

What is Reported Speech and how to use it? with Examples
Published by
Olivia Drake
Reported speech and indirect speech are two terms that refer to the same concept, which is the act of expressing what someone else has said.
On this page:
Reported speech is different from direct speech because it does not use the speaker’s exact words. Instead, the reporting verb is used to introduce the reported speech, and the tense and pronouns are changed to reflect the shift in perspective. There are two main types of reported speech: statements and questions.
1. Reported Statements: In reported statements, the reporting verb is usually “said.” The tense in the reported speech changes from the present simple to the past simple, and any pronouns referring to the speaker or listener are changed to reflect the shift in perspective. For example, “I am going to the store,” becomes “He said that he was going to the store.”
2. Reported Questions: In reported questions, the reporting verb is usually “asked.” The tense in the reported speech changes from the present simple to the past simple, and the word order changes from a question to a statement. For example, “What time is it?” becomes “She asked what time it was.”
It’s important to note that the tense shift in reported speech depends on the context and the time of the reported speech. Here are a few more examples:
- Direct speech: “I will call you later.”Reported speech: He said that he would call me later.
- Direct speech: “Did you finish your homework?”Reported speech: She asked if I had finished my homework.
- Direct speech: “I love pizza.”Reported speech: They said that they loved pizza.
When do we use reported speech?
Reported speech is used to report what someone else has said, thought, or written. It is often used in situations where you want to relate what someone else has said without quoting them directly.
Reported speech can be used in a variety of contexts, such as in news reports, academic writing, and everyday conversation. Some common situations where reported speech is used include:
News reports: Journalists often use reported speech to quote what someone said in an interview or press conference.
Business and professional communication: In professional settings, reported speech can be used to summarize what was discussed in a meeting or to report feedback from a customer.
Conversational English: In everyday conversations, reported speech is used to relate what someone else said. For example, “She told me that she was running late.”
Narration: In written narratives or storytelling, reported speech can be used to convey what a character said or thought.
How to make reported speech?
1. Change the pronouns and adverbs of time and place: In reported speech, you need to change the pronouns, adverbs of time and place to reflect the new speaker or point of view. Here’s an example:
Direct speech: “I’m going to the store now,” she said. Reported speech: She said she was going to the store then.
In this example, the pronoun “I” is changed to “she” and the adverb “now” is changed to “then.”
2. Change the tense: In reported speech, you usually need to change the tense of the verb to reflect the change from direct to indirect speech. Here’s an example:
Direct speech: “I will meet you at the park tomorrow,” he said. Reported speech: He said he would meet me at the park the next day.
In this example, the present tense “will” is changed to the past tense “would.”
3. Change reporting verbs: In reported speech, you can use different reporting verbs such as “say,” “tell,” “ask,” or “inquire” depending on the context of the speech. Here’s an example:
Direct speech: “Did you finish your homework?” she asked. Reported speech: She asked if I had finished my homework.
In this example, the reporting verb “asked” is changed to “said” and “did” is changed to “had.”
Overall, when making reported speech, it’s important to pay attention to the verb tense and the changes in pronouns, adverbs, and reporting verbs to convey the original speaker’s message accurately.
How do I change the pronouns and adverbs in reported speech?
1. Changing Pronouns: In reported speech, the pronouns in the original statement must be changed to reflect the perspective of the new speaker. Generally, the first person pronouns (I, me, my, mine, we, us, our, ours) are changed according to the subject of the reporting verb, while the second and third person pronouns (you, your, yours, he, him, his, she, her, hers, it, its, they, them, their, theirs) are changed according to the object of the reporting verb. For example:
Direct speech: “I love chocolate.” Reported speech: She said she loved chocolate.
Direct speech: “You should study harder.” Reported speech: He advised me to study harder.
Direct speech: “She is reading a book.” Reported speech: They noticed that she was reading a book.
2. Changing Adverbs: In reported speech, the adverbs and adverbial phrases that indicate time or place may need to be changed to reflect the perspective of the new speaker. For example:
Direct speech: “I’m going to the cinema tonight.” Reported speech: She said she was going to the cinema that night.
Direct speech: “He is here.” Reported speech: She said he was there.
Note that the adverb “now” usually changes to “then” or is omitted altogether in reported speech, depending on the context.
It’s important to keep in mind that the changes made to pronouns and adverbs in reported speech depend on the context and the perspective of the new speaker. With practice, you can become more comfortable with making these changes in reported speech.
How do I change the tense in reported speech?
In reported speech, the tense of the reported verb usually changes to reflect the change from direct to indirect speech. Here are some guidelines on how to change the tense in reported speech:
Present simple in direct speech changes to past simple in reported speech. For example: Direct speech: “I like pizza.” Reported speech: She said she liked pizza.
Present continuous in direct speech changes to past continuous in reported speech. For example: Direct speech: “I am studying for my exam.” Reported speech: He said he was studying for his exam.
Present perfect in direct speech changes to past perfect in reported speech. For example: Direct speech: “I have finished my work.” Reported speech: She said she had finished her work.
Past simple in direct speech changes to past perfect in reported speech. For example: Direct speech: “I visited my grandparents last weekend.” Reported speech: She said she had visited her grandparents the previous weekend.
Will in direct speech changes to would in reported speech. For example: Direct speech: “I will help you with your project.” Reported speech: He said he would help me with my project.
Can in direct speech changes to could in reported speech. For example: Direct speech: “I can speak French.” Reported speech: She said she could speak French.
Remember that the tense changes in reported speech depend on the tense of the verb in the direct speech, and the tense you use in reported speech should match the time frame of the new speaker’s perspective. With practice, you can become more comfortable with changing the tense in reported speech.
Do I always need to use a reporting verb in reported speech?
No, you do not always need to use a reporting verb in reported speech. However, using a reporting verb can help to clarify who is speaking and add more context to the reported speech.
In some cases, the reported speech can be introduced by phrases such as “I heard that” or “It seems that” without using a reporting verb. For example:
Direct speech: “I’m going to the cinema tonight.” Reported speech with a reporting verb: She said she was going to the cinema tonight. Reported speech without a reporting verb: It seems that she’s going to the cinema tonight.
However, it’s important to note that using a reporting verb can help to make the reported speech more formal and accurate. When using reported speech in academic writing or journalism, it’s generally recommended to use a reporting verb to make the reporting more clear and credible.
Some common reporting verbs include say, tell, explain, ask, suggest, and advise. For example:
Direct speech: “I think we should invest in renewable energy.” Reported speech with a reporting verb: She suggested that they invest in renewable energy.
Overall, while using a reporting verb is not always required, it can be helpful to make the reported speech more clear and accurate
How to use reported speech to report questions and commands?
1. Reporting Questions: When reporting questions, you need to use an introductory phrase such as “asked” or “wondered” followed by the question word (if applicable), subject, and verb. You also need to change the word order to make it a statement. Here’s an example:
Direct speech: “What time is the meeting?” Reported speech: She asked what time the meeting was.
Note that the question mark is not used in reported speech.
2. Reporting Commands: When reporting commands, you need to use an introductory phrase such as “ordered” or “told” followed by the person, to + infinitive, and any additional information. Here’s an example:
Direct speech: “Clean your room!” Reported speech: She ordered me to clean my room.
Note that the exclamation mark is not used in reported speech.
In both cases, the tense of the reported verb should be changed accordingly. For example, present simple changes to past simple, and future changes to conditional. Here are some examples:
Direct speech: “Will you go to the party with me?”Reported speech: She asked if I would go to the party with her. Direct speech: “Please bring me a glass of water.”Reported speech: She requested that I bring her a glass of water.
Remember that when using reported speech to report questions and commands, the introductory phrases and verb tenses are important to convey the intended meaning accurately.
How to make questions in reported speech?
To make questions in reported speech, you need to use an introductory phrase such as “asked” or “wondered” followed by the question word (if applicable), subject, and verb. You also need to change the word order to make it a statement. Here are the steps to make questions in reported speech:
Identify the reporting verb: The first step is to identify the reporting verb in the sentence. Common reporting verbs used to report questions include “asked,” “inquired,” “wondered,” and “wanted to know.”
Change the tense and pronouns: Next, you need to change the tense and pronouns in the sentence to reflect the shift from direct to reported speech. The tense of the verb is usually shifted back one tense (e.g. from present simple to past simple) in reported speech. The pronouns should also be changed as necessary to reflect the shift in perspective from the original speaker to the reporting speaker.
Use an appropriate question word: If the original question contained a question word (e.g. who, what, where, when, why, how), you should use the same question word in the reported question. If the original question did not contain a question word, you can use “if” or “whether” to introduce the reported question.
Change the word order: In reported speech, the word order of the question changes from the inverted form to a normal statement form. The subject usually comes before the verb, unless the original question started with a question word.
Here are some examples of reported questions:
Direct speech: “Did you finish your homework?”Reported speech: He wanted to know if I had finished my homework. Direct speech: “Where are you going?”Reported speech: She wondered where I was going.
Remember that when making questions in reported speech, the introductory phrases and verb tenses are important to convey the intended meaning accurately.
Here you can find more examples of direct and indirect questions
What is the difference between reported speech an indirect speech?
In reported or indirect speech, you are retelling or reporting what someone said using your own words. The tense of the reported speech is usually shifted back one tense from the tense used in the original statement. For example, if someone said, “I am going to the store,” in reported speech you would say, “He/she said that he/she was going to the store.”
The main difference between reported speech and indirect speech is that reported speech usually refers to spoken language, while indirect speech can refer to both spoken and written language. Additionally, indirect speech is a broader term that includes reported speech as well as other ways of expressing what someone else has said, such as paraphrasing or summarizing.
Examples of direct speech to reported
- Direct speech: “I am hungry,” she said. Reported speech: She said she was hungry.
- Direct speech: “Can you pass the salt, please?” he asked. Reported speech: He asked her to pass the salt.
- Direct speech: “I will meet you at the cinema,” he said. Reported speech: He said he would meet her at the cinema.
- Direct speech: “I have been working on this project for hours,” she said. Reported speech: She said she had been working on the project for hours.
- Direct speech: “What time does the train leave?” he asked. Reported speech: He asked what time the train left.
- Direct speech: “I love playing the piano,” she said. Reported speech: She said she loved playing the piano.
- Direct speech: “I am going to the grocery store,” he said. Reported speech: He said he was going to the grocery store.
- Direct speech: “Did you finish your homework?” the teacher asked. Reported speech: The teacher asked if he had finished his homework.
- Direct speech: “I want to go to the beach,” she said. Reported speech: She said she wanted to go to the beach.
- Direct speech: “Do you need help with that?” he asked. Reported speech: He asked if she needed help with that.
- Direct speech: “I can’t come to the party,” he said. Reported speech: He said he couldn’t come to the party.
- Direct speech: “Please don’t leave me,” she said. Reported speech: She begged him not to leave her.
- Direct speech: “I have never been to London before,” he said. Reported speech: He said he had never been to London before.
- Direct speech: “Where did you put my phone?” she asked. Reported speech: She asked where she had put her phone.
- Direct speech: “I’m sorry for being late,” he said. Reported speech: He apologized for being late.
- Direct speech: “I need some help with this math problem,” she said. Reported speech: She said she needed some help with the math problem.
- Direct speech: “I am going to study abroad next year,” he said. Reported speech: He said he was going to study abroad the following year.
- Direct speech: “Can you give me a ride to the airport?” she asked. Reported speech: She asked him to give her a ride to the airport.
- Direct speech: “I don’t know how to fix this,” he said. Reported speech: He said he didn’t know how to fix it.
- Direct speech: “I hate it when it rains,” she said. Reported speech: She said she hated it when it rained.
If you've read this far, you likely found value in our content. We measure the quality of our articles in various ways, and one significant metric is the number of shares. If you appreciated this piece, please spread the word.
Leave a reply cancel reply, i’m olivia.

