

Understanding Assignments
What this handout is about.
The first step in any successful college writing venture is reading the assignment. While this sounds like a simple task, it can be a tough one. This handout will help you unravel your assignment and begin to craft an effective response. Much of the following advice will involve translating typical assignment terms and practices into meaningful clues to the type of writing your instructor expects. See our short video for more tips.
Basic beginnings
Regardless of the assignment, department, or instructor, adopting these two habits will serve you well :
- Read the assignment carefully as soon as you receive it. Do not put this task off—reading the assignment at the beginning will save you time, stress, and problems later. An assignment can look pretty straightforward at first, particularly if the instructor has provided lots of information. That does not mean it will not take time and effort to complete; you may even have to learn a new skill to complete the assignment.
- Ask the instructor about anything you do not understand. Do not hesitate to approach your instructor. Instructors would prefer to set you straight before you hand the paper in. That’s also when you will find their feedback most useful.
Assignment formats
Many assignments follow a basic format. Assignments often begin with an overview of the topic, include a central verb or verbs that describe the task, and offer some additional suggestions, questions, or prompts to get you started.
An Overview of Some Kind
The instructor might set the stage with some general discussion of the subject of the assignment, introduce the topic, or remind you of something pertinent that you have discussed in class. For example:
“Throughout history, gerbils have played a key role in politics,” or “In the last few weeks of class, we have focused on the evening wear of the housefly …”
The Task of the Assignment
Pay attention; this part tells you what to do when you write the paper. Look for the key verb or verbs in the sentence. Words like analyze, summarize, or compare direct you to think about your topic in a certain way. Also pay attention to words such as how, what, when, where, and why; these words guide your attention toward specific information. (See the section in this handout titled “Key Terms” for more information.)
“Analyze the effect that gerbils had on the Russian Revolution”, or “Suggest an interpretation of housefly undergarments that differs from Darwin’s.”
Additional Material to Think about
Here you will find some questions to use as springboards as you begin to think about the topic. Instructors usually include these questions as suggestions rather than requirements. Do not feel compelled to answer every question unless the instructor asks you to do so. Pay attention to the order of the questions. Sometimes they suggest the thinking process your instructor imagines you will need to follow to begin thinking about the topic.
“You may wish to consider the differing views held by Communist gerbils vs. Monarchist gerbils, or Can there be such a thing as ‘the housefly garment industry’ or is it just a home-based craft?”
These are the instructor’s comments about writing expectations:
“Be concise”, “Write effectively”, or “Argue furiously.”
Technical Details
These instructions usually indicate format rules or guidelines.
“Your paper must be typed in Palatino font on gray paper and must not exceed 600 pages. It is due on the anniversary of Mao Tse-tung’s death.”
The assignment’s parts may not appear in exactly this order, and each part may be very long or really short. Nonetheless, being aware of this standard pattern can help you understand what your instructor wants you to do.
Interpreting the assignment
Ask yourself a few basic questions as you read and jot down the answers on the assignment sheet:
Why did your instructor ask you to do this particular task?
Who is your audience.
- What kind of evidence do you need to support your ideas?
What kind of writing style is acceptable?
- What are the absolute rules of the paper?
Try to look at the question from the point of view of the instructor. Recognize that your instructor has a reason for giving you this assignment and for giving it to you at a particular point in the semester. In every assignment, the instructor has a challenge for you. This challenge could be anything from demonstrating an ability to think clearly to demonstrating an ability to use the library. See the assignment not as a vague suggestion of what to do but as an opportunity to show that you can handle the course material as directed. Paper assignments give you more than a topic to discuss—they ask you to do something with the topic. Keep reminding yourself of that. Be careful to avoid the other extreme as well: do not read more into the assignment than what is there.
Of course, your instructor has given you an assignment so that they will be able to assess your understanding of the course material and give you an appropriate grade. But there is more to it than that. Your instructor has tried to design a learning experience of some kind. Your instructor wants you to think about something in a particular way for a particular reason. If you read the course description at the beginning of your syllabus, review the assigned readings, and consider the assignment itself, you may begin to see the plan, purpose, or approach to the subject matter that your instructor has created for you. If you still aren’t sure of the assignment’s goals, try asking the instructor. For help with this, see our handout on getting feedback .
Given your instructor’s efforts, it helps to answer the question: What is my purpose in completing this assignment? Is it to gather research from a variety of outside sources and present a coherent picture? Is it to take material I have been learning in class and apply it to a new situation? Is it to prove a point one way or another? Key words from the assignment can help you figure this out. Look for key terms in the form of active verbs that tell you what to do.
Key Terms: Finding Those Active Verbs
Here are some common key words and definitions to help you think about assignment terms:
Information words Ask you to demonstrate what you know about the subject, such as who, what, when, where, how, and why.
- define —give the subject’s meaning (according to someone or something). Sometimes you have to give more than one view on the subject’s meaning
- describe —provide details about the subject by answering question words (such as who, what, when, where, how, and why); you might also give details related to the five senses (what you see, hear, feel, taste, and smell)
- explain —give reasons why or examples of how something happened
- illustrate —give descriptive examples of the subject and show how each is connected with the subject
- summarize —briefly list the important ideas you learned about the subject
- trace —outline how something has changed or developed from an earlier time to its current form
- research —gather material from outside sources about the subject, often with the implication or requirement that you will analyze what you have found
Relation words Ask you to demonstrate how things are connected.
- compare —show how two or more things are similar (and, sometimes, different)
- contrast —show how two or more things are dissimilar
- apply —use details that you’ve been given to demonstrate how an idea, theory, or concept works in a particular situation
- cause —show how one event or series of events made something else happen
- relate —show or describe the connections between things
Interpretation words Ask you to defend ideas of your own about the subject. Do not see these words as requesting opinion alone (unless the assignment specifically says so), but as requiring opinion that is supported by concrete evidence. Remember examples, principles, definitions, or concepts from class or research and use them in your interpretation.
- assess —summarize your opinion of the subject and measure it against something
- prove, justify —give reasons or examples to demonstrate how or why something is the truth
- evaluate, respond —state your opinion of the subject as good, bad, or some combination of the two, with examples and reasons
- support —give reasons or evidence for something you believe (be sure to state clearly what it is that you believe)
- synthesize —put two or more things together that have not been put together in class or in your readings before; do not just summarize one and then the other and say that they are similar or different—you must provide a reason for putting them together that runs all the way through the paper
- analyze —determine how individual parts create or relate to the whole, figure out how something works, what it might mean, or why it is important
- argue —take a side and defend it with evidence against the other side
More Clues to Your Purpose As you read the assignment, think about what the teacher does in class:
- What kinds of textbooks or coursepack did your instructor choose for the course—ones that provide background information, explain theories or perspectives, or argue a point of view?
- In lecture, does your instructor ask your opinion, try to prove their point of view, or use keywords that show up again in the assignment?
- What kinds of assignments are typical in this discipline? Social science classes often expect more research. Humanities classes thrive on interpretation and analysis.
- How do the assignments, readings, and lectures work together in the course? Instructors spend time designing courses, sometimes even arguing with their peers about the most effective course materials. Figuring out the overall design to the course will help you understand what each assignment is meant to achieve.
Now, what about your reader? Most undergraduates think of their audience as the instructor. True, your instructor is a good person to keep in mind as you write. But for the purposes of a good paper, think of your audience as someone like your roommate: smart enough to understand a clear, logical argument, but not someone who already knows exactly what is going on in your particular paper. Remember, even if the instructor knows everything there is to know about your paper topic, they still have to read your paper and assess your understanding. In other words, teach the material to your reader.
Aiming a paper at your audience happens in two ways: you make decisions about the tone and the level of information you want to convey.
- Tone means the “voice” of your paper. Should you be chatty, formal, or objective? Usually you will find some happy medium—you do not want to alienate your reader by sounding condescending or superior, but you do not want to, um, like, totally wig on the man, you know? Eschew ostentatious erudition: some students think the way to sound academic is to use big words. Be careful—you can sound ridiculous, especially if you use the wrong big words.
- The level of information you use depends on who you think your audience is. If you imagine your audience as your instructor and they already know everything you have to say, you may find yourself leaving out key information that can cause your argument to be unconvincing and illogical. But you do not have to explain every single word or issue. If you are telling your roommate what happened on your favorite science fiction TV show last night, you do not say, “First a dark-haired white man of average height, wearing a suit and carrying a flashlight, walked into the room. Then a purple alien with fifteen arms and at least three eyes turned around. Then the man smiled slightly. In the background, you could hear a clock ticking. The room was fairly dark and had at least two windows that I saw.” You also do not say, “This guy found some aliens. The end.” Find some balance of useful details that support your main point.
You’ll find a much more detailed discussion of these concepts in our handout on audience .
The Grim Truth
With a few exceptions (including some lab and ethnography reports), you are probably being asked to make an argument. You must convince your audience. It is easy to forget this aim when you are researching and writing; as you become involved in your subject matter, you may become enmeshed in the details and focus on learning or simply telling the information you have found. You need to do more than just repeat what you have read. Your writing should have a point, and you should be able to say it in a sentence. Sometimes instructors call this sentence a “thesis” or a “claim.”
So, if your instructor tells you to write about some aspect of oral hygiene, you do not want to just list: “First, you brush your teeth with a soft brush and some peanut butter. Then, you floss with unwaxed, bologna-flavored string. Finally, gargle with bourbon.” Instead, you could say, “Of all the oral cleaning methods, sandblasting removes the most plaque. Therefore it should be recommended by the American Dental Association.” Or, “From an aesthetic perspective, moldy teeth can be quite charming. However, their joys are short-lived.”
Convincing the reader of your argument is the goal of academic writing. It doesn’t have to say “argument” anywhere in the assignment for you to need one. Look at the assignment and think about what kind of argument you could make about it instead of just seeing it as a checklist of information you have to present. For help with understanding the role of argument in academic writing, see our handout on argument .
What kind of evidence do you need?
There are many kinds of evidence, and what type of evidence will work for your assignment can depend on several factors–the discipline, the parameters of the assignment, and your instructor’s preference. Should you use statistics? Historical examples? Do you need to conduct your own experiment? Can you rely on personal experience? See our handout on evidence for suggestions on how to use evidence appropriately.
Make sure you are clear about this part of the assignment, because your use of evidence will be crucial in writing a successful paper. You are not just learning how to argue; you are learning how to argue with specific types of materials and ideas. Ask your instructor what counts as acceptable evidence. You can also ask a librarian for help. No matter what kind of evidence you use, be sure to cite it correctly—see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial .
You cannot always tell from the assignment just what sort of writing style your instructor expects. The instructor may be really laid back in class but still expect you to sound formal in writing. Or the instructor may be fairly formal in class and ask you to write a reflection paper where you need to use “I” and speak from your own experience.
Try to avoid false associations of a particular field with a style (“art historians like wacky creativity,” or “political scientists are boring and just give facts”) and look instead to the types of readings you have been given in class. No one expects you to write like Plato—just use the readings as a guide for what is standard or preferable to your instructor. When in doubt, ask your instructor about the level of formality they expect.
No matter what field you are writing for or what facts you are including, if you do not write so that your reader can understand your main idea, you have wasted your time. So make clarity your main goal. For specific help with style, see our handout on style .
Technical details about the assignment
The technical information you are given in an assignment always seems like the easy part. This section can actually give you lots of little hints about approaching the task. Find out if elements such as page length and citation format (see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial ) are negotiable. Some professors do not have strong preferences as long as you are consistent and fully answer the assignment. Some professors are very specific and will deduct big points for deviations.
Usually, the page length tells you something important: The instructor thinks the size of the paper is appropriate to the assignment’s parameters. In plain English, your instructor is telling you how many pages it should take for you to answer the question as fully as you are expected to. So if an assignment is two pages long, you cannot pad your paper with examples or reword your main idea several times. Hit your one point early, defend it with the clearest example, and finish quickly. If an assignment is ten pages long, you can be more complex in your main points and examples—and if you can only produce five pages for that assignment, you need to see someone for help—as soon as possible.
Tricks that don’t work
Your instructors are not fooled when you:
- spend more time on the cover page than the essay —graphics, cool binders, and cute titles are no replacement for a well-written paper.
- use huge fonts, wide margins, or extra spacing to pad the page length —these tricks are immediately obvious to the eye. Most instructors use the same word processor you do. They know what’s possible. Such tactics are especially damning when the instructor has a stack of 60 papers to grade and yours is the only one that low-flying airplane pilots could read.
- use a paper from another class that covered “sort of similar” material . Again, the instructor has a particular task for you to fulfill in the assignment that usually relates to course material and lectures. Your other paper may not cover this material, and turning in the same paper for more than one course may constitute an Honor Code violation . Ask the instructor—it can’t hurt.
- get all wacky and “creative” before you answer the question . Showing that you are able to think beyond the boundaries of a simple assignment can be good, but you must do what the assignment calls for first. Again, check with your instructor. A humorous tone can be refreshing for someone grading a stack of papers, but it will not get you a good grade if you have not fulfilled the task.
Critical reading of assignments leads to skills in other types of reading and writing. If you get good at figuring out what the real goals of assignments are, you are going to be better at understanding the goals of all of your classes and fields of study.
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Understanding Writing Assignments

