Business Plan Examples for Students
Ajay Jagtap
- December 29, 2023
26 Min Read

Do you know what’s the most common mistake students and rookie entrepreneurs make while preparing their first business plan?
Of course, it’s the first business plan we’re talking about; there’ll definitely be a few. However, overcomplicating things and failing to consider a business plan example still remain the most common one.
That’s why we decided to come up with a solution. We’ve curated this list of top business plan examples for students to help you get going.
So whether you need a business plan for a college project, start a side hustle, or win a business competition, these examples are just what you need to create business plans that stand out.
Ready to dive in? Let’s start by understanding the key elements of a business plan example:

Key Elements of a Business Plan Example
Business planning is not as complicated of a process as people think it is; they’re just overcomplicating things. (Don’t think so?)
Let’s simplify the key elements that make up a comprehensive business plan; you’ll understand it better that way.
- Executive Summary: A high-level overview or summary of your plan.
- Company Overview: A detailed description of your business idea, its fundamental elements, history, and future goals.
- Market Analysis: A study of your external business environment that includes details about your industry, competitors, and target market.
- Products and Services: Description of the products or services you intend to exchange for money.
- Sales and Marketing Strategies: A section outlining sales and marketing strategies your business will implement to achieve its financial goals.
- Operations Plan: A section outlining the business processes and daily activities involved in ensuring seamless business operations.
- Management Team: Introduction to your founders, key management, and their compensation plan.
- Financial Plan: Your financial plan is a detailed breakdown of your business’s financial projections and financing needs.
That’s pretty much it about the key elements of a business plan example. Next, let’s explore the best business plan examples for students.
Say goodbye to boring templates
Build your business plan faster and easier with AI assistant
Get 30% off for Students and educators

Top Business Plan Examples for Students
Now that you already know about the components of a business plan template, let’s review some of the best business plan examples for students.
1. Startup Business Plan Example
Upmetrics’ startup business plan example is the ideal solution for students planning to start up or participate in a business plan competition. This business plan template follows the SBA-approved business planning format used by thousands of successful entrepreneurs.
Whether your startup is about a new-age AI-based application, an online shopping site, or traditional IT consulting—this sample business plan is just what you need.
Unlike any traditional small business plan, this example of a startup business plan is lean and agile in approach, focuses on innovation, and emphasizes market validation.
2. Lean Business Plan Example
Since you’re transitioning from a student to an entrepreneur, you may not have enough time to spend on creating a detailed business plan. That’s where this lean business plan template can help.
It’s a condensed version of a traditional plan summarizing all its sections with a primary focus on covering only the critical aspects of the business.
This template is best for startups or businesses uncertain about business planning and student-turned-entrepreneurs with limited time and resources to prepare a business plan.
3. SBA Business Plan Example
Following an SBA-recommended business plan format is key to securing bank loans and business grants. Since it can be time-consuming to find a template that follows a similar outline as the SBA, this SBA-approved business plan example is the way to get started.
This SBA business plan template has nine primary sections, that include executive summary, company description, market analysis, organization, product description, marketing, funding request, and financial projections.
SBA business plan examples ensure you stay on track and don’t deviate from your funding needs.
4. One-Page Business Plan Example
As you may have already guessed, a one-page business plan is a one-page version of a traditional business plan. Since it’s a condensed version of a business plan, drafting it can be quite easy and quick compared to a lean or traditional plan.
Employees, partners, and vendors often use one-page business plans as a quick overview of your company and banks and investors as a summary of your operations.
While it may not be the ideal choice for entrepreneurs seeking investment or bank loans, students with side hustles and idea-stage startups can consider this option.
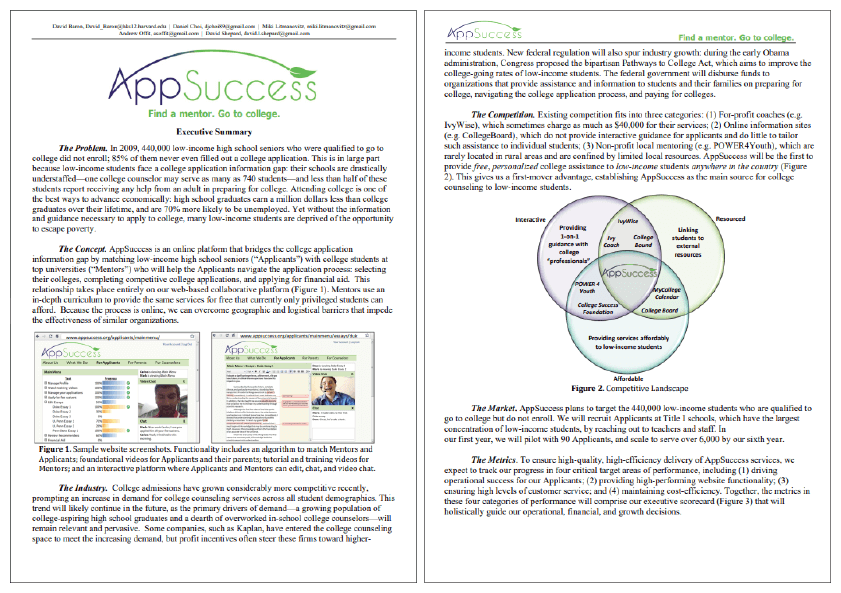
5. HBS Sample Business Plan
Harvard Business School’s new venture competition selected this sample business plan as a finalist in 2011.
This is a business plan of App Success, a collaborative web-based platform that connects low-income high school seniors with college students from top universities; this business will enable them to collaborate on college selection, college applications, and financial aid applications.
This example can be a great reference for those planning to start a mobile or web-based solution.
6. Kean University Sample Business Plan
Kean University organizes a business plan competition every year for its students where students prepare and present business plans to compete, and this is one of the sample business plans the University provides to participants to understand the format.
It’s a business plan of Blue Water Boatworks, Inc., a boat detailing and cleaning company specializing in servicing recreational fiberglass and aluminum watercraft.
This example can be a great reference for those planning to start a business related to housekeeping, cleaning, or maintenance.

7. UVM Sample Business Plan
If you are looking for a strategic business plan for a food business, the University of Vermont’s Fancy Foods Business Plan can be a guiding resource for you.
Despite the fact that it can be a good reference for detailed planning, it was written in 1998, so any statistics and numbers may not seem relevant to today’s market landscape. Make sure you keep that in mind.
You may closely follow this example as a reference if planning to start a food truck, restaurant, or any other business that serves food.
That was the list of best sample business plans for students. However, there’s more to talk about. You now have a business plan example, but what about pitching to investors? Let’s explore free pitch deck examples for students.
Free Pitch Deck Example for Students
Pitching to investors as a first-time founder can be exciting but also overwhelming at times. Worry not; we’ve got a solution—investor pitch templates. We’ve prepared a set of 8 investor pitch templates and examples for students and entrepreneurs to help create winning business pitches.
Whether you need a pitch to find an opportunity, ask for subject matter knowledge, or a problem-solving pitch, these investor pitch examples have got you covered. Download now.
How to write a winning plan for a business plan competition?
Creating a business plan is no different than creating one for a real business. Similar to how entrepreneurs prepare and present business plans to investors, Students in business plan competitions pitch to judges.
In short, the business planning process remains exactly the same. Let’s discuss how you can write a winning plan to help you win a business plan competition.
- Select a compelling business idea : everything starts with a compelling idea. Make sure you have a viable business idea to compete in the competition.
- Refer to winning business plan examples : Once you are sure about your business concept, refer to business plan examples from previous winners and how they planned the sections of their plan.
- Market Research & Industry Analysis : After referring to business plan examples, conduct industry research and market analysis to make your statistical and financial numbers accurate and realistic.
- Understand business model and revenue streams : Since you are preparing a business plan for a company that doesn’t exist, be sure about the business model and how the business will generate profit.
- Use AI business plan generator : Using an AI business plan generator like Upmetrics can be incredibly helpful in speeding up the business planning process. With industry-specific business plan templates and AI assistance to write your plan, you can write the first draft of your plan in literally no time.
- Presentation and visuals : Prepare visuals and graphs to make your business plan visually appealing and numbers digestible. You may not need to prepare these visuals if you use business plan software manually.
- Proofread and edit : Grammatical errors are the last thing judges want to see in a business plan. Make sure you proofread and edit your draft thoroughly before submitting it.
Easy as that, that’s the way to write a perfect business plan that can lead you to victory in any business plan competition on planet Earth. Let’s look at an example of a real-life business and financial plan.

Business and Financial Plan Example for Students
Having learned about business planning for students, let’s quickly discuss a coffee shop sample business plan and financial statements prepared using Upmetrics.
1. Executive Summary
The Cooper’s Cup will be a new cafe in Phoenix, Arizona. The 1,500 square foot café will be located in the newly constructed Market Square Plaza on the northeast corner of 135th Street and Mission Street. The anchor tenant, the Price Chopper grocery store, has already taken occupancy, and the excellent location brings more than 10,000 shoppers weekly.
The Cooper’s Cup, aptly named for the aromatic brown liquid that will fill the cup, fills the void of original cafes in the market and stands out from its corporate peers with its fast food concepts and prompt services. The Cooper’s Cup is the alternative to fast food/commercial/coffee shops and offers a much calmer, civilized gourmet coffee experience.
There are no televisions in the cafe, the background music is subtle, and work from local artists will hang on the walls. The restaurant is well-appointed, with overstuffed leather chairs and sofas in a library-like setting. The cafe is reminiscent of times gone by – yet is cutting edge technologically with WIFI and state-of-the-art espresso machines.
The Cooper’s Cup measures its financial success in terms of increased market share and earnings. This is a tremendous opportunity with a total local market of $54 million! The keys to success will be offering quality gourmet coffees, taking advantage of its small size, and relying on an outstanding barista staff.
To achieve these goals, the cafe will present some of the area’s finest gourmet beans from local distributors. Because of its small size, the restaurant can enjoy larger margins through lower overhead. The cafe will hand-select baristas and offer salaries comparable to the chains. The baristas will be trained to cross-sell and sell higher-margin products.
The primary objectives of the business plan for Cooper’s Cup are below:
- To increase revenues by $36,000 or 5% in Year 2 and $73,000 or 10% by Year 3
- Achieve a profit margin of 5.2% in Year 2 and 6.90% by Year 3
- Be the Cafe of Choice in the Phoenix area and the recipient of the Best Coffeehouse Award.
Guiding Principles
The Cooper’s Cup is committed to values such as excellence, passion, quality, integrity, and leadership, allowing them to navigate challenges and provide for future opportunities. These core beliefs start with their commitment to their products and their employees. Cooper’s Cup rewards excellence and cherishes loyalty. The cafe will work with its employees to build strong businesses and a secure future.
Mission statement
The Cooper’s Cup is committed to its products and employees, which they believe is the recipe for market success.
Key to success
The Cooper’s Cup stands out from the competition. Below are their Keys to Success:
- Great Products : providing exemplary products at market prices – will make customers want to return again and again.
- Hire Quality Baristas : Pay employees rates similar to the larger chains with opportunities for long-term careers and opportunities for advancement with long-term plans to open a second facility.
- Convert Customers to Connoisseurs : Only 40% of the nation’s coffee drinkers consume premium ground and whole bean coffee – this will aid in the continued growth.
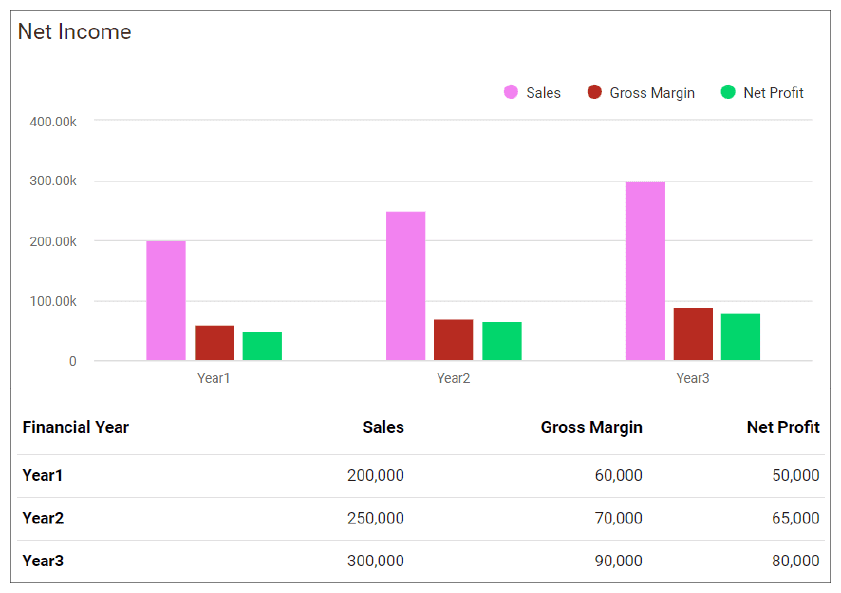
Financial Summary
2. Business Overview
The Cooper’s Cup will be a coffee house/cafe located in Phoenix, Arizona. The cozy cafe will be located in the newly completed Market Square Plaza in the Arizona City area. The cafe will serve gourmet coffee, espresso, drip coffee, lattes, and smoothies. The simple pastry offerings may vary with seasonality, but the primary line will be muffins, bread, cookies, scones, and rolls. All pastries will be supplied daily by a local bakery.
The cafe will be owned and operated by Owen Jones, a veteran restaurateur with several years of experience running and managing chain restaurants. The cafe will be open for business Monday – Thursday 7-10, Fridays and Saturdays, 7-11, and closed Sundays.
The Cooper’s Cup will be formed as an S-Corporation owned by Mr. Doe.
Start-Up Summary
The Cooper’s Cup will have seating for 40 patrons. The rent is $2,075 a month, with a three-five-year lease available. The site comprises 1500 square feet of leased space consisting of a dining room, a coffee bar, two restrooms, and a storage room in the back.
This storefront needs to be plumbed and wired appropriately to be used as a restaurant. Painting, new floors, and countertops are also needed. A custom coffee bar needs to be built. With materials bought on sale and volunteer labor, the cost to renovate will be $71,725.
The coffeehouse equipment will consist of two commercial espresso machines, air pots and urns, a commercial blender, a commercial brewer, top-loading coffee bins, barista syrups, cold drink dispenser, frothing equipment, a commercial refrigerator, microwave, and stainless steel prep bar.
The cost of the equipment is $38,275. The furniture will consist of leather couches and chairs (purchased at auction), coffee tables, bookcases, and window treatments. The artwork will come from local artists and be sold on a consignment basis. The books were secured via donations. The total cost to furnish is $14,000. Other startup expenses will be dishes, furniture, rent deposit, and marketing.
Location and Facilities

The new coffeehouse is located in the highly desirable Phoenix, Arizona, area at the northeastern intersection of 135th Street and Mission Street in the Newmarket Square Plaza. The property is situated in an excellent location, with an easy 6-minute drive time to I-435 and 69 Highway.
The property is 95% leased with Price Chopper as the Anchor Tenant. Other tenants include LifeSpring Med Spa, Jane’s Canines (Pet Store & Boarding), Pride Cleaners Kahn Dental, and Swim U.
Price Chopper brings more than 10,000 shoppers per week to the center. The location comprises a population of 9,420 within a one-mile radius, 61,102 within a 2-mile radius, and 149,550 within a 5-mile radius – with a median household income of $120,856. Sprint / Nextel’s corporate office is within 2 miles of the site.
3. Market Analysis
Phoenix, Arizona, is an award-winning place to live and work and is considered the leading business community in the Midwest. National publications and organizations recognize Phoenix for its business environment and livability. Here’s a sampling: 6th Place, America’s Best Places to Live Money, Top 50 Cities to Live and Play, National Geographic Adventure, 3rd Hottest Town in the U.S., Money, Among 20 Best Places to Live & Work Employment Review, One of only 72 Sterling Tree Cities in the U.S., National Arbor Day Foundation, Top 10 best Locations to Raise a Family, Southern Business and Development, 1st Place, Kid Friendly Report Card, Population Connection, 2nd Best City in America to Live Business Development Outlook.
Phoenix is at the core of one of the most dynamic local markets in the U.S. It offers easy access to the Arizona City region’s amenities, and, as part of the Arizona City metropolitan area, it is within the most centrally located major market in the nation. I-35, I-435, I-635, and U.S. Highway 69 all pass through Phoenix, and no point in the city is more than 3.5 miles from a freeway. The city maintains an excellent arterial street network and plans to construct additional lane-miles as the area grows. Three airports serve the region. Arizona City International Airport (MCI) is just 25 interstate highway miles north of Phoenix. Johnson County Executive Airport—the second busiest in Arizona—provides complete services for private business jets and general aviation. New Century AirCenter, just 12 miles southwest of the city, offers available aviation services and accommodates cargo or passenger jets of any size.
Phoenix supplies some of the most highly educated workers in the nation, with 97% of Phoenix adults over age 25 holding at least a high school diploma. Johnson County, where Phoenix is located, ranks first among the country’s 231 counties with populations greater than 250,000. The county ranks sixth in the percentage of adults with at least a bachelor’s degree and 16th with a graduate or professional degree.
The Phoenix area has a population of 175,265, based on the 2010 census. The median household income is $77,881, and the median age is 37.9. (2010 U.S. Census)
Industry Analysis
The U.S. coffee shop industry includes about 20,000 stores with a combined annual revenue of about $10 billion. Major companies include Caribou Coffee, International Coffee & Tea (The Coffee Bean & Tea Leaf), Peet’s Coffee, and Starbucks. The industry is concentrated: the top 50 companies generate more than 70 percent of sales. Coffee shops are part of the specialty eatery industry, including retail outlets specializing in bagels, donuts, frozen yogurt, and ice cream products. (First Research)
Competitive Landscape
Consumer taste and personal income drive demand. The profitability of individual companies depends on the ability to secure prime locations, drive store traffic, and deliver high-quality products. Large companies have advantages in purchasing, finance, and marketing. Small companies can compete effectively by offering specialized products, serving a local market, or providing superior customer service. Specialty eateries, which include coffee shops, are labor-intensive: average annual revenue per worker is about $50,000. Coffee shops compete with convenience stores, gas stations, quick service, fast food restaurants, gourmet food shops, and donut shops. (First Research)
Market Size
The U.S. coffee shop industry includes about 20,000 stores with a combined annual revenue of about $10 billion. Major companies include Caribou Coffee, International Coffee & Tea (The Coffee Bean & Tea Leaf), Pet’s Coffee, and Starbucks. The industry is concentrated: the top 50 companies generate more than 70 percent of sales. (First Research)
Target Market and Segment Strategy
Most adult coffee drinkers said their lifelong habits began during their teenage years. 54% said they began drinking coffee between 13 and 19. Another 22% reported their coffee cravings started between 20 and 24. This means that 76% of adult coffee drinkers began drinking coffee by the time they were 24. So, despite a large amount of marketing and advertising directed at the younger age groups, savvy coffee shop owners will remember to cater some of their offerings to the adult and senior market. (National Coffee Drinking Study).
The Cooper’s Cup will offer a unique experience for coffee enthusiasts by providing a quiet, cozy, yet sophisticated cafe and a sense of refinement and peace in an otherwise hectic and fast-paced world. While other coffee shops cater to convenience with drive-throughs or loud music venues late into the night, the Cooper’s Cup will stand apart from its competitors with its quiet yet soothing ambiance, capturing a truly unique (and much-needed) market niche.
- Unique products (specialized roasts, local ingredients, locally-themed or named drinks, custom drinks by the star barista, etc.)
- Games, puzzles, mind benders, and other activities that encourage customers to linger over their coffee
- Hosting or sponsoring local events (entertainment, readings, book clubs, etc.)
- Using technology to creatively compete in marketing with big chains — services like FourSquare, Yelp, and Google Places can increase visibility in the local market.
- Delivering amazing service from knowledgeable baristas — spend lots of time training staff and utilizing online services like the American Coffee & Barista School.
- Selling coffee-related items (and tracking down any co-marketing opportunities with a local community college or another student-related group in the area)
4. Products and Services
Product/services descriptions.
The Cooper’s Cup’s primary offering is gourmet roasted coffees with mocha, carmelicious, white mocha, candy bar latte, and brewed coffee. Complementing the coffee will be a smoothie line including wild berry, strawberry, peach, mango, and lemonade. Rounding out the simple menu line will be pastries obtained from an outside supplier, freshly made and delivered daily. The pastry offerings may vary with seasonality, but the primary line will be muffins, bread, cookies, scones, and rolls.

