- +49 (0) 40 639 118 91
- info(at)iot-analytics.com
- Contact Form

- The top 10 IoT use cases
- IoT initiatives appear more successful than ever, as 92% of enterprises report positive ROI from IoT use case implementations, according to IoT Analytics’ 418-page IoT Use Case Adoption Report 2024 .
- The number of IoT use cases being adopted by enterprises grew 53% between 2021 and 2024.
- Complexities related to IoT use case adoption appear to be easing somewhat, which appears to be fueling the adoption growth and ROI.
- Enterprise IoT use case investments continue to grow in 2024, but at a slower pace than in previous years.
- IoT Analytics presents the top 10 IoT use cases, with process automation as the #1 adopted IoT use case.

Why it matters?
- For IoT vendors: With the success of IoT initiatives and the growing adoption rate, IoT vendors can learn about what use cases end users are adopting and tailor their offerings.
- For IoT adopters: Adopting IoT use cases has shown ROI, in many cases, within two years. IoT can help adopters streamline their operations and support digitalization efforts.
Status of IoT initiatives in 2024: More successful than ever before

Over 90% of IoT use case projects have positive ROI. For years, IoT Analytics has been unable to validate common claims that most IoT projects are unsuccessful, such as the following:
- Cisco Survey Reveals Close to Three-Fourths of IoT Projects Are Failing
- It’s the last IT/OT mile that matters in avoiding Industry 4.0’s pilot purgatory
- Why has the Internet of Things failed?
According to IoT Analytics’ research found in the 418-page IoT Use Case Adoption Report 2024 (published July 2024)—which is based on a survey of 200 end users of IoT applications and analyzes 27 IoT use cases—91.7% of organizations have seen ROI from the different IoT use cases they adopted, a 13-percentage-point climb from similar IoT Analytics research in 2021. Further, compared to 2021, 53% more IoT use cases are being adopted by organizations (either in the process of rolling out a use case or have already completed a project), signaling a healthy state of IoT .
IoT project complexity has reduced. In 2021, many respondents to a similar IoT use case survey noted the need for proofs of concept and testing since IoT projects and their technical setups can be complex. However, in 2024, the complexities of usage and onboarding/setup of IoT use case projects ranked 5th and 6th, respectively, in terms of challenges. In IoT Analytics’ opinion, this drop in perceived complexity appears to largely fuel the strong growth in IoT use case adoption.
Restrained IoT spending growth in 2024. 51% of respondents say that their organizations plan to increase their spending in IoT use cases in 2024 compared to 2023; however, they plan to do so by a lower amount than the previous year. According to IoT Analytics’ IoT Software Adoption Report 2023 , companies increased their IoT use case spending, on average, by 8.4% in 2023, while in 2024, respondents stated their companies’ budgets for IoT use cases were increasing 2% on average.
Additional insights from the IoT Use Case Adoption Report 2024 22% of respondents are planning to increase investment in IoT use cases by more than 10% in 2024 (vs. the previous year). In 2021 (for 2022), that share was at 29%, constituting a 7-percentage-point decrease.
Note: The report looks at IoT use cases that apply to most organizations and does not consider industry-specific use cases such as smart heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) (applicable only to buildings) or smart transportation systems (applicable to cities).
The 10 most adopted IoT use cases

Most IoT use cases serve smart operations . The top 10 IoT use cases in 2024 have changed quite a bit since 2021; however, the distribution of use cases by category within the top 10 remains the same: 6 smart operations use cases, 3 smart supply chain use cases, and 1 connected product use case.
Below are the top 10 use cases in 2024, including how IoT Analytics defines them and which organizational KPIs are most affected by each. Also provided are select quotes and implementation examples for some of the use cases from the report.
Note : Each use case and definition below is based on IoT applications—some terms may have broader definitions outside of IoT.
1. Process automation
Process automation definition (by IoT Analytics) The integration of IoT to automate routine processes, enhancing productivity and accuracy
Nearly 3/5 of organizations have adopted process automation. Leading as the most adopted IoT use case at 57.5% of organizations is process automation. This is a stark rise from the 33% adoption rate seen in the 2021 IoT use case report, where it was the second-ranked use case.
Process automation enables companies to streamline and automate processes by integrating interconnected devices and sensors with both new and legacy equipment, such as PLCs and IPCs. This use case helps to reduce the need for manual intervention, increasing efficiency, minimizing errors, and enhancing safety. Technologies such as IoT sensors and edge computing play a crucial role in enabling real-time data collection, analysis, and decision-making. By incorporating IoT into existing systems, companies can optimize workflows, improve production quality, and implement predictive maintenance.
Most important KPI affected
The top KPI affected by process automation is labor efficiency. On average, a major rollout of this use case improves labor efficiency by 8.2%.
Implementation example
When Burnley Brewing , an Australia-based craft brewery, approached its maximum capacity as demand for its beverages grew, it decided to expand. In doing so, it decided also to include automation in its processes . Burnley partnered with Australia-based contract electrical and engineering firm Bon Industry , which leveraged US-based industrial automation technology provider Rockwell Automation ’s FactoryTalk Craft Brew—a process management and automation system developed specifically for the brewing industry. IoT sensors, PLCs, and other action-enabling hardware were placed throughout the brewing process, all connected to FactoryTalk Craft Brew for data collection and process actioning. As a result of this solution, Burnley Brewing lessened the labor of its brewers across the brewing process, from milling and mashing grain at the beginning to controlling fermenters and conditioning tanks near the end.
2. Quality control and management
Quality control and management definition (by IoT Analytics) Integrating IoT (e.g., machine vision) to enhance quality processes
Quality control and management climbed 5 places since 2021. 55% oforganizations have adopted IoT-based quality control and management. In 2021, this use case was 7 th in adoption at 30%, which marks a significant climb. A reason for this climb could be its quick payoff: 53% of companies that have implemented this use case reported amortization in less than 24 months.
Quality control and management allows companies to monitor critical factors like temperature, humidity, and pressure during production. This real-time data allows for immediate detection of quality deviations, enabling swift corrections to prevent defects. IoT solutions can be integrated into both new and legacy equipment, with machine learning analyzing the data to predict potential issues before they arise.
The top KPI affected by quality control and management is, no surprise, product quality. On average, a major rollout of this use case improves product quality by 4.6%.
3. Energy monitoring
Energy monitoring definition (by IoT Analytics) Integrating IoT to monitor energy consumption for individual assets
Companies plan to invest more in energy monitoring than any other smart operations use case. Adoption-wise, energy monitoring has risen to 55%—up from 20% in 2021.It is the rising star among IoT use cases, as new sustainability strategies and high electricity prices (especially in Europe) have led companies to use IoT devices and sensors to closely monitor individual assets’ energy consumption. Within the smart operations category, it has the highest expected investment increase between 2023 and 2024 at 3.5%.
The top KPI affected by energy monitoring is costs. On average, a major rollout of this use case reduced related costs by 8.1%.
4. Real-time inventory management
Real-time inventory management definition (by IoT Analytics) Utilizing IoT for tracking inventory levels in real-time to optimize stock and reduce shortages or excesses
Real-time inventory management leads smart supply chain use cases. 54% of respondents shared that their companies have either fully rolled out or are rolling out real-time inventory management. With the supply chain issues and economic uncertainty following the COVID-19 pandemic, companies have sought smarter inventory management solutions to prevent stockouts and overstocking. In fact, adoption of this use case climbed 35 percentage points between 2021 and 2024, and within the smart supply chain category, it is expected to receive the largest investment increase between 2023 and 2024 at 5.7%.
The top KPI affected by real-time inventory management is the return on equity (ROE)/return on capital employed (ROCE). On average, a major rollout of this use case improves ROE/ROCE by 8.1%.
In 2022, Tyson Foods , a US-based multinational food company, wanted to automate time-consuming manual processes like inventory counts. The company already used computer vision for many of its processes but sought to incorporate machine learning to improve operational efficiency, among other goals. Leveraging AWS ’s Panorama and SageMaker services, Tyson Foods implemented a computer vision-based, real-time inventory management system to deploy a detection model that automated chicken tray counting and identified faulty carriers. This real-time inventory management solution saved Tyson Foods an estimated 15,000 labor hours annually in each facility and helped it avoid over- or underproduction.
Additional insights from the IoT Use Case Adoption Report 2024 The report dives into the challenges companies face when implementing IoT use cases, conveyed by industry, region, and company size. Looking at the process manufacturing industry as an example, 46% of respondents, on average, marked “Integration into legacy systems” as a severe or major challenge, making it the top challenge faced by that industry. “Privacy concerns” and “IT and data security concerns” ranked as the 2nd and 3rd top concerns.
5. Supply chain track and trace
Supply chain track and trace definition (by IoT Analytics) Employing IoT for monitoring the location, condition and/or status of products and materials along the supply chain
Most adopters see fast amortization with supply chain track and trace. Riding just behind real-time inventory management is supplychain track and trace, also at a 54% adoption rate. Approximately 60% of respondents experienced amortization in less than 24 months—second of all IoT use cases in this regard.
Connected sensors, GPS devices, LPWAN, and satellite technologies—all part of IoT’s contribution to supply chain track and trace—help companies monitor and manage the movement of goods throughout their entire supply chain by providing real-time visibility into the location, condition, and status of shipments. Advanced analytics further enhance supply chain operations by predicting disruptions and optimizing routing. With this use case, companies can reduce losses, improve delivery accuracy, and enhance compliance with regulatory requirements.
The top KPI affected by supply chain track and trace is on-time delivery. On average, a major rollout of this use case improves on-time delivery by 8.5%.
Adopter quote
“The drivers drive with more foresight, the wearing parts last longer, the number of accidents goes down, the diesel consumption goes down—the stress is less.” Oliver Nocke – Fleet Manager, Roman Mayer Transport & Logistik (via Samsara )
6. Operations planning and scheduling
Operations planning and scheduling definition (by IoT Analytics) Leveraging IoT for real-time scheduling and planning to improve operational efficiency
Energy companies expect more investment in operations planning and scheduling. 53% of respondents shared that their respective companies have either rolled out or are currently rolling out operations planning and scheduling tools. Approximately 75% of companies in the energy sector are planning to increase investment in this use case in 2024, with an average increase of 5.5%.
By integrating IoT technology with planning systems, companies gain up-to-the-minute insights into production status, machine availability, and workforce capacity, allowing for dynamic adjustments to schedules, which helps reduce downtime and ensure optimal use of assets. Algorithms can further analyze the data to predict demand, identify bottlenecks, and suggest the most efficient scheduling options, resulting in improved operational efficiency and reduced lead times. Many (but not all) of the rollouts are tied to existing planning and scheduling software, such as manufacturing execution systems in the manufacturing sector, energy management systems in the energy sector, or building management systems in the buildings sector.
The top KPI affected by operations planning and scheduling is labor efficiency. On average, a major rollout of this use case improves labor efficiency by 7%.
7. On-site facility track and trace
On-site facility track and trace definition (by IoT Analytics) Employing IoT for real-time tracking and tracing of assets on a site (e.g., in a factory or warehouse)
Wholesale and retail expected to lead in on-site facility track and trace investment. Half of the organizations in the survey have adopted some form of on-site facility track and trace. Of those companies in the wholesale and retail segment that are testing or adopting this use case, 56% expect to increase investment, with an expected increase of 13% on average. Second to them are companies in the healthcare industry at 55%. On-site facility track and trace makes sense for these two segments, as tracking and locating products within a warehouse or equipment in a healthcare facility can aid in timely shipments or urgent medical needs.
The top KPI affected by on-site facility track and trace is on-time delivery. On average, a major rollout of this use case improves on-time delivery by 7.8%.
“Track and trace is a risk mitigation initiative for retailers, making it easier to identify products in the event of a recall, reducing exposure to costly lawsuits and improving overall compliance.” John Merrill – CFO, ReposiTrak , February 14, 2024
8. Asset performance optimization
Asset performance optimization definition (by IoT Analytics) Utilizing IoT to enhance operational efficiency and effectiveness of assets
Asia-Pacific companies to lead in asset performance optimization investment growth. Coming in with an adoption rate of 48% is asset performance optimization. This use case is expected to see a slight decrease in investment in 2024, with Asia-Pacific companies being the only ones foreseeing increased investment by 5% on average.
IoT for asset performance optimization is the modern version of asset performance management, which describes methods of capturing and integrating data, visualizing it, and analyzing it to improve the reliability and availability of physical assets. It combines state-of-the-art data-capture and integration tools (like IoT gateways) and software tools (like IoT platforms) to analyze how assets can operate and be maintained at optimum levels (e.g., optimized asset speed settings, optimized material input settings, or optimized maintenance intervals).
The top KPI affected by asset performance optimization is overall equipment effectiveness (OEE). On average, a major rollout of this use case improves OEE by 9.5%.
When US-based Longroad Energy acquired a 145-megawatt wind farm, it realized the turbines were not yielding as much output as expected due to incorrect setup. Longroad partnered with WindESCo , a US-based renewable energy performance analytics company, which implemented its Swarm System to acquire real-time turbine data, such as angle and energy generated. Data collected by the Swarm System are stored on a cloud server, which feeds into an analytics platform that determines the optimal angles and other turbine settings, optimizing the performance of these assets. As a result, Longroad Energy experienced a 2.5% increase in annual energy production and an annual revenue increase of $430,000.
9. Remote asset monitoring
Remote asset monitoring definition (by IoT Analytics) Utilizing IoT to monitor assets remotely in a read-only format for performance tracking
Remote asset monitoring drops from most adopted use case while seeing strong growth. Approximately 48% of respondents reported adopting remote asset monitoring, up from 34% in 2021. Interestingly, this use case was the most adopted in 2021. At that time, IoT Analytics noted that remote asset monitoring was the cheapest and easiest to set up due to its simplicity compared to other use cases. With other, more complex use cases surpassing remote asset monitoring while it grew significantly, it becomes even harder to believe that IoT is failing. Rather, companies have realized the benefits of IoT use cases and invested more in them.
The top KPI affected by remote asset monitoring is costs. On average, a major rollout of this use case reduced costs by 6.6%.
“We have millions of sensors collecting over 5 trillion rows of data that our AI models, combined with our conventional models used to monitor equipment 24 hours a day, 7 days a week, alerting engineers to anomalies from a distance.” Wael Sawan – CEO, Shell plc , February 01, 2024
10. Location tracking
Location tracking definition (by IoT Analytics) Employing IoT for real-time location tracking of products/assets/devices
Location tracking is the top connected products use case. Approximately 45% of companies in the survey have adopted location tracking. It is also the only connected product use case to make this list of top 10 IoT use cases. IoT location can be applied across various environments, including warehouses, factories, and outdoor work sites. The location data gathered from the machines or devices help companies locate their equipment and personnel, optimize routing, improve asset utilization, and enhance safety. Tracking the location of an asset can also be beneficial to both the vendor of the products (e.g., by understanding usage patterns) and to the user (e.g., by finding a lost item or by mitigating theft).
The top KPI that is affected by location tracking is revenue. On average, a major rollout of this use case improves revenue of the company selling the connected product by 1.6%.
Additional insights from the IoT Use Case Adoption Report 2024 The report shares the top KPIs that respondents’ companies use to measure the success of their IoT strategies by industry. Zooming in on the energy sector as an example, 88% of energy companies, on average, put high importance on decreasing the average time it takes to detect cybersecurity incidents.
Defining IoT
IoT Analytics defines the IoT as connected physical objects that can exchange data to or from one location to another (either directly or indirectly via gateways/hubs). These objects need to be uniquely identifiable and possess the ability to autonomously collect data about their environment. An IoT use case utilizes IoT devices.
Classifying IoT use cases
When looking at IoT use cases, IoT Analytics has four ways to classify them:
- By endpoint
- By functionality
- By application area
- By business objective
In the IoT use case adoption report, IoT Analytics used a mix of functionality and application area . For example, prediction is a functionality, and maintenance is an application area, resulting in predictive maintenance .
Grouping IoT use cases
The report covers 27 IoT use cases and groups them into three categories: Smart operations, smart supply chains, and connected products. The list of the 27 IoT use cases can be found on the report page .

