
- My presentations

Auth with social network:
Download presentation
We think you have liked this presentation. If you wish to download it, please recommend it to your friends in any social system. Share buttons are a little bit lower. Thank you!
Presentation is loading. Please wait.
Writing a Problem Statement
Published by Esmond Tyler Modified over 6 years ago
Similar presentations
Presentation on theme: "Writing a Problem Statement"— Presentation transcript:

Applied Research Center Abraham S. Fischler School of Education

Scientific Research Dr. Noura Al-dayan.

PPA 501 – Analytical Methods in Administration Lecture 2c – The Research Proposal.

Problem Identification

Educational Research by John W. Creswell. Copyright © 2002 by Pearson Education. All rights reserved. Slide 1 Chapter 3 Identifying a Research Problem.

Identifying a Research Problem

WRITING the Research Problem.

Copyright © 2008 by Pearson Education, Inc. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey All rights reserved. John W. Creswell Educational Research: Planning,

Chapter One of Your Thesis

WRITING A RESEARCH PROPOSAL

CHAPTER 3: DEVELOPING LITERATURE REVIEW SKILLS

Developing Business Practice – 302LON Reading for academic success Week 1.

Elke Johanna de Buhr, PhD Tulane University

Literature Review and Parts of Proposal

Northcentral University The Graduate School February 2014
06/10/20151 Business Research Methods Lecture 3. 06/10/20152 Accessing and reviewing literature as part of research Lecture Outline: Why is it so important.

Selection and Definition of a Problem. First Step Identify a general area that is related to your area of expertise and is of particular interest to you.

Research Proposal First three chapters of your research report What you plan to study, why, how.

Critical Thinking Lesson 8
About project
© 2024 SlidePlayer.com Inc. All rights reserved.
Home Blog Business How to Write a Problem Statement: Hands-On Guide With Examples
How to Write a Problem Statement: Hands-On Guide With Examples

When trying to call an audience to action, it is easy to become fixated on coming up with unassailable arguments and bulletproof evidence. Yet, crafting a compelling problem statement is the first step to getting your proposals heard and acknowledged.
In this post, you’ll get a lowdown on how to write an effective problem statement.
Table of Contents
- What is a Problem Statement?
When Should You Write a Problem Statement
How to write a problem statement, common mistakes to avoid when writing a problem statement, what is a problem statement.
A problem statement is a concise and clear description of the issues or challenges that must be addressed. The main objective of this problem-solving strategy is to establish a common ground with your audience about the existence of a problem before moving to more delicate matters, which is the solution. More importantly, it helps garner support from decision-makers, team members, or funding bodies by presenting a compelling case for why the problem needs attention and resources.
A good problem statement should:
- Provide a concise explanation of the specific issue, leaving no room for ambiguity
- Explain why the problem is significant and requires immediate attention
- Highlight the discrepancy or gap between the current state and the desired state.
Crafting a problem statement is often the first step when writing a project proposal to show stakeholders you are solving a realistic problem. A problem statement is also an effective hook when starting a presentation and getting your audience to lean in.
Whether in written documents, presentations, or team discussions, a well-crafted problem statement can be a compelling hook that draws your audience in and paves the way for successful outcomes.
When writing a problem statement, it’s good to have a structure to follow. It helps to articulate the issue, define its scope, and guide the reader’s understanding of the problem. Below are the elements you would want to include in your problem statement.
- Background or context of the problem
- The specific issue being addressed
- The consequences of not solving the problem
- Brief background of the solution (Optional)
Let’s look at a problem statement example for an internal project proposal to test our recipe.

The problem of Healthcare Cost at CompuSoft
Corporate healthcare cost inflation in the U.S. is rising at an alarming rate. The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services recently estimated that medical claims in the country would triple by the year 2025. Such a surge in healthcare expenses poses a formidable challenge for companies like CompuSoft.
In 2017, the average healthcare compensation claim per employee at CompuSoft was $3,136.20. This doubled when the pandemic hit in 2020 at $6,095.49 and has consistently increased since. Controlling these mounting expenses is crucial, as they significantly threaten CompuSoft’s corporate profits.
Maintaining healthy employees offers direct financial benefits to companies, including reduced insurance claims and lower absenteeism rates. I propose that CompuSoft consider implementing an employee fitness program to address this issue.
Step 1. Providing a Background of the Problem
The problem statement should begin with the big picture of the issue and then narrow it down to the specific problem. In the example above, the writer started by providing the context of the problem, which is the rising corporate healthcare cost in the US, with a statement from the health services bureau. This way, the audience understands the extent of the problem and validates the solutions the presenter may propose.
Step 2. Articulating Specific Issue Being Addressed
In the second paragraph, the writer brings the discussion closer to home by focusing on the impact of rising healthcare costs on CompuSoft. This localized approach personalizes the issue and makes it more relatable to the reader, as it directly affects a specific company they can relate to.
The concrete figures quantify the problem and make it more tangible. They add a sense of immediacy and relevance, capturing the reader’s attention and underscoring the significance of the problem for the company’s well-being.
Step 3. Identifying Risks of Not Solving the Problem
This part of the problem statement may be the final blow you need to bring the stakeholders on board with you. When they understand the potential negative consequences and risks of not addressing the problem, they are more likely to recognize the urgency of finding a solution and actively participate in the resolution process.
This statement should be explained concisely – preferably in a one-liner. In the example above, the writer briefly mentioned how escalating healthcare costs could erode the company’s profits.
Step 4. Providing a Background to the Solution
Finally, you should discuss potential solutions that may be implemented. The purpose is to introduce the general approach to solving the problem. This background information serves as a teaser, prompting further discussion with stakeholders.
In the example, the presenter briefly mentioned “implementing an employee fitness program” but did not discuss the specific approach to take. Whether the solution is to build an in-house fitness center or provide fitness-club membership is a topic that should be discussed in the body of the proposal.
1. Being too Vague or Broad
A vague or broad problem statement defeats why you are writing it in the first place – that is, to orient your audience to the significance of your proposal. Vague problem definition lacks insights and often leads to unsuccessful proposals. The broad problem statement, on the other hand, lacks scope and tries to solve multiple problems, diluting the effectiveness of the proposed solution.
You can avoid this mistake by quantifying the problem with concrete figures and focusing on one central issue. A single, specific problem can be more easily measured and evaluated to determine the effectiveness of the solutions.
Bad Problem Statement: The company’s healthcare claim cost is so high. We need to lower the claims, improve the wellness of employees, and increase our profit.
Improved Problem Statement: The company’s average healthcare claim cost per employee has increased by 50% from $3,136.20 in 2021 to $4704.3 in 2022. We need a wellness program that will help decrease the growth rate to 10% this year.
2. Failing to Identify the Root Cause of the Problem
The best approach to resolving any issue begins by analyzing the situation from its foundational elements and gradually working toward a solution. This method allows for a thorough understanding of the problem and its underlying causes. When you fail to identify the root cause of the problem in the problem statement, you are likely to propose an inadequate solution that doesn’t address the core issue.
The Root Cause Analysis (RCA) Diagram is a critical tool in this process. A problem-solving method credited to Sakichi Toyoda , RCA helps find the underlying problem by visually mapping out the potential contributing factors or categories influencing the issue.

Problem: Mounting healthcare expenses of CompuSoft
Causes: national healthcare cost inflation, the impact of COVID-19, the health status of the employees, age of the employees, medical pay for absentee days, and wellness of the employees.
Our fictitious problem statement above pinpointed several causes of the mounting healthcare expenses of CompuSoft, such as (1.) the national healthcare cost inflation, (2.) the impact of COVID-19, (3.) the health status of the employees, and (4.) the absence of fitness programs for employees. While the first two root causes may be external and beyond the direct control of CompuSoft, the organization can still focus on addressing the latter causes to control corporate healthcare costs.
3. Focusing on Symptoms Instead of the Problem Itself
What would you do if you broke your bone? You’d probably take a pain reliever to ease the pain, right? You need to see a doctor and get a cast to heal your injury properly. This is a classic example of differentiating symptoms.
In the workplace, not tackling the underlying problem can result in recurrent issues and an inefficient allocation of resources.
In our example, CompuSoft can switch to a health insurance partner that offers the best deal, but that will only provide temporary relief by reducing immediate healthcare expenses. Encouraging wellness programs and prioritizing employee health is a more comprehensive and sustainable solution.
4. Using Biased or Subjective Language
This needs no lengthy explanation. Biased language may not accurately reflect the facts or reality of the problem. This reinforces the objectivity of the problem statement.
A well-crafted problem statement provides a clear direction for proposal development and increases the odds of gaining buy-in from stakeholders. If, in the end, the audience rejects your solution, at least you leave them convinced of the problem’s existence and that something needs to be done. That’s a win on your part!
Like this article? Please share
Business Analysis Tools, Problem Solving Filed under Business
Related Articles

Filed under Business • April 4th, 2024
Consulting Presentation Slides: A Guide to PPT Consultant Tools
Get to know the best tools to craft a consulting presentation by area of interest. Fully detailed guide plus template list.