Product/Service Sourcing
The Cooper’s Cup has negotiated supplier agreements with several local food-service wholesalers and coffee wholesalers in the Phoenix area that have a reputation for quality and reliability:
- Mean Beans Coffee Roasters
- Phoenix Brewers
- Healthy Harvest Bread Co.
- Mary’s Organics
If one of the abovementioned specialty suppliers cannot meet their needs, the following national suppliers can provide all the food-service products they require. In addition, the following wholesalers will supply the cafe with general restaurant supplies:
- Lawrence Food Products Corp.
- Gerry Food Supply Inc.
Future Products/Services
Young families, which comprise Phoenix’s third largest market share, are often overlooked in the coffee market. Coffeehouses traditionally have not been considered ‘kid’ friendly. To overcome this hurdle, Cooper’s Cup has long-term plans (5 years) to open a 2nd coffee shop: A combination indoor play area/coffee bar. This concept allows parents and caregivers to meet and relax with other adults while the children can enjoy the indoor playground amenities.
Additional future services will include in-store sales for home purchases and an online store.
The website will have the option to purchase a prepaid gift card program – Prepaid gift cards provide immediate cash, reduce credit card transaction charges, and draw new customers to the business.
5. Sales and Marketing Strategies
Swot analysis.
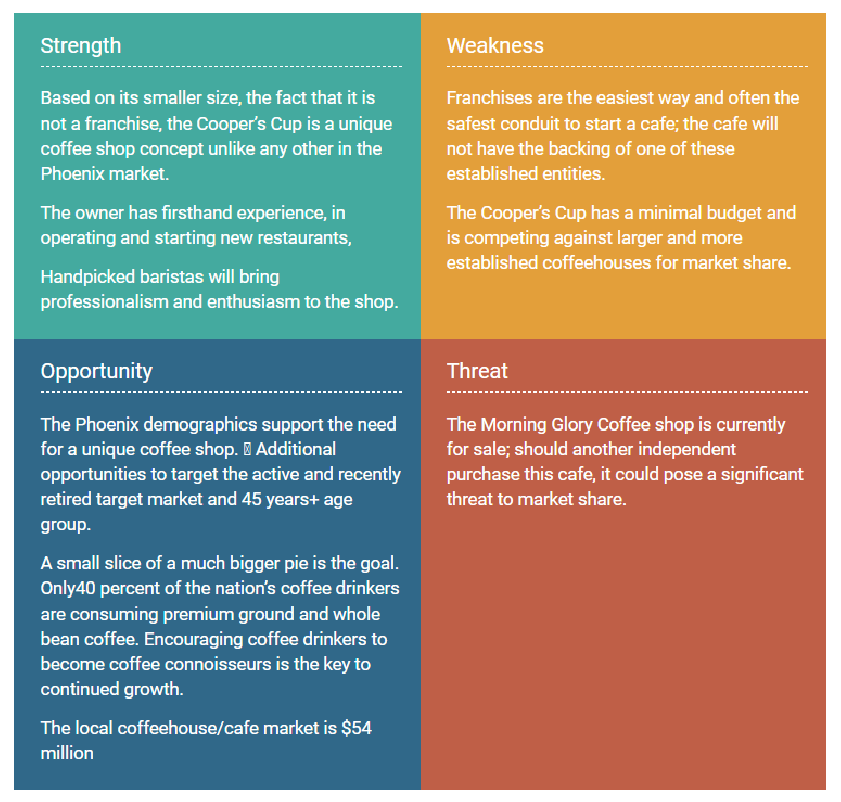
Unique Selling Proposition
The Cooper’s Cup stands out from a crowded sea of coffee chains and franchises. What sets it apart from the competition is primarily its smaller, cozier size combined with premium coffees served by knowledgeable baristas, providing so much energy and enthusiasm for its products.
Market Strategy and Positioning
The Cooper’s Cup utilizes a focus strategy on its Market. By specifically targeting three primary segments, they can cater specifically to their needs.
Senior Market (age 45+)
The Cooper’s Cup will target this Market simply by its well-selected location. Although this demographic group could readily drive downtown, they prefer a local cafe to unwind and relax and historically become some of the most loyal patrons.
Newly Hired Employees
The cafe will attract regular customers (weekly or more) – particularly the newly employed (first job) by providing free WIFI services and providing interesting games in the customer area.
Young Families
The third targeted Market, younger families, often find that coffeehouse is not ‘kid’ friendly. The company has long-term plans to create a combination coffee shop/play area so that parents and caregivers can meet with other adults while the children can enjoy the bounce houses, slides, and indoor playground equipment.
Pricing Strategy
The Cooper’s Cup primarily utilizes competition-based pricing. The cafe does not utilize coupons and discounts (other than opening promotions) because they believe that the most valuable customer demographic of daily coffee consumers is not influenced by discount programs or coupons.
Promotion and Advertising Strategy
- Online Advertising – The Cooper’s Cup will advertise regularly on popular social media sites like Facebook. Compared to traditional print advertising, this is a cost-effective tactic that will allow them to reach prospects in a highly targeted way (e.g., based on criteria such as age, gender, geography, etc.).
- Website – Cooper’s Cup will develop a simple Web site, which will provide basic information about the business, the menu, and links to their presence on the aforementioned social media channels.
- Radio Advertising – During the first six months of operation and the busy holiday shopping season, the business will advertise on local radio stations.
Sales Strategy
The Cooper’s Cup will use the following methods to increase sales revenue (as recommended by Andrew Hetzel on Better Coffee, Better Business):
- The menu will focus on the most profitable products sold. The cafe will always draw customer attention to the best products.
- As warranted, the cafe will raise prices to bolster its brand image. Prices communicate the perceived value of a product, so if set too low, the customers might assume that the beverages are inferior compared to the competition.
- Monitor flavoring inventory – Excess flavoring inventory ties up capital and valuable backroom space for storage. The cafe will utilize 4-6 varieties, including sugar-free offerings.
- Control waste and theft – audit sales and inventory reports to evaluate ingredient waste due to inefficient preparation, returned drinks, and employee consumption. Retail locations can easily waste 20% or more of their daily sales in these three key categories, which is a substantial and unnecessary loss.
- Monitor and evaluate hours of operation.
- Run employee sales contests – The baristas are the salespeople and have great influence over the customer ordering process. All baristas will have some form of sales and customer service training to make each transaction active rather than passive. Sales contests will emphasize high-margin items or cross-selling.
6. Operations Plan
Staffing and training.
An ongoing training and education program will ensure that each staff member learns and implements Cooper’s Cup’s exacting service and operational procedures standards. Staff meetings will reinforce service standards and principles. The Cafe will have detailed work descriptions and training programs for each position, from entry-level employees to the ongoing development of managers and owners. New employees will undergo an extensive training program. This ensures that each guest receives a quality experience from all employees, regardless of how long they have been employed. The Cafe embraces the concept of promoting from within. Excellence in one function typically leads to excellence in another. Regular staff evaluations and training will ensure motivation and address critical issues.
Inventory controls
The founder will be responsible for hiring and training managers who, in turn, will ensure that the day-to-day operations will comply with the standards set by Restaurant policy. Weekly management meetings will provide a forum to review and discuss financial and operational performance. Critical decisions related to purchasing, human resources, marketing, capital expenditures, and customer service will also be addressed.
Purchasing cost controls
Food preparation personnel will follow standardized recipes developed by the founders to control food costs and ensure consistency. The coffee shop will offer an innovative menu with nutritious food and beverages while achieving the most significant margin yield.
Customer Service
The hospitality business recognizes the client’s support experience is the critical driver to replicate business. The direction will Offer a superior degree of Professionalism by hiring individuals who deliver the ideal attitude to work and teaching them the skills required to accommodate guests. The restaurant will keep high levels of consumer satisfaction with talented, educated, and well-trained workers who understand and implement the fundamentals of fantastic service. Ongoing training will be provided to enable staff to perform their jobs with confidence and ability. Employees are well-spoken, well-versed, and trained to provide friendly, prompt, and professional service to each customer. This practice teaches employees who, by producing an exceptional customer experience, can optimize sales and raise their reimbursement. The team will have the knowledge and service required to create excellent daily service for every customer.
Technology & Software
While the quality of the cuisine and dining experience contributes significantly to a restaurant’s profitability, attention to business and financial details can transform small changes into significant returns. Critical sales, cost of sales, labor, inventory, marketing, and overhead metrics are monitored daily. Trends are evaluated, and constructive actions will be taken where improvement is needed. The management team will have access to the restaurant’s transactions and reports available in its real-time POS (point of sale) and accounting systems. Trends will be evaluated, and corrective action will be implemented as required.
7. Organization Structure
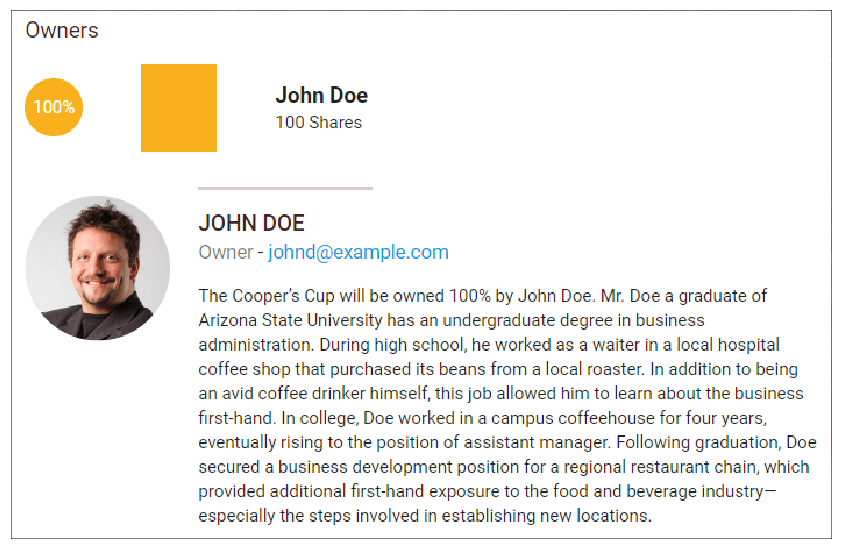
The Cooper’s Cup is formed as an S-Corporation wholly owned by John Doe.
Management Team
The Cooper’s Cup will be owned 100% by John Doe. Mr. Doe, a graduate of Arizona State University, has an undergraduate degree in business administration. During high school, he worked as a waiter in a local hospital coffee shop that purchased its beans from a local roaster. In addition to being an avid coffee drinker, this job allowed him to learn about the business first-hand. In college, Doe worked in a campus coffeehouse for four years, eventually becoming an assistant manager. Following graduation, Doe secured a business development position for a regional restaurant chain, which provided additional first-hand exposure to the food and beverage industry—especially the steps involved in establishing new locations.
Management Team Gaps
The Cooper’s Cup will rely on its POS (Point of Sale) system to generate daily accounting and cost activity reports. Mr. Doe will supply these to an outside bookkeeper for the preparation of annual income taxes.
Personnel Plan
Initially, the cafe will hire 1 manager, 5 baristas, and 2 part-time servers. In Year 2, the cafe plans to hire 1 additional full-time barista.
8. Financial Plan
Important assumptions.
- The sales forecast is conservative and assumes a 5% increase in Year 2 and a 10% in Year 3.
- The analysis accounts for economic seasonality – wherein some month’s revenues peak (such as holidays ) and wane in slower months.
- The analysis assumes the owner will not withdraw any salary till the 3rd year; at any time it is assumed that the owner’s withdrawal is available at his discretion.
- Sales are cash basis – nonaccrual accounting
- Moderate ramp-up in staff over the 5 years forecast
- Barista’s salary in the forecast is $36,000 in 2023.
- In general, most cafes have an 85% gross profit margin
- In general, most cafes have a 3% net profit margin
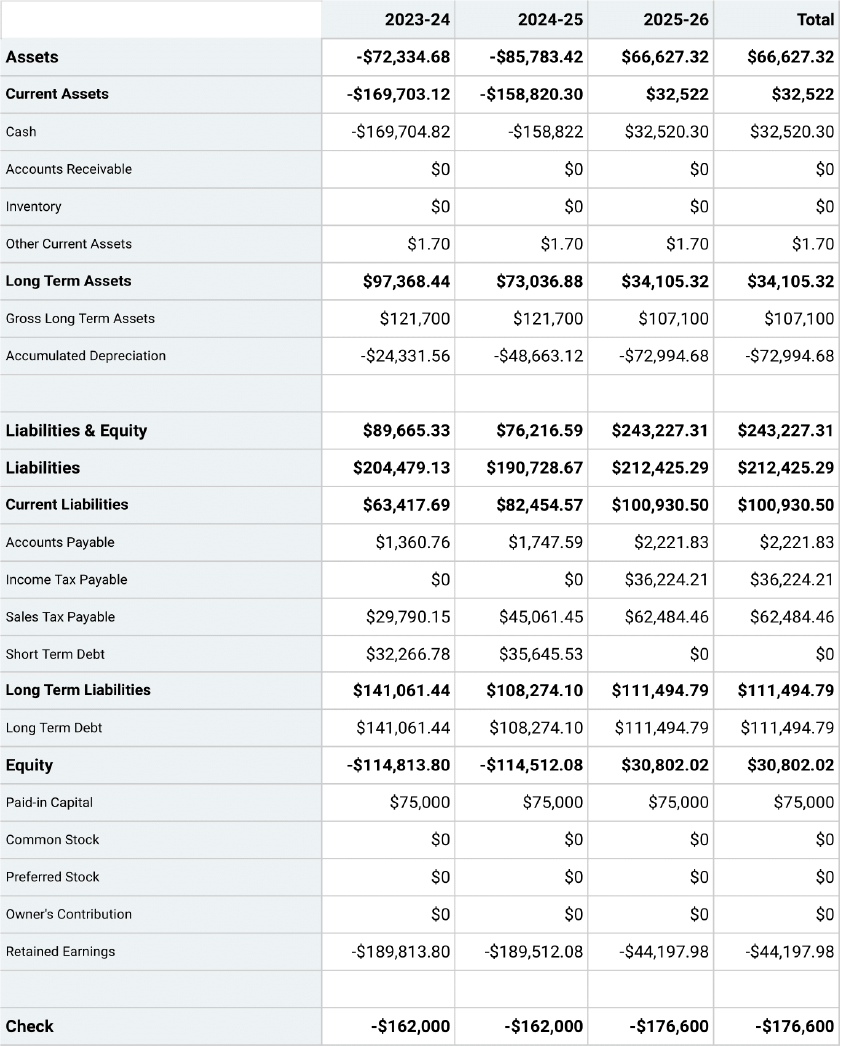
Projected Balance Sheet
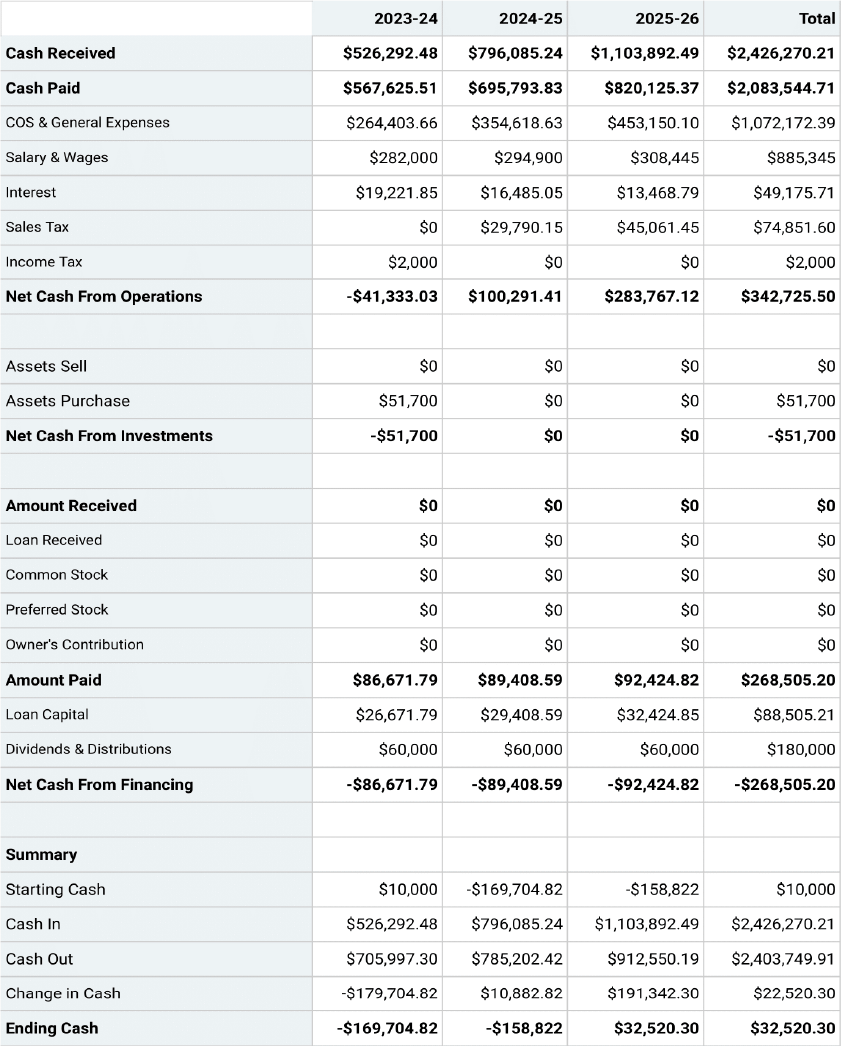
Projected Cash-Flow Statement
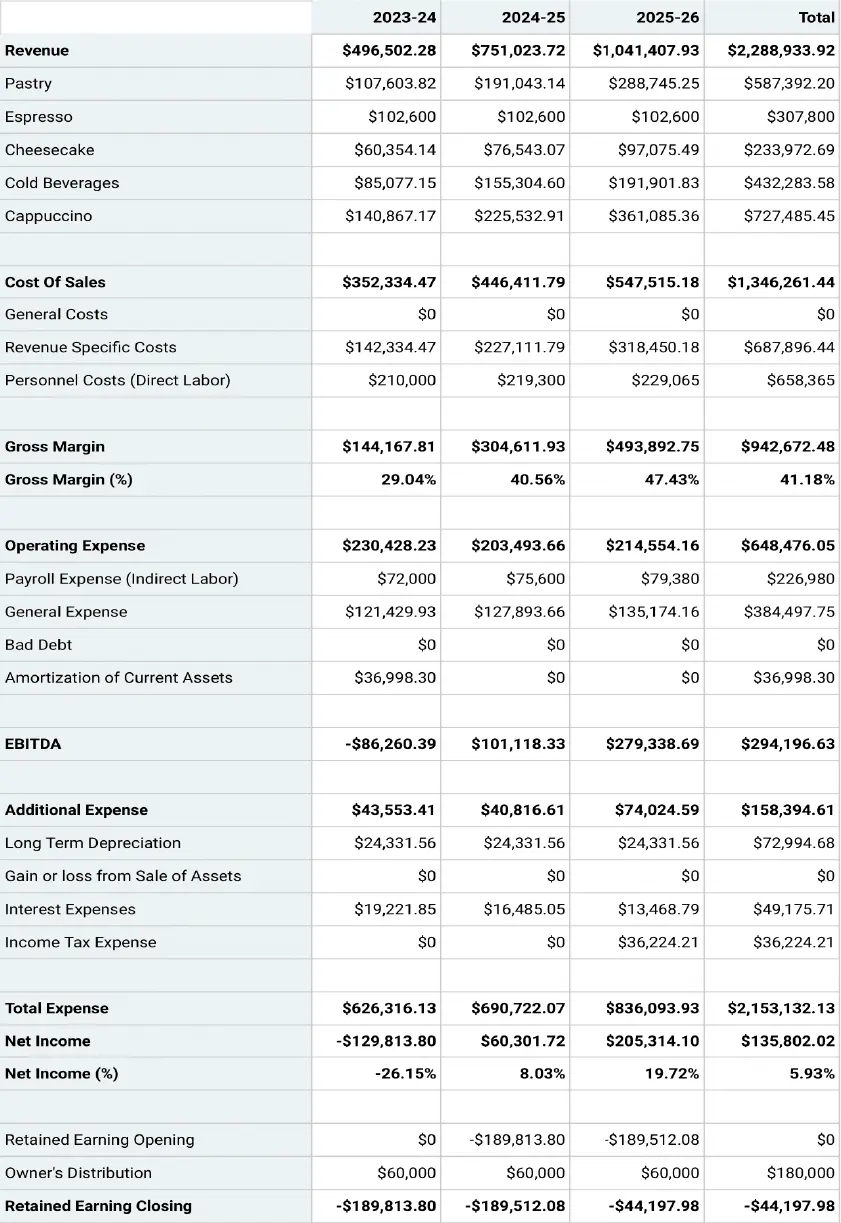
Projected Profit & Loss Statement
Break Even Analysis
Write Your Business Plan With Upmetrics
Whether you need a business plan to compete in a competition, win investors, or gain a competitive advantage in the market landscape, Upmetrics can help you get started.
Upmetrics is an AI business plan software that comes with AI assistance, financial forecasting features, and 400+ sample business plans so that you can prepare a business plan in no time.
So what are you waiting for? Try Upmetrics and create your business plan in a snap.
Make your plan in half the time & twice the impact with Upmetrics
Fill-in-the-blanks, AI-assistance, and automatic financials make it easy.

