Browse Econ Literature
- Working papers
- Software components
- Book chapters
- JEL classification

More features
- Subscribe to new research
RePEc Biblio
Author registration.
- Economics Virtual Seminar Calendar NEW!

Literature reviews as independent studies: guidelines for academic practice
- Author & abstract
- 21 References
- 29 Citations
- Most related
- Related works & more
Corrections
(Free University of Bozen-Bolzano University of Johannesburg)
(Lappeenranta University of Technology)
(Sunway University Business School, Sunway University Swinburne University of Technology Swinburne University of Technology)
(University of Zagreb University of Ljubljana)
(Malaviya National Institute of Technology Jaipur Swinburne University of Technology)
(HHL Leipzig Graduate School of Management Woxsen University)
(The University of Akron)
(University of Messina)
(Santiago de Compostela University)
(Rowan University, Rohrer College of Business)
(Universidad Politécnica de Valencia)
(Parthenope University Paris School of Business)
(University of Turin Ural Federal University)
(University of Beira Interior Centre for Corporate Entrepreneurship and Innovation, Loughborough University)
(University of Beira Interior)
- Marina Dabic
- Alberto Ferraris
- Satish Kumar
Suggested Citation
Download full text from publisher, references listed on ideas.
Follow serials, authors, keywords & more
Public profiles for Economics researchers
Various research rankings in Economics
RePEc Genealogy
Who was a student of whom, using RePEc
Curated articles & papers on economics topics
Upload your paper to be listed on RePEc and IDEAS
New papers by email
Subscribe to new additions to RePEc
EconAcademics
Blog aggregator for economics research
Cases of plagiarism in Economics
About RePEc
Initiative for open bibliographies in Economics
News about RePEc
Questions about IDEAS and RePEc
RePEc volunteers
Participating archives
Publishers indexing in RePEc
Privacy statement
Found an error or omission?
Opportunities to help RePEc
Get papers listed
Have your research listed on RePEc
Open a RePEc archive
Have your institution's/publisher's output listed on RePEc
Get RePEc data
Use data assembled by RePEc
- UConn Library
- Literature Review: The What, Why and How-to Guide
- Introduction
Literature Review: The What, Why and How-to Guide — Introduction
- Getting Started
- How to Pick a Topic
- Strategies to Find Sources
- Evaluating Sources & Lit. Reviews
- Tips for Writing Literature Reviews
- Writing Literature Review: Useful Sites
- Citation Resources
- Other Academic Writings
What are Literature Reviews?
So, what is a literature review? "A literature review is an account of what has been published on a topic by accredited scholars and researchers. In writing the literature review, your purpose is to convey to your reader what knowledge and ideas have been established on a topic, and what their strengths and weaknesses are. As a piece of writing, the literature review must be defined by a guiding concept (e.g., your research objective, the problem or issue you are discussing, or your argumentative thesis). It is not just a descriptive list of the material available, or a set of summaries." Taylor, D. The literature review: A few tips on conducting it . University of Toronto Health Sciences Writing Centre.
Goals of Literature Reviews
What are the goals of creating a Literature Review? A literature could be written to accomplish different aims:
- To develop a theory or evaluate an existing theory
- To summarize the historical or existing state of a research topic
- Identify a problem in a field of research
Baumeister, R. F., & Leary, M. R. (1997). Writing narrative literature reviews . Review of General Psychology , 1 (3), 311-320.
What kinds of sources require a Literature Review?
- A research paper assigned in a course
- A thesis or dissertation
- A grant proposal
- An article intended for publication in a journal
All these instances require you to collect what has been written about your research topic so that you can demonstrate how your own research sheds new light on the topic.
Types of Literature Reviews
What kinds of literature reviews are written?
Narrative review: The purpose of this type of review is to describe the current state of the research on a specific topic/research and to offer a critical analysis of the literature reviewed. Studies are grouped by research/theoretical categories, and themes and trends, strengths and weakness, and gaps are identified. The review ends with a conclusion section which summarizes the findings regarding the state of the research of the specific study, the gaps identify and if applicable, explains how the author's research will address gaps identify in the review and expand the knowledge on the topic reviewed.
- Example : Predictors and Outcomes of U.S. Quality Maternity Leave: A Review and Conceptual Framework: 10.1177/08948453211037398
Systematic review : "The authors of a systematic review use a specific procedure to search the research literature, select the studies to include in their review, and critically evaluate the studies they find." (p. 139). Nelson, L. K. (2013). Research in Communication Sciences and Disorders . Plural Publishing.
- Example : The effect of leave policies on increasing fertility: a systematic review: 10.1057/s41599-022-01270-w
Meta-analysis : "Meta-analysis is a method of reviewing research findings in a quantitative fashion by transforming the data from individual studies into what is called an effect size and then pooling and analyzing this information. The basic goal in meta-analysis is to explain why different outcomes have occurred in different studies." (p. 197). Roberts, M. C., & Ilardi, S. S. (2003). Handbook of Research Methods in Clinical Psychology . Blackwell Publishing.
- Example : Employment Instability and Fertility in Europe: A Meta-Analysis: 10.1215/00703370-9164737
Meta-synthesis : "Qualitative meta-synthesis is a type of qualitative study that uses as data the findings from other qualitative studies linked by the same or related topic." (p.312). Zimmer, L. (2006). Qualitative meta-synthesis: A question of dialoguing with texts . Journal of Advanced Nursing , 53 (3), 311-318.
- Example : Women’s perspectives on career successes and barriers: A qualitative meta-synthesis: 10.1177/05390184221113735
Literature Reviews in the Health Sciences
- UConn Health subject guide on systematic reviews Explanation of the different review types used in health sciences literature as well as tools to help you find the right review type
- << Previous: Getting Started
- Next: How to Pick a Topic >>
- Last Updated: Sep 21, 2022 2:16 PM
- URL: https://guides.lib.uconn.edu/literaturereview

Independent Study
- Formulating the Research Question
- Introduction and Rationale of the Study
Literature Review
- Research Methodology
- Research Design
- Ethical Considerations
- Data Findings
- Data Analysis
- Conclusions
A literature review identifies the boundaries of your study and demonstrates very clearly the focus and purpose of your research.
A literature review is an account of what has been published on a topic by accredited scholars and researchers. Occasionally you will be asked to write one as a separate assignment but more often it is part of the introduction to an essay, research report, or thesis. In writing the literature review, your purpose is to convey to your reader what knowledge and ideas have been established on a topic, and what their strengths and weaknesses are. As a piece of writing, the literature review must be defined by a guiding concept (e.g. your research aim). It is not just a descriptive list of the material available, or a set of summaries.
Besides enlarging your knowledge about the topic, writing a literature review lets you gain and demonstrate skills in two areas:
- information seeking: the ability to scan the literature efficiently, using manual or computerised methods, to identify a set of useful journals and books
- critical appraisal: the ability to apply principles of analysis to identify unbiased and valid studies.
This will be one of the longer sections of the dissertation and will contain a critical review of your reading in books and journals. Learning Resource staff will help you if necessary to use indexes and abstracts in order to secure relevant sources for your work.
The literature reviewed should be closely related to the focus of your study. You should use sub-headings which identify the key issues. This will help you to summarise and synthesise your readings in a structured way.
Ensure that from the start of your work, you keep detailed, accurate notes of all your reading, ensuring that you also note relevant bibliographic data, including: page numbers; author(s); titles; date and place of publication etc.
- An extract from a study based on Explore Wellbeing and Mental Health upon Student Achievement Within Higher Education
- An extract from a study based on Vygotskian theory reflected in classroom practice.pdf
Additional Resources
Purpose of the Literature Review
- << Previous: Introduction and Rationale of the Study
- Next: Research Methodology >>
- Last Updated: Jan 31, 2023 1:04 PM
- URL: https://libguides.derby.ac.uk/independent-study
- USC Libraries
- Research Guides
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper
- 5. The Literature Review
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Reading Research Effectively
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Applying Critical Thinking
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Research Process Video Series
- Executive Summary
- The C.A.R.S. Model
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tiertiary Sources
- Scholarly vs. Popular Publications
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Insiderness
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Writing Concisely
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Generative AI and Writing
- USC Libraries Tutorials and Other Guides
- Bibliography
A literature review surveys prior research published in books, scholarly articles, and any other sources relevant to a particular issue, area of research, or theory, and by so doing, provides a description, summary, and critical evaluation of these works in relation to the research problem being investigated. Literature reviews are designed to provide an overview of sources you have used in researching a particular topic and to demonstrate to your readers how your research fits within existing scholarship about the topic.
Fink, Arlene. Conducting Research Literature Reviews: From the Internet to Paper . Fourth edition. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE, 2014.
Importance of a Good Literature Review
A literature review may consist of simply a summary of key sources, but in the social sciences, a literature review usually has an organizational pattern and combines both summary and synthesis, often within specific conceptual categories . A summary is a recap of the important information of the source, but a synthesis is a re-organization, or a reshuffling, of that information in a way that informs how you are planning to investigate a research problem. The analytical features of a literature review might:
- Give a new interpretation of old material or combine new with old interpretations,
- Trace the intellectual progression of the field, including major debates,
- Depending on the situation, evaluate the sources and advise the reader on the most pertinent or relevant research, or
- Usually in the conclusion of a literature review, identify where gaps exist in how a problem has been researched to date.
Given this, the purpose of a literature review is to:
- Place each work in the context of its contribution to understanding the research problem being studied.
- Describe the relationship of each work to the others under consideration.
- Identify new ways to interpret prior research.
- Reveal any gaps that exist in the literature.
- Resolve conflicts amongst seemingly contradictory previous studies.
- Identify areas of prior scholarship to prevent duplication of effort.
- Point the way in fulfilling a need for additional research.
- Locate your own research within the context of existing literature [very important].
Fink, Arlene. Conducting Research Literature Reviews: From the Internet to Paper. 2nd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2005; Hart, Chris. Doing a Literature Review: Releasing the Social Science Research Imagination . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 1998; Jesson, Jill. Doing Your Literature Review: Traditional and Systematic Techniques . Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2011; Knopf, Jeffrey W. "Doing a Literature Review." PS: Political Science and Politics 39 (January 2006): 127-132; Ridley, Diana. The Literature Review: A Step-by-Step Guide for Students . 2nd ed. Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2012.
Types of Literature Reviews
It is important to think of knowledge in a given field as consisting of three layers. First, there are the primary studies that researchers conduct and publish. Second are the reviews of those studies that summarize and offer new interpretations built from and often extending beyond the primary studies. Third, there are the perceptions, conclusions, opinion, and interpretations that are shared informally among scholars that become part of the body of epistemological traditions within the field.
In composing a literature review, it is important to note that it is often this third layer of knowledge that is cited as "true" even though it often has only a loose relationship to the primary studies and secondary literature reviews. Given this, while literature reviews are designed to provide an overview and synthesis of pertinent sources you have explored, there are a number of approaches you could adopt depending upon the type of analysis underpinning your study.
Argumentative Review This form examines literature selectively in order to support or refute an argument, deeply embedded assumption, or philosophical problem already established in the literature. The purpose is to develop a body of literature that establishes a contrarian viewpoint. Given the value-laden nature of some social science research [e.g., educational reform; immigration control], argumentative approaches to analyzing the literature can be a legitimate and important form of discourse. However, note that they can also introduce problems of bias when they are used to make summary claims of the sort found in systematic reviews [see below].
Integrative Review Considered a form of research that reviews, critiques, and synthesizes representative literature on a topic in an integrated way such that new frameworks and perspectives on the topic are generated. The body of literature includes all studies that address related or identical hypotheses or research problems. A well-done integrative review meets the same standards as primary research in regard to clarity, rigor, and replication. This is the most common form of review in the social sciences.
Historical Review Few things rest in isolation from historical precedent. Historical literature reviews focus on examining research throughout a period of time, often starting with the first time an issue, concept, theory, phenomena emerged in the literature, then tracing its evolution within the scholarship of a discipline. The purpose is to place research in a historical context to show familiarity with state-of-the-art developments and to identify the likely directions for future research.
Methodological Review A review does not always focus on what someone said [findings], but how they came about saying what they say [method of analysis]. Reviewing methods of analysis provides a framework of understanding at different levels [i.e. those of theory, substantive fields, research approaches, and data collection and analysis techniques], how researchers draw upon a wide variety of knowledge ranging from the conceptual level to practical documents for use in fieldwork in the areas of ontological and epistemological consideration, quantitative and qualitative integration, sampling, interviewing, data collection, and data analysis. This approach helps highlight ethical issues which you should be aware of and consider as you go through your own study.
Systematic Review This form consists of an overview of existing evidence pertinent to a clearly formulated research question, which uses pre-specified and standardized methods to identify and critically appraise relevant research, and to collect, report, and analyze data from the studies that are included in the review. The goal is to deliberately document, critically evaluate, and summarize scientifically all of the research about a clearly defined research problem . Typically it focuses on a very specific empirical question, often posed in a cause-and-effect form, such as "To what extent does A contribute to B?" This type of literature review is primarily applied to examining prior research studies in clinical medicine and allied health fields, but it is increasingly being used in the social sciences.
Theoretical Review The purpose of this form is to examine the corpus of theory that has accumulated in regard to an issue, concept, theory, phenomena. The theoretical literature review helps to establish what theories already exist, the relationships between them, to what degree the existing theories have been investigated, and to develop new hypotheses to be tested. Often this form is used to help establish a lack of appropriate theories or reveal that current theories are inadequate for explaining new or emerging research problems. The unit of analysis can focus on a theoretical concept or a whole theory or framework.
NOTE : Most often the literature review will incorporate some combination of types. For example, a review that examines literature supporting or refuting an argument, assumption, or philosophical problem related to the research problem will also need to include writing supported by sources that establish the history of these arguments in the literature.
Baumeister, Roy F. and Mark R. Leary. "Writing Narrative Literature Reviews." Review of General Psychology 1 (September 1997): 311-320; Mark R. Fink, Arlene. Conducting Research Literature Reviews: From the Internet to Paper . 2nd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2005; Hart, Chris. Doing a Literature Review: Releasing the Social Science Research Imagination . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 1998; Kennedy, Mary M. "Defining a Literature." Educational Researcher 36 (April 2007): 139-147; Petticrew, Mark and Helen Roberts. Systematic Reviews in the Social Sciences: A Practical Guide . Malden, MA: Blackwell Publishers, 2006; Torracro, Richard. "Writing Integrative Literature Reviews: Guidelines and Examples." Human Resource Development Review 4 (September 2005): 356-367; Rocco, Tonette S. and Maria S. Plakhotnik. "Literature Reviews, Conceptual Frameworks, and Theoretical Frameworks: Terms, Functions, and Distinctions." Human Ressource Development Review 8 (March 2008): 120-130; Sutton, Anthea. Systematic Approaches to a Successful Literature Review . Los Angeles, CA: Sage Publications, 2016.
Structure and Writing Style
I. Thinking About Your Literature Review
The structure of a literature review should include the following in support of understanding the research problem :
- An overview of the subject, issue, or theory under consideration, along with the objectives of the literature review,
- Division of works under review into themes or categories [e.g. works that support a particular position, those against, and those offering alternative approaches entirely],
- An explanation of how each work is similar to and how it varies from the others,
- Conclusions as to which pieces are best considered in their argument, are most convincing of their opinions, and make the greatest contribution to the understanding and development of their area of research.
The critical evaluation of each work should consider :
- Provenance -- what are the author's credentials? Are the author's arguments supported by evidence [e.g. primary historical material, case studies, narratives, statistics, recent scientific findings]?
- Methodology -- were the techniques used to identify, gather, and analyze the data appropriate to addressing the research problem? Was the sample size appropriate? Were the results effectively interpreted and reported?
- Objectivity -- is the author's perspective even-handed or prejudicial? Is contrary data considered or is certain pertinent information ignored to prove the author's point?
- Persuasiveness -- which of the author's theses are most convincing or least convincing?
- Validity -- are the author's arguments and conclusions convincing? Does the work ultimately contribute in any significant way to an understanding of the subject?
II. Development of the Literature Review
Four Basic Stages of Writing 1. Problem formulation -- which topic or field is being examined and what are its component issues? 2. Literature search -- finding materials relevant to the subject being explored. 3. Data evaluation -- determining which literature makes a significant contribution to the understanding of the topic. 4. Analysis and interpretation -- discussing the findings and conclusions of pertinent literature.
Consider the following issues before writing the literature review: Clarify If your assignment is not specific about what form your literature review should take, seek clarification from your professor by asking these questions: 1. Roughly how many sources would be appropriate to include? 2. What types of sources should I review (books, journal articles, websites; scholarly versus popular sources)? 3. Should I summarize, synthesize, or critique sources by discussing a common theme or issue? 4. Should I evaluate the sources in any way beyond evaluating how they relate to understanding the research problem? 5. Should I provide subheadings and other background information, such as definitions and/or a history? Find Models Use the exercise of reviewing the literature to examine how authors in your discipline or area of interest have composed their literature review sections. Read them to get a sense of the types of themes you might want to look for in your own research or to identify ways to organize your final review. The bibliography or reference section of sources you've already read, such as required readings in the course syllabus, are also excellent entry points into your own research. Narrow the Topic The narrower your topic, the easier it will be to limit the number of sources you need to read in order to obtain a good survey of relevant resources. Your professor will probably not expect you to read everything that's available about the topic, but you'll make the act of reviewing easier if you first limit scope of the research problem. A good strategy is to begin by searching the USC Libraries Catalog for recent books about the topic and review the table of contents for chapters that focuses on specific issues. You can also review the indexes of books to find references to specific issues that can serve as the focus of your research. For example, a book surveying the history of the Israeli-Palestinian conflict may include a chapter on the role Egypt has played in mediating the conflict, or look in the index for the pages where Egypt is mentioned in the text. Consider Whether Your Sources are Current Some disciplines require that you use information that is as current as possible. This is particularly true in disciplines in medicine and the sciences where research conducted becomes obsolete very quickly as new discoveries are made. However, when writing a review in the social sciences, a survey of the history of the literature may be required. In other words, a complete understanding the research problem requires you to deliberately examine how knowledge and perspectives have changed over time. Sort through other current bibliographies or literature reviews in the field to get a sense of what your discipline expects. You can also use this method to explore what is considered by scholars to be a "hot topic" and what is not.
III. Ways to Organize Your Literature Review
Chronology of Events If your review follows the chronological method, you could write about the materials according to when they were published. This approach should only be followed if a clear path of research building on previous research can be identified and that these trends follow a clear chronological order of development. For example, a literature review that focuses on continuing research about the emergence of German economic power after the fall of the Soviet Union. By Publication Order your sources by publication chronology, then, only if the order demonstrates a more important trend. For instance, you could order a review of literature on environmental studies of brown fields if the progression revealed, for example, a change in the soil collection practices of the researchers who wrote and/or conducted the studies. Thematic [“conceptual categories”] A thematic literature review is the most common approach to summarizing prior research in the social and behavioral sciences. Thematic reviews are organized around a topic or issue, rather than the progression of time, although the progression of time may still be incorporated into a thematic review. For example, a review of the Internet’s impact on American presidential politics could focus on the development of online political satire. While the study focuses on one topic, the Internet’s impact on American presidential politics, it would still be organized chronologically reflecting technological developments in media. The difference in this example between a "chronological" and a "thematic" approach is what is emphasized the most: themes related to the role of the Internet in presidential politics. Note that more authentic thematic reviews tend to break away from chronological order. A review organized in this manner would shift between time periods within each section according to the point being made. Methodological A methodological approach focuses on the methods utilized by the researcher. For the Internet in American presidential politics project, one methodological approach would be to look at cultural differences between the portrayal of American presidents on American, British, and French websites. Or the review might focus on the fundraising impact of the Internet on a particular political party. A methodological scope will influence either the types of documents in the review or the way in which these documents are discussed.
Other Sections of Your Literature Review Once you've decided on the organizational method for your literature review, the sections you need to include in the paper should be easy to figure out because they arise from your organizational strategy. In other words, a chronological review would have subsections for each vital time period; a thematic review would have subtopics based upon factors that relate to the theme or issue. However, sometimes you may need to add additional sections that are necessary for your study, but do not fit in the organizational strategy of the body. What other sections you include in the body is up to you. However, only include what is necessary for the reader to locate your study within the larger scholarship about the research problem.
Here are examples of other sections, usually in the form of a single paragraph, you may need to include depending on the type of review you write:
- Current Situation : Information necessary to understand the current topic or focus of the literature review.
- Sources Used : Describes the methods and resources [e.g., databases] you used to identify the literature you reviewed.
- History : The chronological progression of the field, the research literature, or an idea that is necessary to understand the literature review, if the body of the literature review is not already a chronology.
- Selection Methods : Criteria you used to select (and perhaps exclude) sources in your literature review. For instance, you might explain that your review includes only peer-reviewed [i.e., scholarly] sources.
- Standards : Description of the way in which you present your information.
- Questions for Further Research : What questions about the field has the review sparked? How will you further your research as a result of the review?
IV. Writing Your Literature Review
Once you've settled on how to organize your literature review, you're ready to write each section. When writing your review, keep in mind these issues.
Use Evidence A literature review section is, in this sense, just like any other academic research paper. Your interpretation of the available sources must be backed up with evidence [citations] that demonstrates that what you are saying is valid. Be Selective Select only the most important points in each source to highlight in the review. The type of information you choose to mention should relate directly to the research problem, whether it is thematic, methodological, or chronological. Related items that provide additional information, but that are not key to understanding the research problem, can be included in a list of further readings . Use Quotes Sparingly Some short quotes are appropriate if you want to emphasize a point, or if what an author stated cannot be easily paraphrased. Sometimes you may need to quote certain terminology that was coined by the author, is not common knowledge, or taken directly from the study. Do not use extensive quotes as a substitute for using your own words in reviewing the literature. Summarize and Synthesize Remember to summarize and synthesize your sources within each thematic paragraph as well as throughout the review. Recapitulate important features of a research study, but then synthesize it by rephrasing the study's significance and relating it to your own work and the work of others. Keep Your Own Voice While the literature review presents others' ideas, your voice [the writer's] should remain front and center. For example, weave references to other sources into what you are writing but maintain your own voice by starting and ending the paragraph with your own ideas and wording. Use Caution When Paraphrasing When paraphrasing a source that is not your own, be sure to represent the author's information or opinions accurately and in your own words. Even when paraphrasing an author’s work, you still must provide a citation to that work.
V. Common Mistakes to Avoid
These are the most common mistakes made in reviewing social science research literature.
- Sources in your literature review do not clearly relate to the research problem;
- You do not take sufficient time to define and identify the most relevant sources to use in the literature review related to the research problem;
- Relies exclusively on secondary analytical sources rather than including relevant primary research studies or data;
- Uncritically accepts another researcher's findings and interpretations as valid, rather than examining critically all aspects of the research design and analysis;
- Does not describe the search procedures that were used in identifying the literature to review;
- Reports isolated statistical results rather than synthesizing them in chi-squared or meta-analytic methods; and,
- Only includes research that validates assumptions and does not consider contrary findings and alternative interpretations found in the literature.
Cook, Kathleen E. and Elise Murowchick. “Do Literature Review Skills Transfer from One Course to Another?” Psychology Learning and Teaching 13 (March 2014): 3-11; Fink, Arlene. Conducting Research Literature Reviews: From the Internet to Paper . 2nd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2005; Hart, Chris. Doing a Literature Review: Releasing the Social Science Research Imagination . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 1998; Jesson, Jill. Doing Your Literature Review: Traditional and Systematic Techniques . London: SAGE, 2011; Literature Review Handout. Online Writing Center. Liberty University; Literature Reviews. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; Onwuegbuzie, Anthony J. and Rebecca Frels. Seven Steps to a Comprehensive Literature Review: A Multimodal and Cultural Approach . Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2016; Ridley, Diana. The Literature Review: A Step-by-Step Guide for Students . 2nd ed. Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2012; Randolph, Justus J. “A Guide to Writing the Dissertation Literature Review." Practical Assessment, Research, and Evaluation. vol. 14, June 2009; Sutton, Anthea. Systematic Approaches to a Successful Literature Review . Los Angeles, CA: Sage Publications, 2016; Taylor, Dena. The Literature Review: A Few Tips On Conducting It. University College Writing Centre. University of Toronto; Writing a Literature Review. Academic Skills Centre. University of Canberra.
Writing Tip
Break Out of Your Disciplinary Box!
Thinking interdisciplinarily about a research problem can be a rewarding exercise in applying new ideas, theories, or concepts to an old problem. For example, what might cultural anthropologists say about the continuing conflict in the Middle East? In what ways might geographers view the need for better distribution of social service agencies in large cities than how social workers might study the issue? You don’t want to substitute a thorough review of core research literature in your discipline for studies conducted in other fields of study. However, particularly in the social sciences, thinking about research problems from multiple vectors is a key strategy for finding new solutions to a problem or gaining a new perspective. Consult with a librarian about identifying research databases in other disciplines; almost every field of study has at least one comprehensive database devoted to indexing its research literature.
Frodeman, Robert. The Oxford Handbook of Interdisciplinarity . New York: Oxford University Press, 2010.
Another Writing Tip
Don't Just Review for Content!
While conducting a review of the literature, maximize the time you devote to writing this part of your paper by thinking broadly about what you should be looking for and evaluating. Review not just what scholars are saying, but how are they saying it. Some questions to ask:
- How are they organizing their ideas?
- What methods have they used to study the problem?
- What theories have been used to explain, predict, or understand their research problem?
- What sources have they cited to support their conclusions?
- How have they used non-textual elements [e.g., charts, graphs, figures, etc.] to illustrate key points?
When you begin to write your literature review section, you'll be glad you dug deeper into how the research was designed and constructed because it establishes a means for developing more substantial analysis and interpretation of the research problem.
Hart, Chris. Doing a Literature Review: Releasing the Social Science Research Imagination . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 1 998.
Yet Another Writing Tip
When Do I Know I Can Stop Looking and Move On?
Here are several strategies you can utilize to assess whether you've thoroughly reviewed the literature:
- Look for repeating patterns in the research findings . If the same thing is being said, just by different people, then this likely demonstrates that the research problem has hit a conceptual dead end. At this point consider: Does your study extend current research? Does it forge a new path? Or, does is merely add more of the same thing being said?
- Look at sources the authors cite to in their work . If you begin to see the same researchers cited again and again, then this is often an indication that no new ideas have been generated to address the research problem.
- Search Google Scholar to identify who has subsequently cited leading scholars already identified in your literature review [see next sub-tab]. This is called citation tracking and there are a number of sources that can help you identify who has cited whom, particularly scholars from outside of your discipline. Here again, if the same authors are being cited again and again, this may indicate no new literature has been written on the topic.
Onwuegbuzie, Anthony J. and Rebecca Frels. Seven Steps to a Comprehensive Literature Review: A Multimodal and Cultural Approach . Los Angeles, CA: Sage, 2016; Sutton, Anthea. Systematic Approaches to a Successful Literature Review . Los Angeles, CA: Sage Publications, 2016.
- << Previous: Theoretical Framework
- Next: Citation Tracking >>
- Last Updated: May 21, 2024 11:14 AM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide
Harvey Cushing/John Hay Whitney Medical Library
- Collections
- Research Help
YSN Doctoral Programs: Steps in Conducting a Literature Review
- Biomedical Databases
- Global (Public Health) Databases
- Soc. Sci., History, and Law Databases
- Grey Literature
- Trials Registers
- Data and Statistics
- Public Policy
- Google Tips
- Recommended Books
- Steps in Conducting a Literature Review
What is a literature review?
A literature review is an integrated analysis -- not just a summary-- of scholarly writings and other relevant evidence related directly to your research question. That is, it represents a synthesis of the evidence that provides background information on your topic and shows a association between the evidence and your research question.
A literature review may be a stand alone work or the introduction to a larger research paper, depending on the assignment. Rely heavily on the guidelines your instructor has given you.
Why is it important?
A literature review is important because it:
- Explains the background of research on a topic.
- Demonstrates why a topic is significant to a subject area.
- Discovers relationships between research studies/ideas.
- Identifies major themes, concepts, and researchers on a topic.
- Identifies critical gaps and points of disagreement.
- Discusses further research questions that logically come out of the previous studies.
APA7 Style resources
APA Style Blog - for those harder to find answers
1. Choose a topic. Define your research question.
Your literature review should be guided by your central research question. The literature represents background and research developments related to a specific research question, interpreted and analyzed by you in a synthesized way.
- Make sure your research question is not too broad or too narrow. Is it manageable?
- Begin writing down terms that are related to your question. These will be useful for searches later.
- If you have the opportunity, discuss your topic with your professor and your class mates.
2. Decide on the scope of your review
How many studies do you need to look at? How comprehensive should it be? How many years should it cover?
- This may depend on your assignment. How many sources does the assignment require?
3. Select the databases you will use to conduct your searches.
Make a list of the databases you will search.
Where to find databases:
- use the tabs on this guide
- Find other databases in the Nursing Information Resources web page
- More on the Medical Library web page
- ... and more on the Yale University Library web page
4. Conduct your searches to find the evidence. Keep track of your searches.
- Use the key words in your question, as well as synonyms for those words, as terms in your search. Use the database tutorials for help.
- Save the searches in the databases. This saves time when you want to redo, or modify, the searches. It is also helpful to use as a guide is the searches are not finding any useful results.
- Review the abstracts of research studies carefully. This will save you time.
- Use the bibliographies and references of research studies you find to locate others.
- Check with your professor, or a subject expert in the field, if you are missing any key works in the field.
- Ask your librarian for help at any time.
- Use a citation manager, such as EndNote as the repository for your citations. See the EndNote tutorials for help.
Review the literature
Some questions to help you analyze the research:
- What was the research question of the study you are reviewing? What were the authors trying to discover?
- Was the research funded by a source that could influence the findings?
- What were the research methodologies? Analyze its literature review, the samples and variables used, the results, and the conclusions.
- Does the research seem to be complete? Could it have been conducted more soundly? What further questions does it raise?
- If there are conflicting studies, why do you think that is?
- How are the authors viewed in the field? Has this study been cited? If so, how has it been analyzed?
Tips:
- Review the abstracts carefully.
- Keep careful notes so that you may track your thought processes during the research process.
- Create a matrix of the studies for easy analysis, and synthesis, across all of the studies.
- << Previous: Recommended Books
- Last Updated: Jan 4, 2024 10:52 AM
- URL: https://guides.library.yale.edu/YSNDoctoral
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Clinics (Sao Paulo)
Approaching literature review for academic purposes: The Literature Review Checklist
Debora f.b. leite.
I Departamento de Ginecologia e Obstetricia, Faculdade de Ciencias Medicas, Universidade Estadual de Campinas, Campinas, SP, BR
II Universidade Federal de Pernambuco, Pernambuco, PE, BR
III Hospital das Clinicas, Universidade Federal de Pernambuco, Pernambuco, PE, BR
Maria Auxiliadora Soares Padilha
Jose g. cecatti.
A sophisticated literature review (LR) can result in a robust dissertation/thesis by scrutinizing the main problem examined by the academic study; anticipating research hypotheses, methods and results; and maintaining the interest of the audience in how the dissertation/thesis will provide solutions for the current gaps in a particular field. Unfortunately, little guidance is available on elaborating LRs, and writing an LR chapter is not a linear process. An LR translates students’ abilities in information literacy, the language domain, and critical writing. Students in postgraduate programs should be systematically trained in these skills. Therefore, this paper discusses the purposes of LRs in dissertations and theses. Second, the paper considers five steps for developing a review: defining the main topic, searching the literature, analyzing the results, writing the review and reflecting on the writing. Ultimately, this study proposes a twelve-item LR checklist. By clearly stating the desired achievements, this checklist allows Masters and Ph.D. students to continuously assess their own progress in elaborating an LR. Institutions aiming to strengthen students’ necessary skills in critical academic writing should also use this tool.
INTRODUCTION
Writing the literature review (LR) is often viewed as a difficult task that can be a point of writer’s block and procrastination ( 1 ) in postgraduate life. Disagreements on the definitions or classifications of LRs ( 2 ) may confuse students about their purpose and scope, as well as how to perform an LR. Interestingly, at many universities, the LR is still an important element in any academic work, despite the more recent trend of producing scientific articles rather than classical theses.
The LR is not an isolated section of the thesis/dissertation or a copy of the background section of a research proposal. It identifies the state-of-the-art knowledge in a particular field, clarifies information that is already known, elucidates implications of the problem being analyzed, links theory and practice ( 3 - 5 ), highlights gaps in the current literature, and places the dissertation/thesis within the research agenda of that field. Additionally, by writing the LR, postgraduate students will comprehend the structure of the subject and elaborate on their cognitive connections ( 3 ) while analyzing and synthesizing data with increasing maturity.
At the same time, the LR transforms the student and hints at the contents of other chapters for the reader. First, the LR explains the research question; second, it supports the hypothesis, objectives, and methods of the research project; and finally, it facilitates a description of the student’s interpretation of the results and his/her conclusions. For scholars, the LR is an introductory chapter ( 6 ). If it is well written, it demonstrates the student’s understanding of and maturity in a particular topic. A sound and sophisticated LR can indicate a robust dissertation/thesis.
A consensus on the best method to elaborate a dissertation/thesis has not been achieved. The LR can be a distinct chapter or included in different sections; it can be part of the introduction chapter, part of each research topic, or part of each published paper ( 7 ). However, scholars view the LR as an integral part of the main body of an academic work because it is intrinsically connected to other sections ( Figure 1 ) and is frequently present. The structure of the LR depends on the conventions of a particular discipline, the rules of the department, and the student’s and supervisor’s areas of expertise, needs and interests.

