Does Homework Really Help Students Learn?

A conversation with a Wheelock researcher, a BU student, and a fourth-grade teacher

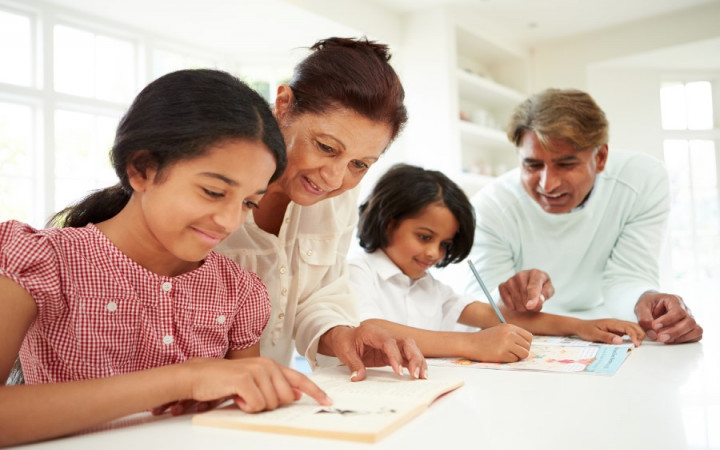
“Quality homework is engaging and relevant to kids’ lives,” says Wheelock’s Janine Bempechat. “It gives them autonomy and engages them in the community and with their families. In some subjects, like math, worksheets can be very helpful. It has to do with the value of practicing over and over.” Photo by iStock/Glenn Cook Photography
Do your homework.
If only it were that simple.
Educators have debated the merits of homework since the late 19th century. In recent years, amid concerns of some parents and teachers that children are being stressed out by too much homework, things have only gotten more fraught.
“Homework is complicated,” says developmental psychologist Janine Bempechat, a Wheelock College of Education & Human Development clinical professor. The author of the essay “ The Case for (Quality) Homework—Why It Improves Learning and How Parents Can Help ” in the winter 2019 issue of Education Next , Bempechat has studied how the debate about homework is influencing teacher preparation, parent and student beliefs about learning, and school policies.
She worries especially about socioeconomically disadvantaged students from low-performing schools who, according to research by Bempechat and others, get little or no homework.
BU Today sat down with Bempechat and Erin Bruce (Wheelock’17,’18), a new fourth-grade teacher at a suburban Boston school, and future teacher freshman Emma Ardizzone (Wheelock) to talk about what quality homework looks like, how it can help children learn, and how schools can equip teachers to design it, evaluate it, and facilitate parents’ role in it.
BU Today: Parents and educators who are against homework in elementary school say there is no research definitively linking it to academic performance for kids in the early grades. You’ve said that they’re missing the point.
Bempechat : I think teachers assign homework in elementary school as a way to help kids develop skills they’ll need when they’re older—to begin to instill a sense of responsibility and to learn planning and organizational skills. That’s what I think is the greatest value of homework—in cultivating beliefs about learning and skills associated with academic success. If we greatly reduce or eliminate homework in elementary school, we deprive kids and parents of opportunities to instill these important learning habits and skills.
We do know that beginning in late middle school, and continuing through high school, there is a strong and positive correlation between homework completion and academic success.
That’s what I think is the greatest value of homework—in cultivating beliefs about learning and skills associated with academic success.
You talk about the importance of quality homework. What is that?
Quality homework is engaging and relevant to kids’ lives. It gives them autonomy and engages them in the community and with their families. In some subjects, like math, worksheets can be very helpful. It has to do with the value of practicing over and over.

What are your concerns about homework and low-income children?
The argument that some people make—that homework “punishes the poor” because lower-income parents may not be as well-equipped as affluent parents to help their children with homework—is very troubling to me. There are no parents who don’t care about their children’s learning. Parents don’t actually have to help with homework completion in order for kids to do well. They can help in other ways—by helping children organize a study space, providing snacks, being there as a support, helping children work in groups with siblings or friends.
Isn’t the discussion about getting rid of homework happening mostly in affluent communities?
Yes, and the stories we hear of kids being stressed out from too much homework—four or five hours of homework a night—are real. That’s problematic for physical and mental health and overall well-being. But the research shows that higher-income students get a lot more homework than lower-income kids.
Teachers may not have as high expectations for lower-income children. Schools should bear responsibility for providing supports for kids to be able to get their homework done—after-school clubs, community support, peer group support. It does kids a disservice when our expectations are lower for them.
The conversation around homework is to some extent a social class and social justice issue. If we eliminate homework for all children because affluent children have too much, we’re really doing a disservice to low-income children. They need the challenge, and every student can rise to the challenge with enough supports in place.
What did you learn by studying how education schools are preparing future teachers to handle homework?
My colleague, Margarita Jimenez-Silva, at the University of California, Davis, School of Education, and I interviewed faculty members at education schools, as well as supervising teachers, to find out how students are being prepared. And it seemed that they weren’t. There didn’t seem to be any readings on the research, or conversations on what high-quality homework is and how to design it.
Erin, what kind of training did you get in handling homework?
Bruce : I had phenomenal professors at Wheelock, but homework just didn’t come up. I did lots of student teaching. I’ve been in classrooms where the teachers didn’t assign any homework, and I’ve been in rooms where they assigned hours of homework a night. But I never even considered homework as something that was my decision. I just thought it was something I’d pull out of a book and it’d be done.
I started giving homework on the first night of school this year. My first assignment was to go home and draw a picture of the room where you do your homework. I want to know if it’s at a table and if there are chairs around it and if mom’s cooking dinner while you’re doing homework.
The second night I asked them to talk to a grown-up about how are you going to be able to get your homework done during the week. The kids really enjoyed it. There’s a running joke that I’m teaching life skills.
Friday nights, I read all my kids’ responses to me on their homework from the week and it’s wonderful. They pour their hearts out. It’s like we’re having a conversation on my couch Friday night.
It matters to know that the teacher cares about you and that what you think matters to the teacher. Homework is a vehicle to connect home and school…for parents to know teachers are welcoming to them and their families.
Bempechat : I can’t imagine that most new teachers would have the intuition Erin had in designing homework the way she did.
Ardizzone : Conversations with kids about homework, feeling you’re being listened to—that’s such a big part of wanting to do homework….I grew up in Westchester County. It was a pretty demanding school district. My junior year English teacher—I loved her—she would give us feedback, have meetings with all of us. She’d say, “If you have any questions, if you have anything you want to talk about, you can talk to me, here are my office hours.” It felt like she actually cared.
Bempechat : It matters to know that the teacher cares about you and that what you think matters to the teacher. Homework is a vehicle to connect home and school…for parents to know teachers are welcoming to them and their families.
Ardizzone : But can’t it lead to parents being overbearing and too involved in their children’s lives as students?
Bempechat : There’s good help and there’s bad help. The bad help is what you’re describing—when parents hover inappropriately, when they micromanage, when they see their children confused and struggling and tell them what to do.
Good help is when parents recognize there’s a struggle going on and instead ask informative questions: “Where do you think you went wrong?” They give hints, or pointers, rather than saying, “You missed this,” or “You didn’t read that.”
Bruce : I hope something comes of this. I hope BU or Wheelock can think of some way to make this a more pressing issue. As a first-year teacher, it was not something I even thought about on the first day of school—until a kid raised his hand and said, “Do we have homework?” It would have been wonderful if I’d had a plan from day one.
Explore Related Topics:
- Share this story
Senior Contributing Editor

Sara Rimer A journalist for more than three decades, Sara Rimer worked at the Miami Herald , Washington Post and, for 26 years, the New York Times , where she was the New England bureau chief, and a national reporter covering education, aging, immigration, and other social justice issues. Her stories on the death penalty’s inequities were nominated for a Pulitzer Prize and cited in the U.S. Supreme Court’s decision outlawing the execution of people with intellectual disabilities. Her journalism honors include Columbia University’s Meyer Berger award for in-depth human interest reporting. She holds a BA degree in American Studies from the University of Michigan. Profile
She can be reached at [email protected] .
Comments & Discussion
Boston University moderates comments to facilitate an informed, substantive, civil conversation. Abusive, profane, self-promotional, misleading, incoherent or off-topic comments will be rejected. Moderators are staffed during regular business hours (EST) and can only accept comments written in English. Statistics or facts must include a citation or a link to the citation.
There are 81 comments on Does Homework Really Help Students Learn?
Insightful! The values about homework in elementary schools are well aligned with my intuition as a parent.
when i finish my work i do my homework and i sometimes forget what to do because i did not get enough sleep
same omg it does not help me it is stressful and if I have it in more than one class I hate it.
Same I think my parent wants to help me but, she doesn’t care if I get bad grades so I just try my best and my grades are great.
I think that last question about Good help from parents is not know to all parents, we do as our parents did or how we best think it can be done, so maybe coaching parents or giving them resources on how to help with homework would be very beneficial for the parent on how to help and for the teacher to have consistency and improve homework results, and of course for the child. I do see how homework helps reaffirm the knowledge obtained in the classroom, I also have the ability to see progress and it is a time I share with my kids
The answer to the headline question is a no-brainer – a more pressing problem is why there is a difference in how students from different cultures succeed. Perfect example is the student population at BU – why is there a majority population of Asian students and only about 3% black students at BU? In fact at some universities there are law suits by Asians to stop discrimination and quotas against admitting Asian students because the real truth is that as a group they are demonstrating better qualifications for admittance, while at the same time there are quotas and reduced requirements for black students to boost their portion of the student population because as a group they do more poorly in meeting admissions standards – and it is not about the Benjamins. The real problem is that in our PC society no one has the gazuntas to explore this issue as it may reveal that all people are not created equal after all. Or is it just environmental cultural differences??????
I get you have a concern about the issue but that is not even what the point of this article is about. If you have an issue please take this to the site we have and only post your opinion about the actual topic
This is not at all what the article is talking about.
This literally has nothing to do with the article brought up. You should really take your opinions somewhere else before you speak about something that doesn’t make sense.
we have the same name
so they have the same name what of it?
lol you tell her
totally agree
What does that have to do with homework, that is not what the article talks about AT ALL.
Yes, I think homework plays an important role in the development of student life. Through homework, students have to face challenges on a daily basis and they try to solve them quickly.I am an intense online tutor at 24x7homeworkhelp and I give homework to my students at that level in which they handle it easily.
More than two-thirds of students said they used alcohol and drugs, primarily marijuana, to cope with stress.
You know what’s funny? I got this assignment to write an argument for homework about homework and this article was really helpful and understandable, and I also agree with this article’s point of view.
I also got the same task as you! I was looking for some good resources and I found this! I really found this article useful and easy to understand, just like you! ^^
i think that homework is the best thing that a child can have on the school because it help them with their thinking and memory.
I am a child myself and i think homework is a terrific pass time because i can’t play video games during the week. It also helps me set goals.
Homework is not harmful ,but it will if there is too much
I feel like, from a minors point of view that we shouldn’t get homework. Not only is the homework stressful, but it takes us away from relaxing and being social. For example, me and my friends was supposed to hang at the mall last week but we had to postpone it since we all had some sort of work to do. Our minds shouldn’t be focused on finishing an assignment that in realty, doesn’t matter. I completely understand that we should have homework. I have to write a paper on the unimportance of homework so thanks.
homework isn’t that bad
Are you a student? if not then i don’t really think you know how much and how severe todays homework really is
i am a student and i do not enjoy homework because i practice my sport 4 out of the five days we have school for 4 hours and that’s not even counting the commute time or the fact i still have to shower and eat dinner when i get home. its draining!
i totally agree with you. these people are such boomers
why just why
they do make a really good point, i think that there should be a limit though. hours and hours of homework can be really stressful, and the extra work isn’t making a difference to our learning, but i do believe homework should be optional and extra credit. that would make it for students to not have the leaning stress of a assignment and if you have a low grade you you can catch up.
Studies show that homework improves student achievement in terms of improved grades, test results, and the likelihood to attend college. Research published in the High School Journal indicates that students who spent between 31 and 90 minutes each day on homework “scored about 40 points higher on the SAT-Mathematics subtest than their peers, who reported spending no time on homework each day, on average.” On both standardized tests and grades, students in classes that were assigned homework outperformed 69% of students who didn’t have homework. A majority of studies on homework’s impact – 64% in one meta-study and 72% in another – showed that take home assignments were effective at improving academic achievement. Research by the Institute for the Study of Labor (IZA) concluded that increased homework led to better GPAs and higher probability of college attendance for high school boys. In fact, boys who attended college did more than three hours of additional homework per week in high school.
So how are your measuring student achievement? That’s the real question. The argument that doing homework is simply a tool for teaching responsibility isn’t enough for me. We can teach responsibility in a number of ways. Also the poor argument that parents don’t need to help with homework, and that students can do it on their own, is wishful thinking at best. It completely ignores neurodiverse students. Students in poverty aren’t magically going to find a space to do homework, a friend’s or siblings to help them do it, and snacks to eat. I feel like the author of this piece has never set foot in a classroom of students.
THIS. This article is pathetic coming from a university. So intellectually dishonest, refusing to address the havoc of capitalism and poverty plays on academic success in life. How can they in one sentence use poor kids in an argument and never once address that poor children have access to damn near 0 of the resources affluent kids have? Draw me a picture and let’s talk about feelings lmao what a joke is that gonna put food in their belly so they can have the calories to burn in order to use their brain to study? What about quiet their 7 other siblings that they share a single bedroom with for hours? Is it gonna force the single mom to magically be at home and at work at the same time to cook food while you study and be there to throw an encouraging word?
Also the “parents don’t need to be a parent and be able to guide their kid at all academically they just need to exist in the next room” is wild. Its one thing if a parent straight up is not equipped but to say kids can just figured it out is…. wow coming from an educator What’s next the teacher doesn’t need to teach cause the kid can just follow the packet and figure it out?
Well then get a tutor right? Oh wait you are poor only affluent kids can afford a tutor for their hours of homework a day were they on average have none of the worries a poor child does. Does this address that poor children are more likely to also suffer abuse and mental illness? Like mentioned what about kids that can’t learn or comprehend the forced standardized way? Just let em fail? These children regularly are not in “special education”(some of those are a joke in their own and full of neglect and abuse) programs cause most aren’t even acknowledged as having disabilities or disorders.
But yes all and all those pesky poor kids just aren’t being worked hard enough lol pretty sure poor children’s existence just in childhood is more work, stress, and responsibility alone than an affluent child’s entire life cycle. Love they never once talked about the quality of education in the classroom being so bad between the poor and affluent it can qualify as segregation, just basically blamed poor people for being lazy, good job capitalism for failing us once again!
why the hell?
you should feel bad for saying this, this article can be helpful for people who has to write a essay about it
This is more of a political rant than it is about homework
I know a teacher who has told his students their homework is to find something they are interested in, pursue it and then come share what they learn. The student responses are quite compelling. One girl taught herself German so she could talk to her grandfather. One boy did a research project on Nelson Mandela because the teacher had mentioned him in class. Another boy, a both on the autism spectrum, fixed his family’s computer. The list goes on. This is fourth grade. I think students are highly motivated to learn, when we step aside and encourage them.
The whole point of homework is to give the students a chance to use the material that they have been presented with in class. If they never have the opportunity to use that information, and discover that it is actually useful, it will be in one ear and out the other. As a science teacher, it is critical that the students are challenged to use the material they have been presented with, which gives them the opportunity to actually think about it rather than regurgitate “facts”. Well designed homework forces the student to think conceptually, as opposed to regurgitation, which is never a pretty sight
Wonderful discussion. and yes, homework helps in learning and building skills in students.
not true it just causes kids to stress
Homework can be both beneficial and unuseful, if you will. There are students who are gifted in all subjects in school and ones with disabilities. Why should the students who are gifted get the lucky break, whereas the people who have disabilities suffer? The people who were born with this “gift” go through school with ease whereas people with disabilities struggle with the work given to them. I speak from experience because I am one of those students: the ones with disabilities. Homework doesn’t benefit “us”, it only tears us down and put us in an abyss of confusion and stress and hopelessness because we can’t learn as fast as others. Or we can’t handle the amount of work given whereas the gifted students go through it with ease. It just brings us down and makes us feel lost; because no mater what, it feels like we are destined to fail. It feels like we weren’t “cut out” for success.
homework does help
here is the thing though, if a child is shoved in the face with a whole ton of homework that isn’t really even considered homework it is assignments, it’s not helpful. the teacher should make homework more of a fun learning experience rather than something that is dreaded
This article was wonderful, I am going to ask my teachers about extra, or at all giving homework.
I agree. Especially when you have homework before an exam. Which is distasteful as you’ll need that time to study. It doesn’t make any sense, nor does us doing homework really matters as It’s just facts thrown at us.
Homework is too severe and is just too much for students, schools need to decrease the amount of homework. When teachers assign homework they forget that the students have other classes that give them the same amount of homework each day. Students need to work on social skills and life skills.
I disagree.
Beyond achievement, proponents of homework argue that it can have many other beneficial effects. They claim it can help students develop good study habits so they are ready to grow as their cognitive capacities mature. It can help students recognize that learning can occur at home as well as at school. Homework can foster independent learning and responsible character traits. And it can give parents an opportunity to see what’s going on at school and let them express positive attitudes toward achievement.
Homework is helpful because homework helps us by teaching us how to learn a specific topic.
As a student myself, I can say that I have almost never gotten the full 9 hours of recommended sleep time, because of homework. (Now I’m writing an essay on it in the middle of the night D=)
I am a 10 year old kid doing a report about “Is homework good or bad” for homework before i was going to do homework is bad but the sources from this site changed my mind!
Homeowkr is god for stusenrs
I agree with hunter because homework can be so stressful especially with this whole covid thing no one has time for homework and every one just wants to get back to there normal lives it is especially stressful when you go on a 2 week vaca 3 weeks into the new school year and and then less then a week after you come back from the vaca you are out for over a month because of covid and you have no way to get the assignment done and turned in
As great as homework is said to be in the is article, I feel like the viewpoint of the students was left out. Every where I go on the internet researching about this topic it almost always has interviews from teachers, professors, and the like. However isn’t that a little biased? Of course teachers are going to be for homework, they’re not the ones that have to stay up past midnight completing the homework from not just one class, but all of them. I just feel like this site is one-sided and you should include what the students of today think of spending four hours every night completing 6-8 classes worth of work.
Are we talking about homework or practice? Those are two very different things and can result in different outcomes.
Homework is a graded assignment. I do not know of research showing the benefits of graded assignments going home.
Practice; however, can be extremely beneficial, especially if there is some sort of feedback (not a grade but feedback). That feedback can come from the teacher, another student or even an automated grading program.
As a former band director, I assigned daily practice. I never once thought it would be appropriate for me to require the students to turn in a recording of their practice for me to grade. Instead, I had in-class assignments/assessments that were graded and directly related to the practice assigned.
I would really like to read articles on “homework” that truly distinguish between the two.
oof i feel bad good luck!
thank you guys for the artical because I have to finish an assingment. yes i did cite it but just thanks
thx for the article guys.
Homework is good
I think homework is helpful AND harmful. Sometimes u can’t get sleep bc of homework but it helps u practice for school too so idk.
I agree with this Article. And does anyone know when this was published. I would like to know.
It was published FEb 19, 2019.
Studies have shown that homework improved student achievement in terms of improved grades, test results, and the likelihood to attend college.
i think homework can help kids but at the same time not help kids
This article is so out of touch with majority of homes it would be laughable if it wasn’t so incredibly sad.
There is no value to homework all it does is add stress to already stressed homes. Parents or adults magically having the time or energy to shepherd kids through homework is dome sort of 1950’s fantasy.
What lala land do these teachers live in?
Homework gives noting to the kid
Homework is Bad
homework is bad.
why do kids even have homework?
Comments are closed.
Latest from Bostonia
Podcast looks at a forgotten chapter of the civil rights struggle, two bu alums take on same roles in leopoldstadt, huntington theatre company’s latest production, this sha alum handles fenway park’s celebrity artists, bu alum chompon boonnak runs mahaniyom, one of greater boston’s hottest thai restaurants, champion of indie films, china scholar merle goldman dies, cfa alum jonathan knight is head of games for the new york times, a commitment to early childhood education, reading list: alum bonnie hammer publishes 15 lies women are told at work —plus fiction, poetry, and short stories, one good deed: jason hurdich (cas’97) is uniting the deaf community, one cup at a time, is our democracy at risk americans think so. bu experts talk about why—and the way forward, space force general b. chance saltzman is a bu alum, law alum steven m. wise, who fought for animal rights, dies, pups wearing custom-designed veterinary collars get star treatment in alum’s new coffee-table book, using glamour for good: alum’s nonprofit organization brings clothes and beauty products to those in need, gallery: shea justice (cfa’93), oscar-nominated actor hong chau (com’01) stars in new action-comedy the instigators, alum’s new book recounts the battle for inclusion in boy scouts, feedback: readers weigh in on a bu superager, the passing of otto lerbinger, and alum’s book fat church, opening doors: ellice patterson (questrom’17).
We sent you SMS, for complete subscription please reply.
You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser or activate Google Chrome Frame to improve your experience.

