- Staff Directory
- Library Policies
- Hege Research Award
- Quaker Archives
- Art Gallery
- Student Support
- Teaching & Learning
- Reserving spaces
- Technology Lending
- Interlibrary Loan
- Course Reserves
- Copyright & Fair Use
- Poster Printing
- Virtual Reference
- Research Guides
- Off-campus access
- Digital Scholarship
- Guilford Sources
- Open Educational Resources
- Quaker Collections
- Digital Collections
- College Archives
- Underground Railroad
- Universities Studying Slavery
- Images & Exhibitions
Service Alert

Hege Library & Learning Technologies

Guide for Thesis Research
- Introduction to the Thesis Process
- Project Planning
- Literature Review
- Theoretical Frameworks
- Research Methodology
- GC Honors Program Theses
- Thesis Submission Instructions This link opens in a new window
- Accessing Guilford Theses from 1898 to 2020 This link opens in a new window
Basics of Methodology
Research is a process of inquiry that is carried out in a pondered, organized, and strategic manner. In order to obtain high quality results, it is important to understand methodology.
Research methodology refers to how your project will be designed, what you will observe or measure, and how you will collect and analyze data. The methods you choose must be appropriate for your field and for the specific research questions you are setting out to answer.
A strong understanding of methodology will help you:
- apply appropriate research techniques
- design effective data collection instruments
- analyze and interpret your data
- develop well-founded conclusions
Below, you will find resources that mostly cover general aspects of research methodology. In the left column, you will find resources that specifically cover qualitative, quantitative, and mixed methods research.
General Works on Methodology
Qualitative Research
Quantitative Research
Mixed Methods Research
- << Previous: Theoretical Frameworks
- Next: Citation >>
- Last Updated: Jul 22, 2024 10:48 AM
- URL: https://library.guilford.edu/thesis-guide
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
- What Is a Research Methodology? | Steps & Tips
What Is a Research Methodology? | Steps & Tips
Published on 25 February 2019 by Shona McCombes . Revised on 10 October 2022.
Your research methodology discusses and explains the data collection and analysis methods you used in your research. A key part of your thesis, dissertation, or research paper, the methodology chapter explains what you did and how you did it, allowing readers to evaluate the reliability and validity of your research.
It should include:
- The type of research you conducted
- How you collected and analysed your data
- Any tools or materials you used in the research
- Why you chose these methods
- Your methodology section should generally be written in the past tense .
- Academic style guides in your field may provide detailed guidelines on what to include for different types of studies.
- Your citation style might provide guidelines for your methodology section (e.g., an APA Style methods section ).
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
How to write a research methodology, why is a methods section important, step 1: explain your methodological approach, step 2: describe your data collection methods, step 3: describe your analysis method, step 4: evaluate and justify the methodological choices you made, tips for writing a strong methodology chapter, frequently asked questions about methodology.
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Your methods section is your opportunity to share how you conducted your research and why you chose the methods you chose. It’s also the place to show that your research was rigorously conducted and can be replicated .
It gives your research legitimacy and situates it within your field, and also gives your readers a place to refer to if they have any questions or critiques in other sections.
You can start by introducing your overall approach to your research. You have two options here.
Option 1: Start with your “what”
What research problem or question did you investigate?
- Aim to describe the characteristics of something?
- Explore an under-researched topic?
- Establish a causal relationship?
And what type of data did you need to achieve this aim?
- Quantitative data , qualitative data , or a mix of both?
- Primary data collected yourself, or secondary data collected by someone else?
- Experimental data gathered by controlling and manipulating variables, or descriptive data gathered via observations?
Option 2: Start with your “why”
Depending on your discipline, you can also start with a discussion of the rationale and assumptions underpinning your methodology. In other words, why did you choose these methods for your study?
- Why is this the best way to answer your research question?
- Is this a standard methodology in your field, or does it require justification?
- Were there any ethical considerations involved in your choices?
- What are the criteria for validity and reliability in this type of research ?
Once you have introduced your reader to your methodological approach, you should share full details about your data collection methods .
Quantitative methods
In order to be considered generalisable, you should describe quantitative research methods in enough detail for another researcher to replicate your study.
Here, explain how you operationalised your concepts and measured your variables. Discuss your sampling method or inclusion/exclusion criteria, as well as any tools, procedures, and materials you used to gather your data.
Surveys Describe where, when, and how the survey was conducted.
- How did you design the questionnaire?
- What form did your questions take (e.g., multiple choice, Likert scale )?
- Were your surveys conducted in-person or virtually?
- What sampling method did you use to select participants?
- What was your sample size and response rate?
Experiments Share full details of the tools, techniques, and procedures you used to conduct your experiment.
- How did you design the experiment ?
- How did you recruit participants?
- How did you manipulate and measure the variables ?
- What tools did you use?
Existing data Explain how you gathered and selected the material (such as datasets or archival data) that you used in your analysis.
- Where did you source the material?
- How was the data originally produced?
- What criteria did you use to select material (e.g., date range)?
The survey consisted of 5 multiple-choice questions and 10 questions measured on a 7-point Likert scale.
The goal was to collect survey responses from 350 customers visiting the fitness apparel company’s brick-and-mortar location in Boston on 4–8 July 2022, between 11:00 and 15:00.
Here, a customer was defined as a person who had purchased a product from the company on the day they took the survey. Participants were given 5 minutes to fill in the survey anonymously. In total, 408 customers responded, but not all surveys were fully completed. Due to this, 371 survey results were included in the analysis.
Qualitative methods
In qualitative research , methods are often more flexible and subjective. For this reason, it’s crucial to robustly explain the methodology choices you made.
Be sure to discuss the criteria you used to select your data, the context in which your research was conducted, and the role you played in collecting your data (e.g., were you an active participant, or a passive observer?)
Interviews or focus groups Describe where, when, and how the interviews were conducted.
- How did you find and select participants?
- How many participants took part?
- What form did the interviews take ( structured , semi-structured , or unstructured )?
- How long were the interviews?
- How were they recorded?
Participant observation Describe where, when, and how you conducted the observation or ethnography .
- What group or community did you observe? How long did you spend there?
- How did you gain access to this group? What role did you play in the community?
- How long did you spend conducting the research? Where was it located?
- How did you record your data (e.g., audiovisual recordings, note-taking)?
Existing data Explain how you selected case study materials for your analysis.
- What type of materials did you analyse?
- How did you select them?
In order to gain better insight into possibilities for future improvement of the fitness shop’s product range, semi-structured interviews were conducted with 8 returning customers.
Here, a returning customer was defined as someone who usually bought products at least twice a week from the store.
Surveys were used to select participants. Interviews were conducted in a small office next to the cash register and lasted approximately 20 minutes each. Answers were recorded by note-taking, and seven interviews were also filmed with consent. One interviewee preferred not to be filmed.
Mixed methods
Mixed methods research combines quantitative and qualitative approaches. If a standalone quantitative or qualitative study is insufficient to answer your research question, mixed methods may be a good fit for you.
Mixed methods are less common than standalone analyses, largely because they require a great deal of effort to pull off successfully. If you choose to pursue mixed methods, it’s especially important to robustly justify your methods here.
Next, you should indicate how you processed and analysed your data. Avoid going into too much detail: you should not start introducing or discussing any of your results at this stage.
In quantitative research , your analysis will be based on numbers. In your methods section, you can include:
- How you prepared the data before analysing it (e.g., checking for missing data , removing outliers , transforming variables)
- Which software you used (e.g., SPSS, Stata or R)
- Which statistical tests you used (e.g., two-tailed t test , simple linear regression )
In qualitative research, your analysis will be based on language, images, and observations (often involving some form of textual analysis ).
Specific methods might include:
- Content analysis : Categorising and discussing the meaning of words, phrases and sentences
- Thematic analysis : Coding and closely examining the data to identify broad themes and patterns
- Discourse analysis : Studying communication and meaning in relation to their social context
Mixed methods combine the above two research methods, integrating both qualitative and quantitative approaches into one coherent analytical process.
Above all, your methodology section should clearly make the case for why you chose the methods you did. This is especially true if you did not take the most standard approach to your topic. In this case, discuss why other methods were not suitable for your objectives, and show how this approach contributes new knowledge or understanding.
In any case, it should be overwhelmingly clear to your reader that you set yourself up for success in terms of your methodology’s design. Show how your methods should lead to results that are valid and reliable, while leaving the analysis of the meaning, importance, and relevance of your results for your discussion section .
- Quantitative: Lab-based experiments cannot always accurately simulate real-life situations and behaviours, but they are effective for testing causal relationships between variables .
- Qualitative: Unstructured interviews usually produce results that cannot be generalised beyond the sample group , but they provide a more in-depth understanding of participants’ perceptions, motivations, and emotions.
- Mixed methods: Despite issues systematically comparing differing types of data, a solely quantitative study would not sufficiently incorporate the lived experience of each participant, while a solely qualitative study would be insufficiently generalisable.
Remember that your aim is not just to describe your methods, but to show how and why you applied them. Again, it’s critical to demonstrate that your research was rigorously conducted and can be replicated.
1. Focus on your objectives and research questions
The methodology section should clearly show why your methods suit your objectives and convince the reader that you chose the best possible approach to answering your problem statement and research questions .
2. Cite relevant sources
Your methodology can be strengthened by referencing existing research in your field. This can help you to:
- Show that you followed established practice for your type of research
- Discuss how you decided on your approach by evaluating existing research
- Present a novel methodological approach to address a gap in the literature
3. Write for your audience
Consider how much information you need to give, and avoid getting too lengthy. If you are using methods that are standard for your discipline, you probably don’t need to give a lot of background or justification.
Regardless, your methodology should be a clear, well-structured text that makes an argument for your approach, not just a list of technical details and procedures.
Methodology refers to the overarching strategy and rationale of your research. Developing your methodology involves studying the research methods used in your field and the theories or principles that underpin them, in order to choose the approach that best matches your objectives.
Methods are the specific tools and procedures you use to collect and analyse data (e.g. interviews, experiments , surveys , statistical tests ).
In a dissertation or scientific paper, the methodology chapter or methods section comes after the introduction and before the results , discussion and conclusion .
Depending on the length and type of document, you might also include a literature review or theoretical framework before the methodology.
Quantitative research deals with numbers and statistics, while qualitative research deals with words and meanings.
Quantitative methods allow you to test a hypothesis by systematically collecting and analysing data, while qualitative methods allow you to explore ideas and experiences in depth.
A sample is a subset of individuals from a larger population. Sampling means selecting the group that you will actually collect data from in your research.
For example, if you are researching the opinions of students in your university, you could survey a sample of 100 students.
Statistical sampling allows you to test a hypothesis about the characteristics of a population. There are various sampling methods you can use to ensure that your sample is representative of the population as a whole.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. (2022, October 10). What Is a Research Methodology? | Steps & Tips. Scribbr. Retrieved 3 September 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/thesis-dissertation/methodology/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to write a dissertation proposal | a step-by-step guide, what is a literature review | guide, template, & examples, what is a theoretical framework | a step-by-step guide.
- Resources Home 🏠
- Try SciSpace Copilot
- Search research papers
- Add Copilot Extension
- Try AI Detector
- Try Paraphraser
- Try Citation Generator
- April Papers
- June Papers
- July Papers

Here's What You Need to Understand About Research Methodology

Table of Contents
Research methodology involves a systematic and well-structured approach to conducting scholarly or scientific inquiries. Knowing the significance of research methodology and its different components is crucial as it serves as the basis for any study.
Typically, your research topic will start as a broad idea you want to investigate more thoroughly. Once you’ve identified a research problem and created research questions , you must choose the appropriate methodology and frameworks to address those questions effectively.
What is the definition of a research methodology?
Research methodology is the process or the way you intend to execute your study. The methodology section of a research paper outlines how you plan to conduct your study. It covers various steps such as collecting data, statistical analysis, observing participants, and other procedures involved in the research process
The methods section should give a description of the process that will convert your idea into a study. Additionally, the outcomes of your process must provide valid and reliable results resonant with the aims and objectives of your research. This thumb rule holds complete validity, no matter whether your paper has inclinations for qualitative or quantitative usage.
Studying research methods used in related studies can provide helpful insights and direction for your own research. Now easily discover papers related to your topic on SciSpace and utilize our AI research assistant, Copilot , to quickly review the methodologies applied in different papers.

The need for a good research methodology
While deciding on your approach towards your research, the reason or factors you weighed in choosing a particular problem and formulating a research topic need to be validated and explained. A research methodology helps you do exactly that. Moreover, a good research methodology lets you build your argument to validate your research work performed through various data collection methods, analytical methods, and other essential points.
Just imagine it as a strategy documented to provide an overview of what you intend to do.
While undertaking any research writing or performing the research itself, you may get drifted in not something of much importance. In such a case, a research methodology helps you to get back to your outlined work methodology.
A research methodology helps in keeping you accountable for your work. Additionally, it can help you evaluate whether your work is in sync with your original aims and objectives or not. Besides, a good research methodology enables you to navigate your research process smoothly and swiftly while providing effective planning to achieve your desired results.
What is the basic structure of a research methodology?
Usually, you must ensure to include the following stated aspects while deciding over the basic structure of your research methodology:
1. Your research procedure
Explain what research methods you’re going to use. Whether you intend to proceed with quantitative or qualitative, or a composite of both approaches, you need to state that explicitly. The option among the three depends on your research’s aim, objectives, and scope.
2. Provide the rationality behind your chosen approach
Based on logic and reason, let your readers know why you have chosen said research methodologies. Additionally, you have to build strong arguments supporting why your chosen research method is the best way to achieve the desired outcome.
3. Explain your mechanism
The mechanism encompasses the research methods or instruments you will use to develop your research methodology. It usually refers to your data collection methods. You can use interviews, surveys, physical questionnaires, etc., of the many available mechanisms as research methodology instruments. The data collection method is determined by the type of research and whether the data is quantitative data(includes numerical data) or qualitative data (perception, morale, etc.) Moreover, you need to put logical reasoning behind choosing a particular instrument.
4. Significance of outcomes
The results will be available once you have finished experimenting. However, you should also explain how you plan to use the data to interpret the findings. This section also aids in understanding the problem from within, breaking it down into pieces, and viewing the research problem from various perspectives.
5. Reader’s advice
Anything that you feel must be explained to spread more awareness among readers and focus groups must be included and described in detail. You should not just specify your research methodology on the assumption that a reader is aware of the topic.
All the relevant information that explains and simplifies your research paper must be included in the methodology section. If you are conducting your research in a non-traditional manner, give a logical justification and list its benefits.
6. Explain your sample space
Include information about the sample and sample space in the methodology section. The term "sample" refers to a smaller set of data that a researcher selects or chooses from a larger group of people or focus groups using a predetermined selection method. Let your readers know how you are going to distinguish between relevant and non-relevant samples. How you figured out those exact numbers to back your research methodology, i.e. the sample spacing of instruments, must be discussed thoroughly.
For example, if you are going to conduct a survey or interview, then by what procedure will you select the interviewees (or sample size in case of surveys), and how exactly will the interview or survey be conducted.
7. Challenges and limitations
This part, which is frequently assumed to be unnecessary, is actually very important. The challenges and limitations that your chosen strategy inherently possesses must be specified while you are conducting different types of research.
The importance of a good research methodology
You must have observed that all research papers, dissertations, or theses carry a chapter entirely dedicated to research methodology. This section helps maintain your credibility as a better interpreter of results rather than a manipulator.
A good research methodology always explains the procedure, data collection methods and techniques, aim, and scope of the research. In a research study, it leads to a well-organized, rationality-based approach, while the paper lacking it is often observed as messy or disorganized.
You should pay special attention to validating your chosen way towards the research methodology. This becomes extremely important in case you select an unconventional or a distinct method of execution.
Curating and developing a strong, effective research methodology can assist you in addressing a variety of situations, such as:
- When someone tries to duplicate or expand upon your research after few years.
- If a contradiction or conflict of facts occurs at a later time. This gives you the security you need to deal with these contradictions while still being able to defend your approach.
- Gaining a tactical approach in getting your research completed in time. Just ensure you are using the right approach while drafting your research methodology, and it can help you achieve your desired outcomes. Additionally, it provides a better explanation and understanding of the research question itself.
- Documenting the results so that the final outcome of the research stays as you intended it to be while starting.
Instruments you could use while writing a good research methodology
As a researcher, you must choose which tools or data collection methods that fit best in terms of the relevance of your research. This decision has to be wise.
There exists many research equipments or tools that you can use to carry out your research process. These are classified as:
a. Interviews (One-on-One or a Group)
An interview aimed to get your desired research outcomes can be undertaken in many different ways. For example, you can design your interview as structured, semi-structured, or unstructured. What sets them apart is the degree of formality in the questions. On the other hand, in a group interview, your aim should be to collect more opinions and group perceptions from the focus groups on a certain topic rather than looking out for some formal answers.
In surveys, you are in better control if you specifically draft the questions you seek the response for. For example, you may choose to include free-style questions that can be answered descriptively, or you may provide a multiple-choice type response for questions. Besides, you can also opt to choose both ways, deciding what suits your research process and purpose better.
c. Sample Groups
Similar to the group interviews, here, you can select a group of individuals and assign them a topic to discuss or freely express their opinions over that. You can simultaneously note down the answers and later draft them appropriately, deciding on the relevance of every response.
d. Observations
If your research domain is humanities or sociology, observations are the best-proven method to draw your research methodology. Of course, you can always include studying the spontaneous response of the participants towards a situation or conducting the same but in a more structured manner. A structured observation means putting the participants in a situation at a previously decided time and then studying their responses.
Of all the tools described above, it is you who should wisely choose the instruments and decide what’s the best fit for your research. You must not restrict yourself from multiple methods or a combination of a few instruments if appropriate in drafting a good research methodology.
Types of research methodology
A research methodology exists in various forms. Depending upon their approach, whether centered around words, numbers, or both, methodologies are distinguished as qualitative, quantitative, or an amalgamation of both.
1. Qualitative research methodology
When a research methodology primarily focuses on words and textual data, then it is generally referred to as qualitative research methodology. This type is usually preferred among researchers when the aim and scope of the research are mainly theoretical and explanatory.
The instruments used are observations, interviews, and sample groups. You can use this methodology if you are trying to study human behavior or response in some situations. Generally, qualitative research methodology is widely used in sociology, psychology, and other related domains.
2. Quantitative research methodology
If your research is majorly centered on data, figures, and stats, then analyzing these numerical data is often referred to as quantitative research methodology. You can use quantitative research methodology if your research requires you to validate or justify the obtained results.
In quantitative methods, surveys, tests, experiments, and evaluations of current databases can be advantageously used as instruments If your research involves testing some hypothesis, then use this methodology.
3. Amalgam methodology
As the name suggests, the amalgam methodology uses both quantitative and qualitative approaches. This methodology is used when a part of the research requires you to verify the facts and figures, whereas the other part demands you to discover the theoretical and explanatory nature of the research question.
The instruments for the amalgam methodology require you to conduct interviews and surveys, including tests and experiments. The outcome of this methodology can be insightful and valuable as it provides precise test results in line with theoretical explanations and reasoning.
The amalgam method, makes your work both factual and rational at the same time.
Final words: How to decide which is the best research methodology?
If you have kept your sincerity and awareness intact with the aims and scope of research well enough, you must have got an idea of which research methodology suits your work best.
Before deciding which research methodology answers your research question, you must invest significant time in reading and doing your homework for that. Taking references that yield relevant results should be your first approach to establishing a research methodology.
Moreover, you should never refrain from exploring other options. Before setting your work in stone, you must try all the available options as it explains why the choice of research methodology that you finally make is more appropriate than the other available options.
You should always go for a quantitative research methodology if your research requires gathering large amounts of data, figures, and statistics. This research methodology will provide you with results if your research paper involves the validation of some hypothesis.
Whereas, if you are looking for more explanations, reasons, opinions, and public perceptions around a theory, you must use qualitative research methodology.The choice of an appropriate research methodology ultimately depends on what you want to achieve through your research.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Research Methodology
1. how to write a research methodology.
You can always provide a separate section for research methodology where you should specify details about the methods and instruments used during the research, discussions on result analysis, including insights into the background information, and conveying the research limitations.
2. What are the types of research methodology?
There generally exists four types of research methodology i.e.
- Observation
- Experimental
- Derivational
3. What is the true meaning of research methodology?
The set of techniques or procedures followed to discover and analyze the information gathered to validate or justify a research outcome is generally called Research Methodology.
4. Where lies the importance of research methodology?
Your research methodology directly reflects the validity of your research outcomes and how well-informed your research work is. Moreover, it can help future researchers cite or refer to your research if they plan to use a similar research methodology.
You might also like

Consensus GPT vs. SciSpace GPT: Choose the Best GPT for Research

Literature Review and Theoretical Framework: Understanding the Differences

Using AI for research: A beginner’s guide

- Privacy Policy

Home » Research Methodology – Types, Examples and writing Guide
Research Methodology – Types, Examples and writing Guide
Table of Contents

