
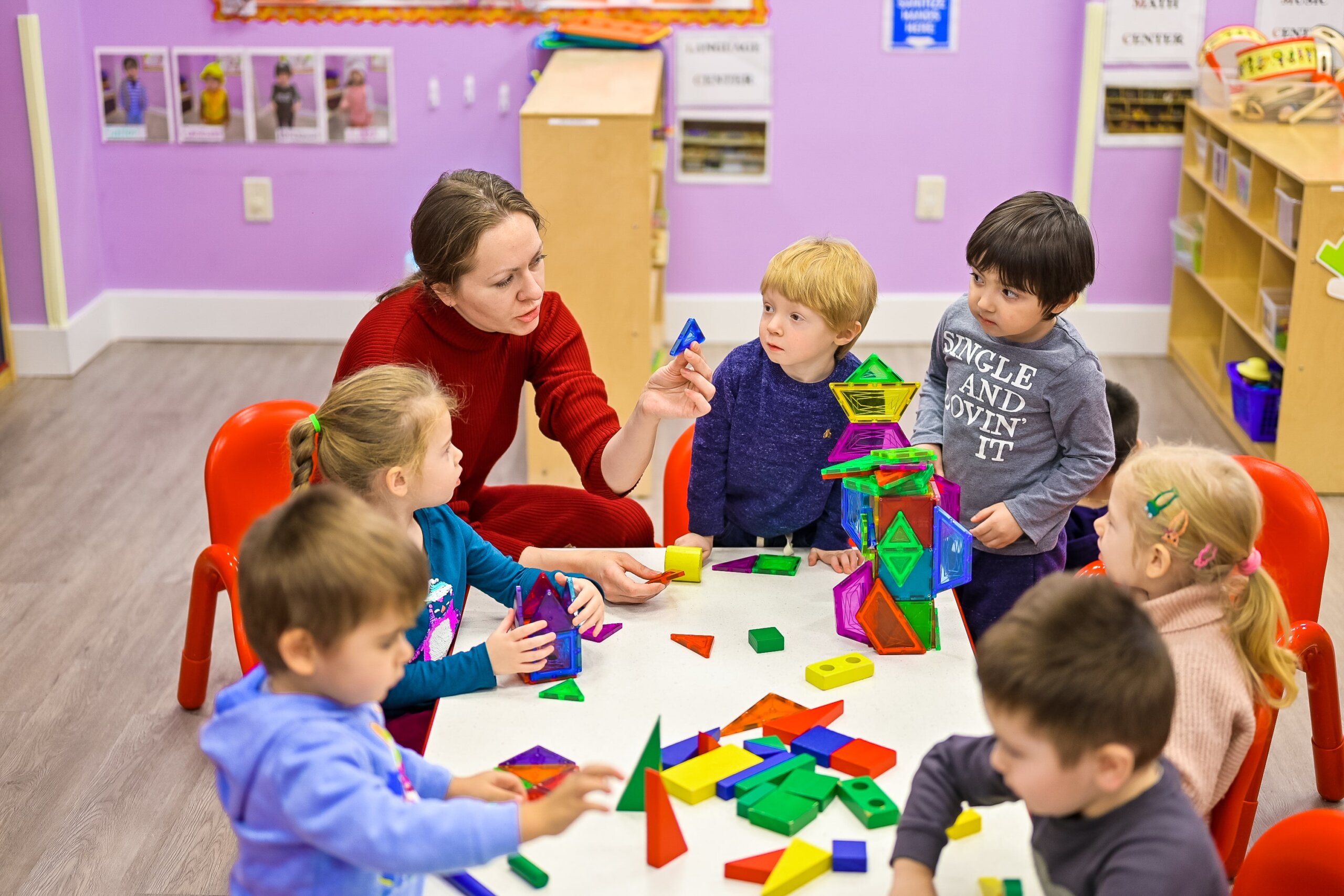
Discovery Play with Littles
2:01 pm ·

15 Powerful Problem Solving Activities for Toddlers and Preschoolers
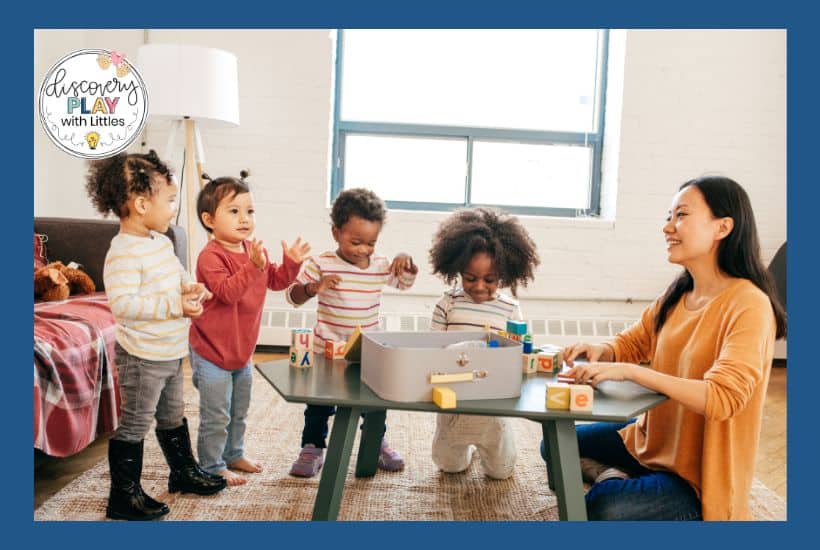
I looked over to her table and she’s crying. Again. While everyone else is happily working away, she sat there, unable to move, just crying.
Not asking for help.
Not trying to solve her problem.
Just crying.
I took a deep breath before heading over. We’ve already been at this for several months…isn’t it about time the problem-solving has kicked in yet?
One glance and I could tell what her problem was. She didn’t have her pencil.
Know how I knew?
It laid on the floor beside her. In plain sight.
As a kindergarten teacher, I don’t jump right in and solve problems for kids. It’s good for them to try to solve the problem themselves. This is something she struggled with.
I reminded myself of the need for patience and empathy as I walked up to her. “What’s wrong, Amanda?”
“I…can’t…find…my…pencil….” she sputtered out between sobs.
“Ok, that’s a problem we can solve. What have you tried?”
“I don’t know.”
After a long time trying to first, calm her down, and second, come up with some strategies she could try, she finally found her pencil. At that point, everyone else had finished the project.

What is Problem Solving?
Problem-solving is the process of finding a solution to your problem . This can be quite tricky for some young children, especially those with little experience in finding more than one way to solve a problem.
Why is Problem Solving Important?
Problem-solving skills are used throughout childhood into adulthood. As adults, we solve problems on a daily basis. Some problems we solve without thinking much- I wanted to make tacos for dinner but forgot to buy the ground beef. What are we going to have for dinner now?
Other problems are significantly more complicated.
Problems for kiddos can be problems with friendships, the inability to find something that’s needed, or even what to do when things don’t go your way.
Kids who lack problem-solving skills struggle to maintain friendships or even begin to attempt to solve their own problems.
Children who lack problem-solving skills are at a higher risk for depression as well.
What Are Problem-Solving Skills?
Problem-solving skills are:
- Breaking Down a Problem into Smaller Parts
- Communication
- Decision-making
- Logical Reasoning
- Perseverance
That’s a big list to teach toddlers and preschoolers. Where do you begin?
The Problem-Solving Steps
Sometimes kids are so overwhelmed with frustration that it affects their ability to solve problems.
Kids feel safe in routines, and routines help them learn and grow. After a few times of repeating this routine, you’ll find your kiddo starts to do this on their own.
It’s important not to skip straight to solving the problem , because your kiddo needs to be in a calm state of mind to solve the problem, and also they need to know their feelings are valid.
- The first thing to do when your kiddo is struggling with problem-solving is to validate their emotions.
In doing this, they will feel more understood and learn that their emotions are okay. There are no bad feelings, and we must learn how to manage our emotions.
This might sound something like “Oh, I can see you are really frustrated that the block won’t fit on there right. Let’s take some deep breaths to help us calm down before we think about what to do next.”
- Next, work through your calm-down process . This may be taking some deep breaths together, hugging a stuffie, or giving your kiddo some quiet time to calm down their heart and mind.
- Identify the problem . This sounds like something you may have already done (before the meltdown) but it’s important to be very clear on the problem you’re solving. Have the child tell you their problem out loud.
- Move on to solution-finding . When your kiddo is ready, talk about what the problem is and three possible solutions. When possible, let your kiddo do all of the talking. This allows him to practice his problem-solving skills. It’s important to remind him that the first thing he tries may not work, and that’s ok. There’s always another way to solve the problem. If he’s prepared for this, solutions that don’t work won’t be such a frustrating experience.
- After you’ve done that, test your solutions one by one. See what works. If you haven’t found a solution yet, go back and think of different ways you might be able to solve your problem and try again.