Wonder of the Day #1385
Why Do We Have Homework?

SCIENCE — Health and Fitness
Have You Ever Wondered...
- Why do we have homework?
- What are the benefits of homework?
- Is there such a thing as too much homework?
- classroom ,
- education ,
- knowledge ,
- mathematics ,
- prioritization ,
- repetition ,
- responsibility ,
- time management ,
- Classroom ,
- Education ,
- Knowledge ,
- Mathematics ,
- Prioritization ,
- Repetition ,
- Responsibility ,
- Time Management
Today’s Wonder of the Day was inspired by Nicolas from fort lauderdale, FL. Nicolas Wonders , “ Who invented homework? ” Thanks for WONDERing with us, Nicolas!
What has eight letters and strikes fear into the hearts of students around the world? No, it's not broccoli, but that was a good guess! Give up? HOMEWORK !
Did you just gasp in fear and anguish ? We're sorry, but homework is a fact of life and it's time we took a closer look at it. Even though it might get in the way of playing outside or watching your favorite television show, it's necessary and, believe it or not, good for you!
Homework creates a bridge between school and home. Parents rarely get to spend much time with you while you're at school. Homework allows them to keep up with what you're doing in your classes on a daily basis. But you don't have homework purely for your parents' benefit . It's good for you, too!
Homework can help you become a better student in several different ways. First of all, homework given in advance of a particular subject can help you make the most of your classroom discussion time. For example, before beginning a discussion of a complex period in history , it can be very helpful to read background information as homework the night before.
Homework also gives you valuable practice with what you've learned in the classroom. Often, the brief period of time you have during class to learn something new is simply not enough. Repeating classroom concepts at home helps to cement in your mind the things you learned.
For example, you've probably experienced the value of homework when it comes to mathematics . A new concept explained in class might seem foreign at first. With repetition via homework, however, you reinforce what you learned in class and it sticks with you. Without homework, a lot of classroom time would be wasted with repetition that could more easily be done outside the classroom.
In these ways, homework expands upon what is done during the day in the classroom. Your overall educational experience is better, because homework helps you to gain and retain more knowledge than would be possible with only classroom work. As you learn more, you know more and you achieve more…and you have homework to thank!
Homework teaches lessons beyond just what's taught in the classroom, too. Bringing homework home, completing it correctly, and turning it in promptly teaches a host of other important life skills, from time management and responsibility to organization and prioritization .
Despite these benefits found by researchers, the topics of who should receive homework and how much homework are hotly debated among educators and researchers. In one study , researchers found that academic gains from homework increased as grade level increased, suggesting homework is more beneficial for older students. Some researchers have found that too much homework can lower or cancel its benefits and become counterproductive , because students become burned out.
How much is too much? That depends upon many complex factors, including the individual abilities of the child, other demands upon time, such as sports, part-time jobs, family responsibilities, and types of classes. If you feel overburdened by homework, the best thing you can do is to open a dialog with your teacher. Be open and honest about your feelings regarding homework and work with your teacher to strike a reasonable balance that helps you achieve your educational goals.
Wonder What's Next?
Tomorrow’s Wonder of the Day feels just like home!
We hope today's Wonder of the Day didn't feel like homework! Be sure to check out the following activities with a friend or family member:
- While some kids don't like any homework, almost every student has homework that he doesn't mind doing on a regular basis. For some, reading a novel for homework is pure joy, because they love to read. For others, doing group projects as homework is great fun, because they get to have fun with their friends in the process. Make a list of the types of homework that you enjoy the most. Once you have your list, think about ways in which you can encourage your teachers to assign more of your favorite types of homework and less of the types you don't enjoy as much. Opening a dialog with your teacher about homework can be a mutually-beneficial conversation that can increase learning both in and out of the classroom!
- You know what goes great with homework? Food! It's true. A healthy snack can give you the energy you need to concentrate and tackle your homework as soon as you get home from school. If you need some ideas, jump online and check out After School Snacks To Power Homework . Share what you learn with your friends and family members. What's your favorite after-school snack? Why?
- Do you have a lot of homework on a regular basis? It can be easy to get overwhelmed. To make sure you make the most of your homework time, it helps to be organized. Setting priorities and sticking to them will help you complete your assignments on time with minimal stress. For help learning how to do this, read through How to Prioritize Homework Assignments: 5 Steps from School Habits. Using what you learn, put a plan into place that will help you make sure you become a homework hero!
Wonder Sources
- http://www.ascd.org/publications/educational-leadership/mar07/vol64/num06/The-Case-For-and-Against-Homework.aspx
- http://www.centerforpubliceducation.org/Main-Menu/Instruction/What-research-says-about-the-value-of-homework-At-a-glance/What-research-says-about-the-value-of-homework-Research-review.html
Did you get it?
Wonder contributors.
We’d like to thank:
quenton , Jaiden , Leo , Grace and Lenysia for contributing questions about today’s Wonder topic!
Keep WONDERing with us!
Wonder Words
- responsibility
- organization
- prioritization
- counterproductive
- overburdened
- educational
Hopefully this article helped you realize why homework is helpful, nyiahna. Keep WONDERing with us!
Don't get homework at this school. :)
Hopefully this article helped you realize why homework is helpful!
yeah me too a lot
Wow, that's great for those schools! Thanks for stopping by, Mister C.
You're welcome, Person!
Thanks for sharing, Joe!
That's a great way to look at it, Adriana!
That's a great way to look at it, Adriana! Thanks for sharing!
I need to vent
Homework could benefit you. It gives your brain an easier time when you get a surprise quiz.
That's a difficult one, Wonder Friend!
It certainly is hard to do homework while at play practice! There are so many cool things going on!
Trying to complete your math homework right after you get home and have had dinner might be the best bet. Good luck!
Ellen The Happy Girl!
We're so glad you liked it, Ellen The Happy Girl!
We like your enthusiasm, tyonna!
Thanks for sharing your thoughts, Student! That's an interesting concept.
clever-name-or-smth
There's nothing wrong with being a big ol' nerd.
And, there's nothing wrong with Invater Zim fanfic, either.
so is checking these comments like a full time job or
Here at Wonderopolis, we do have specific people that check comments, but we do much more than that!
There's a specific amount of time during a school day--and that doesn't make a lot of time for 'independent practice' of skills learned during the school day.
Also, it's a GREAT idea to share your homework with your parents!
Thanks for sharing your opinon, Joe!
That's a great question, Brady. You should post it in the Wonder Bank .
You're welcome, Chase!
That's great, loren! Care to share your fun homework hack?
wegsfvbydgfhnry
Hey, Wonder Friend. We're sorry you think homework is a waste of time. Practice is really important when learning new things.
Hi sofia!
What's your secret for making homework fun? I'm sure a lot of our Wonder Friends would like to try it out!
That seems to be a common theme, ashley.
We're sorry to hear that, harrison.
wonder i already know...
Yikes! Well, it's important to have good time management skills so you can get everything turned in!
Thanks for sharing your opinion, Harold!
Thanks for sharing your thought process, Tyrannie!
That's great, Xavier-B-! Make homework interesting!
Hey, Adriana! We have a wonderful Wonder team that works together to accomplish all the Wonderopolis tasks. There is a core group of three currently, but we have people that pop in occasionally to help with things.
my next wonder is how do you know if a boy likes you because i just got a boyfriend and hes really shy.
Make sure you submit it to the Wonder Bank !
That's legit. We totally understand your position!
CaptainObvious
Thanks bunches, CaptainObvious!
Lil’ Mousey
Hey, Lil' Mousey--
We have some Wonders about cheese already. Check them out !
I know right! ☺️
EverestAndEvetheWarriors
Thanks, E&E!
Thanks for sharing your opinion, kev.
Thanks for sharing your opinion, Giani.
Jeez bro. It’s boring. All you do is sit there and fill out worksheets and assignments. We already do work at school. Why do we need work at home? It’s boring,bro,it’s boring. That’s why nobody likes it.
Thanks for sharing your opinion, Elvisssss.
None taken. ? And, we're glad you respect homework because it's a great way to practice skills.
It's Crule??
...but necessary!
Video gamessssss??????????????
Great reward for finishing homework!
Video games DUH! I have one! Would you rather eat only fried chicken for the rest of your life or suffer from homework every single day for the rest of your life. Plz reply ??
ChickenFries
I would pick fried chicken because I’m a HUGE chicken fan. Not a homework fan. One time my teacher gave the class a big report that day and said it was due the next day. It wasn’t fair because I had to miss football practice because I had to work on it.
We're sorry that happened, ChickenFries.
Homework. Definitely.
Wonder Friend
I love homework it the best i love not being able to play with my friends and doing my homework call me i will do your homework. [redacted]
It may, Catlyn, but practice makes perfect!
Homeworkistheworst
Catlyn smith
Homework is a way for students to practice skills. It takes, on average, doing something right 18 times before it becomes a habit. So, writing a sentence with subject/verb agreement 18 times(ish), means you have mastered that skill.
Until you get to more complicated stuff.
The sources are listed in the left column of the WONDER, ZERVA.
Homework is the independent practice of a skill teachers need to make sure students can perform on their own.
We're sorry homework stresses some people out. That's a great subject to bring up with parents and teachers, though!
We're sorry to hear that, Carter.
Isohatehomework
I'm sure a lot of our Wonder Friends share your opinion! ?
Oh,ha ha ha.???I am not a so called Wonder Friend. Are you a robot?!
? Everyone who comes to Wonderopolis are our Wonder Friends!
We're not robots. We actually respond to most of the comments made.
your not one person, your multiple people who are in the "Wonderopolis" company
Oh...sorry about that...I didn’t mean to say that. I’m sorry x100 ☹️????
It's ?
We think you're not alone in that emotion!
Jack McCrea
OMG YOU ARE SO RIGHT. But to be honest I just hate it
Mason Smolen
That's WONDERful, Mason!
AnonymousPerson31
We're glad we could be of assistance, Wonder Friend!
Maybe this WONDER about expectations will help.
Hi, Lulia! It's important to finish your homework so that you can continue to learn about topics discussed in school! What is your favorite subject in school?
Hi, caileigh! Yeah, though homework isn't the most fun activity after school, it will help you learn more about what you learned in school!
steve savie
Hi, Sara! We're sorry to hear that you're having homework problems ?.
All homework does is make students stressed out and make less time for them to be with their family and relax
no homework is based on the work we do in school and you will get better at your work.
We're so sorry to hear that you're having a tough time with homework, Wonder Friend ?. Homework is important, and time with family and relaxing is important, too!
AngryPerson
u think all of our parents help with our homework? some of them dont, they see this as a "student's responsibility" and let them be and btw, if you delete this comment, it is easy to see that you don't want any negative comments about this and want to eliminate the people who think homework is bad
Hi, AngryPerson. We're so sorry that you're angry. We do want to hear our Wonder Friends' thoughts here at Wonderopolis. If you're having trouble with your homework, we hope that you ask your teacher for help. We appreciate your feedback!
This is so true! In my house, homework never connected me to my parents, because like work at school, I saw it as a test of what I could do individually. Thus, as all my time was taken up by homework, I almost never spent time with my parents. Now I feel isolated from them.
Thanks for sharing your thoughts, Kay. We definitely recommend spending quality time with family, and we hope that learning together is a way to connect with your family!
Thank you for sharing your thoughts, Mii. And we absolutely agree that spending quality time with your family is very important!! Perhaps you could tell your family fun facts that you learned at school? Learning new information is also very important, and it is awesome to share the information you learn with your family so that you can learn together! ?
Homework is both emotionally and mentally hurtful...Physically too-
We're sorry to hear that you are having trouble with your homework, Wonder Friend! We hope that you ask your teacher if you have any specific questions about your homework.
Hi, Llamaz! We hope that you are getting plenty of sleep, too! Check out Wonder 1775: Do Kids Need More Sleep Than Adults? Also, thanks for sharing your thoughts!
Thanks for asking, rather! We ask that Wonderopolis be listed as the author. Also, since we do not list the publish date for our Wonders of the Day, you may put the date you accessed this page for information. The following is how you would cite this page:
"Why Do We Have Homework?" Wonderopolis. https://www.wonderopolis.org/wonder/why-do-we-have-homework . Accessed 25 Apr. 2018.
Hang in there, Louie! It sounds like you're working really hard on your homework and essays, which is awesome!!
Louie ramirez
We appreciate you sharing your thoughts with us, Louie. We know that homework takes a lot of work, but it's also helping you learn and Wonder!
Hi, Louie! What are you writing about in your essay?
Hi, Clara! We have MANY Wonders on these topics!! Our Explore Wonders tab contains over 2,100 Wonders, and if you scroll down on this page, you can search for Wonders by topics that you're interested in! Have fun WONDERing, Clara!
We're sorry to hear that you are having a hard time with your homework, Ben, but we think that you are doing a great job and working hard! Keep up the great work!!
Playing games is fun, but make sure you make time for your homework, too, Mitchell! Once you finish your the homework, you should check out Wonder 1732: How Are Video Games Made? ?
Thank you for sharing your thoughts, Benicio. Though the pros of homework are the focus of this Wonder, the second to last paragraph does list some potential cons:
"Despite these benefits found by researchers, the topics of who should receive homework and how much homework are hotly debated among educators and researchers. In one study , researchers found that academic gains from homework increased as grade level increased, suggesting homework is more beneficial for older students. Some researchers have found that too much homework can lower or cancel its benefits and become counterproductive , because students become burned out."
Hi, kody! We're glad that you're WONDERing with us!
We love hearing that, Jordan!! Thanks for letting us know, and thanks for WONDERing with us!
Thanks for WONDERing with us, Miles!
Hi, Ameir! It looks like you've really done some research on the subject!
Hi, ameir!! If you're having trouble with your homework, you may want to discuss specific questions you're having with your teacher. What is your favorite subject in school?
math and science are my favorite
Those subjects are very interesting!! Have you seen our Math and Science Wonders?
We're sorry to hear that, UJEY, but we're glad you're WONDERing with us!
It is important to take some time to rest, but homework is also important! We hope this Wonder helps explain why!
We're sorry to hear that, Gia, but we hope that this Wonder helps explain the many benefits of homework, too!
homework gets in the way of thing i want to do. I think teachers give homework just because they have nothing else to do. like isn't going to school enough work and it takes time away from my family especially my mom who cancer and i would want to spend more time with my mom. :(
We're so sorry to hear that, digeo! ?
dogs go moo
school is kid preson!
We're sorry you feel that way! We think school is an excellent place to Wonder!!!
why do dogs go moo
Thanks for WONDERing with us!
mkewigyjdfo8ueabsn ry7gtcbsh j
We're glad you liked this Wonder!! ?
Hi, Luke! Have you seen Wonder 1529: Why Do Cats Purr?
Hi, mew mew! Have you seen our Wonders about cats ?
jacob baldwin
Sorry, didn't catch that, jacob! Glad you're WONDERing with us though!!
Hello, Bob! We're always looking to hear more from our Wonder Friends!! ?
Thanks for stopping by to Wonder with us!
dogs say moooooooooooooooooooo
Thanks for sharing your thoughts!!
Thanks for sharing! Sometimes it is difficult to balance homework and other activities. What are some of your favorite things to do when you're not doing homework?
We're sorry you feel that way, CN Olson!! We're glad you're WONDERing with us, though!
Thanks for joining the conversation, davaeh!
im sorry for anyone that feels that way but homework is good for you
Thanks for sharing your thoughts!
Great points, john! We hope you will have some more free time soon!! Thanks for WONDERing with us!!
We appreciate your feedback, jorge!
Agreed aswell
Does your school give homework, bob? Thanks for sharing your thoughts!
xxxtentacion
Sometimes, unfortunately, it does ?. Homework also has benefits too, though! Thanks, gavin!
That certainly does add up the majority of the day! The lessons we learn in school help us to grow up to be thoughtful and intelligent adults. We do agree that everyone needs a break sometimes, though! Hope you and our other friends get a few minutes to kick back and relax today!?
We should discontinue homework because some kids don’t do it or understand it, therefore kids start stressing and saying to there self I’m gonna get in trouble , I’m gonna get a bad grade and it basically leads in to this whole conflict .
Thanks for sharing, Liv!
Sorry you feel that way, Justin, but we're glad that you're WONDERing with us!!
Thank you bob, we should change our studies to something actually helpful.
We appreciate you sharing your thoughts, Bob. Thanks for WONDERing with us!
Homework hater
Homework is a disease I think we need a intercontinental cure research lab for it
But, unfortunately, creating this research lab may require some homework! ?
Thanks for sharing your thoughts, Hi! It's good to keep the conversation going about the amount of homework that students typically get.
Thanks for sharing that, Caden! Have you been back to Mars since being born there?
Yes, I went there with him I will send you a postcard next time we go. I think Mars is wrecking his brain.
Kai's evil twin
My friend trolled me
? Be safe out there, Caden!
Must be a fun class! ?
Thanks for the feedback, Gyanve! Great to hear from you! ?
Perhaps they also suggested some coping strategies, too?
OOOOOOOOOOO
Not a roast
Hi again, Kai! Actually, if you look toward the bottom of the Wonder, under "Sources" you'll see where we got our information. We appreciate you checking up on us with a critical eye! It's always good to be a little skeptical and ask for more research and data. You're a smart Wonder Friend! We Wonder if you could do some research to find support for why schools SHOULDN'T have homework. We're curious to hear what you find!
www.Scholastic.com says that there is no evidence to say that homework benefits kids at all, and Washington Post says that homework on a national level is not related to academic success. Washington post also says that some lower income countries cultures normalize long periods of studying but it is uneffective, nd neotoday.org says that the link between assigned homework and academic achievement is drastically over inflated, What do you have to say about that?(sorry If I was a little harsh in my last two comments I was unhappy at the time) neotoday.org/2014/05/13/should-schools-be-done-with-homework) //www.washingtonpost.com/posteverything/wp/2015/09/02/homework-could-have-an-effect-on-kids-health-should-schools-ban-it
http://www.scholastic.com/browse/subarticle.jsp?id=2953
WOW!! You've really done some EXCELLENT research from some reputable sources, Kai! Our Wonder Salute to you! One thing to note: in the Washington Post article, they do make a distinction that heavy homework loads in elementary can be negative. In higher grades, this might not be the case "Homework, in fact, is an important component of education for students in the middle and upper grades of schooling.". It certainly raises a very good question which is we shouldn't assume homework is helping and adding more homework all the time seems to definitely not be helping. It's a great question that deserves a lot more thought and research. Thank you for WONDERing and researching, Kai!
This might get moderated, but I am curious to see how how many people "talked" with me./?
How many people have responded to my comments
You would just have to look on this comment page and see who "replies" to your comment. Does that help, Kai?
What do you mean, exactly? We don't follow.
? Wow, tough review! Well, research does support that extra practice helps. We DO discuss the debate over how much homework and what kind. Truthfully, homework is probably not going anywhere anytime soon, so we wanted to help show our Wonder Friends how it can be beneficial and how one can get the most out of it. We appreciate hearing from you, Kai!
I'd agree with the fact that practice does help learning on a basic level of memory but, in experience as a student, I cannot say that homework could be considered "practice." I've had many-a-teacher that has given homework out and I've had to google search how to do most of it because I was never taught it in class. Homework is more of busy work in the way of doing hobbies, eating, sleeping, and a happy and healthy life style that could possibly be important in "the real world", as if this torture is as easy as petting a bunny. Homework CAN provide help in small, sparatic, doses. If you are bombarded with homework everyday, it really becomes more harmful than helpful.
Great thoughts, Jillian! Really well said and we appreciate you taking the time to share that with us! We wish more teachers made time to wonder with their class (and we are thankful for the great ones who do!).
jaime lannister
you couldn't be more right school is about seven hours every 5 days a week for about a year and we still get work to take home like school is for learning there needs to be time to separate school life from your life like you can't just do work all day and you also get homework when it's holiday and there are enough going on in childrens lives than homework so this page is bad no one needs homework i learn more from youtube videos than school and children get anxiety enough from life like puberty, family, growing older school is just boring and you need time to settle your mind because in british schools they work you forever and the teachers are tough.
Thanks for sharing your thoughts, Jaime! Hang in there!
I hate homework we do work every day at school teachers know what is is like because they been through homework.Let me put it to you guys i know some people hate homework and some do not.Most teachers just overdo homework.
Good thoughts, Edrick. Thanks for sharing and glad to have you WONDERing with us!
Do they write those essays in class or at home, Brielle? ?
they write the essays at home
Thanks for sharing your thoughts, Yuguj! Glad to have you WONDERing with us on this important topic!
I agree so much I am so scared of not doing my homework or my grade might go down and that really isn't fair for me and my peers so great point!!!
That's a great point, Anonymous! In a perfect world, people would just do the work assigned and see the value in it. Sadly, it's hard to do away with the consequences and still have full participation. It's a challenging problem to try and solve, but we are glad you are WONDERing with us!
I think homework is a waste of time. it takes away from family time and exercise time.
Thanks for sharing your thoughts, Alisa! We think family time and exercise are important, too. The article did mention some reasons why homework has value, even if it doesn't always seem that way. Hang in there! It will all be worth it someday!
I am a very smart student with a brain to fit an adult, but even i get tired of homework. I have spent all day at school so I want a break. We don' need homework.
Yes, I agree and I too get tired of it. In my school they said that HW, was just the same lesson at home than at school. It is just a review. I am smart and don't study (LOL) and yet I have always gotten an A or a B in my tests (BTW, studying is considered homework for some reasons)
The struggle is real, Alisa. We do hope you get some time to give that super-smart brain a break! Thanks for using some of that brain power here with us at Wonderopolis!
Thanks for sharing your thoughts, Kid77! Sometimes in life, the important things are not always the most fun. Some homework assignments might feel unnecessary but (as the article mentioned) there can be many functions of homework. At least in your case, if you learned the material well in class, it shouldn't take up as much time to complete at home. Sometimes, though, that extra practice can make the difference between knowing the information and truly mastering it. Hang in there, Kid77!
ethan (murphy)
If you are bullied, tell a teacher, if the teacher is the bully.... I honestly can’t help you there.
Thanks for sharing your thoughts with us, ethan. We're sorry it feels like you are being bullied by your teachers. Have you spoken with your school counselor or your parents? Perhaps they can help you resolve the issues you are facing.
Thanks for sharing your feedback with us, Alexia. We hope you'll keep exploring Wonders to find one you like!
Thank you for commenting, Boi. We hope you'll visit Wonderopolis again soon.
Thanks for joining the conversation, pretty456 and twanasia! We're glad you stopped by Wonderopolis!
you don't like homework?
Thanks for telling us how you feel, Isaac. We appreciate your feedback.
We're glad we could help with your homework, Pusheen! Since we do not list the publish date, standard MLA formatting says that it's OK to list the date you accessed the page for information. Check out the Purdue OWL website for more guidance.
Thank you for WONDERing with us, Isaac! We hope you'll take a look at Wonder #1534. We think it's right up your alley! ?
Certainly, Liesel! Thank you for asking. We ask that Wonderopolis be listed as the author of this Wonder of the Day. Since we do not list the publish date, you may use the date you accessed this webpage for information (such as November 27). Cheers, Wonder Friend!
We're glad you found this Wonder helpful, sonice! There are both advantages and disadvantages to homework and sometimes those points are contrary to each other. This happens when there are different studies performed by different researchers. Sometimes the results contradict other studies.
I used this source for a case study that I am conducting on homework. I was wondering if I could know who wrote the source and when it was published. If I am allowed to have this information, please respond. Thank you.
Thank you for using Wonderopolis for your homework, Liesel! Please see our response above. ?
I know the heather
Thanks for joining the discussion, D. We're glad you visited Wonderopolis.
We're glad this Wonder helped, suicune300, even if it didn't make you like homework any more! It's great that you're WONDERing! We hope you'll stop by again! :)
Hi, bill! We're not sure we understand your comment. Do you have homework about autism? If so, head over to Wonder #1346 to explore information about autism.
We're glad you joined the conversation, avery! We hope you liked reading this Wonder -- perhaps it helped you understand some of the advantages to homework. :)
We're glad you joined the discussion, Bob. Perhaps this Wonder helped to explain why homework is assigned to students. :)
Hi, amez! Sometimes it is helpful to take a break before starting your homework. Thinking can be tiring sometimes, but it's so important! :)
( ͡° ͜ʖ ͡°)
Thank you for sharing, Wonder Friend! :)
lies lies lies lies lies lies lies lies lies lies
We're sorry you feel this way, bob. Thanks for sharing your opinion. We always value hearing from our Wonder Friends! :)
Hi, Christian. We're sorry you don't agree with this Wonder. We encourage you to also explore the Wonder Sources listed. Thanks for stopping by! :)
i hate homework
Thank you for sharing your opinion, yazzie! We hope this Wonder helped you to understand some of the advantages to homework, along with some of the disadvantages. :)
i really like this article, got an A+ on my report. THANKS!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
Great job, Wonder Friend! Keep up the GREAT work and always keep WONDERing! :)
Hi, Wonder Friend! We appreciate you sharing your opinion about homework! Thanks for WONDERing with us! :)
We appreciate you sharing your opinion about homework, nathan! Try to think about all the extra practice! :)
hey homework is good for your brain and help you to get smarter
Thanks for sharing your opinion, elroi!
Great question, tyler! If we know who submitted the question the author is listed up by the "Listen" button. This Wonder does not have an author listed. Sometimes people submit anonymous questions! Thanks for stopping by! :)
Riley & Anna
Thanks for the KIND words, Riley & Anna! We think our Wonder Friends are pretty AWESOME, too! We encourage you to submit your question to the Wonder Bank! :)
We appreciate you sharing your thoughts about homework, bob! We're glad you think it is helpful! :)
I hate homework
Thanks for joining the discussion and sharing your opinion, Brendon! We're glad you're WONDERing! :)
Thanks for sharing your opinion, Wonder Friend! Spending time with your parents is important, too! We encourage you to share this Wonder with them! :)
Antonio yet King
We appreciate you sharing your thoughts about this Wonder topic, too! Thanks for joining the conversation, Antonio! :)
Thanks for joining the conversation, Caroline! We appreciate you sharing your thoughts! :)
Hi, Makayla! We appreciate you sharing your thoughts about this important topic! Thanks for visiting Wonderopolis! :)
Welcome, Dionna! Thanks for sharing your opinion about homework! We're glad you're WONDERing! :)
Thanks for sharing your thoughts, Bob! We understand that sometimes it is difficult, but try to also think about the positive aspects mentioned in the Wonder! :)
I notice that none of the evidence presented in the article is backed by any tests or studies to show that the claims presented in the wonder is true.
Oh wow. You got us, Unknown. Not a fan of homework, we are guessing? Did you try clicking any of our sources links? We appreciate you keeping us on our toes!
Hi, d! We understand it's important for you to have free time, too! We hope you still have time for that! :)
I think you are wrong I have to stay up all night to do my homework then at school I always fall asleep :(
We're sorry to hear that, Jack. Thanks for sharing your connection. Maybe you can talk to your teacher about that. :)
Thanks for sharing your opinion about homework, avry! We appreciate you joining the discussion! Hopefully you learned some of the positive aspects of homework! :)
Thanks for sharing your opinion, Bumble Bee! We understand that there are many different opinions out there about homework. We tried to address both sides, while also stating the positive aspects of homework. We hope you understand and Wonder with us again soon! :)
wonderopolis is a lier
no your article is mostly one sided. the side being that homework is good
Thanks for sharing your opinion, Wonder Friend. You can read more about the advantages and disadvantages of homework by reviewing the Wonder Sources we provided above.
Hi, Kayla! Thanks for sharing your thoughts! We're sorry to hear homework is so stressful. We hope things get better! Stay positive! :)
That's GREAT, Emma! We love your enthusiasm for learning! Keep up the GREAT work! :)
Trinity Goebel
Hi, Trinity! Thanks for sharing your thoughts about homework. Sometimes it can be frustrating if you have a lot, but try to stay positive! Keep up the GREAT work! :)
homework is stupid why why do we have it mmmmmmm i hate it..
Hi, tyson! Thank you for sharing your thoughts. We're sure there is some good in homework -- just take a look at the Wonder text above to see! :)
A lot of students don't like homework, ..., and it can be challenging to keep up with homework with everything else going on in your life. The important thing is to do your best, because there are lots of benefits to homework even if it doesn't always seem like it. If homework is a regular problem, talk to your teacher or fellow classmates for help. We're glad you took the time to share your thoughts about homework.
To answer your question, Im pretty sure homework is NOT a law, but pretty much every teacher gives you homework. Depending on what grade you are in, usually grades 1-3 get 0-30 minutes of homework each night. grades 4-6 get 0-2 hour of homework each night, and Grades 7 and 8 get 30-3 hours of homework each night..... all of this depends on the student and how he or she learns. but this is what the average student gives to do homework in Elementary school
Thanks for the GREAT explanation, emma! You're right in that there are recommended amounts, but no particular law. We appreciate your comment! :)
Thanks for visiting Wonderopolis for your homework, Maya! Homework is not a law. It depends how much homework you have as to how long it takes. Also, some assignments, like projects, take longer than smaller assignments. We hope this Wonder was helpful in answering your questions! :)
Hi, Maya! No, homework is not a law. It is up to your teacher or school. We hope this Wonder helped explain how homework is helpful for practicing what you learned. We understand it is a pain sometimes, but we hope you understand! Thanks for WONDERing with us! :)
TENNIS is awesome
Hello, TENNIS is awesome! The WONDER mentions some reasons why homework is important, sch as extra practice. We appreciate your comment and you sharing your opinion with us! :)
One opinion
Wonderopolis
We appreciate you sharing your thoughts, One opinion! Thanks for WONDERing with us! :)
Hello, hahahah! Homework can be time consuming sometimes, but keep thinking positively about all you're learning! :)
We appreciate you sharing your opinion, Goopdi! Sometimes it may seem like a chore, but it is always a good idea to practice what you learned at school. WONDERing is a WONDERful way to learn and have fun at the same time! :)
I believe homework is a waste of time!!
Shae Skipper
Hello, Shae Skipper! You make some great points to support your opinion. Thanks for sharing your thoughts with your WONDER friends! :)
Why do we wonder?
That's a GREAT question, Alistair! WONDERing is a GREAT way to learn new things, have fun, and explore the world around us! :)
connor essary
Hello WONDER Friend, connor essary! We are glad you enjoyed this WONDER. Here is another WONDER about homework. Wonder #491: Do Dogs Really Eat Homework? Enjoy! :)
JoHaunn Mainwood
Hi JoHaunn Mainwood! Thanks for commenting on this WONDER! We appreciate our WONDER friends sharing their thoughts! :)
Welcome, Bob! Thanks for WONDERing with us and commenting on the WONDER! :)
McDonald's
Hi McDonald's! Thanks for commenting on this WONDER. We hate to hear you hate homework. Homework is another way to learn and show others what you know. Check back for more WONDERS! :)
Hi Jaheim! We hate to hear you don't enjoy your homework. Homework is a great way to show your family and friends what you are doing in school. Keep working hard and WONDERing!
Thanks for sharing your thoughts, Sara! You do learn more from doing your homework! Keep up the great work! :)
Hi David! We hate to hear you don't like homework because it helps us practice what we learned in school. Homework is different everywhere you go. Keep working hard! :)
Hello, Nicole! We hate to hear you hate homework. Homework can be great practice for what you are learning in school. We know you are working hard and doing a great job. Keep it up! :)
keandre campbell
Welcome to WONDERopolis, keandre campbell! There are over 1,000 WONDERS for you to explore. Thanks for WONDERing with us. Check back every day for more WONDERful WONDERS! :)
That's great, Crazy! Keep up the great WONDERing! :)
Wonder frog
It is not school is amazing!!!
Welcome, Wonder frog! We hate to hear you don't enjoy school. School is a great opportunity to WONDER and learn new things. Then you can share your new knowledge with your friends. Try checking out Wonder #1268: Why Was School Created? Always keep WONDERing! :)
I agree totally!
We appreciate you sharing your opinion about homework, too, Kaytlyn! Thanks for stopping by! :)
We appreciate you joining the discussion, Trinity! We hope this Wonder showed a few reasons why homework can be beneficial! :)
Hello, Jordan! Homework can be great practice. It helps you continue learning! :)
Lukas Wozencraft
That's funny, Lukas Wozencraft! What do you think it will be about? Be sure to check back tomorrow! :)
Jahkeya from DE
Hello WONDER friend, Jahkeya from DE! What would our world be like if dinosaurs weren't extint? Hmmm...? Something to WONDER about! :)
We are glad you enjoyed the video, Jasahn! Homework is very helpful most of the time! Thanks for WONDERing with us! :)
We are glad you liked the video, Makayla! It made us laugh, too! Check out Wonder #1285: What Was Before Dinosaurs? Happy WONDERing! :)
Juilo from DE
Hello, Juilo from DE! Cheer up! Homework helps you practice what you are learning. After all, they say practice makes perfect! If you enjoy video games, check out Wonder #1344: Who Invented the First Video Game? Have fun WONDERing! :)
Autumn from Delaware
Welcome, Autumn from Delaware! The video was silly! Here is another WONDER about dinosaurs! Wonder #275: How Do Dinosaurs Get Their Names? Enjoy! :)
Thanks for WONDERing with us, Sara! Check back everyday for more WONDERful WONDERS!:)
Hello, Gabriel! It sounds like many of our WONDER friends agree with you about the video. We all thought it was funny too! Thanks for commenting! :)
Julian from Delaware
Welcome, Julian from Delaware! You stay busy! That shows true commitment and hard work! :)
Hi Geyonni! We are glad you liked the video. Can you imagine seeing a dinosaur at school? Check out Wonder #491: Do Dogs Really Eat Homework? Happy WONDERing! :)
christina from De
I agree!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
Thanks for commenting, christina from De! You're right, that kids also need time to spend with their family. As the WONDER tells us, it is important to not have too much homework. That leaves time for both! :)
Khyan from DE
Thanks for sharing, Khyan from DE! Homework is helpful practice and playing with your friends is important, too. Hopefully you can find a happy medium between the two! :)
Kainat from Delware
Not really... :(
im just here because of espark, of all you people you domt kn9w what espark is, well its not homework its just were on oir school ipads amd we do this app that novody wants to do and we have (quests) and are a bunch of activities put togethor.
That could be a very fun way to learn and WONDER, Mitchell!
William Weispfenning
Homework is so fun (not) homework = ?
lol really william
Thanks for joining the discussion, William. There are pros and cons to homework and we hope this Wonder helped you learn about them. ?
We appreciate you sharing your thoughts, Trinity! Thanks for visiting Wonderopolis! :)
That's right, Kainat from Delware! Homework is great practice! Keep up the great WONDERing! :)
We are undergoing some spring clearing site maintenance and need to temporarily disable the commenting feature. Thanks for your patience.
Related Wonders for You to Explore

