
Peer Recognized
Make a name in academia

How to Write a Research Paper: the LEAP approach (+cheat sheet)
In this article I will show you how to write a research paper using the four LEAP writing steps. The LEAP academic writing approach is a step-by-step method for turning research results into a published paper .
The LEAP writing approach has been the cornerstone of the 70 + research papers that I have authored and the 3700+ citations these paper have accumulated within 9 years since the completion of my PhD. I hope the LEAP approach will help you just as much as it has helped me to make an real, tangible impact with my research.
What is the LEAP research paper writing approach?
I designed the LEAP writing approach not only for merely writing the papers. My goal with the writing system was to show young scientists how to first think about research results and then how to efficiently write each section of the research paper.
In other words, you will see how to write a research paper by first analyzing the results and then building a logical, persuasive arguments. In this way, instead of being afraid of writing research paper, you will be able to rely on the paper writing process to help you with what is the most demanding task in getting published – thinking.
The four research paper writing steps according to the LEAP approach:

I will show each of these steps in detail. And you will be able to download the LEAP cheat sheet for using with every paper you write.
But before I tell you how to efficiently write a research paper, I want to show you what is the problem with the way scientists typically write a research paper and why the LEAP approach is more efficient.
How scientists typically write a research paper (and why it isn’t efficient)
Writing a research paper can be tough, especially for a young scientist. Your reasoning needs to be persuasive and thorough enough to convince readers of your arguments. The description has to be derived from research evidence, from prior art, and from your own judgment. This is a tough feat to accomplish.
The figure below shows the sequence of the different parts of a typical research paper. Depending on the scientific journal, some sections might be merged or nonexistent, but the general outline of a research paper will remain very similar.

Here is the problem: Most people make the mistake of writing in this same sequence.
While the structure of scientific articles is designed to help the reader follow the research, it does little to help the scientist write the paper. This is because the layout of research articles starts with the broad (introduction) and narrows down to the specifics (results). See in the figure below how the research paper is structured in terms of the breath of information that each section entails.
How to write a research paper according to the LEAP approach
For a scientist, it is much easier to start writing a research paper with laying out the facts in the narrow sections (i.e. results), step back to describe them (i.e. write the discussion), and step back again to explain the broader picture in the introduction.
For example, it might feel intimidating to start writing a research paper by explaining your research’s global significance in the introduction, while it is easy to plot the figures in the results. When plotting the results, there is not much room for wiggle: the results are what they are.
Starting to write a research papers from the results is also more fun because you finally get to see and understand the complete picture of the research that you have worked on.
Most importantly, following the LEAP approach will help you first make sense of the results yourself and then clearly communicate them to the readers. That is because the sequence of writing allows you to slowly understand the meaning of the results and then develop arguments for presenting to your readers.
I have personally been able to write and submit a research article in three short days using this method.
Step 1: Lay Out the Facts

You have worked long hours on a research project that has produced results and are no doubt curious to determine what they exactly mean. There is no better way to do this than by preparing figures, graphics and tables. This is what the first LEAP step is focused on – diving into the results.
How to p repare charts and tables for a research paper
Your first task is to try out different ways of visually demonstrating the research results. In many fields, the central items of a journal paper will be charts that are based on the data generated during research. In other fields, these might be conceptual diagrams, microscopy images, schematics and a number of other types of scientific graphics which should visually communicate the research study and its results to the readers. If you have reasonably small number of data points, data tables might be useful as well.
Tips for preparing charts and tables
- Try multiple chart types but in the finished paper only use the one that best conveys the message you want to present to the readers
- Follow the eight chart design progressions for selecting and refining a data chart for your paper: https://peerrecognized.com/chart-progressions
- Prepare scientific graphics and visualizations for your paper using the scientific graphic design cheat sheet: https://peerrecognized.com/tools-for-creating-scientific-illustrations/
How to describe the results of your research
Now that you have your data charts, graphics and tables laid out in front of you – describe what you see in them. Seek to answer the question: What have I found? Your statements should progress in a logical sequence and be backed by the visual information. Since, at this point, you are simply explaining what everyone should be able to see for themselves, you can use a declarative tone: The figure X demonstrates that…
Tips for describing the research results :
- Answer the question: “ What have I found? “
- Use declarative tone since you are simply describing observations
Step 2: Explain the results