Are you tired of hearing “It’s TOO HARD!” followed by a meltdown?
Using this one simple phrase you’ll get in this powerful lesson, you’ll not only be able to help your kiddo not give up but you’ll:
>Activate their superpower of perseverance so that they can turn around a meltdown and keep trying
>Inspire them to use perseverance …even when it’s hard
>Teach them to recognize the warning signs of giving up , and how to turn it around by taking control of their choices.
Grab your powerful FREE video lesson to teach your kiddo one of the most powerful keys to perseverance.
Powerful Activities that Teach Problem-Solving Skills to Toddlers & Preschoolers
These activities below may look simple, but don’t let that deter you from trying them. A lot happens in little developing brains and these powerful activities help toddlers and preschoolers make connections and develop {many} essential skills-more than just problem-solving.
As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases at no additional cost to you.
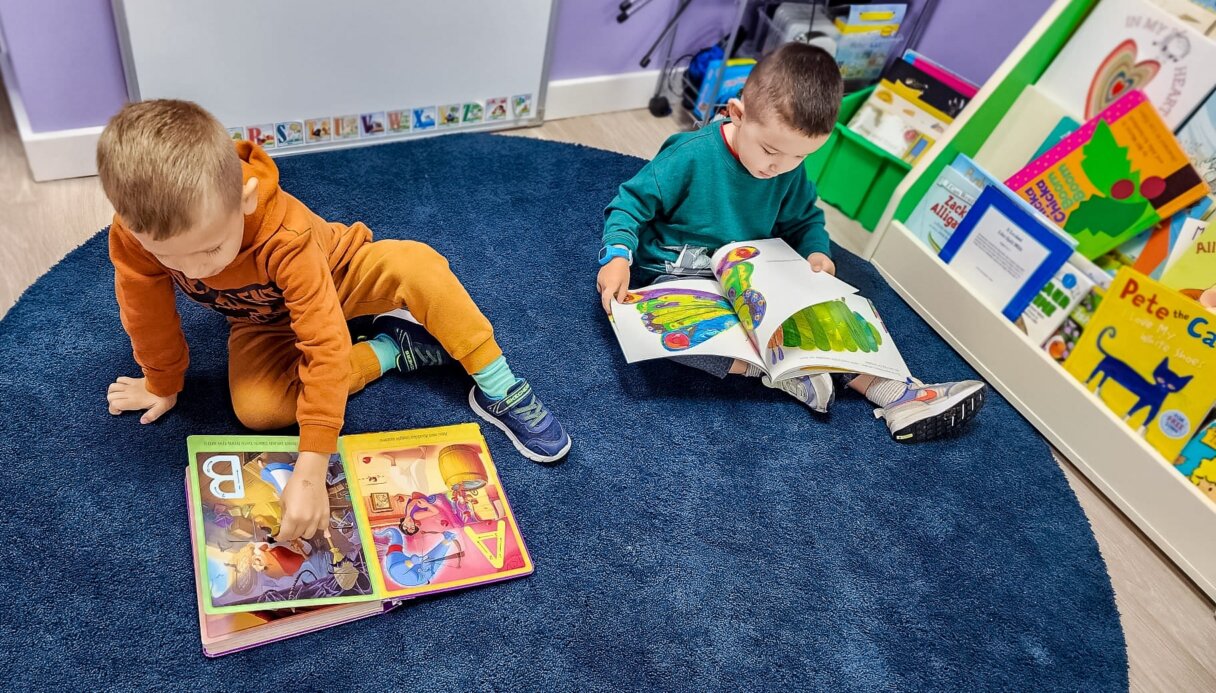
Puzzles are fun and a great way to encourage cognitive development in children. They are great for spacial reasoning and strengthening problem-solving skills. They also develop memory skills, critical thinking, and the ability to plan and execute the plan. Toddlers will enjoy the simple puzzles, and preschoolers will do great with floor puzzles with larger puzzle pieces.

Doing Simple Chores
Doing simple chores is a great way to teach children problem-solving skills, and it strengthens responsibility and perseverance as well.
During the toddler years , you may start with just picking up their toys, or helping you put their dirty clothes in the hamper.
Preschoolers can take their dirty dishes to the sink (or load them in the dishwasher), collect the trash, dust, wipe baseboards, and do their own personal care items like making their bed, taking care of their dirty clothes, and putting clean clothes away.
Stacking Rings
When watching a toddler play with stacking rings it doesn’t look like much is happening, but playing with these toys is full of ways to encourage development. It helps with visual and spacial perception and planning ahead, but it also with balance control, crossing the midline, creative play, and gross motor skills. Not to mention it’s a great opportunity to practice problem-solving.

Playing Hide-and-Seek
Hide and seek has many surprising benefits for kids. Playing hide and seek is like a treasure hunt that helps develop gross motor skills and encourages physical development, as well as problem-solving skills. It also helps young children develop visual tracking, working memory, and social-emotional skills.

Imaginative Play
Imaginative play (also called role-play) builds important skills. Through pretending to be in different situations, kids develop social skills, emotional skills, better communication, and problem-solving skills. Imaginative play is a great idea for young toddlers all the way to older children.
Free Play
Many young children don’t have {enough} time for free play. Free play is important for healthy brain development , not only developing imagination, cooperation, physical skills, and independence but also providing a great opportunity to strengthen problem-solving skills.
Playing with Wooden Blocks
Building blocks are a fun way for children to develop creative thinking, imagination, problem-solving, fine motor skills, and if working with others, cooperation, communication, and friendship.

Playing Memory
Memory games improve attention, focus, visual recognition, and concentration. It helps children recognize details and of course, strengthens problem-solving skills.

Ask Questions
When I see my son struggling with something, my first instinct is to give him choices or at least lead him in the right direction. The better thing to do is to ask very open-ended questions that lead his process, not his thoughts.
Questions like “What’s one way to solve your problem?” are much more effective in teaching problem-solving skills than “Well, where did you last see your stuffy?”
Read Books and Social Stories
Reading books is one of my favorite ways to teach any skill. It’s extremely effective at teaching, and it’s also an amazing bonding time with kids.
When we read stories, our brain reacts as if we’re living in the story. This is why reading books about skills such as problem-solving is so effective.
Kids of all ages learn from the people they love . (Yes, even those older kids who you don’t think are paying attention.) Often as adults, we’re too busy going through our daily routine to think about talking about the way we solved the problem at work that day.
Talking about how you use skills such as problem-solving, perseverance, and integrity is a great way to set an example, and an expectation that this is how we do things, and it will provide encouragement for your kiddo to do the same.
Scavenger Hunts
Scavenger hunts are a great group activity that can strengthen your child’s logical thinking and problem-solving skills.
When Your Kiddo is Ready, Add These Activities
Preschoolers would benefit from all of the fun activities on the list above and when they’re ready, feel free to add in the following activities.
Mazes are great for problem-solving and perseverance, but your kiddo will need to have decent fine motor skills to do these activities. Mazes are one of our favorite activities. We love to take our activity book of mazes in the car with us for road trips.

Board Games
Board games are a good way to strengthen problem-solving, teamwork, planning skills, patience, sportsmanship, and communication skills. They also strengthen family relationships by providing some intentional time of connection .
Any board game can also be turned into an academic game with just a deck of cards for whatever skill you’re working on. If you’re working on the alphabet, put one letter on each card. Before each player’s turn, they draw a letter card and say the letter’s name. (You may accidentally forget the name of a letter every now and then to see if your kiddo is really paying attention!)
Allow Opportunities for Hands-On Investigations
Kids are tactile. They love to touch and explore things with their hands. This is a good activity for toddlers also, as long as they are out of the putting everything in their mouth stage. Hands-on exploration is great for language development, sensory exploration, and problem-solving.
Allowing kids to investigate with their hands allows them to see how the world works up close. It also gives them time and space to try to make things work…and problem-solve when it doesn’t go as they think it should.
The Most Difficult Way (and Most Important Way) To Strengthen Problem-Solving Skills
Watching our kids struggle is hard ! We don’t want to see them having a hard time…and most of the time we don’t want to deal with the impending meltdown. Standing back and giving our kids time and space to work through even simple problems is hard to do. It’s also the most important way to strengthen problem-solving skills.
As parents, we’re like frogs in boiling water. When our kids are infants, they need us to recognize their needs and solve them immediately. As they get older, they can point to what they want, but we still have a lot of interpreting and problem-solving to do on our own. If we aren’t careful, we stay in this stage and don’t teach our kiddos the steps to problem-solving for themselves.
The next most difficult thing? Allowing natural consequences to happen. (As long as your child is safe of course.) If your child saves their money for a long time to buy a new toy, but walks down the toy aisle and picks up something you know they’ll be disappointed with, let it happen. It will teach a valuable lesson that will last for years to come.
Another Essential Part of Problem-Solving
Perseverance is a big part of problem-solving. We are rarely able to solve problems the first time, and it’s essential that kids can find more than one solution to a problem. Studies have found that perseverance is actually the biggest predictor of success, even more than aptitude or raw talent.
An entire module is dedicated to perseverance in our course for kids, Super Kid Adventures . Your kiddo will get 25 teacher-led lessons on character traits (perseverance, empathy, friendship, responsibility, and wellness) and activities that take their learning further.

Want a free preview? Grab a FREE Perseverance video lesson that teaches your kiddo one of the most important secrets that help them use perseverance.
Want More?
If you like this, you’ll love:
The Ultimate List of Books that Teach Perseverance
7 Simple Ways to Encourage Independence in Young Children
How to Help Your Child Develop Self-Help Skills
Your Turn
What are your favorite ways to teach problem-solving skills?
About Elizabeth
Elizabeth is a mama of two boys, a former teacher, and the founder of Discovery Play with Littles. Her mission is to make raising kids with character simple and fun. Join us for our best learning through play ideas, character growth activities, and family connection ideas so you can watch your child thrive.
Reader Interactions
As a SLP trying to guide parents as I work with their child. I would like to know what toys to recommend to my parents as I assist in guiding their child’s development in cognition and expressive language.

