Email Newsletter
Newsletter signup, recent posts from zen and the art of motorcycle maintenance series.
- The importance of using the right tools (Nov 26, 2023)
- Bleeding my brakes (ZAMM series) (Nov 26, 2023)
- Main takeaway: How to incorporate intuitive thinking (ZAMM series) (Dec 1, 2023)
- Why I decided to reread Zen and the Art of Motorcycle Maintenance (ZAMM series) (Nov 26, 2023)

Recent posts from my AI tech comm series
- Use cases for AI: Synthesize insights from granular data (Aug 27, 2023)
- Use cases for AI: Arrange content into information type patterns (Jul 6, 2023)
- Use cases for AI: Develop build and publishing scripts (Jul 19, 2023)
- AI and APIs: What works, what doesn't (Sep 28, 2023)
- Use cases for AI: Summarize long content (Sep 6, 2023)
- Use cases for AI: Understand the meaning of code (Jul 25, 2023)
- Use cases for AI: Seek advice on grammar and style (Aug 4, 2023)
- Use cases for AI: Create glossary definitions (Sep 4, 2023)
- Use cases for AI: Distill needed updates from bug threads (Aug 6, 2023)
- Use cases for AI: Compare API responses to identify discrepancies (Aug 28, 2023)
Recent blog posts
- Get Better at Using Prompts With Deliberate Practice: One technical writer's little experiment — guest post by Diana Cheung (Apr 23, 2024)
- Prompt engineering series: Creating scripts to automate doc build processes (Apr 21, 2024)
- What should your documentation metrics look like? Q&A with Zoomin about their 2024 Technical Content Benchmark Report (Apr 14, 2024)
- AI is accelerating my technical writing output, and other observations (Apr 14, 2024)
- Upcoming conference: AI the API docs (Apr 3, 2024)
- Prompt engineering series: Gathering source input (Mar 20, 2024)
- Prompt engineering series: Error checking the output (Mar 20, 2024)
- Integrating AI with your content delivery platform and documentation: Zoomin Q&A with Keren Brown (Mar 18, 2024)
- Showcasing your API technical writer portfolio and projects — guest post by Peter Gustafson (Mar 12, 2024)
- Prompt engineering series: Reverse engineering the recipe for excellent documentation (Mar 4, 2024)
Popular series
- Reflections on Zen and the Art of Motorcycle Maintenance
- Journey away from smartphones
- Trends to follow or forget
- Simplifying complexity
- Value arguments for docs and tech comm
- See all series
Search results
The ideal number of slides for an hour-long presentation, and other thoughts on preparing slides, comparing two recent presentations, the right number of slides, font size and bulleted lists, avoiding laundry lists, argument overview slide, a good essay makes for a good presentation.
These past two weeks, I gave two presentations — a keynote at an internal writers conference at SAP, and a keynote at an internal writers conference at Amazon. (Sorry that I can’t post the recordings.) Both presentations filled an hour time slot. Because I’ve been in presentation mode this past month, especially preparing slides, I’d like to share some thoughts I have about how to create slides for presentations.
Hands-down, the best advice for creating slides is Guy Kawasaki’s 10-20-30 rule of PowerPoint , which says you should have just 10 slides , your presentation should last no more than 20 minutes , and your font should be no less than 30 points .
I have aspired to follow Kawasaki’s slide rule for a number of years, but one fear always gets in the way: if I have just 10 slides, what if I run out of things to say after 20 minutes? I mean, usually I have to fill an hour presentation slot, right? In order to guard against running out of time, I have a tendency to add more and more slides, helping me remember points I want to make and ensuring I don’t end early.
With my first keynote presentation, I unfortunately had 50 slides (and got through about 40 of them during the presentation). (Granted, many were “sub-slides,” but they were still slides.) For my second presentation, I had only 14 slides (and got through them all). I felt the second presentation went better than the first.
Here’s the problem with having too many slides: the slides lock you into a fixed, rigid presentation order. The more slides you have, the more locked in you are to a fixed set of topics in a predefined order — which may or may not be the right order you want while presenting. With 50+ slides, you won’t have the freedom and flexibility to flow in a more natural way. The more slides you have, the more fixed the order becomes. Instead of a crutch, these slides become a cast that restricts your movement.
The absolute best presentation I’ve ever attended was by David Crystal at UA Europe , and he had no slides at all. He simply had a stool where he occasionally sat, and he spoke for about an hour and a half. It was the most mesmerizing presentation I’ve ever attended, and much of it focused on grammar (and stories about the origins of language). Crystal is the author of some 100+ books on language , and after the presentation, it was clear to me that he was a complete language genius.
I once gave a 20-minute presentation with no slides at all (at a WordPress conference), and I felt a bit naked. It wasn’t a great presentation, but it didn’t tank either. At some point, I’d like to develop the ability to present with just a few slides. I think such a presentation would resemble that of a stand-up comedian or other performer (like the Moth). I don’t have stage performer skills, so I doubt the slide-less presentation will ever be something I pull off. Still, I think as a general rule, the fewer slides one has, the more knowledge and experience the presenter has. Lots of slides is a red flag that the presenter isn’t an expert.
Until I can go slide-less, I have compromised at what I feel is the ideal number of slides for an hour-long presentation: about 15 slides (including the title and conclusion slides). Kawasaki says to limit the number of slides to 10 because no one can retain any more than 10 ideas in an hour, and though I don’t know what data supports this, I generally agree. I bumped my estimate up from 10 to 15 because Kawasaki’s ideal time of 20 minutes seems too short for the hour-long time slot.
Limiting the number of slides to 15 provides the perfect balance between flexibility and structure. You can pursue your ideas in a more freeform, natural way without being locked into a fixed, rigid order that might not fit the idea journey of your presentation.
You might object and say that if you practice your presentation enough, the slides can exactly match the idea journey you want to tell. Hence, you wouldn’t be locked into a structure you don’t want — instead, the slides would help you follow that desired structure.
Well, maybe. But I’ve given about 90 presentations, and it never seems to work out that way for me. Consider the analogy of a conversation. You want to have talking points that allow you to move about in a more freeform way, not necessarily a rigid order in which each topic must be spoken. If you imagine yourself having a conversation with the audience (rather than presenting a presentation), the talking points idea has more merit.
Another Kawasaki principle is to limit the font to no less than 30 points. This is also key. When I see slides with extensive bulleted lists, I cringe. While these bulleted lists might prompt the presenter with details to say, what ends up happening is the presenter more or less reads the slides and presents the presentation rather than telling a story.
Whenever you present a slide with text, the first thing the audience does is tune you out and start reading the text. As an audience member, it’s impossible not to — the screen is huge and directly in front of you.
If you reveal the bulleted list point by point, it has the same effect as flashing multiple, separate slides on the screen: It locks the presenter into a fixed order that potentially interrupts the natural flow of the story.
Ideally, I think good slides should be idea diagrams or visual sketch notes that demonstrate your ideas. Some presenters just put photos from Flickr on their slides to generally depict an idea, but I like more purposeful concept diagrams that might have multiple ideas going on. For example, like this:
Or like this:
Granted, some font on these slides is less than 30 points, but you don’t see extensive bulleted lists here.
For my second presentation slides , I tried to include about 3 stories per slide depicting concept diagrams like this. My thought was that I could glance at the pictures, and each picture would trigger 3 points to cover for the topic. I could cover the 3 stories/points in whatever order I wanted, so I wasn’t locked into a fixed outline. It more or less worked.
I also had slide notes in the presenter view that I could fall back on, but these presenter notes are challenging to read while speaking, and I think most presenters end up ignoring them. Pictures that trigger thought without interfering with one’s language-speaking functions work much better (for me anyway).