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
How to Decipher the Paper Assignment
Many instructors write their assignment prompts differently. By following a few steps, you can better understand the requirements for the assignment. The best way, as always, is to ask the instructor about anything confusing.
- Read the prompt the entire way through once. This gives you an overall view of what is going on.
- Underline or circle the portions that you absolutely must know. This information may include due date, research (source) requirements, page length, and format (MLA, APA, CMS).
- Underline or circle important phrases. You should know your instructor at least a little by now - what phrases do they use in class? Does he repeatedly say a specific word? If these are in the prompt, you know the instructor wants you to use them in the assignment.
- Think about how you will address the prompt. The prompt contains clues on how to write the assignment. Your instructor will often describe the ideas they want discussed either in questions, in bullet points, or in the text of the prompt. Think about each of these sentences and number them so that you can write a paragraph or section of your essay on that portion if necessary.
- Rank ideas in descending order, from most important to least important. Instructors may include more questions or talking points than you can cover in your assignment, so rank them in the order you think is more important. One area of the prompt may be more interesting to you than another.
- Ask your instructor questions if you have any.
After you are finished with these steps, ask yourself the following:
- What is the purpose of this assignment? Is my purpose to provide information without forming an argument, to construct an argument based on research, or analyze a poem and discuss its imagery?
- Who is my audience? Is my instructor my only audience? Who else might read this? Will it be posted online? What are my readers' needs and expectations?
- What resources do I need to begin work? Do I need to conduct literature (hermeneutic or historical) research, or do I need to review important literature on the topic and then conduct empirical research, such as a survey or an observation? How many sources are required?
- Who - beyond my instructor - can I contact to help me if I have questions? Do you have a writing lab or student service center that offers tutorials in writing?
(Notes on prompts made in blue )
Poster or Song Analysis: Poster or Song? Poster!
Goals : To systematically consider the rhetorical choices made in either a poster or a song. She says that all the time.
Things to Consider: ah- talking points
- how the poster addresses its audience and is affected by context I'll do this first - 1.
- general layout, use of color, contours of light and shade, etc.
- use of contrast, alignment, repetition, and proximity C.A.R.P. They say that, too. I'll do this third - 3.
- the point of view the viewer is invited to take, poses of figures in the poster, etc. any text that may be present
- possible cultural ramifications or social issues that have bearing I'll cover this second - 2.
- ethical implications
- how the poster affects us emotionally, or what mood it evokes
- the poster's implicit argument and its effectiveness said that was important in class, so I'll discuss this last - 4.
- how the song addresses its audience
- lyrics: how they rhyme, repeat, what they say
- use of music, tempo, different instruments
- possible cultural ramifications or social issues that have bearing
- emotional effects
- the implicit argument and its effectiveness
These thinking points are not a step-by-step guideline on how to write your paper; instead, they are various means through which you can approach the subject. I do expect to see at least a few of them addressed, and there are other aspects that may be pertinent to your choice that have not been included in these lists. You will want to find a central idea and base your argument around that. Additionally, you must include a copy of the poster or song that you are working with. Really important!
I will be your audience. This is a formal paper, and you should use academic conventions throughout.
Length: 4 pages Format: Typed, double-spaced, 10-12 point Times New Roman, 1 inch margins I need to remember the format stuff. I messed this up last time =(
Academic Argument Essay
5-7 pages, Times New Roman 12 pt. font, 1 inch margins.
Minimum of five cited sources: 3 must be from academic journals or books
- Design Plan due: Thurs. 10/19
- Rough Draft due: Monday 10/30
- Final Draft due: Thurs. 11/9
Remember this! I missed the deadline last time
The design plan is simply a statement of purpose, as described on pages 40-41 of the book, and an outline. The outline may be formal, as we discussed in class, or a printout of an Open Mind project. It must be a minimum of 1 page typed information, plus 1 page outline.
This project is an expansion of your opinion editorial. While you should avoid repeating any of your exact phrases from Project 2, you may reuse some of the same ideas. Your topic should be similar. You must use research to support your position, and you must also demonstrate a fairly thorough knowledge of any opposing position(s). 2 things to do - my position and the opposite.
Your essay should begin with an introduction that encapsulates your topic and indicates 1 the general trajectory of your argument. You need to have a discernable thesis that appears early in your paper. Your conclusion should restate the thesis in different words, 2 and then draw some additional meaningful analysis out of the developments of your argument. Think of this as a "so what" factor. What are some implications for the future, relating to your topic? What does all this (what you have argued) mean for society, or for the section of it to which your argument pertains? A good conclusion moves outside the topic in the paper and deals with a larger issue.
You should spend at least one paragraph acknowledging and describing the opposing position in a manner that is respectful and honestly representative of the opposition’s 3 views. The counterargument does not need to occur in a certain area, but generally begins or ends your argument. Asserting and attempting to prove each aspect of your argument’s structure should comprise the majority of your paper. Ask yourself what your argument assumes and what must be proven in order to validate your claims. Then go step-by-step, paragraph-by-paragraph, addressing each facet of your position. Most important part!
Finally, pay attention to readability . Just because this is a research paper does not mean that it has to be boring. Use examples and allow your opinion to show through word choice and tone. Proofread before you turn in the paper. Your audience is generally the academic community and specifically me, as a representative of that community. Ok, They want this to be easy to read, to contain examples I find, and they want it to be grammatically correct. I can visit the tutoring center if I get stuck, or I can email the OWL Email Tutors short questions if I have any more problems.