Perseverance is the biggest predictor of success, even more than raw talent or aptitude.
Grab a FREE lesson to teach your kiddo one of the keys to perseverance...which is how we talk to our brains.
They'll learn what to say when they encounter something difficult, and why it's so important.
PLAY is often talked about as if it were a relief from serious learning. But for children play is serious learning. Play is really the work of childhood. -Mr. Rogers
Join over 125,000 educators for tips & tricks in the Facebook group .

- Back to School
Teaching Tips
Social emotional, problem solving with little learners (preschool, pre-k, and kindergarten), share this post:.
- Share on Twitter Share on Twitter
- Share on Facebook Share on Facebook
- Share on Pinterest Share on Pinterest
- Share via Email Share via Email

Problem solving is challenging for young students (and many adults too)! To support my little friends, I teach them problem solving strategies that they can use when they encounter a problem. We want our students to become independent thinkers who can solve problems, control their emotions, express empathy, and help others.
I introduce the problem solving techniques a few at a time during a class meeting. Each week, I introduce three new problem solving techniques. We then end up with nine to twelve techniques total based on what my students need that year. I explain the technique to the students in concrete terms so they will understand what the technique is and what it can look/sound like.
We usually start with these four skills: “please stop”, ask, get help, and say how you feel. Many problems can be solved with those solutions, which is why I always start with those. Then, the following week, I introduce take turns, play together, trade, and share. Then, the last four solutions the next week.
Problem Solving Techniques

Singing with puppets is a fun and active way to practice the problem-solving techniques . Preschoolers LOVE puppets! This technique also allows students to role play. Some students will be more verbal if they can pretend to be someone else. At the end of each verse, students act out the problem-solving technique with a buddy using the puppets!As a transition activity to lunch, students took turns sharing a way they have solved a problem. You can also play, “What would you do if….”. State a real problem that could happen and have students pick a problem-solving solution to solve the problem. Some examples would be, “What would you do if your friend took your book?”, “What would you do if you got sticky glue on your hands?”, or “What would you do if you needed the red marker and your friend was coloring with it?” Once they have learned the strategies, stand back and let students try solving their own problems independently. Just a warning: this can take some time with lots of practice and support. As long as the student isn’t frustrated, let them try before you jump in to help. You will be amazed at the problems your child can solve given the opportunity to.
At first, you will be giving students lots of support and giving them the words to use to solve a problem.
- Always approach students at their level, in a calm supporting way.
- Ask, “what’s the problem?” If they don’t respond, comment on what you see such as “I see you have glue all over your hands and it looks sticky.”
- Restate the problem. “So the problem is ….”
- Brainstorm solutions and choose one together. This is the perfect time to use problem solving card visuals! “How can we solve this problem?” Flip through the solution cards and ask “Could we ….?”
- Praise and observe! Cheer on the students for solving the problem and stay close just in case they need more support.
Throughout the day, try to make EVERYTHING a problem to solve. Then model, talk through your thinking out loud, and use visuals to support students as they try to solve a problem. For example, I may put out a big ball of playdough in the center of the table as a small group activity. Students have to problem solve so each student has play dough to play with. It only takes few extra minutes to sneak in problem-solving situations throughout the day. Each time students help solve a problem or observe a friend solve a problem, they learn to self-regulate, express emotions appropriately, develop empathy, and develop problem-solving skills.
State problems for students who look stuck. If a student is just standing there, they need support, but don’t solve the problem for them! It’s so easy to do. Simply state their problem or what you see and ask a probing question. For example, if a student is standing with an empty bowl in their hand, you could say “Your snack spilled on the floor. How can you solve the problem?”
Problem-Solving Necklace or Mini Book!
I hole punched the small cards, put them on a book ring and keep them on a lanyard I wear every day. This way I can support students’ solving problems without having to go to the safe place where they are posted. I can just show the picture cards as a visual on my necklace. The mini book in the safe place works the same way.

Safe Place!
I keep my techniques posted in my circle area at the beginning of the year AND in my safe place. My safe place is a small spot in my classroom where students can go when they are upset, need to calm down, want to be alone, or have a problem.

Once I see students using the problem-solving techniques independently, I remove them from my circle area. They are posted in my safe place ALL YEAR LONG for students to use when they are struggling to solve a problem. In my safe place, you will find a mirror, feeling chart, bean bag, sensory bottles, calm down choices, a stuffed animal, problem solving mini book and problem-solving techniques chart. You can read all about how to set up a safe place in your classroom HERE . Children’s Books!
These are some of my FAVORITE children’s books to teach all about problem-solving. As we read the book, we talk about how the character is or isn’t solving the problem, how it makes the character and others feel, any natural consequences that could occur, and which one of our problem-solving strategies the character could use to solve the problem.

Do you want to use them in your classroom? You can! I did the work for you. Grab them from my TPT store HERE .
LOVE it? Pin this image!

hey, i’m jackie!
I’m Jackie, your go-to girl for early childhood inspiration and research-based curriculum.
Similar Posts

FREE EDITABLE Name Cards to Teach Little Learners their Name
Teaching names is one of the most powerful ways to teach letters and sounds to preschool, pre-k, and kindergarten kiddos. The activities you can do with name cards are endless! …

Center Time Management for Preschool and Pre-K
Center time management is so important for our little learners and the classroom. No matter what system you use, it’s important for students to know the expectations for the classroom…

Printing Help and Support for Teachers Printing PDF Documents
Technology can be tricky and super frustrating, especially when it comes to printing. Honestly, sometimes makes me want to throw my printer out the window! But I’m here to give…

Top 8 Kid Made Gifts for Preschool, Pre-K, and Kindergarten
Need a quick, easy, and cheap kid-made gift for a holiday or celebration like Mother’s Day, Father’s Day, or a classroom event like Muffins in the Morning? Check out my…

STEM and Blocks Center Props for the Whole Year
Take learning into the STEM and blocks center with themed props and STEM I Can Build Cards! Adding new props and engineering challenges will take your Preschool, Pre-k, or Kindergarten…

How to Set Up and Plan for your Art Center in an Early Childhood Classroom
The Art center is a place where students can go to express their feelings, ideas, and be creative! Every child is an artist in the Art center! It is a…
Follow On Instagram

©2023 Pocket of Preschool. All Rights Reserved. Designed by Ashley Hughes
Review Cart
No products in the cart.
Dramatic Play
- Organizations
- ohpikîhakan
- Counselling
- Therapy Groups
- Edmonton Parenting Classes
- Nurturing Newborn Attachment
- Parenting Toddlers and Pre-Schoolers
- Parenting School-Age Children
- Parenting Teens
- Discipline for Children and Youth
- Parenting Communication Skills
- Positive Parenting Strategies
- Parenting in Blended Families
- Couples Workshops
- Couples Communication
- Marriage Preparation
- Self Improvement
- Building Self Esteem
- Healthy Boundaries and Effective Communication
- Journey to Self-Discovery
- Understanding Addictions
- Overcoming Adversity
- Edmonton Anger Management Classes
- Men and Anger
- Women and Anger
- Understanding Anger for Youth
- Training for Organizations
- Staff Skill Development
- Leadership Development
- Indigenous Teachings
- Daycare Management Courses
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Classes FAQs
- Learning & Resources
- Private Workshop Request
- Privacy and return policy
- Guiding Principles
- Partners and Funders
- Social Enterprise Centre
- Video Library
- Internships