Research Methodology
Definition:
Research Methodology refers to the systematic and scientific approach used to conduct research, investigate problems, and gather data and information for a specific purpose. It involves the techniques and procedures used to identify, collect , analyze , and interpret data to answer research questions or solve research problems . Moreover, They are philosophical and theoretical frameworks that guide the research process.
Structure of Research Methodology
Research methodology formats can vary depending on the specific requirements of the research project, but the following is a basic example of a structure for a research methodology section:
I. Introduction
- Provide an overview of the research problem and the need for a research methodology section
- Outline the main research questions and objectives
II. Research Design
- Explain the research design chosen and why it is appropriate for the research question(s) and objectives
- Discuss any alternative research designs considered and why they were not chosen
- Describe the research setting and participants (if applicable)
III. Data Collection Methods
- Describe the methods used to collect data (e.g., surveys, interviews, observations)
- Explain how the data collection methods were chosen and why they are appropriate for the research question(s) and objectives
- Detail any procedures or instruments used for data collection
IV. Data Analysis Methods
- Describe the methods used to analyze the data (e.g., statistical analysis, content analysis )
- Explain how the data analysis methods were chosen and why they are appropriate for the research question(s) and objectives
- Detail any procedures or software used for data analysis
V. Ethical Considerations
- Discuss any ethical issues that may arise from the research and how they were addressed
- Explain how informed consent was obtained (if applicable)
- Detail any measures taken to ensure confidentiality and anonymity
VI. Limitations
- Identify any potential limitations of the research methodology and how they may impact the results and conclusions
VII. Conclusion
- Summarize the key aspects of the research methodology section
- Explain how the research methodology addresses the research question(s) and objectives
Research Methodology Types
Types of Research Methodology are as follows:
Quantitative Research Methodology
This is a research methodology that involves the collection and analysis of numerical data using statistical methods. This type of research is often used to study cause-and-effect relationships and to make predictions.
Qualitative Research Methodology
This is a research methodology that involves the collection and analysis of non-numerical data such as words, images, and observations. This type of research is often used to explore complex phenomena, to gain an in-depth understanding of a particular topic, and to generate hypotheses.
Mixed-Methods Research Methodology
This is a research methodology that combines elements of both quantitative and qualitative research. This approach can be particularly useful for studies that aim to explore complex phenomena and to provide a more comprehensive understanding of a particular topic.
Case Study Research Methodology
This is a research methodology that involves in-depth examination of a single case or a small number of cases. Case studies are often used in psychology, sociology, and anthropology to gain a detailed understanding of a particular individual or group.
Action Research Methodology
This is a research methodology that involves a collaborative process between researchers and practitioners to identify and solve real-world problems. Action research is often used in education, healthcare, and social work.
Experimental Research Methodology
This is a research methodology that involves the manipulation of one or more independent variables to observe their effects on a dependent variable. Experimental research is often used to study cause-and-effect relationships and to make predictions.
Survey Research Methodology
This is a research methodology that involves the collection of data from a sample of individuals using questionnaires or interviews. Survey research is often used to study attitudes, opinions, and behaviors.
Grounded Theory Research Methodology
This is a research methodology that involves the development of theories based on the data collected during the research process. Grounded theory is often used in sociology and anthropology to generate theories about social phenomena.
Research Methodology Example
An Example of Research Methodology could be the following:
Research Methodology for Investigating the Effectiveness of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy in Reducing Symptoms of Depression in Adults
Introduction:
The aim of this research is to investigate the effectiveness of cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) in reducing symptoms of depression in adults. To achieve this objective, a randomized controlled trial (RCT) will be conducted using a mixed-methods approach.
Research Design:
The study will follow a pre-test and post-test design with two groups: an experimental group receiving CBT and a control group receiving no intervention. The study will also include a qualitative component, in which semi-structured interviews will be conducted with a subset of participants to explore their experiences of receiving CBT.
Participants:
Participants will be recruited from community mental health clinics in the local area. The sample will consist of 100 adults aged 18-65 years old who meet the diagnostic criteria for major depressive disorder. Participants will be randomly assigned to either the experimental group or the control group.
Intervention :
The experimental group will receive 12 weekly sessions of CBT, each lasting 60 minutes. The intervention will be delivered by licensed mental health professionals who have been trained in CBT. The control group will receive no intervention during the study period.
Data Collection:
Quantitative data will be collected through the use of standardized measures such as the Beck Depression Inventory-II (BDI-II) and the Generalized Anxiety Disorder-7 (GAD-7). Data will be collected at baseline, immediately after the intervention, and at a 3-month follow-up. Qualitative data will be collected through semi-structured interviews with a subset of participants from the experimental group. The interviews will be conducted at the end of the intervention period, and will explore participants’ experiences of receiving CBT.
Data Analysis:
Quantitative data will be analyzed using descriptive statistics, t-tests, and mixed-model analyses of variance (ANOVA) to assess the effectiveness of the intervention. Qualitative data will be analyzed using thematic analysis to identify common themes and patterns in participants’ experiences of receiving CBT.
Ethical Considerations:
This study will comply with ethical guidelines for research involving human subjects. Participants will provide informed consent before participating in the study, and their privacy and confidentiality will be protected throughout the study. Any adverse events or reactions will be reported and managed appropriately.
Data Management:
All data collected will be kept confidential and stored securely using password-protected databases. Identifying information will be removed from qualitative data transcripts to ensure participants’ anonymity.
Limitations:
One potential limitation of this study is that it only focuses on one type of psychotherapy, CBT, and may not generalize to other types of therapy or interventions. Another limitation is that the study will only include participants from community mental health clinics, which may not be representative of the general population.
Conclusion:
This research aims to investigate the effectiveness of CBT in reducing symptoms of depression in adults. By using a randomized controlled trial and a mixed-methods approach, the study will provide valuable insights into the mechanisms underlying the relationship between CBT and depression. The results of this study will have important implications for the development of effective treatments for depression in clinical settings.
How to Write Research Methodology
Writing a research methodology involves explaining the methods and techniques you used to conduct research, collect data, and analyze results. It’s an essential section of any research paper or thesis, as it helps readers understand the validity and reliability of your findings. Here are the steps to write a research methodology:
- Start by explaining your research question: Begin the methodology section by restating your research question and explaining why it’s important. This helps readers understand the purpose of your research and the rationale behind your methods.
- Describe your research design: Explain the overall approach you used to conduct research. This could be a qualitative or quantitative research design, experimental or non-experimental, case study or survey, etc. Discuss the advantages and limitations of the chosen design.
- Discuss your sample: Describe the participants or subjects you included in your study. Include details such as their demographics, sampling method, sample size, and any exclusion criteria used.
- Describe your data collection methods : Explain how you collected data from your participants. This could include surveys, interviews, observations, questionnaires, or experiments. Include details on how you obtained informed consent, how you administered the tools, and how you minimized the risk of bias.
- Explain your data analysis techniques: Describe the methods you used to analyze the data you collected. This could include statistical analysis, content analysis, thematic analysis, or discourse analysis. Explain how you dealt with missing data, outliers, and any other issues that arose during the analysis.
- Discuss the validity and reliability of your research : Explain how you ensured the validity and reliability of your study. This could include measures such as triangulation, member checking, peer review, or inter-coder reliability.
- Acknowledge any limitations of your research: Discuss any limitations of your study, including any potential threats to validity or generalizability. This helps readers understand the scope of your findings and how they might apply to other contexts.
- Provide a summary: End the methodology section by summarizing the methods and techniques you used to conduct your research. This provides a clear overview of your research methodology and helps readers understand the process you followed to arrive at your findings.
When to Write Research Methodology
Research methodology is typically written after the research proposal has been approved and before the actual research is conducted. It should be written prior to data collection and analysis, as it provides a clear roadmap for the research project.
The research methodology is an important section of any research paper or thesis, as it describes the methods and procedures that will be used to conduct the research. It should include details about the research design, data collection methods, data analysis techniques, and any ethical considerations.
The methodology should be written in a clear and concise manner, and it should be based on established research practices and standards. It is important to provide enough detail so that the reader can understand how the research was conducted and evaluate the validity of the results.
Applications of Research Methodology
Here are some of the applications of research methodology:
- To identify the research problem: Research methodology is used to identify the research problem, which is the first step in conducting any research.
- To design the research: Research methodology helps in designing the research by selecting the appropriate research method, research design, and sampling technique.
- To collect data: Research methodology provides a systematic approach to collect data from primary and secondary sources.
- To analyze data: Research methodology helps in analyzing the collected data using various statistical and non-statistical techniques.
- To test hypotheses: Research methodology provides a framework for testing hypotheses and drawing conclusions based on the analysis of data.
- To generalize findings: Research methodology helps in generalizing the findings of the research to the target population.
- To develop theories : Research methodology is used to develop new theories and modify existing theories based on the findings of the research.
- To evaluate programs and policies : Research methodology is used to evaluate the effectiveness of programs and policies by collecting data and analyzing it.
- To improve decision-making: Research methodology helps in making informed decisions by providing reliable and valid data.
Purpose of Research Methodology
Research methodology serves several important purposes, including:
- To guide the research process: Research methodology provides a systematic framework for conducting research. It helps researchers to plan their research, define their research questions, and select appropriate methods and techniques for collecting and analyzing data.
- To ensure research quality: Research methodology helps researchers to ensure that their research is rigorous, reliable, and valid. It provides guidelines for minimizing bias and error in data collection and analysis, and for ensuring that research findings are accurate and trustworthy.
- To replicate research: Research methodology provides a clear and detailed account of the research process, making it possible for other researchers to replicate the study and verify its findings.
- To advance knowledge: Research methodology enables researchers to generate new knowledge and to contribute to the body of knowledge in their field. It provides a means for testing hypotheses, exploring new ideas, and discovering new insights.
- To inform decision-making: Research methodology provides evidence-based information that can inform policy and decision-making in a variety of fields, including medicine, public health, education, and business.
Advantages of Research Methodology
Research methodology has several advantages that make it a valuable tool for conducting research in various fields. Here are some of the key advantages of research methodology:
- Systematic and structured approach : Research methodology provides a systematic and structured approach to conducting research, which ensures that the research is conducted in a rigorous and comprehensive manner.
- Objectivity : Research methodology aims to ensure objectivity in the research process, which means that the research findings are based on evidence and not influenced by personal bias or subjective opinions.
- Replicability : Research methodology ensures that research can be replicated by other researchers, which is essential for validating research findings and ensuring their accuracy.
- Reliability : Research methodology aims to ensure that the research findings are reliable, which means that they are consistent and can be depended upon.
- Validity : Research methodology ensures that the research findings are valid, which means that they accurately reflect the research question or hypothesis being tested.
- Efficiency : Research methodology provides a structured and efficient way of conducting research, which helps to save time and resources.
- Flexibility : Research methodology allows researchers to choose the most appropriate research methods and techniques based on the research question, data availability, and other relevant factors.
- Scope for innovation: Research methodology provides scope for innovation and creativity in designing research studies and developing new research techniques.
Research Methodology Vs Research Methods
| Research Methodology | Research Methods |
|---|---|
| Research methodology refers to the philosophical and theoretical frameworks that guide the research process. | refer to the techniques and procedures used to collect and analyze data. |
| It is concerned with the underlying principles and assumptions of research. | It is concerned with the practical aspects of research. |
| It provides a rationale for why certain research methods are used. | It determines the specific steps that will be taken to conduct research. |
| It is broader in scope and involves understanding the overall approach to research. | It is narrower in scope and focuses on specific techniques and tools used in research. |
| It is concerned with identifying research questions, defining the research problem, and formulating hypotheses. | It is concerned with collecting data, analyzing data, and interpreting results. |
| It is concerned with the validity and reliability of research. | It is concerned with the accuracy and precision of data. |
| It is concerned with the ethical considerations of research. | It is concerned with the practical considerations of research. |
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Research Gap – Types, Examples and How to...

Research Summary – Structure, Examples and...

Thesis Statement – Examples, Writing Guide

Research Problem – Examples, Types and Guide

Background of The Study – Examples and Writing...

Data Verification – Process, Types and Examples
Still have questions? Leave a comment
Add Comment
Checklist: Dissertation Proposal
Enter your email id to get the downloadable right in your inbox!
Examples: Edited Papers
Need editing and proofreading services, research methodology guide: writing tips, types, & examples.

- Tags: Academic Research , Research
No dissertation or research paper is complete without the research methodology section. Since this is the chapter where you explain how you carried out your research, this is where all the meat is! Here’s where you clearly lay out the steps you have taken to test your hypothesis or research problem.
Through this blog, we’ll unravel the complexities and meaning of research methodology in academic writing , from its fundamental principles and ethics to the diverse types of research methodology in use today. Alongside offering research methodology examples, we aim to guide you on how to write research methodology, ensuring your research endeavors are both impactful and impeccably grounded!
Ensure your research methodology is foolproof. Learn more
Let’s first take a closer look at a simple research methodology definition:
Defining what is research methodology
Research methodology is the set of procedures and techniques used to collect, analyze, and interpret data to understand and solve a research problem. Methodology in research not only includes the design and methods but also the basic principles that guide the choice of specific methods.
Grasping the concept of methodology in research is essential for students and scholars, as it demonstrates the thorough and structured method used to explore a hypothesis or research question. Understanding the definition of methodology in research aids in identifying the methods used to collect data. Be it through any type of research method approach, ensuring adherence to the proper research paper format is crucial.
Now let’s explore some research methodology types:
Types of research methodology
1. qualitative research methodology.
Qualitative research methodology is aimed at understanding concepts, thoughts, or experiences. This approach is descriptive and is often utilized to gather in-depth insights into people’s attitudes, behaviors, or cultures. Qualitative research methodology involves methods like interviews, focus groups, and observation. The strength of this methodology lies in its ability to provide contextual richness.
2. Quantitative research methodology
Quantitative research methodology, on the other hand, is focused on quantifying the problem by generating numerical data or data that can be transformed into usable statistics. It uses measurable data to formulate facts and uncover patterns in research. Quantitative research methodology typically involves surveys, experiments, or statistical analysis. This methodology is appreciated for its ability to produce objective results that are generalizable to a larger population.
3. Mixed-Methods research methodology
Mixed-methods research combines both qualitative and quantitative research methodologies to provide a more comprehensive understanding of the research problem. This approach leverages the strengths of both methodologies to provide a deeper insight into the research question of a research paper .
Research methodology vs. research methods
The research methodology or design is the overall strategy and rationale that you used to carry out the research. Whereas, research methods are the specific tools and processes you use to gather and understand the data you need to test your hypothesis.
Research methodology examples and application
To further understand research methodology, let’s explore some examples of research methodology:
a. Qualitative research methodology example: A study exploring the impact of author branding on author popularity might utilize in-depth interviews to gather personal experiences and perspectives.
b. Quantitative research methodology example: A research project investigating the effects of a book promotion technique on book sales could employ a statistical analysis of profit margins and sales before and after the implementation of the method.
c. Mixed-Methods research methodology example: A study examining the relationship between social media use and academic performance might combine both qualitative and quantitative approaches. It could include surveys to quantitatively assess the frequency of social media usage and its correlation with grades, alongside focus groups or interviews to qualitatively explore students’ perceptions and experiences regarding how social media affects their study habits and academic engagement.
These examples highlight the meaning of methodology in research and how it guides the research process, from data collection to analysis, ensuring the study’s objectives are met efficiently.
Importance of methodology in research papers
When it comes to writing your study, the methodology in research papers or a dissertation plays a pivotal role. A well-crafted methodology section of a research paper or thesis not only enhances the credibility of your research but also provides a roadmap for others to replicate or build upon your work.
How to structure the research methods chapter
Wondering how to write the research methodology section? Follow these steps to create a strong methods chapter:
Step 1: Explain your research methodology
At the start of a research paper , you would have provided the background of your research and stated your hypothesis or research problem. In this section, you will elaborate on your research strategy.
Begin by restating your research question and proceed to explain what type of research you opted for to test it. Depending on your research, here are some questions you can consider:
a. Did you use qualitative or quantitative data to test the hypothesis?
b. Did you perform an experiment where you collected data or are you writing a dissertation that is descriptive/theoretical without data collection?
c. Did you use primary data that you collected or analyze secondary research data or existing data as part of your study?
These questions will help you establish the rationale for your study on a broader level, which you will follow by elaborating on the specific methods you used to collect and understand your data.
Step 2: Explain the methods you used to test your hypothesis
Now that you have told your reader what type of research you’ve undertaken for the dissertation, it’s time to dig into specifics. State what specific methods you used and explain the conditions and variables involved. Explain what the theoretical framework behind the method was, what samples you used for testing it, and what tools and materials you used to collect the data.
Step 3: Explain how you analyzed the results
Once you have explained the data collection process, explain how you analyzed and studied the data. Here, your focus is simply to explain the methods of analysis rather than the results of the study.
Here are some questions you can answer at this stage:
a. What tools or software did you use to analyze your results?
b. What parameters or variables did you consider while understanding and studying the data you’ve collected?
c. Was your analysis based on a theoretical framework?
Your mode of analysis will change depending on whether you used a quantitative or qualitative research methodology in your study. If you’re working within the hard sciences or physical sciences, you are likely to use a quantitative research methodology (relying on numbers and hard data). If you’re doing a qualitative study, in the social sciences or humanities, your analysis may rely on understanding language and socio-political contexts around your topic. This is why it’s important to establish what kind of study you’re undertaking at the onset.
Step 4: Defend your choice of methodology
Now that you have gone through your research process in detail, you’ll also have to make a case for it. Justify your choice of methodology and methods, explaining why it is the best choice for your research question. This is especially important if you have chosen an unconventional approach or you’ve simply chosen to study an existing research problem from a different perspective. Compare it with other methodologies, especially ones attempted by previous researchers, and discuss what contributions using your methodology makes.
Step 5: Discuss the obstacles you encountered and how you overcame them
No matter how thorough a methodology is, it doesn’t come without its hurdles. This is a natural part of scientific research that is important to document so that your peers and future researchers are aware of it. Writing in a research paper about this aspect of your research process also tells your evaluator that you have actively worked to overcome the pitfalls that came your way and you have refined the research process.
Tips to write an effective methodology chapter
1. Remember who you are writing for. Keeping sight of the reader/evaluator will help you know what to elaborate on and what information they are already likely to have. You’re condensing months’ work of research in just a few pages, so you should omit basic definitions and information about general phenomena people already know.
2. Do not give an overly elaborate explanation of every single condition in your study.
3. Skip details and findings irrelevant to the results.
4. Cite references that back your claim and choice of methodology.
5. Consistently emphasize the relationship between your research question and the methodology you adopted to study it.
To sum it up, what is methodology in research? It’s the blueprint of your research, essential for ensuring that your study is systematic, rigorous, and credible. Whether your focus is on qualitative research methodology, quantitative research methodology, or a combination of both, understanding and clearly defining your methodology is key to the success of your research.
Once you write the research methodology and complete writing the entire research paper, the next step is to edit your paper. As experts in research paper editing and proofreading services , we’d love to help you perfect your paper!
Here are some other articles that you might find useful:
- Essential Research Tips for Essay Writing
- How to Write a Lab Report: Examples from Academic Editors
- The Essential Types of Editing Every Writer Needs to Know
- Editing and Proofreading Academic Papers: A Short Guide
- The Top 10 Editing and Proofreading Services of 2023
Frequently Asked Questions
What does research methodology mean, what types of research methodologies are there, what is qualitative research methodology, how to determine sample size in research methodology, what is action research methodology.
Found this article helpful?
One comment on “ Research Methodology Guide: Writing Tips, Types, & Examples ”
This is very simplified and direct. Very helpful to understand the research methodology section of a dissertation
Leave a Comment: Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published.
Your vs. You’re: When to Use Your and You’re
Your organization needs a technical editor: here’s why, your guide to the best ebook readers in 2024, writing for the web: 7 expert tips for web content writing.
Subscribe to our Newsletter
Get carefully curated resources about writing, editing, and publishing in the comfort of your inbox.
How to Copyright Your Book?
If you’ve thought about copyrighting your book, you’re on the right path.
© 2024 All rights reserved
- Terms of service
- Privacy policy
- Self Publishing Guide
- Pre-Publishing Steps
- Fiction Writing Tips
- Traditional Publishing
- Additional Resources
- Dissertation Writing Guide
- Essay Writing Guide
- Academic Writing and Publishing
- Citation and Referencing
- Partner with us
- Annual report
- Website content
- Marketing material
- Job Applicant
- Cover letter
- Resource Center
- Case studies

