
Summarize any | in a click.
TLDR This helps you summarize any piece of text into concise, easy to digest content so you can free yourself from information overload.
Enter an Article URL or paste your Text
Browser extensions.
Use TLDR This browser extensions to summarize any webpage in a click.

Single platform, endless summaries
Transforming information overload into manageable insights — consistently striving for clarity.
100% Automatic Article Summarization with just a click
In the sheer amount of information that bombards Internet users from all sides, hardly anyone wants to devote their valuable time to reading long texts. TLDR This's clever AI analyzes any piece of text and summarizes it automatically, in a way that makes it easy for you to read, understand and act on.
Article Metadata Extraction
TLDR This, the online article summarizer tool, not only condenses lengthy articles into shorter, digestible content, but it also automatically extracts essential metadata such as author and date information, related images, and the title. Additionally, it estimates the reading time for news articles and blog posts, ensuring you have all the necessary information consolidated in one place for efficient reading.
- Automated author-date extraction
- Related images consolidation
- Instant reading time estimation

Distraction and ad-free reading
As an efficient article summarizer tool, TLDR This meticulously eliminates ads, popups, graphics, and other online distractions, providing you with a clean, uncluttered reading experience. Moreover, it enhances your focus and comprehension by presenting the essential content in a concise and straightforward manner, thus transforming the way you consume information online.

Avoid the Clickbait Trap
TLDR This smartly selects the most relevant points from a text, filtering out weak arguments and baseless speculation. It allows for quick comprehension of the essence, without needing to sift through all paragraphs. By focusing on core substance and disregarding fluff, it enhances efficiency in consuming information, freeing more time for valuable content.
- Filters weak arguments and speculation
- Highlights most relevant points
- Saves time by eliminating fluff
Who is TLDR This for?
TLDR This is a summarizing tool designed for students, writers, teachers, institutions, journalists, and any internet user who needs to quickly understand the essence of lengthy content.
Anyone with access to the Internet
TLDR This is for anyone who just needs to get the gist of a long article. You can read this summary, then go read the original article if you want to.
TLDR This is for students studying for exams, who are overwhelmed by information overload. This tool will help them summarize information into a concise, easy to digest piece of text.
TLDR This is for anyone who writes frequently, and wants to quickly summarize their articles for easier writing and easier reading.
TLDR This is for teachers who want to summarize a long document or chapter for their students.
Institutions
TLDR This is for corporations and institutions who want to condense a piece of content into a summary that is easy to digest for their employees/students.
Journalists
TLDR This is for journalists who need to summarize a long article for their newspaper or magazine.
Featured by the world's best websites
Our platform has been recognized and utilized by top-tier websites across the globe, solidifying our reputation for excellence and reliability in the digital world.
Focus on the Value, Not the Noise.
Bulk Content Generator
Brand Voice
AI Text Editor
Research Summary Generator
Craft a detailed research synopsis utilizing the given data for an all-encompassing understanding.
Try Research Summary for free →
Research Summary
Learn how to provide the key points, main findings, and any other relevant information for the research you want to summarize
1 variation
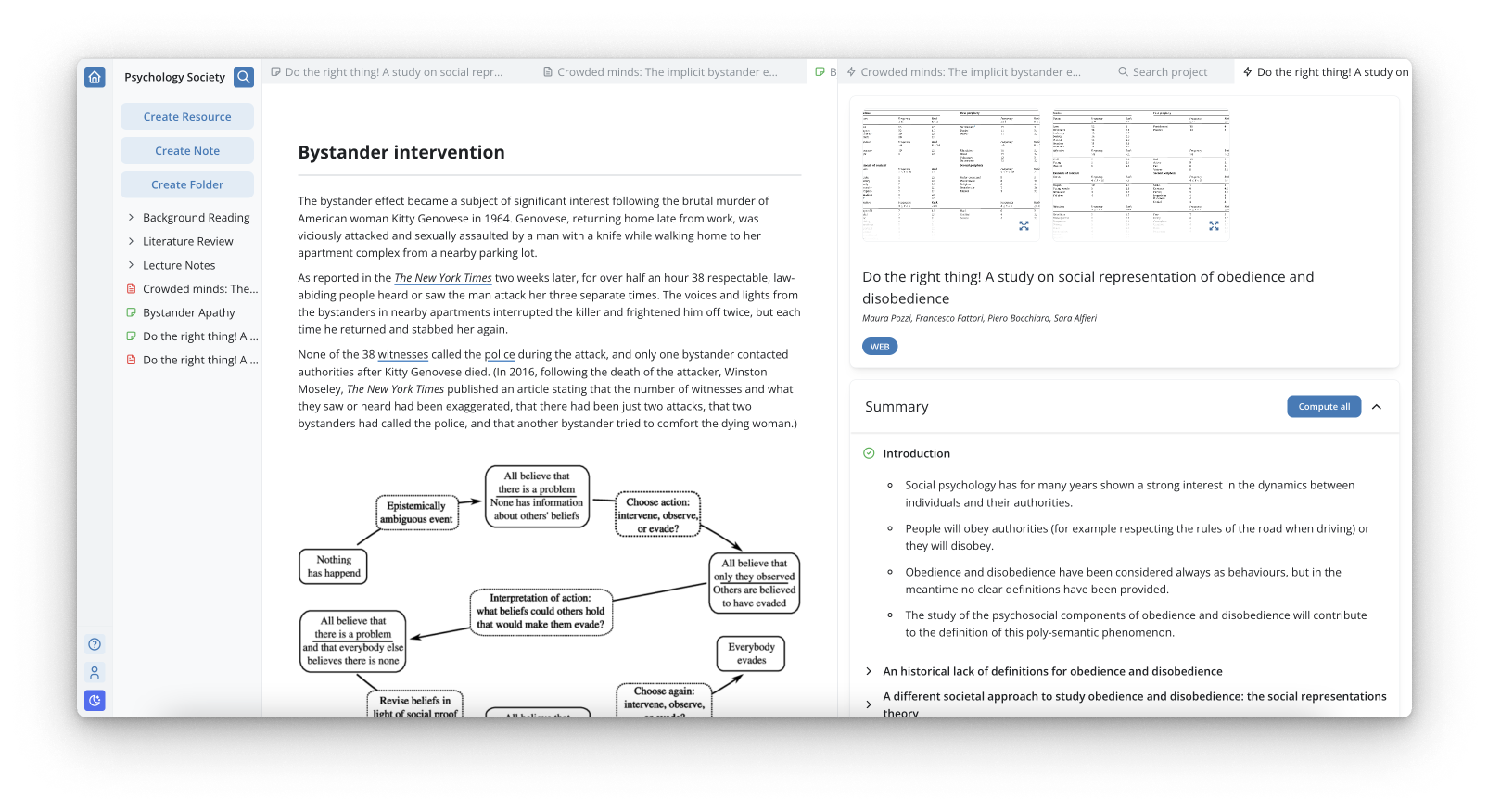
What is a Research Summary?
Have you ever found yourself drowning in a sea of research articles, struggling to make sense of it all? Well, fear not! A research summary is here to save the day. But what exactly is a research summary, and how can it help you navigate the vast ocean of information?
A research summary is a concise and informative overview of a research article, report, or thesis. It aims to provide the reader with a clear understanding of the study's purpose, methods, results, and conclusions without having to read the entire document. Think of it as a mini-version of the original work that highlights its most important aspects.
Now that we know what a research summary is let's dive into why they're so beneficial.
The Benefits of Research Summaries
Research summaries offer several advantages for both readers and writers:
Time-saving : Reading a well-written research summary can save you hours of sifting through dense academic papers. It allows you to quickly grasp the key points and decide if you want to explore the full document further.
Improved comprehension : By breaking down complex ideas into digestible chunks, research summaries make it easier for readers to understand the material. This is particularly helpful for those who are new to a topic or have limited knowledge in the field.
Enhanced communication : Research summaries enable researchers to share their findings with a wider audience, including non-experts and industry professionals. This can lead to increased collaboration and knowledge exchange across disciplines.
Better decision-making : For professionals who rely on evidence-based practices, research summaries provide an accessible way to stay informed about the latest developments in their field. This enables them to make better decisions based on up-to-date information.
With these benefits in mind, let's explore some tips for writing an effective research summary.
Tips for Writing a Great Research Summary
Creating an engaging and informative research summary doesn't have to be a daunting task. Here are some tips to help you craft the perfect summary:
Know your audience : Consider who will be reading your summary and tailor your language and content accordingly. If you're writing for a general audience, avoid jargon and technical terms. If your readers are experts in the field, focus on the most relevant and novel aspects of the research.
Be concise : A research summary should be brief yet informative. Aim to capture the essence of the study without getting bogged down in unnecessary details.
Use clear language : Write in simple, straightforward sentences that are easy to understand. Avoid flowery language or complex sentence structures that may confuse readers.
Highlight key points : Focus on the main elements of the study, such as its purpose, methods, results, and conclusions. Make sure these points stand out by using headings, bullet points, or bold text.
Stay objective : Present the information in a neutral tone and avoid expressing personal opinions or biases. Stick to the facts and let your readers draw their own conclusions.
Proofread : Before submitting your research summary, take the time to proofread it carefully for grammar, spelling, and punctuation errors. A polished summary will make a better impression on your readers.
Generate the Perfect Research Summary with Our Research Summary Generator
Now that we've covered what a research summary is, its benefits, and tips for writing one – wouldn't it be great if there was a tool that could generate a perfect research summary every single time? Well, guess what? There is!
With our Research Summary Generator, you can create an engaging and informative summary in just a few clicks. Say goodbye to hours spent poring over dense academic papers and hello to quick, easy-to-understand summaries tailored to your needs.
Give it a try today and see how our Research Summary Generator can revolutionize your research process!
Example outputs
This Research Summary Generator saves you time and effort by summarizing your research findings in a clear and concise manner, allowing you to easily communicate your results to others.
The Effects of Exercise on Mental Health
A study was conducted to investigate the effects of exercise on mental health. Participants were randomly assigned to either an exercise group or a control group. The exercise group engaged in moderate-intensity aerobic exercise for 30 minutes, three times per week for eight weeks. The results showed that the exercise group had significantly lower levels of depression and anxiety compared to the control group.
Keywords: exercise, mental health, depression, anxiety
The impact of social media on body image.
This study aimed to examine the impact of social media on body image. A sample of young adults completed surveys assessing their use of social media and their perceptions of their own body image. Results indicated that individuals who spent more time on social media reported greater dissatisfaction with their bodies. Additionally, exposure to images of thin and fit individuals on social media was associated with increased body dissatisfaction.
Keywords: social media, body image, young adults, body dissatisfaction
The benefits of meditation for stress reduction.
This meta-analysis aimed to evaluate the effectiveness of meditation for stress reduction. A total of 18 randomized controlled trials were included in the analysis. Results showed that meditation was effective in reducing perceived stress, with larger effect sizes observed for mindfulness-based interventions. Furthermore, the benefits of meditation appeared to be maintained over time.
Keywords: meditation, stress reduction, mindfulness, meta-analysis
What other amazing things can this template help you create.
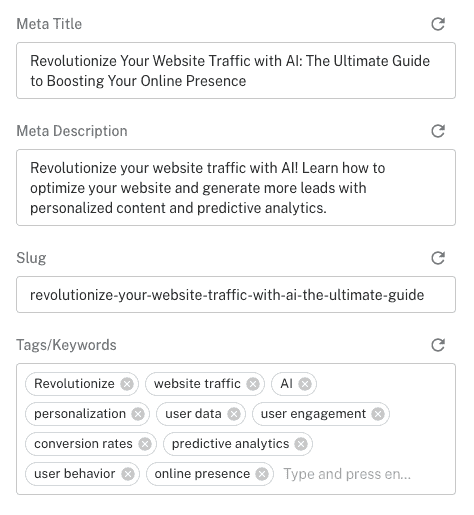
✔ Meta Title
✔ Meta Description
✔ Extract keywords
✔ Feature Image
✔ Soon Internal Linking
Who needs Research Summary Generator?
Researchers
Graduate students
Business professionals
Research Paper Summarizer by AcademicHelp
Free and easy-to-use summarization.

Different Summary Options

Clear and To-The-Point Paragraphs

Customizable Text Length
Free research paper summarizer.

Remember Me
What is your profession ? Student Teacher Writer Other
Forgotten Password?
Username or Email

Research faster with genei
Automatically summarise background reading and produce blogs, articles, and reports faster.
"I could totally see this startup playing the same role as a Grammarly: a helpful extension of workflows that optimizes the way people who write for a living, write." Natasha Mascarenhas Senior Reporter at TechCrunch
Y-combinator summer 2021.
Genei is part of Y-Combinator, a US startup accelerator with over 2000 companies including Stripe, Airbnb, Reddit and Twitch.