Interestingly, many postgraduate students choose to submit their LR to peer-reviewed journals. As LRs are critical evaluations of current knowledge, they are indeed publishable material, even in the form of narrative or systematic reviews. However, systematic reviews have specific patterns 1 ( 8 ) that may not entirely fit with the questions posed in the dissertation/thesis. Additionally, the scope of a systematic review may be too narrow, and the strict criteria for study inclusion may omit important information from the dissertation/thesis. Therefore, this essay discusses the definition of an LR is and methods to develop an LR in the context of an academic dissertation/thesis. Finally, we suggest a checklist to evaluate an LR.
WHAT IS A LITERATURE REVIEW IN A THESIS?
Conducting research and writing a dissertation/thesis translates rational thinking and enthusiasm ( 9 ). While a strong body of literature that instructs students on research methodology, data analysis and writing scientific papers exists, little guidance on performing LRs is available. The LR is a unique opportunity to assess and contrast various arguments and theories, not just summarize them. The research results should not be discussed within the LR, but the postgraduate student tends to write a comprehensive LR while reflecting on his or her own findings ( 10 ).
Many people believe that writing an LR is a lonely and linear process. Supervisors or the institutions assume that the Ph.D. student has mastered the relevant techniques and vocabulary associated with his/her subject and conducts a self-reflection about previously published findings. Indeed, while elaborating the LR, the student should aggregate diverse skills, which mainly rely on his/her own commitment to mastering them. Thus, less supervision should be required ( 11 ). However, the parameters described above might not currently be the case for many students ( 11 , 12 ), and the lack of formal and systematic training on writing LRs is an important concern ( 11 ).
An institutional environment devoted to active learning will provide students the opportunity to continuously reflect on LRs, which will form a dialogue between the postgraduate student and the current literature in a particular field ( 13 ). Postgraduate students will be interpreting studies by other researchers, and, according to Hart (1998) ( 3 ), the outcomes of the LR in a dissertation/thesis include the following:
- To identify what research has been performed and what topics require further investigation in a particular field of knowledge;
- To determine the context of the problem;
- To recognize the main methodologies and techniques that have been used in the past;
- To place the current research project within the historical, methodological and theoretical context of a particular field;
- To identify significant aspects of the topic;
- To elucidate the implications of the topic;
- To offer an alternative perspective;
- To discern how the studied subject is structured;
- To improve the student’s subject vocabulary in a particular field; and
- To characterize the links between theory and practice.
A sound LR translates the postgraduate student’s expertise in academic and scientific writing: it expresses his/her level of comfort with synthesizing ideas ( 11 ). The LR reveals how well the postgraduate student has proceeded in three domains: an effective literature search, the language domain, and critical writing.
Effective literature search
All students should be trained in gathering appropriate data for specific purposes, and information literacy skills are a cornerstone. These skills are defined as “an individual’s ability to know when they need information, to identify information that can help them address the issue or problem at hand, and to locate, evaluate, and use that information effectively” ( 14 ). Librarian support is of vital importance in coaching the appropriate use of Boolean logic (AND, OR, NOT) and other tools for highly efficient literature searches (e.g., quotation marks and truncation), as is the appropriate management of electronic databases.
Language domain
Academic writing must be concise and precise: unnecessary words distract the reader from the essential content ( 15 ). In this context, reading about issues distant from the research topic ( 16 ) may increase students’ general vocabulary and familiarity with grammar. Ultimately, reading diverse materials facilitates and encourages the writing process itself.
Critical writing
Critical judgment includes critical reading, thinking and writing. It supposes a student’s analytical reflection about what he/she has read. The student should delineate the basic elements of the topic, characterize the most relevant claims, identify relationships, and finally contrast those relationships ( 17 ). Each scientific document highlights the perspective of the author, and students will become more confident in judging the supporting evidence and underlying premises of a study and constructing their own counterargument as they read more articles. A paucity of integration or contradictory perspectives indicates lower levels of cognitive complexity ( 12 ).
Thus, while elaborating an LR, the postgraduate student should achieve the highest category of Bloom’s cognitive skills: evaluation ( 12 ). The writer should not only summarize data and understand each topic but also be able to make judgments based on objective criteria, compare resources and findings, identify discrepancies due to methodology, and construct his/her own argument ( 12 ). As a result, the student will be sufficiently confident to show his/her own voice .
Writing a consistent LR is an intense and complex activity that reveals the training and long-lasting academic skills of a writer. It is not a lonely or linear process. However, students are unlikely to be prepared to write an LR if they have not mastered the aforementioned domains ( 10 ). An institutional environment that supports student learning is crucial.
Different institutions employ distinct methods to promote students’ learning processes. First, many universities propose modules to develop behind the scenes activities that enhance self-reflection about general skills (e.g., the skills we have mastered and the skills we need to develop further), behaviors that should be incorporated (e.g., self-criticism about one’s own thoughts), and each student’s role in the advancement of his/her field. Lectures or workshops about LRs themselves are useful because they describe the purposes of the LR and how it fits into the whole picture of a student’s work. These activities may explain what type of discussion an LR must involve, the importance of defining the correct scope, the reasons to include a particular resource, and the main role of critical reading.
Some pedagogic services that promote a continuous improvement in study and academic skills are equally important. Examples include workshops about time management, the accomplishment of personal objectives, active learning, and foreign languages for nonnative speakers. Additionally, opportunities to converse with other students promotes an awareness of others’ experiences and difficulties. Ultimately, the supervisor’s role in providing feedback and setting deadlines is crucial in developing students’ abilities and in strengthening students’ writing quality ( 12 ).
HOW SHOULD A LITERATURE REVIEW BE DEVELOPED?
A consensus on the appropriate method for elaborating an LR is not available, but four main steps are generally accepted: defining the main topic, searching the literature, analyzing the results, and writing ( 6 ). We suggest a fifth step: reflecting on the information that has been written in previous publications ( Figure 2 ).

First step: Defining the main topic
Planning an LR is directly linked to the research main question of the thesis and occurs in parallel to students’ training in the three domains discussed above. The planning stage helps organize ideas, delimit the scope of the LR ( 11 ), and avoid the wasting of time in the process. Planning includes the following steps:
- Reflecting on the scope of the LR: postgraduate students will have assumptions about what material must be addressed and what information is not essential to an LR ( 13 , 18 ). Cooper’s Taxonomy of Literature Reviews 2 systematizes the writing process through six characteristics and nonmutually exclusive categories. The focus refers to the reviewer’s most important points of interest, while the goals concern what students want to achieve with the LR. The perspective assumes answers to the student’s own view of the LR and how he/she presents a particular issue. The coverage defines how comprehensive the student is in presenting the literature, and the organization determines the sequence of arguments. The audience is defined as the group for whom the LR is written.
- Designating sections and subsections: Headings and subheadings should be specific, explanatory and have a coherent sequence throughout the text ( 4 ). They simulate an inverted pyramid, with an increasing level of reflection and depth of argument.
- Identifying keywords: The relevant keywords for each LR section should be listed to guide the literature search. This list should mirror what Hart (1998) ( 3 ) advocates as subject vocabulary . The keywords will also be useful when the student is writing the LR since they guide the reader through the text.
- Delineating the time interval and language of documents to be retrieved in the second step. The most recently published documents should be considered, but relevant texts published before a predefined cutoff year can be included if they are classic documents in that field. Extra care should be employed when translating documents.
Second step: Searching the literature
The ability to gather adequate information from the literature must be addressed in postgraduate programs. Librarian support is important, particularly for accessing difficult texts. This step comprises the following components:
- Searching the literature itself: This process consists of defining which databases (electronic or dissertation/thesis repositories), official documents, and books will be searched and then actively conducting the search. Information literacy skills have a central role in this stage. While searching electronic databases, controlled vocabulary (e.g., Medical Subject Headings, or MeSH, for the PubMed database) or specific standardized syntax rules may need to be applied.
In addition, two other approaches are suggested. First, a review of the reference list of each document might be useful for identifying relevant publications to be included and important opinions to be assessed. This step is also relevant for referencing the original studies and leading authors in that field. Moreover, students can directly contact the experts on a particular topic to consult with them regarding their experience or use them as a source of additional unpublished documents.
Before submitting a dissertation/thesis, the electronic search strategy should be repeated. This process will ensure that the most recently published papers will be considered in the LR.
- Selecting documents for inclusion: Generally, the most recent literature will be included in the form of published peer-reviewed papers. Assess books and unpublished material, such as conference abstracts, academic texts and government reports, are also important to assess since the gray literature also offers valuable information. However, since these materials are not peer-reviewed, we recommend that they are carefully added to the LR.
This task is an important exercise in time management. First, students should read the title and abstract to understand whether that document suits their purposes, addresses the research question, and helps develop the topic of interest. Then, they should scan the full text, determine how it is structured, group it with similar documents, and verify whether other arguments might be considered ( 5 ).
Third step: Analyzing the results
Critical reading and thinking skills are important in this step. This step consists of the following components:
- Reading documents: The student may read various texts in depth according to LR sections and subsections ( defining the main topic ), which is not a passive activity ( 1 ). Some questions should be asked to practice critical analysis skills, as listed below. Is the research question evident and articulated with previous knowledge? What are the authors’ research goals and theoretical orientations, and how do they interact? Are the authors’ claims related to other scholars’ research? Do the authors consider different perspectives? Was the research project designed and conducted properly? Are the results and discussion plausible, and are they consistent with the research objectives and methodology? What are the strengths and limitations of this work? How do the authors support their findings? How does this work contribute to the current research topic? ( 1 , 19 )
- Taking notes: Students who systematically take notes on each document are more readily able to establish similarities or differences with other documents and to highlight personal observations. This approach reinforces the student’s ideas about the next step and helps develop his/her own academic voice ( 1 , 13 ). Voice recognition software ( 16 ), mind maps ( 5 ), flowcharts, tables, spreadsheets, personal comments on the referenced texts, and note-taking apps are all available tools for managing these observations, and the student him/herself should use the tool that best improves his/her learning. Additionally, when a student is considering submitting an LR to a peer-reviewed journal, notes should be taken on the activities performed in all five steps to ensure that they are able to be replicated.
Fourth step: Writing
The recognition of when a student is able and ready to write after a sufficient period of reading and thinking is likely a difficult task. Some students can produce a review in a single long work session. However, as discussed above, writing is not a linear process, and students do not need to write LRs according to a specific sequence of sections. Writing an LR is a time-consuming task, and some scholars believe that a period of at least six months is sufficient ( 6 ). An LR, and academic writing in general, expresses the writer’s proper thoughts, conclusions about others’ work ( 6 , 10 , 13 , 16 ), and decisions about methods to progress in the chosen field of knowledge. Thus, each student is expected to present a different learning and writing trajectory.
In this step, writing methods should be considered; then, editing, citing and correct referencing should complete this stage, at least temporarily. Freewriting techniques may be a good starting point for brainstorming ideas and improving the understanding of the information that has been read ( 1 ). Students should consider the following parameters when creating an agenda for writing the LR: two-hour writing blocks (at minimum), with prespecified tasks that are possible to complete in one section; short (minutes) and long breaks (days or weeks) to allow sufficient time for mental rest and reflection; and short- and long-term goals to motivate the writing itself ( 20 ). With increasing experience, this scheme can vary widely, and it is not a straightforward rule. Importantly, each discipline has a different way of writing ( 1 ), and each department has its own preferred styles for citations and references.
Fifth step: Reflecting on the writing
In this step, the postgraduate student should ask him/herself the same questions as in the analyzing the results step, which can take more time than anticipated. Ambiguities, repeated ideas, and a lack of coherence may not be noted when the student is immersed in the writing task for long periods. The whole effort will likely be a work in progress, and continuous refinements in the written material will occur once the writing process has begun.
LITERATURE REVIEW CHECKLIST
In contrast to review papers, the LR of a dissertation/thesis should not be a standalone piece or work. Instead, it should present the student as a scholar and should maintain the interest of the audience in how that dissertation/thesis will provide solutions for the current gaps in a particular field.
A checklist for evaluating an LR is convenient for students’ continuous academic development and research transparency: it clearly states the desired achievements for the LR of a dissertation/thesis. Here, we present an LR checklist developed from an LR scoring rubric ( 11 ). For a critical analysis of an LR, we maintain the five categories but offer twelve criteria that are not scaled ( Figure 3 ). The criteria all have the same importance and are not mutually exclusive.

First category: Coverage
1. justified criteria exist for the inclusion and exclusion of literature in the review.
This criterion builds on the main topic and areas covered by the LR ( 18 ). While experts may be confident in retrieving and selecting literature, postgraduate students must convince their audience about the adequacy of their search strategy and their reasons for intentionally selecting what material to cover ( 11 ). References from different fields of knowledge provide distinct perspective, but narrowing the scope of coverage may be important in areas with a large body of existing knowledge.
Second category: Synthesis
2. a critical examination of the state of the field exists.
A critical examination is an assessment of distinct aspects in the field ( 1 ) along with a constructive argument. It is not a negative critique but an expression of the student’s understanding of how other scholars have added to the topic ( 1 ), and the student should analyze and contextualize contradictory statements. A writer’s personal bias (beliefs or political involvement) have been shown to influence the structure and writing of a document; therefore, the cultural and paradigmatic background guide how the theories are revised and presented ( 13 ). However, an honest judgment is important when considering different perspectives.
3. The topic or problem is clearly placed in the context of the broader scholarly literature
The broader scholarly literature should be related to the chosen main topic for the LR ( how to develop the literature review section). The LR can cover the literature from one or more disciplines, depending on its scope, but it should always offer a new perspective. In addition, students should be careful in citing and referencing previous publications. As a rule, original studies and primary references should generally be included. Systematic and narrative reviews present summarized data, and it may be important to cite them, particularly for issues that should be understood but do not require a detailed description. Similarly, quotations highlight the exact statement from another publication. However, excessive referencing may disclose lower levels of analysis and synthesis by the student.
4. The LR is critically placed in the historical context of the field
Situating the LR in its historical context shows the level of comfort of the student in addressing a particular topic. Instead of only presenting statements and theories in a temporal approach, which occasionally follows a linear timeline, the LR should authentically characterize the student’s academic work in the state-of-art techniques in their particular field of knowledge. Thus, the LR should reinforce why the dissertation/thesis represents original work in the chosen research field.
5. Ambiguities in definitions are considered and resolved
Distinct theories on the same topic may exist in different disciplines, and one discipline may consider multiple concepts to explain one topic. These misunderstandings should be addressed and contemplated. The LR should not synthesize all theories or concepts at the same time. Although this approach might demonstrate in-depth reading on a particular topic, it can reveal a student’s inability to comprehend and synthesize his/her research problem.
6. Important variables and phenomena relevant to the topic are articulated
The LR is a unique opportunity to articulate ideas and arguments and to purpose new relationships between them ( 10 , 11 ). More importantly, a sound LR will outline to the audience how these important variables and phenomena will be addressed in the current academic work. Indeed, the LR should build a bidirectional link with the remaining sections and ground the connections between all of the sections ( Figure 1 ).
7. A synthesized new perspective on the literature has been established
The LR is a ‘creative inquiry’ ( 13 ) in which the student elaborates his/her own discourse, builds on previous knowledge in the field, and describes his/her own perspective while interpreting others’ work ( 13 , 17 ). Thus, students should articulate the current knowledge, not accept the results at face value ( 11 , 13 , 17 ), and improve their own cognitive abilities ( 12 ).
Third category: Methodology
8. the main methodologies and research techniques that have been used in the field are identified and their advantages and disadvantages are discussed.
The LR is expected to distinguish the research that has been completed from investigations that remain to be performed, address the benefits and limitations of the main methods applied to date, and consider the strategies for addressing the expected limitations described above. While placing his/her research within the methodological context of a particular topic, the LR will justify the methodology of the study and substantiate the student’s interpretations.
9. Ideas and theories in the field are related to research methodologies
The audience expects the writer to analyze and synthesize methodological approaches in the field. The findings should be explained according to the strengths and limitations of previous research methods, and students must avoid interpretations that are not supported by the analyzed literature. This criterion translates to the student’s comprehension of the applicability and types of answers provided by different research methodologies, even those using a quantitative or qualitative research approach.
Fourth category: Significance
10. the scholarly significance of the research problem is rationalized.
The LR is an introductory section of a dissertation/thesis and will present the postgraduate student as a scholar in a particular field ( 11 ). Therefore, the LR should discuss how the research problem is currently addressed in the discipline being investigated or in different disciplines, depending on the scope of the LR. The LR explains the academic paradigms in the topic of interest ( 13 ) and methods to advance the field from these starting points. However, an excess number of personal citations—whether referencing the student’s research or studies by his/her research team—may reflect a narrow literature search and a lack of comprehensive synthesis of ideas and arguments.
11. The practical significance of the research problem is rationalized
The practical significance indicates a student’s comprehensive understanding of research terminology (e.g., risk versus associated factor), methodology (e.g., efficacy versus effectiveness) and plausible interpretations in the context of the field. Notably, the academic argument about a topic may not always reflect the debate in real life terms. For example, using a quantitative approach in epidemiology, statistically significant differences between groups do not explain all of the factors involved in a particular problem ( 21 ). Therefore, excessive faith in p -values may reflect lower levels of critical evaluation of the context and implications of a research problem by the student.
Fifth category: Rhetoric
12. the lr was written with a coherent, clear structure that supported the review.
This category strictly relates to the language domain: the text should be coherent and presented in a logical sequence, regardless of which organizational ( 18 ) approach is chosen. The beginning of each section/subsection should state what themes will be addressed, paragraphs should be carefully linked to each other ( 10 ), and the first sentence of each paragraph should generally summarize the content. Additionally, the student’s statements are clear, sound, and linked to other scholars’ works, and precise and concise language that follows standardized writing conventions (e.g., in terms of active/passive voice and verb tenses) is used. Attention to grammar, such as orthography and punctuation, indicates prudence and supports a robust dissertation/thesis. Ultimately, all of these strategies provide fluency and consistency for the text.
Although the scoring rubric was initially proposed for postgraduate programs in education research, we are convinced that this checklist is a valuable tool for all academic areas. It enables the monitoring of students’ learning curves and a concentrated effort on any criteria that are not yet achieved. For institutions, the checklist is a guide to support supervisors’ feedback, improve students’ writing skills, and highlight the learning goals of each program. These criteria do not form a linear sequence, but ideally, all twelve achievements should be perceived in the LR.
CONCLUSIONS
A single correct method to classify, evaluate and guide the elaboration of an LR has not been established. In this essay, we have suggested directions for planning, structuring and critically evaluating an LR. The planning of the scope of an LR and approaches to complete it is a valuable effort, and the five steps represent a rational starting point. An institutional environment devoted to active learning will support students in continuously reflecting on LRs, which will form a dialogue between the writer and the current literature in a particular field ( 13 ).
The completion of an LR is a challenging and necessary process for understanding one’s own field of expertise. Knowledge is always transitory, but our responsibility as scholars is to provide a critical contribution to our field, allowing others to think through our work. Good researchers are grounded in sophisticated LRs, which reveal a writer’s training and long-lasting academic skills. We recommend using the LR checklist as a tool for strengthening the skills necessary for critical academic writing.
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
Leite DFB has initially conceived the idea and has written the first draft of this review. Padilha MAS and Cecatti JG have supervised data interpretation and critically reviewed the manuscript. All authors have read the draft and agreed with this submission. Authors are responsible for all aspects of this academic piece.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We are grateful to all of the professors of the ‘Getting Started with Graduate Research and Generic Skills’ module at University College Cork, Cork, Ireland, for suggesting and supporting this article. Funding: DFBL has granted scholarship from Brazilian Federal Agency for Support and Evaluation of Graduate Education (CAPES) to take part of her Ph.D. studies in Ireland (process number 88881.134512/2016-01). There is no participation from sponsors on authors’ decision to write or to submit this manuscript.
No potential conflict of interest was reported.
1 The questions posed in systematic reviews usually follow the ‘PICOS’ acronym: Population, Intervention, Comparison, Outcomes, Study design.
2 In 1988, Cooper proposed a taxonomy that aims to facilitate students’ and institutions’ understanding of literature reviews. Six characteristics with specific categories are briefly described: Focus: research outcomes, research methodologies, theories, or practices and applications; Goals: integration (generalization, conflict resolution, and linguistic bridge-building), criticism, or identification of central issues; Perspective: neutral representation or espousal of a position; Coverage: exhaustive, exhaustive with selective citations, representative, central or pivotal; Organization: historical, conceptual, or methodological; and Audience: specialized scholars, general scholars, practitioners or policymakers, or the general public.