Filed under Business • March 13th, 2024
Exploring the Significance of the Fit Gap Analysis (Examples + Templates)
Master the Fit Gap Analysis with this guide featuring professionally designed PPT templates and step-by-step examples.

Filed under PowerPoint Tutorials • February 29th, 2024
How To Present a 5 Why’s Root Cause Analysis
The regular rut of life or the professional wheel, problems can leave you fumbled and dumbstruck at any bend of the road. Mostly unforeseen and uninvited, some problems can have you at your knees while others can bring you to the wits end in an instant. Irrespective of which realm of life you encounter a […]
Leave a Reply
How to Write a Problem Statement Slide (with Examples)
Table of contents, what is a problem statement and why is it important.
Projects should always begin with a thorough definition of the problem as a problem statement.
A problem statement is a concise description of the issue that will be addressed in a project.
It can be tempting to skip the problem statement because you’ve seen this problem before, you already know the solution, or because a stakeholder is pushing you to move faster.
However, many projects have failed because of a false assumption that everybody understands the problem. This misunderstanding is generally not identified until the project is completed and somebody is surprised by the output.
Therefore, good problem solvers take time to define the problem precisely. Then, they socialize the problem with all key stakeholders to ensure that the definition is understood and agreed upon.
Example problem statements
In a business context, problem statements may be:
- Why has revenue growth fallen from 10% in 2021 to 5% in 2022?
- How can ACME Bank increase its market share to 15% by 2025?
- Why are over 50% of customers not renewing their subscription after month 3?
Characteristics of a good problem statement
In order to ensure that your problem statement is concise and informative, it should be:
- Specific: Ensure that you constrain the scope of your problem by making the problem statement should be specific as possible, while still being informative and valuable.
- Time-bound: Ensure that you include time constraints on your problem statement; solutions for the short term might be significantly different than solutions for the long term.
- Measurable and testable: Ensure that your problem statement is quantified, so that there are clear criteria for you to define success.
Problem statement worksheet and downloadable templates
A problem statement worksheet articulates the problem that will be addressed in the project.
It also describes how the problem came about, defines the scope and constraints of the project, and identifies key stakeholders and sources of insight.
The problem statement worksheet looks like this:

You can download this slide (and 30 others) for free below:
Download a free problem statement slide and 29 other slide templates for free
Roadmap slides, recommendations slides, journey slides, key takeaways slides, next steps slides, panel slides, and more!
Free Problem Statement Slide Templates: PowerPoint & Google Slides
By Kate Eby | February 24, 2024
- Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn
Link copied
Write effective problem statements and create engaging presentations for stakeholders with this roundup of problem statement slide templates for PowerPoint and Google Slides. Download these free, customizable templates and edit them for your needs.
On this page, you’ll find a project problem statement worksheet slide template , a customer problem statement slide template , a 5 Ws product problem statement template , and more. You’ll also find tips for writing problem statements and links to related problem-solving templates .
Project Problem Statement Elements Slide Template