I use The Noun Project and Illustrator to create my concept diagrams, as it allows me to more easily manipulate different objects into the slides I want. The images aren’t spectacular, and they’re mostly black and white, but they aren’t embarrassing either, and I have fun making them. I end up exporting these artboards into my presentation. Each artboard is basically a slide in my presentation.
I use RevealJS for my presentations (and have been for the past several years). RevealJS is an HTML/CSS/JS framework that lets you code your slides with simple HTML syntax. For my second presentation, I put the SVGs as slide backgrounds , leaving ample room on the sides to allow for visibility even when the slide show is not in full screen. This worked quite well.
I also put each RevealJS slide presentation into its own GitHub repo. This makes it easy to update the slides. Kawasaki doesn’t say anything about RevealJS, PowerPoint, Google Slides, or Keynote. It really doesn’t matter which tool you use. (I just added some tool-related details here in case you were curious.)
I’ve given many presentations that turn out to be laundry lists of points — a format I regret. This was the problem with my first keynote presentation. After highlighting a trend, I started listing a number of points that could provide solutions to the challenge. These “laundry list” topics tend to be on a lower-level than topics that provide a fuller, richer argument throughout.
Here’s an example of what I mean by a laundry list. In my first presentation, my argument overview was this:
Technology is getting simpler on the front-end for end-users But the code underneath is becoming increasingly specialized/complex Tech writers are generalists, not specialists To provide value in specialist contexts, tech writers must exploit the gaps These gaps are (1) doc tools/processes, (2) understanding user feedback/experiences, and (3) information usability
Then within the “(3) information usability” section, I covered these points:
Give users a map Make information discoverable as needed Ensure harmony across all docs Reduce and distill to its essence Confirm to genre expectations Reduce language complexity Iterative design of docs
Can you see how the presentation just devolved into a laundry list of points rather than focusing on a more focused idea journey? The laundry list comes into focus with the “(1)”, “(2)”, “(3)” points in the last bullet, followed by the 7 bullets later. When I was a composition teacher, I docked student essays for presenting similar laundry lists of ideas rather than going in depth with one point.
For my second presentation, I decided to chop out this laundry list of ideas and instead focus more singularly on my trends argument. So my argument overview was as follows:
Technology is getting more specialized/complex. This complexity drives up the value of technical knowledge, making it more prized than writing skills. To handle the complexity, technical writers must play increasingly collaborative roles with engineers to create documentation
And that’s it. No laundry list at all. I instead spent much more time developing, supporting, and exploring each of these parts of my argument.
Speaking of arguments, I also recommend putting up an “Argument Overview” slide right after your intro hook slide (which usually comes after your title slide). In other words, after you introduce the relevance of your topic, present the audience with your overall argument, so they know where you’re going and what you’re arguing for.
Many presentations will omit this argument overview. When they do, I find myself wondering what the presenter’s overall point is, if they even have one, or if they just have a collage of lots of little ideas. People can often take 10-15 minutes working their way up to some point, which they articulate in fuzzy ways.
I think a good presentation mirrors the elements of an essay:
- relevance hook
- argument/thesis
Many other essay elements might be reflected as well.
Kawasaki says to limit your presentation to 20 minutes. His main scenario isn’t presenters at a conference but rather presentations from startups to venture capitalists (VCs), and he doesn’t really give much reason here for the 20-minute length except to sarcastically say that if you have a Windows machine, it will take 40 minutes to troubleshoot the display. My guess is that VCs are executive types who have a lot of questions and don’t want to be lectured at extensively.
For too many presentations I’ve given, I’ve filled the entire time slot, without leaving any time for questions. This has been a mistake, in part due to having too many slides in the first place. For my second keynote, I spoke for only about 40 minutes and then let Q&A dominate the remaining 20 minutes. Although as an audience member I sometimes dislike listening to other audience members ask questions, I do like to ask my own questions.
Further, very few people can sit patiently listening to a lecture for an hour without engaging with more interactive dialogue. My brain isn’t wired to listen to lectures this long, and neither are many other people’s. You have to be pretty interesting to retain my attention for a full hour in an engaging way.
Probably the biggest reason, though, is that the purpose of a conference is not to present lectures — it’s to confer . You come together to confer with other people, and so you need this space to allow time to discuss your ideas.
What if no one has any questions, and you’re done 20 minutes early? Won’t that feel like you didn’t fill the time, that you short-changed what you promised?
If no one asks questions, it might mean you didn’t make a real argument in your presentation, but instead focused on something everyone already agrees on.
Coming back to the essay comparison, a good presentation focuses on an argument. And an argument must be something that people can take different sides on. If everyone already agrees on the position you’re taking, why bother making it in the first place? Are you already telling people something they already know?
I realize that many presentations at conferences are more information-based rather than argument-based, and people come to “learn” rather than to “debate,” but I’d counter that almost every topic has areas of controversy or uncertainty, and I like to see someone taking a position and defending it with evidence. This shows my bias towards the essay format, as I think good essays reflect this focus as well.
At any rate, if you’ve focused on some argument that people can disagree about, then ending 20 minutes early for Q&A should be ideal, as you will have set the stage for a lively discussion — which is one draw to these gatherings in the first place. You’re setting up the discussion and then allowing for the audience to engage in critical thinking.
Additionally, note that as a presenter, you can also be the one to ask questions. A good teacher doesn’t just lecture to students for 20 minutes and then ask them what questions they have. The teacher asks challenging questions to students and invites them to engage. Why can’t presenters at conferences do the same?
A good essay and a good presentation share many similarities. For many presentations I give, I’ll often write out the content as a blog post or essay before hand. For example, for my second keynote presentation, my Tech comm trends - take two post was the essay form of the post. The essay was about 8,000 words, which is about right for an hour-long presentation. For my first keynote, the essay was an earlier version of the same trends topic .
If the essay doesn’t have a good shape and focus (no idea journey, no story arc, no argument, no evidence, no analysis of opposing views, no interesting questions, etc.), then the presentation will probably lack life as well.
The absolute best advice for any presentation is to structure the idea journey as a story. I don’t mean to pepper in anecdotes everywhere (though that is actually great advice). I mean presentations should follow the general story arc. You have some sort of goal, and you encounter challenges to that goal. The bulk of your work is in getting through these challenges, until you finally come to some realization or conclusion. This flow aligns perfectly with the essay format.
Although I’m not a professional presenter and I lack more training and polish, in the presentations I’ve given over the years, fewer slides work better than more slides. Overall, if I can shape the essay right in the first place, it usually eliminates most of the problems with presentations. That’s why I spend about 90% of the time writing the essay first, and then in the last couple of weeks create the slides.
About Tom Johnson