Roanoke College
- Orientation
- Events Calendar
- &]:text-lg [.small>&]:leading-tight [.large>&]:text-[calc(22rem/16)] ml-[calc(-1*var(--pl))] pl-[var(--pl)] [.no-arrow>&]:ml-0 after:hidden [.lock-icon>&]:after:inline-block [.lock-icon>&]:after:mask-lock [.lock-icon>&]:after:bg-current [.museum-icon>&]:after:inline-block [.museum-icon>&]:after:mask-museum [.museum-icon>&]:after:bg-roanoke-maroon-500 relative after:pointer-events-none after:relative after:top-1 after:left-7 after:-ml-4 after:w-4 after:h-4 after:scale-125 after:origin-bottom-right [.small>&]:after:scale-100 [.small>&]:after:left-6 [.small>&]:after:top-[calc(3rem/16)]" title="Email">Email &]:hidden absolute mask-right-arrowhead-2-by-3 pointer-events-none w-2 h-3 top-1.5 [.small>&]:scale-75 [.large>&]:scale-110 origin-top left-0 peer-hocus:left-1 sm:peer-hocus:left-1.5 motion-reduce:!left-0 bg-theme-fancy-link-color peer-hocus:bg-theme-fancy-link-hocus-color theme-dogwood-bloom-400:peer-aria-current:bg-black theme-dogwood-bloom-400:peer-aria-current:peer-hocus:bg-dogwood-bloom-900 transition-[left,background-color] ease-linear">
- &]:text-lg [.small>&]:leading-tight [.large>&]:text-[calc(22rem/16)] ml-[calc(-1*var(--pl))] pl-[var(--pl)] [.no-arrow>&]:ml-0 after:hidden [.lock-icon>&]:after:inline-block [.lock-icon>&]:after:mask-lock [.lock-icon>&]:after:bg-current [.museum-icon>&]:after:inline-block [.museum-icon>&]:after:mask-museum [.museum-icon>&]:after:bg-roanoke-maroon-500 relative after:pointer-events-none after:relative after:top-1 after:left-7 after:-ml-4 after:w-4 after:h-4 after:scale-125 after:origin-bottom-right [.small>&]:after:scale-100 [.small>&]:after:left-6 [.small>&]:after:top-[calc(3rem/16)]" title="Navigate">Navigate &]:hidden absolute mask-right-arrowhead-2-by-3 pointer-events-none w-2 h-3 top-1.5 [.small>&]:scale-75 [.large>&]:scale-110 origin-top left-0 peer-hocus:left-1 sm:peer-hocus:left-1.5 motion-reduce:!left-0 bg-theme-fancy-link-color peer-hocus:bg-theme-fancy-link-hocus-color theme-dogwood-bloom-400:peer-aria-current:bg-black theme-dogwood-bloom-400:peer-aria-current:peer-hocus:bg-dogwood-bloom-900 transition-[left,background-color] ease-linear">
- &]:text-lg [.small>&]:leading-tight [.large>&]:text-[calc(22rem/16)] ml-[calc(-1*var(--pl))] pl-[var(--pl)] [.no-arrow>&]:ml-0 after:hidden [.lock-icon>&]:after:inline-block [.lock-icon>&]:after:mask-lock [.lock-icon>&]:after:bg-current [.museum-icon>&]:after:inline-block [.museum-icon>&]:after:mask-museum [.museum-icon>&]:after:bg-roanoke-maroon-500 relative after:pointer-events-none after:relative after:top-1 after:left-7 after:-ml-4 after:w-4 after:h-4 after:scale-125 after:origin-bottom-right [.small>&]:after:scale-100 [.small>&]:after:left-6 [.small>&]:after:top-[calc(3rem/16)]" title="Inquire">Inquire &]:hidden absolute mask-right-arrowhead-2-by-3 pointer-events-none w-2 h-3 top-1.5 [.small>&]:scale-75 [.large>&]:scale-110 origin-top left-0 peer-hocus:left-1 sm:peer-hocus:left-1.5 motion-reduce:!left-0 bg-theme-fancy-link-color peer-hocus:bg-theme-fancy-link-hocus-color theme-dogwood-bloom-400:peer-aria-current:bg-black theme-dogwood-bloom-400:peer-aria-current:peer-hocus:bg-dogwood-bloom-900 transition-[left,background-color] ease-linear">
- &]:text-lg [.small>&]:leading-tight [.large>&]:text-[calc(22rem/16)] ml-[calc(-1*var(--pl))] pl-[var(--pl)] [.no-arrow>&]:ml-0 after:hidden [.lock-icon>&]:after:inline-block [.lock-icon>&]:after:mask-lock [.lock-icon>&]:after:bg-current [.museum-icon>&]:after:inline-block [.museum-icon>&]:after:mask-museum [.museum-icon>&]:after:bg-roanoke-maroon-500 relative after:pointer-events-none after:relative after:top-1 after:left-7 after:-ml-4 after:w-4 after:h-4 after:scale-125 after:origin-bottom-right [.small>&]:after:scale-100 [.small>&]:after:left-6 [.small>&]:after:top-[calc(3rem/16)]" title="Self Service">Self Service &]:hidden absolute mask-right-arrowhead-2-by-3 pointer-events-none w-2 h-3 top-1.5 [.small>&]:scale-75 [.large>&]:scale-110 origin-top left-0 peer-hocus:left-1 sm:peer-hocus:left-1.5 motion-reduce:!left-0 bg-theme-fancy-link-color peer-hocus:bg-theme-fancy-link-hocus-color theme-dogwood-bloom-400:peer-aria-current:bg-black theme-dogwood-bloom-400:peer-aria-current:peer-hocus:bg-dogwood-bloom-900 transition-[left,background-color] ease-linear">
- &]:text-lg [.small>&]:leading-tight [.large>&]:text-[calc(22rem/16)] ml-[calc(-1*var(--pl))] pl-[var(--pl)] [.no-arrow>&]:ml-0 after:hidden [.lock-icon>&]:after:inline-block [.lock-icon>&]:after:mask-lock [.lock-icon>&]:after:bg-current [.museum-icon>&]:after:inline-block [.museum-icon>&]:after:mask-museum [.museum-icon>&]:after:bg-roanoke-maroon-500 relative after:pointer-events-none after:relative after:top-1 after:left-7 after:-ml-4 after:w-4 after:h-4 after:scale-125 after:origin-bottom-right [.small>&]:after:scale-100 [.small>&]:after:left-6 [.small>&]:after:top-[calc(3rem/16)]" title="Forms">Forms &]:hidden absolute mask-right-arrowhead-2-by-3 pointer-events-none w-2 h-3 top-1.5 [.small>&]:scale-75 [.large>&]:scale-110 origin-top left-0 peer-hocus:left-1 sm:peer-hocus:left-1.5 motion-reduce:!left-0 bg-theme-fancy-link-color peer-hocus:bg-theme-fancy-link-hocus-color theme-dogwood-bloom-400:peer-aria-current:bg-black theme-dogwood-bloom-400:peer-aria-current:peer-hocus:bg-dogwood-bloom-900 transition-[left,background-color] ease-linear">
- &]:text-lg [.small>&]:leading-tight [.large>&]:text-[calc(22rem/16)] ml-[calc(-1*var(--pl))] pl-[var(--pl)] [.no-arrow>&]:ml-0 after:hidden [.lock-icon>&]:after:inline-block [.lock-icon>&]:after:mask-lock [.lock-icon>&]:after:bg-current [.museum-icon>&]:after:inline-block [.museum-icon>&]:after:mask-museum [.museum-icon>&]:after:bg-roanoke-maroon-500 relative after:pointer-events-none after:relative after:top-1 after:left-7 after:-ml-4 after:w-4 after:h-4 after:scale-125 after:origin-bottom-right [.small>&]:after:scale-100 [.small>&]:after:left-6 [.small>&]:after:top-[calc(3rem/16)]" title="RC Today">RC Today &]:hidden absolute mask-right-arrowhead-2-by-3 pointer-events-none w-2 h-3 top-1.5 [.small>&]:scale-75 [.large>&]:scale-110 origin-top left-0 peer-hocus:left-1 sm:peer-hocus:left-1.5 motion-reduce:!left-0 bg-theme-fancy-link-color peer-hocus:bg-theme-fancy-link-hocus-color theme-dogwood-bloom-400:peer-aria-current:bg-black theme-dogwood-bloom-400:peer-aria-current:peer-hocus:bg-dogwood-bloom-900 transition-[left,background-color] ease-linear">
ACADEMIC SCHEDULES
- &]:text-lg [.small>&]:leading-tight [.large>&]:text-[calc(22rem/16)] ml-[calc(-1*var(--pl))] pl-[var(--pl)] [.no-arrow>&]:ml-0 after:hidden [.lock-icon>&]:after:inline-block [.lock-icon>&]:after:mask-lock [.lock-icon>&]:after:bg-current [.museum-icon>&]:after:inline-block [.museum-icon>&]:after:mask-museum [.museum-icon>&]:after:bg-roanoke-maroon-500 relative after:pointer-events-none after:relative after:top-1 after:left-7 after:-ml-4 after:w-4 after:h-4 after:scale-125 after:origin-bottom-right [.small>&]:after:scale-100 [.small>&]:after:left-6 [.small>&]:after:top-[calc(3rem/16)]" title="Academic Calendar">Academic Calendar &]:hidden absolute mask-right-arrowhead-2-by-3 pointer-events-none w-2 h-3 top-1.5 [.small>&]:scale-75 [.large>&]:scale-110 origin-top left-0 peer-hocus:left-1 sm:peer-hocus:left-1.5 motion-reduce:!left-0 bg-theme-fancy-link-color peer-hocus:bg-theme-fancy-link-hocus-color theme-dogwood-bloom-400:peer-aria-current:bg-black theme-dogwood-bloom-400:peer-aria-current:peer-hocus:bg-dogwood-bloom-900 transition-[left,background-color] ease-linear">
- &]:text-lg [.small>&]:leading-tight [.large>&]:text-[calc(22rem/16)] ml-[calc(-1*var(--pl))] pl-[var(--pl)] [.no-arrow>&]:ml-0 after:hidden [.lock-icon>&]:after:inline-block [.lock-icon>&]:after:mask-lock [.lock-icon>&]:after:bg-current [.museum-icon>&]:after:inline-block [.museum-icon>&]:after:mask-museum [.museum-icon>&]:after:bg-roanoke-maroon-500 relative after:pointer-events-none after:relative after:top-1 after:left-7 after:-ml-4 after:w-4 after:h-4 after:scale-125 after:origin-bottom-right [.small>&]:after:scale-100 [.small>&]:after:left-6 [.small>&]:after:top-[calc(3rem/16)]" title="Academic Catalog">Academic Catalog &]:hidden absolute mask-right-arrowhead-2-by-3 pointer-events-none w-2 h-3 top-1.5 [.small>&]:scale-75 [.large>&]:scale-110 origin-top left-0 peer-hocus:left-1 sm:peer-hocus:left-1.5 motion-reduce:!left-0 bg-theme-fancy-link-color peer-hocus:bg-theme-fancy-link-hocus-color theme-dogwood-bloom-400:peer-aria-current:bg-black theme-dogwood-bloom-400:peer-aria-current:peer-hocus:bg-dogwood-bloom-900 transition-[left,background-color] ease-linear">
- &]:text-lg [.small>&]:leading-tight [.large>&]:text-[calc(22rem/16)] ml-[calc(-1*var(--pl))] pl-[var(--pl)] [.no-arrow>&]:ml-0 after:hidden [.lock-icon>&]:after:inline-block [.lock-icon>&]:after:mask-lock [.lock-icon>&]:after:bg-current [.museum-icon>&]:after:inline-block [.museum-icon>&]:after:mask-museum [.museum-icon>&]:after:bg-roanoke-maroon-500 relative after:pointer-events-none after:relative after:top-1 after:left-7 after:-ml-4 after:w-4 after:h-4 after:scale-125 after:origin-bottom-right [.small>&]:after:scale-100 [.small>&]:after:left-6 [.small>&]:after:top-[calc(3rem/16)]" title="Courses">Courses &]:hidden absolute mask-right-arrowhead-2-by-3 pointer-events-none w-2 h-3 top-1.5 [.small>&]:scale-75 [.large>&]:scale-110 origin-top left-0 peer-hocus:left-1 sm:peer-hocus:left-1.5 motion-reduce:!left-0 bg-theme-fancy-link-color peer-hocus:bg-theme-fancy-link-hocus-color theme-dogwood-bloom-400:peer-aria-current:bg-black theme-dogwood-bloom-400:peer-aria-current:peer-hocus:bg-dogwood-bloom-900 transition-[left,background-color] ease-linear">
- &]:text-lg [.small>&]:leading-tight [.large>&]:text-[calc(22rem/16)] ml-[calc(-1*var(--pl))] pl-[var(--pl)] [.no-arrow>&]:ml-0 after:hidden [.lock-icon>&]:after:inline-block [.lock-icon>&]:after:mask-lock [.lock-icon>&]:after:bg-current [.museum-icon>&]:after:inline-block [.museum-icon>&]:after:mask-museum [.museum-icon>&]:after:bg-roanoke-maroon-500 relative after:pointer-events-none after:relative after:top-1 after:left-7 after:-ml-4 after:w-4 after:h-4 after:scale-125 after:origin-bottom-right [.small>&]:after:scale-100 [.small>&]:after:left-6 [.small>&]:after:top-[calc(3rem/16)]" title="Registrar">Registrar &]:hidden absolute mask-right-arrowhead-2-by-3 pointer-events-none w-2 h-3 top-1.5 [.small>&]:scale-75 [.large>&]:scale-110 origin-top left-0 peer-hocus:left-1 sm:peer-hocus:left-1.5 motion-reduce:!left-0 bg-theme-fancy-link-color peer-hocus:bg-theme-fancy-link-hocus-color theme-dogwood-bloom-400:peer-aria-current:bg-black theme-dogwood-bloom-400:peer-aria-current:peer-hocus:bg-dogwood-bloom-900 transition-[left,background-color] ease-linear">
- &]:text-lg [.small>&]:leading-tight [.large>&]:text-[calc(22rem/16)] ml-[calc(-1*var(--pl))] pl-[var(--pl)] [.no-arrow>&]:ml-0 after:hidden [.lock-icon>&]:after:inline-block [.lock-icon>&]:after:mask-lock [.lock-icon>&]:after:bg-current [.museum-icon>&]:after:inline-block [.museum-icon>&]:after:mask-museum [.museum-icon>&]:after:bg-roanoke-maroon-500 relative after:pointer-events-none after:relative after:top-1 after:left-7 after:-ml-4 after:w-4 after:h-4 after:scale-125 after:origin-bottom-right [.small>&]:after:scale-100 [.small>&]:after:left-6 [.small>&]:after:top-[calc(3rem/16)]" title="Dining Menu">Dining Menu &]:hidden absolute mask-right-arrowhead-2-by-3 pointer-events-none w-2 h-3 top-1.5 [.small>&]:scale-75 [.large>&]:scale-110 origin-top left-0 peer-hocus:left-1 sm:peer-hocus:left-1.5 motion-reduce:!left-0 bg-theme-fancy-link-color peer-hocus:bg-theme-fancy-link-hocus-color theme-dogwood-bloom-400:peer-aria-current:bg-black theme-dogwood-bloom-400:peer-aria-current:peer-hocus:bg-dogwood-bloom-900 transition-[left,background-color] ease-linear">
- &]:text-lg [.small>&]:leading-tight [.large>&]:text-[calc(22rem/16)] ml-[calc(-1*var(--pl))] pl-[var(--pl)] [.no-arrow>&]:ml-0 after:hidden [.lock-icon>&]:after:inline-block [.lock-icon>&]:after:mask-lock [.lock-icon>&]:after:bg-current [.museum-icon>&]:after:inline-block [.museum-icon>&]:after:mask-museum [.museum-icon>&]:after:bg-roanoke-maroon-500 relative after:pointer-events-none after:relative after:top-1 after:left-7 after:-ml-4 after:w-4 after:h-4 after:scale-125 after:origin-bottom-right [.small>&]:after:scale-100 [.small>&]:after:left-6 [.small>&]:after:top-[calc(3rem/16)]" title="Cregger Center">Cregger Center &]:hidden absolute mask-right-arrowhead-2-by-3 pointer-events-none w-2 h-3 top-1.5 [.small>&]:scale-75 [.large>&]:scale-110 origin-top left-0 peer-hocus:left-1 sm:peer-hocus:left-1.5 motion-reduce:!left-0 bg-theme-fancy-link-color peer-hocus:bg-theme-fancy-link-hocus-color theme-dogwood-bloom-400:peer-aria-current:bg-black theme-dogwood-bloom-400:peer-aria-current:peer-hocus:bg-dogwood-bloom-900 transition-[left,background-color] ease-linear">
- &]:text-lg [.small>&]:leading-tight [.large>&]:text-[calc(22rem/16)] ml-[calc(-1*var(--pl))] pl-[var(--pl)] [.no-arrow>&]:ml-0 after:hidden [.lock-icon>&]:after:inline-block [.lock-icon>&]:after:mask-lock [.lock-icon>&]:after:bg-current [.museum-icon>&]:after:inline-block [.museum-icon>&]:after:mask-museum [.museum-icon>&]:after:bg-roanoke-maroon-500 relative after:pointer-events-none after:relative after:top-1 after:left-7 after:-ml-4 after:w-4 after:h-4 after:scale-125 after:origin-bottom-right [.small>&]:after:scale-100 [.small>&]:after:left-6 [.small>&]:after:top-[calc(3rem/16)]" title="Colket Campus Center">Colket Campus Center &]:hidden absolute mask-right-arrowhead-2-by-3 pointer-events-none w-2 h-3 top-1.5 [.small>&]:scale-75 [.large>&]:scale-110 origin-top left-0 peer-hocus:left-1 sm:peer-hocus:left-1.5 motion-reduce:!left-0 bg-theme-fancy-link-color peer-hocus:bg-theme-fancy-link-hocus-color theme-dogwood-bloom-400:peer-aria-current:bg-black theme-dogwood-bloom-400:peer-aria-current:peer-hocus:bg-dogwood-bloom-900 transition-[left,background-color] ease-linear">
- &]:text-lg [.small>&]:leading-tight [.large>&]:text-[calc(22rem/16)] ml-[calc(-1*var(--pl))] pl-[var(--pl)] [.no-arrow>&]:ml-0 after:hidden [.lock-icon>&]:after:inline-block [.lock-icon>&]:after:mask-lock [.lock-icon>&]:after:bg-current [.museum-icon>&]:after:inline-block [.museum-icon>&]:after:mask-museum [.museum-icon>&]:after:bg-roanoke-maroon-500 relative after:pointer-events-none after:relative after:top-1 after:left-7 after:-ml-4 after:w-4 after:h-4 after:scale-125 after:origin-bottom-right [.small>&]:after:scale-100 [.small>&]:after:left-6 [.small>&]:after:top-[calc(3rem/16)]" title="Fintel Library">Fintel Library &]:hidden absolute mask-right-arrowhead-2-by-3 pointer-events-none w-2 h-3 top-1.5 [.small>&]:scale-75 [.large>&]:scale-110 origin-top left-0 peer-hocus:left-1 sm:peer-hocus:left-1.5 motion-reduce:!left-0 bg-theme-fancy-link-color peer-hocus:bg-theme-fancy-link-hocus-color theme-dogwood-bloom-400:peer-aria-current:bg-black theme-dogwood-bloom-400:peer-aria-current:peer-hocus:bg-dogwood-bloom-900 transition-[left,background-color] ease-linear">
- &]:text-lg [.small>&]:leading-tight [.large>&]:text-[calc(22rem/16)] ml-[calc(-1*var(--pl))] pl-[var(--pl)] [.no-arrow>&]:ml-0 after:hidden [.lock-icon>&]:after:inline-block [.lock-icon>&]:after:mask-lock [.lock-icon>&]:after:bg-current [.museum-icon>&]:after:inline-block [.museum-icon>&]:after:mask-museum [.museum-icon>&]:after:bg-roanoke-maroon-500 relative after:pointer-events-none after:relative after:top-1 after:left-7 after:-ml-4 after:w-4 after:h-4 after:scale-125 after:origin-bottom-right [.small>&]:after:scale-100 [.small>&]:after:left-6 [.small>&]:after:top-[calc(3rem/16)]" title="Olin Hall Galleries">Olin Hall Galleries &]:hidden absolute mask-right-arrowhead-2-by-3 pointer-events-none w-2 h-3 top-1.5 [.small>&]:scale-75 [.large>&]:scale-110 origin-top left-0 peer-hocus:left-1 sm:peer-hocus:left-1.5 motion-reduce:!left-0 bg-theme-fancy-link-color peer-hocus:bg-theme-fancy-link-hocus-color theme-dogwood-bloom-400:peer-aria-current:bg-black theme-dogwood-bloom-400:peer-aria-current:peer-hocus:bg-dogwood-bloom-900 transition-[left,background-color] ease-linear">
- &]:text-lg [.small>&]:leading-tight [.large>&]:text-[calc(22rem/16)] ml-[calc(-1*var(--pl))] pl-[var(--pl)] [.no-arrow>&]:ml-0 after:hidden [.lock-icon>&]:after:inline-block [.lock-icon>&]:after:mask-lock [.lock-icon>&]:after:bg-current [.museum-icon>&]:after:inline-block [.museum-icon>&]:after:mask-museum [.museum-icon>&]:after:bg-roanoke-maroon-500 relative after:pointer-events-none after:relative after:top-1 after:left-7 after:-ml-4 after:w-4 after:h-4 after:scale-125 after:origin-bottom-right [.small>&]:after:scale-100 [.small>&]:after:left-6 [.small>&]:after:top-[calc(3rem/16)]" title="A-Z">A-Z &]:hidden absolute mask-right-arrowhead-2-by-3 pointer-events-none w-2 h-3 top-1.5 [.small>&]:scale-75 [.large>&]:scale-110 origin-top left-0 peer-hocus:left-1 sm:peer-hocus:left-1.5 motion-reduce:!left-0 bg-theme-fancy-link-color peer-hocus:bg-theme-fancy-link-hocus-color theme-dogwood-bloom-400:peer-aria-current:bg-black theme-dogwood-bloom-400:peer-aria-current:peer-hocus:bg-dogwood-bloom-900 transition-[left,background-color] ease-linear">
- &]:text-lg [.small>&]:leading-tight [.large>&]:text-[calc(22rem/16)] ml-[calc(-1*var(--pl))] pl-[var(--pl)] [.no-arrow>&]:ml-0 after:hidden [.lock-icon>&]:after:inline-block [.lock-icon>&]:after:mask-lock [.lock-icon>&]:after:bg-current [.museum-icon>&]:after:inline-block [.museum-icon>&]:after:mask-museum [.museum-icon>&]:after:bg-roanoke-maroon-500 relative after:pointer-events-none after:relative after:top-1 after:left-7 after:-ml-4 after:w-4 after:h-4 after:scale-125 after:origin-bottom-right [.small>&]:after:scale-100 [.small>&]:after:left-6 [.small>&]:after:top-[calc(3rem/16)]" title="People Directory">People Directory &]:hidden absolute mask-right-arrowhead-2-by-3 pointer-events-none w-2 h-3 top-1.5 [.small>&]:scale-75 [.large>&]:scale-110 origin-top left-0 peer-hocus:left-1 sm:peer-hocus:left-1.5 motion-reduce:!left-0 bg-theme-fancy-link-color peer-hocus:bg-theme-fancy-link-hocus-color theme-dogwood-bloom-400:peer-aria-current:bg-black theme-dogwood-bloom-400:peer-aria-current:peer-hocus:bg-dogwood-bloom-900 transition-[left,background-color] ease-linear">
- &]:text-lg [.small>&]:leading-tight [.large>&]:text-[calc(22rem/16)] ml-[calc(-1*var(--pl))] pl-[var(--pl)] [.no-arrow>&]:ml-0 after:hidden [.lock-icon>&]:after:inline-block [.lock-icon>&]:after:mask-lock [.lock-icon>&]:after:bg-current [.museum-icon>&]:after:inline-block [.museum-icon>&]:after:mask-museum [.museum-icon>&]:after:bg-roanoke-maroon-500 relative after:pointer-events-none after:relative after:top-1 after:left-7 after:-ml-4 after:w-4 after:h-4 after:scale-125 after:origin-bottom-right [.small>&]:after:scale-100 [.small>&]:after:left-6 [.small>&]:after:top-[calc(3rem/16)]" title="Events Calendar">Events Calendar &]:hidden absolute mask-right-arrowhead-2-by-3 pointer-events-none w-2 h-3 top-1.5 [.small>&]:scale-75 [.large>&]:scale-110 origin-top left-0 peer-hocus:left-1 sm:peer-hocus:left-1.5 motion-reduce:!left-0 bg-theme-fancy-link-color peer-hocus:bg-theme-fancy-link-hocus-color theme-dogwood-bloom-400:peer-aria-current:bg-black theme-dogwood-bloom-400:peer-aria-current:peer-hocus:bg-dogwood-bloom-900 transition-[left,background-color] ease-linear">
- &]:text-lg [.small>&]:leading-tight [.large>&]:text-[calc(22rem/16)] ml-[calc(-1*var(--pl))] pl-[var(--pl)] [.no-arrow>&]:ml-0 after:hidden [.lock-icon>&]:after:inline-block [.lock-icon>&]:after:mask-lock [.lock-icon>&]:after:bg-current [.museum-icon>&]:after:inline-block [.museum-icon>&]:after:mask-museum [.museum-icon>&]:after:bg-roanoke-maroon-500 relative after:pointer-events-none after:relative after:top-1 after:left-7 after:-ml-4 after:w-4 after:h-4 after:scale-125 after:origin-bottom-right [.small>&]:after:scale-100 [.small>&]:after:left-6 [.small>&]:after:top-[calc(3rem/16)]" title="News">News &]:hidden absolute mask-right-arrowhead-2-by-3 pointer-events-none w-2 h-3 top-1.5 [.small>&]:scale-75 [.large>&]:scale-110 origin-top left-0 peer-hocus:left-1 sm:peer-hocus:left-1.5 motion-reduce:!left-0 bg-theme-fancy-link-color peer-hocus:bg-theme-fancy-link-hocus-color theme-dogwood-bloom-400:peer-aria-current:bg-black theme-dogwood-bloom-400:peer-aria-current:peer-hocus:bg-dogwood-bloom-900 transition-[left,background-color] ease-linear">
Independent Study (literature review)
Independent study (PSYC 311, 312, 313) is designed to provide the student with an opportunity to conduct an extensive literature review. The work is carried out independently, with guidance from a faculty mentor. PSYC 311 and 313 are ½-credit courses to spread the work across two semesters; PSYC 312 is a one-credit course. Independent Study is strongly recommended for students who plan to attend graduate school in any of the research areas of psychology. Admission criteria for M.A. and Ph.D. programs often include research experience, and one's likelihood of acceptance into a competitive program is enhanced by having a record of research participation.
To participate in Independent Study , a student must have an overall GPA and a Psychology GPA of at least 3.0, unless special permission is granted by the Psychology faculty. To enroll in an Independent Study, a student must complete a written proposal and the Application for Research in the Department by the first Wednesday of the semester. Note, that your research mentor may require an earlier deadline. If approved by the Department, the Department Chair will contact the registrar's office and register you for the course.
- Independent Study Student Guidelines
- Proposal for a Literature Review Independent Study (EXAMPLE 1)
- Proposal for a Literature Review Independent Study (EXAMPLE 2)
- Final Independent Study - Literature Review Paper (EXAMPLE 1)
- Final Independent Study - Literature Review Paper (EXAMPLE 2)
- Research Assistant Contract
- Student Reflection Guidelines
- Library Hours
- Strategic Plan
- Giving to the Libraries
- Jobs at the Libraries
- Find Your Librarian
- View All →
- Google Scholar
- Research Guides
- Textbook/Reserves
- Government Documents
- Get It For Me
- Print/Copy/Scan
- Renew Materials
- Study Rooms
- Use a Computer
- Borrow Tech Gear
- Student Services
- Faculty Services
- Users with Disabilities
- Visitors & Alumni
- Special Collections
- Find Information
Basics of Systematic Reviews
- About Systematic Review
Types of Reviews
Literature review.
Collects key sources on a topic and discusses those sources in conversation with each other
- Standard for research articles in most disciplines
- Tells the reader what is known, or not known, about a particular issue, topic, or subject
- Demonstrates knowledge and understanding of a topic
- Establishes context or background for a case or argument
- Helps develop the author’s ideas and perspective
Rapid Review
Thorough methodology but with process limitations in place to expeditethe completion of a review.
- For questions that require timely answers
- 3-4 months vs. 12-24 months
- Limitations - scope, comprehensiveness bias, and quality of appraisal
- Discusses potential effects that the limited methods may have had on results
Scoping Review
Determine the scope or coverage of a body of literature on a given topic and give clear indication of the volume of literature and studies available as well as an overview of its focus.
- Identify types of available evidence in a given field
- Clarify key concepts/definitions in the literature
- Examine how research is conducted on a certain topic or field
- Identify key factors related to a concept
- Key difference is focus
- Identify and analyze knowledge gaps
Systematic Review
Attempts to identify, appraise, and summarize all empirical evidence that fits pre-specified eligibility criteria to answer a specific research question.
- clearly defined question with inclusion/exclusion criteria
- rigorous and systematic search of the literature
- thorough screening of results
- data extraction and management
- analysis and interpretation of results
- risk of bias assessment of included studies
Meta-Analysis
Used to systematically synthesize or merge the findings of single, independent studies, using statistical methods to calculate an overall or ‘absolute’ effect.
- Combines results from multiple empirical studies
- Requires systematic review first
- Use well recognized, systematic methods to account for differences in sample size, variability (heterogeneity) in study approach and findings (treatment effects)
- Test how sensitive their results are to their own systematic review protocol
For additional types of reviews please see these articles:
- Sutton, A., Clowes, M., Preston, L. and Booth, A. (2019), Meeting the review family: exploring review types and associated information retrieval requirements. Health Info Libr J, 36: 202-222. https://doi.org/10.1111/hir.12276
- Grant, M.J. and Booth, A. (2009), A typology of reviews: an analysis of 14 review types and associated methodologies. Health Information & Libraries Journal, 26: 91-108. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-1842.2009.00848.x
- << Previous: About Systematic Review
- Next: Sources >>
- Last Updated: May 17, 2024 10:04 AM
- URL: https://libguides.utsa.edu/systematicreview
- Library Locations
- Staff Directory
- 508 Compliance
- Site Search
- © The University of Texas at San Antonio
- Information: 210-458-4011
- Campus Alerts
- Required Links
- UTSA Policies
- Report Fraud

