- Research Process
- Manuscript Preparation
- Manuscript Review
- Publication Process
- Publication Recognition
- Language Editing Services
- Translation Services


How to Write a Journal Article from a Thesis
- 3 minute read
- 238.7K views
Table of Contents
You are almost done with your PhD thesis and want to convert it into a journal article. Or, you’re initiating a career as a journal writer and intend to use your thesis as a starting point for an article. Whatever your situation, turning a thesis into a journal article is a logical step and a process that eventually every researcher completes. But…how to start?
The first thing to know about converting a thesis into a journal article is how different they are:
Thesis Characteristics:
- Meets academic requirements
- Reviewed by select committee members
- Contains chapters
- Lengthy, no word limits
- Table of contents
- Lengthy research of literature
- IRB approval described in detail
- Description and copies of tools used
- All findings presented
- Verb tenses may vary
Journal Article Characteristics:
- Meets journalistic standards
- Reviewed by a panel of “blind” reviewers
- Word limits
- Manuscript format
- Succinct research of literature
- IRB described in 1 to 3 sentences
- Essential and succinct tool information
- Selected findings presented
- Verb tenses are fairly consistent
Converting your thesis to a journal article may be complex, but it’s not impossible.
A thesis is a document of academic nature, so it’s more detailed in content. A journal article, however, is shorter, highlighting key points in a more succinct format. Adapting a thesis for conversion into a journal article is a time-consuming and intricate process that can take you away from other important work. In that case, Elsevier’s Language Editing services may help you focus on important matters and provide a high-quality text for submission in no time at all.
If you are going to convert a thesis into a journal article, with or without professional help, here is a list of some of the steps you will likely have to go through:
1. Identify the best journal for your work
- Ensure that your article is within the journal’s aim and scope. How to find the right journal? Find out more .
- Check the journal’s recommended structure and reference style
2. Shorten the length of your thesis
- Treat your thesis as a separate work
- Paraphrase but do not distort meaning
- Select and repurpose parts of your thesis
3. Reformat the introduction as an abstract
- Shorten the introduction to 100-150 words, but maintain key topics to hold the reader’s attention.
- Use the introduction and discussion as basis for the abstract
4. Modify the introduction
- If your thesis has more than one research question or hypothesis, which are not all relevant for your paper, consider combining your research questions or focusing on just one for the article
- Use previously published papers (at least three) from the target journal as examples
5. Tighten the methods section
- Keep the discussion about your research approach short
6. Report main findings in the results
- Expose your main findings in the results section in concise statements
7. Discussion must be clear and concise
- Begin by providing an interpretation of your results: “What is it that we have learned from your research?”
- Situate the findings to the literature
- Discuss how your findings expand known or previous perspectives
- Briefly present ways in which future studies can build upon your work and address limitations in your study
8. Limit the number of references
- To choose the most relevant and recent
- To format them correctly
- Consider using a reference manager system (e.g. Mendeley ) to make your life easier
If you are not a proficient English speaker, the task of converting a thesis into a journal article might make it even more difficult. At Elsevier’s Language Editing services we ensure that your manuscript is written in correct scientific English before submission. Our professional proofers and editors check your manuscript in detail, taking your text as our own and with the guarantee of maximum text quality.
Language editing services by Elsevier Author Services:

How to Choose a Journal to Submit an Article

How to Submit a Paper for Publication in a Journal
You may also like.

How to Write a Cover Letter for Your Manuscript? Here are the Tips and Examples

Publishing Biomedical Research: What Rules Should You Follow?

Writing an Effective Cover Letter for Manuscript Resubmission

Journal Acceptance Rates: Everything You Need to Know

Research Data Storage and Retention

How to Find and Select Reviewers for Journal Articles

How to Request the Addition of an Extra Author Before Publication

Paper Rejection: Common Reasons
Input your search keywords and press Enter.
- Interesting
- Scholarships
- UGC-CARE Journals
11 Differences Between a Thesis and an Article
Journal article and thesis are two important formats of reports in academia. There are certain differences between the thesis and article. The aim of the thesis is totally different from a journal article. Being a researcher , understanding the differences between both kind of academic writing is very essential.
Differences Between a Thesis and an Article
Courtesy: Elsevier.com
Hope, this article helps you to distinguish the difference between a thesis and an article.
What is the Difference Between Thesis and Dissertation?
What is the difference between sci, scie and esci journals, how to become an academic journal reviewer|step by step guide.
- Difference between
- Peer Reviewed Journals
Top 7 Artificial Intelligence (AI) Tools in Scientific Research 2024
Why mahatma gandhi never won the nobel prize for peace, nomination and selection of nobel prize laureates.
Really it is very very important for a Researcher. Without knowledge of writing an article and thesis research is a dilemma .It is fruitless. Many Many Thanks for your Support in this regard.
[…] 11 Differences Between a Thesis and an Article […]
[…] Also Read: 11 Differences Between a Thesis and an Article | iLovePhD […]
LEAVE A REPLY Cancel reply
Log in to leave a comment
Most Popular
Ugc phd excellence citation to recognize outstanding research, strategies to end the science nobel drought in india, the roadmap to nobel prize-worthy research, annas archive – download research papers for free, ethnographic research examples: exploring cultures through immersive study, advantages and disadvantages of qualitative research methodologies, 150+ cutting-edge chemical engineering research topics, best for you, 24 best online plagiarism checker free – 2024, what is a phd a comprehensive guide for indian scientists and aspiring researchers, popular posts, unethical journal publications, top 100 journal publications in the world 2024, top 488 scopus indexed journals in computer science – open access, popular category.
- POSTDOC 317
- Interesting 259
- Journals 236
- Fellowship 134
- Research Methodology 103
- All Scopus Indexed Journals 94
Mail Subscription

iLovePhD is a research education website to know updated research-related information. It helps researchers to find top journals for publishing research articles and get an easy manual for research tools. The main aim of this website is to help Ph.D. scholars who are working in various domains to get more valuable ideas to carry out their research. Learn the current groundbreaking research activities around the world, love the process of getting a Ph.D.
Contact us: [email protected]
Google News
Copyright © 2024 iLovePhD. All rights reserved
- Artificial intelligence
[email protected]
- English English Spanish German French Turkish