Note : This article was updated in September 2024 to include the latest market data and insights from IoT Analytics.
Article written by Philipp Wegner on October 13, 2021.
The 10 most adopted IoT Use Cases 2021
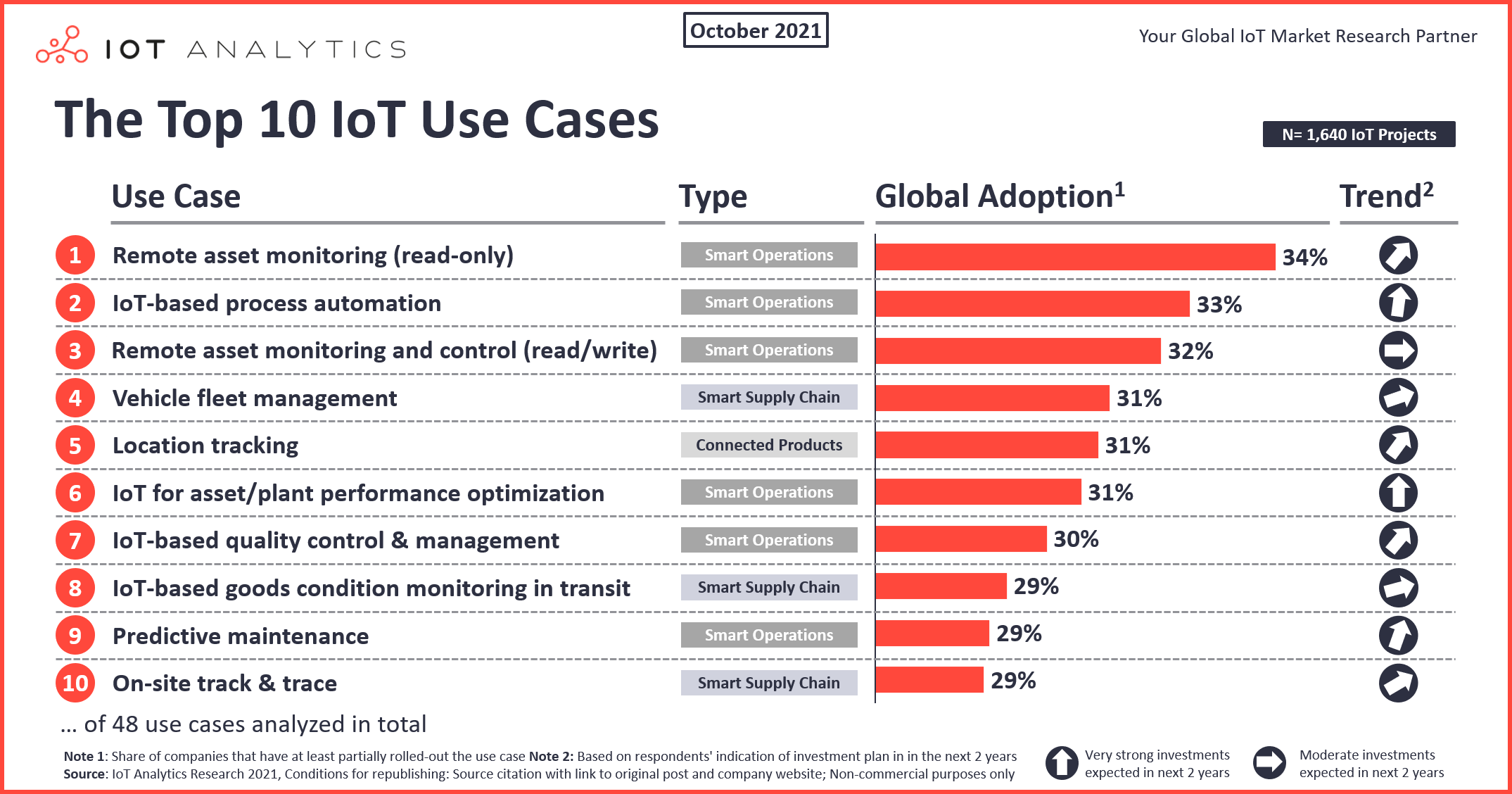
Six of the top 10 IoT use cases today (ranked by adoption) aim at making operations smart, thus improving companies’ production processes for manufacturing, enhancing maintenance operations, or advancing any other operations (e.g., energy generation in the case of an energy company, running healthcare operations in the case of a hospital, or running store operations in the case of a retail company). Three of the top 10 use cases are related to smart supply chains, and only one is related to smart products in the field.
Here are the 10 most adopted use cases, ranked by their adoption rate:
1. Read-only Remote Asset Monitoring
Not surprisingly, the simplest IoT use case is also the most adopted. Read-only remote asset monitoring refers to assets that are connected from afar in a read-only manner (i.e., one can visualize the asset data, but one cannot send back any commands to the asset itself). This use case is one of the easiest and cheapest to set up due to its simplicity. In many cases, remote asset monitoring supersedes the error-prone and costly manual task of checking and documenting asset states in person. Adoption in 2020 was clearly accelerated by the pandemic and is expected to grow even further, as 36% of interviewees say they plan to invest significantly in this use case in the next two years.
Adopter’s quote
“In the future, our engineers and plant operations staff will not need to sit in cars to go from their office location to another sub-station or satellite equipment room to perform daily routine activities. Routine read-only activities could be done more frequently, which could indirectly contribute to the reliability of control systems.” Senior operations manager of a mining company in Qatar
Hindustan Coca-Cola Beverages Pvt. Ltd. , located near Pune, India, adopted remote asset monitoring for its PET and can-bottling lines. T https://aiplindia.com/case-study/ he real-time and continuous monitoring of critical parameters (e.g., syrup flow rate, can-rinse pressure, and water temperature) replaced its MS Excel-based manual reporting. In this specific case, the company combined the remote connectivity of its assets with a condition-monitoring use case that generates alarms based on predefined conditions.
| Use case definition (by IoT Analytics)
Remote Asset Monitoring (read-only) = Real-time, one-way data streaming from machinery/equipment to an offsite location (e.g., cloud), making data accessible from anywhere.
2. IoT-based Process Automation
IoT-based process automation has been rolled out by 33% of companies. This type of process automation describes operational processes that were either entirely manual in the past or relied on antiquated, industrial-automation setups but have now been upgraded with state-of-the-art hardware and software. Companies that introduce this use case to upgrade their existing setups often do so to add flexibility and agility in the operations process so that specific process steps can be changed in the future. This becomes important because companies are increasingly interested in aligning their manufacturing and operations processes to ever-changing customer demands.
“Our manufacturing processes used to have many paper-based steps involved. IoT process automation has reduced many of these paper-based processes, resulting in a reduction in the number of errors, labour cost and real-time access to data.” CIO of a food and beverage manufacturer in Canada
An Australian farmer , reported he was able to use 20% less water thanks to a new IoT-based irrigation system supplied by Lindsay , a US-based manufacturer of pivot-irrigation systems. Farmers increasingly adopt smart IoT-based irrigation systems to automate the process of irrigation and thereby enhance their crop yields.
IoT-based Process Automation = The use of real-time data from connected assets to improve an entire operational process (e.g., a manufacturing process).
3. Remote Asset Monitoring and Control (read/write)
“Read/Write remote asset monitoring and control” is the extension of “Read-only remote asset monitoring.” On top of “reading” the assets data, with this setup one can also communicate back and thereby influence asset control from afar (i.e., “writing” data back).
Just like the read-only asset monitoring use case, this use case was accelerated by the COVID -19 pandemic as service teams, engineers, and other staff needed to find ways to reach an asset that needed their attention while being in a different location.
Because of the added complexity and security risk of controlling an asset, on top of just simply monitoring, this use case comes with significantly higher costs of installation and maintenance. However, it has been proven that such solutions pay off in a relatively short time: Of those decision makers whom IoT Analytics interviewed, 51% reported amortization in less than 24 months.
“Remote monitoring and control of freezers has saved costly materials before being ruined.” Research and development (R&D) manager of a manufacturing company in UK
Schlumberger , an oilfield service company, recently adopted a monitoring and control solution from Advantech and ReStream . These companies had partnered up to supply and develop a new oilfield fluid-monitoring system based on LTE connectivity. The project helped to achieve flow assurance, ensure asset integrity, and optimize production. It also helped to increase labor safety. Oilfield companies suffer from a dynamic chemical environment that, if unchecked, can lead to premature wear, lost productivity, and the release of lethal poisonous gases.
Remote Asset Monitoring and Control (read/write) = Real-time, two-way data streaming of machinery/equipment from/to an offsite location, enabling data access and the sending of commands from anywhere.
4. Vehicle Fleet Management (track/trace)
The management of vehicles in a fleet is the number one IoT supply chain use case right now. The larger the fleet of trucks (or other means of transport) to manage, the higher the complexity. Cross-border fleet management can be especially overwhelming, which is why 31% of companies have rolled out a professional vehicle fleet management solution to gather real-time information.
Today, most fleet management solutions are reliant on wide-area connectivity, such as cellular (2G, 3G, 4G). Several new, low-cost IoT satellite technologies have recently been launched and promise to add another option to this use case so that vehicle fleets are always truly connected at a reasonable price. New companies include Hiber (IoT-focused satellite network) and Starlink (part of SpaceX). Both plan to send thousands of new satellites into space in the coming years to provide low-latency, high-bandwidth connectivity globally.
“Now we know virtually in real time where our wagons are located, which routes we can optimize, and where there is potential for savings for our customers.” Suzy Verachten, project leader, Lineas (European Rail Freight Operator)
Lineas , the largest private rail freight operator in Europe, managed to increase capacity utilization of its fleet by more than 40 percent by implementing the Bosch fleet management solution.
Vehicle Fleet Management (track/trace) = Tracking and tracing the location of individual vehicles either on site while in transit or as general fleet management.
5. Location Tracking (e.g., GPS)
Not every company sells smart-connected IoT products, but of those that do, tracking the location of the asset is the number one use case (31% of companies in our interview set have adopted it). The results from this interview series are in line with results from the IoT Commercialization & Business Model Report 2020 , which found that geolocalization was also the number one use case in terms of customer adoption when original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) were asked which smart product features their end customers were adopting as part of their IoT-enabled assets. Location tracking is therefore important for developing a successful IoT business model .
Tracking the location of an asset can be beneficial to both the vendor of the products (e.g., by understanding usage patterns) and to the user (e.g., by finding a lost item or by mitigating theft).
“Connectivity means we can monitor distance covered, send service alerts, or lock the bike remotely. Things become even more interesting when we mesh this data with other transport data. If we can map the routes of thousands of cyclists, could we help urban planners develop better cycling infrastructure?” Taco Carlier, co-founder, VanMoof
VanMoof, an Amsterdam-based e-bike manufacturer, offers an anti-theft service to its customers that is based on the location tracking of a bike. For a monthly fee, the company sends its “bike hunters” if a customer’s bike is stolen. The bikes are connected and tracked by a combination of Bluetooth and cellular networks. This allows the company to keep its promise of recovering the bike in up to 70% of cases.
Location Tracking (e.g., GPS) = Tracking product location to determine its movement and geographic position.
6. IoT for Asset/Plant Performance Optimization
Asset performance management (APM) is a term in manufacturing to describe methods of capturing and integrating data, visualizing it, and analyzing it to improve the reliability and availability of physical plant–floor assets. IoT for asset/plant performance optimization is the modern version of APM. It integrates state-of-the-art data-capture and integration tools (like IoT gateways) and software tools (like IoT platforms) to analyze how assets can be run and maintained at optimum levels (e.g., optimized asset speed settings, optimized material input settings, or optimized maintenance intervals).
More than 30% of companies in our interview set have adopted IoT for asset/plant performance optimization. With 42% of companies planning to invest significantly in IoT for this purpose, it is among the use cases with the highest expected growth rate.
“The use of IoT for plant performance optimization has been a success since it now allows us to run our CHP power utilities at optimal levels based on variable fuel mix and plant loads for steam and power.” CEO, manufacturing: chemicals and chemical products , India
A beverage manufacturer that was running mostly older equipment used an IoT solution provided by Relayr in one of its bottling plants, which produces 1.2 million bottles per day per production line. It achieved improvements of 11% in performance and 8% in quality. Implementing an IoT retrofit kit and an IoT gateway, the company was able to identify the processes responsible for 90% of the plant’s downtime. Based on the IoT data collected from the legacy machinery of different manufacturers, the company was able to address several issues (e.g., changing the control logic of the machines).
IoT for Asset/Plant Performance Optimization = The use of real-time data from connected assets to optimize individual asset health for better operations performance at a site.
7. IoT- based Quality Control & Management
IoT-based quality control and management involves the use of machine vision or other IoT sensor data to detect quality issues in real time during operations. The use case pays off particularly quickly: Of the 30% of companies that have implemented this IoT use case, two-thirds report amortization in fewer than 24 months.
“We can now tell quickly if the environmental parameters are not quite right at some point, either within the paint shop or in one of the buffer areas. It takes a lot of data to do this, which we collect throughout the process, evaluate historically and analyse in real time” Martin Hilt, innovation and digitalization officer at BMW
A leading global automobile manufacturer automated the testing of the electronic functionality of its cars during the manufacturing process. As the company was adding greater electronic functionality to the cars to stay current with technological developments, it was looking to find ways to optimize its time-consuming, manual method of checking the operation of electronic parts. With the help of Cognizant , the company was able to completely automate vehicle testing and also implement a mixed-mode validation to simulate missing parts that would arrive late due to unforeseen supply chain issues. The solution realized a positive return on investment in four months.
IoT- based Quality Control & Management = The use of IoT sensor data or machine vision to monitor operational process parameters and detect faults (in real time) with the goal of reducing scrap/rework.
8. IoT-based goods condition monitoring in transit
Monitoring the conditions of goods is essential in industries such as pharmaceuticals or food and beverage and can even be seen as a way to help tackle the global food shortage. Temperature sensor data is one of the most important sensor values for this use case; it guarantees the safety of the final product by close monitoring throughout the entire supply chain, both in transit and in storage.
Condition-monitoring solutions were used by 29% of the interviewed decision makers as part of their digital supply chain initiatives.
“The assessment [of goods in transit] was an eye-opener, because we never looked at supply chain risk holistically before. Now we know where the risks are.” An D’haenens, logistics manager EMEA, DuPont
A global life sciences company worked with DHL to enable pallets with smart sensors. The sensors are equipped with low-power wide-area (LPWA) connectivity and track geographic location, movement, delay, shock, and temperature. This ability has enabled the life science company to reduce its life-cycle costs by 6 to 7%, with reported reliability of nearly 100%.
IoT-based goods condition monitoring in transit = The use of IoT sensor data to monitor the condition of transported goods and ensure they remain safe and are not exposed to the wrong temperatures or shocks.
9. Predictive Maintenance
To forecast the remaining useful life of assets and ensure they are repaired before they fail, 29% of all companies have invested in solutions at the intersection of artificial intelligence and maintenance. As IoT Analytics highlighted in a recent blog post, predictive maintenance (PdM) is an en vogue topic, with 40% of interviewed decision makers planning to invest significant amounts of money in the coming two years.
“PdM enabled us to actively monitor highly critical assets, provided us with multiple feeds of various data points (temp, vibration, throughput), allowed [us] to perform analysis of the asset health in real time, and helped us to prevent the need [for] reactive maintenance actions for critical assets.” IT director at an Oil&Gas company in the United States
Colgate-Palmolive Company , a US-based consumer goods manufacturer, leveraged a predictive maintenance solution to optimize its manufacturing capacity and prevent costly downtime. It installed wireless sensors on 2,000 machines (including tube makers and liquid machines) to collect machine data. The predictive maintenance solution detected increased temperatures and alerted staff, thereby preventing nearly 200 hours of downtime and a missing output of 2.8 million tubes of toothpaste.
Predictive Maintenance = The use of real-time IoT sensor data and artificial intelligence (AI) techniques to determine when maintenance should be performed on specific equipment.
10. On-Site Track and Trace
The availability of low-cost sensors and trackers has made it easy and relatively cheap to track goods and tools at construction sites, ports, and even inside buildings (e.g., factories). Of the experts interviewed, 29% have implemented such a solution. The median spending for a fully functional, on-site track-and-trace solution (in our interview set) is only $25,000—one of the lowest in the data set. Costs can scale up, however, as more and more assets get connected.
“Having On-Site Track & Trace has improved our efficiency [and] reduced labor time for tracking items (we have almost 1,000 stock-keeping units). We are now also able to check stock balances in real time.” Head of IT at a retailer in Singapore
Continental , a German automotive supplier, implemented KINEXON’S real-time locating solution at its logistics center and production site in Regensburg. More than 50 transportation vehicles and more than 3,000 load carriers are tracked live inside the 30,000 m² building sites, allowing Continental to locate each of these items within a precision of several centimeters (inches), thereby creating a transparent material flow in the supply chain and increasing overall throughput.
On-Site Track and Trace = Tracking and tracing goods while on site (e.g., at production sites, ports, logistics centers, or warehouses).
More information and further reading
Are you interested in learning more about iot use cases.