Literature Reviews
- Types of reviews
- Getting started
Types of reviews and examples
Choosing a review type.
- 1. Define your research question
- 2. Plan your search
- 3. Search the literature
- 4. Organize your results
- 5. Synthesize your findings
- 6. Write the review
- Artificial intelligence (AI) tools
- Thompson Writing Studio This link opens in a new window
- Need to write a systematic review? This link opens in a new window

Contact a Librarian
Ask a Librarian
- Meta-analysis
- Systematized
Definition:
"A term used to describe a conventional overview of the literature, particularly when contrasted with a systematic review (Booth et al., 2012, p. 265).
Characteristics:
- Provides examination of recent or current literature on a wide range of subjects
- Varying levels of completeness / comprehensiveness, non-standardized methodology
- May or may not include comprehensive searching, quality assessment or critical appraisal
Mitchell, L. E., & Zajchowski, C. A. (2022). The history of air quality in Utah: A narrative review. Sustainability , 14 (15), 9653. doi.org/10.3390/su14159653
Booth, A., Papaioannou, D., & Sutton, A. (2012). Systematic approaches to a successful literature review. London: SAGE Publications Ltd.
"An assessment of what is already known about a policy or practice issue...using systematic review methods to search and critically appraise existing research" (Grant & Booth, 2009, p. 100).
- Assessment of what is already known about an issue
- Similar to a systematic review but within a time-constrained setting
- Typically employs methodological shortcuts, increasing risk of introducing bias, includes basic level of quality assessment
- Best suited for issues needing quick decisions and solutions (i.e., policy recommendations)
Learn more about the method:
Khangura, S., Konnyu, K., Cushman, R., Grimshaw, J., & Moher, D. (2012). Evidence summaries: the evolution of a rapid review approach. Systematic reviews, 1 (1), 1-9. https://doi.org/10.1186/2046-4053-1-10
Virginia Commonwealth University Libraries. (2021). Rapid Review Protocol .
Quarmby, S., Santos, G., & Mathias, M. (2019). Air quality strategies and technologies: A rapid review of the international evidence. Sustainability, 11 (10), 2757. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11102757
Grant, M.J. & Booth, A. (2009). A typology of reviews: an analysis of the 14 review types and associated methodologies. Health Information & Libraries Journal , 26(2), 91-108. https://www.doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-1842.2009.00848.x
Developed and refined by the Evidence for Policy and Practice Information and Co-ordinating Centre (EPPI-Centre), this review "map[s] out and categorize[s] existing literature on a particular topic, identifying gaps in research literature from which to commission further reviews and/or primary research" (Grant & Booth, 2009, p. 97).
Although mapping reviews are sometimes called scoping reviews, the key difference is that mapping reviews focus on a review question, rather than a topic
Mapping reviews are "best used where a clear target for a more focused evidence product has not yet been identified" (Booth, 2016, p. 14)
Mapping review searches are often quick and are intended to provide a broad overview
Mapping reviews can take different approaches in what types of literature is focused on in the search
Cooper I. D. (2016). What is a "mapping study?". Journal of the Medical Library Association: JMLA , 104 (1), 76–78. https://doi.org/10.3163/1536-5050.104.1.013
Miake-Lye, I. M., Hempel, S., Shanman, R., & Shekelle, P. G. (2016). What is an evidence map? A systematic review of published evidence maps and their definitions, methods, and products. Systematic reviews, 5 (1), 1-21. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13643-016-0204-x
Tainio, M., Andersen, Z. J., Nieuwenhuijsen, M. J., Hu, L., De Nazelle, A., An, R., ... & de Sá, T. H. (2021). Air pollution, physical activity and health: A mapping review of the evidence. Environment international , 147 , 105954. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2020.105954
Booth, A. (2016). EVIDENT Guidance for Reviewing the Evidence: a compendium of methodological literature and websites . ResearchGate. https://doi.org/10.13140/RG.2.1.1562.9842 .
Grant, M.J. & Booth, A. (2009). A typology of reviews: an analysis of the 14 review types and associated methodologies. Health Information & Libraries Journal , 26(2), 91-108. https://www.doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-1842.2009.00848.x
"A type of review that has as its primary objective the identification of the size and quality of research in a topic area in order to inform subsequent review" (Booth et al., 2012, p. 269).
- Main purpose is to map out and categorize existing literature, identify gaps in literature—great for informing policy-making
- Search comprehensiveness determined by time/scope constraints, could take longer than a systematic review
- No formal quality assessment or critical appraisal
Learn more about the methods :
Arksey, H., & O'Malley, L. (2005) Scoping studies: towards a methodological framework. International Journal of Social Research Methodology , 8 (1), 19-32. https://doi.org/10.1080/1364557032000119616
Levac, D., Colquhoun, H., & O’Brien, K. K. (2010). Scoping studies: Advancing the methodology. Implementation Science: IS, 5, 69. https://doi.org/10.1186/1748-5908-5-69
Example :
Rahman, A., Sarkar, A., Yadav, O. P., Achari, G., & Slobodnik, J. (2021). Potential human health risks due to environmental exposure to nano-and microplastics and knowledge gaps: A scoping review. Science of the Total Environment, 757 , 143872. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.143872
A review that "[compiles] evidence from multiple...reviews into one accessible and usable document" (Grant & Booth, 2009, p. 103). While originally intended to be a compilation of Cochrane reviews, it now generally refers to any kind of evidence synthesis.
- Compiles evidence from multiple reviews into one document
- Often defines a broader question than is typical of a traditional systematic review
Choi, G. J., & Kang, H. (2022). The umbrella review: a useful strategy in the rain of evidence. The Korean Journal of Pain , 35 (2), 127–128. https://doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2022.35.2.127
Aromataris, E., Fernandez, R., Godfrey, C. M., Holly, C., Khalil, H., & Tungpunkom, P. (2015). Summarizing systematic reviews: Methodological development, conduct and reporting of an umbrella review approach. International Journal of Evidence-Based Healthcare , 13(3), 132–140. https://doi.org/10.1097/XEB.0000000000000055
Rojas-Rueda, D., Morales-Zamora, E., Alsufyani, W. A., Herbst, C. H., Al Balawi, S. M., Alsukait, R., & Alomran, M. (2021). Environmental risk factors and health: An umbrella review of meta-analyses. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Dealth , 18 (2), 704. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18020704
A meta-analysis is a "technique that statistically combines the results of quantitative studies to provide a more precise effect of the result" (Grant & Booth, 2009, p. 98).
- Statistical technique for combining results of quantitative studies to provide more precise effect of results
- Aims for exhaustive, comprehensive searching
- Quality assessment may determine inclusion/exclusion criteria
- May be conducted independently or as part of a systematic review
Berman, N. G., & Parker, R. A. (2002). Meta-analysis: Neither quick nor easy. BMC Medical Research Methodology , 2(1), 10. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2288-2-10
Hites R. A. (2004). Polybrominated diphenyl ethers in the environment and in people: a meta-analysis of concentrations. Environmental Science & Technology , 38 (4), 945–956. https://doi.org/10.1021/es035082g
A systematic review "seeks to systematically search for, appraise, and [synthesize] research evidence, often adhering to the guidelines on the conduct of a review" provided by discipline-specific organizations, such as the Cochrane Collaboration (Grant & Booth, 2009, p. 102).
- Aims to compile and synthesize all known knowledge on a given topic
- Adheres to strict guidelines, protocols, and frameworks
- Time-intensive and often takes months to a year or more to complete
- The most commonly referred to type of evidence synthesis. Sometimes confused as a blanket term for other types of reviews
Gascon, M., Triguero-Mas, M., Martínez, D., Dadvand, P., Forns, J., Plasència, A., & Nieuwenhuijsen, M. J. (2015). Mental health benefits of long-term exposure to residential green and blue spaces: a systematic review. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health , 12 (4), 4354–4379. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph120404354
"Systematized reviews attempt to include one or more elements of the systematic review process while stopping short of claiming that the resultant output is a systematic review" (Grant & Booth, 2009, p. 102). When a systematic review approach is adapted to produce a more manageable scope, while still retaining the rigor of a systematic review such as risk of bias assessment and the use of a protocol, this is often referred to as a structured review (Huelin et al., 2015).
- Typically conducted by postgraduate or graduate students
- Often assigned by instructors to students who don't have the resources to conduct a full systematic review
Salvo, G., Lashewicz, B. M., Doyle-Baker, P. K., & McCormack, G. R. (2018). Neighbourhood built environment influences on physical activity among adults: A systematized review of qualitative evidence. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health , 15 (5), 897. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15050897
Huelin, R., Iheanacho, I., Payne, K., & Sandman, K. (2015). What’s in a name? Systematic and non-systematic literature reviews, and why the distinction matters. https://www.evidera.com/resource/whats-in-a-name-systematic-and-non-systematic-literature-reviews-and-why-the-distinction-matters/

- Review Decision Tree - Cornell University For more information, check out Cornell's review methodology decision tree.
- LitR-Ex.com - Eight literature review methodologies Learn more about 8 different review types (incl. Systematic Reviews and Scoping Reviews) with practical tips about strengths and weaknesses of different methods.
- << Previous: Getting started
- Next: 1. Define your research question >>
- Last Updated: May 17, 2024 8:42 AM
- URL: https://guides.library.duke.edu/litreviews

Services for...
- Faculty & Instructors
- Graduate Students
- Undergraduate Students
- International Students
- Patrons with Disabilities
- Harmful Language Statement
- Re-use & Attribution / Privacy
- Support the Libraries

The burgeoning role of literature review articles in management research: an introduction and outlook
- Open access
- Published: 30 January 2024
- Volume 18 , pages 299–314, ( 2024 )
Cite this article
You have full access to this open access article

- Sascha Kraus ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-4886-7482 1 , 2 ,
- Ricarda B. Bouncken ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-0510-7491 3 &
- Alba Yela Aránega ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-3539-5615 4
3113 Accesses
10 Citations
Explore all metrics
This article delves into the significance and utility of literature review articles in the field of management research, encompassing their three most prominent forms: structured literature reviews, bibliometric analyses, and meta-analyses. It discusses the evolving role of literature reviews as essential tools in a research process, their methodological intricacies, and their contribution to shaping the landscape of management studies. Through a thorough examination of their merits, limitations, and best practices, our article sheds light on how literature review articles serve as valuable resources for scholars, policymakers, and practitioners in the field of management. In addition, the article points towards opportunities for using AI tools, for example Google Colab, ChatGPT, Methods Wizards, or Petal for single or multiple stages and tasks of structured literature analyses.
Similar content being viewed by others

How to conduct systematic literature reviews in management research: a guide in 6 steps and 14 decisions