How to Teach Problem-Solving Skills to Your Child: A Guide for Every Age

Problem-solving is a vital skill that every child should develop as they grow. The ability to problem-solve effectively can not only enhance their performance in school, but is also a critical life skill that will help them navigate life’s challenges successfully as they reach young adulthood.
Developing effective problem-solving skills at an earlier age can also greatly affect a child’s personality, confidence, and trust in themselves. Children who feel like they can handle challenges on their own tend to be more independent and well-adjusted in their environments, and also optimistic about the opportunities available to them later in life.
In this blog post, we’ll explore the benefits of teaching problem-solving skills to your child and provide practical tips for different age groups - from preschoolers to teenagers.
Why Should You Teach Problem-Solving Skills? An Overview of the Benefits
Teaching your child problem-solving skills offers them the advantage of building resiliency at an earlier age. This can help shape them into independent, self-sufficient individuals as they grow up. Below is a summary of a few key developmental abilities that problem-solving skills can help children practice.
1. Cognitive Development
Problem-solving stimulates a child’s critical thinking skills. Critical thinking involves analyzing, evaluating, and synthesizing information.
The process of problem-solving encourages children to gather information, weigh their options, think about the pros and cons, and make thoughtful decisions. Through this process, they practice becoming self-informed to make their judgments independently. This also helps them foster creative thinking, explore different perspectives and ideas, and develop their own strategies for this process.
2. Confidence Building
Self-confidence is built from the experiences where we demonstrate our capabilities in doing and achieving things.
A child who studied hard and got an A on their test will feel more confident in their studying skills the next time an exam rolls around.
If this child grew up with loving parents, caregivers, and a supportive community, they’ll most likely feel more secure in themselves and have an easier time making new friends and connections as they mature.
The positive experiences that a child has reinforces the confidence in their abilities and self-esteem. By practicing problem solving skills early on, it challenges them to develop a stronger sense of reasoning, responsibility, autonomy, and sense of trust in themselves. All of which can lead to a more optimistic outlook on life, healthier relationships, and a sense of fulfillment and satisfaction.
3. Adaptability
The challenges in life are plenty, and not something that we can protect our children from all of the time. One of the most important tools that we can equip our children with for their future success is for them to be adaptable in the face of adversity.
It’s important for children to know that they are able to keep going during tough times, rather than letting it keep them stuck. Knowing how to effectively problem-solve can help them see adversity in a different perspective and find different solutions for it, while building the resilience for them to keep trying.
4. Decision Making
For every individual, feeling confident in making decisions independently is key to leading a fulfilling life, and is a skill that many children may struggle with. This is heavily related to how well they know themselves, their confidence with their choices, and what they think would bring them closer to their life goals.
“Is nursing or accounting the right profession for me? Should I date this person? Does this religion align with my values? Are these the right people to develop friendships with?”
These are all major life decisions, and choosing what is right for them in their life is crucial for their success. Learning how to problem-solve at a young age can help along in this process by letting them explore their values, flex their sense of judgment, and learn about what is meaningful and right for them.
Tips for Teaching Problem-Solving Skills at Every Age
Pre-school Age
Preschoolers often look to their caregivers as role models, so modelling effective problem-solving is key for them to observe and learn.
Strategies:
1. Set a good example
Demonstrate positive problem-solving behaviour through your daily actions. Instead of becoming frustrated and angry, try to approach problems with calm behaviour and demonstrate logical thinking.
For example:
- If you’re feeling angry, take a deep breath and try to keep calm by verbally reminding yourself, in front of your child, of a way to work through the problem such as:
- “I know I am angry right now, but letting it get the best of me will make me feel worse.”
- “I’m allowed to feel angry, but it’s not good for me to hold onto this feeling. I’m going to take a 10 minute break and try to calm down.”
- “I am so angry right now, but for my own peace of mind I choose to let it go.”
- “Being angry won’t help me think better to solve this problem.”
Your child will be able to observe how you worked through your problem. This also sets a good example for how to work through difficult emotion, redirect your thinking, and move forward from situations.
2. Incorporate play
You can use playtime to help children express and understand their emotions when it comes to problems.
If they’re lashing out, help them understand if they are angry or sad. What caused this? Can they self-regulate after a period of intense emotions, or do they hold onto it?
Here are some prompts to use:
- “Do you like playing with this toy?”
- “What are you feeling right now? Are you frustrated because of [toy]?”
- “I understand you’re feeling [emotion]. Figuring out this toy is tough, but I believe you can do it!”
- “You don’t have to play with this if you don’t want to.”
- “If you need help, please ask me politely and I can for sure give you a hand!”
In middle childhood, children start to develop more complex problem-solving skills.
1. Use Family Problems
Involve your child in solving simple family problems, like organizing chores or planning activities. This will help them foster a greater sense of responsibility, learn to accept feedback, and practice their critical thinking and judgment.
Some appropriate topics could include:
- Brushing their teeth
- Putting toys away
- Choosing their own outfits
- Practicing manners - teaching when to say please, thank you, you’re welcome, hellos and goodbyes, sorry, excuse me, waiting their turn, etc.
2. Teach Step-by-Step
Introduce steps to problem solve - state the problem, brainstorm solutions, decide which is best, try it out, and review.
Using homework, for example, try breaking down the problem into steps for them. It could look like this:
1. Identify the Problem:
- Homework is piling up, and your child is feeling overwhelmed! What can we do?
2. Brainstorm Solutions:
- Ask for help from a teacher or classmate?
- Try to manage time better
- Break down homework into smaller, more manageable parts.
3. Make a Decision:
- Create a schedule or a task list
- As a friend for tips
- Choose one subject to start with
4. Give it a Go:
- Follow the schedule
- Try out the study tips
- Complete things in parts
5. Review and Reflect:
- What worked well - schedule or study tips?
- What didn’t work out well - did you procrastinate?
- Adjust and approach the next task differently.

Teenagers are refining their critical thinking and decision-making skills. Children at this age are becoming more independent and learning about themselves in relation to their peers and greater community. They are looking for how they fit into the world, and also how they stand out.
1. Involve them in Simple Chores
Engage teenagers in simple chores so they can practice responsibilities, learn to use logic and judgement, and grow their independence.
Some appropriate topics could include:
- How to make a simple meal (fried eggs, salad)
- Packing their own school lunch
- Help to mow the lawn or shovel snow
- When to do laundry
- How to vacuum
2. Actively Encourage Independence
Encourage and allow them the space to solve problems on their own. If they don’t know what to pack for lunch, give them a few minutes to make a decision independently rather than jumping in and making suggestions for them. If they still need help afterward, try to provide light guidance and not be judgemental about their decisions.
General Strategies for All Ages:
1. Role Play:
Encourage role-playing scenarios where your child can apply problem-solving skills learned. This helps them practice problem-solving in a controlled and fun environment.
Set up a pretend “lost toy” scenario and encourage your child to figure it out. Help them with their thought process, such as where they last saw the toy, and where to look for it first.
2. Skill Teaching:
Break down the problem-solving steps according to their age.
- For 3 - 5 year olds, try to focus on emotions. Teach them to recognize and express their feelings and provide them with an environment that is safe and free of judgment.
- For 5 - 7 year olds, discuss their thoughts and encourage them to consider different perspectives.
- For 7 - 9 year olds, ask them questions that challenge and stimulate their critical thinking, such as “Why do you think this happened” or “What may be a better way to approach this problem?”
3. Encourage Independence:
Support your child in solving their own problems to foster independence and resilience.
If your child is fighting with a friend, guide them towards figuring out a solution themselves. Ask questions such as “Is there anything you could have done differently?” or “If they hurt you, do you think you can forgive them?”
Final Words
Teaching problem-solving skills to your child is an investment in their future success. By adapting the strategies to their age, providing guidance, and encouraging independence, you empower them to navigate life’s challenges with confidence and resilience. Start early, be a positive role model, and watch as your child develops into a capable and confident problem-solver.
To learn more about problem solving, or other practical parenting tips, see our parenting classes:
Parenting Classes
The Family Centre acknowledges that we are on Treaty 6 territory, a traditional meeting ground, gathering place, and traveling route for the Cree, Saulteaux, Blackfoot, Métis, Dene, and Nakota Sioux. We acknowledge all the many First Nations, Métis, and Inuit whose footsteps have marked these lands for centuries.
Subscribe to our mailing list
Please select all that apply:
- I agree to receive The Family Centre's monthly eNewsletter. I can unsubscribe at any time.
- I agree to receive The Family Centre's updated brochures once a year. I can unsubscribe at any time

Building Problem-Solving Skills for Preschoolers
Definition and significance of problem-solving skills in preschoolers, overview of typical problem-solving scenarios for preschoolers, math problem-solving activities for preschoolers, creative problem-solving games and activities, utilizing problem-solving cards for interactive learning, how to teach problem-solving to preschoolers effectively, incorporating problem-solving steps into everyday activities, role of adults in facilitating problem-solving skills, recommended problem-solving books for preschoolers, reputable online resources, using problem-solving worksheets as a learning tool, real-life problem-solving scenarios for preschoolers to navigate.

In the early years of childhood development, problem-solving skills are foundational to cognitive growth and practical learning. This article explores engaging activities, scenarios, and resources designed to foster these critical skills in young learners. Through a variety of methods, including interactive games, math activities, and educational books, preschoolers can develop the ability to navigate challenges, leading to enhanced learning experiences and a solid foundation for future academic success.
To cultivate these essential skills in your preschooler and lay a strong foundation for their future, explore the wealth of problem-solving activities, games, and resources available. Embrace the joy of learning together and watch as your child’s problem-solving abilities flourish. Begin this exciting journey now and open a world of possibilities for your little learner!
Understanding Problem-Solving for Preschoolers
Problem-solving skills in preschoolers refer to their ability to understand a problem, think through solutions, and execute a plan to overcome it. This capability is vital for their cognitive development and helps in navigating daily challenges. Preschoolers encounter problem-solving scenarios in various forms, such as puzzles, social interactions, and play activities, where they learn to make decisions, analyze outcomes, and adapt to new situations. Engaging them in targeted problem-solving activities and games can significantly enhance these skills, preparing them for future more complex tasks and decision-making processes.
Preschoolers encounter various problem-solving scenarios daily, which are crucial for their cognitive, social, and emotional development. These scenarios typically involve challenges or situations that require them to analyze, make decisions, and find solutions. Here’s an overview of common types of problem-solving situations preschoolers might face:
- Social Interactions: Learning to share toys, taking turns, and resolving conflicts with peers are common problems requiring negotiation and empathy.
- Self-care Tasks: Dressing themselves, tying shoelaces, or managing basic hygiene tasks demand practical problem-solving skills and fine motor coordination.
- Academic Challenges: Simple puzzles, building blocks, and age-appropriate educational games encourage critical thinking, pattern recognition, and logical reasoning.
- Emotional Regulation: Identifying and managing their feelings, like frustration or sadness, when things don’t go as planned, teaching them to find constructive solutions.
- Environmental Navigation: Overcoming physical obstacles, like reaching a high shelf or navigating a new play area, requires spatial awareness and physical judgment.
Problem-Solving Activities for Preschoolers