Library Guides
Dissertations 4: methodology: methods.
- Introduction & Philosophy
- Methodology
Primary & Secondary Sources, Primary & Secondary Data
When describing your research methods, you can start by stating what kind of secondary and, if applicable, primary sources you used in your research. Explain why you chose such sources, how well they served your research, and identify possible issues encountered using these sources.
Definitions
There is some confusion on the use of the terms primary and secondary sources, and primary and secondary data. The confusion is also due to disciplinary differences (Lombard 2010). Whilst you are advised to consult the research methods literature in your field, we can generalise as follows:
Secondary sources
Secondary sources normally include the literature (books and articles) with the experts' findings, analysis and discussions on a certain topic (Cottrell, 2014, p123). Secondary sources often interpret primary sources.
Primary sources
Primary sources are "first-hand" information such as raw data, statistics, interviews, surveys, law statutes and law cases. Even literary texts, pictures and films can be primary sources if they are the object of research (rather than, for example, documentaries reporting on something else, in which case they would be secondary sources). The distinction between primary and secondary sources sometimes lies on the use you make of them (Cottrell, 2014, p123).
Primary data
Primary data are data (primary sources) you directly obtained through your empirical work (Saunders, Lewis and Thornhill 2015, p316).
Secondary data
Secondary data are data (primary sources) that were originally collected by someone else (Saunders, Lewis and Thornhill 2015, p316).
Comparison between primary and secondary data
| Primary data | Secondary data |
| Data collected directly | Data collected from previously done research, existing research is summarised and collated to enhance the overall effectiveness of the research. |
| Examples: Interviews (face-to-face or telephonic), Online surveys, Focus groups and Observations | Examples: data available via the internet, non-government and government agencies, public libraries, educational institutions, commercial/business information |
| Advantages: •Data collected is first hand and accurate. •Data collected can be controlled. No dilution of data. •Research method can be customized to suit personal requirements and needs of the research. | Advantages: •Information is readily available •Less expensive and less time-consuming •Quicker to conduct |
| Disadvantages: •Can be quite extensive to conduct, requiring a lot of time and resources •Sometimes one primary research method is not enough; therefore a mixed method is require, which can be even more time consuming. | Disadvantages: •It is necessary to check the credibility of the data •May not be as up to date •Success of your research depends on the quality of research previously conducted by others. |
Use
Virtually all research will use secondary sources, at least as background information.
Often, especially at the postgraduate level, it will also use primary sources - secondary and/or primary data. The engagement with primary sources is generally appreciated, as less reliant on others' interpretations, and closer to 'facts'.
The use of primary data, as opposed to secondary data, demonstrates the researcher's effort to do empirical work and find evidence to answer her specific research question and fulfill her specific research objectives. Thus, primary data contribute to the originality of the research.
Ultimately, you should state in this section of the methodology:
What sources and data you are using and why (how are they going to help you answer the research question and/or test the hypothesis.
If using primary data, why you employed certain strategies to collect them.
What the advantages and disadvantages of your strategies to collect the data (also refer to the research in you field and research methods literature).
Quantitative, Qualitative & Mixed Methods
The methodology chapter should reference your use of quantitative research, qualitative research and/or mixed methods. The following is a description of each along with their advantages and disadvantages.
Quantitative research
Quantitative research uses numerical data (quantities) deriving, for example, from experiments, closed questions in surveys, questionnaires, structured interviews or published data sets (Cottrell, 2014, p93). It normally processes and analyses this data using quantitative analysis techniques like tables, graphs and statistics to explore, present and examine relationships and trends within the data (Saunders, Lewis and Thornhill, 2015, p496).
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| The study can be undertaken on a broader scale, generating large amounts of data that contribute to generalisation of results | Quantitative methods can be difficult, expensive and time consuming (especially if using primary data, rather than secondary data). |
| Suitable when the phenomenon is relatively simple, and can be analysed according to identified variables. | Not everything can be easily measured. |
|
| Less suitable for complex social phenomena. |
|
| Less suitable for why type questions. |
Qualitative research
Qualitative research is generally undertaken to study human behaviour and psyche. It uses methods like in-depth case studies, open-ended survey questions, unstructured interviews, focus groups, or unstructured observations (Cottrell, 2014, p93). The nature of the data is subjective, and also the analysis of the researcher involves a degree of subjective interpretation. Subjectivity can be controlled for in the research design, or has to be acknowledged as a feature of the research. Subject-specific books on (qualitative) research methods offer guidance on such research designs.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Qualitative methods are good for in-depth analysis of individual people, businesses, organisations, events. | The findings can be accurate about the particular case, but not generally applicable. |
| Sample sizes don’t need to be large, so the studies can be cheaper and simpler. | More prone to subjectivity. |
Mixed methods
Mixed-method approaches combine both qualitative and quantitative methods, and therefore combine the strengths of both types of research. Mixed methods have gained popularity in recent years.
When undertaking mixed-methods research you can collect the qualitative and quantitative data either concurrently or sequentially. If sequentially, you can for example, start with a few semi-structured interviews, providing qualitative insights, and then design a questionnaire to obtain quantitative evidence that your qualitative findings can also apply to a wider population (Specht, 2019, p138).
Ultimately, your methodology chapter should state:
Whether you used quantitative research, qualitative research or mixed methods.
Why you chose such methods (and refer to research method sources).
Why you rejected other methods.
How well the method served your research.
The problems or limitations you encountered.
Doug Specht, Senior Lecturer at the Westminster School of Media and Communication, explains mixed methods research in the following video:
LinkedIn Learning Video on Academic Research Foundations: Quantitative
The video covers the characteristics of quantitative research, and explains how to approach different parts of the research process, such as creating a solid research question and developing a literature review. He goes over the elements of a study, explains how to collect and analyze data, and shows how to present your data in written and numeric form.

Link to quantitative research video
Some Types of Methods
There are several methods you can use to get primary data. To reiterate, the choice of the methods should depend on your research question/hypothesis.
Whatever methods you will use, you will need to consider:
why did you choose one technique over another? What were the advantages and disadvantages of the technique you chose?
what was the size of your sample? Who made up your sample? How did you select your sample population? Why did you choose that particular sampling strategy?)
ethical considerations (see also tab...)
safety considerations
validity
feasibility
recording
procedure of the research (see box procedural method...).
Check Stella Cottrell's book Dissertations and Project Reports: A Step by Step Guide for some succinct yet comprehensive information on most methods (the following account draws mostly on her work). Check a research methods book in your discipline for more specific guidance.
Experiments
Experiments are useful to investigate cause and effect, when the variables can be tightly controlled. They can test a theory or hypothesis in controlled conditions. Experiments do not prove or disprove an hypothesis, instead they support or not support an hypothesis. When using the empirical and inductive method it is not possible to achieve conclusive results. The results may only be valid until falsified by other experiments and observations.
For more information on Scientific Method, click here .
Observations
Observational methods are useful for in-depth analyses of behaviours in people, animals, organisations, events or phenomena. They can test a theory or products in real life or simulated settings. They generally a qualitative research method.
Questionnaires and surveys
Questionnaires and surveys are useful to gain opinions, attitudes, preferences, understandings on certain matters. They can provide quantitative data that can be collated systematically; qualitative data, if they include opportunities for open-ended responses; or both qualitative and quantitative elements.
Interviews
Interviews are useful to gain rich, qualitative information about individuals' experiences, attitudes or perspectives. With interviews you can follow up immediately on responses for clarification or further details. There are three main types of interviews: structured (following a strict pattern of questions, which expect short answers), semi-structured (following a list of questions, with the opportunity to follow up the answers with improvised questions), and unstructured (following a short list of broad questions, where the respondent can lead more the conversation) (Specht, 2019, p142).
This short video on qualitative interviews discusses best practices and covers qualitative interview design, preparation and data collection methods.
Focus groups
In this case, a group of people (normally, 4-12) is gathered for an interview where the interviewer asks questions to such group of participants. Group interactions and discussions can be highly productive, but the researcher has to beware of the group effect, whereby certain participants and views dominate the interview (Saunders, Lewis and Thornhill 2015, p419). The researcher can try to minimise this by encouraging involvement of all participants and promoting a multiplicity of views.
This video focuses on strategies for conducting research using focus groups.
Check out the guidance on online focus groups by Aliaksandr Herasimenka, which is attached at the bottom of this text box.
Case study
Case studies are often a convenient way to narrow the focus of your research by studying how a theory or literature fares with regard to a specific person, group, organisation, event or other type of entity or phenomenon you identify. Case studies can be researched using other methods, including those described in this section. Case studies give in-depth insights on the particular reality that has been examined, but may not be representative of what happens in general, they may not be generalisable, and may not be relevant to other contexts. These limitations have to be acknowledged by the researcher.
Content analysis
Content analysis consists in the study of words or images within a text. In its broad definition, texts include books, articles, essays, historical documents, speeches, conversations, advertising, interviews, social media posts, films, theatre, paintings or other visuals. Content analysis can be quantitative (e.g. word frequency) or qualitative (e.g. analysing intention and implications of the communication). It can detect propaganda, identify intentions of writers, and can see differences in types of communication (Specht, 2019, p146). Check this page on collecting, cleaning and visualising Twitter data.
Extra links and resources:
Research Methods
A clear and comprehensive overview of research methods by Emerald Publishing. It includes: crowdsourcing as a research tool; mixed methods research; case study; discourse analysis; ground theory; repertory grid; ethnographic method and participant observation; interviews; focus group; action research; analysis of qualitative data; survey design; questionnaires; statistics; experiments; empirical research; literature review; secondary data and archival materials; data collection.
Doing your dissertation during the COVID-19 pandemic
Resources providing guidance on doing dissertation research during the pandemic: Online research methods; Secondary data sources; Webinars, conferences and podcasts;
- Virtual Focus Groups Guidance on managing virtual focus groups
5 Minute Methods Videos
The following are a series of useful videos that introduce research methods in five minutes. These resources have been produced by lecturers and students with the University of Westminster's School of Media and Communication.

Case Study Research
Research Ethics
Quantitative Content Analysis
Sequential Analysis
Qualitative Content Analysis
Thematic Analysis
Social Media Research
Mixed Method Research
Procedural Method
In this part, provide an accurate, detailed account of the methods and procedures that were used in the study or the experiment (if applicable!).
Include specifics about participants, sample, materials, design and methods.
If the research involves human subjects, then include a detailed description of who and how many participated along with how the participants were selected.
Describe all materials used for the study, including equipment, written materials and testing instruments.
Identify the study's design and any variables or controls employed.
Write out the steps in the order that they were completed.
Indicate what participants were asked to do, how measurements were taken and any calculations made to raw data collected.
Specify statistical techniques applied to the data to reach your conclusions.
Provide evidence that you incorporated rigor into your research. This is the quality of being thorough and accurate and considers the logic behind your research design.
Highlight any drawbacks that may have limited your ability to conduct your research thoroughly.
You have to provide details to allow others to replicate the experiment and/or verify the data, to test the validity of the research.
Bibliography
Cottrell, S. (2014). Dissertations and project reports: a step by step guide. Hampshire, England: Palgrave Macmillan.
Lombard, E. (2010). Primary and secondary sources. The Journal of Academic Librarianship , 36(3), 250-253
Saunders, M.N.K., Lewis, P. and Thornhill, A. (2015). Research Methods for Business Students. New York: Pearson Education.
Specht, D. (2019). The Media And Communications Study Skills Student Guide . London: University of Westminster Press.
- << Previous: Introduction & Philosophy
- Next: Ethics >>
- Last Updated: Sep 14, 2022 12:58 PM
- URL: https://libguides.westminster.ac.uk/methodology-for-dissertations
CONNECT WITH US
- USC Libraries
- Research Guides
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper
- 6. The Methodology
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Reading Research Effectively
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Applying Critical Thinking
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Research Process Video Series
- Executive Summary
- The C.A.R.S. Model
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tiertiary Sources
- Scholarly vs. Popular Publications
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Insiderness
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Writing Concisely
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Generative AI and Writing
- USC Libraries Tutorials and Other Guides
- Bibliography
The methods section describes actions taken to investigate a research problem and the rationale for the application of specific procedures or techniques used to identify, select, process, and analyze information applied to understanding the problem, thereby, allowing the reader to critically evaluate a study’s overall validity and reliability. The methodology section of a research paper answers two main questions: How was the data collected or generated? And, how was it analyzed? The writing should be direct and precise and always written in the past tense.
Kallet, Richard H. "How to Write the Methods Section of a Research Paper." Respiratory Care 49 (October 2004): 1229-1232.
Importance of a Good Methodology Section
You must explain how you obtained and analyzed your results for the following reasons:
- Readers need to know how the data was obtained because the method you chose affects the results and, by extension, how you interpreted their significance in the discussion section of your paper.
- Methodology is crucial for any branch of scholarship because an unreliable method produces unreliable results and, as a consequence, undermines the value of your analysis of the findings.
- In most cases, there are a variety of different methods you can choose to investigate a research problem. The methodology section of your paper should clearly articulate the reasons why you have chosen a particular procedure or technique.
- The reader wants to know that the data was collected or generated in a way that is consistent with accepted practice in the field of study. For example, if you are using a multiple choice questionnaire, readers need to know that it offered your respondents a reasonable range of answers to choose from.
- The method must be appropriate to fulfilling the overall aims of the study. For example, you need to ensure that you have a large enough sample size to be able to generalize and make recommendations based upon the findings.
- The methodology should discuss the problems that were anticipated and the steps you took to prevent them from occurring. For any problems that do arise, you must describe the ways in which they were minimized or why these problems do not impact in any meaningful way your interpretation of the findings.
- In the social and behavioral sciences, it is important to always provide sufficient information to allow other researchers to adopt or replicate your methodology. This information is particularly important when a new method has been developed or an innovative use of an existing method is utilized.
Bem, Daryl J. Writing the Empirical Journal Article. Psychology Writing Center. University of Washington; Denscombe, Martyn. The Good Research Guide: For Small-Scale Social Research Projects . 5th edition. Buckingham, UK: Open University Press, 2014; Lunenburg, Frederick C. Writing a Successful Thesis or Dissertation: Tips and Strategies for Students in the Social and Behavioral Sciences . Thousand Oaks, CA: Corwin Press, 2008.
Structure and Writing Style
I. Groups of Research Methods
There are two main groups of research methods in the social sciences:
- The e mpirical-analytical group approaches the study of social sciences in a similar manner that researchers study the natural sciences . This type of research focuses on objective knowledge, research questions that can be answered yes or no, and operational definitions of variables to be measured. The empirical-analytical group employs deductive reasoning that uses existing theory as a foundation for formulating hypotheses that need to be tested. This approach is focused on explanation.
- The i nterpretative group of methods is focused on understanding phenomenon in a comprehensive, holistic way . Interpretive methods focus on analytically disclosing the meaning-making practices of human subjects [the why, how, or by what means people do what they do], while showing how those practices arrange so that it can be used to generate observable outcomes. Interpretive methods allow you to recognize your connection to the phenomena under investigation. However, the interpretative group requires careful examination of variables because it focuses more on subjective knowledge.
II. Content
The introduction to your methodology section should begin by restating the research problem and underlying assumptions underpinning your study. This is followed by situating the methods you used to gather, analyze, and process information within the overall “tradition” of your field of study and within the particular research design you have chosen to study the problem. If the method you choose lies outside of the tradition of your field [i.e., your review of the literature demonstrates that the method is not commonly used], provide a justification for how your choice of methods specifically addresses the research problem in ways that have not been utilized in prior studies.
The remainder of your methodology section should describe the following:
- Decisions made in selecting the data you have analyzed or, in the case of qualitative research, the subjects and research setting you have examined,
- Tools and methods used to identify and collect information, and how you identified relevant variables,
- The ways in which you processed the data and the procedures you used to analyze that data, and
- The specific research tools or strategies that you utilized to study the underlying hypothesis and research questions.
In addition, an effectively written methodology section should:
- Introduce the overall methodological approach for investigating your research problem . Is your study qualitative or quantitative or a combination of both (mixed method)? Are you going to take a special approach, such as action research, or a more neutral stance?
- Indicate how the approach fits the overall research design . Your methods for gathering data should have a clear connection to your research problem. In other words, make sure that your methods will actually address the problem. One of the most common deficiencies found in research papers is that the proposed methodology is not suitable to achieving the stated objective of your paper.
- Describe the specific methods of data collection you are going to use , such as, surveys, interviews, questionnaires, observation, archival research. If you are analyzing existing data, such as a data set or archival documents, describe how it was originally created or gathered and by whom. Also be sure to explain how older data is still relevant to investigating the current research problem.
- Explain how you intend to analyze your results . Will you use statistical analysis? Will you use specific theoretical perspectives to help you analyze a text or explain observed behaviors? Describe how you plan to obtain an accurate assessment of relationships, patterns, trends, distributions, and possible contradictions found in the data.
- Provide background and a rationale for methodologies that are unfamiliar for your readers . Very often in the social sciences, research problems and the methods for investigating them require more explanation/rationale than widely accepted rules governing the natural and physical sciences. Be clear and concise in your explanation.
- Provide a justification for subject selection and sampling procedure . For instance, if you propose to conduct interviews, how do you intend to select the sample population? If you are analyzing texts, which texts have you chosen, and why? If you are using statistics, why is this set of data being used? If other data sources exist, explain why the data you chose is most appropriate to addressing the research problem.
- Provide a justification for case study selection . A common method of analyzing research problems in the social sciences is to analyze specific cases. These can be a person, place, event, phenomenon, or other type of subject of analysis that are either examined as a singular topic of in-depth investigation or multiple topics of investigation studied for the purpose of comparing or contrasting findings. In either method, you should explain why a case or cases were chosen and how they specifically relate to the research problem.
- Describe potential limitations . Are there any practical limitations that could affect your data collection? How will you attempt to control for potential confounding variables and errors? If your methodology may lead to problems you can anticipate, state this openly and show why pursuing this methodology outweighs the risk of these problems cropping up.
NOTE: Once you have written all of the elements of the methods section, subsequent revisions should focus on how to present those elements as clearly and as logically as possibly. The description of how you prepared to study the research problem, how you gathered the data, and the protocol for analyzing the data should be organized chronologically. For clarity, when a large amount of detail must be presented, information should be presented in sub-sections according to topic. If necessary, consider using appendices for raw data.
ANOTHER NOTE: If you are conducting a qualitative analysis of a research problem , the methodology section generally requires a more elaborate description of the methods used as well as an explanation of the processes applied to gathering and analyzing of data than is generally required for studies using quantitative methods. Because you are the primary instrument for generating the data [e.g., through interviews or observations], the process for collecting that data has a significantly greater impact on producing the findings. Therefore, qualitative research requires a more detailed description of the methods used.
YET ANOTHER NOTE: If your study involves interviews, observations, or other qualitative techniques involving human subjects , you may be required to obtain approval from the university's Office for the Protection of Research Subjects before beginning your research. This is not a common procedure for most undergraduate level student research assignments. However, i f your professor states you need approval, you must include a statement in your methods section that you received official endorsement and adequate informed consent from the office and that there was a clear assessment and minimization of risks to participants and to the university. This statement informs the reader that your study was conducted in an ethical and responsible manner. In some cases, the approval notice is included as an appendix to your paper.
III. Problems to Avoid
Irrelevant Detail The methodology section of your paper should be thorough but concise. Do not provide any background information that does not directly help the reader understand why a particular method was chosen, how the data was gathered or obtained, and how the data was analyzed in relation to the research problem [note: analyzed, not interpreted! Save how you interpreted the findings for the discussion section]. With this in mind, the page length of your methods section will generally be less than any other section of your paper except the conclusion.
Unnecessary Explanation of Basic Procedures Remember that you are not writing a how-to guide about a particular method. You should make the assumption that readers possess a basic understanding of how to investigate the research problem on their own and, therefore, you do not have to go into great detail about specific methodological procedures. The focus should be on how you applied a method , not on the mechanics of doing a method. An exception to this rule is if you select an unconventional methodological approach; if this is the case, be sure to explain why this approach was chosen and how it enhances the overall process of discovery.
Problem Blindness It is almost a given that you will encounter problems when collecting or generating your data, or, gaps will exist in existing data or archival materials. Do not ignore these problems or pretend they did not occur. Often, documenting how you overcame obstacles can form an interesting part of the methodology. It demonstrates to the reader that you can provide a cogent rationale for the decisions you made to minimize the impact of any problems that arose.
Literature Review Just as the literature review section of your paper provides an overview of sources you have examined while researching a particular topic, the methodology section should cite any sources that informed your choice and application of a particular method [i.e., the choice of a survey should include any citations to the works you used to help construct the survey].
It’s More than Sources of Information! A description of a research study's method should not be confused with a description of the sources of information. Such a list of sources is useful in and of itself, especially if it is accompanied by an explanation about the selection and use of the sources. The description of the project's methodology complements a list of sources in that it sets forth the organization and interpretation of information emanating from those sources.
Azevedo, L.F. et al. "How to Write a Scientific Paper: Writing the Methods Section." Revista Portuguesa de Pneumologia 17 (2011): 232-238; Blair Lorrie. “Choosing a Methodology.” In Writing a Graduate Thesis or Dissertation , Teaching Writing Series. (Rotterdam: Sense Publishers 2016), pp. 49-72; Butin, Dan W. The Education Dissertation A Guide for Practitioner Scholars . Thousand Oaks, CA: Corwin, 2010; Carter, Susan. Structuring Your Research Thesis . New York: Palgrave Macmillan, 2012; Kallet, Richard H. “How to Write the Methods Section of a Research Paper.” Respiratory Care 49 (October 2004):1229-1232; Lunenburg, Frederick C. Writing a Successful Thesis or Dissertation: Tips and Strategies for Students in the Social and Behavioral Sciences . Thousand Oaks, CA: Corwin Press, 2008. Methods Section. The Writer’s Handbook. Writing Center. University of Wisconsin, Madison; Rudestam, Kjell Erik and Rae R. Newton. “The Method Chapter: Describing Your Research Plan.” In Surviving Your Dissertation: A Comprehensive Guide to Content and Process . (Thousand Oaks, Sage Publications, 2015), pp. 87-115; What is Interpretive Research. Institute of Public and International Affairs, University of Utah; Writing the Experimental Report: Methods, Results, and Discussion. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University; Methods and Materials. The Structure, Format, Content, and Style of a Journal-Style Scientific Paper. Department of Biology. Bates College.
Writing Tip
Statistical Designs and Tests? Do Not Fear Them!
Don't avoid using a quantitative approach to analyzing your research problem just because you fear the idea of applying statistical designs and tests. A qualitative approach, such as conducting interviews or content analysis of archival texts, can yield exciting new insights about a research problem, but it should not be undertaken simply because you have a disdain for running a simple regression. A well designed quantitative research study can often be accomplished in very clear and direct ways, whereas, a similar study of a qualitative nature usually requires considerable time to analyze large volumes of data and a tremendous burden to create new paths for analysis where previously no path associated with your research problem had existed.
To locate data and statistics, GO HERE .
Another Writing Tip
Knowing the Relationship Between Theories and Methods
There can be multiple meaning associated with the term "theories" and the term "methods" in social sciences research. A helpful way to delineate between them is to understand "theories" as representing different ways of characterizing the social world when you research it and "methods" as representing different ways of generating and analyzing data about that social world. Framed in this way, all empirical social sciences research involves theories and methods, whether they are stated explicitly or not. However, while theories and methods are often related, it is important that, as a researcher, you deliberately separate them in order to avoid your theories playing a disproportionate role in shaping what outcomes your chosen methods produce.
Introspectively engage in an ongoing dialectic between the application of theories and methods to help enable you to use the outcomes from your methods to interrogate and develop new theories, or ways of framing conceptually the research problem. This is how scholarship grows and branches out into new intellectual territory.
Reynolds, R. Larry. Ways of Knowing. Alternative Microeconomics . Part 1, Chapter 3. Boise State University; The Theory-Method Relationship. S-Cool Revision. United Kingdom.
Yet Another Writing Tip
Methods and the Methodology
Do not confuse the terms "methods" and "methodology." As Schneider notes, a method refers to the technical steps taken to do research . Descriptions of methods usually include defining and stating why you have chosen specific techniques to investigate a research problem, followed by an outline of the procedures you used to systematically select, gather, and process the data [remember to always save the interpretation of data for the discussion section of your paper].
The methodology refers to a discussion of the underlying reasoning why particular methods were used . This discussion includes describing the theoretical concepts that inform the choice of methods to be applied, placing the choice of methods within the more general nature of academic work, and reviewing its relevance to examining the research problem. The methodology section also includes a thorough review of the methods other scholars have used to study the topic.
Bryman, Alan. "Of Methods and Methodology." Qualitative Research in Organizations and Management: An International Journal 3 (2008): 159-168; Schneider, Florian. “What's in a Methodology: The Difference between Method, Methodology, and Theory…and How to Get the Balance Right?” PoliticsEastAsia.com. Chinese Department, University of Leiden, Netherlands.
- << Previous: Scholarly vs. Popular Publications
- Next: Qualitative Methods >>
- Last Updated: Sep 3, 2024 1:54 PM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide

Writing the Research Methodology Section of Your Thesis
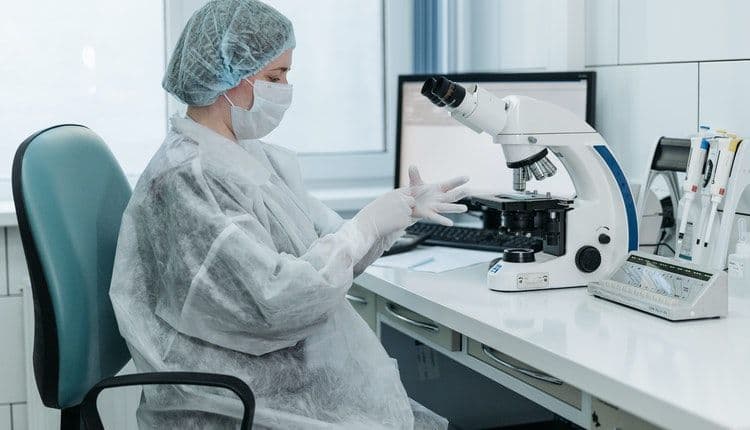

This article explains the meaning of research methodology and the purpose and importance of writing a research methodology section or chapter for your thesis paper. It discusses what to include and not include in a research methodology section, the different approaches to research methodology that can be used, and the steps involved in writing a robust research methodology section.
What is a thesis research methodology?
A thesis research methodology explains the type of research performed, justifies the methods that you chose by linking back to the literature review , and describes the data collection and analysis procedures. It is included in your thesis after the Introduction section . Most importantly, this is the section where the readers of your study evaluate its validity and reliability.
What should the research methodology section in your thesis include?
- The aim of your thesis
- An outline of the research methods chosen (qualitative, quantitative, or mixed methods)
- Background and rationale for the methods chosen, explaining why one method was chosen over another
- Methods used for data collection and data analysis
- Materials and equipment used—keep this brief
- Difficulties encountered during data collection and analysis. It is expected that problems will occur during your research process. Use this as an opportunity to demonstrate your problem-solving abilities by explaining how you overcame all obstacles. This builds your readers’ confidence in your study findings.
- A brief evaluation of your research explaining whether your results were conclusive and whether your choice of methodology was effective in practice
What should not be included in the research methodology section of your thesis?
- Irrelevant details, for example, an extensive review of methodologies (this belongs in the literature review section) or information that does not contribute to the readers’ understanding of your chosen methods
- A description of basic procedures
- Excessive details about materials and equipment used. If an extremely long and detailed list is necessary, add it as an appendix
Types of methodological approaches
The choice of which methodological approach to use depends on your field of research and your thesis question. Your methodology should establish a clear relationship with your thesis question and must also be supported by your literature review . Types of methodological approaches include quantitative, qualitative, or mixed methods.
Quantitative studies generate data in the form of numbers to count, classify, measure, or identify relationships or patterns. Information may be collected by performing experiments and tests, conducting surveys, or using existing data. The data are analyzed using statistical tests and presented as charts or graphs. Quantitative data are typically used in the Sciences domain.
For example, analyzing the effect of a change, such as alterations in electricity consumption by municipalities after installing LED streetlights.
The raw data will need to be prepared for statistical analysis by identifying variables and checking for missing data and outliers. Details of the statistical software program used (name of the package, version number, and supplier name and location) must also be mentioned.
Qualitative studies gather non-numerical data using, for example, observations, focus groups, and in-depth interviews. Open-ended questions are often posed. This yields rich, detailed, and descriptive results. Qualitative studies are usually subjective and are helpful for investigating social and cultural phenomena, which are difficult to quantify. Qualitative studies are typically used in the Humanities and Social Sciences (HSS) domain.
For example, determining customer perceptions on the extension of a range of baking utensils to include silicone muffin trays.
The raw data will need to be prepared for analysis by coding and categorizing ideas and themes to interpret the meaning behind the responses given.
Mixed methods use a combination of quantitative and qualitative approaches to present multiple findings about a single phenomenon. T his enables triangulation: verification of the data from two or more sources.
Data collection
Explain the rationale behind the sampling procedure you have chosen. This could involve probability sampling (a random sample from the study population) or non-probability sampling (does not use a random sample).
For quantitative studies, describe the sampling procedure and whether statistical tests were used to determine the sample size .
Following our example of analyzing the changes in electricity consumption by municipalities after installing LED streetlights, you will need to determine which municipal areas will be sampled and how the information will be gathered (e.g., a physical survey of the streetlights or reviewing purchase orders).
For qualitative research, describe how the participants were chosen and how the data is going to be collected.
Following our example about determining customer perceptions on the extension of a range of baking utensils to include silicone muffin trays, you will need to decide the criteria for inclusion as a study participant (e.g., women aged 20–70 years, bakeries, and bakery supply shops) and how the information will be collected (e.g., interviews, focus groups, online or in-person questionnaires, or video recordings) .
Data analysis
For quantitative research, describe what tests you plan to perform and why you have chosen them. Popular data analysis methods in quantitative research include:
- Descriptive statistics (e.g., means, medians, modes)
- Inferential statistics (e.g., correlation, regression, structural equation modeling)
For qualitative research, describe how the data is going to be analyzed and justify your choice. Popular data analysis methods in qualitative research include:
- Qualitative content analysis
- Thematic analysis
- Discourse analysis
- Narrative analysis
- Grounded theory
- Interpretative phenomenological analysis (IPA)
Evaluate and justify your methodological choices
You need to convince the reader that you have made the correct methodological choices. Once again, this ties back to your thesis question and literature review . Write using a persuasive tone, and use rhetoric to convince the reader of the quality, reliability, and validity of your research.
Ethical considerations
- The young researcher should maintain objectivity at all times
- All participants have the right to privacy and anonymity
- Research participation must be voluntary
- All subjects have the right to withdraw from the research at any time
- Consent must be obtained from all participants before starting the research
- Confidentiality of data provided by individuals must be maintained
- Consider how the interpretation and reporting of the data will affect the participants
Tips for writing a robust thesis research methodology
- Determine what kind of knowledge you are trying to uncover. For example, subjective or objective, experimental or interpretive.
- A thorough literature review is the best starting point for choosing your methods.
- Ensure that there is continuity throughout the research process. The authenticity of your research depends upon the validity of the research data, the reliability of your data measurements, and the time taken to conduct the analysis.
- Choose a research method that is achievable. Consider the time and funds available, feasibility, ethics, and access and availability of equipment to measure the phenomenon or answer your thesis question correctly.
- If you are struggling with a concept, ask for help from your supervisor, academic staff members, or fellow students.
A thesis methodology justifies why you have chosen a specific approach to address your thesis question. It explains how you will collect the data and analyze it. Above all, it allows the readers of your study to evaluate its validity and reliability.
A thesis is the most crucial document that you will write during your academic studies. For professional thesis editing and thesis proofreading services, visit Enago Thesis Editing for more information.
Editor’s pick
Get free updates.
Subscribe to our newsletter for regular insights from the research and publishing industry!
Review Checklist
Introduce your methodological approach , for example, quantitative, qualitative, or mixed methods.
Explain why your chosen approach is relevant to the overall research design and how it links with your thesis question.
Justify your chosen method and why it is more appropriate than others.
Provide background information on methods that may be unfamiliar to readers of your thesis.
Introduce the tools that you will use for data collection , and explain how you plan to use them (e.g., surveys, interviews, experiments, or existing data).
Explain how you will analyze your results. The type of analysis used depends on the methods you chose. For example, exploring theoretical perspectives to support your explanation of observed behaviors in a qualitative study or using statistical analyses in a quantitative study.
Mention any research limitations. All studies are expected to have limitations, such as the sample size, data collection method, or equipment. Discussing the limitations justifies your choice of methodology despite the risks. It also explains under which conditions the results should be interpreted and shows that you have taken a holistic approach to your study.
What is the difference between methodology and methods? +
Methodology refers to the overall rationale and strategy of your thesis project. It involves studying the theories or principles behind the methods used in your field so that you can explain why you chose a particular method for your research approach. Methods , on the other hand, refer to how the data were collected and analyzed (e.g., experiments, surveys, observations, interviews, and statistical tests).
What is the difference between reliability and validity? +
Reliability refers to whether a measurement is consistent (i.e., the results can be reproduced under the same conditions). Validity refers to whether a measurement is accurate (i.e., the results represent what was supposed to be measured). For example, when investigating linguistic and cultural guidelines for administration of the Preschool Language Scales, Fifth Edition (PLS5) in Arab-American preschool children, the normative sample curves should show the same distribution as a monolingual population, which would indicate that the test is valid. The test would be considered reliable if the results obtained were consistent across different sampling sites.
What tense is used to write the methods section? +
The methods section is written in the past tense because it describes what was done.
What software programs are recommended for statistical analysis? +
Recommended programs include Statistical Analysis Software (SAS) , Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (SPSS) , JMP , R software, MATLAB , Microsoft Excel, GraphPad Prism , and Minitab .
- How it works

Research Methods for Dissertation – Types with Comparison
Published by Carmen Troy at August 13th, 2021 , Revised On June 14, 2023
Introduction
“Research methods for a dissertation refer to the specific approaches, procedures, and techniques employed by researchers to investigate and gather data for their dissertation projects.”
These methods provide a systematic and structured framework for conducting research, ensuring the reliability, validity, and rigour of the study.
What are the different research methods for the dissertation, and which one should I use?
Choosing the right research method for a dissertation is a grinding and perplexing aspect of the dissertation research process. A well-defined research methodology helps you conduct your research in the right direction, validates the results of your research, and makes sure that the study you’re conducting answers the set research questions .
The research title, research questions, hypothesis , objectives, and study area generally determine the best research method in the dissertation.
This post’s primary purpose is to highlight what these different types of research methods involve and how you should decide which type of research fits the bill. As you read through this article, think about which one of these research methods will be the most appropriate for your research.
The practical, personal, and academic reasons for choosing any particular method of research are also analysed. You will find our explanation of experimental , descriptive , historical , quantitative , qualitative , and mixed research methods useful regardless of your field of study.
While choosing the right method of research for your own research, you need to:
- Understand the difference between research methods and methodology .
- Think about your research topic, research questions, and research objectives to make an intelligent decision.
- Know about various types of research methods so that you can choose the most suitable and convenient method as per your research requirements.
Research Methodology Vs. Research Methods
A well-defined research methodology helps you conduct your research in the right direction, validates the results of your research, and makes sure that the study you are conducting answers the set research questions .