Thesis vs. Research Paper: Know the Differences
It is not uncommon for individuals, academic and nonacademic to use “thesis” and “research paper” interchangeably. However, while the thesis vs. research paper puzzle might seem amusing to some, for graduate, postgraduate and doctoral students, knowing the differences between the two is crucial. Not only does a clear demarcation of the two terms help you acquire a precise approach toward writing each of them, but it also helps you keep in mind the subtle nuances that go into creating the two documents. This brief guide discusses the main difference between a thesis and a research paper.
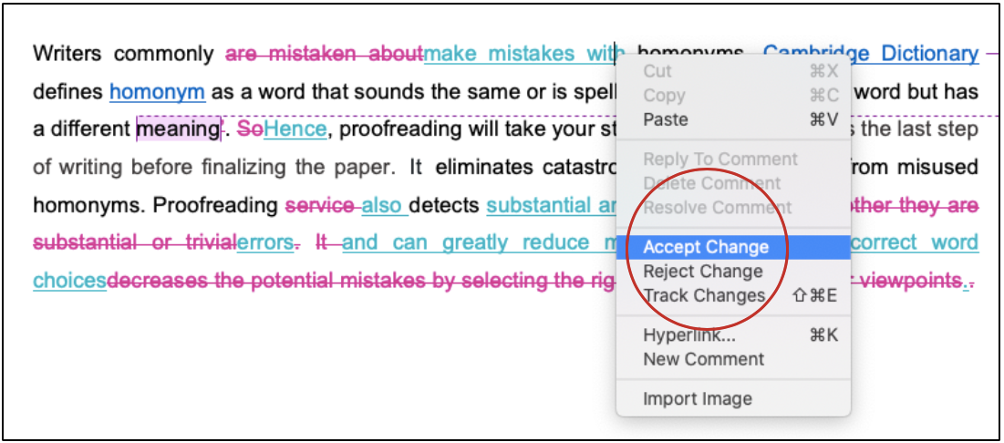
This article discusses the main difference between a thesis and a research paper. To give you an opportunity to practice proofreading, we have left a few spelling, punctuation, or grammatical errors in the text. See if you can spot them! If you spot the errors correctly, you will be entitled to a 10% discount.
It is not uncommon for individuals, academic and nonacademic to use “thesis” and “research paper” interchangeably. After all, both terms share the same domain, academic writing . Moreover, characteristics like the writing style, tone, and structure of a thesis and research paper are also homogenous to a certain degree. Hence, it is not surprising that many people mistake one for the other.
However, while the thesis vs. research paper puzzle might seem amusing to some, for graduate, postgraduate and doctoral students, knowing the differences between the two is crucial. Not only does a clear demarcation of the two terms help you acquire a precise approach toward writing each of them, but it also helps you keep in mind the subtle nuances that go into creating the two documents.
Defining the two terms: thesis vs. research paper
The first step to discerning between a thesis and research paper is to know what they signify.
Thesis: A thesis or a dissertation is an academic document that a candidate writes to acquire a university degree or similar qualification. Students typically submit a thesis at the end of their final academic term. It generally consists of putting forward an argument and backing it up with individual research and existing data.
How to Write a Perfect Ph.D. Thesis
How to Choose a Thesis or Dissertation Topic: 6 Tips
5 Common Mistakes When Writing a Thesis or Dissertation
How to Structure a Dissertation: A Brief Guide
A Step-by-Step Guide on Writing and Structuring Your Dissertation
Research Paper: A research paper is also an academic document, albeit shorter compared to a thesis. It consists of conducting independent and extensive research on a topic and compiling the data in a structured and comprehensible form. A research paper demonstrates a student's academic prowess in their field of study along with strong analytical skills.
7 Tips to Write an Effective Research Paper
7 Steps to Publishing in a Scientific Journal
Publishing Articles in Peer-Reviewed Journals: A Comprehensive Guide
10 Free Online Journal and Research Databases for Researchers
How to Formulate Research Questions
Now that we have a fundamental understanding of a thesis and a research paper, it is time to dig deeper. To the untrained eye, a research paper and a thesis might seem similar. However, there are some differences, concrete and subtle, that set the two apart.
1. Writing objectives
The objective behind writing a thesis is to obtain a master's degree or doctorate and the ilk. Hence, it needs to exemplify the scope of your knowledge in your study field. That is why choosing an intriguing thesis topic and putting forward your arguments convincingly in favor of it is crucial.
A research paper is written as a part of a course's curriculum or written for publication in a peer-review journal. Its purpose is to contribute something new to the knowledge base of its topic.
2. Structure
Although both documents share quite a few similarities in their structures, the framework of a thesis is more rigid. Also, almost every university has its proprietary guidelines set out for thesis writing.
Comparatively, a research paper only needs to keep the IMRAD format consistent throughout its length. When planning to publish your research paper in a peer-review journal, you also must follow your target journal guidelines.
3. Time Taken
A thesis is an extensive document encompassing the entire duration of a master's or doctoral course and as such, it takes months and even years to write.
A research paper, being less lengthy, typically takes a few weeks or a few months to complete.
4. Supervision
Writing a thesis entails working with a faculty supervisor to ensure that you are on the right track. However, a research paper is more of a solo project and rarely needs a dedicated supervisor to oversee.
5. Finalization
The final stage of thesis completion is a viva voce examination and a thesis defense. It includes proffering your thesis to the examination board or a thesis committee for a questionnaire and related discussions. Whether or not you will receive a degree depends on the result of this examination and the defense.
A research paper is said to be complete when you finalize a draft, check it for plagiarism, and proofread for any language and contextual errors . Now all that's left is to submit it to the assigned authority.
What is Plagiarism | How to Avoid It
How to Choose the Right Plagiarism Checker for Your Academic Works
5 Practical Ways to Avoid Plagiarism
10 Common Grammar Mistakes in Academic Writing
Guide to Avoid Common Mistakes in Sentence Structuring
In the context of academic writing, a thesis and a research paper might appear the same. But, there are some fundamental differences that set apart the two writing formats. However, since both the documents come under the scope of academic writing, they also share some similarities. Both require formal language, formal tone, factually correct information & proper citations. Also, editing and proofreading are a must for both. Editing and Proofreading ensure that your document is properly formatted and devoid of all grammatical & contextual errors. So, the next time when you come across a thesis vs. research paper argument, keep these differences in mind.
Editing or Proofreading? Which Service Should I Choose?
Thesis Proofreading and Editing Services
8 Benefits of Using Professional Proofreading and Editing Services
Achieve What You Want with Academic Editing and Proofreading
How Much Do Proofreading and Editing Cost?
If you need us to make your thesis or dissertation, contact us unhesitatingly!
Best Edit & Proof expert editors and proofreaders focus on offering papers with proper tone, content, and style of academic writing, and also provide an upscale editing and proofreading service for you. If you consider our pieces of advice, you will witness a notable increase in the chance for your research manuscript to be accepted by the publishers. We work together as an academic writing style guide by bestowing subject-area editing and proofreading around several categorized writing styles. With the group of our expert editors, you will always find us all set to help you identify the tone and style that your manuscript needs to get a nod from the publishers.
English formatting service
You can also avail of our assistance if you are looking for editors who can format your manuscript, or just check on the particular styles for the formatting task as per the guidelines provided to you, e.g., APA, MLA, or Chicago/Turabian styles. Best Edit & Proof editors and proofreaders provide all sorts of academic writing help, including editing and proofreading services, using our user-friendly website, and a streamlined ordering process.
Get a free quote for editing and proofreading now!
Visit our order page if you want our subject-area editors or language experts to work on your manuscript to improve its tone and style and give it a perfect academic tone and style through proper editing and proofreading. The process of submitting a paper is very easy and quick. Click here to find out how it works.
Our pricing is based on the type of service you avail of here, be it editing or proofreading. We charge on the basis of the word count of your manuscript that you submit for editing and proofreading and the turnaround time it takes to get it done. If you want to get an instant price quote for your project, copy and paste your document or enter your word count into our pricing calculator.

24/7 customer support | Live support
Contact us to get support with academic editing and proofreading. We have a 24/7 active live chat mode to offer you direct support along with qualified editors to refine and furbish your manuscript.

Stay tuned for updated information about editing and proofreading services!
Follow us on Twitter, LinkedIn, Facebook, Instagram, and Medium .
For more posts, click here.
- Editing & Proofreading
- Citation Styles
- Grammar Rules
- Academic Writing
- Proofreading
- Microsoft Tools
- Academic Publishing
- Dissertation & Thesis
- Researching
- Job & Research Application
Similar Posts
How to Determine Variability in a Dataset
How to Determine Central Tendency
How to Specify Study Variables in Research Papers?
Population vs Sample | Sampling Methods for a Dissertation
7 Issues to Avoid That may Dent the Quality of Thesis Writing
How to Ensure the Quality of Academic Writing in a Thesis and Dissertation?
How to Define Population and Sample in a Dissertation?
Recent Posts
ANOVA vs MANOVA: Which Method to Use in Dissertations?
They Also Read

A theoretical framework primarily supports the idea of a research study. It bears all the theories that prove the essence and importance of any research. In a nutshell, it is developed to explain the research and comprehend its circumstances. It may involve all the theory-based logic behind the importance and existence of your research in academics. This step-by-step guide discusses how to build a theoretical framework for a dissertation.