Critical Review as a Method of Inquiry: Issues and Implications
Evolution and trends of the metaverse in business and management: A bibliometric analysis
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
1 Introduction
Management research, as an interdisciplinary field, is marked by a constant influx of new information, theories, and practices (van Grinsven et al. 2016 ; Mas-Tur et al. 2020 ). Keeping abreast of the latest developments and understanding the existing knowledge base serves as a fundamental requirement for making informed decisions in both academic and practical settings (Palmatier et al. 2018 ). Hence, literature review articles, including structured literature reviews, bibliometric analyses, and meta-analyses, play a pivotal role in facilitating this process (Fisch and Block 2018 ). For further embellishing the “art of literature reviews”, our introductory article explores the relevance and use of such articles in management research, elaborating on their multifaceted contributions and complexities.
In the realm of academic research, literature reviews have traditionally been an integral component, serving as a foundation for the development of new ideas, theories, and methodologies (Callahan 2014 ). While literature reviews have long been considered a vital part of scholarly discourse, a relatively recent trend has emerged, one that focuses specifically on standalone literature review articles (Kraus et al. 2022 ). This burgeoning field of literature reviews as own, independent studies not only underscores the importance of comprehensive literature reviews, but also reflects the dynamic evolution of the methods applied to conduct such articles. As research tools and methodologies are constantly further evolving, the discipline of standalone literature review articles is adapting and improving to meet the demands of contemporary management research.
About a decade ago, the publication landscape for literature review articles in the field of academic management faced significant obstacles in attaining the desired level of academic quality and achieving publication. Many journals editorial boards explicitly rejected submissions of this nature, citing concerns about the perceived lack of substantive “contribution” to the field (Wright 2015 ). At the time, literature review articles were frequently perceived as insufficiently impactful and were often deemed outside the scope of what journals sought to publish, as they would not generate new knowledge.
However, the past decade has witnessed a significant shift in the reception and recognition of literature review articles in the management field. This transformation can be attributed to the adoption of more robust methodologies (Breslin and Bailey 2020 ), which have not only improved the academic quality of these articles but have also amplified their impact and citation rates. This transformation has also yielded a notable enhancement in the academic quality of such articles. As a result, they now garner increased attention and “impact” within the academic community (Aguinis et al. 2012 ; 2014 ; Kunisch et al. 2018 ).
The newfound impact of literature review articles is evident through the increased number of citations, enhancing their standing in the academic ecosystem. This ongoing trend not only benefits authors but also elevates the journals themselves. Consequently, the quality and recognition shift positively influences the metrics used to measure the prestige and reach of academic journals, highlighting the evolving importance of literature review articles in the contemporary academic landscape. High-quality literature reviews with improved methodologies have significantly contributed to journal metrics like the “Impact Factor” (from Clarivate) or the “CiteScore” (from Scopus/Elsevier). These metrics mirror the journals' overall influence and status within the academic domain, and well-executed literature reviews have played a pivotal role in elevating these metrics. As a result, journals such as the “International Journal of Management Reviews” now boast some of the highest impact factors in the field, and even the leading journals in the field now–at least occasionally–publish review articles. The “Review of Managerial Science” was one of the few journals to feature an extra category for the type of academic research from its inception, and it continues to be very popular with authors.
2 The evolving role of literature review articles
2.1 most common review article types, 2.1.1 structured literature reviews.
Structured (also called systematic ) literature reviews provide a systematic approach to synthesizing existing research by employing a well-defined methodology (Kraus et al. 2020 ; Sauer and Seuring 2023 ). They assist researchers in organizing, analyzing, and summarizing literature while maintaining transparency in their process. These reviews are instrumental in identifying patterns, trends, and key research questions (Laher and Hassem 2020 ). By following a predefined protocol, structured literature reviews ensure consistency and rigor in the evaluation of existing studies, making them not only valuable for understanding the current state of research but also for setting standards of methodological excellence (Rojon et al. 2021 ; Tranfield et al. 2003 ).
2.1.2 Bibliometric analyses
Bibliometric analyses, rooted in quantitative data analysis (Lawani 1981 ), offer a unique perspective by assessing the impact, connectivity, and evolution of research in management (Donthu et al. 2021 ). Through bibliometric techniques, researchers can identify influential works, key authors, and emerging areas of interest, which are invaluable for understanding the field's dynamics (Zupic and Čater 2015 ). In an era of information overload, bibliometric analyses help researchers identify the most influential and relevant contributions, thus facilitating focused and strategic research efforts (Linnenluecke et al. 2020 ).
2.1.3 Meta-analyses
Meta-analyses, on the other hand, aggregate the results of multiple studies to draw generalizable conclusions (Geyskens et al. 2009 ). They play a significant role in synthesizing empirical evidence, offering statistical rigor, and identifying potential biases or inconsistencies within the literature (King and He 2005 ). This method is particularly valuable in answering specific research questions and quantifying the effects of various management interventions (Combs et al. 2019 ). The transparent and quantitative nature of meta-analyses enhances their credibility, making them essential for resolving debates and informing evidence-based decisions.
2.2 Standalone literature reviews
Literature review articles can be valuable as standalone articles in the academic world and have their own unique place in scholarly publications (Rowe 2014 ). Such standalone literature review articles, as a distinct subfield within the larger arena of academic literature, have gained increasing prominence in recent years (Snyder 2019 ). Unlike traditional literature reviews, which are often embedded within (usually empirical) research papers (Rocco and Plakhotnik 2009 ), standalone literature review articles are comprehensive, self-contained documents that offer a comprehensive survey of the existing literature on a particular topic or research question. These articles are not merely background summaries but serve as authoritative reference points for scholars, researchers, and students seeking to explore a specific subject in depth. This shift towards standalone literature reviews has given rise to a unique branch of academic scholarship.
2.2.1 Evolution
The methods employed in conducting standalone literature review articles have witnessed continuous evolution and improvement (Kraus et al. 2022 ). The field has moved beyond the mere aggregation of existing studies and has evolved into a systematic and structured process. Several key factors contribute to the ongoing refinement of the methods:
Digital Tools and Databases : The proliferation of digital databases and search engines has made it easier to access a vast amount of literature. These tools not only expedite the process of collecting relevant research, but also allow for more precise and targeted searches, enhancing the quality of literature reviews. More than a decade ago, references for bibliometric analyses had to be entered into Excel files largely “by hand”, which meant several weeks of work for the person (often junior scholars) entering the data.
Systematic Review Guidelines : The adaptation of systematic review methodologies to standalone literature reviews has become increasingly common (Aguinis et al. 2020 ; Sauer and Seuring 2023 ). These guidelines ensure a rigorous, reproducible, and unbiased approach to literature selection and analysis, leading to more robust reviews (Simsek et al. 2023 ).
Citation Analysis and Bibliometrics : The use of citation analysis and bibliometric tools has become an essential aspect of standalone literature reviews (Donthu et al. 2021 ). By examining citation patterns and impact metrics, reviewers can assess the influence and relevance of prior research, which aids in determining the significance of various contributions to the field (Mukherjee et al. 2022 ).
Synthesis and Frameworks : Researchers are increasingly employing advanced synthesis methods, such as meta-analysis, content analysis, and thematic frameworks, to organize and present the reviewed literature in a structured manner (Templier and Paré 2015 ). This helps readers gain a clearer understanding of the state of knowledge on a particular topic.
Interdisciplinary Approaches : The boundaries between academic disciplines are becoming increasingly porous. Literature review articles now often encompass interdisciplinary perspectives, allowing for a broader and more holistic understanding of complex topics.
2.2.2 Functions
Literature review articles, while not presenting original empirical research findings, serve several critical functions and are often considered as important contributions to the field. The main functions of such articles are:
Synthesizing Existing Knowledge: Literature review articles are dedicated to summarizing and synthesizing existing knowledge on a specific topic or research area (Rousseau et al. 2008 ). They consolidate information from various primary research studies, providing a holistic overview (Chen and Hitt 2021 ). By doing so, they help readers understand the current state of research on a given subject (Dwertmann and van Knippenberg 2021 ).
Identifying Trends and Gaps: One of the primary roles of a literature review article is to identify trends, patterns, and gaps in the existing body of knowledge. This can be crucial for researchers looking to explore new avenues, formulate research questions, and design studies that address unanswered questions.
Providing Methodological Insights: Some literature review articles delve into the methodologies used in the studies they review. These methodological insights can be valuable for researchers who want to understand the best practices in data collection, analysis, and study design within a particular field.
Supporting Evidence-Based Decision-Making: Literature reviews offer a valuable resource for policymakers, practitioners, and professionals seeking to make informed decisions. They provide a condensed and authoritative source of information, helping stakeholders to apply the most current and reliable knowledge in their work.
Clarifying Complex Concepts: Many fields have complex theories and concepts that may be challenging to grasp for newcomers. Literature reviews often simplify and clarify these ideas, making them accessible to a broader audience, including students and individuals new to the field.
Educational and Teaching Aids: Literature review articles are frequently used in educational settings to teach students about a specific topic or research area, especially in postgraduate or doctoral level courses. Supervisors may assign these articles to help students gain an understanding of foundational knowledge and the history of research within a field.
Influencing Theory Development: In some cases, literature reviews serve as a foundation for advancing new theoretical frameworks or models. They provide a comprehensive perspective on a subject, which can inspire the development of new theories or the refinement of existing ones.
Fostering Debate and Discussion: Sometimes, a literature review article might take a critical stance, highlighting contradictions or controversies in the field. This can stimulate debate and discussions among researchers, contributing to the evolution of knowledge.
While literature review articles primarily summarize and consolidate existing research, they play an essential role in knowledge dissemination and are often a crucial starting point for both seasoned researchers and newcomers to a particular field (Kraus et al. 2023 ). As standalone articles, they offer readers a well-structured and comprehensive overview of a specific topic, making them a valuable resource in academia and beyond.
2.2.3 Use of artificial intelligence AI tools
In the future, researchers may increasingly utilize artificial intelligence (AI) tools like Google Colab, ChatGPT, Methods Wizards, and or Petal in the entire process or enhance specific stages of a systematic literature review and analysis. AI can provide direct or indirect support for various steps in systematic literature analysis, as well as contribute to decision-making during the augmented analysis (Burger et al. 2023 ).
While it is essential that the researcher's decisions guide the research question, AI, such as ChatGPT, can aid in refining research questions and improving terminology. AI also holds the potential to automate search processes across diverse databases, although this potential requires careful research preparation. For instance, employing AI activities necessitates the training of AI models, such as by establishing criteria for paper inclusion or exclusion. Researchers can employ automatic coding of articles through platforms like Petal.org and elicit.org, create word clouds using CodeInterpreter and Python, generate scientometric networks, and visualize research maps.
An integral aspect of supporting literature analysis is the creation of a coding or data extraction sheet by the researcher. AI can assist in the identification and coding of Python scripts. However, limitations persist, and researchers must determine when and based on which criteria they will halt title or abstract screening.
While future research in systematic literature review and analysis may incorporate AI, there are also opportunities for studying and comparing the effectiveness of these methods. For instance, researchers can establish criteria for evaluating and comparing various tools for systematic reviews.
Last, but not least, we would like to emphasize the potential ethical issues associated with the use of generative AI, including ChatGPT, which researchers must take into consideration (see e.g., Dwivedi et al. 2023 ).
2.2.4 Contributions
Advancing Knowledge: Literature review articles contribute significantly to the advancement of knowledge by providing a comprehensive overview of the field (Pittaway et al. 2014 ). They act as stepping stones for subsequent research, helping scholars build on existing work and explore uncharted territory. In this regard, literature reviews serve as catalysts for intellectual growth, encouraging scholars to identify gaps, generate new hypotheses, and design novel research endeavors.
Quality Assurance: Review articles, by evaluating and summarizing a multitude of studies, act as a form of quality assurance. Researchers, policymakers, and practitioners can trust that these reviews have undergone a rigorous evaluation process, which ensures the reliability of the information presented. Furthermore, the transparent methodology employed in structured literature reviews and the quantitative rigor in bibliometric analyses and meta-analyses enhance the credibility of these reviews, making them dependable sources for decision-making.
Informing Theory and Practice: Literature review articles serve as foundational components in the development of theory and practice within the field of management (LePine and King 2010 ). They provide a comprehensive understanding of the existing body of knowledge (DeGeest and Schmidt 2010 ), thus offering valuable insights into both historical and emerging trends. Researchers often employ literature reviews to identify gaps, challenges, and opportunities in the domain, which can stimulate further investigation and innovation. The dual role, as both a beacon illuminating the path of management research and a compass guiding practical applications, underscores the significance of literature review articles.
Policy and Decision-Making: In addition to their academic utility, literature review articles are indispensable for shaping policy and decision-making in the management sector (Aguinis et al. 2022 ). Policymakers and practitioners often rely on these articles to develop strategies and make informed choices based on an evidence-based understanding of current best practices. By synthesizing and summarizing vast bodies of research (Cooper 1988 ), literature review articles act as digestible sources of knowledge, ensuring that decision-makers can navigate the complex landscape of management with a sound understanding of the current state of the art (Dwertmann and van Knippenberg 2021 ).
2.2.5 Limitations and best practices
Potential Biases: Literature review articles, though rigorous, are not immune to potential biases, as the selection of studies and methodologies can introduce subjective judgments. However, adherence to transparent and well-documented procedures can mitigate these biases (Sauer and Seuring 2023 ). Practicing rigorous research ethics and maintaining a commitment to neutrality in the selection and analysis of studies is vital to ensure the objectivity and integrity of literature review articles (Harari et al. 2020 ; Hiebl 2023 ).
Continuous Updates: Given the dynamic nature of management research, literature review articles should be periodically updated to ensure their relevance. Best practices include providing clear guidelines for the frequency of updates and methods for incorporating new research. By setting a standard for regular review updates, researchers can ensure that literature review articles remain current and continue to guide the evolution of the field.
Needs and Justifications for Update: However, on the other side, it is somewhat disturbing to observe that for certain topics, not just one, but two or three literature review articles on the exact or at least almost the same research question have been published at almost the same time or at an extremely short distance from each other, often–but not always–in poorly ranked or even totally unranked journals. This often happens in ignorance or bad research of the editors and reviewers to already published topics. Of course, an update only makes sense if other sub-areas of the subject area are investigated or other questions are addressed, or if the subject area has developed so much in the meantime–also in terms of scope or method–that an update can be justified and, above all, makes sense. If this is not the case, the editors and reviewers should not allow the publication of the more recent contribution, for which there is already a paper with almost the same content.
3 Conclusion: elaborated analyses based on topics and content
Literature review articles, including structured literature reviews, bibliometric analyses, and meta-analyses, are invaluable tools in the realm of management research, significantly contributing to its growth and development (Hulland and Houston 2020 ). They serve as cornerstones for theory development, policy formulation, and evidence-based decision-making, thus playing a pivotal role in the progression of management studies (Short 2009 ). Despite certain limitations, adherence to best practices and a commitment to periodic updates can ensure that these articles remain relevant and continue to guide and shape the field's dynamic evolution. Researchers, policymakers, and practitioners alike can benefit from their contribution to the field's multifaceted landscape, where knowledge is both the destination and the journey. In the future, we expect that the research process will be further augmented by the use of AI tools.
Standalone literature review articles are emerging as a distinctive and essential component of academic scholarship. As this field continues to burgeon, the methods employed for conducting literature reviews are constantly evolving and improving. The utilization of digital tools, the application of systematic review guidelines, the integration of bibliometrics, advanced synthesis methods, and interdisciplinary approaches all contribute to the ongoing refinement of this scholarly practice. These changes reflect the adaptability of the academic community in the face of evolving research methodologies and information technologies, ensuring that standalone literature review articles remain valuable resources in the ever-changing landscape of academia.
The field of standalone literature review articles, as discussed earlier, has witnessed considerable growth and development, marked by a continuous evolution of methodologies. However, there is a pertinent question looming on the horizon: Has the field reached its zenith, and are there signs of saturation in the kind of work produced?
The proliferation of software tools and readily accessible bibliographic databases has made it possible for virtually anyone to conduct descriptive analyses of scholarly literature (e.g., Chen 2003 ; Van Eck and Waltman 2014 ; Ammirato et al. 2023 ). Consequently, a considerable number of literature review articles now seem to produce strikingly similar results, asking the same research questions and presenting almost identical descriptive information. The wealth of available data can sometimes lead to redundancy rather than meaningful insights. Indeed, there are indicators suggesting that this might be the case. In recent years, there has been an influx of literature review articles that, despite employing sophisticated and easy-to-use data analysis tools such as VOSviewer to analyze and visualize Scopus, EBSCO, and similar databases, predominantly produce purely descriptive information. These descriptions often revolve around “most cited authors”, “most cited articles”, “countries with the highest publication rates”, and other similar metrics. While this descriptive information is valuable, it can be argued that the field may have reached a saturation point with regard to this type of analysis.
In this context, the additional benefit of producing literature review articles primarily centered on purely descriptive data is increasingly questionable. While it may serve as a helpful reference for basic background information, these analyses no longer push the boundaries of knowledge or offer new, substantive contributions to a field. Such literature review articles can be seen as a culmination of a specific era, where easy access to data has led to a profusion of descriptive, albeit repetitive, reviews.
The field of standalone literature review articles is evolving, and it is advisable to transition towards more sophisticated analyses and the integration of useful AI tool results. The future of this field should prioritize generating deeper insights through topic, content, and thematic analyses, rather than simply presenting descriptive data. In-depth examinations of existing literature's content, emerging trends, knowledge gaps, and critical assessments of methodologies can provide fresh perspectives and value to readers.
In conclusion, the era of standalone literature review articles centered on purely descriptive data is approaching its conclusion. The field should progress towards more elaborate analyses based on topics and content. This evolution will not only invigorate the discipline but also offer readers valuable insights and a deeper understanding of the state of knowledge in a specific research area. As the field continues to evolve, the focus should shift from “who cites whom” to “what's new” and “what's next” in the world of scholarly literature.
Rather than fixating solely on the most cited sources, the field should embrace a shift towards a more qualitative and substantive approach (Aguinis et al. 2020 ). The content and results should be utilized for theorizing (Post et al. 2020 ; Breslin and Gatrell 2023 ). Analyzing the quality of research, assessing paradigm evolution, exploring interdisciplinary connections, and identifying new research directions are areas that deserve increased attention. Literature reviews that offer meaningful synthesis, critique, and conceptual innovation can form the foundation for advancing knowledge within a specific field. Kunisch et al. ( 2023 ) call this approach–aptly–“review research”.
The key takeaway is that while the age of simplistic, mostly descriptive literature reviews may be nearing its end due to a perceived saturation of such content, it does not diminish the importance of literature review articles in general. Instead, it underscores the need for better, more rigorous, and more insightful approaches to conducting them (Kunisch et al. 2023 ). In conclusion, literature review papers remain vital in the academic landscape, serving as essential foundations for new research, providing historical context, and guiding scholars towards understanding the state of knowledge in their respective fields (Parmigiani and King 2019 ). However, as discussed, there is an urgent need for improvement in how such literature reviews are conducted.
Literature reviews must evolve beyond mere summarization and enumeration of citations to provide deeper insights, critical assessments, and meaningful synthesis. Researchers and scholars should strive for more elaborate and nuanced analyses, focusing on the content, topics, and themes within the literature. By adopting these more advanced and critical approaches, literature review papers will continue to play a crucial role in advancing knowledge and scholarship in various academic disciplines. The future of literature reviews lies not in their obsolescence but in their refinement and their capacity to offer richer, more meaningful contributions to the academic discourse.
4 The review articles in this special issue
This Special Issue of the “Review of Managerial Science” brings together the above mentioned review types in a variety of ways, attempting to provide a state-of-the-art overview of some of the hottest topics in entrepreneurship, innovation, and knowledge in contemporary management research. It consists of ten contributions from 33 authors from 13 countries.
The paper titled “Uncovering the organizational, environmental, and socio-economic sustainability of digitization” by Chopra et al. ( 2023 ) delves into the integration of organizational, environmental, and socioeconomic sustainability with digital technologies, a topic that has garnered increasing attention in recent years. Through a comprehensive bibliometric analysis, this paper provides valuable insights into the social, intellectual, and conceptual structures of this evolving field. The study not only sheds light on the descriptive aspects of this subject but also emphasizes its social and intellectual context, its evolution, and its future agenda. It underscores the benefits of technology adoption in enhancing efficiency, improving performance, and driving profitability for both individuals and companies. Furthermore, it advocates for increased funding to develop environmentally friendly technologies that promote inclusive economic models and sustainable growth. The research also addresses the social and ethical implications of technology integration, emphasizing the importance of considering factors such as gender, race, ethnicity, and location when digitizing the world. By drawing on existing evidence and synthesizing findings, this study offers a fresh academic and policy contribution to the interconnected fields of digitalization and sustainability.
The paper authored by Felicetti et al. ( 2023 ) titled “Digital innovation in entrepreneurial firms” presents a comprehensive systematic literature review that explores the intricate relationship between entrepreneurship and digital innovation. By analyzing 185 papers published over the past two decades, the authors aim to consolidate the state of research at the intersection of these two vital fields. Their review identifies six key topics, such as start-ups' collaboration networks, business-model innovation, and digital ventures. What sets this paper apart is its ability to propose three main research directions for future exploration. These include advocating for multi-level analyses of digital innovation in entrepreneurial ventures, encouraging interdisciplinary approaches, and promoting the development of specific theories for digital innovation. Overall, this research serves as a solid foundation for academics and practitioners by providing a structured overview of the existing knowledge while guiding future research endeavors toward the unexplored territories of entrepreneurship and digital innovation.
In the paper authored by Fernández-Uclés et al. ( 2023 ) titled “Online reputation of agri-food companies and determining factors”, the authors explore the online presence and reputation of agri-food companies in the modern, technology-oriented society. It emphasizes the critical importance of a positive online image as a key intangible asset for companies undergoing technological transformations. The study employs fuzzy-set qualitative comparative analysis to identify the factors influencing online reputation, highlighting the role of legal form and attributes associated with the company's website. These attributes include website quality, the presence of corporate social responsibility information, secure connections, and the sale of organic products. The research's findings provide strategic guidelines for both public and private decision-makers to leverage the full potential of information and communication technologies. In essence, this study emphasizes the need for companies to not only have an online presence but to convey the right image effectively, and it provides concrete insights for achieving this goal.
The paper titled “Overcoming barriers to transformation in manufacturing firms” by Brekke et al. ( 2023 ) tackles the challenges faced by manufacturing firms in their quest to break away from established business models, offerings, routines, and capabilities. They adopt a path-dependence perspective in their analysis, relying on a single longitudinal case study of a leading manufacturing company. Through in-depth interviews with senior executives and managers, the authors uncover four path-breaking mechanisms that offer valuable insights into the process of transformation. These mechanisms include organizational reconfiguration, reconfiguration of value offerings, opportunity exploration, and knowledge reconfiguration. By developing a framework based on these mechanisms, the research provides meaningful guidance for manufacturing firms seeking to deviate from their existing paths, offering fresh perspectives and a systematic approach to the challenge of transformation in this sector.
In the article authored by Ballerini et al. ( 2023 ) titled “E-commerce channel management on the manufacturers' side”, the authors address the evolving landscape of e-commerce channel management from the perspective of manufacturers. As online commerce continues to reshape the global marketplace, this study focuses on the emerging literature concerning online channel management from a manufacturer's point of view. The research starts by providing bibliometric insights into the ongoing work in this field and goes further to identify and review three interconnected thematic clusters. These clusters revolve around strategic marketing issues, pricing policies, and operational interactions among supply chain members. The paper concludes with the development of thirteen original research propositions, offering potential avenues for future research in this rapidly expanding area. In essence, this study provides a comprehensive structure for the existing knowledge on online channel management from the manufacturer's perspective and paves the way for future theoretical advancements and research pathways.
The paper titled “The role of digitalization in business and management” by Calderon-Monge and Ribeiro-Soriano ( 2023 ) is a systematic literature review that explores the role of digitalization in the realms of business and management. In an era where digitalization plays a crucial role in economic growth, the study aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the state-of-the-art digitalization within firms. The authors analyze 119 review articles published in the fields of management, marketing, and finance and accounting. The review reveals key trends in the most mature areas of these disciplines, such as the impact of digital technologies on the analysis of consumer behavior, the intersection of digitalization and green innovation within organizations, and the application of blockchain technology to financial services. This research contributes to a deeper understanding of digitalization's implications and its integration into established points of view within the literature on management, marketing, finance, and accounting. It serves as an essential resource for scholars and practitioners seeking to grasp the evolving landscape of digitalization in the business and management domains.
The article titled “Transformational and entrepreneurial leadership” by Ravet-Brown et al. ( 2023 ) scrutinizes to clarify the distinction and overlap between these two constructs. Entrepreneurship, recognized as a driver of economic growth, hinges on entrepreneurial leadership. Yet, the study notes that research in this area is marked by fragmentation and insufficient integration with the broader leadership literature. This work endeavors to unravel the relationship between the concepts of transformational leadership (TL) and entrepreneurial leadership (EL), which have been suggested by previous research as measured here by a survey study. The authors employ conceptual work, current research findings, and practical insights to examine the conceptual divergence and questionnaire-related challenges associated with EL and TL. While the study provides an overview of EL from a leadership science perspective, it underscores the need for a specific theoretical model to support this evolving field. This research, therefore, represents a significant contribution to the study of leadership styles, providing clarity on the distinctions and overlaps between transformational and entrepreneurial leadership.
In the paper authored by Anwar et al. ( 2023 ) titled “Entrepreneurship in family firms: an updated bibliometric overview”, the authors embark on an ambitious task of unraveling the complexities of entrepreneurial behavior in family firms by conducting a bibliometric analysis. The exponential growth of research in this domain has led to fragmentation due to various theoretical perspectives and contexts. This study integrates two bibliometric methods to paint a comprehensive picture of the field. Through co-citation analysis, the authors cluster the intellectual foundations of entrepreneurship in family firms, highlighting key aspects such as socioemotional wealth and entrepreneurial orientation. A bibliographic coupling of recent publications reveals the current research discourses, encompassing topics like gender and success, family firm internationalization, and more. The research offers a solid foundation for scholars and practitioners seeking to understand the existing knowledge on entrepreneurship in family firms while paving the way for future theoretical advancements and research pathways.
The article “Absorptive capacity in family firms” by Pütz and Werner ( 2023 ) is a systematic literature review that delves into the role of absorptive capacity (AC) in family firms. With two-thirds of businesses worldwide being family firms, understanding AC's impact on these unique entities is crucial. The authors examine 27 articles to shed light on the distinct dynamics of AC in family businesses, emphasizing the influence of family members on the integration of external knowledge. The study reveals that family members both promote the integration of external knowledge and potentially hinder it by isolating the firm and restricting access to external knowledge. Additionally, the research highlights the predominance of conceptual studies in this domain and the need for more empirical research drawing on multidimensional constructs of AC and family influence. This paper provides valuable insights into the intricate relationship between family firms and AC, paving the way for further exploration and understanding in this unique context.
The final article in this issue “Open innovation: status quo and quo vadis–An analysis of a research field” by Bertello et al. ( 2023 ) delves into the evolving field of open innovation. In an era characterized by rapid social and economic changes, the study explores how the research community has adapted to meet new needs and challenges in the open innovation domain. Using bibliometric techniques and content analysis, the paper offers a descriptive analysis of the literature, defines its knowledge structure, and provides an overview of the theoretical landscape. The research shows that the field is consolidating established topics and theoretical approaches while also exploring uncharted dimensions of open innovation. In conclusion, this study offers a comprehensive perspective on the state of research in open innovation and provides valuable insights into its evolving nature.
Data availability
There is no data available for this article.
Aguinis H, Suárez-González I, Lannelongue G, Joo H (2012) Scholarly impact revisited. Acad Manag Perspect 26(2):105–132
Article Google Scholar
Aguinis H, Shapiro DL, Antonacopoulou EP, Cummings TG (2014) Scholarly impact: a pluralist conceptualization. Acad Manage Learn Edu 13(4):623–639
Aguinis H, Ramani RS, Alabduljader N (2020) Best-practice recommendations for producers, evaluators, and users of methodological literature reviews. Organ Res Methods 26(1):46–76
Aguinis H, Jensen SH, Kraus S (2022) Policy implications of organizational behavior and human resource management research. Acad Manage Perspect 36(3):857–878
Ammirato S, Felicetti AM, Rogano D, Linzalone R, Corvello V, Practice, (2023) Digitalising the systematic literature review process: the MySLR platform. Knowl Manag Res Pract 21(4):777–794
Anwar M, Clauss T, Meyer N (2023) Entrepreneurship in family firms: an updated bibliometric overview. Rev Manag Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11846-023-00650-z
Ballerini J, Yahiaoui D, Giovando G, Ferraris A (2023) E-commerce channel management on the manufacturers’ side: ongoing debates and future research pathways. Rev Manag Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11846-023-00645-w
Bertello A, De Bernardi P, Ricciardi F (2023) Open innovation: status quo and quo vadis - an analysis of a research field. Rev Manag Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11846-023-00655-8
Brekke T, Lenka S, Kohtamäki M, Parida V, Solem BAA (2023) Overcoming barriers to transformation in manufacturing firms. A path-dependence perspective of digital servitization. Rev Manag Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11846-023-00641-0
Breslin D, Bailey K (2020) Expanding the conversation through ‘debate essays’ and ‘review methodology’papers. Int J Manag Rev 22(3):219–221
Breslin D, Gatrell C (2023) Theorizing through literature reviews: the miner-prospector continuum. Organ Res Methods 26(1):139–167
Burger B, Kanbach DK, Kraus S, Breier M, Corvello V (2023) On the use of AI-based tools like ChatGPT to support management research. Eur J Innov Manag 26(7):233–241
Calderon-Monge E, Ribeiro-Soriano D (2023) The role of digitalization in business and management: a systematic literature review. Rev Manag Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11846-023-00647-8
Callahan JL (2014) Writing literature reviews: a reprise and update. Hum Resour Dev Rev 13(3):271–275
Chen C (2003) Mapping scientific frontiers: the quest for knowledge visualization. Springer Sci Bus Media 59:364–369
Google Scholar
Chen VZ, Hitt MA (2021) Knowledge synthesis for scientific management: practical integration for complexity versus scientific fragmentation for simplicity. J Manag Inq 30(2):177–192
Chopra R, Agrawal A, Sharma GD, Kallmuenzer A, Vasa L (2023) Uncovering the organizational, environmental, and socio-economic sustainability of digitization: evidence from existing research. Rev Manag Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11846-023-00637-w
Combs JG, Crook TR, Rauch A (2019) Meta-analytic research in management: contemporary approaches, unresolved controversies, and rising standards. J Manage Stud 56(1):1–18
Cooper HM (1988) Organizing knowledge syntheses: a taxonomy of literature reviews. Knowl Soc 1(1):104
DeGeest DS, Schmidt FL (2010) The impact of research synthesis methods on industrial–organizational psychology: the road from pessimism to optimism about cumulative knowledge. Res Synth Methods 1(3–4):185–197
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Donthu N, Kumar S, Mukherjee D, Pandey N, Lim WM (2021) How to conduct a bibliometric analysis: an overview and guidelines. J Bus Res 133:285–296
Dwertmann DJ, van Knippenberg D (2021) Capturing the state of the science to change the state of the science: a categorization approach to integrative reviews. J Organ Behav 42(2):104–117
Dwivedi YK, Kshetri N, Hughes L, Slade EL, Jeyaraj A, Kar AK, Baabdullah AM, Koohang A, Raghavan V, Ahuja M (2023) “So what if ChatGPT wrote it? Multidisciplinary perspectives on opportunities, challenges and implications of generative conversational AI for research, practice and policy. Int J Inf Manag 71:102642
Felicetti AM, Corvello V and Ammirato S (2023) Digital innovation in entrepreneurial firms: a systematic literature review. Rev Manag Sci
Fernández-Uclés D, Mozas-Moral A, Bernal-Jurado E, Puentes-Poyatos R (2023) Online reputation of agri-food companies and determining factors: an empirical investigation. Rev Manag Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11846-023-00639-
Fisch C, Block J (2018) Six tips for your (systematic) literature review in business and management research. Manag Rev Q 68:103–106
Geyskens I, Krishnan R, Steenkamp J-BE, Cunha PV (2009) A review and evaluation of meta-analysis practices in management research. J Manag 35(2):393–419
Harari MB, Parola HR, Hartwell CJ, Riegelman A (2020) Literature searches in systematic reviews and meta-analyses: a review, evaluation, and recommendations. J Vocat Behav 118:103377
Hiebl MR (2023) Sample selection in systematic literature reviews of management research. Organ Res Methods 26(2):229–261
Hulland J, Houston MB (2020) Why systematic review papers and meta-analyses matter: an introduction to the special issue on generalizations in marketing. J Acad Market Sci 48:351–359
King WR, He J (2005) Understanding the role and methods of meta-analysis in IS research. Commun Assoc Inf Syst 16(1):32
Kraus S, Breier M, Dasí-Rodríguez S, Journal M (2020) The art of crafting a systematic literature review in entrepreneurship research. Int Entrep Manag J 16:1023–1042
Kraus S, Breier M, Lim WM, Dabić M, Kumar S, Kanbach D, Mukherjee D, Corvello V, Piñeiro-Chousa J, Liguori, E.e.a. (2022) Literature reviews as independent studies: guidelines for academic practice. RMS 16(8):2577–2595
Kraus S, Mahto RV, Walsh ST (2023) The importance of literature reviews in small business and entrepreneurship research. J Small Bus Manage 61(3):1095–1106
Kunisch S, Menz M, Bartunek JM, Cardinal LB, Denyer D (2018) Feature topic at organizational research methods: how to conduct rigorous and impactful literature reviews? Organ Res Methods 21(3):519–523
Kunisch S, Denyer D, Bartunek JM, Menz M, Cardinal LB (2023) Review research as scientific inquiry. Organ Res Methods 26(1):3–45
Laher S, Hassem T (2020) Doing systematic reviews in psychology. South African J Psychol 50(4):450–468
Lawani S (1981) Bibliometrics: its theoretical foundations, methods and applications. Libri 31(4):294–315
LePine JA, King AW (2010) Editors’ comments: Developing novel theoretical insight from reviews of existing theory and research. Acad Manag Rev 35(4):506–509
Linnenluecke MK, Marrone M, Singh AK (2020) Conducting systematic literature reviews and bibliometric analyses. Aust J Manag 45(2):175–194
Mas-Tur A, Kraus S, Brandtner M, Ewert R, Kürsten W (2020) Advances in management research: a bibliometric overview of the review of managerial science. Rev Manag Sci 14:1–26
Mukherjee D, Lim WM, Kumar S, Donthu N (2022) Guidelines for advancing theory and practice through bibliometric research. J Bus Res 148:101–115
Palmatier RW, Houston MB, Hulland JJ (2018) Review articles: purpose, process, and structure. J Acad Market Sci 46:1–5
Parmigiani A, King E (2019) Successfully proposing and composing review papers. J Manag 45(8):3083–3090
Pittaway L, Holt R, Broad J (2014) Synthesising knowledge in entrepreneurship research-the role of systematic literature reviews. Edward Elgar Publishing, Handbook of research on small business and entrepreneurship
Book Google Scholar
Post C, Sarala R, Gatrell C, Prescott J (2020) Advancing theory with review articles. J Manage Stud 57(2):351–376
Pütz L and Werner A (2023) Absorptive capacity in family firms: a systematic literature review. Rev Manag Sci
Ravet-Brown TÉ, Furtner M and Kallmuenzer A (2023) Transformational and entrepreneurial leadership: a review of distinction and overlap. Rev Manag Sci
Rocco TS, Plakhotnik MS (2009) Literature reviews, conceptual frameworks, and theoretical frameworks: terms, functions, and distinctions. Hum Resour Dev Rev 8(1):120–130
Rojon C, Okupe A, McDowall A (2021) Utilization and development of systematic reviews in management research: what do we know and where do we go from here? Int J Manag Rev 23(2):191–223
Rousseau DM, Manning J, Denyer D (2008) Evidence in management and organizational science: assembling the field’s full weight of scientific knowledge through syntheses. Acad Manag Ann 2(1):475–515
Rowe F (2014) What literature review is not: diversity, boundaries and recommendations. Eur J Inf Syst 23(3):241–255
Sauer PC, Seuring S (2023) How to conduct systematic literature reviews in management research: a guide in 6 steps and 14 decisions. Rev Manag Sci 17:1–35
Short J (2009) The art of writing a review article. J Manag 35(6):1312–1317
Simsek Z, Fox B, Heavey C (2023) Systematicity in organizational research literature reviews: a framework and assessment. Organ Res Methods 26(2):292–321
Snyder H (2019) Literature review as a research methodology: an overview and guidelines. J Bus Res 104:333–339
Templier M, Paré G (2015) A framework for guiding and evaluating literature reviews. Commun Assoc Inf Syst 37(1):6
Tranfield D, Denyer D, Smart P (2003) Towards a methodology for developing evidence-informed management knowledge by means of systematic review. Br J Manag 14(3):207–222
Van Eck NJ, Waltman L (2014) CitNetExplorer: a new software tool for analyzing and visualizing citation networks. J Informet 8(4):802–823
van Grinsven M, Heusinkveld S, Cornelissen J (2016) Translating management concepts: towards a typology of alternative approaches. Int J Manag Rev 18(3):271–289
Wright PM (2015) Rethinking “contribution.” J Manag 41(3):765–768
Zupic I, Čater T (2015) Bibliometric methods in management and organization. Organ Res Methods 18(3):429–472
Download references
Open access funding provided by Libera Università di Bolzano within the CRUI-CARE Agreement.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Faculty of Economics and Management, Free University of Bozen-Bolzano, 39100, Bolzano, Italy
Sascha Kraus
Department of Business Management, University of Johannesburg, 2092, Johannesburg, South Africa
Faculty of Law and Economics, University of Bayreuth, Prieserstraße 2, 95444, Bayreuth, Germany
Ricarda B. Bouncken
Faculty of Economics, Business Studies and Tourism, University of Alcalá, Plaza San Diego, 28801, Alcalá de Henares, Spain
Alba Yela Aránega
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Sascha Kraus .
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest.
The authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Kraus, S., Bouncken, R.B. & Yela Aránega, A. The burgeoning role of literature review articles in management research: an introduction and outlook. Rev Manag Sci 18 , 299–314 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11846-024-00729-1
Download citation
Received : 02 November 2023
Accepted : 04 January 2024
Published : 30 January 2024
Issue Date : February 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s11846-024-00729-1
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Bibliometrics
- Artificial intelligence
JEL Classification
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