Research methods are the techniques and procedures used for conducting research. Choosing the right research method for your writing is an important aspect of the research process .
You need to either collect data or talk to the people while conducting any research. The research methods can be classified based on this distinction.
Hire an Expert Writer
Proposal and dissertation orders completed by our expert writers are
- Formally drafted in an academic style
- Plagiarism free
- 100% Confidential
- Never Resold
- Include unlimited free revisions
- Completed to match exact client requirements
Types of Research Methods
Research methods are broadly divided into six main categories.
Experimental Research Methods
Descriptive research methods, historical research methods, quantitative research methods, qualitative research methods, mixed methods of research.
Experimental research includes the experiments conducted in the laboratory or observation under controlled conditions. Researchers try to study human behavior by performing various experiments. Experiments can vary from personal and informal natural comparisons. It includes three types of variables;
- Independent variable
- Dependent variable
- Controlled variable
Types of Experimental Methods
Laboratory experiments
The experiments were conducted in the laboratory. Researchers have control over the variables of the experiment.
Field experiment
The experiments were conducted in the open field and environment of the participants by incorporating a few artificial changes. Researchers do not have control over variables under measurement. Participants know that they are taking part in the experiment.
Natural experiments
The experiment is conducted in the natural environment of the participants. The participants are generally not informed about the experiment being conducted on them.
Example : Estimating the health condition of the population.
Quasi-experiments
A quasi-experiment is an experiment that takes advantage of natural occurrences. Researchers cannot assign random participants to groups.
Example: Comparing the academic performance of the two schools.
| 1. | 2. Methods of Analysing Data |
|---|---|
What data collection best suits your research?
- Find out by hiring an expert from ResearchProspect today!
- Despite how challenging the subject may be, we are here to help you.
Descriptive research aims at collecting the information to answer the current affairs. It follows the Ex post facto research, which predicts the possible reasons behind the situation that has already occurred. It aims to answer questions like how, what, when, where, and what rather than ‘why.’
| 1. | 2. Methods of Analysing Data |
|---|---|
| It studies the tables containing the groups’ means to compare and distinguish between the categorised and independent variables. It includes the tables containing the data of the participant groups and sub-groups of survey respondents. It is also known as paired testing, where two people are assigned specific identities and qualifications to compare and study types of discrimination. |
In historical research , an investigator collects, analyses the information to understand, describe, and explain the events that occurred in the past. Researchers try to find out what happened exactly during a certain period of time as accurately and as closely as possible. It does not allow any manipulation or control of variables.
| 1. | 2. Methods of Analysing Data |
|---|---|
| Researchers use multiple theories to explain specific phenomena, situations, and types of behavior. It takes a long to go through the textual data. Coding is a way of tagging the data and organising it into a sequence of symbols, numbers, and letters to highlight the relevant points. Quantitative data is used to validate interpretations of historical events or incidents. |
Quantitative research is associated with numerical data or data that can be measured. It is used to study a large group of population. The information is gathered by performing statistical, mathematical, or computational techniques.
Quantitative research isn’t simply based on statistical analysis or quantitative techniques but rather uses a certain approach to theory to address research hypotheses or research questions, establish an appropriate research methodology, and draw findings & conclusions .
Some most commonly employed quantitative research strategies include data-driven dissertations, theory-driven studies, and reflection-driven research. Regardless of the chosen approach, there are some common quantitative research features as listed below.
- Quantitative research is based on testing or building on existing theories proposed by other researchers whilst taking a reflective or extensive route.
- Quantitative research aims to test the research hypothesis or answer established research questions.
- It is primarily justified by positivist or post-positivist research paradigms.
- The research design can be relationship-based, quasi-experimental, experimental, or descriptive.
- It draws on a small sample to make generalisations to a wider population using probability sampling techniques.
- Quantitative data is gathered according to the established research questions and using research vehicles such as structured observation, structured interviews, surveys, questionnaires, and laboratory results.
- The researcher uses statistical analysis tools and techniques to measure variables and gather inferential or descriptive data. In some cases, your tutor or members of the dissertation committee might find it easier to verify your study results with numbers and statistical analysis.
- The accuracy of the study results is based on external and internal validity and the authenticity of the data used.
- Quantitative research answers research questions or tests the hypothesis using charts, graphs, tables, data, and statements.
- It underpins research questions or hypotheses and findings to make conclusions.
- The researcher can provide recommendations for future research and expand or test existing theories.
| 1. | 2. Methods of Analysing Data |
|---|---|
| It is a method of collecting, analysing, and interpreting ample data to discover underlying patterns and details. Statistics are used in every field to make better decisions. The correlational analysis is carried out to discover the interrelationship between the two or more aspects of a situation. It distributes values around some central value, such an average. Example: the distance separating the highest from the lowest value. It counts the maximum and a minimum number of responses to a question or the occurrence of a specific phenomenon. It determines the nature of social problems, such as ethnic or gender discrimination. It explains the relationship between one dependent binary variable and one or more independent variables. This parametric technique is used while comparing two populations or samples. |
Confused between qualitative and quantitative methods of data analysis? No idea what discourse and content analysis are?
We hear you.
- Whether you want a full dissertation written or need help forming a dissertation proposal, we can help you with both.
- Get different dissertation services at ResearchProspect and score amazing grades!
At ResearchProspect, our expert writers can help you with your quantitative dissertation whether you are a sports science student, medical or biological science, education or business, psychology, social sciences, engineering, project management, or any other science-based degree. We guarantee 100% commitment, 100% Plagiarism-free work, 100% Confidentiality and 100% Satisfaction
It is a type of scientific research where a researcher collects evidence to seek answers to a question . It is associated with studying human behaviour from an informative perspective. It aims at obtaining in-depth details of the problem.
As the term suggests, qualitative research is based on qualitative research methods, including participants’ observations, focus groups, and unstructured interviews.
Qualitative research is very different in nature when compared to quantitative research. It takes an established path towards the research process , how research questions are set up, how existing theories are built upon, what research methods are employed, and how the findings are unveiled to the readers.
You may adopt conventional methods, including phenomenological research, narrative-based research, grounded theory research, ethnographies , case studies , and auto-ethnographies.
Again, regardless of the chosen approach to qualitative research, your dissertation will have unique key features as listed below.
- The research questions that you aim to answer will expand or even change as the dissertation writing process continues. This aspect of the research is typically known as an emergent design where the research objectives evolve with time.
- Qualitative research may use existing theories to cultivate new theoretical understandings or fall back on existing theories to support the research process. However, the original goal of testing a certain theoretical understanding remains the same.
- It can be based on various research models, such as critical theory, constructivism, and interpretivism.
- The chosen research design largely influences the analysis and discussion of results and the choices you make. Research design depends on the adopted research path: phenomenological research, narrative-based research, grounded theory-based research, ethnography, case study-based research, or auto-ethnography.
- Qualitative research answers research questions with theoretical sampling, where data gathered from an organisation or people are studied.
- It involves various research methods to gather qualitative data from participants belonging to the field of study. As indicated previously, some of the most notable qualitative research methods include participant observation, focus groups, and unstructured interviews .
- It incorporates an inductive process where the researcher analyses and understands the data through his own eyes and judgments to identify concepts and themes that comprehensively depict the researched material.
- The key quality characteristics of qualitative research are transferability, conformity, confirmability, and reliability.
- Results and discussions are largely based on narratives, case study and personal experiences, which help detect inconsistencies, observations, processes, and ideas.s
- Qualitative research discusses theoretical concepts obtained from the results whilst taking research questions and/or hypotheses to draw general conclusions .
Now that you know the unique differences between quantitative and qualitative research methods, you may want to learn a bit about primary and secondary research methods.
Here is an article that will help you distinguish between primary and secondary research and decide whether you need to use quantitative and/or qualitative primary research methods in your dissertation.
Alternatively, you can base your dissertation on secondary research, which is descriptive and explanatory in essence.
Types of Qualitative Research Methods
Action research
Action research aims at finding an immediate solution to a problem. The researchers can also act as the participants of the research. It is used in the educational field.
A case study includes data collection from multiple sources over time. It is widely used in social sciences to study the underlying information, organisation, community, or event. It does not provide any solution to the problem. Researchers cannot act as the participants of the research.
Ethnography
In this type of research, the researcher examines the people in their natural environment. Ethnographers spend time with people to study people and their culture closely. They can consult the literature before conducting the study.
| 1. | 2. Methods of Analysing Data |
|---|---|
| with open-ended questions | It is a method of studying and retrieving meaningful information from documents. It aims at identifying patterns of themes in the collected information, such as face-to-face interviews, texts, and transcripts. , field observations, and interviews. It is a study of how language is used in texts and contexts. |
When you combine quantitative and qualitative methods of research, the resulting approach becomes mixed methods of research.
Over the last few decades, much of the research in academia has been conducted using mixed methods because of the greater legitimacy this particular technique has gained for several reasons including the feeling that combining the two types of research can provide holistic and more dependable results.
Here is what mixed methods of research involve:
- Interpreting and investigating the information gathered through quantitative and qualitative techniques.
- There could be more than one stage of research. Depending on the research topic, occasionally it would be more appropriate to perform qualitative research in the first stage to figure out and investigate a problem to unveil key themes; and conduct quantitative research in stage two of the process for measuring relationships between the themes.
Note: However, this method has one prominent limitation, which is, as previously mentioned, combining qualitative and quantitative research can be difficult because they both are different in terms of design and approach. In many ways, they are contrasting styles of research, and so care must be exercised when basing your dissertation on mixed methods of research.
When choosing a research method for your own dissertation, it would make sense to carefully think about your research topic , research questions , and research objectives to make an intelligent decision in terms of the philosophy of research design .
Dissertations based on mixed methods of research can be the hardest to tackle even for PhD students.
Our writers have years of experience in writing flawless and to the point mixed methods-based dissertations to be confident that the dissertation they write for you will be according to the technical requirements and the formatting guidelines.
Read our guarantees to learn more about how you can improve your grades with our dissertation services.
Please Find Below an Example of Research Methods Section in a Dissertation or Thesis.
Background and Problem
Diversity management became prominent in the late twentieth century, with foundations in America. Historically homogeneous or nondiverse nations, such as Finland, have not yet experienced the issues associated with rising cultural and ethnic diversity in the workforce. Regardless of the environment, workforce diversity garners greater attention and is characterised by its expanding relevance due to globalised and international companies, global and national worker mobility, demographic shifts, or enhancing productivity.
As a result, challenges of diversity management have been handled through legal, financial, and moral pressures (Hayes et al., 2020). The evolving structure of the working population in terms of language, ethnic background, maturity level, faith, or ethnocultural history is said to pose a challenge to human resource management (HRM) in utilising diversity: the understanding, abilities, and expertise prospects of the entire workforce to deal with possible developments.
The European approach to diversity management is regarded as growing. However, it is found to emphasise the relationship to business and lack competence in diversity management problems. Mass immigration concentrates variety, sometimes treated as cultural minority issues, implying the normalisation of anti-discrimination actions (Yadav and Lenka, 2020).
These causes, in turn, have provided the basis of comprehensive diversity research, which has generated different theories, frameworks, concepts, and guidelines from interdisciplinary viewpoints, such as industrial and organisational psychology and behaviour (OB), cultural studies, anthropology, migration, economics, postcolonialism, and so on. And in the form of international, social and cultural, organisational, group, and individual scale diversity analysis. This dissertation focuses on diversity concerns from impression management, specifically from HRM as an executive-level phenomenon (Seliverstova, 2021).
As conceptual frameworks, organisational structures concentrating on the production of diversity and social psychology, notably social identity theory with diverse ‘identities’ of persons or intergroup connections, are primarily employed. The study’s primary goal in the workplace is to discover inequities or examine the effects of diversity on workplace outcomes.
Individual study interests include behaviours, emotions, intelligence, intercultural skills or competencies, while group research interests include group dynamics, intergroup interactions, effectiveness, and cooperation or collaboration. Organisational studies address themes such as workforce composition, workplace equality, and diversity challenges and how they may be managed accordingly. Domestic diversity, omitting national distinctions, or global diversity, about diverse country cultures, might be studied further (AYDIN and ÖZEREN, 2018).
Diversity is a context-dependent, particular, comparative, complicated, plural phrase or idea with varying interpretations in different organisations and cultures and no unified definition. As a result, in addition to many internal and external elements, diversity may be managed, individuals taught, and organisations have grown in various ways. This dissertation considers diversity in an organisational environment as a construct of ‘differences’ to be handled (Cummings, 2018).
Various management systems have grown in stages, bringing diverse diversity management concepts. Equality/equal opportunities (EO) legislation and diversity management are the two conventional approaches and primary streams with differing theoretical foundations for managing and dealing with workforce diversity challenges (DM).
These approaches relate to whether diversity is handled by increasing sameness by legal pressures or by voluntarily respecting people’s differences, which shows an organisation’s responsiveness and proactivity toward managing diversity. But most of the literature in this area has avoided the impression management theories (Coad and Guenther, 2014). Therefore, this study will add a new dimension in this area by introducing impression management analysis.
Research Aim and Objectives
This research aims to analyse the impact of organisational structure on human resources diversification from the viewpoint of impression managerial theory. It has the following objectives:
- It will examine the existing impression management literature to draw insights into the relationship under consideration.
- It will identify various factors such as competency, social inclusion, etc., affecting the management’s decision to recruit diverse human resources.
- It will recommend appropriate organisational structures and HR policies to improve diversification of HR by reviewing impression management theories.
Research Questions
This research will answer the following questions:
- How does organisational structure affect human resources diversification from the viewpoint of impression managerial theory?
- What factors such as competency, social inclusion, etc., affect the management decision to recruit diverse human resources?
- What are appropriate organisational structures and HR policies to improve diversification of HR by reviewing impression management theories?
Research Hypothesis
The organisational structure significantly impacts the recruitment of diverse human resources.
Literature Review
According to Staniec and Zakrzewska-Bielawska (2010), considering strategy-oriented activities and organisational components are the critical foundation in the organisational structure required to align structure strategy. Each company’s internal organisation is somewhat distinctive, resulting from various corporate initiatives and historical conditions.
Furthermore, each design is based on essential success elements and vital tasks inherent in the firm plan. This article offers empirical research on unique organisational structure elements in Polish firms in the context of concentration and diversification tactics. And companies that adopted concentration techniques mainly used functional organisational structures.
Tasks were primarily classified and categorised based on functions and phases of the technical process, with coordination based on hierarchy. Jobs were also highly centralised and formalised. Organisational structures of an active type were also prevalent in many firms. Only a handful of the evaluated organisations possessed flexible contemporary divisional or matrix structures appropriate to differentiation. However, it appears that even such organisations should adjust their organisational solutions to perform successfully in an immensely complex and chaotic environment.
Similarly, according to Yang and Konrad (2011), diversity management techniques are the institutionalised methods created and applied by organisations to manage diversity among all organisational shareholders. They examined the existing research on the causes and significance of diversity management approaches.
They construct a research model indicating many potential routes for future study using institutional and resource-based theories. They also offer prospective avenues for study on diversity management techniques to further the two theoretical viewpoints. The findings indicate that research on diverse management practises might provide perceptions into the two ideologies. Diversity management provides a method for reconciling the agency vs structure issue for institutional concept.
Furthermore, diversity management is a suitable framework for studying how institutional pressures are translated into organisational action and the relationship between complying with institutional mandates and attaining high performance. Research on diversity management raises the importance of environmental normative elements in resource-based reasoning.
It allows for exploring essential resource sources and the co-evolution of diversity resources and management capacities, potentially developing dynamic resource-based theory. Furthermore, a review of the existing research on diversity management practices reveals that research in this field has nearly entirely concentrated on employee-related activities.
However, in establishing the idea of diversity management practises, we included the practises that companies put in place to manage diversity across all stakeholder groups on purpose. Management techniques for engaging with consumers, dealers, supervisors, board directors, and community members are critical for meeting institutional theory’s social and normative commitments.
Moreover, according to Sippola (2014), this research looks at diversity management from the standpoint of HRM. The study aims to discover the effects of expanding workforce diversity on HRM inside firms. This goal will be accomplished through four papers examining diversity management’s impacts on HRM from various viewpoints and mostly in longitudinal contexts.
The purpose of the first article, as a pilot survey, is to determine the reasons, advantages, and problems of rising cultural diversity and the consequences for HRM to get a preliminary grasp of the issue in the specific setting. According to the report, diversity is vital for productivity but is not often emphasised in HRM strategy.
The key areas that were changed were acquisition, development, and growth. The second article examines how different diversity management paradigms recognised in businesses affect HRM. It offers an experimentally verified typology that explains reactive or proactive strategic and operational level HRM activities in light of four alternative diversity management perspectives.
The third essay will examine how a ‘working culture bridge group’ strategy fosters and enhances workplace diversity. The research looks into how development goals are defined, what training and development techniques are used, and the consequences and causal factors when an analysis measures the training and development approach.
The primary goal of article four is to establish which components of diversity management design are globally integrated into multinational corporations (MNCs) and which integrating (delivery) methods are employed to facilitate it. Another goal is to identify the institutional problems faced by the Finnish national diversity setting during the integration process.
The findings show that the example organisation achieved more excellent global uniformity at the level of diversification concept through effective use of multiple frameworks but was forced to rely on a more multinational approach to implementing diversification policies and procedures. The difficulties faced emphasised the distinctiveness of Finland’s cognitive and normative institutional setting for diversity.
Furthermore, according to Guillaume et al. (2017), to compensate for the dual-edged character of demographic workplace diversity impacts on social inclusion, competence, and well-being-related factors, research has shifted away from straightforward main effect methods and begun to investigate factors that moderate these effects.
While there is no shortage of primary research on the circumstances that lead to favourable or poor results, it is unknown which contextual elements make it work. Using the Classification framework as a theoretical lens, they examine variables that moderate the impacts of workplace diversity on social integration, performance, and well-being outcomes, emphasising characteristics that organisations and managers can influence.
They suggest future study directions and end with practical applications. They concluded that faultlines, cross-categorisation, and status variations across demographic groupings highlight variety. Cross-categorisation has been proven to reduce intergroup prejudice while promoting social inclusion, competence, and well-being. Whether faultlines and subgroup status inequalities promote negative or good intergroup interactions and hinder social integration, performance, and well-being depends on whether situational factors encourage negative or positive intergroup connections. The impacts were not mitigated by team size or diversity type.
Furthermore, our data demonstrate that task characteristics are essential for workgroup diversity. Any demographic diversity in workgroups can promote creativity, but only when combined with task-relevant expertise improves the performance of teams undertaking complicated tasks. The type of team and the industrial context do not appear to play an effect. It is unclear if these findings apply to relational demography and organisational diversity impacts. There is some evidence that, under some settings, relational demography may increase creativity, and, as previously said, demographic variety may help firms function in growth-oriented strategy contexts.
Likewise, according to Ali, Tawfeq, and Dler (2020), diversity management refers to organisational strategies that strive to increase the integration of people from diverse backgrounds into the framework of corporate goals. Organisations should develop productive ways to implement diversity management (DM) policies to establish a creative enterprise that can enhance their operations, goods, and services.
Furthermore, human resource management HRM is a clever tool for any firm to manage resources within the company. As a result, this article explores the link between DM, HR policies, and workers’ creative work-related behaviours in firms in Kurdistan’s Fayoum city. According to the questionnaire, two hypotheses were tested: the influence of HRM on diversity management, HRM on innovation, and the impact of diversity management on innovation.
The first premise is that workplace diversity changes the nature of working relationships, how supervisors and managers connect, and how workers respond to one another. It also addresses human resource functions such as record-keeping, training, recruiting, and employee competence needs. The last premise on the influence of diversity management on innovation is that workplace diversity assists a business in hiring a diverse range of personnel.
In other words, a vibrant population need individuals of varied personalities. Workplace diversity refers to a company’s workforce consisting of employees of various genders, ages, faiths, races, ethnicities, cultural backgrounds, religions, dialects, training, capabilities, etc. According to the study’s findings, human resource management strategies have a substantial influence on diversity management.
Second, diversity management was found to have a considerable impact on creativity. Finally, human resource management techniques influenced innovation significantly. Based on the findings, it was discovered that diversity management had a more significant influence on creation than human resource management.
Lastly, according to Li et al. (2021), the universal trend of rising workplace age diversity has increased the study focus on the organisational effects of age-diverse workforces. Prior research has mainly concentrated on the statistical association between age diversity and organisational success rather than experimentally examining the probable processes behind this relationship.
They argue that age diversity influences organisational performance through human and social capital using an intellectual capital paradigm. Moreover, they investigate workplace functional diversity and age-inclusive management as two confounding factors affecting the benefits of age diversity on physical and human capital.
Their hypotheses were evaluated using data from the Association for Human Resource Management’s major manager-reported workplace survey. Age diversity was favourably linked with organisational performance via the mediation of higher human and social capital. Furthermore, functional diversity and age-inclusive management exacerbated the favourable benefits of age variety on human and social capital. Their study gives insight into how age-diverse workforces might generate value by nurturing knowledge-based organisational resources.
Research Gap/ Contribution
Although there is a vast body of research in diversity in the human resource management area, many researchers explored various dimensions. But no study explicitly discovers the impact of organisational culture on human resource diversification. Moreover, no researchers examined the scope of impression management in this context.
Therefore, this research will fill this considerable literature gap by finding the direct impact of organisational structure on human resource diversification. Secondly, by introducing a new dimension of impression management theory. It will open new avenues for research in this area, and it will help HR managers to formulate better policies for a more inclusive organisational structure.
Research Methodology
It will be mixed quantitative and qualitative research based on the secondary data collected through different research journals and case studies of various companies. Firstly, the quantitative analysis will be conducted through a regression analysis to show the organisational structure’s impact on human resource diversification.
The dummy variable will be used to show organisational structure, and diversification will be captured through the ethnic backgrounds of the employees. Moreover, different variables will be added to the model, such as competency, social inclusion, etc. It will fulfil the objective of identifying various factors which affect the management decision to recruit diverse human resources. Secondly, a systematic review of the literature will be conducted for qualitative analysis to add the impression management dimension to the research. Google Scholar, JSTOR, Scopus, etc., will be used to search keywords such as human resource diversity, impression management, and organisation structure.
Research Limitation
Although research offers a comprehensive empirical analysis on the relationship under consideration due to lack of resources, the study is limited to secondary data. It would be better if the research would’ve been conducted on the primary data collected through the organisations. That would’ve captured the actual views of the working professionals. It would’ve increased the validity of the research.
Ali, M., Tawfeq, A., & Dler, S. (2020). Relationship between Diversity Management and Human Resource Management: Their Effects on Employee Innovation in the Organizations. Black Sea Journal of Management and Marketing, 1 (2), 36-44.
AYDIN, E., & ÖZEREN, E. (2018). Rethinking workforce diversity research through critical perspectives: emerging patterns and research agenda. Business & Management Studies: An International Journal, 6 (3), 650-670.
Coad, A., & Guenther, C. (2014). Processes of firm growth and diversification: theory and evidence. Small Business Economics, 43 (4), 857-871.
Cummings, V. (2018). Economic Diversification and Empowerment of Local Human Resources: Could Singapore Be a Model for the GCC Countries?. In. Economic Diversification in the Gulf Region, II , 241-260.
Guillaume, Y., Dawson, J., Otaye‐Ebede, L., Woods, S., & West, M. (2017). Harnessing demographic differences in organizations: What moderates the effects of workplace diversity? Journal of Organizational Behavior, 38 (2), 276-303.
Hayes, T., Oltman, K., Kaylor, L., & Belgudri, A. (2020). How leaders can become more committed to diversity management. Consulting Psychology Journal: Practice and Research, 72 (4), 247.
Li, Y., Gong, Y., Burmeister, A., Wang, M., Alterman, V., Alonso, A., & Robinson, S. (2021). Leveraging age diversity for organizational performance: An intellectual capital perspective. Journal of Applied Psychology, 106 (1), 71.
Seliverstova, Y. (2021). Workforce diversity management: a systematic literature review. Strategic Management, 26 (2), 3-11.
Sippola, A. (2014). Essays on human resource management perspectives on diversity management. Vaasan yliopisto.
Staniec, I., & Zakrzewska-Bielawska, A. (2010). Organizational structure in the view of single business concentration and diversification strategies—empirical study results. Recent advances in management, marketing, finances. WSEAS Press, Penang, Malaysia .
Yadav, S., & Lenka, U. (2020). Diversity management: a systematic review. Equality, Diversity and Inclusion: An International Journal .
Yang, Y., & Konrad, A. (2011). Understanding diversity management practices: Implications of institutional theory and resource-based theory. Group & Organization Management, 36 (1), 6-38.
FAQs About Research Methods for Dissertations
What is the difference between research methodology and research methods.
Research methodology helps you conduct your research in the right direction, validates the results of your research and makes sure that the study you are conducting answers the set research questions.
Research methods are the techniques and procedures used for conducting research. Choosing the right research method for your writing is an important aspect of the research process.
What are the types of research methods?
The types of research methods include:
- Experimental research methods.
- Descriptive research methods
- Historical Research methods
What is a quantitative research method?
Quantitative research is associated with numerical data or data that can be measured. It is used to study a large group of population. The information is gathered by performing statistical, mathematical, or computational techniques.
What is a qualitative research method?
It is a type of scientific research where a researcher collects evidence to seek answers to a question . It is associated with studying human behavior from an informative perspective. It aims at obtaining in-depth details of the problem.

What is meant by mixed methods research?
Mixed methods of research involve:
- There could be more than one stage of research. Depending on the research topic, occasionally, it would be more appropriate to perform qualitative research in the first stage to figure out and investigate a problem to unveil key themes; and conduct quantitative research in stage two of the process for measuring relationships between the themes.
You May Also Like
This post provides the key disadvantages of secondary research so you know the limitations of secondary research before making a decision.
Action research for my dissertation?, A brief overview of action research as a responsive, action-oriented, participative and reflective research technique.
USEFUL LINKS
LEARNING RESOURCES

COMPANY DETAILS

- How It Works
Breadcrumbs Section. Click here to navigate to respective pages.

Dissertation Research Methods
DOI link for Dissertation Research Methods
Get Citation
Dissertation Research Methods: A Step-by-Step Guide to Writing Up Your Research in the Social Sciences focuses specifically on the methodology for planning, writing and submitting your dissertation thesis. Written by two methodology experts in the social sciences, the book provides a step-by-step guide through each stage of the dissertation process.
It covers all aspects of the methodological considerations needed, from choosing a topic or research question, developing a literature review, identifying research gaps, accessing potential study participants, utilizing the right sampling strategies, analyzing data and writing up findings. Readers are introduced to the main research methods normally used in dissertations and their characteristics, and they are guided to choose an appropriate research method for their study, provide a substantial description of the selected method and articulate strong arguments in support of it. The book is filled with templates, exemplars and tools to help students write about methodology in their thesis and to equip readers to successfully troubleshoot any methodology challenges they may face.
This compact book will be of use to all graduate students and their supervisors in the Social Sciences and Education and Behavioural Sciences who are looking for a guide to working with robust and defensible methodological principles in their dissertation research and theses.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Chapter 1 | 8 pages, planning your dissertation, chapter 2 | 24 pages, conducting a literature review and developing a theoretical/conceptual framework, chapter 3 | 14 pages, understanding the types of dissertation research, chapter 4 | 27 pages, choosing an appropriate research methodology, chapter 5 | 11 pages, understanding the seven types of research gaps, chapter 6 | 10 pages, developing the research problem, chapter 7 | 10 pages, developing the purpose statement, chapter 8 | 16 pages, developing the research statement and research questions, chapter 9 | 15 pages, research alignment, chapter 10 | 11 pages, understanding limitations and delimitations, chapter 11 | 12 pages, understanding assumptions and how to write them in a study, chapter 12 | 15 pages, understanding the differences between contributions and the significance of a study, chapter 13 | 13 pages, deciding on the source of data, chapter 14 | 15 pages, understanding the different kinds of data collection strategies, chapter 15 | 36 pages, planning and implementing the data collection process, chapter 16 | 27 pages, understanding populations and sampling, chapter 17 | 32 pages, planning and implementing the data analysis process, chapter 18 | 25 pages, ensuring quality in the study, chapter 19 | 20 pages, writing your dissertation, chapter 20 | 10 pages, chapter 21 | 41 pages, chapter 22 | 29 pages, chapter 23 | 20 pages.
- Privacy Policy
- Terms & Conditions
- Cookie Policy
- Taylor & Francis Online
- Taylor & Francis Group
- Students/Researchers
- Librarians/Institutions
Connect with us
Registered in England & Wales No. 3099067 5 Howick Place | London | SW1P 1WG © 2024 Informa UK Limited
- Thesis Action Plan New
- Academic Project Planner
Literature Navigator
Thesis dialogue blueprint, writing wizard's template, research proposal compass.
- Why students love us
- Rebels Blog
- Why we are different
- All Products
- Coming Soon
How to Start a Research Project: A Step-by-Step Guide

Starting a research project can feel overwhelming, but breaking it down into manageable steps can make it easier. This guide will walk you through each stage, from choosing a topic to preparing for your final presentation. By following these steps, you'll be well on your way to completing a successful research project.
Key Takeaways
- Choose a topic that interests you and is feasible to research.
- Develop clear research questions and objectives to guide your study.
- Conduct a thorough literature review to understand the existing research.
- Create a detailed research plan with a timeline and methodology.
- Engage with stakeholders and incorporate their feedback throughout the project.
Choosing a Research Topic
Identifying research interests.
Start by thinking about what excites you. Pick a topic that you find fun and fulfilling . This will keep you motivated throughout your research. Make a list of subjects you enjoy and see how they can relate to your field of study.
Evaluating Topic Feasibility
Once you have a few ideas, check if they are too broad or too narrow. A good topic should be manageable within the time you have. Ask yourself if you can cover all aspects of the topic in your thesis.
Consulting with Advisors
If you have difficulty finding a topic, consult with your advisors. Present your ideas to them and seek their guidance. They can provide valuable insights and help you refine your topic to ensure it is both engaging and manageable.
Defining the Research Problem
Formulating research questions.
Once you have a topic, the next step is to formulate research questions . These questions should target what you want to find out. They can focus on describing, comparing, evaluating, or explaining the research problem. A strong research question should be specific enough to be answered thoroughly using appropriate methods. Avoid questions that can be answered with a simple "yes" or "no".
Justifying the Research Problem
After formulating your research questions, you need to justify why your research problem is important . Explain the significance of your research in the context of existing literature. Highlight the gaps your research aims to fill and how it will contribute to the field. This step is crucial for crafting a compelling research proposal.
Setting Research Objectives
Finally, set clear research objectives. These are the specific goals you aim to achieve through your research. They should align with your research questions and provide a roadmap for your study. Establishing well-defined objectives will make it easier to create a research plan and stay on track throughout the research process.
Conducting a Comprehensive Literature Review
Finding credible sources.
Start by gathering reliable sources for your research. Use academic databases, libraries, and journals to find books, articles, and papers related to your topic. Make sure to evaluate the credibility of each source. Primary sources like published articles or autobiographies are firsthand accounts, while secondary sources like critical reviews are more removed.
Analyzing Existing Research
Once you have your sources, read through them and take notes on key points. Look for different viewpoints and how they relate to your research question. This will help you understand the current state of research in your field. Skimming sources initially can save time; set aside useful ones for a full read later.
Identifying Research Gaps
Identify areas that haven't been explored or questions that haven't been answered. These gaps can provide a direction for your own research. For example, if you're studying the impact of WhatsApp on communication, look for what hasn't been covered in existing studies. This will make your research more valuable and original.
Developing a Detailed Research Plan
Creating a solid research plan is crucial for the success of your thesis . It helps you stay organized and ensures that you cover all necessary aspects of your research.
Engaging with Stakeholders
Identifying key stakeholders.
To start, you need to identify all the key stakeholders involved in your research project. Stakeholders can include funders, academic supervisors, and anyone who will be affected by your study. Identifying potential resistance early on can help you address concerns before they become major issues.
Conducting Stakeholder Meetings
Once you have identified your stakeholders, the next step is to conduct meetings with them. These meetings are crucial for understanding their needs and expectations. Here are some steps to ensure productive meetings:
- Identify all stakeholders : Make a list of everyone affected by your project, including customers and end users.
- Keep communication open: Regular updates and open discussions help in aligning everyone's expectations.
- Present your project plan: Explain how your plan addresses stakeholders' expectations and be open to feedback.
- Determine roles: Decide who needs to see which reports and how often, and identify which decisions need approval and by whom.
Incorporating Stakeholder Feedback
Engaging stakeholders allows organizations to identify potential sources of resistance early in the change process. Incorporating their feedback is essential for the success of your project. Make sure to document all feedback and adjust your research plan accordingly. This will not only improve the quality of your research but also ensure that all stakeholders are on board with your project.
Selecting Appropriate Research Methods