Math problem-solving activities for preschoolers should be engaging and hands-on, helping them understand basic mathematical concepts through play and exploration. Here’s a list of activities designed to enhance their math problem-solving skills:
- Sorting and Categorizing: Children sort objects by color, size, shape, or type, which develops their ability to recognize patterns and categories.
- Counting Games: Using toys, beads, or blocks to count aloud helps preschoolers understand numbers and quantity.
- Simple Puzzles: Completing puzzles with different shapes and sizes teaches spatial awareness and geometric concepts.
- Matching Activities: Pairing matching items or numbers with corresponding groups of objects enhances number recognition and counting skills.
- Shape Hunts: Finding objects of specific shapes in their environment helps children identify and classify geometric shapes.
- Measurement Activities: Using rulers, measuring tapes, or comparing objects directly teaches basic measurement and comparison skills.
- Number Stories: Creating simple stories that involve addition or subtraction helps in understanding basic arithmetic operations.
- Pattern Making: Using colored blocks or beads to create and extend patterns teaches sequencing and predictive logic.
Creative problem-solving activities encourage thinking outside the box and foster innovation. Here are some games and activities that can help develop these skills:
- Story Building: Participants add to a story one sentence at a time, promoting creative thinking and collaborative storytelling.
- Invention Scramble: Children use random objects to create a new invention, encouraging imaginative thinking and resourcefulness.
- Obstacle Course: Setting up an obstacle course with specific challenges requires planning and strategy to navigate.
- Riddle Solving: Engaging in riddles and brain teasers enhances critical thinking and comprehension skills.
- Building Challenges: Using blocks or LEGO, children are tasked with constructing a structure based on a theme or specific requirements.
- Role-Playing Games: Children take on different roles and scenarios, promoting empathy and creative problem-solving in social situations.
- Art Projects: Encouraging free-form art or specific thematic projects helps in exploring creativity and expressing ideas visually.
- Treasure Hunts: Organizing a treasure hunt with clues and challenges promotes logical reasoning and teamwork.
Problem-solving cards are a versatile tool that can be used to promote interactive learning. They typically feature scenarios, questions, or challenges that prompt learners to think critically and develop solutions. Here’s how they can be used effectively:
- Scenario-Based Learning: Cards can present real-life situations that require learners to apply knowledge and critical thinking to solve problems.
- Group Discussions: Using cards to initiate group discussions encourages collaboration and the sharing of diverse perspectives.
- Role-Playing Activities : Cards can set up role-playing exercises where learners must navigate and resolve conflicts or challenges.
- Game-Based Learning: Incorporating cards into games can make learning fun and competitive, motivating learners to engage more deeply with the content.
- Skill Development Workshops: Cards can be used in workshops to practice specific skills, such as negotiation, decision-making, or creative thinking.

List of Necessary Elements for Utilizing Problem-Solving Cards
To effectively use problem-solving cards in interactive learning, certain elements are necessary:
- Varied and Relevant Content: Cards should cover various topics and scenarios relevant to the learners’ experiences and learning objectives.
- Clear and Concise Instructions: Each card should have clear, concise instructions to ensure learners understand the problem or task.
- Adaptability: Cards should be versatile enough to be used in different teaching methods and learning environments, whether in-person or online.
- Interactive Design: Engaging visuals and interactive elements on the cards can enhance the learning experience.
- Feedback Mechanism: Incorporating a way to provide feedback on the solutions or discussions generated from the cards helps in assessing understanding and progress.
- Scalability: The difficulty level of the cards should be scalable to cater to different skill levels and learning stages.
- Cultural Sensitivity: Content on the cards should be culturally sensitive and inclusive, reflecting diverse perspectives and experiences.
- Supplementary Materials: Providing additional resources or information related to the scenarios on the cards can deepen understanding and extend learning.

Teaching Strategies
Teaching problem-solving to preschoolers is about guiding them to think independently, make decisions, and learn from outcomes. Here’s how educators and parents can effectively teach problem-solving skills to preschoolers:
- Model Problem-Solving Behavior: Demonstrate how to approach problems calmly and thoughtfully, talking through the process out loud.
- Create a Safe Learning Environment: Ensure that the environment is supportive and non-judgmental, allowing children to explore solutions without fear of failure.
- Encourage Exploration and Play: Through play, children can experiment with different solutions and learn from trial and error.
- Ask Open-Ended Questions: Encourage thinking by asking questions that have no single right answer, prompting children to explore various possibilities.
- Facilitate, Don’t Solve: Guide children through the problem-solving process, helping them think of solutions, rather than providing answers.
- Use Storytelling: Stories can introduce problems in a relatable context, encouraging children to come up with creative solutions.
- Encourage Teamwork: Group activities can teach children how to collaborate, share ideas, and solve problems together.
- Teach Emotional Regulation: Help children recognize and manage their emotions, which is a critical part of solving problems effectively.
List of Necessary Elements for Teaching Problem-Solving to Preschoolers
To teach problem-solving effectively to preschoolers, certain elements are necessary:
- Patience and Time: Problem-solving skills develop over time, requiring patience and practice.
- Age-Appropriate Challenges: Problems should be relevant and challenging but achievable for their developmental stage.
- Variety of Materials: Provide diverse materials and resources to stimulate creative thinking and problem-solving.
- Positive Reinforcement: Celebrate successes and encourage perseverance, reinforcing the value of effort and learning from mistakes.
- Consistent Opportunities: Regularly integrate problem-solving activities into daily routines and learning experiences.
- Clear Guidance and Support: Offer clear instructions and support to help children understand the problem-solving process.
- Reflective Practice: Encourage children to reflect on the problem-solving process and outcomes to enhance learning.
- Cultural and Contextual Relevance: Ensure problems and scenarios are culturally relevant and relatable to the children’s experiences.
Incorporating problem-solving steps into everyday activities offers a practical and seamless way to enhance critical thinking skills. This approach involves identifying daily tasks or challenges and using them as opportunities to practice problem-solving.
For instance, during meal preparation, children can be involved in deciding what to cook, which ingredients are needed, and how to follow the recipe. This engages them in decision-making, sequencing, and logical thinking.
Similarly, when faced with conflicts or decisions, guiding children through identifying the issue, brainstorming possible solutions, evaluating these options, and then implementing and reflecting on the outcome can be very effective. This method makes problem-solving a natural part of daily life and helps children learn to apply these skills autonomously, preparing them for more complex challenges as they grow.

Adults play a crucial role in facilitating problem-solving skills among children by acting as guides, models, and supporters. They set the stage for learning by providing appropriate challenges and resources that encourage critical thinking and experimentation.
Through modeling problem-solving behavior—like verbalizing thought processes, showing how to evaluate options, and demonstrating persistence in the face of difficulties—adults provide a blueprint for children to follow. They also create a safe environment where children feel free to explore solutions without fear of judgment, offering guidance and encouragement rather than solutions, which promotes independence and confidence.
Additionally, by asking open-ended questions, adults can stimulate children’s thought processes and encourage them to see problems from different angles, further developing their critical thinking and decision-making skills. Adults are vital in nurturing an atmosphere where problem-solving can thrive, guiding children to become proficient problem-solvers.

Educational Resources
Books can be a fantastic resource for developing problem-solving skills in preschoolers. Here are some highly recommended titles that engage young readers in the art of problem-solving:
- “Rosie Revere, Engineer” by Andrea Beaty: This book encourages innovation and perseverance, showing that failure is just a step towards success.
- “Curious George” series by H.A. Rey: The adventures of Curious George teach problem-solving and curiosity, as the little monkey often finds himself in tricky situations that require clever solutions.
- “The Most Magnificent Thing” by Ashley Spires: This story is about a girl who learns about frustration and perseverance while trying to create something magnificent.
- “Ish” by Peter H. Reynolds: Reynolds’ book teaches children that thinking “ish-ly” is more important than perfection, encouraging creative problem-solving.
- “Not a Box” by Antoinette Portis: This book stimulates imagination and creativity, showing how a simple box can be much more through innovative thinking.
- “The Dot” by Peter H. Reynolds: Another book by Reynolds, it inspires children to start small and see where their imagination and problem-solving can take them.
- “What Do You Do With a Problem?” by Kobi Yamada: This book personifies problems as opportunities to learn and grow, teaching children to face challenges head-on.
- “Beautiful Oops!” by Barney Saltzberg: Saltzberg’s book encourages finding beauty in mistakes and learning from them, promoting a positive attitude towards problem-solving.
Here’s a list of reputable online resources that provide valuable content on teaching problem-solving skills to preschoolers, including activities, strategies, and educational insights:
- NAEYC (National Association for the Education of Young Children) : Offers a wealth of resources on early childhood development, including articles and tips on promoting problem-solving skills.
- Teaching Strategies : Offers innovative, research-based teaching methods and resources for early childhood educators to enhance problem-solving skills in preschoolers.
- Education.com : Contains a wide range of problem-solving activities, worksheets, and games tailored for preschool-aged children.
These websites are well-regarded in the field of early childhood education and provide a range of tools and insights for effectively teaching problem-solving skills to preschoolers.
Problem-solving worksheets are an effective learning tool for developing critical thinking and analytical skills. They provide structured opportunities for students to practice and refine their approach to solving various types of problems.
List of Necessary Elements for Problem-Solving Worksheets
For problem-solving worksheets to be an effective learning tool, they should include:
- Clear Instructions: Directions should be concise and easy to understand, ensuring students know what is expected.
- Relevant Content: Problems should be age-appropriate and connected to real-world situations to enhance relevance and engagement.
- Structured Approach: Worksheets should guide students through the problem-solving process, possibly outlining steps like understanding the problem, devising a plan, carrying out the plan, and reviewing the solution.
- Variety in Problem Types: Including different types of problems, such as puzzles, logic problems, and word problems, can cater to various learning styles and interests.
- Space for Workings: Providing ample space for students to write down their thought processes and calculations is important for developing their ability to solve problems systematically.
- Engaging Design: Visually appealing worksheets with illustrations or graphics can motivate students and enhance their learning experience.