Frequently Asked Questions
How do you write a business plan for a college project.
As mentioned earlier in the article, business planning for a college project or competition is no different than for a real business. You can write your business plan using these step-by-step instructions.
- Select a compelling business idea
- Refer to business plan examples
- Prepare a business plan outline
- Create a company description section
- Conduct market research and industry analysis
- Describe your product and services
- Outline sales and marketing strategies
- Create an operations plan
- Introduce management team
- Prepare financial projections
- Summarize your plan with an executive summary
What is a business plan for students?
A business plan is a necessary business document that highlights its purpose, business goals, product/service offerings, go-to marketing strategies, operations and financial plan, key people involved in the business operations, and other necessary details.
As a student, consider a business plan example as a document that helps you better understand business and industry dynamics and learn how a business operates inside out.
What is a business plan competition for students?
Business plan competitions are competitions mostly organized by universities for students passionate about entrepreneurship and the business world. These competitions offer students a platform to showcase their entrepreneurial skills while also providing opportunities for mentorship and networking.
How can I increase my chances of winning a business plan competition?
There cannot be a straightforward answer to this question, but there’s surely a method that can increase your chances of winning a competition—Using AI-powered business plan software.
Why? An AI tool will make you 10X more productive while writing a business plan and preparing financial forecasts. So you can spend more time researching the market and brainstorming business ideas.
Where can I find more business plan examples for students?
Upmetrics’ library of 400+ business plan examples could be an incredible source for students to find more industry-specific business plan examples. There are examples for almost every small business category, including real estate, retail, entertainment and media, food & beverages, and more.
About the Author
Ajay is the Head of Content at Upmetrics. Before joining our team, he was a personal finance blogger and SaaS writer, covering topics such as startups, budgeting, and credit cards. If not writing, he’s probably having a power nap. Read more
Reach Your Goals with Accurate Planning
No Risk – Cancel at Any Time – 15 Day Money Back Guarantee
Ready to Kickstart Your Business Planning?

– Don’t Miss It

DECAVERSITY
10 business plan examples for students.

Are you thinking of starting a business? Let’s take a look at some business plan examples for students.
Starting a business as a student is exciting. But, like anyone else, students need support when venturing into entrepreneurship. One of the most important things to start with is learning how to create a strong business plan.
A business plan helps you set clear goals, strategies, and the necessary steps to succeed in the business world. However, not all business plans are the same. There are different types to consider, and choosing the right one depends on your specific business and goals.
In this guide, we'll walk you through the process of creating a solid business plan and introduce you to different plan types. So, let's get started and explore the world of entrepreneurship with a well-structured plan for success.
Writing the Business Plan
Crafting a business plan is a crucial move when you're starting or expanding your business, whether you’re working on a business plan project for students or a fully-fledged business person.
It helps you navigate your journey while also catching the attention of potential investors or lenders. In this guide, we'll break down every part of a business plan and share helpful tips.
What Goes in a Business Plan?
A good business plan typically has several important sections, each with its own job to do.
- Business Overview : Introduction and executive summary.
- Market Analysis : Understanding your target market and competition.
- Marketing and Sales : Strategies to reach and convert customers.
- Product/Service : Description of what you offer.
- Operations and Team : How your business operates and key team members.
- Financial Projection s: Future financial estimates and funding needs.
- Appendix : Supporting documents, if needed.
Now, let’s get into what these sections look like.
Develop a Business Plan Worksheet
Before you start writing your business plan, it's a good idea to start with a business plan worksheet. Think of it as the foundation for your plan—a tool to gather information and get your thoughts organized.
This worksheet will help you come up with your business vision, understand your target market better, and lay out your financial projections. It's the first step to building a solid plan that sets your business on the right track.
The Executive Summary
The executive summary is your business plan's attention-grabbing headline. It's a concise preview of your plan's most critical elements, designed to engage your reader. Here's what to include:
- Mission Statement : Clearly state your business's mission, describing the problem you solve and why your business exists. Define your core values and goals.
- Product/Service Description : Provide a brief, compelling description of your offering, emphasizing its unique features or benefits that set it apart.
- Leadership and Team : Introduce key team members and their qualifications, showcasing their expertise and their role in your business's success.
- Financial Information : Give an overview of your current financial status. Mention revenue and profits if your business is running. If you seek financing, explain how much you need and where you'll invest it.
- Growth Plans : Share your strategy for growth and long-term goals, outlining how you'll expand and achieve profitability.
The executive summary sets the stage for your business plan, making a strong first impression and sparking excitement for what follows.
The Products/Services
In this part, we'll dig deeper into the heart of your business—your products or services. We're going beyond the basics to look at three crucial aspects:
- Benefits to Customers : Discuss how your products or services help your customers. Explain how they solve specific problems or fulfill the needs of your target market. What makes them stand out? What's the unique value they bring compared to what competitors offer?
- Product Lifecycle : Every product or service has a journey. Tell us about the expected lifecycle of yours. Are you planning updates, new versions, or related offerings in the future? Knowing this helps us understand how your business will evolve.
- Intellectual Property : If it applies to your products or services, include any intellectual property rights you have. This might include copyrights, trademarks, or patents. These rights protect your creations and can be valuable assets.
Remember, this section is all about offering the essence of what you're offering and why it's special.
Target Market
Knowing your target market is a cornerstone of business success. Let's simplify:
Who Are Your Customers?
- Demographics : Basic info like age, gender, income, and location helps you target effectively.
What Makes Them Tick?
- Psychographics : Understand their interests, lifestyle, and buying habits to connect personally and tailor your marketing.
Market Trends
- Stay Updated : Keep an eye on industry trends and market shifts. Adapt to capitalize on opportunities.
Why does it matter? Think of it like knowing the weather—it helps you plan. Understanding your target market is your key to getting ahead.

The Marketing Strategy
Your marketing and sales strategies are crucial for attracting and retaining customers.
Marketing Mix
Here, we'll break down each element of your marketing mix—product, price, promotion, and place (distribution).
- Product : Describe your product offerings in detail. What are their unique features and benefits? Why would your target customers choose your products over others in the market? Be clear about what sets you apart.
- Price : Explain your pricing strategy. Will you compete on price, offering lower costs than competitors? Or will you position your products as premium and charge a higher price? Detail any discounts, bundles, or special offers you plan to implement.
- Promotion : Outline your promotional tactics. How will you create awareness and interest in your products? This can include advertising, public relations, content marketing, social media campaigns, and more. Specify your marketing budget and the platforms you'll utilize.
- Place (Distribution) : Describe your distribution strategy. How will your products reach your customers? Will you sell directly to consumers, through retailers, or online? Highlight your distribution channels and logistics. Explain how you'll ensure your products are readily available where your customers want them.
Sales Process
Now it’s time to discuss how you plan to turn potential leads into paying customers.
- Direct Sales : If your strategy involves direct sales, explain how your sales team will engage with potential customers. Provide insights into your sales force, their training, and how they will approach prospects.
- Online Sales : If online sales are a significant part of your strategy, detail your e-commerce platform. Discuss the user experience, payment processing, security measures, and any online marketing tactics to drive traffic and conversions.
- Conversion Strategy : Highlight how you plan to convert leads into paying customers. Will you offer free trials, consultations, or samples? Describe your approach to closing deals and fostering customer loyalty.
By going beyond the surface and addressing these elements in detail, you'll have a marketing and sales strategy that can effectively attract and retain customers for your business.
Discuss Your Distribution Strategy
Your distribution strategy is how you get your products or services to your customers effectively:
- Distribution Channels : These are the paths your products or services take, like physical stores or online platforms.
- Logistics and Transportation : This is how your products move, whether you do it yourself or use other companies.
- Inventory Management : It's about keeping the right amount of stock without having too much or too little.
- Geographic Reach : It's where your customers are, whether nearby, across the country, or worldwide.
- Efficiency and Costs : It's about being fast and not spending too much money.
- Customer Convenience : It means making it easy for customers to buy from you.
- Technology and Automation : Using tools and systems to make things work smoother.
- Scaling and Adaptation : It's about being ready for more customers or changes in the market.
Having a good distribution strategy helps make sure your products or services reach the right customers the right way.
The Competition
It's essential to have a solid grasp of your competitors and strategically position your business to thrive.
Competitive Analysis
To stay ahead of the game, make sure to conduct a thorough competitive analysis. This means rolling up your sleeves and diving deep into the strategies and operations of your rivals.
- In-Depth Examination : Start by examining your competitors meticulously. Look into their products or services, pricing strategies, marketing tactics, and customer base. The goal is to gain a comprehensive understanding of what they do and how they do it.
- Strengths and Weaknesses : Highlight your competitors' strengths and weaknesses. What are they exceptionally good at, and where do they fall short? Identifying these aspects will help them identify opportunities to capitalize on their weaknesses and leverage their strengths.
- Success Insights : Share your insights into what makes your competitors successful. Understand their unique selling propositions, customer engagement strategies, and market positioning. This knowledge will provide you with a foundation for your own strategies.
- Outperforming Plans : Once you've dissected your competitors, outline your plan to outperform them. Whether it's through innovation, superior customer service, or better pricing, make it clear how you intend to gain a competitive edge.
Competitive Advantage
Every business has something that sets it apart from the rest – these are your competitive advantages. In this section, it's time to highlight why customers should choose you over the competition.
- Expert Team : If you have experts on your team, let people know. Customers trust businesses with knowledgeable professionals who offer excellent products or services. If you're new, focus on any relevant experience to build trust as your business grows.
- Unique Partnerships : If your business has forged unique partnerships or collaborations that give you an edge, make it known. These alliances can lead to exclusive offerings, cost advantages, or increased visibility in the market.
- Ideal Location : If your business benefits from an ideal location that attracts foot traffic or serves a specific target demographic, this can be a powerful competitive advantage. Explain how your location enhances your business prospects.
By underlining your competitive advantages, you're essentially telling your audience why you're not just another player in the market.

The operations section is your day-to-day business plan. It helps your team understand how to make your business run smoothly. Here are the key parts:
- Objectives and Goals : State what you want to achieve, both short and long-term. Ensure they align with your overall plan.
- Procedures and Processes : Explain how things will get done, from making your product to customer service.
- Timeline and Milestones : Set dates and goals to track your progress.
- Resource Needs : List what you need to run your business, like equipment and people.
- Supply Chain : Describe how you'll get what you need and manage it.
- Quality Control : Detail how you'll ensure quality, whether through checks or testing.
- Regulations : Mention any rules you need to follow, like permits or licenses.
- Risk Planning : Identify potential problems and your backup plans.
- Growth Strategy : Explain how you'll handle growth, like hiring more people or expanding to new markets.
- Costs : Break down your expenses, both fixed and variable, and how you'll manage them.
By laying out these details, you'll be well-prepared to handle the challenges and growth opportunities that come your way.
The Management Team
In this section of your business plan, you'll want to cover a few key areas:
1. Personal Background : Start by introducing the key people in your management team, if there are any. If it’s just you—don't worry! Give some basic details like names, ages, where they live, their interests, and their educational background. Also, mention any special skills they bring to the table.
2. Business Experience : Talk about their history in the business world. Have they been involved in other businesses? Have they held important positions before? Share their past achievements and roles in previous companies.
3. Track Record : Highlight their successes, the responsibilities they've handled, and their capabilities. Show how their previous experiences have prepared them for the roles they'll play in your business.
4. Education : Mention their formal and informal education, like degrees, certifications, or courses they've taken that are relevant to your business.
5. Financial Standing : Include personal financial statements and supporting documents to demonstrate their financial stability and ability to contribute to the business if necessary.
6. Work History : Detail their direct experience in similar businesses and how it aligns with your current venture.
7. Roles and Responsibilities : Clearly define who does what on the management team. Explain why they're the right fit for their roles and who makes the final decisions.
8. Organization Chart : Create a simple chart that shows how your team is structured and lists each person's responsibilities.
9. Compensation and Benefits : Outline the pay and bonuses each management member will receive. Also, mention any benefits like health insurance or life insurance.
10. External Resources : Tell about any outside resources you can tap into, like lawyers, accountants, or support from organizations that help small businesses.
11. Board of Directors : If you have a board, introduce them and explain how they'll help guide your business.
12. Online Resources : Mention any useful internet resources you'll use for research and networking.
Including these details paints a picture of your team's qualifications and their role in making your business a success.
In this part of your business plan, focus on who will be working with you.
- Current and Future Needs : Start by saying how many people you have on your team right now, if any. Then, talk about how many team members you think you'll need in the near future (like the next year or two) and in the longer term (three to five years from now).
- Skills Required : Describe what skills your team members should have. Think about what makes them good at their jobs and what special skills might be needed for your business.
- Job Descriptions : Explain what each person on your team will be responsible for. This will help everyone better understand their roles. Keep in mind that your roles might change as your business grows.
- Finding People : Discuss how you plan to find and hire the right people. As students, you might use your school's resources and online job platforms or work with other students who have the skills you need.
- Pay and Benefits : Clarify if you'll be paying salaries, hourly wages, or both. You can also mention any extra rewards or bonuses based on performance. Since you're a student, you may not offer extensive benefits initially.
- Extras like Overtime : Say if you'll pay extra for overtime work and when that might happen. Being students, you'll want to manage your workload efficiently, especially during busy times.
By covering these points, you'll show that you've considered your team's needs and are ready to manage your business's human resources effectively, even as students.

Financial Analysis
Think of this section as the pulse of your business plan. It gives you a detailed look at your business's financial health and sustainability. This part is crucial for students because it helps them make informed decisions and attracts potential investors or lenders.
Balance Sheet
Get a certified public accountant (CPA) to help you create a balance sheet. This document paints a picture of your business's financial situation at a specific moment. It has three main parts:
- Assets : What your business owns ( cash, equipment, or inventory).
- Liabilities : What your business owes (such as loans or outstanding bills).
- Owner's Equity : The owner's stake in the business, which is assets minus liabilities. It's basically your business's net worth.
Break-Even Analysis
This is significant because it tells you when your business will start making money. It determines the minimum amount of sales revenue needed to cover both fixed costs (like rent and salaries) and variable costs (like materials and utilities). It's based on info from the income statement and cash flow projections.
Income Statement (Profit and Loss Statement)
The income statement gives you the lowdown on your business's financial performance over a specific time frame, usually monthly or annually. It shows how much money you made and how much you spent. Subtract the expenses from the income, and you've got your profit or loss. It's all about how well your business handles its cash.
Cash Flow Statement
Cash is king in business, and this statement forecasts how money will move in and out of your company. It predicts all cash coming in and going out, helping you ensure you have enough to cover day-to-day costs and investments and pay off any debts. A strong cash flow is crucial to keeping your business going.
As student entrepreneurs, having a CPA set up your accounting system is a smart move for accuracy. When you present these financial documents in your business plan, make sure they're clear and detailed.
These numbers prove the worth and profitability of your business idea, which can be a big draw for potential investors or lenders. So, be thorough and get the figures right.
Supporting Documentation
You'll also want to include various documents that back up the information you've presented in the main part of your plan. Keep in mind that this list might change depending on how far along your business is. Here's what to include:
- Resumes : Put in resumes of the people who are key to your business. Show off their qualifications and experience to give confidence to potential investors or lenders.
- Credit Information (appendix) : If relevant, add credit reports for yourself or your team members. This will prove that you're financially responsible.
- Quotes or Estimates : Include any quotes or cost estimates you've received from suppliers or service providers. This helps prove that you've done your homework on expenses.
- Letters of Intent from Prospective Customers : If you have letters from potential customers saying they want to use your products or services, toss those in. It shows there's a demand.
- Letters of Support from Credible References : If you have supportive letters from mentors, professors, or industry experts, add those. They can vouch for your idea.
- Leases or Buy/Sell Agreements : If you're renting space or buying equipment, include the agreements. It proves you have the physical assets and responsibilities in place.
- Legal Documents Relevant to the Business : If there are any legal papers like incorporation documents, partnership agreements, or licenses, include them. It shows you're following the rules.
- Census/Demographic Data : If your business relies on specific data about people, include statistics or reports from trustworthy sources. This information will support your market analysis and target audience information.
Remember to keep these documents well-organized in the appendix. This list covers the basics, but tailor it to your specific student business plan's needs and stage of development.
Business Plan Program
Creating a strong business plan is essential for any entrepreneur, and with the help of business plan programs and tools, you can make it more effective.
- LivePlan : LivePlan is a user-friendly business planning software that guides users through creating business plans and offers financial forecasting.
- Bizplan : Bizplan focuses on startups and small businesses, providing step-by-step planning, financial tools, and pitch deck creation.
- Enloop : Enloop automates business plan writing using data inputs and offers financial projection tools.
- PlanGuru : PlanGuru is for in-depth financial analysis and creating detailed financial projections.
- Upmetrics : Upmetrics offers customizable templates, financial forecasting, and collaboration features for various business stages.
- Tarkenton GoSmallBiz : Tarkenton GoSmallBiz provides business planning tools, legal resources, and marketing guidance.
- Bplans : Bplans offers free business plan templates and samples for those starting from scratch.
- Canva : Canva provides pitch deck templates and design tools to enhance presentations.
- QuickBooks : QuickBooks aids in financial tracking and management, complementing business planning.

14 Types of Business Plans with Examples
In this section, we'll explore 10 types of business plan examples for student entrepreneurship.
1. Traditional Business Plans
These classic business plans , often prepared on paper, provide a comprehensive overview of the business, detailing its identity, goals, and strategies for success.
2. Standard Plans
Similar to traditional plans, standard business plans are created digitally, typically using software like Microsoft Word or Excel, making them easier to edit and share.
3. One-Page Business Plans
Incredibly concise, these plans condense all crucial information onto a single page, often using bullet points for clarity and brevity.
4. Annual Business Plans
Tailored for a specific year, these plans outline a business's objectives and actions for that particular period, providing a focused strategy.
5. Lean Plans
Lean business plans are streamlined versions, intentionally omitting some details to protect confidential information while offering a concise yet informative summary.
6. Business Plans for Start-ups
Specifically designed for new ventures, these plans may incorporate surveys, customer insights, and visual aids to support their customized approach.
7. Feasibility Studies
These plans investigate the viability of new product or service ideas, helping businesses make informed decisions about their implementation by analyzing their potential success.
Understanding these various types of business plans is essential for your business management studies, as they serve different purposes and contexts within the business world.
8. Strategic Plans
Concentrating on marketing and branding strategies, these plans often involve extensive market research and prioritize effective brand promotion.
9. Operational Plans
Emphasizing practical steps, operational plans use data, charts, and graphs to guide a business's actions toward its goals, with a strong focus on execution.
10. Internal Plans
Highly detailed and meant exclusively for the company's internal team, these plans contain sensitive information and strategic insights for team members' use.
11. What-If plan
This type of plan explores various scenarios and their potential impact on the business. It helps a company prepare for unexpected situations by outlining strategies for different outcomes.
12. Expansion plan
An expansion plan outlines strategies for growing a business, whether through opening new locations, entering new markets, or diversifying product lines. It details the steps and resources needed for expansion.
14. Business Acquisition Plan
When a company intends to acquire another business, this plan outlines the acquisition strategy, financial considerations, and integration plans. It helps ensure a smooth transition and maximizes the value of the acquisition.
These plans cover a range of scenarios and goals, each serving a unique purpose in the world of business strategy. Hopefully, you can choose a business plan template for high school students that suits your needs.
Final Thoughts
Starting and running a business as a student is a journey. A well-structured business plan is essential for success, helping you define your goals and strategies. To create one, feel free to use these business plan examples for students as a source of inspiration.
It’s your tool to guide your entrepreneurial journey and increase your chances of success. So, get started, create your plan, and get started on your path to entrepreneurship with confidence.