Do All Sharks Live In Saltwater?

What Type of Shark Is the Slowest?

Why Do Sharks Have Nostrils?

Who Was Kalpana Chawla?

How Do You Clean Up an Oil Spill?
Drag a word to its definition
Select a Wonder Word:
Match its definition:
Congratulations!
You’ve matched all of the definitions correctly.
Share results
Question 1 of 3
Homework plays an important role for parents by creating a bridge between home and what?
- a school Correct!
- b parents Not Quite!
- c coaches Not Quite!
- d students Not Quite!
Question 2 of 3
Which of the following is NOT an important life skill that can be enhanced via homework?
- a time management Not Quite!
- b prioritization Not Quite!
- c organization Not Quite!
- d photosynthesis Correct!
Question 3 of 3
How much is too much homework per night?
- a 30 minutes Not Quite!
- b 1 hour Not Quite!
- c 2 hours Not Quite!
- d It depends upon a variety of complex factors. Correct!
Quiz Results
Share Results
Spread the joy of wonder, get your wonder daily.
Subscribe to Wonderopolis and receive the Wonder of the Day® via email or SMS
Join the Buzz
Don’t miss our special deals, gifts and promotions. Be the first to know!
Share with the World
Tell everybody about Wonderopolis and its wonders.
Share Wonderopolis
Wonderopolis widget.
Interested in sharing Wonderopolis® every day? Want to add a little wonder to your website? Help spread the wonder of families learning together.
You Got It!

http://wonderopolis.org/wonder/why-do-we-have-homework
© National Center for Families Learning (NCFL)

What’s the Right Amount of Homework?
Decades of research show that homework has some benefits, especially for students in middle and high school—but there are risks to assigning too much.
Your content has been saved!
Many teachers and parents believe that homework helps students build study skills and review concepts learned in class. Others see homework as disruptive and unnecessary, leading to burnout and turning kids off to school. Decades of research show that the issue is more nuanced and complex than most people think: Homework is beneficial, but only to a degree. Students in high school gain the most, while younger kids benefit much less.
The National PTA and the National Education Association support the “ 10-minute homework guideline ”—a nightly 10 minutes of homework per grade level. But many teachers and parents are quick to point out that what matters is the quality of the homework assigned and how well it meets students’ needs, not the amount of time spent on it.
The guideline doesn’t account for students who may need to spend more—or less—time on assignments. In class, teachers can make adjustments to support struggling students, but at home, an assignment that takes one student 30 minutes to complete may take another twice as much time—often for reasons beyond their control. And homework can widen the achievement gap, putting students from low-income households and students with learning disabilities at a disadvantage.
However, the 10-minute guideline is useful in setting a limit: When kids spend too much time on homework, there are real consequences to consider.
Small Benefits for Elementary Students
As young children begin school, the focus should be on cultivating a love of learning, and assigning too much homework can undermine that goal. And young students often don’t have the study skills to benefit fully from homework, so it may be a poor use of time (Cooper, 1989 ; Cooper et al., 2006 ; Marzano & Pickering, 2007 ). A more effective activity may be nightly reading, especially if parents are involved. The benefits of reading are clear: If students aren’t proficient readers by the end of third grade, they’re less likely to succeed academically and graduate from high school (Fiester, 2013 ).
For second-grade teacher Jacqueline Fiorentino, the minor benefits of homework did not outweigh the potential drawback of turning young children against school at an early age, so she experimented with dropping mandatory homework. “Something surprising happened: They started doing more work at home,” Fiorentino writes . “This inspiring group of 8-year-olds used their newfound free time to explore subjects and topics of interest to them.” She encouraged her students to read at home and offered optional homework to extend classroom lessons and help them review material.
Moderate Benefits for Middle School Students
As students mature and develop the study skills necessary to delve deeply into a topic—and to retain what they learn—they also benefit more from homework. Nightly assignments can help prepare them for scholarly work, and research shows that homework can have moderate benefits for middle school students (Cooper et al., 2006 ). Recent research also shows that online math homework, which can be designed to adapt to students’ levels of understanding, can significantly boost test scores (Roschelle et al., 2016 ).
There are risks to assigning too much, however: A 2015 study found that when middle school students were assigned more than 90 to 100 minutes of daily homework, their math and science test scores began to decline (Fernández-Alonso, Suárez-Álvarez, & Muñiz, 2015 ). Crossing that upper limit can drain student motivation and focus. The researchers recommend that “homework should present a certain level of challenge or difficulty, without being so challenging that it discourages effort.” Teachers should avoid low-effort, repetitive assignments, and assign homework “with the aim of instilling work habits and promoting autonomous, self-directed learning.”
In other words, it’s the quality of homework that matters, not the quantity. Brian Sztabnik, a veteran middle and high school English teacher, suggests that teachers take a step back and ask themselves these five questions :
- How long will it take to complete?
- Have all learners been considered?
- Will an assignment encourage future success?
- Will an assignment place material in a context the classroom cannot?
- Does an assignment offer support when a teacher is not there?
More Benefits for High School Students, but Risks as Well
By the time they reach high school, students should be well on their way to becoming independent learners, so homework does provide a boost to learning at this age, as long as it isn’t overwhelming (Cooper et al., 2006 ; Marzano & Pickering, 2007 ). When students spend too much time on homework—more than two hours each night—it takes up valuable time to rest and spend time with family and friends. A 2013 study found that high school students can experience serious mental and physical health problems, from higher stress levels to sleep deprivation, when assigned too much homework (Galloway, Conner, & Pope, 2013 ).
Homework in high school should always relate to the lesson and be doable without any assistance, and feedback should be clear and explicit.
Teachers should also keep in mind that not all students have equal opportunities to finish their homework at home, so incomplete homework may not be a true reflection of their learning—it may be more a result of issues they face outside of school. They may be hindered by issues such as lack of a quiet space at home, resources such as a computer or broadband connectivity, or parental support (OECD, 2014 ). In such cases, giving low homework scores may be unfair.
Since the quantities of time discussed here are totals, teachers in middle and high school should be aware of how much homework other teachers are assigning. It may seem reasonable to assign 30 minutes of daily homework, but across six subjects, that’s three hours—far above a reasonable amount even for a high school senior. Psychologist Maurice Elias sees this as a common mistake: Individual teachers create homework policies that in aggregate can overwhelm students. He suggests that teachers work together to develop a school-wide homework policy and make it a key topic of back-to-school night and the first parent-teacher conferences of the school year.
Parents Play a Key Role
Homework can be a powerful tool to help parents become more involved in their child’s learning (Walker et al., 2004 ). It can provide insights into a child’s strengths and interests, and can also encourage conversations about a child’s life at school. If a parent has positive attitudes toward homework, their children are more likely to share those same values, promoting academic success.
But it’s also possible for parents to be overbearing, putting too much emphasis on test scores or grades, which can be disruptive for children (Madjar, Shklar, & Moshe, 2015 ). Parents should avoid being overly intrusive or controlling—students report feeling less motivated to learn when they don’t have enough space and autonomy to do their homework (Orkin, May, & Wolf, 2017 ; Patall, Cooper, & Robinson, 2008 ; Silinskas & Kikas, 2017 ). So while homework can encourage parents to be more involved with their kids, it’s important to not make it a source of conflict.