While composing a thesis or dissertation, a student must experience some predicted traps. Falling into these traps can affect one’s academic career. However, handling potential blunders and pitfalls wisely, while developing a thesis, can lead you to success. The process of writing may be frustrating but learning about the probable pitfalls may ease your stress. Here, we bring you the list of the most common mistakes we have noticed as a professional proofreading and editing service provider.

A dissertation defense is one of the critical milestones one needs to cross to obtain a doctoral degree. It is a process that helps a candidate proffer their research knowledge to an audience of accomplished academics. Thus, preparing to defend a dissertation can feel distressing and burdensome, for one needs to tick several checkboxes at once. But, with the right set of steps and adequate practice, candidates can successfully overcome this unease.

After gathering and analyzing your data, next is penning the results. You report the primary findings of your study in this section. The most critical issue is that reporting your results must be concise and pursue a logical order.

Finding a dataset's middle or average is critical and involves measuring central tendency. The central tendency's most common measures include the mode, median, and mean. The mode is the most repeated measure in a data set.
Difference Between | Descriptive Analysis and Comparisons
Search form, difference between journal, paper and thesis.
Key Difference: The main difference between journal, paper and thesis is that journal is an article which consists of some specific criteria. A paper is an informative sheet. Thesis includes a deep study under the guidance of some respected person.
A journal is an article type of content which consists of a specific format wherein the thoughts are put into words. A journal is an experience booklet which is to be updated regularly. Journals are informative book logs. They have a pre-defined form of content which are to be followed accordingly. Journals are used for referring purposes.
It contains the desired amount of information which is used for reference. Journals are also reference-books. After studying some specific contents, the content is written in a generalized form and molded into the journal. Journals are specific record keeping booklets. They are periodicals which publish the particular topics. They consist of the reviews regarding any articles or research.
The journals and thesis consists of bunch of papers arranged in a systematic format. The content in a paper gives a systematic approach to the user. Many such research papers together contribute in the work of thesis and journal. The certification obtained in any field acts as a proof in the form of a paper. It narrates the entire subject relevant to the topics.
The meaning of the word thesis means a long piece of writing on a particular subject that is done to earn a degree at a university.
Thesis is a deep study which is done under the guidance of an experienced person; mostly thesis is written after the research is carried on in a particular field. Thesis is especially written in the field of doctorate, post-graduation, masters, etc. After doing the appropriate research in the relevant field along with the master’s degree the individual is allowed to write the relevant experience in the form of a thesis.
Thesis includes research papers and work documents which would be affiliated by a recognized doctorate individual or by a university. A thesis document should be an approved document; its range may vary according to the type of research done. Thesis writing is a proposed form of writing. It includes the detailed study material right from the origin till its final product. It also explains the current status of the product. Theses are mostly written in order to secure the research.
Comparison between Journal, Paper and Thesis:
Image Courtesy: nsl.niscair.res.in, phdthesiswritingservice.blogspot.com, exislepublishing.com
Add new comment
Copyright © 2024, Difference Between | Descriptive Analysis and Comparisons

Journal Article vs Thesis
Which research article can be considered as journal articles? A journal article can be scientific or social science article. These are often called scientific articles, peer-reviewed articles or scholarly articles. They can be categorized as primary literature or as review articles. At times, an article could define an advanced or new tool, technique or methodology. What is a thesis? A thesis is usually a long dissertation written by a candidate for a university degree. The key difference between a journal article and a thesis is that the former is based on specific topics, whereas the latter includes a deep study under expert supervision. A thesis is usually written after a student completes his or her research in a particular field of interest under programs like doctorate, post-graduation, graduation, etc. A thesis is affiliated to any recognized university or a doctoral fellow. Its chapters or sections can be published as individual research papers in reputed journals. Hence, a thesis is considered to be an approved document and its range may vary according to the type of research done. It is generally a proposed form of writing. On the other hand, journal articles are publications including original research papers, scholarly articles, reviews, case studies, etc. A research paper may include a variety of topics, contrary to a thesis which is written on a single topic. Further, a research paper can be completed within few days, depending on the content of the research. In contrast, a thesis takes a much longer time to complete. Journal articles are usually up-to-date researches in a particular field or subject. They can even be short papers presenting innovative ideas. However, a thesis discusses current as well as future research options and presents the research in a more detailed manner, each component divided into one or more chapters.

- X (Twitter)
Related Posts
Combatting microplastics pollution in drinking water.
Microplastics (MPs) have emerged as persistent toxicants in the recent decade. MPs are reported to present in different samples such as soil, water, wastewater, and human samples including placenta, urine etc. Recent studies have reported its presence in drinking water. MPs presence in the Potable water is of concern to the research because MPs are […]
Will Yellow Fever Ever Be Eradicated?
Yellow fever (YF), a mosquito-borne viral infection, historically spread through social and commercial networks, with Barbados serving as a transmission epicenter. Despite a vaccine since the 1930s, YF persists in Africa, South, and Central America, posing risks to residents and travelers. Geographic spread is influenced by social, political, and economic factors. Currently, 44 countries in […]
Inappropriate Reforestation: Threats to Vast Tropical Grasslands in Africa
A recent University of Liverpool-led study sheds light on the perils of misguided reforestation efforts in Africa. Inappropriately executed projects, like the AFR100 initiative, pose a significant threat to an area equivalent to the size of France. The study underlines the crucial need for sustainable and context-specific restoration practices, urging a reevaluation of current initiatives. […]
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Home > Blog > Tips for Online Students > Dissertation vs Thesis: The Differences that Matter
Tips for Online Students , Tips for Students
Dissertation vs Thesis: The Differences that Matter
Updated: June 19, 2024
Published: April 26, 2020

As a graduate student, you will have many different types of challenging coursework and assignments. However, the biggest project that you’ll work on when earning your master’s or doctoral degree will be your thesis or dissertation . The differences between a dissertation vs thesis are plenty. That’s because each of these pieces of writing happen at different times in one’s educational journey.
Let’s break down what a dissertation and thesis are so that you have a strong handle on what’s expected. For both a thesis and a dissertation, there is an obvious fluency and understanding of the subject one studies.
Let’s take a look at their similarities and differences.
Photo by Glenn Carstens-Peters on Unsplash
What is a dissertation.
When you enter a doctoral program to earn a PhD, you will learn a lot about how to conduct your own research. At the culmination of your degree program, you’ll produce a dissertation.
A dissertation is a lengthy piece of written work that includes original research or expanded research on a new or existing topic. As the doctoral student, you get to choose what you want to explore and write about within your field of study.
What is a Thesis?
A thesis is also a scholarly piece of writing, but it is for those who are graduating from a master’s program. A thesis allows students to showcase their knowledge and expertise within the subject matter they have been studying.