I'm an API technical writer based in the Seattle area. On this blog, I write about topics related to technical writing and communication — such as software documentation, API documentation, AI, information architecture, content strategy, writing processes, plain language, tech comm careers, and more. Check out my API documentation course if you're looking for more info about documenting APIs. Or see my posts on AI and AI course section for more on the latest in AI and tech comm.
If you're a technical writer and want to keep on top of the latest trends in the tech comm, be sure to subscribe to email updates below. You can also learn more about me or contact me . Finally, note that the opinions I express on my blog are my own points of view, not that of my employer.
© 2024 Tom Johnson
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Computers and Electronics
- Presentation Software
- PowerPoint Presentations
How to Choose the Right Number of Slides for a Powerpoint Presentation
Last Updated: July 12, 2023 References
Choosing the Right Number of Slides Based on Design Choices
Using time to determine the right number of slides, moving beyond formulaic answers to finding the right number of slides.
This article was co-authored by wikiHow Staff . Our trained team of editors and researchers validate articles for accuracy and comprehensiveness. wikiHow's Content Management Team carefully monitors the work from our editorial staff to ensure that each article is backed by trusted research and meets our high quality standards. There are 10 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been viewed 221,343 times. Learn more...

- Keep the presentation about you, not the slideshow. [2] X Research source The slides are there to support what you have to say. They should be just one part of your presentation, not the whole thing.

- Go through your entire presentation and ask yourself if you really need a given slide. If the answer is no, or if you find you can deliver the info verbally instead, eliminate it.

- If your presentation ended well before the time limit you’ve been given, try to extend the amount of time you spend on each slide, or add extra slides to expand on the info introduced in the presentation.
- Solicit advice from family and friends during your practice presentation. If they feel there are too many or too few slides, or if they feel certain sections of the presentation felt rushed or slow, adjust your presentation to correct these deficiencies.

- One well-known formulation for PowerPoint presentations is the 10/20/30 rule. This rule dictates that you should use about ten slides for a twenty minute presentation, and each slide should utilize thirty point font. In other words, each slide should be about two minutes in length. [8] X Research source Perhaps the 10/20/30 rule works for you. If it does not, don’t feel as if you’re using the wrong number of slides.
- Others argue that an average slide should be onscreen for no more than two minutes, and can be onscreen for as little as 15 seconds. [9] X Research source

- If, on the other hand, you’re in a more intimate environment and can control the lighting, you might be inclined to utilize a greater number of slides. As always, however, don’t feel obligated to use many slides just because you can.
Community Q&A
- If your slide has embedded video, or you aren’t using one slide for each point of your presentation, you can spend longer on each slide. [11] X Research source Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0
- Treat each slide on its own merits. If one slide needs to be onscreen for two minutes, so be it. If it needs to be onscreen for ten seconds, that’s fine too. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0
- If you have a slide with no pictures but several bullet points, each of which you intend to talk about for fifteen to twenty seconds, you might spend well over a minute on that slide. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0

- When you take all of these factors (detail, technicality, audience size and awareness, etc.) into consideration, you can see that the only short answer to "how many slides should I use" is: "it depends." Thanks Helpful 3 Not Helpful 0
You Might Also Like

- ↑ http://www.virtualsalt.com/powerpoint.htm
- ↑ http://www.bloomberg.com/news/articles/2006-06-01/how-to-powerpoint-like-a-pro
- ↑ http://www.shutterstock.com/blog/7-design-tips-for-effective-beautiful-powerpoint-presentations
- ↑ http://www.mrmediatraining.com/2011/03/10/the-five-most-common-powerpoint-mistakes/
- ↑ http://www.free-power-point-templates.com/articles/how-many-slides-for-a-30-minute-presentation/
- ↑ https://owl.english.purdue.edu/media/ppt/20071016041310_686.ppt
About This Article

1. Break complex slides into several simple slides. 2. Include audio and video support only as needed. 3. Time your presentation. 4. Match the number of slides to the subject matter. 5. Tailor to your audience. Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Jun 29, 2017
Is this article up to date?

M. Fernandez
Dec 19, 2017

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
wikiHow Tech Help Pro:
Level up your tech skills and stay ahead of the curve
How Many Slides to Use in a Presentation? 5 Tips
There’s nothing worse than a presentation that goes over time or poorly-designed slides that cram too much information onto the screen at once.
While there are a lot of things that can dictate how many slides to use in a presentation, key factors include how long you have to speak, what content you are presenting, and the visual nature of the content. (Some speakers don’t need slides at all to keep audiences engaged!)
Here, we’re breaking down common presentation times with a guide for how not to overload slides, and use them well—no matter what type of talk you are giving.
How Does Unlimited PowerPoint Templates Sound?
Download thousands of PowerPoint templates, and many other design elements, with a monthly Envato Elements membership. It starts at $16 per month, and gives you unlimited access to a growing library of over 2,000,000 presentation templates, fonts, photos, graphics, and more.

Modern PPT Templates
New & innovative.

Pitch Deck Templates
Startup pitch deck.
Explore PowerPoint Templates
How Many Slides for a 5 Minute Presentation?

When it comes to short presentations, you probably want to keep the number of slides to a minimum. Think about the venue here in particular. How many people are you presenting for?
Often short presentations might be for a small group or on a small screen. That’s a major consideration when it comes to how many slides you need for a 5-minute presentation.
For most speakers that comes down to 5 to 10 slides, up to 2 per minute of speaking time .
- Design for screen size. If you’ll be presenting on a desktop or laptop screen, ensure that text is large enough to read for people standing or sitting a few feet away.
- Practice your timing. Five minutes might seem like a long time until you start talking.
- Put one point on each slide. (That’s probably all you’ll have time for.)
- Include a call to action at the end for the audience. This might include anything from an email address to answer a question or provide feedback to taking a survey or visiting a website.
- Don’t include a questions slide unless you will actually have time to take questions at the end of a short presentation.
How Many Slides for a 10 Minute Presentation?
With a 10-minute you have a little more flexibility in terms of slide count.
With more time, you can vary pacing and might have time to take questions at the end of the talk. (Your slide count will be less if you cut time from your presentation to answer questions.)
For a 10-minute presentation, you’ll probably end up creating 10 to 20 slides, but don’t feel like you have to move through two slides per minute. It really depends on the complexity of the information you are talking about.
Record your presentation as you run through it. Did you finish on time? And were you able to see each slide long enough to understand it during the natural flow of the presentation before moving on to the next one?
- Include plenty of white space for an organized, easy to read design.
- Use a mix of images and text to keep the visual flow moving.
- Use legible fonts that are consistent from slide to slide.
- If a slide looks cluttered, break the content into multiple slides.
- Don’t go crazy with bullets. The goal of each slide is to present an idea, not serve as notes for you.
How Many Slides for a 15 Minute Presentation?

