

Child Marriage: The Devastating End of Childhood
The devastation of child marriage effectively ends a girl’s childhood. How? Forced marriage robs a girl of her education and more, replacing lessons learned in the classroom with adult responsibilities, including forced pregnancy, well before she’s ready. This not only violates her rights, but risks her life, the lives of her children and the future of her community.
Tragically, about 40 million girls worldwide are currently married or in a union – and without our help, an estimated 150 million girls will be married in the next decade. This is unacceptable.
Read more about the issues, Save the Children’s impact – and how you can help end child marriage.
What is child marriage?

Asha, 19, found out that her family were making arrangements for her wedding when she was 15. The union had been agreed when she was 3 years old. She enlisted the Children’s Group and Child Protection Committee to lobby her father who eventually gave in and stopped the marriage. She has since helped other girls stop their marriages and has continued her education.
Child marriage is formal or informal union before age 18. It is a violation of children’s human rights and a form of gender-based violence that robs children of childhood. Child marriage also disrupts their education and drives vulnerability to violence, discrimination and abuse.
Yet these are some of today’s tragic child marriage statistics:
- About 40 million girls ages 15-19 are currently married or in a union worldwide.
- Each year, some 12 million more girls will marry before reaching age 18 – and of those, 4 million are under age 15.
- Save the Children’s Global Girlhood Report estimates that an additional 2.5 million girls are at risk of child marriage globally between 2020 and 2025, as a result of reported increases in all types of gender-based violence due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
- We project that up to 15 million girls and boys will never return to school following pandemic lockdowns and school closures. Children who don’t come back are at greater risk of early marriage, child labor and recruitment into armed forces.
- By 2030, it’s estimated that 150 million girls will lose their childhoods due to child marriage.
What are the effects of child marriage?
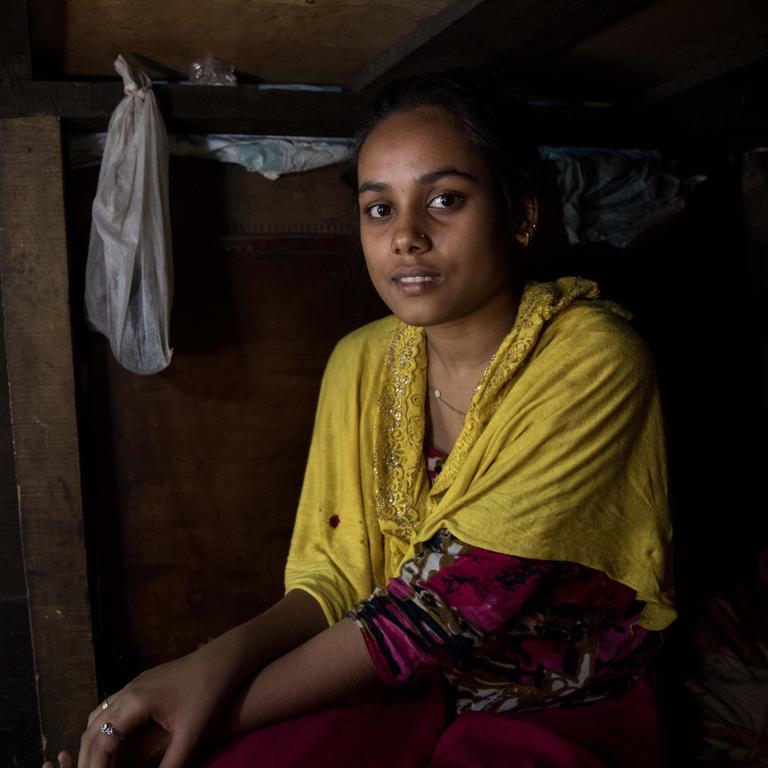

Rizwana inside the the temporary shelters that she calls home. Rizwana had several difficult years but was assisted through them by Save the Children to better educate her family and avoid attempts of child marriage and child labor and eventually continue with her education.
Early marriage has devastating consequences for a girl’s life. Effectively, child marriage ends her childhood. Girls are forced into adulthood before they are physically and mentally ready. Child brides are frequently deprived of their rights to health, education, safety and participation. What’s more, an arranged marriage often means a girl is forced to wed an, at times significantly, older man.
Girls married young are far less likely to stay in school, with lifelong economic impacts. They are often isolated, with their freedom curtailed. They are at higher risk of physical and sexual violence. Child brides are also at greater risk of experiencing dangerous complications in pregnancy and childbirth, contracting HIV/AIDS and suffering domestic violence.
What are the effects of forced pregnancy?

“At the age of thirteen I was forced to marry a man who was much older than me," says 15-year old Aisha, seen here with her two-year old daughter. "I lived with him for awhile but we couldn’t get along because he was so much older than me.
Every year, around 17 million girls give birth. Forced pregnancy and childbearing at a young age, often a result of child marraige, when a girl’s body is not physically mature enough to deliver without complications, can also lead to devastating consequences.
Complications during pregnancy and childbirth represent the number one killer of girls ages 15-19 worldwide. And babies born to adolescent mothers face a substantially higher risk of dying, with a higher likelihood of low birth weight, malnutrition and underdevelopment. Young mothers are far less likely to be in school, and therefore more likely to struggle economically.
Where around the world does child marriage happen?

Amina* was 15 when child marriage threatened to ruin her life. Her father lost his income during COVID-19 lockdown and the family struggled to survive. Amina’s father received a marriage proposal for her and he agreed as the money the family would receive would help solve their financial problems. However, Amina’s mother was furious and went to Save the Children for help. Together they persuaded Amina’s father to reject the marriage offer and to continue her education.
Child marriage is a global problem and is compounded by poverty. Child marriage is a problem that cuts across countries, cultures, religions and ethnicities. Child brides can be found in every region in the world. Major factors that place a girl at risk of marriage include poverty, especially in rural areas, as well as weak laws and enforcement, the perception that marriage will provide “protection,” customs or religious laws, and unequal gender norms.
In Africa, an estimated 12 million girls are still married each year . Despite worldwide progress in reducing child marriage and pregnancy, these are the countries with the highest child marriage rates: Niger , Central African Republic, Mali , Mozambique , and South Sudan .
Why do child marriage rates rise during conflict?

Kadidia*, 14, and her parents were determined that the violence sweeping Africa’s Sahel region – including her homeland Mali – wasn’t going to end her chances of completing her education.
Conflict increases the inequalities that make girls vulnerable to child marriage – and its consequences. Families may arrange marriages for girls, believing marriage will protect their daughters from violence by strangers or armed groups, as well as to ease financial burdens on the family.
For example, child marriage rates have risen in war-ravaged Yemen , one of the few countries in the world without a legal minimum age for marriage. Now more than two-thirds of Yemen’s girls are married before age 18, compared to half before the conflict escalated.
Child marriage is also a growing concern among refugee children, including those from Myanmar and the Central African Republic.
How is Save the Children is a world leader in ending child marriage?

Rizwana’s leadership skills led her to being selected as a Save the Children Youth Champion, and through the additional support she has received through the Youth Champion program, she has continued to advocate for children’s education, the end of child marriage, and financial independence for vulnerable children and youth.
Thanks to compassionate supporters like you, Save the Children has championed equal rights for every child for over 100 years. We helped reduce child marriage worldwide by nearly one-third since 1990 – that’s tens of millions more girls empowered to stay in school or transition to work, and make marriage and motherhood decisions for themselves.
Save the Children puts gender equality at the heart of all we do. Every day, right from the start, we work to empower girls to stay in school, delay marriage and acquire the life and livelihood skills needed to successfully transition to adulthood. We work with girls and boys, families, communities and countries to change harmful gender norms and laws. Plus we empower girls to speak up, lead and succeed. We are the leading advocate for U.S. investment in girls’ leadership around the world.
In addition, Save the Children is proud to be the first nonprofit to be Gender Fair-certified for our commitment to advancing gender equality and empowering the world’s girls.
When you support Save the Children – whether it’s by donating, advocating or participating in an event challenge – you’re helping bridge the gap between the challenges girls face, like child marriage, and the futures they deserve. You’re helping ensure all children have equal opportunities to grow up healthy, educated and safe.
Together, we can change children’s lives – ultimately, transforming the future we all share.
**Sources: Unless otherwise noted, facts and statistics have been sourced from Save the Children’s program and monitoring and evaluation experts, as well as published reports , including our gender equality reports .
Learn More About the Challenges Girls Face Around the World

Insights from Women Deliver 2023 for Companies Ready to Act

Save the Children and the Movie Barbie Are Helping Children Achieve Their Dreams

LGBTQI Children Around the World Celebrate and Love Who They Are This PRIDE Month
Sign Up & Stay Connected
By providing my mobile phone number, I agree to receive recurring text messages from Save the Children (48188) and phone calls with opportunities to donate and ways to engage in our mission to support children around the world. Text STOP to opt-out, HELP for info. Message & data rates may apply. View our Privacy Policy at savethechildren.org/privacy.
Our website has a lot of features which will not display correctly without Javascript.
Please enable Javascript in your browser
Here how you can do it: http://enable-javascript.com

