Insights on the Internet of Things


IoT value set to accelerate through 2030: Where and how to capture it

What is the Internet of Things (IoT)?

Industry 4.0 adoption with the right focus

Laying the foundation to accelerate the enterprise IoT journey

Reliably connecting the workforce of the future (which is now)

A manufacturer’s guide to scaling Industrial IoT

Coronavirus: Industrial IoT in challenging times
Featured publication.

Industry’s fast-mover advantage: Enterprise value from digital factories
Would you like to learn more about how we help clients understand the internet of things, iot in industrial settings.

The 5G era: New horizons for advanced-electronics and industrial companies

Buckets of innovation: How digital has transformed a mining company in Indonesia

Enabling a digital and analytics transformation in heavy-industry manufacturing

Capturing value at scale in discrete manufacturing with Industry 4.0

Korean manufacturing’s digital transformation must escape ‘pilot purgatory’

The coming evolution of field operations

Radically rethink your strategy: How digital B2B ecosystems can help traditional manufacturers create and protect value

A scalable IIoT tech stack starts with business-focused use cases

‘Lighthouse’ manufacturers lead the way—can the rest of the world keep up?

Unlock value with an Industrial IoT technology stack that scales

IIoT platforms: The technology stack as value driver in industrial equipment and machinery
Iot in technology.

The case for committing to greener telecom networks

Connected world: An evolution in connectivity beyond the 5G revolution

A game plan for quantum computing

A 5G manifesto for the CEO

New demand, new markets: What edge computing means for hardware companies
Iot in mobility.

The case for an end-to-end automotive-software platform

The race for cybersecurity: Protecting the connected car in the era of new regulation

The year of future transportation: An interview with Seoul Mayor Park Wonsoon

Development in the mobility technology ecosystem—how can 5G help?
Iot in insurance.

