

Why is biodiversity important?
Biodiversity is essential for the processes that support all life on Earth, including humans. Without a wide range of animals, plants and microorganisms, we cannot have the healthy ecosystems that we rely on to provide us with the air we breathe and the food we eat. And people also value nature of itself.
Some aspects of biodiversity are instinctively widely valued by people but the more we study biodiversity the more we see that all of it is important – even bugs and bacteria that we can’t see or may not like the look of. There are lots of ways that humans depend upon biodiversity and it is vital for us to conserve it. Pollinators such as birds, bees and other insects are estimated to be responsible for a third of the world’s crop production. Without pollinators we would not have apples, cherries, blueberries, almonds and many other foods we eat. Agriculture is also reliant upon invertebrates – they help to maintain the health of the soil crops grow in. Soil is teeming with microbes that are vital for liberating nutrients that plants need to grow, which are then also passed to us when we eat them. Life from the oceans provides the main source of animal protein for many people.
Trees, bushes and wetlands and wild grasslands naturally slow down water and help soil to absorb rainfall. When they are removed it can increase flooding. Trees and other plants clean the air we breathe and help us tackle the global challenge of climate change by absorbing carbon dioxide. Coral reefs and mangrove forests act as natural defences protecting coastlines from waves and storms.
Many of our medicines, along with other complex chemicals that we use in our daily lives such as latex and rubber, also originate from plants. Spending time in nature is increasingly understood to lead to improvements in people’s physical and mental health. Simply having green spaces and trees in cities has been shown to decrease hospital admissions, reduce stress and lower blood pressure.
Further reading
Plural valuation of nature matters for environmental sustainability and justice by Berta Martin-Lopez, Social-Ecological Systems Institute, Faculty of Sustainability, Leuphana University of Lüneburg, Germany
Climate change and biodiversity
Human activities are changing the climate. Science can help us understand what we are doing to habitats and the climate, but also find solutions.
Email updates
We promote excellence in science so that, together, we can benefit humanity and tackle the biggest challenges of our time.
Subscribe to our newsletters to be updated with the latest news on innovation, events, articles and reports.
What subscription are you interested in receiving? (Choose at least one subject)
- Skip to Page Content
- Skip to Navigation
- Skip to Search
- Skip to Footer
- COVID-19 Health and Safety
- Admissions and Ticketing
- Temporary Hall Closures
- Accessibility
- Field Trips
- Adult Group Visits
- Guided Tours
- Transportation
- Davis Family Butterfly Vivarium
- Invisible Worlds: Immersive Experience
- The Secret World of Elephants
- Turtle Odyssey
- Worlds Beyond Earth: Space Show
- Extinct and Endangered: Insects in Peril
- Grounded by Our Roots
- Ice Cold: An Exhibition of Hip-Hop Jewelry
- Opulent Oceans
- What's in a Name?
- Children & Family Programs
- Teen Programs
- Higher Education
- Adult Programs
- Educator Programs
- Evaluation, Research, & Policy
- Master of Arts in Teaching
- Online Courses for Educators
- Urban Advantage
- Climate Week NYC
- Viruses, Vaccines, and COVID-19
- The Science of COVID-19
- OLogy: The Science Website for Kids
- News & Blogs
- Science Topics
- Margaret Mead Festival
- Origami at the Museum
- Astrophysics
- Earth and Planetary Sciences
- Herpetology
- Ichthyology
- Ornithology
- Richard Gilder Graduate School
- Hayden Planetarium
- Center for Biodiversity and Conservation
- Institute for Comparative Genomics
- Southwestern Research Station
- Research Library
- Darwin Manuscripts Project
- Microscopy and Imaging Facility
- Science Conservation
- Computational Sciences
- Staff Directory
- Scientific Publications
- Ways to Donate
- Membership FAQ
- Benefit Events
- Corporate Support
- Planned Giving
- In memoriam: Dr. Eleanor Sterling
What Is Biodiversity?
- Podcasts and Video
- Machine Learning for Conservation
- DotDotGoose
- Conservation Biogeography
- Evidence-informed Conservation
- Integrating Biocultural Knowledge into American Samoa Mangrove Restoration and Conservation
- Biocultural Approaches to Wine Production in France
- Implementing Culturally Attuned Monitoring and Reporting Indicators
- Supporting Resilient Biocultural Land- and Seascapes in the Solomon Islands
- Community Conservation Areas
- Understanding Drivers of Wildlife Trade in Vietnam
- Past Projects
- Mangrove Ecology and Restoration in American Samoa
- Developing a Regional Conservation Strategy for Flamingos in the Americas
- Impact of Human Activity on Black Bear Habitats in the Western Great Basin
- Ecology, Evolution, and Conservation of Primates in Southeast Asia
- Understanding the Role of Palmyra Atoll for Sea Turtles in the Pacific
- Monitoring Landscapes for Conservation Planning
- Building Conservation Capacity in Vietnam
- Advancing Conservation Education
- Developing Global Capacity
- Inclusive Conservation Community Initiative (ICON)
- SCCS-NY Application & Registration
- SCCS-NY Plenaries
- SCCS-NY Code of Conduct
- SCCS-NY Workshops
- SCCS-NY 2023
- SCCS-NY 2022
- SCCS-NY 2021
- SCCS-NY 2020
- SCCS-NY 2019
- SCCS-NY 2018
- SCCS-NY 2017
- SCCS-NY 2016
- SCCS-NY 2015
- SCCS-NY 2014
- SCCS-NY 2013
- SCCS-NY 2012
- SCCS-NY 2010
- SCCS-NY 2011
- Conservation Teaching and Learning Studios
- 2019 Indicator Gathering
- Indicators of Well-being Webinar Series
- 2018 Action Group on Knowledge Systems and Indicators of Wellbeing
- Collaborative Networks
- 2015 GBIF Frontiers of Biodiversity Informatics and Modelling Species Distributions
- 2013 Milstein Science Symposium
- 2009 Exploring the Dynamic Relationship Between Health and the Environment
- 2008 Sustaining Cultural and Biological Diversity in a Rapidly Changing World: Lessons for Global Policy
- 1997-2007 Archive
- Open Source Software and Scripts
- Remote Sensing Interactives
- Lessons in Conservation: Volume 13
- Lessons in Conservation: Volume 12
- Lessons in Conservation: Volume 11
- Lessons in Conservation: Volume 10
- Lessons in Conservation: Volume 9
- Lessons in Conservation: Volume 8
- Lessons in Conservation: Volume 7
- Lessons in Conservation: Volume 6
- Lessons in Conservation: Volume 5
- Lessons in Conservation: Volume 4
- Lessons in Conservation: Volume 3
- Lessons in Conservation: Volume 2
- Lessons in Conservation: Volume 1
- Nature-Culture Indicators and Knowledge Systems Resource Directory
- Conservation Leadership Capacity Building: a Landscape Study
- Nature in Fragments: The Legacy of Sprawl
- Engaging and Learning for Conservation: Workshop on Public Participation in Scientific Research
- Fully-Protected Marine Reserves for the Future of Our Oceans
- Remote Sensing for Ecology and Conservation: A Handbook for Techniques
- For Educators
- Freshwater Mussels of the New York Metropolitan Region
- Remote Sensing Guides
- Learn More About Biodiversity
- Green Your Holidays
- Protecting Nature In Your Community
- Healthy Eating For You and the Planet: Avoiding Pesticides in Produce
- Healthy Eating for You and the Planet: Select Seasonally
- Living With Biodiversity Series
- Living With Nature: Cooking for Biodiversity
- CBC Progress Reports
- Staff Publications
- Exhibitions Created in Conjunction with the CBC

Biodiversity includes not only species we consider rare, threatened, or endangered but also every living thing—from humans to organisms we know little about, such as microbes, fungi, and invertebrates.
At the Center for Biodiversity and Conservation, we include humans and human cultural diversity as a part of biodiversity. We use the term “ biocultural ” to describe the dynamic, continually evolving and interconnected nature of people and place, and the notion that social and biological dimensions are interrelated. This concept recognizes that human use, knowledge, and beliefs influence, and in turn are influenced, by the ecological systems of which human communities are a part. This relationship makes all of biodiversity, including the species, land and seascapes, and the cultural links to the places where we live—be right where we are or in distant lands—important to our wellbeing as they all play a role in maintaining a diverse and healthy planet.
How do we study biodiversity?
Exploration and monitoring.
To study biodiversity, scientists conduct expeditions to survey and monitor species, habitats, and their interactions. On these expeditions, scientists ask questions about, measure, and collect data on various dimensions, such as population sizes and trends, distribution and habitat use, and impacts of management or other human activities. From primates in Southeast Asia to flamingos in the Andes, the CBC is engaged in numerous monitoring projects across the globe.
Tools of the trade
Biodiversity scientists use a variety of tools for collecting and analyzing data at various scales. Landscape monitoring techniques , for instance, use imaging systems such as remote sensing and drones to capture images across an area. Machine learning can be used to identify and count species or classify landscape types captured in these images or in video or audio clips. Mathematical modeling with software such as Maxent enables scientists to model species niches and distributions across these landscapes and predict how they will respond to climate change. New technological advances enhance our ability to monitor biodiversity and implement conservation and management activities.
Read more about the CBC’s Biodiversity Informatics Program to learn how information technology can be used to collect, organize, and analyze biodiversity data.
Synthesizing evidence
The vast knowledge collected through these various methods forms the evidence that decision-makers need to enact effective and sustainable conservation approaches.
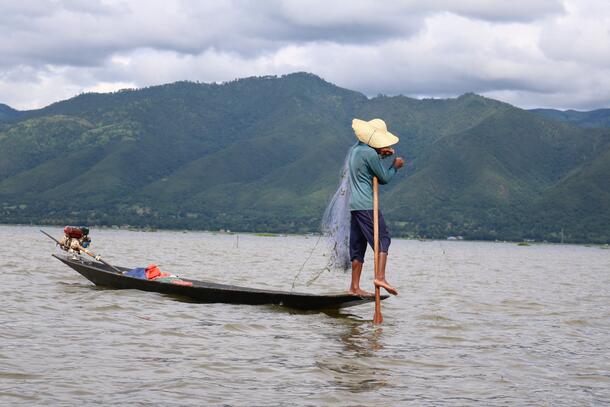

Learn more about our evidence-informed practice by reading about the CBC’s Evidence Initiative .
Building capacity
By strengthening the ability of community leaders, educators, managers, and other professionals to study biodiversity, we improve our ability to effectively manage and conserve the variety of life.
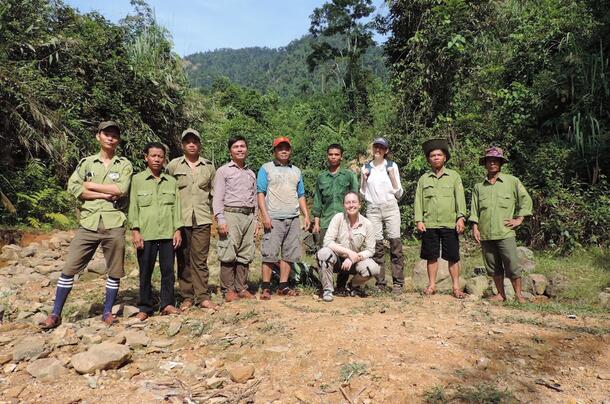

The CBC’s program in Southeast Asia develops capacity for conservation science through multidisciplinary research training of Vietnames graduate and undergraduate students, direct training of protected area staff in survey techniques, and co-leading training workshops on improving wildlife trade management.

The CBC’s Network of Conservation Educators and Practitioners (NCEP) improves training, teaching, and learning in biodiversity conservation with up-to-date, open-access resources for teaching and learning on a range of conservation topics, and by leading training and research initiatives to advance the field of conservation education.
Why is biodiversity important?
Biodiversity is important to most aspects of our lives. We value biodiversity for many reasons, some utilitarian, some intrinsic. This means we value biodiversity both for what it provides to humans, and for the value it has in its own right. Utilitarian values include the many basic needs humans obtain from biodiversity such as food, fuel, shelter, and medicine. Further, ecosystems provide crucial services such as pollination, seed dispersal, climate regulation, water purification, nutrient cycling, and control of agricultural pests. Biodiversity also holds value for potential benefits not yet recognized, such as new medicines and other possible unknown services. Biodiversity has cultural value to humans as well, for spiritual or religious reasons for instance. The intrinsic value of biodiversity refers to its inherent worth, which is independent of its value to anyone or anything else. This is more of a philosophical concept, which can be thought of as the inalienable right to exist. Finally, the value of biodiversity can also be understood through the lens of the relationships we form and strive for with each other and the rest of nature. We may value biodiversity because of how it shapes who we are, our relationships to each other, and social norms. These relational values are part of peoples’ individual or collective sense of wellbeing, responsibility for, and connection with the environment. The different values placed on biodiversity are important because they can influence the conservation decisions people make every day.
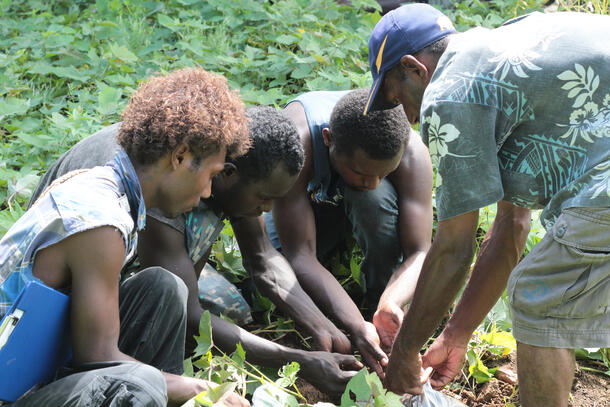

Developing community-based partnerships are crucial for supporting communities in the management and conservation of biodiversity that are vital to their wellbeing.
Threats to Biodiversity
Over the last century, humans have come to dominate the planet, causing rapid ecosystem change and massive loss of biodiversity across the planet. This has led some people to refer to the time we now live in as the “anthropocene.” While the Earth has always experienced changes and extinctions, today they are occurring at an unprecedented rate. Major direct threats to biodiversity include habitat loss and fragmentation, unsustainable resource use, invasive species, pollution, and global climate change. The underlying causes of biodiversity loss, such as a growing human population and overconsumption are often complex and stem from many interrelated factors.
The good news is that it is within our power to change our actions to help ensure the survival of species and the health and integrity of ecological systems. By understanding threats to biodiversity, and how they play out in context, we can be best prepared to manage conservation challenges. The conservation efforts of the last decades have made a significant difference in the state of biodiversity today. Over 100,000 protected areas—including national parks, wildlife refuges, game reserves, and marine protected areas, managed both by governments and local communities—provide habitat for wildlife, and help keep deforestation in check. Other types of conservation actions such as restoration, reintroduction, and the control of invasive species, have also had positive impacts on conservation efforts And these efforts have been bolstered by continuous efforts to improve environmental policies at local, regional, and global scales. It is vitally important that these policies recognize and center local values, needs, and realities to sustainably manage resources for healthy ecological as well as human communities. By acknowledging the interconnections and feedbacks between people and nature, assessing our existing knowledge, and applying evidence to our conservation decisions, we can develop effective approaches for conservation and sustainability for all life on Earth.
Learn more about what we do and what you can do to make a difference today.

Conservation News
News, views and stories from the front lines of conservation
All recent news
Why is biodiversity important.
This post was updated on May 17, 2021.
Humanity must stop the pace of wildlife extinctions — or face extinction itself, according to a growing body of research .
At a time when more than 1 million species are at risk of extinction — and the links between human health and the health of the planet are clear — the stakes have never been higher, experts say.
But how exactly is biodiversity so important to humanity? Why is biodiversity necessary for the stability of the planet? It may not be self-evident, so here are five reasons.
1. Wildlife support healthy ecosystems that we rely on.
Conservation researchers Paul R. and Anne Ehrlich posited in the 1980s that species are to ecosystems what rivets are to a plane’s wing. Losing one might not be a disaster, but each loss adds to the likelihood of a serious problem.
Whether in a village in the Amazon or a metropolis such as Beijing, humans depend on the services ecosystems provide, such as fresh water, pollination, soil fertility and stability, food and medicine. Ecosystems weakened by the loss of biodiversity are less likely to deliver those services, especially given the needs of an ever-growing human population.
One example of this is Kenya’s Lake Turkana — the world’s largest desert lake, a habitat for a variety of wildlife including birds, Nile crocodiles and hippos and a source of food and income for about 300,000 people. The lake is under heavy pressure because of overfishing, cyclical drought, changing rainfall patterns and the diversion of water by upstream developments, and these changes are leading to a loss of biodiversity, declines in fisheries’ yields and a reduced ability to support humans. Without conservation methods in place, this could be the fate of many more ecosystems.
2. Keeping biodiverse ecosystems intact helps humans stay healthy.
Research indicates that there is a close link between disease outbreaks and the degradation of nature.
Seventy percent of emerging viral diseases have spread from animals to humans. As the global wildlife trade continues and development projects expand deeper into tropical forests, humans are increasing their exposure to wild animals — and the diseases they may carry. For example, the COVID-19 pandemic can likely be sourced to a wild animal and fish market in Wuhan, China. This shows that we must take care of nature to take care of ourselves.
- Read more: Poaching, deforestation reportedly on the rise since COVID-19 lockdowns
Deforestation is also accelerating climate breakdown , which in turn may boost the spread of disease by allowing disease carriers like mosquitoes to extend their geographic ranges and infect new populations of humans.
With COVID-19, we’ve seen the damage that diseases can do not only to human health, but also to the global economy. By protecting biodiversity in Earth’s ecosystems, countries could save lives and money, while helping to prevent future pandemics.
3. Biodiversity is an essential part of the solution to climate change.
In a landmark study published in 2017, a group of researchers led by Bronson Griscom, who researches natural climate solutions at Conservation International, discovered that nature can deliver at least 30 percent of the emissions reductions needed by 2030 to prevent climate catastrophe. Protecting biodiversity plays a crucial part in achieving these emissions reductions.
The destruction of forest ecosystems is responsible for 11 percent of all global greenhouse gas emissions caused by humans, so conserving forests would stop the release of these gases into the atmosphere. Trees and plants also store carbon in their tissue, making it even more necessary to protect them.
Some ecosystems, such as mangroves, are particularly good at storing carbon and keeping it out of the atmosphere — where it contributes to climate change. Forests and wetland ecosystems provide crucial buffers to extreme storms and flooding related to climate change. These ecosystems are complex, which means they function best, and are more resilient to the effects of climate change, when all the pieces of the ecosystem are in place — meaning the biodiversity is intact.
“For a relatively small investment, high-biodiversity forests and other ecosystems can be conserved and restored as a powerful means to rein in climate change while also helping communities cope with associated storms, flooding and other impacts,” Langrand said.
4. Biodiversity is good for the economy.
At least 40 percent of the world’s economy and 80 percent of the needs of the poor are derived from biological resources.
Altogether, the food, commercial forestry and ecotourism industries could lose US$ 338 billion per year if the loss of biodiversity continues at its current pace. Around 75 percent of global food crops rely on animals and insects such as bees to pollinate them, but many of these pollinator populations are in decline — which could put more than US$ 235 billion of agricultural products at risk.
Meanwhile The Economics of Ecosystems and Biodiversity (TEEB) initiative estimates that global sustainable business opportunities from investing in natural resources could be worth US$ 2 to 6 trillion by 2050 .
Millions of people also depend on nature and species for their day-to-day livelihoods. This is particularly true for struggling communities in developing countries, who often turn to high-biodiversity ecosystems as their source of food, fuel, medicines and other products made from natural materials for their own use and as sources of income. Nature-related tourism is also a significant income generator for many people as well.
5. Biodiversity is an integral part of culture and identity.
Species are frequently integral to religious, cultural and national identities. All major religions include elements of nature and 231 species are formally used as national symbols in 142 countries. Unfortunately, more than one-third of those species are threatened, but the bald eagle and American bison are examples of conservation successes because of their role as national symbols. Ecosystems such as parks and other protected areas also provide recreation and a knowledge resource for visitors, and biodiversity is a frequent source of inspiration for artists and designers.
Julie Shaw is director of communications for the Critical Ecosystem Partnership Fund. CEPF is a joint initiative of l’Agence Française de Développement, Conservation International, the European Union, the Global Environment Facility, the Government of Japan and the World Bank.
Further Reading:
- Without traditional knowledge, there is no climate change solution
- Protections for African wildlife face growing threat: a lack of money
- We can limit global warming to 1.5 degrees — with nature’s help

45,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today
Meet top uk universities from the comfort of your home, here’s your new year gift, one app for all your, study abroad needs, start your journey, track your progress, grow with the community and so much more.

Verification Code
An OTP has been sent to your registered mobile no. Please verify

Thanks for your comment !
Our team will review it before it's shown to our readers.