Download a Project Problem Statement Elements Slide Template for
PowerPoint | Google Slides
When to Use This Template: This template is perfect for project managers and team leaders who need to articulate the challenges and objectives of a new initiative. It provides a structured format for presenting a project's problems and requirements during planning meetings or proposal presentations. The template is particularly useful in meetings where gaining consensus or approval from decision-makers is crucial.
Notable Template Features: The template breaks down the problem, scope, objectives, benefits, and resources into clear sections, making complicated information easy to understand. This focuses the discussion and ensures that all aspects of the problem are considered. The color-coded sections also help make your presentation clearer and more appealing to stakeholders.
Three-Part Problem Statement Slide Template
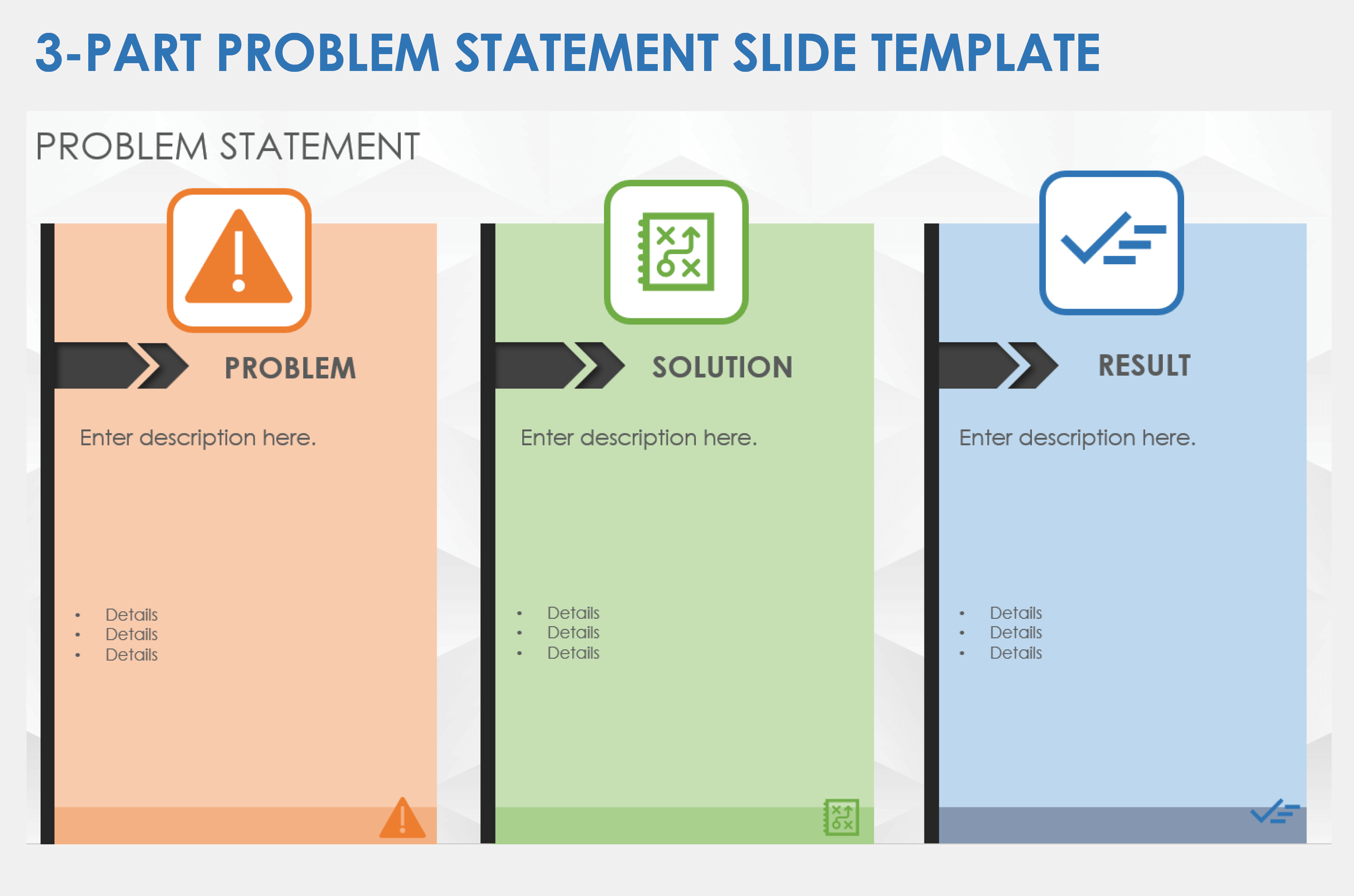
Download a Three-Part Problem Statement Slide Template for
When to Use This Template: Project managers or teams can use this template to clearly communicate challenges, proposed solutions, and expected results. It serves as a foundational tool for project planning and decision-making, helping teams effectively communicate critical issues to stakeholders and align efforts toward shared objectives.
Notable Template Features: This slide template helps guide the audience from problem identification to resolution and final outcomes. The bullet points under each category allow you to list key details and focus on what matters most.
Project Problem Statement Worksheet Slide Template
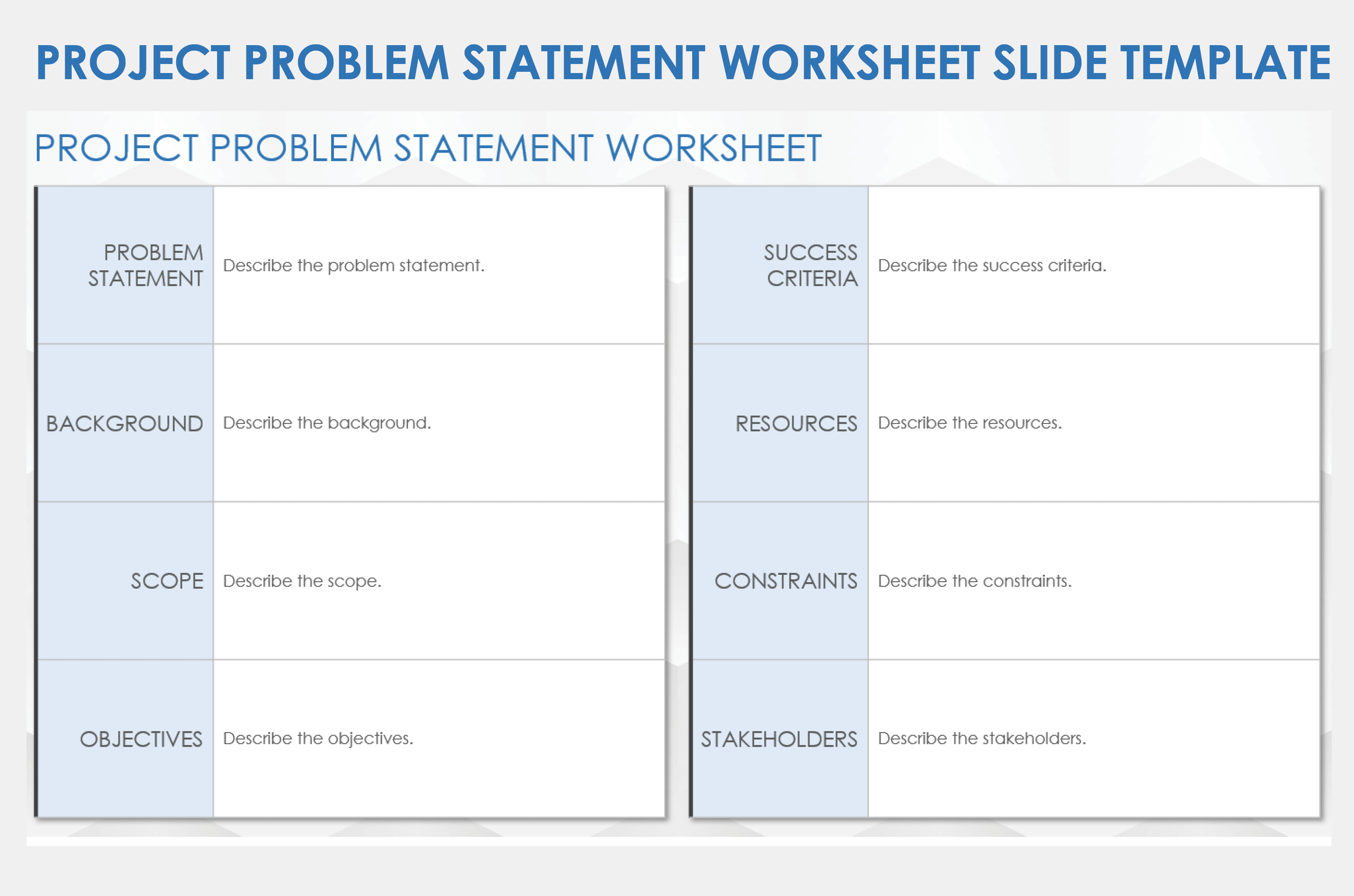
Download a Project Problem Statement Worksheet Slide Template for
When to Use This Template: This worksheet template is designed to clearly outline the central challenge of a new project or initiative. It provides a straightforward way to write a problem statement that is clear and actionable. Teams can use this tool at the outset of the planning stage to ensure that everyone understands the issues being addressed, the criteria for success, and the boundaries of the project.