The core aspect of your research paper is not actually the results; it is the explanation of their meaning. In the second LEAP step, you will do some heavy lifting by guiding the readers through the results using logic backed by previous scientific research.
How to define the Message of a research paper
To define the central message of your research paper, imagine how you would explain your research to a colleague in 20 seconds . If you succeed in effectively communicating your paper’s message, a reader should be able to recount your findings in a similarly concise way even a year after reading it. This clarity will increase the chances that someone uses the knowledge you generated, which in turn raises the likelihood of citations to your research paper.
Tips for defining the paper’s central message :
- Write the paper’s core message in a single sentence or two bullet points
- Write the core message in the header of the research paper manuscript
How to write the Discussion section of a research paper
In the discussion section you have to demonstrate why your research paper is worthy of publishing. In other words, you must now answer the all-important So what? question . How well you do so will ultimately define the success of your research paper.
Here are three steps to get started with writing the discussion section:
- Write bullet points of the things that convey the central message of the research article (these may evolve into subheadings later on).
- Make a list with the arguments or observations that support each idea.
- Finally, expand on each point to make full sentences and paragraphs.
Tips for writing the discussion section:
- What is the meaning of the results?
- Was the hypothesis confirmed?
- Write bullet points that support the core message
- List logical arguments for each bullet point, group them into sections
- Instead of repeating research timeline, use a presentation sequence that best supports your logic
- Convert arguments to full paragraphs; be confident but do not overhype
- Refer to both supportive and contradicting research papers for maximum credibility
How to write the Conclusions of a research paper
Since some readers might just skim through your research paper and turn directly to the conclusions, it is a good idea to make conclusion a standalone piece. In the first few sentences of the conclusions, briefly summarize the methodology and try to avoid using abbreviations (if you do, explain what they mean).
After this introduction, summarize the findings from the discussion section. Either paragraph style or bullet-point style conclusions can be used. I prefer the bullet-point style because it clearly separates the different conclusions and provides an easy-to-digest overview for the casual browser. It also forces me to be more succinct.
Tips for writing the conclusion section :
- Summarize the key findings, starting with the most important one
- Make conclusions standalone (short summary, avoid abbreviations)
- Add an optional take-home message and suggest future research in the last paragraph
How to refine the Objective of a research paper
The objective is a short, clear statement defining the paper’s research goals. It can be included either in the final paragraph of the introduction, or as a separate subsection after the introduction. Avoid writing long paragraphs with in-depth reasoning, references, and explanation of methodology since these belong in other sections. The paper’s objective can often be written in a single crisp sentence.
Tips for writing the objective section :
- The objective should ask the question that is answered by the central message of the research paper
- The research objective should be clear long before writing a paper. At this point, you are simply refining it to make sure it is addressed in the body of the paper.
How to write the Methodology section of your research paper
When writing the methodology section, aim for a depth of explanation that will allow readers to reproduce the study . This means that if you are using a novel method, you will have to describe it thoroughly. If, on the other hand, you applied a standardized method, or used an approach from another paper, it will be enough to briefly describe it with reference to the detailed original source.
Remember to also detail the research population, mention how you ensured representative sampling, and elaborate on what statistical methods you used to analyze the results.
Tips for writing the methodology section :
- Include enough detail to allow reproducing the research
- Provide references if the methods are known
- Create a methodology flow chart to add clarity
- Describe the research population, sampling methodology, statistical methods for result analysis
- Describe what methodology, test methods, materials, and sample groups were used in the research.
Step 3: Advertize the research
Step 3 of the LEAP writing approach is designed to entice the casual browser into reading your research paper. This advertising can be done with an informative title, an intriguing abstract, as well as a thorough explanation of the underlying need for doing the research within the introduction.

