaining organic nutrients are called heterotrophs. Heterotrophic nutrition is of three types: saprophytic, parasitic and holozoic nutrition.
(i) In which of the following groups of organisms food material is broken outside the body and absorbed? (a) Mushroom, green plants, Amoeba (b) Yeast, mushroom, bread mould (c) Paramecium, Amoeba, Cuscuta (d) Cuscuta, lice, tapeworm
(ii) Which of the following is a parasite? (a) Yeast (b) Taenia (c) Amoeba (d) Earthworm
(iii) Which of the following is an example of saprotroph? (a) Grass (b) Mushroom (c) Amoeba (d) Paramecium
(iv) Heterotrophic nutrition involves (a) production of simple sugar from inorganic compounds (b) utilisation of chemical energy to prepare food (c) utilisation of energy obtained by plants (d) all of these.
(v) In Paramecium, food enters the body through (a) mouth (b) pseudopodia (c) cilia (d) cytostome
Download Books – Exam Special
Sample Papers for CBSE 2025 Exams
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 8 All Subjects (for 2025 Exams)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 9 All Subjects (for 2025 Exams)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 10 All Subjects (for 2025 Exams)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 All Subjects (for 2025 Exams)
CBSE Class 10 Most Downloaded Books
- CBSE Important Numerical Problems Class 10 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Practical Based Questions for Class 10 Science Board Exams
- CBSE Important Diagram Based Questions Class 10 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Most Repeated Questions for Class 10 Science Board Exams
CBSE Class 12 Most Downloaded Books
- CBSE Important Diagrams & Graphs Asked in Board Exams Class 12 Physics
- CBSE Important Numericals Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Laws & Principles Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Definitions Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- Master Organic Conversions CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Board Exams
- CBSE Class 12 Physics Chapterwise Important Questions
CBSE Class 8 Most Downloaded Books
- Worksheets for CBSE Class 8 Maths – Chapterwise
ICSE Class 10
- ICSE Important Numericals Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams (215 Numericals)
- ICSE Important Figure Based Questions Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams (230 Questions)
- ICSE Mole Concept and Stoichiometry Numericals Class 10 Chemistry (65 Numericals)
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Chemistry BOARD Exams (150 Qs)
- ICSE Important Functions and Locations Based Questions Class 10 Biology
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Biology BOARD Exams (100 Qs)
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Geography BOARD Exams
- ICSE Revision Notes for Class 10 Chemistry BOARD Exams
- ICSE Revision Notes for Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams
ICSE Class 9
- ICSE Important Figure Based Questions Class 9 Physics Exams
- ICSE Important Numerical Problems for Class 9 Physics Exams
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 9 Geography BOARD Exams (150 Qs)
CBSE Chapter-Wise Test Papers
- CBSE Class 9 Science Chapterwise Test Papers
- CBSE Class 10 Science Chapterwise Test Papers
- CBSE Class 10 Maths Chapterwise Test Papers
- CBSE Class 10 Social Science Chapterwise Test Papers
- CBSE Class 12 Physics Chapterwise Test Papers
- CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Chapterwise Test papers
✨ Join our Online NEET Test Series for 499/- Only for 1 Year
Leave a Reply Cancel reply

Editable Study Materials for Your Institute - CBSE, ICSE, State Boards (Maharashtra & Karnataka), JEE, NEET, FOUNDATION, OLYMPIADS, PPTs
Discover more from Gurukul of Excellence
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading
- Electric Currents and Its Effects Class 7 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 10

Last Updated on October 22, 2024 by XAM CONTENT
Hello students, we are providing case study questions for class 7 science. Case study questions are the new question format that is introduced in CBSE board. The resources for case study questions are very less. So, to help students we have created chapterwise case study questions for class 7 science. In this article, you will find case study questions for cbse class 7 science chapter 10 Electric Currents and Its Effects.