Welcome to my virtual classroom! Join me on a journey of language and learning, where we explore the wonders of English together. Let’s discover the joy of words and education!
Let’s connect
Join the fun!
Stay updated with our latest tutorials and ideas by joining our newsletter.
Type your email…
Recent posts
Modal verbs in conditional sentences with examples, questions in future perfect continuous tense with examples, questions in future perfect tense with examples, questions in future continuous tense with examples, questions in future indefinite (simple) tense with examples, questions in past perfect continuous tense with examples, discover more from fluent english grammar.
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Continue reading
Reported Speech – Rules, Examples
| Candace Osmond
Candace Osmond
Candace Osmond studied Advanced Writing & Editing Essentials at MHC. She’s been an International and USA TODAY Bestselling Author for over a decade. And she’s worked as an Editor for several mid-sized publications. Candace has a keen eye for content editing and a high degree of expertise in Fiction.
They say gossip is a natural part of human life. That’s why language has evolved to develop grammatical rules about the “he said” and “she said” statements. We call them reported speech.
Every time we use reported speech in English, we are talking about something said by someone else in the past. Thinking about it brings me back to high school, when reported speech was the main form of language!
Learn all about the definition, rules, and examples of reported speech as I go over everything. I also included a worksheet at the end of the article so you can test your knowledge of the topic.
What Does Reported Speech Mean?
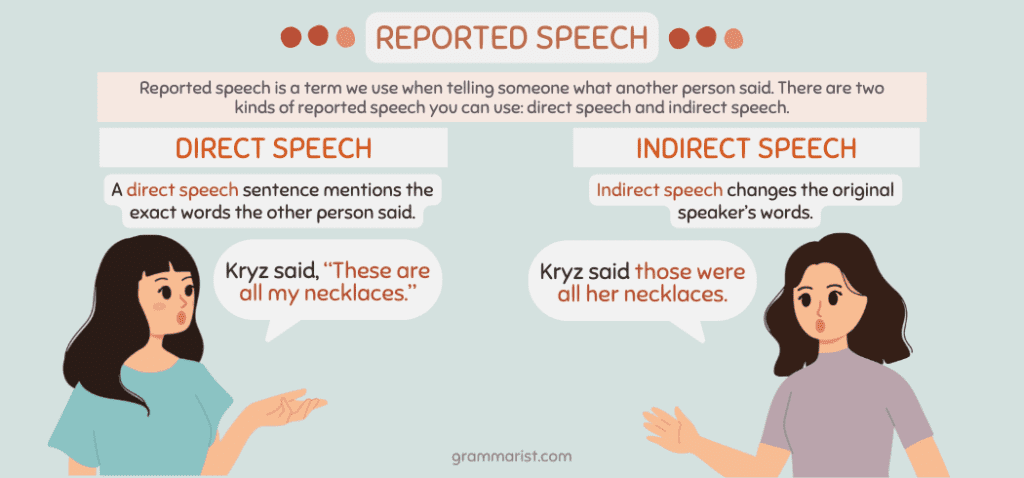
Reported speech is a term we use when telling someone what another person said. You can do this while speaking or writing.
There are two kinds of reported speech you can use: direct speech and indirect speech. I’ll break each down for you.
A direct speech sentence mentions the exact words the other person said. For example:
- Kryz said, “These are all my necklaces.”
Indirect speech changes the original speaker’s words. For example:
- Kryz said those were all her necklaces.
When we tell someone what another individual said, we use reporting verbs like told, asked, convinced, persuaded, and said. We also change the first-person figure in the quotation into the third-person speaker.
Reported Speech Examples
We usually talk about the past every time we use reported speech. That’s because the time of speaking is already done. For example:
- Direct speech: The employer asked me, “Do you have experience with people in the corporate setting?”
Indirect speech: The employer asked me if I had experience with people in the corporate setting.
- Direct speech: “I’m working on my thesis,” I told James.
Indirect speech: I told James that I was working on my thesis.
Reported Speech Structure
A speech report has two parts: the reporting clause and the reported clause. Read the example below:
- Harry said, “You need to help me.”
The reporting clause here is William said. Meanwhile, the reported clause is the 2nd clause, which is I need your help.
What are the 4 Types of Reported Speech?
Aside from direct and indirect, reported speech can also be divided into four. The four types of reported speech are similar to the kinds of sentences: imperative, interrogative, exclamatory, and declarative.
Reported Speech Rules
The rules for reported speech can be complex. But with enough practice, you’ll be able to master them all.
Choose Whether to Use That or If
The most common conjunction in reported speech is that. You can say, “My aunt says she’s outside,” or “My aunt says that she’s outside.”
Use if when you’re reporting a yes-no question. For example:
- Direct speech: “Are you coming with us?”
Indirect speech: She asked if she was coming with them.
Verb Tense Changes
Change the reporting verb into its past form if the statement is irrelevant now. Remember that some of these words are irregular verbs, meaning they don’t follow the typical -d or -ed pattern. For example:
- Direct speech: I dislike fried chicken.
Reported speech: She said she disliked fried chicken.
Note how the main verb in the reported statement is also in the past tense verb form.
Use the simple present tense in your indirect speech if the initial words remain relevant at the time of reporting. This verb tense also works if the report is something someone would repeat. For example:
- Slater says they’re opening a restaurant soon.
- Maya says she likes dogs.
This rule proves that the choice of verb tense is not a black-and-white question. The reporter needs to analyze the context of the action.
Move the tense backward when the reporting verb is in the past tense. That means:
- Present simple becomes past simple.
- Present perfect becomes past perfect.
- Present continuous becomes past continuous.
- Past simple becomes past perfect.
- Past continuous becomes past perfect continuous.
Here are some examples:
- The singer has left the building. (present perfect)
He said that the singers had left the building. (past perfect)
- Her sister gave her new shows. (past simple)
- She said that her sister had given her new shoes. (past perfect)
If the original speaker is discussing the future, change the tense of the reporting verb into the past form. There’ll also be a change in the auxiliary verbs.
- Will or shall becomes would.
- Will be becomes would be.
- Will have been becomes would have been.
- Will have becomes would have.
For example:
- Direct speech: “I will be there in a moment.”
Indirect speech: She said that she would be there in a moment.
Do not change the verb tenses in indirect speech when the sentence has a time clause. This rule applies when the introductory verb is in the future, present, and present perfect. Here are other conditions where you must not change the tense:
- If the sentence is a fact or generally true.
- If the sentence’s verb is in the unreal past (using second or third conditional).
- If the original speaker reports something right away.
- Do not change had better, would, used to, could, might, etc.
Changes in Place and Time Reference
Changing the place and time adverb when using indirect speech is essential. For example, now becomes then and today becomes that day. Here are more transformations in adverbs of time and places.
- This – that.
- These – those.
- Now – then.
- Here – there.
- Tomorrow – the next/following day.
- Two weeks ago – two weeks before.
- Yesterday – the day before.
Here are some examples.
- Direct speech: “I am baking cookies now.”
Indirect speech: He said he was baking cookies then.
- Direct speech: “Myra went here yesterday.”
Indirect speech: She said Myra went there the day before.
- Direct speech: “I will go to the market tomorrow.”
Indirect speech: She said she would go to the market the next day.
Using Modals
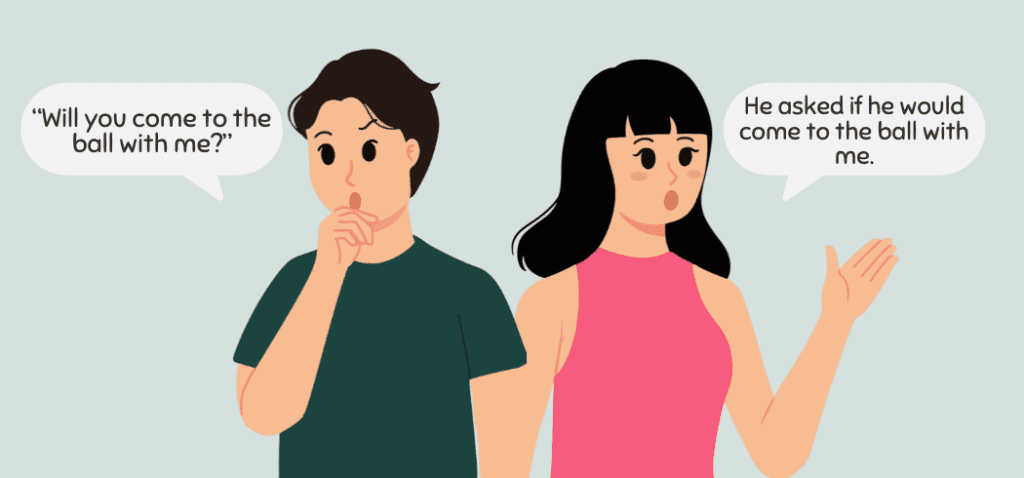