Home > Blog > Tips for Online Students > The Pros and Cons of Homework
School Life Balance , Tips for Online Students
The Pros and Cons of Homework
Updated: July 16, 2024
Published: January 23, 2020

Remember those nights when you’d find yourself staring at a mountain of homework, eyes drooping, wondering if you’d ever see the light at the end of the tunnel? The debate over homework’s role in education is as old as time. Is it a crucial tool for reinforcing learning or just an unnecessary burden?
For college students, this question takes on new dimensions. Juggling homework with the endless amount of classes, part-time jobs, and social lives can feel like walking on thin ice. The pressure to maintain grades, meet deadlines, and still find time for friends and relaxation can be overwhelming. So, is homework a friend or foe?

Photo by energepic.com from Pexels
The homework dilemma.
A large amount of college students report feeling overwhelmed by their academic workload, leading to high levels of stress and anxiety. According to Research.com , 45% of college students in the U.S. experience “more than average” stress, with 36.5% citing stress as a major impediment to their academic performance. This stress often stems directly from the homework load, leading to symptoms like headaches, exhaustion, and difficulty sleeping. The intense pressure to manage homework alongside other responsibilities makes us question the true impact of homework on students’ overall well-being.
And then there’s the digital twist. A whopping 89% of students confessed to using AI tools like ChatGPT for their assignments. While these tools can be a godsend for quick answers and assistance, they can also undermine the personal effort and critical thinking necessary to truly understand the material.
On the brighter side, homework can be a powerful ally. According to Inside Higher Ed , structured assignments can actually help reduce stress by providing a clear learning roadmap and keeping students engaged with the material. But where’s the balance between helpful and harmful?
With these perspectives in mind, let’s dive into the pros and cons of homework for college students. By understanding both sides, we can find a middle ground that maximizes learning while keeping stress at bay.
The Pros of Homework
When thoughtfully assigned, homework can be a valuable tool in a student’s educational journey . Let’s explore how homework can be a beneficial companion to your studies:
Enhances Critical Thinking
Homework isn’t just busywork; it’s an opportunity to stretch your mental muscles. Those late-night problem sets and essays can actually encourage deeper understanding and application of concepts. Think of homework as a mental gym; each assignment is a new exercise, pushing you to analyze, synthesize, and evaluate information in ways that strengthen your critical thinking skills .
Time Management Skills
Do you ever juggle multiple deadlines and wonder how to keep it all together? Regular homework assignments can be a crash course in time management . They teach you to prioritize tasks, manage your schedule, and balance academic responsibilities with personal commitments. The ability to juggle various tasks is a skill that will serve you well beyond your college years.
Reinforcement of Learning
There’s a reason why practice makes perfect. Homework reinforces what you’ve learned in class, helping to cement concepts and theories in your mind. Understanding a concept during a lecture is one thing, but applying it through homework can deepen your comprehension and retention.
Preparation for Exams
Think of homework as a sound check and warm-up for exams. Regular assignments keep you engaged with the material, making it easier to review and prepare when exam time rolls around. By consistently working through problems and writing essays, you build a solid foundation that can make the difference between cramming and confident exam performance.
Encourages Independent Learning
Homework promotes a sense of responsibility and independence. It pushes you to tackle assignments on your own, encouraging problem-solving and self-discipline. This independence prepares you for the academic challenges ahead and the autonomy required in your professional and personal life.

The Cons of Homework
Despite its potential benefits, homework can also have significant downsides. Let’s examine the challenges and drawbacks of homework:
Impact on Mental Health
Homework can be a double-edged sword when it comes to mental health . While it’s meant to reinforce learning, the sheer volume of assignments can lead to stress and anxiety. The constant pressure to meet deadlines and the fear of falling behind can create a relentless cycle of stress. Many students become overwhelmed, leading to burnout and negatively impacting their overall well-being.
Limited Time for Other Activities
College isn’t just about hitting the books. It’s also a time for personal growth, exploring new interests, and building social connections. Excessive homework can eat into the time you might otherwise spend on extracurricular activities, hobbies, or simply hanging out with friends. This lack of balance can lead to a less fulfilling college experience. Shouldn’t education be about more than just academics?
Quality Over Quantity
When it comes to homework, more isn’t always better. Piling on assignments can lead to diminished returns on learning. Instead of diving deep into a subject and gaining a thorough understanding, students might rush through tasks just to get them done. This focus on quantity over quality can undermine the educational value of homework.
Inequity in Education
Homework can sometimes exacerbate educational inequalities. Not all students can access the same resources and support systems at home. While some might have a quiet space and access to the internet, others might struggle with distractions and lack of resources. This disparity can put certain students at a disadvantage, making homework more of a burden than a learning tool.
Dependence on AI Tools
With the advent of AI tools like ChatGPT , homework has taken on a new dimension. While these tools can provide quick answers and assistance, they also pose the risk of students becoming overly reliant on technology. This dependence can take away from the actual learning process, as students might bypass the critical thinking and effort needed to truly understand the material. Is convenience worth the potential loss in learning?
Finding the Balance
Finding the right balance with homework means tackling assignments that challenge and support you. Instead of drowning in a sea of tasks, focus on quality over quantity. Choose projects that spark your critical thinking and connect to real-world situations. Flexibility is key here. Recognize that your circumstances are unique, and adjusting your approach can help reduce stress and create a more inclusive learning environment. Constructive feedback makes homework more than just a chore; it turns it into a tool for growth and improvement.
It’s also about living a well-rounded college life. Don’t let homework overshadow other important parts of your life, like extracurricular activities or personal downtime. Emphasize independent learning and use technology wisely to prepare for future challenges. By balancing thoughtful assignments with your personal needs, homework can shift from being a burden to becoming a helpful companion on your educational journey, enriching your academic and personal growth.
Homework has its pros and cons, especially for college students. It can enhance critical thinking, time management, and learning, but it also brings stress, impacts mental health, and can become overwhelming. Finding the right balance is key.
Focus on quality assignments, maintain flexibility, and make sure your homework complements rather than dominates your life. With a thoughtful approach, homework can support your educational journey, fostering both academic success and personal growth.
How can I manage my time effectively to balance homework and other activities?
Create a schedule that allocates specific times for homework, classes, and personal activities. Use planners or digital calendars to keep track of deadlines and prioritize tasks. Don’t forget to include breaks to avoid burnout.
How can I reduce the stress associated with homework?
To manage stress, practice mindfulness techniques like meditation or deep breathing exercises. Break assignments into smaller, manageable tasks and tackle them one at a time. If needed, seek support from classmates, tutors, or mental health professionals.
Is using AI tools for homework cheating?
While AI tools like ChatGPT can be helpful for quick assistance, relying on them too much can hinder your learning process. Use them as a supplement rather than a replacement for your own effort and critical thinking.
How can teachers make homework more equitable?
Teachers can offer flexible deadlines, provide resources for students who lack them, and design assignments that account for different learning styles and home environments. Open communication between students and teachers can also help address individual challenges.
What are some strategies to make homework more meaningful?
Focus on quality over quantity by designing assignments that encourage deep thinking and application of knowledge. Integrate real-world problems to make homework more relevant and engaging. Provide constructive feedback to help students learn and grow from their assignments.
At UoPeople, our blog writers are thinkers, researchers, and experts dedicated to curating articles relevant to our mission: making higher education accessible to everyone. Read More
In this article
- Future Students
- Current Students
- Faculty/Staff

News and Media
- News & Media Home
- Research Stories
- School’s In
- In the Media
You are here
More than two hours of homework may be counterproductive, research suggests.

A Stanford education researcher found that too much homework can negatively affect kids, especially their lives away from school, where family, friends and activities matter. "Our findings on the effects of homework challenge the traditional assumption that homework is inherently good," wrote Denise Pope , a senior lecturer at the Stanford Graduate School of Education and a co-author of a study published in the Journal of Experimental Education . The researchers used survey data to examine perceptions about homework, student well-being and behavioral engagement in a sample of 4,317 students from 10 high-performing high schools in upper-middle-class California communities. Along with the survey data, Pope and her colleagues used open-ended answers to explore the students' views on homework. Median household income exceeded $90,000 in these communities, and 93 percent of the students went on to college, either two-year or four-year. Students in these schools average about 3.1 hours of homework each night. "The findings address how current homework practices in privileged, high-performing schools sustain students' advantage in competitive climates yet hinder learning, full engagement and well-being," Pope wrote. Pope and her colleagues found that too much homework can diminish its effectiveness and even be counterproductive. They cite prior research indicating that homework benefits plateau at about two hours per night, and that 90 minutes to two and a half hours is optimal for high school. Their study found that too much homework is associated with: • Greater stress : 56 percent of the students considered homework a primary source of stress, according to the survey data. Forty-three percent viewed tests as a primary stressor, while 33 percent put the pressure to get good grades in that category. Less than 1 percent of the students said homework was not a stressor. • Reductions in health : In their open-ended answers, many students said their homework load led to sleep deprivation and other health problems. The researchers asked students whether they experienced health issues such as headaches, exhaustion, sleep deprivation, weight loss and stomach problems. • Less time for friends, family and extracurricular pursuits : Both the survey data and student responses indicate that spending too much time on homework meant that students were "not meeting their developmental needs or cultivating other critical life skills," according to the researchers. Students were more likely to drop activities, not see friends or family, and not pursue hobbies they enjoy. A balancing act The results offer empirical evidence that many students struggle to find balance between homework, extracurricular activities and social time, the researchers said. Many students felt forced or obligated to choose homework over developing other talents or skills. Also, there was no relationship between the time spent on homework and how much the student enjoyed it. The research quoted students as saying they often do homework they see as "pointless" or "mindless" in order to keep their grades up. "This kind of busy work, by its very nature, discourages learning and instead promotes doing homework simply to get points," said Pope, who is also a co-founder of Challenge Success , a nonprofit organization affiliated with the GSE that conducts research and works with schools and parents to improve students' educational experiences.. Pope said the research calls into question the value of assigning large amounts of homework in high-performing schools. Homework should not be simply assigned as a routine practice, she said. "Rather, any homework assigned should have a purpose and benefit, and it should be designed to cultivate learning and development," wrote Pope. High-performing paradox In places where students attend high-performing schools, too much homework can reduce their time to foster skills in the area of personal responsibility, the researchers concluded. "Young people are spending more time alone," they wrote, "which means less time for family and fewer opportunities to engage in their communities." Student perspectives The researchers say that while their open-ended or "self-reporting" methodology to gauge student concerns about homework may have limitations – some might regard it as an opportunity for "typical adolescent complaining" – it was important to learn firsthand what the students believe. The paper was co-authored by Mollie Galloway from Lewis and Clark College and Jerusha Conner from Villanova University.
Clifton B. Parker is a writer at the Stanford News Service .
More Stories

⟵ Go to all Research Stories
Get the Educator
Subscribe to our monthly newsletter.
Stanford Graduate School of Education
482 Galvez Mall Stanford, CA 94305-3096 Tel: (650) 723-2109
- Contact Admissions
- GSE Leadership
- Site Feedback
- Web Accessibility
- Career Resources
- Faculty Open Positions
- Explore Courses
- Academic Calendar
- Office of the Registrar
- Cubberley Library
- StanfordWho
- StanfordYou
Improving lives through learning

- Stanford Home
- Maps & Directions
- Search Stanford
- Emergency Info
- Terms of Use
- Non-Discrimination
- Accessibility
© Stanford University , Stanford , California 94305 .
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Student Opinion
Should We Get Rid of Homework?
Some educators are pushing to get rid of homework. Would that be a good thing?

By Jeremy Engle and Michael Gonchar
Do you like doing homework? Do you think it has benefited you educationally?
Has homework ever helped you practice a difficult skill — in math, for example — until you mastered it? Has it helped you learn new concepts in history or science? Has it helped to teach you life skills, such as independence and responsibility? Or, have you had a more negative experience with homework? Does it stress you out, numb your brain from busywork or actually make you fall behind in your classes?
Should we get rid of homework?
In “ The Movement to End Homework Is Wrong, ” published in July, the Times Opinion writer Jay Caspian Kang argues that homework may be imperfect, but it still serves an important purpose in school. The essay begins:
Do students really need to do their homework? As a parent and a former teacher, I have been pondering this question for quite a long time. The teacher side of me can acknowledge that there were assignments I gave out to my students that probably had little to no academic value. But I also imagine that some of my students never would have done their basic reading if they hadn’t been trained to complete expected assignments, which would have made the task of teaching an English class nearly impossible. As a parent, I would rather my daughter not get stuck doing the sort of pointless homework I would occasionally assign, but I also think there’s a lot of value in saying, “Hey, a lot of work you’re going to end up doing in your life is pointless, so why not just get used to it?” I certainly am not the only person wondering about the value of homework. Recently, the sociologist Jessica McCrory Calarco and the mathematics education scholars Ilana Horn and Grace Chen published a paper, “ You Need to Be More Responsible: The Myth of Meritocracy and Teachers’ Accounts of Homework Inequalities .” They argued that while there’s some evidence that homework might help students learn, it also exacerbates inequalities and reinforces what they call the “meritocratic” narrative that says kids who do well in school do so because of “individual competence, effort and responsibility.” The authors believe this meritocratic narrative is a myth and that homework — math homework in particular — further entrenches the myth in the minds of teachers and their students. Calarco, Horn and Chen write, “Research has highlighted inequalities in students’ homework production and linked those inequalities to differences in students’ home lives and in the support students’ families can provide.”
Mr. Kang argues:
But there’s a defense of homework that doesn’t really have much to do with class mobility, equality or any sense of reinforcing the notion of meritocracy. It’s one that became quite clear to me when I was a teacher: Kids need to learn how to practice things. Homework, in many cases, is the only ritualized thing they have to do every day. Even if we could perfectly equalize opportunity in school and empower all students not to be encumbered by the weight of their socioeconomic status or ethnicity, I’m not sure what good it would do if the kids didn’t know how to do something relentlessly, over and over again, until they perfected it. Most teachers know that type of progress is very difficult to achieve inside the classroom, regardless of a student’s background, which is why, I imagine, Calarco, Horn and Chen found that most teachers weren’t thinking in a structural inequalities frame. Holistic ideas of education, in which learning is emphasized and students can explore concepts and ideas, are largely for the types of kids who don’t need to worry about class mobility. A defense of rote practice through homework might seem revanchist at this moment, but if we truly believe that schools should teach children lessons that fall outside the meritocracy, I can’t think of one that matters more than the simple satisfaction of mastering something that you were once bad at. That takes homework and the acknowledgment that sometimes a student can get a question wrong and, with proper instruction, eventually get it right.
We are having trouble retrieving the article content.
Please enable JavaScript in your browser settings.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access. If you are in Reader mode please exit and log into your Times account, or subscribe for all of The Times.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access.
Already a subscriber? Log in .
Want all of The Times? Subscribe .
Analyzing ‘the homework gap’ among high school students
Subscribe to the brown center on education policy newsletter, michael hansen and michael hansen senior fellow - brown center on education policy , the herman and george r. brown chair - governance studies diana quintero diana quintero former senior research analyst, brown center on education policy - the brookings institution, ph.d. student - vanderbilt university.
August 10, 2017
Researchers have struggled for decades to identify a causal, or even correlational, relationship between time spent in school and improved learning outcomes for students. Some studies have focused on the length of a school year while others have focused on hours in a day and others on hours in the week .
In this blog post, we will look at time spent outside of school–specifically time spent doing homework–among different racial and socio-economic groups. We will use data from the American Time Use Survey (ATUS) to shed light on those differences and then attempt to explain those gaps, using ATUS data and other evidence.
What we know about out-of-school time
Measuring the relationship between out-of-school time and outcomes like test scores can be difficult. Researchers are primarily confounded by an inability to determine what compels students to choose homework during their time off over other activities. Are those who spend more time on homework just extra motivated? Or are they struggling students who need to work harder to keep up? What role do social expectations from parents or peers play?
Previous studies have examined the impact of this outside time use on educational outcomes for students. A 2007 study using data from Berea College in Kentucky identified a causal relationship between hours spent studying and a student’s academic performance through an interesting measure. The researchers took advantage of randomly assigned college roommates, paying attention to those who came to campus with a video game console in tow. They hypothesized students randomly assigned to a roommate without a video game console would study more, since all other factors remained equal. That hypothesis held up, and that group also received significantly higher grades, demonstrating the causal relationship.
Other research has relied on data collected through the American Time Use Survey, a study of how Americans spend their time, and shown the existence of a gender gap and a parental education gap in homework time. Other studies have looked at the relationship between holding a job and student’s time use in discretionary activities , like sleep, media consumption, and time spent on homework. We are curious about out-of-school differences in homework time by race and income.
Descriptive statistics of time use
We began with a general sample of 2,575 full-time high school students between the ages of 15 and 18 from the ATUS, restricting the sample to their answers about time spent on homework during weekdays and school months (September to May). Among all high school students surveyed (those that reported completing their homework and those that did not), the time allocated to complete homework amounted to less than an hour per day, despite the fact that high school teachers report they assign an average of 3.5 hours of homework per day.
To explore racial or income-based differences, in Figure 1, we plot the minutes that students reporting spending on homework separately by their racial/ethnic group and family income. We observed a time gap between racial groups, with Asian students spending the most time on homework (nearly two hours a day). Similarly, we observe a time gap by the students’ family income.

We can also use ATUS data to isolate when students do homework by race and by income. In Figure 2, we plot the percentage of high school students in each racial and income group doing homework by the time of day. Percentages remain low during the school day and then expectedly increase when students get home, with more Asian students doing more homework and working later into the night than other racial groups. Low-income students reported doing less homework per hour than their non-low-income peers.