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
2 What Does the Professor Want? Understanding the Assignment
Writing for whom writing for what.
The first principle of good communication is knowing your audience . This is where writing papers for class gets kind of weird. As Peter Elbow explains: [1]
When you write for a teacher you are usually swimming against the stream of natural communication. The natural direction of communication is to explain what you understand to someone who doesn’t understand it. But in writing an essay for a teacher your task is usually to explain what you are still engaged in trying to understand to someone who understands it better.
Often when you write for an audience of one, you write a letter or email. But college papers aren’t written like letters; they’re written like articles for a hypothetical group of readers that you don’t actually know much about. There’s a fundamental mismatch between the real-life audience and the form your writing takes. It’s kind of bizarre, really.
It helps to remember the key tenet of the university model: you’re a junior scholar joining the academic community. Academic papers, in which scholars report the results of their research and thinking to one another, are the lifeblood of the scholarly world, carrying useful ideas and information to all parts of the academic corpus. Unless there is a particular audience specified in the assignment, you would do well to imagine yourself writing for a group of peers who have some introductory knowledge of the field but are unfamiliar with the specific topic you’re discussing. Imagine them being interested in your topic but also busy; try to write something that is well worth your readers’ time. Keeping an audience like this in mind will help you distinguish common knowledge in the field from that which must be defined and explained in your paper. Understanding your audience like this also resolve the audience mismatch that Elbow describes. As he notes, “You don’t write to teachers, you write for them.” [2]
Another basic tenet of good communication is clarifying the purpose of the communication and letting that purpose shape your decisions. Your professor wants to see you work through complex ideas and deepen your knowledge through the process of producing the paper. Each assignment—be it an argumentative paper, reaction paper, reflective paper, lab report, discussion question, blog post, essay exam, project proposal, or what have you—is ultimately about your learning. To succeed with writing assignments (and benefit from them) you first have to understand their learning-related purposes. As you write for the hypothetical audience of peer junior scholars, you’re demonstrating to your professor how far you’ve gotten in analyzing your topic.
Don’t be scared whenever you are given an assignment. Professors know what it was like to be in college and write all kinds of papers. They aren’t trying to make your lives difficult, but it is their jobs to make us think and ponder about many things. Take your time and enjoy the paper. Make sure you answer the question being asked rather than rant on about something that is irrelevant to the prompt.
Timothée Pizarro
Professors don’t assign writing lightly. Grading student writing is generally the hardest, most intensive work instructors do. [3] With every assignment they give you, professors assign themselves many, many hours of demanding and tedious work that has to be completed while they are also preparing for each class meeting, advancing their scholarly and creative work, advising students, and serving on committees. Often, they’re grading your papers on evenings and weekends because the conventional work day is already saturated with other obligations. You would do well to approach every assignment by putting yourself in the shoes of your instructor and asking yourself, “Why did she give me this assignment? How does it fit into the learning goals of the course? Why is this question/topic/problem so important to my professor that he is willing to spend evenings and weekends reading and commenting on several dozen novice papers on it?”
As I briefly discussed in Chapter 1 , most instructors do a lot to make their pedagogical goals and expectations transparent to students: they explain the course learning goals associated with assignments, provide grading rubrics in advance, and describe several strategies for succeeding. Other professors … not so much. Some students perceive more open-ended assignments as evidence of a lazy, uncaring, or even incompetent instructor. Not so fast! Professors certainly vary in the quantity and specificity of the guidelines and suggestions they distribute with each writing assignment. Some professors make a point to give very few parameters about an assignment—perhaps just a topic and a length requirement—and they likely have some good reasons for doing so. Here are some possible reasons:
- They figured it out themselves when they were students . Unsurprisingly, your instructors were generally successful students who relished the culture and traditions of higher education so much that they strove to build an academic career. The current emphasis on student-centered instruction is relatively recent; your instructors much more often had professors who adhered to the classic model of college instruction: they gave lectures together with, perhaps, one or two exams or papers. Students were on their own to learn the lingo and conventions of each field, to identify the key concepts and ideas within readings and lectures, and to sleuth out instructors’ expectations for written work. Learning goals, rubrics, quizzes, and preparatory assignments were generally rare.
- They think figuring it out yourself is good for you . Because your professors by and large succeeded in a much less supportive environment , they appreciate how learning to thrive in those conditions gave them life-long problem-solving skills. Many think you should be able to figure it out yourself and that it would be good practice for you to do so. Even those who do include a lot of guidance with writing assignments sometimes worry that they’re depriving you of an important personal and intellectual challenge. Figuring out unspoken expectations is a valuable skill in itself.
- They’re egg-heads . As I explained in Chapter 1 , many of your instructors have been so immersed in their fields that they may struggle to remember what it was like to encounter a wholly new discipline for the first time. The assumptions, practices, and culture of their disciplines are like the air they breathe; so much so that it is hard to describe to novices. They may assume that a verb like “analyze” is self-evident, forgetting that it can mean very different things in different fields. As a student, you voluntarily came to study with the scholars, artists, and writers at your institution. Rightly or wrongly, the burden is ultimately on you to meet them where they are.
- Professors value academic freedom ; that is, they firmly believe that their high-level expertise in their fields grants them the privilege of deciding what is important to focus on and how to approach it. As I also explain in Chapter 1 , college professors differ in this way from high school teachers who are usually obligated to address a defined curriculum. Professors are often extremely wary of anything that seems to threaten academic freedom . Some see specified learning goals and standardized rubrics as the first step in a process that would strip higher education of its independence, scholarly innovation, and sense of discovery. While a standardized set of expectations and practices might make it easier to earn a degree, it’s also good to consider the benefits of the more flexible and diversified model.
It is understandably frustrating when you feel you don’t know how to direct your efforts to succeed with an assignment. However, except for rare egregious situations, you would do well to assume the best of your instructor and to appreciate the diversity of learning opportunities you have access to in college. Like one first-year student told Keith Hjortshoj, [4] “I think that every course, every assignment, is a different little puzzle I have to solve. What do I need to do here? When do I need to do it, and how long will it take? What does this teacher expect of me?” The transparency that you get from some professors—along with guides like this one—will be a big help to you in situations where you have to be scrappier and more pro-active, piecing together the clues you get from your professors, the readings, and other course documents.
The prompt: what does “analyze” mean anyway?
Often, the handout or other written text explaining the assignment—what professors call the assignment prompt —will explain the purpose of the assignment, the required parameters (length, number and type of sources, referencing style, etc.), and the criteria for evaluation. Sometimes, though—especially when you are new to a field—you will encounter the baffling situation in which you comprehend every single sentence in the prompt but still have absolutely no idea how to approach the assignment. No one is doing anything wrong in a situation like that. It just means that further discussion of the assignment is in order. Here are some tips:
- Focus on the verbs . Look for verbs like “compare,” “explain,” “justify,” “reflect” or the all-purpose “analyze.” You’re not just producing a paper as an artifact; you’re conveying, in written communication, some intellectual work you have done. So the question is, what kind of thinking are you supposed to do to deepen your learning?
- Put the assignment in context . Many professors think in terms of assignment sequences . For example, a social science professor may ask you to write about a controversial issue three times: first, arguing for one side of the debate; second, arguing for another; and finally, from a more comprehensive and nuanced perspective, incorporating text produced in the first two assignments. A sequence like that is designed to help you think through a complex issue. Another common one is a scaffolded research paper sequence: you first propose a topic, then prepare an annotated bibliography, then a first draft, then a final draft, and, perhaps, a reflective paper. The preparatory assignments help ensure that you’re on the right track, beginning the research process long before the final due date, and taking the time to consider recasting your thesis, finding additional sources, or reorganizing your discussion. [5] If the assignment isn’t part of a sequence, think about where it falls in the semester, and how it relates to readings and other assignments. Are there headings on the syllabus that indicate larger units of material? For example, if you see that a paper comes at the end of a three-week unit on the role of the Internet in organizational behavior, then your professor likely wants you to synthesize that material in your own way. You should also check your notes and online course resources for any other guidelines about the workflow. Maybe you got a rubric a couple weeks ago and forgot about it. Maybe your instructor posted a link about “how to make an annotated bibliography” but then forgot to mention it in class.
- Try a free-write . When I hand out an assignment, I often ask students to do a five-minute or ten-minute free-write. A free-write is when you just write, without stopping, for a set period of time. That doesn’t sound very “free;” it actually sounds kind of coerced. The “free” part is what you write—it can be whatever comes to mind. Professional writers use free-writing to get started on a challenging (or distasteful) writing task or to overcome writers block or a powerful urge to procrastinate. The idea is that if you just make yourself write, you can’t help but produce some kind of useful nugget. Thus, even if the first eight sentences of your free write are all variations on “I don’t understand this” or “I’d really rather be doing something else,” eventually you’ll write something like “I guess the main point of this is …” and—booyah!—you’re off and running. As an instructor, I’ve found that asking students to do a brief free-write right after I hand out an assignment generates useful clarification questions. If your instructor doesn’t make time for that in class, a quick free-write on your own will quickly reveal whether you need clarification about the assignment and, often, what questions to ask.
- Ask for clarification the right way . Even the most skillfully crafted assignments may need some verbal clarification, especially because students’ familiarity with the field can vary enormously. Asking for clarification is a good thing. Be aware, though, that instructors get frustrated when they perceive that students want to skip doing their own thinking and instead receive an exact recipe for an A paper. Go ahead and ask for clarification, but try to convey that you want to learn and you’re ready to work.In general, avoid starting a question with “Do we have to …” because I can guarantee that your instructor is thinking, “You don’t have to do crap. You’re an adult. You chose college. You chose this class. You’re free to exercise your right to fail.” Similarly, avoid asking the professor about what he or she “wants.” You’re not performing some service for the professor when you write a paper. What they “want” is for you to really think about the material.
| Potentially annoying questions | Preferable alternatives |
| I don’t get it. Can you explain this more? or What do you want us to do? | I see that we are comparing and contrasting these two cases. What should be our focus? Their causes? Their impacts? Their implications? All of those things? or I’m unfamiliar with how art historians analyze a painting. Could you say more about what questions I should have in mind to do this kind of analysis? |
| How many sources do we have to cite? | Is there a typical range for the number of sources a well written paper would cite for this assignment? or Could you say more about what the sources are for? Is it more that we’re analyzing these texts in this paper, or are we using these texts to analyze some other case? |
| What do I have to do to get an A on this paper? | Could I meet with you to get feedback on my (pre-prepared) plans/outline/thesis/draft? or I’m not sure how to approach this assignment. Are there any good examples or resources you could point me to? |
Rubrics as road maps
If a professor provides a grading rubric with an assignment prompt, thank your lucky stars (and your professor). If the professor took the trouble to prepare and distribute it, you can be sure that he or she will use it to grade your paper. He or she may not go over it in class, but it’s the clearest possible statement of what the professor is looking for in the paper. If it’s wordy, it may seem like those online “terms and conditions” that we routinely accept without reading. But you really should read it over carefully before you begin and again as your work progresses. A lot of rubrics do have some useful specifics. Mine, for example, often contain phrases like “makes at least six error-free connections to concepts or ideas from the course,” or “gives thorough consideration to at least one plausible counter-argument.” Even less specific criteria (such as “incorporates course concepts” and “considers counter-arguments”) will tell you how you should be spending your writing time.
Even the best rubrics aren’t completely transparent. They simply can’t be. Take, for example, the AAC&U rubric discussed in Chapter 1 . It has been drafted and repeatedly revised by a multidisciplinary expert panel and tested multiple times on sample student work to ensure reliability. But it is still seems kind of vague. What is the real difference between “demonstrating a thorough understanding of context, audience, and purpose” and “demonstrating adequate consideration” of the same? It depends on the specific context. So how can you know whether you’ve done that? A big part of what you’re learning, through feedback from your professors, is to judge the quality of your writing for yourself. Your future bosses are counting on that. At this point, it is better to think of rubrics as roadmaps, displaying your destination, rather than a GPS system directing every move you make.
Behind any rubric is the essential goal of higher education: helping you take charge of your own learning, which means writing like an independently motivated scholar. Are you tasked with proposing a research paper topic? Don’t just tell the professor what you want to do, convince him or her of the salience of your topic, as if you were a scholar seeking grant money. Is it a reflection paper? Then outline both the insights you’ve gained and the intriguing questions that remain, as a scholar would. Are you writing a thesis-driven analytical paper? Then apply the concepts you’ve learned to a new problem or situation. Write as if your scholarly peers around the country are eagerly awaiting your unique insights. Descriptors like “thoroughness” or “mastery” or “detailed attention” convey the vision of student writers making the time and rigorous mental effort to offer something new to the ongoing, multi-stranded academic conversation. What your professor wants, in short, is critical thinking.
What’s critical about critical thinking?
Critical thinking is one of those terms that has been used so often and in so many different ways that if often seems meaningless. It also makes one wonder, is there such a thing as uncritical thinking? If you aren’t thinking critically, then are you even thinking?
Despite the prevalent ambiguities, critical thinking actually does mean something. The Association of American Colleges and Universities usefully defines it as “a habit of mind characterized by the comprehensive exploration of issues, ideas, artifacts, and events before accepting or formulating an opinion or conclusion.” [6]
That definition aligns with the best description of critical thinking I ever heard; it came from my junior high art teacher, Joe Bolger. [7] He once asked us, “What color is the ceiling?” In that withering tween tone, we reluctantly replied, “Whiiiite.” He then asked, “What color is it really?” We deigned to aim our pre-adolescent eyes upwards, and eventually began to offer more accurate answers: “Ivory?” “Yellow-ish tan.” “It’s grey in that corner.” After finally getting a few thoughtful responses, Mr. Bolger said something like, “Making good art is about drawing what you see, not what you think you’re supposed to see.” The AAC&U definition, above, essentially amounts to the same thing: taking a good look and deciding what you really think rather than relying on the first idea or assumption that comes to mind.
The critical thinking rubric produced by the AAC&U describes the relevant activities of critical thinking in more detail. To think critically, one must …
(a) “clearly state and comprehensively describe the issue or problem”,
(b) “independently interpret and evaluate sources”,
(c) “thoroughly analyze assumptions behind and context of your own or others’ ideas”,
(d) “argue a complex position and one that takes counter-arguments into account,” and
(e) “arrive at logical and well informed conclusions”. [8]
While you are probably used to providing some evidence for your claims, you can see that college-level expectations go quite a bit further. When professors assign an analytical paper, they don’t just want you to formulate a plausible-sounding argument. They want you to dig into the evidence, think hard about unspoken assumptions and the influence of context, and then explain what you really think and why.
Interestingly, the AAC&U defines critical thinking as a “habit of mind” rather than a discrete achievement. And there are at least two reasons to see critical thinking as a craft or art to pursue rather than a task to check off. First, the more you think critically, the better you get at it . As you get more and more practice in closely examining claims, their underlying logic, and alternative perspectives on the issue, it’ll begin to feel automatic. You’ll no longer make or accept claims that begin with “Everyone knows that …” or end with “That’s just human nature.” Second, just as artists and craftspersons hone their skills over a lifetime, learners continually expand their critical thinking capacities, both through the feedback they get from others and their own reflections . Artists of all kinds find satisfaction in continually seeking greater challenges. Continual reflection and improvement is part of the craft.
As soon as I see the phrase “critical thinking,” the first thing I think is more work . It always sounds as if you’re going to have to think harder and longer. But I think the AAC&U’s definition is on point, critical thinking is a habit. Seeing that phrase shouldn’t be a scary thing because by this point in many people’s college career this is an automatic response. I never expect an answer to a question to be in the text; by now I realize that my professors want to know what I have to say about something or what I have learned. In a paper or essay, the three-step thesis process explained in Chapter 3 is a tool that will help you get this information across. While you’re doing the hard work (the thinking part), this formula offers you a way to clearly state your position on a subject. It’s as simple as: make a general statement, make an arguable statement, and finally, say why it is important. This is my rule of thumb, and I would not want to start a thesis-driven paper any other way!
Critical thinking is hard work. Even those who actively choose to do it experience it as tedious, difficult, and sometimes surprisingly emotional. Nobel-prize winning psychologist Daniel Kahneman explains that our brains aren’t designed to think; rather, they’re designed to save us from having to think. [9] Our brains are great at developing routines and repertoires that enable us to accomplish fairly complex tasks like driving cars, choosing groceries, and having a conversation without thinking consciously and thoroughly about every move we make. Kahneman calls this “fast thinking.” “Slow thinking,” which is deliberate and painstaking, is something our brains seek to avoid. That built-in tendency can lead us astray. Kahneman and his colleagues often used problems like this one in experiments to gauge how people used fast and slow thinking in different contexts: [10]
A bat and ball cost $1.10.
The bat costs one dollar more than the ball.
How much does the ball cost?
Most people automatically say the ball costs $0.10. However, if the bat costs $1 more, than the bat would cost $1.10 leading to the incorrect total of $1.20. The ball costs $0.05. Kahneman notes, “Many thousands of university students have answered the bat-and-ball puzzle, and the results are shocking. More than 50% of students at Harvard, MIT, and Princeton gave the intuitive—incorrect—answer.” These and other results confirm that “many people are overconfident, prone to place too much faith in their intuitions.” [11] Thinking critically—thoroughly questioning your immediate intuitive responses—is difficult work, but every organization and business in the world needs people who can do that effectively. Some students assume that an unpleasant critical thinking experience means that they’re either doing something wrong or that it’s an inherently uninteresting (and oppressive) activity. While we all relish those times when we’re pleasantly absorbed in a complex activity (what psychologist Mihaly Czikszentmihalyi calls “flow” [12] ), the more tedious experiences can also bring satisfaction, sort of like a good work-out.
Critical thinking can also be emotionally challenging, researchers have found. Facing a new realm of uncertainty and contradiction without relying on familiar assumptions is inherently anxiety-provoking because when you’re doing it, you are, by definition, incompetent. Recent research has highlighted that both children and adults need to be able to regulate their own emotions in order to cope with the challenges of building competence in a new area. [13] The kind of critical thinking your professors are looking for—that is, pursuing a comprehensive, multi-faceted exploration in order to arrive at an arguable, nuanced argument—is inevitably a struggle and it may be an emotional one. Your best bet is to find ways to make those processes as efficient, pleasant, and effective as you can .
The thing no one tells you when you get to college is that critical thinking papers are professors’ favorites. College is all about learning how to think individual thoughts so you’ll have to do quite a few of them. Have no fear though; they do get easier with time. The first step? Think about what you want to focus on in the paper (aka your thesis) and go with it.
Kaethe Leonard
As Chapter 1 explains, the demands students face are not at all unique to their academic pursuits. Professional working roles demand critical thinking, as 81% of major employers reported in an AAC&U-commissioned survey , [14] and it’s pretty easy to imagine how critical thinking helps one make much better decisions in all aspects of life. Embrace it. And just as athletes, artists, and writers sustain their energy and inspiration for hard work by interacting with others who share these passions, look to others in the scholarly community—your professors and fellow students—to keep yourself engaged in these ongoing intellectual challenges. While writing time is often solitary, it’s meant to plug you into a vibrant academic community. What your professors want, overall, is for you to join them in asking and pursuing important questions about the natural, social, and creative worlds.
Other resources
- This website from the Capital Community College Foundation has some good advice about overcoming writer’s block. And student contributor Aly Button recommends this funny clip from SpongeBob Squarepants .
- The Foundation for Critical Thinking maintains a website with many useful articles and tools.
- The Online Writing Laboratory (OWL) at Purdue University is a wonderful set of resources for every aspect of college writing. Especially germane to this chapter is this summary of the most common types of writing assignments.
- This website , BrainBashers.com offers logic puzzles and other brain-teasers for your entertainment.
- Free-write on an assignment prompt. If you have one, do that one. If not, here’s one to practice with:A. “Please write a five-page paper analyzing the controversy surrounding genetically modified organisms (GMOs) in the food supply.”B. What clarification questions would you like to ask your professor? What additional background knowledge do you need to deeply understand the topic? What are some starter ideas that could lead to a good thesis and intriguing argument?
- Find a couple of sample student papers from online paper mills such as this one (Google “free college papers”) and journals featuring excellent undergraduate writing (such as and prize-winning undergraduate papers (such as these from the Norton Writers Prize ), and use the AAC&U rubric on critical thinking to evaluate them. Which descriptor in each row most closely fits the paper?
- Peter Elbow, Writing With Power: Techniques for Mastering the Writing Process (Oxford University Press, 1981), 219. ↵
- Ibid., 220. ↵
- A lot of professors joke, “I teach for free. They pay me to grade.” ↵
- Keith Hjortshoj, The Transition to College Writing , 2nd Edition (New York: Norton, 2009), 4. ↵
- Most professors are perpetually frustrated with the “one-and-done” attitude that most students bring to their work, and some sequences are specifically designed to force you to really rethink your conclusions. ↵
- Terrel Rhodes, ed., Assessing Outcomes and Improving Achievement: Tips and Tools for Using Rubrics (Washington, DC: Association of American Colleges and Universities, 2010). ↵
- Thank you, Mr. Bolger! ↵
- Ibid. ↵
- Daniel Kahneman, Thinking, Fast and Slow (New York: Farrar, Straus and Giroux, 2011). ↵
- Ibid., 44. ↵
- Ibid., 45. ↵
- Mihaly Czikszentmihalyi, Flow: The Psychology of Optimal Experience (New York: Harper & Row, 1990). ↵
- Rosen, Jeffrey A., Elizabeth J. Glennie, Ben W. Dalton, Jean M. Lennon, and Robert N. Bozick. Noncognitive Skills in the Classroom: New Perspectives on Educational Research . RTI International. PO Box 12194, Research Triangle Park, NC 27709-2194, 2010. ↵
- Hart Research Associates, Raising the Bar , 9. ↵
Writing in College Copyright © 2016 by Amy Guptill is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Feedback/errata.
Comments are closed.