Literature reviews as independent studies: guidelines for academic practice

Review of Managerial Science
Review articles or literature reviews are a critical part of scientific research. While numerous guides on literature reviews exist, these are often limited to the philosophy of review procedures, protocols, and nomenclatures, triggering non-parsimonious reporting and confusion due to overlapping similarities. To address the aforementioned limitations, we adopt a pragmatic approach to demystify and shape the academic practice of conducting literature reviews. We concentrate on the types, focuses, considerations, methods, and contributions of literature reviews as independent, standalone studies. As such, our article serves as an overview that scholars can rely upon to navigate the fundamental elements of literature reviews as standalone and independent studies, without getting entangled in the complexities of review procedures, protocols, and nomenclatures.
Related Papers
Publications
Cherley C Du Plessis
The ability to conduct an explicit and robust literature review by students, scholars or scientists is critical in producing excellent journal articles, academic theses, academic dissertations or working papers. A literature review is an evaluation of existing research works on a specific academic topic, theme or subject to identify gaps and propose future research agenda. Many postgraduate students in higher education institutions lack the necessary skills and understanding to conduct in-depth literature reviews. This may lead to the presentation of incorrect, false or biased inferences in their theses or dissertations. This study offers scientific knowledge on how literature reviews in different fields of study could be conducted to mitigate against biased inferences such as unscientific analogies and baseless recommendations. The literature review is presented as a process that involves several activities including searching, identifying, reading, summarising, compiling, analysing, interpreting and referencing. We hope this article serves as reference material to improve the academic rigour in the literature review chapters of postgraduate students' theses or dissertations. This article prompts established scholars to explore more innovative ways through which scientific literature reviews can be conducted to identify gaps (empirical, knowledge, theoretical, methodological, application and population gap) and propose a future research agenda.
Alexandra Gheondea-Eladi
In this paper a general view over literature reviews is given, as well as a short description of the possibilities of two of the current bibliographical referencing software available, EndNote and Mendeley. I argue that unlike other types of literature reviews, a critical literature review cannot be undertaken by writing notes and using the search engines of bibliographical referencing software, but by focusing on a judgment structure which evaluates the theoretical background of the papers, their assumptions and one that provides a logical structure of the paper. Such a judgment structure is likely to be used across many fields in the social sciences. The proposed judgment structure has been provided based on its applications in two different fields from the social sciences.
International Journal of P R O F E S S I O N A L Business Review
With a view to examining the entire proposed structure for an empirical article, this editorial focuses on the Literature Review, also known as the Theoretical Framework. The literature review may be defined as “a documented review of published or unpublished works (articles, books, etc.) in specific fields of interest to the work of the researcher” (Ferreira, 2015: 36). It is to be found in conceptual articles such as empirical articles, whether qualitative or quantitative. It has a clear link to the article as a whole and provides support for the section on the development of the concept and the hypotheses/propositions that follow it in the structure of an empirical article.
Communications of the Association for Information Systems
Murray Jennex
• Learning outcomes • The nature of a literature review • Identifying the main subject and themes • Reviewing previous research • Emphasizing leading research studies • Exploring trends in the literature • Summarizing key ideas in a subject area • Summary A literature review is usually regarded as being an essential part of student projects, research studies and dissertations. This chapter examines the reasons for the importance of the literature review, and the things which it tries to achieve. It also explores the main strategies which you can use to write a good literature review.
Coaching: An International Journal of Theory, Research and Practice
Mark N K Saunders , Céline Rojon
Exploring and evaluating findings from previous research is an essential aspect of all research projects enabling the work to be set in the context of what is known and what is not known. This necessitates a critical review of the literature in which existing research is discussed and evaluated, thereby contextualising and justifying the project. In this research note we consider what is understood by being critical when reviewing prior to outlining the key attributes of a critical literature review. We conclude with a summary checklist to help ensure a literature review is critical.
Paula L Bush
Rebekka Tunombili
Human Resource Development Review
Tonette S Rocco , Maria Plakhotnik
Abstract This essay starts with a discussion of the literature review, theoretical framework, and conceptual framework as components of a manuscript. This discussion includes similarities and distinctions among these components and their relation to other sections of a manuscript such as the problem statement, discussion, and implications. The essay concludes with an overview of the literature review, theoretical framework, and conceptual framework as separate types of manuscripts.
RELATED PAPERS
Psychology of Aesthetics, Creativity, and the Arts
Jean Decety
James Clark
The European Physical Journal B
larissa Aquino
serviceper mobilpurbaratu
Yunan Firdaus
PLANNING MALAYSIA
Mohd. Shahrizan Sahid
Eduardo Fernandes
Kim Sneppen
Journal of Issues in Midwifery
Lilik Indahwati
Anais da Mostra Nacional de Iniciação Científica e Tecnológica Interdisciplinar (MICTI) - e-ISSN 2316-7165
Gabriely Moura
Clinical Chemistry
Patricia Slev
28th IAHR Biennal Congress, Graz, Austria
Hubert Chanson
Kevin Smidt
The Florida Entomologist
Richard Brenner
Journal of Sustainable Development
Hanene Ben Ouada Jamoussi
Shaping the Corporate Landscape : Towards Corporate Reform and Enterprise Diversity
Nina Boeger
Pakistan Journal of Botany
alenka kavcic
IEEE Access
Lukasz Staszewski
Il Quaderno Montessori
Lorenzo Grassi
Proceedings on Engineering Sciences
BOGDAN NEDIC
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
- Systematic Review
- Open access
- Published: 13 May 2024
Sarcopenia and sarcopenic obesity among older adults in the nordic countries: a scoping review
- Fereshteh Baygi 1 na1 ,
- Sussi Friis Buhl 1 na1 ,
- Trine Thilsing 1 ,
- Jens Søndergaard 1 &
- Jesper Bo Nielsen 1
BMC Geriatrics volume 24 , Article number: 421 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
351 Accesses
Metrics details
Sarcopenia and sarcopenic obesity (SO) are age-related syndromes that may compromise physical and mental health among older adults. The Nordic countries differ from other regions on prevalence of disease, life-style behavior, and life expectancy, which may impact prevalence of sarcopenia and SO. Therefore, the aim of this study is to review the available evidence and gaps within this field in the Nordic countries.
PubMed, Embase, and Web of science (WOS) were searched up to February 2023. In addition, grey literature and reference lists of included studies were searched. Two independent researcher assessed papers and extracted data.
Thirty-three studies out of 6,363 searched studies were included in this scoping review. Overall prevalence of sarcopenia varied from 0.9 to 58.5%. A wide prevalence range was still present for community-dwelling older adults when definition criteria and setting were considered. The prevalence of SO ranged from 4 to 11%, according to the only study on this field. Based on the included studies, potential risk factors for sarcopenia include malnutrition, low physical activity, specific diseases (e.g., diabetes), inflammation, polypharmacy, and aging, whereas increased levels of physical activity and improved dietary intake may reduce the risk of sarcopenia. The few available interventions for sarcopenia were mainly focused on resistance training with/without nutritional supplements (e.g., protein, vitamin D).
The findings of our study revealed inadequate research on SO but an increasing trend in the number of studies on sarcopenia. However, most of the included studies had descriptive cross-sectional design, small sample size, and applied different diagnostic criteria. Therefore, larger well-designed cohort studies that adhere to uniform recent guidelines are required to capture a full picture of these two age-related medical conditions in Nordic countries, and plan for prevention/treatment accordingly.
Peer Review reports
The number of older adults with age-related disorders is expected to increase worldwide [ 1 , 2 ]. Sarcopenia and sarcopenic obesity (SO) are both age-related syndromes that may compromise the physical and mental health of older adults and increase their need for health care services in old age [ 3 , 4 ], and this may challenge the sustainability of health care systems economically and by shortage of health care personnel [ 5 ].
Sarcopenia is characterized by low muscle mass in combination with low muscle strength [ 4 ]. SO is characterized by the co-existence of obesity (excessive adipose tissue) and sarcopenia [ 3 ]. Sarcopenia and SO are both associated with physical disability, risk of falls, morbidity, reduced quality of life and early mortality [ 4 , 6 , 7 , 8 , 9 ]. In SO the consequences of sarcopenia and obesity are combined and maximized [ 4 , 6 , 7 , 8 ].
Etiology of sarcopenia and SO is multifactorial and closely linked to multimorbidity [ 3 , 7 , 8 , 9 , 10 ]. Nevertheless, lifestyle and behavioral components particularly diet and physical activity, are important interrelated factors that potentially can be modified. Physical inactivity and sedentary behavior may accelerate age-related loss of muscle mass, reduce energy expenditure, and increase risk of obesity [ 3 , 11 ]. In addition, weight cycling (the fluctuations in weight following dieting and regain) and an unbalanced diet (particularly inadequate protein intake) may accelerate loss of muscle mass and increase severity of sarcopenia and SO in older adults [ 3 , 12 ]. International guideline for the treatment of sarcopenia emphasizes the importance of resistance training potentially in combination with nutritional supplementation to improve muscle mass and physical function [ 13 ]. Similar therapeutic approach is suggested for treatment of SO [ 14 ]. However, more research is needed to confirm optimal treatment of SO [ 14 ].
According to a recently published meta-analysis the global prevalence of sarcopenia ranged from 10 to 27% in populations of older adults ≥ 60 years [ 15 ]. Further the global prevalence of SO among older adults was 11% [ 8 ]. So, sarcopenia and SO are prevalent conditions, with multiple negative health outcomes and should be given special attention [ 16 ]. Despite the large burden on patients and health care systems, the awareness of the importance of skeletal muscle maintenance in obesity is low among clinicians and scientists [ 3 , 16 ].
A recent meta-analysis on publication trends revealed that despite an increase in global research on sarcopenia, the Nordic countries were only limitedly represented [ 6 ]. Nordic countries may differ from other regions on aspects associated with the prevalence and trajectory of sarcopenia and SO and challenge the representativeness of research findings from other parts of the world. These include a different prevalence pattern of noncommunicable diseases [ 17 ], different life-style behavior and life-style associated risk factors [ 15 , 18 ], and higher life expectancy [ 18 ].
The Nordic countries including Sweden, Finland, Iceland, Norway, Denmark, and three autonomous areas (Åland Islands, Greenland and Faroe Islands) share common elements of social and economic policies such as a comprehensive publicly financed health care system [ 18 , 19 ]. Additionally, these countries have a strong tradition of collaboration including a common vision of a socially sustainable region by promoting equal health and inclusive participation in society for older adults [ 20 ]. Therefore, more insight into the etiology, prevalence, and risk factors for sarcopenia and SO among older adults is a prerequisite for the development and implementation of effective strategies to prevent and treat these complex geriatric conditions in this geographic region. So, the aim of this study is to conduct a scoping review to systematically identify and map the available evidence while also addressing knowledge gaps and exploring the following research questions: (1) What are the prevalence of sarcopenia and SO in older adults living in the Nordic countries? (2) Which risk factors or contributing conditions are involved in the development of sarcopenia and SO in the Nordic Countries? (3) Which interventions to prevent or counteract negative health outcomes of sarcopenia and SO have been tested or implemented among older adults living in the Nordic countries?
Identification of relevant studies
The development and reporting of this review were done by following the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-analyses (PRISMA) guidelines [ 21 ].
The literature search was developed to target three main areas: Sarcopenia, sarcopenic obesity, and aging (See Appendix 1 for full search strategy). All studies published before the end of February 2023 were included in this scoping review. The optimal sensitivity of search was obtained by simultaneous search of the following databases: PubMed, Embase, and Web of science (WOS). Additionally, a detailed search for grey literature was performed in relevant databases (e.g., Research Portal Denmark, Libris, Oria, Research.fi). Besides, reference lists of the included studies were reviewed to identify eligible studies. Duplicates and non-peer reviewed evidence (e.g., PhD thesis) were excluded but if the latter contained published articles of relevance, these were included. If more than one publication on similar outcomes (e.g., prevalence) were based on a single study, just one publication was included. Data were extracted from large studies with combined data from several countries only when findings were presented separately for the Nordic countries.
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
The inclusion criteria were as follow : Broad selection criteria were used to be comprehensive: (1) studies with any outcome (e.g., prevalence, risk factors, etc.) to address our research questions on sarcopenia and SO, (2) studies on subjects with age ≥ 60 years in any type of settings (e.g., community, nursing homes, general practice, hospital, outpatients, homecare, etc.), (3) studies using any definition of sarcopenia and SO without restriction for criteria and cutoff values, (4) all type of study designs (e.g., randomized control trials, cohort studies, cross-sectional, etc.), (5) studies should be conducted in the Nordic countries The exclusion criteria are as follow : (1) studies without relevant outcome to sarcopenia or SO, (2) studies without sufficient information to determine eligibility.
Study selection and data extraction
Two independent researchers screened literature and conducted data extraction. Any discrepancies between them were resolved through discussion.
First, duplicates were removed by using EndNote 20.6 software, then titles and abstracts were screened to narrow down the list of potentially eligible studies. Finally, the full text review was done to examine in detail the studies that were not excluded in first step. For more clarification, the reasons for the exclusion were recorded (Fig. 1 ).
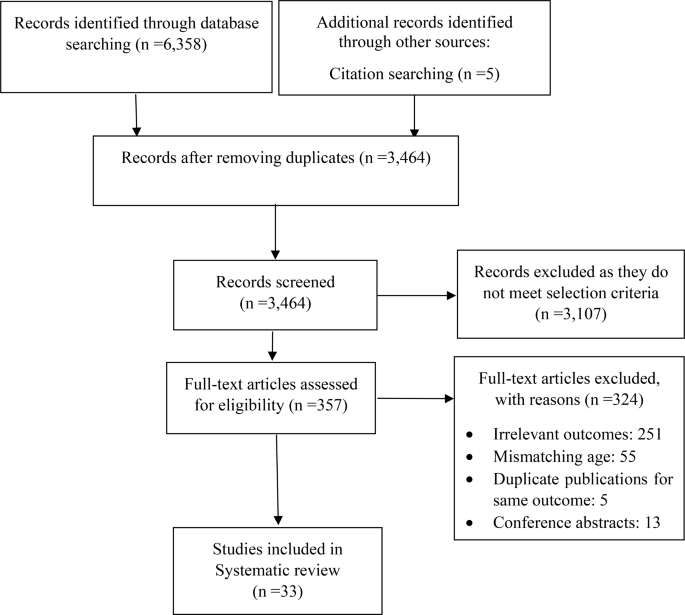
PRISMA diagram for searching resources
The following information was extracted: (1) study characteristics (e.g., first author’s name, country, year of publication), (2) characteristics of the target population (e.g., age, sex), (3) study design, setting, intervention duration and follow-up time (if applicable), measurements, tools, criteria, and results.
Study selection
A combined total of 6,358 studies were identified through the initial electronic database and grey literature searches. An additional five articles were identified through other sources (citation searching). After removing duplication, 3,464 articles remained. A total of 3107 articles were excluded based on screening titles and abstracts. Out of the remaining 357 studies, 324 were excluded after the full-text review. Finally, 33 studies met our inclusion criteria and were included in this current scoping review [ 22 , 23 , 24 , 25 , 26 , 27 , 28 , 29 , 30 , 31 , 32 , 33 , 34 , 35 , 36 , 37 , 38 , 39 , 40 , 41 , 42 , 43 , 44 , 45 , 46 , 47 , 48 , 49 , 50 , 51 , 52 , 53 , 54 ] (Fig. 1 ).
Study characteristics
Table 1 summarized characteristics of the included studies.
The number of documents showed an increasing trend between 2020 and 2021. A peak in the number of publications was observed in 2021 (24.2% of all documents). All the studies were conducted across four (Denmark, Norway, Sweden, and Finland) out of the five Nordic countries and three autonomous areas. The highest contribution in this field was made by Sweden ( n = 12).
Most studies were conducted in community-dwelling settings [ 22 , 23 , 24 , 28 , 30 , 31 , 35 , 36 , 38 , 39 , 40 , 42 , 45 , 46 , 47 , 48 , 49 , 54 ]. Seven studies included patients with acute diseases (hospital-setting) [ 26 , 27 , 33 , 37 , 50 , 51 , 52 ], while four studies included patients with chronic conditions (out-patient setting) [ 25 , 32 , 41 , 44 ], and one study including nursing-home residents [ 34 ]. In terms of study design, most of the studies were observation studies with a cross-sectional or longitudinal design ( 22 , 23 , 24 , 25 , 26 , 27 , 28 , 29 , 30 , 31 , 33 , 34 , 36 , 37 , 38 , 39 , 40 , 41 , 42 , 43 , 44 , 45 , 46 , 47 , 48 , 49 , 50 , 51 , 52 , 53 , 54 ), while three studies [ 32 , 35 , 46 ] applied interventions. It appears, however, that one study [ 32 ] out of the above three interventions is sub-project conducted within the framework of larger intervention program. Sample size ranged from 49 in a cross-sectional case control study [ 52 ] to 3334 in a cohort study [ 30 ].
Five studies were among males only [ 22 , 24 , 36 , 45 , 53 ] and three studies included females only [ 38 , 47 , 54 ]. The rest of the studies had a mixed sample. Top subject area was sarcopenia (31 out of the 33 included studies), and on this subject, publications were categorized into the following research areas (with some studies addressing more areas): prevalence [ 22 , 23 , 24 , 25 , 26 , 27 , 29 , 30 , 33 , 35 , 36 , 37 , 40 , 42 , 44 , 45 , 47 , 49 , 50 , 51 , 52 , 53 , 54 ], risk factors [ 24 , 27 , 28 , 30 , 31 , 34 , 38 , 40 , 42 , 44 , 47 , 49 , 50 , 51 ], and effectiveness of interventions on sarcopenia or indicator of sarcopenia [ 32 , 35 , 46 ].
In most studies sarcopenia was defined according to the criteria set by the European Working Group on Sarcopenia in Older People in the updated version from 2019 (EWGSOP2) ( n = 15) or the original version from 2010 (EWGSOP) ( n = 14). However, in some studies multiple criteria such as EWGSOP, EWGSOP2, and National Institutes of Health Sarcopenia Project definition (FNIH) were applied [ 27 , 39 , 43 ], and in other studies alternative criteria were used [ 26 , 33 , 35 , 45 , 57 ].
Different assessment methods of muscle mass including Dual energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) [ 22 , 24 , 25 , 27 , 29 , 30 , 32 , 33 , 38 , 39 , 40 , 41 , 45 , 46 , 47 , 52 , 53 , 54 ], Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis (BIA) [ 28 , 31 , 34 , 44 , 48 , 49 ], Bioimpedance Spectroscopy (BIS) [ 35 , 42 , 43 ], Computed Tomography (CT) [ 33 ], and Computed Tomography Angiogram (CTA) [ 26 ] were used in the included studies.
SO were defined by the co-existence of sarcopenia with obesity. Studies on SO used the EWGSOP2 criteria [ 39 ], or the EWGSOP2 criteria for hand grip strength only (probable sarcopenia) [ 23 ] in combination with obesity estimated from BMI cut points [ 23 , 39 ], waist circumference [ 23 , 39 ], and fat mass percentage [ 39 ]. Lastly, one study used measures of body composition measures that reflect adiposity as estimates of SO [ 48 ].
Four studies reported the prevalence of “probable sarcopenia” [ 23 , 30 , 36 , 45 ], while two studies reported the prevalence of sarcopenia and comorbidities (e.g., osteopenia, pre-frailty, malnutrition) [ 33 , 40 ].
Narrative synthesis
Due to the heterogeneity of the studies in definition of sarcopenia, settings, and sample size, the overall reported prevalence was variable and ranged from 0.9% [ 54 ] to 58.5% [ 26 ]. However, according to the most commonly used criteria (EWGSOP2) the highest (46%) and lowest (1%) prevalence of sarcopenia was reported in Sweden among inpatients in geriatric care [ 27 ], and community-dwelling older adults [ 30 ], respectively.
Prevalence of sarcopenia according to population and definition criteria is illustrated in Table 2 . Higher prevalence rates of sarcopenia were found in females compared to males among community-dwelling older adults [ 49 ] and in older adults acutely admitted to hospital [ 51 ]. Further, acutely admitted female patients also presented with more severe sarcopenia compared to male patients [ 51 ].
Frequency of sarcopenia was higher (9.1–40.0%) in patients with diabetes (with and without complications of charcot osteoarthropathy), compared to age-matched healthy adults [ 52 ].
The prevalence of “probable sarcopenia” ranged between 20.4% (reduced muscle strength only) and 38.1% (fulfilling one of the following criteria: reduced muscle strength, reduced muscle mass, or low physical function) in Finnish community-dwelling adults [ 23 , 36 ], while longitudinal studies on Swedish community-dwelling old (70 years) and very old adults (≥ 85 years) the prevalence of “probable sarcopenia” (reduced muscle strength only) ranged from 1.8 to 73%, respectively [ 30 , 45 ]. Lastly, in a Swedish study among nursing home residents the prevalence of probable sarcopenia was 44% (evaluated by an impaired chair stand test) [ 34 ].
Prevalence of Osteosarcopenia (sarcopenia and osteoporosis) was 1.5% [ 36 ], and the prevalence of co-occurrence of all three following conditions: pre-frail, malnutrition, and sarcopenia was 7% [ 34 ].
We only identified two studies with prevalence of SO [ 39 ] and probable SO [ 23 ]. The prevalence of SO in a Swedish population was 4% and 11% in females and males, respectively, while the prevalence of probable SO among Finnish community-dwelling ranged between 5.8% and 12.6%, depending on the criteria to define the obesity (e.g., BMI, waist circumference, etc.) [ 23 ].
Several studies investigated aspects of etiology and risk factors for sarcopenia [ 24 , 27 , 28 , 30 , 31 , 34 , 36 , 38 , 40 , 42 , 43 , 44 , 47 , 49 , 50 , 51 ] and one study focused on SO [ 49 ]. Higher physical activity was associated with a decreased likelihood of sarcopenia [ 30 ]. In addition, adhering to world health organization (WHO) guidlines for physical activity and the Nordic nutritional recommendations for protein intake was positively associated with greater physical function and lower fat mass in older female community-dwellers [ 38 ]. In older adults who are physically active, eating a healthy diet (based on the frequency of intake of favorable food like fish, fruits, vegetables, and whole grains versus unfavorable foods like red/processed meats, desserts/sweets/sugar-sweetened beverages, and fried potatoes) was associated with lower risk of sarcopenia [ 28 ]. Further, among older adults who already meet the physical activity guidelines, additional engagement in muscle-strengthening activities was associated with a lower sarcopenia risk score and improved muscle mass and chair rise time [ 31 ].
Associations between sarcopenia, risk of sarcopenia and malnutrition or nutritional status was identified in geriatric patients [ 27 , 51 ], older patients with hip fracture [ 50 ], nursing home residents [ 34 ] and in community-dwelling older adults [ 49 ]. Moreover, the importance of nutritional intake was investigated in the following studies [ 24 , 36 , 47 ]. A study among community-dwelling men revealed an inverse association between total energy intake, protein intake (total, plant, and fish protein), intake of dietary fibers, fat (total and unsaturated), and vitamin D with sarcopenia status [ 36 ]. In a cohort of 71-year-old men a dietary pattern characterized by high consumption of fruit, vegetables, poultry, rice and pasta was associated with lower prevalence of sarcopenia after 16 years [ 24 ]. A longitudinal Finnish study on sarcopenia indices among postmenopausal older women, showed that lower adherence to the Mediterranean (focuses on high consumption of olive oil) or Baltic Sea (focuses on the dietary fat quality and low-fat milk intake) diets resulted in higher loss of lean mass over a 3-year period [ 47 ]. Further, a higher adherence to the Baltic Sea diet was associated with greater lean mass and better physical function, and higher adherence to the Mediterranean diet was associated with greater muscle quality [ 47 ].
In a study of patients with hip fracture age, polypharmacy, and low albumin levels was associated with sarcopenia [ 50 ]. Exocrine pancreatic insufficiency was an independent risk factor for sarcopenia [ 44 ]. This study also revealed that sarcopenia was associated with reduced quality of life, physical function, and increased risk of hospitalization [ 44 ]. In a longitudinal study of community-dwelling adults (+ 75 years) at risk of sarcopenia, high physical function, muscle strength, muscle mass and low BMI predicted better physical function and reduced need for care after four years [ 42 ]. Furthermore, in community-dwelling adults with sarcopenia, muscle mass, muscle strength and physical function are independent predictors of all-cause mortality. As a result, they have been proposed by researchers as targets for the prevention of sarcopenia-related over-mortality [ 43 ]. Lastly, community-dwelling older adults with sarcopenia had lower bone mineral density compared to those without sarcopenia and they were more likely to develop osteoporosis (Osteosarcopenia) [ 40 ].
Regarding SO risk factors, a longitudinal study among community-dwelling older adults in Finland found that SO (operationalized by measures of adiposity) were associated with poorer physical function after ten years [ 48 ].
Our literature search identified three randomized controlled trials investigating the effectiveness of interventions to prevent or counteract sarcopenia in older adults of Norway, Finland, and Sweden, respectively [ 32 , 35 , 46 ]. The Norwegian study [ 32 ] was a double-blinded randomized controlled trial (RCT). The study included those who were at risk of developing sarcopenia, including patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) or individuals who showed diagnostic indications of sarcopenia. Participants received either vitamin D 3 or placebo supplementation for 28 weeks. Additionally, resistance training sessions were provided to all participants from weeks 14 to 27. Vitamin D supplementation did not significantly affect response to resistance training in older adults at risk of sarcopenia with or without COPD [ 32 ].
Furthermore, a RCT among pre-sarcopenic Swedish older adults investigated the effectiveness of three weekly sessions of instructor-led progressive resistance training in combination with a non-mandatory daily nutritional supplement (175 kcal, 19 g protein) compared to control group. The 10 weeks intervention resulted in significant between group improvements of physical function and a significant improvement in body composition in the intervention group [ 46 ].
Another intervention study revealed that a 12-month intervention with two daily nutritional supplements (each containing 20 g whey protein) did not attenuate the deterioration of physical function and muscle mass in sarcopenic older community-dwelling adults compared to isocaloric placebo supplements or no supplementation. All participants were given instructions on home-based exercises, importance of dietary protein and vitamin D supplementation [ 35 ].
Based on our broad literature search 33 studies were identified that concerned sarcopenia and SO and met the inclusion criteria. However, research on SO was very limited with only three studies identified. Narrative synthesis of the included studies revealed that the most reported classification tool for sarcopenia in Nordic countries was the EWGSOP2. Moreover, some studies estimated sarcopenia using EWGSOP. The overall prevalence of sarcopenia in Nordic countries according to EWGSOP2 ranged between 1% and 46% [ 25 , 28 ]. The prevalence of SO, however, was reported only in one study in Sweden (4–11%) [ 39 ]. Even though the previous systematic reviews and meta-analysis have reported the prevalence of sarcopenia and SO in different regions and settings (e.g., community-dwelling, nursing home, etc.) [ 8 , 15 , 55 , 56 ], this current scoping review is to the best of our knowledge the first study that provides an overview of research on sarcopenia and SO in the Nordic countries.
Based on our findings from 24 studies, there were large variability in prevalence of sarcopenia in studies conducted in the Nordic countries. We think that the wide variation in estimated prevalence of sarcopenia in our scoping review might be due to a different definition/diagnostic criterion (e.g., EWGSOP, EWGSOP2, FNIH), methodology to measure muscle mass (DXA, BIA, CT), and heterogeneity in characteristics of the study population (e.g., setting, age, medical conditions, co-occurrence of multiple risk factors). A previous study on prevalence of sarcopenia in Swedish older people showed significant differences between prevalence of sarcopenia based on EWGSOP2 and EWGSOP1 [ 29 ]. Therefore, researchers stressed that prevalence is more dependent on cut-offs than on the operational definition [ 29 , 57 ]. Further, we know that various international sarcopenia working groups have issued expert consensus and such diagnostic criteria are being updated [ 4 , 58 ]. Since the revision of criteria focuses primarily on the adjustment of cut-off values, the main reason for differences in prevalence even when using an updated version of one diagnosis criteria is modification in cut-off values. For instance, if the cut-off value for gait speed was increased by 0.2 m/s, the prevalence of sarcopenia may increase by 8.5% [ 57 ]. Meaning that even a small change in cut-off value can have a big impact on how sarcopenia is diagnosed. Besides when we take definition criteria into account (Table 2 ), the prevalence of sarcopenia is still variable in the population of community-dwelling adults for instance. We believe it is basically because studies have applied different assessment tools and tests to identify older adults with low muscle mass and muscle strength, although using the same definition criteria (Table 1 ). Previous studies have illustrated that choice of methodology to assess muscle strength (e.g., hand grip strength, chair rise) [ 59 ] and muscle mass (e.g., DXA, BIA, anthropometry) [ 60 , 61 , 62 ] in older adults may impact findings and this variability may explain some of the variability in our findings. So, adherence to the latest uniform diagnostic criteria for future studies is recommended to simplify the comparison of findings within the same country, across countries, and regions. Moreover, we suggest that medical community particularly GPs to come to an agreement on assessment methods for muscle mass and muscle strength and the use of one set of definition criteria for sarcopenia.
In previous meta-analyses [ 15 ], sub-group analyses based on region and classification tool, revealed that the prevalence of sarcopenia was higher in European studies using EWGSOP (12%) compared to rest of the studies using Asian Working Group for Sarcopenia (AWGS), FNIH, and EWGSOP (3%) [ 15 ]. In our scoping review, we also found a high prevalence of sarcopenia in Nordic countries. Longevity and life expectancy is higher in the Nordic countries compared to estimates for rest of the world [ 18 ], which means that in this region many people reach old age, and consequently they are more likely to be diagnosed with sarcopenia as an age-related disorder. Therefore, the authors of this current scoping review emphasis the importance of preventive strategies targeted major risk factors and effective interventions to limit the consequences of sarcopenia in the Nordic populations. Besides, we think that the health care system in the Nordic countries should be better equipped with the necessary healthcare resources for both a timely diagnosis and dealing with this major age-related issue in the years to come. However, due to the limitations regarding the timely diagnosis, we highly recommend a comprehensive approach including establishment of support services, implement educational programs, offer training for health care professionals, and engage the community.
Many countries have conducted research on SO [ 7 , 39 , 63 , 64 , 65 ]. Based on our findings, however, among the Nordic countries only Sweden and Finland have investigated the prevalence of probable SO and SO [ 23 , 29 ]. Besides, we only found one study investigating the association between body adiposity and physical function over time [ 54 ]. We did not find any literature on risk factors or interventions among older adults with SO in this region. Therefore, we call on medical and research community in Nordic countries to attach importance to screening of SO in elderly people to capture a full picture of this public health risk to aging society and allocate healthcare resources accordingly.