Main Differences Between a Thesis vs. Dissertation
The biggest difference between a thesis and a dissertation is that a thesis is based on existing research.
On the other hand, a dissertation will more than likely require the doctoral student to conduct their own research and then perform analysis. The other big difference is that a thesis is for master’s students and the dissertation is for PhD students.
Structural Differences Between a Thesis and a Dissertation
Structurally, the two pieces of written analysis have many differences.
- A thesis is at least 100 pages in length
- A dissertation is 2-3x that in length
- A thesis expands upon and analyzes existing research
- A dissertation’s content is mostly attributed to the student as the author
Research Content and Oral Presentation
Once completed, some programs require students to orally present their thesis and dissertation to a panel of faculty members.
Typically, a dissertation oral presentation can take several hours. On the other hand, a thesis only takes about an hour to present and answer questions.
Let’s look at how the two scholarly works are similar and different:
Similarities:
- Each is considered a final project and required to graduate
- Both require immense understanding of the material
- Written skills are key to complete both
- Neither can be plagiarized
- Both are used to defend an argument
- Both require analytical skills
- You will have to draft, rewrite, and edit both pieces of writing
- For both, it is useful to have another person look over before submission
- Both papers are given deadlines
Differences:
- A dissertation is longer than a thesis
- A dissertation requires new research
- A dissertation requires a hypothesis that is then proven
- A thesis chooses a stance on an existing idea and defends it with analysis
- A dissertation has a longer oral presentation component
The Differences in Context: Location Matters
The united states.
In the US, everything that was previously listed is how schools differentiate between a thesis and a dissertation. A thesis is performed by master’s students, and a dissertation is written by PhD candidates.
In Europe, the distinction between a thesis and dissertation becomes a little more cloudy. That’s because PhD programs may require a doctoral thesis to graduate. Then, as a part of a broader post-graduate research project, students may complete a dissertation.
Photo by Russ Ward on Unsplash
The purpose behind written research.
Each piece of writing is an opportunity for a student to demonstrate his or her ability to think critically, express their opinions in writing, and present their findings in front of their department.
Graduate degrees take a lot of time, energy, and hard work to complete. When it comes to writing such lengthy and informative pieces, there is a lot of time management that is involved. The purpose of both a thesis and a dissertation are written proof that you understand and have mastered the subject matter of your degree.
Degree Types
A doctoral degree, or PhD, is the highest degree that one can earn. In most cases, students follow the following path to achieve this level of education: Earn a bachelor’s degree, then a master’s, and then a PhD. While not every job title requires this deep educational knowledge, the salaries that come along with each level of higher education increase accordingly.
Earning Your Degree
Whether you are currently a prospective student considering earning your higher education degree or a student enrolled in a master’s or doctoral program, you know the benefits of education.
However, for some, earning a traditional degree on-campus doesn’t make sense. This could be because of the financial challenges, familial obligations, accessibility, or any other number of reasons.
For students who are seeking their higher education degrees but need a flexible, affordable, and quality alternative to traditional college, take a look at the programs that the University of the People has to offer.
University of the People is an entirely online, US accredited and tuition-free institution dedicated to higher education. You can earn your Master’s in Business Administration or your Master’s in Education . Not to mention, there are a handful of associate’s and bachelor’s degree programs to choose from as well.
If you want to learn more, get in touch with us !
The Bottom Line
Regardless of where and when you earn your master’s or doctoral degree, you will likely have to complete a thesis or dissertation. The main difference between a thesis and dissertation is the level at which you complete them. A thesis is for a master’s degree, and a dissertation is for a doctoral degree.
Don’t be overwhelmed by the prospect of having to research and write so much. Your educational journey has prepared you with the right time management skills and writing skills to make this feat achievable!
In this article
At UoPeople, our blog writers are thinkers, researchers, and experts dedicated to curating articles relevant to our mission: making higher education accessible to everyone. Read More
- Key Differences
Know the Differences & Comparisons
Difference Between Thesis and Research Paper
On the other hand, a research paper is analytical, argumentative and interpretative in nature. It involves the pursuit of knowledge and intelligent analysis of the information collected. It contains the idea of the author, often supported by expert opinions, research and information available in this regard.
Whether you are writing a thesis or research paper, they are equally challenging and take a lot of time to prepare. In this post, we will update you on all the points of difference between thesis and research paper.
Content: Thesis Vs Research Paper
- Key Elements
- Thesis Statement
How to start a research paper?
Comparison chart, what is thesis.
The thesis is a document containing the research and findings that students submit to get the professional qualification or degree . It has to be argumentative, which proposes a debatable point with which people could either agree or disagree. In short, it is a research report in writing that contains a problem which is yet to be dealt with.
In a thesis, the researcher puts forth his/her conclusion. The researcher also gives evidence in support of the conclusion.
Submission of the thesis is a mandatory requirement of a postgraduate course and PhD degree. In this, the primary focus is on the novelty of research along with the research methodology.
It is all about possibilities, by introducing several anti-thesis. Also, it ends up all the possibilities by nullifying all these anti-thesis.
Key Elements of Thesis
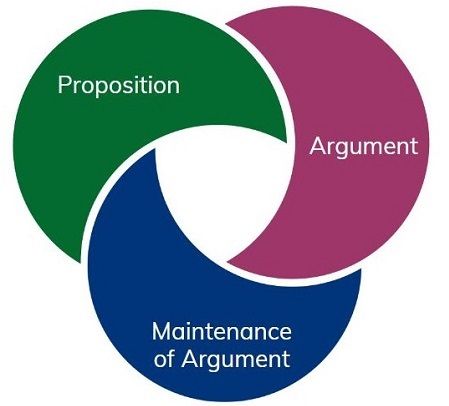
- Proposition : The thesis propagates an idea, hypothesis or recommendation.
- Argument : Gives reasons for accepting the proposition instead of just asserting a point of view.
- Maintenance of argument : The argument should be made cogent enough by providing suitable logic and adequate evidence.
Features of An Ideal Thesis
- An Ideal thesis is expected to add fresh knowledge to the existing theory.
- It communicates the central idea of the research in a clear and concise manner.
- An effective thesis is more than a simple statement, fact or question.
- It answers why and how questions concerned with the topic.
- To avoid confusion, it is worded carefully.
- It outlines the direction and scope of your essay.
- It gives reasons to the reader to continue reading.
Also Read : Difference Between Thesis and Dissertation
What is Thesis Statement?
A thesis statement is a sentence of one line, usually written at the end of your first paragraph. It presents the argument to the reader.
It is a blueprint of your thesis that directs the writer while writing the thesis and guides the reader through it.
What is Research Paper?
Research Paper is a form of academic writing. It is prepared on the basis of the original research conducted by the author on a specific topic, along with its analysis and interpretation of the findings.
An author generally starts writing a research paper on the basis of what he knows about the topic and seeks to find out what experts know. Further, it involves thorough and systematic research on a particular subject to extract the maximum information.
In short, a research paper is a written and published report containing the results of scientific research or a review of published scientific papers. Here, the scientific research is the primary research article, while the review of a published scientific paper is the review article.
In case of the primary research article, the author of the research paper provides important information about the research. This enables the scientific community members to:
- Evaluate it
- Reproduce the experiments
- Assess the reasoning and conclusions drawn
On the other hand, a review article is written to analyze, summarize and synthesize the research carried out previously.
When a research work is published in a scientific journal, it conveys the knowledge to a larger group of people and also makes people aware of the scientific work. Research work published as a research paper passes on knowledge and information to many people. The research paper provides relevant information about the disease and the treatment options at hand .
To start writing a research paper, one should always go for a topic that is interesting and a bit challenging too. Here, the key to choosing the topic is to pick the one that you can manage. So, you could avoid such topics which are very technical or specialized and also those topics for which data is not easily available. Also, do not go for any controversial topic.
The researcher’s approach and attitude towards the topic will decide the amount of effort and enthusiasm.
Steps for writing Research Paper
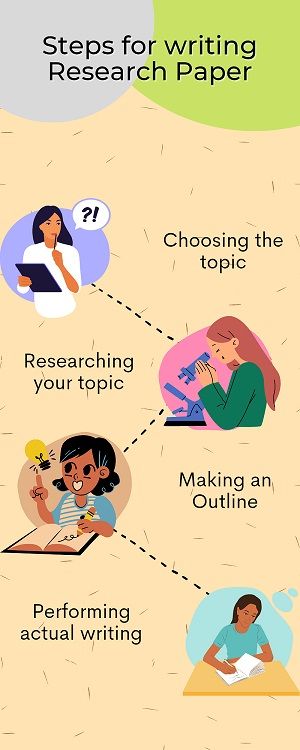
The total number of pages included in a Research Paper relies upon the research topic. It may include 8 to 10 pages, which are:
- Introduction
- Review of Literature
- Methodology
- Research Analysis
- Recommendations
Also Read : Difference Between Research Proposal and Research Report
Key Differences Between Thesis and Research Paper
- A thesis implies an original, plagiarism-free, written academic document that acts as a final project for a university degree of a higher level. But, Research Paper is a novel, plagiarism-free long essay. It portrays the interpretation, evaluation or argument submitted by a researcher.
- The thesis acts as a final project. Whereas a research paper is a kind of research manual of journals.
- The length of the thesis is around 20,000 to 80,000 words. On the contrary, the length of the research paper is relative to the study.
- The thesis focuses on the central question or statement of an intellectual argument that entails further research. On the contrary, the research paper is concerned with proving the central argument.
- The purpose of submitting the thesis is to get the degree or professional qualification. It also presents the knowledge of the candidate in the respective field. Conversely, the aim of publishing research papers is to prove credibility and contribute knowledge in the respective field.
- While the student submits the thesis to the educational committee or panel of professors who review it. In contrast, scientists and other researchers read and review the research paper.
- Preparation and completion of thesis is always under the guidance of a supervisor. For submission of the thesis, the university assigns a supervisor to each student, under whose guidance the thesis must be completed. As against, no supervisor is appointed as a guide in case of a research paper.
- The thesis contains a broader description of the subject matter. In contrast, the research paper contains a narrow description of the subject matter.
Once the research paper is published, it increases the fellowship and job opportunities for new researchers. On the other hand, thesis writing will enable the students to get the desired degree at the end of the course they have opted.
You Might Also Like:

Dr. Owenga says
February 23, 2023 at 2:38 pm
So good and informative. These are quite beneficial insights. Thanks
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Thesis vs. Dissertation: What’s the difference?
Thesis and dissertation are extensive research papers that differ in terms of their requirements, length, and purpose, with the former being associated with a master's degree and the latter with a doctoral degree, but are often used interchangeably.
Updated on September 15, 2023

A thesis and a dissertation are both extensive research papers, and both require literature searches and novel findings, but the two differ in various ways. Their definitions also differ across regions. Typically, in North America, a thesis is required for the completion of a master’s degree, while a dissertation is required for the completion of a doctoral degree. The former is long, while the latter is longer and more intensive.
Despite these differences, the two terms are often used interchangeably, especially among those who haven’t completed one or the other. Here, we’ll compare the components, length, and purpose of these two academic documents to clearly understand the differences between these important papers in the life of a graduate student.
What’s a thesis?
The term “thesis” explained here is generally consistent with how the word is used in North America to describe this substantive research paper.
A thesis is an extended argument (PDF). It is a research-based document that displays the student’s/author’s knowledge and understanding of a specific subject within their field of study. It generally presents findings on a particular topic.
See this and this (PDFs) for examples. These superb master’s theses from Canada will give you an idea of the size and format of these papers.
Who would write a thesis?
You generally write a thesis if you’re undertaking a research-oriented master's degree program (as opposed to a practical program, which may require a capstone, internship, exam, etc.).
The thesis is the essential part of a program’s research component, demonstrating the student's ability to critically analyze the literature and complete independent research. The process of writing a thesis involves exploring a specific research question, conducting a comprehensive literature review, collecting and analyzing data, and presenting findings in a structured and cohesive way.
A thesis' specific requirements and expectations differ depending on the academic institution, department, and program.
Components of a thesis
A thesis is typically presented in chapters. How many chapters will vary, but a common structure is:
- Introduction: Presents the research topic, purpose, and objectives, setting the context for the work.
- Literature review: Comprehensive survey of existing scholarly material related to the research topic, highlighting key theories and findings.
- Methodology: Describes the methods, procedures, and tools used in doing the research.
- Research: The actual performing of the study, collecting, and analyzing data relevant to the research question.
- Findings and conclusions: Gives the results obtained and explains their significance in relation to the research question.
- Limitations and future research: Outlines the study’s shortcomings and suggests potential areas for future investigation.
Within that structure, and in addition to those parts, a thesis may also include:
- Cover page: Contains the thesis title, author's name, institution, department, date, and other relevant information
- Abstract : A brief summary of the thesis, highlighting the research objectives, methods, key findings, and conclusions.
- Certificates of own work
- Certificate of readiness to be included in the library
- Certificate that the research has not been presented to another university
- Acknowledgments
- Table of contents: List of the main sections, subsections, and corresponding page numbers.
- Index of figures and tables
- References: A comprehensive list of all the sources cited in the thesis, following a specific citation style (e.g., APA, MLA).
- Appendices (optional): Additional materials include:
- Abbreviations and/or acronyms used
- Questionnaire or interview schedule/s (if used)
- Data acquired in the form of transcripts or numeric tables
- Research protocol
- Ethics protocol
What’s a dissertation?
This is also viewed from a North American perspective, where a dissertation is usually the main research work toward completing a research-based doctoral program.
A dissertation is a comprehensive and in-depth research project completed as part of the requirements for a doctoral degree. It’s a substantial piece of original work that contributes new knowledge to a specific field of study. Naturally, when it’s completed as the major requirement for earning a PhD, it’s longer, more detailed, and the expectations are higher.
Dissertations themselves can add to the literature in the field. For this reason, some students choose to publish them and have them indexed. The research and the data acquired while working on a dissertation can potentially lead to more publications and help define the researcher’s growing area of expertise.
See this and this (PDFs) top-ranking dissertation on ProQuest for good examples.
Who would write a dissertation?
Completion and defense of a dissertation is a standard requirement for doctoral students to earn a PhD or another doctorate such as an EdD or DM. But some specialized degrees, such as a PsyD (Doctor of Psychology), JD (Juris Doctor) or DPT (Doctor of Physical Therapy) may have practice-based requirements in place of a research project, as these courses of study are geared more toward practical application.
Components of a dissertation
A dissertation’s components are generally the same as those of a thesis. You can look at the list above for a thesis to see what typically goes into a dissertation. But, if compared with a master’s thesis, most aspects are longer and more rigorous.
The word count requirements for theses can vary significantly, but doctoral dissertations often range 40,000–80,000 words or, per Harvard , 100–300 pages.
Differences between a thesis and a dissertation
As already touched on, the key differences are in where the two documents are used, length, and rigor. There are also regional differences.
A thesis typically demonstrates a master’s degree program student's grasp and presentation of a specific subject in their field of study. It normally involves a literature review, data analysis, and original research, but it is usually shorter and less comprehensive than a dissertation. The standards for rigor and novelty may also be lower.
A dissertation requires more extensive research, original contributions to the field, and a deeper exploration of the research topic. A dissertation is typically the output associated with a doctoral degree program.
The main differences in structure between a thesis and a dissertation are in the scope and complexity.
The word count requirement for theses and dissertations can vary depending on the institution and program.
A thesis is usually 20,000–40,000 words. However, there have been cases of mathematics dissertations that were only a few pages long!
Doctoral dissertations may range 60,000 to upward of 100,000 words, and exceed 100 pages. Many universities, however, seek around 80,000 words.
Oversight and process
A thesis may simply be submitted to the student's instructor, though rigorous thesis programs require a committee and defense. A dissertation will nearly always require the student to choose a chair, a committee, and then go through a more rigorous defense and revision (if necessary).
- Committee: Master's thesis committees usually have fewer members (typically 2–3) than doctoral dissertation committees (often 4–5, or even more).
- Guidance: Master's students often receive more detailed direction from advisers than doctoral students, who are expected to work more independently.
- Review: Dissertation reviews are typically more rigorous, often involving external reviewers, while thesis reviews are usually internal.
- Defense: A dissertation defense is generally more intense and formal, as it often involves a presentation to the wider academic community, while a thesis defense might be more confined and informal.
- Revision: The revision process for a doctoral dissertation is typically more extensive, given the larger scope of the project and higher stakes involved, compared with those for a master's thesis.
Regional differences
The terms' use varies among (and even within) countries. Here are some general regional differences:
In the United Kingdom, a thesis is commonly associated with both master's and doctoral degree programs. For example, the University College London refers to a thesis for EngD, MPhil, MD(Res), and PhD degrees. At the University of Nottingham , a dissertation is written for a research master’s degree.
In Australia and New Zealand , “thesis” is generally used to refer to a substantial research project completed for a higher degree, though not limited to a master’s (you’ll find ample references to a “PhD thesis”).
In Latin American countries, the thesis is commonly used to refer to both master's and doctoral research projects.
Closing thoughts
Both theses and dissertations are necessary documents for students in graduate programs. Despite the differences in expectations, and even in definitions of these papers, the student-author must do a diligent and rigorous job to earn their degree.
Here are a few helpful resources if you want to get into greater detail:
- Writing the Winning Thesis or Dissertation: A Step-By-Step Guide
- 100 PhD rules of the game to successfully complete a doctoral dissertation (PDF)
- Theses and Dissertations: A Guide to Writing in Social and Physical Sciences
Perfect the English on your thesis or dissertation
Whether you’re submitting a thesis or a dissertation, if it’s in English, it should:
- Have no grammatical or spelling mistakes
- Use field-appropriate language
- Concisely and clearly communicate your research.
That’s what AJE expert editors will do for you. Within days, you can receive an expert English edit of your work. The editor will be familiar with your field of study and will comprehensively improve both the language quality and the delivery of your message. Look into AJE English Editing .