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Writing Assignments
Kate Derrington; Cristy Bartlett; and Sarah Irvine

Introduction
Assignments are a common method of assessment at university and require careful planning and good quality research. Developing critical thinking and writing skills are also necessary to demonstrate your ability to understand and apply information about your topic. It is not uncommon to be unsure about the processes of writing assignments at university.
- You may be returning to study after a break
- You may have come from an exam based assessment system and never written an assignment before
- Maybe you have written assignments but would like to improve your processes and strategies
This chapter has a collection of resources that will provide you with the skills and strategies to understand assignment requirements and effectively plan, research, write and edit your assignments. It begins with an explanation of how to analyse an assignment task and start putting your ideas together. It continues by breaking down the components of academic writing and exploring the elements you will need to master in your written assignments. This is followed by a discussion of paraphrasing and synthesis, and how you can use these strategies to create a strong, written argument. The chapter concludes with useful checklists for editing and proofreading to help you get the best possible mark for your work.
Task Analysis and Deconstructing an Assignment
It is important that before you begin researching and writing your assignments you spend sufficient time understanding all the requirements. This will help make your research process more efficient and effective. Check your subject information such as task sheets, criteria sheets and any additional information that may be in your subject portal online. Seek clarification from your lecturer or tutor if you are still unsure about how to begin your assignments.
The task sheet typically provides key information about an assessment including the assignment question. It can be helpful to scan this document for topic, task and limiting words to ensure that you fully understand the concepts you are required to research, how to approach the assignment, and the scope of the task you have been set. These words can typically be found in your assignment question and are outlined in more detail in the two tables below (see Table 19.1 and Table 19.2 ).
Table 19.1 Parts of an Assignment Question
| Topic words | These are words and concepts you have to research and write about. |
| Task words | These will tell you how to approach the assignment and structure the information you find in your research (e.g., discuss, analyse). |
| Limiting words | These words define the scope of the assignment, e.g., Australian perspectives, relevant codes or standards or a specific timeframe. |
Make sure you have a clear understanding of what the task word requires you to address.
Table 19.2 Task words
| Give reasons for or explain something has occurred. This task directs you to consider contributing factors to a certain situation or event. You are expected to make a decision about why these occurred, not just describe the events. | the factors that led to the global financial crisis. | |
| Consider the different elements of a concept, statement or situation. Show the different components and show how they connect or relate. Your structure and argument should be logical and methodical. | the political, social and economic impacts of climate change. | |
| Make a judgement on a topic or idea. Consider its reliability, truth and usefulness. In your judgement, consider both the strengths and weaknesses of the opposing arguments to determine your topic’s worth (similar to evaluate). | the efficacy of cogitative behavioural therapy (CBT) for the treatment of depression. | |
| Divide your topic into categories or sub-topics logically (could possibly be part of a more complex task). | the artists studied this semester according to the artistic periods they best represent. Then choose one artist and evaluate their impact on future artists. | |
| State your opinion on an issue or idea. You may explain the issue or idea in more detail. Be objective and support your opinion with reliable evidence. | the government’s proposal to legalise safe injecting rooms. | |
| Show the similarities and differences between two or more ideas, theories, systems, arguments or events. You are expected to provide a balanced response, highlighting similarities and differences. | the efficiency of wind and solar power generation for a construction site. | |
| Point out only the differences between two or more ideas, theories, systems, arguments or events. | virtue ethics and utilitarianism as models for ethical decision making. | |
| (this is often used with another task word, e.g. critically evaluate, critically analyse, critically discuss) | It does not mean to criticise, instead you are required to give a balanced account, highlighting strengths and weaknesses about the topic. Your overall judgment must be supported by reliable evidence and your interpretation of that evidence. | analyse the impacts of mental health on recidivism within youth justice. |
| Provide a precise meaning of a concept. You may need to include the limits or scope of the concept within a given context. | digital disruption as it relates to productivity. | |
| Provide a thorough description, emphasising the most important points. Use words to show appearance, function, process, events or systems. You are not required to make judgements. | the pathophysiology of Asthma. | |
| Highlight the differences between two (possibly confusing) items. | between exothermic and endothermic reactions. | |
| Provide an analysis of a topic. Use evidence to support your argument. Be logical and include different perspectives on the topic (This requires more than a description). | how Brofenbrenner’s ecological system’s theory applies to adolescence. | |
| Review both positive and negative aspects of a topic. You may need to provide an overall judgement regarding the value or usefulness of the topic. Evidence (referencing) must be included to support your writing. | the impact of inclusive early childhood education programs on subsequent high school completion rates for First Nations students. | |
| Describe and clarify the situation or topic. Depending on your discipline area and topic, this may include processes, pathways, cause and effect, impact, or outcomes. | the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the film industry in Australia. | |
| Clarify a point or argument with examples and evidence. | how society’s attitudes to disability have changed from a medical model to a wholistic model of disability. | |
| Give evidence which supports an argument or idea; show why a decision or conclusions were made. Justify may be used with other topic words, such as outline, argue. | Write a report outlining the key issues and implications of a welfare cashless debit card trial and make three recommendations for future improvements. your decision-making process for the recommendations. | |
| A comprehensive description of the situation or topic which provides a critical analysis of the key issues. | Provide a of Australia's asylum policies since the Pacific Solution in 2001. | |
| An overview or brief description of a topic. (This is likely to be part of a larger assessment task.) | the process for calculating the correct load for a plane. |
The criteria sheet , also known as the marking sheet or rubric, is another important document to look at before you begin your assignment. The criteria sheet outlines how your assignment will be marked and should be used as a checklist to make sure you have included all the information required.
The task or criteria sheet will also include the:
- Word limit (or word count)
- Referencing style and research expectations
- Formatting requirements
Task analysis and criteria sheets are also discussed in the chapter Managing Assessments for a more detailed discussion on task analysis, criteria sheets, and marking rubrics.
Preparing your ideas
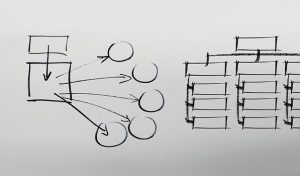
Brainstorm or concept map: List possible ideas to address each part of the assignment task based on what you already know about the topic from lectures and weekly readings.
Finding appropriate information: Learn how to find scholarly information for your assignments which is
See the chapter Working With Information for a more detailed explanation .
What is academic writing?
Academic writing tone and style.
Many of the assessment pieces you prepare will require an academic writing style. This is sometimes called ‘academic tone’ or ‘academic voice’. This section will help you to identify what is required when you are writing academically (see Table 19.3 ). The best way to understand what academic writing looks like, is to read broadly in your discipline area. Look at how your course readings, or scholarly sources, are written. This will help you identify the language of your discipline field, as well as how other writers structure their work.
Table 19.3 Comparison of academic and non-academic writing
| Is clear, concise and well-structured | Is verbose and may use more words than are needed |
| Is formal. It writes numbers under twenty in full. | Writes numbers under twenty as numerals and uses symbols such as “&” instead of writing it in full |
| Is reasoned and supported (logically developed) | Uses humour (puns, sarcasm) |
| Is authoritative (writes in third person- This essay argues…) | Writes in first person (I think, I found) |
| Utilises the language of the field/industry/subject | Uses colloquial language e.g., mate |
Thesis statements
Essays are a common form of assessment that you will likely encounter during your university studies. You should apply an academic tone and style when writing an essay, just as you would in in your other assessment pieces. One of the most important steps in writing an essay is constructing your thesis statement. A thesis statement tells the reader the purpose, argument or direction you will take to answer your assignment question. A thesis statement may not be relevant for some questions, if you are unsure check with your lecturer. The thesis statement:
- Directly relates to the task . Your thesis statement may even contain some of the key words or synonyms from the task description.
- Does more than restate the question.
- Is specific and uses precise language.
- Let’s your reader know your position or the main argument that you will support with evidence throughout your assignment.
- The subject is the key content area you will be covering.
- The contention is the position you are taking in relation to the chosen content.
Your thesis statement helps you to structure your essay. It plays a part in each key section: introduction, body and conclusion.
Planning your assignment structure

When planning and drafting assignments, it is important to consider the structure of your writing. Academic writing should have clear and logical structure and incorporate academic research to support your ideas. It can be hard to get started and at first you may feel nervous about the size of the task, this is normal. If you break your assignment into smaller pieces, it will seem more manageable as you can approach the task in sections. Refer to your brainstorm or plan. These ideas should guide your research and will also inform what you write in your draft. It is sometimes easier to draft your assignment using the 2-3-1 approach, that is, write the body paragraphs first followed by the conclusion and finally the introduction.
Writing introductions and conclusions
Clear and purposeful introductions and conclusions in assignments are fundamental to effective academic writing. Your introduction should tell the reader what is going to be covered and how you intend to approach this. Your conclusion should summarise your argument or discussion and signal to the reader that you have come to a conclusion with a final statement. These tips below are based on the requirements usually needed for an essay assignment, however, they can be applied to other assignment types.
Writing introductions