- School Education /
Essay on Biodiversity in 500 Words for Students

- Updated on
- Dec 7, 2023

Essay on Biodiversity: Biodiversity refers to the variety of animals and plants in the world or a specific area. Even in today’s modern world where so many technological advances have taken place, we still rely on our natural environment and resources to survive, A healthy and vibrant ecosystem is not disturbed by human activities. We humans are the largest consumers of natural resources, and you know what? We are also a real threat to the natural environment? Biodiversity is not just about a variety of animal and plant species, but, also offers us water, climate, disease control, nutrition cycle, oxygen release, etc. According to one report released by the United Nations, around 10 lakh plant and animal species are on the verge of extinction. The worst thing is that this number is almost at a doubling rate.
Also Read: Essay on 5g Technology
Check out all the latest updates on all board exams 2024
Why is Biodiversity Important?
Biodiversity supports all life forms on earth. To understand the importance of biodiversity, we don’t need to think or act like a biologist. All we need is a holistic understanding.
- Biodiversity promotes resilience and stability in our ecosystem. If there is any natural disturbance in the environment, a diverse ecosystem will be able to survive and recover better.
- Fields like agriculture, forestry, and medicine completely rely on biodiversity. We get genetic resources from biodiversity, which is essential for agriculture and medicine fields.
- A healthy biodiversity environment means healthy humans. The medicinal drugs we use are derived from plants, animals, and microorganisms.
- In many parts of the world, biodiversity is an integral part of cultural identity. Indigenous tribes are connected with their natural environment and species.
- Forest areas and oceans play an important role in regulating global temperature and storing carbon dioxide.
- Our environment is constantly changing and the species around it also need to adapt to for to survive. Therefore, genetic diversity within species is also important.
- Natural activities like soil formation, nutrient cycling, water purification, etc, are all dependent on biodiversity.
Also Read: NCERT Solutions Class 9 Natural Vegetation and Wildlife
What is Biodiversity Loss?
Biodiversity loss means the global extinction of various species, resulting in the loss of biological diversity. One of the main factors responsible for biodiversity loss is the conversion of natural habitats into agricultural and urban areas. Cutting down forests and using the land for commercial activities results in destroying the livelihood of all the species in the region. Other factors responsible for biodiversity loss are listed below.
- Overexploitation
- Climate change
- Global trade and transportation
- Emerging diseases
- Pollution
Also Read: Essay on Save Environment
What is Biodiversity Conservation?
Biodiversity conservation refers to the preservation of species, natural resources, and habitats from the rate of extinction. To achieve the goals of biodiversity conservation, effective management, and sustainable practices are required.
- Biodiversity conservation includes protected areas like biodiversity hotspots, national parks, and wildlife sanctuaries.
- One of the most effective ways to conserve biodiversity is rehabilitation and restoring degraded habitats is crucial.
- Promoting sustainable practices in agriculture, forestry, and other resource-dependent activities is essential for the conservation of biodiversity.
- Encouraging the participation of local and indigenous communities can be one solution to achieving the goals of biodiversity conservation. Indigenous and local knowledge can contribute to effective conservation strategies.
Also Read: Essay on Junk Food
Quotes on Biodiversity
Here are some popular quotes on biodiversity. Feel free to add them to your writing topics related to the natural environment.
- ‘Look closely at nature. Every species is a masterclass, exclusively adapted to the particular environment in which it has survived. Who are we to destroy or even diminish biodiversity?’ – E O Wilson
- ‘Biodiversity is our most valuable but least appreciated resource.’ – E O Wilson
- ‘Biodiversity is the greeted treasure we have. It’s diminishment is to be prevented at all cost.’ – Thomas Eisner
- ‘Animal protection is education to humanity.’ – Albert Schweitzer
- ‘Only beautiful animals or ugly people wear fur.’ – Unknown
- ‘Babies and animals are the mirrors of the nature.’ – Epicurus
Also Read: Essay on Globalization
Also Read: How to Prepare for UPSC in 6 Months?
Ans: Biodiversity refers to the variety of plants and animals in our natural environment or a particular region. Biodiversity supports all life forms on earth. To understand the importance of biodiversity, we don’t need to think or act like a biologist. All we need is a holistic understanding. Biodiversity promotes resilience and stability in our ecosystem. If there is any natural disturbance in the environment, a diverse ecosystem will be able to survive and recover better. Fields like agriculture, forestry, and medicine completely rely on biodiversity. We get genetic resources from biodiversity, which is essential for agriculture and medicine fields.
Ans: Biodiversity conservation refers to the preservation of species, natural resources, and habitats from the rate of extinction. To achieve the goals of biodiversity conservation, effective management, and sustainable practices are required.
Ans: Some of the popular biodiversity hotspots in India are the Himalayas, Indo-Burma, Western Ghats & Sundaland.
Related Articles
For more information on such interesting topics, visit our essay writing page and follow Leverage Edu .
Shiva Tyagi
With an experience of over a year, I've developed a passion for writing blogs on wide range of topics. I am mostly inspired from topics related to social and environmental fields, where you come up with a positive outcome.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Contact no. *

Connect With Us
45,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. take the first step today..

Resend OTP in

Need help with?
Study abroad.
UK, Canada, US & More
IELTS, GRE, GMAT & More
Scholarship, Loans & Forex
Country Preference
New Zealand
Which English test are you planning to take?
Which academic test are you planning to take.
Not Sure yet
When are you planning to take the exam?
Already booked my exam slot
Within 2 Months
Want to learn about the test
Which Degree do you wish to pursue?
When do you want to start studying abroad.
January 2024
September 2024
What is your budget to study abroad?

How would you describe this article ?
Please rate this article
We would like to hear more.
Have something on your mind?

Make your study abroad dream a reality in January 2022 with
India's Biggest Virtual University Fair

Essex Direct Admission Day
Why attend .

Don't Miss Out
- Skip to main content
- Skip to secondary menu
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
A Plus Topper
Improve your Grades
Conservation of Biodiversity Essay for Students and Children in English
February 13, 2024 by Prasanna
Conservation of Biodiversity Essay: Mother earth is the home for various species and a place where they can coexist. The term biodiversity is a combination of two words – biological and diversity. It means diverse living organisms simultaneously sustain themselves in an ecosystem. The ecosystem encompasses various communities of creatures, including forests, coral reefs, wildlife, microbes, etc. A surprising number of 8.7 million species inhabit the planet earth.
The existence of biodiversity is an essential element of the planet earth. Every organism is interdependent and interconnected with one another. Everything on this planet is in an intricate web. However, human’s exploitation of the resources is threatening the ecological balance of biodiversity. Thus, it becomes essential to conserve and support all the species.
You can read more Essay Writing about articles, events, people, sports, technology many more.
Long and Short Essays on Conservation of Biodiversity for Children and Kids in English
Given below are two essays in English for students and children about the topic of ‘Conservation of Biodiversity’ in both long and short form. The first essay of 400 to 500 words on ‘Conservation of Biodiversity’ is for students of class 7, 8, 9, and 10. Moreover, it is helpful for the aspirants of competitive exams. Furthermore, 150 – 200 word’s essay on ‘Conservation of Biodiversity ‘will help students and children in class 6 or below.
Long ‘Conservation of Biodiversity’ Essay in English for classes 7, 8, 9, and 10 and Competitive Exam Aspirants. Below we have given a long essay on ‘Conservation of Biodiversity’ of 400 to 500 words. The article on the ‘Conservation of Biodiversity’ topic is best for students of 7 to 10. Furthermore, competitive exam preparation will become easy if students refer to this article.
Long Conservation of Biodiversity Essay 500 words in English
Biodiversity is an amalgamation of two words – biological and diversity. Therefore, the definition of the term ‘biodiversity’ encompasses a large variety of living organisms coexisting in an ecosystem. Biodiversity ranges from the tiniest microbes to the largest mammal. It also includes several species of bacteria, plants, animals, and humans. The recent study discovered 8.7 million different species worldwide, out of which a normal man recognizes only 1.2 million species.
However, the existing biodiversity is at risk. Both natural and human-activities are contributing to degrading the ecosystem. The changing climate and infestation of alien species are threatening the current biodiversity. Furthermore, in the pursuit of modernization, urbanization, and aggressive ambitions, humans are exploiting the natural habitat. Several factors, such as habitat fragmentation, atmospheric pollution, over-consumption of the natural resources by the humans, etc. are putting additional pressure on the planet.
Over one million species are on the verge of extinction. Humans have altered the environment in the quest to dominate the planet. Thus, the vast wealth of the earth is gradually vanishing. There are such thirty or more spots on the planet where several species are under the threat of extinction. Scientists have termed these regions as biodiversity hotspots. These biodiversity hotspots are home to 60% of different kinds of species.
The need of the hour is to participate in conserving biodiversity. Another word for conservation is caring for the environment. The first step to prevent dwindling biodiversity is to protect the plants and animals in their natural habitat.
It would be possible to create a safe habitat for various species by putting an end to the fragmentation of land for selfish purposes. Several species are sensitive to pollution. For instance, salmons can only thrive in freshwater. The concentration of toxic chemicals in the stream may lead to a declining population of salmons. Furthermore, the burning of fossil fuels gives rise to carbon dioxide emission, which is harmful to some species. A large number of species become homeless as a result of deforestation. Moreover, deforestation also leads to climate change. It harms migrating species.
Native plants and animals survive when they interact with the environment freely. It would be best not to disturb them in their natural habitat. Thus, humans need to take responsibility for their actions, and consciously stop polluting the environment.
The government is preserving biodiversity by restoring the natural habitat and assigning protected areas. Furthermore, an initiative to safeguard the forest-dwelling animals, the government is prohibiting wildlife trading and poaching. The government will take further actions to mainstream biodiversity conservation. The government is working towards capping fisheries, mining, farming, concrete construction in green zone areas, etc. enabling multiple species to interact and interconnect freely.
Short Essay on Conservation of Biodiversity 200 words in English
Short Conservation of Biodiversity Essay in English for Classes 6 and Below
Below we have given a short essay on ‘Conservation of Biodiversity’ of 150 to 200 words. This short piece on the topic ‘Conservation of Biodiversity’ is perfect for all students of grade 6 and below. Biodiversity consists of all living organisms on the earth. It includes a variety of life forms, from plants, animals, bacteria, to fungi. However, in today’s time, the earth is losing flora and fauna as well as genetic diversity.
Owing to the dominating human species, several other species of plants and animals are becoming extinct at an alarming rate. Pollution, deforestation, global warming, over-exploitation of the ecosystem, and impulsive hunting of animals diminish the earth’s natural biodiversity.
Human beings are the greatest threat to biodiversity. Scientists have identified more than thirty regions in the world as global biodiversity hotspots. On the one hand, these areas have abundant resources. On the other hand, these are high-risk areas of endangered species. In ecosystems, every creature is interdependent and interconnected. Elimination of a single species can disrupt the entire food chain.
In the quest to conserve biodiversity, it is compelling to reduce carbon footprints. Afforestation, reusing, recycling, and reducing waste can contribute to protecting biodiversity from further harm. The creation of wildlife sanctuary and biodiversity reserves can aid in the natural restoration of biodiversity. Thus, for the survival of every species, including humans, we must conserve biodiversity. We should set an example to inspire the next generation to follow the same path.
10 lines on Conservation of Biodiversity Essay in English
Students who are preparing for competitive examinations or entrance examinations can use this piece on ‘Conservation of Biodiversity’ for reference. Moreover, children can take note of these points to help them deliver a speech on the stage. Children who are planning to participate in literary work or debate competition can also find it very useful.
- Biodiversity is a mixture of several species of plants, animals, and microbial organisms coexisting on the planet earth.
- The recent study reveals the existence of 8.7 million different species worldwide.
- Human activities worldwide are threatening biodiversity.
- Deforestation, burning of fossil fuels, an infestation of alien species, climate change, fragmentation of habitat are some of the reasons behind dwindling biodiversity.
- Scientists have identified more than thirty regions in the world as biodiversity hotspots.
- We should participate in conserving biodiversity.
- We should not disturb the native plants and animals so they can live freely in their natural habitat.
- Land fragmentation and deforestation is making several species homeless.
- The government made law to preserve biodiversity and create wildlife sanctuaries.
- Humans also need to take responsibility for their actions, and consciously stop polluting the environment.
FAQ’s on Conservation of Biodiversity Essay
Question 1. Which factor is responsible for dwindling biodiversity?
Answer: Humans are responsible for dwindling biodiversity.
Question 2. What is the figure of different species that inhabit the planet earth?
Answer: Approximately 8.7 million different species inhabit the planet earth.
Question 3. What do you mean by biodiversity hotspots, and how many are there currently?
Answer: Biodiversity hotspots are biological-rich regions around the world that are threatened by the loss of inhabitants. Currently, there are over 30 biodiversity hotspots that the world recognizes.
Question 4. How can an ordinary person conserve biodiversity?
Answer: It is essential to cut down on exploiting the earth’s resources. Humans should restrict their activities that are harming the natural environment. We should make a collective effort to stabilize various species around the world.
- Picture Dictionary
- English Speech
- English Slogans
- English Letter Writing
- English Essay Writing
- English Textbook Answers
- Types of Certificates
- ICSE Solutions
- Selina ICSE Solutions
- ML Aggarwal Solutions
- HSSLive Plus One
- HSSLive Plus Two
- Kerala SSLC
- Distance Education
Essay on Biodiversity for Students and Children
500+ words essay on biodiversity.
Essay on Biodiversity – Biodiversity is the presence of different species of plants and animals on the earth. Moreover, it is also called biological diversity as it is related to the variety of species of flora and fauna. Biodiversity plays a major role in maintaining the balance of the earth.

Furthermore, everything depends upon the biological diversity of different plants and animals. But due to some reasons, biodiversity is decreasing day by day. If it does not stop then our earth could no longer be a place to live in. Therefore different measures help in increasing the biodiversity of the earth.
Methods to Increase Biodiversity
Building wildlife corridors- This means to build connections between wildlife spaces. In other words, many animals are incapable to cross huge barriers. Therefore they are no able to migrate the barrier and breed. So different engineering techniques can make wildlife corridors. Also, help animals to move from one place to the other.
Set up gardens- Setting up gardens in the houses is the easiest way to increase biodiversity. You can grow different types of plants and animals in the yard or even in the balcony. Further, this would help in increasing the amount of fresh air in the house.
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas
Protected areas- protected areas like wildlife sanctuaries and zoo conserve biodiversity. For instance, they maintain the natural habitat of plants and animals. Furthermore, these places are away from any human civilization. Therefore the ecosystem is well maintained which makes it a perfect breeding ground for flora and fauna. In our country, their various wildlife sanctuaries are build that is today spread over a vast area. Moreover, these areas are the only reason some of the animal species are not getting extinct. Therefore the protected areas should increase all over the globe.
Re-wilding – Re-wilding is necessary to avert the damage that has been taking place over centuries. Furthermore, the meaning of re-wilding is introducing the endangered species in the areas where it is extinct. Over the past years, by various human activities like hunting and cutting down of trees the biodiversity is in danger. So we must take the necessary steps to conserve our wildlife and different species of plants.
Importance of Biodiversity
Biodiversity is extremely important to maintain the ecological system. Most Noteworthy many species of plants and animals are dependent on each other.
Therefore if one of them gets extinct, the others will start getting endangered too. Moreover, it is important for humans too because our survival depends on plants and animals. For instance, the human needs food to survive which we get from plants. If the earth does not give us a favorable environment then we cannot grow any crops. As a result, it will no longer be possible for us to sustain on this planet.
Biodiversity in flora and fauna is the need of the hour. Therefore we should take various countermeasures to stop the reduction of endangering of species. Furthermore, pollution from vehicles should decrease. So that animals can get fresh air to breathe. Moreover, it will also decrease global warming which is the major cause of the extinction of the species.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Travelling Essay
- Picnic Essay
- Our Country Essay
- My Parents Essay
- Essay on Favourite Personality
- Essay on Memorable Day of My Life
- Essay on Knowledge is Power
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on My Favourite Season
- Essay on Types of Sports
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App


Essay on Biodiversity 1000+ Words
Biodiversity, short for biological diversity, is a remarkable tapestry of life that blankets our planet. It encompasses the variety of living organisms, ecosystems, and habitats that make Earth a vibrant and thriving place. In this essay, we will delve into the importance of biodiversity, the threats it faces, and why we should protect it.
The Marvelous World of Biodiversity
Imagine a world without colorful flowers, buzzing bees, towering trees, or majestic tigers. Biodiversity is what makes our world so diverse and beautiful. It includes everything from tiny microbes in the soil to the largest whales in the ocean. Earth’s rich biodiversity provides us with essential resources, from food to medicine, and enriches our lives in countless ways.
The Benefits of Biodiversity
Biodiversity is not just about pretty landscapes and exotic animals; it plays a crucial role in sustaining life on Earth. It helps maintain a stable and healthy environment. For instance, forests with diverse tree species are better at absorbing carbon dioxide, a greenhouse gas that contributes to climate change. Biodiversity also supports pollinators like bees and butterflies, which are essential for our food supply. The more diverse our ecosystems, the more resilient they are to threats like diseases and extreme weather.
Food and Medicine
Biodiversity is the foundation of our food system. Different plant and animal species provide us with a wide range of foods, from fruits and vegetables to grains and meats. Moreover, many of the medicines we rely on come from plants and animals. For example, the bark of the willow tree gave us aspirin, and the Madagascar periwinkle plant provides a lifesaving medicine for cancer patients. Protecting biodiversity ensures that we have a diverse and healthy diet and access to essential medicines.
Cultural and Recreational Value
Biodiversity isn’t just about science and survival; it also enriches our cultures and leisure activities. Many indigenous communities around the world have deep cultural connections to the land and its diverse species. Biodiversity inspires art, literature, and music. Imagine a world without the fascinating stories of animals like the African elephant or the enchanting songs of birds like the nightingale. Biodiversity enhances our quality of life in ways we might not even realize.
Threats to Biodiversity
Despite its immense value, biodiversity is under threat. Human activities, such as deforestation, pollution, overfishing, and habitat destruction, are driving many species to the brink of extinction. Climate change, fueled by the burning of fossil fuels, poses another significant threat. Rising temperatures can disrupt ecosystems and push species out of their habitats. These threats not only endanger the creatures themselves but also disrupt the delicate balance of our planet.
Conservation Efforts
The good news is that people around the world are working hard to protect biodiversity. Conservation organizations, scientists, and governments are implementing measures to safeguard endangered species and preserve critical habitats. National parks and wildlife reserves provide safe havens for countless plants and animals. Additionally, there are international agreements like the Convention on Biological Diversity aimed at preserving biodiversity on a global scale.
What You Can Do
You, as a young environmental advocate, can also play a crucial role in protecting biodiversity. You can start by learning more about the species and ecosystems in your area. Participate in local conservation efforts, like planting trees or cleaning up parks. Reduce your environmental footprint by conserving water, reducing waste, and using energy-efficient appliances. Spread the word about the importance of biodiversity to inspire others to take action.
Conclusion of Essay on Biodiversity
In conclusion, biodiversity is a precious gift that we must cherish and protect. It sustains life on Earth, provides us with essential resources, and enriches our cultures and enjoyment of the natural world. However, it faces serious threats from human activities and climate change. By understanding the importance of biodiversity and taking action to conserve it, we can ensure a healthier and more vibrant planet for future generations. Let us celebrate the wonders of biodiversity and work together to safeguard the incredible diversity of life on Earth.
Also Check: Simple Guide on How To Write An Essay