Essay on Child Marriage
Students are often asked to write an essay on Child Marriage in their schools and colleges. And if you’re also looking for the same, we have created 100-word, 250-word, and 500-word essays on the topic.
Let’s take a look…
100 Words Essay on Child Marriage
Introduction.
Child marriage is a global issue where a child, usually under 18 years, is married off. This practice affects both girls and boys but it’s more prevalent among girls.
Causes of Child Marriage
Many factors contribute to child marriage. Poverty, cultural traditions, and lack of education often drive families to marry off their children at a young age.
Consequences
Child marriage has severe consequences. It often leads to early pregnancies, health risks, and limits opportunities for education and career growth.
To end child marriage, we need to focus on education, enforce laws against it, and change societal attitudes.
Also check:
- 10 Lines on Child Marriage
250 Words Essay on Child Marriage
Child marriage, a deeply entrenched social issue, is a practice that involves the marriage of one or both parties before they reach the age of 18. Globally, it is considered a violation of human rights, yet it continues to persist in many societies due to a complex interplay of socio-economic and cultural factors.
The roots of child marriage are multifaceted. Poverty is a significant driver, with families marrying off young daughters to reduce their economic burden. Traditional norms and gender stereotypes also play a role, perpetuating the belief that a girl’s value lies in her ability to become a wife and mother. Furthermore, in some societies, child marriage is used as a strategy to strengthen familial ties or secure political alliances.
Consequences of Child Marriage
The consequences of child marriage are profound and far-reaching. It often results in early pregnancy, posing substantial health risks to young girls whose bodies are not yet mature enough for childbirth. It also hinders girls’ education and personal development, limiting their opportunities and perpetuating cycles of poverty.
Efforts to Combat Child Marriage
Efforts to combat child marriage span from local to global levels. They encompass law enforcement, advocacy for girls’ education, and initiatives to empower girls. However, for these efforts to be effective, it is crucial to address the underlying socio-economic factors that give rise to child marriage.
Child marriage is a complex issue that requires comprehensive, multi-faceted approaches to eradicate. By promoting education, gender equality, and economic stability, societies can help ensure that every child is afforded the right to a safe and fulfilling childhood.
500 Words Essay on Child Marriage
Child marriage, a prevalent practice in many cultures and societies, is a complex issue that infringes upon the rights and development of children, particularly girls. It is a deep-rooted practice, often perpetuated by poverty, gender inequality, traditions, and lack of education. This essay delves into the implications, causes, and potential solutions to child marriage.
The Implications of Child Marriage
Child marriage poses significant risks to the physical, psychological, and emotional well-being of children. It often leads to early pregnancies, which present health risks for both the mother and the child. Moreover, child brides are more likely to experience domestic violence and are less likely to receive proper education. This practice also perpetuates the cycle of poverty, as child brides are less likely to contribute economically to their communities.
Underlying Causes
The causes of child marriage are multifaceted and deeply entrenched in societal norms and structures. Poverty is a significant factor, with families marrying off their daughters to lessen financial burdens. Gender inequality also plays a crucial role, with girls often valued less in societies, leading to their early marriage. Additionally, traditional beliefs and lack of education contribute to the persistence of this practice.
Legislation and Its Limitations
Many countries have enacted laws to prevent child marriage, setting the minimum age for marriage at 18. However, the enforcement of these laws often proves challenging due to societal norms and lack of awareness. Moreover, in some societies, legal loopholes allow child marriage to continue under the guise of cultural or religious practices.
Addressing Child Marriage
Addressing child marriage requires a multifaceted approach. Education is a powerful tool in this regard. Empowering girls through education can help them understand their rights and resist early marriage. Furthermore, educating communities about the detrimental effects of child marriage can foster change in societal attitudes.
Economic empowerment is also crucial. By providing families with financial stability, the economic incentive for child marriage decreases. Social protection measures, such as cash transfers, can help achieve this.
Lastly, legal measures need to be strengthened. Laws against child marriage should be enforced strictly, and legal loopholes need to be addressed.
Child marriage is a violation of children’s rights and a practice that hampers societal development. While it is deeply entrenched in many societies, a combination of education, economic empowerment, and legal measures can help combat this practice. It is crucial for all stakeholders, including governments, NGOs, and communities, to work together to end child marriage and ensure a better future for all children.
That’s it! I hope the essay helped you.
If you’re looking for more, here are essays on other interesting topics:
- Essay on Arranged Marriage
- Essay on Army Officer
- Essay on Army Man
Apart from these, you can look at all the essays by clicking here .
Happy studying!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Child Marriage: Legal Dilemmas and Cultural Clash
How it works
Child marriage is the marriage that an individual performs without reaching the physical and mental maturity necessary to act as an adult. Child marriage usually means the marriage of a 18-year-old child. Early marriage, these minors are from their families, friends and future; education, deprives the school of life and pushes it under very difficult responsibilities. We see such marriages more especially in developing and underdeveloped countries.
In our country’s legal system; According to the Turkish Civil Code, the Turkish Penal Code and the Turkish Child Protection Law, it is possible to come up with different definitions as girls who are not over the age of 17 and who are not over 18 years of age respectively.
The United Nations (1989) has classified child marriages as an application that should be eliminated in which women and children are exploited for the benefit of men.
If we look at the factors that prepare the girls’ early marriage; it is thought that the economic level of the family, educational status, unrest in the family, the perspective of the family and the individual stereotypes and the traditional practices provide an environment for early marriage of girls. Early marriages have been observed more frequently in families with poor socio-cultural structure. In such families different early marriage plans are made for boys and girls. While the marriage of boys depends on the minimum level of education and military service, girls do not need to be educated and the limited income of the family is spent on the education of boys. For this reason, girls are engaged immediately after they begin to enter adolescence and then they are married.
Violations of women’s basic human rights and freedoms and gender inequalities that cause unequal power relations between men and women are a reason for the continuation of early marriages. There is a share of women’s perspective on early marriages, mostly under the exposure of girls. In traditional societies, women are considered to be predisposed to innate domestic roles, and there is a widespread belief that no matter how old they are, they can fulfill their household’s mistress and partner duties. One of the reasons that differ in the regions where early marriages are most common is the wars and natural disasters that occur.
The famine in Kenya, the war and drought in Afghanistan, the tsunami in Indonesia, as well as the emergence of early marriages in natural disasters appear as effective events. Some post-disaster marriages are seen as an act of economic income, while others are aimed at protecting individuals who are left alone after the disaster. The choice of early marriage of girls is a protection goal from rape events. By marrying daughterS to a “good” family, parents also establish social ties between tribes or clans and improve their social status. Parents also believe that marrying their daughters young protects them from rape, premarital sexual activity, unintended pregnancies, and sexually transmitted infections, especially human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and AIDS.
Parents believe that marrying their daughters early protects them from HIV/AIDS. Research has shown the opposite: marriage by the age of 20 years is a risk factor for HIV infection in girls. Risks for Infants Mothers under the age of 18 have a 35% to 55% higher risk of delivering a preterm or low-birthweight infant than mothers older than 19 years. The infant mortality rate is 60% higher when the mother is under the age of 18 years. Data demonstrate that even after surviving the first year, children younger than 5 years had a 28% higher mortality rate in the young mothers cohort.
Religion, Culture and Civil Law Although the general age of marriage in most countries is 18, most countries may allow young people under the age of majority, or even a person who is 16 years of age, with the consent of their parents or legal representative, to obtain a dominant marriage in exceptional circumstances under Turkish Civil Code. In some countries, a religious marriage is not enough and civil marriage is not done. In this case, although the Turkish civil code allows children under the age of 16 to be married by listening to them together with legal representatives and guardians, but these early marriages are legitimized by relying on religion and society in the areas in which minors under the age of 16 are married. Mothers do not have any right to speak on marriages held at a child’s age.
In fact, this is a cultural problem that has come from the past and is still continuing. The woman who has been married without her consent and who is a mother when the time comes does not make any statement of the future of her own daughter. There is no statement of opinion on the future of the child. In the Turkish Grand National Assembly’S report , another reason for child marriages is tradition, traditions and religious belief: ‘traditional family sees the girl as an entity entrusted to the family for a certain period of time, and believes that the real home of the girl is the home of the wife. As a result of discrimination created by gender inequality, it is thought that girls should be married without being aware of sexuality. Marriage at a young age is believed to be easier for the husband to obey and adapt to the new home.
Male families also want to get a bride as young as possible in order to make it easier for them to adapt. It is believed that girls can be protected from sexual harassment and violence that can occur when they are put under the protection of a man as soon as possible. In addition, it is seen as a common belief that these marriages will prevent young girls from getting pregnant and getting pregnant with the opposite sex. In a study conducted in our country, it was reported that early marriage was nourished by traditional practices such as protecting the reputation of the woman, transferring the economic burden of the woman to another, and gaining the prestige of the marriage for women and family.
Child Marriage And The Law Turkish Law According to Article 10 of the Turkish Civil Code numbered 4721, which regulates the general conditions of the act of competence, each person who has the power to differentiate and who is not limited has the capacity to act. According to article 11 titled adolescence 18, adolescence begins with the filling of 18 years of age. Marriage makes the person mature. According to Article 12 of the Turkish Civil Code, the age of 15 years of age can be made available to the court with the consent of the parents.
The Turkish Civil Code regulates the age issue, which is one of the conditions of marriage license, in Article 124. According to this, male or female cannot marry unless they are seventeen years old. However, the judge may allow the marriage of men or women who have reached the age of sixteen in exceptional circumstances and for a very important reason. The parent and father or guardian will be heard before the decision is made. According to the first paragraph of Article 103 of the Turkish Penal Code, the offense of sexual abuse against children under 15 years of age, whether with or without the consent, is between three years and eight years; will be punished. In our society, families marry girls under fifteen years of age.
If this situation is noticed in some way, the defendant and his mother and father and the victim’s mother and father due to the involvement of the judicial proceedings. Even if the victim is seventeen and has a formal marriage with the accused, an arrangement similar to the article 434 of the Turkish Penal Code No. 765 does not exist in the new Turkish Penal Code. Therefore, it is not possible to get rid of this penalty. Therefore, the victim’s husband (defendant), his mother, his father, his father-in-law and his mother-in-law are put on trial for this crime and are being punished. According to Article 104 of the Turkish Penal Code entitled sexual intercourse with minors; “The person who has sex with a child who has completed his fifteen years of age without coercion, threats and deceit shall be sentenced to imprisonment of six months to two years upon complaint.”
In this article, when an unofficial marriage of a child over the age of fifteen is defined as an independent crime, the spouse who has sexual relations with that child is not punished unless the complaint is made. Why Is It Important For Countries To Set 18 As The Minimum Legal Age Of Marriage? A minimum age of law is an important way for boys and girls to protect them from being ready for marriage. In some cultures, the concept of child recognized by the constitution may conflict with the perception of child recognized by the culture that has the Constitution. Therefore, the government must have a consistent and clear legislation.
Age was defined as 18. The primary aims of the law should be to protect children, taking into account the public perception. especially for people who force girls to marry, imposing sanctions must be among the priorities of the law. What Does International Law Say About Child Marriages? The Universal Declaration of Human Rights, the Convention on the Rights of the Child, the Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Discrimination Against Women all directly or indirectly forbid the degrading and mistreatment of girls, inherent in child marriage.
Nevertheless, child marriage is common in many parts of the world, claiming millions of victims annually—and hundreds of thousands of injuries or death resulting from abuse or complications from pregnancy and childbirth. Child Marriage Restraint Act, 1929, Section, “Child” means a person who, if a male, has not completed twenty one years of age, and if a female, has not completed eighteen years of age. Early marriages have been accepted as a child right, women’s rights and human rights violations. An analysis of descriptive and multivariate data can be used to find out who is married as a child. Data from demographic and health surveys are used when doing this. This gives us reliable results. Education is a very important obstacle in preventing child marriages.
The more educated a girl is, the less likely she is to marry as a child. Improving access to education is an important strategy for both girls and boys in finishing child marriages. Legislative, free and mandatory education as well as programmed and advocacy efforts to expand should demonstrate the strong importance of education in reducing the number of married girls. International and regional agreements prohibit child marriage and set controllable rules for governments to protect children who are not ready physically and mentally from marriage. In this way, governments should report to the committees to ensure that they are able to effectively control how they implement these standards.
According to the laws adopted by some governments, preventing children from getting married requires international protection. Instead of the West, we come across child marriages in Eastern countries, and in countries like Pakistan, we learn that the age of child marriage is 6 years old. It is stated that the increase in child marriages in some regions increased from 25% to 75% and this increase was possible to achieve this degree among regions due to some economic reasons. Because a person is missing from the family and this situation is seen as an advantage for the family. Among the reasons for parents ‘ misunderstanding of child marriage is the misinterpretation of religion. We see that a lot of people are inclined to learn religion from the clergy.
For this reason, as a solution, it is possible for many children to get rid of this situation and continue their lives in a manner that is worthy of human dignity by explaining that child marriages are wrong, convincing people that religion does not promote child marriages, and informing people of criminal sanctions along with the laws. Another reason why child marriages can not be prevented is that these marriages do not take place under the legal framework. Child marriage occurs in rural areas where there is little resources to implement the law. As a solution to this, child protection systems should be created and strengthened, as well as supporting legal aid systems and services.
Cite this page
Child Marriage: Legal Dilemmas and Cultural Clash. (2019, Jan 28). Retrieved from https://papersowl.com/examples/child-marriage-legal-dilemmas-and-cultural-clash/
"Child Marriage: Legal Dilemmas and Cultural Clash." PapersOwl.com , 28 Jan 2019, https://papersowl.com/examples/child-marriage-legal-dilemmas-and-cultural-clash/
PapersOwl.com. (2019). Child Marriage: Legal Dilemmas and Cultural Clash . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/child-marriage-legal-dilemmas-and-cultural-clash/ [Accessed: 30 Oct. 2024]
"Child Marriage: Legal Dilemmas and Cultural Clash." PapersOwl.com, Jan 28, 2019. Accessed October 30, 2024. https://papersowl.com/examples/child-marriage-legal-dilemmas-and-cultural-clash/
"Child Marriage: Legal Dilemmas and Cultural Clash," PapersOwl.com , 28-Jan-2019. [Online]. Available: https://papersowl.com/examples/child-marriage-legal-dilemmas-and-cultural-clash/. [Accessed: 30-Oct-2024]
PapersOwl.com. (2019). Child Marriage: Legal Dilemmas and Cultural Clash . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/child-marriage-legal-dilemmas-and-cultural-clash/ [Accessed: 30-Oct-2024]
Don't let plagiarism ruin your grade
Hire a writer to get a unique paper crafted to your needs.