Download a sample of the full adoption report
The sample of the report gives you a holistic overview of the available analysis (outline, key slides). The sample also provides additional context on the topic and describes the methodology of the analysis.
Company email address
Company name
Country Aruba Afghanistan Angola Anguilla Åland Islands Albania Andorra United Arab Emirates Argentina Armenia American Samoa Antarctica French Southern Territories Antigua and Barbuda Australia Austria Azerbaijan Burundi Belgium Benin Bonaire, Sint Eustatius and Saba Burkina Faso Bangladesh Bulgaria Bahrain Bahamas Bosnia and Herzegovina Saint Barthélemy Belarus Belize Bermuda Bolivia, Plurinational State of Brazil Barbados Brunei Darussalam Bhutan Bouvet Island Botswana Central African Republic Canada Cocos (Keeling) Islands Switzerland Chile China Côte d'Ivoire Cameroon Congo, Democratic Republic of the Congo Cook Islands Colombia Comoros Cabo Verde Costa Rica Cuba Curaçao Christmas Island Cayman Islands Cyprus Czechia Germany Djibouti Dominica Denmark Dominican Republic Algeria Ecuador Egypt Eritrea Western Sahara Spain Estonia Ethiopia Finland Fiji Falkland Islands (Malvinas) France Faroe Islands Micronesia, Federated States of Gabon United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland Georgia Guernsey Ghana Gibraltar Guinea Guadeloupe Gambia Guinea-Bissau Equatorial Guinea Greece Grenada Greenland Guatemala French Guiana Guam Guyana Hong Kong Heard Island and McDonald Islands Honduras Croatia Haiti Hungary Indonesia Isle of Man India British Indian Ocean Territory Ireland Iran, Islamic Republic of Iraq Iceland Israel Italy Jamaica Jersey Jordan Japan Kazakhstan Kenya Kyrgyzstan Cambodia Kiribati Saint Kitts and Nevis Korea, Republic of Kuwait Lao People's Democratic Republic Lebanon Liberia Libya Saint Lucia Liechtenstein Sri Lanka Lesotho Lithuania Luxembourg Latvia Macao Saint Martin (French part) Morocco Monaco Moldova, Republic of Madagascar Maldives Mexico Marshall Islands North Macedonia Mali Malta Myanmar Montenegro Mongolia Northern Mariana Islands Mozambique Mauritania Montserrat Martinique Mauritius Malawi Malaysia Mayotte Namibia New Caledonia Niger Norfolk Island Nigeria Nicaragua Niue Netherlands, Kingdom of the Norway Nepal Nauru New Zealand Oman Pakistan Panama Pitcairn Peru Philippines Palau Papua New Guinea Poland Puerto Rico Korea, Democratic People's Republic of Portugal Paraguay Palestine, State of French Polynesia Qatar Réunion Romania Russian Federation Rwanda Saudi Arabia Sudan Senegal Singapore South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha Svalbard and Jan Mayen Solomon Islands Sierra Leone El Salvador San Marino Somalia Saint Pierre and Miquelon Serbia South Sudan Sao Tome and Principe Suriname Slovakia Slovenia Sweden Eswatini Sint Maarten (Dutch part) Seychelles Syrian Arab Republic Turks and Caicos Islands Chad Togo Thailand Tajikistan Tokelau Turkmenistan Timor-Leste Tonga Trinidad and Tobago Tunisia Türkiye Tuvalu Taiwan Tanzania, United Republic of Uganda Ukraine United States Minor Outlying Islands Uruguay United States of America Uzbekistan Holy See Saint Vincent and the Grenadines Venezuela, Bolivarian Republic of Virgin Islands, British Virgin Islands, U.S. Viet Nam Vanuatu Wallis and Futuna Samoa Yemen South Africa Zambia Zimbabwe
Which specific insights are you interested in?
IMPORTANT: Please tick the box prior to sending your request. All fields are required.
I agree that IoT Analytics GmbH may process my information to contact me and notify me of future research updates in accordance with its privacy statement .
Already a subscriber? See your reports here →
The IoT Use Case Adoption Report 2024 is a 418-page report on the adoption, spending, ROI, future investments for use cases in smart operations, supply chain and connected products. Based on insights from 200 IoT adopters across various verticals, regions, company sizes
This report provides answers to the following questions (among others):
- What are the most adopted IoT use cases (out of a list of 27)?
- Which IoT use cases have the highest return on investment (ROI)?
- Which KPIs are most important for a company’s IoT strategy, and how are the KPIs affected by implementing IoT use cases?
- How much do companies spend on hardware, software, and services for individual IoT use cases?
- Which IoT use cases do companies plan to invest in the most in 2024?
- Who are the leading vendors for IoT use cases, how satisfied are end users, and what are the strengths and weaknesses of the top vendors?
- What challenges do IoT end users face when implementing use cases?
- How do companies ensure their workforce has the necessary IoT skills?
- How much are companies’ IoT strategies impacting their sustainability goals?
Related publications
You may be interested in the following publications:
- IoT Use Case Adoption Report 2024
- State of IoT Summer 2024
- IoT Startup Landscape and Database 2024
- IoT Enterprise Projects Adoption Report 2024
Related market data
You may be interested in the following IoT market data products:
- Global IoT Enterprise Spending
Related articles
You may also be interested in the following recent articles:
- State of IoT 2024: Number of connected IoT devices growing 13% to 18.8 billion globally
- IoT Startup Landscape 2024: 7 notable insights
- IoT market update: Enterprise IoT market size reached $269 billion in 2023, with growth deceleration in 2024
- Top 5 enterprise technology priorities: AI on the rise, but cybersecurity remains on top
Are you interested in continued IoT coverage and updates?
Subscribe to our newsletter and follow us on LinkedIn and Twitter to stay up-to-date on the latest trends shaping the IoT markets. For complete enterprise IoT coverage with access to all of IoT Analytics’ paid content & reports including dedicated analyst time check out the Enterprise subscription.
Share this with others:

Dimitris Paraskevopoulos
Iot research newsletter.
Sign up for our exclusive email updates today, and receive the latest market insights before others.
Most Recent Articles
- The role of eSIM for IoT: Better security, simplified roaming, and easier provisioning—but only 33% of cellular IoT devices use it
- What CEOs talked about in Q3 2024: Practical AI applications, renewable energy sources, and unpredictable IT outages
- Avoiding digital transformation icebergs: Can industrial DataOps steer projects away from disaster?
- State of private 5G in 2024: Key growth trends, use cases, and forecast
Search the Blog
Blog categories.
- Industrial IoT
- Non-industrial IoT applications
- IoT Platforms & Software
- IoT Connectivity & Hardware
- General IoT
IoT Analytics, founded and operating out of Germany, is a leading provider of strategic IoT market insights and a trusted advisor for 1000+ corporate partners worldwide.
Learn more about how we can help you achieve your goals faster with the right data-driven insights and intelligence.
We need your consent before you can continue on our website. We use cookies and other technologies on our website. Some of them are essential, while others help us to improve this website and your experience. You can find more information about the use of your data in our privacy policy .
- External Media
Accept only essential cookies
Individual Privacy Preferences
Cookie Details Privacy Policy Legal Notice
We use cookies and other technologies on our website. Some of them are essential, while others help us to improve this website and your experience. You can find more information about the use of your data in our privacy policy . Here you will find an overview of all cookies used. You can give your consent to whole categories or display further information and select certain cookies.
Accept all Save Accept only essential cookies
Essential cookies enable basic functions and are necessary for the proper function of the website.
Show Cookie Information Hide Cookie Information
| Name | |
|---|---|
| Provider | Owner of this website, |
| Purpose | Saves the visitors preferences selected in the Cookie Box of Borlabs Cookie. |
| Cookie Name | borlabs-cookie |
| Cookie Expiry | 1 Year |
Statistics cookies collect information anonymously. This information helps us to understand how our visitors use our website.
| Accept | |
|---|---|
| Name | |
| Provider | Google Ireland Limited, Gordon House, Barrow Street, Dublin 4, Ireland |
| Purpose | Cookie by Google used for website analytics. Generates statistical data on how the visitor uses the website. |
| Privacy Policy | |
| Cookie Name | _ga,_gat,_gid |
| Cookie Expiry | 2 Months |
Marketing cookies are used by third-party advertisers or publishers to display personalized ads. They do this by tracking visitors across websites.
| Accept | |
|---|---|
| Name | |
| Provider | Crisp IM SAS |
| Purpose | Cookie by Crisp used for live chat and messaging. |
| Privacy Policy | |
| Cookie Name | crisp-client* |
| Accept | |
|---|---|
| Name | |
| Provider | HubSpot Inc., 25 First Street, 2nd Floor, Cambridge, MA 02141, USA |
| Purpose | HubSpot is a user database management service provided by HubSpot, Inc. We use HubSpot on this website for our online marketing activities. |
| Privacy Policy | |
| Host(s) | *.hubspot.com, hubspot-avatars.s3.amazonaws.com, hubspot-realtime.ably.io, hubspot-rest.ably.io, js.hs-scripts.com |
| Cookie Name | __hs_opt_out, __hs_d_not_track, hs_ab_test, hs-messages-is-open, hs-messages-hide-welcome-message, __hstc, hubspotutk, __hssc, __hssrc, messagesUtk |
| Cookie Expiry | Session / 30 Minutes / 1 Day / 1 Year / 13 Months |
| Accept | |
|---|---|
| Name | |
| Provider | OneSignal, Inc. |
| Purpose | Cookie by OneSignal used for in-browser push notifications. |
| Privacy Policy | |
| Cookie Name | __cf_bm |
Content from video platforms and social media platforms is blocked by default. If External Media cookies are accepted, access to those contents no longer requires manual consent.
| Accept | |
|---|---|
| Name | |
| Provider | Meta Platforms Ireland Limited, 4 Grand Canal Square, Dublin 2, Ireland |
| Purpose | Used to unblock Facebook content. |
| Privacy Policy | |
| Host(s) | .facebook.com |
| Accept | |
|---|---|
| Name | |
| Provider | Google Ireland Limited, Gordon House, Barrow Street, Dublin 4, Ireland |
| Purpose | Used to unblock Google Maps content. |
| Privacy Policy | |
| Host(s) | .google.com |
| Cookie Name | NID |
| Cookie Expiry | 6 Month |
| Accept | |
|---|---|
| Name | |
| Provider | Meta Platforms Ireland Limited, 4 Grand Canal Square, Dublin 2, Ireland |
| Purpose | Used to unblock Instagram content. |
| Privacy Policy | |
| Host(s) | .instagram.com |
| Cookie Name | pigeon_state |
| Cookie Expiry | Session |
| Accept | |
|---|---|
| Name | |
| Provider | Openstreetmap Foundation, St John’s Innovation Centre, Cowley Road, Cambridge CB4 0WS, United Kingdom |
| Purpose | Used to unblock OpenStreetMap content. |
| Privacy Policy | |
| Host(s) | .openstreetmap.org |
| Cookie Name | _osm_location, _osm_session, _osm_totp_token, _osm_welcome, _pk_id., _pk_ref., _pk_ses., qos_token |
| Cookie Expiry | 1-10 Years |
| Accept | |
|---|---|
| Name | |
| Provider | Twitter International Company, One Cumberland Place, Fenian Street, Dublin 2, D02 AX07, Ireland |
| Purpose | Used to unblock Twitter content. |
| Privacy Policy | |
| Host(s) | .twimg.com, .twitter.com |
| Cookie Name | __widgetsettings, local_storage_support_test |
| Cookie Expiry | Unlimited |
| Accept | |
|---|---|
| Name | |
| Provider | Vimeo Inc., 555 West 18th Street, New York, New York 10011, USA |
| Purpose | Used to unblock Vimeo content. |
| Privacy Policy | |
| Host(s) | player.vimeo.com |
| Cookie Name | vuid |
| Cookie Expiry | 2 Years |
| Accept | |
|---|---|
| Name | |
| Provider | Google Ireland Limited, Gordon House, Barrow Street, Dublin 4, Ireland |
| Purpose | Used to unblock YouTube content. |
| Privacy Policy | |
| Host(s) | google.com |
| Cookie Name | NID |
| Cookie Expiry | 6 Month |
Privacy Policy Legal Notice
IoT Applications: 7 Real-World Examples Across Industries
Healthcare, supply chain management, agriculture, and manufacturing – these are just a few examples of industries currently being revolutionized by the Internet of Things. Explore 7 types of IoT applications across various sectors, draw inspiration from real-world examples, and see how this technology can reshape your business.
Agnieszka Mroczkowska Content Marketing Manager
Karol wrótniak mobile developer.
Table of contents
There’s a reason why the Internet of Things market is expected to be worth over $1 trillion by 2024. IoT applications automate processes and generate brand-new product offerings thanks to the continuous connection between machines, humans, and data. Together with enhanced sensor connectivity and new technologies like artificial intelligence, IoT has the potential to drive innovation across industries ranging from healthcare to manufacturing.
Apart from technology improvements, the Internet of Things also presents a number of solutions addressing the most pressing concerns of our time: climate change, access to healthcare services, and growing urbanization. To achieve their sustainability goals and optimize operations, companies and governments are investing in IoT-based energy and resource management solutions such as smart grid technology or telemedicine.
This article dives into real-world IoT applications that perfectly encapsulate the potential of this technology for solving the most important issues societies are facing now.
What is the Internet of Things (IoT)?
The Internet of Things (IoT) is a network of physical objects embedded with sensors, software, and other technologies for connecting and sharing data with other devices and systems over the Internet.
The global number of IoT devices is expected to nearly double, from 15.1 billion in 2020 to more than 29 billion in 2030 .
IoT technology has emerged as one of the most important technologies in recent years, enabling us to connect common objects to the internet (embedded devices) that include things such as kitchen appliances, vehicles, vibrators (like OhMiBod ), digital displays (like Loop ), thermostats, and baby monitors, building seamless communication between people, processes, and things.
Thanks to IoT, physical objects can exchange and gather data with minimum human interaction using smart sensors, the cloud, big data, analytics, and mobile devices. Such digital systems can record, monitor, and alter each interaction between linked devices in a hyperconnected environment where the physical and digital worlds come together
What are the core components of IoT?
Device connection layer.
The device connection layer is made up of devices and sensors. Smart sensors continually collect data from their surroundings and relay it to the following layer. The most recent semiconductor technology approaches can manufacture tiny smart sensors for a variety of applications.
Some common types of sensors include:
- Thermostats and temperature sensors,
- Pressure sensors,
- Light intensity sensors,
- Humidity/moisture level sensors,
- RFID labels.
Connectivity via wireless networks
The majority of current smart devices and sensors can connect to low-power wireless networks such as Wi-Fi, Bluetooth Low Energy, ZigBee, Z-wave, LoRAWAN, and others. Each of these wireless technologies offers unique advantages and disadvantages in terms of power, data transmission rate, and overall efficiency.
IoT gateway
An IoT gateway is responsible for managing the bidirectional data flow between multiple networks and protocols. The gateway can also translate multiple network protocols and ensure the compatibility of linked devices and sensors.
Gateways can be set to locally analyze data obtained from thousands of sensors before passing it to the next level. With higher-order encryption algorithms, IoT gateways provide a certain level of security for the network and transmitted data, serving as a barrier between devices and the cloud.
The Internet of Things generates vast amounts of data from devices, apps, and users, which must be managed efficiently. The IoT cloud provides the capabilities required for collecting, processing, managing, and storing massive volumes of data in real-time. Businesses and services can access this data remotely for enhanced decision-making.
The Internet of Things cloud is essentially a complex, high-performance network of computers designed to do high-speed data processing on billions of devices, traffic control, and precise analytics.
IoT analytics
Transforming analog data from billions of smart devices and sensors into usable insights that teams can use for decision-making is a vital part of IoT.
For IoT systems to be managed and optimized as a whole, they need smart analytics solutions. For example, real-time smart analytics lets engineers find problems with the data devices collect and act quickly to prevent a minor issue from snowballing into a massive problem.
User interface
IoT applications / simple websites equipped with user interfaces are the visible, physical components of the IoT system that users can interact with. Modern approaches propose a more interactive design to simplify complicated processes into an understandable interface – for example, simple touch panel controls.
In today’s competitive market, user interface design is a key factor in customers’ purchasing decisions. Users are more likely to purchase new devices or smart gadgets if they’re easy to use and compatible with popular wireless protocols.
Do all IoT projects require the same components?
In IoT (Internet of Things) projects, the components such as devices/sensors, gateways, cloud services, analytics, apps (user interfaces), and wireless networks can vary depending on the project’s specific needs and objectives.
- Devices/sensors and wireless networks are essential in every IoT system for data collection and communication.
- Wireless networks are a fundamental component in the majority of IoT systems, facilitating the transmission of data from devices/sensors. While almost always necessary, there are some IoT setups where alternative communication methods (like wired connections) might be used, especially in environments where wireless communication is impractical or poses security risks.
- Gateways , which link devices/sensors to the cloud, are commonly needed but may be omitted in simpler setups where devices directly connect to the cloud.
- Cloud services are widely used for data storage and processing in IoT, although some projects might manage these tasks locally or through decentralized methods.
- Analytics plays a key role in projects focused on data analysis and decision-making, but might not be central to basic data-gathering tasks.
- The user interface , whether it’s a mobile/web app, an Apple Watch app, or a simple web page, is critical when human interaction or monitoring is required, but it is not necessary for automated, behind-the-scenes processes.
To sum up, while certain components like devices/sensors and wireless networks are almost universally present, others, such as gateways or cloud services, may vary based on the complexity and specific needs of the project.
Why is IoT important today?
Businesses can boost efficiency and production by deploying IoT devices to automate and optimize operations . IoT sensors, for example, help to monitor equipment performance and detect or even address possible issues before they create downtime, lowering maintenance costs and increasing uptime.
Smart devices provide massive volumes of data that teams can use to make better-informed business decisions and create new products. IoT applications also provide insights into consumer behavior, market trends, and operational performance.
IoT technology also helps organizations save costs and boost profitability by automating repetitive tasks and reducing manual processes that are prone to human-made errors.
- You may also like: How Much Does it Cost to Develop an App in 2023? New Cost Breakdown
The Internet of Things plays a role in customer experience as well, helping businesses build more tailored and engaging experiences for customers . Retail is a great example of that – a store can implement IoT devices to track client movements in stores and give targeted offers depending on their actions.
Finally, there’s the sustainability benefit of IoT. Take the concept of smart cities as an example. It emerged as a potential solution to the environmental issues caused by growing urbanization. A survey from 2019 showed that 4 in 5 people believe that such cities can be created with IoT. Today, this number is likely even bigger.
7 Popular IoT applications across industries
Before we delve into the details, let’s take a brief look at the most popular types of IoT applications and their impact on changes across various industries:
1. IoT in healthcare
Connected devices in the healthcare industry, also known as the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT), are one of the fastest-growing segments of the IoT space, with a projected market value of $177 billion by 2026 .
Here are some examples of IoT applications in healthcare:
- Patient health monitoring – Doctors can use IoT applications to remotely monitor high-risk patients at home, such as the elderly and those with chronic conditions. Good examples of that are continuous glucose monitors (CGM) that use sensors placed into the skin to monitor diabetes patients, giving a bird’s-eye perspective of the patient’s hyperglycemia trends. Since these devices provide real-time and continuous data, doctors can adjust prescriptions and propose modifications as needed.
- Improved access to patient medical records – The Internet of Things also improves access to patient medical records by making real-time data available across various departments and professionals.
- Real-time data enhancing medical research – Until now, medical research has always relied on data obtained in a controlled setting or generated after the event. Vast amounts of real-time data via IoT significantly benefit research.
- Improved drug development and production – IoT is used by pharma companies to enhance the pharmaceutical production process. Lower medicine prices are the direct result of this. Another use case is smart inventory management.
- Telemedicine – During the COVID pandemic, the Internet of Things started to be used in a variety of ways, from telemedicine to vaccine cold chain monitoring.
A real-life example of a healthcare IoT app: QardioCore
Find the app on the App Store | Google Play Store
QardioCore is a smart device that works as an ECG monitor, which lets users better monitor health issues such as high blood pressure and cholesterol. It also provides data to healthcare facilities, which monitor illnesses like diabetes, heart problems, and weight gain without requiring physical visits.
QardioCore monitors heart rate and heart rate variability, skin temperature, respiration rate, and activity monitoring in addition to continually collecting ECG data, offering clinicians a better understanding of their patients’ entire heart health and behavior.
2. IoT & smart cities
A smart city is a city that uses sensors and cellular or wireless technologies in common areas like lampposts, electricity, and heat systems, as well as water and waste management systems.
Here are a few ways to incorporate IoT into the running of a city:
- Air pollution control – Air pollution is a major issue in every country throughout the world. Temperature, CO2 levels, smoke, and humidity can all be easily measured using current sensors. Modern cities use IoT to collect data on air quality and build mitigation strategies.
- Traffic management – Road sensors and traffic lights send data to IoT systems via smart lighting systems. When gathered over time, this data enables officials to examine traffic patterns during peak hours and develop bottleneck remedies. Commuters can use this data to evaluate which regions are busy and which other routes are available.
- Parking – Parking may sound trivial, but it plays a vital role in traffic management. Smart parking systems provide vehicles with real-time information about available unoccupied spaces.
- Waste, water, and electricity management – Sensors installed internally or externally in water meters help with water management, helping cities better understand consumption patterns. Water waste trends can be used to design an effective water recycling system. An IoT-powered smart waste management system creates a geographical map of trash production, starts the clearing process, and improves garbage segregation.
- Infrastructure management – Maintaining public infrastructure such as streetlights, roads, parks, and gas supply lines is expensive. Repair work in any of these creates disturbances in daily operations. Maintenance and monitoring systems based on IoT seek out symptoms of wear and tear while evaluating trends, helping cities save a significant amount of money thanks to predictive maintenance.
- Management of disasters – Disaster-prone locations can be linked to a warning system using the Internet of Things. A forest fire, for example, can be discovered and extinguished before it spreads out of control.
A real-life example of a smart city app: Parker
Find the app on the App Store | Google Play Store
Available across many cities in the United States, Parker directs drivers to available on-street and off-street parking lots/garages in real-time. Users can easily find prices, time limitations, operating hours, and parking regulations to park without anxiety. Users also benefit from easy mobile payment methods.
In places where Parker has real-time sensors, the app can provide real-time guidance with dynamic routing. It also features an automatic “Find My Car” feature that helps users locate their vehicles.
3. IoT in supply chain management
Supply chain management (SCM) is all about streamlining the flow of products and services from raw material purchases to customer delivery. Inventory management, fleet management, vendor connections, and planned maintenance are all part of this field.
Many companies were impacted by supply chain concerns during the pandemic, which inspired them to incorporate modern solutions based on IoT. The number of companies using IoT in supply chain management increases by 27% on average year over year .
The Internet of Things is used throughout the supply chain management process:
- Trackers – Shipping businesses often struggle to keep track of assets. This is where trackers help. They also let companies examine shipping routes to determine the quickest and most fuel-efficient routes. Other use cases are monitoring and regulating other characteristics such as container temperature and humidity.
- Smart routing – The Internet of Things technology lets teams redesign the supply chain process by offering smart routing options. This enhances the durability of supply chains.
- Real-time and remote fleet management – This solution guarantees a great experience for both managers and customers. Any transportation delays or problems can instantly alert the proper people thanks to the end-to-end communication between vehicles and managers and between vehicles and drivers. Aside from asset management, IoT also monitors vehicle health, ensuring that emissions regulations are obeyed.
A real-life example of a supply chain management IoT app: ZillionSource
ZillionSource combines the power of hardware with new technology, providing companies with insights into their asset monitoring or supply chain goods. In addition to global map tracing and trip notes, the IoT platform analyzes data and presents it in reports and graphs.
Even with millions of devices, the scalable and expandable platform runs seamlessly. Customization and security devices are handled via its business cloud application for dynamic control and its advanced pattern-recognition rule engine, which allows users to adjust and define rules according to their preferences.
4. IoT in agriculture
Agriculture stands to greatly benefit from the Internet of Things as governments around the world prioritize the expansion of agricultural systems. Farmers are using technology in farming to improve production yields and, at the same time, fight climate change by making their operations more sustainable. The global smart farming market will reach almost $30 billion by 2023 .
Here are some common IoT applications in agriculture:
- Sensors – They offer data on soil chemistry and fertilizer profiles, as well as CO2 levels, moisture, temperature, acidity level, and the presence of adequate nutrients. This data is key for understanding future harvest
- RFID chips – Agriculture companies can use them for livestock tracking to maintain track of an animal’s vitals, vaccination data, and whereabouts.
- Smart greenhouses – Instead of relying on changing weather patterns, a smart greenhouse uses microclimate to grow food. Sensors monitor and regulate all parameters, and light and water systems are automated.
- Smart irrigation – This is an Internet of Things application that regulates and effectively uses water in agriculture. The IoT system only starts the water flow when the soil reaches a specified level of dryness. It also cuts off the flow when a particular level is reached to cut down on waste caused by human error.
- Prediction farming – This is a technique of honing and implementing agricultural strategies based on information gathered over time. The data generated by sensors enables farmers to choose the best growth parameters and fertilizers.
A real-life example of an agriculture IoT app: Farmalyzer
Farmalyzer is a platform that connects IoT sensors, weather data, climate analysis, and horticulture advice. Users can get free weather data, soil maps, topographical maps, and satellite pictures.
The app also lets users manage weather stations and soil sensors. It includes a smartphone location service, AR mode for quickly locating sensors and effective recommendations for optimizing local growth management by accounting for microclimate differences.
- You may also like: What is Flutter App Development and How Can It Benefit Your Business?
5. IoT in energy
Utility companies are looking to IoT to improve energy efficiency. Energy meters, transmission lines, manufacturing plants, and distribution terminals can all have appropriate sensors to create a smart grid.
According to a McKinsey estimate , IoT in the energy sector might provide annual advantages of $40-70 billion by 2025.
Here are some examples of IoT applications in the energy sector:
- Sensors and the smart grid – Sensors have a rich array of use cases: they can generate notifications in the event of a power transmission breakdown at any point, detect line irregularities, keep track of energy consumption, and collect data on consumption at the regional, organizational, and individual levels.
- Reduction of carbon footprint – Data coming from sensors helps everyday users assess their energy use, take steps towards energy saving, and reduce their carbon footprints. It’s also a solution for reducing expenses when energy prices soar.
- Bringing together multiple energy sources – Utilities companies are departing from fuel-only systems and instead relying on a number of energy sources, including renewables, heat pumps, biomass, and others. Using a smart grid, they can easily switch between these various energy sources and make sure that specific parameters are in line with user expectations.
- Predictive maintenance – Smart grids and intelligent energy meters enable predictive maintenance, which significantly reduces operational costs.
A real-life example of an energy IoT app: Oma Helen
Oma Helen is a mobile app from the Finnish utilities provider Helen that offers unique insights into energy statistics and the fundamentals of energy consumption to individual users.
The app helps users manage their contract-related issues, get information on the energy use and output, right down to the hourly level, and see how their individual use affects the fixed pricing component of the contract.
- You may also like: Agile Roles and Responsibilities – From Theory to Practice
6. IoT in manufacturing
The Internet of Things is all about bringing physical items into the digital spotlight. What better place to use this than on the production floor? The Internet of Things (IoT) at the industrial level is known as Industrial IoT (IIoT), also called Industry 4.0 or the fourth wave of the industrial revolution.
The worldwide IoT manufacturing market was valued at $50.0 billion in 2021 and is expected to produce $87.9 billion by the end of 2026.
Here are some common applications of IoT in manufacturing:
- Maintenance management – Most manufacturers use enterprise asset management (EAM) and computerized maintenance management systems (CMMS). Combining them with IoT-enabled sensors increases the machine’s physical life while also ensuring availability and dependability.
- Real-time device monitoring – This allows predictive maintenance and optimal machine health. Condition-based maintenance (CBM) is a maintenance method that monitors asset health and conducts maintenance only when necessary. IoT facilitates this while also lowering expenses.
- Optimization of product development and quality testing – This area of innovation has the potential to enhance everything from packaging to management. The IIoT can automate many manual maintenance tasks, which in turn automates mass manufacturing, and leverage machine learning systems to constantly improve the output.
A real-life example of: Digital Factory Wizard
Find the app on the App Store | Google Play Store
Digital Factory Wizard is an app that allows users to track their factory floor activities in new ways. All the linked “things” are transformed into valuable data to help companies operate their businesses. Dedicated reports help to continually improve everyday procedures and employee performance.
7. IoT, wearables and consumer tech
Wearable technology is another tangible manifestation of the Internet of Things. Smartwatches, fitness trackers, smart eyeglasses, and even connected fabric are all examples of wearable technology. The worldwide consumer IoT technology market was valued at $221.74 billion in 2022, and it’s expected to reach $616.75 billion by 2032 .
Here are a few examples of IoT wearable devices and their functionalities:
- Notifications and reminders – Smartwatches can do anything from read text messages and display notifications to monitor locations and display reminders.
- Fintech wearables – Wearable payment devices include clothing, gadgets, and accessories that let users make contactless payments. Smartwatches, belts, jackets, fitness trackers, and even rings are the most popular types. They link the smartphone to the consumer’s bank account through services such as Apple Pay, Samsung Pay, and Google Pay.
- Augmented Reality – When combined with head-mounted augmented reality (AR) equipment, wearables give surgeons access to patient history, previous data collected, and real-time current data during surgery.
A real-life example: OhMiBod
OhMiBod for Apple Watch – it’s a remote intimacy app that allows partners to connect and control one another’s pleasure gadgets from anywhere in the world. It was launched at CES 2019.
A real-life example: WHOOP
WHOOP is a wearable device and mobile app that monitors sleep, strain, recovery, stress, and health biometrics 24 hours a day. The product provides individualized coaching based on user goals to help them achieve peak performance.
WHOOP converts data into actionable next steps and recommends anything from when to sleep to what habits to adopt to help users attain their objectives. WHOOP measures heart rate variability, resting heart rate, sleep, and respiratory rate to determine how prepared the user is to perform.
The future of the Internet of Things
Thanks to its ability to link a wide range of equipment and sensors to the internet, IoT has already transformed numerous industries, from manufacturing to healthcare. The potential value of IoT is growing. McKinsey estimates that its value will grow to $12.5 trillion globally by 2030 . But what’s in store for this fast-growing technology?
IoT security is one of the biggest challenges that impact the adoption of this technology trend. A solution to that is the shift to edge computing , which involves analyzing data on the device itself rather than transferring it to the cloud. Edge computing has the potential to reduce latency, increase dependability, and improve privacy and security.
You may also like:
- 8 Key IoT Security Challenges and Proven Solutions from the Field
- Today’s 11 IoT Challenges and Solutions That Work
- Why Flutter for IoT is Your Best Bet – Top 10 Reasons
Another IoT trend is the increased use of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) to evaluate data from connected devices. Businesses can obtain insights into IoT data by applying sophisticated analytics to it, but only systems based on machine learning algorithms can deliver accurate and valuable insights when circumstances change.
Moreover, alongside these advancements in AI and ML, there’s a growing integration of blockchain technology in the IoT landscape. It’s being used to improve security and privacy in the IoT as well. Data from an IoT device could be kept in a decentralized, tamper-proof ledger using blockchain, making it more secure and less subject to attack.
Our experience in IoT app development
If you’re looking for an IoT application development company , you’re in the right place. With over 10 years of experience, we specialize in building both native and Flutter-based IoT apps. Just to name a few, we’ve created OhMiBod , OhMiBod Remote for Apple Watch , and Loop .
Our work speaks for itself – just check out our reviews on Clutch . Skip the time-consuming in-house recruitment and tap into our experts from day one. Contact us .
IoT applications – wrap up
The Internet of Things has a bright future ahead of it, with numerous applications poised to transform industries and enhance our daily lives. The potential for IoT devices, systems, and apps is essentially unlimited, ranging from edge computing and AI to smart cities and smart farming.
We can expect even more fascinating advancements in the next few years as developers and businesses continue to innovate and push the boundaries of what is possible when using an IoT device.
Related posts
- Top Flutter Apps: Real-World Examples & Business Stories
- 5 Scrum Values: Guide for App Owners with Real-life Examples
- How to Measure Your Digital Product Success | Guide with Examples
- Driving Sustainability Awareness – Emerging Green Apps Trends & Examples
- User Story Mapping: Examples, Templates, and Best Practices | Guide for App Owners
About the authors
Agnieszka mroczkowska.
Content Marketing Manager
As a Content Marketing Manager with a deep dive into the tech world, Agnieszka brings over 6 years of experience in the IT industry. She excels at transforming complex app development topics into engaging reads, collaborating with our brilliant Developers, Business Analysts, Scrum Masters, Designers, and more to uncover insights. When not immersed in tech, Aga enjoys outdoor adventures and Lindy Hop dancing.
Karol Wrótniak
Mobile Developer
Flutter & Android Developer with 12 years of experience. A warhorse with impressive experience and skills in native and Flutter app development. Karol is probably the most active contributor to open source libraries you've ever met. He develops Gradle plugins and Bitrise steps, and he is engaged in many projects, in particular those related to testing. Karol has been engaged as a speaker in many events and meetups like DevFest, 4Developers Wrocław, JDD Conference, Linux Academy, and more. He is an active member of Google Developers Group Wrocław, Flutter Wrocław, and Bitrise User Group.
Hire experienced IoT development team
Together, we will get your project off the ground and achieve amazing results
Hey, good to see you!
We're Droids On Roids – digital product creators and consultants, turning ideas into industry benchmarks . We build software from concept to launch, and beyond. All under one roof.
See how we can help
- [Free] Digital product strategy workshop
- Digital product discovery services
- Digital product design services
- iOS (iPhone) app development services
- Android app development services
- Flutter app development services
- Kotlin Multiplatform app development
- Web app development services
Keep your budget safe, not sorry.
How? Through our Product Discovery. It's your finances' best friend, letting you:
- 👉 Verify your assumptions
- 👉 Fast-track your launch!
Knock, knock... Next super reads want to get to your inbox!
Let them in for the latest and greatest on creating digital products. No fluff, just real insights from the Droids On Roids pros.
- Ebook Flutter
- Ebook PO Guide
- Blog Newsletter
- Checklist Google Play
- Checklist iOS App Store
- Checklist Old Google Play
- Checklist Old iOS App Store
More discoveries await!
Droids on roids sa.
[email protected] Company Presentation VAT-UE: PL8971771342 KRS: 0000940155
- Mobile App Development
- Web App Development
- UI/UX App Design
- Product Design Workshops
- Android App Development
- iOS App Development
- Flutter App Development
- Mobile Commerce
- Internet of Things
- Health and Fitness
- App Development Cost Explained
- App Development Process Explained
- Flutter vs React Native – What to choose
- Flutter Pros and Cons
- React Native Pros and Cons
- Native vs Cross-platform App Development
Wroclaw (HQ) ul. Ruska 51B, 50-079 Poland
London 85 Great Portland Street United Kingdom
San Francisco 75 Broadway, 94111 United States
Programs and Partnerships
© 2011-2024 All rights reserved. Privacy Policy Walne Zgromadzenie
Sign up now and turn your vision into a success story!
- Bahasa Indonesia
- Sign out of AWS Builder ID
- AWS Management Console
- Account Settings
- Billing & Cost Management
- Security Credentials
- AWS Personal Health Dashboard
- Support Center
- Expert Help
- Knowledge Center
- AWS Support Overview
- AWS re:Post
Customer Stories / Consumer Packaged Goods / Global