There’s a fairly logical relationship between the time you have to present information and how complicated the content is. The number of slides you need for a 15-minute presentation might not be that much different than at 10 minutes.
That’s because what’s on each slide might need to sit with the audience a little longer. You need to leave a chart on the screen long enough for the audience to understand it. A photo, on the other hand, can flash up and go away quickly and still be understood.
Carefully consider your presentation topic and then use this recommendation as needed: Allow for 20-30 slides for a 15-minute presentation .
- Pick a theme for each slide: Image or text? Don’t expect the audience to “read” both on every slide.
- Use image based slides to connect a short text point (or no text at all) to an idea the audience can see.
- Use text-based slides without images for more complex information or to show bullet points, charts or numbers.
- You don’t have to have a new photo and image for each slide. Use the same image and change the text if you need to. Or don’t use an image at all. Nice typography is pretty awesome.
- Include more detailed information in the notes area for you as you are giving the presentation or to the audience to download and print later.
How Many Slides for a 30 Minute Presentation?
Once you get into the territory of longer presentations, you might want to use slides of varying types – some that are super quick and others that stay visible longer – to get different points across and fit the conversational flow.
This varying approach can be interesting for the audience but might require a little math and planning on your part to determine the exact right number of slides.
Start with this formula for a 30-minute presentation :
- 4 minutes: Amount of time for opening and closing (1 slide each)
- 2 minutes: Time for each point in your presentation (1 slide per point)
- 1 minute: Time for each sub-point in your presentation (1 slide per sub-point)
- 3 minutes: Deep dive for one or two key takeways (1-2 slides)
- Flash slide (quick on and off the screen): For transitions between large topic areas or polling the audience to keep them engaged
Now you can look at your content and do a few quick calculations to get a rough idea of how many slides you might need. For a 30-minute presentation with 5 points with two subpoints each and a takeaway, that’s in the neighborhood of 20 slides.
How Many Slides for a 45 Minute Presentation?

For longer presentations, pace and energy are key. Some presenters can go through an exceptional number of slides because of the way they speak.
Seasoned speakers, often giving a presentation that they’ve done a lot of times, can average 5 slides per minute. These are fast-paced quick hit images that really keep the audience thinking and engaged. It’s a fun style but can be difficult to pull off.
A more moderate estimate is 1 to 2 slides per minute at a varying pace. That’s what you commonly see in corporate presentations and talks. (The content is often complex as well.)
- Consider location with longer presentations. Will the slides be projected on a large screen? Design for that environment.
- Include mixed media clips if appropriate in longer presentations. Varying formats can keep the audience interested.
- Use a design theme for a consistent look and feel for the entire presentation.
- Don’t let slides sit on the screen for too long. Mix it up with a new photo even if the content theme hasn’t changed much. Once you set an expectation for the audience with visuals, you don’t want them to check out.
- Make the most of the top half of the slides. If you are in a big room, sometimes the lower portion is obscured for some audience members. Even if you need to use more slides to keep content toward the top, do it.
How-To Geek
How to time your powerpoint slides for more effective presentations.
Delivering a presentation is not just about giving good slides, it is also about making sure that our presentation finishes by the time our audience w
Delivering a presentation is not just about giving good slides, it is also about making sure that our presentation finishes by the time our audience wants to have their tea break---so practicing how long to speak for each slide is essential for a proper presentation.
Rehearsing our Slides
Before we rehearse, make sure that we select our first slide. Now open the 'Slide Show' tab and click the 'Rehearse Timings' button.
Powerpoint will start the usual presentation mode with a timer panel. The clock on the panel will start ticking once we enter the presentation mode.
Click on the arrow button to move on the next slide and Microsoft Powerpoint will record each timing as you progress from one slide to the next one. You can also click on the pause button just in case you need to answer the phone or turn off the oven while you're rehearsing your slides.
You will see a summary on how much time you have spent on each slide at the end of the rehearsal.
Create a Self-Running Presentation
You can even set a self-running power point slides and let it run according to these timing, relieving us from the need to manually navigate the slides. Bear in mind that we can run into a situation where Powerpoint changes the slides before we finish, so make sure that you can deliver each slide based on your rehearsal timing.
Click on the setup slide show button.
Select the 'Browsed at a kiosk (full screen)' option to setup a self-running Powerpoint presentation. Press the 'esc' key to stop the self-running presentation.
You can re-adjust the presentation timing by recording back from the beginning or from the current slide.
If we're still not happy with the timing, we can clear all the slides timing and redo our presentation rehearsal.
Delivering a good presentation is not an easy task and requires a lot of practice. There are tons of great things that we can do with Powerpoint to add punch to our presentation, for example:
- Adding live web pages to our presentation
- Animating text and objects
- Putting video from the web in our presentation
- Using your mouse as a laser pointer in PowerPoint 2010
What other tips do you have for giving an effective presentation?
ATLANTA, MAY 23-24 PUBLIC SPEAKING CLASS IS ALMOST FULL! RESERVE YOUR SPOT NOW

- Public Speaking Classes
- Corporate Presentation Training
- Online Public Speaking Course
- Northeast Region
- Midwest Region
- Southeast Region
- Central Region
- Western Region
- Presentation Skills
- 101 Public Speaking Tips
- Fear of Public Speaking
How Many PowerPoint Slides Should You Use in a Presentation?

Instead, you want to figure out what you want to say first . Then, after you have designed a great presentation, go back and figure out what visual aids you will need to better make your key points. The main rule of thumb is to provide only the number of slides that you absolutely need and absolutely no more than that.
So in this session, I’m going to cover a few examples for the right number of slides needed in short presentations, the long presentation, the best way to give corporate presentations.
The Max Number of Slides for a 15-Minute Presentation (or Less.)

Instead, especially for short talks, the first thing you want to do is make a list of the most important items that need to be covered in your presentation. Then, rank these items based on their list of importance. As you go down the list, you should notice that the level of importance for each item drops exponentially as you go down the list. So, instead of covering all of the items, just cover the three (or five) most important items in your presentation.
On your first slide, give an overview of all of the points. Just list them out for the audience so they can see what you will be covering. Then, create a separate slide for each of the three (or five) main points. Finally, on your last slide, just copy the content from your first slide and your introduction now becomes a nice conclusion as well.
By the way, for most business presentations, if you can deliver the important things in a 10-minute speech, you will be loved. If you require a 30-minute presentation time, the audience will like you about three times less.
For more details about how to design presentations or to use our helpful online presentation generator click here.
What If You Have an Hour-Long Talk? How Many Slides Do You Need?