TechCrunch favourite startups 2021
Genei was recently named among Tech Crunch's favourite startups of summer 2021.
Oxford University All Innovate 2020
Prize winning company in Oxford University's prestigious "All Innovate" startup competition.
Trusted by thought leaders and experts
"genei is a company that excites me a lot. Their AI has the potential to offer massive productivity boosts in research and writing."
"We can perform research using genei's keyword extraction tool to optimize our article content better than before."
"Genei’s summarisation provides a whole new dimension to our research and reporting, and helps contribute towards the clarity and conciseness of our work."

Add, organise, and manage information with ease.
95% of users say genei enables them work more productively. Documents can be stored in customisable projects and folders, whilst content can be linked to any part of a document to generate automatic references.

Ask questions and our AI will find answers.
95% of users say they find greater answers and insights from their work when using genei.
Finish your reading list faster.
AI-powered summarisation and keyword extraction for any group of PDFs or webpages. 98% of users say genei saves them time by paraphrasing complex ideas and enabling them to find crucial information faster.
.png)
Improve the quality & efficiency of your research today
Never miss important reading again.
Our chrome extension add-on means you can summarize webpages or save them for later reading as you browse.

- Import, view, summarise & analyse PDFs and webpages
- Document management and file storage system
- Full notepad & annotation capabilities
- In-built citation management and reference generator
- Export functionality
- Everything in basic
- 70% higher quality AI
- Access to GPT3 - the world's most advanced language based AI
- Multi-document summarisation, search, and question answering
- Rephrasing and Paraphrasing functionality
Loved by thousands of users worldwide
Find out how genei can benefit you.
AI Summary Generator | Summary Maker
AI Summary Generator offers a free, online summary generator and summary maker. Perfect for quickly condensing articles, papers, and paragraphs into clear, concise summaries. Ideal for students and professionals needing efficient content and text summarization.
AI Summary Generator & Summary Maker
Ever found yourself in a situation where you need to go through an entire document to understand the key points? Or spend hours of time reading news articles, essays, or business reports? Then you are in dire need of a tool that makes the whole thing a lot simpler and smoother.
This is where the summary generator - an AI-powered online tool comes to rescue you. It is built to transform the way you consume textual information. In this digital world, the information is overloaded. Whether it is to stay updated with global news, or to study for our exams, we often find ourselves buried in a big heap of information.
Manually summarizing this whole data would be a tremendous task. It's not just time-consuming but it requires a lot of effort and is always prone to missing out on crucial information. But with summarizing tools like this summarygenerator.ai, it is a cakewalk.
Revolutionizing Text Summarization
Summary generators utilize AI to condense extensive text into concise summaries, saving time and ensuring key information is retained amidst the daily deluge of data. These tools are particularly useful given the average American's exposure to about 34 gigabytes or 100,000 words of non-essential information each day
AI-driven summary generators excel by understanding semantics and context, moving beyond basic text reduction to deliver nuanced summaries. This capability helps users efficiently navigate large documents, focusing on relevant and crucial content without manual effort.

Struggling with slow and inefficient summarization tools?
Common issues with traditional summarization tools.
- Costly subscriptions or fees
- Single mode of summarization
- Delayed results due to processing time
- Fixed and rigid summary lengths
- Often requires software installation or updates
Benefits of Using SummaryGenerator.AI
- 100% Free, no hidden costs
- Dual modes: Summary Text or Bullet Points
- Generate summaries in seconds with real-time summarization
- Choose from Short, Medium, or Long summaries
- Fully online with no need for downloads or updates
AI Powered Online Summary Generator
Free to use.
- Completely free access to advanced text summarization.
- No cost involved at any stage of usage.
- Allows unlimited usage without any financial commitment.
How to Use Summary Generator tool?
Using SummaryGenerator.ai is a straightforward process. Let's walk through the steps you need to follow to generate your first summary.
Visit SummaryGenerator.ai website. Our platform is designed to be responsive, so you can use it on any device of your choice.
On the homepage, you will find a text input box. paste the text you want to summarize into this box., choose your summary mode - 'summary text mode' or 'summary points mode'. you can leave this option as is to get the summary in text mode., next, select the length of your summary. depending on your needs, you can choose from short, medium, or long summary options. this is an optional field., click on the 'generate summary' button. in just a few seconds, you'll have a summary of your text.
Using SummaryGenerator.ai is as simple as that! Our platform is designed to make summarizing a hassle-free process for you. With clean UI and clear navigation, anyone can use the platform with ease.
There are certain points you need to keep in mind to get the best results out of this tool. The quality of the summary text is highly dependent on the kind of input we are feeding. We have kept restrictions on the minimum length of the text we need to keep it to get the summary.
- Input length should be between 100-500 words.
- Choose the summary mode and length for the best results.
- You can review and refine the results by adding more clear input text.
By following these tips, you will always get a simple and readable summary format.
Leveraging Summarizer Generators for Students, Professionals, and More
An online summary generator is a versatile platform that offers a wide range of applications for different sets of users.Whether you are a student struggling to go through lengthy study material or a professional dealing with complex reports, this tool can streamline your summarization process.
For Students:
- In the academic world, tools like summarizers help students to condense lengthy study materials or prepare notes for exams. This is one of the go-to software for them to prepare and consume knowledge better.
- You can summarize text from research papers, books, or lecture notes in a matter of seconds. By going through the summarized concepts, students can focus on the core knowledge without getting lost in the details.
For Professionals:
- Time is a priceless commodity in the professional world. Whether you are going through annual reports, technical documents, or news, professionals need to process a huge wealth of information in a short span. This is where the summary generator helps you boost productivity.
- Our platform is designed and tested to distill lengthy texts to produce the key points out of it. From business analytics to technical managers, marketers to content creators, this platform is the perfect choice for you.
- Get the gist of news data or any market research data much easier now with a free online text summarizer tool like this one.
Feature of this Summary Generator
This summarizing tool is not any other ordinary text summarize tool, it is equipped with advanced features designed to provide comprehensive and flexible summaries.
Let's take a look at a few features that make summarygenerator.ai stand out from other platforms and best for your requirements.
1. Dual Mode for Comprehensive Summaries
Have you ever been in a need of summary of a document in a list of bullet points? With this tool, you can have the leverage to generate summaries in two different formats - Summary mode and Summary Points mode.
- 1. Summary Mode: This mode is the classic text summary mode. It condenses your input text into a concise summary in paragraphs. It maintains the essential points while reducing the overall length. It's perfect for anyone who needs shorter paragraphs of what is there in a lengthy text.
- 2. Summary Points mode: Need a quick overview at a glance? Switch to the points mode. This mode represents the summary in the form of bullet points, making it clear to go through the text in easy-to-read bullet points.
With these dual modes in place, you can select anything that suits your needs.
2. Customizable Summary Length
What's the use when you feed 1000 words news article and it summarizes in 500 words? Every content is different and we understand it is pretty tough to generalize on the summary length. That's why we implemented this customization option for the users to choose the summary length.
- 1. Short - Choose this option when you want a brief overview or if you are short on time. It’s the perfect option to quickly understand what the content is about.
- 2. Medium - When you need a little more details but still want to keep things concise, opt for a medium summary. It offers that balance between the length and depth of the information.
- 3. Long - If you don’t want to miss out on any key points from the lengthy document, choose this option.
This customizable feature is one of the cool and truly makes the "summary generator" It puts you in control of your summaries, ensuring that you are the best one to decide on how you want to read.
Frequently Asked Questions
SummaryGenerator.ai employs advanced AI algorithms to analyze the context and main ideas of the input text. It then condenses these ideas into a coherent and concise summary, making it easier to grasp the essential information quickly.
Yes! SummaryGenerator.ai is completely free to use. You can summarize as many texts as you need without any charge, providing an accessible tool for users across various disciplines.
Absolutely, you can! Our AI-powered summary generator is designed to handle a wide range of text types. Whether it's academic papers, business reports, news articles, or blog posts, SummaryGenerator.ai efficiently produces summaries that capture the core content of your documents.
Empower Your Academic Journey
AI Summarizer & Summary Generator
Jenni AI stands as a comprehensive academic writing assistant, encompassing an AI summarizer and summary generator among its key features. This specialized functionality is meticulously crafted to facilitate the creation of concise summaries, effectively condensing extensive research papers, articles, or essays. Jenni AI simplifies the process, enabling you to focus more on your analysis and less on summarization. Our tool is built with the ethos of promoting authentic academic endeavors, not replacing them.

Loved by over 3 million academics

Trusted By Academics Worldwide
Academics from leading institutions rely on Jenni AI for efficient summary generation

Crafting Quality Academic Writing Solutions with Our Text Summarizer
Discover how Jenni AI stands out as the solution for your summarization needs
Effortless Summarization
Jenni AI takes the hassle out of summarization. Just paste your text, and watch as Jenni AI distills the core ideas into a clear, concise summary.
Get started

Interactive Editing
Don’t just settle for the first draft. Interact with the summary, tweak, and refine it to meet your specific requirements, ensuring that every summary is precisely what you need.
Learning and Improvement
Jenni AI is not just a tool, but a companion in your academic journey. Learn from the summarization process and improve your writing skills with every interaction.

Our Commitment to Academic Integrity
At Jenni AI, we uphold the principle of academic integrity with the utmost regard. Our tool is devised to assist, not to replace your original work.
How Does Jenni AI Summarizing Tool Work?
Navigating the Realm of Academic Writing Has Never Been Easier
Create Your Account
Sign up for a free Jenni AI account to embark on a simplified summarization journey.
Paste Your Text
Copy and paste the text you wish to summarize. Whether it's a research article, essay, or a complex thesis, Jenni AI is here to assist.
Generate Your Summary
Ask Jenni to summarize and watch as it employs advanced algorithms to distill the core essence of your text, presenting a coherent and concise summary.
Review and edit your summary. Jenni AI's interactive platform allows you to tweak and refine the summary to align perfectly with your academic objectives.
What Scholars Are Saying
Hear from our satisfied users and elevate your writing to the next level

· Aug 26
I thought AI writing was useless. Then I found Jenni AI, the AI-powered assistant for academic writing. It turned out to be much more advanced than I ever could have imagined. Jenni AI = ChatGPT x 10.

Charlie Cuddy
@sonofgorkhali
· 23 Aug
Love this use of AI to assist with, not replace, writing! Keep crushing it @Davidjpark96 💪

Waqar Younas, PhD
@waqaryofficial
· 6 Apr
4/9 Jenni AI's Outline Builder is a game-changer for organizing your thoughts and structuring your content. Create detailed outlines effortlessly, ensuring your writing is clear and coherent. #OutlineBuilder #WritingTools #JenniAI

I started with Jenni-who & Jenni-what. But now I can't write without Jenni. I love Jenni AI and am amazed to see how far Jenni has come. Kudos to http://Jenni.AI team.