If the direct speech contains a modal verb, make sure to change them accordingly.
- Will becomes would
- Can becomes could
- Shall becomes should or would.
- Direct speech: “Will you come to the ball with me?”
Indirect speech: He asked if he would come to the ball with me.
- Direct speech: “Gina can inspect the room tomorrow because she’s free.”
Indirect speech: He said Gina could inspect the room the next day because she’s free.
However, sometimes, the modal verb should does not change grammatically. For example:
- Direct speech: “He should go to the park.”
Indirect speech: She said that he should go to the park.
Imperative Sentences
To change an imperative sentence into a reported indirect sentence, use to for imperative and not to for negative sentences. Never use the word that in your indirect speech. Another rule is to remove the word please . Instead, say request or say. For example:
- “Please don’t interrupt the event,” said the host.
The host requested them not to interrupt the event.
- Jonah told her, “Be careful.”
- Jonah ordered her to be careful.
Reported Questions
When reporting a direct question, I would use verbs like inquire, wonder, ask, etc. Remember that we don’t use a question mark or exclamation mark for reports of questions. Below is an example I made of how to change question forms.
- Incorrect: He asked me where I live?
Correct: He asked me where I live.
Here’s another example. The first sentence uses direct speech in a present simple question form, while the second is the reported speech.
- Where do you live?
She asked me where I live.
Wrapping Up Reported Speech
My guide has shown you an explanation of reported statements in English. Do you have a better grasp on how to use it now?
Reported speech refers to something that someone else said. It contains a subject, reporting verb, and a reported cause.
Don’t forget my rules for using reported speech. Practice the correct verb tense, modal verbs, time expressions, and place references.
Grammarist is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for sites to earn advertising fees by advertising and linking to Amazon.com. When you buy via the links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commission at no cost to you.
2024 © Grammarist, a Found First Marketing company. All rights reserved.
- English Grammar
- Clause structure and verb patterns
Reported speech
Level: intermediate
Reporting and summarising
When we want to report what people say, we don't usually try to report their exact words. We usually give a summary , for example:
Direct speech (exact words) :
Mary : Oh dear. We've been walking for hours! I'm exhausted. I don't think I can go any further. I really need to stop for a rest. Peter : Don't worry. I'm not surprised you're tired. I'm tired too. I'll tell you what, let's see if we can find a place to sit down, and then we can stop and have our picnic.
Reported speech (summary) :
When Mary complained that she was tired out after walking so far, Peter said they could stop for a picnic.
Reporting verbs
When we want to report what people say, we use reporting verbs . Different reporting verbs have different patterns, for example:
Mary complained (that) she was tired . (verb + that clause) She asked if they could stop for a rest . (verb + if clause) Peter told her not to worry . (verb + to -infinitive) He suggested stopping and having a picnic . (verb + - ing form)
See reporting verbs with that , wh- and if clauses , verbs followed by the infinitive , verbs followed by the -ing form .
GapFillDragAndDrop_MTY1NTE=
GapFillTyping_MTY1NTI=
Tenses in reported speech
When reporting what people say or think in English, we need to remember that the rules for tense forms in reported speech are exactly the same as in the rest of the language.
This is a letter that Andrew wrote ten years ago:
If we wanted to report what Andrew said in his letter, we might say something like this:
Andrew said that when he was 22, he was an engineering student in his last month at university. He wanted to travel abroad after he had finished his course at the university, but he would need to earn some money while he was abroad so he wanted to learn to teach English as a foreign language. A friend had recommended a course but Andrew needed more information, so he wrote to the school and asked them when their courses started and how much they were . He also wanted to know if there was an examination at the end of the course.
We would naturally use past tense forms to talk about things which happened ten years ago. So, tenses in reports and summaries in English are the same as in the rest of the language.
Sometimes we can choose between a past tense form and a present tense form. If we're talking about the past but we mention something that's still true , we can use the present tense:
John said he'd stayed at the Shangri-la because it' s the best hotel in town. Mary said she enjoyed the film because Robert de Niro is her favourite actor. Helen said she loves visiting New York.
or the past tense:
John said he'd stayed at the Shangri-la because it was the best hotel in town. Mary said she enjoyed the film because Robert de Niro was her favourite actor. Helen said she loved visiting New York.
If we're talking about something that everybody knows is true , we normally use the present tense :
Michael said he'd always wanted to climb Everest because it' s the highest mountain in the world. Mary said she loved visiting New York because it' s such an exciting city.
Hi! I found the following paragraph from a grammar site while I was studying the reported speech. Can you help me? It says; --> We can use a perfect form with have + -ed form after modal verbs, especially where the report looks back to a hypothetical event in the past: He said the noise might have been the postman delivering letters. (original statement: ‘The noise might be the postman delivering letters.’)
And my question is: How do we understand if it is a hypothetical event in the past or not? We normally don't change 'might' in reported speech. (e.g. ‘It might snow tonight,’ he warned. --> He warned that it might snow that night.) But why do we say 'He said the noise might have been the postman delivering letters.' instead of 'He said that the noise might be the postman delivering letters.’ What's the difference between these two indirect reported speeches? Could you please explain the difference? And I also found this example which is about the same rule above: --> He said he would have helped us if we’d needed a volunteer. (original statement: a) ‘I’ll help you if you need a volunteer’ or b) ‘I’d help you if you needed a volunteer.’) Can you also explain why we report this sentence like that. How can we both change a) and b) into the same indirect reported speech? Thank you very much!
- Log in or register to post comments
Hello Melis_06,
1. He said the noise might have been the postman delivering letters. 2. He said that the noise might be the postman delivering letters.
In sentence 1 it is clear that the noise has ended; it is a noise that 'he' could hear but it is not a noise that you can hear now. In sentence 2 the noise could have ended or it could be a noise that you can still hear now. For example, if the noise is one which is constant, such as a noise that comes from your car engine that you are still trying to identify, then you would use sentence 2. In other words, sentence 2 allows for a wider range of time possibilities - both past (ended) and present (still current).
Your second question is similar:
He said he would have helped us if we needed a volunteer - you no longer need a volunteer
He said he would help us if we needed a volunteer - this could still be relevant; you may still need a volunteer.
The LearnEnglish Team
Hello my friend : what are you doing now? me : I'm eating an apple now and My friend repeated his question now
my question
Can I repeat the sentence in the past ( I was eating an apple) and mean( I'm eating an apple now) ?
You can but it is unusual. If you say I was eating an apple (past continuous), it means that it was in the past. You already finished eating the apple and you are not eating it now. But if your friend asked you just a moment ago, I guess you are still eating the apple when she/he asks the second question, so I would say I'm eating an apple (because you are still doing it).
Alternatively, you can use a past tense reporting verb e.g. I said I was eating an apple (referring to the time of the first question), or I said I 'm eating an apple (to show that you are still eating it now, at the moment of speaking).
LearnEnglish team
Am I correct then? When someone wants us to repeat the sentence we have just said a moment ago we say 'I said I am doing...' if we are still doing that action. But if we are done with that action, then we say 'I said I was doing...' Did I get it right? Thanks!
Hello Meldo,
Yes, that's correct. Well done!
Hi. I wish to enquire if the verb tense used after a conjunction also changes in complex sentences as per tense transition rules, especially if it is already in simple past tense. In order to explain, could you please solve the following for me: 1. It has been quite a while since I last saw you. 2. Nevertheless, she has been quite desensitized to such perverse actions to the extent that it seldom ever seems obnoxious to her. 3. Let me keep this in my cupboard lest I misplace this. 4. I had arrived at the station before you even left your house. 5. I met my grandfather before he died.
Hi Aamna bluemoon,
The verb may or may not be backshifted, depending on whether the original speaker's point of view and the reporter's point of view are the same or not. For example:
- She said it had been quite a while since she last saw me . (it seems relatively recent, for both the original speaker and the reporter)
- She said it had been quite a while since she had last seen us . (a lot of time has passed between speaking and reporting this, or the situation has changed a lot since then e.g. they have met frequently since then)
- She said she had met her grandfather before he died . (seems quite recent)
- She said she had met her grandfather before he'd died . (a lot of time has passed between speaking and reporting this)
I hope that helps.
Hi, can you help me, please? How could I report this famous quotation: 'There's no such things as good news in America'.
Hi bri.q630,
First of all, the sentence is not grammatically correct. The phrase is 'no such thing' (singular), not 'things'.
How you report it depends. Using 'said' as the reporting verb we have two possibilities:
1. They said (that) there's no such thing as good news in America. 2. They said (that) there was no such thing as good news in America.
Sentence 2 tells that only about the time when 'they' said it. It does not tell us if it is still true or not.
Sentence 1 tells us that what 'they' said is still relevant today. In other words there was no good news (in their opinion) when they spoke, and there is still no good news now.
Thank you Peter,
All things are getting clear to me.
So, you mean, I can use both sentences depending on what I want to indicate, can't I?
then the possible indications are bellow, are those correct?
1-a I remembered the World War 2 ended in 1945. (This would be indicated the statement is still ture.)
1-b I remembered the World War 2 had ended in 1945. (This would be indicated I might missunderstand.)
2-a I felt time is money. (This would be indicated the statement is still ture.)
2-b I felf time was money. (This would be indicated I might not feel any more.)
3-a I knew the sun rises in the east. (This would be indicated the statement is still true.)