Initial attempts to explain the homework gap
We hypothesized that these racial and income-based time gaps could potentially be explained by other factors, like work, time spent caring for others, and parental education. We tested these hypotheses by separating groups based on particular characteristics and comparing the average number of minutes per day spent on homework amongst the comparison groups.
Students who work predictably reported spending less time on educational activities, so if working disproportionately affected particular racial or income groups, then work could help explain the time gap. Students who worked allocated on average 20 minutes less for homework than their counterparts who did not work. Though low-income students worked more hours than their peers, they largely maintained a similar level of homework time by reducing their leisure or extracurricular activities. Therefore, the time gap on homework changed only slightly with the inclusion of work as a factor.
We also incorporated time spent taking care of others in the household. Though a greater percentage of low-income students take care of other household members, we found that this does not have a statistically significant effect on homework because students reduce leisure, rather than homework, in an attempt to help their families. Therefore, this variable again does not explain the time gaps.
Finally, we considered parental education, since parents with more education have been shown to encourage their children to value school more and have the resources to ensure homework is completed more easily. Our analysis showed students with at least one parent with any post-secondary degree (associate or above) reported spending more time on homework than their counterparts whose parents do not hold a degree; however, gaps by race still existed, even holding parental education constant. Turning to income levels, we found that parental education is more correlated with homework time among low-income students, reducing the time gap between income groups to only eight minutes.
Societal explanations
Our analysis of ATUS could not fully explain this gap in time spent on homework, especially among racial groups. Instead, we believe that viewing homework as an outcome of the culture of the school and the expectations of teachers, rather than an outcome of a student’s effort, may provide some reasons for its persistence.
Many studies, including recent research , have shown that teachers perceive students of color as academically inferior to their white peers. A 2016 study by Seth Gershenson et al. showed that this expectations gap can also depend on the race of the teacher. In a country where minority students make up nearly half of all public school students, yet minority teachers comprise just 18 percent of the teacher workforce, these differences in expectations matter.
Students of color are also less likely to attend high schools that offer advanced courses (including Advanced Placement courses) that would likely assign more homework, and thus access to rigorous courses may partially explain the gaps as well.
Research shows a similar, if less well-documented, gap by income, with teachers reporting lower expectations and dimmer futures for their low-income students. Low-income students and students of color may be assigned less homework based on lower expectations for their success, thus preventing them from learning as much and creating a self-fulfilling prophecy .
In conclusion, these analyses of time use revealed a substantial gap in homework by race and by income group that could not be entirely explained by work, taking care of others, or parental education. Additionally, differences in educational achievement, especially as measured on standardized tests, have been well-documented by race and by income . These gaps deserve our attention, but we should be wary of blaming disadvantaged groups. Time use is an outcome reflecting multiple factors, not simply motivation, and a greater understanding of that should help raise expectations–and therefore, educational achievement–all around.
Sarah Novicoff contributed to this post.
Related Content
Michael Hansen, Diana Quintero
October 5, 2016
Sarah Novicoff, Matthew A. Kraft
November 15, 2022
September 10, 2015
K-12 Education
Governance Studies
Brown Center on Education Policy
Michael Trucano, Sopiko Beriashvili
September 20, 2024
Megan Kuhfeld, Karyn Lewis
Sweta Shah, Juanita Morales

Homework Struggles May Not Be a Behavior Problem
Exploring some options to understand and help..
Posted August 2, 2022 | Reviewed by Abigail Fagan
- What Is Anxiety?
- Take our Generalized Anxiety Disorder Test
- Find a therapist to overcome anxiety
- Mental health challenges and neurodevelopmental differences directly affect children's ability to do homework.
- Understanding what difficulties are getting in the way—beyond the usual explanation of a behavior problem—is key.
- Sleep and mental health needs can take priority over homework completion.
Chelsea was in 10th grade the first time I told her directly to stop doing her homework and get some sleep. I had been working with her since she was in middle school, treating her anxiety disorder. She deeply feared disappointing anyone—especially her teachers—and spent hours trying to finish homework perfectly. The more tired and anxious she got, the harder it got for her to finish the assignments.

One night Chelsea called me in despair, feeling hopeless. She was exhausted and couldn’t think straight. She felt like a failure and that she was a burden to everyone because she couldn’t finish her homework.
She was shocked when I told her that my prescription for her was to go to sleep now—not to figure out how to finish her work. I told her to leave her homework incomplete and go to sleep. We briefly discussed how we would figure it out the next day, with her mom and her teachers. At that moment, it clicked for her that it was futile to keep working—because nothing was getting done.
This was an inflection point for her awareness of when she was emotionally over-cooked and when she needed to stop and take a break or get some sleep. We repeated versions of this phone call several times over the course of her high school and college years, but she got much better at being able to do this for herself most of the time.

When Mental Health Symptoms Interfere with Homework
Kids with mental health or neurodevelopmental challenges often struggle mightily with homework. Challenges can come up in every step of the homework process, including, but not limited to:
- Remembering and tracking assignments and materials
- Getting the mental energy/organization to start homework
- Filtering distractions enough to persist with assignments
- Understanding unspoken or implied parts of the homework
- Remembering to bring finished homework to class
- Being in class long enough to know the material
- Tolerating the fear of not knowing or failing
- Not giving up the assignment because of a panic attack
- Tolerating frustration—such as not understanding—without emotional dysregulation
- Being able to ask for help—from a peer or a teacher and not being afraid to reach out
This list is hardly comprehensive. ADHD , autism spectrum disorder, social anxiety , generalized anxiety, panic disorder, depression , dysregulation, and a range of other neurodevelopmental and mental health challenges cause numerous learning differences and symptoms that can specifically and frequently interfere with getting homework done.

The Usual Diagnosis for Homework Problems is "Not Trying Hard Enough"
Unfortunately, when kids frequently struggle to meet homework demands, teachers and parents typically default to one explanation of the problem: The child is making a choice not to do their homework. That is the default “diagnosis” in classrooms and living rooms. And once this framework is drawn, the student is often seen as not trying hard enough, disrespectful, manipulative, or just plain lazy.
The fundamental disconnect here is that the diagnosis of homework struggles as a behavioral choice is, in fact, only one explanation, while there are so many other diagnoses and differences that impair children's ability to consistently do their homework. If we are trying to create solutions based on only one understanding of the problem, the solutions will not work. More devastatingly, the wrong solutions can worsen the child’s mental health and their long-term engagement with school and learning.
To be clear, we aren’t talking about children who sometimes struggle with or skip homework—kids who can change and adapt their behaviors and patterns in response to the outcomes of that struggle. For this discussion, we are talking about children with mental health and/or neurodevelopmental symptoms and challenges that create chronic difficulties with meeting homework demands.
How Can You Help a Child Who Struggles with Homework?
How can you help your child who is struggling to meet homework demands because of their ADHD, depression, anxiety, OCD , school avoidance, or any other neurodevelopmental or mental health differences? Let’s break this down into two broad areas—things you can do at home, and things you can do in communication with the school.

Helping at Home
The following suggestions for managing school demands at home can feel counterintuitive to parents—because we usually focus on helping our kids to complete their tasks. But mental health needs jump the line ahead of task completion. And starting at home will be key to developing an idea of what needs to change at school.
- Set an end time in the evening after which no more homework will be attempted. Kids need time to decompress and they need sleep—and pushing homework too close to or past bedtime doesn’t serve their educational needs. Even if your child hasn’t been able to approach the homework at all, even if they have avoided and argued the whole evening, it is still important for everyone to have a predictable time to shut down the whole process.
- If there are arguments almost every night about homework, if your child isn’t starting homework or finishing it, reframe it from failure into information. It’s data to put into problem-solving. We need to consider other possible explanations besides “behavioral choice” when trying to understand the problem and create effective solutions. What problems are getting in the way of our child’s meeting homework demands that their peers are meeting most of the time?
- Try not to argue about homework. If you can check your own anxiety and frustration, it can be more productive to ally with your child and be curious with them. Kids usually can’t tell you a clear “why” but maybe they can tell you how they are feeling and what they are thinking. And if your child can’t talk about it or just keeps saying “I don't know,” try not to push. Come back another time. Rushing, forcing, yelling, and threatening will predictably not help kids do homework.

Helping at School
The second area to explore when your neurodiverse child struggles frequently with homework is building communication and connections with school and teachers. Some places to focus on include the following.
- Label your child’s diagnoses and break down specific symptoms for the teachers and school team. Nonjudgmental, but specific language is essential for teachers to understand your child’s struggles. Breaking their challenges down into the problems specific to homework can help with building solutions. As your child gets older, help them identify their difficulties and communicate them to teachers.
- Let teachers and the school team know that your child’s mental health needs—including sleep—take priority over finishing homework. If your child is always struggling to complete homework and get enough sleep, or if completing homework is leading to emotional meltdowns every night, adjusting their homework demands will be more successful than continuing to push them into sleep deprivation or meltdowns.
- Request a child study team evaluation to determine if your child qualifies for services under special education law such as an IEP, or accommodations through section 504—and be sure that homework adjustments are included in any plan. Or if such a plan is already in place, be clear that modification of homework expectations needs to be part of it.
The Long-Term Story
I still work with Chelsea and she recently mentioned how those conversations so many years ago are still part of how she approaches work tasks or other demands that are spiking her anxiety when she finds herself in a vortex of distress. She stops what she is doing and prioritizes reducing her anxiety—whether it’s a break during her day or an ending to the task for the evening. She sees that this is crucial to managing her anxiety in her life and still succeeding at what she is doing.
Task completion at all costs is not a solution for kids with emotional needs. Her story (and the story of many of my patients) make this crystal clear.

Candida Fink, M.D. , is board certified in child/adolescent and general psychiatry. She practices in New York and has co-authored two books— The Ups and Downs of Raising a Bipolar Child and Bipolar Disorder for Dummies.
- Find a Therapist
- Find a Treatment Center
- Find a Psychiatrist
- Find a Support Group
- Find Online Therapy
- United States
- Brooklyn, NY
- Chicago, IL
- Houston, TX
- Los Angeles, CA
- New York, NY
- Portland, OR
- San Diego, CA
- San Francisco, CA
- Seattle, WA
- Washington, DC
- Asperger's
- Bipolar Disorder
- Chronic Pain
- Eating Disorders
- Passive Aggression
- Personality
- Goal Setting
- Positive Psychology
- Stopping Smoking
- Low Sexual Desire
- Relationships
- Child Development
- Self Tests NEW
- Therapy Center
- Diagnosis Dictionary
- Types of Therapy

It’s increasingly common for someone to be diagnosed with a condition such as ADHD or autism as an adult. A diagnosis often brings relief, but it can also come with as many questions as answers.
- Emotional Intelligence
- Gaslighting
- Affective Forecasting
- Neuroscience
Homework – Top 3 Pros and Cons
Pro/Con Arguments | Discussion Questions | Take Action | Sources | More Debates

From dioramas to book reports, from algebraic word problems to research projects, whether students should be given homework, as well as the type and amount of homework, has been debated for over a century. [ 1 ]
While we are unsure who invented homework, we do know that the word “homework” dates back to ancient Rome. Pliny the Younger asked his followers to practice their speeches at home. Memorization exercises as homework continued through the Middle Ages and Enlightenment by monks and other scholars. [ 45 ]
In the 19th century, German students of the Volksschulen or “People’s Schools” were given assignments to complete outside of the school day. This concept of homework quickly spread across Europe and was brought to the United States by Horace Mann , who encountered the idea in Prussia. [ 45 ]
In the early 1900s, progressive education theorists, championed by the magazine Ladies’ Home Journal , decried homework’s negative impact on children’s physical and mental health, leading California to ban homework for students under 15 from 1901 until 1917. In the 1930s, homework was portrayed as child labor, which was newly illegal, but the prevailing argument was that kids needed time to do household chores. [ 1 ] [ 2 ] [ 45 ] [ 46 ]
Public opinion swayed again in favor of homework in the 1950s due to concerns about keeping up with the Soviet Union’s technological advances during the Cold War . And, in 1986, the US government included homework as an educational quality boosting tool. [ 3 ] [ 45 ]
A 2014 study found kindergarteners to fifth graders averaged 2.9 hours of homework per week, sixth to eighth graders 3.2 hours per teacher, and ninth to twelfth graders 3.5 hours per teacher. A 2014-2019 study found that teens spent about an hour a day on homework. [ 4 ] [ 44 ]
Beginning in 2020, the COVID-19 pandemic complicated the very idea of homework as students were schooling remotely and many were doing all school work from home. Washington Post journalist Valerie Strauss asked, “Does homework work when kids are learning all day at home?” While students were mostly back in school buildings in fall 2021, the question remains of how effective homework is as an educational tool. [ 47 ]
Is Homework Beneficial?
Pro 1 Homework improves student achievement. Studies have shown that homework improved student achievement in terms of improved grades, test results, and the likelihood to attend college. Research published in the High School Journal indicated that students who spent between 31 and 90 minutes each day on homework “scored about 40 points higher on the SAT-Mathematics subtest than their peers, who reported spending no time on homework each day, on average.” [ 6 ] Students in classes that were assigned homework outperformed 69% of students who didn’t have homework on both standardized tests and grades. A majority of studies on homework’s impact – 64% in one meta-study and 72% in another – showed that take-home assignments were effective at improving academic achievement. [ 7 ] [ 8 ] Research by the Institute for the Study of Labor (IZA) concluded that increased homework led to better GPAs and higher probability of college attendance for high school boys. In fact, boys who attended college did more than three hours of additional homework per week in high school. [ 10 ] Read More
Pro 2 Homework helps to reinforce classroom learning, while developing good study habits and life skills. Students typically retain only 50% of the information teachers provide in class, and they need to apply that information in order to truly learn it. Abby Freireich and Brian Platzer, co-founders of Teachers Who Tutor NYC, explained, “at-home assignments help students learn the material taught in class. Students require independent practice to internalize new concepts… [And] these assignments can provide valuable data for teachers about how well students understand the curriculum.” [ 11 ] [ 49 ] Elementary school students who were taught “strategies to organize and complete homework,” such as prioritizing homework activities, collecting study materials, note-taking, and following directions, showed increased grades and more positive comments on report cards. [ 17 ] Research by the City University of New York noted that “students who engage in self-regulatory processes while completing homework,” such as goal-setting, time management, and remaining focused, “are generally more motivated and are higher achievers than those who do not use these processes.” [ 18 ] Homework also helps students develop key skills that they’ll use throughout their lives: accountability, autonomy, discipline, time management, self-direction, critical thinking, and independent problem-solving. Freireich and Platzer noted that “homework helps students acquire the skills needed to plan, organize, and complete their work.” [ 12 ] [ 13 ] [ 14 ] [ 15 ] [ 49 ] Read More
Pro 3 Homework allows parents to be involved with children’s learning. Thanks to take-home assignments, parents are able to track what their children are learning at school as well as their academic strengths and weaknesses. [ 12 ] Data from a nationwide sample of elementary school students show that parental involvement in homework can improve class performance, especially among economically disadvantaged African-American and Hispanic students. [ 20 ] Research from Johns Hopkins University found that an interactive homework process known as TIPS (Teachers Involve Parents in Schoolwork) improves student achievement: “Students in the TIPS group earned significantly higher report card grades after 18 weeks (1 TIPS assignment per week) than did non-TIPS students.” [ 21 ] Homework can also help clue parents in to the existence of any learning disabilities their children may have, allowing them to get help and adjust learning strategies as needed. Duke University Professor Harris Cooper noted, “Two parents once told me they refused to believe their child had a learning disability until homework revealed it to them.” [ 12 ] Read More
Con 1 Too much homework can be harmful. A poll of California high school students found that 59% thought they had too much homework. 82% of respondents said that they were “often or always stressed by schoolwork.” High-achieving high school students said too much homework leads to sleep deprivation and other health problems such as headaches, exhaustion, weight loss, and stomach problems. [ 24 ] [ 28 ] [ 29 ] Alfie Kohn, an education and parenting expert, said, “Kids should have a chance to just be kids… it’s absurd to insist that children must be engaged in constructive activities right up until their heads hit the pillow.” [ 27 ] Emmy Kang, a mental health counselor, explained, “More than half of students say that homework is their primary source of stress, and we know what stress can do on our bodies.” [ 48 ] Excessive homework can also lead to cheating: 90% of middle school students and 67% of high school students admit to copying someone else’s homework, and 43% of college students engaged in “unauthorized collaboration” on out-of-class assignments. Even parents take shortcuts on homework: 43% of those surveyed admitted to having completed a child’s assignment for them. [ 30 ] [ 31 ] [ 32 ] Read More
Con 2 Homework exacerbates the digital divide or homework gap. Kiara Taylor, financial expert, defined the digital divide as “the gap between demographics and regions that have access to modern information and communications technology and those that don’t. Though the term now encompasses the technical and financial ability to utilize available technology—along with access (or a lack of access) to the Internet—the gap it refers to is constantly shifting with the development of technology.” For students, this is often called the homework gap. [ 50 ] [ 51 ] 30% (about 15 to 16 million) public school students either did not have an adequate internet connection or an appropriate device, or both, for distance learning. Completing homework for these students is more complicated (having to find a safe place with an internet connection, or borrowing a laptop, for example) or impossible. [ 51 ] A Hispanic Heritage Foundation study found that 96.5% of students across the country needed to use the internet for homework, and nearly half reported they were sometimes unable to complete their homework due to lack of access to the internet or a computer, which often resulted in lower grades. [ 37 ] [ 38 ] One study concluded that homework increases social inequality because it “potentially serves as a mechanism to further advantage those students who already experience some privilege in the school system while further disadvantaging those who may already be in a marginalized position.” [ 39 ] Read More
Con 3 Homework does not help younger students, and may not help high school students. We’ve known for a while that homework does not help elementary students. A 2006 study found that “homework had no association with achievement gains” when measured by standardized tests results or grades. [ 7 ] Fourth grade students who did no homework got roughly the same score on the National Assessment of Educational Progress (NAEP) math exam as those who did 30 minutes of homework a night. Students who did 45 minutes or more of homework a night actually did worse. [ 41 ] Temple University professor Kathryn Hirsh-Pasek said that homework is not the most effective tool for young learners to apply new information: “They’re learning way more important skills when they’re not doing their homework.” [ 42 ] In fact, homework may not be helpful at the high school level either. Alfie Kohn, author of The Homework Myth, stated, “I interviewed high school teachers who completely stopped giving homework and there was no downside, it was all upside.” He explains, “just because the same kids who get more homework do a little better on tests, doesn’t mean the homework made that happen.” [ 52 ] Read More
Discussion Questions
1. Is homework beneficial? Consider the study data, your personal experience, and other types of information. Explain your answer(s).
2. If homework were banned, what other educational strategies would help students learn classroom material? Explain your answer(s).
3. How has homework been helpful to you personally? How has homework been unhelpful to you personally? Make carefully considered lists for both sides.
Take Action
1. Examine an argument in favor of quality homework assignments from Janine Bempechat.
2. Explore Oxford Learning’s infographic on the effects of homework on students.
3. Consider Joseph Lathan’s argument that homework promotes inequality .
4. Consider how you felt about the issue before reading this article. After reading the pros and cons on this topic, has your thinking changed? If so, how? List two to three ways. If your thoughts have not changed, list two to three ways your better understanding of the “other side of the issue” now helps you better argue your position.
5. Push for the position and policies you support by writing US national senators and representatives .
| 1. | Tom Loveless, “Homework in America: Part II of the 2014 Brown Center Report of American Education,” brookings.edu, Mar. 18, 2014 | |
| 2. | Edward Bok, “A National Crime at the Feet of American Parents,” , Jan. 1900 | |
| 3. | Tim Walker, “The Great Homework Debate: What’s Getting Lost in the Hype,” neatoday.org, Sep. 23, 2015 | |
| 4. | University of Phoenix College of Education, “Homework Anxiety: Survey Reveals How Much Homework K-12 Students Are Assigned and Why Teachers Deem It Beneficial,” phoenix.edu, Feb. 24, 2014 | |
| 5. | Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD), “PISA in Focus No. 46: Does Homework Perpetuate Inequities in Education?,” oecd.org, Dec. 2014 | |
| 6. | Adam V. Maltese, Robert H. Tai, and Xitao Fan, “When is Homework Worth the Time?: Evaluating the Association between Homework and Achievement in High School Science and Math,” , 2012 | |
| 7. | Harris Cooper, Jorgianne Civey Robinson, and Erika A. Patall, “Does Homework Improve Academic Achievement? A Synthesis of Researcher, 1987-2003,” , 2006 | |
| 8. | Gökhan Bas, Cihad Sentürk, and Fatih Mehmet Cigerci, “Homework and Academic Achievement: A Meta-Analytic Review of Research,” , 2017 | |
| 9. | Huiyong Fan, Jianzhong Xu, Zhihui Cai, Jinbo He, and Xitao Fan, “Homework and Students’ Achievement in Math and Science: A 30-Year Meta-Analysis, 1986-2015,” , 2017 | |
| 10. | Charlene Marie Kalenkoski and Sabrina Wulff Pabilonia, “Does High School Homework Increase Academic Achievement?,” iza.og, Apr. 2014 | |
| 11. | Ron Kurtus, “Purpose of Homework,” school-for-champions.com, July 8, 2012 | |
| 12. | Harris Cooper, “Yes, Teachers Should Give Homework – The Benefits Are Many,” newsobserver.com, Sep. 2, 2016 | |
| 13. | Tammi A. Minke, “Types of Homework and Their Effect on Student Achievement,” repository.stcloudstate.edu, 2017 | |
| 14. | LakkshyaEducation.com, “How Does Homework Help Students: Suggestions From Experts,” LakkshyaEducation.com (accessed Aug. 29, 2018) | |
| 15. | University of Montreal, “Do Kids Benefit from Homework?,” teaching.monster.com (accessed Aug. 30, 2018) | |
| 16. | Glenda Faye Pryor-Johnson, “Why Homework Is Actually Good for Kids,” memphisparent.com, Feb. 1, 2012 | |
| 17. | Joan M. Shepard, “Developing Responsibility for Completing and Handing in Daily Homework Assignments for Students in Grades Three, Four, and Five,” eric.ed.gov, 1999 | |
| 18. | Darshanand Ramdass and Barry J. Zimmerman, “Developing Self-Regulation Skills: The Important Role of Homework,” , 2011 | |
| 19. | US Department of Education, “Let’s Do Homework!,” ed.gov (accessed Aug. 29, 2018) | |
| 20. | Loretta Waldman, “Sociologist Upends Notions about Parental Help with Homework,” phys.org, Apr. 12, 2014 | |
| 21. | Frances L. Van Voorhis, “Reflecting on the Homework Ritual: Assignments and Designs,” , June 2010 | |
| 22. | Roel J. F. J. Aries and Sofie J. Cabus, “Parental Homework Involvement Improves Test Scores? A Review of the Literature,” , June 2015 | |
| 23. | Jamie Ballard, “40% of People Say Elementary School Students Have Too Much Homework,” yougov.com, July 31, 2018 | |
| 24. | Stanford University, “Stanford Survey of Adolescent School Experiences Report: Mira Costa High School, Winter 2017,” stanford.edu, 2017 | |
| 25. | Cathy Vatterott, “Rethinking Homework: Best Practices That Support Diverse Needs,” ascd.org, 2009 | |
| 26. | End the Race, “Homework: You Can Make a Difference,” racetonowhere.com (accessed Aug. 24, 2018) | |
| 27. | Elissa Strauss, “Opinion: Your Kid Is Right, Homework Is Pointless. Here’s What You Should Do Instead.,” cnn.com, Jan. 28, 2020 | |
| 28. | Jeanne Fratello, “Survey: Homework Is Biggest Source of Stress for Mira Costa Students,” digmb.com, Dec. 15, 2017 | |
| 29. | Clifton B. Parker, “Stanford Research Shows Pitfalls of Homework,” stanford.edu, Mar. 10, 2014 | |
| 30. | AdCouncil, “Cheating Is a Personal Foul: Academic Cheating Background,” glass-castle.com (accessed Aug. 16, 2018) | |
| 31. | Jeffrey R. Young, “High-Tech Cheating Abounds, and Professors Bear Some Blame,” chronicle.com, Mar. 28, 2010 | |
| 32. | Robin McClure, “Do You Do Your Child’s Homework?,” verywellfamily.com, Mar. 14, 2018 | |
| 33. | Robert M. Pressman, David B. Sugarman, Melissa L. Nemon, Jennifer, Desjarlais, Judith A. Owens, and Allison Schettini-Evans, “Homework and Family Stress: With Consideration of Parents’ Self Confidence, Educational Level, and Cultural Background,” , 2015 | |
| 34. | Heather Koball and Yang Jiang, “Basic Facts about Low-Income Children,” nccp.org, Jan. 2018 | |
| 35. | Meagan McGovern, “Homework Is for Rich Kids,” huffingtonpost.com, Sep. 2, 2016 | |
| 36. | H. Richard Milner IV, “Not All Students Have Access to Homework Help,” nytimes.com, Nov. 13, 2014 | |
| 37. | Claire McLaughlin, “The Homework Gap: The ‘Cruelest Part of the Digital Divide’,” neatoday.org, Apr. 20, 2016 | |
| 38. | Doug Levin, “This Evening’s Homework Requires the Use of the Internet,” edtechstrategies.com, May 1, 2015 | |
| 39. | Amy Lutz and Lakshmi Jayaram, “Getting the Homework Done: Social Class and Parents’ Relationship to Homework,” , June 2015 | |
| 40. | Sandra L. Hofferth and John F. Sandberg, “How American Children Spend Their Time,” psc.isr.umich.edu, Apr. 17, 2000 | |
| 41. | Alfie Kohn, “Does Homework Improve Learning?,” alfiekohn.org, 2006 | |
| 42. | Patrick A. Coleman, “Elementary School Homework Probably Isn’t Good for Kids,” fatherly.com, Feb. 8, 2018 | |
| 43. | Valerie Strauss, “Why This Superintendent Is Banning Homework – and Asking Kids to Read Instead,” washingtonpost.com, July 17, 2017 | |
| 44. | Pew Research Center, “The Way U.S. Teens Spend Their Time Is Changing, but Differences between Boys and Girls Persist,” pewresearch.org, Feb. 20, 2019 | |
| 45. | ThroughEducation, “The History of Homework: Why Was It Invented and Who Was behind It?,” , Feb. 14, 2020 | |
| 46. | History, “Why Homework Was Banned,” (accessed Feb. 24, 2022) | |
| 47. | Valerie Strauss, “Does Homework Work When Kids Are Learning All Day at Home?,” , Sep. 2, 2020 | |
| 48. | Sara M Moniuszko, “Is It Time to Get Rid of Homework? Mental Health Experts Weigh In,” , Aug. 17, 2021 | |
| 49. | Abby Freireich and Brian Platzer, “The Worsening Homework Problem,” , Apr. 13, 2021 | |
| 50. | Kiara Taylor, “Digital Divide,” , Feb. 12, 2022 | |
| 51. | Marguerite Reardon, “The Digital Divide Has Left Millions of School Kids Behind,” , May 5, 2021 | |
| 52. | Rachel Paula Abrahamson, “Why More and More Teachers Are Joining the Anti-Homework Movement,” , Sep. 10, 2021 |
More School Debate Topics
Should K-12 Students Dissect Animals in Science Classrooms? – Proponents say dissecting real animals is a better learning experience. Opponents say the practice is bad for the environment.
Should Students Have to Wear School Uniforms? – Proponents say uniforms may increase student safety. Opponents say uniforms restrict expression.
Should Corporal Punishment Be Used in K-12 Schools? – Proponents say corporal punishment is an appropriate discipline. Opponents say it inflicts long-lasting physical and mental harm on students.
ProCon/Encyclopaedia Britannica, Inc. 325 N. LaSalle Street, Suite 200 Chicago, Illinois 60654 USA
Natalie Leppard Managing Editor [email protected]
© 2023 Encyclopaedia Britannica, Inc. All rights reserved
- Social Media
- Death Penalty
- School Uniforms
- Video Games
- Animal Testing
- Gun Control
- Banned Books
- Teachers’ Corner
Cite This Page
ProCon.org is the institutional or organization author for all ProCon.org pages. Proper citation depends on your preferred or required style manual. Below are the proper citations for this page according to four style manuals (in alphabetical order): the Modern Language Association Style Manual (MLA), the Chicago Manual of Style (Chicago), the Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association (APA), and Kate Turabian's A Manual for Writers of Term Papers, Theses, and Dissertations (Turabian). Here are the proper bibliographic citations for this page according to four style manuals (in alphabetical order):
[Editor's Note: The APA citation style requires double spacing within entries.]
[Editor’s Note: The MLA citation style requires double spacing within entries.]
Along with Stanford news and stories, show me:
- Student information
- Faculty/Staff information
We want to provide announcements, events, leadership messages and resources that are relevant to you. Your selection is stored in a browser cookie which you can remove at any time using “Clear all personalization” below.