· 28 Jul
Jenni is perfect for writing research docs, SOPs, study projects presentations 👌🏽

Stéphane Prud'homme
http://jenni.ai is awesome and super useful! thanks to @Davidjpark96 and @whoisjenniai fyi @Phd_jeu @DoctoralStories @WriteThatPhD
Frequently asked questions
How does jenni ai generate summaries, is jenni ai suitable for all academic fields.
How does the citation helper work?
Can I use Jenni AI for professional or non-academic writing?
How does Jenni AI help with writer’s block?
How does Jenni AI compare to other summarization tools?
Choosing the Right Academic Writing Companion
Get ready to make an informed decision and uncover the key reasons why Jenni AI is your ultimate tool for academic excellence.
Feature Featire
COMPETITORS
Academic Orientation
Designed with academic rigor in mind, ensuring your summaries uphold scholarly standards.
Often lack academic focus, potentially diluting the essence of scholarly texts.
Contextual Understanding
Employs advanced AI to grasp the context, ensuring summaries are meaningful and coherent.
May struggle with contextual understanding, leading to disjointed or misleading summaries.
Customization
Offers customization options to tailor summaries according to your specific needs and preferences.
Generic summarization often with limited customization, risking loss of critical information.
User-Friendly Interface
Intuitive interface makes summarization a breeze, enhancing the user experience.
Clunky interfaces can hinder the summarization process, making it less user-friendly.
Promotes an interactive learning environment, aiding in improving your summarization skills over time.
Merely provide summarization with no added value in terms of learning or skill enhancement.
Ready to Elevate Your Academic Writing?
Create your free Jenni AI account today and discover a new horizon of academic excellence!
Best Summarizing Tool for Academic Texts
Copy and paste your text
Number of sentences in results:
⚙️ 11 Best Summarizing Tools
- 🤔 How to Summarize an Article without Plagiarizing?
- 📝 How to Proofread Your Summary?
⭐ Best Summarizing Tool: the Benefits
🔗 references, ✅ 11 best summary generators to consider.
We’re here to offer the whole list of text summarizers in this article. Every tool has a strong algorithm so you won’t have to proofread a lot in order to make the summary look hand-written. The usage of such websites can be productive for your studying as long as you can focus on more important tasks and leave this routine work to online tools.
In this blog post, you’ll also find tips on successful summarizing and proofreading. These are basic skills that you will need for many assignments. To summarize text better, you’ll need to read it critically, spot the main idea, underline the essential points, and so on. As for proofreading, this skill is useful not only to students but also to professional writers.
To summarize a text, a paragraph or even an essay, you can find a lot of tools online. Here we’ll list some of these, including those that allow choose the percent of similarity and define the length of the text you’ll get.
If you’re asked to summarize some article or paragraph in your own words, one of these summary makers can become significant for getting fast results. Their user-friendly design and accurate algorithms play an important role in the summary development.
1. Summarize Bot
Summarize Bot is an easy-to-use and ad-free software for fast and accurate summary creation in our list. With its help, you can save your time for research by compressing texts. The summary maker shows the reading time, which it saves for you, and other useful statistics. To summarize any text, you should only send the message in Facebook or add the bot to Slack. The app works with various file types: including PDF, mp3, DOC, TXT, jpg, etc., and supports almost every language.
The only drawback is the absence of web version. If you don’t have a Facebook account and don’t want to install Slack, you won’t be able to enjoy this app’s features.
SMMRY has everything you need for a perfect summary—easy to use design, lots of features, and advanced settings (URL usage). If you look for a web service that changes the wording, this one would never disappoint you.
SMMRY allows you to summarize the text not only by copy-pasting but also with the file uploading or URL inserting. The last one is especially interesting. With this option, you don’t have to edit an article in any way. Just put the URL into the field and get the result. The tool is ad-free and doesn’t require registration.
Jasper is an AI-powered summary generator. It creates unique, plagiarism-free summaries, so it’s a perfect option for those who don’t want to change the wording on their own.
When using this tool, you can summarize a text of up to 12,000 characters (roughly 2,000-3,000 words) in more than 30 languages. Although Jasper doesn’t have a free plan, it offers a 7-day free trial to let you see whether this tool meets your needs.
4. Quillbot
Quillbot offers many tools for students and writers, and summarizer is one of them. With this tool, you can customize your summary length and choose between two modes: paragraph and key sentences. The former presents a summary as a coherent paragraph, while the latter gives you key ideas of the text in the form of bullet points.
What is great about Quillbot is that you can use it for free. However, there’s a limitation: you can only summarize a text of up to 1,200 words on a free plan. A premium plan extends this limit to 6,000 words. In addition, you don’t need to register to use Quillbot summarizer; just input your text and get the result.
5. TLDR This
TLDR This is a summary generator that can help you quickly summarize long text. You can paste your paper directly into the tool or provide it with a URL of the article you want to shorten.
With a free plan, you have unlimited attempts to summarize texts in the form of key sentences. TLDR This also provides advanced AI summaries, but you have only 10 of these on a free plan. To get more of them, you have to go premium, which starts at $4 per month.
HIX.AI summarizer is an AI-powered tool that can help you summarize texts of up to 10,000 characters. If you use Google Chrome or Microsoft Edge, HIX.AI has a convenient extension for you.
You can use the tool for free to check 1,000 words per week. Along with this, you get access to over 120 other AI-powered tools to help you with your writing tasks. These include essay checker, essay rewriter, essay topic generator, and many others. With a premium plan, which starts at $19.99 a month billed yearly, you also get access to GPT-4 and other advanced features.
7. Scholarcy
Scholarcy is one of the best tools for summarizing academic articles. It presents summaries in the form of flashcards, which can be downloaded as Word, PowerPoint, or Markdown files.
This tool has some outstanding features for students and researchers. For example, it creates a referenced summary, which makes it easier for you to cite the information correctly in your paper. In addition, it can find the references from the summarized article and provide you with open-access links to them. The tool can also extract tables and figures from the text and let you download them as Excel files.
Unregistered users can summarize one article per day. With a free registered account, you can make 3 summary flashcards a day. Moreover, Scholarcy offers free Chrome, Edge, and Firefox extensions that allow you to summarize short and medium-sized articles.
Frase is an AI-powered summary generator that is available for free. The tool can summarize texts of up to 600-700 words. Therefore, it’s good if you want to, say, summarize the main points of your short essay or blog post to write a conclusion. However, if you need summaries of long research articles, you should choose another option.
This summary generator allows you to adjust the level of creativity, meaning that you can generate original, plagiarism-free summaries. Frase also has lots of extra features for SEO and project management, which makes it a good option for website content creators.
9. Resoomer
Resoomer is another paraphrasing and summarizing tool that works with several languages. You’re free to use the app in English, French, German, Italian, and Spanish.
This online tool may be considered as one of the best text summarizers in IvyPanda ranking, because it allows performing many custom settings. For example, you can click to Manual and set the size of the summary (in percent or words). You can also set the number of keywords for the tool to focus on.
Among its drawbacks, we would mention that the software works only with argumentative texts and won’t reword other types correctly. Also, free version contains lots of ads and does not allow its users to import files. The premium subscription costs 4.90€ per month or 39.90€/year.
10. Summarizer
Summarizer is another good way to summarize any article you read online. This simple Chrome extension will provide you with a summary within a couple of clicks. Install the add-on, open the article or select the piece of text you want to summarize and click the button “Summarize”.
The software processes various texts in your browser, including long PDF articles. The result of summarizing has only 7% of the original article. This app is great for all who don’t want to read long publications. However, it doesn’t allow you to import file or download the result.
11. Summary Generator
The last article and essay Summary Generator in our list which can be helpful for your experience in college or university. This is free open software everyone can use.
The tool has only two buttons—one to summarize the document and the other to clear the field. With this software, you’ll get a brief summary based on your text. You don’t have to register there to get your document shortened.
Speaking about drawbacks of the website, we would mention too many ads and no options to summarize a URL or document, set up the length of the result and export it to the popular file types.
These were the best online summarizing tools to deal with the task effectively. We hope some of them became your favorite summarizers, and you’ll use them often in the future.
Not sure if a summarizer will work for your paper? Check out this short tutorial on how the text summarizing tool can come in handy for essay writing.
🤔 Techniques & Tools to Summarize without Plagiarizing
Of course, there are times when you can’t depend on online tools. For example, you may be restricted to use them in a class or maybe you have to highlight some specific paragraphs and customizing the tool’s settings would take more time and efforts than summary writing itself.
In this chapter, you’ll learn to summarize a long article, essay, research paper, report, or a book chapter with the help of helpful tips, a logical approach, and a little bit of creativity.
Here are some methods to let you create a fantastic summary.
- Know your goal. To choose the right route to your goal, you need to understand it perfectly. Why should you summarize the text? What is its style: scientific or publicistic? Who is the author? Where was the article published? There are many significant questions that can help to adapt your text better. Develop a short interview to use during the summary writing. Include all the important information on where you need to post the text and for what purpose.
- Thorough reading. To systemize your thoughts about the text, it’s significant to investigate it in detail. Read the text two or more times to grasp the basic ideas of the article and understand its goals and motives. Give yourself all the time you need to process the text. Often we need a couple of hours to extract the right results from the study or learn to paraphrase the text properly.
- Highlight the main idea. When writing a summary, you bear a responsibility for the author. Not only you have to extract the significant idea of the text but to paraphrase it correctly. It’s important not to misrepresent any of the author’s conclusions in your summary. That’s why you should find the main idea and make sure, you can paraphrase it without a loss of meaning. If possible, read a couple of professional reviews of a targeted book chapter or article. It can help you to analyze the text better.
- Mark the arguments. The process of summarizing is always easier if you have a marker to highlight important details in the text. If you don’t have a printed text, there’s always Microsoft Word to use a highlight tool on the paper. Try to mark all arguments, statistics, and facts in the text to represent them in your summary. This information will turn into key elements of the summary you’ll create, so keep attention on what you highlight exactly.
- Take care of plagiarism. Before you start writing, learn what percent of originality should you aim at. Various projects have different requirements. And they determine how many efforts you should put into writing to get a perfect summary your teacher will like. Depending on the percent of originality, build a plan for your short text. Allow yourself copy as much information as allowed to save your time.
- Build a structure. With the help of key elements, which you’ve highlighted in the text, it’s possible to create a powerful structure including all the interesting facts and arguments. Develop an outline according to a basic structure – introduction, body, and conclusion. Even if your summary is extremely short, the main idea should sound in both the first and last sentences.
- Write a draft. If you’re not a professional writer, it can be extremely difficult to develop a text with the correct word count on the first try. We advise you to develop a general text firstly – include all the information without controlling the number of sentences.
- Cut out the unnecessary parts. On this step, you should edit the draft and eliminate the unnecessary parts. Keep in mind, the number of sentences your summary must contain. Make sure the main point is fully represented in the text. You can cut out any sentence except those concluding the significant arguments.
- Wordiness – you should delete unnecessary words, which make it difficult to understand the text
- Common mistakes – mistakes made in academic papers are basically the same, so it’s helpful to have an article like this one when you’re proofreading
- Appropriate terminology – for each topic, there’s a list of the terminology you can use
- Facts and statistics – you can accidently write a wrong year or percent, make sure to avoid these mistakes
- Quotes – every quote should be written correctly and have a link to its source.
📝 How to Proofread the Summarized Text?
Now, when you know how to summarize an article, it’s time to edit your text whether it’s your own writing or a summary generator’s results.
In this chapter, you’ll see the basic ways to proofread any type of text: academic paper (essay, research paper, etc.), article, letter, book’s chapter, and so on.
- Proofread your summary. Are there times when you can’t remember an appropriate synonym? Then you should use Thesaurus and analogous services from time to time. They can expand your vocabulary a lot and help to find the right words even in the most challenging situations.
- Pay attention to easily confused words. It’s especially significant if you edit a nonfiction text – there’s a number of words people often confuse without even realizing. English Oxford Living Dictionaries have a list of these word pairs so you won’t miss any.
- Proofread one type of mistakes at a time. To edit a paper properly don’t split your attention to grammar and punctuation—this way you can miss dozens of mistakes. To get more accurate results, read the first time to edit the style, the second to eliminate grammar mistakes, and the third to proofread punctuation. Take as many times as you need to concentrate on each type.
- Take a rest from your paper. If you use an online summarizing tool, you can skip this step. But if you’ve been writing a paper for several hours and now trying to edit it without taking a break, it may be a bad idea. Why? Because without a fresh pair of eyes there’s a great possibility not to spot even obvious mistakes. Give yourself some time to slightly forget the text—go for a walk or call a friend, and then return to work as a new person.
- Hire a proofreader. If you need to get perfect results, think about hiring a professional. Skills and qualification, which they have, guarantee a perfect text without any mistakes or style issues. Once you find a proofreader, you can optimize your work perfectly. Search for specialists on freelance websites like UpWork — it’s comfortable and safe to use. Of course, there’s one flaw you should think about—hiring a pro is expensive. So, everyone should decide on their own whether they need to spend this money or not.
- Switch your paper with a friend. If you can’t afford a professional editor, there’s a less expensive option—ask a friend to look through your paper and proofread theirs in return. Make sure, you both make manual editing, not just check it with Microsoft Office or analogous software. Although there are great grammar tools, they still can’t spot many mistakes obvious to a human.
- Use grammar checking tools. We recommend you not to depend on multiple grammar tools. But the assistance it can offer is irreplaceable. Start your proofreading by scanning your text with Grammarly or an analogous tool. The service detects many types of errors including confusing words’ pairs, punctuation, misspellings, wordiness, incorrect word order, unfinished sentences, and so on. Of course, you should never correct the mistakes without thinking on every specific issue. Tools not only miss a lot of mistakes but they also can be wrong about your errors.
- Read aloud. It’s amazing how different the written text can sound when read aloud. If you practice this proofreading method, you know that many mistakes can be spotted if you actually pronounce the text. Why does it happen? People understand information better if they perceive it with the help of different senses. You can use this trick even in learning— memorize the materials with the help of reading, listening, and speaking.
These tips are developed to help students proofread their papers easily. We hope this chapter and the post itself create a helpful guide on how to summarize an article.
Here you found the best summarizing tools, which are accessible online and completely free, and learned to summarize various texts and articles on your own.
Updated: Dec 19th, 2023
- Summarizing: Academic Integrity at MIT
- 4 of the Best Online Summarizer Tools to Shorten Text: maketecheasier
- Summarizing: University of Toronto
- 5 Easy Summarizing Strategies for Students: ThoughtCo.
- Summarizing: Texas A&M University Writing Center
- Comparative Study of Text Summarization Methods: Semantic Scholar
- How to Write a Summary: UTEP
- How to Write a Summary: UW
- Free Essays
- Writing Tools
- Lit. Guides
- Donate a Paper
- Referencing Guides
- Free Textbooks
- Tongue Twisters
- Job Openings
- Expert Application
- Video Contest
- Writing Scholarship
- Discount Codes
- IvyPanda Shop
- Terms and Conditions
- Privacy Policy
- Cookies Policy
- Copyright Principles
- DMCA Request
- Service Notice
This page is for anyone interested in creating a summary for an essay or any other written work. It lists the best online summarizing tools and gives advice on how to summarize an article well. Finally, you'll find tips on how to properly proofread your summary.
Use AI to summarize scientific articles in seconds

Send a document, get a summary. It's that easy.