3-b I knew the sun rase in the east. (This would be indicated I might misunderstand or forget.)
4-a I guessed* that Darth Vader is Luke's father. (This would be indicated I still believe he is.*sorry for the typo)
4-2 I guessed that Darth Vader was Luke's father. (This would be indicated I might know he is not.)
Thank you in advance.
Hello again Nobori,
1-a I remembered the World War 2 ended in 1945. (This would be indicated the statement is still ture.) 1-b I remembered the World War 2 had ended in 1945. (This would be indicated I might missunderstand.)
Both forms are possible here. The 'ending' is a moment in the past; after this there is no war. By the way, we treat 'World War 2' as a name so there is no article before it.
2-a I felt time is money. (This would be indicated the statement is still ture.) 2-b I felf time was money. (This would be indicated I might not feel any more.)
That's correct. Remember that backshifting the verb does not mean something is no longer true; it simply does not tell us anything about the present. Here, it tells the reader how you felt at a given moment in time; you may
3-a I knew the sun rises in the east. (This would be indicated the statement is still true.) 3-b I knew the sun rase in the east. (This would be indicated I might misunderstand or forget.)
That's also correct. Again, remember that backshifting the verb does not mean something is no longer true; it simply does not tell us anything about the present.
4-a I guessed* that Darth Vader is Luke's father. (This would be indicated I still believe he is.*sorry for the typo) 4-2 I guessed that Darth Vader was Luke's father. (This would be indicated I might know he is not.)
Again, correct. In the second example it might still be true that he is Luke's father, or it might have turned out to be not true. The sentence does not tell us.
Hi Peter, Thank you for your thoughtful answer. Allthing is now very clear to me. Best
Hi, I am translating a fiction novel into English and need your help regarding the reporting speech as for few things I am not getting any clear understanding over the internet. As you know in fiction, we need to write in non-ordinary way to create unique impressions of the word and academic writing is different than speaking. Will be grateful if you could give your insight below, especially considering in the context of fiction/academic writing.
1) Let’s say If someone is giving a speech or presentation, I want to mix their speech, indirect-direct and past tense- present tense. Below are three examples:
-He said, their company makes excellent profit every year OR their company made excellent profit every year ( can both be correct? As the sentence)
- Roger had given his speech yesterday. He said, their company makes excellent profit every year and your company will sustain for next hundred years.(Can YOUR be used in the sentence)
- Roger said people wants to feel important OR Roger said people wanted to feel important (which will be correct as this is a trait which is true in past and present)
2) He thought why he is talking to her OR He thought why he was talking to her (are both write? As usually I see in novels the second example with WAS)
3) Gia was sitting with Jake and she told him she had met with her last year. Her mother had taken her to the dinner. Her mother had told her about her future plans. Her mother also had paid the bill for the dinner. (Do I need to use every time past perfect in this example though it doesn’t feel natural? As a rule of thumb I think past perfect needs to be used when we talk about another past event in the past )
Hello Alamgir3,
We're happy to help with a few specific grammar questions, but I'm afraid we can't help you with your translation -- I'd suggest you find an editor for that.
1) In the second clause, you can use present or past. We often use the present when it's still true now, but the past is not wrong. FYI we don't normally use a comma after 'said' in reported speech.
2) 'Why was he talking to her?' he thought.
3) This is really more of a question of style than grammar. Here I would suggest doing something like combining the four sentences into two and then leaving out 'had' in the second verb in each sentence. Even if it isn't written, it's understood to be past perfect.
All the best, Kirk LearnEnglish team
Hello teachers, I'm sorry, I could not find where to new post. Could you tell me about the back-sifting of thoughts bellow? Which forms are correct?
1-a I remembered the World War 2 ended in 1945. 1-b I remembered the World War 2 had ended in 1945.
2-a I felt time is money. 2-b I felf time was money.
3-a I knew the sun rises in the east. 3-b I knew the sun rase in the east.
4-a I guess that Darth Vader is Luke's father. 4-2 I guessed that Darth Vader was Luke's father.
Do those questions have the same conclusion as indirect speech, such as say and tell?
Hello Nobori,
The verb form remains the same when we want to make it clear that the situation described by the verb is still true, and this works in the same way as indirect speech. For example:
She said she loves me. [she loved me then and she loves me still] She said she loved me. [she loved me then; no information on how she feels now]
Other than this rule, the choice is really contextual and stylistic (up to the speaker). Sometimes a choice implies something. For example, the saying 'time is money' is a general statement, so if you choose to backshift here the listener will know it is an intentional choice and suspect that something has changed (you no longer believe it).
Hi teachers, I've read almost the section of comments below and my summarize is the present tense only can be used if the statement is still true now and past simple only tells the statement was true in the past and doesn't tell the statement is true or not now. Just to make sure, I wanna ask, If I'm not sure whether the statement is still true or not now, can I choose backshift instead (this is still apply to past tense become past perfect)? Thank you
Hello rahmanagustiansyah,
It sounds to me as if you've got the right general idea. Could you please give a couple of example sentences that illustrate your question?
Thanks in advance, Kirk The LearnEnglish Team
For example, Steve said "Anna hates you." Then I wanna tell about that to my friend, but I'm not sure whether Anna still hates me or not now. What should I choose between these two options. Answer 1:Steve said Anna hates me or Answer 2 : Steve said Anna hated me. Thank you
Hi rahmanagustiansyah,
In that case, I would choose answer 2. I might even add "... but I don't know if she still does" to the sentence to clarify, if that is the key point you want to communicate.
Jonathan The LearnEnglish Team
Hello Natasa Tanasa,
Both sentences are grammatically possible.
The first sentence is only possible if when the person asks the original question the woman is no longer there (she has already gone). The second sentence can be used in this situation too, or in a situation in which the woman was still there when the original question was asked. As the past tense is used in the original question ( Who was... ), both sentences are possible.
Hello Ahmed Imam,
When the situation is still true at the time of reporting, we can leave the verb form unchanged. For example:
1. She told me she loved me.
2. She told me she loves me.
In sentence 1 we know she loved me when she told me but we don't know whether or not she loves me now. In sentence 2, we know she loved me when she told me and we know that she loves me now.
In your example, if the supermarket is still in the same place then we can use either form. If the supermarket has been closed down or moved to another location then we need to use was .
As for which is 'safer', you'll need to make your own mind up! Keeping the verb in the same form carries more specific information and that may be appropriate or even important.
Hello eugelatina87,
I'll give you a hint: a verb is missing from the question.
Does that help you complete it?
All the best,
The first two sentences are possible and they can both mean that he is still Mary's boyfriend now. The first one makes this more clear, but the second one doesn't only refer to the past.
Hello magnuslin
Regarding your first question, the most common way of saying it is the second one. In some very specific situation, perhaps the first option would be possible.
This also answers your second question. It is not necessary to always backshift using the tenses you mention.
As for your third question, no, it is not necessary. In fact, it is probably more common to use the past simple in the reported speech as well.
All the best
Hello manu,
Both forms are possible. If you use had been then we understand that he was there earlier but not when he said it - in other words, when he said it he had already left. If you use was then he may have left at the time of speaking, or he may have still been there.
Hello _princess_
I would recommend using answer a) because this is the general pattern used in reported speech. Sometimes the verb in the reported clause can be in the present tense when we are speaking about a situation that is still true, but the reported verb in the past tense can also have the same meaning. Since here the time referred to could be either past or present, I'd recommend using the past form.
Hello mwright,
This is an example of an indirect question. An indirect question reports a question, but is not a question itself, which is why we do not use a question mark at the end. Since it is not a question, we use the normal word order without inversion or auxiliary verbs. For example:
Indicative: He lives in Rome. Interrogative: Does he live in Rome? (Where does he live?) Reported: She asked if he lives in Rome. (She asked where he lives.)
Hello ahlinthit
There are different styles of punctuating direct speech -- in other words, you might find other sources that will disagree with me -- but what I would use here is something different: "The boss is dead!" said the doctor.
Hope this helps.
Best wishes
Hello Timmosky,
The form that comes after the auxiliary verb 'do' (or 'does' or 'did') is not the plural present simple verb, but rather the bare infinitive (also known as 'base form' or 'first form') of the verb. Does that make sense?
All the best, Kirk The LearnEnglish Team
Hello sky-high,
This is very formal language. The phrase 'to the effect that' means 'with the meaning that'. In this context it can be understood to mean 'with the result that'.
Best wishes,
The difference is quite logical. If we use 'said' then we are talking about a claim by Peter in the past which he may or may not still maintain. If we use 'says' then we are talking about an opinion expressed by Peter which he still holds.
The reported information (whether or not Rooney is in good shape) can refer to only the past or to the present as well and the statement (what Peter thinks) can separately refer to only the past or the present as well. Of course, all of this is from the point of view of the person reporting Peter's opinion, and whether or not they think that Peter still thinks now what he thought then.
Both are possible. If you use the present tense then it is clear that the statement is still true (i.e. the business was not growing when Mary spoke and is still not growing now). If you use the past tense then no information is given regarding the present (i.e. the business was growing when Mary spoke and may or may not be growing now).
Hello aseel aftab,
It should be 'if they had'. This is not from this page, is it? I don't see it anywhere here, but if I've missed it please let me know.
Online courses