Education scholar Denise Pope has found that too much homework has negative effects on student well-being and behavioral engagement. (Image credit: L.A. Cicero)
A Stanford researcher found that too much homework can negatively affect kids, especially their lives away from school, where family, friends and activities matter.
“Our findings on the effects of homework challenge the traditional assumption that homework is inherently good,” wrote Denise Pope , a senior lecturer at the Stanford Graduate School of Education and a co-author of a study published in the Journal of Experimental Education .
The researchers used survey data to examine perceptions about homework, student well-being and behavioral engagement in a sample of 4,317 students from 10 high-performing high schools in upper-middle-class California communities. Along with the survey data, Pope and her colleagues used open-ended answers to explore the students’ views on homework.
Median household income exceeded $90,000 in these communities, and 93 percent of the students went on to college, either two-year or four-year.
Students in these schools average about 3.1 hours of homework each night.
“The findings address how current homework practices in privileged, high-performing schools sustain students’ advantage in competitive climates yet hinder learning, full engagement and well-being,” Pope wrote.
Pope and her colleagues found that too much homework can diminish its effectiveness and even be counterproductive. They cite prior research indicating that homework benefits plateau at about two hours per night, and that 90 minutes to two and a half hours is optimal for high school.
Their study found that too much homework is associated with:
* Greater stress: 56 percent of the students considered homework a primary source of stress, according to the survey data. Forty-three percent viewed tests as a primary stressor, while 33 percent put the pressure to get good grades in that category. Less than 1 percent of the students said homework was not a stressor.
* Reductions in health: In their open-ended answers, many students said their homework load led to sleep deprivation and other health problems. The researchers asked students whether they experienced health issues such as headaches, exhaustion, sleep deprivation, weight loss and stomach problems.
* Less time for friends, family and extracurricular pursuits: Both the survey data and student responses indicate that spending too much time on homework meant that students were “not meeting their developmental needs or cultivating other critical life skills,” according to the researchers. Students were more likely to drop activities, not see friends or family, and not pursue hobbies they enjoy.
A balancing act
The results offer empirical evidence that many students struggle to find balance between homework, extracurricular activities and social time, the researchers said. Many students felt forced or obligated to choose homework over developing other talents or skills.
Also, there was no relationship between the time spent on homework and how much the student enjoyed it. The research quoted students as saying they often do homework they see as “pointless” or “mindless” in order to keep their grades up.
“This kind of busy work, by its very nature, discourages learning and instead promotes doing homework simply to get points,” Pope said.
She said the research calls into question the value of assigning large amounts of homework in high-performing schools. Homework should not be simply assigned as a routine practice, she said.
“Rather, any homework assigned should have a purpose and benefit, and it should be designed to cultivate learning and development,” wrote Pope.
High-performing paradox
In places where students attend high-performing schools, too much homework can reduce their time to foster skills in the area of personal responsibility, the researchers concluded. “Young people are spending more time alone,” they wrote, “which means less time for family and fewer opportunities to engage in their communities.”
Student perspectives
The researchers say that while their open-ended or “self-reporting” methodology to gauge student concerns about homework may have limitations – some might regard it as an opportunity for “typical adolescent complaining” – it was important to learn firsthand what the students believe.
The paper was co-authored by Mollie Galloway from Lewis and Clark College and Jerusha Conner from Villanova University.
Media Contacts
Denise Pope, Stanford Graduate School of Education: (650) 725-7412, [email protected] Clifton B. Parker, Stanford News Service: (650) 725-0224, [email protected]
You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser to improve your experience.

Health & Nursing
Courses and certificates.
- Bachelor's Degrees
- View all Business Bachelor's Degrees
- Business Management – B.S. Business Administration
- Healthcare Administration – B.S.
- Human Resource Management – B.S. Business Administration
- Information Technology Management – B.S. Business Administration
- Marketing – B.S. Business Administration
- Accounting – B.S. Business Administration
- Finance – B.S.
- Supply Chain and Operations Management – B.S.
- Communications – B.S.
- User Experience Design – B.S.
- Accelerated Information Technology Bachelor's and Master's Degree (from the School of Technology)
- Health Information Management – B.S. (from the Leavitt School of Health)
- View all Business Degrees
Master's Degrees
- View all Business Master's Degrees
- Master of Business Administration (MBA)
- MBA Information Technology Management
- MBA Healthcare Management
- Management and Leadership – M.S.
- Accounting – M.S.
- Marketing – M.S.
- Human Resource Management – M.S.
- Master of Healthcare Administration (from the Leavitt School of Health)
- Data Analytics – M.S. (from the School of Technology)
- Information Technology Management – M.S. (from the School of Technology)
- Education Technology and Instructional Design – M.Ed. (from the School of Education)
Certificates
- Supply Chain
- Accounting Fundamentals
- Digital Marketing and E-Commerce
Bachelor's Preparing For Licensure
- View all Education Bachelor's Degrees
- Elementary Education – B.A.
- Special Education and Elementary Education (Dual Licensure) – B.A.
- Special Education (Mild-to-Moderate) – B.A.
- Mathematics Education (Middle Grades) – B.S.
- Mathematics Education (Secondary)– B.S.
- Science Education (Middle Grades) – B.S.
- Science Education (Secondary Chemistry) – B.S.
- Science Education (Secondary Physics) – B.S.
- Science Education (Secondary Biological Sciences) – B.S.
- Science Education (Secondary Earth Science)– B.S.
- View all Education Degrees
Bachelor of Arts in Education Degrees
- Educational Studies – B.A.
Master of Science in Education Degrees
- View all Education Master's Degrees
- Curriculum and Instruction – M.S.
- Educational Leadership – M.S.
- Education Technology and Instructional Design – M.Ed.
Master's Preparing for Licensure
- Teaching, Elementary Education – M.A.
- Teaching, English Education (Secondary) – M.A.
- Teaching, Mathematics Education (Middle Grades) – M.A.
- Teaching, Mathematics Education (Secondary) – M.A.
- Teaching, Science Education (Secondary) – M.A.
- Teaching, Special Education (K-12) – M.A.
Licensure Information
- State Teaching Licensure Information
Master's Degrees for Teachers
- Mathematics Education (K-6) – M.A.
- Mathematics Education (Middle Grade) – M.A.
- Mathematics Education (Secondary) – M.A.
- English Language Learning (PreK-12) – M.A.
- Endorsement Preparation Program, English Language Learning (PreK-12)
- Science Education (Middle Grades) – M.A.
- Science Education (Secondary Chemistry) – M.A.
- Science Education (Secondary Physics) – M.A.
- Science Education (Secondary Biological Sciences) – M.A.
- Science Education (Secondary Earth Science)– M.A.
- View all Technology Bachelor's Degrees
- Cloud Computing – B.S.
- Computer Science – B.S.
- Cybersecurity and Information Assurance – B.S.
- Data Analytics – B.S.
- Information Technology – B.S.
- Network Engineering and Security – B.S.
- Software Engineering – B.S.
- Accelerated Information Technology Bachelor's and Master's Degree
- Information Technology Management – B.S. Business Administration (from the School of Business)
- User Experience Design – B.S. (from the School of Business)
- View all Technology Master's Degrees
- Cybersecurity and Information Assurance – M.S.
- Data Analytics – M.S.
- Information Technology Management – M.S.
- MBA Information Technology Management (from the School of Business)
- Full Stack Engineering
- Web Application Deployment and Support
- Front End Web Development
- Back End Web Development
3rd Party Certifications
- IT Certifications Included in WGU Degrees
- View all Technology Degrees
- View all Health & Nursing Bachelor's Degrees
- Nursing (RN-to-BSN online) – B.S.
- Nursing (Prelicensure) – B.S. (Available in select states)
- Health Information Management – B.S.
- Health and Human Services – B.S.
- Psychology – B.S.
- Health Science – B.S.
- Public Health – B.S.
- Healthcare Administration – B.S. (from the School of Business)
- View all Nursing Post-Master's Certificates
- Nursing Education—Post-Master's Certificate
- Nursing Leadership and Management—Post-Master's Certificate
- Family Nurse Practitioner—Post-Master's Certificate
- Psychiatric Mental Health Nurse Practitioner —Post-Master's Certificate
- View all Health & Nursing Degrees
- View all Nursing & Health Master's Degrees
- Nursing – Education (BSN-to-MSN Program) – M.S.
- Nursing – Leadership and Management (BSN-to-MSN Program) – M.S.
- Nursing – Nursing Informatics (BSN-to-MSN Program) – M.S.
- Nursing – Family Nurse Practitioner (BSN-to-MSN Program) – M.S. (Available in select states)
- Nursing – Psychiatric Mental Health Nurse Practitioner (BSN-to-MSN Program) – M.S. (Available in select states)
- Nursing – Education (RN-to-MSN Program) – M.S.
- Nursing – Leadership and Management (RN-to-MSN Program) – M.S.
- Nursing – Nursing Informatics (RN-to-MSN Program) – M.S.
- Master of Healthcare Administration
- Master of Public Health
- MBA Healthcare Management (from the School of Business)
- Business Leadership (with the School of Business)
- Supply Chain (with the School of Business)
- Accounting Fundamentals (with the School of Business)
- Digital Marketing and E-Commerce (with the School of Business)
- Back End Web Development (with the School of Technology)
- Front End Web Development (with the School of Technology)
- Web Application Deployment and Support (with the School of Technology)
- Full Stack Engineering (with the School of Technology)
- Single Courses
- Course Bundles
Apply for Admission
Admission requirements.
- New Students
- WGU Returning Graduates
- WGU Readmission
- Enrollment Checklist
- Accessibility
- Accommodation Request
- School of Education Admission Requirements
- School of Business Admission Requirements
- School of Technology Admission Requirements
- Leavitt School of Health Admission Requirements
Additional Requirements
- Computer Requirements
- No Standardized Testing
- Clinical and Student Teaching Information
Transferring
- FAQs about Transferring
- Transfer to WGU
- Transferrable Certifications
- Request WGU Transcripts
- International Transfer Credit
- Tuition and Fees
- Financial Aid
- Scholarships
Other Ways to Pay for School
- Tuition—School of Business
- Tuition—School of Education
- Tuition—School of Technology
- Tuition—Leavitt School of Health
- Your Financial Obligations
- Tuition Comparison
- Applying for Financial Aid
- State Grants
- Consumer Information Guide
- Responsible Borrowing Initiative
- Higher Education Relief Fund
FAFSA Support
- Net Price Calculator
- FAFSA Simplification
- See All Scholarships
- Military Scholarships
- State Scholarships
- Scholarship FAQs
Payment Options
- Payment Plans
- Corporate Reimbursement
- Current Student Hardship Assistance
- Military Tuition Assistance
WGU Experience
- How You'll Learn
- Scheduling/Assessments
- Accreditation
- Student Support/Faculty
- Military Students
- Part-Time Options
- Virtual Military Education Resource Center
- Student Outcomes
- Return on Investment
- Students and Gradutes
- Career Growth
- Student Resources
- Communities
- Testimonials
- Career Guides
- Skills Guides
- Online Degrees
- All Degrees
- Explore Your Options
Admissions & Transfers
- Admissions Overview
Tuition & Financial Aid
Student Success
- Prospective Students
- Current Students
- Military and Veterans
- Commencement
- Careers at WGU
- Advancement & Giving
- Partnering with WGU
Should Students Have Homework?
- Classroom Strategies
- See More Tags