Most writing at university will require a strong and logically structured introduction. An effective introduction should provide some background or context for your assignment, clearly state your thesis and include the key points you will cover in the body of the essay in order to prove your thesis.
Usually, your introduction is approximately 10% of your total assignment word count. It is much easier to write your introduction once you have drafted your body paragraphs and conclusion, as you know what your assignment is going to be about. An effective introduction needs to inform your reader by establishing what the paper is about and provide four basic things:
- A brief background or overview of your assignment topic
- A thesis statement (see section above)
- An outline of your essay structure
- An indication of any parameters or scope that will/ will not be covered, e.g. From an Australian perspective.
The below example demonstrates the four different elements of an introductory paragraph.
1) Information technology is having significant effects on the communication of individuals and organisations in different professions. 2) This essay will discuss the impact of information technology on the communication of health professionals. 3) First, the provision of information technology for the educational needs of nurses will be discussed. 4) This will be followed by an explanation of the significant effects that information technology can have on the role of general practitioner in the area of public health. 5) Considerations will then be made regarding the lack of knowledge about the potential of computers among hospital administrators and nursing executives. 6) The final section will explore how information technology assists health professionals in the delivery of services in rural areas . 7) It will be argued that information technology has significant potential to improve health care and medical education, but health professionals are reluctant to use it.
1 Brief background/ overview | 2 Indicates the scope of what will be covered | 3-6 Outline of the main ideas (structure) | 7 The thesis statement
Note : The examples in this document are taken from the University of Canberra and used under a CC-BY-SA-3.0 licence.
Writing conclusions
You should aim to end your assignments with a strong conclusion. Your conclusion should restate your thesis and summarise the key points you have used to prove this thesis. Finish with a key point as a final impactful statement. Similar to your introduction, your conclusion should be approximately 10% of the total assignment word length. If your assessment task asks you to make recommendations, you may need to allocate more words to the conclusion or add a separate recommendations section before the conclusion. Use the checklist below to check your conclusion is doing the right job.
Conclusion checklist
- Have you referred to the assignment question and restated your argument (or thesis statement), as outlined in the introduction?
- Have you pulled together all the threads of your essay into a logical ending and given it a sense of unity?
- Have you presented implications or recommendations in your conclusion? (if required by your task).
- Have you added to the overall quality and impact of your essay? This is your final statement about this topic; thus, a key take-away point can make a great impact on the reader.
- Remember, do not add any new material or direct quotes in your conclusion.
This below example demonstrates the different elements of a concluding paragraph.
1) It is evident, therefore, that not only do employees need to be trained for working in the Australian multicultural workplace, but managers also need to be trained. 2) Managers must ensure that effective in-house training programs are provided for migrant workers, so that they become more familiar with the English language, Australian communication norms and the Australian work culture. 3) In addition, Australian native English speakers need to be made aware of the differing cultural values of their workmates; particularly the different forms of non-verbal communication used by other cultures. 4) Furthermore, all employees must be provided with clear and detailed guidelines about company expectations. 5) Above all, in order to minimise communication problems and to maintain an atmosphere of tolerance, understanding and cooperation in the multicultural workplace, managers need to have an effective knowledge about their employees. This will help employers understand how their employee’s social conditioning affects their beliefs about work. It will develop their communication skills to develop confidence and self-esteem among diverse work groups. 6) The culturally diverse Australian workplace may never be completely free of communication problems, however, further studies to identify potential problems and solutions, as well as better training in cross cultural communication for managers and employees, should result in a much more understanding and cooperative environment.
1 Reference to thesis statement – In this essay the writer has taken the position that training is required for both employees and employers . | 2-5 Structure overview – Here the writer pulls together the main ideas in the essay. | 6 Final summary statement that is based on the evidence.
Note: The examples in this document are taken from the University of Canberra and used under a CC-BY-SA-3.0 licence.
Writing paragraphs
Paragraph writing is a key skill that enables you to incorporate your academic research into your written work. Each paragraph should have its own clearly identified topic sentence or main idea which relates to the argument or point (thesis) you are developing. This idea should then be explained by additional sentences which you have paraphrased from good quality sources and referenced according to the recommended guidelines of your subject (see the chapter Working with Information ). Paragraphs are characterised by increasing specificity; that is, they move from the general to the specific, increasingly refining the reader’s understanding. A common structure for paragraphs in academic writing is as follows.
Topic Sentence
This is the main idea of the paragraph and should relate to the overall issue or purpose of your assignment is addressing. Often it will be expressed as an assertion or claim which supports the overall argument or purpose of your writing.
Explanation/ Elaboration
The main idea must have its meaning explained and elaborated upon. Think critically, do not just describe the idea.
These explanations must include evidence to support your main idea. This information should be paraphrased and referenced according to the appropriate referencing style of your course.
Concluding sentence (critical thinking)
This should explain why the topic of the paragraph is relevant to the assignment question and link to the following paragraph.
Use the checklist below to check your paragraphs are clear and well formed.
Paragraph checklist
- Does your paragraph have a clear main idea?
- Is everything in the paragraph related to this main idea?
- Is the main idea adequately developed and explained?
- Do your sentences run together smoothly?
- Have you included evidence to support your ideas?
- Have you concluded the paragraph by connecting it to your overall topic?
Writing sentences
Make sure all the sentences in your paragraphs make sense. Each sentence must contain a verb to be a complete sentence. Avoid sentence fragments . These are incomplete sentences or ideas that are unfinished and create confusion for your reader. Avoid also run on sentences . This happens when you join two ideas or clauses without using the appropriate punctuation. This also confuses your meaning (See the chapter English Language Foundations for examples and further explanation).
Use transitions (linking words and phrases) to connect your ideas between paragraphs and make your writing flow. The order that you structure the ideas in your assignment should reflect the structure you have outlined in your introduction. Refer to transition words table in the chapter English Language Foundations.
Paraphrasing and Synthesising
Paraphrasing and synthesising are powerful tools that you can use to support the main idea of a paragraph. It is likely that you will regularly use these skills at university to incorporate evidence into explanatory sentences and strengthen your essay. It is important to paraphrase and synthesise because:
- Paraphrasing is regarded more highly at university than direct quoting.
- Paraphrasing can also help you better understand the material.
- Paraphrasing and synthesising demonstrate you have understood what you have read through your ability to summarise and combine arguments from the literature using your own words.
What is paraphrasing?
Paraphrasing is changing the writing of another author into your words while retaining the original meaning. You must acknowledge the original author as the source of the information in your citation. Follow the steps in this table to help you build your skills in paraphrasing (see Table 19.4 ).
Table 19.4 Paraphrasing techniques
| 1 | Make sure you understand what you are reading. Look up keywords to understand their meanings. |
| 2 | Record the details of the source so you will be able to cite it correctly in text and in your reference list. |
| 3 | Identify words that you can change to synonyms (but do not change the key/topic words). |
| 4 | Change the type of word in a sentence (for example change a noun to a verb or vice versa). |
| 5 | Eliminate unnecessary words or phrases from the original that you don’t need in your paraphrase. |
| 6 | Change the sentence structure (for example change a long sentence to several shorter ones or combine shorter sentences to form a longer sentence). |
Example of paraphrasing
Please note that these examples and in text citations are for instructional purposes only.
Original text
Health care professionals assist people often when they are at their most vulnerable . To provide the best care and understand their needs, workers must demonstrate good communication skills . They must develop patient trust and provide empathy to effectively work with patients who are experiencing a variety of situations including those who may be suffering from trauma or violence, physical or mental illness or substance abuse (French & Saunders, 2018).
Poor quality paraphrase example
This is a poor example of paraphrasing. Some synonyms have been used and the order of a few words changed within the sentences however the colours of the sentences indicate that the paragraph follows the same structure as the original text.
Health care sector workers are often responsible for vulnerable patients. To understand patients and deliver good service , they need to be excellent communicators . They must establish patient rapport and show empathy if they are to successfully care for patients from a variety of backgrounds and with different medical, psychological and social needs (French & Saunders, 2018).
A good quality paraphrase example
This example demonstrates a better quality paraphrase. The author has demonstrated more understanding of the overall concept in the text by using the keywords as the basis to reconstruct the paragraph. Note how the blocks of colour have been broken up to see how much the structure has changed from the original text.
Empathetic communication is a vital skill for health care workers. Professionals in these fields are often responsible for patients with complex medical, psychological and social needs. Empathetic communication assists in building rapport and gaining the necessary trust to assist these vulnerable patients by providing appropriate supportive care (French & Saunders, 2018).
The good quality paraphrase example demonstrates understanding of the overall concept in the text by using key words as the basis to reconstruct the paragraph. Note how the blocks of colour have been broken up, which indicates how much the structure has changed from the original text.
What is synthesising?
Synthesising means to bring together more than one source of information to strengthen your argument. Once you have learnt how to paraphrase the ideas of one source at a time, you can consider adding additional sources to support your argument. Synthesis demonstrates your understanding and ability to show connections between multiple pieces of evidence to support your ideas and is a more advanced academic thinking and writing skill.
Follow the steps in this table to improve your synthesis techniques (see Table 19.5 ).
Table 19.5 Synthesising techniques
| 1 | Check your referencing guide to learn how to correctly reference more than one author at a time in your paper. |
| 2 | While taking notes for your research, try organising your notes into themes. This way you can keep similar ideas from different authors together. |
| 3 | Identify similar language and tone used by authors so that you can group similar ideas together. |
| 4 | Synthesis can not only be about grouping ideas together that are similar, but also those that are different. See how you can contrast authors in your writing to also strengthen your argument. |
Example of synthesis
There is a relationship between academic procrastination and mental health outcomes. Procrastination has been found to have a negative effect on students’ well-being (Balkis, & Duru, 2016). Yerdelen, McCaffrey, and Klassens’ (2016) research results suggested that there was a positive association between procrastination and anxiety. This was corroborated by Custer’s (2018) findings which indicated that students with higher levels of procrastination also reported greater levels of the anxiety. Therefore, it could be argued that procrastination is an ineffective learning strategy that leads to increased levels of distress.
Topic sentence | Statements using paraphrased evidence | Critical thinking (student voice) | Concluding statement – linking to topic sentence
This example demonstrates a simple synthesis. The author has developed a paragraph with one central theme and included explanatory sentences complete with in-text citations from multiple sources. Note how the blocks of colour have been used to illustrate the paragraph structure and synthesis (i.e., statements using paraphrased evidence from several sources). A more complex synthesis may include more than one citation per sentence.
Creating an argument
What does this mean.
Throughout your university studies, you may be asked to ‘argue’ a particular point or position in your writing. You may already be familiar with the idea of an argument, which in general terms means to have a disagreement with someone. Similarly, in academic writing, if you are asked to create an argument, this means you are asked to have a position on a particular topic, and then justify your position using evidence.
What skills do you need to create an argument?
In order to create a good and effective argument, you need to be able to:
- Read critically to find evidence
- Plan your argument
- Think and write critically throughout your paper to enhance your argument
For tips on how to read and write critically, refer to the chapter Thinking for more information. A formula for developing a strong argument is presented below.
A formula for a good argument
What does an argument look like?
As can be seen from the figure above, including evidence is a key element of a good argument. While this may seem like a straightforward task, it can be difficult to think of wording to express your argument. The table below provides examples of how you can illustrate your argument in academic writing (see Table 19.6 ).
Table 19.6 Argument
| Introducing your argument | • This paper will argue/claim that... • ...is an important factor/concept/idea/ to consider because... • … will be argued/outlined in this paper. |
| Introducing evidence for your argument | • Smith (2014) outlines that.... • This evidence demonstrates that... • According to Smith (2014)… • For example, evidence/research provided by Smith (2014) indicates that... |
| Giving the reason why your point/evidence is important | • Therefore this indicates... • This evidence clearly demonstrates.... • This is important/significant because... • This data highlights... |
| Concluding a point | • Overall, it is clear that... • Therefore, … are reasons which should be considered because... • Consequently, this leads to.... • The research presented therefore indicates... |
Editing and proofreading (reviewing)
Once you have finished writing your first draft it is recommended that you spend time revising your work. Proofreading and editing are two different stages of the revision process.
- Editing considers the overall focus or bigger picture of the assignment
- Proofreading considers the finer details
As can be seen in the figure above there are four main areas that you should review during the editing phase of the revision process. The main things to consider when editing include content, structure, style, and sources. It is important to check that all the content relates to the assignment task, the structure is appropriate for the purposes of the assignment, the writing is academic in style, and that sources have been adequately acknowledged. Use the checklist below when editing your work.
Editing checklist
- Have I answered the question accurately?
- Do I have enough credible, scholarly supporting evidence?
- Is my writing tone objective and formal enough or have I used emotive and informal language?
- Have I written in the third person not the first person?
- Do I have appropriate in-text citations for all my information?
- Have I included the full details for all my in-text citations in my reference list?
There are also several key things to look out for during the proofreading phase of the revision process. In this stage it is important to check your work for word choice, grammar and spelling, punctuation and referencing errors. It can be easy to mis-type words like ‘from’ and ‘form’ or mix up words like ‘trail’ and ‘trial’ when writing about research, apply American rather than Australian spelling, include unnecessary commas or incorrectly format your references list. The checklist below is a useful guide that you can use when proofreading your work.
Proofreading checklist
- Is my spelling and grammar accurate?
- Are they complete?
- Do they all make sense?
- Do they only contain only one idea?
- Do the different elements (subject, verb, nouns, pronouns) within my sentences agree?
- Are my sentences too long and complicated?
- Do they contain only one idea per sentence?
- Is my writing concise? Take out words that do not add meaning to your sentences.
- Have I used appropriate discipline specific language but avoided words I don’t know or understand that could possibly be out of context?
- Have I avoided discriminatory language and colloquial expressions (slang)?
- Is my referencing formatted correctly according to my assignment guidelines? (for more information on referencing refer to the Managing Assessment feedback section).
This chapter has examined the experience of writing assignments. It began by focusing on how to read and break down an assignment question, then highlighted the key components of essays. Next, it examined some techniques for paraphrasing and summarising, and how to build an argument. It concluded with a discussion on planning and structuring your assignment and giving it that essential polish with editing and proof-reading. Combining these skills and practising them, can greatly improve your success with this very common form of assessment.
- Academic writing requires clear and logical structure, critical thinking and the use of credible scholarly sources.
- A thesis statement is important as it tells the reader the position or argument you have adopted in your assignment. Not all assignments will require a thesis statement.
- Spending time analysing your task and planning your structure before you start to write your assignment is time well spent.
- Information you use in your assignment should come from credible scholarly sources such as textbooks and peer reviewed journals. This information needs to be paraphrased and referenced appropriately.
- Paraphrasing means putting something into your own words and synthesising means to bring together several ideas from sources.
- Creating an argument is a four step process and can be applied to all types of academic writing.
- Editing and proofreading are two separate processes.
Academic Skills Centre. (2013). Writing an introduction and conclusion . University of Canberra, accessed 13 August, 2013, http://www.canberra.edu.au/studyskills/writing/conclusions
Balkis, M., & Duru, E. (2016). Procrastination, self-regulation failure, academic life satisfaction, and affective well-being: underregulation or misregulation form. European Journal of Psychology of Education, 31 (3), 439-459.
Custer, N. (2018). Test anxiety and academic procrastination among prelicensure nursing students. Nursing education perspectives, 39 (3), 162-163.
Yerdelen, S., McCaffrey, A., & Klassen, R. M. (2016). Longitudinal examination of procrastination and anxiety, and their relation to self-efficacy for self-regulated learning: Latent growth curve modeling. Educational Sciences: Theory & Practice, 16 (1).
Writing Assignments Copyright © 2021 by Kate Derrington; Cristy Bartlett; and Sarah Irvine is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
- Utility Menu
fa3d988da6f218669ec27d6b6019a0cd
A publication of the harvard college writing program.
Harvard Guide to Using Sources
- The Honor Code
- Understanding Your Assignment
Before you visit the library, you should make sure you understand what you're being asked to do and what constraints, if any, have been placed on your assignment. If you have been asked to review the literature on post-traumatic stress disorder, for example, do you understand how far back you should go? If you have been asked to write a paper about American policy in relation to Vietnam, do you know what policies to focus on? Or is the choice of policies up to you? Has your professor offered any guidance in narrowing your topic? If you are researching a genetic disorder, are there any guidelines for what you should be seeking to learn about the disorder beyond what it is and how it presents itself?
Even when you understand the basic expectations of your assignment, you should be prepared for the fact that you won't necessarily know exactly what you're looking for—and that you shouldn't know what you want to find before you start looking. Research is an iterative process—the more you learn about what's available and what's been written already, the clearer your own project becomes, which in turn means you need to go back to the library to further narrow and continue your search. Before you take the first plunge into your research, it will be helpful to ask the following questions:
How wide a net should I cast, given the scope of my assignment?
What is required what is optional.
Some professors will tell you how many outside sources to consult. When this is the case, try to think of this as a guideline for how much work seems reasonable rather than as a quota you must meet. If you think of the number of sources as a quota, you'll be less likely to look for sources that help you build your own argument and more likely to simply check off a number. If you choose the first three sources you find, you risk ending up with a paper that strings together unrelated ideas, rather than one that truly integrates the most important ideas to make a compelling argument.
Sometimes requirements laid out in an assignment will help you shape your paper. For example, an assignment might tell you to "look for an argument to critique" or to "use at least one source that puts forth a counterargument." If your assignment doesn't offer possible approaches, you can come up with your own. Consult the section of this guide on the roles that a source can play in your paper for some ideas on what sources can do in your paper that might, in turn, help you think about what types of sources to look for.

