Social Work Practice with Carers


Case Study 2: Josef
Download the whole case study as a PDF file
Josef is 16 and lives with his mother, Dorota, who was diagnosed with Bipolar disorder seven years ago. Josef was born in England. His parents are Polish and his father sees him infrequently.
This case study looks at the impact of caring for someone with a mental health problem and of being a young carer , in particular the impact on education and future employment .
When you have looked at the materials for the case study and considered these topics, you can use the critical reflection tool and the action planning tool to consider your own practice.
- One-page profile
Support plan
Transcript (.pdf, 48KB)
Name : Josef Mazur
Gender : Male
Ethnicity : White European
Download resource as a PDF file
First language : English/ Polish
Religion : Roman Catholic
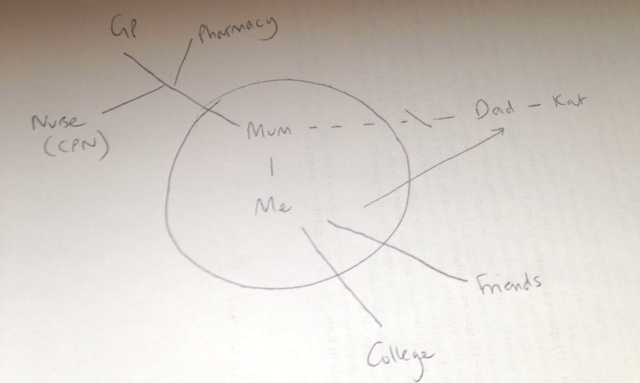
Josef lives in a small town with his mother Dorota who is 39. Dorota was diagnosed with Bi-polar disorder seven years ago after she was admitted to hospital. She is currently unable to work. Josef’s father, Stefan, lives in the same town and he sees him every few weeks. Josef was born in England. His parents are Polish and he speaks Polish at home.
Josef is doing a foundation art course at college. Dorota is quite isolated because she often finds it difficult to leave the house. Dorota takes medication and had regular visits from the Community Psychiatric Nurse when she was diagnosed and support from the Community Mental Health team to sort out her finances. Josef does the shopping and collects prescriptions. He also helps with letters and forms because Dorota doesn’t understand all the English. Dorota gets worried when Josef is out. When Dorota is feeling depressed, Josef stays at home with her. When Dorota is heading for a high, she tries to take Josef to do ‘exciting stuff’ as she calls it. She also spends a lot of money and is very restless.
Josef worries about his mother’s moods. He is worried about her not being happy and concerned at the money she spends when she is in a high mood state. Josef struggles to manage his day around his mother’s demands and to sleep when she is high. Josef has not told anyone about the support he gives to his mother. He is embarrassed by some of the things she does and is teased by his friends, and he does not think of himself as a carer. Josef has recently had trouble keeping up with course work and attendance. He has been invited to a meeting with his tutor to formally review attendance and is worried he will get kicked out. Josef has some friends but he doesn’t have anyone he can confide in. His father doesn’t speak to his mother.
Josef sees some information on line about having a parent with a mental health problem. He sends a contact form to ask for information. Someone rings him and he agrees to come into the young carers’ team and talk to the social worker. You have completed the assessment form with Josef in his words and then done a support plan with him.
Back to Summary
Josef Mazur
What others like and admire about me
Good at football
Finished Arkham Asylum on expert level
What is important to me
Mum being well and happy
Seeing my dad
Being an artist
Seeing my friends
How best to support me
Tell me how to help mum better
Don’t talk down to me
Talk to me 1 to 1
Let me know who to contact if I am worried about something
Work out how I can have some time on my own so I can do my college work and see my friends
Don’t tell mum and my friends
Date chronology completed : 7 March 2016
Date chronology shared with person: 7 March 2016
| 1997 | Josef’s mother and father moved to England from Poznan. | Both worked at the warehouse – Father still works there. |
| 11.11.1999 | Josef born. | Mother worked for some of the time that Josef was young. |
| 2006 | Josef reports that his mother and father started arguing about this time because of money and Josef’s mother not looking after household tasks. | Josef started doing household tasks e.g. cleaning, washing and ironing. |
| 2008 | Josef reports that his mother didn’t get out of bed for a few months. | Josef managed the household during this period. |
| October 2008 | Josef reports that his mother spent lots of money in catalogues and didn’t sleep. She was admitted to hospital. | Mother was in hospital for 6 weeks and was diagnosed with bipolar disorder. Josef began looking after his mother’s medication and says that he started to ‘keep an eye on her.’ |
| May 2010 | Josef’s father moved out to live with his friend Kat. Josef stayed with his mother. | Josef reports that his mother was ‘really sad for a while and then she went round and shouted at them.’ Mother started on different medication and had regular visits from the Community Psychiatric Nurse. Josef said that the CPN told him about his mum’s illness and to let him know if he needed any help but he was managing ok. Josef saw his father every week for a few years and then it was more like every month. Father does not visit Josef or speak to his mother. |
| 2013/14 | Josef reports that his mother got into a lot of debt and they had eviction letters. | Josef’s father paid some of the bills and his mother was referred by the Community Mental Health Team for advice from CAB and started getting benefits. Josef started doing the correspondence. |
| 2015 | Josef left school and went to college. | Josef got an A (art), 4 Cs and 3 Ds GCSE. He says that he ‘would have done better but I didn’t do much work.’ |
| 26 Feb 2016 | Josef got a letter from his tutor at college saying he had to go to a formal review about attendance. | Josef saw information on-line about having a parent with a mental health problem and asked for some information. |
| 2 March 2016 | Phone call from young carer’s team to Josef. | Josef agreed to come in for an assessment. |
| 4 March 2016 | Social worker meets with Josef. | Carer’s assessment and support plan completed. |
| 7 March 2016 | Paperwork completed. | Sent to Josef. |
Young Carers Assessment
Do you look after or care for someone at home?
The questions in this paper are designed to help you think about your caring role and what support you might need to make your life a little easier or help you make time for more fun stuff.
Please feel free to make notes, draw pictures or use the form however is best for you.
What will happen to this booklet?
This is your booklet and it is your way to tell an adult who you trust about your caring at home. This will help you and the adult find ways to make your life and your caring role easier.
The adult who works with you on your booklet might be able to help you with everything you need. If they can’t, they might know other people who can.
Our Agreement
- I will share this booklet with people if I think they can help you or your family
- I will let you know who I share this with, unless I am worried about your safety, about crime or cannot contact you
- Only I or someone from my team will share this booklet
- I will make sure this booklet is stored securely
- Some details from this booklet might be used for monitoring purposes, which is how we check that we are working with everyone we should be
Signed: ___________________________________
Young person:
- I know that this booklet might get shared with other people who can help me and my family so that I don’t have to explain it all over again
- I understand what my worker will do with this booklet and the information in it (written above).
Signed: ____________________________________
Name : Josef Mazur Address : 1 Green Avenue, Churchville, ZZ1 Z11 Telephone: 012345 123456 Email: [email protected] Gender : Male Date of birth : 11.11.1999 Age: 16 School : Green College, Churchville Ethnicity : White European First language : English/ Polish Religion : Baptised Roman Catholic GP : Dr Amp, Hill Surgery
The best way to get in touch with me is:
Do you need any support with communication?