Group and one-to-one classes with expert teachers.

Learn English in your own time, at your own pace.

One-to-one sessions focused on a personal plan.

Get the score you need with private and group classes.
- English Grammar
- Reported Speech
Reported Speech - Definition, Rules and Usage with Examples
Reported speech or indirect speech is the form of speech used to convey what was said by someone at some point of time. This article will help you with all that you need to know about reported speech, its meaning, definition, how and when to use them along with examples. Furthermore, try out the practice questions given to check how far you have understood the topic.

Table of Contents
Definition of reported speech, rules to be followed when using reported speech, table 1 – change of pronouns, table 2 – change of adverbs of place and adverbs of time, table 3 – change of tense, table 4 – change of modal verbs, tips to practise reported speech, examples of reported speech, check your understanding of reported speech, frequently asked questions on reported speech in english, what is reported speech.
Reported speech is the form in which one can convey a message said by oneself or someone else, mostly in the past. It can also be said to be the third person view of what someone has said. In this form of speech, you need not use quotation marks as you are not quoting the exact words spoken by the speaker, but just conveying the message.
Now, take a look at the following dictionary definitions for a clearer idea of what it is.
Reported speech, according to the Oxford Learner’s Dictionary, is defined as “a report of what somebody has said that does not use their exact words.” The Collins Dictionary defines reported speech as “speech which tells you what someone said, but does not use the person’s actual words.” According to the Cambridge Dictionary, reported speech is defined as “the act of reporting something that was said, but not using exactly the same words.” The Macmillan Dictionary defines reported speech as “the words that you use to report what someone else has said.”
Reported speech is a little different from direct speech . As it has been discussed already, reported speech is used to tell what someone said and does not use the exact words of the speaker. Take a look at the following rules so that you can make use of reported speech effectively.
- The first thing you have to keep in mind is that you need not use any quotation marks as you are not using the exact words of the speaker.
- You can use the following formula to construct a sentence in the reported speech.
- You can use verbs like said, asked, requested, ordered, complained, exclaimed, screamed, told, etc. If you are just reporting a declarative sentence , you can use verbs like told, said, etc. followed by ‘that’ and end the sentence with a full stop . When you are reporting interrogative sentences, you can use the verbs – enquired, inquired, asked, etc. and remove the question mark . In case you are reporting imperative sentences , you can use verbs like requested, commanded, pleaded, ordered, etc. If you are reporting exclamatory sentences , you can use the verb exclaimed and remove the exclamation mark . Remember that the structure of the sentences also changes accordingly.
- Furthermore, keep in mind that the sentence structure , tense , pronouns , modal verbs , some specific adverbs of place and adverbs of time change when a sentence is transformed into indirect/reported speech.
Transforming Direct Speech into Reported Speech
As discussed earlier, when transforming a sentence from direct speech into reported speech, you will have to change the pronouns, tense and adverbs of time and place used by the speaker. Let us look at the following tables to see how they work.
Here are some tips you can follow to become a pro in using reported speech.
- Select a play, a drama or a short story with dialogues and try transforming the sentences in direct speech into reported speech.
- Write about an incident or speak about a day in your life using reported speech.
- Develop a story by following prompts or on your own using reported speech.
Given below are a few examples to show you how reported speech can be written. Check them out.
- Santana said that she would be auditioning for the lead role in Funny Girl.
- Blaine requested us to help him with the algebraic equations.
- Karishma asked me if I knew where her car keys were.
- The judges announced that the Warblers were the winners of the annual acapella competition.
- Binsha assured that she would reach Bangalore by 8 p.m.
- Kumar said that he had gone to the doctor the previous day.
- Lakshmi asked Teena if she would accompany her to the railway station.
- Jibin told me that he would help me out after lunch.
- The police ordered everyone to leave from the bus stop immediately.
- Rahul said that he was drawing a caricature.
Transform the following sentences into reported speech by making the necessary changes.
1. Rachel said, “I have an interview tomorrow.”
2. Mahesh said, “What is he doing?”
3. Sherly said, “My daughter is playing the lead role in the skit.”
4. Dinesh said, “It is a wonderful movie!”
5. Suresh said, “My son is getting married next month.”
6. Preetha said, “Can you please help me with the invitations?”
7. Anna said, “I look forward to meeting you.”
8. The teacher said, “Make sure you complete the homework before tomorrow.”
9. Sylvester said, “I am not going to cry anymore.”
10. Jade said, “My sister is moving to Los Angeles.”
Now, find out if you have answered all of them correctly.
1. Rachel said that she had an interview the next day.
2. Mahesh asked what he was doing.
3. Sherly said that her daughter was playing the lead role in the skit.
4. Dinesh exclaimed that it was a wonderful movie.
5. Suresh said that his son was getting married the following month.
6. Preetha asked if I could help her with the invitations.
7. Anna said that she looked forward to meeting me.
8. The teacher told us to make sure we completed the homework before the next day.
9. Sylvester said that he was not going to cry anymore.
10. Jade said that his sister was moving to Los Angeles.
What is reported speech?
What is the definition of reported speech.
Reported speech, according to the Oxford Learner’s Dictionary, is defined as “a report of what somebody has said that does not use their exact words.” The Collins Dictionary defines reported speech as “speech which tells you what someone said, but does not use the person’s actual words.” According to the Cambridge Dictionary, reported speech is defined as “the act of reporting something that was said, but not using exactly the same words.” The Macmillan Dictionary defines reported speech as “the words that you use to report what someone else has said.”
What is the formula of reported speech?
You can use the following formula to construct a sentence in the reported speech. Subject said that (report whatever the speaker said)
Give some examples of reported speech.
Given below are a few examples to show you how reported speech can be written.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.

Reported Speech
Perfect english grammar.

Reported Statements
Here's how it works:
We use a 'reporting verb' like 'say' or 'tell'. ( Click here for more about using 'say' and 'tell' .) If this verb is in the present tense, it's easy. We just put 'she says' and then the sentence:
- Direct speech: I like ice cream.
- Reported speech: She says (that) she likes ice cream.
We don't need to change the tense, though probably we do need to change the 'person' from 'I' to 'she', for example. We also may need to change words like 'my' and 'your'. (As I'm sure you know, often, we can choose if we want to use 'that' or not in English. I've put it in brackets () to show that it's optional. It's exactly the same if you use 'that' or if you don't use 'that'.)
But , if the reporting verb is in the past tense, then usually we change the tenses in the reported speech:
- Reported speech: She said (that) she liked ice cream.
* doesn't change.
- Direct speech: The sky is blue.
- Reported speech: She said (that) the sky is/was blue.
Click here for a mixed tense exercise about practise reported statements. Click here for a list of all the reported speech exercises.
Reported Questions
So now you have no problem with making reported speech from positive and negative sentences. But how about questions?
- Direct speech: Where do you live?
- Reported speech: She asked me where I lived.
- Direct speech: Where is Julie?
- Reported speech: She asked me where Julie was.
- Direct speech: Do you like chocolate?
- Reported speech: She asked me if I liked chocolate.
Click here to practise reported 'wh' questions. Click here to practise reported 'yes / no' questions. Reported Requests