How to write the Introduction of a research paper
The introduction section should leave no doubt in the mind of the reader that what you are doing is important and that this work could push scientific knowledge forward. To do this convincingly, you will need to have a good knowledge of what is state-of-the-art in your field. You also need be able to see the bigger picture in order to demonstrate the potential impacts of your research work.
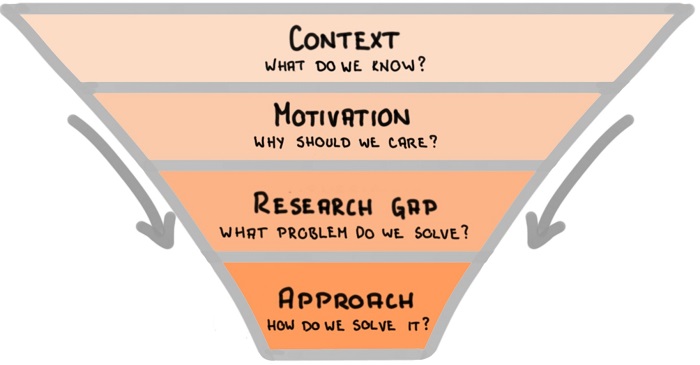
Think of the introduction as a funnel, going from wide to narrow, as shown in the figure below:
- Start with a brief context to explain what do we already know,
- Follow with the motivation for the research study and explain why should we care about it,
- Explain the research gap you are going to bridge within this research paper,
- Describe the approach you will take to solve the problem.
Tips for writing the introduction section :
- Follow the Context – Motivation – Research gap – Approach funnel for writing the introduction
- Explain how others tried and how you plan to solve the research problem
- Do a thorough literature review before writing the introduction
- Start writing the introduction by using your own words, then add references from the literature
How to prepare the Abstract of a research paper
The abstract acts as your paper’s elevator pitch and is therefore best written only after the main text is finished. In this one short paragraph you must convince someone to take on the time-consuming task of reading your whole research article. So, make the paper easy to read, intriguing, and self-explanatory; avoid jargon and abbreviations.
How to structure the abstract of a research paper:
- The abstract is a single paragraph that follows this structure:
- Problem: why did we research this
- Methodology: typically starts with the words “Here we…” that signal the start of own contribution.
- Results: what we found from the research.
- Conclusions: show why are the findings important
How to compose a research paper Title
The title is the ultimate summary of a research paper. It must therefore entice someone looking for information to click on a link to it and continue reading the article. A title is also used for indexing purposes in scientific databases, so a representative and optimized title will play large role in determining if your research paper appears in search results at all.
Tips for coming up with a research paper title:
- Capture curiosity of potential readers using a clear and descriptive title
- Include broad terms that are often searched
- Add details that uniquely identify the researched subject of your research paper
- Avoid jargon and abbreviations
- Use keywords as title extension (instead of duplicating the words) to increase the chance of appearing in search results
How to prepare Highlights and Graphical Abstract
Highlights are three to five short bullet-point style statements that convey the core findings of the research paper. Notice that the focus is on the findings, not on the process of getting there.
A graphical abstract placed next to the textual abstract visually summarizes the entire research paper in a single, easy-to-follow figure. I show how to create a graphical abstract in my book Research Data Visualization and Scientific Graphics.
Tips for preparing highlights and graphical abstract:
- In highlights show core findings of the research paper (instead of what you did in the study).
- In graphical abstract show take-home message or methodology of the research paper. Learn more about creating a graphical abstract in this article.