Our writers will help you fix any mistakes and get an A+!
Please check your inbox.
You can order an original essay written according to your instructions.
Trusted by over 1 million students worldwide
1. Tell Us Your Requirements
2. Pick your perfect writer
3. Get Your Paper and Pay
Hi! I'm Amy, your personal assistant!
Don't know where to start? Give me your paper requirements and I connect you to an academic expert.
short deadlines
100% Plagiarism-Free
Certified writers
About child marriage
Child marriage is a global issue. It is fuelled by gender inequality, poverty, social norms and insecurity, and has devastating consequences all over the world.
Find out more
Why it happens
Where it happens, how to end it, the law and child marriage.
Explore our vision and mission to end child marriage, learn about our organisational structure, and discover how we work as a global partnership to drive change and empower girls worldwide.
- How we work
- Partnership Strategy
- How we are funded
- Our Board of Trustees
- Our Champions
Our Partnership
Girls Not Brides members are civil society organisations committed to working together to end child marriage and support married girls. Our strength is our diversity.
- National Partnerships & Coalitions
- Member directory
- Become a member
Learning and Resources
Discover tools, resources and events to learn more about child marriage and related issues, and be successful in your advocacy, youth activism and fundraising.
- Resource centre
- Child marriage atlas
Child Marriage Research to Action Network
Stories and impact.
Here you'll find the latest news and stories about child marriage, and the work our member organisations and partners in the broader movement are doing to end the harmful practice.
Child marriage is a global issue. It is fuelled by gender inequality, poverty, social norms and insecurity, and has devastating consequences all over the world. Here, you can discover more about the extent and impacts of child marriage and the progress we’ve made towards ending it.
12 million girls are married before the age of 18 each year
That is 23 girls every minute, nearly 1 every 3 seconds [1].
View sources
Child marriage is rooted in gender inequality and the belief that girls and women are inferior to boys and men. It is made worse by poverty, lack of education, harmful social norms and practices, and insecurity. Its drivers vary between communities and it looks different across the world.
Child marriage is a truly global problem. It happens across countries, cultures, religions and ethnicities. Use our interactive atlas to understand the scale of the problem and what is being done to end it. You can also find data to support your advocacy and fundraising, and to connect with others working on the issue in your location.
Child marriage looks different from one community to the next. There is no single solution, actor or sector to end it; we must all work together. Solutions must be local, contextual and integrated. The Girls Not Brides Theory of Change shows the range and combination of approaches needed, and the role everyone has to play.
Child marriage or marriage without the free and full consent of both spouses is a human rights violation. Progressive legal frameworks are one element of the comprehensive response needed to successfully address child marriage, as reflected within the Girls Not Brides Theory of Change.
Further information about child marriage
More than 650 million women alive today already suffer the direct consequences of child marriage.
Globally, the rates of child marriage are slowly declining but progress isn't happening fast enough.
If pre-pandemic trends continue, 150 million more girls will be married by 2030 [2] . Because of the COVID-19 pandemic, this may increase by a further 13 million girls [3] .
Child marriage violates girls’ rights to health, education and opportunity.
Child marriage is any formal marriage or informal union where one or both parties are under 18 years of age. It is rooted in gender inequality.
Girls who formally marry or cohabit as if married before the age of 18 are more likely to have early pregnancies, experience dangerous complications in pregnancy and childbirth, acquire HIV, and experience domestic violence. Ending child marriage will improve the health of millions of girls, and their children. Find out more on our Health learning page .
When a girl gets married she is often expected to drop out of school to look after the home, children and extended family. For the same reasons – and sometimes because of official school or national policies – it is difficult for married girls, pregnant girls and young mothers to return to school. Find out more on our Education learning page .
When they marry as children, girls miss out on developing the skills, knowledge and confidence they need to make informed decisions, negotiate, access paid employment and live independent lives. With little access to education and economic opportunities, girls and their families are more likely to live in poverty. Find out more on our Economic Justice learning page (coming soon).
Systems that undervalue the contribution and participation of girls and women limit their own possibilities for growth, stability and transformation.
Child marriage directly hinders the achievement of at least six of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). Find out more on our SDG and Gender learning pages (coming soon).
Ending child marriage and guaranteeing girls’ rights means a fairer, more secure and prosperous future for us all.

At Girls Not Brides we want to see local and national governments, regional bodies, and global institutions direct money and resources towards ending child marriage. We advocate for child marriage laws, policies and programmes that empower girls and their communities. We want them to be well-financed, comprehensive, and multi-sectoral.


Youth Activism
Resources, tools and information for young activists, member organisations, civil society actors and donors to support and promote meaningful inclusion of youth in the collective efforts of the Partnership to end child marriage.

The CRANK is a joint initiative and platform for a coordinated global research agenda on child marriage, and to encourage the uptake of research by policy makers and practitioners. On…
Data sources
- [1] UNICEF, Child marriage database , 2020
- [3] UNFPA, UNFPA projections predict calamitous impact on women’s health as COVID-19 pandemic continues , 2020
We use cookies to give you a better online experience and for marketing purposes.
Read the Girls Not Brides' privacy policy
Allow all cookies Essential cookies only

- High contrast
- Our history
- Children in India
- Partner With Us
- Where we work
- Frequently asked questions
- Press centre
Search UNICEF
Ending child marriage and adolescent empowerment, child marriage negatively affects the indian economy and can lead to an intergenerational cycle of poverty .

- End child marriage
- Available in:
Child marriage violates children’s rights and places them at high risk of violence, exploitation, and abuse. Child marriage affects both girls and boys, but it affects girls disproportionately.
It is defined as a marriage of a girl or boy before the age of 18 and refers to both formal marriages and informal unions in which children under the age of 18 live with a partner as if married.
Child marriage ends childhood. It negatively influences children’s rights to education, health and protection. These consequences impact not just the girl directly, but also her family and community.
A girl who is married as a child is more likely to be out of school and not earn money and contribute to the community. She is more likely to experience domestic violence and become infected with HIV/AIDS. She is more likely to have children when she is still a child. There are more chances of her dying due to complications during pregnancy and childbirth.
Estimates suggest that each year, at least 1.5 million girls under 18 get married in India. Nearly 16 per cent adolescent girls aged 15-19 are currently married.
While the prevalence of girls getting married before age 18 has declined from 47 per cent to 27 per cent between 2005-2006 and 2015-2016 it is still too high.
The significant progress in the reduction of child marriages in India has contributed to a large extent to the global decrease in the prevalence of the practice. The decline may be the result of multiple factors such as increased literacy of mothers, better access to education for girls, strong legislation and migration from rural areas to urban centres. Increased rates of girls’ education, proactive government investments in adolescent girls, and strong public messaging around the illegality of child marriage and the harm it causes are also among the reasons for the shift.
Child marriage, a deeply rooted social norm, provides glaring evidence of widespread gender inequality and discrimination. It is the result of the interplay of economic and social forces. In communities where the practice is prevalent, marrying a girl as a child is part of a cluster of social norms and attitudes that reflect the low value accorded to the human rights of girls.
Child marriage negatively affects the Indian economy and can lead to an intergenerational cycle of poverty.
Girls and boys married as children more likely lack the skills, knowledge and job prospects needed to lift their families out of poverty and contribute to their country’s social and economic growth. Early marriage leads girls to have children earlier and more children over their lifetime, increasing economic burden on the household. The lack of adequate investments in many countries to end child marriage is likely due in part to the fact that the economic case for ending the practice has not yet been made forcefully.
As a result of norms assigning lower value to girls, as compared to boys, girls are perceived to have no alternative role other than to get married. And are expected to help with domestic chores and undertake household responsibilities in preparation for their marriage.
Evidence shows that critical game changers for adolescent girls’ empowerment include postponing marriage beyond the legal age , improving their health and nutritional status, supporting girls to transition to secondary school, and helping them develop marketable skills so that they can realize their economic potential and transition into healthy, productive and empowered adults.
UNICEF’s approach to ending child marriage in India recognizes the complex nature of the problem, and the socio-cultural and structural factors underpinning the practice. UNICEF India accomplished its ‘scale-up strategy’ to prevent child marriage and increase adolescent empowerment by working with government, partners and relevant stakeholders from the national level down to the district level. The most significant development has been the gradual shift from interventions that are small in scope and mainly sector-based to large scale district models on adolescent empowerment and reduction of child marriage which rely on existing large government programmes.
UNICEF and UNFPA have joined forces through a Global Programme to Accelerate Action to End Child Marriage, where for the first time existing strategies in areas such as health, education, child protection, nutrition and water and sanitation have been brought together to address child marriage in a holistic manner. The approach is to address child marriage through the entire lifecycle of a child especially by addressing persisting negative social norms which are key drivers for the high prevalence of child marriage in India. The programme works in partnership with governments, civil society organizations and young people themselves and adopt methods that have proven to work at scale. At the global level, child marriage is included in Goal 5 “Achieve gender equality and empower all women and girls” under Target 5.3 “Eliminate all harmful practices, such as child, early and forced marriage and female genital mutilation”.
Explore more

Akha: The Boat of Hope
Solar-powered refrigeration units on Assam's Boat Clinics have revolutionized immunization services for over three million poor people in remote areas.

Dove and UNICEF aim to reach 16.4 million young people in India with self-esteem education materials
Boat clinics serve as lifelines, reaching approximately 20,000 people every month with essential medical care and compassion