Tackling the IoT opportunity for commercial lines insurance

Digital ecosystems for insurers: Opportunities through the Internet of Things

Commercial lines insurtech: A pathway to digital
Connect with our internet of things experts.
30+ IoT Applications & Use Cases
Internet of Things (IoT) applications are becoming more widespread. According to Statista , worldwide expenditure on IoT in 2022 is expected to be $1B.
IoT enables a myriad of different business applications. Knowing those IoT examples and use cases can help businesses integrate IoT technologies into their future investment decisions. We have created the most comprehensive list of IoT use cases in industries.
The image below shows the potential impact of IoT technologies in various industries in 2025.
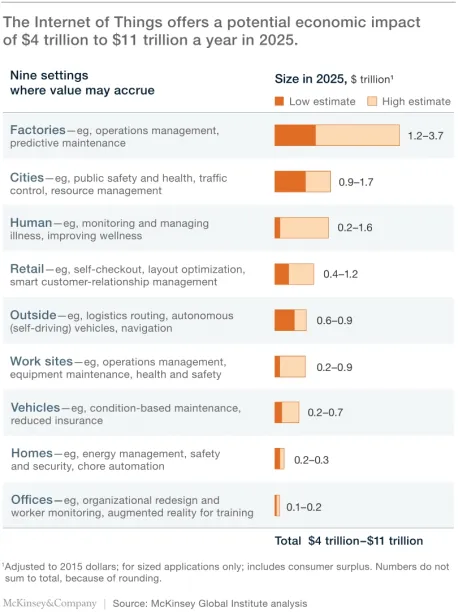
We have compiled 33 IoT applications for business leaders to select the correct use case for their IoT implementation . Use cases include:
Smart Factories
1. enterprise asset management.
Enterprise asset management involves work management, asset maintenance, planning and scheduling, supply chain management, and environmental, health, and safety (EHS) initiatives. Businesses collect real-time data from an asset with IoT sensors.
Businesses are rapidly adopting smart asset management systems into their businesses. Due to their asset-intensive environments, we mostly encounter IoT asset monitoring in industries such as logistics, retail, and manufacturing.
IoT-powered asset management increases real-time visibility of assets and helps businesses optimize their resource while providing benefits such as:
- Increased operational efficiency
- Better control over the sales lifecycle
- More efficient safety and compliance checks
- More responsive smart environment.
2. Predictive maintenance
Maintenance is conducted to prevent predicted problems. So over the lifetime of a machine, some components may never be checked if they are not predicted to cause problems.
For example, Fanuc is a robotics company that is working on reducing the downtime of machines with IoT technology. Fanuc uses sensors to predict when the failure of the component will happen.
3. Industrial process automation/optimization
Organizations can keep a real-time record of the metrics of all the machines inside a plant using IoT and IP networks. Manufacturers can use this data to automate workflows and optimize production systems. Automation and optimization support industrial companies to reduce costs and increase the quality and volume of output.
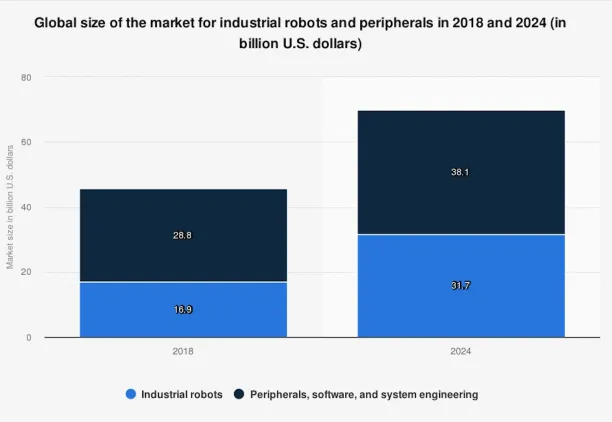
The market for automated industrial robots is proliferating. The market size was 41 billion U.S. dollars in 2017 and is expected to reach 73 billion U.S. dollars in 2023.
4. Energy management
Energy can be a costly input for industrial businesses. With fluctuating energy costs and strict government requirements for efficiency, managing energy distribution becomes important.
IoT devices can help manufacturers manage energy consumption based on real-time data collected from devices. Intelligent energy management systems reduce energy bills, operational expenditures, and the carbon footprint of the factory while increasing energy efficiency. WebNMS is an IoT platform that provides IoT applications, including energy management, to optimize the energy consumption of businesses.
Smart Cities
Kay Sharpington from Gartner, states “The COVID-19 pandemic is slowing down spending, however, governments across the globe continue to use IoT technologies and solutions to improve citizen safety. At the same time, the falling endpoint and connectivity costs make smart city initiatives more viable”.
Gartner estimated that the global government Internet of Things (IoT) endpoint electronics and communications market totaled $15 billion in 2020, an increase of 6% from 2019. The same study also reveals the top 5 government IoT applications and revenue generated by each use case, as seen below:
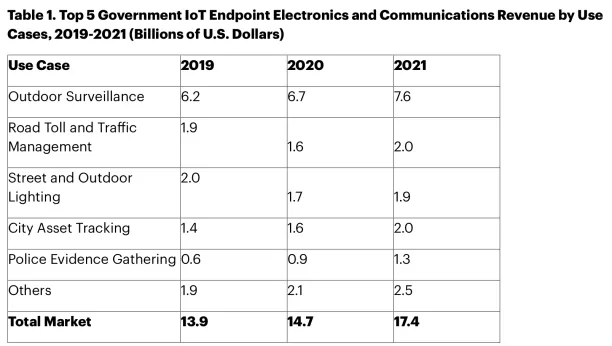