Biodiversity Explained: Facts, Myths, and the Race to Protect It

By MJ Altman on January 4, 2023

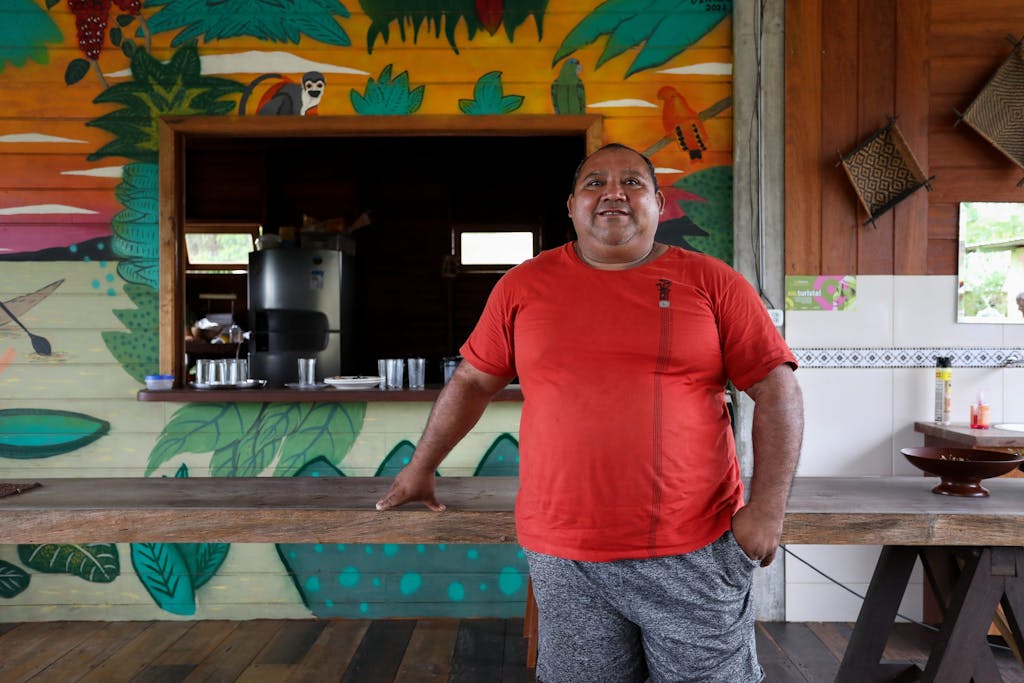
A baby sloth hangs in a tree at the Bosque da Ciência in Manaus, Brazil. PHOTO: Michael Dantas/United Nations Foundation
As ecosystems and habitats degrade and disappear worldwide, biodiversity — the interconnectedness of all forms of life on our planet — is in jeopardy. In light of a new global agreement to protect our lands, ocean, and waters, explore what biodiversity really means and what it will take to preserve life on Earth.
From microscopic fungi to mega forests, “biodiversity” is the collective term for the variety of life on Earth in all its forms. It is 4.5 billion years of evolution, embodied.
Biodiversity is responsible for our food, our soil, our water, our weather, even the air we breathe. Yet despite being a crucial foundation for our collective future, biodiversity is often lost amid conversations on climate change — until recently.
In December 2022, leaders from nearly 200 nations adopted a landmark UN agreement to reverse nature’s rapid decline before it’s too late. Known as the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework , it calls for protecting 30% of the planet’s land, ocean, and inland waters and includes 23 other targets to help restore and protect ecosystems and endangered species worldwide.
Here are 12 things you should know:
1. Biodiversity is more than just the total number of species on Earth.
“It is actually more complex than that,” Dr. Thomas Lovejoy, the late ecologist, told the United Nations Foundation in 2018. “It’s about the genetic diversity within species, the diversity of habitats, and the large biological units known as biomes.”
This includes the interactions that occur between species within ecosystems – primordial relationships that shape our environment in countless, often unseen ways.
“Without biological diversity, there is no other life on Earth — including our own,” he explained. “Even though we are often oblivious to it, this diversity of life is what provides clean water, oxygen, and all other things that end up being part of our diet, as well as clothing and shelter. It provides a lot of psychological benefits too, which are not much appreciated.”
2. We’re only just beginning to understand biodiversity’s influence and importance in our lives.
Earth’s many ecosystems rely on a delicate, complicated, and fascinating tangle of life that, in many ways, remains a mystery. In fact, the term “biological diversity” wasn’t introduced to the scientific community until 1980 in a research paper on species loss by Dr. Lovejoy. Scientists still haven’t identified all forms of life on the planet. New species are discovered every year.
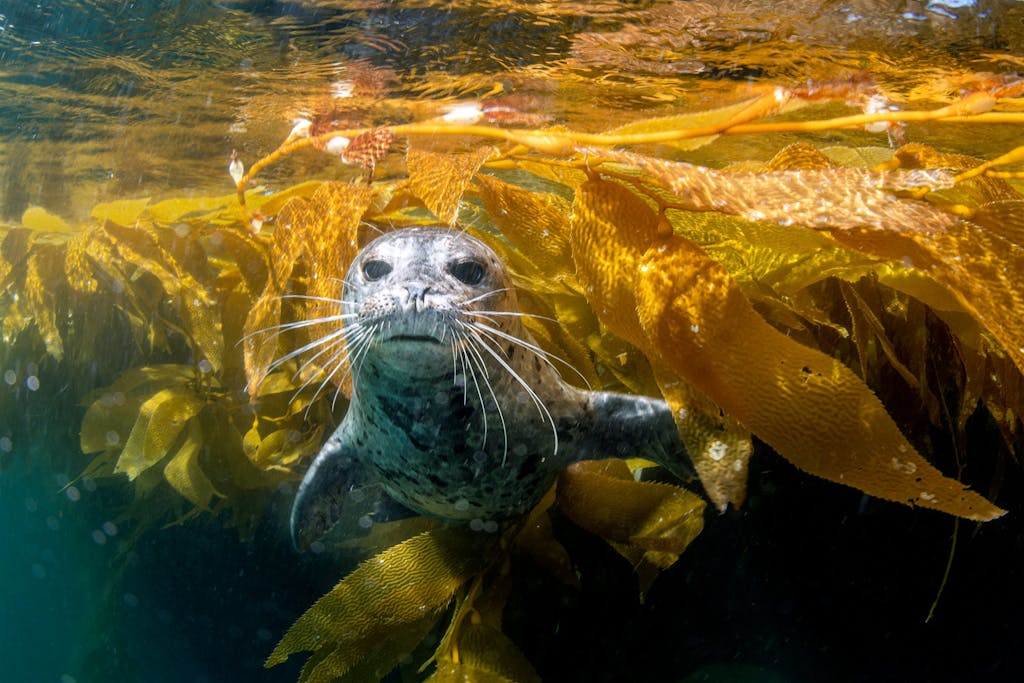

A harbor seal swims through kelp off the coast of Southern California's Channel Islands. Seals are among the thousands of species that rely on kelp forests for food and shelter. PHOTO: Shutterstock/Joe Belanger
Take kelp, for example. These undersea forests provide sustenance and shelter for marine species like chinook salmon, which, in turn, serve as a staple food for orcas. And kelp also absorb excess carbon dioxide, which can help mitigate climate change.
3. The planet’s biodiversity holds enormous, untapped potential for medical and scientific breakthroughs.
Lovejoy described each species on the planet as a unique set of solutions for a particular set of biological problems. “Whoever would have thought a bacterium from a Yellowstone hot spring would revolutionize forensic and diagnostic medicine, make the human genome project possible, and confer benefits in the trillion-dollar range?” he wrote as a Senior Fellow at the United Nations Foundation, citing a previously unknown and seemingly inconsequential microbe discovered in 1966 that revolutionized genetic testing and immunization development, including the COVID-19 vaccine.
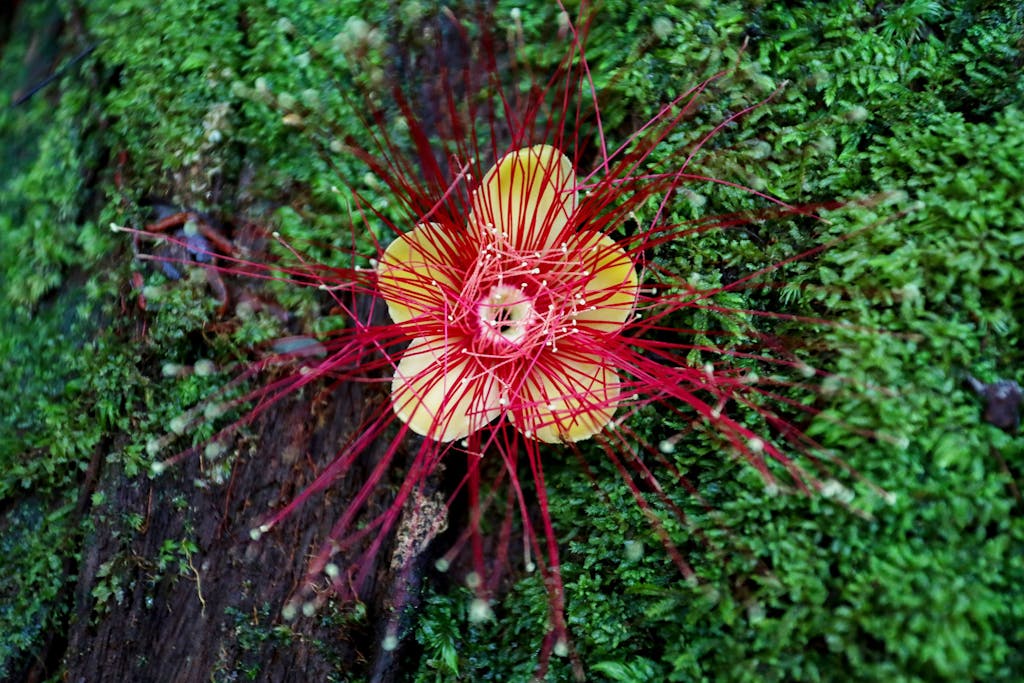

A flowering plant grows from a tree in the Amazon Rainforest, near the research station known as Camp 41 north of Manaus, Brazil. PHOTO: Michael Dantas/United Nations Foundation
Today, one-fourth of all modern medicines are derived from tropical plants, and 70% of all cancer drugs are natural or bio-inspired products. In the past decade, researchers in Nova Scotia found a soil fungus that can disarm antibiotic-resistant bacteria — a discovery that could transform the fields of medicine and agriculture. The possibilities for discovery and innovation are monumental.
4. Climate change and biodiversity are interconnected.
Climate change is causing biodiversity loss, and biodiversity loss is causing climate change. Here’s how: Destroying and degrading ecosystems releases more carbon dioxide into the atmosphere than burning fossil fuels.
Meanwhile, the consequences of burning fossil fuels — rising global temperatures, an increase in wildfires, and ocean acidification, to name a few — are threatening habitats and wildlife alike. In late 2019 and early 2020, for example, more than 60,000 koalas were killed by wildfires in Australia so massive that nearly 3 billion animals died or were displaced as a result. Earlier this year, the Australian government officially listed koalas as an endangered species.
At COP 27 last year, world leaders reached a historic agreement to create a “loss and damage” fund to support communities that are already feeling climate change’s disastrous impact, including biodiversity loss and its impact on livelihoods.
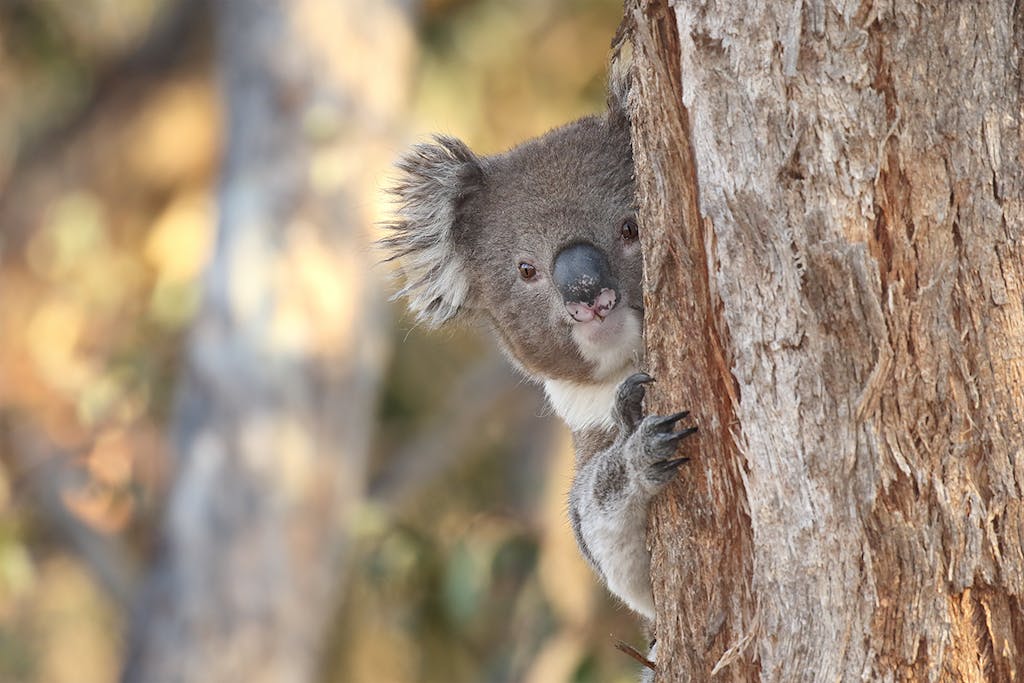

More than 60,000 koalas were killed by wildfires in Australia in late 2019 and early 2020. Increased wildfires and subsequent habitat loss are just one of the consequences of climate change. PHOTO: Patrick Kavanagh
5. Biodiversity can help us adapt to climate change.
The UN considers biodiversity our strongest natural defense against climate change. Land and ocean ecosystems currently absorb 60% of human-caused emissions , and they are the planet’s only way of storing massive amounts of carbon dioxide. Coastal wetlands, for example, protect against storm surges and flooding during extreme weather while also storing carbon dioxide and creating oxygen.
According to a joint estimate by the UN Development Programme and the Government of Papua New Guinea, every dollar invested in environmental protection generates more than $2,500 in so-called ecosystem services — water regulation, coastal protection, carbon storage, and other invisible functions that nature provides. It’s one of the reasons that Papua New Guinea launched the first-ever national, independent Biodiversity and Climate Fund to protect its status as one of just 17 “megadiverse” countries.
6. Less biodiversity means a higher risk of disease.
For decades, the scientific community has warned that biodiversity loss increases the spread of infectious disease . Why? Because extinction upsets the ecosystem in unpredictable ways, and the destruction of natural habitats increases interaction between humans and wildlife. Biodiversity essentially acts as a barrier between humans and animal-borne disease.
Species that tend to survive logging, farming, mining, wildlife trade and consumption, and other human activities behind widespread biodiversity loss are often “vectors of disease” like mice and mosquitoes, which host pathogens that are able to make the jump to humans. It’s one of the reasons why cases of Lyme disease in the northeast United States have spiked in recent decades: With fewer mammals to prey on, ticks are increasingly seeking out people. In fact, roughly 75% of emerging infectious diseases are zoonotic .
It’s also why researchers like Dr. Alessandra Nava and her team of virus hunters at Brazil’s Fiocruz Amazônia are tracking the spread of disease in bats, monkeys, and rodents in the world’s largest rainforest. Their goal is to stay a step ahead of future pandemics by better understanding the pathogens contained within the jungle’s creatures before they come in contact with humans — encounters that become more likely as the human footprint expands.
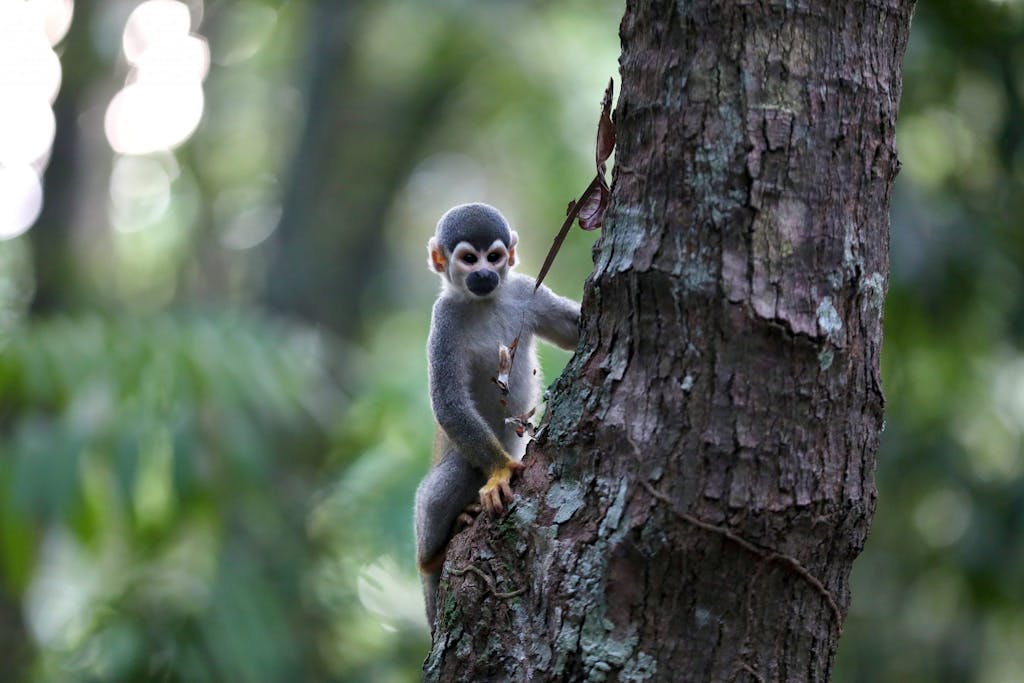

A golden-backed squirrel monkey at the Bosque da Ciência, a rainforest park in Manaus, Brazil. PHOTO: Michael Dantas/United Nations Foundation
7. Biodiversity on land depends on biodiversity in water.
Maintaining the ocean’s ecological balance is crucial for protecting biodiversity on land, as well as maintaining our ability to feed future generations. The ocean plays a vital role in regulating the planet’s weather and water and the air we breathe. It is also the planet’s largest source of protein , feeding more than 3 billion people every day who rely on fish as a staple food.
Yet the ocean remains a vastly unexplored ecological frontier. While scientists have identified 200,000 marine species , the actual number is estimated to be in the millions. Unsustainable fishing practices, pollution, climate change, and habitat destruction are threatening creatures that may vanish before we even knew they existed.
8. Our planet’s biodiversity is on the brink.
Some 1 million species are threatened with extinction right now. That’s more than any other time in history, and they’re disappearing at a rate that is 1,000 times the norm. The culprit is the way most humans consume, produce, travel, and live.
A 2019 UN report found that we have altered 75% of the planet’s terrestrial environment, 40% of its marine environment, and 50% of streams and rivers. Nearly three-fourths of our freshwater resources are devoted to crop or livestock production, which often means using pesticides, fertilizers, fuels, and antibiotics that pollute our rivers, streams, seas, and soil. Every day we are destroying habitats and degrading massive amounts of soil and water through industrial manufacturing and agriculture while jeopardizing precious natural resources that could be lost forever in our lifetime; in the past two decades, we’ve lost half of the planet’s coral reefs . Deforestation in the Amazon rainforest hit a record high last year; some 18% is gone already, with scientists warning that we’re approaching a tipping point toward potential collapse .
9. Sustainability is the only way forward.
Such irresponsible production and consumption of our natural resources come at a catastrophic cost. We are destroying our planet at an unprecedented rate and losing a vast number of plants, animals, insects, and marine life in the process — to the detriment of our own future. Humanity’s health and well-being are dependent on a biodiverse planet.
Fortunately, examples are emerging of a greener, more sustainable way of doing business. Circular economic models are becoming more common as companies realize the economic and environmental value of reducing, reusing, and recycling their supply chain. At the same time, more citizens are demanding sustainable sourcing and socially just labor practices from their consumer goods. In 2022, the founder of the outdoor retailer Patagonia announced plans to invest all of the company’s profits toward combating climate change . “If we have any hope of a thriving planet — much less a business — 50 years from now, it is going to take all of us doing what we can with the resources we have,” Yvon Chouinard wrote .

Along Brazil’s Rio Negro, fourth-generation logger Roberto Brito de Mendonça stands in the dining lodge of his community’s ecotourism lodge. He retired from the family business to help start the operation, which includes a newly built classroom named in honor of Dr. Lovejoy. PHOTO: Michael Dantas/United Nations Foundation
10. Indigenous communities are crucial.
For thousands of years, Indigenous communities have served as the planet’s most effective environmental stewards. Today, according to the UN, Indigenous people manage more than 20% of the planet’s land and 80% of its biodiversity. “For us, it is not a passion, or a job,” Hindou Ibrahim of the Mbororo tribe in Chad, an SDG (Sustainable Development Goal) Advocate and Indigenous rights activist, told the UN last year. “It is our way of living. And that’s what we have done for all generations.”
In 2015, the UN created the Local Communities and Indigenous Peoples Platform to ensure their formal participation in global negotiations on climate change.
11. Conservation is critical.
One of our most promising solutions is preservation. Restoring degraded ecosystems alone could provide up to one-third of the climate mitigation needed to keep the Earth from warming too far above pre-industrial levels. This means creating protected areas, curbing extractive capitalism, and restoring the planet’s enormous amount of degraded land.
People across the globe are leading efforts to do just that. One inspiring example is Rita Mesquita, who expanded the amount of protected rainforest in Brazil by 76% during her time in the country’s Ministry of the Environment. Today, she oversees programs that encourage residents and visitors alike in Manaus to interact with the surrounding Amazon rainforest.
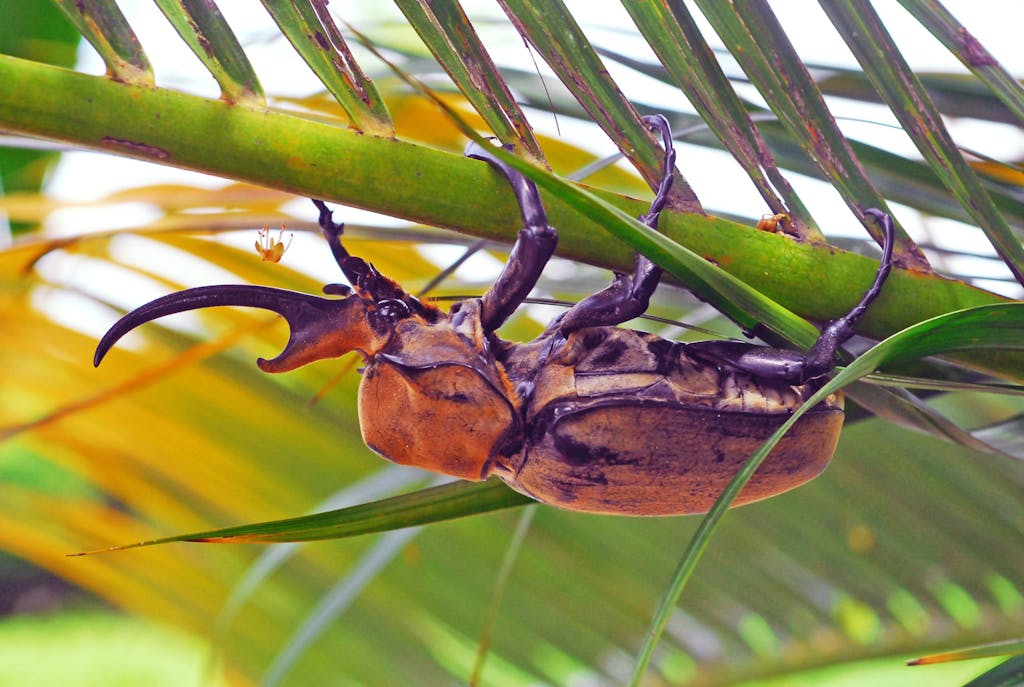

A Rhinoceros Beetle in Costa Rica’s National Park Tortuguero. The rhino beetle is one of the strongest insects in the world with relation to its body size, but because its tropical lowland habitat has been deforested and overcut, it is struggling to survive. PHOTO: GRID-Arendal/Peter Prokosch
12. We need cooperation — and revolution — at all levels.
We need partnerships among countries, communities, consumers, and corporations. And we’re seeing signs of progress every day. In fact, at COP 27, the Governments of Brazil, Democratic Republic of Congo, and Indonesia announced an alliance to protect their respective rainforests. Their historic agreement could pave the way for more multilateral action and impact. Coming just a month later, the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework represents an enormous and long-awaited step toward halting extinction rates that some scientists are calling an existential crisis akin to climate change.
A huge part of the solution to the biodiversity challenge will be transforming how we approach the natural world and our place within it. As Dr. Lovejoy told the UN Foundation in 2018 , “There needs to be a major shift in perception from thinking of nature as something with a fence around it in the middle of an expansive, human-dominated landscape … to thinking about embedding our aspirations in nature.”