How will my use of sources help me meet the terms of the assignments?
If you have a sense of why you're using sources to write a particular paper, you will be able to begin the process of locating them efficiently. If you are doing a literature review and your goal is to analyze past research on a particular topic, then your use of sources is fairly straightforward, and you know what you're looking for. If your assignment is to come up with your own question based on course readings and then find your own sources to answer that question, your task may be less clear cut. Here are some questions to ask yourself as you search for sources:
- Am I surveying the literature on a particular topic?
- Am I looking for sources in order to better understand a particular topic so that I can come up with a question to ask?
- Am I looking for sources to help me develop my thesis and argument?
- As you begin your research process, keep in mind that it's important to avoid looking only for sources that back up a position you've already decided to argue. Rather, you should see what ideas are out there and then decide how those ideas affect your thinking on a topic. It may be that someone disagrees with your interpretation, but rather than weakening your argument, this source may well prompt you to strengthen your position. On the other hand, if you find that every source seems to validate your position, it's worth asking yourself if your thesis is, in fact, arguable.
How will I know when I'm done with my research?
Writing a research paper is rarely a linear process. In many cases you won't be able to narrow your focus to a research question until you begin reading about your chosen topic. Once you formulate your question, you'll need to go back to the library resources you've identified and look for the sources that are most useful to you as you answer your question. As you read those sources, you'll likely refine your thesis and consult even more sources as your paper takes shape. This doesn't mean that you'll never be finished with your paper, however. Remember that you need to decide what's reasonable for the scope of your assignment, and that your goal is to answer your research question, not to report on every source that has ever been produced on your topic. If you're having trouble knowing when to stop reading, consult your instructor.
Library research can be overwhelming, especially given the many resources available at Harvard. You might find it helpful to remember that most research assignments are designed to provide you with an opportunity to learn something about a topic related to your course material that interests you. With that in mind, use the resources available to you through the Harvard library system, and don't be afraid to ask for help.
- Navigating the Harvard Libraries
- Online Library Tools
- Evaluating Sources
- Integrating Sources
PDFs for This Section
- Using sources
- Locating Sources
- Online Library and Citation Tools
- Instasolving
Unraveling the Essence of Assignments: Your Path to Academic Success
A Journey to Excellence: Understanding and Conquering Academic Assignments
Assignments play a crucial role in shaping your academic journey and are essential for achieving success. They provide a platform to apply theoretical knowledge, develop critical thinking skills, and enhance your understanding of various subjects. Completing assignments with diligence and dedication not only improves your grades but also prepares you for future challenges. This process encourages independent learning, time management, and problem-solving abilities, all of which are vital for academic and professional growth. By unraveling the essence of assignments, students can unlock their full potential and pave the way for a successful academic career. Embracing assignments as opportunities rather than burdens transforms the learning experience, making it more engaging and rewarding. As you navigate through your educational journey, recognizing the value of assignments will empower you to excel and achieve your academic goals with confidence and competence.
Defining the Assignment
At its core, an assignment is a task assigned to students by their educators, whether teachers or professors. These tasks serve as a medium through which students can demonstrate their knowledge and ability to apply it effectively. It's not merely an exercise in regurgitating facts and figures; it's an opportunity to showcase one's grasp of a subject, critical thinking skills, and creativity.
But let's peel back the layers and examine the concept of assignments on a deeper level. Assignments are not just educational chores but the keys to success and the beacons of a brighter future. Imagine a student aspiring to be admitted to a prestigious college or securing a coveted position at a renowned institution like Lloyds Bank. The path to such achievements is paved with grades; each assignment contributes to that mosaic of success. Therefore, the quality of assignments submitted is not merely a matter of academic performance but a stepping stone toward future accomplishments.
The Purpose of Assignments
To truly appreciate the significance of assignments, we must delve into their purpose. Why do students invest time and effort in completing these tasks? The answer lies in the multifaceted benefits that assignments offer:
1. Consolidation of Knowledge : Attending lectures and absorbing information is crucial but often fleeting. Assignments bridge the gap between theory and practical understanding. They require students to dive deeper into a subject, conduct research, and apply what they've learned. For example, consider historical accounts of World War II. While initial class discussions might cover the basics, in-depth research during assignment preparation ensures the details will be etched in memory for years to come.
2. Stimulating Critical Thinking : Stimulating Critical Thinking: In a classroom, students are passive participants in the learning process. Assignments, on the other hand, transform them into active thinkers and investigators. At home, students have access to a wealth of resources and the opportunity to seek online assignment help in USA , enabling them to explore various perspectives, gather advice, and engage in critical thinking. Assignments could be essays, asking students to present their unique viewpoints on a subject and require persuasive skills and research acumen. These skills are not just essential for academic success but for all future endeavors.

The Typical Assignment Structure
Now that we understand why assignments are vital, let's dissect their typical structure, which serves as a roadmap to successful assignment completion. There are five main aspects you're bound to encounter when tackling an assignment:
1. Overview : Before delving into the specifics of an assignment, professors typically provide an overview. This initial step clarifies the task's nature, what should be explored, and whether it's an individual or group endeavor. It's the foundation upon which your assignment journey begins.
2. Description of the Task : Once you've grasped the assignment's scope, the next step is to define the specific task you should undertake. Professors may provide a topic or present a list of potential themes from which you can choose. This phase outlines the assignment's goals and objectives, giving you a clear direction for your work.
3. Additional Materials : In many cases, assignments come with a list of recommended sources or materials. While some sources may need to be found independently, others may be specifically assigned by the professor. This step helps students learn to integrate various resources effectively. Additionally, you might be required to prepare supplementary materials like mini-presentations to enhance your assignment. Always clarify with your instructor whether additional materials are necessary, as being over-prepared is preferable to being unprepared.
4. Style Tips : Every assignment at the college or university level must adhere to specific style requirements. This includes adhering to rules of academic writing, such as avoiding first and second-person pronouns, contractions, and maintaining formality. Furthermore, academic assignments often require specific formatting styles like MLA, APA, Harvard, Chicago, and more. Your professor usually dictates the formatting style, so carefully consult the template provided, which typically contains samples of formatting styles. Pay attention to headings, title pages, references, titles, citations, and other style-related aspects. Even minor formatting errors can impact your grade significantly, so meticulous attention to academic and formatting styles is crucial.
5. Technical Details: The final important aspect of an assignment pertains to technical details. These include specifications such as the required number of pages, acceptable word count deviations, the deadline for submission, and source age requirements. In most cases, only recent sources from the last 5-7 years are permitted to ensure the information is current and relevant.
Assignment-Related Terms You Should Know
As you embark on your assignment journey, you must familiarize yourself with certain terms and processes you're likely to encounter. These terms elucidate the various dimensions of assignments and provide insight into what tasks usually involve:
1. Analyzing : This involves considering an issue or concept from all perspectives. It entails breaking down the subject into its constituent parts and providing fact-based explanations for each part, often establishing connections and outcomes. When you analyze a topic, you dissect it to gain a deeper understanding.
2. Summarizing : Summarizing requires you to retell what you have read or seen in your own words. It involves distilling the most critical aspects of the information while disregarding insignificant details. Summarizing is a valuable skill that helps you extract the essence of a subject.
3. Evaluating : To evaluate is to assess a topic or idea from all sides before reaching a judgment. It involves considering specific criteria, such as whether something is effective, dangerous, promising, or any other relevant measure. Evaluation is a critical thinking skill that aids in forming well-informed opinions.
4. Describing : When you describe, you present an overview of a subject. This can include comprehensively understanding a topic or simply introducing it to the reader.
5. Comparing : Comparison involves taking at least two objects, ideas, or concepts and examining what sets them apart and what they have in common. Comparative analysis helps in drawing distinctions and identifying similarities.
6. Research : Research is studying a subject's background, meaning, and implications by applying credible sources. It explores available information systematically to gather evidence and support your arguments.
7. Relating : Relating involves establishing a connection between at least two different objects or concepts. It aims to demonstrate how these entities are interconnected and how one influences the other.
8. Applying : Applying requires bringing a particular idea or theory into practical use and relating it to a specific object or situation. It entails studying the latter through the lens of the former, often showcasing real-world applications.
9. Illustrating : To illustrate is to prove a point by providing detailed examples. Examples are used to support arguments and make complex concepts more accessible.
You May Also Like
Assignment help
5 common assignment writing problems for students.
Decoding Student Struggles Insights into Common Assignment Writing Challenges and Strategies for Academic Success.

Pro-Tips For Overcoming Time Management Struggles For Assignments
Unlock success with pro tips! Conquer time management hurdles for assignments effortlessly. Elevate your productivity with expert strategies.

Learn Quick Tips to Solve Math Assignment Faster
Math Made Swift: Unlock Efficiency with Quick Tips to Solve Assignments Faster. Accelerate your problem-solving skills for academic success!

How to complete when you have lots of assignments ?
Assignment Juggling Mastery: Strategies to Efficiently Navigate and Excel When Facing a Pile-Up of Academic Tasks.

Using Examples in Your Assignment- Reasons & Benefits
Empower Your Academic Journey with Tailored Assignment Help Solutions - Achieve Excellence, Stress-Free!
12 Tips for writing an academic assignments
The Write Way: Strategies to Enhance Clarity and Coherence in Assignments

4 Reasons Why Students find Programming Assignment help Difficult
Maximize Success: Uncover the Top Benefits of Choosing Online Programming Assignment Help for Academic Excellence!
Expert Guidance On How to Structure An Assignment
Strategic Blueprint: Unlock Academic Success with Expert Guidance on Crafting a Well-Structured Assignment for Optimal Impact and Excellence.

Engineering Assignment Writing From Experts To Change Your Learning Experience
Transform your learning journey with expert engineering assignment writing. Unlock new levels of understanding and excellence.

5 Best Chegg Alternatives and Competitors
Explore top Chegg alternatives and competitors! Discover websites like Chegg offering quality study resources and services.

How Math Assignment Helpers Simplify Mathematics For College Students?
Empower your math skills with expert math assignment helpers. Overcome difficulties, grasp concepts, and succeed in college mathematics!

Role of Assignment Help Sites to Enhance Knowledge & Skills in Management Students
Unlock Your Academic Success with Premium Management Assignment Help Services - Expert Assistance Tailored to Your Needs!

How to Write Perfect Hook For Your Assignments
Craft compelling assignments with our guide: Write the perfect hook. Engage your audience from the start for impactful academic success.

Top-Rated Tips From Experts: How to Write a Maths Assignment
Mathematics Mastery: Trust Our Experts for Impeccable Assignment Writing, Ensuring Precision and Academic Excellence.

10+ Practical Tips For Effective Assignment Writing
Craft A+ essays with our Effective Assignment Writing guide – Your key to academic excellence and top-notch grades!

Overcoming Study Challenges with Accounting Assignments Help
Overcome study challenges with expert accounting assignments help. Tailored solutions for academic success from professionals in the field.

How to write an “academic assignments"
Unlocking Your Potential: Proven Techniques for Excelling in Assignments

Why Are Students Opting For Statistics Assignment Help?
Get expert statistics assignment help! Our professionals offer assistance with data analysis, hypothesis testing, and more. Score high grades!

Improve Your Performance with Statistics Assignment Help
Boost Your Grades with Expert Statistics Assignment Help - Enhance Your Performance Today!
Amazing Assignment Significance For Students That Blew Your Mind
Unveiling the Mind-Blowing Significance of Amazing Assignments for Students – Transformative Insights That Reshape Academic Excellence!

How Assignment Help USA Assist University Students
Elevate Your Grades with Assignment Help USA - Supporting University Students for Academic Excellence!

50+ Essay and Dissertation Assignment Topics For College Students
Exploring Diverse Dimensions: Essay and Dissertation Assignment Topics to Ignite Academic Curiosity and Foster Critical Thinking.

Chegg vs. Quizlet: What Every Student Should Know
Comparing Chegg and Quizlet: Key Features, Benefits, and Drawbacks for Students

350 Research Paper Topics By Chemistry Help Experts
Unlock Your Chemistry Potential with Expert Guidance from Chemistry Help Experts
- IN > -->
- IWP > -->
- Understanding the Assignment
Contact the LWC

Understanding the assignment
Are you sure that your professor wants a hard copy? Did the professor require a title page? Stapled? Single-spaced or double spaced?