5. Outdoor surveillance
When IoT CCTV cameras are combined with artificial intelligence and machine vision, governments can automate the surveillance of streets through cameras. As IoT enables connectivity of machines, they can record and analyze video data in real-time, and they can provide police officers with insights instead of single pieces of images.
However, outdoor surveillance processes personal information and there is potential for abuse in the use of such technologies. Therefore appropriate checks and balances need to be implemented in such systems to ensure that personal information is not abused while the risk of crime is minimized.
6. Smart lighting
According to the 2018 Gartner IoT hype cycle report, smart lighting is the fourth-most mature IoT tech application. Smart lighting aims to optimize energy management.
Smart lighting is made up of street lighting with IoT sensors. Sensors collect data about the condition of traffic and pedestrians. With that data, street lights provide optimum lighting so that street lighting systems can save up to 80% of the energy.
Smart lighting can also be applied to factories or homes.
7. Electronic road toll collection and traffic management
Traffic engineers augmented by smart systems at a central traffic management center (TMC) can analyze data from IoT sensors and then optimize the timing of traffic lights throughout the day. This can help divide the traffic more evenly over roads as traffic volume fluctuates.
8. Smart parking
In cities like San Francisco, parking is a big problem. With IoT sensors, parking problems in a city can be minimized.
The working principle of smart parking is:
- Sensors are attached to parking lots to detect parked cars
- Measurements are periodically sent to the cloud by microcontrollers
- Mobile Apps use cloud data to identify empty parking spaces,
- Drivers check mobile apps to identify vacant parking spaces close to the location they aim to go to.
Noise Monitoring
In smart cities, sound monitoring systems can monitor noise levels, warn companies that they violate limits, and help manage noise levels.
9. Structural health monitoring
IoT allows remote collection of architectural data to monitor events such as vibrations and changes in material conditions, predict structural damage, and prepare action plans for structures such as bridges, buildings, stadiums, ships, airplanes, etc.
10. Waste management
Traditional waste collections are complicated and costly since a fleet of trucks drives along busy streets using inefficient routes. Fill levels of garbage containers differ for each container, ranging from overflowing to partially filled to empty. IoT sensors can monitor fill levels for conventional bins and send the data to the relevant department of the city hall. With that information, the garbage truck routes can be optimized for trash collection.
Machine learning methods can also be implemented in IoT sensors (i.e. edge analytics ) so that sensors can predict the fill levels of containers by learning from historical data.
Below the video, you can find how Proximus, an IoT solutions vendor, uses IoT to manage waste:
Water Management
Due to the drastic increase in urbanization levels and the importance of water quality in human health, water management is a key topic for cities. A water management system is based on real-time data collected from sensors. Water management can provide the following applications:
11. Water conservation
Sensors detect the water level in tanks and alert when the water level is lower than the threshold. Well™, a smart home water conservation system developed by Mindtribe , uses IoT sensors to monitor water usage.
12. Smart irrigation
IoT sensors determine the weather conditions and the soil moisture, which will help in getting the appropriate amount of water that the soil needs. For instance, greenIQ is a vendor that offers a sprinkler sensor that optimizes its functionality based on the dryness of the soil.