Nestlé Efficiently Scales to 2.8 Million Connected Devices with AWS IoT
Learn how Nestlé developed a global framework for Internet of Things products using AWS IoT Core.
Overview | Opportunity | Solution | Outcome | AWS Services Used
2.8M devices connected
to a centralized IoT Platform
Reduced IoT solution development time
from months to weeks
Supports connected consumer devices
across 97 countries
Created a repeatable and scalable
technology model to accelerate innovation
Unlocked new functionality
to improve customer experience
Consumer packaged goods (CPG) giant Nestlé wanted to accelerate the development of Internet of Things (IoT) solutions across its global business units, including coffee brand Nespresso and pet care brand Nestlé Purina Petcare (Purina). Rather than have each business unit build its own IoT offering, Nestlé set out to build a single centralized framework, the IoT Platform, that could be adopted by numerous brands. “Our main goal is to reuse common components across solutions and accelerate the creation of new customer experiences,” says Víctor García, senior product manager for the consumer IoT Platform at Nestlé.
It’s safe to say that there has never been a project quite like this in Nestlé’s storied history, which stretches across well over 150 years. Yet, the IT team was determined to break down walls and deliver a first-of-a-kind initiative. Nestlé chose to build the IoT Platform on Amazon Web Services (AWS) to unlock scale and take advantage of serverless architecture. “We have no doubt that we picked the right provider when we chose AWS,” says Adrian Matellanes, global head of digital experience technologies at Nestlé.