Start with an introduction slide with an overview of all five bullet points. On your internal slides, just cover the single main idea for each bullet. You will have five internal slides. Then, end with your summary slide with the main concepts one more time. This repetition of the main concepts will increase the audience’s retention of the material. For the more seasoned presenter, you can use just three main bullet points but add an extra relevant story to each point. The more that you use this technique the easier you will find it to fit your content into the correct presentation length.
For instance, if you find yourself rushing at the end without enough time to finish, you can give fewer details in your stories. If you finish early, you can add more details into your examples and stories.
For a 60-minute presentation, use five bullet points and seven slides . This time insert a couple of different stories as evidence of each bullet point. I like to use the “bad example/good example” technique. On each of the internal slides, give your audience an example of yourself or someone else who did the opposite of the point. Then, follow up with a good example.
The “Bad Example/Good Example” Technique.
If I were to use the technique to prove the point that you need seven slides for an hour presentation, I could use the following…
Bad Example : A few years ago, I went to a three-day seminar where the presenter taught about how to market to universities. On the first morning, his team gave each of us a three-ring binder with hundreds of pages. I was actually pretty excited as I scanned the binder. It was full of a ton of great information. During the first hour, the speaker gave us over 50 great tips and techniques. In the next hour, he covered another 50. He did this over and over for two and a half days. Because I am a public speaking
However, a better example is…
Good Example : A few weeks ago, a long-time client asked me to design a custom workshop for his team. He had a team who were working on a project that had been discontinued. So, he wanted to help the team members have an easier time getting rehired elsewhere in the company. We created a short class for them on how to do well in a job interview. I started by making a list of the most important items they would likely want to know. Art the top of the list was how to reduce nervousness. I spent the first few minutes covering details on how to do this. Second, I gave them a simple process to help them answer questions with credibility. Finally, I gave them a list of questions they would likely be asked. I could have covered hundreds of other tips. However, these were the things that would give them the most bang-for-their-buck.
How Many Slides for a Longer Presentation
Basically, if you design a 120-minute PowerPoint presentation, start by creating two 60-minute presentations. Then, just insert a short break in between each session. When I created the two-day Fearless Presentations ® class, I didn’t start with two days of content. On the contrary, I started with an outline of the “most important” items just like what I suggested you do in your 15-minute presentation.
Here is the list that I started with:
- How to Reduce Public Speaking Fear.
- Designing Short Impromptu Speeches.
- How to Create a Presentation that Is Easier to Deliver.
- Adding Energy and Enthusiasm to Boring Topics.
- Ways to Add Impact and Interactivity to a Presentation.
If I wanted to, I could deliver the entire content of this speech in an hour-long keynote. I’d just need to insert a few examples for each point. That is pretty easy. However, if I want to turn the list into a 2-day seminar, that is pretty easy as well. I’d start with the first point, “How to Reduce Public Speaking Fear.” This becomes the topic of a new one-hour presentation. I use the same technique. “What is the most important thing I can teach the audience about reducing nervousness? What is the second most important thing? And the third thing?”
Basically, the entire two-day class is just a collection of five shorter presentations. In my entire slide deck, I use about 30 different slides in two full days.
The Guy Kawasaki 10/20/30 Rule of PowerPoint
Guy Kawasaki created an interesting PowerPoint rule for entrepreneurs coming to him for venture capital. He calls it his 10/20/30 PowerPoint Rule . This general rule is what he requires presenters to use when they come to him for help. Basically, he noticed that presenters spend too much time blathering about unimportant things. So, he gave them a guide and set time limits for each presenter.
- 10 PowerPoint Slides
- 20-Minute Presentation
- 30 Point Font
Obviously, he created these criteria for a certain type of presentation. However, his logic is sound. In fact, the only thing I might argue with him about is the 10 slides rule. Kawasaki says, “Ten is the optimal number of slides in a PowerPoint presentation because a normal human being cannot comprehend more than ten concepts in a meeting.”
Let me reiterate that. A normal human being cannot comprehend. He doesn’t say retain. The average person can comprehend more information than he or she can retain. For instance, if I read an entire book on accounting, I might comprehend all of the content. However, because the book covers so many concepts, I’m likely to retain only a few. Knowing this, reduce your number of slides and you will increase retention of your important points.

Podcasts , presentation skills
View More Posts By Category: Free Public Speaking Tips | leadership tips | Online Courses | Past Fearless Presentations ® Classes | Podcasts | presentation skills | Uncategorized
Managing Time Effectively in Your Presentation: 4 Expert Tips – How to Stay on Track!
We’ve all been there. Halfway through a presentation, you suddenly realise that you don‘t have enough time left! This despite the fact that you‘ve practiced the presentation again and again and have always come in under time.
Presentations are often time-limited. In particular, pitch presentations, and occasions where there are several speakers, generally have rigid time limits that you must stick to. This article will give you four great tips for managing time effectively.
How to keep your presentation to time – 4 expert tips
Here are our four best tips for managing time during your presentation effectively – why not give them a try?
Tip #1: Prepare thoroughly
You need to start thinking about the timing of your presentation from the beginning of your preparation . One way of doing this is to take a sheet of paper and sketch out your slides in sequence , making a note of the maximum presentation time you anticipate for each slide.
This helps you see which slides are essential, and which can be left out. You should end up with a coherent narrative line, where each slide adds to your argument.
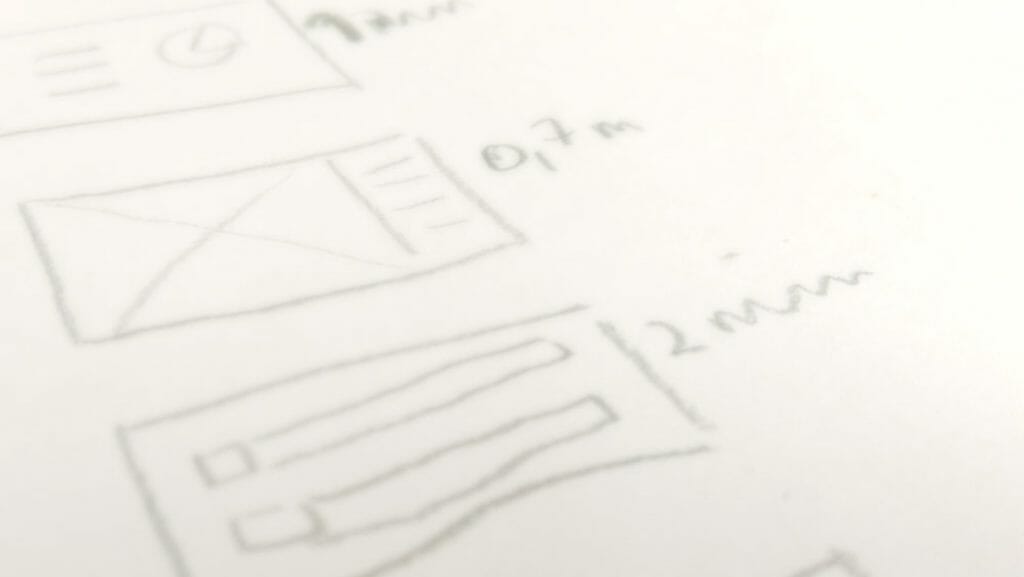