Notable Template Features: The template's comprehensive structure breaks down the problem statement into specific components, such as context, success criteria, stakeholders, and scope. This helps teams focus their discussions and ensure a shared understanding of the problem. Teams can also use this template in presentations to provide stakeholders with context for the problem statement.
Traffic Light Problem Statement Slide Template
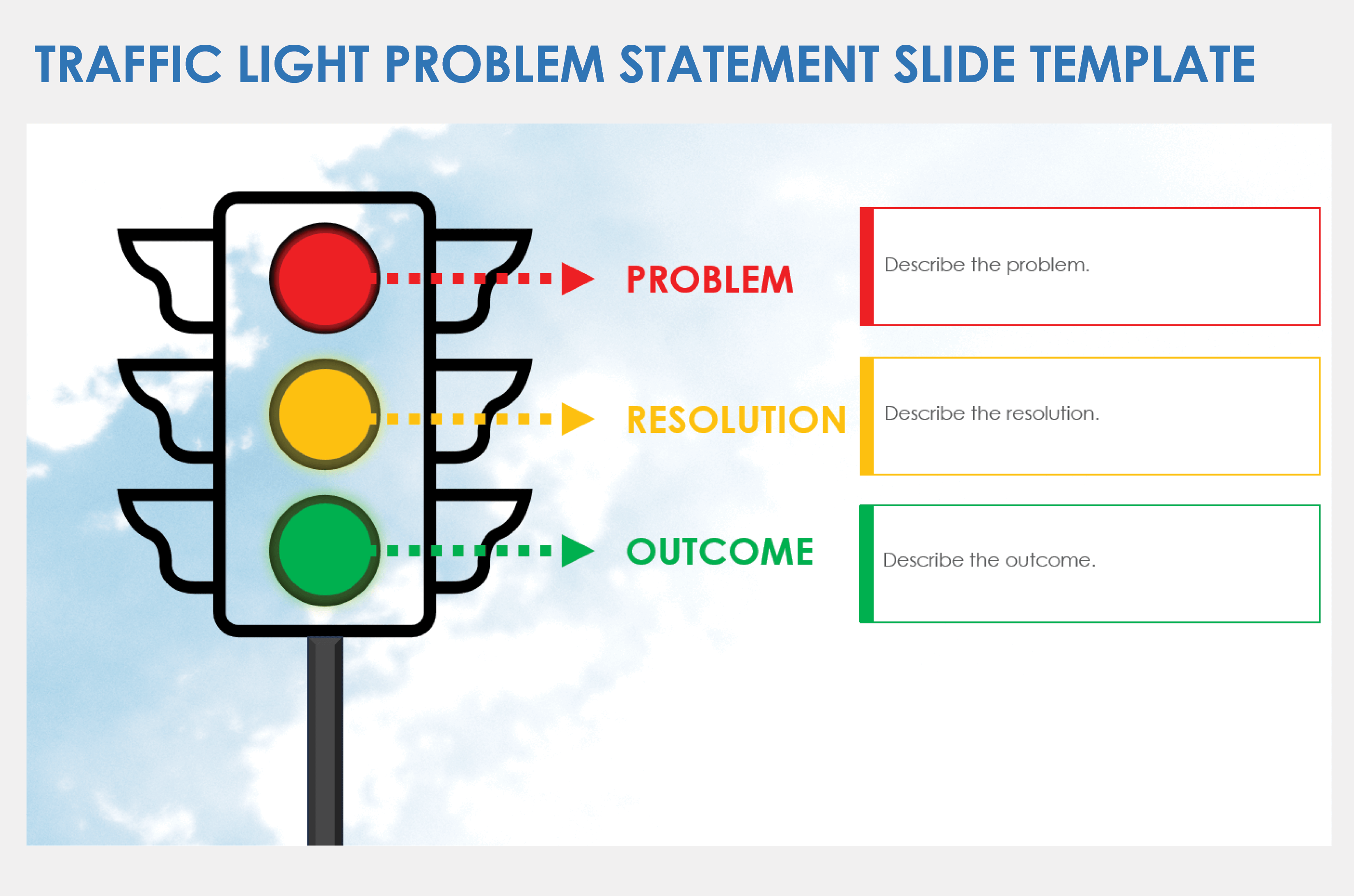
Download a Traffic Light Problem Statement Slide Template for
When to Use This Template: Project or product managers can use this template to present a clear problem statement in meetings or in documents. This template is particularly useful during the initial stages of project planning or when addressing project roadblocks.
Notable Template Features: The template includes sections for identifying a problem, how to solve it, and what the results should be. Each part corresponds to the colors in the traffic light graphic, which reinforces the importance of a careful approach to problem-solving.
Single-Problem Statement and Solution Slide Template
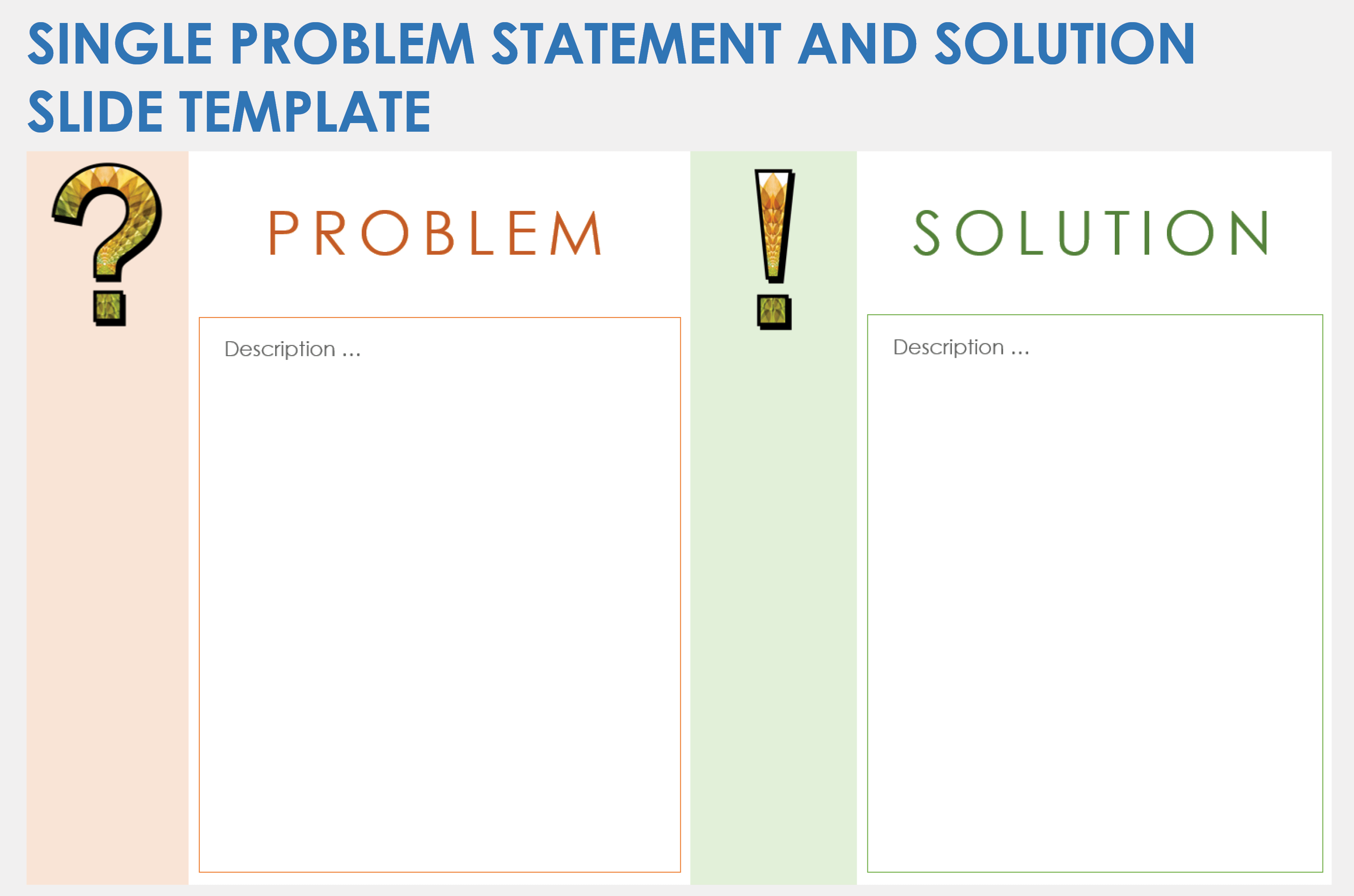
Download a Single-Problem Statement and Solution Slide Template for
When to Use This Template: This template is ideal for project proposals, strategy meetings, or pitches where a clearly defined problem and solution can drive decision-making. The visual juxtaposition of problems versus solutions helps stakeholders quickly grasp the core issues and the strategy for resolution.
Notable Template Features: This template has a two-column layout that visually distinguishes challenges and solutions. Each section contains placeholders for text and icons, enhancing the presentation’s visual appeal. Icons such as question and check marks guide the audience from problem to solution.