Step 4: Prepare for submission

Sometimes it seems that nuclear fusion will stop on the star closest to us (read: the sun will stop to shine) before a submitted manuscript is published in a scientific journal. The publication process routinely takes a long time, and after submitting the manuscript you have very little control over what happens. To increase the chances of a quick publication, you must do your homework before submitting the manuscript. In the fourth LEAP step, you make sure that your research paper is published in the most appropriate journal as quickly and painlessly as possible.
How to select a scientific Journal for your research paper
The best way to find a journal for your research paper is it to review which journals you used while preparing your manuscript. This source listing should provide some assurance that your own research paper, once published, will be among similar articles and, thus, among your field’s trusted sources.
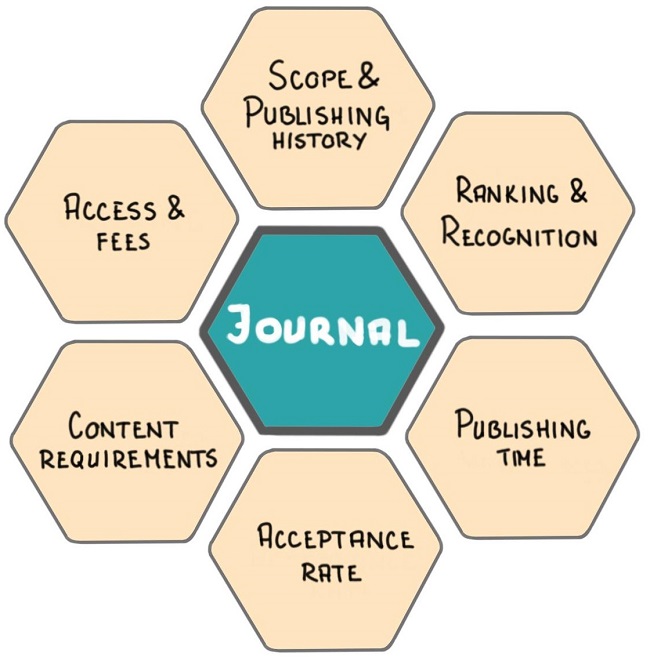
After this initial selection of hand-full of scientific journals, consider the following six parameters for selecting the most appropriate journal for your research paper (read this article to review each step in detail):
- Scope and publishing history
- Ranking and Recognition
- Publishing time
- Acceptance rate
- Content requirements
- Access and Fees
How to select a journal for your research paper:
- Use the six parameters to select the most appropriate scientific journal for your research paper
- Use the following tools for journal selection: https://peerrecognized.com/journals
- Follow the journal’s “Authors guide” formatting requirements
How to Edit you manuscript
No one can write a finished research paper on their first attempt. Before submitting, make sure to take a break from your work for a couple of days, or even weeks. Try not to think about the manuscript during this time. Once it has faded from your memory, it is time to return and edit. The pause will allow you to read the manuscript from a fresh perspective and make edits as necessary.
I have summarized the most useful research paper editing tools in this article.
Tips for editing a research paper:
- Take time away from the research paper to forget about it; then returning to edit,
- Start by editing the content: structure, headings, paragraphs, logic, figures
- Continue by editing the grammar and language; perform a thorough language check using academic writing tools
- Read the entire paper out loud and correct what sounds weird
How to write a compelling Cover Letter for your paper
Begin the cover letter by stating the paper’s title and the type of paper you are submitting (review paper, research paper, short communication). Next, concisely explain why your study was performed, what was done, and what the key findings are. State why the results are important and what impact they might have in the field. Make sure you mention how your approach and findings relate to the scope of the journal in order to show why the article would be of interest to the journal’s readers.
I wrote a separate article that explains what to include in a cover letter here. You can also download a cover letter template from the article.
Tips for writing a cover letter:
- Explain how the findings of your research relate to journal’s scope
- Tell what impact the research results will have
- Show why the research paper will interest the journal’s audience
- Add any legal statements as required in journal’s guide for authors
How to Answer the Reviewers
Reviewers will often ask for new experiments, extended discussion, additional details on the experimental setup, and so forth. In principle, your primary winning tactic will be to agree with the reviewers and follow their suggestions whenever possible. After all, you must earn their blessing in order to get your paper published.
Be sure to answer each review query and stick to the point. In the response to the reviewers document write exactly where in the paper you have made any changes. In the paper itself, highlight the changes using a different color. This way the reviewers are less likely to re-read the entire article and suggest new edits.
In cases when you don’t agree with the reviewers, it makes sense to answer more thoroughly. Reviewers are scientifically minded people and so, with enough logical and supported argument, they will eventually be willing to see things your way.
Tips for answering the reviewers:
- Agree with most review comments, but if you don’t, thoroughly explain why
- Highlight changes in the manuscript
- Do not take the comments personally and cool down before answering
The LEAP research paper writing cheat sheet
Imagine that you are back in grad school and preparing to take an exam on the topic: “How to write a research paper”. As an exemplary student, you would, most naturally, create a cheat sheet summarizing the subject… Well, I did it for you.
This one-page summary of the LEAP research paper writing technique will remind you of the key research paper writing steps. Print it out and stick it to a wall in your office so that you can review it whenever you are writing a new research paper.