*Josef is bilingual – English and Polish. He speaks English at school and with his friends, and Polish at home. Josef was happy to have this assessment in English, however, another time he may want to have a Polish interpreter. It will be important to ensure that Josef is able to use the words he feels best express himself.
About the person/ people I care for
I look after my mum who has bipolar disorder. Mum doesn’t work and doesn’t really leave the house unless she is heading for a high. When Mum is sad she just stays at home. When she is getting hyper then she wants to do exciting stuff and she spends lots of money and she doesn’t sleep.
Do you wish you knew more about their illness?
Do you live with the person you care for?
What I do as a carer It depends on if my mum has a bad day or not. When she is depressed she likes me to stay home with her and when she is getting hyper then she wants me to go out with her. If she has new meds then I like to be around. Mum doesn’t understand English very well (she is from Poland) so I do all the letters. I help out at home and help her with getting her medication.
Tell us what an average week is like for you, what kind of things do you usually do?
Monday to Friday
Get up, get breakfast, make sure mum has her pills, tell her to get up and remind her if she’s got something to do.
If mum hasn’t been to bed then encourage her to sleep a bit and set an alarm
College – keep phone on in case mum needs to call – she usually does to ask me to get something or check when I’m coming home
Go home – go to shops on the way
Remind mum about tablets, make tea and pudding for both of us as well as cleaning the house and fitting tea in-between, ironing, hoovering, hanging out and bringing in washing
Do college work when mum goes to bed if not too tired
More chores
Do proper shop
Get prescription
See my friends, do college work
Sunday – do paper round
Physical things I do….
(for example cooking, cleaning, medication, shopping, dressing, lifting, carrying, caring in the night, making doctors appointments, bathing, paying bills, caring for brothers & sisters)
I do all the housework and shopping and cooking and get medication
Things I find difficult
Emotional support I provide…. (please tell us about the things you do to support the person you care for with their feelings; this might include, reassuring them, stopping them from getting angry, looking after them if they have been drinking alcohol or taking drugs, keeping an eye on them, helping them to relax)
If mum is stressed I stay with her
If mum is depressed I have to keep things calm and try to lighten the mood
She likes me to be around
When mum is heading for a high wants to go to theme parks or book holidays and we can’t afford it
I worry that mum might end up in hospital again
Mum gets cross if I go out
Other support
Please tell us about any other support the person you care for already has in place like a doctor or nurse, or other family or friends.
The GP sees mum sometimes. She has a nurse who she can call if things get bad.
Mum’s medication comes from Morrison’s pharmacy.
Dad lives nearby but he doesn’t talk to mum.
Mum doesn’t really have any friends.
Do you ever have to stop the person you care for from trying to harm themselves or others?
Some things I need help with
Sorting out bills and having more time for myself
I would like mum to have more support and to have some friends and things to do
On a normal week, what are the best bits? What do you enjoy the most? (eg, seeing friends, playing sports, your favourite lessons at school)
Seeing friends
When mum is up and smiling
Playing football
On a normal week, what are the worst bits? What do you enjoy the least? (eg cleaning up, particular lessons at school, things you find boring or upsetting)
Nagging mum to get up
Reading letters
Missing class
Mum shouting
Friends laugh because I have to go home but they don’t have to do anything
What things do you like to do in your spare time?
Do you feel you have enough time to spend with your friends or family doing things you enjoy, most weeks?
Do you have enough time for yourself to do the things you enjoy, most weeks? (for example, spending time with friends, hobbies, sports)
Are there things that you would like to do, but can’t because of your role as a carer?
Can you say what some of these things are?
See friends after college
Go out at the weekend
Time to myself at home
It can feel a bit lonely
I’d like my mum to be like a normal mum
School/ College Do you think being your caring role makes school/college more difficult for you in any way?
If you ticked YES, please tell us what things are made difficult and what things might help you.
Things I find difficult at school/ college
Sometimes I get stressed about college and end up doing college work really late at night – I get a bit angry when I’m stressed
I don’t get all my college work done and I miss days
I am tired a lot of the time
Things I need help with…
I am really worried they will kick me out because I am behind and I miss class. I have to meet my tutor about it.
Do your teachers know about your caring role?
Are you happy for your teachers and other staff at school/college to know about your caring role?
Do you think that being a carer will make it more difficult for you to find or keep a job?
Why do you think being a carer is/ will make finding a job more difficult?
I haven’t thought about it. I don’t know if I’ll be able to finish my course and do art and then I won’t be able to be an artist.
Who will look after mum?
What would make it easier for you to find a job after school/college?
Finishing my course
Mum being ok
How I feel about life…
Do you feel confident both in school and outside of school?
Somewhere in the middle
In your life in general, how happy do you feel?
Quite unhappy
In your life in general, how safe do you feel?
How healthy do you feel at the moment?
Quite healthy
Being heard
Do you think people listen to what you are saying and how you are feeling?
If you said no, can you tell us who you feel isn’t listening or understanding you sometimes (eg, you parents, your teachers, your friends, professionals)
I haven’t told anyone
I can’t talk to mum
My friends laugh at me because I don’t go out
Do you think you are included in important decisions about you and your life? (eg, where you live, where you go to school etc)
Do you think that you’re free to make your own choices about what you do and who you spend your time with?
Not often enough
Is there anybody who knows about the caring you’re doing at the moment?
If so, who?
I told dad but he can’t do anything
Would you like someone to talk to?
Supporting me Some things that would make my life easier, help me with my caring or make me feel better
I don’t know
Fix mum’s brain
People to help me if I’m worried and they can do something about it
Not getting kicked out of college
Free time – time on my own to calm down and do work or have time to myself
Time to go out with my friends
Get some friends for mum
I don’t want my mum to get into trouble
Who can I turn to for advice or support?
I would like to be able to talk to someone without mum or friends knowing
Would you like a break from your caring role?
How easy is it to see a Doctor if you need to?
To be used by social care assessors to consider and record measures which can be taken to assist the carer with their caring role to reduce the significant impact of any needs. This should include networks of support, community services and the persons own strengths. To be eligible the carer must have significant difficulty achieving 1 or more outcomes without support; it is the assessors’ professional judgement that unless this need is met there will be a significant impact on the carer’s wellbeing. Social care funding will only be made available to meet eligible outcomes that cannot be met in any other way, i.e. social care funding is only available to meet unmet eligible needs.
Date assessment completed : 7 March 2016
Social care assessor conclusion
Josef provides daily support to his mum, Dorota, who was diagnosed with bipolar disorder seven years ago. Josef helps Dorota with managing correspondence, medication and all household tasks including shopping. When Dorota has a low mood, Josef provides support and encouragement to get up. When Dorota has a high mood, Josef helps to calm her and prevent her spending lots of money. Josef reports that Dorota has some input from community health services but there is no other support. Josef’s dad is not involved though Josef sees him sometimes, and there are no friends who can support Dorota.
Josef is a great support to his mum and is a loving son. He wants to make sure his mum is ok. However, caring for his mum is impacting: on Josef’s health because he is tired and stressed; on his emotional wellbeing as he can get angry and anxious; on his relationship with his mother and his friends; and on his education. Josef is at risk of leaving college. Josef wants to be able to support his mum better. He also needs time for himself, to develop and to relax, and to plan his future.