Qualitative vs Quantitative Methods
When choosing research methods , you need to decide between qualitative and quantitative approaches. Qualitative methods involve collecting non-numerical data, such as interviews and focus groups, to understand experiences and opinions. On the other hand, quantitative methods focus on numerical data and statistical analysis, like surveys and experiments. Sometimes, a mixed-method approach, combining both qualitative and quantitative techniques, can provide a more comprehensive understanding of your research problem.
Choosing Data Collection Tools
Selecting the right data collection tools is crucial for gathering accurate and reliable data. Common tools include:
- Surveys : Useful for collecting data from a large number of participants.
- Interviews : Provide in-depth insights through one-on-one conversations.
- Focus Groups : Gather diverse perspectives through group discussions.
- Observations : Allow you to study behaviors in natural settings.
Each tool has its strengths and weaknesses, so choose the one that best aligns with your research objectives.
Ensuring Ethical Compliance
Ethical compliance is a fundamental aspect of any research project. Make sure to obtain informed consent from all participants and ensure their privacy and confidentiality. Additionally, consider any potential risks to participants and take steps to minimize them. Ethical research not only protects participants but also enhances the credibility of your study.
Implementing the Research Plan

Data Collection Procedures
To start, you need to establish clear data collection procedures . This involves selecting the right tools and methods for gathering data. Whether you choose surveys, interviews, or experiments, ensure that your methods align with your research objectives. It's crucial to define the purpose of your project and identify research objectives before diving into data collection.
Data Analysis Techniques
Once data is collected, the next step is to analyze it. Choose appropriate data analysis techniques that suit your research design. This could involve statistical analysis for quantitative data or thematic analysis for qualitative data. Remember, the goal is to derive meaningful insights that address your research questions.
Maintaining Research Integrity
Maintaining research integrity is essential throughout the implementation phase. This means adhering to ethical guidelines, ensuring data accuracy, and avoiding any form of bias. By maintaining high standards, you ensure the credibility and reliability of your research findings.
Writing the Research Proposal
Structuring the proposal.
Creating a well-structured research proposal is essential for clearly communicating your research plan. Start with an introduction that outlines the background and significance of your study. Follow this with a literature review that situates your research within the existing body of work. Next, detail your research design and methodology, explaining how you will collect and analyze data. Finally, include a timeline and budget if required. A clear structure helps reviewers understand your research plan and its feasibility.
Articulating the Research Statement
Your research statement is the heart of your proposal. It should clearly define the problem you aim to address and why it is important. Make sure your statement is specific, measurable, and achievable. This will guide your entire research process and help you stay focused. A strong research statement is crucial for convincing reviewers of the value of your study.
Defining KPIs and Metrics
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) and metrics are essential for measuring the success of your research. Identify the specific outcomes you aim to achieve and how you will measure them. Common metrics include data accuracy, response rates, and completion times. Including KPIs in your proposal shows that you have a clear plan for evaluating your research's impact.
Managing the Research Project
Setting milestones.
Creating a timeline with specific milestones is essential for tracking your progress. For example, aim to complete your literature review by the end of the first month. These milestones will help you stay on track and make adjustments as needed. Regularly review and update your timeline to reflect your current status and any changes in your schedule.
Tracking Progress
To ensure that you are meeting your milestones, it's important to track your progress consistently. Use tools like Gantt charts or project management software to visualize your progress. Regular check-ins with your team can also help identify any issues early on and keep everyone aligned with the project goals.
Adjusting the Plan as Needed
Flexibility is key in managing a research project. Unexpected challenges may arise, requiring you to adjust your plan. Be prepared to reallocate resources or extend deadlines if necessary. Consulting with your advisors can provide valuable insights and help you make informed decisions when adjustments are needed.
Drafting and Revising the Research Paper
Organizing the paper.
Start by creating a clear structure for your paper. This includes an introduction, body, and conclusion. Use a mind map or outline to group your ideas logically . This will help you stay organized and ensure that your paper flows smoothly.
Revising for Clarity and Coherence
Revising is a crucial part of the writing process. Read your paper out loud to catch any awkward sentences or unclear points. Make sure each paragraph supports your thesis statement and that your ideas are clearly organized. Don't hesitate to remove or revise sections that don't fit.
Maintaining Academic Integrity
Always cite your sources correctly to avoid plagiarism. Use a consistent citation style and double-check your references. This not only upholds academic standards but also enhances the credibility of your work.
Preparing for the Final Presentation
Creating visual aids.
Visual aids are essential for making your presentation engaging and easy to follow. Use slides, charts, and graphs to highlight key points . Ensure that your visuals are clear and not cluttered with too much information. Effective visual aids can make complex data more understandable and keep your audience engaged.
Practicing the Presentation
Practice is crucial for a successful presentation. Rehearse multiple times to get comfortable with the material and the flow of your talk. Consider practicing in front of friends or family to get feedback. This will help you refine your delivery and timing. Remember, the goal is to communicate your research clearly and confidently.
Handling Q&A Sessions
Anticipate questions that your audience might ask and prepare answers in advance. This will help you handle the Q&A session smoothly. Be honest if you don't know an answer and offer to follow up later. Handling questions well can demonstrate your deep understanding of the topic and leave a positive impression on your audience.
Getting ready for your final presentation can be nerve-wracking, but it doesn't have to be. Start by organizing your main points and practicing your delivery. Remember, confidence comes from preparation. For more tips and a step-by-step guide to ace your presentation, visit our website today !
Starting a research project may seem daunting, but breaking it down into manageable steps can make the process much more approachable. By clearly defining your research subject, engaging with stakeholders, crafting a precise research statement, and establishing key performance indicators, you set a strong foundation for your project. Choosing the right methodology and creating a detailed timeline will help ensure that your research is well-organized and on track. Remember, the key to a successful research project is thorough planning and consistent effort. With these steps, you can confidently navigate your research journey and achieve meaningful results.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do i choose a good research topic.
Start by thinking about what interests you. Pick a topic that you find fun and fulfilling. This will keep you motivated throughout your research. Make a list of subjects you enjoy and see how they can relate to your field of study.
What should I include in the introduction of my research paper?
Your introduction should set the stage for your research. Provide some background information and clearly state what your research will cover. This helps readers understand the context and significance of your work.
How do I create a timeline for my research project?
Break down your research into smaller tasks and assign time frames to each. This helps you manage your time and stay organized throughout the project. Use a table or chart to keep track of deadlines.
What is the best way to organize my research data?
Review the data you have and reorganize it so that the most important parts are central to your research. Set aside any information that is less relevant. Use digital folders or reference management software to keep everything organized.
How do I choose a thesis supervisor?
Look for a supervisor who is supportive and knowledgeable in your area of study. Good communication is key, so make sure you establish a good rapport with them from the start.
Where should I place my thesis statement?
A good place for your thesis statement is at the end of your introduction. This helps to clearly outline your main argument or point right from the start.
What should I do if I feel stuck during my research project?
If you feel stuck, take a break and revisit your work with fresh eyes. Talk to your advisor or peers for new perspectives. Sometimes, stepping away for a bit can help you see things more clearly.
How do I ensure my research is ethical?
Make sure your research complies with ethical guidelines. This includes getting consent from participants, ensuring their privacy, and being honest about your findings. Consult your institution's ethics board if you have questions.

Discovering Statistics Using IBM SPSS Statistics: A Fun and Informative Guide

Unlocking the Power of Data: A Review of 'Essentials of Modern Business Statistics with Microsoft Excel'

Discovering Statistics Using SAS: A Comprehensive Review

Trending Topics for Your Thesis: What's Hot in 2024

How to Deal with a Total Lack of Motivation, Stress, and Anxiety When Finishing Your Master's Thesis

Mastering the First Step: How to Start Your Thesis with Confidence

Thesis Action Plan

Thesis Revision Made Simple: Techniques for Perfecting Your Academic Work
Integrating calm into your study routine: the power of mindfulness in education.
- Blog Articles
- Affiliate Program
- Terms and Conditions
- Payment and Shipping Terms
- Privacy Policy
- Return Policy
© 2024 Research Rebels, All rights reserved.
Your cart is currently empty.

Online Students
For All Online Programs
International Students
On Campus, need or have Visa
Campus Students
For All Campus Programs
What a Thesis Paper is and How to Write One

From choosing a topic and conducting research to crafting a strong argument, writing a thesis paper can be a rewarding experience.
It can also be a challenging experience. If you've never written a thesis paper before, you may not know where to start. You may not even be sure exactly what a thesis paper is. But don't worry; the right support and resources can help you navigate this writing process.
What is a Thesis Paper?

A thesis paper is a type of academic essay that you might write as a graduation requirement for certain bachelor's, master's or honors programs. Thesis papers present your own original research or analysis on a specific topic related to your field.
“In some ways, a thesis paper can look a lot like a novella,” said Shana Chartier , director of information literacy at Southern New Hampshire University (SNHU). “It’s too short to be a full-length novel, but with the standard size of 40-60 pages (for a bachelor’s) and 60-100 pages (for a master’s), it is a robust exploration of a topic, explaining one’s understanding of a topic based on personal research.”
Chartier has worked in academia for over 13 years and at SNHU for nearly eight. In her role as an instructor and director, Chartier has helped to guide students through the writing process, like editing and providing resources.
Chartier has written and published academic papers such as "Augmented Reality Gamifies the Library: A Ride Through the Technological Frontier" and "Going Beyond the One-Shot: Spiraling Information Literacy Across Four Years." Both of these academic papers required Chartier to have hands-on experience with the subject matter. Like a thesis paper, they also involved hypothesizing and doing original research to come to a conclusion.
“When writing a thesis paper, the importance of staying organized cannot be overstated,” said Chartier. “Mapping out each step of the way, making firm and soft deadlines... and having other pairs of eyes on your work to ensure academic accuracy and clean editing are crucial to writing a successful paper.”
How Do I Choose a Topic For My Thesis Paper?

What your thesis paper is for will determine some of the specific requirements and steps you might take, but the first step is usually the same: Choosing a topic.
“Choosing a topic can be daunting," said Rochelle Attari , a peer tutor at SNHU. "But if (you) stick with a subject (you're) interested in... choosing a topic is much more manageable.”
Similar to a thesis, Attari recently finished the capstone for her bachelor’s in psychology . Her bachelor’s concentration is in forensics, and her capstone focused on the topic of using a combined therapy model for inmates who experience substance abuse issues to reduce recidivism.
“The hardest part was deciding what I wanted to focus on,” Attari said. “But once I nailed down my topic, each milestone was more straightforward.”
In her own writing experience, Attari said brainstorming was an important step when choosing her topic. She recommends writing down different ideas on a piece of paper and doing some preliminary research on what’s already been written on your topic.
By doing this exercise, you can narrow or broaden your ideas until you’ve found a topic you’re excited about. " Brainstorming is essential when writing a paper and is not a last-minute activity,” Attari said.
How Do I Structure My Thesis Paper?
Thesis papers tend to have a standard format with common sections as the building blocks.
While the structure Attari describes below will work for many theses, it’s important to double-check with your program to see if there are any specific requirements. Writing a thesis for a Master of Fine Arts, for example, might actually look more like a fiction novel.
According to Attari, a thesis paper is often structured with the following major sections:
Introduction
- Literature review
- Methods, results
Now, let’s take a closer look at what each different section should include.
Your introduction is your opportunity to present the topic of your thesis paper. In this section, you can explain why that topic is important. The introduction is also the place to include your thesis statement, which shows your stance in the paper.
Attari said that writing an introduction can be tricky, especially when you're trying to capture your reader’s attention and state your argument.
“I have found that starting with a statement of truth about a topic that pertains to an issue I am writing about typically does the trick,” Attari said. She demonstrated this advice in an example introduction she wrote for a paper on the effects of daylight in Alaska:
In the continental United States, we can always count on the sun rising and setting around the same time each day, but in Alaska, during certain times of the year, the sun rises and does not set for weeks. Research has shown that the sun provides vitamin D and is an essential part of our health, but little is known about how daylight twenty-four hours a day affects the circadian rhythm and sleep.
In the example Attari wrote, she introduces the topic and informs the reader what the paper will cover. Somewhere in her intro, she said she would also include her thesis statement, which might be:
Twenty-four hours of daylight over an extended period does not affect sleep patterns in humans and is not the cause of daytime fatigue in northern Alaska .
Literature Review
In the literature review, you'll look at what information is already out there about your topic. “This is where scholarly articles about your topic are essential,” said Attari. “These articles will help you find the gap in research that you have identified and will also support your thesis statement."
Telling your reader what research has already been done will help them see how your research fits into the larger conversation. Most university libraries offer databases of scholarly/peer-reviewed articles that can be helpful in your search.
In the methods section of your thesis paper, you get to explain how you learned what you learned. This might include what experiment you conducted as a part of your independent research.
“For instance,” Attari said, “if you are a psychology major and have identified a gap in research on which therapies are effective for anxiety, your methods section would consist of the number of participants, the type of experiment and any other particulars you would use for that experiment.”
In this section, you'll explain the results of your study. For example, building on the psychology example Attari outlined, you might share self-reported anxiety levels for participants trying different kinds of therapies. To help you communicate your results clearly, you might include data, charts, tables or other visualizations.
The discussion section of your thesis paper is where you will analyze and interpret the results you presented in the previous section. This is where you can discuss what your findings really mean or compare them to the research you found in your literature review.
The discussion section is your chance to show why the data you collected matters and how it fits into bigger conversations in your field.
The conclusion of your thesis paper is your opportunity to sum up your argument and leave your reader thinking about why your research matters.
Attari breaks the conclusion down into simple parts. “You restate the original issue and thesis statement, explain the experiment's results and discuss possible next steps for further research,” she said.
Find Your Program
Resources to help write your thesis paper.
While your thesis paper may be based on your independent research, writing it doesn’t have to be a solitary process. Asking for help and using the resources that are available to you can make the process easier.
If you're writing a thesis paper, some resources Chartier encourages you to use are:
- Citation Handbooks: An online citation guide or handbook can help you ensure your citations are correct. APA , MLA and Chicago styles have all published their own guides.
- Citation Generators: There are many citation generator tools that help you to create citations. Some — like RefWorks — even let you directly import citations from library databases as you research.
- Your Library's Website: Many academic and public libraries allow patrons to access resources like databases or FAQs. Some FAQs at the SNHU library that might be helpful in your thesis writing process include “ How do I read a scholarly article? ” or “ What is a research question and how do I develop one? ”
It can also be helpful to check out what coaching or tutoring options are available through your school. At SNHU, for example, the Academic Support Center offers writing and grammar workshops , and students can access 24/7 tutoring and 1:1 sessions with peer tutors, like Attari.
"Students can even submit their papers and receive written feedback... like revisions and editing suggestions," she said.
If you are writing a thesis paper, there are many resources available to you. It's a long paper, but with the right mindset and support, you can successfully navigate the process.
“Pace yourself,” said Chartier. “This is a marathon, not a sprint. Setting smaller goals to get to the big finish line can make the process seem less daunting, and remember to be proud of yourself and celebrate your accomplishment once you’re done. Writing a thesis is no small task, and it’s important work for the scholarly community.”
A degree can change your life. Choose your program from 200+ SNHU degrees that can take you where you want to go.
Meg Palmer ’18 is a writer and scholar by trade who loves reading, riding her bike and singing in a barbershop quartet. She earned her bachelor’s degree in English, language and literature at Southern New Hampshire University (SNHU) and her master’s degree in writing, rhetoric and discourse at DePaul University (’20). While attending SNHU, she served as the editor-in-chief of the campus student newspaper, The Penmen Press, where she deepened her passion for writing. Meg is an adjunct professor at Johnson and Wales University, where she teaches first year writing, honors composition, and public speaking. Connect with her on LinkedIn .
Explore more content like this article

What is the Difference Between Bachelor’s and Master’s Degrees?

Academic Referencing: How to Cite a Research Paper

What is Considered Plagiarism And How to Avoid It
About southern new hampshire university.

SNHU is a nonprofit, accredited university with a mission to make high-quality education more accessible and affordable for everyone.
Founded in 1932, and online since 1995, we’ve helped countless students reach their goals with flexible, career-focused programs . Our 300-acre campus in Manchester, NH is home to over 3,000 students, and we serve over 135,000 students online. Visit our about SNHU page to learn more about our mission, accreditations, leadership team, national recognitions and awards.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Methodology
- What Is a Research Design | Types, Guide & Examples
What Is a Research Design | Types, Guide & Examples
Published on June 7, 2021 by Shona McCombes . Revised on November 20, 2023 by Pritha Bhandari.
A research design is a strategy for answering your research question using empirical data. Creating a research design means making decisions about:
- Your overall research objectives and approach
- Whether you’ll rely on primary research or secondary research
- Your sampling methods or criteria for selecting subjects
- Your data collection methods
- The procedures you’ll follow to collect data
- Your data analysis methods
A well-planned research design helps ensure that your methods match your research objectives and that you use the right kind of analysis for your data.
Table of contents
Step 1: consider your aims and approach, step 2: choose a type of research design, step 3: identify your population and sampling method, step 4: choose your data collection methods, step 5: plan your data collection procedures, step 6: decide on your data analysis strategies, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about research design.
- Introduction
Before you can start designing your research, you should already have a clear idea of the research question you want to investigate.
There are many different ways you could go about answering this question. Your research design choices should be driven by your aims and priorities—start by thinking carefully about what you want to achieve.
The first choice you need to make is whether you’ll take a qualitative or quantitative approach.
| Qualitative approach | Quantitative approach |
|---|---|
| and describe frequencies, averages, and correlations about relationships between variables |
Qualitative research designs tend to be more flexible and inductive , allowing you to adjust your approach based on what you find throughout the research process.
Quantitative research designs tend to be more fixed and deductive , with variables and hypotheses clearly defined in advance of data collection.
It’s also possible to use a mixed-methods design that integrates aspects of both approaches. By combining qualitative and quantitative insights, you can gain a more complete picture of the problem you’re studying and strengthen the credibility of your conclusions.
Practical and ethical considerations when designing research
As well as scientific considerations, you need to think practically when designing your research. If your research involves people or animals, you also need to consider research ethics .
- How much time do you have to collect data and write up the research?
- Will you be able to gain access to the data you need (e.g., by travelling to a specific location or contacting specific people)?
- Do you have the necessary research skills (e.g., statistical analysis or interview techniques)?
- Will you need ethical approval ?
At each stage of the research design process, make sure that your choices are practically feasible.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