13. Leakage management
IoT sensors can detect temperature changes, water leakage, chemical leakage, and pressure levels in water tanks.
14. Water quality management
IoT sensors determine what kind of chemicals are in the water. They also identify metrics such as total dissolved solids (TDS), bacteria, chlorine, electrical conductivity, etc.
Learn more about IoT in agriculture.
Digital Health
15. ultraviolet radiation monitoring.
Sunlight consists of three major components:
- Visible light: Wavelengths between 0.4 and 0.8 micrometers,
- Ultraviolet light: Wavelengths shorter than 0.4 micrometers,
- Infrared light: Wavelengths longer than 0.8 micrometers.
Ultraviolet (UV) rays are electromagnetic waves that account for about 10% of solar light. When overexposed, UV rays have harmful effects such as skin cancer, premature aging, cataracts, and immune system suppression. IoT sensors measure UV sun rays to warn people not to be exposed during certain hours.
16. Fall detection
Falling to the ground and not being able to get up or request help can be a scary experience for senior citizens. IoT sensors can detect falls using geolocation data and summon help so that it reduces the time the elderly remain on the floor after a fall which could lead to lethal consequences.
The below video is an example of how fall detection systems work from a vendor called Walabot:

17. Companion robots
A companion robot is a robot that is designed to create companionship mostly for elderly and single children. IoT sensors are essential for robotics and it is the same for companion robots as well. Sensors detect objects that surround the robot and enable the robot to move.
Researchers claim that people have become more receptive to companion robots during the pandemic. Social isolation may lead people to loneliness, anxiety, and frustration, especially the elderly.
18. Medical fridges
Medical fridges monitor the temperature of vaccines, medicines, and organic elements for clinics and health centers. Medical fridges provide an opportunity to follow all safety standards and national regulations of the pharmaceutical market using IoT sensors. They prevent medicines and vaccines from spoiling.
Efento is an IoT sensor and IoT platform vendor that has a variety of temperature measurement products and wireless temperature monitoring in medical refrigerators.
19. Patient surveillance/remote patient monitoring
20% of patients who had surgery are readmitted to the hospital within just 30 days. Remote patient monitoring (RPM) systems use wearables to monitor the condition of patients who are resting at home after surgery. RPM enables real-time data collection about patients’ body temperature, which is the main indicator of infections.
With RPM, doctors can observe patients’ data and provide early diagnoses without requiring patients to be physically present at the hospital.
Telit is an IoT solution vendor and offers its customers a remote patient monitoring (RPM) solution that enhances patient monitoring capabilities and patient satisfaction. Telit’s offering can reduce:
- Patients hospital stay duration thanks to early diagnosis of complications
- Hospital readmissions
Smart Retail
20. supply chain control.
IoT devices have transformed supply chain management. Sensors, which are attached to storage containers or products themselves,
- show the location of goods using GPS,
- track the speed of movement, providing an accurate estimated time of arrival (ETA) for goods,
- monitor warehouse conditions such as temperature, humidity, light intensity, and other environmental factors
21. Near-field communication (NFC) payment
NFC enables contactless payments. POS vendors include NFC support in their systems, and customers are adopting contactless payments via their smartphones.
22. Layout optimization
Sensors in the store collect data like voice, image, or video to better understand customer habits and preferences. Retailers can get insights to redesign the layout of their stores. The optimized layout can enhance sales.
23. Smart product management
IoT sensors enable retailers to control the rotation of products on shelves and warehouses to automate merchandising decisions. We have already written about retail analytics use cases, feel free to check it out if you want to learn more.
Smart Workplace
24. sociometric badges.
Sociometric sensors are wearable IoT devices that measure the amount of face-to-face interaction, conversational time, physical proximity to other people, and physical activity levels using social signals derived from vocal features, body motion, and relative location.