Eligibility decision : Eligible for support
What’s happening next : Create support plan
Completed by Name : Role : Organisation :
Name: Josef Mazur
Address 1 Green Avenue, Churchville, ZZ1 Z11
Telephone 012345 123456
Email [email protected]
Gender: Male
Date of birth: 11.11.1999 Age: 16
School Green College, Churchville
Ethnicity White European
First language English/ Polish
Religion Baptised Roman Catholic
GP Dr Amp, Hill Surgery
My relationship to this person son
Name Dorota Mazur
Gender Female
Date of birth 12.6.79 Age 36
First language Polish
Religion Roman Catholic
Support plan completed by
Organisation
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
| ||
|
| ||
Date of support plan: 7 March 2016
This plan will be reviewed on: 7 September 2016
Signing this form
Please ensure you read the statement below in bold, then sign and date the form.
I understand that completing this form will lead to a computer record being made which will be treated confidentially. The council will hold this information for the purpose of providing information, advice and support to meet my needs. To be able to do this the information may be shared with relevant NHS Agencies and providers of carers’ services. This will also help reduce the number of times I am asked for the same information.
If I have given details about someone else, I will make sure that they know about this.
I understand that the information I provide on this form will only be shared as allowed by the Data Protection Act.
Josef has given consent to share this support plan with the CPN but does not want it to be shared with his mum.
Mental health
The social work role with carers in adult mental health services has been described as: intervening and showing professional leadership and skill in situations characterised by high levels of social, family and interpersonal complexity, risk and ambiguity (Allen 2014). Social work with carers of people with mental health needs, is dependent on good practice with the Mental Capacity Act where practitioner knowledge and understanding has been found to be variable (Iliffe et al 2015).
- Carers Trust (2015) Mental Health Act 1983 – Revised Code of Practice Briefing
- Carers Trust (2013) The Triangle of Care Carers Included: A Guide to Best Practice in Mental Health Care in England
- Mind, Talking about mental health
- Tool 1: Triangle of care: self-assessment for mental health professionals – Carers Trust (2013) The Triangle of Care Carers Included: A Guide to Best Practice in Mental Health Care in England Second Edition (page 23 Self-assessment tool for organisations)
Mental capacity, confidentiality and consent
Social work with carers of people with mental health needs, is dependent on good practice with the Mental Capacity Act where practitioner knowledge and understanding has been found to be variable (Iliffe et al 2015). Research highlights important issues about involvement, consent and confidentiality in working with carers (RiPfA 2016, SCIE 2015, Mental Welfare Commission for Scotland 2013).
- Beddow, A., Cooper, M., Morriss, L., (2015) A CPD curriculum guide for social workers on the application of the Mental Capacity Act 2005 . Department of Health
- Bogg, D. and Chamberlain, S. (2015) Mental Capacity Act 2005 in Practice Learning Materials for Adult Social Workers . Department of Health
- Department of Health (2015) Best Interest Assessor Capabilities , The College of Social Work
- RiPfA Good Decision Making Practitioner Handbook
- SCIE Mental Capacity Act resource
- Tool 2: Making good decisions, capacity tool (page 70-71 in good decision making handbook)
Young carers
A young carer is defined as a person under 18 who provides or intends to provide care for another person. The concept of care includes practical or emotional support. It is the case that this definition excludes children providing care as part of contracted work or as voluntary work. However, the local authority can ignore this and carry out a young carer’s need assessment if they think it would be appropriate. Young carers, young adult carers and their families now have stronger rights to be identified, offered information, receive an assessment and be supported using a whole-family approach (Carers Trust 2015).
- SCIE (2015) Young carer transition in practice under the Care Act 2014
- SCIE (2015) Care Act: Transition from children’s to adult services – early and comprehensive identification
- Carers Trust (2015) Rights for young carers and young adult carers in the Children and Families Act
- Carers Trust (2015) Know your Rights: Support for Young Carers and Young Adult Carers in England
- The Children’s Society (2015) Hidden from view: The experiences of young carers in England
- DfE (2011) Improving support for young carers – family focused approaches
- ADASS and ADCS (2015) No wrong doors: working together to support young carers and their families
- Carers Trust, Supporting Young Carers and their Families: Examples of Practice
- Refugee toolkit webpage: Children and informal interpreting
- SCIE (2010) Supporting carers: the cared for person
- SCIE (2015) Care Act Transition from children’s to adults’ services – Video diaries
- Tool 3: Young carers’ rights – The Children’s Society (2014) The Know Your Rights pack for young carers in England!
- Tool 4: Vision and principles for adults’ and children’s services to work together
Young carers of parents with mental health problems
The Care Act places a duty on local authorities to assess young carers before they turn 18, so that they have the information they need to plan for their future. This is referred to as a transition assessment. Guidance, advocating a whole family approach, is available to social workers (LGA 2015, SCIE 2015, ADASS/ADCS 2011).
- SCIE (2012) At a glance 55: Think child, think parent, think family: Putting it into practice
- SCIE (2008) Research briefing 24: Experiences of children and young people caring for a parent with a mental health problem
- SCIE (2008) SCIE Research briefing 29: Black and minority ethnic parents with mental health problems and their children
- Carers Trust (2015) The Triangle of Care for Young Carers and Young Adult Carers: A Guide for Mental Health Professionals
- ADASS and ADCS (2011) Working together to improve outcomes for young carers in families affected by enduring parental mental illness or substance misuse
- Ofsted (2013) What about the children? Joint working between adult and children’s services when parents or carers have mental ill health and/or drug and alcohol problems
- Mental health foundation (2010) MyCare The challenges facing young carers of parents with a severe mental illness
- Children’s Commissioner (2012) Silent voices: supporting children and young people affected by parental alcohol misuse
- SCIE, Parental mental health and child welfare – a young person’s story
Tool 5: Family model for assessment
- Tool 6: Engaging young carers of parents with mental health problems or substance misuse
Young carers and education/ employment
Transition moments are highlighted in the research across the life course (Blythe 2010, Grant et al 2010). Complex transitions required smooth transfers, adequate support and dedicated professionals (Petch 2010). Understanding transition theory remains essential in social work practice (Crawford and Walker 2010). Partnership building expertise used by practitioners was seen as particular pertinent to transition for a young carer (Heyman 2013).
- TLAP (2013) Making it real for young carers
- Learning and Work Institute (2018) Barriers to employment for young adult carers
- Carers Trust (2014) Young Adult Carers at College and University
- Carers Trust (2013) Young Adult Carers at School: Experiences and Perceptions of Caring and Education
- Carers Trust (2014) Young Adult Carers and Employment
- Family Action (2012) BE BOTHERED! Making Education Count for Young Carers

Download The Triangle of Care as a PDF file
The Triangle of Care Carers Included: A Guide to Best Practice in Mental Health Care in England
The Triangle of Care is a therapeutic alliance between service user, staff member and carer that promotes safety, supports recovery and sustains wellbeing…

Download the Capacity Tool as a PDF file
Capacity Tool Good decision-making Practitioners’ Handbook
The Capacity tool on page 71 has been developed to take into account the lessons from research and the case CC v KK. In particular:
- that capacity assessors often do not clearly present the available options (especially those they find undesirable) to the person being assessed
- that capacity assessors often do not explore and enable a person’s own understanding and perception of the risks and advantages of different options
- that capacity assessors often do not reflect upon the extent to which their ‘protection imperative’ has influenced an assessment, which may lead them to conclude that a person’s tolerance of risks is evidence of incapacity.