Practical Application
Preschoolers can learn valuable problem-solving skills through real-life scenarios they can relate to and navigate. Here’s a list of scenarios that can help preschoolers develop and practice these skills:
- Sharing Toys: Navigating how to share toys with siblings or friends, deciding who plays with what, and for how long.
- Dressing for the Weather: Choosing appropriate clothing for the day based on the weather conditions, like selecting a raincoat on a rainy day or a sunhat when it’s sunny.
- Meal Choices: Making decisions about what to eat for snacks or meals, balancing between healthy options and favorite treats.
- Cleaning Up: Figuring out how to organize and clean up toys and supplies efficiently after playtime.
- Lost Items: Developing strategies to find a lost toy or belonging, retracing steps, and thinking of places where it could be.
- Turn-taking Games: Learning to wait for a turn and cope with the delay in gratification during group games or activities.
- Building Structures: Deciding how to build a stable structure using blocks or other materials, which involves planning and adjusting techniques.
- Resolving Conflicts : Finding peaceful solutions to disputes with peers, like taking turns, sharing, or finding a compromise.
- Planning a Playdate: Participating in planning activities, considering what games to play and what snacks to have.
- Handling Emotions: Identifying and managing emotions when things don’t go as planned, such as calming down after a disappointment.
Nurturing problem-solving skills from a young age is beneficial and crucial for children’s cognitive and emotional development. As detailed in this article, integrating problem-solving activities into the daily routines of preschoolers can significantly enhance their ability to navigate and overcome challenges, fostering independence, creativity, and resilience.
Therefore, parents, educators, and caregivers must incorporate a variety of problem-solving activities into their interactions with young learners. From math games to social scenarios and creative play, every moment can be an opportunity to develop these vital skills. Let’s embrace the joy and responsibility of guiding our preschoolers through their problem-solving journey, equipping them with the tools they need to thrive in an ever-changing world. Encourage, facilitate, and revel in the process of discovery, and watch as the seeds of today’s problem-solving activities blossom into the critical thinking abilities of tomorrow.
Empower your little scholar with the gift of problem-solving! Join us at Little Scholars Daycare, where we turn everyday moments into exciting learning opportunities. Enroll your child today and watch them grow into confident, creative problem-solvers ready to take on the world!
Related articles

Celebrating St. Patrick’s Day with Kids

Balancing Screen Time and Playtime

A Journey Through the Senses: Unlocking the World for Our Little Scholars

Understanding and Supporting Social-Emotional Development in Young Children

AI Assistant
Hi, I am a personal AI assistant, ask me anything you want to know about The Little Scholars Childcare Center!
Select a location to tour:

HelloParent
13 Problem-Solving Activities For Toddlers And Preschoolers

Problem-Solving Activities
Problem-solving skills are vital for a child’s cognitive development. They help kids think critically, make decisions, and become more independent. As a parent or caregiver, you can nurture these skills in toddlers and preschoolers through a variety of engaging activities. Let’s explore 13 problem-solving activities that will not only entertain but also educate your little ones.
1. Building with Blocks
Age Group: Toddlers and Preschoolers
Description: Encourage your child to build structures with blocks. Start with simple designs and gradually increase complexity. This activity enhances spatial reasoning and problem-solving abilities.
Playing with building blocks is a timeless and versatile activity that promotes problem-solving skills in young children. As they stack blocks to create structures, kids learn about balance, stability, and the concept of cause and effect. They discover that if they place a block in a certain way, the structure becomes more stable. This understanding is fundamental to problem-solving.
2. Shape Sorters
Age Group: Toddlers
Description: Shape sorters teach toddlers about shapes, sizes, and how objects fit together. It’s a fun way to introduce problem-solving concepts.
Shape sorters are classic toys that introduce toddlers to basic problem-solving. The child must figure out which shape corresponds to each slot in the sorter. This activity enhances their ability to categorize and match objects based on their attributes. It’s a simple yet effective way to lay the foundation for more complex problem-solving skills.
Age Group: Preschoolers
Description: Jigsaw puzzles challenge preschoolers to solve problems by finding the right fit for each piece. They improve spatial awareness and patience.
Puzzles are excellent tools for enhancing problem-solving skills in preschoolers. When kids work on jigsaw puzzles, they learn to analyze the shape, color, and pattern of each piece. They must figure out where each piece fits in the overall picture. This process involves trial and error, spatial reasoning, and the development of patience—an essential component of problem-solving.
4. Sorting Games
Description: Sorting games with colored objects or shapes help kids categorize and organize, promoting logical thinking.
Sorting games engage children’s problem-solving abilities by encouraging them to categorize and organize objects based on specific criteria. For instance, you can provide a mix of colored objects and ask your child to sort them by color. This activity promotes logical thinking as they identify patterns and make decisions about where each item belongs.
5. Scavenger Hunts
Description: Create scavenger hunts at home or in your backyard. Give clues to find hidden treasures, stimulating critical thinking and problem-solving.
Scavenger hunts are not only thrilling but also fantastic for developing problem-solving skills. You can organize indoor or outdoor hunts with clues that require critical thinking and problem-solving to decipher. Children must follow clues, make connections, and strategize to locate hidden treasures, fostering their problem-solving abilities.
6. Building Simple Machines
Description: Use everyday materials like cardboard, string, and pulleys to create simple machines. Children can experiment and learn about cause and effect.
Engaging in hands-on activities like building simple machines is a fantastic way to introduce problem-solving concepts. Children can use everyday materials to create pulleys, levers, or ramps. As they experiment with these simple machines, they observe cause-and-effect relationships, encouraging them to think critically and find solutions to challenges they encounter during the construction process.
7. Storytelling
Description: Encourage imaginative problem-solving by asking your child to come up with solutions to challenges in their stories.
Storytelling not only stimulates creativity but also encourages problem-solving in young children. When kids invent stories, they often encounter dilemmas that require resolution. By asking your child how the characters in their stories overcome challenges, you prompt them to think creatively and find solutions—an invaluable problem-solving skill.
8. Cooking Together
Description: Involve your child in age-appropriate cooking activities. They’ll have to follow instructions and make choices, enhancing decision-making skills.
Cooking together is a delightful way to introduce problem-solving to children. It involves following recipes, making choices about ingredients, and adapting to unexpected situations (like a spill). These activities encourage decision-making and critical thinking as children participate in the cooking process.
9. Obstacle Courses
Description: Set up indoor or outdoor obstacle courses with challenges that require problem-solving and decision-making.
Creating obstacle courses at home or in the yard provides opportunities for preschoolers to engage in problem-solving and decision-making. Children must figure out how to navigate the course, overcome obstacles, and make choices along the way. This physical activity complements cognitive development by promoting quick thinking and strategizing.
10. Pattern Recognition
Description: Use everyday objects or cards to create simple patterns. Ask your child to continue the pattern or identify what comes next.
Pattern recognition is a fundamental problem-solving skill that can be introduced through simple activities. You can use everyday objects like buttons or cards with patterns to engage your child. Encourage them to identify and extend patterns, which enhances their ability to recognize sequences and make predictions—a critical component of problem-solving.
11. Planting and Gardening
Description: Gardening teaches children about cause and effect as they care for plants and watch them grow.
Gardening is a hands-on activity that teaches children about cause and effect—a crucial aspect of problem-solving. When kids care for plants and witness their growth, they learn how their actions impact the world around them. Gardening fosters a sense of responsibility and encourages children to think about the consequences of their actions.
12. Role-Playing
Description: Role-playing scenarios where your child has to solve problems, like playing doctor or chef, fosters creativity and critical thinking.
Role-playing scenarios, such as playing doctor or chef, provide opportunities for children to engage in imaginative problem-solving. These activities encourage creativity as children devise solutions to various role-playing challenges. Whether they’re diagnosing a stuffed animal or creating a pretend meal, kids develop problem-solving skills through these scenarios.
13. Science Experiments
Description: Conduct age-appropriate science experiments that encourage hypothesis testing and problem-solving.
Age-appropriate science experiments are perfect for fostering problem-solving skills in preschoolers. These experiments often involve forming hypotheses, conducting tests, and analyzing results—key elements of problem-solving. Encourage your child’s curiosity by engaging in safe and enjoyable science experiments together.
These problem-solving preschool activities for toddlers and preschoolers not only promote cognitive development but also provide hours of fun and quality time together. Remember to adapt activities to your child’s age and developmental stage, allowing them to explore, learn, and grow at their own pace.
In conclusion, nurturing problem-solving skills in young children is essential for their overall development. These activities offer a balance between education and enjoyment, helping your child build critical thinking skills that will benefit them throughout their lives.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are the problems in joining my kid in a Preschool?
Joining your child in a preschool can have several challenges, including separation anxiety, adjustment to a new routine, socialization issues, and concerns about the quality of education and care provided. It’s essential to communicate with the preschool staff, address your child’s needs, and gradually ease the transition to make the process smoother.
2. How to teach problem-solving skills to children and preteens?
To teach problem-solving skills to children and preteens, encourage them to:
Identify the problem.
Brainstorm possible solutions.
Evaluate the pros and cons of each solution.
Make a decision and implement it.
Reflect on the results and learn from the experience.
3. How to keep children busy during their pre-school time?
To keep children engaged during their preschool time, consider activities like art and craft, storytelling, outdoor play, educational games, music, and group activities. Preschools often offer a variety of structured and creative activities to stimulate children’s minds and bodies.
4. What are some preschool programs for kids?
Preschool programs for kids often include activities like early literacy and numeracy, creative arts, physical play, socialization, and learning through play. Many preschools also follow specific educational approaches like Montessori, Waldorf, or play-based programs to cater to different learning styles.
5. How preschool activities impact a child’s learning pace?
Preschool activities play a significant role in a child’s learning pace. They help children develop cognitive, social, and emotional skills, which are essential for academic success. Engaging in age-appropriate activities can foster a love for learning, improve attention span, and enhance problem-solving abilities.
6. What are problem-solving activities that kids can do at home?
There are various problem-solving activities kids can do at home, such as puzzles, board games, scavenger hunts, building challenges with blocks or LEGO, cooking and following recipes, and science experiments. These activities promote critical thinking and decision-making while having fun.
Also Check: Preschools in India
Share this:
Leave a reply cancel reply, discover more from helloparent.
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading

Want to boost your child's problem solving skills? Look no further. This article offers nine engaging problem solving activities for kids that build critical thinking. From simple puzzles to interactive storytelling, discover fun and practical ideas to help your child tackle challenges with confidence.
Introduction to Problem Solving
Problem solving is a vital skill that enables individuals to navigate complex situations, overcome obstacles, and achieve their goals. It involves critical thinking, creativity, and analytical reasoning to identify and resolve problems. Developing problem solving skills is essential for children to become independent, confident, and successful individuals. When children learn to solve problems, they enhance their cognitive abilities, build resilience, and improve their decision-making skills. Whether it’s figuring out how to share toys with friends or deciding the best way to build a fort, problem solving is a crucial part of their growth and development.