Share on Mastodon
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
- Biodiversity Essay

Essay on Biodiversity
Biodiversity is a term made up of two words - Bio meaning Life, and Diversity meaning Variety. The term biodiversity refers to the variety of life on Earth. Plants, animals, microbes, and fungi are all examples of living species on the planet.
Types of Biodiversity
Genetic Biodiversity- Genetic diversity is the variation in genes and genotypes within a species, e.g., every human looks different from the other.
Species Biodiversity- Species Diversity is the variety of species within a habitat or a region. It is the biodiversity observed within a community.
Ecosystem Biodiversity- Ecological biodiversity refers to the variations in the plant and animal species living together and connected by food chains and food webs.
Importance of Biodiversity
Biodiversity is an integral part of cultural identity. Human cultures co-evolve with their environment and conservation is a priority for cultural identity. Biodiversity is used for Medicinal purposes.
Many plants and animals are used for medicinal purposes, like vitamins and painkillers. It contributes to climate stability. It helps in controlling the effects of climate change and managing greenhouse gases.
Biodiversity provides more food resources. It supplies many vital ecosystems, such as creating and maintaining soil quality, controlling pests, and providing habitat for wildlife. Biodiversity has a relationship with Industry. Biological sources provide many Industrial materials including rubber, cotton, leather, food, paper, etc.
There are many economic benefits of Biodiversity. Biodiversity also helps in controlling pollution. Biodiversity helps in forming a healthy ecosystem. Biodiversity also acts as a source of recreation. Along with other factors, biodiversity helps in improving soil quality.
Long Essay on Biodiversity
There are many economic benefits of Biodiversity. Biodiversity is a source of economic wealth for many regions of the world. Biodiversity facilitates Tourism and the Recreational industry. Natural Reserves and National Parks benefit a lot from it. Forest, wildlife, biosphere reserve, sanctuaries are prime spots for ecotourism, photography, painting, filmmaking, and literary works.
Biodiversity plays a vital role in the maintenance of the gaseous composition of the atmosphere, breakdown of waste material, and removal of pollutants.
Conservation of Biodiversity
Biodiversity is very important for human existence as all life forms are interlinked with each other and one single disturbance can have multiple effects on another. If we fail to protect our biodiversity, we can endanger our plants, animals, and environment, as well as human life. Therefore, it is necessary to protect our biodiversity at all costs. Conservation of Biodiversity can be done by educating the people to adopt more environment-friendly methods and activities and develop a more harmonious and empathetic nature towards the environment. The involvement and cooperation of communities are very important. The process of continuous protection of Biodiversity is the need of the hour.
The Government of India, along with 155 other nations, has signed the convention of Biodiversity at the Earth Summit to protect it. According to the summit, efforts should be made in preserving endangered species.
The preservation and proper management methods for wildlife should be made. Food crops, animals, and plants should be preserved. Usage of various food crops should be kept at a minimum. Every country must realize the importance of protecting the ecosystem and safeguarding the habitat.
The Government of India has launched the Wild Life Protection Act 1972 to protect, preserve, and propagate a variety of species. The Government has also launched a scheme to protect national parks and sanctuaries. There are 12 countries - Mexico, Columbia, Peru, Brasil, Ecuador, Democratic Republic of Congo, Madagascar, India, China, Malaysia, Indonesia, and Australia, in which Mega Diversity Centres are located. These countries are tropical and they possess a large number of the world’s species.
Various hotspots have been made to protect the vegetation. There are various methods for conserving biodiversity.
If biodiversity conservation is not done efficiently, each species would eventually become extinct due to a lack of appetite and hunger. This scenario has been a big issue for the last few decades, and many unique species have already become extinct. As a result of a lack of biodiversity protection, several species are still on the verge of extinction.

FAQs on Biodiversity Essay
1. What are the three types of Biodiversity?
Biodiversity is referred to as the variability that exists between the living organisms from different sources of nature, such as terrestrial, marine, and other aquatic ecosystems. Biodiversity has three levels, which are genetic, species, and ecosystem diversity. This is also considered as the type of ecosystem.
2. What is Biodiversity and why is it important?
Biodiversity is responsible for boosting the productivity of the ecosystems in which every species, no matter how small, has an important role to play. For example, a greater variety of crops can be obtained from a plant species which is in large numbers. If species diversity is in a greater amount, then it ensures natural sustainability for all life forms.
3. What is the connection between Biodiversity and the Food Chain?
If a single species goes extinct from the food chain, it will have an impact on the species that survive on it, putting them on the verge of extinction.
4. How are human beings affecting biodiversity?
Pollution- Pollution not only affects human beings, but also affects our flora and fauna, and we should control the pollution to conserve our biodiversity.
Population- Population control is a must to maintain a balance in our ecological system. Humans contribute to pollution by bursting crackers and by not following all the traffic rules.
5. How does Deforestation affect biodiversity?
Deforestation- Trees are very important for survival. They help in balancing out the ecosystem. Deforestation leads to the destruction of habitat. Deforestation should be stopped to protect our animals and plants. Deforestation not only removes vegetation that is important for removing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, but it also emits greenhouse gases.
Home — Essay Samples — Environment — Biodiversity — The Importance of Conserving Biodiversity
The Importance of Conserving Biodiversity
- Categories: Biodiversity Wildlife Conservation
About this sample

Words: 2133 |
11 min read
Published: Oct 31, 2018
Words: 2133 | Pages: 5 | 11 min read

Cite this Essay
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing style below:
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Prof. Kifaru
Verified writer
- Expert in: Environment

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
1 pages / 551 words
5 pages / 2102 words
2 pages / 923 words
1 pages / 696 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online

Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Biodiversity
Imagine walking through a forest, surrounded by an array of vibrant colors. The leaves of trees are changing, creating a breathtaking scene that seems almost magical. This is the beauty of a deciduous forest, a unique ecosystem [...]
Deforestation, the process of clearing forests for agriculture, urban development, and other purposes, has been a hotly debated topic for decades. While some argue that deforestation is essential for economic growth and human [...]
Nature has always been a source of inspiration and wonder for humanity. From the majestic mountains to the serene lakes, the beauty of nature has captivated our hearts and minds for centuries. The natural world provides us with [...]
In the intricate web of life that constitutes our planet's biodiversity, each species, regardless of its size or role, holds intrinsic value and contributes to the overall health of ecosystems. However, the alarming rate at [...]
Igea Lissoni's research paper titled "The Impact of Climate Change on Biodiversity: A Comprehensive Analysis" provides a deep analysis of the effects of climate change on biodiversity and highlights the urgent need for action to [...]
The issue of endangered animals is a pressing concern in today's world. As human activities continue to encroach upon natural habitats and disrupt ecosystems, numerous species are facing the threat of extinction. This essay aims [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Perspective
- Published: 13 May 2021
Biodiversity conservation as a promising frontier for behavioural science
- Kristian Steensen Nielsen ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-8395-4007 1 ,
- Theresa M. Marteau ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-3025-1129 2 ,
- Jan M. Bauer 3 ,
- Richard B. Bradbury ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-1245-2763 1 , 4 ,
- Steven Broad ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-1826-6400 5 ,
- Gayle Burgess 5 ,
- Mark Burgman 6 ,
- Hilary Byerly ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-7445-2099 7 ,
- Susan Clayton 8 ,
- Dulce Espelosin 9 ,
- Paul J. Ferraro ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-4777-5108 10 ,
- Brendan Fisher 11 , 12 ,
- Emma E. Garnett ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-1664-9029 1 , 13 ,
- Julia P. G. Jones 14 ,
- Mark Otieno 15 , 16 ,
- Stephen Polasky ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-4934-2434 17 , 18 ,
- Taylor H. Ricketts 11 , 12 ,
- Rosie Trevelyan 19 ,
- Sander van der Linden ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-0269-1744 20 ,
- Diogo Veríssimo 21 &
- Andrew Balmford 1
Nature Human Behaviour volume 5 , pages 550–556 ( 2021 ) Cite this article
25k Accesses
66 Citations
124 Altmetric
Metrics details
- Environmental studies
- Human behaviour
- Psychology and behaviour
- Sustainability
Human activities are degrading ecosystems worldwide, posing existential threats for biodiversity and humankind. Slowing and reversing this degradation will require profound and widespread changes to human behaviour. Behavioural scientists are therefore well placed to contribute intellectual leadership in this area. This Perspective aims to stimulate a marked increase in the amount and breadth of behavioural research addressing this challenge. First, we describe the importance of the biodiversity crisis for human and non-human prosperity and the central role of human behaviour in reversing this decline. Next, we discuss key gaps in our understanding of how to achieve behaviour change for biodiversity conservation and suggest how to identify key behaviour changes and actors capable of improving biodiversity outcomes. Finally, we outline the core components for building a robust evidence base and suggest priority research questions for behavioural scientists to explore in opening a new frontier of behavioural science for the benefit of nature and human wellbeing.
Similar content being viewed by others
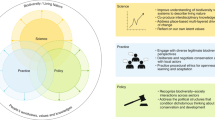
Biodiversity and the challenge of pluralism
The evolution and future of research on Nature-based Solutions to address societal challenges