The AJE Team
See our "Privacy Policy"
AJE will edit your thesis or dissertation
Choose between our expert academic editing services to prepare your thesis or dissertation.
Journal vs conference papers: Key differences & advice
Journal and conference papers are not the same, and both formats have advantages and disadvantages. A good understanding of the key differences between journal and conference papers avoid s pitfalls, such as copyright issues when wanting to turn a conference into a journal paper at a later stage.
Disclosure: This post may contain affiliate links, which means I may earn a small commission if you make a purchase using the links below at no additional cost to you . I only recommend products or services that I truly believe can benefit my audience. As always, my opinions are my own.
What is a journal paper?
What is a conference paper, advantages of journal papers, disadvantages of journal papers, advantages of conference papers, disadvantages of conference papers, differences between journal and conference papers, questions to ask yourself before submitting a conference paper, is conference paper better than journal paper, can you use a conference paper in a journal, are all conference papers automatically published in conference proceedings, do conference papers count as publications.
A journal paper is a written piece of academic work – presenting empirical research, a theoretical discussion, or both – published in an academic journal. Most journal papers or articles are peer-reviewed , meaning they undergo a rigorous review process involving several stages and rounds of revisions before they are published.
Most academic journals have an impact factor, which is an index calculated based on the number of citations of articles published within a specific journal. The higher the impact factor of a journal, the wider the (potential) reach of journal papers that it publishes. And the better the reputation of the journal.
Therefore, authors of journal papers tend to target journals with a high impact factor to publish their work. There are other criteria that play a role when selecting a journal to publish research . However, the impact factor remains a crucial one, as publications in high-impact factor journals strongly influence academic promotions.
A conference paper is a piece of academic work that is specifically written for an academic conference, and mostly accompanies a conference presentation. While there are some exceptions, most conference papers are not peer-reviewed.
Conference papers are usually submitted several weeks before the actual conference, and circulated among conference participants in preparation for the actual presentations. However, not all conferences require conference papers. And some conferences make the submission of a conference paper optional.
Many conferences that require or allow the submission of a conference paper have ‘best conference paper’ awards, rewarding outstanding submissions. Furthermore, some conferences publish a collection of conference papers after the event, in the so-called conference proceedings. Many conference proceedings do not have an impact factor.

If you are looking to elevate your writing and editing skills, I highly recommend enrolling in the course “ Good with Words: Writing and Editing Specialization “, which is a 4 course series offered by the University of Michigan. This comprehensive program is conveniently available as an online course on Coursera, allowing you to learn at your own pace. Plus, upon successful completion, you’ll have the opportunity to earn a valuable certificate to showcase your newfound expertise!
Advantages and disadvantages of journal and conference papers
The choice between a journal or a conference paper should be a careful one. Both formats fulfill important but different roles in academia. Therefore, a good understanding of the benefits and drawbacks of both formats can help to make an informed decision.
Please notice that the following points are developed from a social sciences perspective. Other fields and specific disciplines may have different standards.
- Journal papers are more prestigious in academia. Especially if you strive for an academic career , publishing peer-reviewed journal papers in high-impact journals should be your priority.
- Journal papers are more frequently cited than conference papers. Journal impact factors are not the only metric that strongly influences academic promotions: The so-called h-index is a metric that measures your ‘impact’ in terms of how often your publications have been cited. And journal papers are cited more often than conference papers, as they are considered more reputable.
- Journal papers undergo revisions, which often means they are of higher quality. Due to the rigorous peer-review process that most journal papers are subjected to, the quality of journal papers tends to be better than that of conference papers. During peer review, experts on a topic point out flaws in the draft paper, challenge your thinking and provide suggestions for improvement. While dealing with peer review comments can be a tedious process, the final result is often a much better paper compared to the initial manuscript.
- Publishing a journal paper takes time. The whole process from manuscript to published paper can be lengthy, and take from anywhere between several months to several years.
- Most journals do not publish preliminary results. Even if you make a groundbreaking discovery in your preliminary analysis, most journals will not consider it worthy of a publication before more final conclusions can be drawn.
- There is a risk of outdated data in journal papers. For instance, if you want to publish your academic work to contribute to a current societal discussion, a journal paper may not be the best option. In the worst case, the publishing process takes more than a year and by the time of publication, your data may be outdated. Furthermore, your conclusions may be irrelevant for practice as a lot can change in a year.
- Journal papers have to follow strict rules set by journals. Journals set, for example, rules in terms of length, structure, or reference style that have to be followed. Conference papers, on the other hand, are often more flexible.
- Conference papers tend to have a lower threshold of acceptance than journal papers. It is much easier to publish a conference paper in conference proceedings than publish academic work in a high-impact journal. Therefore, conference papers can be a valuable option to learn about paper writing and publishing, and an easier way for early career researchers to get their name on a publication.
- Conference papers are published relatively fast. Some conference papers undergo peer review before being published in conference proceedings, but many don’t. In general, conference proceedings are published relatively soon after the actual conference takes places. Thus, a conference paper can be a good way to publish fast.
- Conference papers can discuss ongoing research and preliminary results. Contrary to journal papers, conference papers often address ongoing research and tentative conclusions. Furthermore, the format tends to be more open than in journal papers, providing authors of conference papers more freedom in terms of content and structure.
- Conference papers can often compete for ‘best conference paper’ aw ards . And having such an award to your name certainly looks good on your academic CV !
- Conference papers do not count as much as journal publications for career advancement. This is because many conference papers are not peer-reviewed and because many conference proceedings do not have an impact factor. Thus, in terms of career promotion or trajectories, conference papers are less relevant than journal papers.
- Conference papers can create copyright issues. It is a very common scenario: an author writes a conference paper first, then makes some edits and submits it to an academic journal for publication. If the conference paper has been published in conference proceedings, it will likely be flagged as plagiarised by the journal. Journals do not like to publish articles which have been published elsewhere in a similar fashion, and some use any indication of plagiarism (even if it is self-plagiarism) as a reason to desk-reject a manuscript.
- Sharing great ideas prematurely in a conference paper can make you vulnerable. Unfortunately, there is a lot of competition in academia, and not everyone plays by the rules. Therefore, you should always carefully consider how much of your work you share, without linking it to a publication of your own. Sharing an excellent idea that is sent around to hundreds of conference participants creates a risk that someone copies or steals your idea or approach, and tries to publish it faster in a journal article than you do.
Based on the discussion of the advantages and disadvantages of journal and conference papers above, the following key differences come to light:
- Content and requirements : Conference papers are more open to include preliminary results and are more flexible in terms of requirements than journal papers. The target audience of conference papers are conference participants, while journal papers target the wider academic community.
- Submission and peer review process : Journal papers tend to be submitted via an online system and undergo a structured peer review process. Conference papers are often simply sent to the conference organisers by email and are not peer-reviewed.
- Time to publication: Conference papers are often published more quickly in conference proceedings than journal papers are published in academic journals.
- Career relevance: Journal papers are much more relevant for academic careers than conference papers. Most journals have impact factors, while most conference proceedings do not have impact factors.
Even though journal papers are more important for academic promotions, submitting a conference paper is not per se the wrong choice. A ‘best conference paper’ award, for instance, can make you stand out when applying for academic jobs.
When embarking on writing a conference paper, it is better to be safe than sorry: At times, it may require reaching out to conference organisers or target journals to make sure that you will not run into copyright or plagiarism issues at a later point.
Oftentimes, conferences still allow you to present even without submitting a conference paper. Or you can ask the conference organisers not to include your paper in the conference proceedings. Furthermore, some journals are okay with publishing a paper that has been published in a conference proceeding earlier. Just make sure to ask in advance to prevent bad surprises!
Thus, when considering a conference paper, first answer the following questions:
- What are the benefits of submitting a conference paper to the specific conference, and do they outweigh the drawbacks?
- How can I mitigate the drawbacks? (Would my conference paper be published in the conference proceedings and can I opt out? Can I participate in the conference without a conference paper?)
- Do I share too many original ideas in my conference paper, which someone could copy without referring to my work as I haven’t published on the topic yet?
- Could I face copyright issues if I want to turn my conference paper into a journal paper at a later point?
Frequently Asked Questions
In academia, journal papers are considered ‘better’ than conference papers because they have a stronger positive impact on academic careers. Reasons for this are the more rigorous peer-review process that journal papers tend to undergo before publication, the higher standards of journals compared to conference proceedings, and the impact factor of journals.
You should never simply submit a conference paper to a journal without making substantial edits beforehand. That said, it is okay to use similar data or arguments. If your conference paper has been published in conference proceedings, it is best to inform the journal about it in your letter to the editor , which accompanies your journal paper submission. Otherwise, it may be flagged as plagiarised and immediately desk-rejected by the journal editors before it even has the chance to enter the peer-review process.
Not all conference papers are automatically published in conference proceedings. Different conferences have different rules when it comes to publishing papers in conference proceedings. Therefore, you should check the rules and procedures of a specific conference in advance. If you cannot find the information online, you can send an email to the conference organisers. You can also always ask if it is possible to present without submitting a conference paper or to not have your conference paper published in the conference proceedings.
Conference papers often do not count as academic publications. Therefore, on academic CVs, conference papers tend to be listed under ‘Conferences’ instead of ‘Publications’. Alternatively, they are listed as a separate sub-category under ‘Publications’, but in a way that they are clearly differentiated from other (peer-reviewed) publications.
Master Academia
Get new content delivered directly to your inbox.
Subscribe and receive Master Academia's quarterly newsletter.
The best answers to "What are your plans after graduation?"
How many people have a phd data from oecd countries, related articles.