How much speaking time should you allow per slide?
It would be great if we could calculate the speaking time per slide , adding up to the time you’re allowed for your presentation, thus solving the problem of time management. Unfortunately, there aren’t any hard and fast rules. The approximate speaking time per slide depends on the content of that slide and your presentation topic.
As a rule, however, aim to speak for no more than 3-4 minutes per slide. In general, keep it shorter rather than too long – this keeps your audience attentive.
Bonus tip: Keep in mind that your presentation will almost always take longer than when you rehearse it at home beforehand. This is because you are interacting with the audience and follow-up questions are asked. Allow about 20%-40% more time for the actual presentation.
Tip #2: Look at your subject from an outsider’s perspective, and present it accordingly
Think like an outsider. Instead of considering the individual points of your presentation from your own point of view, imagine how long it would take someone without your prior knowledge and background to understand them . Use the latter times as a guide. This way you allow as much room as possible for questions.
You know yourself and your strengths best. When is your energy level at its highest? Do you start strong or do you need a few minutes to get into flow? Tailor your presentation accordingly. Who is your audience and where are you going to give your presentation?
If you are presenting on the evening of the last day of a conference, for example, you need to be prepared for a tired audience. If you are introducing a conference, you may need to clarify terms first. Also, plan your presentation time carefully in light of your surroundings. T hat way, you won’t run out of time or breath.
As a general rule, make sure you meet the needs of your audience . Ask yourself what points you really want to include in your presentation to get your core message across. You can find further tips in our short article “ Focus on audience’s needs “.
Tip #3: Use PowerPoint Speaker View
Another simple trick you can use to keep your presentation time is the PowerPoint Speaker View. This handy PowerPoint feature offers lots of helpful options. For example, you could set it to show the next slide along in your presentation, or display notes that only you, and not your audience, can see.
A really useful feature here is the timer. It shows how much time of your presentation has already passed, allowing you to keep the presentation on time.
We go through how to set the timer in our article “ PowerPoint Presenter View” .
Tip #4: Use shortcuts for PowerPoint for managing time better!
With the right keyboard shortcuts, you can save a lot of time, whether in PowerPoint presentations or generally when working on the computer. The best thing is: they are easy to learn and work on every computer! You can find out exactly which shortcuts there are and how to get the most out of working with shortcuts in our blog post on “ Shortcuts .”
With the help of shortcuts, you can work much more efficiently in the future and invest more time in presenting itself . Not only you, but also your audience will thank you!
Extra Tip: Use add-ins from PresentationLoad!
Our customers often ask whether there is an add-in available that makes it possible to display time periods, countdowns or the current time in presentations . We listened, and developed such an add-in ourselves! With the help of our revolutionary time presentation tool, you can now incorporate time management and efficiency into your next presentation in a professional way.
Until now, the only way to get an overview of time in PowerPoint presentations was to use PowerPoint Speaker View. Unfortunately, this function is only visible to the presenter. That’s why our new Dynamic Time Add-In tool equips your current PowerPoint version with the features needed to show time, date and time periods in the way that best suits your presentation.
The add-in is compatible with:
- Microsoft Office 2010 (32bit & 64bit)
- Microsoft Office 2013 (32bit & 64bit)
- Windows 7 (32bit & 64bit)
- Windows 8.1 (32bit & 64bit)
Four for one: time, date, counter and countdown
Whether it’s a presentation, a lecture, self-running info screens, or trade fair presentations, showing the time, whether faded in or as a countdown, can be a great tool . For example, you could announce an upcoming deadline for an important product or the launch of your website by fading in a countdown.
By doing so, you not only add interest to your presentation, but also have the use of a unique tool known only to a few. To help you get started, we provide a short tutorial below, to help get you up to speed. Follow the simple instructions to get started!
Just install and go: instructions
The add-in is installed by executing the downloaded file (admin rights may be required) and is automatically integrated within your PowerPoint window as a tab.
To activate the range of functions, click the DynamicElements tab. Then select the Time button to open the Time Panel options window. The editing interface for Dynamic Time now appears on the right of the screen.
As soon as you create a new textbox and select a mode in the Time Panel, it will automatically include the date (or time/countdown) you want.
Any number of text fields can be assigned with time and date display. To do this, create a text field in the conventional way, then activate it via the Time Panel (on the right of the page) by assigning a new mode (the default is none).
We’ve put in four modes (functions with setting options) for this purpose:
- Clock for the time display
- Date to show the date
- Counter to display a counter
- Countdown to see a countdown
When choosing time- or date-based displays, you need to select a time zone if the one you want is not the default.
You can display any time or date using a single field, or split it into components (e.g. the time in hours, minutes and seconds).
To see what the dynamic element looks like once inserted, switch to presentation mode via the Slide Show tab and choose From current slide .
(For further instructions, please see the ReadMeFirst file included in the add-in).
Possible uses:
- Dynamic time display
- Show the current time (including seconds) on your PowerPoint slides during the presentation:

- Show a start screen with live time in digital format (for your event, lecture, self-running presentation/info screen):

- Display a world clock with different time zones. By setting different time zones you can, for example, display an individualized company world clock, including all your company locations:

Display the date in different formats . The days of the week can be automatically included if so desired. Combine the date and time for attractive calendar pages!

3. Dynamic Counter
Show the time which has elapsed since a specified point in time (giving the date and time). For example, show the time since the launch of a new product or of your website, the founding of your company or the opening of a particular location.
4. Dynamic Countdown
Show the time remaining until a particular event (in days, hours, minutes and seconds).
Click here to get to the add-in: Download
To sum up: Managing time in presentations the right way
The chances are that your next presentation is coming up. Using our expert tips, you can plan and achieve sticking to the time you’re given for your presentation . You should find it far easier to manage that time effectively.
If you have any further questions about managing presentation time, or indeed about PowerPoint in general, do feel free to email us at [email protected] . We’re always glad to help!
Looking for professionally designed slide templates for your presentation? Take a look around our store! We have a fabulous range of slides for download covering the business topics you need! ► Shop
You might also be interested in the following articles:
- PowerPoint Presenter View
- Concentrate on Audience’s Needs
- Preparing Presentatios: 11 tips
- Target Group Analysis
Share this post
- share
- save