If GPT had a PhD
- 50,000 words summarized
- First article summarized per month can be up to 200,000 words
- 50 documents indexed for semantic search
- 100 Chat Messages
- Unlimited article searches
- Import and summarize references with the click of a button
- 1,000,000 words summarized per month
- Maximum document length of 200,000 words
- Unlimited bulk summaries
- 10,000 chat messages per month
- 1,000 documents indexed for semantic search
- Resources Home 🏠
- Try SciSpace Copilot
- Search research papers
- Add Copilot Extension
- Try AI Detector
- Try Paraphraser
- Try Citation Generator
- April Papers
- June Papers
- July Papers

How To Write A Research Summary

It’s a common perception that writing a research summary is a quick and easy task. After all, how hard can jotting down 300 words be? But when you consider the weight those 300 words carry, writing a research summary as a part of your dissertation, essay or compelling draft for your paper instantly becomes daunting task.
A research summary requires you to synthesize a complex research paper into an informative, self-explanatory snapshot. It needs to portray what your article contains. Thus, writing it often comes at the end of the task list.
Regardless of when you’re planning to write, it is no less of a challenge, particularly if you’re doing it for the first time. This blog will take you through everything you need to know about research summary so that you have an easier time with it.
What is a Research Summary?
A research summary is the part of your research paper that describes its findings to the audience in a brief yet concise manner. A well-curated research summary represents you and your knowledge about the information written in the research paper.
While writing a quality research summary, you need to discover and identify the significant points in the research and condense it in a more straightforward form. A research summary is like a doorway that provides access to the structure of a research paper's sections.
Since the purpose of a summary is to give an overview of the topic, methodology, and conclusions employed in a paper, it requires an objective approach. No analysis or criticism.
Research summary or Abstract. What’s the Difference?
They’re both brief, concise, and give an overview of an aspect of the research paper. So, it’s easy to understand why many new researchers get the two confused. However, a research summary and abstract are two very different things with individual purpose. To start with, a research summary is written at the end while the abstract comes at the beginning of a research paper.
A research summary captures the essence of the paper at the end of your document. It focuses on your topic, methods, and findings. More like a TL;DR, if you will. An abstract, on the other hand, is a description of what your research paper is about. It tells your reader what your topic or hypothesis is, and sets a context around why you have embarked on your research.
Getting Started with a Research Summary
Before you start writing, you need to get insights into your research’s content, style, and organization. There are three fundamental areas of a research summary that you should focus on.
- While deciding the contents of your research summary, you must include a section on its importance as a whole, the techniques, and the tools that were used to formulate the conclusion. Additionally, there needs to be a short but thorough explanation of how the findings of the research paper have a significance.
- To keep the summary well-organized, try to cover the various sections of the research paper in separate paragraphs. Besides, how the idea of particular factual research came up first must be explained in a separate paragraph.
- As a general practice worldwide, research summaries are restricted to 300-400 words. However, if you have chosen a lengthy research paper, try not to exceed the word limit of 10% of the entire research paper.
How to Structure Your Research Summary
The research summary is nothing but a concise form of the entire research paper. Therefore, the structure of a summary stays the same as the paper. So, include all the section titles and write a little about them. The structural elements that a research summary must consist of are:
It represents the topic of the research. Try to phrase it so that it includes the key findings or conclusion of the task.
The abstract gives a context of the research paper. Unlike the abstract at the beginning of a paper, the abstract here, should be very short since you’ll be working with a limited word count.
Introduction
This is the most crucial section of a research summary as it helps readers get familiarized with the topic. You should include the definition of your topic, the current state of the investigation, and practical relevance in this part. Additionally, you should present the problem statement, investigative measures, and any hypothesis in this section.
Methodology
This section provides details about the methodology and the methods adopted to conduct the study. You should write a brief description of the surveys, sampling, type of experiments, statistical analysis, and the rationality behind choosing those particular methods.
Create a list of evidence obtained from the various experiments with a primary analysis, conclusions, and interpretations made upon that. In the paper research paper, you will find the results section as the most detailed and lengthy part. Therefore, you must pick up the key elements and wisely decide which elements are worth including and which are worth skipping.
This is where you present the interpretation of results in the context of their application. Discussion usually covers results, inferences, and theoretical models explaining the obtained values, key strengths, and limitations. All of these are vital elements that you must include in the summary.
Most research papers merge conclusion with discussions. However, depending upon the instructions, you may have to prepare this as a separate section in your research summary. Usually, conclusion revisits the hypothesis and provides the details about the validation or denial about the arguments made in the research paper, based upon how convincing the results were obtained.
The structure of a research summary closely resembles the anatomy of a scholarly article . Additionally, you should keep your research and references limited to authentic and scholarly sources only.
Tips for Writing a Research Summary
The core concept behind undertaking a research summary is to present a simple and clear understanding of your research paper to the reader. The biggest hurdle while doing that is the number of words you have at your disposal. So, follow the steps below to write a research summary that sticks.
1. Read the parent paper thoroughly
You should go through the research paper thoroughly multiple times to ensure that you have a complete understanding of its contents. A 3-stage reading process helps.
a. Scan: In the first read, go through it to get an understanding of its basic concept and methodologies.
b. Read: For the second step, read the article attentively by going through each section, highlighting the key elements, and subsequently listing the topics that you will include in your research summary.
c. Skim: Flip through the article a few more times to study the interpretation of various experimental results, statistical analysis, and application in different contexts.
Sincerely go through different headings and subheadings as it will allow you to understand the underlying concept of each section. You can try reading the introduction and conclusion simultaneously to understand the motive of the task and how obtained results stay fit to the expected outcome.
2. Identify the key elements in different sections
While exploring different sections of an article, you can try finding answers to simple what, why, and how. Below are a few pointers to give you an idea:
- What is the research question and how is it addressed?
- Is there a hypothesis in the introductory part?
- What type of methods are being adopted?
- What is the sample size for data collection and how is it being analyzed?
- What are the most vital findings?
- Do the results support the hypothesis?
Discussion/Conclusion
- What is the final solution to the problem statement?
- What is the explanation for the obtained results?
- What is the drawn inference?
- What are the various limitations of the study?
3. Prepare the first draft
Now that you’ve listed the key points that the paper tries to demonstrate, you can start writing the summary following the standard structure of a research summary. Just make sure you’re not writing statements from the parent research paper verbatim.
Instead, try writing down each section in your own words. This will not only help in avoiding plagiarism but will also show your complete understanding of the subject. Alternatively, you can use a summarizing tool (AI-based summary generators) to shorten the content or summarize the content without disrupting the actual meaning of the article.
SciSpace Copilot is one such helpful feature! You can easily upload your research paper and ask Copilot to summarize it. You will get an AI-generated, condensed research summary. SciSpace Copilot also enables you to highlight text, clip math and tables, and ask any question relevant to the research paper; it will give you instant answers with deeper context of the article..
4. Include visuals
One of the best ways to summarize and consolidate a research paper is to provide visuals like graphs, charts, pie diagrams, etc.. Visuals make getting across the facts, the past trends, and the probabilistic figures around a concept much more engaging.
5. Double check for plagiarism
It can be very tempting to copy-paste a few statements or the entire paragraphs depending upon the clarity of those sections. But it’s best to stay away from the practice. Even paraphrasing should be done with utmost care and attention.
Also: QuillBot vs SciSpace: Choose the best AI-paraphrasing tool
6. Religiously follow the word count limit
You need to have strict control while writing different sections of a research summary. In many cases, it has been observed that the research summary and the parent research paper become the same length. If that happens, it can lead to discrediting of your efforts and research summary itself. Whatever the standard word limit has been imposed, you must observe that carefully.
7. Proofread your research summary multiple times
The process of writing the research summary can be exhausting and tiring. However, you shouldn’t allow this to become a reason to skip checking your academic writing several times for mistakes like misspellings, grammar, wordiness, and formatting issues. Proofread and edit until you think your research summary can stand out from the others, provided it is drafted perfectly on both technicality and comprehension parameters. You can also seek assistance from editing and proofreading services , and other free tools that help you keep these annoying grammatical errors at bay.
8. Watch while you write
Keep a keen observation of your writing style. You should use the words very precisely, and in any situation, it should not represent your personal opinions on the topic. You should write the entire research summary in utmost impersonal, precise, factually correct, and evidence-based writing.
9. Ask a friend/colleague to help
Once you are done with the final copy of your research summary, you must ask a friend or colleague to read it. You must test whether your friend or colleague could grasp everything without referring to the parent paper. This will help you in ensuring the clarity of the article.
Once you become familiar with the research paper summary concept and understand how to apply the tips discussed above in your current task, summarizing a research summary won’t be that challenging. While traversing the different stages of your academic career, you will face different scenarios where you may have to create several research summaries.
In such cases, you just need to look for answers to simple questions like “Why this study is necessary,” “what were the methods,” “who were the participants,” “what conclusions were drawn from the research,” and “how it is relevant to the wider world.” Once you find out the answers to these questions, you can easily create a good research summary following the standard structure and a precise writing style.
You might also like

Consensus GPT vs. SciSpace GPT: Choose the Best GPT for Research

Literature Review and Theoretical Framework: Understanding the Differences

Types of Essays in Academic Writing - Quick Guide (2024)
Upload your PDF, EPUB, DOCX, ODT, or TXT file here.
PDF, EPUB, DOCX, ODT, TXT
Or import your images / photos by clicking below
(JPEG / PNG)
Please wait... or cancel
Reading speed : 0.8
Go to the main ideas in your texts, summarize them « relevantly » in 1 Click
We advice + we design + we develope.
- Text example
Text example
Initialisation...
Identify the important ideas and facts
To help you summarize and analyze your argumentative texts , your articles, your scientific texts, your history texts as well as your well-structured analyses work of art, Resoomer provides you with a "Summary text tool" : an educational tool that identifies and summarizes the important ideas and facts of your documents. Summarize in 1-Click, go to the main idea or skim through so that you can then interpret your texts quickly and develop your syntheses .
Who is Resoomer for ?
College students.
With Resoomer, summarize your Wikipedia pages in a matter of seconds for your productivity.
Identify the most important ideas and arguments of your texts so that you can prepare your lessons.
JOURNALISTS
If you prefer simplified information that summarizes the major events, then Resoomer is for you !
Identify and understand very fast the facts and the ideas of your texts that are part of the current news and events.
PRESS RELEASES
With the help of Resoomer, go to the main idea of your articles to write your arguments and critiques .
Save time, summarize your digital documents for a relevant and fast uptake of information.
Need to summarize your books' presentations ? Identify the arguments in a matter of seconds.
Too many documents ? Simplify your readings with Resoomer like a desktop tool.
Need to summarize your chapters ? With Resoomer, go to the heart of your ideas.
Identify your books' or your authors' ideas quickly. Summarize the most important main points.
From now on, create quick summaries of your artists' presentation and their artworks .
INSTITUTIONS
Identify the most important passages in texts that contains a lot of words for detailed analyses .
They Tweeted
Follow @resoomer_ Tweeter
SUMMARIZE YOUR ONLINE ARTICLES IN 1-CLICK
Download the extension for your browser
Surf online and save time when reading on internet ! Resoomer summarizes your articles in 500 words so that you can go to the main idea of your text.
HOW DOES RESOOMER WORK ?
Popular articles.
- Summary and synthesis: the difference?
- The text summarizer
- Summarize a text
- Summarize a document online
- Summarize an online article
- Read more and faster documents
- Argue and find arguments in a text
- Learn more": How to increase your knowledge?
Our partners that like Resoom(er)ing their texts :


Research Assistant
Ai-powered research summarizer.
- Summarize academic papers: Quickly understand the main points of research papers without reading the entire document.
- Extract insights from reports: Identify key findings and trends from industry reports, surveys, or reviews.
- Prepare for presentations: Create concise summaries of research materials to include in your presentations or talking points.
- Enhance your understanding: Improve your comprehension of complex subjects by summarizing the main ideas and insights.
- Save time: Reduce the time spent on reading lengthy research documents by focusing on the most important points.
New & Trending Tools
Resume improvement assistant, global branding and cultural considerations tutor, brand extensions and line extensions tutor.
Training videos | Faqs