Opportunity | Using AWS IoT Core to Accelerate Innovation for Nestlé
As one of the largest CPG corporations in the world, Nestlé is home to many household names. To accelerate time to market for IoT innovation across its global businesses, Nestlé needed a unified and secure solution framework that would liberate teams to focus on the customer experience. “Some of our brands wouldn’t have been able to afford or develop IoT solutions in house if we didn’t have a common solution ready for them to use,” says Matellanes. Nestlé used AWS IoT Core , a service that offers cloud connectivity for billions of IoT devices across the globe without managing infrastructure, to build its central offering.
With the IoT Platform available, Nestlé business units have been freed to innovate and focus their resources on building differentiated products. At Purina, for example, teams used the IoT Platform to bring essential and often complex IoT functionalities—such as device-to-cloud connectivity, data ingestion, security certificate management, and software update management—to its newly developed Smart Litterbox offering, which uses artificial intelligence (AI) to alert people when their cats may need to see the veterinarian. “The IoT Platform was a significant catalyst for us to get buy-ins from business stakeholders and to off-load complex IoT workflows,” says Ann Scharenberg, director of architecture and services for new business models at Purina US. “We’re using it to build a number of new products.”

We have no doubt that we picked the right provider when we chose AWS.”
Adrian Matellanes Global Head of Digital Experience Technologies, Nestlé
Solution | Global Head of Digital Experience Technologies, Nestlé
From the moment the IoT Platform initiative started in 2016, Nestlé IT leaders were set on using serverless architecture. “The single most important differentiator for AWS was its serverless computing service,” says García. “Just as we wanted to take common components out of our IT solutions so teams could focus on business value, we wanted to use AWS to reduce the load of managing infrastructure.” Nestlé uses AWS Lambda , a serverless, event-driven compute service, so its teams can focus on the consumer experience.
Seven years is a long time, and Nestlé has been busy. After its success with its first proof of concept, which was for a Nescafé product, the corporation has incrementally expanded its IoT operations throughout its global business units. Today, over 2.8 million devices in 97 countries are connected through the IoT Platform, which has ingested 2.1 billion data points in that time. “When so many of our companies grew and extended the solution’s features, the technology spoke for itself,” says Matellanes. And as the enterprise gains more experience building IoT products, development times have shrunk from months to weeks.
Purina is the most recent Nestlé company to bring a connected device to consumers using the IoT Platform, which is powered by AWS IoT Core. The business worked closely with AWS Professional Services , a team that assists organizations with enterprise cloud computing initiatives, to realize its AI-powered Smart Litterbox project. “Working with AWS Professional Services, we mapped out a service-based architecture to meet many requirements for customers with multiple devices, all with the IoT Platform continuing to drive the consistency and quality that we’ve seen for years,” says Scharenberg. Purina also used Amazon SageMaker , a service to build, train, and deploy machine learning models, to develop the AI for the Smart Litterbox. Once the device shipped to retail stores and Amazon in May of 2023, the team started seeing more detailed data than it’s ever received from any product.
For Purina, IoT devices are about more than data—they’re about building a relationship with consumers. The Smart Litterbox is a case in point. Purina engineered the product to provide pet owners with detailed information and proactive health predictions throughout the full pet life cycle. By helping people care for their beloved pets, Purina is building trust that will elevate its brand identity. “We think this product will change our consumer relationships in a way that wouldn’t be possible with our other products,” says Scharenberg. “From our perspective, the potential is huge, and it will only grow as we add more devices into our IoT portfolio.”
Outcome | Advancing IoT Innovation around the World on AWS
Armed with the IoT Platform, Nestlé teams are ready to pick up the pace of innovation. In the coming years, business units, including Purina, are set to roll out numerous IoT products. “The constant evolution of AWS offerings keeps us on our toes,” says Matellanes. “We have absolute peace of mind with our systems on AWS.”
Due to the sheer scale and complexity of a global enterprise like Nestlé, consistency has been key to the success of IoT initiatives. “The story of this solution’s continuous evolution over 7 years is one of constant standardization and improvement,” says García. “And as we worked, AWS kept up a constant pace of innovation, delivering new specialized services that we used to accelerate our platform’s value proposition.”
About Nestlé
Nestlé is a global CPG company headquartered in Switzerland. It has several business units, including Nespresso, Stouffer’s, Nestlé Purina Healthcare, and many more, to fit virtually any aspect of life under its motto: Good Food, Good Life.
AWS Services Used
Aws iot core.
AWS IoT Core lets you connect billions of IoT devices and route trillions of messages to AWS services without managing infrastructure.
Learn more »
AWS Lambda is a serverless, event-driven compute service that lets you run code for virtually any type of application or backend service without provisioning or managing servers.
Amazon SageMaker
Build, train, and deploy machine learning (ML) models for any use case with fully managed infrastructure, tools, and workflows.
AWS Professional Services
The AWS Professional Services organization is a global team of experts that can help you realize your desired business outcomes when using the AWS Cloud.
More Consumer Packaged Goods Customer Stories
no items found
Get Started
Organizations of all sizes across all industries are transforming their businesses and delivering on their missions every day using AWS. Contact our experts and start your own AWS journey today.

Ending Support for Internet Explorer
- There are no suggestions because the search field is empty.
SUGGESTED CONTENT:
Book a Demo of MachineMetrics
See the Platform in Action [Video]
.png?width=1960&height=1300&name=01_comp_Downtime-%26-Quality_laptop%20(1).png)
Learn How to Run a Downtime Analysis
Machinemetrics blog, production planning and scheduling: taking a modern approach, machinemetrics unveils revolutionary automated schedule..., how manufacturing production scheduling software tackles an..., the challenges of manufacturing scheduling and how modern....
Ready to empower your shop floor?
- MachineMetrics
- Product Updates
- Data Science
- Lean Manufacturing
Machine Monitoring
IoT in Manufacturing: Top Use Cases and Case Studies
Updated May 17, 2021
Within this article, we’ll be discussing practical IoT applications in manufacturing and use cases of industrial IoT technology in manufacturing
What is IoT?
What is iiot, the benefits of iot in manufacturing.
IoT represents a digital transformation in manufacturing processes and business operations. Using it alongside an advanced machine data platform can be transformational. And there are many benefits of IoT in manufacturing:
Process Optimization
Inventory Management
Predictive Maintenance
IoT in Manufacturing Use Cases [+Case Studies]
Remote monitoring.
Learn more about remote monitoring for machine builders and OEMs.
Supply Chain Management and Optimization
- Real-time tracking of assets and products
- Automation of warehouse tasks
- Digitized paperwork management
- Forecasting accuracy improvement
- Greater control of inventory
Digital Twins
Real-Time Machine Monitoring
Production visibility.

Integrating Systems
Compiling kpis.