Contributions of human cultures to biodiversity and ecosystem conservation
A recent global synthesis estimates that 75% of Earth’s land surface has been fundamentally altered by human activities, 66% of the ocean has been negatively affected, and 85% of wetland areas have been lost 1 . The combined effects of land-use change and habitat fragmentation, overharvesting, invasive species, pollution and climate change have resulted in an average decline in monitored populations of vertebrates of nearly 70% since 1970 and extinction rates that are orders of magnitude higher than the average seen in the geological record 2 , 3 , 4 . The threats to species are so severe that there is growing scientific consensus that we are entering the sixth mass extinction—the fifth being the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event 66 million years ago that eliminated all non-avian dinosaurs 5 .
The rapid degradation of ecosystems and associated loss of species is of profound importance for at least three reasons. First, there are powerful moral arguments that people should not cause the avoidable extinction of perhaps one million or more species 6 . It is beyond the scope of this paper to describe such arguments, but philosophers have discussed the ethics of biodiversity conservation 7 , 8 , 9 and social scientists have identified public support for assigning moral value to nature 10 , 11 , 12 . Second, human prosperity depends on wild habitats and species for a host of essential benefits, from climate regulation, biogeochemical and flood regulation to food production and the maintenance of mental wellbeing 13 , 14 . Their deterioration thus presents an existential challenge 1 . Third, evidence suggests that pandemics resulting from greater disease transmission between humans and wild animals 15 , 16 will become more regular features of the future unless our interactions with wild species changes fundamentally 15 , 17 , 18 , 19 , 20 . The COVID-19 pandemic—with devastating effects on societies and economies worldwide—most probably emerged from interactions between people and wild animals in China and illustrates the unforeseen consequences that can arise from human encroachment into wild habitats and from poorly regulated exploitation of biodiversity 17 , 21 .
Humanity’s impacts on biodiversity are the result of our actions, from unsustainable wildlife harvesting to the rising demand for environmentally damaging foods 1 , 22 , 23 , 24 , 25 . Importantly, these actions are undertaken by actors in myriad roles—including consumers, producers and policymakers—who directly or indirectly impact ecosystems and wild species 26 . For example, the rapid clearance of the Amazon is driven by the actions of consumers across the globe who eat beef, regional policymakers who undervalue forest retention, and ultimately local ranchers who are incentivised to convert forest to pasture 27 , 28 . Similarly, the illegal trade in wildlife (for example, rhino horn, pangolin scales, tiger bones and elephant ivory) involves suppliers who hunt the animals, intermediaries (and perhaps corrupt enforcement agents) who facilitate trade and transport the products to market, and domestic and international consumers 24 , 29 , 30 , 31 . The impacts of people’s behaviour on biodiversity are of course not only manifest in less developed countries. For example, the continued illegal persecution of birds of prey in UK uplands is the result of choices by some gamekeepers to shoot and poison raptors to limit their predation of red grouse, by some hunters to pay exceptionally high prices for large daily ‘bags’ of grouse, and by policymakers to resist attempts at tighter regulation of the shooting industry 32 .
Because human activities are responsible for driving ecosystem decline, reversing current trends will require profound and persistent changes to human behaviour across actors and scales 33 . Despite its critical importance, the science of behaviour change has not been a principal focus of research in conservation science and is rarely applied in practical efforts to address major threats to biodiversity (for example, habitat loss and degradation, overharvesting of resources and species, and invasive species) 33 , 34 , 35 , 36 , 37 (A.B. et al., manuscript in preparation). Conservation scientists (defined broadly to include researchers across the natural and social sciences seeking to understand and mitigate these threats) have generally been slow to incorporate evidence from behavioural science into their theories and interventions 33 , 36 , 38 , 39 , 40 , 41 . Conversely, biodiversity conservation has also not been a strong focus of study for behavioural scientists (defined broadly to include those engaged in the scientific study of behaviour across diverse disciplines, including psychology, sociology, economics, anthropology and political science). One exception is research on common-pool resource management and commons dilemmas, which has a long history tracing back to the 1970s 42 , 43 , 44 , 45 . This research tradition has tackled issues closely linked to biodiversity conservation and foreshadows many contemporary and interdisciplinary analyses. More recently, social-marketing techniques have been used to tackle a variety of biodiversity problems and their potential is increasingly recognised 46 , 47 , 48 , 49 , 50 . For example, a recent study in the Philippines, Indonesia and Brazil used locally tailored social-marketing campaigns to shift social norms and increase sustainable fishing among communities of small-scale fisheries 50 . But while the number of successful applications of behavioural science to biodiversity conservation is increasing, they remain rare and often suffer from methodological limitations 51 . The conservation evidence base is consequently patchy and generally poorly informed by behavioural science 36 , 52 .
Meanwhile, in other contexts, behavioural science has made substantial gains in understanding how to encourage prosocial behaviour, including actions that ultimately affect biodiversity outcomes. A growing body of research related to climate change suggests the importance of social norms, risk communication, emotion and choice architecture in changing behaviour 53 , 54 , 55 , 56 , 57 . Behavioural science has been incorporated into some public efforts to encourage sustainable land management in the United States and the European Union 58 , 59 , 60 , 61 , 62 . Nevertheless, there are still few applications of behavioural science to explicitly address the most important proximate causes of biodiversity loss. Behavioural insights from research related to climate change, land management, consumer behaviour, voting, collective action and programme enrolment can inform the multi-scale approach needed to deliver effective biodiversity conservation, but this research has not been systematically linked to address biodiversity conservation problems. Moreover, the literature is heavily focused on households and is not well-developed for other important actors 57 , 63 . We therefore see unrealised potential for behavioural science to address the escalating biodiversity crisis.
Increasing scientific engagement
Behavioural scientists might be motivated to become engaged in biodiversity conservation research for at least three reasons. First, biodiversity conservation is essential for the long-term prosperity of people and nature. Its particular characteristics (see below) mean that it would be unhelpful simply to adopt behaviour-change interventions found effective in other domains: indeed, these do not necessarily generalize to biodiversity conservation 52 , 64 . Instead, the field offers a new arena for exploring important research questions and for testing novel interventions. Behavioural science research that focuses specifically on biodiversity conservation can contribute to the mitigation of a global and existential threat.
Second, engaging in biodiversity conservation research offers behavioural scientists a chance to investigate theories and interventions in new contexts and populations 65 , 66 , 67 . A key requirement for increasing the generalizability of behavioural science is to ramp up research activities outside North America, Australia and Europe 68 , 69 . Due to the importance of the tropics for biodiversity, the focus of many conservation interventions is in Africa, Latin America and Asia, providing opportunities to test theory and interventions in contexts which are less ‘WEIRD’ (western, educated, industrialized, rich and democratic). A related challenge is the need to shift behaviours of many different kinds of actors. Behaviour-change interventions in other sectors have been criticised for being too narrowly focused on end-users 70 , 71 : Conservation problems provide opportunities for targeting the behaviours of a far broader array of stakeholders. Moreover, conserving biodiversity often requires coordinated action across local, national and global actors, heterogeneous cultures and divergent financial interests, with the benefits of conservation commonly accruing to geographically and psychologically distant communities and indeed non-human species.
Finally, conservation scientists and practitioners are keen to collaborate more with behavioural scientists 72 , 73 . An increasing number of conservation scientists and practitioners recognise the need for stronger integration with behavioural science in order to design interventions that are grounded in greater understanding of the social, motivational and contextual drivers of people’s actions 33 , 39 , 74 , 75 . Naturally, as with all interdisciplinary collaborations, these collaborations will have their challenges 75 . However, recent examples show that effective collaborations can produce novel and mutually beneficial research that suggests practical routes to achieving behaviour change for biodiversity conservation 50 , 64 , 76 , 77 , 78 .
The remainder of this Perspective seeks to encourage greater engagement of behavioural scientists in conservation-targeted research and practice. We first highlight the diversity of actors involved in threats to biodiversity and the scope of behaviour changes required. In doing so, we propose routes to identifying key behaviour changes and prioritising among them on the basis of their potential for improving biodiversity outcomes. We suggest research questions for better understanding how to influence different actors’ behaviours and for improving conservation interventions, and close by making recommendations for how to expand the conservation evidence base systematically.
Identifying key actors and behaviour changes
Threats to biodiversity are rarely caused by a single action of a single actor. Rather, they typically result from multiple behaviours by multiple actors over large spatial and temporal scales 36 , 79 . It can thus be very challenging to identify those behaviour changes with the greatest promise of being achieved and of positively impacting biodiversity. Doing so requires specifying conservation targets (e.g., particular populations or ecosystems), and then systematically considering the proximate causes and underlying drivers of threats to them, the actors involved (for example, producers and consumers), and the harmful behaviours performed by those actors 26 , 39 , 45 , 80 .
The proximate threats to wild species and the places they live can be categorised into four main groups: habitat loss and degradation, overharvesting, invasive species, and climate change and pollution 81 , 82 , 83 . These threats also interact, with species or ecosystems commonly impacted by multiple threats, sometimes with amplifying effects. For example, the spread of some invasive plants is thought to be exacerbated by elevated nitrogen deposition and atmospheric CO 2 concentrations 84 , 85 . Proximate threats are driven by broader societal processes, including rising demand for food and consumer goods, weak local, national and international institutions that struggle to ensure the protection of public goods (including against corrupt actors), population growth and the growing disconnect of people from nature due to increasing urbanization and indoor recreation 86 . Many of the interventions conservationists deploy to tackle proximate threats, such as removing invasive species, restoring wetlands or propagating threatened species in captivity, are not primarily about changing people’s behaviour (although even in these examples those carrying out the management actions must be trained and incentivised, and behaviours must change if these threats are not to recur). However, given the pervasive importance of human activities in conservation problems, many interventions do involve attempts to alter behaviour. If behavioural science is to improve the effectiveness of these efforts, an important first step is to identify the main actors responsible for a given threat and the changes in their behaviour that might be required to alleviate it.
One tool for mapping the actors and behaviours impacting a conservation target is to build a threat chain (A.B. et al., manuscript in preparation). This is a simplified summary of knowledge of the reasons for the unfavourable status of a species or ecosystem, from changes in ecological dynamics to the socioeconomic mechanisms thought to be responsible, and their underlying drivers. Once this putative causal chain has been constructed, the main actors in the chain can be identified, along with changes in their behaviour that might potentially reduce the particular threat. Where conservation targets are impacted by multiple threats this process can be repeated, with the likely impact of different behaviour changes compared across threats in order to identify the most promising interventions for delivering those changes.
Using Amazon deforestation (as an example of habitat loss) for illustration 27 , 28 (Fig. 1 , red boxes), the extirpation of forest-dependent species and ecosystem processes resulting from conversion to pasture has been caused (inter alia) by a combination of rising global demand for beef, poor pasture and livestock management, the absence of incentives for forest retention and the practice of establishing de facto land tenure via forest clearance. Underlying drivers include weak governance at multiple levels and rising per capita demand for beef among a growing population in Brazil and beyond. Potential behaviour changes that might be targeted to reduce deforestation (blue boxes) include increased enforcement of forest protection legislation by government agencies, improved pasture and stock management by ranchers, a reduction in per capita demand for beef among domestic and international consumers, and an accelerated decline in human population growth in high-consumption countries.
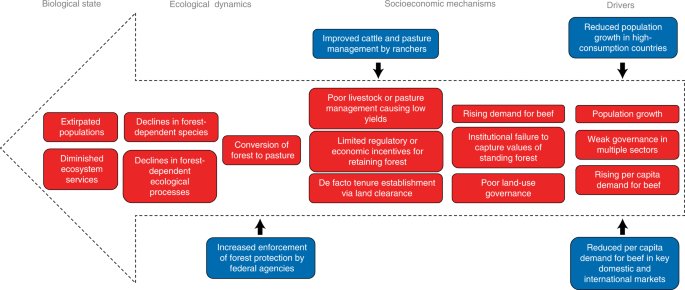
This example characterizes (in red boxes) the threat to the Amazon forest from conversion to cattle pasture. Potentially beneficial changes in the behaviours are in blue boxes. This threat chain addresses only one of several interacting threats impacting the conservation target. The threat chain model is adapted from Balmford et al. 26 .
As a heuristic, we conducted this threat-mapping exercise for 12 examples chosen to represent different threat processes and the diversity of ecological and socioeconomic contexts in which they arise (A.B. et al., manuscript in preparation). We identified nine main clusters of actors (rows in Fig. 2 ), classified by how their behaviour impacts conservation targets. Producers and extractors of natural resources, conservation managers and consumers are commonly identified as targets for behaviour-change interventions in conservation and other sectors. However, we also identified other actor groupings, including manufacturers and sellers, investors, policymakers, voters, communicators and lobbyists, all of whom may have considerable—usually indirect—influences on conservation outcomes, yet are commonly overlooked when it comes to behaviour-change interventions. Because our clusters of actors are operationally defined, they align well with the diversity of behaviour changes we identified (Fig. 2 , right column), including reducing consumers’ purchases of high-footprint items and directing investors’ investments towards less damaging production technologies. Our clusters can also be mapped onto more conventional organisational groups (such as citizens or businesses; Fig. 2 , ‘Actor—defined by group’ columns), but because such organizational groups impact conservation targets in heterogeneous ways, their correspondence with behaviour changes is much weaker than for our typology.
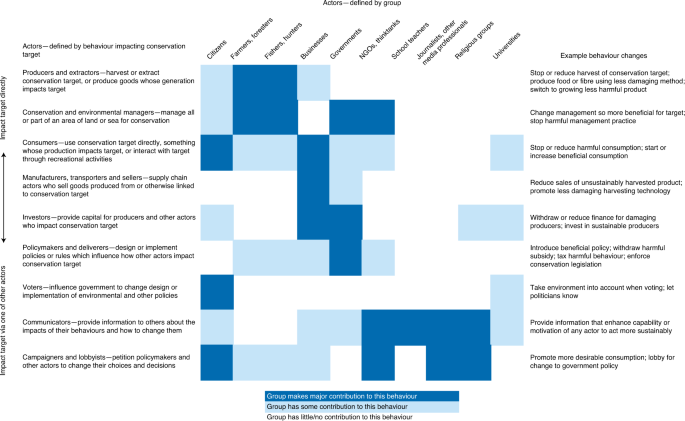
Actors classified according to their behavioural impacts on conservation targets (rows) and by their organizational affiliation. NGO, non-governmental organization.
Prioritising behaviour changes
After examining all major threats to a given conservation target and identifying promising behaviour changes involving specified actors, the next step is to prioritise behaviour changes and, in turn, the interventions potentially capable of achieving them. We suggest this should focus on two main characteristics that together determine the impact of behaviour-change interventions 57 , 87 . The first is the target behaviour’s potential, if changed, to improve the state of the conservation objective (by analogy with the climate change literature, its technical potential). In the Amazon example (Fig. 1 ), both enforcing forest protection laws and providing herd management support that is conditional on ranchers stopping clearance might be considered to have greater technical potential than slowing population growth in beef-consuming countries (which may have only limited effect if per capita demand continues to rise). Prioritising behaviours for research and intervention on the basis of their technical potential—considered an omission in behavioural science contributions to climate change mitigation 57 , 88 , 89 , 90 —ensures that resources and efforts are allocated toward the behaviours with the greatest potential to effectively mitigate biodiversity threats.
The second aspect to consider in prioritization is the behaviour’s plasticity, which refers to the degree to which a target behaviour can be changed by a specified intervention 57 . For example, to what extent can behaviour-change interventions increase the share of plant-based food in overseas or Brazilian diets, or improve the cattle and pasture management of Amazonian farmers? Due to the current paucity of conservation-focused behaviour-change interventions, good estimates of behavioural plasticity will often be lacking. Instead, it will often be necessary to use evidence from interventions targeting comparable behaviours relating to other actors, contexts or domains until more direct data become available 87 . Although considerations of technical potential and behavioural plasticity should guide the selection of behaviours to study and intervene against, we note that additional considerations may become pertinent when selecting interventions for implementation (for example, feasibility, stakeholder support and costs) 91 , 92 , 93 .
Given the range of actors involved in causing ecosystem change and the complexity of their behaviour, standalone behaviour-change interventions are unlikely to effectively mitigate a biodiversity threat (as illustrated in Fig. 1 ). Individual-level interventions—for example, targeting specific farmers, manufacturers, or investors—may well form an important part of the solution, but they will usually be insufficient on their own. For example, successfully incentivising ranchers in one Amazonian municipality to retain their remaining forests will be of little benefit to biodiversity if prevailing market failure or weak institutions continue to incentivise forest clearance elsewhere. Tackling more systemic drivers, such as environmentally damaging subsidy regimes, corporate interests, poor governance and persistent norms, also necessitates population-level interventions that can alter economic systems, institutional systems and physical infrastructure. Importantly, the intent here is not to undermine the legitimacy of individual-level interventions—quite the contrary. Systemic changes also cannot be achieved without individual-level behaviour changes and support 57 , 94 , 95 . Different levels of intervention must work in concert, which requires a holistic understanding of the determinants of human behaviour.
Building a robust evidence base
Generating evidence on behaviour-change interventions for biodiversity conservation demands a mix of methods, including experimental and observational studies using quantitative and qualitative techniques 96 , 97 , 98 . Critically, to build an evidence base, these studies must be based on mapping and synthesizing the existing literature 99 . They also need to be embedded in relevant conceptual or theoretical frameworks, coupled with a theory of change, and designed with the statistical power to answer the study questions. This might include, for example, taking a systems perspective 98 , as well as using a taxonomy or typology of interventions 100 , 101 .
Behavioural responses and the effectiveness of interventions are likely to vary between social and cultural contexts. Assessing the effect size of interventions in different settings will be key to building a robust evidence base that has global application. Improving the cross-cultural profile of behavioural science evidence is thus imperative, and particularly so for biodiversity conservation, where many problems are centred outside Europe and North America. Achieving this will, however, be challenging given that the research capacity in behavioural science remains low in high-income countries and even lower elsewhere. International partnerships will therefore be an important strand of building capacity across regions.
Emergent research questions
Given that behavioural science research into conservation-related problems is still in its infancy, many important questions remain unanswered. In this final section, we outline four higher-order questions that we believe could impact the effectiveness of interventions aimed at reducing people’s negative impacts on biodiversity, natural habitats and the services provided by ecosystems. While these questions can apply to prosocial behaviour more broadly, we believe that there is considerable merit in tackling them within the context of biodiversity conservation, in part through devising and testing novel interventions in the field. This will necessitate close collaboration between behavioural scientists and conservation scientists and practitioners.
The first research question deals with prioritization. As with climate change interventions, there is a clear need for a more systematic understanding of the technical potential of different behaviour changes: which ones, if delivered, would be most likely to reduce a threat and thereby enhance the status of the conservation target, taking into account other threats it faces 80 , 91 ? Given the focus of many recent environmental interventions on appealing, tractable but relatively low-impact behaviour changes (for example, eating more locally grown food or avoiding plastic drinking straws), such prioritization is badly needed 88 , 90 . One challenge in identifying priorities may be the complexity of conservation outcomes: estimating probable impacts of behaviour changes on highly interconnected ecosystems may be more difficult than impacts on greenhouse gas levels 80 , but we suggest that this is a surmountable problem. A further consideration here is how far a behaviour change addressing one conservation issue might reduce (or indeed increase) threats to other conservation targets 102 .
The remaining research questions are all aimed at improving our understanding of the plasticity of priority behaviours (that is, those with high technical potential to improve biodiversity outcomes 91 ). Our second suggested question is which interventions work best to alter priority behaviours, and how does this vary across contexts? One key aspect is exploring how the suitability of behaviour-change interventions varies with the level of deliberation and perceived importance of the decision being made. Consider contrasting interventions aimed at increasing how often consumers buy sustainably (rather than unsustainably) sourced fish. For someone making a weekly shopping trip such a choice may be performed with limited deliberation, which means that interventions targeting automatic decision-making processes may be effective 103 . However, for other actors, such as supply-chain managers making bulk purchases for supermarkets, different interventions—perhaps motivated by limiting reputational risk—will probably be required. At the level of decision makers designing national or international fisheries policy, other sorts of interventions 104 —potentially linked to cessation or realignment of taxpayer subsidies—might need to be considered.
This example also illustrates our third suggested research question: how does the effectiveness of behaviour-change interventions vary with the financial and psychological costs of the change for the target actor? Differences in motivation will be important here. In some instances, actors may benefit directly from pro-conservation behaviour (for example, because eating more sustainably sourced fish aligns with health values, or keeping their pet cat indoors reduces its risk of injury). But sometimes those choices may carry costs (for example, sustainable seafood may be more expensive or difficult to source). In the case of the supermarket chains, there may be financial and administrative costs to switching suppliers, at least over the short term. Policymakers will also face strong lobbying pressure to continue to support the policy status quo. Clearly, different interventions will be needed across such diverse contexts. Varied interventions may also be needed within actor groups. For example, supermarket chains may differ in their motivations, knowledge, demographics and other interests in ways that warrant different types of behaviour-change interventions.
Lastly, how can practitioners design interventions to ensure that behaviour changes persist over the long term? Although many intervention studies do not evaluate persistence over time, those that do commonly observe that effectiveness wanes 105 , 106 , 107 . In some contexts, it might be possible to design one-off interventions with long-lasting effects, but in others, delivering lasting change may necessitate recurring rounds of intervention or the repeated introduction of novel interventions. Better understanding the persistence of intervention effects will be key to sustaining beneficial behaviour change.
Many more questions will emerge as this field develops. Addressing them will require fresh partnerships and continued commitment to work across disciplines and in unfamiliar circumstances. Such partnerships may follow recommendations for interdisciplinary collaborations around biodiversity conservation 108 , 109 or be inspired by existing programmes and networks (some of which collaborate closely with practitioners), such as the Cambridge Conservation Initiative, Center for Behavioral and Experimental Agri-environmental Research, and Science for Nature and People Partnership. We submit that there are few other opportunities where behavioural scientists have such potential to tackle one of the great challenges of our age. We hope this Perspective can help inspire this critical work.
Summary for Policymakers of the Global Assessment Report on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services of the Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services http://rid.unrn.edu.ar/handle/20.500.12049/4223 (IPBES Secretariat, 2019).
Maxwell, S. L., Fuller, R. A., Brooks, T. M. & Watson, J. E. M. Biodiversity: The ravages of guns, nets and bulldozers. Nature 536 , 143–145 (2016).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Living Planet Report 2020—Bending the Curve of Biodiversity Loss (WWF, 2020).
Ceballos, G. et al. Accelerated modern human-induced species losses: entering the sixth mass extinction. Sci. Adv. 1 , e1400253 (2015).
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Ceballos, G., Ehrlich, P. R. & Dirzo, R. Biological annihilation via the ongoing sixth mass extinction signaled by vertebrate population losses and declines. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 114 , E6089–E6096 (2017).
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Tilman, D. et al. Future threats to biodiversity and pathways to their prevention. Nature 546 , 73–81 (2017).
Partridge, E. Nature as a moral resource. Environ. Ethics 6 , 101–130 (1984).
Article Google Scholar
Ehrenfeld, D. in Biodiversity (ed. Wilson, E. O.) 212–216 (National Academy Press, 1988).
Taylor, P. W. The ethics of respect for nature. Environ. Ethics 3 , 197–218 (1981).
Clayton, S. in The Virtues of Sustainability (ed. Kawall, J.) Ch. 1 (Oxford Univ. Press, 2021).
Feinberg, M. & Willer, R. The moral roots of environmental attitudes. Psychol. Sci. 24 , 56–62 (2013).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Kellert, S. R. The Value of Life: Biological Diversity and Human Society (Island Press, 1997).
Bratman, G. N. et al. Nature and mental health: an ecosystem service perspective. Sci. Adv. 5 , eaax0903 (2019).
Díaz, S. et al. Assessing nature’s contributions to people. Science 359 , 270–272 (2018).
Gibb, R. et al. Zoonotic host diversity increases in human-dominated ecosystems. Nature 584 , 398–402 (2020).
Balmford, A., Fisher, B., Mace, G. M., Wilcove, D. S. & Balmford, B. COVID-19: Analogues and lessons for tackling the extinction and climate crises. Curr. Biol. 30 , R969–R971 (2020).
Dobson, A. P. et al. Ecology and economics for pandemic prevention. Science 369 , 379–381 (2020).
Allen, T. et al. Global hotspots and correlates of emerging zoonotic diseases. Nat. Commun. 8 , 1124 (2017).
Morens, D. M., Daszak, P., Markel, H. & Taubenberger, J. K. Pandemic COVID-19 joins history’s pandemic legion. mBio 11 , e00812-20 (2020).
Wilkinson, D. A., Marshall, J. C., French, N. P., Hayman, D. T. S. & Wilkinson, D. A. Habitat fragmentation, biodiversity loss and the risk of novel infectious disease emergence. J. R. Soc. Interface 15 , 20180403 (2018).
Mallapaty, S. Where did COVID come from? WHO investigation begins but faces challenges. Nature 587 , 341–342 (2020).
Tilman, D. & Clark, M. Global diets link environmental sustainability and human health. Nature 515 , 518–522 (2014).
Poore, J. & Nemecek, T. Reducing food’s environmental impacts through producers and consumers. Science 992 , 987–992 (2018).
‘t Sas-Rolfes, M., Challender, D. W. S., Hinsley, A., Veríssimo, D. & Milner-Gulland, E. J. Illegal wildlife trade: scale, processes, and governance. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 44 , 201–230 (2019).
Dietz, T. Drivers of human stress on the environment in the twenty-first century. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 42 , 189–213 (2017).
Balmford, A. et al. Capturing the many dimensions of threat: comment on Salafsky et al. Conserv. Biol. 23 , 482–487 (2009).
Nepstad, D. C., Stickler, C. M. & Almeida, O. T. Globalization of the Amazon soy and beef industries: opportunities for conservation. Conserv. Biol. 20 , 1595–1603 (2006).
zu Ermgassen, E. K. H. J. et al. Results from on-the-ground efforts to promote sustainable cattle ranching in the Brazilian Amazon. Sustainability 10 , 1301 (2018).
MacFarlane, D. et al. Reducing demand for overexploited wildlife products: Lessons from systematic reviews from outside conservation science. Preprint at OSF https://osf.io/preprints/8935b/ (2020).
Thomas-Walters, L. et al. Motivations for the use and consumption of wildlife products. Conserv. Biol. 35 , 483–491 (2021).
Johnson, C. K. et al. Global shifts in mammalian population trends reveal key predictors of virus spillover risk. Proc. R. Soc. B 287 , 20192736 (2020).
Avery, M. Inglorious: Conflict in the Uplands (Bloomsbury, 2015).
Cowling, R. M. Let’s get serious about human behavior and conservation. Conserv. Lett. 7 , 147–148 (2014).
Marselle, M., Turbe, A., Shwartz, A., Bonn, A. & Colléony, A. Addressing behavior in pollinator conservation policies to combat the implementation gap. Conserv. Biol. 35 , 610–622 (2021).
Saunders, C. D. The emerging field of conservation psychology. Hum. Ecol. Rev. 10 , 137–149 (2003).
Google Scholar
Selinske, M. J. et al. Revisiting the promise of conservation psychology. Conserv. Biol. 32 , 1464–1468 (2018).
Schultz, P. W. Conservation means behavior. Conserv. Biol. 25 , 1080–1083 (2011).
Cinner, J. How behavioral science can help conservation. Science 362 , 889–891 (2018).
Reddy, S. M. W. et al. Advancing conservation by understanding and influencing human behavior. Conserv. Lett. 10 , 248–256 (2017).
Burgess, G. Powers of persuasion? Conservation communications, behavioural change and reducing demand for illegal wildlife products. TRAFFIC Bull. 28 , 65–73 (2016).
Kidd, L. R. et al. Messaging matters: A systematic review of the conservation messaging literature. Biol. Conserv. 236 , 92–99 (2019).
Ostrom, E. et al. The Drama of the Commons (National Academy Press, 2002).
Dietz, T., Ostrom, E. & Stern, P. C. The struggle to govern the commons. Science 302 , 1907–1912 (2003).
Ostrom, E. Governing the Commons: The evolution of Institutions for Collective Action (Cambridge Univ. Press, 1990).
Stern, P. C., Young, O. R. & Druckman, D. E. Global Environmental Change: Understanding the Human Dimensions (National Academy Press, 1992).
Veríssimo, D. The past, present, and future of using social marketing to conserve biodiversity. Soc. Mar. Q. 25 , 3–8 (2019).
Veríssimo, D. et al. Does it work for biodiversity? Experiences and challenges in the evaluation of social marketing campaigns. Soc. Mar. Q. 24 , 18–34 (2018).
Green, K. M., Crawford, B. A., Williamson, K. A. & DeWan, A. A. A meta-analysis of social marketing campaigns to improve global conservation outcomes. Soc. Mar. Q. 25 , 69–87 (2019).
DeWan, A., Green, K., Li, X. & Hayden, D. Using social marketing tools to increase fuel-efficient stove adoption for conservation of the golden snub-nosed monkey, Gansu Province, China. Conserv. Evid. 10 , 32–36 (2013).
McDonald, G. et al. Catalyzing sustainable fisheries management though behavior change interventions. Conserv. Biol. 35 , 1176–1189 (2020).
Veríssimo, D. & Wan, A. K. Y. Characterizing efforts to reduce consumer demand for wildlife products. Conserv. Biol. 33 , 623–633 (2019).
Byerly, H. et al. Nudging pro-environmental behavior: evidence and opportunities. Front. Ecol. Environ. 16 , 159–168 (2018).
van der Linden, S., Maibach, E. & Leiserowitz, A. Improving public engagement with climate change: five ‘best practice’ insights from psychological science. Perspect. Psychol. Sci. 10 , 758–763 (2015).
Chapman, D. A., Lickel, B. & Markowitz, E. M. Reassessing emotion in climate change communication. Nat. Clim. Chang. 7 , 850–852 (2017).
Nisa, C. F., Bélanger, J. J., Schumpe, B. M. & Faller, D. G. Meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials testing behavioural interventions to promote household action on climate change. Nat. Commun. 10 , 4545 (2019).
Valkengoed, A. M. Van & Steg, L. Meta-analyses of factors motivating climate change adaptation behaviour. Nat. Clim. Chang. 9 , 158–163 (2019).
Nielsen, K. S. et al. How psychology can help limit climate change. Am. Psychol. 76 , 130–144 (2021).
Dessart, F. J., Barreiro-Hurlé, J. & van Bavel, R. Behavioural factors affecting the adoption of sustainable farming practices: a policy-oriented review. Eur. Rev. Agric. Econ. 46 , 417–471 (2019).
Palm-Forster, L. H., Ferraro, P. J., Janusch, N., Vossler, C. A. & Messer, K. D. Behavioral and experimental agri-environmental research: methodological challenges, literature gaps, and recommendations. Environ. Resour. Econ. 73 , 719–742 (2019).
Wallen, K. E. & Kyle, G. T. The efficacy of message frames on recreational boaters’ aquatic invasive species mitigation behavioral intentions. Hum. Dimens. Wildl. 23 , 297–312 (2018).
Metcalf, A. L., Angle, J. W., Phelan, C. N., Muth, B. A. & Finley, J. C. More ‘bank’ for the buck: microtargeting and normative appeals to increase social marketing efficiency. Soc. Mar. Q. 25 , 26–39 (2019).
Green, K. M., DeWan, A., Arias, A. B. & Hayden, D. Driving adoption of payments for ecosystem services through social marketing, Veracruz, Mexico. Conserv. Evid. 10 , 48–52 (2013).
Stern, P. C. & Dietz, T. A broader social science research agenda on sustainability: Nongovernmental influences on climate footprints. Energy Res. Soc. Sci. 60 , 101401 (2020).
Niemiec, R. M., Sekar, S., Gonzalez, M. & Mertens, A. The influence of message framing on public beliefs and behaviors related to species reintroduction. Biol. Conserv. 248 , 108522 (2020).
Watts, D. J. Should social science be more solution-oriented?. Nat. Hum. Behav. 1 , 0015 (2017).
Berkman, E. T. & Wilson, S. M. So useful as a good theory? The practicality crisis in (social) psychological theory. Perspect. Psychol. Sci . https://doi.org/10.1177/1745691620969650 (2021).
Giner-Sorolla, R. From crisis of evidence to a ‘crisis’ of relevance? Incentive-based answers for social psychology’s perennial relevance worries. Eur. Rev. Soc. Psychol. 30 , 1–38 (2019).
Henrich, J., Heine, S. J. & Norenzayan, A. The weirdest people in the world? Behav. Brain Sci. 33 , 61–83 (2010).
Rad, M. S., Martingano, A. J. & Ginges, J. Toward a psychology of Homo sapiens : making psychological science more representative of the human population. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 115 , 11401–11405 (2018).
Ewert, B. Moving beyond the obsession with nudging individual behaviour: towards a broader understanding of behavioural public policy. Public Policy Adm. 35 , 337–360 (2020).
Bhargava, B. S. & Loewenstein, G. Behavioral economics and public policy 102: beyond nudging. Am. Econ. Rev. 105 , 396–401 (2015).
Wright, A. J. et al. Competitive outreach in the 21st century: why we need conservation marketing. Ocean Coast. Manag. 115 , 41–48 (2015).
Veríssimo, D. & McKinley, E. Introducing conservation marketing: why should the devil have all the best tunes? Oryx 50 , 14 (2016).
Nilsson, D., Fielding, K. & Dean, A. J. Achieving conservation impact by shifting focus from human attitudes to behaviors. Conserv. Biol. 34 , 93–102 (2020).
Bennett, N. J. et al. Mainstreaming the social sciences in conservation. Conserv. Biol. 31 , 56–66 (2017).
Nelson, K. M., Partelow, S. & Schlüter, A. Nudging tourists to donate for conservation: experimental evidence on soliciting voluntary contributions for coastal management. J. Environ. Manag. 237 , 30–43 (2019).
Niemiec, R. M., Willer, R., Ardoin, N. M. & Brewer, F. K. Motivating landowners to recruit neighbors for private land conservation. Conserv. Biol. 33 , 930–941 (2019).
Byerly, H., D’Amato, A. W., Hagenbuch, S. & Fisher, B. Social influence and forest habitat conservation: experimental evidence from Vermont’s maple producers. Conserv. Sci. Pract. 1 , e98 (2019).
Amel, E., Manning, C., Scott, B. & Koger, S. Beyond the roots of human inaction: fostering collective effort toward ecosystem conservation. Science 279 , 275–279 (2017).
Selinske, M. J. et al. Identifying and prioritizing human behaviors that benefit biodiversity. Conserv. Sci. Pr. 2 , e249 (2020).
Diamond, J. M. in Extinctions (ed. Nitecki, M. H.) 191–246 (Univ. Chicago Press, 1984).
Millennium Ecosystem Assessment. Ecosystems and Human Well-being: Synthesis (Island Press, 2005).
Wilson, E. O. The Future of Life (Vintage, 2002).
Dukes, J. S. & Mooney, H. A. Does global change increase the success of biological invaders? Trends Ecol. Evol. 14 , 135–139 (1999).
Smith, S. D. et al. Elevated CO 2 increases productivity and invasive species success in an arid ecosystem. Nature 408 , 79–82 (2000).
Díaz, S. et al. Pervasive human-driven decline of life on Earth points to the need for transformative change. Science 366 , eaax3100 (2019).
Dietz, T., Gardner, G. T., Gilligan, J., Stern, P. C. & Vandenbergh, M. P. Household actions can provide a behavioral wedge to rapidly reduce U.S. carbon emissions. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 106 , 18452–18456 (2009).
Stern, P. C. Toward a coherent theory of environmentally significant behavior. J. Soc. Issues 56 , 407–424 (2000).
Stern, P. C. Contributions of psychology to limiting climate change. Am. Psychol. 66 , 303–314 (2011).
Nielsen, K. S., Cologna, V., Lange, F., Brick, C. & Stern, P. C. The case for impact-focused environmental psychology. J. Environ. Psychol . https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvp.2021.101559 (2021).
Nielsen, K. S. et al. Improving climate change mitigation analysis: a framework for examining feasibility. One Earth 3 , 325–336 (2020).
Vandenbergh, M. P. & Gilligan, J. M. Beyond Politics (Cambridge Univ. Press, 2017).
Selinske, M. J. et al. We have a steak in it: eliciting interventions to reduce beef consumption and its impact on biodiversity. Conserv. Lett. 13 , e12721 (2020).
Seto, K. C. et al. Carbon lock-in: types, causes, and policy implications. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 41 , 425–452 (2016).
Marteau, T. M. Towards environmentally sustainable human behaviour: targeting non-conscious and conscious processes for effective and acceptable policies. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A 375 , 20160371 (2017).
Ogilvie, D. et al. Using natural experimental studies to guide public health action: turning the evidence-based medicine paradigm on its head. J. Epidemiol. Community Health 74 , 203–208 (2020).
Marteau, T. M., Fletcher, P. C., Hollands, G. J. & Munafo, M. R. in Handbook of Behavior Change (eds. Hagger, M. S. et al.) 193–207 (Cambridge University Press, 2020).
Rutter, H. et al. The need for a complex systems model of evidence for public health. Lancet 390 , 2602–2604 (2017).
Sutherland, W. J., Fleishman, E., Mascia, M. B., Pretty, J. & Rudd, M. A. Methods for collaboratively identifying research priorities and emerging issues in science and policy. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2 , 238–247 (2011).
Hollands, G. J. et al. The TIPPME intervention typology for changing environments to change behaviour. Nat. Hum. Behav. 1 , 0140 (2017).
Michie, S. et al. The behavior change technique taxonomy (v1) of 93 hierarchically clustered techniques: Building an international consensus for the reporting of behavior change interventions. Ann. Behav. Med. 46 , 81–95 (2013).
Liu, J. et al. Framing sustainability in a telecoupled world. Ecol. Soc. 18 , 26 (2013).
Article CAS Google Scholar
Marteau, T. M., Hollands, G. J. & Fletcher, P. C. Changing human behavior to prevent disease: the importance of targeting automatic processes. Science 337 , 1492–1495 (2012).
Sumaila, U. R. et al. Updated estimates and analysis of global fisheries subsidies. Mar. Policy 109 , 103695 (2019).
Bernedo, M., Ferraro, P. J. & Price, M. The persistent impacts of norm-based messaging and their implications for water conservation. J. Consum. Policy 37 , 437–452 (2014).
Ferraro, P. J. & Price, M. K. Using nonpecuniary strategies to influence behavior: evidence from a large-scale field experiment. Rev. Econ. Stat. 95 , 64–73 (2013).
Dayer, A. A., Lutter, S. H., Sesser, K. A., Hickey, C. M. & Gardali, T. Private landowner conservation behavior following participation in voluntary incentive programs: recommendations to facilitate behavioral persistence. Conserv. Lett. 11 , e12394 (2018).
Kelly, R. et al. Ten tips for developing interdisciplinary socio-ecological researchers. SEPR 1 , 149–161 (2019).
Campbell, L. M. Overcoming obstacles to interdisciplinary research. Conserv. Biol. 19 , 574–577 (2005).
Download references
Acknowledgements
We are grateful for funding from the Cambridge Conservation Initiative Collaborative, Fund and Arcadia, RSPB and the Gund Institute for Environment, University of Vermont. A.B. is supported by a Royal Society Wolfson Research Merit award. E.E.G. was supported by a NERC studentship (grant number NE/L002507/1). We thank P. C. Stern for helpful discussion and feedback.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Zoology, University of Cambridge, Cambridge, UK
Kristian Steensen Nielsen, Richard B. Bradbury, Emma E. Garnett & Andrew Balmford
Behaviour and Health Research Unit, University of Cambridge, Cambridge, UK
Theresa M. Marteau
Department of Management, Society and Communication, Copenhagen Business School, Frederiksberg, Denmark
Jan M. Bauer
Centre for Conservation Science, RSPB, Sandy, UK
Richard B. Bradbury
TRAFFIC, Cambridge, UK
Steven Broad & Gayle Burgess
Centre for Environmental Policy, Imperial College London, London, UK
Mark Burgman
Institute of Behavioral Science, University of Colorado, Boulder, CO, USA
Hilary Byerly
Psychology Department, The College of Wooster, Wooster, OH, USA
Susan Clayton
Center for Behavior and the Environment, Rare, Querétaro, México
Dulce Espelosin
Carey Business School and the Department of Environmental Health and Engineering, a joint department of the Bloomberg School of Public Health and the Whiting School of Engineering, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, MD, USA
Paul J. Ferraro
Gund Institute for Environment, University of Vermont, Burlington, VT, USA
Brendan Fisher & Taylor H. Ricketts
Environmental Program, Rubinstein School of Environment and Natural Resources, University of Vermont, Burlington, VT, USA
Cambridge Institute for Sustainability Leadership, University of Cambridge, Cambridge, UK
Emma E. Garnett
College of Environmental Sciences and Engineering, Bangor University, Bangor, UK
- Julia P. G. Jones
Department of Animal Ecology and Tropical Biology, University of Würzburg, Würzburg, Germany
Mark Otieno
Department of Agricultural Resource Management, University of Embu, Embu, Kenya
Department of Applied Economics, University of Minnesota, St Paul, MN, USA
Stephen Polasky
Natural Capital Project, University of Minnesota, St Paul, MN, USA
Tropical Biology Association, Cambridge, UK
Rosie Trevelyan
Department of Psychology, University of Cambridge, Cambridge, UK
Sander van der Linden
Department of Zoology, University of Oxford, Oxford, UK
Diogo Veríssimo
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
All authors contributed to the conceptualization of the research. K.S.N., T.M.M. and A.B. wrote the manuscript. The other contributing authors (J.M.B., R.B.B., S.B., G.B., M.B., H.B., S.C., D.E., P.J.F., B.F., E.E.G., J.P.G.J., M.O., S.P., T.H.R., R.T., S.v.d.L. and D.V.) provided critical comments and revisions. All authors approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Kristian Steensen Nielsen .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Peer review information Nature Human Behaviour thanks Rebecca Niemiec, Philip Seddon and Matthew Selinske for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Nielsen, K.S., Marteau, T.M., Bauer, J.M. et al. Biodiversity conservation as a promising frontier for behavioural science. Nat Hum Behav 5 , 550–556 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41562-021-01109-5
Download citation
Received : 30 November 2020
Accepted : 31 March 2021
Published : 13 May 2021
Issue Date : May 2021
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1038/s41562-021-01109-5
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
This article is cited by
Behavioural sciences need behavioural ecology.
- Marlen Z. Gonzalez
- Marissa A. Rice
Nature Human Behaviour (2024)
The causal revolution in biodiversity conservation
- Ganga Shreedhar
Realizing the full potential of behavioural science for climate change mitigation
- Kristian S. Nielsen
- Viktoria Cologna
- Kimberly S. Wolske
Nature Climate Change (2024)
Leveraging the link between pro-environmental behaviour and well-being to encourage sustainable lifestyle shifts
- Michael M. Prinzing
- Kate Laffan
npj Climate Action (2024)
Empathy for wildlife: The importance of the individual
- Pauline Smith
- Abigail Marsh
Ambio (2024)
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
133 Biodiversity Topics & Examples
🔝 top-10 biodiversity topics for presentation, 🏆 best biodiversity project topics, 💡 most interesting biodiversity assignment topics, 📌 simple & easy biodiversity related topics, 👍 good biodiversity title ideas, ❓ biodiversity research topics.
- Biodiversity loss.
- Global biodiversity conservation.
- The Amazon rainforest.
- Animal ecology research.
- Sub Saharan Africa.
- Marine biodiversity.
- Threats to ecosystems.
- Plant ecology.
- Importance of environmental conservation.
- Evolution of animal species.
- Habitat Destruction and Biodiversity Extinctions The instance of extinction is by and large regarded as the demise of the very last character of the genus. Habitat obliteration has played a major part in wiping out of species, and it is […]
- Biology Lab Report: Biodiversity Study of Lichens As a consequence of these results, the variety of foods found in forest flora that include lichens may be linked to varying optimum conditions for establishment and development.
- Biodiversity Benefits for Ecology This variation of species in the ecosystem is a very important concept and factor that indeed is the basis for sustaining life on our planet. Moreover, the most important supporter of life, which is soil […]
- Biodiversity Hotspots: The Philippines The International Conservation has classified the Philippines as one of the biodiversity hotspots in the world. Additionally, the country is said to be one of the areas that are endangered in the world.
- How Biodiversity Is Threatened by Human Activity Most of the marine biodiversity is found in the tropics, especially coral reefs that support the growth of organisms. Overexploitation in the oceans is caused by overfishing and fishing practices that cause destruction of biodiversity.
- Biodiversity Conservation: Tropical Rainforest The forest is not a threat to many species and that, therefore, helps in showing that conserving this forest will be of great benefit to many species. The disadvantage of conserving the Mangrove Forest is […]
- Conserving Biodiversity: The Loggerhead Turtle The loggerhead sea turtle is the species of oceanic turtle which is spread all over the world and belongs to the Cheloniidae family.
- Biodiversity Hotspots and Environmental Ethics The magnitude of the problem of losing biodiversity hotspots is too great, to the extend of extinction of various species from the face of the earth.
- Marine Biodiversity Conservation and Impure Public Goods The fact that the issue concerning the global marine biodiversity and the effects that impure public goods may possibly have on these rates can lead to the development of a range of externalities that should […]
- The Importance of Biodiversity in Ecosystem The most urgent problem right now is to maintain the level of biodiversity in this world but it has to begin with a more in-depth understanding of how different species of flora and fauna can […]
- Aspects, Importance and Issues of Biodiversity Genetic diversity is a term used to refer to the dissimilitude of organisms of the same species. Species diversity is used to refer to dissimilitude of organisms in a given region.
- Introduced Species and Biodiversity Rhymer and Simberloff explain that the seriousness of the phenomenon may not be very evident from direct observation of the morphological traits of the species.
- Loss of Biodiversity and Extinctions It is estimated that the number of species that have become extinct is greater than the number of species that are currently found on earth.
- Climate Change’s Negative Impact on Biodiversity This essay’s primary objective is to trace and evaluate the impact of climate change on biological diversity through the lens of transformations in the marine and forest ecosystems and evaluation of the agricultural sector both […]
- Essentials of Biodiversity At the same time, the knowledge and a more informed understanding of the whole concept of biodiversity gives us the power to intervene in the event that we are faced by the loss of biodiversity, […]
- Biodiversity: Aspects Within the Sphere of Biology Finally, living objects consist of cells, which are the basic units of their function and structure. The viruses’ structure depends on which nucleic acid is included, which denotes that there are DNA and RNA viruses.
- Coral Reef and Biodiversity in Ecosystems Coral reefs are formed only in the tropical zone of the ocean; the temperature limits their life – are from +18 to +29oS, and at the slightest deviation from the boundaries of the coral die.
- Biodiversity and the Health of Ecosystems Various opinions are revealed concerning biodiversity, including the human impact, reversal of biodiversity loss, the impact of overpopulation, the future of biodiversity, and the rate of extinction.
- Wild Crops and Biodiversity Threats However, out of millions of existing types of wild crop cultures, the vast majority have been abandoned and eradicated, as the agricultural companies placed major emphasis on the breeding of domesticated cultures that are easy […]
- Biodiversity, Interdependency: Threatened and Endhangered Species In the above table, humans rely on bees to facilitate pollination among food crops and use their honey as food. Concurrently, lichens break down rocks to provide nutrient-rich soil in the relationship.
- Invasive Processes’ Impact on Ecosystem’s Biodiversity If the invasive ones prove to be more adaptive, this will bring about the oppression of the native species and radical changes in the ecosystem.
- Biodiversity and Dynamics of Mountainous Area Near the House It should be emphasized that the term ecosystem used in this paper is considered a natural community characterized by a constant cycle of energy and resources, the presence of consumers, producers, and decomposers, as well […]
- National Biodiversity Strategy By this decision, the UN seeks to draw the attention of the world community and the leaders of all countries to the protection and rational use of natural resources.
- Rewilding Our Cities: Beauty, Biodiversity and the Biophilic Cities Movement What is the source of your news item? The Guardian.
- Biodiversity and Food Production This paper will analyze the importance of biodiversity in food production and the implications for human existence. Edible organisms are few as compared to the total number of organisms in the ecosystem.
- Restoring the Everglades Wetlands: Biodiversity The Act lays out the functions and roles of the Department of Environmental Protection and the South Florida Water Management District in restoration of the Everglades.
- Biodiversity: Importance and Benefits This is due to the fact that man is evolving from the tendency of valuing long term benefits to a tendency of valuing short terms benefits.
- A Benchmarking Biodiversity Survey of the Inter-Tidal Zone at Goat Island Bay, Leigh Marine Laboratory Within each quadrant, the common species were counted or, in the case of seaweed and moss, proliferation estimated as a percentage of the quadrant occupied.
- Natural Selection and Biodiversity These are featured by the ways in which the inhabiting organisms adapt to them and it is the existence of these organisms on which the ecosystems depend and therefore it is evident that this diversity […]
- Loss of Biodiversity in the Amazon Ecosystem The growth of the human population and the expansion of global economies have contributed to the significant loss of biodiversity despite the initial belief that the increase of resources can halt the adverse consequences of […]
- Urban Plants’ Role in Insects’ Biodiversity The plants provide food, shelter and promote the defensive mechanisms of the insects. The observation was also an instrumental method that was used to assess the behavior and the existence of insects in relation to […]
- Brazilian Amazonia: Biodiversity and Deforestation Secondly, the mayor persuaded the people to stop deforestation to save the Amazon. Additionally, deforestation leads to displacement of indigenous people living in the Amazonia.
- Defining and Measuring Biodiversity Biodiversity is measured in terms of attributes that explore the quality of nature; richness and evenness of the living organisms within an ecological niche.
- Biodiversity, Its Importance and Benefits Apart from that, the paper is going to speculate on the most and least diverse species in the local area. The biodiversity can be measured in terms of the number of different species in the […]
- Biodiversity, Its Evolutionary and Genetic Reasons The occurrence of natural selection is hinged on the hypothesis that offspring inherit their characteristics from their parents in the form of genes and that members of any particular population must have some inconsiderable disparity […]
- Biodiversity Hotspots: Evaluation and Analysis The region also boasts with the endangered freshwater turtle species, which are under a threat of extinction due to over-harvesting and destroyed habitat.
- Natural Sciences: Biodiversity and Human Civilisation The author in conjunction with a team of other researchers used a modelling study to illustrate the fact approximately 2 percent of global energy is currently being deployed in the generation of wind and solar […]
- How Human Health Depends on Biodiversity The disturbance of the ecosystem has some effects on the dynamics of vectors and infectious diseases. Change of climate is a contributing factor in the emergence of new species and infectious diseases.
- Biodiversity and Business Risk In conclusion, biodiversity risk affects businesses since the loss of biodiversity leads to: coastal flooding, desertification and food insecurity, all of which have impacts on business organizations.
- Measurement of Biodiversity It is the “sum total of all biotic variation from the level of genes to ecosystems” according to Andy Purvus and Andy Hector in their article entitled “Getting the Measure of Diversity” which appeared in […]
- Ecosystems: Biodiversity and Habitat Loss The review of the topic shows that the relationship between urban developmental patterns and the dynamics of ecosystem are concepts that are still not clearly understood in the scholarly world as well as in general.
- When Human Diet Costs Too Much: Biodiversity as the Ultimate Answer to the Global Problems Because of the unreasonable use of the natural resources, environmental pollution and inadequate protection, people have led a number of species to extinction; moreover, due to the increasing rates of consumerist approach towards the food […]
- The Impact of Burmese Pythons on Florida’s Native Biodiversity Scientists from the South Florida Natural Resource Center, the Smithsonian institute and the University of Florida have undertaken studies to assess the predation behavior of the Burmese pythons on birds in the area.
- Threat to Biodiversity Is Just as Important as Climate Change This paper shall articulate the truth of this statement by demonstrating that threats to biodiversity pose significant threat to the sustainability of human life on earth and are therefore the protection of biodiversity is as […]
- Cold Water Coral Ecosystems and Their Biodiversity: A Review of Their Economic and Social Value
- Benchmarking DNA Metabarcoding for Biodiversity-Based Monitoring and Assessment
- Prospects for Integrating Disturbances, Biodiversity and Ecosystem Functioning Using Microbial Systems
- Enterprising Nature: Economics, Markets, and Finance in Global Biodiversity Politics
- Institutional Economics and the Behaviour of Conservation Organizations: Implications for Biodiversity Conservation
- Fisheries, Fish Pollution and Biodiversity: Choice Experiments With Fishermen, Traders and Consumers
- Last Stand: Protected Areas and the Defense of Tropical Biodiversity
- Hardwiring Green: How Banks Account For Biodiversity Risks and Opportunities
- Governance Criteria for Effective Transboundary Biodiversity Conservation
- Marine Important Bird and Biodiversity Areas for Penguins in Antarctica: Targets for Conservation Action
- Ecological and Economic Assessment of Forests Biodiversity: Formation of Theoretical and Methodological Instruments
- Environment and Biodiversity Impacts of Organic and Conventional Agriculture
- Food From the Water: How the Fish Production Revolution Affects Aquatic Biodiversity and Food Security
- Biodiversity and World Food Security: Nourishing the Planet and Its People
- Climate Change and Energy Economics: Key Indicators and Approaches to Measuring Biodiversity
- Conflicts Between Biodiversity and Carbon Sequestration Programs: Economic and Legal Implications
- Models for Sample Selection Bias in Contingent Valuation: Application to Forest Biodiversity
- Optimal Land Conversion and Growth With Uncertain Biodiversity Costs
- Internalizing Global Externalities From Biodiversity: Protected Areas and Multilateral Mechanisms of Transfer
- Combining Internal and External Motivations in Multi-Actor Governance Arrangements for Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services
- Balancing State and Volunteer Investment in Biodiversity Monitoring for the Implementation of CBD Indicators
- Differences and Similarities Between Ecological and Economic Models for Biodiversity Conservation
- Globalization and the Connection of Remote Communities: Household Effects and Their Biodiversity Implications
- Shaded Coffee and Cocoa – Double Dividend for Biodiversity and Small-Scale Farmers
- Spatial Priorities for Marine Biodiversity Conservation in the Coral Triangle
- One World, One Experiment: Addressing the Biodiversity and Economics Conflict
- Alternative Targets and Economic Efficiency of Selecting Protected Areas for Biodiversity Conservation in Boreal Forest
- Analysing Multi Level Water and Biodiversity Governance in Their Context
- Agricultural Biotechnology: Productivity, Biodiversity, and Intellectual Property Rights
- Renewable Energy and Biodiversity: Implications for Transitioning to a Green Economy
- Agricultural Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services of Major Farming Systems
- Integrated Land Use Modelling of Agri-Environmental Measures to Maintain Biodiversity at Landscape Level
- Changing Business Perceptions Regarding Biodiversity: From Impact Mitigation Towards New Strategies and Practices
- Forest Biodiversity and Timber Extraction: An Analysis of the Interaction of Market and Non-market Mechanisms
- Poverty and Biodiversity: Measuring the Overlap of Human Poverty and the Biodiversity Hotspots
- Protecting Agro-Biodiversity by Promoting Rural Livelihoods
- Maintaining Biodiversity and Environmental Sustainability
- Landscape, Legal, and Biodiversity Threats That Windows Pose to Birds: A Review of an Important Conservation Issue
- Variable Mating Behaviors and the Maintenance of Tropical Biodiversity
- Species Preservation and Biodiversity Value: A Real Options Approach
- What Is Being Done to Preserve Biodiversity and Its Hotspots?
- How Are Argentina and Chile Facing Shared Biodiversity Loss?
- Are Diverse Ecosystems More Valuable?
- How Can Biodiversity Loss Be Prevented?
- Can Payments for Watershed Services Help Save Biodiversity?
- How Can Business Reduce Impacts on the World’s Biodiversity?
- Are National Biodiversity Strategies Appropriate for Building Responsibilities for Mainstreaming Biodiversity Across Policy Sectors?
- How Does Agriculture Effect Biodiversity?
- Are There Income Effects on Global Willingness to Pay For Biodiversity Conservation?
- How Does the Economic Risk Aversion Affect Biodiversity?
- What Are the Threats of Biodiversity?
- How Has the Increased Usage of Synthetic Pesticides Impacted Biodiversity?
- What Does Drive Biodiversity Conservation Effort in the Developing World?
- How Does the Plantation Affect Biodiversity?
- What Does Drive Long-Run Biodiversity Change?
- How Does the United Nations Deal With Biodiversity?
- What Factors Affect Biodiversity?
- How Are Timber Harvesting and Biodiversity Managed in Uneven-Aged Forests?
- When Should Biodiversity Tenders Contract on Outcomes?
- Who Cares About Biodiversity?
- Why Can Financial Incentives Destroy Economically Valuable Biodiversity in Ethiopia?
- What Factors Affect an Area’s Biodiversity?
- In What Ways Is Biodiversity Economically Valuable?
- Which Human Activities Threaten Biodiversity?
- How Can Biodiversity Be Protected?
- In What Ways Is Biodiversity Ecologically Value?
- In Which Countries Is Biodiversity Economically Valuable?
- Does Species Diversity Follow Any Patterns?
- How Is Biodiversity Measured?
- What Is a Biodiversity Hotspot?
- Ecosystem Essay Topics
- Climate Change Titles
- Environment Research Topics
- Disaster Essay Titles
- Evolution Topics
- Glaciers Topics
- Hunting Questions
- Global Warming Essay Titles
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2024, February 22). 133 Biodiversity Topics & Examples. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/biodiversity-essay-topics/
"133 Biodiversity Topics & Examples." IvyPanda , 22 Feb. 2024, ivypanda.com/essays/topic/biodiversity-essay-topics/.
IvyPanda . (2024) '133 Biodiversity Topics & Examples'. 22 February.
IvyPanda . 2024. "133 Biodiversity Topics & Examples." February 22, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/biodiversity-essay-topics/.
1. IvyPanda . "133 Biodiversity Topics & Examples." February 22, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/biodiversity-essay-topics/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "133 Biodiversity Topics & Examples." February 22, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/biodiversity-essay-topics/.
- About Project
- Testimonials
Business Management Ideas