Table of Contents
Case Study Questions on Electric Currents and Its Effects
Question 1:
Read the given passage below and answer the question:
Electricity is the form of energy which we use electricity for many purposes to make our tasks easier. Electricity makes it possible to light our homes, roads, offices, markets and factories even after sunset. A bulb has a thin wire that gives off light. The wire of an electric bulb gets heated to such a high temperature that it starts glowing. Nowadays The fluorescent CFLs and LED bulbs are being used for lighting as they are considered to much better than incandescent electric bulbs. However, damaged CFLs need to be disposed off safely. It is advised to use electrical appliances and gadgets, which are electricity efficient. It also advisable to use ISI marked electrical appliances and gadgets
Q.1. What is the name of thin wire in the electric bulb? (a) Element (b) Coil (c) Filament (d) Fuse
Difficulty Level: Easy
Ans. Option (c) is correct. Explanation: An electric bulb has a filament that is connected to its terminals. The filament of an electric bulb gets heated to such a high temperature that it starts glowing.
Q.2. CFLs and LED stand for: (a) Compact fluorescent lamps and light emitting diode. (b) Composed fluorescent lamps and light emitting diode. (c) Compact fluorescent lamps and light emission diode. (d) Composed fluorescent lamps and light emission diode.
Difficulty Level: Medium
Ans. Option (a) is correct. Explanation: CFLs – Compact fluorescent lamps, LED – light emitting diode.
Q.3. Fluorescent tubes and CFLs contain toxic gas: (a) carbon monoxide (b) water vapour (c) mercury vapours (d) Chlorofluorocarbons
Difficulty Level: Hard
Ans. Option (c) is correct. Explanation: Fluorescent tubes and CFLs contain mercury vapour, toxic in nature. Therefore, damaged fluorescent tubes or CFLs need to be disposed off safely.
Q.4. What is a disadvantage of using incandescent electric bulbs? How LED bulbs are better than incandescent bulbs and CFLs?
Ans. Incandescent electric bulbs give heat therefor, a part of electricity consumed is used in producing heat which results in the wastage of electricity. LED bulbs consume less electricity as compared to incandescent bulbs or CFLs. Thus, LED bulbs are much electricity efficient.
Q.5. Who assigns ISI mark? Why is it suggested to use ISI mark products?
Ans. Bureau of Indian Standards, New Delhi assigns a Standard Mark on products, called ISI mark. The ISI mark is an assurance of conformity to the specifications given on the products. It is therefore suggested to use ISI mark products.
- Motion and Time Class 7 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 9
- Reproduction in Plants Class 7 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 8
- Transpirations in Animals and Plants Class 7 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 7
- Respiration in Organisms Class 7 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 6
- Physical and Chemical Changes Class 7 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 5
- Acids Bases and Salts Class 7 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 4
- Heat Class 7 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 3
Nutrition in Animals Class 7 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 2
Nutrition in plants class 7 case study questions science chapter 1, topics from which case study questions may be asked.
- Define electric current.
- Define electricity.
- Discuss electric circuits and its components.
- Describe the heating effect of electric current.
- Explain the magnetic effect of electric current.
We use electrical appliances in everyday life from morning to night. We use electric bulbs, air conditioners, refrigerators, etc., They run with the help of electrical energy.
- Electricity is the form of energy, which is used to run appliances, move things and to do work using these appliances.
- Electricity can be generated naturally through lightning or artificially through the generator.
- Electric circuit is a continuous and closed circuit of electric current.
Components of electric circuit: Bulb, electric cell, switch (key), conductors, bulb and other devices which are used .
For further practice on case study questions related to Class 7 Science Chapter 10 Electric Currents and Its Effects, we recommend exploring the link given below.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Electric Currents and Its Effects Case Study Questions
Q1: what are case study questions for cbse examinations.
A1: Case study questions in CBSE examinations typically involve scenarios or real-life examples, requiring students to apply their understanding of concepts to solve problems or analyze situations.
Q2: Why are case study questions important for understanding class 7 science chapters?
A2: Case study questions provide a practical context for students to apply theoretical knowledge to real-world situations, fostering deeper understanding and critical thinking skills.
Q3: How do case study questions differ from other question types?
A3: Unlike direct questions that test specific knowledge, case study questions involve analyzing a scenario, understanding the context, and applying various scientific concepts to answer the questions. They test higher-order thinking skills such as analysis, synthesis, and evaluation.