How to Make Your Study Limitations Sound Positive?
The important trick you have to learn while presenting your limitations is to present them in a constructive way rather than being too negative about them. You must try to use positive language even when you are talking about major limitations of your work. In this blog, we will look at some clever techniques to present the study limitations in your research paper without reducing the impact of your work.
1. Use Less Negative Words

In the example below, the authors are trying to tell the readers that one of the drawbacks of their study was that a lot of parameters were approximated. In the first example, the authors start the sentence with the word ‘Unfortunately’. This is a negative word. Don’t use strong negative words like ‘unfortunately’, ‘disappointing’, ‘regrettably’, etc. Try to use slightly less negative words like ‘limitations’, ‘pitfalls’, ‘drawbacks’, ‘shortcomings’ etc. In the second example, the authors have used the word ‘limitation’ which is a slightly less negative word.
✖ The authors have used strong negative words such as ‘Unfortunately’ and ‘Regrettably’ Unfortunately, due to lack of reliable data a lot of parameters were approximated from available literature. Regrettably, there wasn’t enough literature on the topic. ✔ The authors have used slightly less negative words like ‘Limitations’ and ‘Scarcely available’ One of the limitations of the study is that certain parameters were approximated from scarcely available literature data.
2. Clarify Exactly What Your Limitations Are
In the example below, the authors are trying to tell the readers that one of the drawbacks of their study is the small sample size. In the first example, the authors have not given any further explanation as to why the sample size is small. Whereas in the second example, the authors have clearly explained the reason. They are saying that the sample size is small because the cases were limited to one hospital. They are also finishing the passage with a positive note saying that even though it is a small study it has yielded useful results, and future work should try to replicate these findings in larger studies.
You can imagine the type of impact both examples might have on the readers. The first example undermines the credibility of the research, whereas the second example sets a slightly different tone and sounds a bit positive.
✖ The author has provided no reason for the small sample size. This is a very blunt statement and undermines the crediblity of the research. Unfortunately, the sample size was too small in study. ✔ The author has clearly explained why their sample size was small and their explanation sounds credible One limitation is that the sample size was small. This is because the number of cases was limited to one hospital. Nevertheless, the study has yielded important results. Larger yet similar studies are required to reconfirm the findings.
3. Distance Yourself from the Limitation
Here is a slightly different way of presenting the same limitations. The authors have used some clever tactics here to make the limitations sound more positive.
✔ The authors have take a neutal stance and telling the readers that this is a common problem faced by most studies of this nature Although the study has yielded important results, it is limited by the small sample size. Due to financial constraints, the majority of such studies are limited to cases from one hospital.
You can see that the author has used the adverb ‘Although’ at the start of the sentence, so this immediately tells the readers that something negative is about to follow. They are saying that although the study has yielded very important results, the sample size is a bit small.
There is something else they are doing here that is quite clever. They are saying that this is because of financial constraints, and most studies of this nature suffer from this limitation. The authors are distancing themselves from the data and taking a neutral stance by saying they are not the only ones experiencing this problem, and this is a well-known problem in the field. After reading this passage, you get a feeling that although the study has some limitations, it may not be the author’s fault. This is a very good example demonstrating how to strike a constructive and positive tone when talking about limitations.
You must talk about the limitations of your work in the discussion section of the paper. One of the important qualities that the scientific community expects from a researcher is honesty and admitting when they have made a mistake. However, the trick is not to make your readers feel too negative about your work. We have covered a few strategies in this blog to make your limitations sound less negative. For further reading, please refer to our blogs on handling negative results and research limitations examples .
If you have any questions, please drop a comment below, and we will answer as soon as possible. We also recommend you to refer to our other blogs on academic writing tools , academic writing resources , academic writing phrases and research paper examples which are relevant to the topic discussed in this blog.
Similar Posts

How to Create a Research Paper Outline?
In this blog we will see how to create a research paper outline and start writing your research paper.

Results Section Examples and Writing Tips
In this blog, we will go through many results section examples and understand how to write a great results section for your paper.

Paraphrasing – Techniques for Rephrasing, Rewording, and Rewriting.
In this blog, we explain good paraphrasing techniques. We also discuss how paraphrasing tools and plagiarism checkers can be used to avoid academic misconduct.

Research Methodology – 5 Beginner Writing Mistakes to Avoid
In this blog, we will look at five common mistakes to avoid while writing the methodology section of your research paper.

How to Reuse a Method from a Previous Paper?
In this blog, we will look at how to replicate someone’s methodology in your paper.

Introduction Paragraph Examples and Writing Tips
In this blog, we will go through a few introduction paragraph examples and understand how to construct a great introduction paragraph for your research paper.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- 10 Share Facebook
- 0 Share Twitter
- 0 Share LinkedIn
- 0 Share Email

Research Specialist
- Madison, Wisconsin
- SCHOOL OF EDUCATION/WIS CENTER FOR EDUCATION RESCH-GEN
- Partially Remote
- Staff-Full Time
- Staff-Part Time
- Opening at: May 7 2024 at 13:55 CDT
- Closing at: May 21 2024 at 23:55 CDT
Job Summary:
The Teaming Up for Equity in Science: Supporting NGSS Three-dimensional Learning and Achievement through Actionable Assessment project seeks an education researcher to join a team investigating how to make middle school assessment more meaningful for students. The research specialist will support quantitative and qualitative research into the educational efficacy of an innovative middle school science assessment system called ONPAR. Research activities include surveys, interviews, analysis of assessment results, education data, and user feedback. This is a grant-funded position which ends 12/31/2026. The Teaming Up for Equity in Science: Supporting NGSS Three-dimensional Learning and Achievement through Actionable Assessment project will examine the use of the ONPAR NGSS-based assessment system to leverage data to inform teaching and learning and conduct a randomized controlled trial to assess its effectiveness. The project will refine and validate ONPAR materials to meet the needs of users, increase teacher efficacy for NGSS assessment and data-driven instruction through professional development, improve outcomes for high-need middle school science learners, particularly ELs and students who struggle with reading, and build capacity for sustaining and expanding the use of the ONPAR assessment system. More information on the project can be found at http://iiassessment.wceruw.org/ .
Responsibilities:
- 30% Conducts research experiments according to established research protocols with moderate impact to the project(s). Collects data and monitors test results
- 20% Operates, cleans, and maintains organization of research equipment and research area. Tracks inventory levels and places replenishment orders
- 20% Reviews, analyzes, and interprets data and/or documents results for presentations and/or reporting to internal and external audiences
- 10% Participates in the development, interpretation, and implementation of research methodology and materials
- 10% Provides operational guidance on day-to-day activities of unit or program staff and/or student workers
- 10% Performs literature reviews and writes reports
Institutional Statement on Diversity:
Diversity is a source of strength, creativity, and innovation for UW-Madison. We value the contributions of each person and respect the profound ways their identity, culture, background, experience, status, abilities, and opinion enrich the university community. We commit ourselves to the pursuit of excellence in teaching, research, outreach, and diversity as inextricably linked goals. The University of Wisconsin-Madison fulfills its public mission by creating a welcoming and inclusive community for people from every background - people who as students, faculty, and staff serve Wisconsin and the world. For more information on diversity and inclusion on campus, please visit: Diversity and Inclusion
Required Bachelor's Degree minimum in science education or closely related field Preferred Master's Degree MA in science education preferred
Qualifications:
Required: -experience working in K-12 science education (classroom, research or other related position) -experience assisting with or conducting quantitative and qualitative research and following research procedures -excellent written and oral communication skills -self-motivated -able to thrive in a minimal supervision environment Preferred: -experience organizing and cleaning quantitative data -familiarity with science assessment -experience conducting literature reviews and writing reports -attentive to detail -strong collaboration skills
Full or Part Time: 80% - 100% This position may require some work to be performed in-person, onsite, at a designated campus work location. Some work may be performed remotely, at an offsite, non-campus work location. The balance of in-person and remote work for this position will be discussed at the time of hire.
Appointment Type, Duration:
Terminal, 30 month appointment. This position has the possibility to be extended or converted to an ongoing appointment based on need and/or funding
Minimum $44,543 ANNUAL (12 months) Depending on Qualifications Employees in this position can expect to receive benefits such as generous vacation, holidays, and paid time off; competitive insurances and savings accounts; retirement benefits.
Additional Information:
The Wisconsin Center for Education Research (WCER), established in 1964, is one of the first, most productive, and largest university-based education research and development centers in the world. WCER's researchers and staff work to make teaching and learning as effective as possible for all ages and all people. WCER's mission is to improve educational outcomes for diverse student populations, impact education practice positively and foster collaborations among academic disciplines and practitioners. To this end, our center helps scholars and practitioners develop, submit, conduct, and share grant-funded education research. At WCER, all employees share five fundamental organization values to guide the purpose and quality of our work and interactions within ourselves and our outside stakeholders. The values that the work and people of WCER strive to uphold are: - Innovation and Excellence. Continuous improvement is a driver for excellence. We innovate and improve in our work to advance education through leading research and development. - Equitable Education. Equitable education is essential to a healthy society. We aim to reverse imbalances and injustices in education through our work. - Affirming and Increasing Diversity. Individual differences and group diversity inspire creative and equitable outcomes. We actively affirm and seek to increase such diversity in our center. - Healthy Workplace. The well-being of our workplace enhances success for all. We commit to a workplace based on mutual respect and transparency. - Partnering Across Differences. Diverse backgrounds and expertise improve the quality of our work. We collaborate across disciplines, methodologies, organizations, and communities to strengthen our research and development outcomes. If you need to request an accommodation because of a disability during the recruitment process, please email [email protected] and one of our Division Disability Representatives will contact you. More information can also be found at https://employeedisabilities.wisc.edu/disability-accommodation-information-for-applicants/ .
How to Apply:
Please click on the "Apply Now" button to start the application process. As part of the application process, you will be required to submit: - A cover letter addressed to Laura Wright describing how your experience and qualifications meet the requirements of this position - A current resume - A list with the contact information of at least three professional references
Becky Ohan [email protected] 608-262-5158 Relay Access (WTRS): 7-1-1. See RELAY_SERVICE for further information.
Official Title:
Research Specialist(RE047)
Department(s):
A17-SCHOOL OF EDUCATION/WCER
Employment Class:
Academic Staff-Terminal
Job Number:
The university of wisconsin-madison is an equal opportunity and affirmative action employer..
You will be redirected to the application to launch your career momentarily. Thank you!
Frequently Asked Questions
Applicant Tutorial
Disability Accommodations
Pay Transparency Policy Statement
Refer a Friend
You've sent this job to a friend!
Website feedback, questions or accessibility issues: [email protected] .
Learn more about accessibility at UW–Madison .
© 2016–2024 Board of Regents of the University of Wisconsin System • Privacy Statement
Religious Worship Attendance in America: Evidence from Cellphone Data

Religious worship is integral to the lives of millions of Americans, and has increasingly been shown to be an important driver of important economic outcomes . To date, most studies on religion have relied on surveys where respondents self-report their worship, potentially limiting the reliability of results. In this paper, the author uses anonymized location data from smartphones to provide a descriptive analysis of religious worship attendance in the United States.
The author uses geolocation data from Veraset, a company that provides de-identified geospatial data for millions of smartphones in the United States. He narrows his sample to the roughly 2.1 million cellphones that generate consistent location data over a one-year period between April 2019 and February 2020. The author shows that his sample is reasonably representative of the broader population and can therefore be used to make estimates about religious behavior for the full country. He discovers the following concerning religious worship attendance in the United States:
- Seventy-three percent of people step into a religious place of worship at least once during the year on the primary day of worship (e.g. Sundays for most Christian churches). However, only 5% of Americans attend services “weekly,” far fewer than the roughly 22% who report they do so in surveys.
- The number of occasional versus frequent attenders varies substantially by religion. Members of some religions, such as Latter-day Saints and Jehovah’s Witnesses, have a relatively high fraction of members who are weekly attenders, while members of other religions, such as Catholics and Jews, have a relatively low fraction of members who are weekly attenders.
- Approximately 45 million Americans attend worship services in a typical week. There is limited week-to-week variation/seasonality in attendance, with holidays being the major exceptions. Easter Sunday and Christmas, for example, have nearly 50% greater religious attendance than a typical week.
- Start times and duration of attendance differ meaningfully across religious traditions. There is extreme consistency/uniformity in some religions both in terms of start times and durations (Muslims, Latter-day Saints, and Jehovah’s Witnesses) while other religions are much less uniform (Buddhists and Hindus).
- Religious individuals have very similar income to non-religious individuals ($79k versus $80k). However, individuals that attend weekly have slightly lower incomes ($74k) than less-frequent attenders ($78k) and never attenders ($80k).
- Cold temperatures and precipitation on the day of service lead to less attendance.
- The intensity of religious observance correlates with a host of other activities. For example, relative to non-attenders and infrequent attenders, frequent religious attenders are less likely to go to strip clubs, liquor stores, and casinos.
This research paints a newly detailed picture of religious worship attendance in the United States. Even though the author finds that the frequency of religious worship visits is lower than claimed in surveys, he still shows that approximately 45 million Americans spend more than an hour each week attending religious worship, underscoring the important role of religion in American life. By releasing new granular measures of religious attendance, the author hopes to support future research on some of the most important questions related to religion, such as what leads to increased or decreased religiosity and how religiosity impacts peoples’ attitudes and behaviors.