Essay on Biodiversity
List of short and long essays on biodiversity, biodiversity essay for kids and school students, essay on biodiversity – essay 1 (150 words), essay on biodiversity: types, importance and conclusion – essay 2 (250 words), essay on biodiversity: with threats and importance – essay 3 (300 words), essay on biodiversity: introduction, importance, decline and steps – essay 4 (400 words), essay on biodiversity – essay 5 (500 words), biodiversity essay for competitive exam and upsc civil services exam, essay on biodiversity: with conclusion – essay 6 (600 words), essay on biodiversity: facts, importance and preservation – essay 7 (750 words), essay on biodiversity in india – essay 8 (1000 words).
Introduction:
Biodiversity also known as biological diversity is the variables that exist among several species living in the ecosystem. These living organisms include marine, terrestrial and aquatic life. Biodiversity aims to understand the positions these organisms occupy in the broader ecosystem.
Importance of Biodiversity:
When there is biodiversity in our ecosystem it translates to a greener environment. This is because plant life thrives in a balanced ecosystem. This invariably affects humans as we consume plants for our survival. Also, a healthy ecosystem can help to reduce the risk of diseases and the way we respond to them.
Increasing Biodiversity:
Some changes could be encouraged to improve biodiversity in our environment.
Some of them are:
1. Stopping penetration of invasive alien species.
2. Using sustainable agricultural methods.
3. Having protected areas for spices to thrive.
4. Having an organic maintenance culture for fertilizers.
Conclusion:
To make the world a safe place for all organisms, we must maintain good health in all the ecosystems. This is the benefit of paying attention to biodiversity.
Diversity is the hallmark of nature. Things exist in different forms which creates diversity. Biodiversity is a significant and desirable variation in plant and animal existence on the surface of the earth. The variation exists due to genetics, species and the ecosystem or the habitat. Biodiversity is an important aspect in the world because it enables the survival and sustainability of living things on earth.
Types of Biodiversity:
The variation in living things has resulted in different types of biodiversity depending on the certain variables. Genetic diversity is due to the genetic components shared by living organisms. The species that have similar genes diverge and they develop differently thus creating biodiversity. Species diversity occurs when a habitat comprises different kinds of living things. Ecological diversity is through the interaction of living things that share common sources of energy in an ecosystem which contributes to biodiversity.
The existence of living things in an ecosystem and the functioning of the ecosystem contribute to the relevance of biodiversity in nature. Through biodiversity, living organisms are able to acquire food and other important resources to sustain their lives. The climate and environmental changes are regulated because of biodiversity. The culture is enriched through biodiversity as it involves existence of several groups of species and people in one environment.
All the three types of biodiversity are important to the existence of living organisms. The ecosystem is the hallmark of diversity because it helps to sustain the lives of diverse living things.
Biodiversity is the variability or the diversity of the different species of life forms. The planet earth is habitat for a wide variety of flora and fauna like plants, animals and other life forms.
What is Biodiversity?
Biodiversity or Biological diversity refers to the variety and variability of living beings on planet earth and it is the degree of variation of life. It represents the wealth of biological assets available on earth and encompasses microorganism, plants, animals and ecosystems such as coral reefs, forests, rainforests, deserts etc.
Threats to Biodiversity:
The growing population, industrialization, technology, etc., all are impacting biodiversity. The increased human activities have been reducing the natural area for plants, animals and other living things. A number of plants and animals have gone extinct because of increased deforestation and other factors. Growing pollution, causing global warming and climate change, is a big threat to biodiversity. The decline in biodiversity would in turn lead to imbalance in the ecosystem and would become a threat to the human race as well as other living organisms.
Different plants and animals are dependent on others to live and keep the natural surroundings in a balanced state. For example, human beings are dependent on various plants and animals for their food, shelter, safety, clothes etc. Similarly, every living species is dependent on some other species. It is, therefore, important to preserve biodiversity in our planet in order to maintain the ecological balance.
Protecting Biodiversity:
As we know, the biodiversity loss is a serious threat for human race, we all should work for maintaining biodiversity, and find out solutions to reduce the biodiversity decline. Since, air pollution and deforestation are major threats to biodiversity, these are the first things that need to be controlled. Government should frame stricter laws and organizations should sensitize people to be concerned about it and contribute their bit.
Biodiversity, also referred to as the biological diversity refers to the diversified form of plants and animals that exists in our planet . It also denotes each and every aspect of the ecosystem such as micro-organisms, coral reefs, rainforests, deserts, forests etc.,
A good balance in biodiversity supports human race and humans on the other hand must ensure to save biodiversity. This essay is going to talk about the importance of biodiversity and the role of human beings in safeguarding the ecosystem.
There are more than 300,000 species of flora that has been identified and there should be many more unidentified varieties. Similarly there must be infinite variety of other species in our Earth and these together form a perfect natural protection for the human race. Biodiversity supports human race in different ways.
Few of them are listed below:
1. Some of the species capture and stores energy and releases it back in the atmosphere for human consumption.
2. Some biological species help in decomposing organic materials and thus acts as a natural recycling agent.
3. Plants and trees help in reducing pollution and maintain the purity of atmospheric air.
4. It is from the biological resources that humans receive food and shelter.
5. The astonishing beauty of biodiversity is the base for tourism industry to flourish.
Decline in Biodiversity:
The Earth’s biodiversity is undergoing a severe decline and this is a great threat to the human race. There are several factors that lead to the decline in biological species, the most significant one being the behavior of human beings.
1. Human beings destroy forests to build houses and offices. Through deforestation humans are actually destroying the natural habitat of many plants and animals.
2. All new scientific inventions are causing harm to the environment. We cannot even find some species of birds today because of the increase in noise pollution.
3. Global warming is another reason for the decline in biodiversity. Some species require specific climate to survive and when the climatic conditions change continuously these species either migrate or become extinct. Decline in the number of coral reefs are a perfect example.
Steps to Be Taken:
The Government and different voluntary organizations must act upon immediately to create awareness among people on environmental issues and its consequences. It is also the responsibility of every common man to save mother Earth by maintaining a rich biodiversity .
If proper care is not taken, the biodiversity of Earth may become extinct one day and if it happens then, humans have to find another planet to live. It’s better to act now before it gets too late.
Biodiversity can be said to mean the extreme importance of a very wide variety of animals and plants that are resident on the planet earth or in a particular habitat. It is very necessary to maintain the level of biodiversity on the earth so that the environmental harmony can be balanced. Biological diversity is another name for biodiversity and is widely the variability or diversity of all the different species of animals and plants on this planet. Having a very high biodiversity is extremely essential to help maintain the surroundings in a state of harmony. Biodiversity can be loosely defined as a variety of fauna and flora that are available in a specific habitat or the planet earth. Biodiversity is largely originated from the terms – species diversity and species richness.
Biodiversity is mainly a united view of the biological varieties. A lot of other words and terms have been at one time or another used to explain diversity. Some of these terms include taxonomic diversity (this comes from a species diversity point of view), ecological diversity (this comes from an ecosystem diversity point of view), morphological diversity (this comes from a genetic diversity point of view) and functional diversity (this comes from the point of view of the functions of the species). Biodiversity gives quite a uniform view of the above discussed biological varieties.
Biological diversity is quite important because its helps maintain the ecological balance in a system. Different animals and plants depend on one another to fulfill all of their needs. For example, we human beings depend on various animals and plants for our clothes, shelter and food. Other species also do the same and depend on a variety of other species to sustain them and provide them with the basics. Biodiversity and its beautiful richness ensure that the earth is fit enough for the survival of each and every one of the organism living on the earth. However, the ever increasing pollution is negatively affecting biodiversity. Quite a lot of animals and plants have gone into extinction as a result of this pollution and a lot more are going to become extinct if proper care is not taken and the pollution of the environment continues to exponentially and this would cause a sharp decline in the biodiversity.
We human beings have to understand how important the maintenance of the immensely rich biodiversity is. Smokes from vehicles causes a high rate of air pollution and this causes harm to a lot of species. The level of pollution in the atmosphere has to be put under control. Water bodies like seas, oceans and rivers are polluted by the release of industrial wastes into the. These wastes are very harmful to the marine organism and life in the water bodies. There is therefore a need to try as much as possible to dispose industrial wastes through other means and methods that do not harm the environment. The industrial wastes can be primarily treated before being disposed into the water properly and safely.
When you are a biology student biodiversity is one of the most important words you can learn. Not only that but it also becomes your lives calling to maintain it. But let’s not get ahead of ourselves before we can understand why it is important, we need to understand what it is.
This term refers to the many different life forms that inhabit the earth at this moment, this includes bacteria, plants, animals and humans and it also refers to their shared environment. Life has manifested itself in many different forms we do not know why exactly but we are certain that they all exist and depend on each other for survival.
Why is biodiversity important?
The answer to this question is more important than just simply stating what biodiversity is. My personal experience as a student has thought me that I learn best when I have an example so I will give you an example of the importance of biodiversity.
The famous Yellowstone Park is a natural reserve and national park but before it was declared as such it was just another forest that man wanted to hunt in. The geographical region had many wolfs inhabiting its plains, for generations they were hunted until they became extinct in the region. After a while, the coyotes began to reproduce as they hade more space and they started hunting the small mammals, which lead to a decrease in the population of eagles in the area but the most significant change came because of the deer. After fifty years of no wolfs in the park the number of roe deer rose and since they had no natural predators, they no longer feared open grasslands. That’s when they started grazing extensively which depleted the grass on the shore of the Yellow stone river and this, in turn, made the soil loos. The river began to take away a lot of soil and to deposit it in other places flooding certain areas while at the same time causing droughts to happen in other places.
Biologists came to the park with a wish to restore its wolf population and after a decade of planning and working they restored one pack to the park. The pack soon made the deer go back to the forest so they could be harder to hunt, the coyote’s population dropped because they couldn’t compete with the wolf, that led to the increase of small rodents which let to the return of carnivores’ grate birds. But above all the grazing on the river edge stopped and after a few years, the Yellowstone river returned to its natural flow.
This story is completely true and I love to use it as an example of the importance of maintaining biodiversity. There are many regions in the world that have similar problems and if we do not do our best to conserve biodiversity, we could be looking at similar or even worst natural catastrophes.
People tend to mass produce and they do this with most things. They will destroy a forest of many thousands of life forms to make a plantation with one single plant, the same is true of animal farming. With our need to be productive all the time we lose sight of the small things that make the system function as whole. Even though an insignificant thing as a bug or a wolf pack might seem the least important for our daily lives once we take them out of the picture, we see that the balance and wealth biodiversity gives to the planet is not something that can be easily compensated.
The genetic, species and ecosystem variability of flora and fauna on earth are known as Biodiversity. For painting what exactly is Biodiversity, we need a large canvas beyond imagination. Such is the volume of the subject. But, the actual meaning and terms are still not clear.
Keeping it very simple and to the point, the term ‘Biodiversity’ comprises of two words. The first word is Bio, and the other one is Diversity. Bio means the forms of life and Diversity means mixture or variety. So, when both the words combine they form a definition like this ‘Biodiversity means various and mixed forms of life on earth.’ The variety of life forms on earth includes plants and animals and their natural habitat.
Facts about Biodiversity:
Digging into the term ‘Biodiversity’ more generously makes us realize that we have over 10,000 species of birds on earth. The amazing number blows everyone’s mind. Insects have a different counting, and their species are in millions. Plants are also a part of this biological system, and hence there are more than 20,000 species of plants.
Even after so many species of plants, animals and insects have specified there are still over millions of species which are not known by anyone. These species cannot be counted under any head as they don’t pursue an identity. The actual picture says that earth is home to almost 50 million species or even more than that. These facts do not conclude the point because one or the other day there may be many new species evolving.
Biodiversity is essential for survival. The importance of Biodiversity not only related to plants, animals and natural habitat. But it also provides us so many natural products such as fibre and timber and the fresh water to carry out our daily lives. Therefore we need to understand the importance of Biodiversity.
1. The natural and organic resources:
In the happiness of living our lives, we often forget that Biodiversity is a part of nature. We should protect it no matter whatever be the limitations. Mother Nature has provided us with enough resources which are the Biological Resources. These include wood, medicines, food, etc., which are direct blessings of Biological System or by-product of the Biological Systems. Herbs and plants play a vital role in producing medicines. They may get their final touch from the pharmaceutical companies, but the original source is plants which are again a part of Biodiversity.
2. Biodiversity provides fibres:
It is important to know that wool, jute, palms, etc., use to produce various types of fibres after processing which are again part of the Biological Systems. So, if biodiversity does not persist how people will have access to these fibres? Flax plants use for the production of linen, which is extensively using for making clothes. Similarly, Corchorus plants and Agave plants are using for the production of Jute and sisal respectively. These fibres are no doubt essential for the cloth industry. Therefore it becomes our duty to maintain the Biodiversity.
3. Powerful benefits of Biodiversity:
People may not be aware of the importance, but there are many spiritual benefits of biodiversity. Our folk dances, mythology, and history have a deep link with the Biodiversity in one or the other way. Everyone enjoys or experience the Biodiversity in a different format. Biological diversity also contributes to attracting tourists, especially flora and fauna, which is a rare phenomenon in cities. Therefore it is our ethical duty to preserve Biodiversity.
Preserve Biodiversity:
There are different ways in which we can preserve our Biological environment. Biodiversity should be protected by following these ways.
i. People should stop the process of hunting and poaching the animals. They are a part of Biodiversity.
ii. Protection of endangered species and their surroundings.
iii. We need to curb pollution for protecting Biodiversity.
iv. The explosive growth of population is a threat to Biodiversity. So, to maintain the biological balance, we need to have the population growth under control. Otherwise, people will be exploiting natural resources unethically for survival.
All steps must be taken to protect biodiversity. Things may seem difficult in the initial stages but practicing them will lead to genuine results. Creating awareness on environmental issues and the negative impact of the loss of biodiversity will let people understand the inevitable need for biodiversity conservation.
It is our responsibility to protect the endangered species of plant and animals. If one wants to reach their destination, then it is imperative to take the first step. Without taking a step forward, things will never change on their own. To make a better tomorrow, we need to take steps for preserving our very own Biodiversity.
Biodiversity is a term used to refer the different forms of life on the Earth. It also includes the variety of species in the ecosystem. There is an uneven distribution of the biodiversity on the Earth due to the extreme variation of temperatures in different regions. For instance, it is more in regions near the equator due to warm climatic conditions. However, near the pole, the extreme cold and unfavourable weather conditions do not support a majority of life forms. Additionally, changes in climatic conditions on the Earth over a period of time have also led to the extinction of a number of species.
Biodiversity is often defined at different levels depending upon the category of species. For example, taxonomic diversity is used to measure the species diversity level of different forms of life on the Earth. Ecological diversity is a broader term used for the ecosystem diversity. Similarly, functional diversity is a type used to measure diversity based on their feeding mechanisms along with other functions of species within a population.
Distribution:
There is an uneven distribution of biodiversity on the Earth. In fact, it increases from pole to equator. The climatic conditions of a region decide the presence of different species in an area. Not all species can survive in all weather conditions. Moreover, lower altitudes have a high concentration of species as compared to higher altitudes.
The importance of biodiversity does not only lie in the survival of various species of the earth. There is social, cultural as well as the economic importance of it as well. Biodiversity is of extreme importance to maintain the balance of nature. It is vital to maintaining the food chain as well. One species may be the food for another species and various species are linked to each other through this food chain. Apart from this, there is scientific importance of the biodiversity as well. The research and breeding programmes involve the variety of species. If these species cease to exist then such programmes shall not be possible.
Also, most of the drugs and medicine which are vital for the cure of many diseases are also made from many plants and animals. For instance, penicillin is a fungus through which the penicillin antibiotic is extracted.
Another important importance of biodiversity is that it provides food to all including human beings. All the food we consume is either derived from plants or animals such as fishes and other marine animals. They are also the source of new crops, pesticides and source material for agricultural practices.
Biodiversity is also important for industrial use. We get many products such as fur, honey, leather and pearls from animals. Moreover, we get timber for plants which are the basis of the paper we use in our everyday life. Tea, coffee and other drinks along with dry fruits and our regular fruits and vegetables, all are obtained from the various plants.
There is cultural and religious importance of many species as well. Many plants and animals are worshipped in different cultures and religions such as Ocitnum sanctum (Tulsi) which is a plant worshipped by Hindus.
Biodiversity in India:
India ranks among the top 12 nations which have a rich heritage of biodiversity. There are about 350 different species of mammals along with 12000 different species of birds which are found in India. Additionally, there are around 50000 species of insects which have their habitat in our country. There are a wide variety of domestic animals such as cows and buffaloes along with marine life which is found in India. Moreover, India is a land of 10 different biographical regions which include islands, Trans Himalayas, Desert, Western Ghats, Gangetic Plain, Semi-arid zone, Northeastern zone, Deccan Plateau, Coastal islands and the Western Ghats.
The Gradual Decrease:
Not all species which existed in the ancient times exist today as well. For example, dinosaurs used to exist on our planet in older times. But they were not able to adapt to the changing environmental conditions which led to their extinction from the Earth. Similarly, there are many other species which are on the verge of extinction due to the urbanisation and modernisation of the world. With the increase in population, there has been a constant need to reduce the forest areas and make way for new cities. This has led to the reduction in forests which are the natural habitat for many wild animals and plants. Due to this many wild plants have become extinct and there has been an increase in the man-animal conflict as well. Hence there has been a need to conserve the biodiversity so as to maintain the balance of nature.
Initiatives for the Conservation of Biodiversity:
There have been initiatives by the governments all over the world to conserve the existing biodiversity on the earth. For example, there are dedicated national parks which earmark the area for wild animals and plants and reduce human intervention in their lives. There are various wildlife conservation programmes in place to protect the vulnerable and endangered species. For example, Project Tiger is one such measure in place to increase the population of tigers in our country.
There are also many laws in place which make the hunting of endangered and vulnerable animals a punishable offence. At the international level, UNESCO (United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization) and IUCN (International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources) have also initiated many programmes in order to preserve various species.
It is not possible for the human to live all alone on the Earth. Various other life forms are equally important and play their roles in the mutual survival of the various species on the Earth. Each one of species has its own set of contribution for the environment. Already many species have become extinct as they were not able to survive in the changing weather conditions. Hence it is our duty to ensure that our activities do not affect the other flora and fauna on the planet. Although there are a number of steps taken by the government so as to preserve the various life forms, we should also contribute individually towards this cause. If we do not act today, we may yet again witness the extinction of the vulnerable biodiversity which may further disturb the balance of nature.
Biodiversity , Ecosystem , Environment
Get FREE Work-at-Home Job Leads Delivered Weekly!