For example, Humanyze is a vendor that uses sociometric sensors to perform people analytics. The company helps organizations understand how their teams interact to increase performance.
Smart Homes
25. remote control appliances.
IoT-powered home appliances let residents remotely switch on and off devices using smartphone apps to avoid incidents and save energy. Additionally, these devices can make autonomous decisions based on sensor inputs, such as preparing fresh coffee when a resident is identified to wake up. Other examples of autonomous or remote-controlled actions include:
- Turning on lights,
- Starting the coffee maker,
- Setting temperature,
- Open up a music playlist,
- And locking doors.
Home Intrusion Detection Systems:
IoT-based home security applications give users capabilities such as smart locks and security cameras that detect motions and send alerts to their smartphones so that they can monitor the safety conditions of their homes from anywhere.
26. Smart locks
Eyelock is a security provider vendor that offers its clients an iris-based authentication solution.
27. Motion detection
Manything is another vendor in the IoT-based home security market. It streams home/office videos and lets users receive alerts when it detects any activity.
Smart Logistics
28. fleet tracking.
IoT fleet tracking systems improve security and provide precise and complete reports that give the fleet managers full transparency regarding the fleet’s activities. Through GPS monitoring and geo-location tools, companies can track the location of their trucks, optimize routes, and monitor their fleet utilization in detail.
For instance, Canadian delivery service Sure Track Courier saved 6-10% per month on fuel costs by optimizing routes using IoT data from trucks.
29. Platooning
Platooning involves a group of self-driving trucks that follow a lead truck at high speed safely and efficiently. Trucks use IoT sensors so that each truck communicates with the other trucks to adapt its speed and braking accordingly.
30. Connected vehicles
Sensors are enhancing vehicles along with AI and analytical capabilities. These sensors provide communication with the driver to supply useful information about other cars on the road and roadside infrastructure to the driver to help the driver make safer or more informed decisions. For example, these vehicles provide GPS-enabled location detection features that help them detect traffic congestion.
Autonomous vehicles are also applications of IoT devices. Though it is not commonly used in logistics yet, we will witness this approach soon. For instance, the Mercedes-Benz prototype of the semi-autonomous truck is scheduled for release in 2025.
Smart Metering
31. smart grid.
With the increasing attention regarding climate change and carbon emissions, utilities focus on reducing energy consumption. For utility companies, IoT enables remote data management and monitoring capabilities to manage better power flows into and out of their grids, and give users the insights needed to understand their energy infrastructure investments.
32. Digital Twins
A digital twin is a virtual replica of physical entities such as devices, people, processes, or systems that help businesses make model-driven decisions. With the help of IoT sensors, businesses collect data that is needed to create a digital twin.
Digital twins enable businesses to gain a deeper understanding of real-world conditions so that they make necessary adjustments to their products & services.
33. IoT devices in healthcare
In healthcare , the ecosystem of IoT-enabled devices such as wearables (smartwatches, rings, vests, etc.), monitors (heart monitors, sleep monitors, temperature monitors, etc.), and trackers (medication refill reminder, drug effectiveness tracking, etc.) can be used for:
- Constant monitoring of patients’ vitals (blood pressure, heart rate, temperature rate, etc.),
- And more accurate diagnoses of patients, thanks to real-time data from IoT devices, thus reducing the possibility of readmission and rising hospital bills.
Further reading
We have written articles about IoT technologies before, feel free to read our other articles on:
- Increase Speed to Market Using an IoT Platform
- Edge Analytics in 2022: What it is, Why it Matters & Use Cases
- IoT Testing: Framework, Challenges, Case Studies & Tools 2022
We also have some in-depth articles on other use cases of IoT in different industries:
- Top 6 Use Cases of IoT in Manufacturing
- 5 Use Cases of IoT in Automotive in 2022
- 7 Ways IoT Will Improve Your Banking Experience in 2022
Finally, if you believe your business could benefit from implementing an IoT solution, we have a data-driven list of vendors prepared .