Business Plan Development Guide
(6 reviews)
Lee Swanson, University of Saskatchewan
Copyright Year: 2017
Publisher: OPENPRESS.USASK.CA
Language: English
Formats Available
Conditions of use.
Learn more about reviews.
Reviewed by Kevin Heupel, Affiliate Faculty, Metropolitan State University of Denver on 3/4/20
The text does a good job of providing a general outline about writing and developing a written business plan. All of the important steps and components are included. However, the text is light on details, examples, and rationale for each element... read more
Comprehensiveness rating: 3 see less
The text does a good job of providing a general outline about writing and developing a written business plan. All of the important steps and components are included. However, the text is light on details, examples, and rationale for each element of the business plan. Some examples from actual business plans would be helpful.
Content Accuracy rating: 4
For the most part, the content is accurate. The content covers all important aspects of drafting a business plan. I thought the industry analysis could use more information about collecting primary and secondary sources; instead, this information was referenced in the marketing plan section.
Relevance/Longevity rating: 5
Most of the content relies on cites as far back as 2006; however, when it comes to developing and writing a business plan nothing has changed. Thus, the content is current and there is no concern about it becoming obsolete in the near future.
Clarity rating: 4
The text is clear. There are no difficult terms used and the writing is simple. The text uses a lot of bullet points though, which gets tedious to read for a few pages.
Consistency rating: 5
The text does a good job of maintaining consistency in terms of framework and terminology. The text is organized where it's easy to find the information you want in a quick manner.
Modularity rating: 3
The text has a lot of bullet points and the paragraphs are dense. However, the use of subheading is excellent.
Organization/Structure/Flow rating: 5
The book is organized as if you're writing a business plan from start to finish, which is helpful as a practical guide.
Interface rating: 5
There are no navigation problems, distortion of images/charts, or any other display features that may distract or confuse the reader.
Grammatical Errors rating: 5
The text is free of grammatical errors. The sentence structure is simple with many bullet points, which helps to avoid any grammatical issues.
Cultural Relevance rating: 5
This book was written by a Canadian professor and provides references to Canadian sources. However, the information in this text can be used for U.S. schools.
This book is very short and provides a good, general overview about the process of creating and writing a business plan. It won't help a reader if he/she is confused about a certain part of the business plan. The reader will have to find another source, such as "Preparing Effective Business Plans" by Bruce Barringer, Ph.D. The book provides links to good resources and a finished business plan that the reader can reference. I would recommend the book for undergraduate courses.
Reviewed by Kenneth Lacho, Professor of Management, The University of New Orleans on 6/19/18
1. Text is relevant to Canada. Not the United States 2. Needs to cover resources available to entrepreneur, e.g., federal government agencies, trade associations, chambers of commerce, economic development agencies. 3. Discuss local economy or... read more
1. Text is relevant to Canada. Not the United States 2. Needs to cover resources available to entrepreneur, e.g., federal government agencies, trade associations, chambers of commerce, economic development agencies. 3. Discuss local economy or economic area relevant to this proposed business. 4. Business model ok as a guide. 5. Suggested mission statement to cover: product/business, target customer, geographical area covered. 6. Need detailed promotion plan, e.g., personal selling, advertising, sales promotion, networking publicity, and social media. 7. How do you find the target market? 8. Chapter 6 too much detail on debt and equity financing. 9. Discuss how to find sources of financing, e.g., angels. 10. Expand coverage of bootstring, crowdfunding. 11. Chapter 4 – good checklist. 12. Chapter 3 - overlaps. 13. Chapter 7 – 3 pages of executive summary – double or single spaced typing. Number all tables, graphs. 14. Some references out-of-date, mostly academic. Bring in trade magazines such as Entrepreneur.
Content Accuracy rating: 5
In my opinion, the content is accurate and error free.
Relevance/Longevity rating: 4
The material is relevant to writing a business plan. I wonder if the Porter, SWOT VRIO, etc. material is too high level for students who may not be seniors or have non-business degrees (e.g., liberal arts). Porter has been around for a while and does have longevity. The author has to be more alert to changes in promotion, e.g., social media and sources of financing, e.g., crowdfunding.
Clarity rating: 3
As noted in No. 9, the tone of the writing is too academic, thus making the material difficult to understand. Paragraphs are too long. Need to define: Porter, TOWS Matrix, VRIO, PESTEL. A student less from a senior or a non-business major would not be familiar with these terms.
Consistency rating: 4
The text is internally consistent. The model approach helps keep the process consistent.
Modularity rating: 4
The process of developing a business plan is divided into blocks which are parts of the business plan. Paragraphs tend to be too long in some spots.
Organization/Structure/Flow rating: 4
The topics are presented in a logical step-wise flow. The language style is too academic in parts, paragraphs too long. Leaves out the citations. Provides excellent check lists.
There are no display features which confuse the reader.
Grammatical Errors rating: 4
The text has no grammatical errors. On the other hand, I found the writing to be too academic in nature. Some paragraphs are too long. The material is more like an academic conference paper or journal submission. Academic citations references are not needed. The material is not exciting to read.
The text is culturally neutral. There are no examples which are inclusive of a variety of races, ethnicities, and backgrounds.
This book best for a graduate class.
Reviewed by Louis Bruneau, Part Time Faculty, Portland Community College on 6/19/18
The text provides appropriate discussion and illustration of all major concepts and useful references to source and resource materials. read more
Comprehensiveness rating: 5 see less
The text provides appropriate discussion and illustration of all major concepts and useful references to source and resource materials.
Contents of the book were accurate, although it could have benefited from editing/proofreading; there was no evidence of bias. As to editing/proofreading, a couple of examples: A. “Figure 1 – Business Plan… “ is shown at the top of the page following the diagram vs. the bottom of the page the diagram is on. (There are other problems with what is placed on each page.) B. First paragraph under heading “Essential Initial Research” there is reference to pages 21 to 30 though page numbering is missing from the book. (Page numbers are used in the Table of Contents.)
The book is current in that business planning has been stable for sometime. The references and resources will age in time, but are limited and look easy to update.
Clarity rating: 5
The book is written in a straightforward way, technical terms that needed explanations got them, jargon was avoided and generally it was an easy read.
The text is internally consistent in terms of terminology and framework.
Modularity rating: 5
The book lends itself to a multi-week course. A chapter could be presented and students could work on that stage of Plan development. It could also be pre-meeting reading for a workshop presentation. Reorganizing the book would be inappropriate.
The topics in the text are presented in a logical, clear fashion.
Generally, the book is free of interface problems. The financial tables in the Sample Plan were turned 90° to maintain legibility. One potential problem was with Figure 6 – Business Model Canvas. The print within the cells was too small to read; the author mitigated the problem by presenting the information, following Figure 6, in the type font of the text.
I found no grammatical errors.
The text is not culturally insensitive or offensive in any way.
I require a business plan in a course I teach; for most of the students the assignment is a course project that they do not intend to pursue in real life. I shared the book with five students that intended to develop an actual start-up business; three of them found it helpful while the other two decided not to do that much work on their plans. If I were planning a start-up, I would use/follow the book.
Reviewed by Todd Johnson, Faculty of Business, North Hennepin Community College on 5/21/18
The text is a thorough overview of all elements of a business plan. read more
Comprehensiveness rating: 4 see less
The text is a thorough overview of all elements of a business plan.
The content is accurate and seems to lack bias.
Content seems relevant and useful . It does not help an entrepreneur generate ideas, and is very light on crowdfunding and other novel funding source content. It is more traditional. This can be easily updated in future versions, however. "Social Media" appears once in the book, as does "Crowd Funding".
The book is comprehensive, but perhaps not written in the most lucid, accessible prose. I am not sure any college student could pick this up and just read and learn. It would be best used as a "teach along guide" for students to process with an instructor.
The text seems consistent. The author does a nice job of consistently staying on task and using bullets and brevity.
Here I am not so certain. The table of contents is not a good guide for this book. It does make the book look nicely laid out, but there is a lot of complexity within these sections. I read it uncertain that it was well organized. Yes there are many good bits of information, however it is not as if I could spend time on one swathe of text at a time. I would need to go back and forth throughout the text.
Organization/Structure/Flow rating: 2
Similar to the above. I did not like the flow and organization of this. An editor would help things be in a more logical order.
Interface rating: 2
The interface is just OK. It is not an attractice interface, as it presents text in a very dense manner. The images and charts are hard to follow.
I did not find any grammatical errors.
Cultural Relevance rating: 4
I a not certain of the origins of Saskatchewan, but I do feel this is a different read. It is more formal and dense than it has to be. This would be a difficult read for my students. I do not feel it is insensitive in any way, or offensive in any way.
I would not adopt this book if given the chance. It is too dense, and not organized very well, even though the information is very good. The density and lack of modularity are barriers to understanding what is obviously very good information.
Reviewed by Mariana Mitova, Lecturer, Bowling Green State University on 2/1/18
Though this textbook has a prescriptive nature, it is quite comprehensive. The author strikes a good balance between presenting concepts in a concise way and providing enough information to explain them. Many every-day examples and live links to... read more
Though this textbook has a prescriptive nature, it is quite comprehensive. The author strikes a good balance between presenting concepts in a concise way and providing enough information to explain them. Many every-day examples and live links to other resources add to the completeness of the textbook.
Content seems accurate.
Since the content is somewhat conceptual, the text will not become obsolete quickly. In addition, the author seems to be updating and editing content often hence the relevance to current developments is on target.
The text is very clear, written in clear and straight-to-the point language.
The organization of content is consistent throughout the entire text.
The textbook is organized by chapters, beginning with overview of the model used and followed by chapters for each concept within the model. Nicely done.
The flow is clear, logical and easy to follow.
Overall, images, links, and text are well organized. Some headlines were misaligned but still easy to follow.
No concerns for grammar.
No concerns for cultural irrelevance.
Reviewed by Darlene Weibye, Cosmetology Instructor, Minnesota State Community and Technical College on 2/1/18
The text is comprehensive and covers the information needed to develop a business plan. The book provides all the means necessary in business planning. read more
The text is comprehensive and covers the information needed to develop a business plan. The book provides all the means necessary in business planning.
The text was accurate, and error-free. I did not find the book to be biased.
The content is up-to-date. I am reviewing the book in 2017, the same year the book was published.
The content was very clear. A business plan sample included operation timelines, start up costs, and all relevant material in starting a business.
The book is very consistent and is well organized.
The book has a table of contents and is broken down into specific chapters. The chapters are not divided into sub topics. I do not feel it is necessary for sub topics because the chapters are brief and to the point.
There is a great flow from chapter to chapter. One topic clearly leads into the next without repeating.
The table of contents has direct links to each chapter. The appearance of the chapters are easy to read and the charts are very beneficial.
Does not appear to have any grammatical errors.
The text is not culturally insensitive or offensive.
I am incorporating some of the text into the salon business course. Very well written book.
Table of Contents
Introduction
- Chapter 1 – Developing a Business Plan
- Chapter 2 – Essential Initial Research
- Chapter 3 – Business Models
- Chapter 4 – Initial Business Plan Draft
- Chapter 5 – Making the Business Plan Realistic
- Chapter 6 – Making the Plan Appeal to Stakeholders and Desirable to the Entrepreneur
- Chapter 7 – Finishing the Business Plan
- Chapter 8 – Business Plan Pitches
References Appendix A – Business Plan Development Checklist and Project Planner Appendix B – Fashion Importers Inc. Business Plan Business Plan Excel Template
Ancillary Material
About the book.
This textbook and its accompanying spreadsheet templates were designed with and for students wanting a practical and easy-to-follow guide for developing a business plan. It follows a unique format that both explains what to do and demonstrates how to do it.
About the Contributors
Dr. Lee Swanson is an Associate Professor of Management and Marketing at the Edwards School of Business at the University of Saskatchewan. His research focuses on entrepreneurship, social entrepreneurship, Aboriginal entrepreneurship, community capacity-building through entrepreneurship, and institutional-stakeholder engagement. Dr. Swanson’s current research is funded through a Social Sciences Humanities Research Council grant and focuses on social and economic capacity building in Northern Saskatchewan and Northern Scandinavia. He is also actively studying Aboriginal community partnerships with resource based companies, entrepreneurship centres at universities, community-based entrepreneurship, and entrepreneurial attitudes and intentions. He teaches upper-year and MBA entrepreneurship classes and conducts seminars on business planning and business development.
Contribute to this Page

- Entrepreneurship
- Affiliate Marketing
- WordPress And Webdesign
- Sales Funnel
- Motivation And Affirmation
- Get in Touch
10 Business Plan Examples for Students (2024)
Written by Peter Keszegh
Starting a business isn’t just for the established entrepreneurs. If you’re a student with a great business idea, or if you’re just looking to earn extra money on the side, you can set up your own business with the right steps and preparation, too!
In this article, we’ll list some business plan examples for students and how you can turn your business ideas into reality.

What is a business plan?
In simple terms, a business plan is a detailed document that explains everything you need to know about your business idea . It includes your goals for your business and how exactly you plan to achieve them.
A business plan should be able to explain why your product or service is valuable, your target market for your business, and your future plans for the business.
Having a well-written business plan is important, especially if you’re looking at seeking external funding from investors. Even if you’re planning to use personal funds for your business, the business plan will help outline all your operational and management strategies.
Tailoring your plan to your business
While business plans have some standard sections used by all industries, it’s best to tailor your business plan depending on what your market is. For instance, if you’re planning to sell food products, you need to write sections on sourcing ingredients and quality control.
Think about what’s special about your business, and make sure to incorporate that in your business plan. Put yourselves in the shoes of an external investor – what would they want to know about your business? Don’t be afraid to think outside the box, too.

Parts of a business plan
You might be wondering – how should we structure a business plan? Here are some key sections you might want to include when writing your business plan:
Executive summary
An executive summary is exactly that – a summary of what your business is all about and your goals for the future. Make sure to include what your product or service plans to do, your target market, and key milestones you’d like to achieve. If you have plans to source external funding, mention this here, too.
Company description
You can use this section to expound on what you plan to achieve and what your business vision is . Use this section to highlight what makes your business unique , and why your product or service offers an innovative solution.
Market analysis
If you’re looking to start a business, you need to have a good understanding of the market and who your competitors are. Do the research to make sure there’s a real need for your product or service , and make sure you know what sets your business apart from competitors.
Organizational structure
If you’re working with a team and you all have different responsibilities, make sure to put that into writing. This doesn’t have to be too formal – all you have to do is make sure everyone’s tasks are clearly delineated so there’s no overstepping.
Product line or services offered
Talk about what you plan to sell or offer as a business. What exactly does your product or service do? What makes it so special, and what can your product or service do that isn’t already offered by your competitors?
Marketing and sales strategies
How do you plan to promote your business to attract customers and secure sales ? You can talk about where you plan to sell your products or offer your services, and how you plan to advertise your business.
Financial projections and funding requests
Set financial goals for your business and identify when your business will likely break even . If you need to secure external funding, make sure to mention this here, and mention how much money you’ll be needing and how you’ll be spending it.
Relevant documents that you mentioned earlier in your business plan should be included here. For instance, if you conducted market research via a survey, put your survey data here.
Of course, don’t be limited by the sections listed here. If there are other relevant details you’d like to talk about in your business plan, don’t be afraid to explore them. For instance, if you’re looking at using new technologies and tools for your product or service, you can write a relevant section in your business plan as well.

Why students need to master business plans
Businesses aren’t just for more seasoned entrepreneurs – starting a business can prove to be useful for students who want to hone their skills and become more business-minded.
Here’s how business plans can help students:
Enhancing strategic decision-making
You’ll have to make a lot of decisions when running a business, and business plans will force you to make smarter decisions. You don’t want to make things unnecessarily difficult for you and your team only to get mediocre results – you want to make sure you make the most out of your resources!
This kind of strategic decision-making isn’t something you learn in the classroom. Hands-on business experience will be useful for you to make wise decisions, even if it means learning from mistakes.
Improving market research and analysis skills
As students, you already do a lot of research for different school projects. When setting up a business, you’ll have to do research of your own to get a better understanding of the market your business plans to work in.
Having a good understanding of the market will also improve your analysis skills. For instance, doing enough research on the retail industry will give you a better idea of who the average retail customer is, allowing you to tweak your marketing and sales strategies to capture that target market.
Honing financial literacy and forecasting
Discussions about money and numbers can get pretty confusing. When you’re setting up a business and dealing with real, tangible figures, you’ll gain a better understanding of how finances work, how profitable your business might be, and what you’ll likely be spending money on.

Business plan examples for students
If you need a little help in thinking about the kind of business you want to set up, here are 10 business plan examples for students that you can use as inspiration:

Tu toring services
Some students will understand subjects better than others, which means there are a number of students who’ll need a little bit of help when it comes to their academic requirements and upcoming exams.
If you’re academically gifted and have a talent for teaching, you might want to consider offering tutoring services in your school.
- Executive summary : Mission, services offered, and target client demographic.
- Business description: Subjects covered, and technologies used (if applicable).
- Services provided: Individual tutoring, group workshops, and ongoing support options.
- Market analysis: Demographic trends, existing offerings, and unmet needs.
- Marketing strategy: Flyers, community center partnerships, and word-of-mouth referral programs .
- Operational plan: Scheduling system, session formats (in-person, online), and materials preparation.
- Management and organization: Tutor recruitment, training programs, and operational leadership.
- Financial summary: Basic costs, session pricing, financial goals, and sustainability plan.

Campus delivery service business
Especially during finals weeks, students can get pretty busy and can often forget to take care of themselves. How many all-nighters have you pulled as a student, and how many times have you skipped a meal to work on a deadline?
If this sounds like the kind of culture in your university, you might want to consider setting up a campus delivery service to cater to busy students. Here’s how you can set up your business plan:
- Executive summary: Service overview, mission, and objectives.
- Company description: Origins, campus focus, and service differentiation.
- Service offering: Types of delivery services offered (e.g., food, groceries).
- Market analysis: Campus demographics, needs assessment, and competitor analysis.
- Marketing strategy: Promotional tactics targeting students and staff, partnerships with local businesses.
- Operations plan: Delivery logistics, technology use (e.g., apps, GPS tracking), and hours of operation.
- Management and organization: Team roles, volunteer vs. paid staff, and management hierarchy.
- Financial plan: Start-up costs, pricing strategy, revenue projections, and break-even analysis.

Campus fitness and wellness programs
Another way you can help students in your school become healthier is to offer services that focus on fitness and wellness . If there’s a need for students in your school to become more physically active or to just take better care of their overall wellness, you could offer relevant programs on campus.
- Executive summary: Concept, target audience, and objectives of the fitness programs.
- Business description: Range of services (classes, personal training, wellness workshops).
- Market analysis: Campus health trends, competitor offerings, and student wellness needs.
- Services: Detailed look at program offerings, schedules, and customization options.
- Marketing plan: Engagement strategies, campus events, and partnership with student health services.
- Operational plan: Instructor qualifications, equipment needs, and location logistics.
- Management and organization: Structure of the team, roles, and experience in health and wellness.
- Financial overview: Initial setup costs, pricing strategy, revenue streams, and financial projections.

Student freelance platform
Freelancing is a popular way for students to earn extra income on the side, in the middle of their busy class schedules. If you have enough know-how when it comes to setting up websites or apps, you might want to consider launching a portal where student freelancers can conveniently find more freelance gigs.
- Executive summary: Platform purpose, target market, and value proposition.
- Business description: Niche focus (e.g., design, tutoring, programming), platform features.
- Market analysis: Demand for freelance work among students, analysis of existing platforms, gap identification.
- Service description: User interface, service categories, payment processing system.
- Marketing and sales strategy: Campus outreach, online presence, and user acquisition strategies.
- Technology plan: Website architecture, user security measures, and scalability.
- Operations plan: Customer support, dispute resolution process, and freelancer vetting process.
- Financial summary: Funding requirements, monetization strategy, and financial forecasts.

Mobile app for campus services and networking business
Maybe you’ve got an enormous campus that boasts a lot of helpful activities and services that most students might not already be aware of. If you want to promote these services in an innovative way, you could think about setting up a mobile app that students can use as a one-stop-shop for all their campus service needs.
- Executive summary: Introduction to the app, its core functionalities, and target user base.
- Business description: Insight into how the app facilitates campus life, services offered, and networking features.
- Market analysis: Current apps in the market, student needs analysis, and potential for growth.
- Product description: Detailed functionalities, user interface design, and privacy features.
- Marketing plan: Strategies for app launch, user acquisition, and partnerships with university departments.
- Technology plan: Development roadmap, platform compatibility, and maintenance plan.
- Management and operations: Team structure, developer roles, and operational milestones.
- Financial projections: Budget for app development, marketing costs, monetization strategies, and revenue forecasts.

Eco-friendly apparel brand
Everyone’s becoming more eco-conscious nowadays, and brands who often highlight their environmentally-friendly practices do get a good reputation. If you want to tap into that market and mix it with a bit of fashion design, you can choose to set up an eco-friendly apparel business.
- Executive summary: Brand mission, product range, and sustainability goals.
- Company background: Inspiration behind the brand, target demographic, and brand story.
- Products and services: Description of apparel line, materials used, and production process.
- Market analysis: Trends in sustainable fashion, target market behavior, and competitive landscape.
- Marketing strategy: Branding, social media campaigns, and collaborations with eco-conscious influencers.
- Operational plan: Supply chain management, ethical sourcing, and online versus physical sales approach.
- Management team: Roles, responsibilities, and background of team members.
- Financial plan: Initial investment, cost structure, sales forecast, and profitability analysis.

Sustainable campus living products
Maybe you’re not too keen on selling apparel, but you’d still like to tap into the market of students who prioritize sustainable brands and products.
If you also share the same passion for sustainability and have ideas on how to cater to students’ needs, you might want to consider selling sustainable products instead that dormers and other students will find useful for everyday life.
- Executive summary: Mission statement, product line overview, and sustainability goals.
- Company overview: Background on the inspiration for eco-friendly products targeted at students.
- Market analysis: Trends in sustainability, potential campus markets, and niche opportunities.
- Products offered: Description of eco-friendly living products (reusable containers, biodegradable goods).
- Marketing and sales strategy: Campus-based initiatives, eco-friendly partnerships, and social media.
- Operations: Sourcing of materials, product manufacturing, and logistics.
- Management team: Founder’s background, operational management, and advisory board.
- Financial projections: Cost analysis, sales forecast, funding requirements, and profitability timeline.

Student event planning service
A big part of student life is all about events and getting to meet new people. Not only is event planning a big thing for official student organizations, it’s also helpful for smaller communities who want to organize events to meet like-minded people.
If events are a popular thing in your school, you might benefit from setting up a student event planning service.
- Executive summary: Overview of services, unique selling points, and business goals.
- Company description: Types of events covered (e.g., academic, social, sporting).
- Service offering: Full event planning, day-of coordination, and consultation services.
- Market analysis: Campus event culture, demand for event planning services, competitor overview.
- Marketing plan: Outreach strategies, partnerships with campus organizations, and promotional materials.
- Operational strategy: Event logistics, vendor relationships, and event execution checklist.
- Management structure: Leadership team, volunteer opportunities, and staffing needs.
- Financial projections: Pricing model, expected expenses, revenue estimates, and growth potential.

Campus event photography service
Every big event needs good documentation to go with it. Even if your school isn’t big on events, you can choose to offer photography services to groups of friends who want cute little photoshoots in the most Instagrammable parts of your campus.
If you have a knack for photography, here’s how you can start offering photography services on campus:
- Executive summary: Concept and goals for providing photography services for campus events and personal photoshoots.
- Company description: Insights into the types of events covered (e.g., graduations, parties, portraits).
- Services offered: Packages available, including event coverage, individual portraits, and group sessions.
- Market analysis: Demand for photography services on campus, existing offerings, and unique selling points.
- Marketing strategy: Portfolio development, social media presence, partnerships with event organizers.
- Operational plan: Booking process, event execution, post-processing, and delivery of images.
- Management team: Background of the photographer(s), roles in business management , marketing, and customer service.
- Financial plan: Pricing strategy, cost of equipment and travel, revenue projections, and growth potential.