Within both qualitative and quantitative approaches, there are several types of research design to choose from. Each type provides a framework for the overall shape of your research.
Types of quantitative research designs
Quantitative designs can be split into four main types.
- Experimental and quasi-experimental designs allow you to test cause-and-effect relationships
- Descriptive and correlational designs allow you to measure variables and describe relationships between them.
| Type of design | Purpose and characteristics |
|---|---|
| Experimental | relationships effect on a |
| Quasi-experimental | ) |
| Correlational | |
| Descriptive |
With descriptive and correlational designs, you can get a clear picture of characteristics, trends and relationships as they exist in the real world. However, you can’t draw conclusions about cause and effect (because correlation doesn’t imply causation ).
Experiments are the strongest way to test cause-and-effect relationships without the risk of other variables influencing the results. However, their controlled conditions may not always reflect how things work in the real world. They’re often also more difficult and expensive to implement.
Types of qualitative research designs
Qualitative designs are less strictly defined. This approach is about gaining a rich, detailed understanding of a specific context or phenomenon, and you can often be more creative and flexible in designing your research.
The table below shows some common types of qualitative design. They often have similar approaches in terms of data collection, but focus on different aspects when analyzing the data.
| Type of design | Purpose and characteristics |
|---|---|
| Grounded theory | |
| Phenomenology |
Your research design should clearly define who or what your research will focus on, and how you’ll go about choosing your participants or subjects.
In research, a population is the entire group that you want to draw conclusions about, while a sample is the smaller group of individuals you’ll actually collect data from.
Defining the population
A population can be made up of anything you want to study—plants, animals, organizations, texts, countries, etc. In the social sciences, it most often refers to a group of people.
For example, will you focus on people from a specific demographic, region or background? Are you interested in people with a certain job or medical condition, or users of a particular product?
The more precisely you define your population, the easier it will be to gather a representative sample.
- Sampling methods
Even with a narrowly defined population, it’s rarely possible to collect data from every individual. Instead, you’ll collect data from a sample.
To select a sample, there are two main approaches: probability sampling and non-probability sampling . The sampling method you use affects how confidently you can generalize your results to the population as a whole.
| Probability sampling | Non-probability sampling |
|---|---|
Probability sampling is the most statistically valid option, but it’s often difficult to achieve unless you’re dealing with a very small and accessible population.
For practical reasons, many studies use non-probability sampling, but it’s important to be aware of the limitations and carefully consider potential biases. You should always make an effort to gather a sample that’s as representative as possible of the population.
Case selection in qualitative research
In some types of qualitative designs, sampling may not be relevant.
For example, in an ethnography or a case study , your aim is to deeply understand a specific context, not to generalize to a population. Instead of sampling, you may simply aim to collect as much data as possible about the context you are studying.
In these types of design, you still have to carefully consider your choice of case or community. You should have a clear rationale for why this particular case is suitable for answering your research question .
For example, you might choose a case study that reveals an unusual or neglected aspect of your research problem, or you might choose several very similar or very different cases in order to compare them.
Data collection methods are ways of directly measuring variables and gathering information. They allow you to gain first-hand knowledge and original insights into your research problem.
You can choose just one data collection method, or use several methods in the same study.
Survey methods
Surveys allow you to collect data about opinions, behaviors, experiences, and characteristics by asking people directly. There are two main survey methods to choose from: questionnaires and interviews .
| Questionnaires | Interviews |
|---|---|
| ) |
Observation methods
Observational studies allow you to collect data unobtrusively, observing characteristics, behaviors or social interactions without relying on self-reporting.
Observations may be conducted in real time, taking notes as you observe, or you might make audiovisual recordings for later analysis. They can be qualitative or quantitative.
| Quantitative observation | |
|---|---|
Other methods of data collection
There are many other ways you might collect data depending on your field and topic.
| Field | Examples of data collection methods |
|---|---|
| Media & communication | Collecting a sample of texts (e.g., speeches, articles, or social media posts) for data on cultural norms and narratives |
| Psychology | Using technologies like neuroimaging, eye-tracking, or computer-based tasks to collect data on things like attention, emotional response, or reaction time |
| Education | Using tests or assignments to collect data on knowledge and skills |
| Physical sciences | Using scientific instruments to collect data on things like weight, blood pressure, or chemical composition |
If you’re not sure which methods will work best for your research design, try reading some papers in your field to see what kinds of data collection methods they used.
Secondary data
If you don’t have the time or resources to collect data from the population you’re interested in, you can also choose to use secondary data that other researchers already collected—for example, datasets from government surveys or previous studies on your topic.
With this raw data, you can do your own analysis to answer new research questions that weren’t addressed by the original study.
Using secondary data can expand the scope of your research, as you may be able to access much larger and more varied samples than you could collect yourself.
However, it also means you don’t have any control over which variables to measure or how to measure them, so the conclusions you can draw may be limited.
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
As well as deciding on your methods, you need to plan exactly how you’ll use these methods to collect data that’s consistent, accurate, and unbiased.
Planning systematic procedures is especially important in quantitative research, where you need to precisely define your variables and ensure your measurements are high in reliability and validity.
Operationalization
Some variables, like height or age, are easily measured. But often you’ll be dealing with more abstract concepts, like satisfaction, anxiety, or competence. Operationalization means turning these fuzzy ideas into measurable indicators.
If you’re using observations , which events or actions will you count?
If you’re using surveys , which questions will you ask and what range of responses will be offered?
You may also choose to use or adapt existing materials designed to measure the concept you’re interested in—for example, questionnaires or inventories whose reliability and validity has already been established.
Reliability and validity
Reliability means your results can be consistently reproduced, while validity means that you’re actually measuring the concept you’re interested in.
| Reliability | Validity |
|---|---|
| ) ) |
For valid and reliable results, your measurement materials should be thoroughly researched and carefully designed. Plan your procedures to make sure you carry out the same steps in the same way for each participant.
If you’re developing a new questionnaire or other instrument to measure a specific concept, running a pilot study allows you to check its validity and reliability in advance.
Sampling procedures
As well as choosing an appropriate sampling method , you need a concrete plan for how you’ll actually contact and recruit your selected sample.
That means making decisions about things like:
- How many participants do you need for an adequate sample size?
- What inclusion and exclusion criteria will you use to identify eligible participants?
- How will you contact your sample—by mail, online, by phone, or in person?
If you’re using a probability sampling method , it’s important that everyone who is randomly selected actually participates in the study. How will you ensure a high response rate?
If you’re using a non-probability method , how will you avoid research bias and ensure a representative sample?
Data management
It’s also important to create a data management plan for organizing and storing your data.
Will you need to transcribe interviews or perform data entry for observations? You should anonymize and safeguard any sensitive data, and make sure it’s backed up regularly.
Keeping your data well-organized will save time when it comes to analyzing it. It can also help other researchers validate and add to your findings (high replicability ).
On its own, raw data can’t answer your research question. The last step of designing your research is planning how you’ll analyze the data.
Quantitative data analysis
In quantitative research, you’ll most likely use some form of statistical analysis . With statistics, you can summarize your sample data, make estimates, and test hypotheses.
Using descriptive statistics , you can summarize your sample data in terms of:
- The distribution of the data (e.g., the frequency of each score on a test)
- The central tendency of the data (e.g., the mean to describe the average score)
- The variability of the data (e.g., the standard deviation to describe how spread out the scores are)
The specific calculations you can do depend on the level of measurement of your variables.
Using inferential statistics , you can:
- Make estimates about the population based on your sample data.
- Test hypotheses about a relationship between variables.
Regression and correlation tests look for associations between two or more variables, while comparison tests (such as t tests and ANOVAs ) look for differences in the outcomes of different groups.
Your choice of statistical test depends on various aspects of your research design, including the types of variables you’re dealing with and the distribution of your data.
Qualitative data analysis
In qualitative research, your data will usually be very dense with information and ideas. Instead of summing it up in numbers, you’ll need to comb through the data in detail, interpret its meanings, identify patterns, and extract the parts that are most relevant to your research question.
Two of the most common approaches to doing this are thematic analysis and discourse analysis .
| Approach | Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Thematic analysis | |
| Discourse analysis |
There are many other ways of analyzing qualitative data depending on the aims of your research. To get a sense of potential approaches, try reading some qualitative research papers in your field.
If you want to know more about the research process , methodology , research bias , or statistics , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Simple random sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Cluster sampling
- Likert scales
- Reproducibility
Statistics
- Null hypothesis
- Statistical power
- Probability distribution
- Effect size
- Poisson distribution
Research bias
- Optimism bias
- Cognitive bias
- Implicit bias
- Hawthorne effect
- Anchoring bias
- Explicit bias
A research design is a strategy for answering your research question . It defines your overall approach and determines how you will collect and analyze data.
A well-planned research design helps ensure that your methods match your research aims, that you collect high-quality data, and that you use the right kind of analysis to answer your questions, utilizing credible sources . This allows you to draw valid , trustworthy conclusions.
Quantitative research designs can be divided into two main categories:
- Correlational and descriptive designs are used to investigate characteristics, averages, trends, and associations between variables.
- Experimental and quasi-experimental designs are used to test causal relationships .
Qualitative research designs tend to be more flexible. Common types of qualitative design include case study , ethnography , and grounded theory designs.
The priorities of a research design can vary depending on the field, but you usually have to specify:
- Your research questions and/or hypotheses
- Your overall approach (e.g., qualitative or quantitative )
- The type of design you’re using (e.g., a survey , experiment , or case study )
- Your data collection methods (e.g., questionnaires , observations)
- Your data collection procedures (e.g., operationalization , timing and data management)
- Your data analysis methods (e.g., statistical tests or thematic analysis )
A sample is a subset of individuals from a larger population . Sampling means selecting the group that you will actually collect data from in your research. For example, if you are researching the opinions of students in your university, you could survey a sample of 100 students.
In statistics, sampling allows you to test a hypothesis about the characteristics of a population.
Operationalization means turning abstract conceptual ideas into measurable observations.
For example, the concept of social anxiety isn’t directly observable, but it can be operationally defined in terms of self-rating scores, behavioral avoidance of crowded places, or physical anxiety symptoms in social situations.
Before collecting data , it’s important to consider how you will operationalize the variables that you want to measure.
A research project is an academic, scientific, or professional undertaking to answer a research question . Research projects can take many forms, such as qualitative or quantitative , descriptive , longitudinal , experimental , or correlational . What kind of research approach you choose will depend on your topic.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, November 20). What Is a Research Design | Types, Guide & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved September 3, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/methodology/research-design/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, guide to experimental design | overview, steps, & examples, how to write a research proposal | examples & templates, ethical considerations in research | types & examples, what is your plagiarism score.

Home > Blog >
Data analysis in qualitative research, theertha raj, august 30, 2024.
While numbers tell us "what" and "how much," qualitative data reveals the crucial "why" and "how." But let's face it - turning mountains of text, images, and observations into meaningful insights can be daunting.
This guide dives deep into the art and science of how to analyze qualitative data. We'll explore cutting-edge techniques, free qualitative data analysis software, and strategies to make your analysis more rigorous and insightful. Expect practical, actionable advice on qualitative data analysis methods, whether you're a seasoned researcher looking to refine your skills or a team leader aiming to extract more value from your qualitative data.
What is qualitative data?
Qualitative data is non-numerical information that describes qualities or characteristics. It includes text, images, audio, and video.
This data type captures complex human experiences, behaviors, and opinions that numbers alone can't express.
A qualitative data example can include interview transcripts, open-ended survey responses, field notes from observations, social media posts and customer reviews
Importance of qualitative data
Qualitative data is vital for several reasons:
- It provides a deep, nuanced understanding of complex phenomena.
- It captures the 'why' behind behaviors and opinions.
- It allows for unexpected discoveries and new research directions.
- It puts people's experiences and perspectives at the forefront.
- It enhances quantitative findings with depth and detail.
What is data analysis in qualitative research?
Data analysis in qualitative research is the process of examining and interpreting non-numerical data to uncover patterns, themes, and insights. It aims to make sense of rich, detailed information gathered through methods like interviews, focus groups, or observations.
This analysis moves beyond simple description. It seeks to understand the underlying meanings, contexts, and relationships within the data. The goal is to create a coherent narrative that answers research questions and generates new knowledge.
How is qualitative data analysis different from quantitative data analysis?
Qualitative and quantitative data analyses differ in several key ways:
- Data type: Qualitative analysis uses non-numerical data (text, images), while quantitative analysis uses numerical data.
- Approach: Qualitative analysis is inductive and exploratory. Quantitative analysis is deductive and confirmatory.
- Sample size: Qualitative studies often use smaller samples. Quantitative studies typically need larger samples for statistical validity.
- Depth vs. breadth: Qualitative analysis provides in-depth insights about a few cases. Quantitative analysis offers broader insights across many cases.
- Subjectivity: Qualitative analysis involves more subjective interpretation. Quantitative analysis aims for objective, statistical measures.
What are the 3 main components of qualitative data analysis?
The three main components of qualitative data analysis are:
- Data reduction: Simplifying and focusing the raw data through coding and categorization.
- Data display: Organizing the reduced data into visual formats like matrices, charts, or networks.
- Conclusion drawing/verification: Interpreting the displayed data and verifying the conclusions.
These components aren't linear steps. Instead, they form an iterative process where researchers move back and forth between them throughout the analysis.
How do you write a qualitative analysis?
Step 1: organize your data.
Start with bringing all your qualitative research data in one place. A repository can be of immense help here. Transcribe interviews , compile field notes, and gather all relevant materials.
Immerse yourself in the data. Read through everything multiple times.
Step 2: Code & identify themes
Identify and label key concepts, themes, or patterns. Group related codes into broader themes or categories. Try to connect themes to tell a coherent story that answers your research questions.
Pick out direct quotes from your data to illustrate key points.
Step 3: Interpret and reflect
Explain what your results mean in the context of your research and existing literature.
Als discuss, identify and try to eliminate potential biases or limitations in your analysis.
Summarize main insights and their implications.
What are the 5 qualitative data analysis methods?
Thematic Analysis Identifying, analyzing, and reporting patterns (themes) within data.
Content Analysis Systematically categorizing and counting the occurrence of specific elements in text.
Grounded Theory Developing theory from data through iterative coding and analysis.
Discourse Analysis Examining language use and meaning in social contexts.
Narrative Analysis Interpreting stories and personal accounts to understand experiences and meanings.
Each method suits different research goals and data types. Researchers often combine methods for comprehensive analysis.
What are the 4 data collection methods in qualitative research?
When it comes to collecting qualitative data, researchers primarily rely on four methods.
- Interviews : One-on-one conversations to gather in-depth information.
- Focus Groups : Group discussions to explore collective opinions and experiences.
- Observations : Watching and recording behaviors in natural settings.
- Document Analysis : Examining existing texts, images, or artifacts.
Researchers often use multiple methods to gain a comprehensive understanding of their topic.
How is qualitative data analysis measured?
Unlike quantitative data, qualitative data analysis isn't measured in traditional numerical terms. Instead, its quality is evaluated based on several criteria.
Trustworthiness is key, encompassing the credibility, transferability, dependability, and confirmability of the findings. The rigor of the analysis - the thoroughness and care taken in data collection and analysis - is another crucial factor.
Transparency in documenting the analysis process and decision-making is essential, as is reflexivity - acknowledging and examining the researcher's own biases and influences.
Employing techniques like member checking and triangulation all contribute to the strength of qualitative analysis.
Benefits of qualitative data analysis
The benefits of qualitative data analysis are numerous. It uncovers rich, nuanced understanding of complex phenomena and allows for unexpected discoveries and new research directions.
By capturing the 'why' behind behaviors and opinions, qualitative data analysis methods provide crucial context.
Qualitative analysis can also lead to new theoretical frameworks or hypotheses and enhances quantitative findings with depth and detail. It's particularly adept at capturing cultural nuances that might be missed in quantitative studies.
Challenges of Qualitative Data Analysis
Researchers face several challenges when conducting qualitative data analysis.
Managing and making sense of large volumes of rich, complex data can lead to data overload. Maintaining consistent coding across large datasets or between multiple coders can be difficult.
There's a delicate balance to strike between providing enough context and maintaining focus on analysis. Recognizing and mitigating researcher biases in data interpretation is an ongoing challenge.
The learning curve for qualitative data analysis software can be steep and time-consuming. Ethical considerations, particularly around protecting participant anonymity while presenting rich, detailed data, require careful navigation. Integrating different types of data from various sources can be complex. Time management is crucial, as researchers must balance the depth of analysis with project timelines and resources. Finally, communicating complex qualitative insights in clear, compelling ways can be challenging.
Best Software to Analyze Qualitative Data
G2 rating: 4.6/5
Pricing: Starts at $30 monthly.
Looppanel is an AI-powered research assistant and repository platform that can make it 5x faster to get to insights, by automating all the manual, tedious parts of your job.
Here’s how Looppanel’s features can help with qualitative data analysis:
- Automatic Transcription: Quickly turn speech into accurate text; it works across 8 languages and even heavy accents, with over 90% accuracy.
- AI Note-Taking: The research assistant can join you on calls and take notes, as well as automatically sort your notes based on your interview questions.
- Automatic Tagging: Easily tag and organize your data with free AI tools.
- Insight Generation: Create shareable insights that fit right into your other tools.
- Repository Search: Run Google-like searches within your projects and calls to find a data snippet/quote in seconds
- Smart Summary: Ask the AI a question on your research, and it will give you an answer, using extracts from your data as citations.
Looppanel’s focus on automating research tasks makes it perfect for researchers who want to save time and work smarter.
G2 rating: 4.7/5
Pricing: Free version available, with the Plus version costing $20 monthly.
ChatGPT, developed by OpenAI, offers a range of capabilities for qualitative data analysis including:
- Document analysis : It can easily extract and analyze text from various file formats.
- Summarization : GPT can condense lengthy documents into concise summaries.
- Advanced Data Analysis (ADA) : For paid users, Chat-GPT offers quantitative analysis of data documents.
- Sentiment analysis: Although not Chat-GPT’s specialty, it can still perform basic sentiment analysis on text data.
ChatGPT's versatility makes it valuable for researchers who need quick insights from diverse text sources.
How to use ChatGPT for qualitative data analysis
ChatGPT can be a handy sidekick in your qualitative analysis, if you do the following:
- Use it to summarize long documents or transcripts
- Ask it to identify key themes in your data
- Use it for basic sentiment analysis
- Have it generate potential codes based on your research questions
- Use it to brainstorm interpretations of your findings
G2 rating: 4.7/5 Pricing: Custom
Atlas.ti is a powerful platform built for detailed qualitative and mixed-methods research, offering a lot of capabilities for running both quantitative and qualitative research.
It’s key data analysis features include:
- Multi-format Support: Analyze text, PDFs, images, audio, video, and geo data all within one platform.
- AI-Powered Coding: Uses AI to suggest codes and summarize documents.
- Collaboration Tools: Ideal for teams working on complex research projects.
- Data Visualization: Create network views and other visualizations to showcase relationships in your data.
G2 rating: 4.1/5 Pricing: Custom
NVivo is another powerful platform for qualitative and mixed-methods research. It’s analysis features include:
- Data Import and Organization: Easily manage different data types, including text, audio, and video.
- AI-Powered Coding: Speeds up the coding process with machine learning.
- Visualization Tools: Create charts, graphs, and diagrams to represent your findings.
- Collaboration Features: Suitable for team-based research projects.
NVivo combines AI capabilities with traditional qualitative analysis tools, making it versatile for various research needs.
Can Excel do qualitative data analysis?
Excel can be a handy tool for qualitative data analysis, especially if you're just starting out or working on a smaller project. While it's not specialized qualitative data analysis software, you can use it to organize your data, maybe putting different themes in different columns. It's good for basic coding, where you label bits of text with keywords. You can use its filter feature to focus on specific themes. Excel can also create simple charts to visualize your findings. But for bigger or more complex projects, you might want to look into software designed specifically for qualitative data analysis. These tools often have more advanced features that can save you time and help you dig deeper into your data.
How do you show qualitative analysis?
Showing qualitative data analysis is about telling the story of your data. In qualitative data analysis methods, we use quotes from interviews or documents to back up our points. Create charts or mind maps to show how different ideas connect, which is a common practice in data analysis in qualitative research. Group your findings into themes that make sense. Then, write it all up in a way that flows, explaining what you found and why it matters.
What is the best way to analyze qualitative data?
There's no one-size-fits-all approach to how to analyze qualitative data, but there are some tried-and-true steps.
Start by getting your data in order. Then, read through it a few times to get familiar with it. As you go, start marking important bits with codes - this is a fundamental qualitative data analysis method. Group similar codes into bigger themes. Look for patterns in these themes - how do they connect?
Finally, think about what it all means in the bigger picture of your research. Remember, it's okay to go back and forth between these steps as you dig deeper into your data. Qualitative data analysis software can be a big help in this process, especially for managing large amounts of data.
In qualitative methods of test analysis, what do test developers do to generate data?
Test developers in qualitative research might sit down with people for in-depth chats or run group discussions, which are key qualitative data analysis methods. They often use surveys with open-ended questions that let people express themselves freely. Sometimes, they'll observe people in their natural environment, taking notes on what they see. They might also dig into existing documents or artifacts that relate to their topic. The goal is to gather rich, detailed information that helps them understand the full picture, which is crucial in data analysis in qualitative research.
Which is not a purpose of reflexivity during qualitative data analysis?
Reflexivity in qualitative data analysis isn't about proving you're completely objective. That's not the goal. Instead, it's about being honest about who you are as a researcher. It's recognizing that your own experiences and views might influence how you see the data. By being upfront about this, you actually make your research more trustworthy. It's also a way to dig deeper into your data, seeing things you might have missed at first glance. This self-awareness is a crucial part of qualitative data analysis methods.
What is a qualitative data analysis example?
A simple example is analyzing customer feedback for a new product. You might collect feedback, read through responses, create codes like "ease of use" or "design," and group similar codes into themes. You'd then identify patterns and support findings with specific quotes. This process helps transform raw feedback into actionable insights.
How to analyze qualitative data from a survey?
First, gather all your responses in one place. Read through them to get a feel for what people are saying. Then, start labeling responses with codes - short descriptions of what each bit is about. This coding process is a fundamental qualitative data analysis method. Group similar codes into bigger themes. Look for patterns in these themes. Are certain ideas coming up a lot? Do different groups of people have different views? Use actual quotes from your survey to back up what you're seeing. Think about how your findings relate to your original research questions.
Which one is better, NVivo or Atlas.ti?
NVivo is known for being user-friendly and great for team projects. Atlas.ti shines when it comes to visual mapping of concepts and handling geographic data. Both can handle a variety of data types and have powerful tools for qualitative data analysis. The best way to decide is to try out both if you can.
While these are powerful tools, the core of qualitative data analysis still relies on your analytical skills and understanding of qualitative data analysis methods.
Do I need to use NVivo for qualitative data analysis?
You don't necessarily need NVivo for qualitative data analysis, but it can definitely make your life easier, especially for bigger projects. Think of it like using a power tool versus a hand tool - you can get the job done either way, but the power tool might save you time and effort. For smaller projects or if you're just starting out, you might be fine with simpler tools or even free qualitative data analysis software. But if you're dealing with lots of data, or if you need to collaborate with a team, or if you want to do more complex analysis, then specialized qualitative data analysis software like NVivo can be a big help. It's all about finding the right tool for your specific research needs and the qualitative data analysis methods you're using.
Here’s a guide that can help you decide.
How to use NVivo for qualitative data analysis
First, you import all your data - interviews, documents, videos, whatever you've got. Then you start creating "nodes," which are like folders for different themes or ideas in your data. As you read through your material, you highlight bits that relate to these themes and file them under the right nodes. NVivo lets you easily search through all this organized data, find connections between different themes, and even create visual maps of how everything relates.
How much does NVivo cost?
NVivo's pricing isn't one-size-fits-all. They offer different plans for individuals, teams, and large organizations, but they don't publish their prices openly. Contact the team here for a custom quote.
What are the four steps of qualitative data analysis?
While qualitative data analysis is often iterative, it generally follows these four main steps:
1. Data Collection: Gathering raw data through interviews, observations, or documents.
2. Data Preparation: Organizing and transcribing the collected data.
3. Data Coding: Identifying and labeling important concepts or themes in the data.
4. Interpretation: Drawing meaning from the coded data and developing insights.
Follow us on
Get the best resources for ux research, in your inbox, related articles.