Why and how to conduct a systematic literature review

Theoretical vs. conceptual frameworks: Simple definitions and an overview of key differences

How to write a good research proposal (in 9 steps)

How to properly use AI in academic research

Thesis Vs. Dissertation — Know the difference and similarities!
The academic world is filled with many different types of writing assignments, each with its own unique set of requirements and expectations. One common source of confusion for students is the distinction between a thesis and a dissertation. Both are long-form academic works, but there are several key differences between the two that are important to understand.
In Shakespeare’s day, a candidate for a master’s degree would write a thesis, an original paper in which he maintained a certain proposition. Whereas, completion of a doctoral program required submission and defense of a dissertation. He would read his thesis to his committee, after which he sat in silence while two faculty members gave point-by-point refutations of everything the candidate said.
The focus here was on the student’s ideas and his ability to arrange and express them clearly. If a student wished to advance further in academia he could pursue a dissertation. This was more of a literature review . He would read widely in a particular area and write up his findings, discussing the various authorities and their opinions. The point was to demonstrate that he was well-versed in the literature of the field. While the confusion between the two terms is understandable, we shall tackle the dissertation vs. thesis topic in this article and provide unambiguous insights on it.
Table of Contents
What Is a Thesis?
A thesis is a critically written scholarly piece of research work. Typically, it is submitted by students graduating from a master’s program. The purpose of a thesis is to allow students to showcase their knowledge and expertise within the subject matter they have been studying as part of the program.
What Is a Dissertation?
A dissertation is a comparatively lengthier piece of scholarly writing that accounts for your research work throughout the doctoral program. A researcher earns the Ph.D. after submitting and defending his/her dissertation. It includes all information about the original research or expanded research on a new or existing topic conducted by the Ph.D. candidate.
Dissertation vs. Thesis: Differences
- The primary difference between a thesis and a dissertation is the time when they are completed. As mentioned earlier, a thesis is presented at the culmination of a master’s program, whereas, a dissertation is presented to earn a Ph.D.
- A thesis is a compilation of research ensuring that the researcher is well-informed and has knowledge about the research topic learned in the study program. On the other hand, a dissertation provides an opportunity for the researcher to contribute new theories and information to the existing literature in the research field.
- A thesis is a presentation of learned and existing information, while the purpose of a dissertation is to develop a unique concept and defend it based on theoretical and practical results.
- A master’s thesis is approximately 100 pages in length. However, a Ph.D. dissertation should be much longer than a thesis and must include background and research information. A dissertation must include your research proposal, grant proposal, literature review , ideation of research topic, and every other minute detail about your research. Ideally, a dissertation inclusive of all details mentioned above should be three times the length of a master’s thesis.
Dissertation vs. Thesis: Similarities
- Both a thesis and a dissertation are considered final projects and are required to graduate from respective programs.
- The thesis and dissertation both require a deep and accurate understanding of the research problem.
- Both forms of scholarly written pieces must address specific research questions.
- Academic writing skills are imperative for a thesis as well as a dissertation.
- Ethical practices must be followed while collating and documenting research data.
- Plagiarism is not accepted in either.
- Both require analytical skills to support the findings.
- It is essential that both undergo intense dissertation/ thesis editing and critical proofreading before final submission.
Dissertation vs. Thesis: Europe
In Europe, the original distinction between a thesis and a dissertation has been largely retained. A doctoral thesis is a focused piece of original research that is performed to obtain a Ph.D. A dissertation is part of a broader post-graduate research project.