Student art gallery and workshop space
Maybe you’re from an art school, or your campus boasts a rich and talented artistic community. If your school’s artists are looking for a space to display their art, setting up a gallery and workshop space might be a profitable and sustainable business opportunity.
- Executive summary: Vision, goals, and unique aspects of the art gallery and workshop space.
- Company overview: Concept behind promoting student art, workshop themes, and community benefits.
- Market analysis: Interest in local art, campus cultural activities, and potential for art sales.
- Services and products: Exhibition schedules, workshop offerings, and art sales.
- Marketing strategy: Promotions through campus channels, local art scenes, and social media.
- Operations: Gallery setup, workshop logistics, and artist collaboration processes.
- Management team: Backgrounds in art management, curation, and education.
- Financials: Start-up expenses, pricing for art and workshops, expected revenue, and growth potential.

Common mistakes to avoid for student businesses
Setting up a business is no walk in the park, especially for young and inexperienced students. Here are some common mistakes that you can avoid when planning your own business, so you can steer clear of bigger problems down the road:
Lack of a well-defined business plan
It should go without saying that insufficient planning will make it difficult to get your business off the ground. Make sure you put down all important details in writing , and consult experts and get insights from successful small businesses if you need to.
Underestimating the importance of market research
You’ll need more than just a cool idea to start a business. There needs to be a real need or demand for your product or service, and if there’s another business already offering the same thing, you need to make sure your product or service is different or unique.
Familiarize yourself with the existing market and what the market gaps are. Once you identify what that market needs, you can tailor your business plans to try to fill in that gap.
Overlooking legal and financial regulations
Being a student doesn’t exempt you from following standard business regulations. Double check with experts and do extra research to make sure your business complies with all necessary regulations. For instance, you may need to officially register your business, or secure necessary permits.
Inadequate financial planning and management
Your business needs to be on financially stable ground for it to stay sustainable. Make sure you know if you’re in good financial standing to launch your business , and make sure you aren’t spending more than what you can actually afford.
Ignoring the importance of a strong team
It’s tempting to do everything yourself, especially if you lack funds or the ability to delegate tasks. However, you might benefit from having a team of members with various skills. A strong team will bring in more ideas to the table , and will be helpful in managing heavy workloads.
Overlooking customer feedback
You need to listen to what your customers are saying to adapt to their needs and wants. Are your products too expensive? Are people looking for different colors of your products? Engage with your customers so they can let you know how you can improve your business.
Neglecting online marketing
Social media is everything in today’s digital age! You’ll be able to reach a wider audience if you set up social media accounts on different platforms to advertise your services or products.

Future steps for student business owners
So you’ve made your business plan – congratulations! But where do you go from here?
If you want to know whether or not your business is taking off and what future opportunities you can secure, here are some ideas:
Evaluating business performance
Regularly review how well your business is performing by checking product sales, total profits, and how wide your customer base is. If you’ve been earning a good amount of money and are selling popular products or services, that’s a great sign!
Make sure to listen to customer feedback , too, as your customers might give you helpful insights that you might not immediately be aware of. You can do this via informal chats with your customers, or via more formal means like customer surveys.
Exploring growth strategies
Once you’ve evaluated how well your business is performing, you might want to consider growing your business if there’s a demand for a product or service you aren’t already offering, or if there’s an adjacent market you can tap into.
For instance, if you’re offering tutoring services for basic algebra classes, you might want to offer sessions for more complicated math subjects if your tutees need them. If you’ve set up an art space that can also be used as a venue for student events, you can consider expanding your offerings.
Scaling the business
Maybe your business has really taken off and has hit a point that you can no longer meet the customer demand with your tiny team. If that’s the case, you might want to consider scaling.
You can scale your business by adding more people to your team , or ramping up your production efforts.
Building a brand
Don’t be afraid to make a name for yourself! Explore how you can create a brand for your business. This is where you can let your creative juices flow – do you want to appear like a sophisticated and professional brand, or are you going for a more quirky approach?

Takeaways for business plan examples for students
The opportunities are endless if you want to set up a business as a student. Let your imagination run wild and look through business plan examples for students if you want to start selling or offering something new to your school’s community.
Don’t be intimidated by your lack of expertise or resources just yet – with the right mindset and enough determination, you’ll be able to set up your business for success and start your journey as a solid business owner!
About the Author
Peter Keszegh
Peter K. is an experienced digital marketer with a decade of expertise in driving business growth through innovative strategies. His data-driven approach and deep understanding of SEO, PPC, social media, and content marketing have propelled brands to new heights. With a client-centric mindset, Peter builds strong relationships and aligns strategies with business goals. A sought-after thought leader and speaker, his insights have helped professionals navigate the digital landscape. Trust Peter to elevate your brand and achieve success in the digital era.
Business Plan Template for College Students
- Great for beginners
- Ready-to-use, fully customizable Subcategory
- Get started in seconds

Starting a business as a college student can be both exciting and challenging. You have big dreams and innovative ideas, but how do you turn them into a successful reality? ClickUp's Business Plan Template for College Students is here to guide you every step of the way!
With this template, you can:
- Clearly define your business goals and strategies for success
- Create a comprehensive financial plan and projections to attract investors
- Identify potential obstacles and develop contingency plans
- Effectively communicate your business ideas to stakeholders and secure funding or resources
Don't let your entrepreneurial dreams fade away. Use ClickUp's Business Plan Template for College Students to bring your vision to life and make a lasting impact in the business world. Start planning and building your future today!
Business Plan Template for College Students Benefits
Starting a business as a college student is an exciting and challenging endeavor. With a Business Plan Template for College Students, you can:
- Clearly articulate your business goals and strategies, giving potential investors and partners a comprehensive understanding of your vision
- Create a solid financial forecast that demonstrates the potential profitability of your venture, increasing your chances of securing funding or resources
- Identify potential obstacles and develop contingency plans to mitigate risks, ensuring your business is well-prepared for any challenges that may arise
- Effectively communicate your business idea to others, including professors, mentors, and potential customers, gaining valuable feedback and support for your startup.
Main Elements of College Students Business Plan Template
ClickUp's Business Plan Template for College Students provides a comprehensive framework for college students to develop and present their business ideas effectively:
- Custom Statuses: Easily track the progress of each section of your business plan with statuses such as Complete, In Progress, Needs Revision, and To Do.
- Custom Fields: Use custom fields like Reference, Approved, and Section to add important details to your business plan, such as references, approval status, and specific sections.
- Custom Views: Access different views like Topics, Status, Timeline, Business Plan, and Getting Started Guide to organize your business plan information, track progress, create a timeline, and refer to a guide to get started.
- Collaboration Tools: Collaborate with team members, mentors, or advisors by assigning tasks, adding comments, and attaching files directly within the template.
- Goal Tracking: Set goals within your business plan and use ClickUp's Goals feature to track their progress and measure success.
- Document Management: Store important documents, financial projections, and market research within ClickUp's Docs feature for easy access and reference.
How To Use Business Plan Template for College Students
If you're a college student looking to start your own business, using ClickUp's Business Plan Template can help you get organized and create a solid plan for success. Just follow these six steps:
1. Define your business idea and goals
Start by clearly defining your business idea and the goals you want to achieve. What problem does your business solve? Who is your target audience? What are your short-term and long-term goals? Take the time to brainstorm and outline these key details.
Use a Doc in ClickUp to document your business idea and goals.
2. Conduct market research
Next, conduct thorough market research to understand your industry, competition, and target market. Identify trends, customer needs, and potential challenges. This research will help you refine your business idea, identify opportunities, and develop strategies to stand out in the market.
Use the Table view in ClickUp to organize and analyze your market research data.
3. Plan your products or services
Based on your market research, plan out the products or services you will offer. Determine their unique selling points, pricing strategy, and how they will meet the needs of your target market. Consider any additional features or benefits that will set you apart from competitors.
Create tasks in ClickUp to outline and organize your product or service plans.
4. Develop a marketing strategy
Now it's time to develop a comprehensive marketing strategy to promote your business and attract customers. Identify the most effective channels to reach your target audience, such as social media, content marketing, or email campaigns. Outline your branding, messaging, and promotional tactics.
Use the Board view in ClickUp to visually plan and track your marketing initiatives.
5. Create a financial plan
A solid financial plan is crucial for any business. Determine your startup costs, revenue projections, and expenses. Create a budget that includes marketing, operations, and any other necessary expenses. Consider different funding options and outline your financial goals for the first year and beyond.
Use custom fields in ClickUp to track and analyze your financial projections.
6. Review and revise
Once you have completed your business plan using ClickUp's template, review it thoroughly and make any necessary revisions. Share it with trusted mentors, advisors, or teammates for feedback. Continuously update and refine your plan as your business evolves.
Set recurring tasks in ClickUp to regularly review and update your business plan.
Get Started with ClickUp’s Business Plan Template for College Students
College students who are starting their own businesses or pursuing entrepreneurial ventures can use the ClickUp Business Plan Template to effectively communicate their business ideas and secure funding or resources for their startups.
First, hit “Add Template” to sign up for ClickUp and add the template to your Workspace. Make sure you designate which Space or location in your Workspace you’d like this template applied.
Next, invite relevant members or guests to your Workspace to start collaborating.
Now you can take advantage of the full potential of this template to create a comprehensive business plan:
- Use the Topics View to outline and organize different sections of your business plan, such as Executive Summary, Market Analysis, Marketing Strategy, Financial Projections, etc.
- The Status View will help you track the progress of each section, with statuses like Complete, In Progress, Needs Revision, and To Do
- The Timeline View will allow you to set deadlines and visualize the timeline for completing each section of your business plan
- The Business Plan View will provide a holistic overview of your entire business plan, allowing you to see how different sections fit together
- The Getting Started Guide View will provide step-by-step instructions and resources to help you navigate through the business planning process
- Utilize custom fields like Reference, Approved, and Section to add additional information and categorize different aspects of your business plan
- Regularly update and revise your business plan as you progress, ensuring that it reflects the most accurate and up-to-date information.
- Business Plan Template for Lululemon
- Business Plan Template for Hotel Industry
- Business Plan Template for Packaging Manufacturers
- Business Plan Template for Sales Teams
- Business Plan Template for Photography Business
Template details
Free forever with 100mb storage.
Free training & 24-hours support
Serious about security & privacy
Highest levels of uptime the last 12 months
- Product Roadmap
- Affiliate & Referrals
- On-Demand Demo
- Integrations
- Consultants
- Gantt Chart
- Native Time Tracking
- Automations
- Kanban Board
- vs Airtable
- vs Basecamp
- vs MS Project
- vs Smartsheet
- Software Team Hub
- PM Software Guide
See in 90 seconds how LivePlan simplifies
financials for students: Watch
Garretts Bike Shop
Provide real–world business plan examples for your students, inspire confidence in future entrepreneurs and easily create your class syllabus using industry–best business plans., liveplan gives students access to actual business plans so they can practice business planning in and outside of the classroom., it's not just a classroom project. it's your students planning for their futures..

Teach by example
LivePlan's examples of actual business plans show students how they can identify opportunities, meet challenges, and plan their path to profits. Just like real-world entrepreneurs.

No spreadsheets necessary
With all–in–one spreadsheet–free forecasting and pitching tools–students can use LivePlan to build a realistic business plan with accurate projections and compelling pitches. Analyze scenarios. Track progress. Set goals. All in LivePlan.

Works seamlessly with your classroom setup
With LivePlan you can simplify syllabus creation. LivePlan can also be used alongside classroom tools such as Blackboard and Canvas. LivePlan's optional instructional resources can enhance your syllabus with materials that introduce lean planning principles, growth metrics, financial forecasting, and more.
Instructors looking for a great tool to help students develop business plans need to look at Live Plan. The step–by–step process walks students through the entire process from Pitch to Financials. As the Instructor you can also have online access to their plan and provide feedback and comments as the plan develops.

Mike Allen Business Instructor, North Idaho College, Coeur d'Alene, ID
Bring out the best in every student
LivePlan's business plan examples help students turn ideas into top–notch business plans for class projects and startups. The tools, features, and instructional content allow you to focus on bringing out the best in your students for every plan and project.
Before using LivePlan, my students were intimidated by the business planning process. LivePlan breaks it down into manageable steps and takes the mystery out of developing a business plan.

Amy Schulz NACCE Vice President of Education, Membership and Associate Faculty, Feather River College, Quincy, CA
I used LivePlan to develop a business plan for a class project. Turns out, the project became part of a business plan competition where I placed second out of over 200 entries.

Sheila Austin Student
LivePlan provides your students with the tools to

Know the competition
No business operates in a vacuum. LivePlan incorporates real–world industry data, so students can better understand competitors, plan businesses around industry realities, and confidently execute data–driven strategies.

Build business dreams together
From sharing feedback and engaging in discussions, to simultaneously working on different parts of the plan, students can easily collaborate in groups using LivePlan.

Create a plan that fits their needs
Whether small or big, LivePlan can build out the right–sized business plan for your classroom projects. In LivePlan, students can develop a simple lean plan that focuses their ideas, or create a full business plan with all the details and steps necessary to persuade investors, attract partners, and turn their idea into a profitable reality.

With so much happening in the classroom, you need a tool that works with you, not one that makes you do extra work. Used by educators, consultants, entrepreneurs, and students all around the world, LivePlan has been regularly improved and streamlined so it's easy to use.

Develop confidence in their plan and themselves
It's one thing to plan a business. It's another thing to know how to talk about a business plan. Students can develop talking points and practice their pitch in LivePlan so they can discuss their enterprise with confidence and authority.
With LivePlan your students exceed expectations
With LivePlan, students create business plans that:
- Guide them from concept to actionable plan
- Build the confidence necessary to be entrepreneurs
- Combine pitching, forecasting, and collaboration
LivePlan streamlines projects for educators
LivePlan eases project management in the classroom, so instructors can:
- Pinpoint feedback and suggest improvements
- Monitor project progress
- Teach business planning instead of managing multiple apps
Go beyond business plan examples
LivePlan easily integrates into business courses, includes all materials and curriculum to support classroom business projects, and comes with free phone, email, and chat technical support.
The students very much appreciate the guidance the LivePlan program offers. I love the ability to act as a contributor to their plans. The help resources are phenomenal and easy to navigate.

John Shaw Assistant Professor of Management, Davis College of Business – Jacksonville University, Jacksonville, FL
See how LivePlan can upgrade your student's education
Fill out the form below and our LivePlan Partnership Team will be in touch shortly.
Get Your Free LivePlan Account Today
Thanks an educator advocate will be contacting you shortly to set up your free liveplan account..
If you'd like to talk to us before then, please call 1–888–498–6136 Phones are open M–F, 8am–5pm (Pacific time)
Teachers and students love LivePlan
LivePlan really facilitated communication between students who were in a team on the business plan project. Students could comment on sections of their business plan and collaborate on what to change in their plan without having to meet face–to–face.

Amy Valente Assistant Professor of Business, Cayuga Community College, Auburn, New York
LivePlan helped us easily set up the business plan for our startup during our MBA. As soon as the other students saw it, they also wanted LivePlan. The time we saved on planning we could use for operational tasks. It was the ideal solution for us.

The product we produced by using Live Plan was exceptional, far exceeded our expectations, and came out so much better than we could have ever done on our own.

This product is a game-changer. It allows the non–MBA founder to unleash their potential through strategic planning and beautiful design. Highly recommended.

Answers Neuroscience
LivePlan is simply awesome.

Amit Agrawal
Financial modeling spreadsheets and templates in Excel & Google Sheets
- Your cart is empty.

Business Plan Examples For Students Entrepreneurship To Inspire Your Journey

Venturing into the world of entrepreneurship as a student can be both exciting and challenging. One of the pivotal steps in turning a business idea into reality is creating a robust business plan. This foundational document helps in organizing the vision, setting clear objectives, and outlining the necessary steps to achieve entrepreneurial success. Whether you’re eyeing a new coffee shop or a cutting-edge tech start-up, a well-structured business plan is indispensable. This article delves into the critical components of a business plan and provides practical examples tailored for student entrepreneurs.
Understanding the intricacies of business planning can significantly elevate the chances of your venture’s success. Not only does a comprehensive business plan facilitate better decision-making, but it also helps in securing investments and managing resources effectively. For students, crafting this document might seem daunting, but with the right guidance, it becomes a manageable and enlightening process. By exploring various business plan examples for students entrepreneurship, you will learn how to construct a blueprint that resonates with your business goals and market needs. Let’s dive into the essential elements you need to include and see how to bring your entrepreneurial vision to life.
Business Plan Examples for Students Entrepreneurs: Key Components to Success
Creating a solid business plan is crucial for students venturing into entrepreneurship. A well-crafted business plan not only helps in outlining the business vision but also serves as a roadmap to guide the venture toward success. Here are some vital components to include in a business plan, along with illustrative examples to empower student entrepreneurs.
Understanding the Executive Summary
The executive summary encapsulates the entire business plan into a succinct overview. It should answer key questions: What is the business? What are its goals? Who are the target customers? For example, if a student wants to start a coffee shop targeting college students, the executive summary might outline how the shop will provide affordable, quality coffee in a cozy atmosphere conducive to studying.
Market Analysis: Know Your Audience
Conducting thorough market research is vital. This section should analyze the industry landscape, target market, competitors, and potential challenges. For instance, a student starting a clothing line should identify their target demographics (e.g., college-age students) and evaluate competitors like local boutiques and online shops. Including statistics, such as the percentage of students who regularly purchase new clothing, adds depth to the analysis.
Sample Market Analysis Points:
- Industry Overview
- Target Market Description
- Competitor Analysis
- Marketing Strategy
Defining the Business Model
Clearly defining how the business will operate is essential. This involves laying out the revenue streams, pricing strategies, and sales channels. If the student plans to launch a tutoring service, they need to specify whether they will charge per session, offer subscriptions, or partner with schools. Each option has distinct implications for revenue generation.
Marketing Strategy: Reaching Your Customers
A comprehensive marketing strategy outlines how a business will attract and retain customers. For students, this might mean using social media platforms to promote their products. For example, if presenting a startup focused on handmade jewelry, the marketing strategy could detail how platforms like Instagram and TikTok will be leveraged to share product images and testimonials, and how promotions will be structured to appeal to fellow students.
Key Elements of a Marketing Strategy:
- Brand Positioning
- Promotional Tactics
- Social Media Plans
- Partnership and Collaboration Ideas
Operations Plan: Day-to-Day Functionality
The operations plan covers the logistics of running the business. This includes the location, equipment, staff requirements, and any necessary licenses or permits. For example, a student opening a food truck needs to discuss the physical location of the food truck, any partnerships with local festivals for events, and the number of employees required to operate the truck successfully.
Financial Projections: Planning for Profit
Financial projections are critical in demonstrating the viability of the business. This section must include forecasts for income, expenses, and profitability. For a student looking to begin a tech service, projecting potential earnings based on market size and pricing strategy is essential. It’s beneficial to create a sales forecast that outlines expected revenue based on different scenarios, such as an average case where the service captures 10% of the market.
Essential Financial Projection Components:
- Start-Up Costs
- Projected Income Statement
- Cash Flow Statement
- Break-Even Analysis
Funding Requirements: Securing Investment
If the business will require external funding, detailing the funding requirements is necessary. Students should define how much capital is needed and outline where they expect to obtain it—whether through loans, investors, or personal savings. For instance, if launching an app, a student should clearly state how much investment they need to cover development and marketing expenses and what potential return they offer to investors.
Appendix: Supporting Documents
The appendix serves as a place for additional documents that support the business plan, such as resumes, reference letters, or detailed research findings. Including this information lends credibility to the plan and provides additional context for potential investors or mentors.
Learning to craft a compelling business plan can significantly benefit student entrepreneurs. By incorporating these core components, they can construct a roadmap for success and attract the necessary resources to bring their business ideas to fruition. Whether aspiring to manage a café, launch a tech startup, or create an online boutique, a carefully structured business plan is one of the first steps toward entrepreneurship.
The Importance of Market Research in Student Business Plans
In today’s competitive business landscape, aspiring entrepreneurs, particularly students, must grasp the significance of market research when crafting their business plans. Utilizing thorough market research not only enhances the quality of a student’s business plan but also establishes a solid foundation for their entrepreneurial journey. Understanding the target market, identifying competitors, and recognizing industry trends are crucial steps that students should take before launching their businesses.
Understanding the Target Market
Knowing the target market is essential for any business. It helps students to design products or services that cater specifically to their audience’s needs. Conducting market research allows students to:
- Identify demographics: Understanding age, gender, income levels, and preferences can guide students in tailoring their offerings.
- Gather customer feedback: Engaging with potential customers through surveys or focus groups can provide invaluable insights into their expectations and desires.
- Analyze purchasing behavior: Recognizing patterns in how and why customers make purchases can help students strategize their marketing efforts effectively.
Identifying Competitors
Another vital aspect of market research is competitor analysis. Students must understand who their competitors are, what they offer, and how they position themselves in the market. Familiarity with competitors allows students to:
- Differentiate their offerings: By analyzing competitors, students can identify gaps in the market and develop unique selling propositions that set them apart.
- Learn from competitors’ successes and failures: Understanding what works in the industry gives students insight into best practices and potential pitfalls.
- Adjust pricing strategies: Observing competitor pricing can help students set competitive prices while ensuring profitability.
Recognizing Industry Trends
Staying abreast of industry trends is equally crucial. The business environment is dynamic, and trends can significantly influence consumer behavior and market demand . Through diligent market research, students can:
- Spot emerging trends: Identifying shifts in consumer preferences, technology advancements, or economic changes can help students position their companies for future success.
- Assess market viability: Understanding current and future trends allows students to determine if their business ideas are sustainable in the long run.
- Adapt marketing strategies: With awareness of trending topics or interests within their market, students can align their marketing efforts to resonate with potential customers effectively.
Tools and Techniques for Market Research
Various tools and techniques can aid students in their market research endeavors. They should consider using:
- Online surveys: Platforms like SurveyMonkey or Google Forms enable students to create and distribute surveys easily.
- Social media polls: Utilizing social media channels can provide insights into consumer sentiment and preferences with immediate feedback.
- Industry reports: Many organizations publish valuable research data that can be accessed for free or at a reasonable cost.
- Competitor websites: Regularly analyzing competitors’ Websites and marketing materials can provide insights into their strategies.
Implementing Research Findings
After gathering relevant data, students must take action on their findings. This includes:
- Revising business plans: research findings can enhance and refine the business plan, making it more robust and convincing to potential investors.
- Tailoring marketing campaigns: Properly analyzing target marketing insights will enable students to craft campaigns that resonate with their audience effectively.
- Innovating products or services: Insights from market research can lead to improvements or iterations on offerings, better meeting customer needs.
Market research into student business plans is not merely an academic exercise; it serves as a practical foundation for entrepreneurial success. When students understand their market, analyze competitors, recognize trends, and actively implement their findings, they greatly increase their chances of building sustainable businesses. Thorough preparation using market insights paves the way for innovative ideas, successful launches, and thriving ventures.
How to Financially Forecast When Writing a Business Plan as a Student
When diving into the world of entrepreneurship, especially as a student, understanding how to financially forecast is crucial. A financial forecast provides a roadmap for potential investors and helps outline what the future holds for your business. It’s essential to approach this important component of your business plan with clarity and a sound strategy.
Define Your Financial Goals
The first step in effective financial forecasting is defining your financial goals. Knowing precisely what you aim to achieve will serve as the foundation for all your calculations. Consider these key factors:
- Revenue milestones: What sales figures do you wish to achieve within the first year?
- Profit margins: How much profit do you aim to make after expenses are deducted?
- Funding needs: Do you require external funding, and if so, how much?
Understanding these elements helps shape your forecast and prepares you for deeper insights into your business’s financial health.
Gather Historical Data
Even as a student, it’s possible to compile relevant data that can influence your forecast. If you’re launching a business similar to existing companies, use their financial data as references. Look into:
- Industry benchmarks: Find statistics that reflect average sales and growth rates in your sector.
- Competitor performance: Analyze the financial success of competitors to gauge realistic expectations for your projections.
- Market trends: Investigate whether the demand for your product or service is rising or falling.
Each data point will enhance the accuracy of your financial forecasts, positioning you for greater business success.
Estimate Income and Expenses
At the core of financial forecasting are your estimates of income and expenses. It’s vital to break down these elements in detail.
Estimating Income
Begin by predicting how much you will earn from sales. Use the following strategies:
- Pricing strategy: What price will you set for your product/service?
- Sales volume: Estimate how many units you expect to sell over a defined period.
By multiplying the price by the expected sales volume, you can arrive at your forecasted revenue.