Join more than 50,000 subscribers receiving regular updates! Plus, get a FREE copy of How to Make Money Blogging!
Message from Sophia!
Like this post? Don’t forget to share it!
Here are a few recommended articles for you to read next:
- Essay on Noise Pollution
- Essay on Deforestation
- Essay on Environmental Pollution
- Essay on Acid Rain
No comments yet.
Leave a reply click here to cancel reply..
You must be logged in to post a comment.
Billionaires
- Donald Trump
- Warren Buffett
- Email Address
- Free Stock Photos
- Keyword Research Tools
- URL Shortener Tools
- WordPress Theme
Book Summaries
- How To Win Friends
- Rich Dad Poor Dad
- The Code of the Extraordinary Mind
- The Luck Factor
- The Millionaire Fastlane
- The ONE Thing
- Think and Grow Rich
- 100 Million Dollar Business
- Business Ideas
Digital Marketing
- Mobile Addiction
- Social Media Addiction
- Computer Addiction
- Drug Addiction
- Internet Addiction
- TV Addiction
- Healthy Habits
- Morning Rituals
- Wake up Early
- Cholesterol
- Reducing Cholesterol
- Fat Loss Diet Plan
- Reducing Hair Fall
- Sleep Apnea
- Weight Loss
Internet Marketing
- Email Marketing
Law of Attraction
- Subconscious Mind
- Vision Board
- Visualization
Law of Vibration
- Professional Life
Motivational Speakers
- Bob Proctor
- Robert Kiyosaki
- Vivek Bindra
- Inner Peace
Productivity
- Not To-do List
- Project Management Software
- Negative Energies
Relationship
- Getting Back Your Ex
Self-help 21 and 14 Days Course
Self-improvement.
- Body Language
- Complainers
- Emotional Intelligence
- Personality
Social Media
- Project Management
- Anik Singal
- Baba Ramdev
- Dwayne Johnson
- Jackie Chan
- Leonardo DiCaprio
- Narendra Modi
- Nikola Tesla
- Sachin Tendulkar
- Sandeep Maheshwari
- Shaqir Hussyin
Website Development
Wisdom post, worlds most.
- Expensive Cars
Our Portals: Gulf Canada USA Italy Gulf UK
Privacy Overview
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-analytics | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-functional | 11 months | The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-necessary | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-others | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Other. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-performance | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". |
| viewed_cookie_policy | 11 months | The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. It does not store any personal data. |
Birds, the Best Ambassadors of Biodiversity