However, the thesis has evolved since original research nowadays requires plenty of background research . So, a thesis will contain extensive citations and references to earlier work, although the focus remains on the original work that comes out of it.
Dissertation vs. Thesis: USA
In the United States, the definition of a thesis is almost the opposite of that in Europe. Because a thesis is shorter than a dissertation it gradually came to mean a preliminary degree on the way to a doctorate. A thesis is now performed to earn a Master’s degree. In scientific fields, a master’s candidate takes advanced coursework and gains hands-on experience in a research project but does not direct the project to the same extent that he would in a doctoral program. In a master’s project, the student’s ideas are welcomed and expected but the focus is on obtaining technical expertise, not doing original research. Engineering students commonly obtain Master’s degrees and seldom go on to get PhDs. In other fields such as Chemistry, the opposite is true, with a Master’s degree no longer being required as the first step for a doctorate. Almost everyone I know who received a Master’s degree in Chemistry got one because they dropped out of graduate school and wrote their truncated research as a Master’s project.
In a Nutshell
Needless to say, the dissertation vs. thesis facts are real. Therefore, using one term instead of another is not acceptable as an academic. One must remember the purpose of each and use them accordingly. However, one is not undermined by the other. Whether you are writing a thesis or a dissertation, both must be done with the same seriousness. Both require critical technical and soft skills. Improving your time management and academic writing skills plays a major role in acing both forms of scholarly writing.
How do you decipher dissertation vs. thesis? Should the interchanged usage of these terms be acceptable? How is your approach to writing a thesis different from that of a dissertation? What are the other differences associated with the thesis and dissertation? Let us know in the comments section below!
Frequently Asked Questions
"Dissertation" and "thesis" are used interchangeably but differ in: Academic Level: Thesis for master's, dissertation for doctoral degrees (US). Scope and Depth: Thesis shorter, demonstrates mastery; dissertation extensive, original research. Originality: Thesis may involve original analysis; dissertation presents significant new insights. Time and Effort: Dissertations require more resources and time than theses.
The length of a dissertation varies depending on factors like academic discipline, research topic, institution, and country. Generally, dissertations are longer than theses, ranging from 10,000 to over 100,000 words. However, word count alone does not reflect the quality or depth of the research. Guidelines from the academic institution should be consulted for specific requirements.
The length of a thesis varies depending on factors like academic discipline, research topic, institution, and country. Generally, the word count ranges from around 10,000 to 50,000 words. Specific guidelines from the academic institution should be consulted for precise requirements.
Has helped develop my writing skills through science-based study.
Rate this article Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published.

Enago Academy's Most Popular Articles

- Reporting Research
Choosing the Right Analytical Approach: Thematic analysis vs. content analysis for data interpretation
In research, choosing the right approach to understand data is crucial for deriving meaningful insights.…

Comparing Cross Sectional and Longitudinal Studies: 5 steps for choosing the right approach
The process of choosing the right research design can put ourselves at the crossroads of…

- Career Corner
Unlocking the Power of Networking in Academic Conferences
Embarking on your first academic conference experience? Fear not, we got you covered! Academic conferences…

Research Recommendations – Guiding policy-makers for evidence-based decision making
Research recommendations play a crucial role in guiding scholars and researchers toward fruitful avenues of…

- AI in Academia
Disclosing the Use of Generative AI: Best practices for authors in manuscript preparation
The rapid proliferation of generative and other AI-based tools in research writing has ignited an…
Choosing the Right Analytical Approach: Thematic analysis vs. content analysis for…
Comparing Cross Sectional and Longitudinal Studies: 5 steps for choosing the right…
How to Design Effective Research Questionnaires for Robust Findings

Sign-up to read more
Subscribe for free to get unrestricted access to all our resources on research writing and academic publishing including:
- 2000+ blog articles
- 50+ Webinars
- 10+ Expert podcasts
- 50+ Infographics
- 10+ Checklists
- Research Guides
We hate spam too. We promise to protect your privacy and never spam you.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
This infographic lists nine ways in which a thesis is different from a journal article. The idea is to help you understand how the two are distinct types of academic writing, meant for different audiences and written for different purposes. Feel free to download a PDF version of this infographic and print it out as handy reference.
The structure of a thesis allows for an extensive exploration of the research problem, thorough analysis of the findings, and comprehensive discussion of their implications. In contrast, a journal article adheres to a more concise and standardized structure. It typically includes an abstract, introduction, methodology, results, discussion, and ...
Adapting a Dissertation or Thesis Into a Journal Article. Dissertations or theses are typically required of graduate students. Undergraduate students completing advanced research projects may also write senior theses or similar types of papers. Once completed, the dissertation or thesis is often submitted (with modifications) as a manuscript ...
2. Shorten the length of your thesis. Treat your thesis as a separate work. Paraphrase but do not distort meaning. Select and repurpose parts of your thesis. 3. Reformat the introduction as an abstract. Shorten the introduction to 100-150 words, but maintain key topics to hold the reader's attention.
Thesis formatted as a table of content manner. A journal article should follow a manuscript format. Abstract. The length of the thesis abstract is longer than a journal paper. (approx 350 words) Abstract in the article is smaller in length. (approx 150 to 250 words) Introduction. A detailed introduction is required.
To the untrained eye, a research paper and a thesis might seem similar. However, there are some differences, concrete and subtle, that set the two apart. 1. Writing objectives. The objective behind writing a thesis is to obtain a master's degree or doctorate and the ilk.
Key Difference: The main difference between journal, paper and thesis is that journal is an article which consists of some specific criteria. A paper is an informative sheet. Thesis includes a deep study under the guidance of some respected person. The meaning of the word journal means a book in which you write down your personal experiences ...
The main difference is how you organize your written content. Traditional Style Theses are organized by chapters or sections. Journal Style Theses are organized by manuscripts tied into an overarching Introduction and Conclusion. Reference the tables below for an in-depth description of the differences between the two Thesis Template Styles.
However, the points discussed in the infographic 9 differences between thesis and journal article can be applied to research articles. This is because theses involve original research, and therefore, the type of journal articles that a thesis is converted into are almost always original research articles.
The main difference between a master's thesis and a PhD thesis is really the scope of the work. The master's thesis is assumed to be over a shorter period and therefore should have a slightly smaller scope. One might extract just one or two journal papers out of a master's thesis, but four or five out of a PhD thesis.
The key difference between a journal article and a thesis is that the former is based on specific topics, whereas the latter includes a deep study under expert supervision. A thesis is usually written after a student completes his or her research in a particular field of interest under programs like doctorate, post-graduation, graduation, etc.
Both papers are given deadlines. Differences: A dissertation is longer than a thesis. A dissertation requires new research. A dissertation requires a hypothesis that is then proven. A thesis chooses a stance on an existing idea and defends it with analysis. A dissertation has a longer oral presentation component.
It portrays the interpretation, evaluation or argument submitted by a researcher. The thesis acts as a final project. Whereas a research paper is a kind of research manual of journals. The length of the thesis is around 20,000 to 80,000 words. On the contrary, the length of the research paper is relative to the study.
Dissertations and theses (the plural of thesis) are often confused because they're both lengthy research papers written for higher education. In American English, a dissertation is written to earn a doctorate whereas a thesis is written to earn a master's (or sometimes a bachelor's). In many informal situations, however, the terms ...
The main differences in structure between a thesis and a dissertation are in the scope and complexity. Length. The word count requirement for theses and dissertations can vary depending on the institution and program. A thesis is usually 20,000-40,000 words. However, there have been cases of mathematics dissertations that were only a few ...
9 Differences between a thesis and a journal article. Top. About Editage Insights. Editage Insights offers a wealth of free academic research and publishing resources and is a one-stop guide for authors and others involved in scholarly publishing. Our original resources for authors and journals will help you become an expert in academic publishing.
Journal and conference papers are not the same, and both formats have advantages and disadvantages. A good understanding of the key differences between journal and conference papers avoids pitfalls, such as copyright issues when wanting to turn a conference into a journal paper at a later stage. Disclosure: This post may contain affiliate links, which
Dissertation vs. Thesis: Differences. The primary difference between a thesis and a dissertation is the time when they are completed. As mentioned earlier, a thesis is presented at the culmination of a master's program, whereas, a dissertation is presented to earn a Ph.D. A thesis is a compilation of research ensuring that the researcher is ...
While writing their research papers, many researchers are sligthly unclear about what they should include in the Results and Discussions sections. To effectively write both these sections you need to clearly understand the distinction between the two. This infographic explains the five main differences between these two sections of a manuscript.