Next to Read
7 benefits of iot in banking, iot analytics: benefits, challenges, use cases & vendors.
Your email address will not be published. All fields are required.
Related research
Top 10 iot communication protocols & their features, 25 iot stats from reputable sources.
We use cookies to improve our site and your experience. By continuing to browse our site, you accept our cookie policy. Read more. I understand
- Customer log-in
- Get Free IoT Trial
- 中文 (Chinese)
- 한국어 (Korean)
- 日本語 (Japanese)
15 IoT Examples for Business Applications
The IoT, or Internet of Things, is all around us, from consumer IoT applications such as connected cars and wearables to robotic lawn movers. But what about industrial or smart city IoT examples, that might not get much hype, but provide real benefits?

On this page, explore 15 Internet of Things use cases and several case studies.
Smart Cities Internet of Things Examples
Smart cities are quickly expanding and there is a growing need for connected solutions that support the management of urban infrastructure, parking and traffic, electric vehicle charging, waste handling, information sharing and security services. Smart city technologies and IoT smart city solutions present a compelling solution to the problems caused by urbanisation.
1. Smart Pest Removal
Rats and mice are a major problem to citizens and businesses, and it is very costly in man-hours to get rid of the pests in an efficient way.
Digital rat traps can reduce a large part of the working time by manually checking if traps are filled. With the help of small sensors and automatic status messages the trap gives notification when a rat has walked in or has been near the trap.
IoT-powered traps digitize the manual work with small sensors and instant messages. This gives a full overview of the traps and improves the ability to take early action against the pests.
How does it work?
1. Rat traps are equipped with IoT devices 2. Sensors monitor whether there are rats in or around the traps 3. Devices send data, e.g. via an NB-IoT connection 4. Service personnel monitors the traps remotely 5. Service personnel visits only the traps that require emptying
What are the benefits?
The digital traps eliminate wasted time for manually overhauling empty traps, and they help to speed up maintenance of traps.
- Save time on unnecessarily checking traps
- Reduce transportation costs
- More efficient rat control
- Reduce CO2 by less transportation
- Better understanding of the rats' whereabouts
Related Case Studies
- Case study with Anticimex (PDF)
2. Smart Meters for Utilities
Collecting meter data is expensive, and it is difficult to get 100% correct data for production and billing.
IoT-sensors in electricity/water/gas/heat meters send the precise data to the supplier’s back office who can track consumption in real time.
Insight into consumption and distribution paves the way for great savings and efficiencies. At the same time, leaks are detected more quickly.
Read more about IoT for Utilities.
Related Case Study and Blog Posts
- Blog: Smart Meters to Transform Utilities
- Case: Connecting around 1 Million Smart Meters
- Case: Water Leak Detection using IoT
3. Smart Road Signs
It is dangerous when signs overturn on highways and elsewhere in traffic, and it is very expensive to manually check that all signs are in place.
Internet-connected road signs that, for instance, are placed at roadworks or other places, can save a big part of the time spent manually checking if the signs stand upright as they should. Using smart tilt sensors and a digital monitoring platform, service personnel just drive out to the signs that actually require service.
With NB-IoT trackers, signs can automatically notify if they are overturned or in any way relocated.
1. Road signs are equipped with IoT device 2. Sensors monitor, whether the sign stands upright as it should 3. Devices send data, e.g. via an NB-IoT connection 4. Service personnel gets notified when a sign is overturned 5. Service personnel only moves out to overturned signs
Digital monitoring of signs provides increased security and massive savings, avoiding manual inspection of the signs.
- Reduce man hours on controlling the signs
- Increase security in traffic
4. IoT Smoke Detectors
The consequences are fatal when smoke detectors do not function effectively in the event of a fire – either because the battery is flat or because no one hears them.
IoT-powered smoke detectors communicate digitally so that all relevant people are notified quickly in the event of a fire. The smart sensors detect smoke, temperature and battery levels.
Digital smoke detectors can save human lives, minimize damages and help protect business-critical assets for companies.
5. Smart Climate Control
Poor indoor climate translates into bad business. A strained indoor climate results in inefficient meetings, poor concentration and more sick days.
Small IoT devices can monitor the indoor climate and automatically notify if airing is bad or the heat should be lowered in the room.
A good indoor climate is key to optimize the well-being and productivity of employees, students, healthcare professionals, etc.
- Case: Smart Buildings Create Significant Energy Savings
- Case: Energy Management from Home to Cloud
6. Smog, Noise and Traffic Monitoring
Noise, smog and traffic jam are all harmful to public health and an economic burden to society.
Intelligent sensors that detect everything from air pollution and noise levels to the number of cars on the roads provide valuable insights that can be used for better infrastructure planning.
There are great benefits from improving the environment and space on the roads in cities – both economically and in terms of creating a more clean and healthy city.
- Case: Smart City IoT Applications for a Greener World
7. Digital Sewers
Heavy rainfall and clogged sewers typically cause overflow and spillage of sewage into the natural streams.