Key Takeaways
- Problem solving skills are essential for cognitive growth in children, enhancing creativity, decision-making, and resilience.
- Engaging activities like puzzles, building challenges, and coding foster critical thinking and practical applications of problem solving skills.
- Role-playing and interactive storytelling encourage creativity and collaborative problem solving, preparing children for real-life challenges.
Why Problem Solving Skills Matter
Nurturing children’s problem solving abilities is essential for their intellectual development. These capabilities are pivotal in bolstering critical thinking, making well-informed choices, and sparking creative thought—all of which are instrumental across life’s journey.
Engaging in activities such as online games, storytelling, and coding helps children develop problem solving skills, encouraging creativity, logical thinking, and the ability to navigate challenges, ultimately leading to enhanced problem solving abilities that are applicable in real-life situations.
Learning to start a lemonade stand can be a practical way for kids to apply these skills and understand the basics of entrepreneurship. Children learn true lessons through engaging in activities that present challenges—like selecting the prime spot for a lemonade stand or adeptly utilizing resources—which instill resilience and self-assurance while teaching them to regulate emotions during adversity. To further enrich their entrepreneurial journey, introducing a business plan for kids can provide structured guidance and insights.
Each child develops these solving skills at their own pace, highlighting the need for customized approaches in teaching problem solving. This could entail adjusting recipes or experimenting with different pricing techniques at a lemonade stand to suit individual learning trajectories effectively. problem solving expertise holds relevance across myriad spheres such as business ventures, scientific inquiries, personal endeavors, or academic pursuits—a concept mirrored by running a small-scale lemonade enterprise that imparts valuable insights.
A robust approach to effective problem solving involves assessing alternatives before settling on an optimal resolution. This might resemble trying out new combinations when concocting a tantalizing lemonade mix aimed at boosting sales figures. Engaging children in such processes cultivates their capacity for both analytical reasoning and innovative thinking while fostering resilience along with assurance of self-worth – traits that can be honed. By urging youngsters to seek advice and accept errors as ubiquitous stepping stones towards enhancing one’s ability to solve problems efficiently.
Instilling step-wise strategies within the realm of problem solving into young minds—such as identifying issues clearly, generating potential solutions collaboratively, carefully selecting and applying viable fixes swiftly followed up by reflective pondering—can provide impactful lifelong benefits through captivating activities rooted deeply within practicality. Employing open-ended questions fosters yet another layer of depth into cultivating productive critical analysis combined seamlessly alongside prolific creative ideation necessary throughout successful decision-making journeys.
In essence, whenever your offspring embark upon entrepreneurial ventures like managing a lemonade stand selling cold drinks they’re not merely engaged in simple commercial transactions; instead, they’re laying down solid foundations equipped thoroughly with comprehensive competencies allowing them ultimately master artful maneuverings required consistently amid future situations demanding astute resolutions.
Developing Problem Solving Skills
Developing problem solving skills in children requires a combination of teaching, guidance, and practice. Here are some strategies to help children develop their problem solving skills:
- Encourage Critical Thinking: Ask open-ended questions that prompt children to think deeply and analyze situations. Engage them in discussions that require them to consider different perspectives and solutions.
- Provide Opportunities for Practice: Offer a variety of games, puzzles, and real-world challenges that allow children to practice their problem solving skills. Activities like building a model or planning a small event can be both fun and educational.
- Foster Creativity: Encourage children to think outside the box and explore multiple solutions to problems. Creative thinking can be nurtured through activities like drawing, storytelling, and imaginative play.
- Teach problem solving Strategies: Introduce children to structured problem solving strategies such as identifying the problem, generating possible solutions, evaluating options, and selecting the best solution. These steps can be applied to various scenarios, from academic tasks to everyday challenges.
Encourage Perseverance: Teach children the value of persistence and resilience. Encourage them to keep trying even when they encounter difficulties, and celebrate their efforts and successes.
By incorporating these strategies into daily activities, you can help children develop strong problem solving skills that will serve them well throughout their lives.
Simple Puzzles to Kickstart Critical Thinking
Engaging children in activities like jigsaw puzzles, crosswords, and Sudoku can act as a catalyst for fostering critical thinking. These types of games promote the development of vital problem solving skills such as logical reasoning and pattern recognition, which are integral to successfully navigating complex situations. Similarly, just as organizing a lemonade stand demands tactical foresight and planning abilities akin to puzzle-solving.

Not only do these puzzles bolster one’s abilities to solve problems, but they also cultivate essential cognitive traits like imaginative thinking and tenacity. For instance, strategizing on how best to compete with neighboring lemonade stands requires an equivalent degree of analytical thought that comes into play when tackling an intricate puzzle. Such undertakings push children towards innovative ideas for overcoming obstacles.
By engaging in puzzles, youngsters have the opportunity for hands-on practice with their solving skills within a relaxed environment where trial and error is part of the learning process—they experiment with various tactics and learn from any slip-ups made along the way until they reach successful conclusions.
Encouraging children to participate in self esteem activities for kids can further enhance their confidence and willingness to tackle new challenges, contributing to their overall development. This iterative method reflects real-world steps taken during problem solving exercises such as running a lemonade stand—determining eye-catching setups or efficiently handling supply levels—to achieve effective results.
Understanding how much to sell lemonade for is another crucial decision that can significantly influence the success of the stand. Engaging in these activities helps children practice problem solving skills, making them more adept at tackling challenges in various contexts.
Building Challenges with Blocks
Engaging children in building challenges, such as creating the tallest structure or crafting a robust lemonade stand , is an excellent method for cultivating problem solving skills. These activities make use of different materials like wooden blocks or Legos to foster various creative solutions and enhance diverse solving skills.
Such construction tasks also bolster spatial awareness and comprehension of three-dimensional geometry, similar to planning out a functional lemonade stand. Through cycles of envisioning, measuring, experimenting with designs and refining them, kids sharpen their critical thinking along with their ability to solve problems—much like ensuring that a lemonade stand holds up against light wind mimics engineering a bridge capable of supporting weight.
These building challenges are adaptable across age groups, enabling progressive complexity from elementary structures to intricate configurations. By giving youngsters themed projects for these solving activities, stimulates both creativity and innovative problem solving just as concocting special-themed versions would do for actual lemonade stands.
Undertaking these endeavors encourages ingenuity and exploration, which arms young minds with the resilience needed to confront real-world problems effectively. Engaging in these activities is a practical way to introduce children to the problem solving process, helping them master essential skills through consistent practice and reflection.
Interactive Storytelling for Creative Problem Solving
Utilizing interactive storytelling can significantly enhance children’s creative problem solving skills. When children are involved in stories, their imagination and critical thinking skills are activated as they navigate various predicaments encountered by the characters within these tales. This immersive process promotes a multifaceted approach to thinking and expands their creative problem solving abilities.
Through platforms like Scratch, which merge block-based coding with narrative creation, kids gain an opportunity to enrich their solving skills while delving into the realm of programming logic. A practical example would be crafting digital ads for a homemade lemonade stand, integrating lessons on both code and commerce. These tasks serve not only as educational tools, but also infuse fun into skill development.
Identifying with story protagonists allows young learners to extrapolate how these figures might tackle obstacles—a stepping stone toward refining one’s own problem solving strategies. Blending this form of engagement with arts-and-crafts activities—for instance devising marketing narratives for their product—enhances relevance by linking fictional endeavors with tangible outcomes in real life scenarios. Ultimately converting learning into a delightful pursuit that carries substantial real-world applicability.
Brain-Boosting Board Games
Engaging in board games offers not only entertainment, but is a powerful means to enhance problem solving skills. Titles such as Cluedo, Codenames, Mastermind, and Scrabble are particularly beneficial for honing these competencies. Imagine your lemonade stand as if it were a tangible board game where strategic insight and careful preparation pave the way to triumph.
While engaging in Cluedo’s mystery unraveling through clue acquisition mirrors the analytical process of identifying what delights customers at your lemonade stand, Uno demands tactful gameplay and decision-making that bolsters critical thinking along with tactical prowess—key components when determining optimal timing and location for your beverage enterprise.
Chess cultivates children’s ability to foresee outcomes strategically—a pivotal element necessary for devising plans essential in operating a prosperous lemonade venture. Through their promotion of forward-thinking, exploration of various outcomes, and making judicious choices based on available information—in an atmosphere filled with amusement—board games serve as an excellent practice ground for sharpening solving skills applicable within real-world contexts.
Outdoor Scavenger Hunts
Engaging in outdoor scavenger hunts is an enjoyable way to enhance problem solving skills. Participants decipher clues and unravel puzzles during these pursuits, honing both critical thinking and creativity as they search for hidden rewards—much like the journey of identifying prime locations and arrangements when starting a lemonade stand.
To elevate the complexity and engagement levels of a scavenger hunt, incorporating riddles as part of the clue trail can be effective. Constructing shelters or mastering an obstacle course outdoors are types of problem solving activities that foster inventive approaches and tactical reasoning. They reflect real-life challenges similar to those encountered while establishing a thriving lemonade business , such as selecting optimal spots for customer attraction.
Undertaking a scavenger hunt necessitates collective effort and cooperation—key abilities crucial for managing something like a lemonade stand successfully. Collaborating on unraveling mysteries and seeking objects allows youngsters to practice productive communication methods alongside sharing innovative ideas with one another. These solving activities serve as an entertaining educational approach to build upon essential skills applicable within various life scenarios.
Coding Activities for Logical Reasoning
Coding activities are great for developing problem solving skills and logical reasoning in children. Coding teaches creativity, logic, planning, and persistence, all essential for running a successful lemonade stand. By learning to code, children can enhance their critical thinking and problem solving abilities in a fun and engaging way.
There are numerous tools and online or in-person programs available for children to learn coding. These programs make coding accessible and enjoyable, encouraging children to explore and experiment with different solutions. For example, they can plan their lemonade stand setup and sales strategies using coding principles.