Empowered Voices—Girls Leading the Way with Kanyashree
Kanyashree Prakalpa: Building a Brighter Future for Every Girl in West Bengal
- Open access
- Published: 14 February 2022
The health consequences of child marriage: a systematic review of the evidence
- Suiqiong Fan 1 &
- Alissa Koski 1 , 2
BMC Public Health volume 22 , Article number: 309 ( 2022 ) Cite this article
38k Accesses
44 Citations
21 Altmetric
Metrics details
Child marriage, defined as marriage before 18 years of age, is a violation of human rights and a marker of gender inequality. Growing attention to this issue on the global development agenda also reflects concerns that it may negatively impact health. We conducted a systematic review to synthesize existing research on the consequences of child marriage on health and to assess the risk of bias in this body of literature.
Methods and findings
We searched databases focused on biomedicine and global health for studies that estimated the effect of marrying before the age of 18 on any physical or mental health outcome or health behaviour. We identified 58 eligible articles, nearly all of which relied on cross-sectional data sources from sub-Saharan Africa or South Asia. The most studied health outcomes were indicators of fertility and fertility control, maternal health care, and intimate partner violence. All studies were at serious to critical risk of bias. Research consistently found that women who marry before the age of 18 begin having children at earlier ages and give birth to a larger number of children when compared to those who marry at 18 or later, but whether these outcomes were desired was not considered. Across studies, women who married as children were also consistently less likely to give birth in health care facilities or with assistance from skilled providers. Studies also uniformly concluded that child marriage increases the likelihood of experiencing physical violence from an intimate partner. However, research in many other domains, including use of contraception, unwanted pregnancy, and sexual violence came to divergent conclusions and challenge some common narratives regarding child marriage.
Conclusions
There are many reasons to be concerned about child marriage. However, evidence that child marriage causes the health outcomes described in this review is severely limited. There is more heterogeneity in the results of these studies than is often recognized. For these reasons, greater caution is warranted when discussing the potential impact of child marriage on health. We provide suggestions for avoiding common biases and improving the strength of the evidence on this subject.
Trial registration
The protocol of this systematic review was registered with PROSPERO (CRD42020182652) in May 2020.
Peer Review reports
Introduction
Marriage before the age of 18, often referred to as child marriage, is a violation of human rights that hinders educational attainment and literacy and may increase the likelihood of living in poverty in adulthood [ 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 ]. Girls are far more likely to marry than boys, and these consequences contribute to existing gender gaps in educational outcomes in some settings [ 6 , 7 ]. The United Nations Sustainable Development Goals list child marriage as an indicator of gender inequality and call for an end to the practice by the year 2030 [ 8 ]. Child marriage remains ongoing throughout much of the world despite intensifying efforts to eliminate it [ 9 ].
In addition to its consequences on education, growing attention to child marriage as a global development issue also seems to reflect increasing consideration of its potential impacts on population health. Multinational organizations including the World Bank, the United Nations Population Fund (UNFPA), and the United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF) include the potential for harmful consequences on health among the foremost concerns regarding this practice [ 2 , 10 , 11 , 12 , 13 ]. These organizations highlight relationships between child marriage and early childbearing [ 11 , 12 , 13 ], obstetric complications [ 12 , 13 ], violence [ 2 , 12 ], and sexually transmitted infections [ 12 ], among other adverse outcomes.
We undertook this systematic review to synthesize the results of existing research regarding the impact of child marriage on the health of persons who marry before the age of 18. We evaluated the range of health outcomes that have been studied and the geographic distribution of those studies. We also assessed the risk of bias in individual studies and the likelihood that their results reflect causal relationships.
We searched three databases for literature on the relationship between child marriage and health: MEDLINE, Embase, and Ovid Global Health. These databases were chosen because they focus on biomedicine and human health. We aimed to include as broad a range of health outcomes as possible and focusing our search within these databases allowed us to avoid defining specific health outcomes within our search terms. Instead, we searched for studies of child marriage within these databases. This approach made our search terms more concise and the range of outcomes more inclusive. Specific search terms used for each database are included in Supplementary File 1 . We registered our protocol with PROSPERO (CRD42020182652) in May 2020 and conducted our database searches shortly afterward.
We also searched Google Scholar to identify relevant grey literature. Haddaway et al. [ 14 ] found that the majority of grey literature tends to appear within the first 200 citations returned by Google Scholar and recommend focusing on the first 200-300 records. We followed this recommendation and evaluated the first 300 records returned, as sorted by relevance. Search terms used in Google Scholar are also included in Supplementary File 1 . We reviewed the bibliographies of all included studies in an effort to identify any relevant citations not picked up through searches of the databases described above. The search strategy was developed with assistance from a research librarian at McGill University.
Citations returned from searches of all four databases were imported into EndNote X9 and duplicate citations removed [ 15 ]. We transferred all unique citations into Rayyan to facilitate the review process [ 16 ]. A single reviewer (SF) examined the title and abstract of each unique citation for eligibility according to pre-defined criteria specified in the registered protocol. Articles were brought forward for full-text review if they described etiologic studies that used quantitative methods to estimate the effect of child marriage on one or more health outcomes. We defined child marriage as formal or informal union prior to the age of 18. If the title and abstract did not specify the age thresholds used to define child marriage, they were brought forward for full-text review. For example, abstracts that referred to the effect of adolescent or teen marriage without explicitly stating how those exposures were defined were brought forward. Eligible health outcomes included physical or mental health disorders or symptoms of those disorders, as well as health behaviours. Eligible health behaviours included actions like smoking or dietary habits as well as health care seeking, such as prenatal care. We restricted our review to studies in which outcomes were measured at the individual level and to those that measured the effect of child marriage on the individuals married; studies that examined the effect of age at marriage on the offspring of the persons who married were excluded. Studies written in English, French or Chinese were eligible for inclusion.
We excluded studies that used solely qualitative methods and quantitative studies that relied exclusively on hypothesis testing to indicate differences between groups. For example, studies that used chi-squared tests to indicate whether the distribution of some characteristic differed between persons married before the age of 18 and those married at older ages were excluded, even if the authors seemed to interpret their results as causal, because such testing does not result in a comparative effect measure (e.g., a risk difference or an odds ratio) and does not account for potential biases. We also excluded studies in which persons who married before the age of 18 were incorporated into a larger aggregate age category, making the effect of child marriage unidentifiable. For example, comparisons of outcomes among persons who married between 15 and 19 years of age with those who married between 20 and 24 years of age were not eligible for inclusion. Conference presentations and abstracts were also excluded.
Both authors read the full text of each article brought forward from the title and abstract review and independently judged their eligibility according to the inclusion and exclusion criteria described above. Discrepancies were resolved through discussion. The following information was extracted from each included study: authors, title, year of publication, the language of publication, country/region in which the study was conducted, study design, study population, sample size, data sources, statistical methods, outcomes, and results.
Risk of bias assessment
We assessed the risk of bias within each included study using the Risk Of Bias In Non-randomised Studies - of Interventions (ROBINS-I) tool developed by members of the Cochrane Bias Methods Group and the Cochrane Non-Randomised Studies Methods Group [ 17 ]. ROBINS-I is designed to evaluate the risk of bias in non-randomized studies by considering how closely the study’s design and methods approximate an ideal randomized trial. To illustrate, in a hypothetical cluster-randomized trial to estimate the causal effect of child marriage on a specified health outcome, the treatment or intervention would be marriage before the age of 18 years. All children in a specific area (a region, a state, a community, etc.) would be randomized at a very young age to one of two treatment groups: those randomized to the intervention would marry at some point prior to their 18th birthdays (a = 1), while those randomized to the control group would marry on their 18th birthday or any later age (a = 0). All children would then be followed up over a period of time sufficient to observe the specified outcome of interest. In the ideal randomized trial, all persons would adhere to their assigned treatment (i.e., remain married) and would remain in the study until follow-up was complete. After the follow-up period, the probability of the outcome among those assigned to a = 1 would be compared with the same probability among those assigned to a = 0. Under these conditions, we could expect that there would be no differences between those children who married before the age of 18 and those who married afterward aside from age at marriage. As a result, if the probability of the outcome among those randomly assigned to marry as children differed from the probability among those randomly assigned to marry after their 18th birthdays, one could interpret that difference as the causal effect of child marriage [ 18 ].
Of course, a randomized trial like this would be unethical and could never actually be conducted. Researchers interested in the effects of child marriage on health must rely on non-randomized study designs to estimate the causal effect of interest. Without the benefit of randomization, it becomes challenging to identify the causal effect of child marriage because those who marry as children are different from those who marry at later ages in many ways. For example, girls who marry before the age of 18 come from poorer households and from communities with greater gender inequality, on average, compared to those who marry at later ages. These differences are likely to affect their health through causal pathways other than age at marriage, such as the experience of violence or limited ability to access education or health care. This means that a naïve comparison of health outcomes between those who marry as children and those who marry as adults is likely to mix up the consequences of age at marriage with the consequences of childhood poverty and gender inequality.
The ROBINS-I tool requires assessors to carefully consider the potential for multiple sources of bias including confounding, inappropriate selection of participants into the study (i.e., selection bias), mishandling of missing data, and problems with the measurement of exposures and outcomes (i.e., information bias). The potential for bias in each domain is assessed through a series of signaling questions and a summary judgement of low, moderate, serious, or critical risk of bias is then made within each domain. A cross-domain judgement of the risk of bias for the entire study is made based on the risk within each individual domain. Both authors independently assessed the risk of bias in each included study. Disagreements in any single domain or across domains were resolved by discussion.
We identified a set of variables likely to confound estimates of the effect of child marriage on a wide range of health outcomes in advance to facilitate assessment of bias in this domain. These variables and their relationships to child marriage and health, broadly defined, are illustrated in the simplified Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) in Fig. 1 . The prevalence of child marriage has fallen over time in many countries, which means that the likelihood of marrying before the age of 18 differs across birth cohorts [ 6 , 19 ]. As discussed above, childhood socioeconomic conditions and gender inequality may lead to child marriage. They may also influence health later in life through a variety of causal pathways. We also considered spousal characteristics a source of confounding because the presence of an available spouse may drive child marriage. For example, a potential husband willing to pay a bride price for a young wife may motivate a family to marry a girl child. The same characteristics of the spouse that may motivate the marriage, such as his age, wealth, and attitudes regarding gender equity, may influence the married child’s health later in life through mechanisms like controlling behaviour. In studies that use pooled data from across multiple regions or countries, it is also important to control for confounding by country/regional-level variables that affect both the probability of child marriage and health. The DAG also illustrates our assumption that the effects of child marriage on health are often mediated through educational attainment and socioeconomic conditions after marriage.
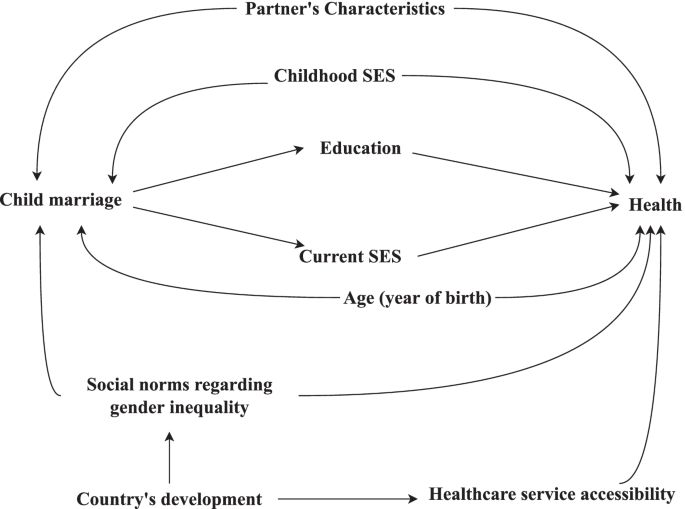
Directed acyclic graph illustrating assumed causal relationships between child marriage and a wide range of health outcomes