Estimating Expenses
Expenses can range widely, so consider both fixed and variable costs:
- Fixed costs: These remain unchanged regardless of your sales volume, such as rent and salaries.
- Variable costs: These fluctuate based on sales, such as materials and shipping expenses.
Be thorough in your calculations, as underestimating costs can jeopardize your entire plan.
Cash Flow Projections
Maintaining positive cash flow is vital for a thriving business. Cash flow projections display your incoming and outgoing cash over time. Follow these steps:
- Create a cash flow statement : Outline your estimated cash inflows (from sales) and cash outflows (expenses).
- Forecast monthly : Project cash flow on a monthly basis to observe trends and adjust your strategy accordingly.
This level of detail will help you anticipate periods of surplus or shortfall in funds, making it easier to plan for unexpected costs.
Create a Break-Even Analysis
A break-even analysis determines when your business will become profitable. It’s critical for understanding how much you need to sell before generating a profit. To conduct this analysis:
- Calculate total fixed costs.
- Determine the contribution margin per unit (selling price minus variable costs).
- Divide total fixed costs by the contribution margin to find the break-even point.
This calculation not only guides your pricing strategy but also shapes your investment pitches.
Review and Revise Regularly
Forecasting is not a one-time task. Regularly review and revise your projections based on actual performance:
- Compare actual results to projections to identify discrepancies.
- Adjust assumptions according to market changes.
Feedback and adaptability are indispensable for refining your forecasting approach and ensuring continued growth.
By following these strategies, you can develop a comprehensive financial forecast for your business plan, positioning yourself as a credible entrepreneur despite being a student. Each component will contribute to a well-rounded, realistic view of your business’s potential, boosting your confidence as you embark on your entrepreneurial journey.
Creative Business Ideas for Student Entrepreneurs and Their Plans
Embarking on an entrepreneurial journey as a student can be both thrilling and daunting. With the right creative business ideas and well-structured plans, aspiring entrepreneurs can navigate this exciting phase with confidence. Here are some innovative concepts and essential elements that can form the foundation for your business venture.
Freelance Graphic Design
Students with a knack for creativity can consider offering freelance graphic design services. With the increasing demand for logos, promotional materials, and social media content, this field offers significant opportunities.
- Identify your niche—branding, social media graphics, or print design.
- Create a portfolio website to showcase your work.
- Utilize social media platforms to reach potential clients.
- Set competitive pricing based on market research.
E-commerce Store for Handmade Crafts
For students with crafting skills, starting an e-commerce website to sell handmade goods can be an excellent business model. Platforms like Etsy make it easy to reach a global audience.
- Source sustainable and quality materials for crafting.
- Develop a captivating brand story that resonates with customers.
- Implement an SEO strategy to enhance visibility on search engines.
- Market your products via social media campaigns and influencer collaborations.
Online Tutoring Services
With the rise of remote education, online tutoring remains a great option for student entrepreneurs who excel in academics. By offering tutoring services in subjects like math, science, or even languages, students can leverage their knowledge.
- Identify subject areas where you have expertise.
- Set up a website to schedule sessions and process payments.
- Build trust through testimonials and reviews from satisfied students.
- Offer free trial sessions to attract new clients.
Blogging or Vlogging
If you’re passionate about a specific topic—be it fashion, travel, or tech—consider blogging or vlogging as a way to monetize your interest. By building a personal brand, you can attract sponsorships and affiliate marketing opportunities.
- Choose a specific niche to focus on to establish authority.
- Develop a content calendar to maintain consistent postings.
- Engage with your audience through social media channels.
- Utilize analytics tools to track your audience’s interests and optimize content accordingly.
Mobile Car Wash and Detailing Services
This business idea caters to busy professionals who lack time for car maintenance. Offering a mobile car washing and detailing service can be both profitable and relatively low-cost to start.
- Invest in quality cleaning supplies and equipment.
- Market your services through local advertising and online platforms.
- Provide various packages to cater to different budgets.
- Use a scheduling tool to manage appointments easily.
Event Planning and Coordination
If you’re organized and enjoy planning parties or events, consider starting an event planning business. You can begin by coordinating student events and gradually expand to corporate ones.
- Network with local vendors to secure deals and discounts.
- Create a detailed checklist for each type of event to streamline the process.
- Leverage social media to showcase past events and gain new clients.
- Offer packages that include venue sourcing, décor, and logistics planning.
As student entrepreneurs explore these creative business ideas, they must remember that a solid business plan is the backbone of any successful venture. Tailor your strategies based on personal interests and market needs to enhance your chances of success. With dedication and a clear vision, the sky’s the limit!
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Student Business Plans
Creating a business plan is a crucial step for student entrepreneurs who aspire to turn their innovative ideas into successful ventures. However, there are common pitfalls that can undermine the effectiveness of these plans. Here are some mistakes students should avoid when crafting a business plan to enhance their chances of success.
Avoid Ambiguity
It’s essential to be precise about your business goals, target market, and the unique value proposition of your product or service. Vague statements can lead to confusion and may mislead potential investors or partners. Instead of writing, “We want to be the best in our market,” specify what that means—identify your metrics and how you plan to achieve them.
Neglecting Market Research
One of the biggest mistakes is skipping thorough market research. Failing to understand your target audience’s needs, preferences, and behaviors can be detrimental. Comprehensive market research aids in identifying opportunities and challenges. Consider these steps to ensure you are well-informed:
- Conduct surveys or interviews with potential customers.
- Analyze competitors and their market positioning.
- Utilize statistical data to grasp market trends.
Overly Optimistic Financial Projections
Many student entrepreneurs fall into the trap of presenting overly ambitious financial forecasts. While being optimistic is important, basing projections solely on hope can discredit the business plan. Aim to create realistic financial expectations by:
- Researching industry benchmarks to inform your projections.
- Including a break-even analysis to show when you expect to become profitable.
- Projecting conservative estimates of revenue growth and expenses.
Ignoring the Competition
Understanding your competitors is critical for positioning your business. Common mistakes include neglecting to analyze competitors or underestimating their impact. It’s important to:
- Identify main competitors in your niche.
- Examine their strengths and weaknesses.
- Describe how your business differs and the advantages you will have over them.
Failure to Secure Relevant Skills and Expertise
Another widespread error is trying to cover all aspects of the business without acknowledging personal limitations. Successful entrepreneurship often requires a team effort. Consider bringing in partners or advisors who possess skills you may lack. This can strengthen your business plan by:
- Highlighting diverse expertise in finance, marketing, and operations.
- Demonstrating a well-rounded team to potential investors.
Underestimating the Importance of an Executive Summary
Many overlook the significance of an impactful executive summary. It is often the first impression decision-makers will have of your business plan. This section should succinctly summarize your mission, market strategy, and financial outlook. Key elements to include are:
- A brief description of your business idea.
- Insights into your target market.
- An overview of your financial projections.
Forgetting to Outline Realistic Milestones
Milestones are essential for tracking progress and motivating your team. A business plan without clear, achievable milestones may appear unstructured and lessen its credibility. When defining your milestones:
- Set specific, measurable goals.
- Establish timelines for each milestone to maintain accountability.
- Regularly evaluate and adjust your milestones based on progress.
Neglecting to Revise the Plan Regularly
An effective business plan is not static. Many students make the mistake of treating it as a one-time task. As market conditions and business dynamics change, revising your plan regularly is necessary to stay aligned with your goals and strategies. Conduct regular reviews to:
- Evaluate your progress against set milestones.
- Revise your strategies based on feedback and new opportunities.
By steering clear of these common mistakes, student entrepreneurs can craft strong, persuasive business plans that attract support, investment, and guidance. Remember, the process of creating a business plan is just as important as the final document. Strive for clarity, research, collaboration, and adaptability, and you will put yourself on a path to entrepreneurial success.
The Role of Mentorship in Developing Effective Business Plans for Students
Mentorship has emerged as a powerful tool for students venturing into entrepreneurship, particularly in the context of developing effective business plans. The relationship between a mentor and a mentee can serve as a catalyst for growth, guiding students through the intricate process of business planning. There are several key aspects where mentorship significantly enhances the ability of students to create robust business plans.
Personalized Guidance and Insights
One of the most significant advantages of having a mentor is the personalized guidance they provide. Mentors often bring years of experience and practical knowledge to the table. This experience proves invaluable for students who may be new to entrepreneurship. With their insights, mentors can help students identify potential pitfalls and recognize opportunities specific to their business idea.
- Expert Consultation: Mentors can offer expertise in particular fields, whether it’s marketing, finance, or operations, allowing students to tailor their business plans effectively.
- Networking Opportunities: Mentors often have vast professional networks they can leverage, helping students connect with potential partners, investors, and customers.
Encouraging Critical Thinking and Creativity
Effective business plans are not just about numbers; they reflect creative thinking and strategic foresight. Mentors can challenge students to think critically about their business ideas, encouraging them to explore various avenues and possible outcomes. By posing thought-provoking questions, mentors assist students in considering multiple perspectives.
- Idea Generation: Mentors can facilitate brainstorming sessions that lead to innovative ideas and potential revenue streams.
- Problem-Solving: With the mentor’s guidance, students can develop their problem-solving skills, preparing them for potential challenges they may face in the business landscape.
Structuring the Business Plan
A well-structured business plan is vital for attracting investors and ensuring the viability of the business. Mentors help students identify essential components that should be included in their plans, such as:
- Executive Summary: A concise overview of the business and its goals.
- Market Analysis: Understanding the industry landscape and target audience.
- Marketing Strategy: Outlining how to reach and engage customers.
- Financial Projections: Estimating revenue, costs, and profitability.
- Operational Plan: Detailing the logistics of running the business.
By helping students structure their business plans effectively, mentors ensure that the plans meet the expectations of stakeholders and investors alike.
Providing Accountability and Motivation
Having a mentor inherently establishes a framework of accountability. When students know they need to report back to their mentors, they are more likely to stay committed to their objectives. Moreover, mentors can motivate students, especially during challenging times. The entrepreneurial journey often comes with ups and downs, and a mentor can provide reassurance, guidance, and the necessary nudge to keep pushing forward.
Fostering a Growth Mindset
With a mentor’s support, students can cultivate a growth mindset. They learn to view challenges as opportunities for learning and growth rather than insurmountable obstacles. This shift in perspective is crucial for entrepreneurship, where resilience and adaptability are key predictors of success.
- Encouraging Continuous Learning: Mentors instill the importance of ongoing education and self-improvement.
- Reflective Practice: Regular discussions with mentors encourage students to reflect on their experiences, leading to better decision-making in the future.
Ultimately, mentorship plays a pivotal role in developing effective business plans for students pursuing entrepreneurship. By providing guidance, fostering critical thinking, enhancing accountability, and encouraging a growth mindset, mentorship transforms students’ ideas into actionable, well-structured business plans. For aspiring entrepreneurs, finding the right mentor can be one of the most impactful steps they take in their journey.
Leveraging Technology to Streamline Business Plan Development for Students
In a world where technology shapes how we operate, students venturing into entrepreneurship can greatly benefit from leveraging various tools to develop their business plans. A well-crafted business plan not only serves as a roadmap for budding entrepreneurs but also enhances their chances of success. By using technological advancements, students can streamline this critical process and ensure they remain competitive in today’s fast-paced market.
Understanding the Importance of a Business Plan
Before exploring the technological tools available, it’s essential to grasp why a solid business plan is vital. A business plan acts as a blueprint that outlines the operational structure, market analysis, financial projections, and marketing strategies of a venture. For students, grasping the components and key performance indicators (KPIs) of their business is crucial. This understanding helps them secure funding from investors, manage resources effectively, and evaluate business performance over time.
Online Business Plan Tools
Several online platforms provide templates and tools to aid students in writing their business plans. These resources not only simplify the process but also offer guidance on how to present ideas effectively. Popular online tools include:
- LivePlan: This tool allows users to create business plans with ease. It provides step-by-step instructions and visual aids to help articulate each section clearly.
- BizPlan: BizPlan offers a visual planner that helps users develop their ideas intuitively. It allows for seamless collaboration if students wish to work in teams.
- Enloop: Enloop uses your input to create a draft business plan and automatically generates a performance score to evaluate the feasibility of your ideas.
- Canva: While primarily a graphic design tool, Canva offers stunning templates for business plans that can elevate any presentation. Students can easily combine text with visuals for a more impactful proposal.
Utilizing Financial Modeling Software
Financial projections are a necessary component of any business plan. Missing this crucial detail could lead to misunderstandings and miscalculations. Fortunately, technology offers robust financial modeling software tailored for students and entrepreneurs. Some noteworthy options include:
- Excel: A staple in any student’s toolkit, Excel allows for detailed financial modeling. With templates readily available, students can practice creating budgets, cash flow projections, and profit-loss statements.
- QuickBooks: This accounting software provides valuable insights into the financial health of a business and offers tools to create forecasts.
Collaboration Tools for Team Projects
For those working in groups, collaboration tools are indispensable. They enable seamless communication and project management. Here are a few tools to consider:
- Trello: This visual project management tool helps teams keep track of tasks and deadlines efficiently. Each member can update their progress and ensure everyone is aligned.
- Slack: A communication platform that allows for real-time discussions, file sharing, and organization within channels that can be tailored to specific project aspects.
Research and Market Analysis Tools
Accurate market analysis is integral to developing a successful business plan. Students can explore the following tools to gather data effectively:
- Google Trends: This tool allows students to analyze trending keywords in their industry. Understanding consumer interests can shape how they position their business.
- SurveyMonkey: Gathering insights directly from potential customers is essential. SurveyMonkey enables students to create surveys that yield valuable feedback.
Final Thoughts on Streamlining Your Plan
With technology rapidly changing the landscape of entrepreneurship, students have an unprecedented opportunity to refine their business plans efficiently. By utilizing online tools and software dedicated to business planning and market analysis, students can boost their confidence and structure their ideas more clearly. Moreover, these resources not only save time but also enhance creativity and reduce the stress associated with creating comprehensive business plans.
Ultimately, the integration of technology into business plan development equips students with essential skills and an edge in the competitive entrepreneurial world. They can confidently present their ideas, back them with data, and demonstrate the viability of their business concepts, paving the way for future success.
Crafting a business plan is not just essential for aspiring entrepreneurs; it is also a rite of passage that helps students visualize their entrepreneurial dreams and understand the intricacies of running a business. As we’ve explored, several key components contribute to the success of student business plans. By understanding these elements, students can create comprehensive and actionable plans that are tailored to their unique ideas and goals.
Market research stands out as a vital step in developing a business plan. It allows students to grasp their target audience’s needs, assess the competition, and identify market trends. With this information, they can make informed decisions that are crucial during the planning phase. Conducting thorough market research not only enhances a business idea’s viability but also showcases a student’s commitment and professionalism when presenting their plan to potential investors or mentors. The data gleaned from this research can serve as a powerful tool for justifying the feasibility of the proposed business, which is especially important in convincing stakeholders of its potential success.
When it comes to the financial aspect, students often encounter challenges in forecasting and budgeting. However, accurate financial projections are crucial in any business plan. Students must learn to create realistic forecasts that reflect potential revenue, operating costs, and profit margins. This section of the plan should be based on the market research findings and supported by concrete data. tools and software can simplify this process, allowing for more precise calculations and easier adjustments when needed. A sound financial plan not only guides the student’s actions but also establishes credibility among potential investors.
Creative business ideas flourish amongst students, inspired by their unique experiences and perspectives. However, the cultivation of these ideas must be underpinned by a concrete plan. Outlining the business concept, defining the target market, and detailing the operational strategy can transform a simple idea into a promising venture. Moreover, by highlighting their ingenuity and adaptability, students can develop distinct strategies that set them apart in the marketplace. Whether starting an innovative app or a niche product line, students can showcase their creativity by crafting plans that are as dynamic as their ideas.
Avoiding common mistakes in business plan development can significantly impact a student’s success. Many students overlook the importance of clarity and specificity. Failing to clearly outline objectives, strategies, and metrics can leave a plan feeling vague and unconvincing. Additionally, neglecting to address potential risks and challenges can lead to unrealistic expectations. By understanding and navigating these pitfalls, students can create robust plans that anticipate obstacles and outline contingency strategies. Educators and mentors can provide valuable feedback to help students refine their plans and better prepare them for future challenges.
Mentorship plays an instrumental role in shaping successful business plans. Engaging with experienced entrepreneurs allows students to gain insights that they may not have considered. Mentors can provide constructive criticism, offer guidance on best practices, and share their own experiences, all of which are invaluable to a student entrepreneur. Developing a relationship with a mentor enriches the planning process and can even open doors to networking opportunities that can elevate the student’s entrepreneurial journey.
Today’s digital landscape offers numerous tools and technologies to streamline the business plan development process. From agile project management applications to financial modeling software, students are better equipped than ever to craft comprehensive plans. Utilizing these resources can enhance collaboration, improve organization, and facilitate adjustments throughout the planning phase. Students should take advantage of these technological advancements to save time and focus more on the creative aspects of their business ideas.
As students embark on their entrepreneurial journeys, they must remember that a business plan is not merely a document but a living entity that evolves as their ideas develop. By integrating market research, financial forecasting, mentorship, creativity, and technology, students can build compelling business plans that inspire confidence and drive action. The entrepreneurial path is filled with uncertainties, but with a well-structured plan and a clear vision, student entrepreneurs can navigate these challenges and work towards turning their dreams into reality. Preparing a business plan is not just about generating a product or service; it is about establishing a foundation for a future filled with opportunities, personal growth, and, ultimately, success.