When Product Markets Become Collective Traps: The Case of Social Media
Research progress of epileptic seizure prediction methods based on EEG
- Review Paper
- Published: 07 May 2024
Cite this article

- Zhongpeng Wang 1 , 2 ,
- Xiaoxin Song ORCID: orcid.org/0009-0008-0176-2310 1 ,
- Long Chen 1 , 2 ,
- Jinxiang Nan 1 ,
- Yulin Sun 1 ,
- Meijun Pang 1 , 2 ,
- Kuo Zhang 1 , 2 ,
- Xiuyun Liu 1 , 2 &
- Dong Ming 1 , 2
At present, at least 30% of refractory epilepsy patients in the world cannot be effectively controlled and treated. The suddenness and unpredictability of seizures greatly affect the physical and mental health and even the life safety of patients, and the realization of early prediction of seizures and the adoption of interventions are of great significance to the improvement of patients’ quality of life. In this paper, we firstly introduce the design process of EEG-based seizure prediction methods, introduce several databases commonly used in the research, and summarize the commonly used methods in pre-processing, feature extraction, classification and identification, and post-processing. Then, based on scalp EEG and intracranial EEG respectively, we reviewed the current status of epileptic seizure prediction research from five commonly used feature analysis methods, and make a comprehensive evaluation of both. Finally, this paper describes the reasons why the current algorithms cannot be applied to the clinic, summarizes their limitations, and gives corresponding suggestions, aiming to provide improvement directions for subsequent research. In addition, deep learning algorithms have emerged in recent years, and this paper also compares the advantages and disadvantages of deep learning algorithms with traditional machine learning methods, in the hope of providing researchers with new technologies and new ideas and making significant breakthroughs in the field of epileptic seizure prediction.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Price includes VAT (Russian Federation)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions
Aarabi A, Fazel-Rezai R, Aghakhani Y (2009) EEG seizure prediction: measures and challenges. In: 2009 Annual international conference of the IEEE engineering in medicine and biology society, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 03–06 September 2009
Aarabi A, He B (2017) Seizure prediction in patients with focal hippocampal epilepsy. Clin Neurophysiol 128(7):1299–1307. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinph.2017.04.026
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Abbasi B, Goldenholz DM (2019) Machine learning applications in epilepsy. Epilepsia 60(10):2037–2047. https://doi.org/10.1111/epi.16333
Acharya UR, Vinitha Sree S, Swapna G, Martis RJ, Suri JS (2013) Automated EEG analysis of epilepsy: a review. Knowl-Based Syst 45:147–165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2013.02.014
Article Google Scholar
Acharya UR, Hagiwara Y, Adeli H (2018a) Automated seizure prediction. Epilepsy Behav 88:251–261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yebeh.2018.09.030
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Acharya UR, Oh SL, Hagiwara Y, Tan JH, Adeli H (2018b) Deep convolutional neural network for the automated detection and diagnosis of seizure using EEG signals. Comput Biol Med 100:270–278. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiomed.2017.09.017
Alexandre Teixeira C, Direito B, Bandarabadi M, Le Van QM, Valderrama M, Schelter B, Schulze-Bonhage A, Navarro V, Sales F, Dourado A (2014) Epileptic seizure predictors based on computational intelligence techniques: a comparative study with 278 patients. Comput Methods Programs Biomed 114(3):324–336. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmpb.2014.02.007
Alotaiby TN, Alshebeili SA, Alotaibi FM, Alrshoud SR (2017) Epileptic seizure prediction using CSP and LDA for scalp EEG signals. Comput Intell Neurosci 2017:1240323. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/1240323
Bandarabadi M, Teixeira CA, Rasekhi J, Dourado A (2015) Epileptic seizure prediction using relative spectral power features. Clin Neurophysiol 126(2):237–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinph.2014.05.022
Beniczky S, Karoly P, Nurse E, Ryvlin P, Cook M (2021) Machine learning and wearable devices of the future. Epilepsia 62(Suppl 2):S116–S124. https://doi.org/10.1111/epi.16555
Bishop CM (2006) Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning. Springer New York, New York. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-0-387-45528-0
Book Google Scholar
Blanco S, Garay A, Coulombie D (2013) Comparison of frequency bands using spectral entropy for epileptic seizure prediction. ISRN Neurol 2013:1–5. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/287327
Bonn E a U. Epileptologie Bonn / Forschung / AG Lehnertz / EEG Data Download n.d. https://www.ukbonn.de/epileptologie/?idcat=193&lang=3
Brázdil M, Pail M, Halámek J, Plešinger F, Cimbálník J, Roman R, Klimeš P, Daniel P, Chrastina J, Brichtová E, Rektor I, Worrell GA, Jurák P (2017) Very high-frequency oscillations: Novel biomarkers of the epileptogenic zone. Ann Neurol 82(2):299–310. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.25006
Burges CJC (1998) A tutorial on support vector machines for pattern recognition. Data Min Knowl Disc 2(2):121–167. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1009715923555
Chen H, Ji T, Zhan X, Liu X, Yu G, Wang W, Jiang Y, Zhou X-H, Ullah I (2022) An explainable statistical method for seizure prediction using brain functional connectivity from EEG. Comput Intell Neurosci 2022:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/2183562
Chu H, Chung CK, Jeong W, Cho KH (2017) Predicting epileptic seizures from scalp EEG based on attractor state analysis. Comput Methods Programs Biomed 143:75–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmpb.2017.03.002
Competition RP (2014) American Epilepsy Society seizure prediction challenge. https://www.kaggle.com/competitions/seizure-prediction/data
Cui S, Duan L, Qiao Y, Xiao Y (2018) Learning EEG synchronization patterns for epileptic seizure prediction using bag-of-wave features. J Ambient Intell Humaniz Comput (prepublish). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-018-1000-3
D’Alessandro M, Esteller R, Vachtsevanos G, Hinson A, Echauz J, Litt B (2003) Epileptic seizure prediction using hybrid feature selection over multiple intracranial EEG electrode contacts: a report of four patients. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 50(5):603–615. https://doi.org/10.1109/tbme.2003.810706
Delamont RS, Walker MC (2011) Pre-ictal autonomic changes. Epilepsy Res 97(3):267–272. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2011.10.016
Detti P, Vatti G, Zabalo Manrique de Lara G (2020) EEG synchronization analysis for seizure prediction: a study on data of noninvasive recordings. Processes 8(7). https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8070846
Direito B, Teixeira CA, Sales F, Castelo-Branco M, Dourado A (2017) A realistic seizure prediction study based on multiclass SVM. Int J Neural Syst 27(3):1750006. https://doi.org/10.1142/s012906571750006x
Duun-Henriksen J, Kjaer TW, Madsen RE, Remvig LS, Thomsen CE, Sorensen HB (2012) Channel selection for automatic seizure detection. Clin Neurophysiol 123(1):84–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinph.2011.06.001
Elger CE, Lehnertz K (1998) Seizure prediction by non-linear time series analysis of brain electrical activity. Eur J Neurosci 10(2):786–789. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1460-9568.1998.00090.x
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
EPMoghaddam D, Sheth SA, Haneef Z, Gavvala J, Aazhang B (2022) Epileptic seizure prediction using spectral width of the covariance matrix. J Neural Eng 19(2). https://doi.org/10.1088/1741-2552/ac6063
Fei K, Wang W, Yang Q, Tang S (2017) Chaos feature study in fractional Fourier domain for preictal prediction of epileptic seizure. Neurocomputing 249:290–298. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2017.04.019
Freiburg UO (2003) Seizure prediction project Freiburg. https://epilepsy.uni-freiburg.de/
Freiman TM, Eismann-Schweimler J, Frotscher M (2011) Granule cell dispersion in temporal lobe epilepsy is associated with changes in dendritic orientation and spine distribution. Exp Neurol 229(2):332–338. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2011.02.017
Gao Y, Liu A, Wang L, Qian R, Chen X (2023) A self-interpretable deep learning model for seizure prediction using a multi-scale prototypical part network. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng 31:1847–1856. https://doi.org/10.1109/tnsre.2023.3260845
Ghosh A, Sarkar A, Das T, Basak P (2017) Pre-ictal epileptic seizure prediction based on ECG signal analysis. In: 2017 2nd International conference for convergence in technology (I2CT), Mumbai, India, 07–09 April 2017
Goldberger AL, Amaral LA, Glass L, Hausdorff JM, Ivanov PC, Mark RG, Mietus JE, Moody GB, Peng CK, Stanley HE (2000) PhysioBank, PhysioToolkit, and PhysioNet: components of a new research resource for complex physiologic signals. Circulation 101(23):E215–E220. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.cir.101.23.e215
Han C, Peng F, Chen C, Li W, Zhang X, Wang X, Zhou W (2021) Research progress of epileptic seizure predictions based on electroencephalogram signals. Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi 38(6):1193–1202. https://doi.org/10.7507/1001-5515.202105052
Hao J, Cui Y, Niu B, Yu L, Lin Y, Xia Y, Yao D, Guo D (2021) Roles of very fast ripple (500–1000[Formula: see text]Hz) in the hippocampal network during status epilepticus. Int J Neural Syst 31(4):2150002. https://doi.org/10.1142/s0129065721500027
Hassan AR, Subasi A (2016) Automatic identification of epileptic seizures from EEG signals using linear programming boosting. Comput Methods Programs Biomed 136:65–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmpb.2016.08.013
Honghong H, Feng Z, Liangfu L, Xiaopeng S (2023) A review of the application of neural networks in epileptic seizure prediction. J Front Comput Sci Technol 17(11):2543–2556. https://doi.org/10.3778/j.issn.1673-9418.2302001
Howbert JJ, Patterson EE, Stead SM, Brinkmann B, Vasoli V, Crepeau D, Vite CH, Sturges B, Ruedebusch V, Mavoori J, Leyde K, Sheffield WD, Litt B, Worrell GA (2014) Forecasting seizures in dogs with naturally occurring epilepsy. PLoS ONE 9(1):e81920. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0081920
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Iasemidis LD, Sackellares JC, Zaveri HP, Williams WJ (1990) Phase space topography and the Lyapunov exponent of electrocorticograms in partial seizures. Brain Topogr 2(3):187–201. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf01140588
Iasemidis LD, Deng-Shan S, Chaovalitwongse W, Sackellares JC, Pardalos PM, Principe JC, Carney PR, Prasad A, Veeramani B, Tsakalis K (2003) Adaptive epileptic seizure prediction system. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 50(5):616–627. https://doi.org/10.1109/tbme.2003.810689
Ibrahim F, Abd-Elateif El-Gindy S, El-Dolil SM, El-Fishawy AS, El-Rabaie E-SM, Dessouky MI, Eldokany IM, Alotaiby TN, Alshebeili SA, Abd El-Samie FE (2019) A statistical framework for EEG channel selection and seizure prediction on mobile. Int J Speech Technol 22(1):191–203. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10772-018-09565-7
Islam MS, El-Hajj AM, Alawieh H, Dawy Z, Abbas N, El-Imad J (2020) EEG mobility artifact removal for ambulatory epileptic seizure prediction applications. Biomed Signal Process Control 55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bspc.2019.101638
Jacobs J, LeVan P, Chander R, Hall J, Dubeau F, Gotman J (2008) Interictal high-frequency oscillations (80–500 Hz) are an indicator of seizure onset areas independent of spikes in the human epileptic brain. Epilepsia 49(11):1893–1907. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1528-1167.2008.01656.x
Jacobs J, Zijlmans M, Zelmann R, Chatillon CE, Hall J, Olivier A, Dubeau F, Gotman J (2010) High-frequency electroencephalographic oscillations correlate with outcome of epilepsy surgery. Ann Neurol 67(2):209–220. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.21847
Jemal I, Mitiche A, Mezghani N (2021) A study of EEG feature complexity in epileptic seizure prediction. Appl Sci 11(4). https://doi.org/10.3390/app11041579
Khan H, Marcuse L, Fields M, Swann K, Yener B (2018) Focal onset seizure prediction using convolutional networks. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 65(9):2109–2118. https://doi.org/10.1109/tbme.2017.2785401
Klatt J, Feldwisch-Drentrup H, Ihle M, Navarro V, Neufang M, Teixeira C, Adam C, Valderrama M, Alvarado-Rojas C, Witon A, Le Van QM, Sales F, Dourado A, Timmer J, Schulze-Bonhage A, Schelter B (2012) The EPILEPSIAE database: an extensive electroencephalography database of epilepsy patients. Epilepsia 53(9):1669–1676. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1528-1167.2012.03564.x
Le Douget JE, Fouad A, Maskani Filali M, Pyrzowski J, Le Van QM (2017) Surface and intracranial EEG spike detection based on discrete wavelet decomposition and random forest classification. Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc 2017:475–478. https://doi.org/10.1109/embc.2017.8036865
Lekshmy HO, Panickar D, Harikumar S (2022) Comparative analysis of multiple machine learning algorithms for epileptic seizure prediction. J Phys Conf Ser 2161(1). https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/2161/1/012055
Li S, Zhou W, Yuan Q, Liu Y (2013) Seizure prediction using spike rate of intracranial EEG. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng 21(6):880–886. https://doi.org/10.1109/tnsre.2013.2282153
Li Y, Liu Y, Guo YZ, Liao XF, Hu B, Yu T (2022) Spatio-temporal-spectral hierarchical graph convolutional network with semisupervised active learning for patient-specific seizure prediction. IEEE Trans Cybern 52(11):12189–12204. https://doi.org/10.1109/tcyb.2021.3071860
Litt B, Echauz J (2002) Prediction of epileptic seizures. Lancet Neurol 1(1):22–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1474-4422(02)00003-0
Lu L, Zhang F, Wu Y, Ma S, Zhang X, Ni G (2022) A multi-frame network model for predicting seizure based on sEEG and iEEG data. Front Comput Neurosci 16:1059565. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncom.2022.1059565
Maimaiti B, Meng H, Lv Y, Qiu J, Zhu Z, Xie Y, Li Y, Yu C, Zhao W, Liu J, Li M (2022) An overview of EEG-based machine learning methods in seizure prediction and opportunities for neurologists in this field. Neuroscience 481:197–218. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2021.11.017
Mirowski P, Madhavan D, LeCun Y, Kuzniecky R (2009) Classification of patterns of EEG synchronization for seizure prediction. Clin Neurophysiol 120(11):1927–1940. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinph.2009.09.002
Mormann F, Lehnertz K, David P, Elger CE (2000) Mean phase coherence as a measure for phase synchronization and its application to the EEG of epilepsy patients. Physica D 144(3–4):358–369. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0167-2789(00)00087-7
Mormann F, Kreuz T, Rieke C, Andrzejak RG, Kraskov A, David P, Elger CE, Lehnertz K (2005) On the predictability of epileptic seizures. Clin Neurophysiol 116(3):569–587. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinph.2004.08.025
Nabil D, Benali R, Reguig FB (2020) Epileptic seizure recognition using EEG wavelet decomposition based on nonlinear and statistical features with support vector machine classification. Biomed Eng Biomed Tech 65(2):133–148. https://doi.org/10.1515/bmt-2018-0246