We synthesized results narratively. Included studies considered a wide range of health outcomes, as intended given our search strategy. We found it most intuitive and pragmatic to synthesize results within broad outcome categories, such as the effects of child marriage on contraceptive use, on maternal health care, and on mental health. These categories emerged from the data and were not pre-specified. Meta-analyses were not conducted because the studies examined a wide range of health outcomes that were measured in different ways. The serious risk of bias in all included studies, discussed below, also made quantitative synthesis inappropriate.
Our search strategy returned a total of 2767 unique records from MEDLINE, Embase, Ovid Global Health and Google Scholar, as shown in Fig. 2 . After title and abstracting screening, the full text of 126 articles was reviewed. Fifty-six of these studies met our inclusion criteria and two additional eligible studies were identified through citation tracking, for a total of 58 included articles.
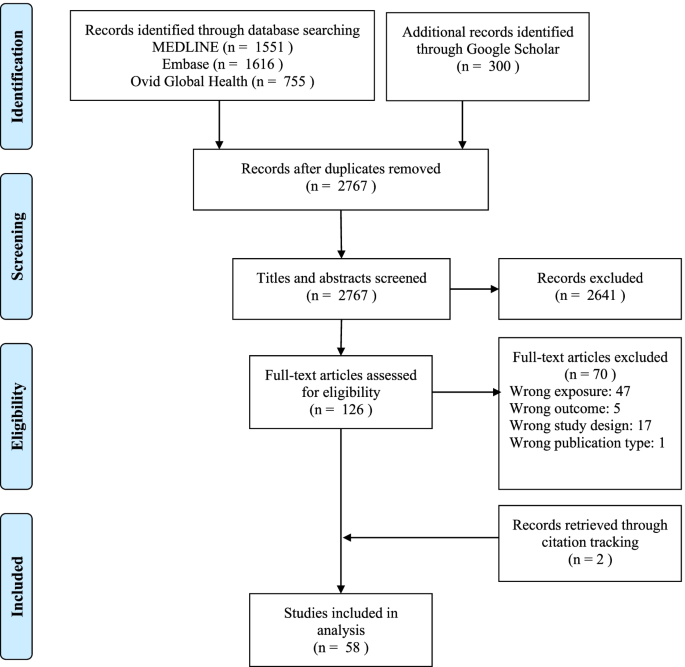
PRISMA flow diagram illustrating the process used to identify eligible studies
Selected characteristics of all 58 studies included in our review are presented in Table 1 . These studies were published between 1989 and 2020 but the vast majority ( n = 55, 95%) were published in 2010 or later and more than half ( n = 31, 53%) were published between 2016 and 2020, which reflects the relatively recent rise of child marriage on global health and development agendas. Included studies were based in 70 countries across the globe, as illustrated in Fig. 3 . Nearly all studies, 57 of 58, were based in low- and middle-income countries according to World Bank classifications [ 20 ]; the single exception was a study based in the United States [ 21 ]. The geographic distribution of studies included in our review was heavily focused in South Asia ( n = 30, 52%) and Sub-Saharan Africa ( n = 27, 47%), which is perhaps unsurprising given that countries in these regions have some of the highest rates of child marriage in the world [ 9 ]. However, more than half of the studies included in our review were based in just three countries: India ( n = 13), Bangladesh ( n = 8) and Ethiopia ( n = 11). Studies from regions other than South Asia or Sub-Saharan Africa were nearly all included in a handful of studies that analyzed survey data from multiple countries simultaneously [ 22 , 23 , 24 ].
Nearly all included studies, 55 of 58 (95%), were based on the analysis of cross-sectional survey data. More than half ( n = 34, 59%) relied on data from a single source, the Demographic and Health Surveys (DHS), or their precursor, the World Fertility Surveys (WFS).
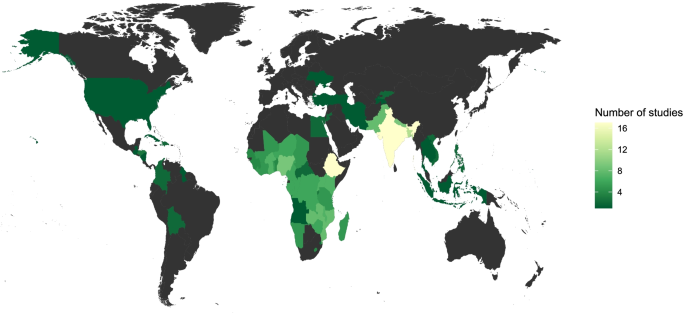
Geographic distribution of included studies
Bias assessment
All studies included in our review were determined to be at serious or critical risk of bias based on assessment using ROBINS-I. The summary risk of bias assessment for each study is listed in Table 1 ; risk of bias within each ROBINS-I domain in each study is detailed in Supplementary File 2 . Confounding was the most prevalent concern. Every study was deemed to be at serious to critical risk of bias in this domain, most often because of failure to account for important sources of confounding and inappropriate adjustment for variables affected by age at marriage that are on the causal pathway. Cross-sectional surveys like the DHS often do not collect information necessary to control for confounding. Failure to control for major sources of confounding like childhood poverty and gender inequality may result in overestimation of the harmful effects of child marriage. The second common source of bias was adjustment for variables measured after marriage that are likely on the causal pathway between age at marriage and the health outcomes being studied. To illustrate, the authors of many studies included in this review acknowledged that age at marriage may dictate how long a girl stays in school and that her educational attainment may subsequently influence a wide range of health outcomes. Unfortunately, they then adjusted for educational attainment in regression analyses. This will very likely result in biased estimates because educational attainment was measured after marriage and is more likely to be a mediator than a confounder (Fig. 1 ) [ 79 , 80 ]. Adjusting for it may remove some of the effect of child marriage on health and lead to underestimates of effect. Given that these two issues may bias results in different directions, predicting the net direction of confounding within studies is challenging. Other sources of bias also affected many of the studies in this review, including selection and measurement biases. Few authors discussed the potential influence of bias on their estimates or their conclusions.
The health consequences of child marriage
Studies included in our review estimated the effect of child marriage on a variety of health outcomes. The most common outcomes were measures of reproductive health, such as fertility and fertility control, maternal health care utilization, intimate partner violence, mental health, and nutritional status. The following paragraphs synthesize the literature in each of these categories. In light of the serious risk of bias in all included studies, we interpreted these results with a high degree of caution. We assessed the direction of effect measures, meaning whether the study found that child marriage increased or decreased the probability of experiencing the outcome, and the consistency of directionality across studies within each outcome category. We also assessed the precision of effect measures by evaluating the width of confidence intervals surrounding those measures. We did not interpret the magnitude of the effect estimates from individual studies due to the risk of bias.
The effect of child marriage on the number and timing of births
Eleven studies estimated the effect of child marriage on the number of children born, though this outcome was not consistently measured. Some studies estimated the effect of child marriage on the odds of having given birth to any children [ 34 , 50 , 63 ], the odds of having three or more children [ 24 , 46 , 50 , 63 , 75 ], four or more children [ 34 ], five or more children [ 37 , 69 ], or a continuous measure of the total number of children ever born [ 24 , 25 , 30 , 46 , 54 ]. The age ranges of the people included in these studies also differed, leading to variation in the time frame over which these births could have occurred. Child marriage was correlated with higher fertility in nearly all studies regardless of how the outcome was defined. The only exception was a study from Ethiopia that found no effect [ 30 ]. Ten of these studies focused on fertility exclusively among women. Misunas et al. [ 24 ] focused on men and came to similar conclusions: child marriage increased the odds that men aged 20-29 had fathered three or more children and increased the average number of children fathered by the ages of 40-49 [ 24 ].
A second commonly examined outcome was the likelihood of giving birth within the first year of marriage. Four studies based on data from South Asia [ 39 , 46 , 50 , 63 ] and one study based on pooled data from multiple countries in Africa [ 75 ] examined this outcome. Three of these studies [ 46 , 50 , 75 ] reported that marriage before the age of 18 decreased the odds of giving birth within the first year of marriage. The remaining two [ 39 , 63 ] did not find any evidence of a relationship between child marriage and this outcome.
We also identified five studies that estimated the effect of child marriage on the likelihood of giving birth before a specified age, often referred to as early, teen, or adolescent pregnancy [ 23 , 26 , 31 , 32 , 34 ]. Three of these studies found that child marriage increased the odds of giving birth before the age of 20 [ 26 , 31 , 32 ], the other two reported that child marriage increased the odds of giving birth before the age of 18 [ 23 , 34 ]. Two studies also estimated the effect of child marriage on mean age at first birth and found that those who married before the age of 18 gave birth for the first time at younger ages, on average, than those who married at older ages [ 32 , 46 ].
Collectively, this evidence indicates that women who marry as children often begin having children of their own at earlier ages when compared to their peers who marry after their 18th birthdays, and that they tend to have a larger number of children over their lifetimes. This is not surprising, given that marriage changes sexual behavior in ways that increase the risk of pregnancy. Essentially, girls who marry at earlier ages spend a longer time at risk of pregnancy than those who marry later.
The effect of child marriage on birth intervals
The World Health Organization recommends an interval of at least 24 months between a live birth and a subsequent pregnancy to reduce the risk of poor maternal health outcomes [ 81 ]. Five studies included in our review estimated the effect of child marriage on the likelihood of repeated childbirths in less than two years [ 39 , 50 , 62 , 63 , 75 ]. All five used samples of women between the ages of 20 and 24 who were included in DHS. A sixth study based on a small cross-sectional sample of women aged 15-49 from Ethiopia estimated the effect on repeated childbirth in less than three years [ 27 ]. These studies came to different conclusions. Two studies by the same author reported that child marriage increased the odds of repeated childbirth within two years in India [ 62 , 63 ] but another study based on the same data source found that women who married as children were less likely to have two births within a two-year period than those who married at older ages [ 39 ]. There were also differences in the results of research from Pakistan: one study reported that child marriage made it more likely that women would have two births within two years [ 50 ] while another found no evidence that child marriage influenced this outcome [ 39 ]. Child marriage protected against short birth intervals in Nepal [ 39 ] and in an analysis of data from 34 African countries [ 75 ]. There was no evidence that child marriage influence the likelihood of short birth intervals in Bangladesh [ 39 ].
These results, which range from harmful to protective effects, indicate that child marriage is not clearly or consistently correlated with short birth intervals.
Child marriage, unwanted or mistimed pregnancy, and pregnancy termination
Seven studies estimated the effect of child marriage on the likelihood of experiencing a mistimed or unwanted pregnancy [ 39 , 46 , 47 , 50 , 62 , 63 , 75 ]. All seven were based on analyses of DHS data. The DHS typically asks women whether pregnancies were wanted at the time they occurred, wanted later (i.e., mistimed), or not wanted. Interestingly, six of the seven studies that examined this outcome reduced these categorical responses into a binary measure: women were categorized as having an unwanted pregnancy if they reported that they had a mistimed pregnancy or if they became pregnant when they did not want any more children [ 39 , 46 , 50 , 62 , 63 , 75 ]. The rationale for doing this was not explained in any of the studies. The remaining study [ 47 ] only categorized instances in which a woman became pregnant at a time when she did not want any more children as unwanted.
Estimates of the effect of child marriage on this outcome are mixed. A study from 34 countries in Africa reported that child marriage protected against mistimed/unwanted pregnancies [ 75 ]. Studies from India, Pakistan, and Nepal concluded that child marriage increased the odds of experiencing mistimed/unwanted pregnancy [ 39 , 50 ]. Three studies from Bangladesh came to different conclusions. One found no relationship between child marriage and this outcome [ 39 ] while another reported that child marriage increased the odds of mistimed/unwanted pregnancy [ 46 ]. The third used a different definition of the outcome and found that marriage before the age of 15 was positively associated with unwanted pregnancy (mistimed pregnancies were treated as wanted) but no evidence that marriage between the ages of 15 and 17 affected the likelihood of unwanted pregnancy [ 47 ].
Three of these studies also estimated the effect of child marriage on the likelihood of experiencing two or more mistimed or unwanted pregnancies [ 39 , 62 , 63 ]. Godha et al. reported a large effect of child marriage on having multiple mistimed/unwanted pregnancies in India, Bangladesh, and Pakistan but results were inconclusive in Nepal [ 39 ]. Two studies by the same author reported that child marriage increased the odds of having multiple mistimed/unwanted pregnancies in India [ 62 , 63 ].
We identified eight studies of the effect of child marriage on pregnancy outcomes [ 39 , 47 , 48 , 50 , 57 , 63 , 66 , 75 ]. Six of these relied on the DHS, which typically asks female respondents, “Have you ever had a pregnancy that miscarried, was aborted, or ended in a stillbirth?” [ 82 ]. The wording of this question makes it impossible to examine these outcomes separately. As a result, most studies based on the DHS used a composite outcome that grouped these three events despite differences in their intendedness. Five studies based on the DHS concluded that child marriage increased the odds of having a pregnancy end in either miscarriage, abortion, or stillbirth [ 39 , 48 , 50 , 63 , 75 ]. Exceptionally, the 2007 Bangladesh DHS asked a yes or no question regarding whether a woman had ever terminated a pregnancy. Using responses to this question, Kamal reported that marriage before the age of 15 was correlated with higher odds of termination but no evidence that marriage between 15 and 17 years of age influenced this outcome [ 47 ].
Two studies from India used other cross-sectional data sources and defined their outcomes differently. Santhya et al. used a combined outcome of miscarriage and stillbirth and found that child marriage increased the likelihood of experiencing either of these birth outcomes. [ 66 ]. Paul considered stillbirth and miscarriage separately. Marriage before the age of 15 increased the odds of stillbirth and miscarriage, but marriage between the ages of 15-17 was no less risky in this regard than marriage at 18 or later [ 57 ].
Child marriage and contraceptive use
Fifteen of the studies included in our review estimated the effect of child marriage on various aspects of contraceptive use [ 23 , 24 , 32 , 39 , 40 , 41 , 43 , 46 , 53 , 56 , 62 , 63 , 65 , 66 , 75 ]. All were based on cross-sectional data and thirteen used data from the DHS.