By Suzanne Capek Tingley, Veteran Educator, M.A. Degree
It used to be that students were the only ones complaining about the practice of assigning homework. For years, teachers and parents thought that homework was a necessary tool when educating children. But studies about the effectiveness of homework have been conflicting and inconclusive, leading some adults to argue that homework should become a thing of the past.
What Research Says about Homework
According to Duke professor Harris Cooper, it's important that students have homework. His meta-analysis of homework studies showed a correlation between completing homework and academic success, at least in older grades. He recommends following a "10 minute rule" : students should receive 10 minutes of homework per day in first grade, and 10 additional minutes each subsequent year, so that by twelfth grade they are completing 120 minutes of homework daily.
But his analysis didn't prove that students did better because they did homework; it simply showed a correlation . This could simply mean that kids who do homework are more committed to doing well in school. Cooper also found that some research showed that homework caused physical and emotional stress, and created negative attitudes about learning. He suggested that more research needed to be done on homework's effect on kids.
Some researchers say that the question isn't whether kids should have homework. It's more about what kind of homework students have and how much. To be effective, homework has to meet students' needs. For example, some middle school teachers have found success with online math homework that's adapted to each student's level of understanding. But when middle school students were assigned more than an hour and a half of homework, their math and science test scores went down .
Researchers at Indiana University discovered that math and science homework may improve standardized test grades, but they found no difference in course grades between students who did homework and those who didn't. These researchers theorize that homework doesn't result in more content mastery, but in greater familiarity with the kinds of questions that appear on standardized tests. According to Professor Adam Maltese, one of the study's authors, "Our results hint that maybe homework is not being used as well as it could be."
So while many teachers and parents support daily homework, it's hard to find strong evidence that the long-held practice produces positive results.
Problems with Homework
In an article in Education Week Teacher , teacher Samantha Hulsman said she's frequently heard parents complain that a 30-minute homework assignment turns into a three-hour battle with their kids. Now, she's facing the same problem with her own kids, which has her rethinking her former beliefs about homework. "I think parents expect their children to have homework nightly, and teachers assign daily homework because it's what we've always done," she explained. Today, Hulsman said, it's more important to know how to collaborate and solve problems than it is to know specific facts.
Child psychologist Kenneth Barish wrote in Psychology Today that battles over homework rarely result in a child's improvement in school . Children who don't do their homework are not lazy, he said, but they may be frustrated, discouraged, or anxious. And for kids with learning disabilities, homework is like "running with a sprained ankle. It's doable, but painful."
Barish suggests that parents and kids have a "homework plan" that limits the time spent on homework. The plan should include turning off all devices—not just the student's, but those belonging to all family members.
One of the best-known critics of homework, Alfie Kohn , says that some people wrongly believe "kids are like vending machines—put in an assignment, get out learning." Kohn points to the lack of evidence that homework is an effective learning tool; in fact, he calls it "the greatest single extinguisher of children's curiosity that we have yet invented."
Homework Bans
Last year, the public schools in Marion County, Florida, decided on a no-homework policy for all of their elementary students . Instead, kids read nightly for 20 minutes. Superintendent Heidi Maier said the decision was based on Cooper's research showing that elementary students gain little from homework, but a lot from reading.
Orchard Elementary School in South Burlington, Vermont, followed the same path, substituting reading for homework. The homework policy has four parts : read nightly, go outside and play, have dinner with your family, and get a good night's sleep. Principal Mark Trifilio says that his staff and parents support the idea.
But while many elementary schools are considering no-homework policies, middle schools and high schools have been reluctant to abandon homework. Schools say parents support homework and teachers know it can be helpful when it is specific and follows certain guidelines. For example, practicing solving word problems can be helpful, but there's no reason to assign 50 problems when 10 will do. Recognizing that not all kids have the time, space, and home support to do homework is important, so it shouldn't be counted as part of a student's grade.
So Should Students Have Homework?
Should you ban homework in your classroom? If you teach lower grades, it's possible. If you teach middle or high school, probably not. But all teachers should think carefully about their homework policies. By limiting the amount of homework and improving the quality of assignments, you can improve learning outcomes for your students.
Ready to Start Your Journey?
HEALTH & NURSING
Recommended Articles
Take a look at other articles from WGU. Our articles feature information on a wide variety of subjects, written with the help of subject matter experts and researchers who are well-versed in their industries. This allows us to provide articles with interesting, relevant, and accurate information.
{{item.date}}
{{item.preTitleTag}}
{{item.title}}
The university, for students.
- Student Portal
- Alumni Services
Most Visited Links
- Business Programs
- Student Experience
- Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion
- Student Communities
7 Research-Based Reasons Why Students Should Not Have Homework: Academic Insights, Opposing Perspectives & Alternatives
Checking 13yo’s math homework & I have just one question. I can catch mistakes & help her correct. But what do kids do when their parent isn’t an Algebra teacher? Answer: They get frustrated. Quit. Get a bad grade. Think they aren’t good at math. How is homework fair??? — Jay Wamsted (@JayWamsted) March 24, 2022
Insights from Teachers and Education Industry Experts: Diverse Perspectives on Homework
Check out this video featuring Courtney White, a high school language arts teacher who gained widespread attention for her explanation of why she chooses not to assign homework.
“I teach 1st grade. I had parents ask for homework. I explained that I don’t give homework. Home time is family time. Time to play, cook, explore and spend time together. I do send books home, but there is no requirement or checklist for reading them. Read them, enjoy them, and return them when your child is ready for more. I explained that as a parent myself, I know they are busy—and what a waste of energy it is to sit and force their kids to do work at home—when they could use that time to form relationships and build a loving home. Something kids need more than a few math problems a week.” — Colleen S. , 1st grade teacher
“The lasting educational value of homework at that age is not proven. A kid says the times tables [at school] because he studied the times tables last night. But over a long period of time, a kid who is drilled on the times tables at school, rather than as homework, will also memorize their times tables. We are worried about young children and their social emotional learning. And that has to do with physical activity, it has to do with playing with peers, it has to do with family time. All of those are very important and can be removed by too much homework.” — David Bloomfield , education professor at Brooklyn College and the City University of New York graduate center
“Homework in primary school has an effect of around zero. In high school it’s larger. (…) Which is why we need to get it right. Not why we need to get rid of it. It’s one of those lower hanging fruit that we should be looking in our primary schools to say, ‘Is it really making a difference?’” — John Hattie , professor
”Many kids are working as many hours as their overscheduled parents and it is taking a toll – psychologically and in many other ways too. We see kids getting up hours before school starts just to get their homework done from the night before… While homework may give kids one more responsibility, it ignores the fact that kids do not need to grow up and become adults at ages 10 or 12. With schools cutting recess time or eliminating playgrounds, kids absorb every single stress there is, only on an even higher level. Their brains and bodies need time to be curious, have fun, be creative and just be a kid.” — Pat Wayman, teacher and CEO of HowtoLearn.com
7 Reasons Why Students Should Not Have Homework
1. elevated stress and health consequences.
By addressing the issue of homework-related stress and health consequences, we can take a significant step toward creating a more nurturing and effective educational environment. This environment would not only prioritize academic achievement but also the overall well-being and happiness of students, preparing them for a balanced and healthy life both inside and outside the classroom.
2. Inequitable Impact and Socioeconomic Disparities
Moreover, the approach to homework varies significantly across different types of schools. While some rigorous private and preparatory schools in both marginalized and affluent communities assign extreme levels of homework, many progressive schools focusing on holistic learning and self-actualization opt for no homework, yet achieve similar levels of college and career success. This contrast raises questions about the efficacy and necessity of heavy homework loads in achieving educational outcomes.
3. Negative Impact on Family Dynamics
The issue is not confined to specific demographics but is a widespread concern. Samantha Hulsman, a teacher featured in Education Week Teacher , shared her personal experience with the toll that homework can take on family time. She observed that a seemingly simple 30-minute assignment could escalate into a three-hour ordeal, causing stress and strife between parents and children. Hulsman’s insights challenge the traditional mindset about homework, highlighting a shift towards the need for skills such as collaboration and problem-solving over rote memorization of facts.
4. Consumption of Free Time
Authors Sara Bennett and Nancy Kalish , in their book “The Case Against Homework,” offer an insightful window into the lives of families grappling with the demands of excessive homework. They share stories from numerous interviews conducted in the mid-2000s, highlighting the universal struggle faced by families across different demographics. A poignant account from a parent in Menlo Park, California, describes nightly sessions extending until 11 p.m., filled with stress and frustration, leading to a soured attitude towards school in both the child and the parent. This narrative is not isolated, as about one-third of the families interviewed expressed feeling crushed by the overwhelming workload.
Furthermore, the intense homework routine’s effectiveness is doubtful, as it can overwhelm students and detract from the joy of learning. Effective learning builds on prior knowledge in an engaging way, but excessive homework in a home setting may be irrelevant and uninteresting. The key challenge is balancing homework to enhance learning without overburdening students, allowing time for holistic growth and activities beyond academics. It’s crucial to reassess homework policies to support well-rounded development.
5. Challenges for Students with Learning Disabilities
Homework, a standard educational tool, poses unique challenges for students with learning disabilities, often leading to a frustrating and disheartening experience. These challenges go beyond the typical struggles faced by most students and can significantly impede their educational progress and emotional well-being.
Child psychologist Kenneth Barish’s insights in Psychology Today shed light on the complex relationship between homework and students with learning disabilities:
6. Critique of Underlying Assumptions about Learning
These findings bring to light several critical points:
The emerging consensus from these studies suggests that the traditional approach to homework needs rethinking. Rather than focusing on the quantity of assignments, educators should consider the quality and relevance of homework, ensuring it truly contributes to learning and development. This reassessment is crucial for fostering an educational environment that nurtures curiosity and a love for learning, rather than extinguishing it.
7. Issues with Homework Enforcement, Reliability, and Temptation to Cheat
In the academic realm, the enforcement of homework is a subject of ongoing debate, primarily due to its implications on student integrity and the true value of assignments. The challenges associated with homework enforcement often lead to unintended yet significant issues, such as cheating, copying, and a general undermining of educational values.
In conclusion, the challenges of homework enforcement present a complex problem that requires careful consideration. The focus should shift towards creating meaningful, manageable, and quality-driven assignments that encourage genuine learning and integrity, rather than overwhelming students and prompting counterproductive behaviors.
Addressing Opposing Views on Homework Practices
While opinions on homework policies are diverse, understanding different viewpoints is crucial. In the following sections, we will examine common arguments supporting homework assignments, along with counterarguments that offer alternative perspectives on this educational practice.
1. Improvement of Academic Performance
2. reinforcement of learning.
Homework is traditionally viewed as a tool to reinforce classroom learning, enabling students to practice and retain material. However, research suggests its effectiveness is ambiguous. In instances where homework is well-aligned with students’ abilities and classroom teachings, it can indeed be beneficial. Particularly for younger students , excessive homework can cause burnout and a loss of interest in learning, counteracting its intended purpose.
3. Development of Time Management Skills
Homework is often considered a crucial tool in helping students develop important life skills such as time management and organization. The idea is that by regularly completing assignments, students learn to allocate their time efficiently and organize their tasks effectively, skills that are invaluable in both academic and personal life.
However, the impact of homework on developing these skills is not always positive. For younger students, especially, an overwhelming amount of homework can be more of a hindrance than a help. Instead of fostering time management and organizational skills, an excessive workload often leads to stress and anxiety . These negative effects can impede the learning process and make it difficult for students to manage their time and tasks effectively, contradicting the original purpose of homework.
4. Preparation for Future Academic Challenges
Homework is often touted as a preparatory tool for future academic challenges that students will encounter in higher education and their professional lives. The argument is that by tackling homework, students build a foundation of knowledge and skills necessary for success in more advanced studies and in the workforce, fostering a sense of readiness and confidence.
5. Parental Involvement in Education
Homework often acts as a vital link connecting parents to their child’s educational journey, offering insights into the school’s curriculum and their child’s learning process. This involvement is key in fostering a supportive home environment and encouraging a collaborative relationship between parents and the school. When parents understand and engage with what their children are learning, it can significantly enhance the educational experience for the child.
Exploring Alternatives to Homework and Finding a Middle Ground
Alternatives to traditional homework, ideas for minimizing homework.
For teachers who are not ready to fully eliminate homework, these strategies offer a compromise, ensuring that homework supports rather than hinders student learning. By focusing on quality, relevance, and student engagement, educators can transform homework from a chore into a meaningful component of education that genuinely contributes to students’ academic growth and personal development. In this way, we can move towards a more balanced and student-centric approach to learning, both in and out of the classroom.
Useful Resources
Leave a comment cancel reply.
Internet Explorer is no longer supported
Please upgrade to Microsoft Edge , Google Chrome , or Firefox .
Lo sentimos, la página que usted busca no se ha podido encontrar. Puede intentar su búsqueda de nuevo o visitar la lista de temas populares.
Get this as a PDF
Enter email to download and get news and resources in your inbox.
Share this on social
Strategies to make homework go more smoothly.
Routines and incentive systems to help kids succeed
Writer: Peg Dawson, EdD, NCSP
Clinical Experts: Peg Dawson, EdD, NCSP , Karol Espejo, LCSW
Here is the best guide to helping kids do homework successfully that we’ve seen, published by the National Association of School Psychologists on their website, NASPonline.org . Our thanks to NASP for sharing it with us.
There are two key strategies parents can draw on to reduce homework hassles. The first is to establish clear routines around homework, including when and where homework gets done and setting up daily schedules for homework. The second is to build in rewards or incentives to use with children for whom “good grades” is not a sufficient reward for doing homework.
Homework Routines
Tasks are easiest to accomplish when tied to specific routines. By establishing daily routines for homework completion, you will not only make homework go more smoothly, but you will also be fostering a sense of order your child can apply to later life, including college and work.
Step 1. Find a location in the house where homework will be done. The right location will depend on your child and the culture of your family. Some children do best at a desk in their bedroom. It is a quiet location, away from the hubbub of family noise. Other children become too distracted by the things they keep in their bedroom and do better at a place removed from those distractions, like the dining room table. Some children need to work by themselves. Others need to have parents nearby to help keep them on task and to answer questions when problems arise. Ask your child where the best place is to work. Both you and your child need to discuss pros and cons of different settings to arrive at a mutually agreed upon location.
Step 2. Set up a homework center. Once you and your child have identified a location, fix it up as a home office/homework center. Make sure there is a clear workspace large enough to set out all the materials necessary for completing assignments. Outfit the homework center with the kinds of supplies your child is most likely to need, such as pencils, pens, colored markers, rulers, scissors, a dictionary and thesaurus, graph paper, construction paper, glue and cellophane tape, lined paper, a calculator, spell checker, and, depending on the age and needs of your child, a computer or laptop. If the homework center is a place that will be used for other things (such as the dining room table), then your child can keep the supplies in a portable crate or bin. If possible, the homework center should include a bulletin board that can hold a monthly calendar on which your child can keep track of longterm assignments. Allowing children some leeway in decorating the homework center can help them feel at home there, but you should be careful that it does not become too cluttered with distracting materials.
Step 3. Establish a homework time. Your child should get in the habit of doing homework at the same time every day. The time may vary depending on the individual child. Some children need a break right after school to get some exercise and have a snack. Others need to start homework while they are still in a school mode (i.e., right after school when there is still some momentum left from getting through the day). In general, it may be best to get homework done either before dinner or as early in the evening as the child can tolerate. The later it gets, the more tired the child becomes and the more slowly the homework gets done.
Step 4. Establish a daily homework schedule. In general, at least into middle school, the homework session should begin with your sitting down with your child and drawing up a homework schedule. You should review all the assignments and make sure your child understands them and has all the necessary materials. Ask your child to estimate how long it will take to complete each assignment. Then ask when each assignment will get started. If your child needs help with any assignment , then this should be determined at the beginning so that the start times can take into account parent availability. A Daily Homework Planner is included at the end of this handout and contains a place for identifying when breaks may be taken and what rewards may be earned.
Incentive Systems
Many children who are not motivated by the enjoyment of doing homework are motivated by the high grade they hope to earn as a result of doing a quality job. Thus, the grade is an incentive, motivating the child to do homework with care and in a timely manner. For children who are not motivated by grades, parents will need to look for other rewards to help them get through their nightly chores. Incentive systems fall into two categories: simple and elaborate.
Simple incentive systems. The simplest incentive system is reminding the child of a fun activity to do when homework is done. It may be a favorite television show, a chance to spend some time with a video or computer game, talking on the telephone or instant messaging, or playing a game with a parent. This system of withholding fun things until the drudgery is over is sometimes called Grandma’s Law because grandmothers often use it quite effectively (“First take out the trash, then you can have chocolate chip cookies.”). Having something to look forward to can be a powerful incentive to get the hard work done. When parents remind children of this as they sit down at their desks they may be able to spark the engine that drives the child to stick with the work until it is done.
Elaborate incentive systems. These involve more planning and more work on the part of parents but in some cases are necessary to address more significant homework problems. More complex incentives systems might include a structure for earning points that could be used to “purchase” privileges or rewards or a system that provides greater reward for accomplishing more difficult homework tasks. These systems work best when parents and children together develop them. Giving children input gives them a sense of control and ownership, making the system more likely to succeed. We have found that children are generally realistic in setting goals and deciding on rewards and penalties when they are involved in the decision-making process.
Building in breaks. These are good for the child who cannot quite make it to the end without a small reward en route. When creating the daily homework schedule, it may be useful with these children to identify when they will take their breaks. Some children prefer to take breaks at specific time intervals (every 15 minutes), while others do better when the breaks occur after they finish an activity. If you use this approach, you should discuss with your child how long the breaks will last and what will be done during the breaks (get a snack, call a friend, play one level on a video game). The Daily Homework Planner includes sections where breaks and end-of-homework rewards can be identified.
Building in choice. This can be an effective strategy for parents to use with children who resist homework. Choice can be incorporated into both the order in which the child agrees to complete assignments and the schedule they will follow to get the work done. Building in choice not only helps motivate children but can also reduce power struggles between parents and children.
Developing Incentive Systems
Step 1. Describe the problem behaviors. Parents and children decide which behaviors are causing problems at homework time. For some children putting homework off to the last minute is the problem; for others, it is forgetting materials or neglecting to write down assignments. Still others rush through their work and make careless mistakes, while others dawdle over assignments, taking hours to complete what should take only a few minutes. It is important to be as specific as possible when describing the problem behaviors. The problem behavior should be described as behaviors that can be seen or heard; for instance, complains about h omework or rushes through homework, making many mistakes are better descriptors than has a bad attitude or is lazy.
Step 2. Set a goal. Usually the goal relates directly to the problem behavior. For instance, if not writing down assignments is the problem, the goal might be: “Joe will write down his assignments in his assignment book for every class.”
Step 3. Decide on possible rewards and penalties. Homework incentive systems work best when children have a menu of rewards to choose from, since no single reward will be attractive for long. We recommend a point system in which points can be earned for the goal behaviors and traded in for the reward the child wants to earn. The bigger the reward, the more points the child will need to earn it. The menu should include both larger, more expensive rewards that may take a week or a month to earn and smaller, inexpensive rewards that can be earned daily. It may also be necessary to build penalties into the system. This is usually the loss of a privilege (such as the chance to watch a favorite TV show or the chance to talk on the telephone to a friend).
Once the system is up and running, and if you find your child is earning more penalties than rewards, then the program needs to be revised so that your child can be more successful. Usually when this kind of system fails, we think of it as a design failure rather than the failure of the child to respond to rewards. It may be a good idea if you are having difficulty designing a system that works to consult a specialist, such as a school psychologist or counselor, for assistance.
Step 4. Write a homework contract. The contract should say exactly what the child agrees to do and exactly what the parents’ roles and responsibilities will be. When the contract is in place, it should reduce some of the tension parents and kids often experience around homework. For instance, if part of the contract is that the child will earn a point for not complaining about homework, then if the child does complain, this should not be cause for a battle between parent and child: the child simply does not earn that point. Parents should also be sure to praise their children for following the contract. It will be important for parents to agree to a contract they can live with; that is, avoiding penalties they are either unable or unwilling to impose (e.g., if both parents work and are not at home, they cannot monitor whether a child is beginning homework right after school, so an alternative contract may need to be written).
We have found that it is a rare incentive system that works the first time. Parents should expect to try it out and redesign it to work the kinks out. Eventually, once the child is used to doing the behaviors specified in the contract, the contract can be rewritten to work on another problem behavior. Your child over time may be willing to drop the use of an incentive system altogether. This is often a long-term goal, however, and you should be ready to write a new contract if your child slips back to bad habits once a system is dropped.
Click here to download the homework planner and incentive sheet .
Frequently Asked Questions
To help homework go more smoothly, e stablish a routine that includes a time and place where it will be done, a planner that lists each assignment, scheduled breaks when some of the work is done, and a reward system for kids who are not motivated by good grades alone.
Set a good homework routine following these steps: Find a location in the house where homework will be done. Set up a homework center stocked with needed materials . Establish a homework time. Use a daily homework planner so that your child has everything in writing.
One tool that can make homework go more smoothly i s a Daily Homework Planner , which lists each assignment, how long it should take to complete, and what rewards may be earned for completing each assignment.
Was this article helpful?
Explore popular topics, subscribe to our newsletters.
" * " indicates required fields
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.