Netoff T, Park Y, Parhi K (2009) Seizure prediction using cost-sensitive support vector machine. Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc 2009:3322–3325. https://doi.org/10.1109/iembs.2009.5333711
Ngamga EJ, Bialonski S, Marwan N, Kurths J, Geier C, Lehnertz K (2016) Evaluation of selected recurrence measures in discriminating pre-ictal and inter-ictal periods from epileptic EEG data. Phys Lett A 380(16):1419–1425. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physleta.2016.02.024
Article CAS Google Scholar
Osmond E, Billetop A, Jary S, Likeman M, Thoresen M, Luyt K (2014) Neonatal seizures: magnetic resonance imaging adds value in the diagnosis and prediction of neurodisability. Acta Paediatr 103(8):820–826. https://doi.org/10.1111/apa.12583
Oyrer J, Maljevic S, Scheffer IE, Berkovic SF, Petrou S, Reid CA (2018) Ion channels in genetic epilepsy: from genes and mechanisms to disease-targeted therapies. Pharmacol Rev 70(1):142–173. https://doi.org/10.1124/pr.117.014456
Parhi KK, Zhang Z (2019) Discriminative ratio of spectral power and relative power features derived via frequency-domain model ratio with application to seizure prediction. IEEE Trans Biomed Circuits Syst 13(4):645–657. https://doi.org/10.1109/tbcas.2019.2917184
Park Y, Luo L, Parhi KK, Netoff T (2011) Seizure prediction with spectral power of EEG using cost-sensitive support vector machines. Epilepsia 52(10):1761–1770. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1528-1167.2011.03138.x
Patel AD, Moss R, Rust SW, Patterson J, Strouse R, Gedela S, Haines J, Lin SM (2016) Patient-centered design criteria for wearable seizure detection devices. Epilepsy Behav 64(Pt A):116–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yebeh.2016.09.012
Peters B (2022) Risks and complications of seizures. https://www.verywellhealth.com/risks-and-complications-of-seizures-4685790
Qin Y, Zheng H, Chen W, Qin Q, Han C, Che Y (2020). Patient-specific seizure prediction with scalp EEG using convolutional neural network and extreme learning machine. In: 2020 39th Chinese control conference (CCC), Shenyang, China, 27–29 July 2020
Rajkomar A, Dean J, Kohane I (2019) Machine learning in medicine. N Engl J Med 380(14):1347–1358. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMra1814259
Rasekhi J, Mollaei MR, Bandarabadi M, Teixeira CA, Dourado A (2013) Preprocessing effects of 22 linear univariate features on the performance of seizure prediction methods. J Neurosci Methods 217(1–2):9–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneumeth.2013.03.019
Savadkoohi M, Oladunni T, Thompson L (2020) A machine learning approach to epileptic seizure prediction using Electroencephalogram (EEG) Signal. Biocybern Biomed Eng 40(3):1328–1341. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbe.2020.07.004
Schelter B, Winterhalder M, Maiwald T, Brandt A, Schad A, Schulze-Bonhage A, Timmer J (2006) Testing statistical significance of multivariate time series analysis techniques for epileptic seizure prediction. Chaos 16(1):013108. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2137623
Schulze-Bonhage A, Sales F, Wagner K, Teotonio R, Carius A, Schelle A, Ihle M (2010) Views of patients with epilepsy on seizure prediction devices. Epilepsy Behav 18(4):388–396. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yebeh.2010.05.008
Shahidi Zandi A, Tafreshi R, Javidan M, Dumont GA (2013) Predicting epileptic seizures in scalp EEG based on a variational Bayesian Gaussian mixture model of zero-crossing intervals. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 60(5):1401–1413. https://doi.org/10.1109/tbme.2012.2237399
Sharif B, Jafari AH (2017) Prediction of epileptic seizures from EEG using analysis of ictal rules on Poincaré plane. Comput Methods Programs Biomed 145:11–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmpb.2017.04.001
Slimen IB, Boubchir L, Seddik H (2020) Epileptic seizure prediction based on EEG spikes detection of ictal-preictal states. J Biomed Res 34(3). https://doi.org/10.7555/jbr.34.20190097
Sun Y, Jin W, Si X, Zhang X, Cao J, Wang L, Yin S, Ming D (2022) Continuous seizure detection based on transformer and long-term iEEG. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform 26(11):5418–5427. https://doi.org/10.1109/jbhi.2022.3199206
Sun B, Lv J-J, Rui L-G, Yang Y-X, Chen Y-G, Ma C, Gao Z-K (2021) Seizure prediction in scalp EEG based channel attention dual-input convolutional neural network. Physica A Stat Mech Appl 584. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physa.2021.126376
Tamanna T, Rahman M A, Sultana S, Haque M H, Parvez MZ (2021) Predicting seizure onset based on time-frequency analysis of EEG signals. Chaos Solitons Fractals 145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chaos.2021.110796
Tomlinson SB, Porter BE, Marsh ED (2017) Interictal network synchrony and local heterogeneity predict epilepsy surgery outcome among pediatric patients. Epilepsia 58(3):402–411. https://doi.org/10.1111/epi.13657
Truong ND, Nguyen AD, Kuhlmann L, Bonyadi MR, Yang J, Ippolito S, Kavehei O (2018) Convolutional neural networks for seizure prediction using intracranial and scalp electroencephalogram. Neural Netw 105:104–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neunet.2018.04.018
Tsiouris Κ, Pezoulas VC, Zervakis M, Konitsiotis S, Koutsouris DD, Fotiadis DI (2018) A long short-term memory deep learning network for the prediction of epileptic seizures using EEG signals. Comput Biol Med 99:24–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiomed.2018.05.019
Usman SM, Khalid S, Akhtar R, Bortolotto Z, Bashir Z, Qiu H (2019a) Using scalp EEG and intracranial EEG signals for predicting epileptic seizures: review of available methodologies. Seizure 71:258–269. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seizure.2019.08.006
Usman SM, Khalid S, Akhtar R, Bortolotto Z, Bashir Z, Qiu HY (2019b) Using scalp EEG and intracranial EEG signals for predicting epileptic seizures: review of available methodologies. Seizure-Eur J Epilepsy 71:258–269. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seizure.2019.08.006
Usman SM, Latif S, Beg A (2019c) Principle components analysis for seizures prediction using wavelet transform. Int J Adv Appl Sci 6(3):50–55. https://doi.org/10.21833/ijaas.2019.03.008
Varotto G, Tassi L, Franceschetti S, Spreafico R, Panzica F (2012) Epileptogenic networks of type II focal cortical dysplasia: a stereo-EEG study. Neuroimage 61(3):591–598. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2012.03.090
Velmurugan J, Nagarajan SS, Mariyappa N, Mundlamuri RC, Raghavendra K, Bharath RD, Saini J, Arivazhagan A, Rajeswaran J, Mahadevan A, Malla BR, Satishchandra P, Sinha S (2019) Magnetoencephalography imaging of high frequency oscillations strengthens presurgical localization and outcome prediction. Brain 142(11):3514–3529. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awz284
Vezzani A, French J, Bartfai T, Baram TZ (2011a) The role of inflammation in epilepsy. Nat Rev Neurol 7(1):31–40. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrneurol.2010.178
Vezzani A, Maroso M, Balosso S, Sanchez MA, Bartfai T (2011b) IL-1 receptor/Toll-like receptor signaling in infection, inflammation, stress and neurodegeneration couples hyperexcitability and seizures. Brain Behav Immun 25(7):1281–1289. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2011.03.018
Wang G, Wang D, Du C, Li K, Zhang J, Liu Z, Tao Y, Wang M, Cao Z, Yan X (2020a) Seizure Prediction Using Directed Transfer Function and Convolution Neural Network on Intracranial EEG. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng 28(12):2711–2720. https://doi.org/10.1109/tnsre.2020.3035836
Wang Y, Shi Y, Cheng Y, He Z, Wei X, Chen Z, Zhou Y (2023) A spatiotemporal graph attention network based on synchronization for epileptic seizure prediction. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform 27(2):900–911. https://doi.org/10.1109/jbhi.2022.3221211
Wang Y, Zhou D, Yang X, Xu X, Ren L, Yu T, Zhou W, Shao X, Yang Z, Wang S, Cao D, Liu C, Kwan SY, Xiang J (2020b) Expert consensus on clinical applications of high-frequency oscillations in epilepsy. Acta Epileptol 2(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s42494-020-00018-w
WHO (2023) World Health Organization. Epilepsy. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/epilepsy
Williamson JR, Bliss DW, Browne DW, Narayanan JT (2012) Seizure prediction using EEG spatiotemporal correlation structure. Epilepsy Behav 25(2):230–238. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yebeh.2012.07.007
Wong M, Guo D (2013) Dendritic spine pathology in epilepsy: cause or consequence? Neuroscience 251:141–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2012.03.048
Wu G, Li Z, Zhang Y, Dong X, Ye L (2019) Study of feature extraction algorithms for epileptic seizure prediction based on SVM. In: Communications, signal processing, and systems pp 2370–2377. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-6571-2_289
Wu J, Zhou T, Li T (2020) Detecting epileptic seizures in EEG signals with complementary ensemble empirical mode decomposition and extreme gradient boosting. Entropy (Basel), 22(2). https://doi.org/10.3390/e22020140
Xiang J, Li C, Li H, Cao R, Wang B, Han X, Chen J (2015) The detection of epileptic seizure signals based on fuzzy entropy. J Neurosci Methods 243:18–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneumeth.2015.01.015
Yang S, Li B, Zhang Y, Duan M, Liu S, Zhang Y, Feng X, Tan R, Huang L, Zhou F (2020) Selection of features for patient-independent detection of seizure events using scalp EEG signals. Comput Biol Med 119:103671. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiomed.2020.103671
Yang X, Zhao J, Sun Q, Lu J, Ma X (2021) An effective dual self-attention residual network for seizure prediction. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng 29:1604–1613. https://doi.org/10.1109/tnsre.2021.3103210
Yu Z, Nie W, Zhou W, Xu F, Yuan S, Leng Y, Yuan Q (2018) Epileptic seizure prediction based on local mean decomposition and deep convolutional neural network. J Supercomput 76(5):3462–3476. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-018-2600-6
Yuan S, Zhou W, Chen L (2018) Epileptic seizure prediction using diffusion distance and Bayesian linear discriminate analysis on intracranial EEG. Int J Neural Syst 28(1):1750043. https://doi.org/10.1142/s0129065717500435
Zelig D, Goldberg I, Shor O, Ben Dor S, Yaniv-Rosenfeld A, Milikovsky DZ, Ofer J, Imtiaz H, Friedman A, Benninger F (2022) Paroxysmal slow wave events predict epilepsy following a first seizure. Epilepsia 63(1):190–198. https://doi.org/10.1111/epi.17110
Zhang Y, Yang S, Liu Y, Zhang Y, Han B, Zhou F (2018) Integration of 24 feature types to accurately detect and predict seizures using scalp EEG signals. Sensors (Basel), 18(5). https://doi.org/10.3390/s18051372
Zheng Y, Wang G, Li K, Bao G, Wang J (2014) Epileptic seizure prediction using phase synchronization based on bivariate empirical mode decomposition. Clin Neurophysiol 125(6):1104–1111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinph.2013.09.047
Zhu J, Lin H, Su C, Shen Q, Jiang D (2003) The roles of different components of EEGs for seizure prediction-wavelet energy evaluation. Acta Bioch Bioph Sin 01:73–78
Google Scholar
Zurich (2018) The SWEC-ETHZ iEEG database and algorithms. http://ieeg-swez.ethz.ch/
Download references
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by the National Key Research and Development Program of China under Grant 2022YFF1202304; in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant 62376190, Grant 81925020, and Grant 82001939; and in part by the Natural Science Foundation of Tianjin under Grant 22JCYBJC01430.
National Natural Science Foundation of China 62376190, Zhongpeng Wang, 81925020, Dong Ming, 82001939, Long Chen
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Academy of Medical Engineering and Translational Medicine, Tianjin University, Tianjin, 300072, China
Zhongpeng Wang, Xiaoxin Song, Long Chen, Jinxiang Nan, Yulin Sun, Meijun Pang, Kuo Zhang, Xiuyun Liu & Dong Ming
Haihe Laboratory of Brain-Computer Interaction and Human-Machine Integration, Tianjin, 300392, China
Zhongpeng Wang, Long Chen, Meijun Pang, Kuo Zhang, Xiuyun Liu & Dong Ming
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
All authors wrote the paper.
Corresponding authors
Correspondence to Long Chen or Xiuyun Liu .
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest.
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Data Availability
No data was used for the research described in the article.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Wang, Z., Song, X., Chen, L. et al. Research progress of epileptic seizure prediction methods based on EEG. Cogn Neurodyn (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11571-024-10109-w
Download citation
Received : 20 September 2023
Revised : 09 March 2024
Accepted : 14 March 2024
Published : 07 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s11571-024-10109-w
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Seizure prediction
- Intracranial EEG (iEEG)
- Feature extraction
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
Is the Wisconsin Taxpayer Stingy?
Junjie Guo, Kim Ruhl and Ananth Seshadri
Executive Summary:
- Recent reports note that Wisconsin is 42nd in the nation when it comes to funding the UW-System. Wisconsin allocates a larger share of higher-education appropriations to 2-year institutions than most other states and a smaller share to 4-year This distinction is becoming less meaningful as the 2-year technical colleges offer liberal arts transfer degrees as a pathway to a 4-year institution and the UW-System schools are increasingly focused on majors that satisfy workforce demands.
- This paper addresses the question: Is the Wisconsin taxpayer rather stingy in funding higher education in Wisconsin and, in particular, funding UW-Madison?
- Wisconsin is 22nd in the nation when it comes to total higher-education appropriations per full-time equivalent (FTE) undergraduate, which includes both UW-System and technical college While this measure declined in the last decade, it also declined between 2003 and 2010. Despite the decline, it has remained higher than the median in the United States for more than the last two decades.
- After accounting for state income per capita, Wisconsin’s appropriations per FTE undergraduate are appreciably higher than the national average, casting doubt on the notion that the Wisconsin taxpayer is stingy.
- State appropriations per FTE undergraduate are higher for UW-Madison than the median of other Big-10 universities and the median of other public institutions in the Association of American Universities (AAU).
- As a share of university revenue, state appropriations for UW-Madison are similar to the median of other Big-10 universities and the median of other public AAU institutions.
- States exert influence over in-state Reservegate led to a decade-long tuition freeze in Wisconsin. Focusing on the sum of tuition and fees and state appropriations, we find that UW-Madison is slightly below the median of Big-10 peers.
- In the past, UW System tuition rose to offset declines in state support to protect the university system. That implicit contract is now broken. If the state deems UW- Madison worthy of additional support, it ought to come from increases in in-state tuition and not on the backs of the Wisconsin taxpayer.
Read White Paper #5
- Facebook Logo
- Twitter Logo
- Linkedin Logo