The tool allows you to follow steps to ensure you support people as far as possible to make their own decisions and that you record what you have done.

Download Know your rights as a PDF file
Tool 3: Know Your Rights Young Carers in Focus
This pack aims to make you aware of your rights – your human rights, your legal rights, and your rights to access things like benefits, support and advice.
Need to know where to find things out in a hurry? Our pack has lots of links to useful and interesting resources that can help you – and help raise awareness about young carers’ issues!
Know Your Rights has been produced by Young Carers in Focus (YCiF), and funded by the Big Lottery Fund.
Tool 4: Vision and principles for adults’ and children’s services to work together to support young carers
Download the tool as a PDF file
You can use this tool to consider how well adults’ and children’s services work together, and how to improve this.

Click on the diagram to open full size in a new window
This is based on ADASS and ADCS (2015) No wrong doors : working together to support young carers and their families
Download the tool as a PDF file
You can use this tool to help you consider the whole family in an assessment or review.
What are the risk, stressors and vulnerability factors?
How is the child/ young person’s wellbeing affected?
How is the adult’s wellbeing affected?

What are the protective factors and available resources?
This tool is based on SCIE (2009) Think child, think parent, think family: a guide to parental mental health and child welfare
Tool 6: Engaging young carers
Young carers have told us these ten things are important. So we will do them.
- Introduce yourself. Tell us who you are and what your job is.
- Give us as much information as you can.
- Tell us what is wrong with our parents.
- Tell us what is going to happen next.
- Talk to us and listen to us. Remember it is not hard to speak to us we are not aliens.
- Ask us what we know and what we think. We live with our parents; we know how they have been behaving.
- Tell us it is not our fault. We can feel guilty if our mum or dad is ill. We need to know we are not to blame.
- Please don’t ignore us. Remember we are part of the family and we live there too.
- Keep on talking to us and keeping us informed. We need to know what is happening.
- Tell us if there is anyone we can talk to. Maybe it could be you.

- Equal opportunities
- Complaints procedure
- Terms and conditions
- Privacy policy
- Cookie policy
- Accessibility

Case studies in child welfare
About this guide, child welfare case studies, real-life stories, and scenarios, social services and organizational case studies, other case studies, using case studies.
This guide is intended as a supplementary resource for staff at Children's Aid Societies and Indigenous Well-being Agencies. It is not intended as an authority on social work or legal practice, nor is it meant to be representative of all perspectives in child welfare. Staff are encouraged to think critically when reviewing publications and other materials, and to always confirm practice and policy at their agency.
Case studies and real-life stories can be a powerful tool for teaching and learning about child welfare issues and practice applications. This guide provides access to a variety of sources of social work case studies and scenarios, with a specific focus on child welfare and child welfare organizations.
- Real cases project Three case studies, drawn from the New York City Administration for Children's Services. Website also includes teaching guides
- Protective factors in practice vignettes These vignettes illustrate how multiple protective factors support and strengthen families who are experiencing stress. From the National Child Abuse Prevention Month website
- Child welfare case studies and competencies Each of these cases was developed, in partnership, by a faculty representative from an Alabama college or university social work education program and a social worker, with child welfare experience, from the Alabama Department of Human Resources
- Immigration in the child welfare system: Case studies Case studies related to immigrant children and families in the U.S. from the American Bar Association
- White privilege and racism in child welfare scenarios From the Center for Advanced Studies in Child Welfare more... less... https://web.archive.org/web/20190131213630/https://cascw.umn.edu/wp-content/uploads/2013/12/WhitePrivilegeScenarios.pdf
- You decide: Would you remove these children from their families? Interactive piece from the Australian Broadcasting Corporation featuring cases based on real-life situations
- A case study involving complex trauma This case study complements a series of blog posts dedicated to the topic of complex trauma and how children learn to cope with complex trauma
- Fostering and adoption: Case studies Four case studies from Research in Practice (UK)
- Troubled families case studies This document describes how different families in the UK were helped through family intervention projects
- Parenting case studies From of the Pennsylvania Child Welfare Resource Center's training entitled "Understanding Reactive Attachment Disorder"
- Children’s Social Work Matters: Case studies Collections of narratives and case studies
- Race for Results case studies Series of case studies from the Annie E. Casey Foundation looking at ways of addressing racial inequities and supporting better outcomes for racialized children and communities
- Systems of care implementation case studies This report presents case studies that synthesize the findings, strategies, and approaches used by two grant communities to develop a principle-guided approach to child welfare service delivery for children and families more... less... https://web.archive.org/web/20190108153624/https://www.childwelfare.gov/pubPDFs/ImplementationCaseStudies.pdf
- Child Outcomes Research Consortium: Case studies Case studies from the Child Outcomes Research Consortium, a membership organization in the UK that collects and uses evidence to improve children and young people’s mental health and well-being
- Social work practice with carers: Case studies
- Social Care Institute for Excellence: Case studies
- Learning to address implicit bias towards LGBTQ patients: Case scenarios [2018] more... less... https://web.archive.org/web/20190212165359/https://www.lgbthealtheducation.org/wp-content/uploads/2018/10/Implicit-Bias-Guide-2018_Final.pdf
- Using case studies to teach
- Last Updated: Aug 12, 2022 11:21 AM
- URL: https://oacas.libguides.com/case-studies
Bridging Community-Based Human Services and Health Care: Case Study Series
Health care and community-based organizations (CBOs) across the country are increasingly working together to address social needs that may be contributing to poor health outcomes. These cross-sector relationships are occurring under a variety of partnership models, yet little is known about the factors that contribute to their success. With support from the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation, Nonprofit Finance Fund, the Center for Health Care Strategies, and the Alliance for Strong Families and Communities worked together through the Partnership for Healthy Outcomes to capture insights on partnerships between health care organizations and CBOs, particularly those that serve low-income and/or vulnerable populations.
The following case studies illustrate the potential for diverse and effective models between CBOs and health care organizations. They provide important lessons for how successful partnerships deliver services, share information, secure funding, engage their communities, and evaluate success:
Read the Executive Summary for key learnings from Partnership for Healthy Outcomes:
Ensuring Healthy Outcomes for Louisville’s Vulnerable Children: Health Access Nurturing Development Services Program – This case study looks at a partnership between Family & Children’s Place and the Louisville Metro Department of Public Health and Wellness that provides home visitation services for new and expectant parents to equip them with the skills to support a healthy family.
Housing is a Health Intervention: Transitional Respite Care Program in Spokane – This case study explores a collaboration among Catholic Charities Spokane, Providence Sacred Heart Medical Center (part of the Providence Health & Services health system), and Volunteers of America that provides post-hospitalization care and tailored, coordinated services to homeless clients to give them a better chance at healing.
Collaborating to Reduce Hospital Readmissions for Older Adults with Complex Needs: Eastern Virginia Care Transitions Partnership – This case study features a collaborative in Virginia including more than 80 health care and social services organizations, which is designed to reduce hospital readmissions and improve quality of care by using evidence-based care transition coaching and in-home assessments.