Multiple-Problem Statement and Solution Slide Template
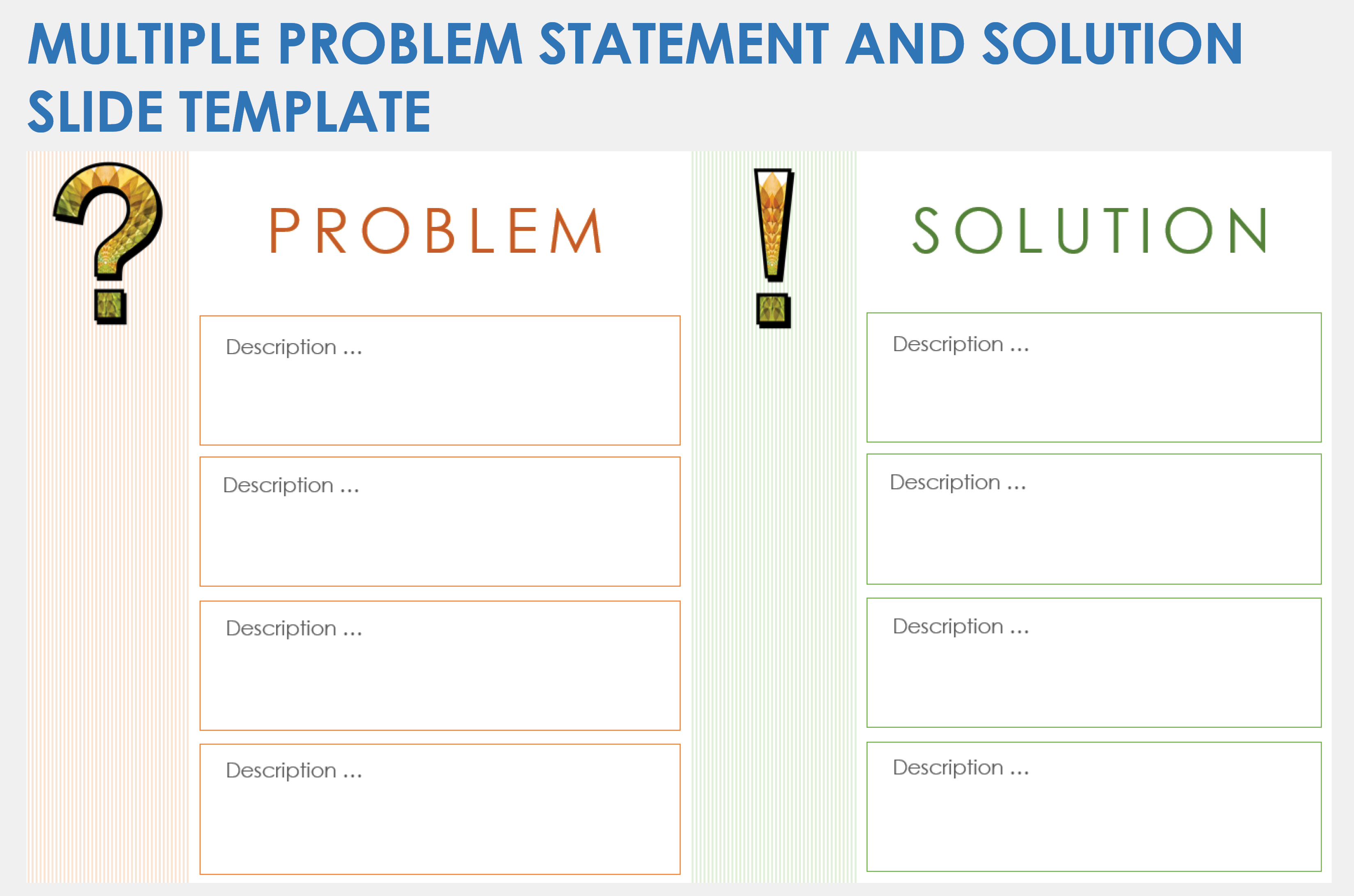
Download a Multiple-Problem Statement and Solution Slide Template for
When to Use This Template: Project or product managers can use this template in strategic planning sessions, problem-solving meetings, or any scenario where a clear comparative analysis is needed. The slide format, which shows each challenge next to its proposed solution, can be useful during team meetings where alignment on issues and remedies is crucial.
Notable Template Features: This template has a two-column layout that guides the viewer from problems on the left to solutions on the right. Each problem and solution pair is clearly marked, making complex information more accessible for the audience.
Customer Problem Statement Slide Template
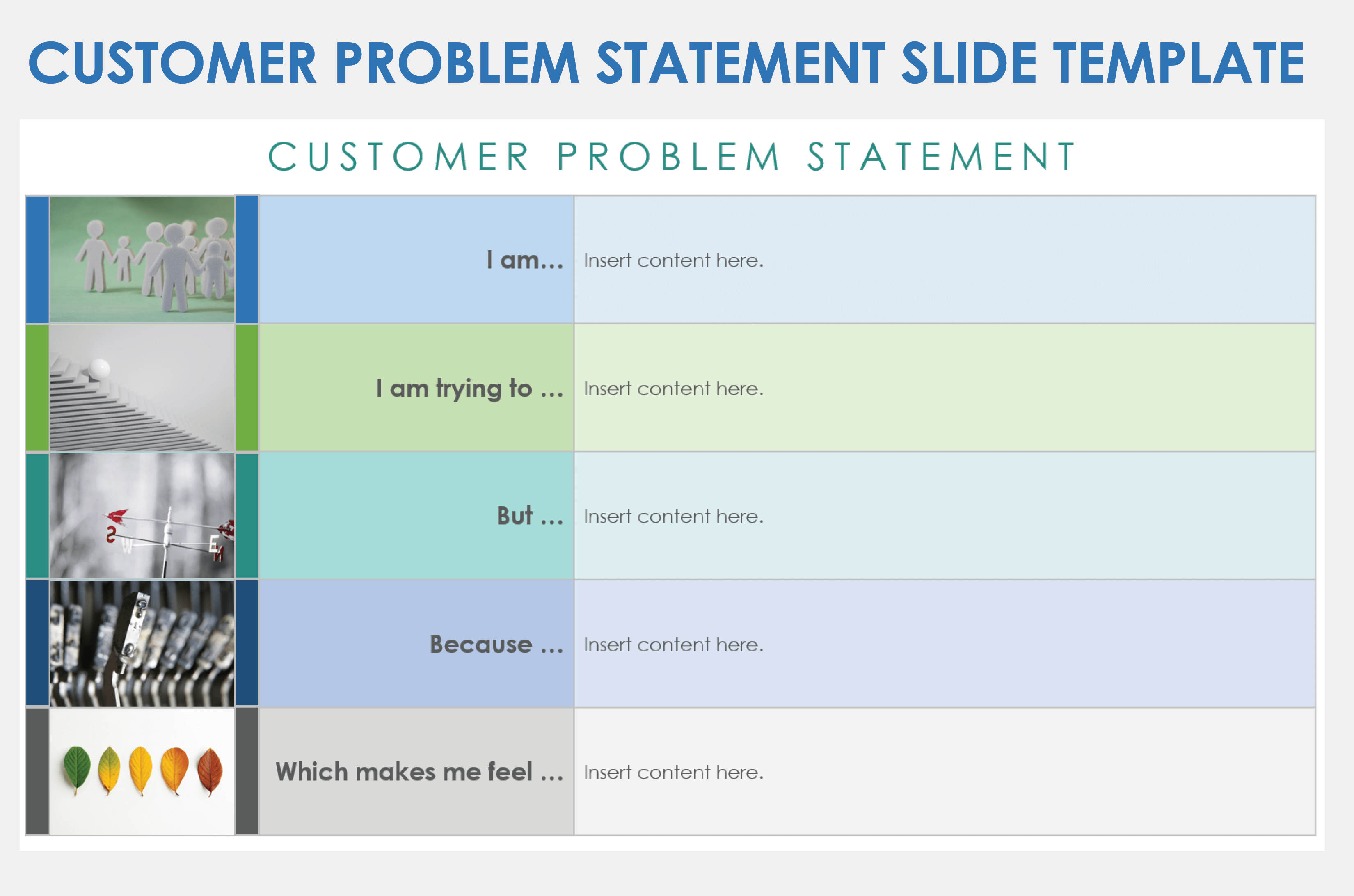
Download a Customer Problem Statement Slide Template for
When to Use This Template: Product managers and customer service teams can use this template to break down a customer's problem into tangible parts, clarifying the issue, the attempts to resolve it, the obstacles faced, and its emotional impact. This template is particularly effective for internal presentations that aim to align team members on customer pain points and drive home the urgency of finding a solution.
Notable Template Features: The template provides a step-by-step layout that guides the presenter through the different aspects of a customer's dilemma. Color-coded sections make the narrative easy to follow through each step of the statement. This breakdown not only captures the complexity of the issue but also fosters a deeper understanding of the problem among team members.
Circular Customer Problem Statement Slide Template
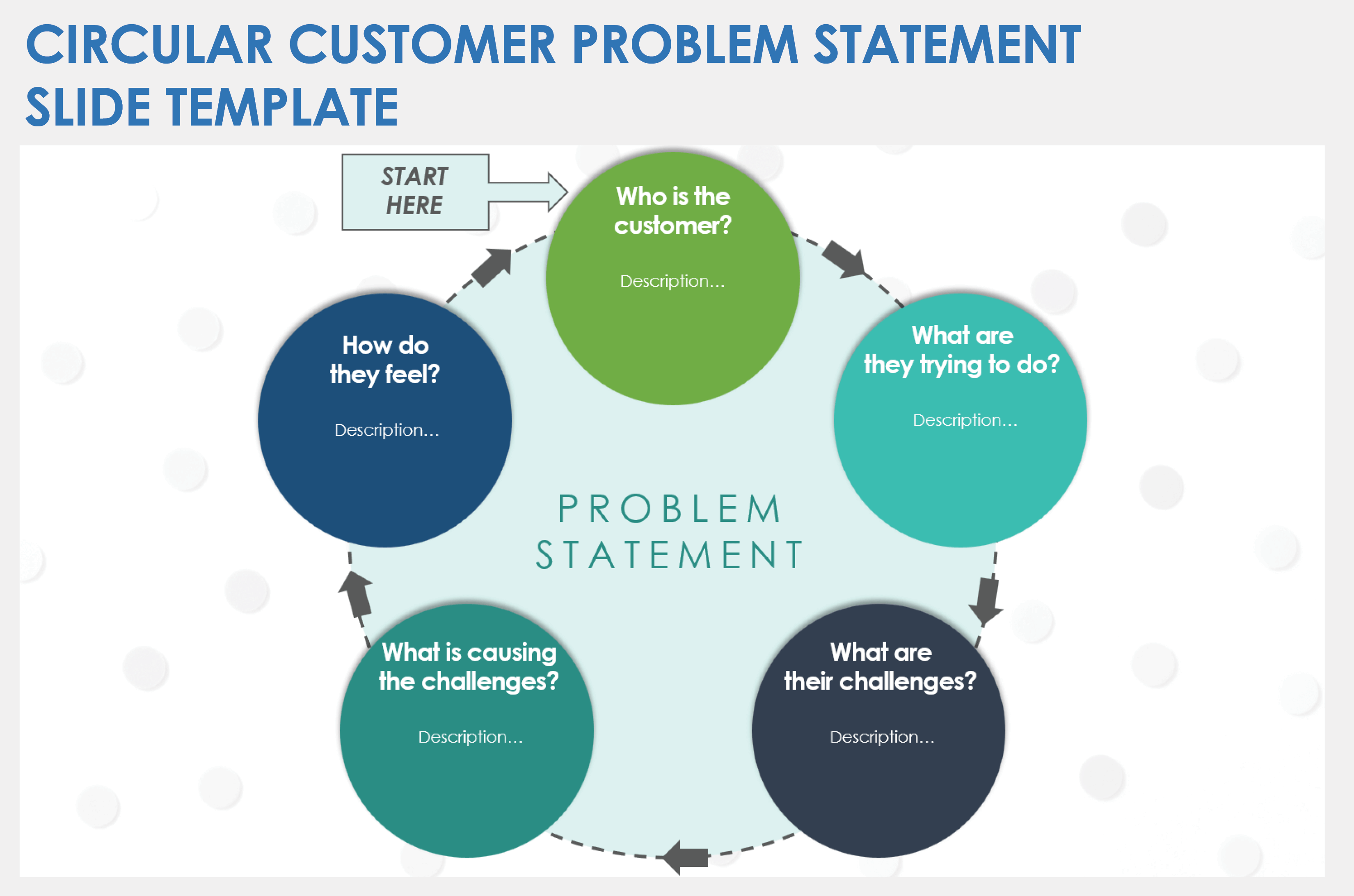
Download a Circular Customer Problem Statement Slide Template for
When to Use This Template: Use this customer problem statement template to get a full picture of a customer's issue, from who the customer is to their goals, challenges, and emotional responses. It is ideal for sessions focused on understanding and addressing customer experiences, ensuring that teams explore every facet of the problem and link it back to the customer's perspective.
Notable Template Features: This template features a circular flow that tells the whole story of the customer’s issue, with each segment prompting a key part of the problem. Its design encourages comprehensive analysis, and the arrangement of sections ensures that thoughts flow logically. You can also customize the template to focus on the workflow around the problem or other details rather than only the customer story.
Product Problem Statement Slide Template
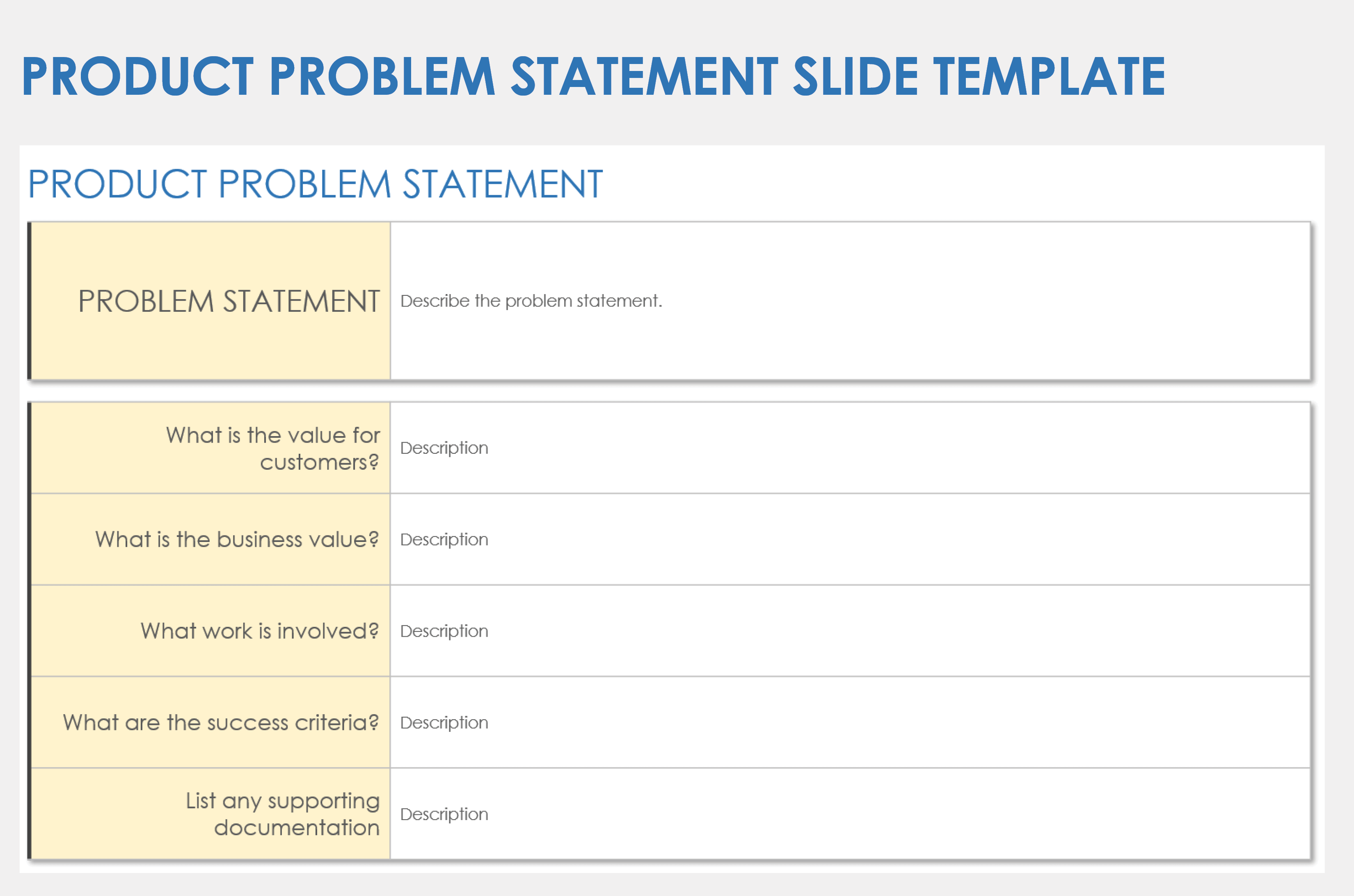
Download a Product Problem Statement Slide Template for
When to Use This Template: Product managers can use this template to clearly articulate the problem their product aims to solve. This serves as an essential tool during the initial stages of product development or when proposing enhancements to existing products. By structuring thoughts and research systematically, this template helps managers secure stakeholder buy-in and align cross-functional teams toward a common objective.
Notable Template Features: Each section prompts users to delve deeply into understanding the problem and its potential impacts, customer value, and business significance. The template allows you to link externally to supporting documentation to show that all claims and assumptions are backed by research. The template's simple structure helps to streamline the problem-solving process, while its thoroughness makes the problem statement more compelling.
5 Ws Product Problem Statement Slide Template
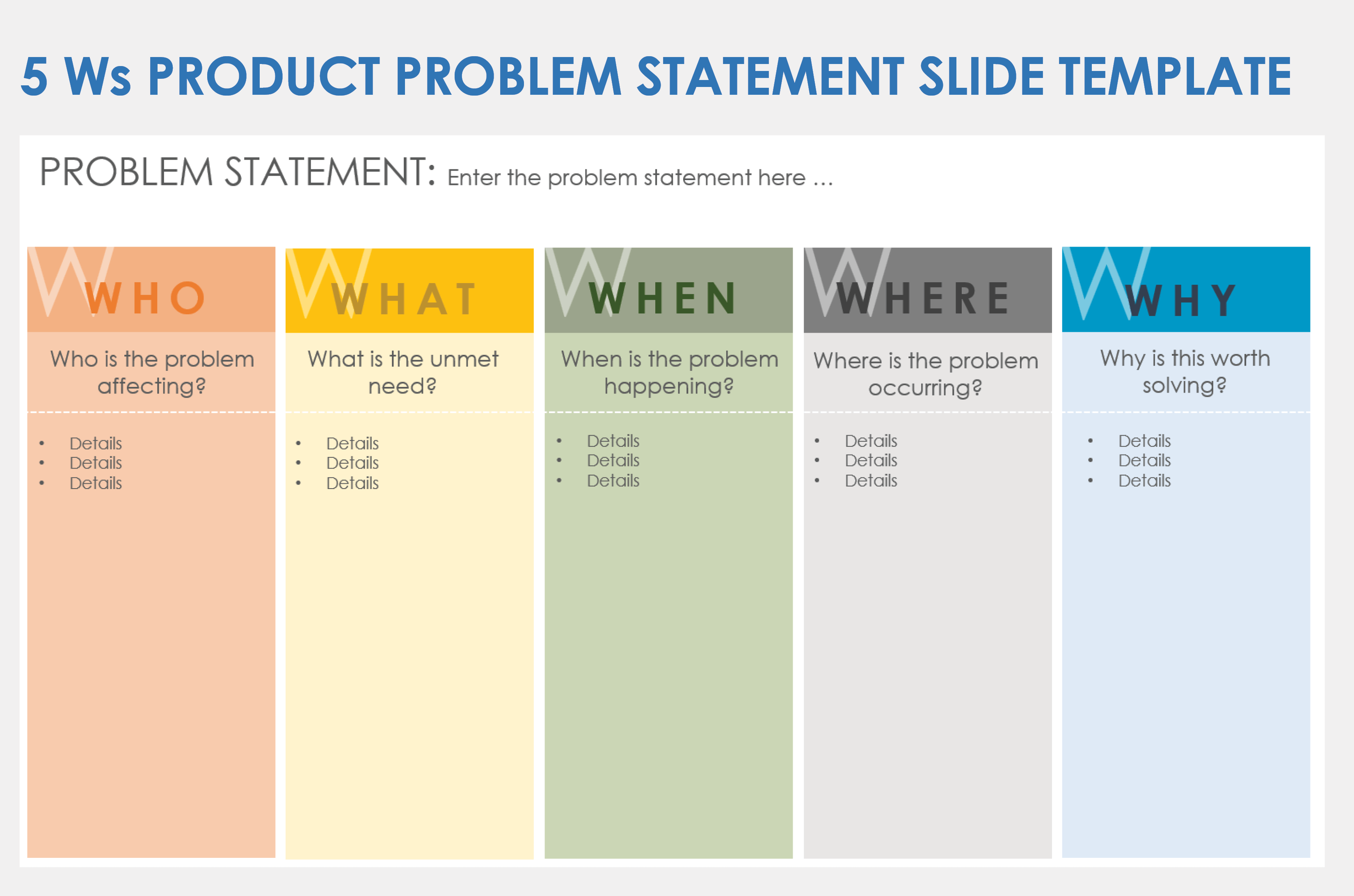
Download a Five Ws Product Problem Statement Slide Template for
When to Use This Template: Product managers and teams can use this template to define and document the who, what, when, where, and why of a problem. This ensures that team members align on the problem before moving toward solutions, fostering a focused approach to product development.
Notable Template Features: This template prompts users to consider all aspects of a problem statement: who it affects, what the problem is, when and where it occurs, and why it is critical to address. Each column uses color-coding and clear bullet points for organized note-taking.
How to Write a Problem Statement
A problem statement serves as the foundation for any project, ensuring that everyone involved understands the core of the problem they need to solve. Crafting a well-defined statement is crucial for guiding a team toward a solution efficiently.
Follow these steps to create a compelling problem statement:
- Identify the Problem: Gather information about the issue through research, observations, or discussions with stakeholders. For customer problem statements, this might include using surveys or customer service calls to gather data on customer pain points. Use templates such as the 5 Ws to thoroughly understand the who, what, when, where, and why of the problem.
- Explain the Impact: Describe how the problem affects the organization, customers, or stakeholders. Provide data or examples to illustrate the extent of the problem's impact.
- Analyze the Cause: Investigate and identify the root causes of the problem. Understanding why the problem exists is crucial for finding an effective solution. Keep asking why and drilling down to the root cause to ensure that your problem statement describes the core problem rather than a symptom.
- Set Objectives: Define what a successful solution would look like. Outline the desired outcome and what changes or improvements you aim to achieve. Use financial and other measurable data to illustrate the benefits of your proposed solution.
- Specify Constraints and Requirements: Highlight any limitations — such as budget, time, or resources — that could impact the solution. Also, list any necessary criteria that the solution must meet, providing measurable benchmarks for success.
- Review and Refine: Once you draft the problem statement, review it to ensure clarity. The statement can be referenced throughout the project to keep work on track, but keep in mind that factors can change, impacting solutions and action plans. Be prepared to pivot as the project progresses.
The key to an effective problem statement lies in its clarity and precision. Keep it succinct, focused on the problem, and free of jargon to ensure that it's accessible to everyone involved.
For more tools, see this complete collection of free problem statement templates .
How Do You Present a Problem Statement?
Presenting a problem statement is your opportunity to bring the problem to life, engage your audience, and set the stage for collaborative problem-solving. While a written problem statement can be as short as an elevator pitch, stakeholders need context to understand the significance of a problem and the reasoning behind any proposed solutions.
Here are the elements to include in a problem statement presentation:
- State the Problem Clearly: Present the problem statement in a clear and concise manner. Use simple language to ensure that everyone understands the issue at hand.
- Discuss Causes and Impact: Briefly introduce the background and relevance of the problem to your audience. Share your insights into the causes of the problem. This helps in building a common understanding of the problem's roots and complexity. Use data, anecdotes, or real-life examples to illustrate the significance of the problem and how it affects the organization, stakeholders, or customers.
- Clarify Outcomes: Clearly state what you aim to achieve by solving the problem. Define the desired outcomes and success criteria to give your audience a clear idea of the direction you propose. Acknowledge any limitations or specific requirements that could influence the approach to solving the problem. This transparency helps in setting realistic expectations.
- Invite Feedback: Encourage your audience to share their thoughts, questions, and suggestions. Foster an open dialogue to promote collaborative problem-solving.
- Conclude With Next Steps: End your presentation by summarizing the key points and outlining next steps to ensure everyone leaves with a clear understanding of the problem and the actions required.
Keep your presentation focused, clear, and interactive to maximize understanding and participation. The goal is not only to present a problem but to motivate and guide your audience toward finding a solution together.
Related Problem-Solving Templates
Using problem-solving templates can transform complex challenges into manageable tasks, guiding you from analysis to actionable solutions. Download one of the problem-solving templates below to clearly define problems, identify root causes, and create more successful outcomes.
Root Cause Analysis Template
This root cause analysis template provides a comprehensive report with a list of questions to help you identify the cause of an event or issue, identify actions already taken, and recommend preventative strategies.
DMAIC Analysis Template
DMAIC stands for define, measure, analyze, implement, and control . This DMAIC template takes you through this process of defining the problem, measuring its significance, analyzing factors contributing to the problem, identifying potential solutions, and planning to prevent a recurrence of the problem.