Level sensors under well covers can monitor sewers and alert if a too high-water level is detected.
With real-time digital monitoring service providers can act in time and do proactive clean-ups at blocked sewers.
IoT Examples in Healthcare
IoT in healthcare use cases is growing rapidly. According to a report by Grand View Research the global IoT in healthcare market size is projected to reach USD 534.3 billion by 2025. IoT devices can for instance help medical device manufacturers identify operational problems and save lives during emergencies, they can remotely monitor the status of patients or provide cold chain monitoring of pharmaceuticals.
8. Better Care for Dementia Patients
The Danish society spend billions every year on dementia and the decease creates great insecurity for patients and relatives.
With smart trackers in watches and bracelets, healthcare professionals and caregivers can easily locate any missing dementia patient.
Tracking solutions save society resources and minimize the risk of dementia patients are putting themselves and others at risk.
- Case: Digital Monitoring of Defibrillators
- Case: Delivering Lifesaving Connectivity when it’s Needed most
- Case: Weathering the Coronavirus Storm in the Caribbean
- Case: Creating the Next Generation of Pharmaceutical Supply Chains
Industrial IoT Devices
Explore a couple of B2B use cases that highlight how IoT is being used by enterprises to lower costs by reducing working hours, minimizing down-time in production and machines, and avoiding waste of expensive equipment.
Lower Costs by Reducing Working Hours
Every day, companies use many hours on manual workflows. It can be service checks of products at the customer, supervision of equipment and machines in production, or similar tasks. Much of that time can be reduced with IoT.
Manual workflows are often critical for companies to deliver quality service to their customers. However, manual working hours sometimes result in high costs, including labor costs.
By equipping your products and equipment with IoT devices that are connected to the internet, they can be monitored digitally, for instance directly via a mobile application.
Here are some instances of IoT applications that help to lower costs by reducing working hours.
9. Reduce Downtime on Production Sites
Downtime on the production site can be very expensive, e.g. if the assembly line needs service or if components are to be replaced.
By installing trackers on critical production machines, you can collect important usage data and get the machines to notify you well in advance before they need service.
IoT trackers and predictive maintenance can cut downtime and deliver serious savings by better maintenance planning.
10. Fill-level Sensors for Silos and Tanks
Manual fill-level monitoring in tanks and silos is costly, time consuming and can be expensive if supplies run out.
Small sensors in tanks and silos can read the fill-level in real time and proactively send alarms when it’s time to fill up the tanks.
The remote fill-level monitoring saves man-hours, transport costs and avoids expensive emergency fillings.
- Case: Pioneering Water-as-a-Service Solutions through IoT
Save Costs and Avoid Waste of Expensive Equipment
Every day, companies lose expensive equipment when transporting goods to and from customers or when carrying equipment to perform work outside the company. It can be anything from roller cages and pallets to machinery and tools. IoT offers new opportunities to digitally track equipment so that it automatically sends notifications when it disappears.
There are big gains to reap for companies that track their equipment through IoT. They save time and money on the purchase of new equipment, they avoid wasted time on manual tracing, and better utilization of existing equipment.
By installing small IoT devices on the equipment, they can easily and quickly be tracked digitally. The devices can be configured, so that they automatically send messages, when they move, stand still at places where they should not be, or disappear.
11. Digital Tracking of Roller Cages
Companies often waste resources on handling their assets, such as pallets and roller cages , when they are left unused in a warehouse or disappear during transport. Many companies use a large number of roller cages to move goods between customers and suppliers. It is often difficult to know where the assets are located and how many the company has available.
By installing small battery-powered trackers directly on the assets you can track their location and status at any time.
1. Roller cages are equipped with IoT devices 2. GPS tracker monitors the roller cage location 3. Devices send data, e.g. via an LTE-M connection 4. Employees get message when a roller cage disappears from the route 5. Roller cages can effectively be retrieved as needed
Insights like these deliver great savings, for instance by reducing lost assets, improving the inventory management or reducing ‘bottlenecks’.
- Fewer lost roller cages (less cost for replacements)
- Save time on manual tracing
- Avoid bottlenecks by lack of roller cages
- Minimize costs for unused roller cages (tied capital)
- Reduce costs for handling roller cages
12. Efficient Logistics with Smart Containers
It is expensive and inefficient for suppliers if they are driving around in half-empty trucks or if they cannot deliver due to low inventory.
With IoT suppliers can equip their containers with smart sensors so that they can always be tracked throughout the value chain and automatically report on fill level data.
Digitization of containers, e.g. for chemicals or water, gives the supplier opportunity to provide new services and to streamline their logistics and inventory management.
Related Case Studies and Blog Posts
- Case: Smart Shipping Containers on the Silk Road
- Case: Sony’s IoT Asset Tracking Solution