Of these fifteen studies, eight estimated the effect of child marriage on the likelihood that women were using contraception at the time the surveys were conducted [ 32 , 39 , 40 , 46 , 53 , 62 , 63 , 65 ]. As with other outcomes, results were mixed. Child marriage reportedly increased the likelihood of using modern contraception in India and Bangladesh [ 39 ]. Results from Pakistan and Nepal indicate that the same may be true in those countries but the estimates were imprecise [ 39 ]. A second study from Nepal concluded that child marriage led to lower odds of using modern contraception [ 65 ]. The two studies from Nepal used different samples of women, which may partially explain the differences in their results. A study based on pooled data from 18 African countries found that child marriage was correlated with a lower likelihood of using modern contraception [ 53 ]. However, results varied markedly between countries and across geographic regions; in some, child marriage appeared to increase the likelihood of using modern contraception [ 53 ]. In Ghana, de Groot et al. found that child marriage was not correlated with the odds of using any form of contraception or with the use of modern contraceptives [ 32 ].
Two other studies investigated the effect of child marriage on the use of any method of contraception, including those not classified as modern [ 40 , 46 ]. Marriage prior to the age of 15 led to lower odds of contraceptive use in Rwanda, but there was no indication that those who married between 15 and 17 years of age were any more or less likely to use contraception than those who married at older ages [ 40 ]. In Bangladesh, women who married as children were more likely to be using some form of contraception at the time of the survey than those who married at the age of 18 or older [ 46 ]. In yet another iteration of this outcome, Yaya [ 75 ] reported that women who married as children were more likely to have ever used modern contraception. A single study estimated the effect of child marriage among men on the likelihood that they were using modern contraception [ 24 ]. In five of ten countries studied, child marriage was not related to modern contraceptive use. In two (Honduras and Nepal), child marriage seemed to slightly increase the odds of contraceptive use, but it decreased the likelihood in Madagascar [ 24 ].
A second outcome that has received particular focus is whether a woman used contraception before her first pregnancy. All four studies that examined the effect of child marriage on this outcome were based on data from South Asia [ 39 , 56 , 63 , 66 ] and concluded that marrying as a child decreased the likelihood that a woman used contraception prior to her first pregnancy [ 39 , 56 , 63 , 66 ]. The authors of these studies frequently interpreted their results as an indicator of uncontrolled fertility that may place girls and their children at risk of poor health outcomes [ 39 , 56 , 63 ]. However, this relationship is more challenging to interpret because the outcome variables used did not capture whether pregnancies were desired shortly after marriage or the outcomes of those pregnancies.
Four studies estimated the impact of child marriage on the likelihood that a woman had an unmet need for contraception [ 23 , 32 , 41 , 43 ]. This outcome was conceptually defined as a woman who is sexually active but not using contraception and who reports a desire to delay the next birth (a need for spacing), have no more births (a need for limiting), or a combination of the two. Once again, conclusions differ between studies. Using pooled DHS data from 47 countries, Kidman and Heymann found that marrying as a child increased the likelihood that women had an unmet need for contraception to either space or limit births [ 23 ]. An analysis of DHS data from Ethiopia found that women who married as children were less likely to have an unmet need for spacing and less likely to have an unmet need for limiting births compared to women who married at older ages [ 41 ]. In Zambia, child marriage was correlated with a greater unmet need for spacing and for limiting [ 43 ]. In Ghana, de Groot et al. found that child marriage was not correlated with an unmet need for limiting [ 32 ]. These studies all used different samples, which may partially explain the differences in their results.
Child marriage and use of maternal health care
Nine of the studies included in our review estimated the effect of child marriage on the use of health care during pregnancy, at the time of delivery, and during the post-partum period, which we collectively refer to as maternal health care [ 33 , 39 , 49 , 53 , 58 , 62 , 66 , 67 , 74 ].
Studies of prenatal care defined their outcomes as the receipt of at least one prenatal checkup [ 49 , 62 ], the receipt of four or more prenatal checkups [ 49 , 58 , 67 ], or a count of the total number of prenatal checkups received [ 39 , 53 ]. Once again, results within countries come to different conclusions. In Nepal, one study found that women who married as children were less likely to receive four or more prenatal checkups [ 67 ] while another found no evidence that child marriage influenced this outcome [ 39 ]. A study from India found no indication that child marriage affected prenatal care [ 39 ] but two others concluded that child marriage decreased the likelihood of receiving at least one checkup and of receiving at least four checkups [ 58 , 62 ]. In one study from Pakistan, women who married as children were less likely to receive any prenatal care than those who married at older ages, but there was no difference in the likelihood of receiving four or more checkups [ 49 ]. A separate study from the same country reported that child marriage had no effect on the number of prenatal care checkups [ 39 ]. The effect of child marriage on the number of prenatal care visits varied between geographic regions in Africa. In some, child marriage appeared correlated with a decrease the number of visits while in others there was no effect [ 53 ].
Compared to other outcomes, the results of studies that estimated the impact of child marriage on the likelihood of delivering in a health care facility were remarkably consistent. Across geographic locations, all seven studies that examined this outcome concluded that child marriage reduced the likelihood of delivery in a health care facility [ 39 , 49 , 53 , 58 , 66 , 67 , 74 ]. Six of the same studies also found that women who married as children were less likely to have a skilled health care provider present during delivery [ 39 , 49 , 53 , 58 , 67 , 74 ].
Only two studies considered post-natal care [ 58 , 67 ]. One reported that child marriage led to lower likelihood of a post-natal checkup within 42 days of delivery in India [ 66 ] while the other found a lower likelihood of a checkup within 24 h of delivery in Nepal [ 75 ].
Child marriage and intimate partner violence
Sixteen studies estimated the effect of child marriage on the likelihood of experiencing intimate partner violence [ 22 , 23 , 29 , 35 , 38 , 42 , 51 , 53 , 55 , 60 , 62 , 64 , 66 , 70 , 71 , 77 ]. Fifteen of these studies were based on cross-sectional data [ 22 , 23 , 29 , 35 , 38 , 42 , 51 , 53 , 55 , 60 , 62 , 64 , 66 , 70 , 71 ] and eight (50%) were based on the DHS [ 22 , 23 , 51 , 53 , 60 , 62 , 64 , 70 ]. The DHS measures intimate partner violence by asking female respondents a series of questions regarding their experience of specific acts. For example, physical violence is assessed by asking women whether they have been slapped, kicked, or pushed, among other actions. Sexual violence is assessed by asking whether the respondent’s husband has forced her to have sex or perform sex acts when she did not want to. Emotional violence is measured by asking whether her spouse has humiliated or threatened her [ 83 ]. Studies based on data from sources other than the DHS tended to use the same or very similar questions to measure the experience of violence.
Physical violence was the most frequently examined outcome but was measured over different time frames across studies. Some estimated the likelihood of ever having experienced physical violence from a husband or partner while others considered only the year prior to the survey. Still, others focused on the 3 months prior to the survey [ 35 ], the 9 months between survey waves [ 77 ], or during pregnancy [ 38 ]. Regardless of the time period during which violence was measured, the conclusions of these studies were fairly consistent: nearly all reported that marrying as a child increased the likelihood of experiencing physical violence [ 22 , 38 , 51 , 55 , 60 , 64 , 66 , 71 , 77 ]. A study from Ethiopia found no indication that child marriage had an effect on this outcome but it considered a relatively short time period of 3 months [ 35 ].
Estimates of the effect of child marriage on the experience of sexual violence were much less consistent. Two studies from India came to conflicting conclusions. Raj et al. found that child marriage did not increase the likelihood of experiencing sexual violence at any point or in the year prior to the 2005-06 National Family Health Survey [ 64 ]. However, a study by Santhya et al. based on survey data collected from five Indian states between 2006 and 2008 found that child marriage did increase the likelihood of ever experiencing sexual violence [ 66 ]. Studies from Bangladesh and Ghana reported that women who married as children were no more or less likely to experience sexual violence than those who married at later ages [ 60 , 71 ]. Two studies that pooled DHS data across multiple countries also found mixed results [ 22 , 53 ]. Olamijuwon used data from 18 African countries and found that child marriage increased the odds of experiencing sexual violence in Central, East, and Southern Africa, but there was no evidence of a statistical relationship in West Africa [ 53 ]. Kidman used DHS data from 34 countries across the globe and reported that child marriage seemed to increase the odds of experiencing sexual violence in the year prior to the surveys in all included geographic regions except Europe and Central Asia [ 22 ]. Erulkar found that women who married as children in Ethiopia were more likely to report that their first sexual experience was forced [ 35 ].
Only two studies, one from Pakistan and one from Ghana, considered emotional violence as a stand-alone outcome. Both concluded the child marriage led to an increase in the likelihood of ever experiencing emotional violence from an intimate partner [ 51 , 71 ].
Five studies considered only combined outcomes that mixed indicators of physical and sexual violence [ 62 , 70 ], or physical, sexual, and emotional violence [ 23 , 29 , 42 ]. All of these found that child marriage was associated with increased reporting of these composite measures of violence, but some results were sensitive to the sample used and were inconsistent across locations [ 70 ]. Hong Le et al. considered whether child marriage affected the likelihood of violence among boys but was underpowered to detect any effect [ 42 ].
Child marriage and mental health
Five of the studies included in our review estimated the effect of child marriage on various aspects of mental health. These studies relied on cross-sectional data collected from Ghana, Iran, Ethiopia, Niger and the United States [ 21 , 32 , 36 , 44 , 45 ]. Women in the United States who married before the age of 18 were more likely to report experiencing a wide range of mood, anxiety, and other psychiatric disorders in adulthood when compared to those who married at later ages [ 21 ]. The authors of a small study from a single county in Iran found that women who married as children reported more depressive symptoms than those who married at the age of 18 or older [ 36 ]. John, Edmeades, and Murithi examined the relationship between child marriage and multiple domains of psychological well-being in Niger and Ethiopia [ 44 ]. The authors found that marriage before the age of 16 was correlated with poorer overall psychological well-being, but no evidence that marriage between the ages of 16 and 17 was associated with poorer outcomes when compared to women who married at the age of 18 or later [ 44 ]. In Ghana, child marriage seemed to protect against measures of stress. The Ghanaian study also found no indication of differences in levels of social support between women who married before the age of 18 and those who married after their 18th birthdays, though these odds ratio estimates were very imprecise [ 32 ].
Child marriage and nutritional status
Six studies included in our review estimated the effect of child marriage on indicators of nutritional status [ 28 , 34 , 52 , 61 , 76 , 78 ]. Four focused exclusively on pregnant women. Two studies from Ethiopia examined the relationship between child marriage and mid-upper arm circumference (MUAC) [ 52 , 76 ]. One reported that pregnant women who married before the age of 18 were more likely to have an MUAC less than 22 cm, often interpreted as a marker of undernutrition [ 84 , 85 ], compared to those who married later on [ 52 ]. The other found that marrying before the age of 15 increased the likelihood of MUAC <22 cm but no evidence that marrying between the ages of 15 and 17 affected this outcome [ 76 ]. A third study from Ethiopia reported that child marriage led to an increase in the prevalence of Vitamin A deficiency among pregnant or recently post-partum women [ 28 ].
Two other studies focused on women who were not pregnant and used body mass index (BMI) as the indicator of nutritional status [ 34 , 78 ]. Their results diverge. Yusuf et al. found that women in Nigeria who married as children were more likely to have a BMI less than 18.5, frequently interpreted as underweight among adults. However, in a study of 35 African countries, Efevbera et al. reported that child marriage was protective against being underweight (BMI<18.5) [ 44 ]. Interestingly, the authors of these studies offered plausible explanations for effects in either direction. Efevbera et al. hypothesize that girls who marry as children may gain access to more plentiful food at an earlier age and that repeated pregnancies during adolescence might result in greater weight gain relative to those who marry at later ages [ 34 ]. In contrast, Nigatu et al. note that repeat pregnancies in quick succession may have a detrimental impact on cumulative nutritional status [ 52 ]. This suggests that the mechanisms through which age at marriage may affect subsequent nutritional status have not been thoroughly considered.
Other health consequences of child marriage