Want More Resources Like This?
Get advice from our clinical experts, guides on common conditions and concerns, and much more.
Why I Think All Schools Should Abolish Homework

H ow long is your child’s workweek? Thirty hours? Forty? Would it surprise you to learn that some elementary school kids have workweeks comparable to adults’ schedules? For most children, mandatory homework assignments push their workweek far beyond the school day and deep into what any other laborers would consider overtime. Even without sports or music or other school-sponsored extracurriculars, the daily homework slog keeps many students on the clock as long as lawyers, teachers, medical residents, truck drivers and other overworked adults. Is it any wonder that,deprived of the labor protections that we provide adults, our kids are suffering an epidemic of disengagement, anxiety and depression ?
With my youngest child just months away from finishing high school, I’m remembering all the needless misery and missed opportunities all three of my kids suffered because of their endless assignments. When my daughters were in middle school, I would urge them into bed before midnight and then find them clandestinely studying under the covers with a flashlight. We cut back on their activities but still found ourselves stuck in a system on overdrive, returning home from hectic days at 6 p.m. only to face hours more of homework. Now, even as a senior with a moderate course load, my son, Zak, has spent many weekends studying, finding little time for the exercise and fresh air essential to his well-being. Week after week, and without any extracurriculars, Zak logs a lot more than the 40 hours adults traditionally work each week — and with no recognition from his “bosses” that it’s too much. I can’t count the number of shared evenings, weekend outings and dinners that our family has missed and will never get back.
How much after-school time should our schools really own?
In the midst of the madness last fall, Zak said to me, “I feel like I’m working towards my death. The constant demands on my time since 5th grade are just going to continue through graduation, into college, and then into my job. It’s like I’m on an endless treadmill with no time for living.”
My spirit crumbled along with his.
Like Zak, many people are now questioning the point of putting so much demand on children and teens that they become thinly stretched and overworked. Studies have long shown that there is no academic benefit to high school homework that consumes more than a modest number of hours each week. In a study of high schoolers conducted by the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD), researchers concluded that “after around four hours of homework per week, the additional time invested in homework has a negligible impact on performance.”
In elementary school, where we often assign overtime even to the youngest children, studies have shown there’s no academic benefit to any amount of homework at all.
Our unquestioned acceptance of homework also flies in the face of all we know about human health, brain function and learning. Brain scientists know that rest and exercise are essential to good health and real learning . Even top adult professionals in specialized fields take care to limit their work to concentrated periods of focus. A landmark study of how humans develop expertise found that elite musicians, scientists and athletes do their most productive work only about four hours per day .
Yet we continue to overwork our children, depriving them of the chance to cultivate health and learn deeply, burdening them with an imbalance of sedentary, academic tasks. American high school students , in fact, do more homework each week than their peers in the average country in the OECD, a 2014 report found.
It’s time for an uprising.
Already, small rebellions are starting. High schools in Ridgewood, N.J. , and Fairfax County, Va., among others, have banned homework over school breaks. The entire second grade at Taylor Elementary School in Arlington, Va., abolished homework this academic year. Burton Valley Elementary School in Lafayette, Calif., has eliminated homework in grades K through 4. Henry West Laboratory School , a public K-8 school in Coral Gables, Fla., eliminated mandatory, graded homework for optional assignments. One Lexington, Mass., elementary school is piloting a homework-free year, replacing it with reading for pleasure.
More from TIME
Across the Atlantic, students in Spain launched a national strike against excessive assignments in November. And a second-grade teacher in Texas, made headlines this fall when she quit sending home extra work , instead urging families to “spend your evenings doing things that are proven to correlate with student success. Eat dinner as a family, read together, play outside and get your child to bed early.”
It is time that we call loudly for a clear and simple change: a workweek limit for children, counting time on the clock before and after the final bell. Why should schools extend their authority far beyond the boundaries of campus, dictating activities in our homes in the hours that belong to families? An all-out ban on after-school assignments would be optimal. Short of that, we can at least sensibly agree on a cap limiting kids to a 40-hour workweek — and fewer hours for younger children.
Resistance even to this reasonable limit will be rife. Mike Miller, an English teacher at Thomas Jefferson High School for Science and Technology in Alexandria, Va., found this out firsthand when he spearheaded a homework committee to rethink the usual approach. He had read the education research and found a forgotten policy on the county books limiting homework to two hours a night, total, including all classes. “I thought it would be a slam dunk” to put the two-hour cap firmly in place, Miller said.
But immediately, people started balking. “There was a lot of fear in the community,” Miller said. “It’s like jumping off a high dive with your kids’ future. If we reduce homework to two hours or less, is my kid really going to be okay?” In the end, the committee only agreed to a homework ban over school breaks.
Miller’s response is a great model for us all. He decided to limit assignments in his own class to 20 minutes a night (the most allowed for a student with six classes to hit the two-hour max). His students didn’t suddenly fail. Their test scores remained stable. And they started using their more breathable schedule to do more creative, thoughtful work.
That’s the way we will get to a sane work schedule for kids: by simultaneously pursuing changes big and small. Even as we collaboratively press for policy changes at the district or individual school level, all teachers can act now, as individuals, to ease the strain on overworked kids.
As parents and students, we can also organize to make homework the exception rather than the rule. We can insist that every family, teacher and student be allowed to opt out of assignments without penalty to make room for important activities, and we can seek changes that shift practice exercises and assignments into the actual school day.
We’ll know our work is done only when Zak and every other child can clock out, eat dinner, sleep well and stay healthy — the very things needed to engage and learn deeply. That’s the basic standard the law applies to working adults. Let’s do the same for our kids.
Vicki Abeles is the author of the bestseller Beyond Measure: Rescuing an Overscheduled, Overtested, Underestimated Generation, and director and producer of the documentaries “ Race to Nowhere ” and “ Beyond Measure. ”
More Must-Reads from TIME
- Welcome to the Golden Age of Scams
- Introducing TIME's 2024 Latino Leaders
- How to Make an Argument That’s Actually Persuasive
- Did the Pandemic Break Our Brains?
- 33 True Crime Documentaries That Shaped the Genre
- The Ordained Rabbi Who Bought a Porn Company
- Why Gut Health Issues Are More Common in Women
- The 100 Most Influential People in AI 2024
Contact us at [email protected]
You are using an outdated browser. Upgrade your browser today or install Google Chrome Frame to better experience this site.
Pros and cons of school assignments: Should kids have homework?

Do you think homework is good for kids? Should it be abolished? Find out the pros and cons of homework for students and join our education poll and debate.
Should kids have homework?
Pros and cons of homework.
Some researchers have identified a strong correlation between homework and academic success. Harris Cooper, professor of psychology and neuroscience at Duke University, led a meta-analysis in 2006, " Does homework improve academic achievement?, " which showed that homework can improve students' scores on class tests. The study demonstrated that accross different topics, including Math, English, American History, and Social studies, student who had done homework performed better than their classmates who had not.
In addition to improving grades and results in standardized tests, there are many other pros to homework such as:
- Homework provides parents with the opportunity to participate in their children's education.
- Possibility for kids to further explore a subject at their own pace. Not all children have the same capacity to assimilate all the information covered in class.
- School assignments can help develop a sense of responsibility and time management.
- It facilitates rote learning.
- It reduces the time kids spend watching TV as well as playing video games and with their cell phones .
- Homework is an opportunity to practice some research and study skills and deepen understanding of some concepts which cannot be fully developed in class.
However, some voices have started to point out some disadvantages of doing homework and questioned the traditional education model in place. Some of them claim that homework should be abolished. The publication “The End of Homework: How Homework Disrupts Families, Overburdens Children, and Limits Learning” by Kralovec and Buell (2000) has brought into the discussion a very interesting new angle. Kralovec and Buell argue that homework contributes to a competitive culture that overvalues work to the detriment of personal and family well-being . Moreover, there are several other problems associated to homework, such as:
- Homework is very unfair because economically disadvantaged students can’t study at home with the same conditions and support as the wealthier children.
- Too many school assignments can excessively reduce the time for playing, doing sports or simply interacting socially with friends and family. Homework can also interfere with kids' household chores .
- Cheating is easy. Often students simply plagiarize their assignments from others or from the Internet and therefore the learning objectives of homework are not fulfilled. In occasions parents or older relatives do children's coursework.
- Sometimes homework is not well designed and do not really contribute to learning. In other cases homework is not marked shortly after being submitted and, therefore, feedback does not reach students as soon as it should. Students may get frustrated and lose interest.
- It may keep students up late at night, reduce their sleeping time and therefore their performance in class the following day.
- As Galloway et al (2013) show, homework can be a source of stress and physical health problems for children.
To summarize, there are several pros and cons to the use of homework as educational tool for children. What side of the debate are you on? Do you think homework is overall good or bad for the development and education of children? Vote and tell us why (see below).
Watch these videos on the homework debate:
Vote to see result and collect 1 XP. Your vote is anonymous. If you change your mind, you can change your vote simply by clicking on another option.
Voting results
New to netivist?
Join with confidence, netivist is completely advertisement free. You will not receive any promotional materials from third parties.
Or sign in with your favourite Social Network:
Join the debate
In order to join the debate you must be logged in.
Already have an account on netivist? Just login . New to netivist? Create your account for free .
Report Abuse and Offensive language
Was there any kind of offensive or inappropriate language used in this comment.
If you feel this user's conduct is unappropriate, please report this comment and our moderaters will review its content and deal with this matter as soon as possible.
NOTE: Your account might be penalized should we not find any wrongdoing by this user. Only use this feature if you are certain this user has infringed netivist's Terms of Service .
Our moderators will now review this comment and act accordingly. If it contains abusive or inappropriate language its author will be penalized.
Posting Comment
Your comment is being posted. This might take a few seconds, please wait.
Error Posting Comment
error.
We are having trouble saving your comment. Please try again .
Most Voted Debates
| Rank | |
|---|---|
Start a Debate
Would you like to create a debate and share it with the netivist community? We will help you do it!
Found a technical issue?

Are you experiencing any technical problem with netivist? Please let us know!
Help netivist
Help netivist continue running free!
Please consider making a small donation today. This will allow us to keep netivist alive and available to a wide audience and to keep on introducing new debates and features to improve your experience.

- What is netivist?
- Entertainment
- Top Debates
- Top Campaigns
- Provide Feedback

Follow us on social media:

Share by Email
There was an error...
Email successfully sent to:

Join with confidence, netivist is completely advertisement free You will not recive any promotional materials from third parties
Join netivist
Already have a netivist account?
If you already created your netivist account, please log in using the button below.
If you are new to netivist, please create your account for free and start collecting your netivist points!
You just leveled up!
Congrats you just reached a new level on Netivist. Keep up the good work.

Together we can make a difference
Follow us and don't miss out on the latest debates!
share this!
September 19, 2024
This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies . Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
Study reveals impact of homework on student achievement in math and science
by Maynooth University

Researchers at Maynooth University's Hamilton Institute and Department of Mathematics and Statistics in Ireland have unveiled significant findings on the role of homework in student achievement. The research, led by Prof Andrew Parnell, Nathan McJames and Prof Ann O'Shea, used a new AI model to analyze data from the "Trends in International Mathematics and Science Study" (TIMSS 2019).
Focusing on 4,118 Irish students in their second year of secondary school, the research assessed the impact of varying homework patterns on their mathematics and science performance.
The study titled, "Little and often: Causal inference machine learning demonstrates the benefits of homework for improving achievement in mathematics and science" was published in the journal Learning and Instruction .
It offers new evidence on how homework frequency and duration affect academic performance among Irish secondary school students.
Frequency over duration
The study highlights that the frequency of homework is more important than its duration. Daily homework assignments were found to be most effective for improving mathematics achievement, while science performance benefited most from homework assigned three to four times a week.
Effectiveness of shorter assignments
Short-duration homework tasks, lasting up to 15 minutes, were shown to be just as effective as longer assignments. This suggests that regular, concise homework can promote learning without overwhelming students with excessive work.
Equity in benefits
Contrary to previous research, this study found that all students, regardless of socioeconomic background, experienced similar benefits from homework, indicating equitable advantages across diverse student populations. The researchers advocate for homework policies prioritizing regular, short-duration assignments to optimize student engagement and academic success without causing undue stress.
Nathan McJames, the lead author, commented, "Our study provides strong evidence that regular homework can significantly enhance student performance, especially when given 'little and often'. By avoiding very long homework assignments, this also allows students to balance schoolwork with other important activities outside of school."
Prof Andrew Parnell added, "Our use of advanced causal inference methods ensures the reliability of our findings. This research provides valuable insights that can guide evidence-based policy changes in education, ultimately benefiting students across the board."
Journal information: Learning and Instruction
Provided by Maynooth University
Explore further
Feedback to editors

New data science tool greatly speeds up molecular analysis of our environment
7 hours ago

AI tools help uncover enzyme mechanisms for lasso peptides
8 hours ago

Light momentum turns pure silicon from an indirect to a direct bandgap semiconductor
9 hours ago

Study reveals large ocean heat storage efficiency during the last deglaciation

Citizen science collaboration yields precise data on exoplanet WASP-77 A b

A possible explanation for the 'missing plastic problem': New detection technique finds microplastics in coral skeletons

Genome sequence analysis identifies new driver of antimicrobial resistance
10 hours ago

Analysis of heterostructures for spintronics shows how two desired quantum-physical effects reinforce each other

Evolved in the lab, found in nature: Uncovering hidden pH sensing abilities in microbial cultures

Harnessing exosomes and hydrogels for advanced diabetic wound healing
11 hours ago
Relevant PhysicsForums posts
Sources to study basic logic for precocious 10-year old.
22 hours ago
How to explain Bell's theorem to non-scientists
Sep 19, 2024
Worksheets for Physics Experiments with Smartphones
How is physics taught without calculus.
Sep 18, 2024
I want to start Tutoring Online -- Looking for Advice
Sep 13, 2024
Are excuses for academic parties getting thinner or is it just me?
Sep 7, 2024
More from STEM Educators and Teaching
Related Stories

Doing homework is associated with change in students' personality
Oct 6, 2017

How parents' support and emotional guidance shape homework success
Sep 5, 2024

The numbers do not add up for mathematics homework, according to a new study
Mar 12, 2024

Q&A: Does homework still have value? An education expert weighs in
Jan 18, 2024

Should parents help their kids with homework?
Aug 29, 2019

Type of maternal homework assistance affects child's persistence
May 9, 2018
Recommended for you

Learning mindset could be key to addressing medical students' alarming burnout

Researchers test ChatGPT, other AI models against real-world students
Sep 16, 2024
Virtual learning linked to rise in chronic absenteeism, study finds

AI tools like ChatGPT popular among students who struggle with concentration and attention
Aug 28, 2024

Researchers find academic equivalent of a Great Gatsby Curve in science mentorships
Aug 27, 2024

More academic freedom leads to more innovation, reports study
Aug 21, 2024
Let us know if there is a problem with our content
Use this form if you have come across a typo, inaccuracy or would like to send an edit request for the content on this page. For general inquiries, please use our contact form . For general feedback, use the public comments section below (please adhere to guidelines ).
Please select the most appropriate category to facilitate processing of your request
Thank you for taking time to provide your feedback to the editors.
Your feedback is important to us. However, we do not guarantee individual replies due to the high volume of messages.
E-mail the story
Your email address is used only to let the recipient know who sent the email. Neither your address nor the recipient's address will be used for any other purpose. The information you enter will appear in your e-mail message and is not retained by Phys.org in any form.
Newsletter sign up
Get weekly and/or daily updates delivered to your inbox. You can unsubscribe at any time and we'll never share your details to third parties.
More information Privacy policy
Donate and enjoy an ad-free experience
We keep our content available to everyone. Consider supporting Science X's mission by getting a premium account.
E-mail newsletter

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A conversation with a Wheelock researcher, a BU student, and a fourth-grade teacher. "Quality homework is engaging and relevant to kids' lives," says Wheelock's Janine Bempechat. "It gives them autonomy and engages them in the community and with their families. In some subjects, like math, worksheets can be very helpful.
Homework allows them to keep up with what you're doing in your classes on a daily basis. But you don't have homework purely for your parents' benefit. It's good for you, too! Homework can help you become a better student in several different ways. First of all, homework given in advance of a particular subject can help you make the most of your ...
The National PTA and the National Education Association support the " 10-minute homework guideline "—a nightly 10 minutes of homework per grade level. But many teachers and parents are quick to point out that what matters is the quality of the homework assigned and how well it meets students' needs, not the amount of time spent on it.
Homework has its pros and cons, especially for college students. It can enhance critical thinking, time management, and learning, but it also brings stress, impacts mental health, and can become overwhelming. Finding the right balance is key. Focus on quality assignments, maintain flexibility, and make sure your homework complements rather than ...
Pope and her colleagues found that too much homework can diminish its effectiveness and even be counterproductive. They cite prior research indicating that homework benefits plateau at about two hours per night, and that 90 minutes to two and a half hours is optimal for high school. • Greater stress: 56 percent of the students considered ...
The authors believe this meritocratic narrative is a myth and that homework — math homework in particular — further entrenches the myth in the minds of teachers and their students.
A TIME cover in 1999 read: "Too much homework! How it's hurting our kids, and what parents should do about it.". The accompanying story noted that the launch of Sputnik in 1957 led to a push ...
We can also use ATUS data to isolate when students do homework by race and by income. In Figure 2, we plot the percentage of high school students in each racial and income group doing homework by ...
And homework has a greater positive effect on students in secondary school (grades 7-12) than those in elementary. "Every child should be doing homework, but the amount and type that they're doing ...
Too much homework may diminish its effectiveness. While research on the optimum amount of time students should spend on homework is limited, there are indications that for high school students, 1½ to 2½ hours per night is optimum. Middle school students appear to benefit from smaller amounts (less than 1 hour per night).
Unfortunately, when kids frequently struggle to meet homework demands, teachers and parents typically default to one explanation of the problem: The child is making a choice not to do their ...
Regardless, research has shown that doing more than two hours of homework per night does not benefit high school students. Having lots of homework to do every day makes it difficult for teens to ...
Homework also helps students develop key skills that they'll use throughout their lives: Accountability. Autonomy. Discipline. Time management. Self-direction. Critical thinking. Independent problem-solving. The skills learned in homework can then be applied to other subjects and practical situations in students' daily lives.
From dioramas to book reports, from algebraic word problems to research projects, whether students should be given homework, as well as the type and amount of homework, has been debated for over a century. []While we are unsure who invented homework, we do know that the word "homework" dates back to ancient Rome. Pliny the Younger asked his followers to practice their speeches at home.
Homework can affect both students' physical and mental health. According to a study by Stanford University, 56 per cent of students considered homework a primary source of stress. Too much homework can result in lack of sleep, headaches, exhaustion and weight loss. Excessive homework can also result in poor eating habits, with families ...
The research quoted students as saying they often do homework they see as "pointless" or "mindless" in order to keep their grades up. "This kind of busy work, by its very nature ...
In 1st grade, children should have 10 minutes of daily homework; in 2nd grade, 20 minutes; and so on to the 12th grade, when on average they should have 120 minutes of homework each day, which is ...
According to Duke professor Harris Cooper, it's important that students have homework. His meta-analysis of homework studies showed a correlation between completing homework and academic success, at least in older grades. He recommends following a "10 minute rule": students should receive 10 minutes of homework per day in first grade, and 10 ...
Examining these arguments offers important perspectives on the wider educational and developmental consequences of homework practices. 1. Elevated Stress and Health Consequences. According to Gitnux, U.S. high school students who have over 20 hours of homework per week are 27% more likely to encounter health issues.
That was when kids were in school for classes and went home to do homework. But now, school for millions of students means working at home doing school work all day, because school buildings are ...
Others need to have parents nearby to help keep them on task and to answer questions when problems arise. Ask your child where the best place is to work. Both you and your child need to discuss pros and cons of different settings to arrive at a mutually agreed upon location. Step 2. Set up a homework center.
American high school students, in fact, do more homework each week than their peers in the average country in the OECD, a 2014 report found. It's time for an uprising. Already, small rebellions ...
Homework can also interfere with kids' household chores. Cheating is easy. Often students simply plagiarize their assignments from others or from the Internet and therefore the learning objectives of homework are not fulfilled. In occasions parents or older relatives do children's coursework. Sometimes homework is not well designed and do not ...
Focusing on 4,118 Irish students in their second year of secondary school, the research assessed the impact of varying homework patterns on their mathematics and science performance.. The study ...
Compared with no homework, students who received homework obtained higher test scores (g = 0.45), particularly in arithmetic computation (g = 0.46) and problem-solving (g = 0.17). Two experiments explored the effectiveness of homework moderated by the homework time (Dolean & Lervag, 2021; Koch, 1965).