Now that we have gone through the four LEAP research paper writing steps, I hope you have a good idea of how to write a research paper. It can be an enjoyable process and once you get the hang of it, the four LEAP writing steps should even help you think about and interpret the research results. This process should enable you to write a well-structured, concise, and compelling research paper.
Have fund with writing your next research paper. I hope it will turn out great!
Learn writing papers that get cited
The LEAP writing approach is a blueprint for writing research papers. But to be efficient and write papers that get cited, you need more than that.
My name is Martins Zaumanis and in my interactive course Research Paper Writing Masterclass I will show you how to visualize your research results, frame a message that convinces your readers, and write each section of the paper. Step-by-step.
And of course – you will learn to respond the infamous Reviewer No.2.

Hey! My name is Martins Zaumanis and I am a materials scientist in Switzerland ( Google Scholar ). As the first person in my family with a PhD, I have first-hand experience of the challenges starting scientists face in academia. With this blog, I want to help young researchers succeed in academia. I call the blog “Peer Recognized”, because peer recognition is what lifts academic careers and pushes science forward.
Besides this blog, I have written the Peer Recognized book series and created the Peer Recognized Academy offering interactive online courses.
Related articles:
One comment
- Pingback: Research Paper Outline with Key Sentence Skeleton (+Paper Template)
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
I want to join the Peer Recognized newsletter!
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
Privacy Overview
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-analytics | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-functional | 11 months | The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-necessary | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-others | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Other. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-performance | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". |
| viewed_cookie_policy | 11 months | The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. It does not store any personal data. |
Copyright © 2024 Martins Zaumanis
Contacts: [email protected]
Privacy Policy
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Research paper
Writing a Research Paper Introduction | Step-by-Step Guide
Published on September 24, 2022 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on September 5, 2024.

The introduction to a research paper is where you set up your topic and approach for the reader. It has several key goals:
- Present your topic and get the reader interested
- Provide background or summarize existing research
- Position your own approach
- Detail your specific research problem and problem statement
- Give an overview of the paper’s structure
The introduction looks slightly different depending on whether your paper presents the results of original empirical research or constructs an argument by engaging with a variety of sources.
The five steps in this article will help you put together an effective introduction for either type of research paper.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Step 1: introduce your topic, step 2: describe the background, step 3: establish your research problem, step 4: specify your objective(s), step 5: map out your paper, research paper introduction examples, frequently asked questions about the research paper introduction.
The first job of the introduction is to tell the reader what your topic is and why it’s interesting or important. This is generally accomplished with a strong opening hook.
The hook is a striking opening sentence that clearly conveys the relevance of your topic. Think of an interesting fact or statistic, a strong statement, a question, or a brief anecdote that will get the reader wondering about your topic.
For example, the following could be an effective hook for an argumentative paper about the environmental impact of cattle farming:
A more empirical paper investigating the relationship of Instagram use with body image issues in adolescent girls might use the following hook:
Don’t feel that your hook necessarily has to be deeply impressive or creative. Clarity and relevance are still more important than catchiness. The key thing is to guide the reader into your topic and situate your ideas.
Scribbr Citation Checker New
The AI-powered Citation Checker helps you avoid common mistakes such as:
- Missing commas and periods
- Incorrect usage of “et al.”
- Ampersands (&) in narrative citations
- Missing reference entries