Meeting the Health and Social Service Needs of High-Risk LGBTQ Youth in Detroit: The Ruth Ellis Health & Wellness Center – This case study looks at a partnership between the Ruth Ellis Center and the Henry Ford Health System, an integrated health care organization, which aims to improve the long-term health outcomes for one of the region’s most vulnerable populations.
Other Reports
It takes a village. let’s make the village equitable., the promise, pitfalls, and potential of calaim, strengthening the los angeles food access ecosystem.
- Clear All Filters
- Arts and Culture
- Human Services
- Nonprofit Sector
- Financial Management
- Impact Investing
- All Programs
- Pillars of Work
- Standards of Excellence
- Implementation Support
- Mobilization
- For Policymakers
- Local Policymakers
- State Policymakers
- Federal Policymakers
- All Resources
- Economic Mobility Catalog
- Evaluation Policy Guide
- Spending Guides
- Job Quality Playbook
- Local Infrastructure Hub
- EdResearch for Recovery
- ARP Dashboard
- Moneyball for Government
- Our Leadership
- Our Partners
- Our Supporters
- Racial Justice
- Upcoming Events
- Previous Events
- Press Releases
Read more: Democracy depends on a government that works — here’s how we get there
An RFI Guide: How Requests for Information Can Improve Government Human Services Contracting
Case studies, leading examples, and perspectives, rfi case studies and leading examples.
An increasing number of innovative governments have already improved outcomes by implementing the concepts outlined in the Collaborative Procurement Questions and Steps to Effectively Integrate an RFI into the Procurement Process sections of this guide. The sample Requests for Information (RFIs) and case studies below provide leading examples that can be employed by other governments to solicit feedback from human services providers and community stakeholders as a way to increase collaboration, enhance competition, and prioritize evidence-based programs.
Together these sample RFIs and case studies provide strong examples of how local and state governments have employed a more collaborative procurement process to achieve improved outcomes for their residents. It is worth noting that while a number of the examples below are related to Pay for Success projects, they can nonetheless be used for a much wider range of procurements. In fact, one of the key takeaways from local and state Pay for Success initiatives has been that increased collaboration between governments and human services providers leads to better outcomes.
Through its Office of State Planning and Budgeting, the State of Colorado released a Call for Innovation in January 2017 for proposals highlighting innovative approaches to measurably improving outcomes for Colorado youth involved or at high risk of involvement in the child welfare and juvenile justice systems. Overall, 61 proposals were submitted in response to this Call for Innovation resulting in three state-funded Pay for Success projects to serve Colorado youth and their families.
New York City
New York City has taken a comprehensive approach to increasing collaboration with human services providers and community stakeholders. This effort included the creation of a Nonprofit Resiliency Committee composed of city government officials, human services providers, and community groups. This Committee developed a Guide to Collaborative Communication which provides practical examples of how to use RFIs to increase the overall level of collaboration between government and human services providers. 8
Rhode Island
The Strategies to Identify and Prevent At-Risk Families RFI developed by the Rhode Island Department of Children, Youth, and Families contains in-depth questions on how to better structure, measure, and fund programs for children and families. In a related effort, this same Department moved to outcomes-focused contracts to expand family-based services by asking providers to propose the services, supports, and resources that would best enable children and families to achieve the outcomes prioritized by the Department. This approach, coupled with an institutionalized system of performance feedback loops, allowed the Department to make a 50% expansion in foster care resources for children with the highest need.
South Carolina
Through its Adapting Pay-for-Success Methods to Managed Care Incentives to Improve Health and Social Outcomes for Medicaid Beneficiaries RFI , the South Carolina Department of Health and Human Services requested input on the specific outcomes, intervention strategies, payment structure, and potential barriers to improving the health of its residents. This RFI gathered information on innovative approaches to rewarding demonstrated improvement in health and social outcomes for beneficiaries
The Washington State Health Care Authority’s Community Engagement in Supportive Housing Interventions RFI provides an example of a clear project overview accompanied by very specific questions to elicit feedback about the best program models and potential partnerships for supportive housing. In its Best Starts for Kids program, King County (WA) used an equity lens to design its contracting process and focused on building trust between human services providers and King County government agencies. This focus led to major shifts in the King County contracting process including greater engagement of community members and local organizations to jointly develop shared goals and values for government contracts.
Harvard Kennedy School Government Performance Lab
The Government Performance Lab at the Harvard Kennedy School has a collection of exemplary RFIs and other government procurement documents. In addition, through Bloomberg Philanthropies’ What Works Cities initiative, the Government Performance Lab has also helped a variety of jurisdictions use an RFI to improve outcomes, including Tempe (AZ) and Boston . In Boston, the city used a web form as an RFI to collect information from vendors; this led to a problem-based RFP that outlined outcome goals rather than specific solutions, allowing vendors to use their expertise to identify the best solutions. As part of What Works Cities, the Government Performance Lab has also developed strategies for governments to increase collaboration.
Sector Perspectives
Governments and human services providers bring unique perspectives to the work of solving community challenges. While governments often control budget and policy decisions, human services providers have significant expertise in how best to meet the needs of residents. In order to successfully increase collaboration and achieve more meaningful outcomes for those residents, it is important to understand the unique perspectives each of these stakeholders bring to their primary point of intersection: the human services contracting process.
Human Services Providers Perspective
For human services providers, developing, implementing, and continuously improving an evidence-based intervention that reliably produces meaningful and cost-effective outcomes requires significant and ongoing investment. The process to implement, evaluate, learn, and continually refine an intervention model is very resource intensive. A lack of sustainable funding for ongoing service delivery, even for the most proven intervention models, means that few providers have the resources needed for ongoing program improvement, evaluation, and evidence generation activities. As a result, few human services providers are engaged in continuous evidence building, few of their interventions have strong evidence demonstrating meaningful and sustained results, and government contracts continue to focus primarily on pricing and buying short-term inputs and outputs rather than outcomes of critical importance to communities and practitioners.
Furthermore, government practices, regulations, and laws far too often restrict human services providers’ access to critical data sources needed to produce evidence of impact across social service interventions. Government practices, regulations, and laws also present other obstacles to human services providers’ data analysis and evaluation efforts, including duplicative and conflicting data collection requirements and underfunded or unfunded data collection, analysis, and reporting requirements. Governments can play a critical role in providing the financial resources and access to administrative data needed by human services providers to develop their ability to regularly assess and report their evidence of impact. By strengthening human services providers access to outcomes data and providing sustainable funding for evidence-based programs, the government can serve as a crucial partner in scaling evidence-based interventions.
Public Sector Perspective
Local, state, and federal governments increasingly depend on human services providers to meet the needs of their residents. According to the 2013 National Survey of Nonprofit Government Contracting and Grants, “governments paid close to $81 billion to human services providers for services through contracts and grants in 2012.” 9 Despite the size of this spending, many governments do not have strong partnerships with their contracted human services providers which impedes their ability to get the best outcomes for their residents.
Innovative government leaders who want to establish effective partnerships with human services providers to increase impact face several barriers to changing the status quo. First, procurement and privacy laws are often interpreted in ways that do not incentivize collaboration with human services providers or the sharing of administrative data with them. Second, administrative data are collected with diverse and inconsistent goals, definitions, and reporting units and are not always useful for measuring the impact of interventions. Furthermore, many government agencies have a culture of restricting access to critical data sources, rather than fostering a sharing and learning organizational mindset.