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Scholarcy's AI summarization tool is designed to generate accurate, reliable article summaries. Our summarizer tool is trained to identify key terms, claims, and findings in academic papers. These insights are turned into digestible Summary Flashcards. The knowledge extraction and summarization methods we use focus on accuracy.
Our plagiarism checker, AI Detector, Citation Generator, proofreading services, paraphrasing tool, grammar checker, summarizer, and free Knowledge Base content are designed to help students produce quality academic papers. We make every effort to prevent our software from being used for fraudulent or manipulative purposes.
Article Metadata Extraction. TLDR This, the online article summarizer tool, not only condenses lengthy articles into shorter, digestible content, but it also automatically extracts essential metadata such as author and date information, related images, and the title. Additionally, it estimates the reading time for news articles and blog posts ...
Summarize anything, understand complex research, and organise your knowledge with Scholarcy. Home Features. Uses for. Students Researchers International students. Pricing Help Login Start Free. Join over 500,000 people saving time. ... Summarize any paper, article or textbook.
Summarize an article, a document, or a Youtube video with HIX.AI is as easy as 123: Just copy-paste your text, upload a document, or drop a URL of a webpage or Youtube video. Specify whether you want the summary to be in paragraph or bullet point format. Click on the 'Generate' button, and an instant, concise summary will be generated for you.
With our Research Summary Generator, you can create an engaging and informative summary in just a few clicks. Say goodbye to hours spent poring over dense academic papers and hello to quick, easy-to-understand summaries tailored to your needs. Give it a try today and see how our Research Summary Generator can revolutionize your research process!
Our Research Paper Summarizing Tool helps you get to the heart of the papers quickly, making them easier to understand. It's not just about making the text shorter; it's about making sure you get the key information you need for your studies or research. With this summarizer, you can focus more on applying what you learn and less on trying to ...
1. QuillBot. Produces the clearest and most accurate summaries. Summarizes text in a creative way, combining sentences. Can summarize long texts (up to 6,000 words with premium) Options for length, format of summary, and keywords to focus on. Highlights text that was used in the summary.
genei is a intelligent research tool enabling you to improve productivity by using a custom AI algorithm to summarise articles, analyse research and find key information, instantly. ... Our chrome extension add-on means you can summarize webpages or save them for later reading as you browse. ... In-built citation management and reference generator;
Reads, understands, and summarizes the main points and conclusions of a research paper. HyperWrite's Research Paper Summarizer is an AI-powered tool designed to read and summarize research papers. It identifies the main points, arguments, and conclusions, providing a clear and concise summary. This tool is perfect for students, researchers, and professionals who need to quickly understand the ...
AI Summary Generator offers a free, online summary generator and summary maker. Perfect for quickly condensing articles, papers, and paragraphs into clear, concise summaries. Ideal for students and professionals needing efficient content and text summarization. ... You can summarize text from research papers, books, or lecture notes in a matter ...
Use our research paper summarizer to shorten any text in 3 easy steps: Enter the text you want to reduce. Choose how long you want the summary to be. Press the "summarize" button and get the new text. 15,000 characters left. Number of sentences in the summary:
Jenni AI stands as a comprehensive academic writing assistant, encompassing an AI summarizer and summary generator among its key features. This specialized functionality is meticulously crafted to facilitate the creation of concise summaries, effectively condensing extensive research papers, articles, or essays.
3. Jasper. Jasper is an AI-powered summary generator. It creates unique, plagiarism-free summaries, so it's a perfect option for those who don't want to change the wording on their own. When using this tool, you can summarize a text of up to 12,000 characters (roughly 2,000-3,000 words) in more than 30 languages.
QuillBot's AI Text Summarizer, trusted by millions globally, utilizes cutting-edge AI to summarize articles, papers, or documents into key summary paragraphs. Try our free AI text summarization tool now!
SciSummary uses GPT-3.5 and GPT-4 models to provide summaries of any scientific articles or research papers. The technology learns as it goes as our team of PhDs analyze requested summaries and guides the training of the model. SciSummary makes it easy to stay up-to-date with the latest scientific breakthroughs and research findings, without ...
Research paper summarizer is an AI-powered article summarizer tool designed to condense extensive academic papers into concise summaries. These summaries capture the critical points, key findings, and main arguments of a research article and represent them in the most succinct way possible. As a result, researchers quickly grasp the scope of ...
One of the best ways to summarize and consolidate a research paper is to provide visuals like graphs, charts, pie diagrams, etc.. Visuals make getting across the facts, the past trends, and the probabilistic figures around a concept much more engaging. 5. Double check for plagiarism.
Identify the important ideas and facts. To help you summarize and analyze your argumentative texts, your articles, your scientific texts, your history texts as well as your well-structured analyses work of art, Resoomer provides you with a "Summary text tool" : an educational tool that identifies and summarizes the important ideas and facts of your documents.
The Summarizer Tool can help researchers quickly extract the main points, methodologies, and findings from academic papers, allowing them to identify relevant sources efficiently. This tool can save researchers valuable time during the initial stages of their research, enabling them to focus on analyzing the information and drawing meaningful ...
Summarize main points from research, papers, or reviews. HyperWrite's Research Assistant is an AI-powered tool that helps you quickly understand the main points of research inputs, sections of papers, or reviews. Utilizing GPT-4 and ChatGPT AI models, this tool generates a concise paragraph that highlights the key findings and insights from your input.
And they are also suggesting that future studies can explore treating certain types of animal diseases with ultrasound. This is a very good example of how to finish the discussion section of your paper on a positive note. 3. Summary. Limitations are a vital component of the discussion section of your research paper. Remember, every study has ...
4. Summary. You must talk about the limitations of your work in the discussion section of the paper. One of the important qualities that the scientific community expects from a researcher is honesty and admitting when they have made a mistake. However, the trick is not to make your readers feel too negative about your work.
Insights / Research Brief • May 08, 2024 Marginal Returns to Public Universities The typical marginally admitted university student completes an additional year of four-year education, is 12 percentage points more likely to earn a bachelor's degree, and eventually earns 5-10 percent more than their marginally rejected but otherwise ...
Job Summary: The Teaming Up for Equity in Science: Supporting NGSS Three-dimensional Learning and Achievement through Actionable Assessment project seeks an education researcher to join a team investigating how to make middle school assessment more meaningful for students. The research specialist will support quantitative and qualitative research into the educational efficacy of an innovative ...
In this paper, the author uses anonymized location data from smartphones to provide a descriptive analysis of religious worship attendance in the United States. ... This research paints a newly detailed picture of religious worship attendance in the United States. Even though the author finds that the frequency of religious worship visits is ...
In this paper, we firstly introduce the design process of EEG-based seizure prediction methods, introduce several databases commonly used in the research, and summarize the commonly used methods in pre-processing, feature extraction, classification and identification, and post-processing.
Occasionally, circumstances make it necessary for students to test late. To preserve the security of AP Exams, alternate versions of the exams are used for late testing. All students who participate in late testing at a given school must take these alternate exams on the scheduled late-testing dates at the scheduled times.
5.6.24. Junjie Guo, Kim Ruhl and Ananth Seshadri. In this fifth report in "The Economics of UW-Madison" white paper series we addresses the question: Is the Wisconsin taxpayer rather ungenerous in funding higher education?