In terms of risk factors for sarcopenia, our study revealed that malnutrition, low levels of physical activity, specific diseases (e.g., diabetes, osteoporosis), inflammation, polypharmacy (multiple medicines), BMI, and ageing are potential risk factor for sarcopenia in populations of the Nordic region. However, evidence on risk factors derived mainly from cross-sectional associations [ 27 , 28 , 30 , 31 , 34 , 40 , 44 , 49 , 50 , 51 ], and only to a limited extend from longitudinal studies [ 24 , 38 , 43 , 47 ]. Therefore, the associations between risk factors and sarcopenia should be interpreted with caution due to the possibility of reverse causality and confounding affecting the results. Moreover, our findings on risk factors mainly came from community-dwelling older adults, and only to a limited extend hospital and nursing home settings. We think that risk factors may vary depending on population characteristics (e.g., age, sex, health condition) and setting (e.g., hospital, nursing home, community). Therefore, we encourage researchers of the Nordic countries to perform well-designed prospective cohort studies in different settings to enhance the possibility to establish causal inference as well as understanding degree and direction of changes over time.
A recently published meta-analyses revealed a higher risk of having polypharmacy in Europe among individuals with sarcopenia compared to people without this condition [ 66 ]. A nationwide register-based study in Swedish population also showed that the prevalence of polypharmacy has increased in Sweden over the last decade [ 67 ]. Sarcopenia itself is associated with morbidity (identified by specific disease or inflammatory markers) and different health-related outcomes (e.g., disability) [ 7 ]; therefore, future research should investigate whether polypharmacy is a major factor to sarcopenia development [ 66 ]. Although we lack information on polypharmacy in Nordic countries other than Sweden, we encourage researchers in this region to examine the above research gap in their future studies.
According to previous studies physiological changes in ageing include systemic low-grade inflammation which results in insulin resistance, affect protein metabolism and leads to increased muscle wasting [ 68 ]. Acute and chronic disease may increase the inflammatory response and accelerate age-related loss of muscle mass and increase risk of sarcopenia [ 68 , 69 ]. Hence, we think that special attention should be made by health care professionals particularly GPs to older adults with acute or chronic conditions to limit the risk of sarcopenia.
Literature from the Nordic countries also indicated that higher levels of physical activity and different dietary patterns (e.g., higher protein intake, fruit, vegetables, fibers) were associated with reduced risk of sarcopenia or improvement in indicators of sarcopenia. There was a large heterogeneity in the studied aspect which makes direct comparison of studies difficult. Nevertheless, according to findings from a recent systematic review of meta-analyses on sarcopenia the identified risk factors are in alignment with previously identified risk factors globally [ 70 ]. Other potential lifestyle-related risk factors suggested from the above meta-analysis included smoking and extreme sleep duration. However, we did not identify studies investigating these health behaviors in the Nordic populations. Therefore, high-quality cohort studies are needed to deeply understand such associations with the risk of sarcopenia.
In this current review, we only found three intervention studies in Nordic countries. However, two of them were sub-projects of big intervention programs, meaning that such studies were not designed explicitly for the prevention/treatment of sarcopenia. Therefore, explicit intervention studies on sarcopenia in this region is recommended.
We believe that on a global level, research on sarcopenia will carry on with nutrition, exercise, and understanding of molecular mechanisms. Furthermore, examining the link between sarcopenia and other medical conditions/diseases would be the next step [ 6 ]. In the Nordic countries, however, already performed studies have a basic and descriptive design, so that, well-designed research and advanced analyses are lacking. Hence, we recommend conducting large well-designed and adequately powered studies to (a) explore the scale of this age-related health issue on country and regional level, (b) investigate the patterns of physical activity and sedentary behavior to understand if this should be a target in older adults with SO and sarcopenia, (c) determine whether elderly populations are suffering from nutritional deficiency or are at risk of malnutrition. The latest can support further studies to assess the impact of combined physical activity and dietary intake, which are still lacking globally [ 6 ].
A previous systematic review on therapeutic strategies for SO revealed that exercise-based interventions (e.g., resistance training) reduced total adiposity and consequently improved body composition. However, evidence of other therapeutic strategies (e.g., nutritional supplementation) was limited due to scarcity of data and lack of unique definition for SO [ 69 ]. Therefore, authors suggested that more research should be done to clarify optimal treatment options for various age-groups and not only for older adults [ 14 ].
In our scoping review, the included studies, did not provide a status of either SO or the prevention/treatment methods in this region. We believe that SO is practically neglected in clinical practice and research as well, and this is mainly because it is difficult to separate it from general obesity. The consequence of lacking knowledge in this research area is that when older adults with SO are recommended weight loss- a frequently used strategy for management of general obesity- this may accelerate the loss of muscle mass and increase the severity of the sarcopenia [ 3 ]. Consequently, we think that this issue may have adverse effects both on patients (e.g., decreasing quality of their life) and on the health care system (e.g., increasing the health care demands) of this region. Therefore, we encourage researchers to perform cohort studies to understand the epidemiology and etiological basis of SO, which are poorly understood even on a global scale [ 8 ]. We think that the consensus definition on SO from the European Society for Clinical Nutrition and Metabolism (ESPEN) and European Association for the Study of Obesity (EASO) which was published in 2022 [ 3 ], can positively affect the ability to define studies on prevalence and prevention of SO. Besides, we recommend conducting further research to find the optimal treatment for SO and reduce its adverse consequences both at individual and society levels. Additionally, we think that the concepts of sarcopenia and SO might be somehow unfamiliar to health care personnel. Therefore, it is highly recommended that more information be provided to bring their attention to the significance of prevention, timely diagnosis, and treatment of these two aging disorders.
Strengths and limitations of the study
This is the first study providing an overview of available evidence on sarcopenia and SO among older adults in the Nordic countries. These countries have important similarities in welfare sectors and on a population level and we believe that our findings will be a significant benefit for researchers and health care providers to understand the knowledge gaps and plan for future studies in this geographical region. However, the current scoping review has limitations. This review was limited to studies among individuals more than 60 years old which may limit the overview of available research in this field, as well as understanding risk factors, confounders for prevention, and the potential for early detection of these two diseases in younger age population. The included cross-sectional studies in our review cannot provide information on causality of the associations.
Sarcopenia and SO are generally prevalent syndromes among older adults in Nordic countries, even though the prevalence of them varies according to the criteria for definition, population, and setting. Research among older adults with SO was very limited in this region. Besides, studies on risk factors were primarily cross-sectional and only few intervention studies were identified. Therefore, we encourage researchers performing well-designed studies (e.g., prospective cohorts) to understand the epidemiology and etiological basis of these two age-related disorders. For the next step, implementation of interventions targeting risk factors (e.g., combined physical activity and dietary intake) and evaluating of their impact on prevention or treatment of sarcopenia and SO is recommended. Furthermore, for the comprehensive advancement of muscle health in older adults, we recommend implementing interventions directed at health care personnel and encouraging more collaboration among clinicians, professional societies, researchers, and policy makers to ensure comprehensive and effective approach to health care initiatives.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
sarcopenic obesity
Web of science
Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-analyses
European Working Group on Sarcopenia in Older People in the updated version from 2019
National Institutes of Health Sarcopenia Project definition
Dual energy X-ray absorptiometry
Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis
Bioimpedance Spectroscopy
Computed Tomography
Computed Tomography Angiogram
World Health Organization
General Practitioner
Randomized Controlled Trial
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
European Association for the Study of Obesity
United, Nations, Department of Economic and Social Affairs., Population Division (2019). World Population Prospects 2019: Highlights (ST/ESA/SER.A/423).
United, Nations, Department of Economic and Social Affairs., Population Division (2019). World Population Ageing 2019: Highlights (ST/ESA/SER.A/430).
Donini LM, Busetto L, Bischoff SC, Cederholm T, Ballesteros-Pomar MD, Batsis JA, Bauer JM, Boirie Y, Cruz-Jentoft AJ, Dicker D, Frara S, Frühbeck G, Genton L, Gepner Y, Giustina A, Gonzalez MC, Han HS, Heymsfield SB, Higashiguchi T, Laviano A, Lenzi A, Nyulasi I, Parrinello E, Poggiogalle E, Prado CM, Salvador J, Rolland Y, Santini F, Serlie MJ, Shi H, Sieber CC, Siervo M, Vettor R, Villareal DT, Volkert D, Yu J, Zamboni M, Barazzoni R. Definition and diagnostic criteria for sarcopenic obesity: ESPEN and EASO Consensus Statement. Obes Facts. 2022;15(3):321–35. doi: 10.1159/000521241. Epub 2022 Feb 23. PMID: 35196654; PMCID: PMC9210010.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Cruz-Jentoft AJ, Bahat G, Bauer J, Boirie Y, Bruyère O, Cederholm T, Cooper C, Landi F, Rolland Y, Sayer AA, Schneider SM, Sieber CC, Topinkova E, Vandewoude M, Visser M, Zamboni M, Writing Group for the European Working Group on Sarcopenia in Older People 2 (EWGSOP2), and the Extended Group for EWGSOP2. Sarcopenia: revised European consensus on definition and diagnosis. Age Ageing. 2019;48(1):16–31. https://doi.org/10.1093/ageing/afy169 . Erratum in: Age Ageing. 2019;48(4):601. PMID: 30312372; PMCID: PMC6322506.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Cylus J, Figueras J, Normand C. Will population ageing spell the end of the welfare state? A review of evidence and policy options [Internet]. Sagan A, Richardson E, North J, White C, editors. Copenhagen (Denmark): European Observatory on Health Systems and Policies; 2019. PMID: 31820887.
Yuan D, Jin H, Liu Q, Zhang J, Ma B, Xiao W, Li Y. Publication trends for Sarcopenia in the World: a 20-Year bibliometric analysis. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022;9:802651. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmed.2022.802651 . PMID: 35223902; PMCID: PMC8873525.
Marengoni A, Angleman S, Melis R, Mangialasche F, Karp A, Garmen A, Meinow B, Fratiglioni L. Aging with multimorbidity: a systematic review of the literature. Ageing Res Rev. 2011;10(4):430–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arr.2011.03.003 . Epub 2011 Mar 23. PMID: 21402176.
Gao Q, Mei F, Shang Y, Hu K, Chen F, Zhao L, Ma B. Global prevalence of sarcopenic obesity in older adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Nutr. 2021;40(7):4633–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clnu.2021.06.009 . Epub 2021 Jun 21. PMID: 34229269.
Molino S, Dossena M, Buonocore D, Verri M. Sarcopenic obesity: an appraisal of the current status of knowledge and management in elderly people. J Nutr Health Aging. 2016;20(7):780-8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12603-015-0631-8 . PMID: 27499312.
Khadra D, Itani L, Tannir H, Kreidieh D, El Masri D, El Ghoch M. Association between sarcopenic obesity and higher risk of type 2 diabetes in adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. World J Diabetes. 2019;10(5):311–23. https://doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v10.i5.311 . PMID: 31139318; PMCID: PMC6522758.
Aggio DA, Sartini C, Papacosta O, Lennon LT, Ash S, Whincup PH, Wannamethee SG, Jefferis BJ. Cross-sectional associations of objectively measured physical activity and sedentary time with Sarcopenia and sarcopenic obesity in older men. Prev Med. 2016;91:264–72. Epub 2016 Aug 26. PMID: 27575317; PMCID: PMC5061552.
Rossi AP, Rubele S, Calugi S, Caliari C, Pedelini F, Soave F, Chignola E, Vittoria Bazzani P, Mazzali G, Dalle Grave R, Zamboni M. Weight cycling as a risk factor for low muscle mass and strength in a population of males and females with obesity. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2019;27(7):1068–1075. https://doi.org/10.1002/oby.22493 . PMID: 31231958.
Dent E, Morley JE, Cruz-Jentoft AJ, Arai H, Kritchevsky SB, Guralnik J, Bauer JM, Pahor M, Clark BC, Cesari M, Ruiz J, Sieber CC, Aubertin-Leheudre M, Waters DL, Visvanathan R, Landi F, Villareal DT, Fielding R, Won CW, Theou O, Martin FC, Dong B, Woo J, Flicker L, Ferrucci L, Merchant RA, Cao L, Cederholm T, Ribeiro SML, Rodríguez-Mañas L, Anker SD, Lundy J, Gutiérrez Robledo LM, Bautmans I, Aprahamian I, Schols JMGA, Izquierdo M, Vellas B. International clinical practice guidelines for sarcopenia (ICFSR): screening, diagnosis and management. J Nutr Health Aging. 2018;22(10):1148–1161. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12603-018-1139-9 . PMID: 30498820.
Poggiogalle E, Parrinello E, Barazzoni R, Busetto L, Donini LM. Therapeutic strategies for sarcopenic obesity: a systematic review. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2021;24(1):33–41. https://doi.org/10.1097/MCO.0000000000000714 . PMID: 33323715.
Petermann-Rocha F, Balntzi V, Gray SR, Lara J, Ho FK, Pell JP, Celis-Morales C. Global prevalence of Sarcopenia and severe Sarcopenia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2022;13(1):86–99. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcsm.12783 . Epub 2021 Nov 23. PMID: 34816624; PMCID: PMC8818604.
Prado CM, Wells JC, Smith SR, Stephan BC, Siervo M. Sarcopenic obesity: a critical appraisal of the current evidence. Clin Nutr. 2012;31(5):583–601. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clnu.2012.06.010 . Epub 2012 Jul 17. PMID: 22809635.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Balaj M, Huijts T, McNamara CL, Stornes P, Bambra C, Eikemo TA. Non-communicable diseases and the social determinants of health in the nordic countries: findings from the European Social Survey (2014) special module on the social determinants of health. Scand J Public Health. 2017;45(2):90–102. Epub 2017 Jan 27. PMID: 28128015.
Nordic Burden of Disease Collaborators. Life expectancy and disease burden in the Nordic countries: results from the Global Burden of Diseases, Injuries, and Risk Factors Study 2017. Lancet Public Health. 2019;4(12): e658-e669. doi: 10.1016/S2468-2667(19)30224-5. Epub 2019 Nov 20. PMID: 31759894; PMCID: PMC7098475.
Stockmarr A, Hejgaard T, Matthiessen J. Obesity prevention in the Nordic Countries. Curr Obes Rep. 2016;5(2):156 – 65. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13679-016-0206-y . PMID: 27033877.
Cuadrado A, Stjernberg M, Huynh D. Active and healthy ageing: heterogenous perspectives and nordic indicators. Nordens välfärdscenter/Nordic Welfare Centre; 2022.
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, PRISMA Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. Int J Surg. 2010;8(5):336 – 41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijsu.2010.02.007 . Epub 2010 Feb 18. Erratum in: Int J Surg. 2010;8(8):658. PMID: 20171303.
Sallfeldt ES, Mallmin H, Karlsson MK, Mellström D, Hailer NP, Ribom EL. Sarcopenia prevalence and incidence in older men - a MrOs Sweden study. Geriatr Nurs. 2023 Mar-Apr;50:102–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gerinurse.2023.01.003 . Epub 2023 Feb 10. PMID: 36774676.
Sääksjärvi K, Härkänen T, Stenholm S, Schaap L, Lundqvist A, Koskinen S, Borodulin K, Visser M. Probable Sarcopenia, obesity, and risk of all-cause mortality: a pooled analysis of 4,612 participants. Gerontology. 2023;69(6):706–15. Epub 2023 Jan 30. PMID: 36716714.
Karlsson M, Becker W, Cederholm TE, Byberg L. A posteriori dietary patterns in 71-year-old Swedish men and the prevalence of Sarcopenia 16 years later. Br J Nutr Camb Univ Press. 2022;128(5):909–20. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0007114521003901 .
Article CAS Google Scholar
Dolin TG, Mikkelsen MK, Jakobsen HL, Vinther A, Zerahn B, Nielsen DL, Johansen JS, Lund CM, Suetta C. The prevalence of Sarcopenia and cachexia in older patients with localized colorectal cancer. J Geriatr Oncol. 2023;14(1):101402. Epub 2022 Nov 21. PMID: 36424269.
Paajanen P, Lindström I, Oksala N, Väärämäki S, Saari P, Mäkinen K, Kärkkäinen JM. Radiographically quantified Sarcopenia and traditional cardiovascular risk assessment in predicting long-term mortality after endovascular aortic repair. J Vasc Surg. 2022;76(4):908–e9152. Epub 2022 Mar 31. PMID: 35367563.
Sobestiansky S, Åberg AC, Cederholm T. Sarcopenia and malnutrition in relation to mortality in hospitalised patients in geriatric care - predictive validity of updated diagnoses. Clin Nutr ESPEN. 2021;45:442–8. Epub 2021 Jul 16. PMID: 34620352.
Papaioannou KG, Nilsson A, Nilsson LM, Kadi F. Healthy eating is Associated with Sarcopenia Risk in physically active older adults. Nutrients. 2021;13(8):2813. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13082813 . PMID: 34444973; PMCID: PMC8401667.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Wallengren O, Bosaeus I, Frändin K, Lissner L, Falk Erhag H, Wetterberg H, Rydberg Sterner T, Rydén L, Rothenberg E, Skoog I. Comparison of the 2010 and 2019 diagnostic criteria for Sarcopenia by the European Working Group on Sarcopenia in Older people (EWGSOP) in two cohorts of Swedish older adults. BMC Geriatr. 2021;21(1):600. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12877-021-02533-y . PMID: 34702174; PMCID: PMC8547086.
Scott D, Johansson J, Gandham A, Ebeling PR, Nordstrom P, Nordstrom A. Associations of accelerometer-determined physical activity and sedentary behavior with Sarcopenia and incident falls over 12 months in community-dwelling Swedish older adults. J Sport Health Sci. 2021;10(5):577–84. Epub 2020 Feb 5. PMID: 34088651; PMCID: PMC8500807.
Veen J, Montiel-Rojas D, Nilsson A, Kadi F. Engagement in muscle-strengthening activities lowers Sarcopenia Risk in older adults already adhering to the Aerobic Physical Activity guidelines. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021;18(3):989. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18030989 . PMID: 33499423; PMCID: PMC7908493.
Mølmen KS, Hammarström D, Pedersen K, Lian Lie AC, Steile RB, Nygaard H, Khan Y, Hamarsland H, Koll L, Hanestadhaugen M, Eriksen AL, Grindaker E, Whist JE, Buck D, Ahmad R, Strand TA, Rønnestad BR, Ellefsen S. Vitamin D3 supplementation does not enhance the effects of resistance training in older adults. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2021;12(3):599–628. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcsm.12688 . Epub 2021 Mar 31. PMID: 33788419; PMCID: PMC8200443.
Simonsen C, Kristensen TS, Sundberg A, Wielsøe S, Christensen J, Hansen CP, Burgdorf SK, Suetta C, de Heer P, Svendsen LB, Achiam MP, Christensen JF. Assessment of Sarcopenia in patients with upper gastrointestinal tumors: prevalence and agreement between computed tomography and dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry. Clin Nutr. 2021;40(5):2809–16. Epub 2021 Mar 26. PMID: 33933747.
Faxén-Irving G, Luiking Y, Grönstedt H, Franzén E, Seiger Å, Vikström S, Wimo A, Boström AM, Cederholm T. Do malnutrition, sarcopenia and frailty overlap in nursing-home residents? J Frailty Aging. 2021;10(1):17–21. https://doi.org/10.14283/jfa.2020.45 . PMID: 33331617.
Björkman MP, Suominen MH, Kautiainen H, Jyväkorpi SK, Finne-Soveri HU, Strandberg TE, Pitkälä KH, Tilvis RS. Effect of protein supplementation on physical performance in older people with sarcopenia-a randomized controlled trial. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2020;21(2):226–e2321. Epub 2019 Nov 14. PMID: 31734121.
Jyväkorpi SK, Urtamo A, Kivimäki M, Strandberg TE. Macronutrient composition and sarcopenia in the oldest-old men: the Helsinki businessmen study (HBS). Clin Nutr. 2020;39(12):3839–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clnu.2020.04.024 . Epub 2020 Apr 24. PMID: 32376097.
Probert N, Lööw A, Akner G, Wretenberg P, Andersson ÅG. A comparison of patients with hip fracture, ten years apart: morbidity, malnutrition and sarcopenia. J Nutr Health Aging. 2020;24(8):870–877. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12603-020-1408-2 . PMID: 33009538.
Sjöblom S, Sirola J, Rikkonen T, Erkkilä AT, Kröger H, Qazi SL, Isanejad M. Interaction of recommended levels of physical activity and protein intake is associated with greater physical function and lower fat mass in older women: Kuopio osteoporosis risk Factor- (OSTPRE) and fracture-Prevention Study. Br J Nutr. 2020;123(7):826–39. Epub 2020 Jan 8. PMID: 31910914; PMCID: PMC7054249.
von Berens Å, Obling SR, Nydahl M, Koochek A, Lissner L, Skoog I, Frändin K, Skoglund E, Rothenberg E, Cederholm T. Sarcopenic obesity and associations with mortality in older women and men - a prospective observational study. BMC Geriatr. 2020;20(1):199. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12877-020-01578-9 . PMID: 32517653; PMCID: PMC7285448.
Nielsen BR, Andersen HE, Haddock B, Hovind P, Schwarz P, Suetta C. Prevalence of muscle dysfunction concomitant with osteoporosis in a home-dwelling Danish population aged 65–93 years -the Copenhagen Sarcopenia Study. Exp Gerontol. 2020;138:110974. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exger.2020.110974 . Epub 2020 May 25. PMID: 32464171.
Van Ancum JM, Alcazar J, Meskers CGM, Nielsen BR, Suetta C, Maier AB. Impact of using the updated EWGSOP2 definition in diagnosing Sarcopenia: a clinical perspective. Arch Gerontol Geriatr 2020 Sep-Oct;90:104125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.archger.2020.104125 . Epub 2020 May 23. PMID: 32534364.
Björkman M, Jyväkorpi SK, Strandberg TE, Pitkälä KH, Tilvis RS. Sarcopenia indicators as predictors of functional decline and need for care among older people. J Nutr Health Aging. 2019;23(10):916–922. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12603-019-1280-0 . PMID: 31781719.
Björkman MP, Pitkala KH, Jyväkorpi S, Strandberg TE, Tilvis RS. Bioimpedance analysis and physical functioning as mortality indicators among older sarcopenic people. Exp Gerontol. 2019;122:42–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exger.2019.04.012 . Epub 2019 Apr 24. PMID: 31026498.
Olesen SS, Büyükuslu A, Køhler M, Rasmussen HH, Drewes AM. Sarcopenia associates with increased hospitalization rates and reduced survival in patients with chronic pancreatitis. Pancreatology. 2019;19(2):245–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pan.2019.01.006 . Epub 2019 Jan 14. PMID: 30665702.
Sobestiansky S, Michaelsson K, Cederholm T. Sarcopenia prevalence and associations with mortality and hospitalisation by various sarcopenia definitions in 85–89 year old community-dwelling men: a report from the ULSAM study. BMC Geriatr. 2019;19(1):318. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12877-019-1338-1 . PMID: 31747923; PMCID: PMC6864927.
Vikberg S, Sörlén N, Brandén L, Johansson J, Nordström A, Hult A, Nordström P. Effects of resistance training on functional strength and muscle mass in 70-Year-old individuals with pre-sarcopenia: a randomized controlled trial. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2019;20(1):28–34. Epub 2018 Nov 7. PMID: 30414822.
Isanejad M, Sirola J, Mursu J, Rikkonen T, Kröger H, Tuppurainen M, Erkkilä AT. Association of the baltic sea and mediterranean diets with indices of sarcopenia in elderly women, OSPTRE-FPS study. Eur J Nutr. 2018;57(4):1435–48. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-017-1422-2 . Epub 2017 Mar 16. PMID: 28303397.
Mikkola TM, von Bonsdorff MB, Salonen MK, Simonen M, Pohjolainen P, Osmond C, Perälä MM, Rantanen T, Kajantie E, Eriksson JG. Body composition as a predictor of physical performance in older age: a ten-year follow-up of the Helsinki Birth Cohort Study. Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2018 Jul-Aug;77:163–8. doi: 10.1016/j.archger.2018.05.009. Epub 2018 May 14. PMID: 29783137; PMCID: PMC5994345.
Ottestad I, Ulven SM, Øyri LKL, Sandvei KS, Gjevestad GO, Bye A, Sheikh NA, Biong AS, Andersen LF, Holven KB. Reduced plasma concentration of branched-chain amino acids in sarcopenic older subjects: a cross-sectional study. Br J Nutr. 2018;120(4):445–53. Epub 2018 Jun 18. PMID: 29909813.
Steihaug OM, Gjesdal CG, Bogen B, Kristoffersen MH, Lien G, Ranhoff AH. Sarcopenia in patients with hip fracture: a multicenter cross-sectional study. PLoS ONE. 2017;12(9):e0184780. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0184780 . PMID: 28902873; PMCID: PMC5597226.
Jacobsen EL, Brovold T, Bergland A, Bye A. Prevalence of factors associated with malnutrition among acute geriatric patients in Norway: a cross-sectional study. BMJ Open. 2016;6(9):e011512. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2016-011512 . PMID: 27601491; PMCID: PMC5020767.
Jansen RB, Christensen TM, Bülow J, Rørdam L, Holstein PE, Svendsen OL. Sarcopenia and body composition in diabetic Charcot osteoarthropathy. J Diabetes Complications. 2015 Sep-Oct;29(7):937–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2015.05.020 . Epub 2015 Jun 5. PMID: 26139557.
Frost M, Nielsen TL, Brixen K, Andersen M. Peak muscle mass in young men and Sarcopenia in the ageing male. Osteoporos Int. 2015;26(2):749–56. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00198-014-2960-6 . Epub 2014 Nov 22. PMID: 25416073.
Patil R, Uusi-Rasi K, Pasanen M, Kannus P, Karinkanta S, Sievänen H. Sarcopenia and osteopenia among 70-80-year-old home-dwelling finnish women: prevalence and association with functional performance. Osteoporos Int. 2013;24(3):787–96. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00198-012-2046-2 . Epub 2012 Jun 12. PMID: 22688541.
Papadopoulou SK, Tsintavis P, Potsaki P, Papandreou D. Differences in the prevalence of sarcopenia in community-dwelling, nursing home and hospitalized individuals. a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Nutr Health Aging. 2020;24(1):83–90. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12603-019-1267-x . PMID: 31886813.
Mayhew AJ, Amog K, Phillips S, Parise G, McNicholas PD, de Souza RJ, Thabane L, Raina P. The prevalence of sarcopenia in community-dwelling older adults, an exploration of differences between studies and within definitions: a systematic review and meta-analyses. Age Ageing. 2019;48(1):48–56. https://doi.org/10.1093/ageing/afy106 . PMID: 30052707.
Cao M, Lian J, Lin X, Liu J, Chen C, Xu S, Ma S, Wang F, Zhang N, Qi X, Xu G, Peng N. Prevalence of Sarcopenia under different diagnostic criteria and the changes in muscle mass, muscle strength, and physical function with age in Chinese old adults. BMC Geriatr. 2022;22(1):889. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12877-022-03601-7 . PMID: 36418979; PMCID: PMC9682713.
Cruz-Jentoft AJ, Baeyens JP, Bauer JM, Boirie Y, Cederholm T, Landi F, Martin FC, Michel JP, Rolland Y, Schneider SM, Topinková E, Vandewoude M, Zamboni M, European working group on sarcopenia in older people. sarcopenia: European consensus on definition and diagnosis: report of the European working group on sarcopenia in older people. Age Ageing. 2010;39(4):412–23. https://doi.org/10.1093/ageing/afq034 . Epub 2010 Apr 13. PMID: 20392703; PMCID: PMC2886201.
Verstraeten LMG, de Haan NJ, Verbeet E, van Wijngaarden JP, Meskers CGM, Maier AB. Handgrip strength rather than chair stand test should be used to diagnose s in geriatric rehabilitation inpatients: restoring health of acutely unwell adulTs (RESORT). Age Ageing. 2022;51(11):afac242. https://doi.org/10.1093/ageing/afac242 . PMID: 36413590; PMCID: PMC9681126.
Cheng KY, Chow SK, Hung VW, Wong CH, Wong RM, Tsang CS, Kwok T, Cheung WH. Diagnosis of sarcopenia by evaluating skeletal muscle mass by adjusted bioimpedance analysis validated with dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2021;12(6):2163–73. Epub 2021 Oct 4. PMID: 34609065; PMCID: PMC8718029.
Sousa-Santos AR, Barros D, Montanha TL, Carvalho J, Amaral TF. Which is the best alternative to estimate muscle mass for sarcopenia diagnosis when DXA is unavailable? Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2021 Nov-Dec;97:104517. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.archger.2021.104517 . Epub 2021 Sep 3. PMID: 34547538.
González Correa CH, Marulanda Mejía F, Castaño González PA, Vidarte Claros JA, Castiblanco Arroyabe HD. Bioelectrical impedance analysis and dual x-ray absorptiometry agreement for skeletal muscle mass index evaluation in sarcopenia diagnosis. Physiol Meas. 2020;41(6):064005. https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6579/ab8e5f . PMID: 32348971.
Hwang B, Lim JY, Lee J, Choi NK, Ahn YO, Park BJ. Prevalence rate and associated factors of sarcopenic obesity in Korean elderly population. J Korean Med Sci. 2012;27(7):748–55. https://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2012.27.7.748 . Epub 2012 Jun 29. PMID: 22787369; PMCID: PMC3390722.
Kera T, Kawai H, Hirano H, Kojima M, Fujiwara Y, Ihara K, Obuchi S. Differences in body composition and physical function related to pure Sarcopenia and sarcopenic obesity: a study of community-dwelling older adults in Japan. Geriatr Gerontol Int. 2017;17(12):2602–9. https://doi.org/10.1111/ggi.13119 . Epub 2017 Jun 28. PMID: 28657168.
Aibar-Almazán A, Martínez-Amat A, Cruz-Díaz D, Jiménez-García JD, Achalandabaso A, Sánchez-Montesinos I, de la Torre-Cruz M, Hita-Contreras F. Sarcopenia and sarcopenic obesity in Spanish community-dwelling middle-aged and older women: Association with balance confidence, fear of falling and fall risk. Maturitas. 2018;107:26–32. Epub 2017 Oct 7. PMID: 29169576.
Prokopidis K, Giannos P, Reginster JY, Bruyere O, Petrovic M, Cherubini A, Triantafyllidis KK, Kechagias KS, Dionyssiotis Y, Cesari M, Ibrahim K, Scott D, Barbagallo M, Veronese N, the Task Force on Pharmaceutical Strategy of the European Geriatric Medicine Society (EuGMS). Special interest group in Systematic Reviews and Meta-analyses and sarcopenia is associated with a greater risk of polypharmacy and number of medications: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2023;14(2):671–683. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcsm.13190 . Epub 2023 Feb 13. PMID: 36781175; PMCID: PMC10067503.
Zhang N, Sundquist J, Sundquist K, Ji J. An increasing Trend in the prevalence of polypharmacy in Sweden: a nationwide register-based study. Front Pharmacol. 2020;11:326. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2020.00326 . PMID: 32265705; PMCID: PMC7103636.
Dalle S, Rossmeislova L, Koppo K. The role of inflammation in age-related sarcopenia. Front Physiol. 2017;8:1045. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2017.01045 . PMID: 29311975; PMCID: PMC5733049.
Riuzzi F, Sorci G, Arcuri C, Giambanco I, Bellezza I, Minelli A, Donato R. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of sarcopenia: the S100B perspective. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2018;9(7):1255–68. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcsm.12363 . Epub 2018 Nov 30. PMID: 30499235; PMCID: PMC6351675.
Yuan S, Larsson SC. Epidemiology of sarcopenia: prevalence, risk factors, and consequences. Metabolism. 2023;144:155533. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.metabol.2023.155533 . Epub 2023 Mar 11. PMID: 36907247.
Download references
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Open access funding provided by University of Southern Denmark
This work was done without any fund.
Author information
Fereshteh Baygi, Sussi Friis Buhl contributed equally to this work.
Authors and Affiliations
Research Unit of General Practice, Department of Public Health, University of Southern Denmark, Odense, Denmark
Fereshteh Baygi, Sussi Friis Buhl, Trine Thilsing, Jens Søndergaard & Jesper Bo Nielsen
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
FB conceived and designed the review, participated in literature review, data extraction, interpretation of the results and wrote the manuscript. SFB designed the review, participated in literature review, data extraction, and revised the manuscript. TT, JBN and JS contributed to the conception of the study and revised the manuscript critically. All the authors approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Correspondence to Fereshteh Baygi or Sussi Friis Buhl .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate, consent for publication, competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Material 1
Rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Baygi, F., Buhl, S.F., Thilsing, T. et al. Sarcopenia and sarcopenic obesity among older adults in the nordic countries: a scoping review. BMC Geriatr 24 , 421 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12877-024-04970-x
Download citation
Received : 12 November 2023
Accepted : 12 April 2024
Published : 13 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12877-024-04970-x
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Sarcopenic obesity
- Nordic countries
BMC Geriatrics
ISSN: 1471-2318
- Submission enquiries: [email protected]
- General enquiries: [email protected]