Check out our online resources designed to help you improve your writing in the University and beyond.
Understanding the assignment is critical before you begin writing the paper. The purpose, audience, and structure are usually included in the prompt and is your guide to completing the assignment correctly.
We have created resources below to support students identifying key aspects of written assignments and how to best approach completing it.
Purpose Tab Open
Audience tab closed, structure tab closed, additional resources tab closed, purpose accordion open.
How does your professor know that you are learning new concepts and approaches to new material? You will be asked to show your knowledge and understanding through:
- Essay Exams
- Lab notes and field notes
- Projects and project reports
- Papers written to academic or professional audiences
- Informal papers
In most cases, you will get instructions from the professor who wants to know that you:
- Listen, think, and read critically
- Apply the new concepts you learned in your courses and major by writing about it, by completing a project and writing a report and/or by presenting your findings
- Adjust your writing based on the audience and disciplinary writing conventions
Each professor has specific goals in mind when teaching a course. You will find those goals when you look at the course objectives. Similarly, for writing tasks, your professor’s goal is stated in the assignment task and/or it is related to the course objectives.
Next steps and additional information
Writing assignments don’t all have the same purpose. Because of different majors and different audiences, the purpose of an assignment changes.
To make sure that you understand the assignment purpose:
- Underline, circle, or highlight key words that help define the purpose. Does your professor want to test your knowledge or see that you can apply theoretical principles you learned about in last week’s class?
- Restate the assignment’s purpose in your own words and check with your peers.
- Ask yourself some questions: “What questions am I supposed to answer?” “How am I supposed to structure this essay?” “What am I supposed to focus on?”
- If you have any doubt, talk to your professor during office hours. If online, post a question in your Discussions Area. Sometimes your classmates are your best resources.
- Start early
- Make an appointment at the University Writing Commons
Audience Accordion Closed
Writing always has an audience. Who the audience is is not always as clearly defined as it could be. When you write for an academic course, you often walk a precarious line when you imagine your audience:
- Your professor might tell you that she is the audience. Does that mean that you don’t need to be explicit and cite sources since she knows a great deal about the subject? Then why do you get feedback that states “More details” or “Expand here” or “Examples?”
- Your professor might tell you to write to a specified outside reader – an expert in your major field, your best friend, the governor of the state, a city official, your classmates. You know, however, that the grade comes from your professor, and it doesn’t make much difference that your outside reader thought that you are the greatest writer ever.
- Your professor doesn’t say anything about the audience in the assignment sheet and you are not sure who you are supposed to focus on. You decide to write to “the public” – pretty much everybody – which makes your task even more difficult since you have no sense of who that amorphous public might be.
In many cases, you are asked to write because your professor wants to know that you:
- Understand the class materials.
- Apply the class materials.
- Remember the class materials.
- Make connections between the class materials and outside resources.
- Understand the implications of class materials on your research, project, or world peace.
Whoever your audience for your writing assignment is, keep in mind that your professor wants clear, concise, detailed, specific, and well-structured writing that can be read by an expert audience (somebody in your major and field of study) or a lay audience (somebody interested but unfamiliar with the terminology used in your major). In both cases, you can’t assume.
Your audience, whether it’s an expert or lay audience, expects to learn something from your writing assignment. To make sure that your writing meets your professors expectations:
- Do not assume that your audience has knowledge that you gained in your course, even if the audience is your professor.
- Use the knowledge that you gained in your course to write your report, essay, presentation, blog entry to show that you understood the class lectures and class readings.
- Before you get too deep into the writing process, let your professor know who your intended audience for your writing is, and how that influences what and how you write. If your professor had another audience in mind, adjust your work to keep this audience in mind.
- Start Early!
- Make an appointment at the University Writing Commons.
Adapting to your audience : Colorado State University’s Writing Center gives you a comprehensive understanding of how audience influences your writing. You can click on the links to the right to get information on types of audiences, how to develop audience awareness, how to analyze your audience, and how to write for an audience.
Audience : The University of North Carolina-Chapel Hill’s Writing Center provides a handout that provides answers to questions such as “How do I identify my audience” and “How much should I explain.”
Structure Accordion Closed
A professor often writes an assignment to guide their students’ work with the new materials presented in the course. You have to be able to interpret the assignment so that you can write a successful essay exam, lab notes, report, or paper. Common components of an assignment include:
- Introduction
Disciplinary conventions will guide specifics. When you read the assignment, look for instructions on what should go into your introduction, whether the body of your paper needs to include a synthesis and/or an analysis of the course readings, a methodology section, a section on data collection, a results section, and so on.
- In the humanities and social sciences, it is common for writing assignments to require student-writers to include themselves (first-person pronouns) in their analyses and conclusions.
- In the natural sciences, health professions, and technological fields, it is common that classroom assignments, especially in the undergraduate years, are especially interested in how the student-writer conveys an understanding of the process, the elements, the definitions of materials. They require third person in passive-voice.
- Sometimes, the assignment asks students to work on materials for a client. This changes the writing conventions that you will be using. You will need to find out who your client (audience) is before you can make choices on writing conventions.
Pay attention to your professor’s word choice:
- “Discuss how gender influences…”
- “Analyze the impact of presidential elections on…”
- “Summarize the main reasons for Chavez’ involvement in…”
Words such as discuss, analyze, and summarize ask you for different writing responses. If you are not sure, use your professor’s office hours to get clarification on the assignment. You can also make an appointment with the University Writing Commons to make sure that you understand the assignment.
Professors are usually not trying to trick students through writing assignments. When you talk to your professor, your classmates, or the UWC Writing Assistants, it is often helpful when you:
- Let the professor know what your understanding of the assignment is before asking questions. This shows that you have read the assignment sheet.
- Underline, circle, or highlight key words that help define the purpose.
- Restate the assignment’s purpose in your own words.
- Check with classmates. Sometimes they are your best resource.
Additional resources Accordion Closed
Specifications are part of all majors. Whether they are explicitly explained in the assignment instructions, or whether they are implicitly assumed as part of your knowledge of writing in your major, pay attention to how an assignment is supposed to look once you finished revising and editing it. To make sure that you understand assignment specifications:
- Establish a habit of reviewing specifications early in the writing process.
- Keep a list of specifications close by when you write your assignment. This way, you can make sure that you remember to use upper or lower case for titles.
- Ask your professor during office hours if you are not clear about the writing assignment’s specifications.
- Make use of your major-specific handbooks. Purchase one for the duration of your studies.
Understanding the writing assignments: The UNC-Chapel Hill’s Writing Center gives you a good idea of what you can expect from a writing assignment, and what you need to pay attention to when reading an assignment. They provide specific details on format and also show you how to interpret the assignment.
How to decipher the assignment : Purdue University’s Online Writing Lab provides this handout with information on the steps to take to understand the requirements of the assignment.
Common writing assignments : Purdue University’s Online Writing Lab’s page on common writing assignments will give you a good sense of what kinds of writing assignments your professors might have in mind, and what generally accepted structures for various assignments are.
Sample lab assignment : The University of Wisconsin-Madison’s Writing Center offers this page with a common outline of a sample lab assignment, with brief notes on what needs to be part of each section.
Levels of formality : Purdue University’s Online Writing Lab shows you the levels of formality you should use in your academic writing. They distinguish writing as formal, semi-formal, and informal.
Academic tone, diction, and style : The University of North Texas at Dallas shows you what you need to pay attention to when you decide on the level of formality and informality in your writing.
Effective E-mail communication : The University of North Carolina – Chapel Hill offers this handout on one form of communication often underestimated by students: email communication with professors or community members.
Writing and speaking guidelines : Pennsylvania State University has developed guidelines for engineering and science writers with great information on the structures of various genres and styles that you might need to use in engineering and the sciences.
Writing the basic business letter : Purdue University’s Online Writing Lab outlines the technical specifications for a business letter. It includes a pdf file that shows a business letter with annotations.
How to write, outline, proofread and everything in-between : The Community for Accredited Online Schools provides some excellent resources for understanding the kind of essay, writing outlines, how to do academic research, how to evaluate a source, and more!
Fold a paper R2-D2 and other awesome star wars origami : Wired.com offers this fun and challenging article on origami with complete instructions.
The University of North Carolina-Chapel Hill developed several handouts that discuss genre in different fields. Each handout includes tips on how to strengthen your writer’s voice:
- Science writing
- Art history writing
- Communication Studies
- Mailing List
- Search Search
Username or Email Address
Remember Me

Resources for Teachers: Creating Writing Assignments
This page contains four specific areas:
Creating Effective Assignments
Checking the assignment, sequencing writing assignments, selecting an effective writing assignment format.
Research has shown that the more detailed a writing assignment is, the better the student papers are in response to that assignment. Instructors can often help students write more effective papers by giving students written instructions about that assignment. Explicit descriptions of assignments on the syllabus or on an “assignment sheet” tend to produce the best results. These instructions might make explicit the process or steps necessary to complete the assignment. Assignment sheets should detail:
- the kind of writing expected
- the scope of acceptable subject matter
- the length requirements
- formatting requirements
- documentation format
- the amount and type of research expected (if any)
- the writer’s role
- deadlines for the first draft and its revision
Providing questions or needed data in the assignment helps students get started. For instance, some questions can suggest a mode of organization to the students. Other questions might suggest a procedure to follow. The questions posed should require that students assert a thesis.
The following areas should help you create effective writing assignments.
Examining your goals for the assignment
- How exactly does this assignment fit with the objectives of your course?
- Should this assignment relate only to the class and the texts for the class, or should it also relate to the world beyond the classroom?
- What do you want the students to learn or experience from this writing assignment?
- Should this assignment be an individual or a collaborative effort?
- What do you want students to show you in this assignment? To demonstrate mastery of concepts or texts? To demonstrate logical and critical thinking? To develop an original idea? To learn and demonstrate the procedures, practices, and tools of your field of study?
Defining the writing task
- Is the assignment sequenced so that students: (1) write a draft, (2) receive feedback (from you, fellow students, or staff members at the Writing and Communication Center), and (3) then revise it? Such a procedure has been proven to accomplish at least two goals: it improves the student’s writing and it discourages plagiarism.
- Does the assignment include so many sub-questions that students will be confused about the major issue they should examine? Can you give more guidance about what the paper’s main focus should be? Can you reduce the number of sub-questions?
- What is the purpose of the assignment (e.g., review knowledge already learned, find additional information, synthesize research, examine a new hypothesis)? Making the purpose(s) of the assignment explicit helps students write the kind of paper you want.
- What is the required form (e.g., expository essay, lab report, memo, business report)?
- What mode is required for the assignment (e.g., description, narration, analysis, persuasion, a combination of two or more of these)?
Defining the audience for the paper
- Can you define a hypothetical audience to help students determine which concepts to define and explain? When students write only to the instructor, they may assume that little, if anything, requires explanation. Defining the whole class as the intended audience will clarify this issue for students.
- What is the probable attitude of the intended readers toward the topic itself? Toward the student writer’s thesis? Toward the student writer?
- What is the probable educational and economic background of the intended readers?
Defining the writer’s role
- Can you make explicit what persona you wish the students to assume? For example, a very effective role for student writers is that of a “professional in training” who uses the assumptions, the perspective, and the conceptual tools of the discipline.
Defining your evaluative criteria
1. If possible, explain the relative weight in grading assigned to the quality of writing and the assignment’s content:
- depth of coverage
- organization
- critical thinking
- original thinking
- use of research
- logical demonstration
- appropriate mode of structure and analysis (e.g., comparison, argument)
- correct use of sources
- grammar and mechanics
- professional tone
- correct use of course-specific concepts and terms.
Here’s a checklist for writing assignments:
- Have you used explicit command words in your instructions (e.g., “compare and contrast” and “explain” are more explicit than “explore” or “consider”)? The more explicit the command words, the better chance the students will write the type of paper you wish.
- Does the assignment suggest a topic, thesis, and format? Should it?
- Have you told students the kind of audience they are addressing — the level of knowledge they can assume the readers have and your particular preferences (e.g., “avoid slang, use the first-person sparingly”)?
- If the assignment has several stages of completion, have you made the various deadlines clear? Is your policy on due dates clear?
- Have you presented the assignment in a manageable form? For instance, a 5-page assignment sheet for a 1-page paper may overwhelm students. Similarly, a 1-sentence assignment for a 25-page paper may offer insufficient guidance.
There are several benefits of sequencing writing assignments:
- Sequencing provides a sense of coherence for the course.
- This approach helps students see progress and purpose in their work rather than seeing the writing assignments as separate exercises.
- It encourages complexity through sustained attention, revision, and consideration of multiple perspectives.
- If you have only one large paper due near the end of the course, you might create a sequence of smaller assignments leading up to and providing a foundation for that larger paper (e.g., proposal of the topic, an annotated bibliography, a progress report, a summary of the paper’s key argument, a first draft of the paper itself). This approach allows you to give students guidance and also discourages plagiarism.
- It mirrors the approach to written work in many professions.
The concept of sequencing writing assignments also allows for a wide range of options in creating the assignment. It is often beneficial to have students submit the components suggested below to your course’s STELLAR web site.
Use the writing process itself. In its simplest form, “sequencing an assignment” can mean establishing some sort of “official” check of the prewriting and drafting steps in the writing process. This step guarantees that students will not write the whole paper in one sitting and also gives students more time to let their ideas develop. This check might be something as informal as having students work on their prewriting or draft for a few minutes at the end of class. Or it might be something more formal such as collecting the prewriting and giving a few suggestions and comments.
Have students submit drafts. You might ask students to submit a first draft in order to receive your quick responses to its content, or have them submit written questions about the content and scope of their projects after they have completed their first draft.
Establish small groups. Set up small writing groups of three-five students from the class. Allow them to meet for a few minutes in class or have them arrange a meeting outside of class to comment constructively on each other’s drafts. The students do not need to be writing on the same topic.
Require consultations. Have students consult with someone in the Writing and Communication Center about their prewriting and/or drafts. The Center has yellow forms that we can give to students to inform you that such a visit was made.
Explore a subject in increasingly complex ways. A series of reading and writing assignments may be linked by the same subject matter or topic. Students encounter new perspectives and competing ideas with each new reading, and thus must evaluate and balance various views and adopt a position that considers the various points of view.
Change modes of discourse. In this approach, students’ assignments move from less complex to more complex modes of discourse (e.g., from expressive to analytic to argumentative; or from lab report to position paper to research article).
Change audiences. In this approach, students create drafts for different audiences, moving from personal to public (e.g., from self-reflection to an audience of peers to an audience of specialists). Each change would require different tasks and more extensive knowledge.
Change perspective through time. In this approach, students might write a statement of their understanding of a subject or issue at the beginning of a course and then return at the end of the semester to write an analysis of that original stance in the light of the experiences and knowledge gained in the course.
Use a natural sequence. A different approach to sequencing is to create a series of assignments culminating in a final writing project. In scientific and technical writing, for example, students could write a proposal requesting approval of a particular topic. The next assignment might be a progress report (or a series of progress reports), and the final assignment could be the report or document itself. For humanities and social science courses, students might write a proposal requesting approval of a particular topic, then hand in an annotated bibliography, and then a draft, and then the final version of the paper.
Have students submit sections. A variation of the previous approach is to have students submit various sections of their final document throughout the semester (e.g., their bibliography, review of the literature, methods section).
In addition to the standard essay and report formats, several other formats exist that might give students a different slant on the course material or allow them to use slightly different writing skills. Here are some suggestions:
Journals. Journals have become a popular format in recent years for courses that require some writing. In-class journal entries can spark discussions and reveal gaps in students’ understanding of the material. Having students write an in-class entry summarizing the material covered that day can aid the learning process and also reveal concepts that require more elaboration. Out-of-class entries involve short summaries or analyses of texts, or are a testing ground for ideas for student papers and reports. Although journals may seem to add a huge burden for instructors to correct, in fact many instructors either spot-check journals (looking at a few particular key entries) or grade them based on the number of entries completed. Journals are usually not graded for their prose style. STELLAR forums work well for out-of-class entries.
Letters. Students can define and defend a position on an issue in a letter written to someone in authority. They can also explain a concept or a process to someone in need of that particular information. They can write a letter to a friend explaining their concerns about an upcoming paper assignment or explaining their ideas for an upcoming paper assignment. If you wish to add a creative element to the writing assignment, you might have students adopt the persona of an important person discussed in your course (e.g., an historical figure) and write a letter explaining his/her actions, process, or theory to an interested person (e.g., “pretend that you are John Wilkes Booth and write a letter to the Congress justifying your assassination of Abraham Lincoln,” or “pretend you are Henry VIII writing to Thomas More explaining your break from the Catholic Church”).
Editorials . Students can define and defend a position on a controversial issue in the format of an editorial for the campus or local newspaper or for a national journal.
Cases . Students might create a case study particular to the course’s subject matter.
Position Papers . Students can define and defend a position, perhaps as a preliminary step in the creation of a formal research paper or essay.
Imitation of a Text . Students can create a new document “in the style of” a particular writer (e.g., “Create a government document the way Woody Allen might write it” or “Write your own ‘Modest Proposal’ about a modern issue”).
Instruction Manuals . Students write a step-by-step explanation of a process.
Dialogues . Students create a dialogue between two major figures studied in which they not only reveal those people’s theories or thoughts but also explore areas of possible disagreement (e.g., “Write a dialogue between Claude Monet and Jackson Pollock about the nature and uses of art”).
Collaborative projects . Students work together to create such works as reports, questions, and critiques.