This part of the introduction differs depending on what approach your paper is taking.
In a more argumentative paper, you’ll explore some general background here. In a more empirical paper, this is the place to review previous research and establish how yours fits in.
Argumentative paper: Background information
After you’ve caught your reader’s attention, specify a bit more, providing context and narrowing down your topic.
Provide only the most relevant background information. The introduction isn’t the place to get too in-depth; if more background is essential to your paper, it can appear in the body .
Empirical paper: Describing previous research
For a paper describing original research, you’ll instead provide an overview of the most relevant research that has already been conducted. This is a sort of miniature literature review —a sketch of the current state of research into your topic, boiled down to a few sentences.
This should be informed by genuine engagement with the literature. Your search can be less extensive than in a full literature review, but a clear sense of the relevant research is crucial to inform your own work.
Begin by establishing the kinds of research that have been done, and end with limitations or gaps in the research that you intend to respond to.
The next step is to clarify how your own research fits in and what problem it addresses.
Argumentative paper: Emphasize importance
In an argumentative research paper, you can simply state the problem you intend to discuss, and what is original or important about your argument.
Empirical paper: Relate to the literature
In an empirical research paper, try to lead into the problem on the basis of your discussion of the literature. Think in terms of these questions:
- What research gap is your work intended to fill?
- What limitations in previous work does it address?
- What contribution to knowledge does it make?
You can make the connection between your problem and the existing research using phrases like the following.
| Although has been studied in detail, insufficient attention has been paid to . | You will address a previously overlooked aspect of your topic. |
| The implications of study deserve to be explored further. | You will build on something suggested by a previous study, exploring it in greater depth. |
| It is generally assumed that . However, this paper suggests that … | You will depart from the consensus on your topic, establishing a new position. |
Now you’ll get into the specifics of what you intend to find out or express in your research paper.
The way you frame your research objectives varies. An argumentative paper presents a thesis statement, while an empirical paper generally poses a research question (sometimes with a hypothesis as to the answer).
Argumentative paper: Thesis statement
The thesis statement expresses the position that the rest of the paper will present evidence and arguments for. It can be presented in one or two sentences, and should state your position clearly and directly, without providing specific arguments for it at this point.
Empirical paper: Research question and hypothesis
The research question is the question you want to answer in an empirical research paper.
Present your research question clearly and directly, with a minimum of discussion at this point. The rest of the paper will be taken up with discussing and investigating this question; here you just need to express it.
A research question can be framed either directly or indirectly.
- This study set out to answer the following question: What effects does daily use of Instagram have on the prevalence of body image issues among adolescent girls?
- We investigated the effects of daily Instagram use on the prevalence of body image issues among adolescent girls.
If your research involved testing hypotheses , these should be stated along with your research question. They are usually presented in the past tense, since the hypothesis will already have been tested by the time you are writing up your paper.
For example, the following hypothesis might respond to the research question above:
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