There's more! What if someone asks you to do something (in a polite way)? For example:
- Direct speech: Close the window, please
- Or: Could you close the window please?
- Or: Would you mind closing the window please?
- Reported speech: She asked me to close the window.
- Direct speech: Please don't be late.
- Reported speech: She asked us not to be late.
Reported Orders
- Direct speech: Sit down!
- Reported speech: She told me to sit down.
- Click here for an exercise to practise reported requests and orders.
- Click here for an exercise about using 'say' and 'tell'.
- Click here for a list of all the reported speech exercises.

Hello! I'm Seonaid! I'm here to help you understand grammar and speak correct, fluent English.

- Cambridge Dictionary +Plus
Reported speech: indirect speech
Indirect speech focuses more on the content of what someone said rather than their exact words. In indirect speech , the structure of the reported clause depends on whether the speaker is reporting a statement, a question or a command.
Indirect speech: reporting statements
Indirect reports of statements consist of a reporting clause and a that -clause. We often omit that , especially in informal situations:
The pilot commented that the weather had been extremely bad as the plane came in to land. (The pilot’s words were: ‘The weather was extremely bad as the plane came in to land.’ )
I told my wife I didn’t want a party on my 50th birthday. ( that -clause without that ) (or I told my wife that I didn’t want a party on my 50th birthday .)
Indirect speech: reporting questions
Reporting yes-no questions and alternative questions.
Indirect reports of yes-no questions and questions with or consist of a reporting clause and a reported clause introduced by if or whether . If is more common than whether . The reported clause is in statement form (subject + verb), not question form:
She asked if [S] [V] I was Scottish. (original yes-no question: ‘Are you Scottish?’ )
The waiter asked whether [S] we [V] wanted a table near the window. (original yes-no question: ‘Do you want a table near the window? )
He asked me if [S] [V] I had come by train or by bus. (original alternative question: ‘Did you come by train or by bus?’ )
Questions: yes-no questions ( Are you feeling cold? )
Reporting wh -questions
Indirect reports of wh -questions consist of a reporting clause, and a reported clause beginning with a wh -word ( who, what, when, where, why, how ). We don’t use a question mark:
He asked me what I wanted.
Not: He asked me what I wanted?
The reported clause is in statement form (subject + verb), not question form:
She wanted to know who [S] we [V] had invited to the party.
Not: … who had we invited …
Who , whom and what
In indirect questions with who, whom and what , the wh- word may be the subject or the object of the reported clause:
I asked them who came to meet them at the airport. ( who is the subject of came ; original question: ‘Who came to meet you at the airport?’ )
He wondered what the repairs would cost. ( what is the object of cost ; original question: ‘What will the repairs cost?’ )
She asked us what [S] we [V] were doing . (original question: ‘What are you doing?’ )
Not: She asked us what were we doing?
When , where , why and how
We also use statement word order (subject + verb) with when , where, why and how :
I asked her when [S] it [V] had happened (original question: ‘When did it happen?’ ).
Not: I asked her when had it happened?
I asked her where [S] the bus station [V] was . (original question: ‘Where is the bus station?’ )
Not: I asked her where was the bus station?
The teacher asked them how [S] they [V] wanted to do the activity . (original question: ‘How do you want to do the activity?’ )
Not: The teacher asked them how did they want to do the activity?
Questions: wh- questions
Indirect speech: reporting commands
Indirect reports of commands consist of a reporting clause, and a reported clause beginning with a to -infinitive:
The General ordered the troops to advance . (original command: ‘Advance!’ )
The chairperson told him to sit down and to stop interrupting . (original command: ‘Sit down and stop interrupting!’ )
We also use a to -infinitive clause in indirect reports with other verbs that mean wanting or getting people to do something, for example, advise, encourage, warn :
They advised me to wait till the following day. (original statement: ‘You should wait till the following day.’ )
The guard warned us not to enter the area. (original statement: ‘You must not enter the area.’ )
Verbs followed by a to -infinitive
Indirect speech: present simple reporting verb
We can use the reporting verb in the present simple in indirect speech if the original words are still true or relevant at the time of reporting, or if the report is of something someone often says or repeats:
Sheila says they’re closing the motorway tomorrow for repairs.
Henry tells me he’s thinking of getting married next year.
Rupert says dogs shouldn’t be allowed on the beach. (Rupert probably often repeats this statement.)
Newspaper headlines
We often use the present simple in newspaper headlines. It makes the reported speech more dramatic:
JUDGE TELLS REPORTER TO LEAVE COURTROOM
PRIME MINISTER SAYS FAMILIES ARE TOP PRIORITY IN TAX REFORM
Present simple ( I work )
Reported speech
Reported speech: direct speech
Indirect speech: past continuous reporting verb
In indirect speech, we can use the past continuous form of the reporting verb (usually say or tell ). This happens mostly in conversation, when the speaker wants to focus on the content of the report, usually because it is interesting news or important information, or because it is a new topic in the conversation:
Rory was telling me the big cinema in James Street is going to close down. Is that true?
Alex was saying that book sales have gone up a lot this year thanks to the Internet.
‘Backshift’ refers to the changes we make to the original verbs in indirect speech because time has passed between the moment of speaking and the time of the report.
In these examples, the present ( am ) has become the past ( was ), the future ( will ) has become the future-in-the-past ( would ) and the past ( happened ) has become the past perfect ( had happened ). The tenses have ‘shifted’ or ‘moved back’ in time.
The past perfect does not shift back; it stays the same:
Modal verbs
Some, but not all, modal verbs ‘shift back’ in time and change in indirect speech.
We can use a perfect form with have + - ed form after modal verbs, especially where the report looks back to a hypothetical event in the past:
He said the noise might have been the postman delivering letters. (original statement: ‘The noise might be the postman delivering letters.’ )
He said he would have helped us if we’d needed a volunteer. (original statement: ‘I’ll help you if you need a volunteer’ or ‘I’d help you if you needed a volunteer.’ )
Used to and ought to do not change in indirect speech:
She said she used to live in Oxford. (original statement: ‘I used to live in Oxford.’ )
The guard warned us that we ought to leave immediately. (original statement: ‘You ought to leave immediately.’ )
No backshift
We don’t need to change the tense in indirect speech if what a person said is still true or relevant or has not happened yet. This often happens when someone talks about the future, or when someone uses the present simple, present continuous or present perfect in their original words:
He told me his brother works for an Italian company. (It is still true that his brother works for an Italian company.)
She said she ’s getting married next year. (For the speakers, the time at the moment of speaking is ‘this year’.)
He said he ’s finished painting the door. (He probably said it just a short time ago.)
She promised she ’ll help us. (The promise applies to the future.)
Indirect speech: changes to pronouns
Changes to personal pronouns in indirect reports depend on whether the person reporting the speech and the person(s) who said the original words are the same or different.
Indirect speech: changes to adverbs and demonstratives
We often change demonstratives ( this, that ) and adverbs of time and place ( now, here, today , etc.) because indirect speech happens at a later time than the original speech, and perhaps in a different place.
Typical changes to demonstratives, adverbs and adverbial expressions
Indirect speech: typical errors.
The word order in indirect reports of wh- questions is the same as statement word order (subject + verb), not question word order:
She always asks me where [S] [V] I am going .
Not: She always asks me where am I going .
We don’t use a question mark when reporting wh- questions:
I asked him what he was doing.
Not: I asked him what he was doing?