Resources & Guides
February 15, 2024
How to use AI for Qualitative Data Analysis

August 15, 2024
Transcription in Qualitative Research: A Comprehensive Guide for UX Researchers

May 22, 2024
Triangulation in Qualitative Research: A Comprehensive Guide [2024]
Looppanel automatically records your calls, transcribes them, and centralizes all your research data in one place
- Essay Editor
How to Restate a Thesis: an Overview of Useful Methods

The thesis is a significant part of any academic project. It serves as a compass in the research process. Moreover, it helps the readers to get interested in the work and tune into the narration. Here we'd like to explain the essence of its paraphrasing and present a few effective strategies and tips on how to restate the thesis in a conclusion successfully.
Restating a Thesis: a Short Review
It may seem surprising but to reformulate a thesis in the course of the project is crucial. As a rule, it helps to reinforce the main idea and provides more efficient communication with the audience.
How to Define a Restated Thesis?
It is not only the synonymous version of the original statement but a restructured and reworded one. Being restated, a thesis must convey the same concept, letting people watch it from different angles. Besides, the author sounds more convincing and gripping when removing repeated expressions.
The following situation is rather popular among students when preparing an essay or a research project.
A tutor asks, 'How do you restate a thesis?'
'Am I supposed to?', he answers.
To understand the sense of restating it is necessary to learn its goals.
What are the Purposes of Restating the Thesis?
Generally, the process of reformulating has a few purposes. They are
- to make the speech more smooth and keep the audience interested throughout the whole narration;
- to accentuate different nuances of the thesis;
- to organize the writing coherently, emphasizing the stem of the work (the idea, hypothesis, or whatnot, mentioned in the thesis).
A Brief Guide on How to Restate The Thesis
This is a compact step-by-step guide for effective restating.
- Realize the importance of the core idea and its aim.
- Select appropriate synonyms and think of new sentence structures, thus staying logical and consistent.
- Highlight different angles of the stated idea.
- Use transition phrases when introducing the reformulated issue ( furthermore, additionally, moreover, etc. ).
- Proofread the text to ensure that it is fluent and clear, and restated issues strengthen the argumentation.
TOP Strategies to Restate the Thesis Effectively
'How do I restate my thesis?' This is the first question the student may ask when learning about the necessity of changes. It is not a desperately terrifying matter, there are some traditional strategies to get a successful result.
- Operate with synonyms. Using different words of the same notion, you demonstrate the richness of the vocabulary and get rid of speech monotony.
Studying abroad is a fine experience, useful for personal enrichment. | Getting an education in a foreign country provides a good background for self-development. |
- Intermix the sentences. When you are modifying the sentence structure, you uncover a new perspective on the issue and arouse the audience's attention.
Veganism is widely spread among the representatives of the privileged circle. | Would veganism be popular among the socially deprived? |
- Use a focus transition. By restatement of this type, you are accentuating a specific aspect of the thesis and showing an in-depth investigation of the main issue.
The dramatist usually touched on the theme of love in his plays. | The dramatist underlined the nonexistence of a happy end in love in his plays. |
- Perform a tense shift. If you are changing the verb tense from present to past, it testifies to the development of the argumentation.
Social media is becoming popular among younger schoolchildren. | For the last decade, social media has grown in popularity among youngsters. |
- Play with active and passive voices. The active voice usage makes the sentence easier to understand, and the passive – creates an atmosphere of objectivity and neutrality. The active voice emphasizes the importance of the doer, thus the passive one highlights the significance of the affected matter.
The importance of regular physical training is accentuated by coaches. | Coaches underline the importance of regular physical training. |
How to Restate Your Thesis: Examples
In this section, we offer some more practical restatements based on the recommendations and strategies above.
Thesis | Variant 1 | Variant 2 |
Reading fiction books produces a positive impact on the development of imagination. | Everyone is to read fiction to develop his or her imagination. | How would one's imagination develop if a person didn't read fairy-tales, stories, or novellas? |
Mobile applications may be an effective educational tool, upgrading creativity and problem-solving skills. | Mobile apps proved their effectiveness in developing a wide range of soft skills. | The education experts advise using mobile applications for advancing personal creativity and other soft skills. |
We hope that both theoretical data and practical examples of the issue will be helpful in realizing the advantages of paraphrasing. Now you know how to restate the thesis statement successfully and what methods to use in this field. Just master the skill by creating different versions of one sentence, keeping the sense and logic.
If you still find any difficulty in this process, try Aithor , a professional AI-powered text-generator. It may be used for rewriting, rephrasing, creating fool projects, or separate passages. However, do not forget to practice on your own, as well.
Related articles
Plagiarism: 7 types in detail.
Your professor says that it is necessary to avoid plagiarism when writing a research paper, essay, or any project based on the works of other people, so to say, any reference source. But what does plagiarism mean? What types of it exist? And how to formulate the material to get rid of potential bad consequences while rendering original texts? Today we try to answer these very questions. Plagiarism: Aspect in Brief Plagiarism is considered to be a serious breach, able to spoil your successful ...
Top 10 Use Cases for AI Writers
Writing is changing a lot because of AI. But don't worry — AI won't take human writers' jobs. It's a tool that can make our work easier and help us write better. When we use AI along with our own skills, we can create good content faster and better. AI can help with many parts of writing, from coming up with ideas to fixing the final version. Let's look at the top 10 ways how to use AI for content creation and how it can make your writing better. What Is AI Content Writing? AI content writin ...
Paraphrasing vs Plagiarism: Do They Really Differ?
Academic assignments require much knowledge and skill. One of the most important points is rendering and interpreting material one has ever studied. A person should avoid presenting word-for-word plagiarism but express his or her thoughts and ideas as much as possible. However, every fine research is certain to be based on the previous issues, data given, or concepts suggested. And here it's high time to differentiate plagiarism and paraphrasing, to realize its peculiarities and cases of usage. ...
What Is Self-Plagiarism & How To Avoid It
Have you ever thought about whether using your own work again could be seen as copying? It might seem strange, but self-plagiarism is a real issue in school and work writing. Let's look at what this means and learn how to avoid self-plagiarism so your work stays original and ethical. What is self-plagiarism? Self-plagiarism, also called auto-plagiarism or duplicate plagiarism, happens when a writer uses parts of their old work without saying where it came from. This isn't just about copying w ...
Can Plagiarism Be Detected on PDF?
Plagiarism has been a challenge for a long time in writing. It's easy to find information online, which might make some people use it without saying where it came from. But plagiarism isn't just taking someone else's words. Sometimes, we might do it by accident or even use our own old work without mentioning it. When people plagiarize, they can get into serious trouble. They might lose others' trust or even face legal problems. Luckily, we now have tools to detect plagiarism. But what about PDF ...
What is Citation and Why Should You Cite the Sources When Writing Content
When we write something for school, work, or just for fun, we often use ideas and facts from other places. This makes us ask: what is a citation in writing? Let's find out what this means and why it's really important when we write. What is Citation? Citation in research refers to the practice of telling your readers where you got your information, ideas, or exact words from. It's like showing them the path to the original information you used in your writing. When you cite something, you us ...
How To Write Essays Faster Using AI?
Creating various topical texts is an obligatory assignment during studies. For a majority of students, it seems like a real headache. It is quite difficult to write a smooth and complex work, meeting all the professors' requirements. However, thanks to modern technologies there appeared a good way of getting a decent project – using AI to write essays. We'd like to acquaint you with Aithor, an effective tool of this kind, able to perform fine and elaborated texts, and, of course, inspiration, i ...
How to Write a Dialogue in an Essay: Useful Tips
A correct usage of dialogues in essays may seem quite difficult at first sight. Still there are special issues, for instance, narrative or descriptive papers, where this literary technique will be a good helper in depicting anyone's character. How to add dialogues to the work? How to format them correctly? Let's discuss all relevant matters to master putting conversation episodes into academic essays. Essay Dialogue: Definition & Purpose A dialogue is a literary technique for presenting a con ...

Writing The Methodology Chapter
5 Time-Saving Tips & Tools
By: David Phair (PhD) and Amy Murdock (PhD) | July 2022
The methodology chapter is a crucial part of your dissertation or thesis – it’s where you provide context and justification for your study’s design. This in turn demonstrates your understanding of research theory, which is what earns you marks .
Over the years, we’ve helped thousands of students navigate this tricky section of the research process. In this post, we’ll share 5 time-saving tips to help you effectively write up your research methodology chapter .
Overview: Writing The Methodology Chapter
- Develop a (rough) outline before you start writing
- Draw inspiration from similar studies in your topic area
- Justify every research design choice that you make
- Err on the side of too much detail , rather than too little
- Back up every design choice by referencing literature

1. Develop an outline before you start writing
The first thing to keep in mind when writing your methodology chapter (and the rest of your dissertation) is that it’s always a good idea to sketch out a rough outline of what you are going to write about before you start writing . This will ensure that you stay focused and have a clear structural logic – thereby making the writing process simpler and faster.
An easy method of finding a structure for this chapter is to use frameworks that already exist, such as Saunder’s “ research onion ” as an example. Alternatively, there are many free methodology chapter templates for you to use as a starting point, so don’t feel like you have to create a new one from scratch.
Next, you’ll want to consider what your research approach is , and how you can break it down from a top-down angle, i.e., from the philosophical down to the concrete/tactical level. For example, you’ll need to articulate the following:
- Are you using a positivist , interpretivist , or pragmatist approach ?
- Are you using inductive or deductive reasoning?
- Are you using a qualitative , quantitative, or mixed methods study?
Keep these questions front of mind to ensure that you have a clear, well-aligned line of argument that will maintain your chapter’s internal and external consistency.
Remember, it’s okay if you feel overwhelmed when you first start the methodology chapter. Nobody is born with an innate knowledge of how to do this, so be prepared for the learning curve associated with new research projects. It’s no small task to write up a dissertation or thesis, so be kind to yourself!

2. Take inspiration from other studies
Generally, there are plenty of existing journal articles that will share similar methodological approaches to your study. With any luck, there will also be existing dissertations and theses that adopt a similar methodological approach and topic. So, consider taking inspiration from these studies to help curate the contents of your methodology chapter.
Students often find it difficult to choose what content to include in the methodology chapter and what to leave for the appendix. By reviewing other studies with similar approaches, you will get a clearer sense of your discipline’s norms and characteristics . This will help you, especially in terms of deciding on the structure and depth of discussion.
While you can draw inspiration from other studies, remember that it’s vital to pay close attention to your university’s specific guidelines, so you can anticipate departmental expectations of this section’s layout and content (and make it easier to work with your supervisor). Doing this is also a great way to figure out how in-depth your discussion should be. For example, word-count guidelines can help you decide whether to include or omit certain information.
Need a helping hand?
3. Justify every design choice you make
The golden rule of the methodology chapter is that you need to justify each and every design choice that you make, no matter how small or inconsequential it may seem. We often see that students merely state what they did instead of why they did what they did – and this costs them marks.
Keep in mind that you need to illustrate the strength of your study’s methodological foundation. By discussing the “what”, “why” and “how” of your choices, you demonstrate your understanding of research design and simultaneously justify the relevancy and efficacy of your methodology – both of which will earn you marks.
It’s never an easy task to conduct research. So, it’s seldom the case that you’ll be able to use the very best possible methodology for your research (e.g. due to time or budgetary constraints ). That’s okay – but make sure that you explain and justify your use of an alternate methodology to help justify your approach.
Ultimately, if you don’t justify and explain the logic behind each of your choices, your marker will have to assume that you simply didn’t know any better . So, make sure that you justify every choice, especially when it is a subpar choice (due to a practical constraint, for example). You can see an example of how this is done here.

4. Err on the side of too much detail
We often see a tendency in students to mistakenly give more of an overview of their methodology instead of a step-by-step breakdown . Since the methodology chapter needs to be detailed enough for another researcher to replicate your study, your chapter should be particularly granular in terms of detail.
Whether you’re doing a qualitative or quantitative study, it’s crucial to convey rigor in your research. You can do this by being especially detailed when you discuss your data, so be absolutely clear about your:
- Sampling strategy
- Data collection method(s)
- Data preparation
- Analysis technique(s)
As you will likely face an extensive period of editing at your supervisor/reviewer’s direction, you’ll make it much easier for yourself if you have more information than you’d need. Some supervisors expect extensive detail around a certain aspect of your dissertation (like your research philosophy), while others may not expect it at all.
Remember, it’s quicker and easier to remove/ trim down information than it is to add information after the fact, so take the time to show your supervisor that you know what you’re talking about (methodologically) and you’re doing your best to be rigorous in your research.

5. Provide citations to support each design choice
Related to the issue of poor justification (tip #3), it’s important include high-quality academic citations to support the justification of your design choices. In other words, it’s not enough to simply explain why you chose a specific approach – you need to support each justification with reference to academic material.
Simply put, you should avoid thinking of your methodology chapter as a citation-less section in your dissertation. As with your literature review, your methods section must include citations for every decision you make, since you are building on prior research. You must show that you are making decisions based on methods that are proven to be effective, and not just because you “feel” that they are effective.
When considering the source of your citations, you should stick to peer-reviewed academic papers and journals and avoid using websites or blog posts (like us, hehe). Doing this will demonstrate that you are familiar with the literature and that you are factoring in what credible academics have to say about your methodology.
As a final tip, it’s always a good idea to cite as you go . If you leave this for the end, then you’ll end up spending a lot of precious time retracing your steps to find your citations and risk losing track of them entirely. So, be proactive and drop in those citations as you write up . You’ll thank yourself later!
Let’s Recap…
In this post, we covered 5 time-saving tips for writing up the methodology chapter:
- Look at similar studies in your topic area
- Justify every design choice that you make
- Back up every design choice by referencing methodology literature
If you’ve got any questions relating to the methodology chapter, feel free to drop a comment below. Alternatively, if you’re interested in getting 1-on-1 help with your thesis or dissertation, be sure to check out our private coaching service .

Psst... there’s more!
This post was based on one of our popular Research Bootcamps . If you're working on a research project, you'll definitely want to check this out ...
What data analysis method can work best for my study. I am using a mixed method in the study. I am developing a framework to address the challenges faced by the taxi operators as entrepreneurs. I will need to analyse both using qualitative and quantitative.
How to find standard deviation for non numerical data
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
Quantitative Methods for Undergraduate Students
This workshop introduces concepts such as descriptive vs. inferential statistics, running exploratory data analysis, testing data for normality, and parametric vs. non-parametric data analysis. Participants will learn about different statistical methods for exploring and analyzing their data.
This session will be held online via Zoom.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
What Is a Research Methodology? | Steps & Tips. Published on August 25, 2022 by Shona McCombes and Tegan George. Revised on November 20, 2023. Your research methodology discusses and explains the data collection and analysis methods you used in your research. A key part of your thesis, dissertation, or research paper, the methodology chapter explains what you did and how you did it, allowing ...
ISBN: 9788132105961. Publication Date: 2010. A Gentle Guide to Research Methods Gordon Rugg Provides an overview of research methods, including research design, data collection methods, statistics, and academic writing. This book also includes a coverage of data collection methods - from interviews to indirect observation to card sorts.
Summary of Methods Chapter Strategies ! Most important: Explain each of your methodology choices by linking it to what you want to learn. Show how your methods are the best way to answer your research question - how various methodological choices you made (e.g., decision to do multiple site comparison) provided leverage for understanding
Dissertation Methodology. In any research, the methodology chapter is one of the key components of your dissertation. It provides a detailed description of the methods you used to conduct your research and helps readers understand how you obtained your data and how you plan to analyze it. This section is crucial for replicating the study and ...
Research methods are specific procedures for collecting and analyzing data. Developing your research methods is an integral part of your research design. When planning your methods, there are two key decisions you will make. First, decide how you will collect data. Your methods depend on what type of data you need to answer your research question:
How to choose a research methodology. To choose the right research methodology for your dissertation or thesis, you need to consider three important factors. Based on these three factors, you can decide on your overarching approach - qualitative, quantitative or mixed methods. Once you've made that decision, you can flesh out the finer ...
Revised on 10 October 2022. Your research methodology discusses and explains the data collection and analysis methods you used in your research. A key part of your thesis, dissertation, or research paper, the methodology chapter explains what you did and how you did it, allowing readers to evaluate the reliability and validity of your research.
Research Methodology Example. Detailed Walkthrough + Free Methodology Chapter Template. If you're working on a dissertation or thesis and are looking for an example of a research methodology chapter, you've come to the right place. In this video, we walk you through a research methodology from a dissertation that earned full distinction ...
Revised on April 16, 2024. A thesis is a type of research paper based on your original research. It is usually submitted as the final step of a master's program or a capstone to a bachelor's degree. Writing a thesis can be a daunting experience. Other than a dissertation, it is one of the longest pieces of writing students typically complete.
Provide the rationality behind your chosen approach. Based on logic and reason, let your readers know why you have chosen said research methodologies. Additionally, you have to build strong arguments supporting why your chosen research method is the best way to achieve the desired outcome. 3. Explain your mechanism.
Do yourself a favour and start with the end in mind. Section 1 - Introduction. As with all chapters in your dissertation or thesis, the methodology chapter should have a brief introduction. In this section, you should remind your readers what the focus of your study is, especially the research aims. As we've discussed many times on the blog ...
Thesis. Definition: Thesis is a scholarly document that presents a student's original research and findings on a particular topic or question. It is usually written as a requirement for a graduate degree program and is intended to demonstrate the student's mastery of the subject matter and their ability to conduct independent research.
The research methodology is an important section of any research paper or thesis, as it describes the methods and procedures that will be used to conduct the research. It should include details about the research design, data collection methods, data analysis techniques, and any ethical considerations.
1. Qualitative research methodology. Qualitative research methodology is aimed at understanding concepts, thoughts, or experiences. This approach is descriptive and is often utilized to gather in-depth insights into people's attitudes, behaviors, or cultures. Qualitative research methodology involves methods like interviews, focus groups, and ...
Observational methods are useful for in-depth analyses of behaviours in people, animals, organisations, events or phenomena. They can test a theory or products in real life or simulated settings. They generally a qualitative research method. Questionnaires and surveys.
Bem, Daryl J. Writing the Empirical Journal Article. Psychology Writing Center. University of Washington; Denscombe, Martyn. The Good Research Guide: For Small-Scale Social Research Projects. 5th edition.Buckingham, UK: Open University Press, 2014; Lunenburg, Frederick C. Writing a Successful Thesis or Dissertation: Tips and Strategies for Students in the Social and Behavioral Sciences.
A thesis research methodology explains the type of research performed, justifies the methods that you chose by linking back to the literature review, and describes the data collection and analysis procedures.It is included in your thesis after the Introduction section.Most importantly, this is the section where the readers of your study evaluate its validity and reliability.
The research title, research questions, hypothesis, objectives, and study area generally determine the best research method in the dissertation. This post's primary purpose is to highlight what these different types of research methods involve and how you should decide which type of research fits the bill.
As we mentioned, research methodology refers to the collection of practical decisions regarding what data you'll collect, from who, how you'll collect it and how you'll analyse it. Research design, on the other hand, is more about the overall strategy you'll adopt in your study. For example, whether you'll use an experimental design ...
Dissertation Research Methods: A Step-by-Step Guide to Writing Up Your Research in the Social Sciences focuses specifically on the methodology for planning, writing and submitting your dissertation thesis. Written by two methodology experts in the social sciences, the book provides a step-by-step guide through each stage of the dissertation process.
Qualitative methods involve collecting non-numerical data, such as interviews and focus groups, to understand experiences and opinions. On the other hand, quantitative methods focus on numerical data and statistical analysis, like surveys and experiments. Sometimes, a mixed-method approach, combining both qualitative and quantitative techniques ...
Research has shown that the sun provides vitamin D and is an essential part of our health, but little is known about how daylight twenty-four hours a day affects the circadian rhythm and sleep. ... Methods. In the methods section of your thesis paper, you get to explain how you learned what you learned. ...
A research design is a strategy for answering your research question using empirical data. Creating a research design means making decisions about: Your overall research objectives and approach. Whether you'll rely on primary research or secondary research. Your sampling methods or criteria for selecting subjects. Your data collection methods.
This template covers all the core components required in the methodology section of a typical dissertation, thesis or research paper, including: The opening section. Research philosophy. Research type. Research strategy. Time horizon. Sampling strategy. Data collection methods. Data analysis methods.
Each method suits different research goals and data types. Researchers often combine methods for comprehensive analysis. What are the 4 data collection methods in qualitative research? When it comes to collecting qualitative data, researchers primarily rely on four methods. Interviews: One-on-one conversations to gather in-depth information.
The thesis is a significant part of any academic project. It serves as a compass in the research process. Moreover, it helps the readers to get interested in the work and tune into the narration. Here we'd like to explain the essence of its paraphrasing and present a few effective strategies and tips on how to restate the thesis in a conclusion successfully. Restating a Thesis: a Short Review ...
The methodology chapter is a crucial part of your dissertation or thesis - it's where you provide context and justification for your study's design. This in turn demonstrates your understanding of research theory, which is what earns you marks.. Over the years, we've helped thousands of students navigate this tricky section of the research process.
This workshop introduces concepts such as descriptive vs. inferential statistics, running exploratory data analysis, testing data for normality, and parametric vs. non-parametric data analysis. Participants will learn about different statistical methods for exploring and analyzing their data. This session will be held online via Zoom.