The final part of the introduction is often dedicated to a brief overview of the rest of the paper.
In a paper structured using the standard scientific “introduction, methods, results, discussion” format, this isn’t always necessary. But if your paper is structured in a less predictable way, it’s important to describe the shape of it for the reader.
If included, the overview should be concise, direct, and written in the present tense.
- This paper will first discuss several examples of survey-based research into adolescent social media use, then will go on to …
- This paper first discusses several examples of survey-based research into adolescent social media use, then goes on to …
Scribbr’s paraphrasing tool can help you rephrase sentences to give a clear overview of your arguments.
Full examples of research paper introductions are shown in the tabs below: one for an argumentative paper, the other for an empirical paper.
- Argumentative paper
- Empirical paper
Are cows responsible for climate change? A recent study (RIVM, 2019) shows that cattle farmers account for two thirds of agricultural nitrogen emissions in the Netherlands. These emissions result from nitrogen in manure, which can degrade into ammonia and enter the atmosphere. The study’s calculations show that agriculture is the main source of nitrogen pollution, accounting for 46% of the country’s total emissions. By comparison, road traffic and households are responsible for 6.1% each, the industrial sector for 1%. While efforts are being made to mitigate these emissions, policymakers are reluctant to reckon with the scale of the problem. The approach presented here is a radical one, but commensurate with the issue. This paper argues that the Dutch government must stimulate and subsidize livestock farmers, especially cattle farmers, to transition to sustainable vegetable farming. It first establishes the inadequacy of current mitigation measures, then discusses the various advantages of the results proposed, and finally addresses potential objections to the plan on economic grounds.
The rise of social media has been accompanied by a sharp increase in the prevalence of body image issues among women and girls. This correlation has received significant academic attention: Various empirical studies have been conducted into Facebook usage among adolescent girls (Tiggermann & Slater, 2013; Meier & Gray, 2014). These studies have consistently found that the visual and interactive aspects of the platform have the greatest influence on body image issues. Despite this, highly visual social media (HVSM) such as Instagram have yet to be robustly researched. This paper sets out to address this research gap. We investigated the effects of daily Instagram use on the prevalence of body image issues among adolescent girls. It was hypothesized that daily Instagram use would be associated with an increase in body image concerns and a decrease in self-esteem ratings.
The introduction of a research paper includes several key elements:
- A hook to catch the reader’s interest
- Relevant background on the topic
- Details of your research problem
and your problem statement
- A thesis statement or research question
- Sometimes an overview of the paper
Don’t feel that you have to write the introduction first. The introduction is often one of the last parts of the research paper you’ll write, along with the conclusion.
This is because it can be easier to introduce your paper once you’ve already written the body ; you may not have the clearest idea of your arguments until you’ve written them, and things can change during the writing process .
The way you present your research problem in your introduction varies depending on the nature of your research paper . A research paper that presents a sustained argument will usually encapsulate this argument in a thesis statement .
A research paper designed to present the results of empirical research tends to present a research question that it seeks to answer. It may also include a hypothesis —a prediction that will be confirmed or disproved by your research.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2024, September 05). Writing a Research Paper Introduction | Step-by-Step Guide. Scribbr. Retrieved October 20, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/research-paper/research-paper-introduction/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, writing strong research questions | criteria & examples, writing a research paper conclusion | step-by-step guide, research paper format | apa, mla, & chicago templates, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Lay out the facts. Explain the results. Advertize the research. Prepare for submission. I will show each of these steps in detail. And you will be able to download the LEAP cheat sheet for using with every paper you write.
Writing a research paper requires you to demonstrate a strong knowledge of your topic, engage with a variety of sources, and make an original contribution to the debate. This step-by-step guide takes you through the entire writing process, from understanding your assignment to proofreading your final draft.
Step 1: Choose your topic. Step 2: Identify a problem. Step 3: Formulate research questions. Step 4: Create a research design. Step 5: Write a research proposal. Other interesting articles. Step 1: Choose your topic. First you have to come up with some ideas. Your thesis or dissertation topic can start out very broad.
In this guide we concisely explain how to write an academic research paper step by step. We’ll cover areas like how to start a research paper, how to write a research paper outline, how to use citations and evidence, and how to write a conclusion for a research paper.
How to Write Research Paper. You can write Research Paper by the following guide: Choose a Topic: The first step is to select a topic that interests you and is relevant to your field of study. Brainstorm ideas and narrow down to a research question that is specific and researchable.
The introduction to a research paper is where you set up your topic and approach for the reader. It has several key goals: Present your topic and get the reader interested. Provide background or summarize existing research. Position your own approach. Detail your specific research problem and problem statement.