- Blog Post: IoT-powered connected shipping for vaccine delivery
13. Tracking Machinery and Equipment on Construction Sites
Downtime is expensive on the construction site, e.g. when excavators needs maintenance or when tools disappear from the site.
There is a huge shrinkage of tools on construction sites. It costs the contractor dearly in the purchase of new tools and lost working hours when their employees are looking for the tools. By installing IoT devices in everything from screwdrivers to angle grinders, tools can automatically send notifications when it disappears.
With IoT trackers, tools and equipment can always be tracked and localized. Additionally, sensors provide usage data that can be used for optimizing maintenance plans.
1. IoT devices are installed in the tool, e.g. in a screwdriver 2. Sensors monitor the location of the tool 3. Devices send data, e.g. via an NB-IoT connection 4. Company is notified if tools disappear from the construction site 5. Tools can easily and effectively be tracked down and retrieved
There are big savings to be made – partly by avoiding downtime, and partly by tracking expensive machines and equipment that are stolen or lost.
- Save costs for new-procurement of tools
- Reduce downtime at the construction site
- Achieve better utilization of the available tools
- Minimize the amount of stolen devices
Asset Tracking
Asset tracking IoT systems enable companies to track assets in a smart way. With connected devices expected to rise from hundreds of millions to billions over the next few years, smart tracking with cloud service, analytics and alarms functionalities is becoming a clear expectation for asset owners and companies transporting high-value goods.
Minimize Transportation Costs
Many companies make a living from transporting goods, equipment and services to customers and business partners. With IoT, businesses can deliver their service with fewer miles spent on the road – and most often with a higher quality for the customer as a result.
Transportation costs are one of the major records in many companies’ budgets. In addition, there are increasing pressure – both politically and from customers – for businesses to reduce their CO2 emissions. Therefore, IoT solutions that reduce transportation time, are increasingly in demand by companies across industries and sectors.
Remote data reading with IoT technology typically works by installing small IoT devices in the places where one wish to obtain data from, and monitoring can take place remotely.
14. Waste Management with Smart Bins
Today, waste is collected inefficiently. This is expensive to citizens, the government and not least the climate due to CO2 emissions.
Garbage trucks drive out every day to empty and half-filled garbage cans, although they do not require emptying. It is expensive in transport and working hours, creates traffic jams and discharges unnecessarily a lot of CO2. IoT can eliminate wasted time on the road.
By installing IoT sensors in the bins, the garbage collectors can measure the fill level in each container remotely and use data for better route planning. By mounting fill level- sensors in the containers the garbage collectors get insight into which bins require emptying and which they can disregard on their route. Data from all the bins are analysed and translates into an optimized route plan.
1. Garbage cans are equipped with IoT devices 2. Sensors monitor the fill level in the bins 3. Devices send data, e.g. via an NB-IoT connection 4. Data is analyzed and translates into daily routes 5. Garbage trucks only drive out to the places where buckets are full (dynamic emptying)
Better route planning can deliver significant savings by lowering transportation costs, CO2 emissions and by cutting inefficient man hours on the road.
- Save man hours
- Save fuel and reduce CO2 emissions
- Better use of capacity and fleet
- Minimize queues around garbage trucks in traffic
- Case: Hitachi Construction Machinery Enables IoT Innovation with ConSite
- Case: Sony’s IoT asset tracking solution
- Case: A Platform for Transport Management in the Light Commercial Vehicle Market
15. Digital Moisture Meters
Water damage is one of the most frequent damage to both companies and consumers. Damage service companies are helping customers dehumidify their buildings. After installing dehumidification equipment at the site of damage; damage service companies use a lot of their time with transport from customer to customer, in order to measure the moisture values. It takes various readings until they know when the place is dry, and the customer can come again back to everyday life. A lot of this transportation time can be saved with IoT.
By installing small IoT devices in floors and walls, service employees can remotely read the moisture values, without having to visit the customer.
1. IoT devices with moisture sensors are installed in walls and floors 2. Sensors monitor the moisture values in the room 3. Devices transmits data, e.g. via an NB-IoT connection 4. Service Officer is notified when the place is dehumidified 5. Service Officer visits damage site and uninstalls dehumidification equipment
- Save working hours
- Save fuel and CO2 emissions
- Better utilization of fleet and dehumidification equipment
- Customers come back faster into their home after a moisture damage
IoT devices are all around us. Innovative enterprises and consumers are finding creative ways to leverage on the power of IoT and disrupt industries and traditional business models. From our daily work providing IoT Connectivity and IoT Cloud services, we have selected 15 real-life Internet of Things examples together with concrete customer cases for you to get inspired.
Many of these use cases were published for the first time in a white paper by Telenor Denmark (Note: The white paper is in Danish).
On this Page:
Iot use cases.
Resources & News

Join Us for a Webinar

IMAGES
VIDEO