Word of the Day
Your browser doesn't support HTML5 audio
of a yellowish-brown or greenish-brown colour

Wise, brainy, or astute: words for describing intelligent people

Learn more with +Plus
- Recent and Recommended {{#preferredDictionaries}} {{name}} {{/preferredDictionaries}}
- Definitions Clear explanations of natural written and spoken English English Learner’s Dictionary Essential British English Essential American English
- Grammar and thesaurus Usage explanations of natural written and spoken English Grammar Thesaurus
- Pronunciation British and American pronunciations with audio English Pronunciation
- English–Chinese (Simplified) Chinese (Simplified)–English
- English–Chinese (Traditional) Chinese (Traditional)–English
- English–Dutch Dutch–English
- English–French French–English
- English–German German–English
- English–Indonesian Indonesian–English
- English–Italian Italian–English
- English–Japanese Japanese–English
- English–Norwegian Norwegian–English
- English–Polish Polish–English
- English–Portuguese Portuguese–English
- English–Spanish Spanish–English
- English–Swedish Swedish–English
- Dictionary +Plus Word Lists
To add ${headword} to a word list please sign up or log in.
Add ${headword} to one of your lists below, or create a new one.
{{message}}
Something went wrong.
There was a problem sending your report.

Reporting Verbs in English Grammar
In this reference, you will learn about reporting verbs in English, how they are used in indirect speech , important grammar rules, and helpful examples. You will find sections that explain what reporting verbs are, a comprehensive list of reporting verbs with examples, and illustrative images to support your learning.
What is a Reporting Verb?

Direct speech is where the speaker gives first-hand information, while indirect speech reports what someone else said. For example, “I am watching TV” is direct speech, and “She said that she was watching TV” is indirect speech.
We use reported speech to tell what another person said without using their exact words, adapting them to the new circumstances.
A reported speech sentence has two parts:
- Introductory Clause + Indirect Clause
Example: He said that they were classmates. (Introductory clause: He said that , Indirect clause: They were classmates. )
In the introductory clause, a reporting verb is needed. There are about 248 verbs to introduce reported speech in English.
List of Reporting Verbs (with Examples)
Tell, say & ask.
The most common verbs to introduce reported speech are Tell , Say , and Ask . Important aspects of these verbs include:
- Can be followed by THAT but it can be omitted.
- Needs an indirect object.
Example: He told me that she was his wife.
- Can have an indirect object introduced by the particle “to.”
- He said that Sarah was working. (no indirect object)
- He said to me that Sarah was working. (with indirect object)
- Can have an indirect object or not.
- Can be used to report questions .
Example: She asked (me) where I lived.
- Can be used to report imperatives or requests.
Example: She asked (me) to babysit for her on Friday.
Verb + that + Clause
Example: She complained that I was always late.
Example: She denied that she had flown in an aeroplane.
Example: He explained that it was an easy recipe to follow.
Exclaim/Remark
Example: She exclaimed/remarked that he was a beautiful baby.
Example: She promised that she would call me.
Example: He boasted that he was a brilliant dentist.
Inform somebody
Example: He informed me that I would be called for an interview.
Example: He claimed that he knew the answer.
Example: He agreed that it was a beautiful hat.
Example: He suggested that I (should) take the other road.
Verb + to + Infinitive
Example: He agreed to cook for me.
Example: He offered to carry her baby.
Example: She refused to buy me a car.
Example: He demanded to be told the truth.
Example: He threatened to punish me if I didn’t behave myself.
Example: He promised to marry her when he returned.
Example: He claimed to have heard her say that.
Verb + Indirect Object + to + Infinitive
Example: He advised me to take a coat.
Example: He allowed me to park over there.
Example: She begged me to call the police.
Example: He commanded them to drop their weapons.
Example: He encouraged me to phone her.
Example: My doctor forbade me to eat sweets.
Example: She invited me to go to his house.
Example: He wanted me to drink a cup of tea.
Example: He instructed me to insert coin.
Example: My parents permitted me to travel with my friends.
Example: He urged me to finish reading the book.
Example: She ordered me to get out of bed.
Example: She reminded me to take out the garbage.
Example: She warned me not to go near the oven.
Verb + “ing” Form
Example: He admitted (to) stealing/having stolen her money.
Accuse somebody of
Example: She accused me of breaking the cup.
Apologize for
Example: He apologized for shouting/having shouted at me.
Boast about/of
Example: He boasted of/about being the cleverest of all.
Complain to somebody of
Example: She complained to me of having a toothache.
Example: He denied murdering/having murdered his wife.
Example: She insisted on me/my wearing warm clothes.
Example: She suggested going to the theatre.
Explain to somebody
Example: He explained to me how to make polite conversation.
Wonder where/what/why/how + clause
When the subject of the reporting verb is not the same as the subject in the reported question .
- She wondered how he could reach the top.
- He wondered where Joan was.
- He wondered why she was crying.
‘Wonder + whether + to-inf or clause’ or ‘Wonder where/what/how + to-inf or clause’
When the subject of the infinitive is the same as the subject of the verb.
- He wondered whether to buy that blender.
- He wondered where he had gone wrong in his calculations.
- He wondered what he should wear.
- He wondered how to get to the post office.