A few of the studies included in our review examined outcomes other than those discussed above. We note them briefly here. A case-control study from India reported that women diagnosed with cervical cancer were more likely to have been married before the age of 18 [ 72 ]. A large, pooled analysis of DHS data from 47 countries reported that child marriage was associated with symptoms of sexually transmitted infections [ 23 ]. A small, cross-sectional study from a single Indian state found no evidence that child marriage led to an increase in the odds of obstetric fistula [ 68 ]. A third study from India examined the effect of child marriage on the odds of experiencing at least one complication during pregnancy, delivery, or within two months after delivery [ 57 ]. Marriage before the age of 15 seemed to increase the likelihood of pregnancy complications, but there was no evidence of an effect for marriage between 15 and 17 years. Child marriage was not associated with delivery complications, but was associated with postnatal complications [ 57 ]. A study from Ghana found no indication that child marriage influenced the likelihood of self-reported poor health, of being ill in the two weeks prior to the survey, or of having a health insurance card but did report that child marriage increased the odds of having difficulty with activities of daily living, such as bending or walking [ 32 ].
Our systematic review synthesized research on the health consequences of marrying before the age of 18. Studies almost uniformly found that women who married before the age of 18 began having children of their own at earlier ages and gave birth to more children over the course of their reproductive lives when compared to those who married at the age of 18 or later. Whether these outcomes, considered alone, are harmful to health is not clear. Though there are many reasons to be concerned about adolescent childbearing, none of the studies of the effect of child marriage on the timing of births considered whether those pregnancies were planned or desired or whether they resulted in obstetric complications or maternal morbidity or mortality [ 23 , 26 , 31 , 32 , 34 , 39 , 46 , 50 , 63 , 75 ]. Similarly, having multiple births, especially at short intervals, may increase the risk of obstetric complications and subsequent morbidity or mortality. However, studies that compared the number of children born to women who married before the age of 18 with the number born to those who married at later ages also did not measure whether those pregnancies were planned or whether they led to harm [ 24 , 25 , 30 , 34 , 37 , 46 , 50 , 54 , 63 , 69 , 75 ]. Rather, studies seemed to assume that these are negative outcomes without directly measuring intentions or harms.
A separate set of studies that estimated the effect of child marriage on the experience of mistimed or unwanted pregnancies came to divergent conclusions: some found that child marriage increased the likelihood of these outcomes but others found that child marriage protected against them or had no effect. Studies of whether child marriage affected the likelihood of obstetric complications, miscarriage or stillbirth did not consider maternal age when those events occurred [ 39 , 47 , 48 , 50 , 57 , 63 , 66 , 75 ]. Moreover, the fact that child marriage corresponds with a larger number of pregnancies means that girls who married prior to the age of 18 had more opportunities to experience these events compared to those who married later; this was not discussed in any of the studies we identified.
The results of studies in other outcome domains are very mixed and challenge some common narratives regarding child marriage. To illustrate, studies included in this review came to conflicting conclusions regarding whether child marriage increases or decreases the use of modern contraception, the likelihood of giving birth within the first year of marriage, and the likelihood of repeated childbirth within two years. Conclusions regarding mistimed and unwanted pregnancies were also mixed, as noted above. Collectively, these results suggest that child marriage is not uniformly characterized by an inability to control the number or timing of births and suggests that a more cautious approach to discussions of agency within these marriages is warranted, at least regarding fertility and fertility control.
Across studies, women who married as children were less likely to give birth in a health care facility or with assistance from a skilled health care provider. These findings raise concerns about access to emergency obstetric care and subsequent birth outcomes for both mother and child. However, we found only one study that estimated the effect of child marriage on the likelihood of complications during pregnancy, delivery, and the postpartum period [ 57 ] and consideration of the consequences for the infants born was beyond the scope of this review. This statistical relationship could be confounded by lack of access due to geographic distance. Child marriage is more common in rural areas, where health care facilities and skilled health care providers may be more spread out. It may also be a function of gender inequality, which may manifest as an inability to seek care without permission. Future research should consider the potential for confounding by these and other variables and investigate whether place modifies this relationship.
Child marriage could plausibly affect many aspects of maternal and reproductive health through complex causal pathways. However, most of the studies included in our review did not discuss causal mechanisms in detail, which may have hindered their ability to identify and account for various sources of bias. More thorough consideration and discussion of these mechanisms would strengthen the theoretical underpinnings of this body of literature and help mitigate biases. For example, use of Directed Acyclic Graphs to illustrate assumed causal relationships would help to clarify the causal pathways being studied and identify sources of bias [ 86 ].
The effects of child marriage among boys have been almost entirely overlooked. Only 2 of the 58 studies included in this review considered boys or men and one of them was underpowered to generate informative estimates [ 42 ]. This intense focus on child marriage among girls reflects the gendered nature of the practice. However, a substantial proportion of boys also marry before the age of 18 in some countries [ 7 , 24 ] and further inquiry into the health consequences among boys is warranted.
The geographic distribution of research on child marriage and health is highly skewed. The focus on South Asia and sub-Saharan Africa may be justified since these regions have some of the highest rates of child marriage in the world. However, it is unclear why just three countries, India, Bangladesh, and Ethiopia, have received such focused attention while other countries in these regions have received very little. Child marriage is certainly ongoing in many other regions of the world that have received little or no research attention, including high-income countries [ 9 , 87 , 88 ].
The geographic distribution of these studies and the range of outcomes considered is clearly reflective of heavy reliance on the DHS. The DHS is appealing because it collects information on age at marriage that is comparable across settings and over time, data are readily accessible and of high quality, and samples are typically nationally representative. However, defaulting to this data source may also have restricted the range of outcomes studied. The DHS focuses primarily on reproductive health and our review included many studies of the effect of child marriage on fertility, contraceptive use, and intimate partner violence. Far less attention has been paid to other potential harms of child marriage that are not included in the surveys, such as indicators of mental health. Importantly, the DHS does not collect information on some of the strongest confounders of many relationships between child marriage and health, including childhood socioeconomic conditions and measures of gender equality. Other data sources will be necessary to increase the geographic scope of this body of research and to overcome some of the limitations inherent in the use of cross-sectional data to estimate causal effects.
All studies included in our review were at serious to critical risk of bias. Quantification of the net magnitude of different biases on the results of each study would have made the project untenable. Considering pervasive bias, we avoided interpreting the magnitude of reported estimates from individual studies and instead took only the directionality of the estimates at face value. This allowed us to assess the (in)consistency of conclusions within domains of health. However, it is entirely possible that bias could lead to a reversal of effects, i.e., estimating a positive effect when the true effect is negative or vice versa. The bias in these studies means that it is unclear whether any of the relationships described are causal.
Nearly all studies included in our review relied on cross-sectional data. There are severe limitations to using cross-sectional research designs to estimate causal effects, and more rigorous designs are needed to further our understanding of the consequences of child marriage. Quasi-experimental designs that more effectively mitigate confounding would strengthen this body of literature and have already been used to study the effect of child marriage on educational attainment and literacy. For example, Field and Ambrus and Sunder used age at menarche as an instrumental variable to study the effect of child marriage on these outcomes [ 3 , 4 ]. Encouragement trials that randomly assign exposure to interventions meant to prevent child marriage could also be used to estimate the effects of child marriage on health outcomes, though such trials are more resource intensive to conduct [ 89 ]. However, given that the DHS and other cross-sectional data sources will likely continue to be used to investigate these relationships, the use of quantitative bias analyses to examine how sensitive estimates are to various sources of bias would be an improvement [ 90 ].
There are several limitations to this systematic review. First, to capture as wide a range of health outcomes as possible, we searched databases focused on human health and biomedicine. Relevant studies from other academic disciplines such as economics and sociology may have been missed using this approach. Second, our search was conducted in English and all included studies were published in English. Eligible studies published in other languages may have been missed, which could influence our conclusions regarding the geographic distribution of research. Finally, as noted in the introduction, child marriage may have consequences beyond the domain of health. We focused our systematic review on the health consequences of child marriage in response to growing rhetoric regarding child marriage as a population health concern. Rigorous systematic reviews of the effect of child marriage on educational and economic outcomes would be a valuable addition to the literature.
Availability of data and materials
The PROSPERO protocol and the data extraction form are publicly available through the Open Science Foundation at https://osf.io/32mu7/ .
Abbreviations
Body Mass Index
Cross-Sectional
Directed Acyclic Graph
Demographic and Health Surveys
Mid-Upper Arm Circumference
Risk Of Bias In Non-randomised Studies - of Interventions tool
Socio-Economic Status
United Nations Population Fund
United Nations Children’s Fund
United Nations Office of the High Commissioner for Human Rights. Recommendations for Action Against Child and Forced Marriages [Internet]. 2017. Report No.: UNICEF/UN05222/Dragaj. Available from: https://www.ohchr.org/Documents/Issues/Women/WRGS/CEFM/RecommendationsForActionEbook.pdf
UNICEF. Early marriage: a harmful traditional practice. New York: UNICEF; 2005.
Google Scholar
Field E, Ambrus A. Early Marriage, Age of Menarche, and Female Schooling Attainment in Bangladesh. J Polit Econ. 2008;116(5):881–930.
Sunder N. Marriage age, social status, and intergenerational effects in Uganda. Demography. 2019;56(6):2123–46.
Dahl GB. Early teen marriage and future poverty. Demography. 2010;47(3):30.
Article Google Scholar
Koski A, Clark S, Nandi A. Has child marriage declined in sub-Saharan Africa? An analysis of trends in 31 countries. Popul Dev Rev. 2017;43(1):7–29.
Gastón CM, Misunas C, Cappa C. Child marriage among boys: a global overview of available data. Vulnerable Child Youth Stud. 2019;14(3):219–28.
United Nations. The Sustainable Development Goals Report 2018. New York, NY; 2018.
Girls Not Brides. Child Marriage Atlas. [cited 2021 Jul 3]. Available from: https://atlas.girlsnotbrides.org/map/
UNICEF. Ending Child Marriage: Progress and Prospects. New York; 2014. Available from: https://www.unicef.org/media/files/Child_Marriage_Report_7_17_LR.pdf
Wodon Q. Child marriage: A persistent hurdle to health and prosperity. World Bank. 2015 [cited 2020 Jul 28]. Available from: https://blogs.worldbank.org/health/child-marriage-persistent-hurdle-health-and-prosperity
United Nations Population Fund. Marrying too young: end child marriage [Internet]. New York, NY: United Nations Population Fund; 2012 [cited 2020 Apr 27]. Available from: http://www.unfpa.org/webdav/site/global/shared/documents/publications/2012/MarryingTooYoung.pdf
UNICEF. Child Marriage. 2021 [cited 2020 Jul 30]. Available from: https://www.unicef.org/protection/child-marriage
Haddaway NR, Collins AM, Coughlin D, Kirk S. The Role of Google Scholar in Evidence Reviews and Its Applicability to Grey Literature Searching. PLOS ONE. 2015;17(9):e0138237.
Clarivate Analytics. EndNote. 2019 [cited 2020 May 11]. Available from: https://endnote.com/
Ouzzani M, Hammady H, Fedorowicz Z, Elmagarmid A. Rayyan—a web and mobile app for systematic reviews. Syst Rev. 2016;5(1):210.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Sterne JA, Hernán MA, Reeves BC, Savović J, Berkman ND, Viswanathan M, et al. ROBINS-I: a tool for assessing risk of bias in non-randomised studies of interventions. BMJ. 2016 [cited 2020 Apr 27];355. Available from: https://www.bmj.com/content/355/bmj.i4919
Hernán MA, Robins JM. Causal Inference: What If. Boca Raton: Chapman & Hall/CRC; 2020.
Male C, Wodon Q. Girls’ Education and Child Marriage in West and Central Africa: Trends, Impacts, Costs, and Solutions. Forum Soc Econ. 2018;47(2):262–74.
World Bank. World Bank Country and Lending Groups [Internet]. 2020 [cited 2020 Aug 17]. Available from: https://datahelpdesk.worldbank.org/knowledgebase/articles/906519-world-bank-country-and-lending-groups
Le Strat Y, Dubertret C, Le Foll B. Child marriage in the United States and its association with mental health in women. Pediatrics. 2011;128(3):524–30.
Kidman R. Child marriage and intimate partner violence: a comparative study of 34 countries. Int J Epidemiol. 2016;dyw225.
Kidman R, Heymann J. Prioritising action to accelerate gender equity and health for women and girls: Microdata analysis of 47 countries. Glob Public Health. 2018;13(11):1634–49.