5 Whys Template
The 5 Why process is a method for investigating the root cause of a problem by asking why the issue is occurring, then repeating the question until you get to the root cause. Download this 5 Whys template to evaluate a problem and determine corrective actions.

Fishbone Diagram Template
Brainstorm the possible causes of an issue with a fishbone diagram template. The diagram provides a visual tool for identifying cause-and-effect relationships and getting at the root of an issue.
Corrective Action Plan Template
Use this corrective action plan template to identify problems, plan action steps to mitigate the issues, and track progress.

For more related templates, including a cause mapping template and an example report, see this full selection of root cause analysis templates .
Use Smartsheet to Solve Your Project Problems
From simple task management and project planning to complex resource and portfolio management, Smartsheet helps you improve collaboration and increase work velocity -- empowering you to get more done.
The Smartsheet platform makes it easy to plan, capture, manage, and report on work from anywhere, helping your team be more effective and get more done. Report on key metrics and get real-time visibility into work as it happens with roll-up reports, dashboards, and automated workflows built to keep your team connected and informed.
When teams have clarity into the work getting done, there’s no telling how much more they can accomplish in the same amount of time. Try Smartsheet for free, today.
Discover a better way to streamline workflows and eliminate silos for good.
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Problem Statements PowerPoint Presentation

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.

The Research Problem & Statement

I f you’re new to academic research, you’re bound to encounter the concept of a “ research problem ” or “ problem statement ” fairly early in your learning journey. Having a good research problem is essential, as it provides a foundation for developing high-quality research, from relatively small research papers to a full-length PhD dissertations and theses.
In this post, we’ll unpack what a research problem is and how it’s related to a problem statement . We’ll also share some examples and provide a step-by-step process you can follow to identify and evaluate study-worthy research problems for your own project.
Overview: Research Problem 101
What is a research problem.
- What is a problem statement?
Where do research problems come from?
- How to find a suitable research problem
- Key takeaways
A research problem is, at the simplest level, the core issue that a study will try to solve or (at least) examine. In other words, it’s an explicit declaration about the problem that your dissertation, thesis or research paper will address. More technically, it identifies the research gap that the study will attempt to fill (more on that later).
Let’s look at an example to make the research problem a little more tangible.
To justify a hypothetical study, you might argue that there’s currently a lack of research regarding the challenges experienced by first-generation college students when writing their dissertations [ PROBLEM ] . As a result, these students struggle to successfully complete their dissertations, leading to higher-than-average dropout rates [ CONSEQUENCE ]. Therefore, your study will aim to address this lack of research – i.e., this research problem [ SOLUTION ].
A research problem can be theoretical in nature, focusing on an area of academic research that is lacking in some way. Alternatively, a research problem can be more applied in nature, focused on finding a practical solution to an established problem within an industry or an organisation. In other words, theoretical research problems are motivated by the desire to grow the overall body of knowledge , while applied research problems are motivated by the need to find practical solutions to current real-world problems (such as the one in the example above).
As you can probably see, the research problem acts as the driving force behind any study , as it directly shapes the research aims, objectives and research questions , as well as the research approach. Therefore, it’s really important to develop a very clearly articulated research problem before you even start your research proposal . A vague research problem will lead to unfocused, potentially conflicting research aims, objectives and research questions .