Q4: Are there any resources available online for students to practice case study questions on class 7 science chapters for CBSE exams?
A4: Yes, several educational websites offer case study questions for CBSE students preparing for science examinations. We also offer a collection of case study questions for all classes and subject on our website. Visit our website to access these questions and enhance your learning experience. There is another website Physics Gurukul that offers a large collection of case study questions.
Q5: How can students effectively prepare for case study questions on Electric Currents and Its Effects for CBSE exams?
A5: Effective preparation strategies include regular revision of concepts, solving practice questions, analyzing case studies from previous exams, seeking clarification on doubts, and consulting with teachers or peers for guidance and support.
Q6: How can teachers incorporate case study questions on Electric Currents and Its Effects class 7 science into classroom teaching?
A6: Teachers can integrate case studies into lesson plans, group discussions, or interactive activities to engage students in active learning, promote problem-solving skills, and facilitate a deeper understanding of Electric Currents and Its Effects.
Q7: What steps should I follow to correctly answer case study questions?
A7: Follow these steps: Read the case study carefully. Understand the scenario and the information provided. Identify the key concepts. Determine which scientific principles or concepts are relevant to the case study. Analyze the information. Break down the information, identify relationships, and note any data or facts given. Answer the questions. Apply your knowledge to answer the questions, ensuring that your responses are based on the case study and the relevant scientific concepts.
Q8: What should I check when reading a case study?
A8: Check the following: Context and background: Understand the setting and context of the case study. Key facts and data: Identify important details, data points, and observations mentioned. Relevant concepts: Recognize which scientific concepts and principles are applicable. Questions asked: Carefully read each question to understand what is being asked and how it relates to the case study.
Q9: What are common mistakes to avoid when answering case study questions?
A9: Common mistakes include: Not reading the case study carefully: Missing important details and context. Ignoring key concepts: Failing to identify and apply relevant scientific principles. Superficial analysis: Providing answers that lack depth and do not fully address the questions. Making assumptions: Adding information not provided in the case study or making unsupported assumptions.
Q10: How can I ensure my answers are thorough and well-structured?
A10: Ensure your answers are thorough and well-structured by: Organizing your thoughts: Structure your answer logically with a clear introduction, body, and conclusion. Using evidence: Support your answers with specific information from the case study. Applying relevant concepts: Clearly explain how scientific principles relate to the case study. Reviewing your answers: Check for completeness and accuracy, ensuring all parts of the question are addressed.
Q11: What are the important keywords from the chapter “Electric Currents and Its Effects”?
A11: Important keywords from the chapter “Electric Currents and Its Effects” are given below: Appliances: A machine or device designed to perform a specific task or function. Generator: A machine which generates something for example electricity. Circuit: A circular path in which electricity flows. Resistance: An electrical component which resists or opposes the flow of electric current. Fuse: A safety device used in electric circuits. Coil: A long thin piece of wire spiralled into circles.

Related Posts


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
6&,(1&( &odvv ; 6dpsoh &dvh 6wxglhv 5hdg wkh iroorzlqj dqg dqvzhu dq\ irxu txhvwlrqv iurp wr 0dueoh¶v srsxodulw\ ehjdq lq dqflhqw 5rph dqg *uhhfh zkhuh zklwh dqg rii zklwh pdueoh zhuh
As mentioned above, Case Based Questions will carry a total of 12 marks i.e about 15 percent of the total CBSE Class 10 Science marks will come from the Case Study Based Question.
The Science Subject case study for class 10th covers a wide range of chapters from the Science. Students willing to score good marks in their board exams can use it. The questions are highly interactive and it allows students to use their thoughts and skills to solve such kinds of questions. Case Study Questions Class 10 Science
As you have already gone through the four questions provided in the CBSE model question paper, we are proving you with other examples of the case-based questions in the CBSE class 10 Science. If you wish to get similar questions, you can download the myCBSEguide App and access the Sample question papers with case study-type questions.