Coffee Shop Financial Model Excel Template
Download Coffee Shop Financial Model Template. Allows you to start planning with no fuss and maximum of help Highly versatile and user-fri... read more
- Excel - Multi-User – $129.00 Version 1
- Excel - Single-User – $99.00 Version 1
- Free Demo – $0.00 Version 1

All My Financial Models, Spreadsheets, Templates, and Tools: 120+
Lifetime access to all future templates as well! Here is a set of spreadsheets that have some of the most valuable logic in the world. I have been thr... read more
- All My Excel Tools – $499.00 Version 1

Cafe Financial Model Excel Template
Check Our Cafe Budget Template. Creates a financial summary formatted for your Pitch Deck. Ready to Raise Capital. Creates 5-year cafe financial model... read more
- Excel - Multi-User – $129.00
- Excel - Single-User – $99.00
- Free Demo – $0.00

Juice Bar Financial Model Excel Template
Get Your Juice Bar Financial Model. Impress bankers and investors with a proven, strategic business plan that impresses every time. Five year juice ba... read more

Restaurant Key Performance Indicator Tracker (Sales, Average Customer, Top 10 Menu & Worst 10 Menu, etc.)
This financial report explained the trend in quantity sold, sales per day, number of pax, average spending per person, and customer turnover for the r... read more

Tea Cafe Financial Model Excel Template
Check Our Tea Cafe Pro-forma Template. Excel template - robust and powerful. This is your solid foundation to plan your business model. Five year tea ... read more

Coffee Truck Financial Model Excel Template
Get the Best Coffee Truck Financial Projection Template. Creates a financial summary formatted for your Pitch Deck. Ready to Raise Capital. Coff... read more

The Customer-Centric Financial Model for Restaurants
Starting a restaurant without a financial plan is like driving a car blindfolded. You wouldn´t do it because you are a careful person! As a business ... read more
- Full Excel Version – $79.00 Version 1.2
- Free PDF Demo – $0.00 Version 1.0

All-day Restaurant & Bar – 5 Year Financial Model
Financial Model providing an advanced 5-year financial plan for an All Day Restaurant & Bar.
- Financial Model - Premium Version – $109.00 Version 1
- Financial Model - Standard Version – $89.00 Version 1
- PDF Free Demo – $0.00 Version 1

Gourmet Food Store Financial Model Excel Template
Gourmet Food Store Financial Model Allows you to start planning with no fuss and maximum of help . Shop Now Highly versatile and user-friendly Gourmet... read more

Cigar Lounge Financial Model Excel Template
Order Your Cigar Lounge Pro Forma Projection. There's power in Cash Flow Projections and the insight they can provide your business. Five-year financi... read more

Golf & Entertainment Center – 5 Year Financial Model
Financial Model providing an advanced 5-year financial plan for a startup or operating Golf & Entertainment Center.
- Financial Model - Standard Version – $69.00 Version 1
- Financial Model - Premium Version – $99.00 Version 1

Karaoke Bar Business Plan Financial Model Excel Template
Order Karaoke Bar Pro Forma Projection. Spend less time on Cash Flow forecasting and more time on your products. Generates 5-year Karaoke Bar Cashflow... read more

Wine Bar Financial Model Excel Template
Download Wine Bar Financial Model. Generate fully-integrated Pro-forma for 5 years. Automatic aggregation of annual summaries on outputs tabs. G... read more

Multi Cuisine Cafe – 3 Statement Financial Model with 5 years Monthly Projection & Valuation
This Multi-Cuisine Café business Plan Model is a perfect tool for a financial feasibility study on launching a cafe.

Coffee Shop – The Customer-Centric Financial Model
Starting a Coffee Shop without a financial plan is like driving a car blindfolded. You wouldn´t do it because you are a careful person! As a business... read more
- Full Excel Version – $79.00 Version 1.3
- Free PDF Demo – $0.00 Version 1.2

Coffee and Snack Financial Model
This is a financial model for starting a coffee shop with snacks. The model supports both sitting clients as well as take away, additionally the model... read more
- Full Excel Model – $79.00
- FREE PDF Preview – $0.00

Pizzeria – 3 Statement Financial Model with 5 years Monthly Projection and Valuation
The Pizzeria FM is a perfect tool for financial feasibility of launching a Pizzeria.

Food Sector Bundle (6 Models)
Planning to start a food business but can’t decide on the profitability of your investment? Why don’t you use our food bundle with 6 templates as... read more
- Template Bundle – $370.00 Version 1

All Day Bar & Restaurant Financial Model Excel Template
All Day Bar & Restaurant Budget Template There's power in Cash Flow Projections and the insight they can provide your business . Shop Now Five-yea... read more

Bubble Tea Cafe Financial Model Excel Template
Discover Bubble Tea Cafe Financial Model Template. Creates a financial summary formatted for your Pitch Deck. Ready to Raise Capital. Five year bubble... read more

Start Up Bar Financial Model
Start Up Bar Business Financial Model presents the case of an investment in a bar business and its operations. The model generates the three financial... read more
- Excel Model – $79.00
- Free PDF – $0.00

Cat Cafe Financial Model Excel Template
Cat Cafe Budget Template Enhance your pitches and impress potential investors with the expected financial metrics. Buy Now Five-year Cat Cafe budgetin... read more

Brewery – 3 Statement Financial Model with 5 years Monthly Projection & Valuation
This Brewery Business Plan Model is a perfect tool for a financial feasibility study on launching a brewery. The model can be used by the start-up to ... read more
- Excel Model – $99.00 Version 1

Coffee Shop – 5 Year Financial Model
Financial Model providing an advanced 5-year financial plan for a startup or operating Coffee Shop.
- Excel Model - Standard Version – $69.00 Version 1
- Excel Model - Premium Version – $89.00 Version 1

Coffeehouse Financial Model Excel Template
Discover Coffeehouse Financial Projection Template. Creates 5-year financial projection and financial ratios in GAAP or IFRS formats on the fly.... read more

Karaoke Lounge Financial Model
The idea of this Karaoke Lounge Financial Model is, that you offer 3 separate Karaoke rooms for little private groups, that can be rented, a bar/resta... read more
- Full Excel Version – $79.00
- Free PDF Demo – $0.00

Startup Business Plan – Coffee Shop
If you dream of owning a coffee shop, the template is the first step in making your dream into reality, It is constructed based on solid experience an... read more
- Excel Version – $69.00 Version 1
- PDF Version – $0.00 Version 1

Beer Bar Financial Model Excel Template
Get the Best Beer Bar Financial Plan. Create fully-integrated financial projection for 5 years. With 3 way financial statements inside. A sophis... read more

Juice Bar- 3 Statement Financial Model with 5 years Monthly Projection and Valuation
This Juice bar FM is a perfect tool for financial feasibility of operating a Juice Bar.

Snack Bar Financial Model Excel Template
Get Snack Bar Financial Model Template. Creates 5-year financial projection and financial ratios in GAAP or IFRS formats on the fly. Generates 5... read more

Confectionery Shop Financial Model Excel Template
Confectionery Shop Financial Plan Allows investors and business owners to make a complete financial projection in less than 90 mins. Buy Now Highly ve... read more

Market Entry Feasibility Study for Coffee Shops Industry
This model include market entry feasibility study in word format and business plan to convert the literature into numbers excel format for coffee shop... read more
- PDF Demo Version – $0.00 Version 1
- Excel Model + Feasibility Study – $195.00 Version 1

Sports Bar Financial Model Excel Template
Discover Sports Bar Financial Model Template. Creates a financial summary formatted for your Pitch Deck. Ready to Raise Capital. Creates 5-year ... read more

Tea Store Financial Model Excel Template
Try Tea Store Budget Template. Enhance your pitches and impress potential investors with the expected financial metrics. Five-year tea store 3 way fin... read more

Restaurant Financial Model
This Restaurant Financial Model is tailored for those who aim to start a business from scratch, and it is specifically designed for restaurants, cafes... read more
- Excel Model – $89.99 Version 1
- PDF Preview – $0.00 Version 1

Restaurant Financial Model: Adaptable to all Types of Outlets
Our full-fledged financial model in excel format has the functionality to run unlimited activity scenarios. It is built due to our vast experience in ... read more

FAST FOOD The Customer-Centric Financial Restaurant Model
Starting a fast food restaurant without a financial plan is like driving a car blindfolded. You wouldn´t do it because you are a careful person! As a... read more

Fast Food Franchise – Financial Plan
The Franchise Fast Food Excel Financial Model is tailored to evaluate the feasibility of a Fast Food Franchise, and will give you full visibility into... read more
- PDF Preview – $0.00
- Full Excel File – $40.00

Coffee/Tea Lounge – 3 Statement Financial Model with 5 years Monthly Projection and Valuation
This Coffee/Tea Lounge FM is a perfect tool for financial feasibility of operating a lounge.

Golf Range & Restaurant Financial Model
The idea of this financial model is a golf range with a restaurant, like the concept of Topgolf in the USA. The model assumes to set up a building wit... read more

Breakfast Restaurant Financial Model Excel Template
Order Breakfast Restaurant Financial Projection Template. Allows you to start planning with no fuss and maximum of help Five-year horizon financial mo... read more

Ice Cream Shop – 5 Year Financial Model
Financial Model providing an advanced 5-year financial plan for a startup or operating Ice Cream Shop.
- Financial Model - Premium Version – $89.00 Version 1

Coffee And Snack Financial Model Excel Template
Coffee And Snack Pro Forma Template Create fully-integrated financial projection for 5 years With 3 way financial statements inside. Shop Now Creates ... read more

Sandwich Bar Financial Model Excel Template
Download Sandwich Bar Pro-forma Template. Allows investors and business owners to make a complete financial projection in less than 90 mins. Cre... read more

Subway Cafe Financial Model Excel Template
Subway Cafe Financial Model Allows investors and business owners to make a complete financial projection in less than 90 mins. Shop Now Highly versati... read more

Tapas Bar Financial Model Excel Template
Get Your Tapas Bar Financial Model. Spend less time on Cash Flow forecasting and more time on your products. Five year tapas bar 3 way forecast ... read more

Restaurant Monthly Forecast Model Template
The Restaurant Monthly Forecast Model provides a 3-year annual and monthly forecast specific to a restaurant operation.
- Full Excel Version – $55.00

Bistro Financial Model Excel Template
Check Our Bistro Financial Model. Requesting a loan without a financial model for paying it back is a common way to land in the rejection pile. Create... read more

Restaurant and Bar Financial Model Template
Financial model template for an eating establishment in which customers are served food and drinks at their tables. The model uses a detailed breakdow... read more
- Excel model – $30.00 Version 1
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
20+ SAMPLE College Business Plan in PDF | MS Word
College business plan | ms word, 20+ sample college business plan, what is a college business plan, what are the benefits gained from a college business plan, how to create a college business plan, where do public universities get their funding, what are some of the main types of universities, what are vocational or technical colleges.
College Business Plan Template

College Business Plan Example

Basic Business Plan

College Business Plan in PDF

College of Business and Administration Plan

City College Business Plan

University College Business Plan
Standard College Business Plan

College Preparatory Schools Business Plan
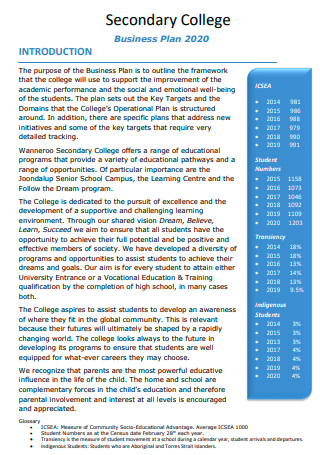
Secondary College Business Plan

College of Applied Biology Business Plan

National College Business Plan

College Multi Year Business Plan

Printable College Business Plan

College of Entrepreneurship Center Business Plan

College of Applied Arts and Technology Business Plan

College Business Plan and Budget

Draft College Business Plan

College of Medicine Business Plan
Sample College Business Plan

College Business Plan in DOC
1. executive summary, 2. college features and offerings, 3. marketing analysis, 4. marketing strategy, share this post on your network, you may also like these articles.
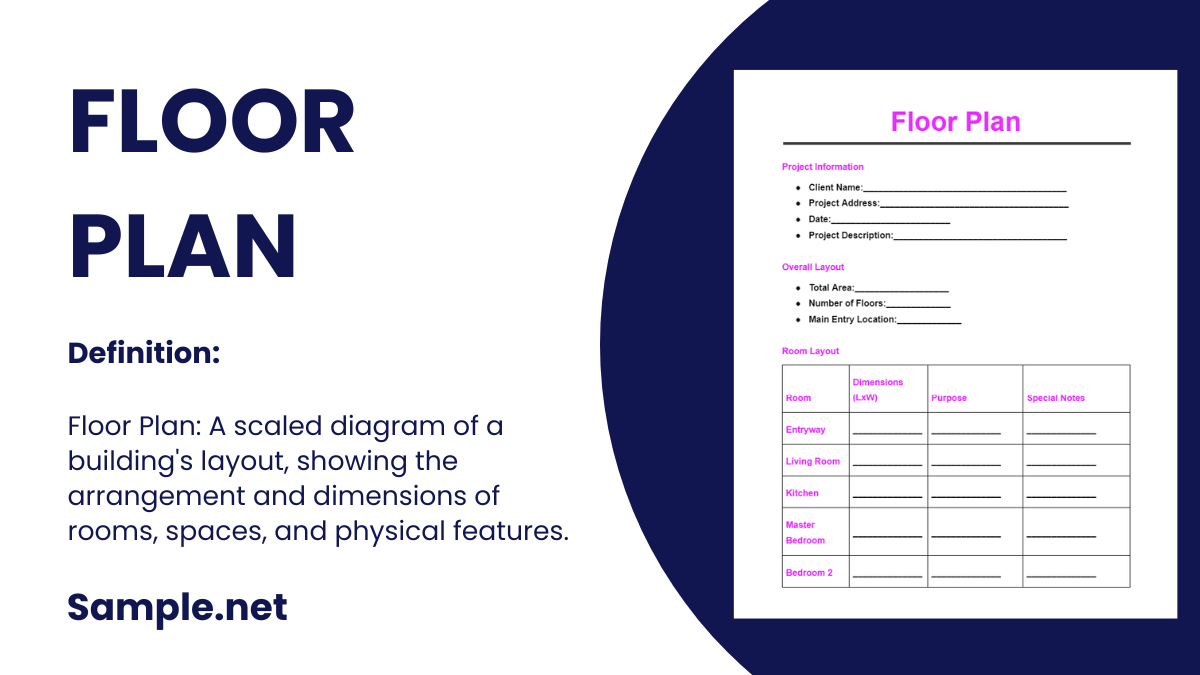
In this comprehensive guide, we explore the essentials of creating an effective Floor Plan. Whether you are designing a new home, renovating an existing space, or planning an office…
Nursing Care Plan

In this comprehensive guide, we explore the essentials of creating an effective Nursing Care Plan. Whether you are a nursing student, a new graduate, or an experienced nurse, this…
browse by categories
- Questionnaire
- Description
- Reconciliation
- Certificate
- Spreadsheet
Information
- privacy policy
- Terms & Conditions
Simple Business Plan Templates
By Joe Weller | April 2, 2020
- Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn
Link copied
In this article, we’ve compiled a variety of simple business plan templates, all of which are free to download in PDF, Word, and Excel formats.
On this page, you’ll find a one-page business plan template , a simple business plan for startups , a small-business plan template , a business plan outline , and more. We also include a business plan sample and the main components of a business plan to help get you started.
Simple Business Plan Template

Download Simple Business Plan Template
Word | PDF
This simple business plan template lays out each element of a traditional business plan to assist you as you build your own, and it provides space to add financing information for startups seeking funding. You can use and customize this simple business plan template to fit the needs for organizations of any size.
One-Page Business Plan Template
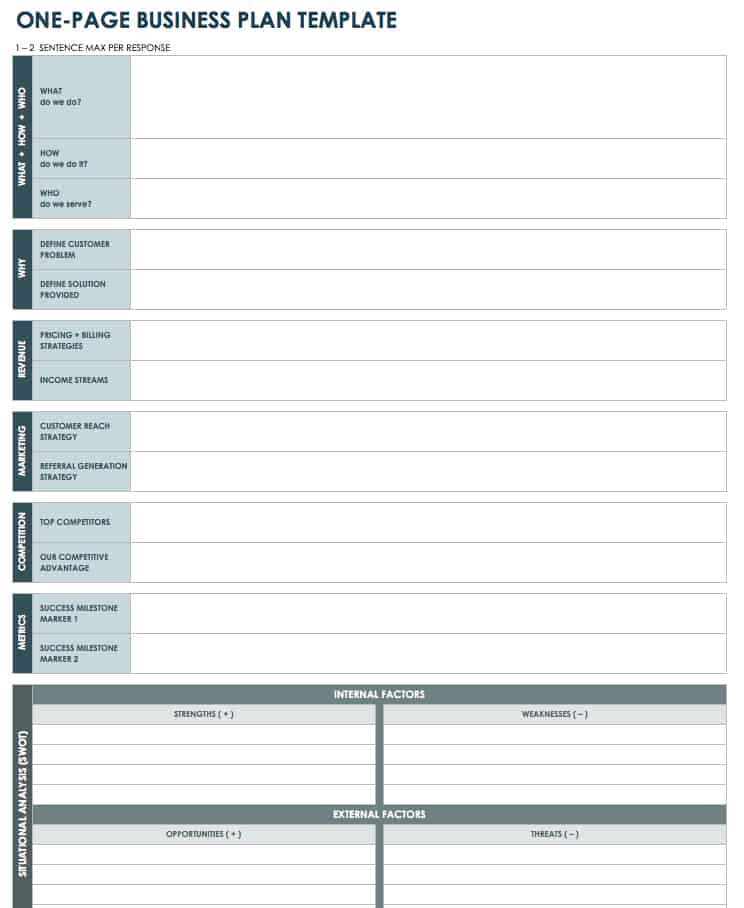
Download One-Page Business Plan Template
Excel | Word | PDF | Smartsheet
Use this one-page business plan to document your key ideas in an organized manner. The template can help you create a high-level view of your business plan, and it provides easy scannability for stakeholders. You can use this one-page plan as a reference to build a more detailed blueprint for your business.
For additional single page plans, take a look at " One-Page Business Plan Templates with a Quick How-To Guide ."
Simple Fill-in-the-Blank Business Plan Template
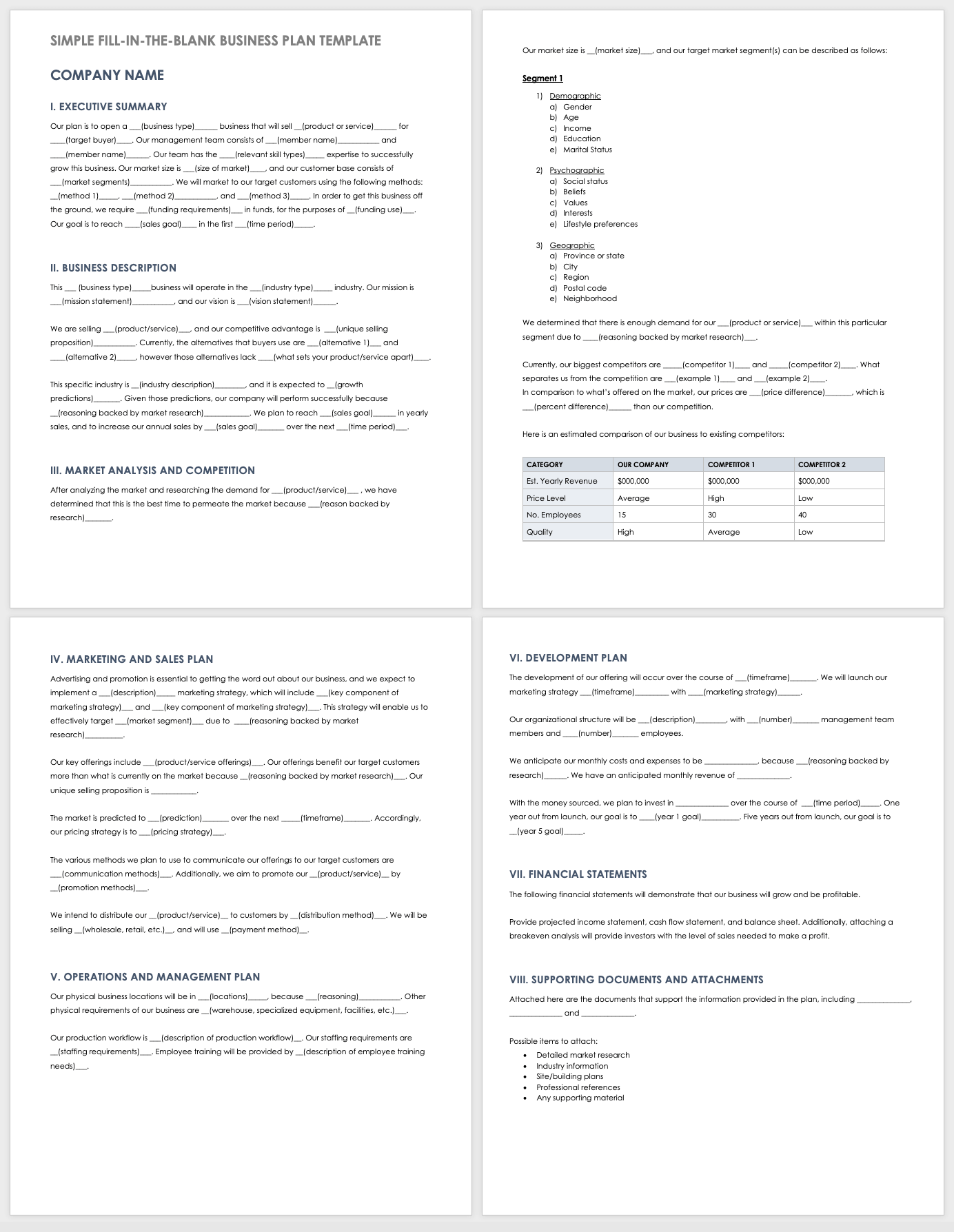
Download Simple Fill-in-the-Blank Business Plan Template
Use this fill-in-the-blank business plan template to guide you as you build your business plan. Each section comes pre-filled with sample content, with space to add customized verbiage relevant to your product or service.
For additional free, downloadable resources, visit " Free Fill-In-the-Blank Business Plan Templates ."
Simple Business Plan for Startup