Understanding the Assignment: Writing
- The Tension
- The Question
Overview of understanding the assignment
So you have been given an essay title: now what? Many writers move straight from reading the assignment prompt to paddling around in a swimming pool of bewildered dread. If that's you, please hop out of the dread-pool and inhale. It's going to be okay!
Getting to grips with the expectations for an assignment can take a lot of back-and-forth: read the prompt or title; jot down some ideas; take a walk; revisit the prompt to highlight key phrases; read a couple journal articles; and so on. Please don't expect to read the essay title and immediately sit down to write a focused rough draft. That's not how writing works.
That said, there are organised approaches you can deploy when you don't get what you're supposed to do. Stick with this guide to discover quick activities that will help you lay a productive foundation.
Guide contents
The tabs of this guide will support you in unpicking assignment prompts and learning what to do with them. The sections are organised as follows:
- The Verb - Begin breaking down the essay title, and get to grips with what you are actually meant to do .
- The Tension - Identify the zone of uncertainty where ideas start to take shape.
- The Question - Use question-based tactics to begin moving from essay title to essay plan.
- The Scope - Learn why instructors love to assign essay titles that feel totally mismatched to the word count limits, and how to navigate this.
What's the verb?
Highlighting key words in the essay title or assignment brief is a great first step in understanding the assignment. Among those words, make sure you pay close attention to the verb – that is, the action word that indicates what you are expected to do . Consider this example:
" Critically evaluate whether the Magna Carta is still relevant today."
To evaluate , you reach a conclusion about a topic by considering evidence that supports different positions on, or perspectives about, that topic. The adverb critically emphasizes the need not only to explore a range of evidence, but to assess it in an argumentative (rather than simply descriptive) manner.
What if we slightly amend the verb? Consider this change:
" Critically discuss whether the Magna Carta is still relevant today."
Does changing the verb from evaluate to discuss meaningfully change your goal? To be honest, most instructors use these verbs interchangeably in essay briefs. For some, though, discuss would suggest greater emphasis on forging a dialogue between sources, demonstrating where perspectives align and where they diverge.
Importantly, the expectation to be critical exists with essay verbs like discuss, evaluate, analyse, examine , etc. even if the adverb critically isn’t used. Unless you are specifically asked to summarise or describe something in an objective way, criticality is key.
The likely suspects
Instructors describe assignment aims in any number of ways, but there tends to be shared language when it comes to the key verbs. Below, you will find a sampling of the most common "actions" to conduct as a writer, with explanations and tips to help you out.
Advise, suggest, recommend, propose
- With verbs like these, you need to use informed logic and relevant supporting evidence to put forward an approach, idea, solution, or similar. For example, you might propose a specific treatment protocol based on critically synthesizing a patient's case history, NHS guidelines, and evidence from medical journals. You might recommend a specific advertising approach based on a company's financial goals, their target consumers, and marketing research.
- When asked to suggest a path forward, don't sit on the fence : it would be unwise to list a variety of options without critically and clearly "backing" one of them. However, it does demonstrate good critical thought to address any shortcomings or risks in your proposal, and how these might be mitigated.
Analyse, examine
- Here, you are being asked to break something down and consider its parts . This requires close critical attention.
- Imagine your topic as a cube. Instead of standing back and saying, "That's a cube," you will take the cube into your hands and rotate it again and again, carefully investigating each of its facets.
- For example, to analyse a business model, you would break the model down into its parts (e.g. management, target clients, production, distribution, etc.) and "dig into" those. Depending on the scope of the assignment, you might need to further break down the parts you identify.
Assess, appraise, evaluate
- Here, you are being asked to reach conclusions about the validity, efficacy, reliability, impacts, etc. of something. That "something" could be a piece of academic literature (e.g. critical appraisals of medical studies). It might be a policy, law, or similar (e.g. assessment of a judicial change intended to reduce crime). Maybe it's a business campaign or financial restructure – many options exist!
- In any case, ensure you understand not only what you are meant to assess (the object), but how that object is best evaluated in your field (the approach/method). Are there industry standards that govern "success"? Do you need to use a particular appraisal tool that features set steps?
Compare, contrast
- C ompare suggests the need to find the similarities and differences between two things; contrast calls for you to compare two things with more attention paid to differences.
- Instructors will almost never ask you to compare/contrast in a merely descriptive way, so look for the next step: what are you expected to do with , or make of , the comparison(s)? For example, you might contrast two interpretations of a cultural artefact in order to analyse how and why the differences exist.
Defend, argue, make an argument
- These verbs call for you to back a stance or perspective . You should focus on making clear claims and offering solid academic evidence to support them.
- When you have to argue a point, don't forget to engage with counterarguments. Think of it this way: your instructor KNOWS that multiple perspectives exist, or they wouldn't have assigned the essay! Actively grappling with any counterarguments (and conceding minor points as needed) boosts the sense that a) you are trustworthy, and b) you conducted balanced research.
Discuss, explore
- These verbs are worryingly vague, but don't fret. Discuss and explore imply that you should consider the topic from more than one angle, using academic literature to capture multiple perspectives.
- Hint: if you pretend the assignment says analyse , instead, this tends to produce what the instructor was hoping for.
Outline, delineate
- The goal with these verbs is to identify the main beats of something. For example, if you are asked to "outline the political strategy used by Politician ABC in Election XYZ," make sure you communicate the primary components or elements of the overall strategy. Imagine boiling the whole strategy down into a TL;DR version .
- As with compare/contrast, you should look out for an additional step or expectation that takes the assignment from descriptive to critical . For example, you might have to delineate a diagnostic procedure in order to critically reflect on its relevance to your nursing practice.
Reflect, write a critical reflection/account
- The assignment verbs can get redundant, but reflect is its own beast. Unlike most essays, reflective assignments prioritise your own relevant experience . Project work, for example, may culminate in a reflective component (i.e., reflecting on how a business presentation went; reflecting on the process of creating a video game).
- Although reflection centres something you completed or did, avoid relying on biased feelings and personal opinion: this is still academic writing!
- Think of it as a reflective analysis . Break the subject down into parts: namely, decisions you made along the way, why you made them, their effects (good, bad, or neutral), and what you learned . Justify the "why" with evidence relevant to your field. In nursing, tying your actions to best practices from NHS guidelines would make sense. In a creative writing module, you might cite craft manuals when discussing your approach to backstory and dialogue.
Synthesize, "use a range of literature to..."
- To synthesize means to create a new thing by combining parts of other things. For example, you are synthesizing if you write a paragraph that defines "influencer" by weaving together how the concept has been defined in two academic articles, in a digital newspaper, and on social media platforms. Synthesis demonstrates your ability to draw relevant connections between multiple sources of information.
- Synthesis is the heart of academic writing . Odds are that you ought to be synthesizing ideas, facts, and data from different sources even if the assignment prompt doesn't use this term.
- As with compare/contrast and outline/delineate, look for additional cues on how to use your synthesis . Are you meant to synthesize in order to defend an argument, support a reflective account, etc.?
What's the tension?
With any essay title you receive, you'll notice that some tension or uncertainty exists at the heart of it. It would be rare (and pointless!) for an instructor to assign an essay title that has one clear answer. Consider this invented essay question:
"How many people own houseplants in the UK now compared to pre-COVID?"
This is a terrible essay title because it is flat. There is nothing to explore or think through critically: just the expectation to provide the pre-pandemic number, find the post-pandemic number, and...then what? There is no tension.
Now, consider this essay question:
“Analyse the rising popularity of houseplants that began in the UK during the pandemic.”
This is a better essay prompt because it leaves room for the writer to discover and develop an angle. The question itself begets more questions. For example, what factors (social, personal, economic, etc.) influenced this change? Did popularity shift across all demographics or just some (and which, and why)? In other words, this question reveals layers of uncertainty that you can dig into as a writer.
Let’s return to examine the tension in an earlier essay prompt:
“Critically evaluate whether the Magna Carta is still relevant today .”
The word still suggests potential change over time, and there we discover a tension between the past and present. The writer will need to closely consider if/how the Magna Carta (i.e., a legal document of the past ) translates or applies to contemporary society (i.e., the present ).
If you are still struggling to identify the tension in an essay title, turning it into a question can help. We'll explore that trick in the next tab of this guide.
Can you turn the statement into a question?
Instructors often use statements as essay titles. Keep the required title when you submit, of course, but as you plan your approach to the essay, it often helps to reformat the statement as a question for yourself. Returning to our now familiar example…
“Critically evaluate whether the Magna Carta is still relevant today.”
This could be posed in question form as the following:
“ Is the Magna Carta still relevant today?”
This slight change gives you something more tangible to focus on since, by nature, questions spark the mind to begin contemplating answers . You can also play with more specific variations of the questions you form to get your ideas flowing:
“Is the Magna Carta still relevant today, and if so, how ?”
" Which tenets of the Magna Carta are still relevant today? How can the relevance of those tenets be proven ?”
" What factors or qualities make the Magna Carta less relevant today?”
As you can see, framing and reframing such questions in new ways lays the groundwork for you to truly dig in and analyse the situation as a writer.
– Check out our Developing Research Questions guide for further guidance on developing effective questions.
What if it's already a question?
If the assignment prompt is already in question form, you can still build it out with relevant questions to help you think through your writing strategy and potential content. For example, let's say this is the essay question:
"How do a nurse's communication practices influence trust when treating gender-diverse patients?"
Try putting this central question at the centre of a mind map, then adding branches for questions that help you dig in. You can also use a bulleted list to try this out, as so:
- "What kinds of literature could I use to unpack and define this?"
- "And why is 'trust' imperative? What risks exist when trust is absent?"
- "And how might negative/damaging 'influence' arise?"
- "Do LGBTQ+ groups and medical literature define this differently?"
- "What could make 'communication practices' more inclusive of gender-diverse patients?"
Note that each grouping of questions expands on keywords from the original question. By interrogating the question itself with further questions, you can really get the ball rolling! This will help you develop an initial sense of the research you need to conduct and points that might be relevant to make.
Can you narrow the scope?
By design, most assignment titles give you a great deal of breadth or scope . The seeming bigness of an assignment can be daunting: you might panic and ask yourself, “How in the world am I supposed to discuss ALL OF THIS in just 2,000 words?!”
The short answer? You likely aren’t supposed to discuss all of it, so take a deep breath! When the essay title is broad, instructors generally expect you to narrow the scope of your response. This means you limit your evaluation in some manner, finding one “angle” of exploration amongst the many options that exist. Let's return to our old title friend:

Okay, the Magna Carta is a very long, significant document. So if you're responding to this title, your essay will lack depth and feel rushed if you try to evaluate whether EVERY aspect of the Magna Carta is relevant in EVERY way in EVERY place, today. Instead, you can narrow the scope by doing things like…
- Focusing on a specific clause or a couple related clauses of the Magna Carta (i.e., not the whole document);
- Limiting the evaluation of relevance to a specific legal area, such as criminal court or land rights (i.e., not the entirety of LAW).
The way you choose to narrow the scope will vary according to the essay and field. Analysing a situation through one theoretical lens might sufficiently limit the scope: for example, analysing a poem using ecocritical theory rather than analysing the poem "in general." In other cases, the narrowing might relate to the evidence bank you choose to use, the demographic/population discussed, a tool or model used, etc.
Once you have found your angle, remember to use your introduction to clearly communicate your focus and argument (see our Crafting the Introduction guide for tips on thesis statements, aim statements, and essay maps).

- Last Updated: Sep 2, 2024 9:49 AM
- URL: https://library.soton.ac.uk/understanding_assignments

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
This handout will help you unravel your assignment and begin to craft an effective response. Much of the following advice will involve translating typical assignment terms and practices into meaningful clues to the type of writing your instructor expects. See our short video for more tips.
This resource describes some steps you can take to better understand the requirements of your writing assignments. This resource works for either in-class, teacher-led discussion or for personal use.
Often, the handout or other written text explaining the assignment—what professors call the assignment prompt—will explain the purpose of the assignment, the required parameters (length, number and type of sources, referencing style, etc.), and the criteria for evaluation. Sometimes, though—especially when you are new to a field—you ...
Assignments are a common method of assessment at university and require careful planning and good quality research. Developing critical thinking and writing skills are also necessary to demonstrate your ability to understand and apply information about your topic.
If you choose the first three sources you find, you risk ending up with a paper that strings together unrelated ideas, rather than one that truly integrates the most important ideas to make a compelling argument. Sometimes requirements laid out in an assignment will help you shape your paper.
Types of writing assignments vary from department to department, from course to course, and from instructor to instructor, so it is important to understand thoroughly the requirements of a particular assignment.
Assignments bridge the gap between theory and practical understanding. They require students to dive deeper into a subject, conduct research, and apply what they've learned. For example, consider historical accounts of World War II.
Understanding the assignment is critical before you begin writing the paper. The purpose, audience, and structure are usually included in the prompt and is your guide to completing the assignment correctly.
Research has shown that the more detailed a writing assignment is, the better the student papers are in response to that assignment. Instructors can often help students write more effective papers by giving students written instructions about that assignment.
Guide contents. The tabs of this guide will support you in unpicking assignment prompts and learning what to do with them. The sections are organised as follows: The Verb - Begin breaking down the essay title, and get to grips with what you are actually meant to do. The Tension - Identify the zone of uncertainty where ideas start to take shape.