These CBSE Class 10 Science Case Studies have been developed by experienced teachers of schools.studyrate.in for the benefit of Class 10 students. Class 10th Maths Case Study Questions; Benefits of Case Study Questions. Engaging with case study questions in Class 10 Science offers several benefits. Let's explore some of them:
A8: Check the following: Context and background: Understand the setting and context of the case study. Key facts and data: Identify important details, data points, and observations mentioned. Relevant concepts: Recognize which scientific concepts and principles are applicable. Questions asked: Carefully read each question to understand what is being asked and how it relates to the case study.
Hello students, we are providing case study questions for class 10 science. Case study questions are the new question format that is introduced in CBSE board. The resources for case study questions are very less. So, to help students we have created chapterwise case study questions for class 10 science.
Case Study Class 10 Science: Here, you will get class 10 Science case study questions and answers pdf at free of cost. Along with you can also download case study questions class 10 Science chapter wise for getting higher marks in board examinations.
Hello students, we are providing case study questions for class 10 science. Case study questions are the new question format that is introduced in CBSE board. The resources for case study questions are very less. So, to help students we have created chapterwise case study questions for class 10 science.
There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage-based as well. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then the MCQ questions based on it will be asked. Acids, Bases, and Salts Case Study Questions With Answers. Here, we have provided case-based/passage-based questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 2 Acids, Bases, and Salts
In CBSE Class 10 Science Paper, Students will have to answer some questions based on Assertion and Reason. There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage based as well. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then the MCQ questions based on it will be asked. Here, we have provided … Continue reading Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 1 ...
QB365 Provides the updated CASE Study Questions for Class 10 , and also provide the detail solution for each and every case study questions . Case study questions are latest updated question pattern from NCERT, QB365 will helps to get more marks in Exams
At Case Study Questions there will given a Paragraph. In where some Important Questions will made on that respective Case Based Study. There will various types of marks will given 1 marks, 2 marks, 3 marks, 4 marks. CBSE Case Based Questions Class 10 Science Biology Chapter 7 CASE STUDY : 1
The Assertion & Reasoning questions along with the solutions are given in the CBSE Class 10 Science case study 2021-2022 PDF that is available here. Class 10th has very basic and important chapters that are necessary to solve.
In CBSE Class 10 Science Paper, Students will have to answer some questions based on Assertion and Reason.There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage-based as well.
A8: Check the following: Context and background: Understand the setting and context of the case study. Key facts and data: Identify important details, data points, and observations mentioned. Relevant concepts: Recognize which scientific concepts and principles are applicable. Questions asked: Carefully read each question to understand what is being asked and how it relates to the case study.
In CBSE Class 10 Science Paper, Students will have to answer some questions based on Assertion and Reason. There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage based as well. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then the MCQ questions based on it will be asked. Here, we have provided case … Continue reading Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 10 ...
Here we are providing you with Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Life Processes Case Study Questions, by practicing this Case Study and Passage Based Questions will help you in your Class 10th Board Exam. ... Here, we have provided case-based/passage-based questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Life Processes. Case Study/Passage-Based Questions ...
Hello students, we are providing case study questions for class 10 science. Case study questions are the new question format that is introduced in CBSE board. The resources for case study questions are very less. So, to help students we have created chapterwise case study questions for class 10 science.
In CBSE Class 10 Science Paper, Students will have to answer some questions based on Assertion and Reason. There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage based as well. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then the MCQ questions based on it will be asked. Here, we have provided case … Continue reading Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 11 ...
In CBSE Class 10 Science Paper, Students will have to answer some questions based on Assertion and Reason. There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage based as well. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then the MCQ questions based on it will be asked. Here, we have provided … Continue reading Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 2 Acids ...
In CBSE Class 10 Science Paper, Students will have to answer some questions based on Assertion and Reason. There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage based as well. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then the MCQ questions based on it will be asked. Here, we have provided case … Continue reading Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 6 ...
A8: Check the following: Context and background: Understand the setting and context of the case study. Key facts and data: Identify important details, data points, and observations mentioned. Relevant concepts: Recognize which scientific concepts and principles are applicable. Questions asked: Carefully read each question to understand what is being asked and how it relates to the case study.