Misunas C, Gastón CM, Cappa C. Child marriage among boys in high-prevalence countries: an analysis of sexual and reproductive health outcomes. BMC Int Health Hum Rights. 2019;19(1):25.
Agyei WKA, Mbamanya J. Determinants of cumulative fertility in Kenya. J Biosoc Sci. 1989;21(2):135–44.
Ali M, Alauddin S, Khatun MostF, Maniruzzaman Md, Islam SMS. Determinants of early age of mother at first birth in Bangladesh: a statistical analysis using a two-level multiple logistic regression model. J Public Health. 2020 [cited 2020 Jul 2]; Available from: http://link.springer.com/ https://doi.org/10.1007/s10389-020-01228-9
Ayane GB, Desta KW, Demissie BW, Assefa NA, Woldemariam EB. Suboptimal child spacing practice and its associated factors among women of child bearing age in Serbo town, JIMMA zone, Southwest Ethiopia. Contracept Reprod Med. 2019;4(1):4.
Baytekus A, Tariku A, Debie A. Clinical vitamin-A deficiency and associated factors among pregnant and lactating women in Northwest Ethiopia: a community-based cross-sectional study. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2019 Dec;19(1):506.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Begum S, Donta B, Nair S, Prakasam C. Socio-demographic factors associated with domestic violence in urban slums, Mumbai, Maharashtra, India. Indian J Med Res. 2015;141(6):783.
Berlie AB, Alamerew YT. Determinants of Fertility Rate among Reproductive Age Women (15-49) in Gonji-Kollela District of the Amhara National Regional State, Ethiopia. Ethiop J Health Dev.:12.
Birhanu BE, Kebede DL, Kahsay AB, Belachew AB. Predictors of teenage pregnancy in Ethiopia: a multilevel analysis. BMC Public Health. 2019;19(1):601.
de Groot R, Kuunyem MY, Palermo T. Child marriage and associated outcomes in northern Ghana: a cross-sectional study. BMC Public Health. 2018;18(1):285.
Delprato M, Akyeampong K. The Effect of Early Marriage Timing on Women’s and Children’s Health in Sub-Saharan Africa and Southwest Asia. Ann Glob Health. 2017;83(3–4):557.
Efevbera Y, Bhabha J, Farmer P, Fink G. Girl child marriage, socioeconomic status, and undernutrition: evidence from 35 countries in Sub-Saharan Africa. BMC Med. 2019;17(1):55.
Erulkar A. Early marriage, marital relations and intimate partner violence in Ethiopia. Int Perspect Sex Reprod Health. 2013 Mar;39(01):006–13.
Fakhari A, Farahbakhsh M, Azizi H, Esmaeili ED, Mirzapour M, Rahimi VA, et al. Early Marriage and Negative Life Events Affect on Depression in Young Adults and Adolescents. Arch Iran Med. 2020;23(2):10.
Gebremedhin S, Betre M. Level and differentials of fertility in Awassa town, Southern Ethiopia. Afr J Reprod Health. 2009;13(1):93–112.
PubMed Google Scholar
Gebrezgi BH, Badi MB, Cherkose EA, Weldehaweria NB. Factors associated with intimate partner physical violence among women attending antenatal care in Shire Endaselassie town, Tigray, northern Ethiopia: a cross-sectional study, July 2015. Reprod Health. 2017;14(1):76.
Godha D, Hotchkiss DR, Gage AJ. Association between child marriage and reproductive health outcomes and service utilization: A multi-country study from South Asia. J Adolesc Health. 2013;52(5):552–8.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Habyarimana F, Ramroop S. The Analysis of Socio-Economic and Demographic Factors Associated with Contraceptive Use Among Married Women of Reproductive Age in Rwanda. Open Public Health J. 2018;11(1):348–59.
Hailemariam A, Haddis F. Factors Affecting Unmet Need for Family Planning In Southern Nations, Nationalities and Peoples Region, Ethiopia. Ethiop J Health Sci. 2011;21(2):77–90.
Hong Le MT, Tran TD, Nguyen HT, Fisher J. Early marriage and intimate partner violence among adolescents and young adults in Viet Nam. J Interpers Violence. 2014;29(5):889–910.
Imasiku ENS, Odimegwu CO, Adedini SA, Ononokpono DN. VARIATIONS IN UNMET NEED FOR CONTRACEPTION IN ZAMBIA: DOES ETHNICITY PLAY A ROLE? J Biosoc Sci. 2014;46(3):294–315.
John NA, Edmeades J, Murithi L. Child marriage and psychological well-being in Niger and Ethiopia. BMC Public Health. 2019;19(1):1029.
John NA, Edmeades J, Murithi L, Barre I. Child marriage and relationship quality in Ethiopia. Cult Health Sex. 2019;21(8):853–66.
Kamal SM. Decline in Child Marriage and Changes in Its Effect on Reproductive Outcomes in Bangladesh. J Health Popul Nutr. 2012;20(3):317–30.
Kamal SMM. Domestic Violence, Unwanted Pregnancy and Pregnancy Termination among Urban Women of Bangladesh. J Fam Reprod Health. 2013;7(1):11–22.
Kamal SMM, Hassan CH. Child Marriage and Its Association With Adverse Reproductive Outcomes for Women in Bangladesh. Asia Pac J Public Health. 2015;27(2):NP1492-506.
Nasrullah M, Zakar R, Krämer A. Effect of Child Marriage on Use of Maternal Health Care Services in Pakistan: Obstet Gynecol. 2013;122(3):517–24.
Nasrullah M, Muazzam S, Bhutta ZA, Raj A. Girl Child Marriage and Its Effect on Fertility in Pakistan: Findings from Pakistan Demographic and Health Survey, 2006–2007. Matern Child Health J. 2014;18(3):534–43.
Nasrullah M, Zakar R, Zakar MZ. Child Marriage and Its Associations With Controlling Behaviors and Spousal Violence Against Adolescent and Young Women in Pakistan. J Adolesc Health. 2014;55(6):804–9.
Nigatu M, Gebrehiwot TT, Gemeda DH. Household Food Insecurity, Low Dietary Diversity, and Early Marriage Were Predictors for Undernutrition among Pregnant Women Residing in Gambella, Ethiopia. Adv Public Health. 2018;2018:1–10.
Olamijuwon EO, Chisumpa VH, Akinyemi JO. Unveiling the realities of marrying too young: implications of child marriage on sexual and reproductive health of girls and infant survival in sub-Sahara Africa. (Special issue on family demography in Africa: determinants and consequences.). Afr Popul Stud. 2017;31(1):3594–610.
Onagoruwa A, Wodon Q. Measuring the impact of child marriage on total fertility: a study for fifteen countries. J Biosoc Sci. 2018;50(5):626–39.
Oshiro A, Poudyal AK, Poudel KC, Jimba M, Hokama T. Intimate Partner Violence Among General and Urban Poor Populations in Kathmandu, Nepal. J Interpers Violence. 2011;26(10):2073–92.
Pandey A, Singh KK. Contraceptive use before first pregnancy by women in India (2005–2006): determinants and differentials. BMC Public Health. 2015;15(1):1316.
Paul P. Maternal Age at Marriage and Adverse Pregnancy Outcomes: Findings from the India Human Development Survey, 2011-2012. J Pediatr Adolesc Gynecol. 2018;31(6):620–4.
Paul P, Chouhan P. Association between child marriage and utilization of maternal health care services in India: Evidence from a nationally representative cross-sectional survey. Midwifery. 2019;75:66–71.
Prakash R, Singh A, Pathak PK, Parasuraman S. Early marriage, poor reproductive health status of mother and child well-being in India. J Fam Plann Reprod Health Care. 2011;37(3):136–45.
Rahman M, Hoque MdA, Mostofa MdG, Makinoda S. Association Between Adolescent Marriage and Intimate Partner Violence: A Study of Young Adult Women in Bangladesh. Asia Pac J Public Health. 2014;26(2):160–8.
Rahman ML, Kile ML, Rodrigues EG, Valeri L, Raj A, Mazumdar M, et al. Prenatal arsenic exposure, child marriage, and pregnancy weight gain: Associations with preterm birth in Bangladesh. Environ Int. 2018;112:23–32.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Raj A. When the mother is a child: the impact of child marriage on the health and human rights of girls. Arch Dis Child. 2010 Nov 1;95(11):931–5.
Raj A, Saggurti N, Balaiah D, Silverman JG. Prevalence of child marriage and its effect on fertility and fertility-control outcomes of young women in India: a cross-sectional, observational study. The Lancet. 2009;30(9678):1883–9.
Raj A, Saggurti N, Lawrence D, Balaiah D, Silverman JG. Association between adolescent marriage and marital violence among young adult women in India. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2010;110(1):35–9.
Raj A, Vilms RJ, McDougal L, Silverman JG. Association between having no sons and using no contraception among a nationally representative sample of young wives in Nepal. Int J Gynecol Obstet. 2013;121(2):162–5.
Santhya KG, Ram U, Acharya R, Jejeebhoy SJ, Ram F, Singh A. Associations Between Early Marriage and Young Women’s Marital and Reproductive Health Outcomes: Evidence from India. Int Perspect Sex Reprod Health. 2010;36(03):132–9.
Sekine K, Carter DJ. The effect of child marriage on the utilization of maternal health care in Nepal: A cross-sectional analysis of Demographic and Health Survey 2016. Wilunda C, editor. PLOS ONE. 2019;14(9):e0222643.
Singh JP, Gupta SD, Khanna A, Sharma LS. Prevalence of Obstetric Fistula and Associated Factors in Rajasthan, India. J Health Manag. 2019;21(2):193–8.
Solanke BL. Maternal socio-demographic factors associated with low parity and grand multiparity in Nigeria. Women Health. 2019;59(7):730–47.
Speizer IS, Pearson E. Association between Early Marriage and Intimate Partner Violence in India: A Focus on Youth from Bihar and Rajasthan. J Interpers Violence. 2011;26(10):1963–81.
Tenkorang EY. Explaining the links between child marriage and intimate partner violence: Evidence from Ghana. Child Abuse Negl. 2019;89:48–57.
Thakur A, Gupta B, Gupta A, Chauhan R. Risk factors for cancer cervix among rural women of a hilly state: A case-control study. Indian J Public Health. 2015;59(1):45.
Thekdi KP, Mehta PI, Thekdi PI, Kartha GP. Fertility profile, anxiety, depression of married women and its association with reproductive tract infections in the rural area of Surendranagar district. Sch J Appl Med Sci. 2014;2(1):104–8.
Uddin J, Pulok MH, Johnson RB, Rana J, Baker E. Public Health. 2019;171:6–14.
Yaya S, Odusina EK, Bishwajit G. Prevalence of child marriage and its impact on fertility outcomes in 34 sub-Saharan African countries. BMC Int Health Hum Rights. 2019;19(1):33.
Yimer B. Under Nutrition and Associated Factors among Adolescent Pregnant Women in Shashemenne District, West Arsi Zone, Ethiopia: A Communitybased Study. J Nutr Food Sci [Internet]. 2016 [cited 2020 Jul 2];06(01). Available from: https://www.omicsonline.org/open-access/under-nutrition-and-associated-factors-among-adolescent-pregnantwomen-in-shashemenne-district-west-arsi-zone-ethiopia-a-communityb-2155-9600-1000454.php?aid=66531
Yount KM, Crandall A, Cheong YF, Osypuk TL, Bates LM, Naved RT, et al. Child Marriage and Intimate Partner Violence in Rural Bangladesh: A Longitudinal Multilevel Analysis. Demography. 2016;53(6):1821–52.
Yusuf OB, Gbadebo BM, Afolabi RF, Adebowale AS. Trends, pattern and socioeconomic predictors of underweight among young married women in Nigeria. Public Health Res. 2018;8(2):35–45.
Elwert F, Winship C. Endogenous Selection Bias: The Problem of Conditioning on a Collider Variable. Annu Rev Sociol. 2014;40(1):31–53.
Schisterman EF, Cole SR, Platt RW. Overadjustment Bias and Unnecessary Adjustment in Epidemiologic Studies. Epidemiol Camb Mass. 2009;20(4):488–95.
World Health Organization. Report of a WHO technical consultation on birth spacing: Geneva, Switzerland 13-15 June 2005. 2007;(WHO/RHR/07.1). Available from: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/69855
ICF International. Demographic and Health Surveys Methodology - Questionnaires: Household, Woman’s, and Man’s. [Internet]. Calverton, Maryland, USA; 2011. (MEASURE DHS Phase III). Available from: http://www.measuredhs.com/publications/publication-DHSQ6-DHS-Questionnaires-and-Manuals.cfm
ICF International. DHS Questionnaire Modules: Domestic Violence [Internet]. Calverton, Maryland, USA; 2019 [cited 2021 Jul 3]. Available from: https://dhsprogram.com/publications/publication-DHSQM-DHS-Questionnaires-and-Manuals.cfm
Kumar P, Sareen N, Agrawal S, Kathuria N, Yadav S, Sethi V. Screening Maternal Acute Malnutrition Using Adult Mid-Upper Arm Circumference in Resource-Poor Settings. Indian J Community Med Off Publ Indian Assoc Prev Soc Med. 2018;43(2):132–4.
Ververs M, Antierens A, Sackl A, Staderini N, Captier V. Which Anthropometric Indicators Identify a Pregnant Woman as Acutely Malnourished and Predict Adverse Birth Outcomes in the Humanitarian Context? PLoS Curr [Internet]. 2013 Jun 7 [cited 2020 Aug 19];5. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3682760/
Shrier I, Platt RW. Reducing bias through directed acyclic graphs. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2008;8(1):70.
Koski A, Clark S. Child Marriage in Canada. Popul Dev Rev. 2021;47(1):57–78.
Koski A, Heymann J. Child marriage in the United States: How common is the practice, and which children are at greatest risk? Perspect Sex Reprod Health. 2018;50(2):59–65.
Baird S, Chirwa E, McIntosh C, Özler B. The short-term impacts of a schooling conditional cash transfer program on the sexual behavior of young women. Health Econ. 2010;19(S1):55–68.
Lash T, Fox M, MacLehose R. Applying Quantitative Bias Analysis to Epidemiologic Data [Internet]. 2nd ed. Springer International Publishing; 2021 [cited 2021 Jul 6]. (Statistics for Biology and Health). Available from: https://www.springer.com/gp/book/9783030826727
Download references
Acknowledgements
We thank Genevieve Gore at the McGill University Library for her assistance in developing the search terms used in this review.
No funding was received for the study.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Epidemiology, Biostatistics and Occupational Health, McGill University, 2001 McGill College Avenue, Montreal, Quebec, H3A 1G1, Canada
Suiqiong Fan & Alissa Koski
Institute for Health and Social Policy, McGill University, 2001 McGill College Avenue, Montreal, Quebec, H3A 1G1, Canada
Alissa Koski
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
SF and AK were responsible for the study conception and design. SF conducted database searches. SF and AK screened eligible studies and extracted data from included studies. SF and AK conducted the analysis, interpreted the results, and collaboratively wrote the manuscript. SF prepared the tables and figures. AK supervised the study. The author(s) read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Alissa Koski .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Competing interests.
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1., additional file 2., additional file 3., rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Fan, S., Koski, A. The health consequences of child marriage: a systematic review of the evidence. BMC Public Health 22 , 309 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-022-12707-x
Download citation
Received : 16 September 2021
Accepted : 31 January 2022
Published : 14 February 2022
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-022-12707-x
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Child marriage
- Social determinants of health
- Systematic review
BMC Public Health
ISSN: 1471-2458
- General enquiries: [email protected]

IMAGES
VIDEO