What is a research problem statement?
As the name suggests, a problem statement (within a research context, at least) is an explicit statement that clearly and concisely articulates the specific research problem your study will address. While your research problem can span over multiple paragraphs, your problem statement should be brief , ideally no longer than one paragraph . Importantly, it must clearly state what the problem is (whether theoretical or practical in nature) and how the study will address it.
Here’s an example of a statement of the problem in a research context:
Rural communities across Ghana lack access to clean water, leading to high rates of waterborne illnesses and infant mortality. Despite this, there is little research investigating the effectiveness of community-led water supply projects within the Ghanaian context. Therefore, this study aims to investigate the effectiveness of such projects in improving access to clean water and reducing rates of waterborne illnesses in these communities.
As you can see, this problem statement clearly and concisely identifies the issue that needs to be addressed (i.e., a lack of research regarding the effectiveness of community-led water supply projects) and the research question that the study aims to answer (i.e., are community-led water supply projects effective in reducing waterborne illnesses?), all within one short paragraph.
Need a helping hand?
Wherever there is a lack of well-established and agreed-upon academic literature , there is an opportunity for research problems to arise, since there is a paucity of (credible) knowledge. In other words, research problems are derived from research gaps . These gaps can arise from various sources, including the emergence of new frontiers or new contexts, as well as disagreements within the existing research.
Let’s look at each of these scenarios:
New frontiers – new technologies, discoveries or breakthroughs can open up entirely new frontiers where there is very little existing research, thereby creating fresh research gaps. For example, as generative AI technology became accessible to the general public in 2023, the full implications and knock-on effects of this were (or perhaps, still are) largely unknown and therefore present multiple avenues for researchers to explore.
New contexts – very often, existing research tends to be concentrated on specific contexts and geographies. Therefore, even within well-studied fields, there is often a lack of research within niche contexts. For example, just because a study finds certain results within a western context doesn’t mean that it would necessarily find the same within an eastern context. If there’s reason to believe that results may vary across these geographies, a potential research gap emerges.
Disagreements – within many areas of existing research, there are (quite naturally) conflicting views between researchers, where each side presents strong points that pull in opposing directions. In such cases, it’s still somewhat uncertain as to which viewpoint (if any) is more accurate. As a result, there is room for further research in an attempt to “settle” the debate.
Of course, many other potential scenarios can give rise to research gaps, and consequently, research problems, but these common ones are a useful starting point. If you’re interested in research gaps, you can learn more here .
How to find a research problem
Given that research problems flow from research gaps , finding a strong research problem for your research project means that you’ll need to first identify a clear research gap. Below, we’ll present a four-step process to help you find and evaluate potential research problems.
If you’ve read our other articles about finding a research topic , you’ll find the process below very familiar as the research problem is the foundation of any study . In other words, finding a research problem is much the same as finding a research topic.
Step 1 – Identify your area of interest
Naturally, the starting point is to first identify a general area of interest . Chances are you already have something in mind, but if not, have a look at past dissertations and theses within your institution to get some inspiration. These present a goldmine of information as they’ll not only give you ideas for your own research, but they’ll also help you see exactly what the norms and expectations are for these types of projects.
At this stage, you don’t need to get super specific. The objective is simply to identify a couple of potential research areas that interest you. For example, if you’re undertaking research as part of a business degree, you may be interested in social media marketing strategies for small businesses, leadership strategies for multinational companies, etc.
Depending on the type of project you’re undertaking, there may also be restrictions or requirements regarding what topic areas you’re allowed to investigate, what type of methodology you can utilise, etc. So, be sure to first familiarise yourself with your institution’s specific requirements and keep these front of mind as you explore potential research ideas.
Step 2 – Review the literature and develop a shortlist
Once you’ve decided on an area that interests you, it’s time to sink your teeth into the literature . In other words, you’ll need to familiarise yourself with the existing research regarding your interest area. Google Scholar is a good starting point for this, as you can simply enter a few keywords and quickly get a feel for what’s out there. Keep an eye out for recent literature reviews and systematic review-type journal articles, as these will provide a good overview of the current state of research.
At this stage, you don’t need to read every journal article from start to finish . A good strategy is to pay attention to the abstract, intro and conclusion , as together these provide a snapshot of the key takeaways. As you work your way through the literature, keep an eye out for what’s missing – in other words, what questions does the current research not answer adequately (or at all)? Importantly, pay attention to the section titled “ further research is needed ”, typically found towards the very end of each journal article. This section will specifically outline potential research gaps that you can explore, based on the current state of knowledge (provided the article you’re looking at is recent).
Take the time to engage with the literature and develop a big-picture understanding of the current state of knowledge. Reviewing the literature takes time and is an iterative process , but it’s an essential part of the research process, so don’t cut corners at this stage.
As you work through the review process, take note of any potential research gaps that are of interest to you. From there, develop a shortlist of potential research gaps (and resultant research problems) – ideally 3 – 5 options that interest you.

Step 3 – Evaluate your potential options
Once you’ve developed your shortlist, you’ll need to evaluate your options to identify a winner. There are many potential evaluation criteria that you can use, but we’ll outline three common ones here: value, practicality and personal appeal.
Value – a good research problem needs to create value when successfully addressed. Ask yourself:
- Who will this study benefit (e.g., practitioners, researchers, academia)?
- How will it benefit them specifically?
- How much will it benefit them?
Practicality – a good research problem needs to be manageable in light of your resources. Ask yourself:
- What data will I need access to?
- What knowledge and skills will I need to undertake the analysis?
- What equipment or software will I need to process and/or analyse the data?
- How much time will I need?
- What costs might I incur?
Personal appeal – a research project is a commitment, so the research problem that you choose needs to be genuinely attractive and interesting to you. Ask yourself:
- How appealing is the prospect of solving this research problem (on a scale of 1 – 10)?
- Why, specifically, is it attractive (or unattractive) to me?
- Does the research align with my longer-term goals (e.g., career goals, educational path, etc)?
Depending on how many potential options you have, you may want to consider creating a spreadsheet where you numerically rate each of the options in terms of these criteria. Remember to also include any criteria specified by your institution . From there, tally up the numbers and pick a winner.
Step 4 – Craft your problem statement
Once you’ve selected your research problem, the final step is to craft a problem statement. Remember, your problem statement needs to be a concise outline of what the core issue is and how your study will address it. Aim to fit this within one paragraph – don’t waffle on. Have a look at the problem statement example we mentioned earlier if you need some inspiration.
Key Takeaways
We’ve covered a lot of ground. Let’s do a quick recap of the key takeaways:
- A research problem is an explanation of the issue that your study will try to solve. This explanation needs to highlight the problem , the consequence and the solution or response.
- A problem statement is a clear and concise summary of the research problem , typically contained within one paragraph.
- Research problems emerge from research gaps , which themselves can emerge from multiple potential sources, including new frontiers, new contexts or disagreements within the existing literature.
- To find a research problem, you need to first identify your area of interest , then review the literature and develop a shortlist, after which you’ll evaluate your options, select a winner and craft a problem statement .

You Might Also Like:

How To Choose A Tutor For Your Dissertation
Hiring the right tutor for your dissertation or thesis can make the difference between passing and failing. Here’s what you need to consider.

5 Signs You Need A Dissertation Helper
Discover the 5 signs that suggest you need a dissertation helper to get unstuck, finish your degree and get your life back.

Writing A Dissertation While Working: A How-To Guide
Struggling to balance your dissertation with a full-time job and family? Learn practical strategies to achieve success.

How To Review & Understand Academic Literature Quickly
Learn how to fast-track your literature review by reading with intention and clarity. Dr E and Amy Murdock explain how.

Dissertation Writing Services: Far Worse Than You Think
Thinking about using a dissertation or thesis writing service? You might want to reconsider that move. Here’s what you need to know.
📄 FREE TEMPLATES
Research Topic Ideation
Proposal Writing
Literature Review
Methodology & Analysis
Academic Writing
Referencing & Citing
Apps, Tools & Tricks
The Grad Coach Podcast
I APPRECIATE YOUR CONCISE AND MIND-CAPTIVATING INSIGHTS ON THE STATEMENT OF PROBLEMS. PLEASE I STILL NEED SOME SAMPLES RELATED TO SUICIDES.
Very pleased and appreciate clear information.
Your videos and information have been a life saver for me throughout my dissertation journey. I wish I’d discovered them sooner. Thank you!
Very interesting. Thank you. Please I need a PhD topic in climate change in relation to health.
Your posts have provided a clear, easy to understand, motivating literature, mainly when these topics tend to be considered “boring” in some careers.
Thank you, but i am requesting for a topic in records management
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Submit Comment
- Print Friendly

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
1) The document discusses how to write an effective statement of the problem for a research proposal. It provides guidelines for selecting a research problem, considerations in selecting a problem, criteria for a good problem, and the key parts and characteristics of an effective statement.
Statement of the problem (final) This document provides an outline for developing a research proposal. It includes sections for background information, defining the research problem, formulating objectives, selecting a research topic, and identifying variables and measurements.
In academic research, writing a problem statement can help you contextualize and understand the significance of your research problem. It is often several paragraphs long, and serves as the basis for your research proposal. Alternatively, it can be condensed into just a few sentences in your introduction.
The document discusses research problem statements and their components. It provides definitions of a research problem and notes that a good problem statement clearly describes the issue to be addressed, generates the research questions, and identifies gaps in previous literature.
A research problem is an educational issue or question in the study. An objective is the major intent of the study. Research questions are those that the researcher would like answered or addressed in the study.
Crafting a problem statement is often the first step when writing a project proposal to show stakeholders you are solving a realistic problem. A problem statement is also an effective hook when starting a presentation and getting your audience to lean in.
A problem statement worksheet articulates the problem that will be addressed in the project. It also describes how the problem came about, defines the scope and constraints of the project, and identifies key stakeholders and sources of insight.
Write effective problem statements and create engaging presentations for stakeholders with this roundup of problem statement slide templates for PowerPoint and Google Slides. Download these free, customizable templates and edit them for your needs.
Problem Statements PowerPoint Presentation. This resource is enhanced by a PowerPoint file. If you have a Microsoft Account, you can view this file with PowerPoint Online.
In this post, we’ll unpack what a research problem is and how it’s related to a problem statement. We’ll also share some examples and provide a step-by-step process you can follow to identify and evaluate study-worthy research problems for your own project.