As a result, government contracts are typically focused on measuring inputs and outputs rather than longer-term outcomes, which makes it difficult to structure flexible contracts that allow resources to be redirected to meet changing program needs without time consuming contract amendments. Along with this focus on output targets, an overemphasis on compliance and contracting minutiae means that contracts are too often renewed year after year regardless of impact. As a result, there is a wide gulf between the status quo and the ideal state of collaborative, outcomes-focused, and community-first contracting.
Aligning Sector Perspectives to Build a Better Government Procurement Process
This Request for Information (RFI) Guide is one tool that can help governments and human services providers move away from the output-focused status quo to create partnerships that focus on delivering meaningful outcomes for communities in need. As one example, King County (WA), through their Best Starts for Kids initiative, implemented a more accessible, collaborative, and outcomes-focused contracting system that resulted in a significant increase in new organizations applying for publicly available funds . Collaborative planning and partnership development position both government and human services providers to better accomplish their respective goals: successful outcomes-based human services contracts that make a measurable difference for communities.
Governments and human services providers can improve outcomes for residents through strong collaboration. This Request for Information (RFI) Guide uses a series of Collaborative Procurement Questions to help governments and human services providers jointly improve results at their primary point of intersection: the human services contracting process. By identifying the key questions that governments and human services providers should answer during every human services procurement, this guide is designed to increase collaboration and meet shared outcome goals. In sum, when governments and human services providers work together to implement accessible, collaborative, and outcomes-focused contracting, they can enhance positive results and better serve the young people, families, and communities who depend on them to provide the services they need to reach their fullest potential.
Acknowledgements
Project Evident and Results for America gratefully acknowledge the assistance of the individuals and organizations who provided their insight, advice, and expertise during the development of this Request for Information (RFI) Guide over the course of 2018. Results for America is also grateful to have received generous support from the Kresge Foundation and the Laura and John Arnold Foundation to help support the production of this RFI Guide.
RFI Guide Project Team:
Tamar Bauer, Entrepreneur in Residence, Project Evident Sophie Bergmann, Program Associate, Results for America Nichole Dunn, Vice President for Innovation and Community Impact, Results for America (former) Jed Herrmann, Senior Policy Advisor, Results for America Sara Peters, Senior Director of Policy and Evidence, Project Evident
8 See page 14 of the Guide to Collaborative Communication for details on using an RFI.
9 The Urban Institute, Nonprofit-Government Contracts and Grants: Findings from the 2013 National Survey

An official website of the United States government
Here’s how you know
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
Office of the Assistant Secretary for Planning and Evaluation
Case Management
Displaying 1 - 10 of 43. 10 per page. Page 1.
Case Studies in Supporting Prevention through Human Services Program Integration
Coordinating integrated prevention approaches to serve the whole person, integrating services to strengthen children, youth, and families and prevent involvement in the child welfare system, advancing equity for fathers in human services programs, continuity of care services following coordinated specialty care: an environmental scan, transition options, opportunities for integration, and funding considerations following coordinated specialty care issue brief, the coordinated specialty care transition study: final report, network adequacy for behavioral health: existing standards and considerations for designing standards, virtual case management considerations and resources for human services programs, final outcome evaluation of the balancing incentive program.
Social Work Graduate
Resources for social work graduates
Various social work practice approaches
Blogs added to / updated regularly
https://www.facebook.com/socialworkgraduate
https://www.instagram.com/socialworkgraduate/
Definition, importance, information included, presentation, amending, legislation, terminating client, sharing with client, templates: SOAP, DAP, BIRP, BPSS, Intake report
Three sections follow:
1. Background Material that provides the context for the topic
2. A suggested Practice Approach
3. A list of Supporting Material / References
Feedback welcome!

Background Material

What are case notes?
Sommers-Flanagan (2009) suggest case notes reflect the information provided at an interview and usually cover the following three broad areas:
Identifying, evaluating, and exploring the client's chief complaint and associated therapy goals.
Obtaining data related to the client's interpersonal style, interpersonal skills, and personal history.
Evaluating the client's current life situation and functioning.
AASW (2016) add a fourth point: case notes should also include actions to be taken with regard to the client. Lillis (2017) elaborates: case notes could include reference to or inclusion of other documents, e.g. a care plan, a purchase order and a review summary. For Lillis, case notes are a combination of documents that successfully describe the situation, needs and actual services provided.
Why are case notes important?
Case notes have been emphasized as central to the work in which social workers engage. Case notes:
help focus work,
support effective partnerships with service users and carers,
provide a comprehensive, documented account of work with service users and their families,
assist continuity when workers change,
provide an essential tool for managers to monitor work,
can becomes a major source of evidence for investigations and enquiries.
Inadequate case records result in poor decision-making and adverse client outcomes (AASW, 2016; Lillis, 2017).
Healy and Mulholland (2007) expand many of the above points as follows. Case records are:
a vital information base for client work
formal and factual information—what the case consists of, what has been done to deal with it, when the case began, when the situation changed, the service modifications that took place, when the case ended and the final outcome
situational data on the client’s needs (phone calls, notes, emails, face-to-face interviews)
a way of clarifying the case situation for both the practice worker and the client
having the client speak, and the subsequent work presenting the case in a coherent and focused written form helps clarify the complex issues of the case for both worker and client
a means by which social workers and service users can make visible to others, such as team members, aspects of the social context of the client’s needs that might otherwise be ignored
recording case notes provides a focused social work coherence to them, frames the individuality of the client’s situation, and makes it easier for others dealing with the client to understand the situation
a method of promoting opportunities for collaborative responses in health and community services teams
a means of promoting the recognition of good practice
assist accountability, demonstrate efficiency and quality work as well as commitment and dedication
a vital information base for the achievement of consistency in social work intervention.
How and when should case notes be recorded?
Case notes can be recorded manually or electronically and should:
include on each page the name and DOB or other identifying information of the client
be recorded as soon as possible after an interaction or event
be typed or, if handwritten, clearly readable
include the name, signature and profession/role of the author
include the time of contact, particularly where there are a high volume of interactions in a day (AASW, 2016; Sommers-Flanagan, 2009).
What information should be included in a case note?
There are no prescribed rules for what we put in or out of case notes. It depends on the agency rules and our view. However they are legal documents that can be called for by the court. So in writing them consider
Who is going to read them?
How will / can the information be interpreted?
What needs to be there so someone else can go on with the case if you leave?
Put context around any judgements you make, do not just give your opinion (Maple, 2012).