When was the last time you saw a bird? Perhaps this morning while you were exercising outside, or yesterday during a stroll through a park. If you are on holiday, you have probably seen one in a forest, village square, in the countryside, flying low over the ocean at the beach, skimming rivers or other bodies of water. It makes no difference if it's winter in the Southern Hemisphere or Summer in the Northern Hemisphere, daytime or night, on a busy city street, in a moor, jungle, or desert. Birds are everywhere! For that reason, Audubon believes that birds should take center stage at the next COP16 to be held in Cali.
Birds are found in almost every ecosystem on the planet. Their continuous presence is a warning and a reminder to take action. Birds do not only elicit joy and admiration. They are excellent indicators of an ecosystem's health, making them unparalleled umbrella species. On the other hand, the absence or decline of bird populations points to the degradation and disappearance of our natural world. This has increasingly been the case for decades. The reason? - climate change, habitat loss, pollution, invasive species, pesticides, and pollutants, among other factors.
We are well aware that biodiversity and the conservation of our natural resources are the basis for our growth and survival as a species. Healthy ecosystems provide invaluable services, such as storm protection and water regulation. Nevertheless, we are losing our biodiversity and ecosystems at an alarming rate. How do we reverse this trend and ensure a sustainable future for everyone? One option is to turn to birds for a solution. By protecting birds we also preserve our ecosystems.
Birds can be our guides and ambassadors in this collective effort towards a more sustainable future. A study by Audubon shows how the most important areas for conservation of migratory, endemic and globally endangered birds in Colombia overlap key water regulation sites by 85% and sites that are vulnerable or highly vulnerable to climate change by 42%.
Mangroves, corals, and seagrasses are not only a refuge for various species and the home of fisheries, but also act as natural barriers against storms and tsunamis. Studies have shown that marine ecosystems can reduce wave energy on shores by 95%. More effective protection of river basins improves water quality and regulates water flow, so vital for human life and agriculture. Four of the world´s five major cities could improve water quality and regulation by harnessing the power of nature. One out of every six of these cities can also save resources by investing in river basin conservation rather than only investing in more treatment plants or grey infrastructure.
The annual financial gap associated with managing natural resources and mitigating the future effects of climate change is estimated to range from $598 and $824 billion. Financial resources are earmarked and business cases exist to justify why biodiversity conservation should be internalised in decision-making. Based on my experience at Audubon, I can honestly say that we possess the tools, methodologies, citizen engagement, and insight into rural science to spur this movement. We are also counting on the unrivaled convening power of birds.
Recent studies show that birding is on the rise in the Americas with more than 96 million birdwatchers in the United States alone. We have an opportunity to connect these euphoric birders and make the necessary policy and investment changes for that purpose. That, indeed, reflects the power of birds. What I am referring to, here, is galvanizing civil society to create local, national, and global movements, and call on our governments to make this a priority investment. Colombia, home to nearly 2000 bird species, is truly, a country of birds. The National Bird Conservation Strategy ENCA2030 facilitated by Audubon, RNOA, and the Humboldt Institute with support from the Colombian Ministry of Environment is an inspirational example of how society can organize itself to protect its natural resources. The strategy encompasses more than 2,000 people from diverse socio-economic backgrounds as well as the environmental, academic, public, private, regional, autonomous, and corporate sectors. The objective is the conservation and sustainable management of key habitats for birds, nature, and local communities.
Birdwatchers, civil society, and businesses must coordinate efforts and work together to address climate change adaptation and mitigation. They must collaborate with governments to effectively implement ENCA as well as other conservation initiatives. Birds can serve as our guides and ambassadors in this collective effort towards a more sustainable future.
Audubon and its local and hemispheric partners look to the next COP and beyond as an opportunity to demonstrate how birds connect us to the needs of nature and humanity. The time to act together is now. We must endeavor to protect our birds and biodiversity and ensure the well-being of local communities and us all.
Originally published in El Espectador newspaper, June 27, 2024.

Pledge to stand with Audubon to call on elected officials to listen to science and work towards climate solutions.

Essay on Conservation of Biodiversity in English for Children and Students

Table of Contents
Biodiversity is essential for maintaining the ecological system of our planet. Rich biodiversity is a sign of a healthy environment. Conservation of biodiversity is vital for the survival of human beings as well as other living beings on Earth. A lot of emphasis is being given on the conservation of biodiversity these days. This is because rich biodiversity is what makes our planet fit for living.
Fill Out the Form for Expert Academic Guidance!
Please indicate your interest Live Classes Books Test Series Self Learning
Verify OTP Code (required)
I agree to the terms and conditions and privacy policy .
Fill complete details
Target Exam ---
Long and Short Essay on Conservation of Biodiversity in English
Here are essay on Conservation of Biodiversity of varying lengths to help you with the topic in your exam. You can choose any Conservation of Biodiversity essay as per your interest and requirement:
Short Essay on Conservation of Biodiversity – Essay 1 (200 words)
Biodiversity refers to the variety of flora and fauna in a given region on earth as a whole. The greater the variety of flora and fauna, the better it is for the survival of different species. This is because it helps in the process of food chain. Different species of animals are dependent upon other species to satiate their hunger while some species are dependent on plants. If one species goes extinct for some reason, those dependent on them for food will also starve to death and we will keep losing various species resulting in decline in the biodiversity. This is what has been happening since a long time especially during the last few decades.
The advancement in technology and various other activities such as industrialization, deforestation, growing pollution, global warming and the ever growing population of human beings are some of the reasons for lowered biodiversity. We are losing numerous species of plants, animals, marine creatures, insects and other organisms each year.
It is imperative to maintain high level of biodiversity. The activities causing a decline in biodiversity have already been identified. We now need to keep a check on all these activities for the conservation of biodiversity. The joint efforts of the government and general public across the globe can help in this direction.

Essay on Biodiversity and Conservation – Essay 2 (300 words)
Introduction
Biodiversity is vital for the environmental harmony. God has created numerous species of flora and fauna and there is a reason behind these diverse creations. But, we humans seem to have turned a blind eye towards the need to maintain biodiversity and are indulging in various activities that are causing a decline in the same.
What is Biodiversity?
Biodiversity, also known as biological diversity or ecological diversity, is the diversity of the species of plants, animals and other living organisms in the world or in a particular habitat. There is a need to maintain rich biodiversity as it helps in maintaining the ecological balance on Earth. This is because each species of flora and fauna has its own role to play in the ecological system to keep it intact.
Why do We Need to Conserve Biodiversity?
Our beautiful planet has given us numerous things that occur here naturally. Natural resources, rivers, valleys, oceans, different species of animals and beautiful varieties of plants and trees are among some of these. But man is so busy growing and developing his own artificial world that he is spoiling these beautiful natural things. Today, we have exploited most of the things that were available abundantly in nature. There is a dire need to conserve these natural things. Among other things, there is a serious need for the conservation of biodiversity.
The requirement to maintain biodiversity has often been overlooked. This is because we think that we are doing well for ourselves, even though many species have gone extinct until now and that we would remain unaffected even if few more go extinct. However, this is a misconception. Richness of biodiversity is essential for the proper functioning of our environment. We would not be able to survive in the times to come if the biodiversity continues to decline.
Humans must keep a check on their activities and stop exploiting flora and fauna for serving their own selfish purposes. They must instead contribute towards the conservation of biodiversity.
Essay on Importance of Conservation of Biodiversity – Essay 3 (400 words)
All the species of plants and animals present on Earth together form biodiversity. We depend upon each other to fulfil various needs so as to live comfortably on this planet. Rich biodiversity is vital for our survival. However, unfortunately it is declining at a fast pace and this may put us in deep trouble in the times to come. Conservation of biodiversity is the need of the hour. We must all contribute towards the same to ensure a comfortable and peaceful life ahead.
Importance of Conservation of Biodiversity
Conservation of biodiversity is important for many reasons. Here are some of the main reasons why we must conserve biodiversity:
- Process of Food Chain
Different species of animals and plants serve as the source of food for other animals and living organisms. When one species goes extinct or shifts from one habitat to another, it results in different kinds of deficiencies for others species. Some species even starve to death as their main source of food goes extinct. Rich biodiversity thus helps in the process of food chain.
- Nutritional Needs
We eat different kinds of fruits, vegetables, meats, fishes and other things as they satisfy different nutritional needs for the proper functioning of our body. The decline in the variety of plants and animals would mean the decline in the variety of food we eat and this is likely to result in nutritional deficiencies.
- Cleaner Air
Trees and plants inhale carbon dioxide and other harmful gases from the atmosphere and exhale the life giving oxygen. Some plants and trees have a greater ability to purify the air and keep the atmosphere clean. The decline in the number and types of trees and plants can impact the quality of air negatively.
- Better Cultivation of Crops
Many insects, organisms and microorganisms such as earthworms, fungi and bacteria work on different levels and make the soil fertile and maintain its health. Healthy and fertile soil is certainly better for the cultivation of crops. Loss of such species can thus be a great loss for us.
- For Medical Reasons
Many species of trees and plants are used to derive different medicines to cure various diseases. Many plants serving medicinal purposes have gone extinct in the past and many others are likely to go extinct even before the scientists discover their utility.
Thus, the richness of biodiversity is essential for the survival of living beings on Earth. This issue must be taken up seriously and stern measures must be taken to conserve biodiversity.
Essay on Conservation Methods of Biodiversity – Essay 4 (500 words)
The need for conservation of biodiversity has been stressed upon numerous times as it is of utmost importance for the survival of the mankind and other living beings on Earth. In addition to emphasizing upon the importance and need to protect and conserve biodiversity, it is essential to share the methods to conserve it.
Methods to Conserve Biodiversity
Here are some of the methods that can help in the conservation of biodiversity:
- Control Population
One of the reasons why biodiversity is declining is because of the growing human population. Trees are being cut and animals are being harmed at a large scale in order to satiate various human needs. The greater the population the higher the needs which would result in further exploitation of flora and fauna and decline in biodiversity. The first and foremost thing that needs to be done for the conservation of biodiversity is to control human population and allow other species of plants and animals to thrive on our planet.
- Control Pollution
The growing pollution is causing harm to our beautiful planet. The temperature is rising and subsequently causing global warming. The changing climate, deteriorating air quality and the growing amount of pollution on land and in water bodies is leading to different types of diseases in many species and has also caused the extinction of several of them. Many species of flora and fauna are unable to withstand these changes in the atmosphere and it becomes extremely difficult for them to survive. It is essential to cut down on the activities leading to pollution in order to lower it.
- Keep a Tab on Deforestation
Forests are a habitat for different varieties of flora and fauna. Deforestation has been one of the main reasons for the extinction of numerous wild creatures as well as various beautiful plants. The loss of habitat makes wild animals vulnerable. They are unable to survive in the new environment. While some struggle for survival by shifting to other places others are unable to adapt to new surroundings and die.
- Avoid Wastage
It is imperative for us to avoid wastage of any kind. Most of the things we use are derived from natural resources. From the electricity we consume, to the fuel we use, from the clothes we wear to the paper we write on, everything has been prepared directly or indirectly from the natural resources. We need to understand that natural resources are not only essential for us but are also vital for the survival of other species. We must thus utilise only as much as we require so that these remain available in abundance in the nature for future use.
- Spread Awareness
Apart from this, one of the best methods to conserve biodiversity is by spreading awareness. People need to be sensitized about the issue so that they act responsibly and contribute towards conserving biodiversity. The government can do so at a bigger level while we can spread awareness by word of mouth and through social media.
Conservation of biodiversity is extremely important to maintain a healthy environment and ensure a comfortable life for future generations. There are many ways in which we can conserve it. We must all contribute our bit towards conserving the same.

Long Essay on Conservation of Biodiversity – Essay 5 (600 words)
Conservation of biodiversity is vital for maintaining the Earth’s environment and sustaining life on the planet. There are a number of ways in which the richness of biodiversity helps in maintaining the ecological system and serves us. Different kind of foods available fulfils different nutritional needs, plants clean the air, many organisms keep the soil health in check and survival of different species is possible due to the process of food chain. These are some of the examples to show the importance of conserving biodiversity on Earth.
The Decline in Biodiversity
The continual decline in biodiversity has become a cause of concern world over. Many regions in the world have seen a major dip in the biodiversity owing to the changes in climate and increasing pollution levels. This has had a big impact on the other species living in those areas. Biodiversity is declining world over. Research shows that numerous varieties of animals go extinct each year largely due to human activities.
Western Black Rhinoceros, Dodo, Tasmanian tiger, Golden Toad, Woolly Mammoth, Caribbean Monk Seal, Ivory-billed Woodpecker and Japanese Sea Lion are some of the species of animals that have gone extinct. Lemur, Mountain Gorilla, Vaquita, Sea Turtles, Amur Leopard and Tiger are some of the species that are on the verge of extinction. Apart from these many species of plants and trees including Lepidodendron, Araucaria Mirabilis, Wood Cycad and Kokia Cookei have gone extinct and many others are endangered.
Need for Conservation of Biodiversity
If we continue to lose different species of flora and fauna at this speed, our survival will become extremely difficult on Earth. This is because every species of plant and animal either big or small, contributes towards the maintenance of the ecological balance in its own unique way. Loss of these can have a huge impact on the environment as well as other living beings. For instance, we depend on different kind of plants and animals as they serve as a source of food for us.
They satisfy different nutritional needs. Trees provide wood and other raw material that are used to craft numerous things that are vital for us. Similarly, different kinds of herbs are used for preparing medicines. Likewise, different species of insects and animals contribute in their own way in making the environment fit for living. If this richness of diversity is not maintained we shall lose out on many things and it will make our life difficult. This is why it is extremely important to conserve biodiversity.
How Can We Help in the Conservation of Biodiversity?
We as general public can help in the conservation of biodiversity by avoiding wastage of the natural resources. We can also do out bit by avoiding activities that lead to pollution as pollution is the main cause of decline in biodiversity.
Besides, we must plant trees and plants and encourage those around us to do the same. People mostly think that their contribution may not affect much and thus do not make any effort. If each one of us thinks this way we will soon be making life difficult for us. We must contribute our bit towards the conservation of biodiversity. These small contributions can lead to major change over the course of time.
Government’s Role in the Conservation of Biodiversity
The government must sensitize people about the need for conservation of biodiversity through media, hoardings and other means. The government must also keep a tab on the human activities that are causing a decline in the biodiversity. Strict action must be taken against individuals, groups and organizations indulging in these.
Conservation of biodiversity is of utmost importance. We must all make efforts to conserve biodiversity rather than contributing towards its decline.
More Information:
Essay on Biodiversity
Related content

Get access to free Mock Test and Master Class
Register to Get Free Mock Test and Study Material
Offer Ends in 5:00
Select your Course
Please select class.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
500+ Words Essay on Conservation of Biodiversity. Conservation of biodiversity is vital for maintaining the Earth's environment and sustaining life on the planet. There are a number of ways in which the richness of biodiversity helps in maintaining the ecological system. Conservation of biodiversity is important for the survival of living beings on Earth.
Find high quality essays on the 'Conservation of Biodiversity' especially written for school, college and university students. These essays will also guide you to learn about the need, importance, methods and ways of conservation of biodiversity. ... Importance of Conservation of Biodiversity: India is an ancient civilization where the ...
Why is biodiversity important?
Biodiversity is important to most aspects of our lives. We value biodiversity for many reasons, some utilitarian, some intrinsic. This means we value biodiversity both for what it provides to humans, and for the value it has in its own right. Utilitarian values include the many basic needs humans obtain from biodiversity such as food, fuel ...
Why is biodiversity important?
3.2. (33) Essay on Biodiversity: Biodiversity refers to the variety of animals and plants in the world or a specific area. Even in today's modern world where so many technological advances have taken place, we still rely on our natural environment and resources to survive, A healthy and vibrant ecosystem is not disturbed by human activities.
Biodiversity is the description of the natural state of the planet. It is not something that humans can create, they can only manage it. Biodiversity is an important aspect of the earth's ecosystem. It is extremely unfortunate that mankind will realize this when it is already too late. The most urgent problem right now is to maintain the ...
Essay on Biodiversity - The process of continuous biodiversity conservation is essential right now. A greater level of biodiversity is necessary to maintain the harmony of the natural environment. ... Importance Of Biodiversity. Maintaining biodiversity is crucial for the health of the ecological system. Many species of plants and animals are ...
The first essay of 400 to 500 words on 'Conservation of Biodiversity' is for students of class 7, 8, 9, and 10. Moreover, it is helpful for the aspirants of competitive exams. Furthermore, 150 - 200 word's essay on 'Conservation of Biodiversity 'will help students and children in class 6 or below. Long 'Conservation of ...
500+ Words Essay on Biodiversity. Essay on Biodiversity - Biodiversity is the presence of different species of plants and animals on the earth. Moreover, it is also called biological diversity as it is related to the variety of species of flora and fauna. Biodiversity plays a major role in maintaining the balance of the earth.
Human beings get so many benefits from biodiversity. These services may include food, wood, nitrogen fixation, pollination, and beauty. Other services include maintenance of climate and life, prevention of overflow of water and famine, natural bug's control, and even spiritual enrichment.
Essay on Biodiversity 1000+ Words. Biodiversity, short for biological diversity, is a remarkable tapestry of life that blankets our planet. It encompasses the variety of living organisms, ecosystems, and habitats that make Earth a vibrant and thriving place. In this essay, we will delve into the importance of biodiversity, the threats it faces ...
Biodiversity Explained: Facts, Myths, and the Race to ...
Human beings are not only a part of our planet's ecosystems, but also, they are massively overusing them. This makes ecosystem protection, including biodiversity preservation, vital for humanity's future. The speed and scale of the threat are unprecedented in human history. The long arch of evolution has been confronted with such a high level ...
Importance of Biodiversity. Biodiversity is an integral part of cultural identity. Human cultures co-evolve with their environment and conservation is a priority for cultural identity. Biodiversity is used for Medicinal purposes. Many plants and animals are used for medicinal purposes, like vitamins and painkillers.
Having a great amount of biodiversity guarantees natural sustainability for all life forms, healthy ecosystems and creates a stronger foundation from a variety of disasters (McCarty, 2008). Biodiversity also provides a plethora of natural services such as ecosystem/ biological resources, and social benefits.
With the overarching goal to sustainably provide sufficient food for people while conserving and restoring biodiversity, Delabre et al. (7) examine how, and under what conditions, the post-2020 global biodiversity framework can support leverage points for transformative change, with a specific focus on food production and consumption.
What is biodiversity and why is it important? Biodiversity is the variety of all life on Earth - animals, plants, fungi and micro-organisms like bacteria. Animals and plants provide humans with ...
Due to the importance of the tropics for biodiversity, the focus of many conservation interventions is in Africa, Latin America and Asia, providing opportunities to test theory and interventions ...
Biodiversity is measured in terms of attributes that explore the quality of nature; richness and evenness of the living organisms within an ecological niche. Biodiversity, Its Importance and Benefits. Apart from that, the paper is going to speculate on the most and least diverse species in the local area.
Essay on Biodiversity: Types, Importance and Conclusion - Essay 2 (250 Words) Introduction: Diversity is the hallmark of nature. Things exist in different forms which creates diversity. ... issues and the negative impact of the loss of biodiversity will let people understand the inevitable need for biodiversity conservation.
pollutants is also an important element to reduce adverse impacts on biodiversity. SDG 15: Life on Land. The conservation, restoration and sustainable use of terrestrial ecosystems is essential for sustainable development and for achieving the 2030 Agenda and all of the SDGs.
A study by Audubon shows how the most important sites for the conservation of migratory, endemic and globally threatened birds in Colombia overlap 85% with important sites for water regulation. ... Financial resources are earmarked and business cases exist to justify why biodiversity conservation should be internalised in decision-making. Based ...
Essay on Conservation Methods of Biodiversity - Essay 4 (500 words) Introduction The need for conservation of biodiversity has been stressed upon numerous times as it is of utmost importance for the survival of the mankind and other living beings on Earth.