Design Thinking: Problem Solving with a Difference

Why Corporate Mission Statements Are So Important

7 Tips & Learnings from the Apple Keynote
Home Blog PowerPoint Tutorials How To Set Time Duration To Switch Slides in PowerPoint
How To Set Time Duration To Switch Slides in PowerPoint
Usually, presenters use mouse clicks, keys from a keyboard or a remote to switch slides in PowerPoint . However, if you have your presentation well-timed or have to account for every second in a presentation due to time constraints, you might want to make sure that your slides are well-timed. To do this, you can add a time duration to switch your slides. In this tutorial we will show you how to set time duration to switch slides in PowerPoint. For the purpose of this post, we will be using the Financial PowerPoint Template .
Select Your Slides from Slides Pane
In the first step, click the slide preview for the slide you wish to set time for. In case you want all your slides to switch according to a set time limit (e.g. 10 seconds), select one slide and hit CTRL+A to select all slides.
In case you want to set a different time for each slide, you will have to select each slide one by one and follow the steps shown below.
Select a Time Duration for Your Slides from the Transitions Tab
From the Transitions tab, go to ‘After’ and add a time duration after which you wish to switch your slide(s). Also make sure that ‘ On Mouse Click’ is unchecked.
The process for switching slides is similar in various versions across PowerPoint and while we are demonstrating this method using PowerPoint 2013, you will find similar options in older versions (e.g. PowerPoint 2010).
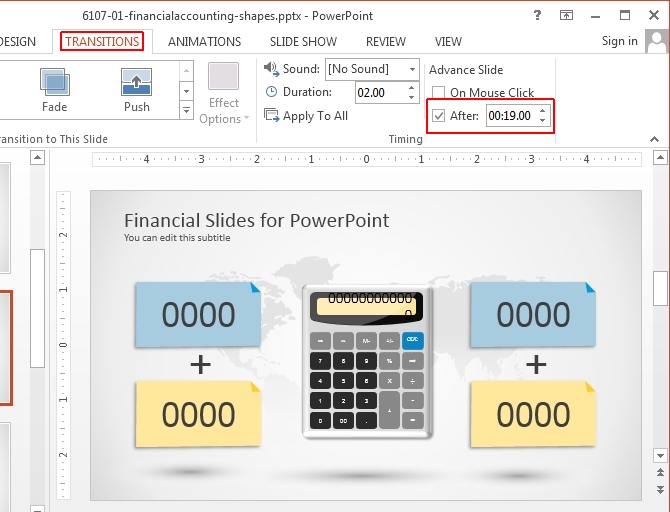
For a Single slide: For a single slide, select the respective slide from the Preview pane and add a time duration for switching the slide.
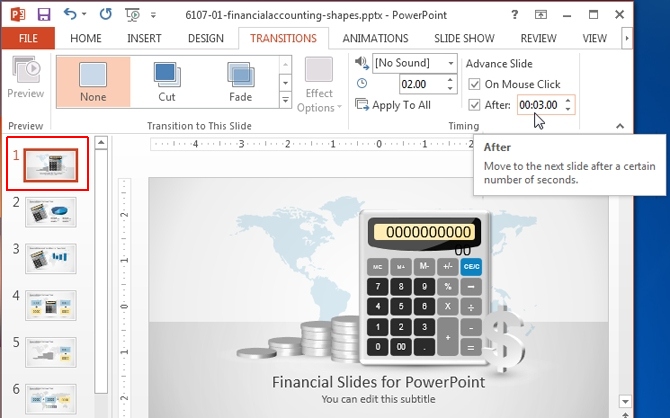
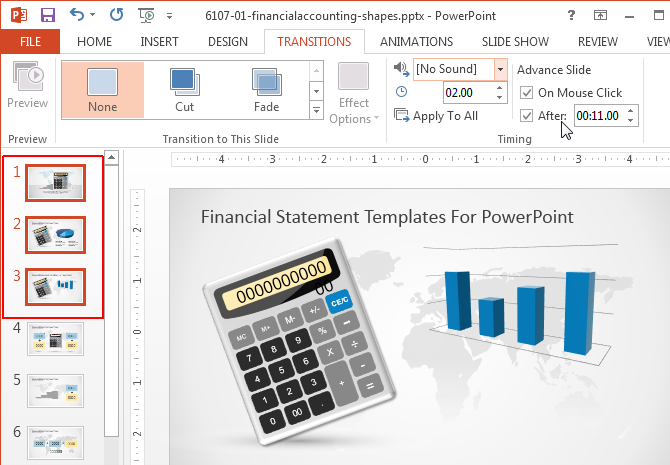
For Multiple Slides: To apply the same time duration to multiple slides, select the slides from the Preview pane using CTRL+Mouse Click, go to the Transitions tab and set a time to switch them. As mentioned earlier, you can also select all slides by clicking a single slide preview, followed by CTRL+A.
In case you have applied slide transitions, you can also set the length of the transitions using the ‘Duration’ option from the same section.
Once you have followed the aforementioned steps, switch to Slide Show mode and your slides will switch according to the set time duration.

While having well-timed slides might help in good time management, you nevertheless need good presentation slides to make an impression on your audience. Slide Model provides High-Quality PowerPoint Templates with editable slide elements which have been designed by expert professionals to give you the imagery that can be attention grabbing and visually appealing. For more details, see our plans and pricing.
Like this article? Please share
PowerPoint 2013, PowerPoint Tips, Presentation, Presentation Tips, Time, Time Management, View Presentation Filed under PowerPoint Tutorials
Related Articles

Filed under Google Slides Tutorials • May 3rd, 2024
How to Work with Google Slides Version History
Go back to previous changes or check who edited your presentation. Learn how to work with Google Slides Version History here.

Filed under Google Slides Tutorials • April 29th, 2024
Best Google Slides Add-Ons
Optimize your Google Slides experience by installing the best Google Slides add-ons available in the market. Full list with photos.

Filed under Design • April 23rd, 2024
How to Create the Perfect Handouts for a Presentation
Learn how to create effective handouts for presentations and the recommended structure for handouts with this guide.
Leave a Reply

- Get started with computers
- Learn Microsoft Office
- Apply for a job
- Improve my work skills
- Design nice-looking docs
- Getting Started
- Smartphones & Tablets
- Typing Tutorial
- Online Learning
- Basic Internet Skills
- Online Safety
- Social Media
- Zoom Basics
- Google Docs
- Google Sheets
- Career Planning
- Resume Writing
- Cover Letters
- Job Search and Networking
- Business Communication
- Entrepreneurship 101
- Careers without College
- Job Hunt for Today
- 3D Printing
- Freelancing 101
- Personal Finance
- Sharing Economy
- Decision-Making
- Graphic Design
- Photography
- Image Editing
- Learning WordPress
- Language Learning
- Critical Thinking
- For Educators
- Translations
- Staff Picks
- English expand_more expand_less
PowerPoint Tips - Simple Rules for Better PowerPoint Presentations
Powerpoint tips -, simple rules for better powerpoint presentations, powerpoint tips simple rules for better powerpoint presentations.