COMMENTS
A literature review - or a review article - is "a study that analyzes and synthesizes an existing body of literature by identifying, challenging, and advancing the building blocks of a theory through an examination of a body (or several bodies) of prior work (Post et al. 2020, p. 352).Literature reviews as standalone pieces of work may allow researchers to enhance their understanding of ...
1 Introduction. A literature review - or a review article - is "a study that analyzes and synthesizes. an existing body of literature by identifying, challenging, and advancing the building ...
This is why the literature review as a research method is more relevant than ever. Traditional literature reviews often lack thoroughness and rigor and are conducted ad hoc, rather than following a specific methodology. ... However, independent of type of review, pay close attention to what studies have been included and for what reasons as ...
Literature reviews as independent studies: guidelines for academic practice. S. Kraus, M. Breier, +12 authors. João J. Ferreira. Published in Reviews of Management… 14 October 2022. Education. Review articles or literature reviews are a critical part of scientific research. While numerous guides on literature reviews exist, these are often ...
Examples of literature reviews. Step 1 - Search for relevant literature. Step 2 - Evaluate and select sources. Step 3 - Identify themes, debates, and gaps. Step 4 - Outline your literature review's structure. Step 5 - Write your literature review.
As an independent study, the literature review takes center stage in and thus represents. the main contribution of the study. Here, the literature review fundamentally serves as an.
Review articles or literature reviews are a critical part of scientific research. While numerous guides on literature reviews exist, these are often limited to the philosophy of review procedures, pr ... "Literature reviews as independent studies: guidelines for academic practice," Review of Managerial Science, Springer, vol. 16(8), pages 2577 ...
A literature review is probably the most common academic writing activity that is performed by scholars and graduate students. Imel [] identified a literature review as being either part of a larger study or as a research effort on its own.As a part of a larger study, Imel [] identified the literature is "the foundation for the study."It has been suggested that the literature review for a ...
Example: Predictors and Outcomes of U.S. Quality Maternity Leave: A Review and Conceptual Framework: 10.1177/08948453211037398 ; Systematic review: "The authors of a systematic review use a specific procedure to search the research literature, select the studies to include in their review, and critically evaluate the studies they find." (p. 139).
Literature review is an essential feature of academic research. Fundamentally, knowledge advancement must be built on prior existing work. To push the knowledge frontier, we must know where the frontier is. By reviewing relevant literature, we understand the breadth and depth of the existing body of work and identify gaps to explore.
A formal literature review is an evidence-based, in-depth analysis of a subject. There are many reasons for writing one and these will influence the length and style of your review, but in essence a literature review is a critical appraisal of the current collective knowledge on a subject. Rather than just being an exhaustive list of all that ...
Literature Review. A literature review identifies the boundaries of your study and demonstrates very clearly the focus and purpose of your research. A literature review is an account of what has been published on a topic by accredited scholars and researchers. Occasionally you will be asked to write one as a separate assignment but more often ...
A literature review should connect to the study question, guide the study methodology, and be central in the discussion by indicating how the analyzed data advances what is known in the field. A theoretical framework drives the question, guides the types of methods for data collection and analysis, informs the discussion of the findings, and ...
Literature reviews can take two major forms. The most prevalent one is the "literature review" or "background" section within a journal paper or a chapter in a graduate thesis. This section synthesizes the extant literature and usually identifies the gaps in knowledge that the empirical study addresses (Sylvester, Tate, & Johnstone, 2013).
A literature review may consist of simply a summary of key sources, but in the social sciences, a literature review usually has an organizational pattern and combines both summary and synthesis, often within specific conceptual categories.A summary is a recap of the important information of the source, but a synthesis is a re-organization, or a reshuffling, of that information in a way that ...
A literature review is an integrated analysis-- not just a summary-- of scholarly writings and other relevant evidence related directly to your research question. That is, it represents a synthesis of the evidence that provides background information on your topic and shows a association between the evidence and your research question ...
A sophisticated literature review (LR) can result in a robust dissertation/thesis by scrutinizing the main problem examined by the academic study; anticipating research hypotheses, methods and results; and maintaining the interest of the audience in how the dissertation/thesis will provide solutions for the current gaps in a particular field.
the proliferation of literature reviews as independent studies. To contribute a solu-tion toward addressing this gap, we aim to demystify review articles as independent studies from a pragmatic standpoint (i.e., practicality). To do so, we deliberately (i) move away from review procedures, protocols, and nomenclatures, and (ii) invest our
Independent Study (literature review) Independent study (PSYC 311, 312, 313) is designed to provide the student with an opportunity to conduct an extensive literature review. The work is carried out independently, with guidance from a faculty mentor. PSYC 311 and 313 are ½-credit courses to spread the work across two semesters; PSYC 312 is a ...
Systematic Review. Attempts to identify, appraise, and summarize all empirical evidence that fits pre-specified eligibility criteria to answer a specific research question. clearly defined question with inclusion/exclusion criteria. rigorous and systematic search of the literature. thorough screening of results. data extraction and management.
Types of reviews and examples. Definition: "A term used to describe a conventional overview of the literature, particularly when contrasted with a systematic review (Booth et al., 2012, p. 265). Characteristics: Example: Mitchell, L. E., & Zajchowski, C. A. (2022). The history of air quality in Utah: A narrative review.
The literature review and result-discussion sections show the highest number of mentions, which indicates that the 37 selected articles are related in terms of the theoretical basis, the study results, and the discussion (thus theory reflects reality). These results show that previous studies prove that CT theory is related to PS.
Seven independent reviewers screened identified studies, including title and abstract review to determine if studies met the following inclusion criteria: (1) targeted samples with mental health symptomology or disorders, (2) studied youth participants aged 6-17 years, and (3) examined the use of a mobile app-based platform for intervention.
The PubMed and Scopus databases were accessed by two independent investigators concerning robotic rSBRT for liver metastases, up to 3 October 2023. ... The aim of this study was to systematically review the literature regarding the role of rSBRT in the management of metastatic liver disease from tumors of various origins, with a focus on ...
Literature review articles, including structured literature reviews, bibliometric analyses, and meta-analyses, are invaluable tools in the realm of management research, significantly contributing to its growth and development (Hulland and Houston 2020).They serve as cornerstones for theory development, policy formulation, and evidence-based decision-making, thus playing a pivotal role in the ...
A comprehensive literature search until October 2023 was performed on ScienceDirect, PubMed, Web of Science, and Cochrane Library by two independent reviewers adhering to the PRISMA framework. ... was used to evaluate the methodological quality of studies. Out of 198 results, 8 studies were included in this qualitative synthesis, accounting for ...
Introduction. Narrative reviews are a type of knowledge synthesis grounded in a distinct research tradition. They are often framed as non-systematic, which implies that there is a hierarchy of evidence placing narrative reviews below other review forms. 1 However, narrative reviews are highly useful to medical educators and researchers. While a systematic review often focuses on a narrow ...
Having a foundational knowledge of the fundamental elements of literature reviews as independent studies is valuable, as it can help scholars to (i) gain a good grasp of the fundamental elements of literature reviews as independent studies (1st contribution), and (ii) mindfully adopt or adapt existing review procedures, protocols, and ...
Therefore, the aim of this study is to review the available evidence and gaps within this field in the Nordic countries. PubMed, Embase, and Web of science (WOS) were searched up to February 2023. In addition, grey literature and reference lists of included studies were searched. Two independent researcher assessed papers and extracted data.
Increasingly, urban planners are adopting virtual reality (VR) in designing urban green spaces (UGS) to visualize landscape designs in immersive 3D. However, the psychological effect of green spaces from the experience in VR may differ from the actual experience in the real world. In this paper, we systematically reviewed studies in the literature that conducted experiments to investigate the ...