Download Startup Business Plan Template — Word
This business plan template is designed with a startup business in mind and contains the essential elements needed to convey key product or service details to investors and stakeholders. Keep all your information organized with this template, which provides space to include an executive summary, a company overview, competitive analysis, a marketing strategy, financial data, and more. For additional resources, visit " Free Startup Business Plan Templates and Examples ."
Simple Small-Business Plan Template

Download Simple Small-Business Plan Template
This template walks you through each component of a small-business plan, including the company background, the introduction of the management team, market analysis, product or service offerings, a financial plan, and more. This template also comes with a built-in table of contents to keep your plan in order, and it can be customized to fit your requirements.
Lean Business Plan Template

Download Lean Business Plan Template
This lean business plan template is a stripped-down version of a traditional business plan that provides only the most essential aspects. Briefly outline your company and industry overview, along with the problem you are solving, as well as your unique value proposition, target market, and key performance metrics. There is also room to list out a timeline of key activities.
Simple Business Plan Outline Template

Download Simple Business Plan Outline Template
Use this simple business plan outline as a basis to create your own business plan. This template contains 11 sections, including a title page and a table of contents, which details what each section should cover in a traditional business plan. Simplify or expand this outline to create the foundation for a business plan that fits your business needs.
Simple Business Planning Template with Timeline
Download Simple Business Planning Template with Timeline
Excel | Smartsheet
This template doubles as a project plan and timeline to track progress as you develop your business plan. This business planning template enables you to break down your work into phases and provides room to add key tasks and dates for each activity. Easily fill in the cells according to the start and end dates to create a visual timeline, as well as to ensure your plan stays on track.
Simple Business Plan Rubric Template
Download Simple Business Plan Rubric
Once you complete your business plan, use this business plan rubric template to assess and score each component of your plan. This rubric helps you identify elements of your plan that meet or exceed requirements and pinpoint areas where you need to improve or further elaborate. This template is an invaluable tool to ensure your business plan clearly defines your goals, objectives, and plan of action in order to gain buy-in from potential investors, stakeholders, and partners.
Basic Business Plan Sample
Download Basic Business Plan Sample
This business plan sample serves as an example of a basic business plan that contains all the traditional components. The sample provides a model of what a business plan might look like for a fictional food truck business. Reference this sample as you develop your own business plan.
For additional resources to help support your business planning efforts, check out “ Free Strategic Planning Templates .”
Main Components of a Business Plan
The elements you include in your business plan will depend on your product or service offerings, as well as the size and needs of your business.
Below are the components of a standard business plan and details you should include in each section:
- Company name and contact information
- Website address
- The name of the company or individual viewing the presentation
- Table of Contents
- Company background and purpose
- Mission and vision statement
- Management team introduction
- Core product and service offerings
- Target customers and segments
- Marketing plan
- Competitive analysis
- Unique value proposition
- Financial plan (and requirements, if applicable)
- Business and industry overview
- Historical timeline of your business
- Offerings and the problem they solve
- Current alternatives
- Competitive advantage
- Market size
- Target market segment(s)
- Projected volume and value of sales compared to competitors
- Differentiation from competitors
- Pricing strategy
- Marketing channels
- Promotional plan
- Distribution methods
- Legal structure of your business
- Names of founders, owners, advisors, etc.
- Management team’s roles, relevant experience, and compensation plan
- Staffing requirements and training plans
- Physical location(s) of your business
- Additional physical requirements (e.g., warehouse, specialized equipment, facilities, etc.)
- Production workflow
- Raw materials and sourcing methods
- Projected income statement
- Projected cash flow statement
- Projected balance sheet
- Break-even analysis
- Charts and graphs
- Market research and competitive analysis
- Information about your industry
- Information about your offerings
- Samples of marketing materials
- Other supporting materials
Tips for Creating a Business Plan
It’s easy to feel overwhelmed at the thought of putting together a business plan. Below, you’ll find top tips to help simplify the process as you develop your own plan.
- Use a business plan template (you can choose from the variety above), or refer to the previous section to create a standard outline for your plan.
- Modify your outline to reflect the requirements of your specific business. If you use a standard business plan outline, remove sections that aren’t relevant to you or aren’t necessary to run your business.
- Gather all the information you currently have about your business first, and then use that information to fill out each section in your plan outline.
- Use your resources and conduct additional research to fill in the remaining gaps. (Note: It isn’t necessary to fill out your plan in order, but the executive summary needs to be completed last, as it summarizes the key points in your plan.)
- Ensure your plan clearly communicates the relationship between your marketing, sales, and financial objectives.
- Provide details in your plan that illustrate your strategic plan of action, looking forward three to five years.
- Revisit your plan regularly as strategies and objectives evolve.
- What product or service are we offering?
- Who is the product or service for?
- What problem does our product or service offering solve?
- How will we get the product or service to our target customers?
- Why is our product or service better than the alternatives?
- How can we outperform our competitors?
- What is our unique value proposition?
- When will things get done, and who is responsible for doing them?
- If you need to obtain funding, how will you use the funding?
- When are payments due, and when do payments come in?
- What is the ultimate purpose of your business?
- When do you expect to be profitable?
To identify which type of business plan you should write, and for more helpful tips, take a look at our guide to writing a simple business plan .
Benefits of Using a Business Plan Template
Creating a business plan can be very time-consuming, especially if you aren’t sure where to begin. Finding the right template for your business needs can be beneficial for a variety of reasons.
Using a business plan template — instead of creating your plan from scratch — can benefit you in the following ways:
- Enables you to immediately write down your thoughts and ideas in an organized manner
- Provides structure to help outline your plan
- Saves time and valuable resources
- Helps ensure you don’t miss essential details
Limitations of a Business Plan Template
A business plan template can be convenient, but it has its drawbacks — especially if you use a template that doesn’t fit the specific needs of your business.
Below are some limitations of using a business plan template:
- Each business is unique and needs a business plan that reflects that. A template may not fit your needs.
- A template may restrict collaboration with other team members on different aspects of the plan’s development (sales, marketing, and accounting teams).
- Multiple files containing different versions of the plan may be stored in more than one place.
- You still have to manually create charts and graphs to add to the plan to support your strategy.
- Updates to the plan, spreadsheets, and supporting documents have to be made in multiple places (all documents may not update in real time as changes are made).
Improve Your Business Plan with Real-Time Work Management in Smartsheet
Empower your people to go above and beyond with a flexible platform designed to match the needs of your team — and adapt as those needs change.
The Smartsheet platform makes it easy to plan, capture, manage, and report on work from anywhere, helping your team be more effective and get more done. Report on key metrics and get real-time visibility into work as it happens with roll-up reports, dashboards, and automated workflows built to keep your team connected and informed.
When teams have clarity into the work getting done, there’s no telling how much more they can accomplish in the same amount of time. Try Smartsheet for free, today.
Discover why over 90% of Fortune 100 companies trust Smartsheet to get work done.
Access our library of 134 Business Templates
Wow you’ve unlocked access to our library of 134 business templates.
Get started by checking out some of our top business templates:
Featured business templates

Weekly Schedule Template
Tracking employees’ work time and wages is easy with this free weekly schedule template.

Monthly Report
Provide a professional, concise summary of project activities with this monthly report template.

One Page Business Plan
Need to write a business plan but don’t know where to begin? Download our free 1-page business plan ...
7 Free Startup | Business Plans | PDF Templates & Examples
All startup | business plans | pdf business templates..
Showing 1 - 7 of 7
.png)
Business Case

Executive Summary Template

Risk Assessment Template

Simple Business Plan Template

Startup Business Plan Template

Strategic Planning
Explore template collections.

Customer Service

Spreadsheets

Get all Startup | Business Plans | PDF templates and more.
Choose from 550+ free, downloadable sample business plans.
Search Sample Business Plans

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software

Simple Business Plan

To reach your goals in business , you need to have strategies in mind. There must be somewhere you can list down all the variables to your success; all the necessary factors to get to where you want to be. If you know how to create a business plan , then you’re a step closer to what you want. Allow this article to shed some light on its complexity. Learn about its purpose, its formats, and browse through an amazing list of sample business plans . Without further ado, here are some of the most useful templates and examples that you can ever find online!
46+ Simple Business Plan Examples
1. simple business plan template.

- Apple Pages
- Google Docs
Size: A4, US
2. Spa Business Plan Template

3. Nonprofit Business Plan Template

Size: 39 KB
4. Trucking Business Plan Template

Size: 31 KB
5. Business Plan Template

Size: 35 KB
6. Business Plan Table of Contents Template

- MS Publisher
Size: 57 KB
7. Sports Bar Business Plan Template

8. Saas Business Plan Template

Size: A4 & US
9. Startup Business Plan Template

Size: 33 KB
10. Rental Property Business Plan Template

11. Construction Business Plan Template

Size: 34 KB
12. Sample Construction Business Plan Template

Size: 58 KB
13. Restaurant Business Plan Template

Size: 36 KB
14. Generic Business Plan Template

15. Freight Trucking Business Plan Template

Size: 40 KB
16. Mortgage Broker Business Plan Template

17. Boutique Business Plan Template

Size: 42 KB
18. Recruitment/Staffing Agency Business Plan Template

Size: 45 KB
19. Modern Business Plan Template

20. Travel Business Plan Template

21. Veterinary Business Plan Template

22. Renovation Business Plan Template

23. Sample Business Plan Template

24. Simple Business Plan Template

25. Business Plan Outline Template

26. Sample Marketing Business Plan Template

27. Business Operational Plan Template

Free Download
28. 30 60 90 Day Business Plan Template

29. Business Plan Presentation Template

30. Business Plan Outline

Size: 79 kB
31. Small Business Sample
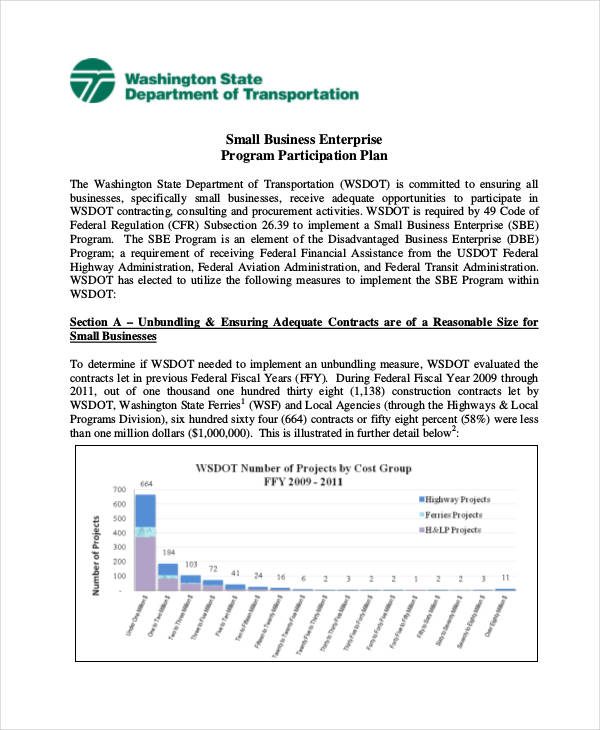
Size: 199 kB
32. Cafe Business Plan

Size: 151 kB
33. Restaurant Business Example

34. Mini Business Plan

35. Farm Business Plan

Size: 32 kB
36. Social Business Sample

37. Presentation Business Plan

Size: 774 kB
38. Start-up Business Example

39. Bakery Business Plan

40. Car Wash Business Sample

Size: 125 kB
41. Cleaning Business Plan

Size: 140 kB
42. Daycare Business Example

Size: 171 kB
43. Insurance Business Sample

Size: 324 kB
44. Lawn Care Business Plan

Size: 397 kB
45. Personal Business Plan

Size: 237 kB
46. Real Estate Business Sample

47. Retail Business Plan

48. Student Business Plan

What Is the Purpose of a Business Plan?
A business plan has one true purpose and that is to help determine the success of a company. No organization makes it to the top of their industry on sheer luck and hard work alone. Writing a business plan becomes essential so that a company can have as much direction as it needs as it claws its way towards the point of success. Such is the role of a quality plan for business and is defined by the following:
- To explain the business model – A good business plan clarifies what the business is about and what is needed to be done to attain success.
- Set goals – Business plans, like work plans , are made to ascertain specific goals detailed in strategic plans directed towards the profitability and success of a company or business
- Detect potential problems – A sure way of finding out problems within a business is the inclusion of an evaluation as a result of actions being done in a business plan.
- Measure development – Having a budget plan for business provides the owner or decision-maker a guide of sorts in determining where the current business is and the next step of the management plan to take in progressing towards the success set by the business plan.
Tips on How to Pick the Right Business Plan Format
Remember that there’s no such thing as right or wrong when you want to learn how to write a business plan. Instead, adjust your thinking towards what is more effective or appropriate for your needs. Keep in mind that formatting is always an important consideration. You can stay up all night working on your simple analysis plan or spend hours browsing for the right business plan template, but if the formatting is wrong, then you still won’t be able to guarantee your document’s efficacy. Nowadays, there are two major formats that you can select. One is the traditional business plan format while the other is the lean start-up format . To help you decide between either of these, here are some important tips to consider:
1. Determine Your Specific Need for the Business Plan
As stated in the previous section, the main purpose of a business plan is to serve as a guide. What hasn’t been said yet is that it doesn’t necessarily have to be your guide alone. Those who want to attract investors or lenders will want the traditional business plan format for reasons that will become apparent soon. Otherwise, the lean start-up format may be more suitable.
2. Look into the Characteristics of Each Type
After you’ve determined why there’s a need for a business plan, now it’s time to tackle the elements of the formats. The traditional format, for example, is much longer and more detailed. Its precise nature is what makes this format attractive to investors or lenders—people who normally require a lot of information. On the other hand, the lean start-up format focuses only on the significant bits of info, such as the company’s organizational infrastructure, finances, and value proposal.
3. Determine Whether or Not Time is on Your Side
The lengthy and specific nature of traditional business plans requires a lot of time and effort to do. If you only have a longer time to prepare, then perhaps that is the best choice for you. Yet those who only have a few hours or days to prepare one may have to go for the lean start-up format instead.
4. Look into Which Type is Better for You
Both of these business plan outline formats have their weaknesses and strengths. It is up to you to choose which of these will you apply in composing your business plan. Remember, consider not your wants but your needs. If you need to obtain a simple, less hassle and faster yet more likely to be ambiguous, you may utilize the lean start-up format. Conversely, if you need to have a precise and detailed business plan which is paired with challenging and time-consuming composition then use the traditional one.
General FAQs
1. what is a business plan.
A business plan is a formal and comprehensive document that is prepared by a business to outline the goals of the business and how it can be attained. It states the time frame within which these goals should be achieved, along with the product details, manpower, and financial estimates.
2. What are the main components of a business plan?
Each business plan examples share common components such as the executive summary , company description, marketing plan, operational plan , and so much more. However, how these components are expressed or explained will differ according to the needs and designs of the business owner.
3. What is the purpose of a business plan?
The purpose of a business plan is to define the goals of a business along with the steps needed to reach them. It also helps in maintaining the focus of your business and securing long-term financing .
If you weren’t so sure before about how to make a business plan, well you are now. Whether it is a simple one-page version, a non-profit business plan , or even a business continuity plan , you now have the skills and knowledge necessary to make a highly effective document. Should that be something you aren’t too keen on yet, then there are always templates like the ones above. Stop hesitating and get started on your plan today!
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
Create a study plan for final exams in high school
Develop a project timeline for a middle school science fair.

COMMENTS
Objectives. The primary objectives of the business plan for Cooper's Cup are below: To increase revenues by $36,000 or 5% in Year 2 and $73,000 or 10% by Year 3. Achieve a profit margin of 5.2% in Year 2 and 6.90% by Year 3. Be the Cafe of Choice in the Phoenix area and the recipient of the Best Coffeehouse Award.
In this section, we'll explore 10 types of business plan examples for student entrepreneurship. 1. Traditional Business Plans. These classic business plans, often prepared on paper, provide a comprehensive overview of the business, detailing its identity, goals, and strategies for success. 2.
Lean Business Plan Template PDF. This scannable business plan template allows you to easily identify the most important elements of your plan. Use this template to outline key details pertaining to your business and industry, product or service offerings, target customer segments (and channels to reach them), and to identify sources of revenue.
Here are the key components students should consider: Executive Summary: This is a snapshot of the business plan, summarizing the key details. It should be engaging and clearly explain the business goals and objectives. Business Description: This section provides an overview of your business.
Chapter 1 - Developing a Business Plan. Chapter 2 - Essential Initial Research. Chapter 3 - Business Models. Chapter 4 - Initial Business Plan Draft. Chapter 5 - Making the Business Plan Realistic. Chapter 6 - Making the Plan Appeal to Stakeholders and Desirable to the Entrepreneur. Chapter 7 - Finishing the Business Plan.
Start with a cogent and concise one sentence statement of the business idea. A sentence that is so clear and appealing that the reader can immediately visualise or 'see' the business. You can then go on to describe: The market at which you are aiming. The specific benefits offered by your product or service.
Takeaways for business plan examples for students The opportunities are endless if you want to set up a business as a student. Let your imagination run wild and look through business plan examples for students if you want to start selling or offering something new to your school's community.
Creating a business plan as a student can be a daunting task, but with the help of ClickUp's Business Plan Template, you can break it down into manageable steps. Follow these six steps to create a comprehensive business plan that sets you up for success: 1. Define your business idea. Start by clearly defining your business idea.
ClickUp's Business Plan Template for College Students is here to guide you every step of the way! With this template, you can: Clearly define your business goals and strategies for success. Create a comprehensive financial plan and projections to attract investors. Identify potential obstacles and develop contingency plans.
LivePlan's business plan examples help students turn ideas into top-notch business plans for class projects and startups. The tools, features, and instructional content allow you to focus on bringing out the best in your students for every plan and project. Before using LivePlan, my students were intimidated by the business planning process.
The vision/mission statements are clear summaries of where the business is headed. It describes what the business produces, who products are produced for, and unique business characteristics. It will reflect the values of the management team and the type of business culture you are trying to create. B. Goals and Objectives.
rk in small groups to brainstorm ideas. (15 min)4. As the class comes back, the teacher writes the words "Business Plan" on the board, and asks the class what they thi. k. eeds to be included in a business plan. (5 min)5. From there the teacher will pass out copies of the first part of a transcript from the article Ho.
BizPlan: BizPlan offers a visual planner that helps users develop their ideas intuitively. It allows for seamless collaboration if students wish to work in teams. Enloop: Enloop uses your input to create a draft business plan and automatically generates a performance score to evaluate the feasibility of your ideas.
4. Marketing Strategy. A college business plan should also come with a good marketing strategy. A marketing strategy is perhaps the most important of a business plan. It is the strategic part where plans are made on how to achieve a college's goal, especially when it comes to the number of its enrollees.
Download Simple Small-Business Plan Template. Word | PDF. This template walks you through each component of a small-business plan, including the company background, the introduction of the management team, market analysis, product or service offerings, a financial plan, and more. This template also comes with a built-in table of contents to ...
You've Unlocked Access to Our Library of 134 Business Templates! Get started by checking out some of our top business templates: Tracking employees' work time and wages is easy with this free weekly schedule template. Provide a professional, concise summary of project activities with this monthly report template.
A fill-in-the-blank business plan built for small businesses. Download Business Plan Template. Sample Plans. Popular Plans. Coffee Shop Agricultural Farm Hair & Beauty Salon Bakery Cleaning Service See All. Top Categories. Food & Beverage Fitness & Beauty Cleaning, Repairs & Maintenance Clothing & Fashion Brand Retail & eCommerce See All.
BUSINESS PLAN . WRITTEN PORTION 1. Title Page a. Name and address of business and owners of the business. 2. Table of Contents. 3. Executvi e Summary a. This is the most important section of the whole business plan!! If you turn off your potential inve stor they will not even read the rest of the information. b.
1. Executive Summary. The executive summary is among the most important or the heart of a business plan or any financial plan. The summary includes the founders, principal employees, or the management team and the skills they will bring to the business. 2.
1. What is a business plan? A business plan is a formal and comprehensive document that is prepared by a business to outline the goals of the business and how it can be attained. It states the time frame within which these goals should be achieved, along with the product details, manpower, and financial estimates. 2.
Get your commercial cleaning business plan template. Use our free template to create a complete commercial cleaning business plan. Download Free Template Let's take a look at what to include in a business plan for commercial cleaning company success. 1. Executive summary. The executive summary is the first part of your commercial cleaning ...