Information recorded about a client should be impartial , accurate and complete with care taken to ensure that:
only details relevant to the provision of a support or service to which the client has consented are recorded
when working with involuntary clients this means recording information relevant to statutory practice
notes are free from derogatory or emotive language
subjective opinions are qualified with relevant background information, theory or research
relevant information is not omitted. (AASW, 2016)
It is important to listen for what is important to the client. Signs that a matter is important are:
Word, phrase or topic repetitions (e.g. “money” may be mentioned four times)
Use of colloquial phrases of emphasis (e.g. ‘after all I said last time’, ‘I mean’, ‘and then where will she be’)
Swearwords (e.g. ‘it’s bloody awful’)
Tone of voice , such as extra loudness or long pauses followed by a strongly expressed phrase (Healy & Mulholland, 2007)
The guiding principle for deciding what information should be included in a case note is whether it is relevant to the service or support being provided. The type of information that is considered relevant may include:
a range of biopsychosocial, environmental and systemic factors impacting on the client; this includes consideration of an individual's culture, religion and spirituality
risk and resilience factors
facts, theory or research underpinning an assessment
a record of all discussions and interactions with the client and persons/services involved in the provision of support including referral information, telephone and email correspondence
a record of non-attendance, either by the Social Worker or client, at scheduled and agreed meetings or activities
evidence that the Social Worker and client have discussed their respective legal and ethical responsibilities. This may include:
client rights, responsibilities and complaints processes
the parameters of the service and support being offered and agreed to
issues relating to informed consent, information sharing, confidentiality and privacy
efforts to promote and support client self-determination and autonomy
specific responsibilities to clients in particular settings such as private practice or rural settings as per the relevant Association’s Code of Ethics document
professional boundaries and how dual relationships may be managed
record keeping and freedom of information
discharge planning
relevant legislative requirements and their possible implications for practice
details of reasons and any related actions or outcomes leading up to or following the termination or interruption of a service or support (AASW, 2016). Professional views may often be missing in case notes because social workers position their own subjectivity as irrelevant, or as threatening the achievement of accuracy and comprehensiveness. However, at times it is important to express it, e.g. where it is needed to justify an action (Lillis, 2017).
Other writers provide their own details of what should be included in case notes. In particular Oranga Tamariki (2022a) (the New Zealand Ministry for Children) provides general points when writing case notes. TheraNest (2020) draws together three sources to present a detailed list. This information is included under each of the references in the Supporting Material/References section that concludes this topic.
How should information be presented?
There are a number of case-writing models available to social workers. Some of them provide general guidance for writing case notes while others are specific to a service type or context. In addition, many organisations have policies and procedures around case recording (AASW, 2016). Case note templates are discussed further in the Practice Approach section that follows.
Sommers-Flanagan (2009) suggests the following should be used to structure case notes:
Most reports begin with identifying the reason for referral.
They then examine specific behavioural observations made by the interviewer.
The client’s specific problem is stated in some detail, along with its unique evolution. The history and description of several problems may be included.
For some clients past treatments or history of counselling can be listed.
Relevant medical history should be included, e.g. general health, recent illnesses, chronic physical illnesses or hospitalizations, prescription medications.
Include a social and family history where relevant.
Current ability to manage activities around daily living (ADLs) should be mentioned where relevant. This section can be expanded to include a description of the client’s psychological functioning, cognitive functioning, emotional functioning, or personality functioning.
Include some discussion of diagnostic issues, even if they are broad (e.g. depression, anxiety, substance use, eating disorder). For some clients, more detail may be appropriate.
Include a paragraph around case formulation and treatment plan: how the worker views the case and how the worker is likely to proceed in working with the client.
Can case notes be amended or changed at a later date?
If a change must be made to correct an error or omission, the change can be recorded as a new and separate case note. It is advisable to provide an explanation for its earlier absence or inaccuracy. Add, if possible, a note in the margin of the original case note referring the reader to the additional or amended detail (AASW, 2016).
What are the legislative responsibilities with regard to case notes?
Case notes may be subject to, and can be subpoenaed, for a range of legislative processes and requirements. The nature of these requirements may differ between organisations, districts, States and countries. Therefore it is important for Social Workers to:
be familiar with the specific legal requirements and processes impacting on practice
consider the implications of Federal and State legislation to the recording of case notes
understand how these requirements are implemented within their organisation (where relevant)
understand what policies and procedures may need to be implemented when working in private practice (AASW, 2016).
What should happen with case notes on termination of a service or support?
Termination or interruption of services should be included in case notes. Given termination may be unanticipated (e.g. departure of a social worker), it is particularly important to ensure that case notes are maintained and updated as soon after an interaction or event as practicable (AASW, 2016).
Sharing case notes with the client
It is important that clients can view reports, but they may also misinterpret information in a report unless offered guidance. The following guidelines are suggested:
Inform clients at the outset that records will be kept, and clients can have access to them.
Inform clients that some portions of the records are written in language designed to communicate with other professionals; consequently, the records may not be especially easy to read or understand.
If clients request their records, tell them you would like to review the records with them before releasing them, so as to minimize the possibility that the records are misinterpreted.
When clients request records, schedule an appointment (free of charge) with them to review the records together.
If clients are no longer seeing you, are angry with you, or refuse to meet with you, you can (a) release the records to them without a meeting (and hope the records are not misinterpreted), or (b) agree to release the records only to another licensed professional (who will review them with the client).
Whatever the situation, always discuss the issue of releasing records with your supervisor, rather than acting impulsively on your client's request (Sommers-Flanagan, 2009).
- Practice Approach
One of the themes to emerge from the literature around case notes is how they are “setting dependent” (AASW, 2016); Maple, 2012; TheraNest, 2020). Prescribed rules for what is included or excluded varies from agency to agency. However a number of key points from the Background Material section above. They include the following:
Each page should have the client's name, client's date of birth, social worker’s name and date of the interaction.
Case notes should be written as soon as possible after the interaction.
Consider who is going to read notes and how this should impact on writing style.
Information about a client should be impartial, accurate, complete, and free from emotive language.
Subjective opinions should be qualified with relevant background information, theory or research.
Be clear and consistent – don’t include extra details that are not to the point.
Sign and date the case notes when completed
Relevant information recorded in case notes may include:
The reason for the referral; the client’s specific problems
Evidence that legal and ethical responsibilities of both worker and client have been discussed
Relevant behavioural observations
A range of biopsychosocial, environmental and systemic factors impacting on the client. When relevant:
medical history
social and family history
ability to manage activities of daily living
culture, religion and spirituality
Risk and resilience factors
An assessment supported by facts, theory and/or research
A plan of action based on this assessment
A Selection of Formats for Writing Case Notes
Several different formats exist for writing case notes. TheraNest (2020) highlights three:
S.O.A.P. (Subjective, Objective, Assessment, Plan
D.A.P. (Data, Assessment, Plan)
B.I.R.P. (Behavior, Interventions, Response, Plan)
SOAP (Subjective, Objective, Assessment, Plan)
These four sections try to ensure case notes are complete, yet concise.
Subjective: What the client says about the problem; opinion-based information from the client including their goals, concerns, feelings, perceptions of their own problems. Also include relevant information from other family members or close friends.
Objective: Information that is fact-based, verifiable and quantifiable. This can be direct observations of the client. This might include things like the client’s appearance, body language and other obvious behaviour.
Assessment: Using subjective and objective information to assess the situation; a conclusion or recommendation could be included, with evidence as to why conclusions have been drawn.
Plan: The plan of action, e.g. referrals to other agencies, goals, timeline targets, i.e. the steps to take to assist the client meet their needs (AGS, 2019; Government of Northwest Territories Canada, n.d.; Moore, 2022a).
AGS (2019) provides two examples of case notes to illustrate the above. The AGS website also provides a template social workers can use to record case notes.
Examples of SOAP case notes
| what the client says | ||
| facts and observations | ||
| assess the situation + conclusion | ||
| steps to take; referrals | ||
DAP (Data, Assessment, Plan)
The Data heading covers everything that occurred during a counselling session, including but not limited to a client’s observable responses, affect, traits, and behavior. This section includes specific, objective information about the session’s focus, what was said, and more, in order to answer the question: “What did I observe?”