PowerPoint Tips: Simple Rules for Better PowerPoint Presentations
Lesson 17: simple rules for better powerpoint presentations.
/en/powerpoint-tips/embed-excel-charts-in-a-slide/content/
Simple rules for better PowerPoint presentations
Have you ever given a PowerPoint presentation and noticed that something about it just seemed a little … off? If you’re unfamiliar with basic PowerPoint design principles, it can be difficult to create a slide show that presents your information in the best light.
Poorly designed presentations can leave an audience feeling confused, bored, and even irritated. Review these tips to make your next presentation more engaging.
Don't read your presentation straight from the slides
If your audience can both read and hear, it’s a waste of time for you to simply read your slides aloud. Your audience will zone out and stop listening to what you’re saying, which means they won’t hear any extra information you include.
Instead of typing out your entire presentation, include only main ideas, keywords, and talking points in your slide show text. Engage your audience by sharing the details out loud.

Follow the 5/5/5 rule
To keep your audience from feeling overwhelmed, you should keep the text on each slide short and to the point. Some experts suggest using the 5/5/5 rule : no more than five words per line of text, five lines of text per slide, or five text-heavy slides in a row.

Don't forget your audience
Who will be watching your presentation? The same goofy effects and funny clip art that would entertain a classroom full of middle-school students might make you look unprofessional in front of business colleagues and clients.
Humor can lighten up a presentation, but if you use it inappropriately your audience might think you don’t know what you’re doing. Know your audience, and tailor your presentation to their tastes and expectations.
Choose readable colors and fonts
Your text should be easy to read and pleasant to look at. Large, simple fonts and theme colors are always your best bet. The best fonts and colors can vary depending on your presentation setting. Presenting in a large room? Make your text larger than usual so people in the back can read it. Presenting with the lights on? Dark text on a light background is your best bet for visibility.

Don't overload your presentation with animations
As anyone who’s sat through a presentation while every letter of every paragraph zoomed across the screen can tell you, being inundated with complicated animations and exciting slide transitions can become irritating.
Before including effects like this in your presentation, ask yourself: Would this moment in the presentation be equally strong without an added effect? Does it unnecessarily delay information? If the answer to either question is yes—or even maybe—leave out the effect.
Use animations sparingly to enhance your presentation
Don’t take the last tip to mean you should avoid animations and other effects entirely. When used sparingly, subtle effects and animations can add to your presentation. For example, having bullet points appear as you address them rather than before can help keep your audience’s attention.
Keep these tips in mind the next time you create a presentation—your audience will thank you. For more detailed information on creating a PowerPoint presentation, visit our Office tutorials .
/en/powerpoint-tips/three-tips-for-beautiful-powerpoint-presentations/content/
How Many Slides Do You Need For A Whatever-Minute Presentation?
Yousef "yoyo" abu ghaidah.
- May 9, 2018
- One Comment
“How many slides do I need for a 10 minutes presentation?”
“I have 30 minutes. Do I need 30 slides?”
“I have a 60-minute presentation coming up and I don’t want to bore my audience to death with slide-overload. What do I do?”
If I had a dollar for every time I get a question like these, I’d be a millionaire.
It’s time to put the age-old PowerPoint question to rest. How many slides do you really need for your next presentation, regardless of the time set?
Here’s your answer: As many as you need, but within reason .
I know, I know. You’re looking for a quick and simple solution that you can use right now. But trust me, you’ll get what I mean after reading this post.
Rules Don’t Apply … Sort Of
There are so many rules out there that you’ve probably heard of.
“Only use five slides.”
“Keep it to one slide for every three minutes.”
Even presentation pros like Guy Kawasaki will advocate for the 10/20/30 rule (10 slides, 20 minutes, 30 point font).
These rules aren’t necessarily wrong, but I do feel they overlook one of the most important factors in your presentation: Your message.
When you apply a general rule-of-thumb to the content you want to present, you’re going to end up limiting yourself. That sort of practice can be bad for you, and even worse for your audience.
Look at it this way: Do you think J. K. Rowling was thinking about how many pages she would need to get Harry Potter out to the world?

Of course not. Her priorities were centered down to the plot, how the characters express themselves, the intricacies between the hero and the villain, and so on.
Rowling’s only true goal was to write a fictional novel so epic that it would appeal to the masses.
Do I need to tell you how hugely successful she was a result of that approach?
Take the same principle and develop as many slides as you need to capture every meaningful component of your message.
Remember, slides are empty canvases for your information. You can put a single word and a picture to demonstrate your point or 500 words and a chart to do the exact same thing.
But practice this approach with caution. Don’t just cram in slides for the sake of doing so.
Only bring the slides that express the value of your content. Nothing more, nothing less.
Time Allocation is Crucial
Time is the most precious thing we have in this world , and it is certainly the one thing you NEED to respect when it comes to your audience.
That said, there is a misconception about time limits in presentations that you need to be aware of.

Avoid going for the minute(s)-per-slide approach. Many presenters feel that sustaining this number is crucial for delivery. For example, if someone was preparing 10 slides for a 10-minute presentation, then that same person may feel dedicating 1 minute per slide is the way to go.
Don’t do this, because how you allocate your time should be completely up to you.
I’ve witnessed presenters spend 10 seconds on one slide only to spend five minutes on another, and they were extremely effective in their delivery.
The slide that took five minutes to present was also the slide that needed five minutes of my time to understand. This highlighted that the slide in question was meaningful, insightful, and followed a pace that I was comfortable with.
That’s the key take away. Dedicate more of the time given to you to the content that matters most. This approach should allow you to gauge just how many slides you need to bring in.
So, How Many Slides Do You Really Need?
All you have to do is answer two simple questions:
- “How many slides do I need to get my message across?”
- “What pace would my audience feel comfortable with?”
With the ‘right’ answers, you’re almost certain to get the perfect number of slides for your presentation, every single time.
You’re The Special Ingredient
Whatever number you go for, remember that your slides should only be seen as the tools you need to get your message across.
Sure, designing beautiful slides will help, but they won’t do the work for you.
Rely on yourself to get your message out there. Your tone, body-language, and passion are what truly can make or break your presentation.
Dang…I needed this LOL. Thank you for decreasing my stress.
Got a project for us?
© Slide Cow. All rights reserved.
Session expired
Please log in again. The login page will open in a new tab. After logging in you can close it and return to this page.

Presentation Time Calculator
PT Time Controller
보다 정확하게 측정하고 싶다면, Customize를 이용하세요.
1. If you scroll right or left, it will calculate PT time according to corresponding speed. 2. You can consider your speech speed and the interval of your PPT pages .
140 WPM (Words Per Minute)
* 매우 천천히 설명하는 발표는 330 CPM까지도 내려갑니다.
1. Read your script for 20 seconds using below stopwatch. 2. Enter the script as much as you just read and it will calculate PT time about total script. 3. If you have PPT, enter the number of PPT pages, the interval of PPT pages and the time to view materials.
2021.03.18. Modified