Online interactive games help children develop perseverance, goal-setting abilities, and skills to overcome challenges. These games encourage creative solutions to puzzles, teaching effective problem solving approaches applicable to real-life scenarios. Coding activities provide a valuable foundation for logical reasoning and critical thinking, preparing children for future challenges.
Craft-Based Problem Solving
Activities involving crafts are a potent tool for nurturing children’s problem solving skills and enhancing their capacity for critical thinking. When kids create decorations and signage for a lemonade stand , they engage in independent ideation and the pursuit of original solutions. Such hands-on solving activities allow youngsters to delve into creative expression as they navigate challenges.
Posing open-ended questions during craft projects stimulates young minds by advancing their critical thinking skills through crafting ventures that prompt them to conceive numerous potential outcomes and strategies, fostering individualized approaches to tackling problems. Through structured building challenge cards provided within these activities, creativity is bolstered alongside honing problem solving capabilities.
Introducing prompts tailored toward problem solving can inspire children to cultivate critical thinking abilities while inventing distinctive resolutions. Utilizing common items like straws, cotton balls, yarns, and Popsicle sticks propels resourcefulness paired with out-of-the-box reasoning—essential when creating compelling lemonade stand decor which sets it apart from competitors.
Partaking in crafting endeavors grants youth an avenue to showcase inventive responses to difficulties encountered—a fundamental practice that guides them towards advanced problem solving abilities crucial when approaching complex issues or devising enterprising answers rooted in real-life scenarios.
Fun with Riddles and Brain Teasers
Engaging children in riddles and brain teasers is an entertaining method to enhance their problem solving abilities. These exercises encourage youngsters to apply creative thought and deduce solutions, akin to devising captivating strategies for marketing a lemonade stand. Brain teasers serve as intellectual calisthenics that demand increased mental exertion for resolution.
Brain teasers bestow the advantage of promoting various pathways toward finding resolutions, instilling flexibility within young minds. This adaptability aids children in honing their solving skills by evaluating diverse methods and potential answers. Utilizing brain teasers as a morning routine can be an effective strategy for activating the cognitive functions of students, equipping them with readiness for challenges throughout the day.
Incorporating these puzzles into breaks from conventional teaching plans also provides stimulation and amusement for students. Tackling riddles encourages kids to interpret information metaphorically while fostering a sense of humor during education—thus enhancing engagement levels significantly. Riddles along with brain teaser activities present not just enjoyment, but also pave the way into interactive practice sessions that bolster problem solving skills transferable to real-world scenarios.
Real-Life Problem Solving Through Role Play
Engaging in role-play scenarios is an excellent method to hone problem solving skills among youngsters. When children take part in a lemonade stand simulation, they are presented with the chance to consider different viewpoints and build empathy by assuming various roles like patrons or proprietors of the business. This activity prompts them to examine issues carefully and work together in search of viable solutions.
Such role-playing exercises solidify understanding about problem solving while presenting potential solutions for consideration. Through these enactments, kids get an opportunity to rehearse how they would manage real situations that could arise at their makeshift stands — from handling rushes of customers to sorting out service-related dilemmas — thereby enhancing their solving skills through active participation.
Implementing a tangible lemonade stand calls upon collective effort and creative problem solving abilities as children join forces on aspects such as aesthetics, promotional tactics, and transactional strategies. Their involvement teaches them crucial communication techniques, informed decision-making processes, and innovative approaches for tackling hurdles encountered along the way.
By offering realistic scenarios through role-playing activities where fun intersects with learning experiences tailor-made for developing solving abilities, it discreetly teaches invaluable lessons about finding imaginative resolutions within collaborative settings.
Real-World Applications
problem solving skills have numerous real-world applications, including:
- Academic Success: problem solving skills are essential for academic success. They enable students to analyze complex information, evaluate evidence, and develop well-supported arguments. For example, solving math problems or conducting science experiments requires critical thinking and analytical reasoning.
- Career Success: In the workplace, problem solving skills are highly valued. Employees who can analyze complex problems, develop creative solutions, and implement effective strategies are often more successful. Whether it’s managing a project or resolving a customer complaint, problem solving abilities are crucial.
- Personal Growth: problem solving skills help individuals develop a growth mindset which helps them to navigate personal challenges, develop resilience, and achieve their goals. From managing time effectively to resolving conflicts with friends or family, these skills are essential for personal development.
- Social Impact: problem solving skills can be used to address social challenges and create positive change. Individuals who can think critically and develop innovative solutions are better equipped to tackle issues like environmental sustainability, community development, and social justice.
By understanding and applying problem solving skills in various contexts, children can become more capable and confident individuals.
Teaching Problem Solving Skills
Teaching problem solving skills requires a combination of explicit instruction, guided practice, and independent practice. Here are some strategies for teaching problem solving skills:
- Use Real-World Examples: Illustrate the importance and relevance of problem solving skills by using real-world examples. Discuss scenarios that children can relate to, such as planning a birthday party or resolving a disagreement with a friend.
- Provide Explicit Instruction: Teach children specific problem solving strategies, including identifying the problem, generating solutions, evaluating options, and selecting the best solution. Use clear and simple language to explain each step.
- Encourage Collaboration: Promote teamwork and communication by encouraging children to work together on problem solving tasks. Collaborative activities help children develop skills like negotiation, compromise, and conflict resolution .
- Provide Feedback: Offer constructive feedback on children’s problem solving efforts. Highlight their strengths, identify areas for improvement, and provide guidance on how to enhance their skills. Positive reinforcement can boost their confidence and motivation.
By incorporating these strategies into your teaching approach, you can help children develop strong problem solving skills that will benefit them in all areas of life.
Final Thoughts on Problem Solving Activities for Kids
Fostering problem solving abilities in kids is crucial for their mental growth and eventual achievements. Children can bolster their critical thinking capabilities and unleash creative potential by diving into a variety of solving activities, including assembling puzzles, tackling building challenges, immersing themselves in interactive storytelling, indulging in board games, exploring scavenger hunts, practicing coding exercises, creating crafts projects, deciphering riddles and engaging in role-playing scenarios. These pursuits offer delightful and hands-on methods to hone children’s problem solving skills with direct ties to situations encountered in everyday life.
Motivating youngsters to dive into these types of solving activities not only aids them in developing tenacity, but also boosts self-assurance and emotional regulation when faced with difficulties. It’s essential that as guardians or educators we provide support yet still give the young ones ample room for autonomous exploration to arrive at unique solutions on their own terms. Let us journey together on this educational quest empowering our youth with the invaluable tools necessary for triumph!
Frequently Asked Questions
How do puzzles help in developing problem solving skills in children?
Puzzles are a fantastic way to boost children’s problem solving skills by enhancing logical reasoning and critical thinking. By encouraging them to experiment and learn from their mistakes, you’re equipping them with essential tools for tackling challenges in life.
What are some examples of board games that foster problem solving skills?
Engaging in games such as Cluedo, Codenames, Mastermind, and Scrabble can substantially improve your problem solving abilities.
Immerse yourself in these captivating activities to refine your strategic planning and enhance your decision-making skills!
How can coding activities benefit children's problem solving abilities?
Participating in coding exercises greatly enhances your child’s capacity for problem solving as it nurtures imagination, logical reasoning, and critical thinking skills.
Through the process of addressing coding problems, they acquire a strategic approach to handling real-world issues, equipping them with the tools needed to thrive in various circumstances.
Why is role-playing effective for teaching problem solving skills?
Role-playing is effective for teaching problem solving skills because it encourages exploration of different perspectives and fosters empathy. Engaging in scenarios helps students collaboratively analyze issues and practice real-life reactions, empowering them with valuable problem solving techniques.
What benefits do craft-based problem solving activities offer?
Craft-based problem solving activities spark creativity and enhance critical thinking skills in children by promoting independent idea generation and innovative solutions.
Embrace these fun opportunities to inspire kids to tackle challenges with confidence!
back to blog

STAY CONNECTED TO LEMONADE DAY NATIONAL
@LemonadeDayNational

IMAGES
VIDEO