- Latest Posts
- Active vs. Passive Voice Exercises – Active vs. Passive Voice Worksheet - December 25, 2023
- Phrase Exercises – Phrase Worksheet - December 23, 2023
- Sentence Exercises – Sentence Worksheet - December 23, 2023

My English Path
Online resources for English teachers and students
- Reported Speech
Grammar Explanations
Table of Contents
Direct speech and reported speech
Reported speech (also called indirect speech) gives the meaning of what someone said, not the exact words, while direct speech gives the exact words of the speaker, enclosed in quotation marks (or inverted commas.
With reported speech, we do not use quotation marks.
We use that to connect the introduction with the reported words. Using the connecting word that is optional.
- Direct: I am going to help you,” he said.
- Reported: He said (that) he was going to help us.
Introductory verbs
There are certain verbs that we use to introduce reported speech. Here are the most common of them. (More introductory verbs with examples are given below.)
1. say / said
- Direct: “I need a break,” she said.
- Reported: She said (that) she needed a break.
2. tell / told
- Direct: “I need a break,” she said to me.
- Reported: She told me (that) she needed a break.
3. ask / asked
- Direct: “Are you ready?” she asked me.
- Reported: She asked me if I was ready.
Note: Unlike told and asked , with the verb said , we do not mention the person to whom the words were said.
Change of verb tenses
Because speech is often reported after it was said, verb tenses in the original statements change.
Here is a summary of tense changes with examples
When not to change verb tenses?
If the speech is reported immediately , the tense does not change.
- Direct: “It is hot these days,” she said.
- Reported: She said it is hot these days.
If the introductory verb used is in the present simple, future simple or present perfect , we do not change verb tense.
- Direct: “This information is confidential.”
- Reported: She says this information is confidential.
- Reported: She has said this information is confidential.
- Reported: She will say this information is confidential.
In addition, tense does not change when we talk about general truths, permanent states, and conditions .
- Direct: He said, “Earth travels around the sun. ”
- Reported: He said Earth travels around the sun.
We do not change verb tense when we report wishes, preferences, and unreal past.
- Direct: He said, “I wish I could fly. ”
- Reported: He said he wishes he could fly.
⇔ Try this quiz on reporting statements.
How to report imperatives
To report imperative verbs (commands, requests, suggestions), we use an infinitive verb and we use tell / told or ask / asked , but not say / said.
Other verbs that can be used to report imperatives are: a dvise, order, beg, etc.
- Direct: “ Open the door.”
- Reported: He told me to open the door.
- Direct: “Will you pass the salt, please?”
- Reported: He asked me to pass the salt.
- Direct: “ Forgive my son, please.”
- Reported: He begged me to forgive his son.
To report a negative imperative, we use not to infinitive .
- Direct: “ Don’t open this document.”
- Reported: He ordered them not to open that document.
With the verb suggest, we use that-clause or verb-ing.
- Direct: “I suggest that you go to the doctor.”
- Reported: He suggested that I (should) go to the doctor.
- Direct: “I suggest that you take a home remedy.”
- Reported: He suggested taking a home remedy.
⇔ Take a quiz on how to report imperatives.
How to report questions
When we report questions we change the helping verb-subject order to subject-helping verb/verb .
We follow the same rules of tense changes.
Yes/No questions
We use if or whether to connect the introduction with reported words.
- Direct: “ Are you tired?”
- Reported: He asked me if I was tired.
- Direct: “ Does she eat tuna fish?”
- Reported: He asked me if she ate tuna fish.
- Direct: “ Did they arrive ?”
- Reported: He asked me if they had arrived .
- Direct: “ Has she resigned ?”
- Reported: He asked me whether she had resigned or not.
Wh-questions
- Direct: “What are you doing ?”
- Reported: He wanted to know what I was doing .
- Direct: “When will they arrive ?”
- Reported: He wanted to know when they would arrive.
- Direct: “What has she eaten ?”
- Reported: He wanted to know what she had eaten.
- Direct: “When do they wake up ?”
- Reported: He wanted to know when they woke up .
- Direct: “Why did they leave early?”
- Reported: He wanted to know why they had left early.
⇔ Take a quiz on how to report questions.
Change of time expressions
Because the time of reported speech is later than that of direct speech, time reference will be different. As a result, time expressions in reported speech change according to the context.
This is a table of the most common time expressions and how they change.
Special introductory verbs
Sometimes we use verbs other than say , tell , ask to introduce reported speech. We need to choose an appropriate reporting verb because each verb expresses how the reporting person interprets the speech. Here are some of these verbs with examples.
advise somebody to infinitive
- “ You should visit the doctor.”
- She advised me to visit a doctor.
accuse somebody of verb-ing
- “ You spoiled my plan.”
- She accused me of spoiling her plan.
admit verb-ing
- “ I broke the screen.”
- She admitted breaking the screen.
apologize for + verb-ing
- “ I apologize for breaking the screen.”
- She apologized for breaking the screen.
- “ I was the one who developed the app.”
- She boasted that she had developed the app.
- “ I fixed the errors in the program.”
- She claimed that she had fixed the errors in the program.
complain that
- “ The place is not clean.”
- She complained that the place was not clean.
demand that
- “Pull down the curtains immediately.”
- She demanded that I should pull down the curtains immediately.
deny verb-ing
- “ I didn’t use your laptop.”
- She denied using (or having used) my laptop.
encourage somebody to infinitive
- “ You should read more about the topic.”
- She encouraged me to read more about the topic.
inform somebody that
- “ The parental meeting will be tomorrow.”
- She informed us that the parental meeting would be the following day.
insist that
- “ You have to pay immediately.”
- She insisted that I had to pay immediately.
refuse to infinitive
- “ I won’t let you use my car.”
- She refused to lend me her car.
remind somebody to
- “ Remember to switch off the lights.”
- She reminded me to switch off the lights.
- “ Our company ranking has improved.”
- The manager stated that the company ranking had improved.
threaten to infinitive
- “ If you keep annoying me, I will tell the teacher.”
- She threatened to tell the teacher if he kept annoying her.
suggest verb-ing
- “ Why don’t you try the new software?”
- She suggested trying the new software.
warn somebody to infinitive
- “ Don’t throw the ball.”
- She warned him not to throw the ball.
More resources on the Site:
Reported Speech (Statements) Quiz
Grammar FAQs
Verb Tenses: A Complete Guide
Google Slides for Teachers
Join our newsletter!
Grammar explanations, quizzes, and tips in your inbox
Please enable JavaScript in your browser to complete this form. Name: * Email: * Enter a valid email Submit
We respect your privacy.

COMMENTS
Reported speech is used to report what someone else has said, thought, or written. It is often used in situations where you want to relate what someone else has said without quoting them directly. Reported speech can be used in a variety of contexts, such as in news reports, academic writing, and everyday conversation.
In short, reported speech is the linguistic technique that you use to tell somebody what someone else’s direct speech was. In reported speech though, you may need to make certain changes to the grammar to make the sentence make sense. Some examples below highlight what needs to be changed.
Reported speech is a term we use when telling someone what another person said. You can do this while speaking or writing. There are two kinds of reported speech you can use: direct speech and indirect speech. I’ll break each down for you. A direct speech sentence mentions the exact words the other person said. For example:
English Grammar. Verbs. Clause structure and verb patterns. Reported speech. Oops, something went wrong. Check your browser's developer console for more details. Level: intermediate. Reporting and summarising. When we want to report what people say, we don't usually try to report their exact words. We usually give a summary, for example:
Reported speech or indirect speech is the form of speech used to convey what was said by someone at some point of time. This article will help you with all that you need to know about reported speech, its meaning, definition, how and when to use them along with examples.
Reported speech: She says (that) she likes ice cream. We don't need to change the tense, though probably we do need to change the 'person' from 'I' to 'she', for example. We also may need to change words like 'my' and 'your'.
Indirect reports of yes-no questions and questions with or consist of a reporting clause and a reported clause introduced by if or whether. If is more common than whether. The reported clause is in statement form (subject + verb), not question form: She asked if [S] [V] I was Scottish. (original yes-no question: ‘Are you Scottish?’)
What is reported speech? Reported speech is when we repeat what another person has said but instead of using their exact words in quotation marks (direct speech), we use subordinate clause introduced by a reporting verb like the ones below: Examples: He says/said … She explains/explained … She tells/told me … He asks/asked …
Direct and Indirect Speech. Comprehensive guide to reporting verbs in English: definitions, detailed list, practical examples, and illustrative images for better understanding and usage.
Reported speech (also called indirect speech) gives the meaning of what someone said, not the exact words, while direct speech gives the exact words of the speaker, enclosed in quotation marks (or inverted commas. With reported speech, we do not use quotation marks.