Asset Utilization
Difficulties of Adopting IoT in Manufactur ing
1. large investments are required and the roi is questionable, 2. concerns about data security, 3. employees who aren’t qualified, 4. integration with operational technology and older systems, how to use iot and machine data for remote operations, boosting your operational efficiency with iiot, subscribe to our mailing list, related posts, read the latest.
Lists by Topic
- MachineMetrics (387)
- Lean Manufacturing (72)
- Industry 4.0 (50)
- Manufacturing data (23)
- Manufacturing News (20)
- Data Science (15)
- data collection (14)
- Product Updates (12)
- Connected Factory (10)
- Machine Monitoring (10)
- manufacturing analytics (10)
- Smart Manufacturing (9)
- industrial iot (9)
- CNC Machines (8)
- Productivity (8)
- Downtime (7)
- Industrial Automation (7)
- Tool Monitoring (7)
- Big Data (6)
- Data Visualisation (5)
- Edge Computing (5)
- Maintenance (5)
- Process Optimization (5)
- Shop Floor (5)
- digital manufacturing (5)
- Automotive (4)
- Death of MES (4)
- MES software (4)
- Machine Learning (4)
- Production Scheduling (4)
- Quality Assurance (4)
- Aerospace and Defense (3)
- Contract Manufacturing (3)
- Data Cleaning (3)
- Heavy Machinery Manufacturing (3)
- Medical Device Manufacturing (3)
- OEE Software (3)
- Oil and Gas Manufacturing (3)
- capacity (3)
- continuous improvement (3)
- inustrial IOT (3)
- press release (3)
- preventative maintenance (3)
- security (3)
- 8 wastes (2)
- Condition Monitoring (2)
- Dashboards (2)
- Internet of things (2)
- Production Monitoring (2)
- Strategic Partnerships (2)
- management (2)
- real-time analytics (2)
- Digital Transformation (1)
- Downtime Categorization (1)
- FANUC FOCAS (1)
- Line Balancing (1)
- Machine Tool Distributors (1)
- Machinery (1)
- Manufacturing Innovation (1)
- Quality Control (1)
- Supply Chain (1)
- Turnkey contracts (1)
- coaching (1)
- elon musk (1)
- employee engagement (1)
- link roundup (1)
- manufacturing (1)
- manufacturing software (1)
- networks (1)
- release notes (1)
844-822-0664
Easthampton Office
116 Pleasant St, Suite 316, Easthampton, MA 01027
Edge Platform
Cloud Platform
APIs & Applications
Industrial IoT Platform
Production Monitoring
Condition Monitoring
For Machine Builders and Distributors
For Developers
Production Schedule Intelligence
Aerospace & Defense
Contract Manufacturers
Heavy Machinery
Medical devices
Oil & Gas
Precision Metalworking
ERP Integration
Metal Stamping & Fabrication
Tool, Die & Mold CNC
ROI Calculator
Waste Calculator
Connectivity Hub
Partner Program
Privacy Policy
Data Processing Addendum
Service Level Agreement
Website Terms
IoT Applications : 30+ Use Cases
Internet of Things (IoT) applications are becoming more widespread. According to Statista , worldwide expenditure on IoT in 2022 is expected to be $1B.
IoT enables a myriad of different business applications. Knowing those IoT examples and use cases can help businesses integrate IoT technologies into their future investment decisions. That is why we set out to create the most comprehensive list of IoT use cases in industries.
The image below shows the potential impact of IoT technologies in various industries in 2025.
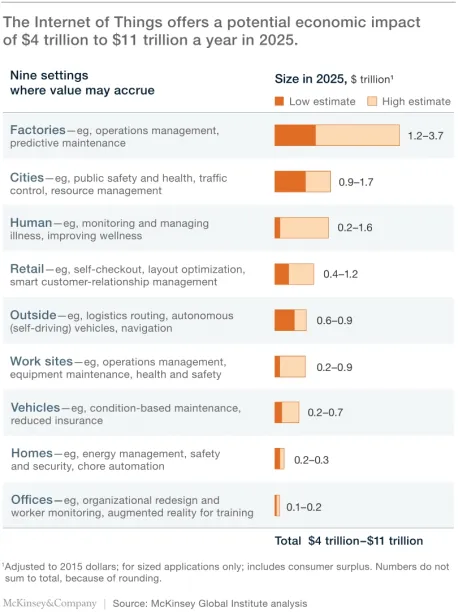
We have compiled 33 IoT applications for business leaders to select the correct use case for their IoT implementation . Use cases include:
Smart Factories
1. enterprise asset management.
Enterprise asset management involves work management, asset maintenance, planning and scheduling, supply chain management, and environmental, health, and safety (EHS) initiatives. Businesses collect real-time data from an asset with IoT sensors.
Businesses are rapidly adopting smart asset management systems into their businesses. Due to their asset-intensive environments, we mostly encounter IoT asset monitoring in industries such as logistics, retail, and manufacturing.
IoT-powered asset management increases real-time visibility of assets and helps businesses optimize their resource while providing benefits such as:
- Increased operational efficiency
- Better control over the sales lifecycle
- More efficient safety and compliance checks
- More responsive smart environment.
2. Predictive maintenance
Maintenance is conducted to prevent predicted problems. So over the lifetime of a machine, some components may never be checked if they are not predicted to cause problems.
For example, Fanuc is a robotics company that is working on reducing the downtime of machines with IoT technology. Fanuc uses sensors to predict when the failure of the component will happen.
3. Industrial process automation/optimization
Organizations can keep a real-time record of the metrics of all the machines inside a plant using IoT and IP networks. Manufacturers can use this data to automate workflows and optimize production systems. Automation and optimization support industrial companies to reduce costs and increase the quality and volume of output.
The market for automated industrial robots is proliferating. The market size was 41 billion U.S. dollars in 2017 and is expected to reach 73 billion U.S. dollars in 2023.
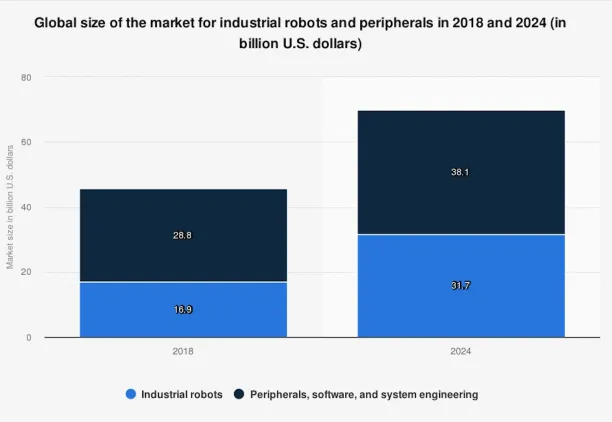
4. Energy management
Energy can be a costly input for industrial businesses. With fluctuating energy costs and strict government requirements for efficiency, managing energy distribution becomes important.
IoT devices can help manufacturers manage energy consumption based on real-time data collected from devices. Intelligent energy management systems reduce energy bills, operational expenditures, and the carbon footprint of the factory while increasing energy efficiency. WebNMS is an IoT platform that provides IoT applications including energy management to optimize the energy consumption of businesses.
Smart Cities
Kay Sharpington from Gartner, states “The COVID-19 pandemic is slowing down spending, however, governments across the globe continue to use IoT technologies and solutions to improve citizen safety. At the same time, the falling endpoint and connectivity costs make smart city initiatives more viable”.
Gartner estimated that the global government Internet of Things (IoT) endpoint electronics and communications market totaled $15 billion in 2020, an increase of 6% from 2019. Same study also reveals the top 5 government IoT applications and revenue generated by each use case as seen below:
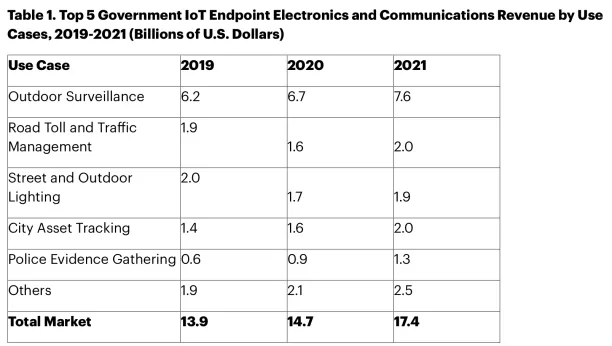
5. Outdoor surveillance
When IoT CCTV cameras are combined with artificial intelligence and machine vision, governments can automate the surveillance of streets through cameras. As IoT enables connectivity of machines, they can record and analyze video data in real-time, and they can provide police officers with insights instead of single pieces of images.
However, outdoor surveillance processes personal information and there is potential for abuse in the use of such technologies. Therefore appropriate checks and balances need to be implemented in such systems to ensure that personal information is not abused while the risk of crime is minimized.
6. Smart lighting
According to the 2018 Gartner IoT hype cycle report, smart lighting is the fourth-most mature IoT tech application. Smart lighting aims to optimize energy management.
Smart lighting is made up of street lighting with IoT sensors. Sensors collect data about the condition of traffic and pedestrians. With that data, street lights provide optimum lighting so that street lighting systems can save up to 80% of the energy.
Smart lighting can also be applied to factories or homes.
7. Electronic road toll collection and traffic management
Traffic engineers augmented by smart systems at a central traffic management center (TMC) can analyze data from IoT sensors and then optimize the timing of traffic lights throughout the day. This can help divide the traffic more evenly over roads as traffic volume fluctuates.
8. Smart parking
In cities like San Francisco, parking is a big problem. With IoT sensors, parking problems in a city can be minimized.
The working principle of smart parking is:
- Sensors are attached to parking lots to detect parked cars
- Measurements are periodically sent to the cloud by microcontrollers
- Mobile Apps use cloud data to identify empty parking spaces,
- Drivers check mobile apps to identify vacant parking spaces close to the location they aim to go to.
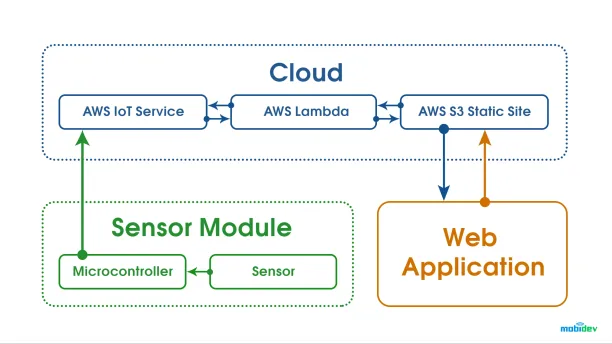
Noise Monitoring
In smart cities, sound monitoring systems can monitor noise levels warn companies that violate limits, and help manage noise levels.
9. Structural health monitoring
IoT allows remote collection of architectural data to monitor events such as vibrations and changes in material conditions, predict structural damage, and prepare action plans for structures such as bridges, buildings, stadiums, ships, airplanes, etc.
10. Waste management
Traditional waste collections are complicated and costly since a fleet of trucks drives along busy streets using inefficient routes. Fill levels of garbage containers differ for each container: ranging from overflowing, partially filled, and empty. IoT sensors can monitor fill levels for conventional bins and send the data to the relevant department of the city hall. With that information, the garbage truck routes can be optimized for trash collection.
Machine learning methods can also be implemented in IoT sensors (i.e. edge analytics ) so that sensors can predict the fill levels of containers by learning from historical data.
Below the video, you can find how Proximus, an IoT solutions vendor, uses IoT to manage waste:
Water Management
Due to the drastic increase in urbanization levels and the importance of water quality in human health, water management is a key topic for cities. A water management system is based on real-time data collected from sensors. Water management can provide the following applications:
11. Water conservation
Sensors detect the water level in tanks and alert when the water level is lower than the threshold. Well™, a smart home water conservation system developed by Mindtribe , uses IoT sensors to monitor water usage.
12. Smart irrigation
IoT sensors determine the weather conditions and the soil moisture, which will help in getting the appropriate amount of water that the soil needs. For instance, greenIQ is a vendor that offers a sprinkler sensor that optimizes its functionality based on the dryness of the soil.

13. Leakage management
IoT sensors can detect temperature changes, water leakage, chemical leakage, and pressure levels in water tanks.
14. Water quality management
IoT sensors determine what kind of chemicals are in the water. They also identify metrics such as total dissolved solids (TDS), bacteria, chlorine, electrical conductivity, etc.
Learn more about IoT in agriculture.
Digital Health
15. ultraviolet radiation monitoring.
Sunlight consists of three major components:
- Visible light: Wavelengths between 0.4 and 0.8 micrometers,
- Ultraviolet light: Wavelengths shorter than 0.4 micrometers,
- Infrared light: Wavelengths longer than 0.8 micrometers.
Ultraviolet (UV) rays are electromagnetic waves that account for about 10% of solar light. When overexposed, UV rays have harmful effects such as skin cancer, premature aging, cataracts, and immune system suppression. IoT sensors measure UV sun rays to warn people not to be exposed during certain hours.
16. Fall detection
Falling to the ground and not being able to get up or request help can be a scary experience for senior citizens. IoT sensors can detect falls using geolocation data and summon help so that it reduces the time the elderly remain on the floor after a fall which could lead to lethal consequences.
The below video is an example of how fall detection systems work from a vendor called Walabot:
17. Companion robots
A companion robot is a robot that is designed to create companionship mostly for elderly and single children. IoT sensors are essential for robotics and it is the same for companion robots as well. Sensors detect objects that surround the robot and enable the robot to move.
Researchers claim that people have become more receptive to companion robots during the pandemic. Social isolation may lead people to loneliness, anxiety, and frustration, especially the elderly.
18. Medical fridges
Medical fridges monitor the temperature of vaccines, medicines, and organic elements for clinics and health centers. Medical fridges provide an opportunity to follow all safety standards and national regulations of the pharmaceutical market using IoT sensors. They prevent medicines and vaccines from spoiling.
Efento is an IoT sensor and IoT platform vendor that has a variety of temperature measurement products along with wireless monitoring of temperature in medical refrigerators.
19. Patient surveillance/remote patient monitoring
20% of patients who had surgery are readmitted to the hospital within just 30 days. Remote patient monitoring (RPM) systems use wearables to monitor the condition of patients who are resting at home after surgery. RPM enables real-time data collection about patients’ body temperature which is the main indicator of infections. With RPM, doctors can observe patients’ data and provide early diagnoses without requiring patients to be physically present at the hospital.
Telit is an IoT solution vendor and offers its customers a remote patient monitoring (RPM) solution that enhances patient monitoring capabilities and patient satisfaction. Telit’s offering can reduce:
- Patients hospital stay duration thanks to early diagnosis of complications
- Hospital readmissions
Smart Retail
20. supply chain control.
IoT devices have transformed supply chain management. Sensors, which are attached to storage containers or products themselves,
- show the location of goods using GPS,
- track the speed of movement providing an accurate estimated time of arrival (ETA) for goods,
- monitor warehouse conditions such as temperature, humidity, light intensity, and other environmental factors
21. Near field communication (NFC) payment
NFC enables contactless payments. POS vendors include NFC support in their systems, and customers are adopting contactless payments via their smartphones.
22. Layout optimization
Sensors in the store collect data like voice, image, or video to better understand customer habits and preferences. Retailers can get insights to redesign the layout of their stores. The optimized layout can enhance sales.
23. Smart product management
IoT sensors enable retailers to control the rotation of products on shelves and warehouses to automate merchandising decisions. We have already written about retail analytics use cases, feel free to check it out if you want to learn more.
Smart Workplace
24. sociometric badges.
Sociometric sensors are wearable IoT devices that measure the amount of face-to-face interaction, conversational time, physical proximity to other people, and physical activity levels using social signals derived from vocal features, body motion, and relative location.
For example, Humanyze is a vendor that uses sociometric sensors to perform people analytics. The company helps organizations understand how their teams interact to increase performance.
Smart Homes
25. remote control appliances.
IoT-powered home appliances let residents remotely switch on and off devices using smartphone apps to avoid incidents and save energy. Additionally, these devices can make autonomous decisions based on sensor inputs such as preparing fresh coffee when a resident is identified to wake up. Other examples of autonomous or remote-controlled actions include:
- Turning on lights,
- Starting the coffee maker,
- Setting temperature,
- Open up a music playlist,
- And locking doors.
Home Intrusion Detection Systems:
IoT-based home security applications give users capabilities such as smart locks and security cameras that detect motions and send alerts to their smartphones so that they can monitor the safety conditions of their homes from anywhere.
26. Smart locks
Eyelock is a security provider vendor that offers its clients an iris-based authentication solution.
27. Motion detection
Manything is another vendor in IoT IoT-based home security market. It streams home/office videos and lets users receive alerts when it detects any activity.
Smart Logistics
28. fleet tracking.
IoT fleet tracking systems improve security and provide precise and complete reports that give the fleet managers full transparency regarding the fleet’s activities. Through GPS monitoring and geo-location tools, companies can track the location of their trucks, optimize routes, and monitor their fleet utilization in detail.
For instance, Canadian delivery service Sure Track Courier saved 6-10% per month on fuel costs by optimizing routes using IoT data from trucks.
29. Platooning
Platooning involves a group of self-driving trucks that follow a lead truck at high speed safely and efficiently. Trucks use IoT sensors so that each truck communicates with the other trucks to adapt its speed and braking accordingly.
30. Connected vehicles
Sensors are enhancing vehicles along with AI and analytical capabilities. These sensors provide communication with the driver to supply useful information about other cars on the road and roadside infrastructure to the driver to help the driver make safer or more informed decisions. For example, these vehicles provide GPS-enabled location detection feature that helps them detect traffic congestion.
Autonomous vehicles are also an application of IoT devices. Though it is not commonly used in logistics yet, we will witness this approach soon. For instance, the Mercedes-Benz prototype of the semi-autonomous truck is scheduled for release in 2025.
Smart Metering
31. smart grid.
With the increasing attention regarding climate change and carbon emissions, utilities focus on reducing energy consumption. For utility companies, IoT enables remote data management and monitoring capabilities to manage better power flows into and out of their grids, and give users the insights needed to understand their energy infrastructure investments.
32. Digital Twins
A digital twin is a virtual replica of physical entities such as devices, people, processes, or systems that help businesses make model-driven decisions. With the help of IoT sensors, businesses collect data that is needed to create a digital twin.
Digital twins enable businesses to gain a deeper understanding of real-world conditions so that they make necessary adjustments to their products & services.
33. IoT devices in healthcare
In healthcare , the ecosystem of IoT-enabled devices such as wearables (smartwatches, rings, vests, etc.), monitors (heart monitors, sleep monitors, temperature monitors, etc.), and trackers (medication refill reminder, drug effectiveness tracking, etc.) can be used for:
- Constant monitoring of patients’ vitals (blood pressure, heart rate, temperature rate, etc.),
- And more accurate diagnoses of patients, thanks to real-time data from IoT devices, thus reducing the possibility of readmission and rising hospital bills.
Read more on IoT
We have written articles about IoT technologies before, feel free to read our other articles on:
- Increase Speed to Market Using an IoT Platform
- Edge Analytics in 2022: What it is, Why it Matters & Use Cases
- IoT Testing: Framework, Challenges, Case Studies & Tools 2022
We also have some in-depth articles on other use cases of IoT in different industries:
- Top 6 Use Cases of IoT in Manufacturing
- 5 Use Cases of IoT in Automotive in 2022
- 7 Ways IoT Will Improve Your Banking Experience in 2022
Finally, if you believe your business could benefit from implementing an IoT solution, we have a data-driven list of vendors prepared .
We will help you choose the best one for your business:

Next to Read
Iot analytics: benefits, challenges, use cases & vendors.
Your email address will not be published. All fields are required.
Related research
IoT Cloud : Benefits, Challenges, Platforms&Functionality
IoT Implementation: Steps & Best Practices
We use cookies to improve our site and your experience. By continuing to browse our site, you accept our cookie policy. Read more. I understand
- Customer log-in
- Get Free IoT Trial
- 中文 (Chinese)
- 한국어 (Korean)
- 日本語 (Japanese)
IoT Case Studies
Explore our IoT case studies and learn how our customers have leveraged IoT connectivity to gain a competitive edge and create one-of-a-kind experiences.
Featured IoT Business Cases
{{post.post_title}}, no posts found. try to change filter, follow the iot pioneers.
For two decades, we have helped leading companies succeed with pioneering IoT solutions. In these IoT use cases, learn more about their strategies, and how you can succeed with connected products.
Outsource specialized knowledge and focus on your customers
Reduce vendor complexity with one partner for global connectivity, mitigate risk with guaranteed service levels and data security, speed up time to market with help from an experienced partner, gain peace of mind with a top rated service team on call 24/7.
Successful global IoT deployments require pioneering IoT solutions. Gain insights here on how connected products unlock value and deliver a competitive edge in these comprehensive IoT business cases.
We are working with many verticals. You can read detailed IoT case studies with global managed connectivity solutions for verticals such as smart cities, utilities, automotive, and industrial manufacturing, as well as transport and logistics.
More IoT Cases and Examples
15 iot examples for business applications.
When Sony proposed mSafety with connectivity from Telenor IoT, we seized the opportunity based on LTE-M's connectivity and battery life benefits. It is also very important that our connectivity provider has global roaming capabilities. LTE-M is the state of the art, offering carrier-grade machine-to- machine network connectivity.

We were looking for a partner to provide plug & play global connectivity. Telenor IoT has also guided us with technical decisions. Overall, this has helped focus our development resources to deliver a world-class application for our customers. Trusting Telenor's robust global connectivity is important for our application.

Telenor IoT are the backbone of our operation and have been our partner from early scale-up through to today. We selected Telenor IoT as our global connectivity partner, because they had the best performing SIMs and have proved to be trustworthy partners. Their global managed connectivity is reliable and secure which is critical.

Our target market is global customers who want the best-of-the-best. Telenor IoT was the obvious choice for connecting our cars, with their broad and extensive experience in connected automotive solutions. Also, their technical expertise and ability to trouble-shoot is industry-leading.

As industry leader, partnering with Telenor IoT has enabled us to move into new markets with comparative ease. Their support and troubleshooting tech team is world-class and when we need them, they are always available for questions and support.

Resources & News

Join Us for a Webinar
- Data Center
- Applications
- Open Source

Datamation content and product recommendations are editorially independent. We may make money when you click on links to our partners. Learn More .
When decision-makers consider implementing Internet of Things (IoT) solutions, they typically want assurance that their investments will pay off and that service providers’ offerings will meet or exceed their needs.
Reading IoT case studies can show business leaders what’s possible and help them make more confident choices about when and how to implement the technology.
These studies below show how the IoT opens diverse possibilities for businesses, helping them meet current and future goals.
See more: The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) Market
5 IoT case studies
1. improving insights at a vineyard.
Industry: Agriculture
Use case: Applying the IoT and data analytics to track statistics from fields and equipment across the complete grape-growing process.
Outcome: Deep Sky Vineyards has locations in Arizona and Argentina. Business leaders wanted a better way to oversee operations after a broken valve caused a flood. The company used a Google Cloud IoT solution that caused a 75% reduction in human error costs. Since the technology gives water flow and soil moisture metrics, it raised crop efficiency by 50% by preventing adverse conditions that could cause rot.
Cloud technology also allowed pushing over-the-air updates to remote devices. That convenience allowed the vineyard to maintain visibility over its sites and use the latest software versions.
2. Streamlining Contactless COVID-19 Testing
Industry: Health care
Use case: Building pods for contactless COVID-19 testing
Outcome: As the coronavirus spread around the world, it became critical to care for people without putting providers at unnecessary risk. For example, one Italian hospital used robots to take patients’ vitals. In this IoT case study, Microsoft Azure’s cloud and IoT solutions allowed for creating contactless testing stations in less than two months.
The solutions served as stations where people could drive or walk up to a window for their tests. The portability allowed setting up testing centers in remote locations or anywhere they’d most likely reach the most at-risk groups.
The testing pods have computerized translation services to help non-English speakers as well as artificial intelligence (AI) cameras that ensure everyone wears masks.
IoT innovations: 85 Top IoT Devices
3. Minimizing Labeling Errors During Automotive Production
Industry: Manufacturing
Use case: Using smart cameras and machine learning (ML) to help team members apply the correct regulatory labels to vehicles in a factory.
Outcome: Since the IoT can alert people to issues before they cause outages , manufacturing and industrial brands are particularly interested in its potential. It can bring attention to faulty equipment and also reduce human errors. Brands under the Volkswagen Group umbrella must apply 25 different labels during vehicle production, and each one has more than 2,000 variations based on country specifics.
Amazon Web Services (AWS) provided a cloud-based IoT solution that uses machine learning, automated cameras and IoT apps to identify label errors and alert workers to the issues.
The labels are in several languages, but this method translates them into an employee’s native tongue. Volkswagen Group representatives reported that this process improvement reduced the complexity of workers’ tasks and led to an overall improvement in vehicle quality.
4. Enhancing the Management of Solar-Powered Trash Receptacles
Industry: Waste management
Use case: Using IoT and the cloud to improve oversight of solar trash cans in a given location or community.
Outcome: BigBelly Solar relied on Telit to develop a better way for people to manage waste disposal points. This IoT case study caused an 80% reduction in management costs and gave customers a browser-based console for better visibility. The associated cloud functionality also facilitated remote diagnostics if a particular trash can malfunctioned in a customer’s network.
Moreover, an authorized party could use the cloud interface to remotely update a garbage receptacle’s software, keeping it functioning smoothly. BigBelly Solar has compacting and non-compacting versions. This technology works with both kinds to verify the fullness level of a given container, saving waste managers from having their staff members make unnecessary trips to check it.
5. Narrowing the Digital Divide to Facilitate Learning
Industry: Education
Use case: Bringing reliable internet access to the 70% of students in a Texas school district who did not have it at home. This approach also created secure outdoor access points.
Outcome: The COVID-19 pandemic caused a quick shift to remote learning for many students around the world. This IoT use case involved using products from Cisco’s IoT line to extend the school’s internet access into the homes of children who needed it to continue their studies.
After first testing this method by bringing dependable, private Wi-Fi to one cluster of houses, the school district’s leaders decided to roll out the technology to eight other groups of residences in the area. The people who worked on this project are developing a blueprint for use across the country, helping kids connect beyond the COVID-19 pandemic.
Oscar Rico is the school district’s executive director of technology. He explains his drive to find a solution, saying, “When your family can afford internet, you can get up, log in, and do your schoolwork from home. But 70% of our students don’t have internet access at home. Maybe some have access to a parent’s cell phone with unreliable internet. But I knew most would be sitting at a makeshift desk, working their way through a pile of paper. I wanted to find a way to change that.”
See more: Best IoT Platforms & Software
Subscribe to Data Insider
Learn the latest news and best practices about data science, big data analytics, artificial intelligence, data security, and more.
Similar articles
Exploring multi-tenant architecture: a comprehensive guide, 8 best data analytics tools: gain data-driven advantage in 2024, common data visualization examples: transform numbers into narratives, get the free newsletter.
Subscribe to Data Insider for top news, trends & analysis
Latest Articles
Exploring multi-tenant architecture: a..., 8 best data analytics..., common data visualization examples:..., what is data management....


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
IoT Analytics presents the top 10 IoT use cases, with process automation as the #1 adopted IoT use case. Why it matters? For IoT vendors: With the success of IoT initiatives and the growing adoption rate, IoT vendors can learn about what use cases end users are adopting and tailor their offerings.
Discover 7 types of IoT apps from different industries, each with unique examples, in this insightful guide on the Internet of Things. Learn how IoT transforms each sector and how you can use this technology to advance your business.
Consumer packaged goods (CPG) giant Nestlé wanted to accelerate the development of Internet of Things (IoT) solutions across its global business units, including coffee brand Nespresso and pet care brand Nestlé Purina Petcare (Purina).
The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) takes IoT further by using it to drive a digital transformation in manufacturing. IIoT uses embedded sensors to capture and analyze machine data to improve operational processes using networked industrial control systems.
Explore 15 IoT examples and a number of IoT case studies for B2B applications within Smart Cities, asset tracking, healthcare, manufacturing.
Internet of Things (IoT) applications are becoming more widespread. According to Statista, worldwide expenditure on IoT in 2022 is expected to be $1B. IoT enables a myriad of different business applications. Knowing those IoT examples and use cases can help businesses integrate IoT technologies into their future investment decisions.
global standards, the primary Mobile IoT technologies – LTE-M and NB-IoT – are making it cost-effective to roll out IoT solutions, such as smart metering and asset tracking, that don’t require high levels of throughput and low latency connectivity.
The IoT ONE database contains 19,090 case studies that are tagged by industry, function, use case, supplier, and technology.
You can read detailed IoT case studies with global managed connectivity solutions for verticals such as smart cities, utilities, automotive, and industrial manufacturing, as well as transport and logistics. More IoT Cases and Examples. 15 IoT Examples for Business Applications.
Reading IoT case studies can show business leaders what’s possible and help them make more confident choices about when and how to implement the technology. These studies below show how the IoT opens diverse possibilities for businesses, helping them meet current and future goals.