Under Assessment, social workers interpret and analyze the data in the previous session. This involves applying some professional subjectivity and may result in clinical hypotheses or findings. Here, social workers might record things like how a session related to a client’s overall treatment goals, a working hypothesis, and/or a probable diagnosis of a client’s condition.
The Plan section is used for making decisions and recommending a plan of treatment for the client. Here, the objective and subjective data from the previous two sections are used to inform a social worker’s strategy or next actions – often between the current session and the next. This could include recommendations for therapy or lifestyle changes, among other short- and long-term treatments (Moore, 2022b).
The key difference between SOAP and DAP formats is that the former breaks down the information about a session into two discrete sections, which can be highly useful in healthcare contexts where medications, blood results, and other clinical data can inform a patient’s treatment (Moore, 2022b).
BIRP (Behaviour, Interventions, Response, Plan)
Behavior (Presenting the Problem) This section records the subjective and objective details that were observed (CF SOAP outline above). This section can also contain details about the session itself, such as where it took place.
Example: Met with client X in the office. The most recent assessment shows they are presenting symptoms of anxiety. Today they showed signs of exhaustion, lack of focus, and looked tired. They reported not being able to sleep in the past week and feeling overwhelmed by work.
Interventions This section outlines the methods used to reach the goals and objectives of the therapy. It’s a concise summary of the conversation, focusing strongly on the therapist’s actions and the patient’s reactions.
Example: Through client-centered techniques, this writer encouraged the patient to expand their thoughts about their work. Negative thoughts were identified and challenged. The patient was asked to see if there is a link between their insomnia and the stressful period at work. The connection was successfully made and normalized through discussion. The conversation then focused on the specific work-related triggers that may have led to insomnia. A mild sleep aid was prescribed.
Response In this section, the therapist should record the client’s response to the intervention, including what the client said and how they reacted.
Example: The patient initially rejected the link between their insomnia and stress at work. When asked how work made them feel, the patient became silent, reduced eye contact, and disengaged from the conversation with the writer. After a few moments of thinking, the patient was able to describe their own feelings in relation to their work.
Plan The plan outlines when the next session will take place, and its focus.
Example: The next appointment scheduled for September 16, will assess the client’s response to the sleep aid and reassess their feelings about work.
https://quenza.com/blog/girp-notes/
The GIRP framework offers a powerful communication tool by delivering a streamlined, concise, and organized account of a patient or client’s journey. GIRP notes highlight key developments and treatment plans , becoming an invaluable asset for all stakeholders.
What is a GIRP note?
The acronym GIRP stands for: G oal, I ntervention, R esponse, and P lan.
Goal GIRP notes always start with a goal. The goal describes what the patient wants to get out of therapy or coaching. You might include both short and long-term goals in this first section. For example: Janine has been attending fortnightly psychotherapy sessions to get better control of her social anxiety and agoraphobia. Long-term, she would like to have a more active social life. However, at present, her main goal is to start doing her grocery shopping in person again. Janine feels this is a safe and achievable goal for her to build some positive momentum.
Intervention The intervention simply describes the techniques, methods, or strategies the practitioner and client are using to work toward the desired change.
So, in Janine’s case, the intervention section might read: Therapist and client discussed gradual exposure techniques to start working up to completing a full in-person grocery shop. Or, for another person: Discussed client’s limiting beliefs around her capacity to successfully launch an online business. Introduced the concept of focusing on strengths rather than weaknesses. Then, prompted the client to come up with some empowering affirmations she can use when self-doubt is becoming an issue.
Response The response section provides an objective account of the individual’s reaction or progress in response to the intervention. This forces the practitioner to hone in on whether what they are doing in session is working and adjust course if necessary. In coaching, an example would be: Client struggled immensely with identifying strengths. By the end of the session we identified 3: creativity, persistence, and ability to learn new things. Did not get to move onto affirmations before the end of the session.
Plan The plan sets out the forthcoming steps, giving a clear roadmap for future treatment, services, and/or client tasks, based on insights gained from the individual’s response to past interventions.
For example: Janine to undertake 2 more trips for grocery shopping before next session. If successful, therapist and patient to decide on a new goal. May be suitable to include more social interaction, in line with long-term goal of having an active social life.
Benefits of GIRP Notes
The two most significant benefits of GIRP notes are that they:
1. Enhance communication between the client and professionals involved in a case resulting in a collaborative approach to care and a strong therapeutic relationship.
2. Maintain a focus on the individual’s goals.
Biopsychosocial-Spiritual Approach (BPSS)
The BPSS is used quite frequently by social workers, especially in their initial dealings with clients. The following is a template that could be adapted as necessary for different clients. Other templates for the BPSS can be found in a separate topic on this website at https://www.thesocialworkgraduate.com/post/bio-psychosocial-spiritual-assessment
_________________________________________________________________________________
Client Name:
Client D.O.B:
Client address:
Client contact details:
Referred by:
Presenting problem:
Family Structure/genogram:
Medical / psychological history:
Current medications:
Employment / education:
Other issues: Should check areas in BPSS to see if any other topics should be included
Planned intervention and referrals:
_____________________________________________________________________________

Pacheco (2014) suggests social workers can develop a template that can be written over when taking notes.The template can contain prompts to ensure the social worker does not forget to touch on certain areas. An example using the BPSS approach is shown on the right.
This is quite simple to make: type up your page with the prompts, highlight the prompts, and choose a light colour from the available font colours, e.g.tan background 2.
Pacheco’s approach could be used with other approaches too, such as SOAP, DAP and BIRP.
A number of other writers suggest case notes templates, and these have been included under their reference in the following Supporting Material / References section.
Healy and Mulholland (2007) suggest three approaches: topic sentences, problems to be solved, and expressing client concerns.
Oranga Tamariki (2022b) provide an example of a good and poor case note
Social Work Haven (2021) has developed a case notes cheat sheet
Sommers-Flanagan (2009) provide a detailed intake report template.
Supporting Material/References
AASW: Australian Association of Social Workers. (2016). Case notes . Retrieved from https://www.aasw.asn.au/document/item/2356
AGS: Airiodion Global Services. (2019). A simple (but detailed) guide on different types & stages of social work processes . Retrieved frpm https://www.airiodion.com/social-work-process/
Healy, K., & Mulholland, J. (2007). Writing Case Records. In K Healy & J Mulholland (Eds.), Writing Skills for Social Workers (pp. 68-86) . Sage Publications.
Three Methods for Writing Case Notes
Topic sentences—provide the gist but leave out the detail
Problems to be solved
Expressing client concerns—state the client’s concerns as well as the social worker’s professional judgement
An example of each of the above follows based on this situation: The grandmother said: It was last Friday she came round, late as usual, and she hadn’t brought me any money to buy food for the kid after all I said last time it happened - no money and no food either - I mean I don’t mind looking after the kid - it’s bloody awful the way she treats that child - but on my pension I can’t pay for its food and that - I mean if she doesn’t give me some money soon I will have to stop caring for the kid and then where will she be?’
Topic sentences :
This case is about childcare by grandmother. Grandmother is client. The mother is in paid employment; she finds it difficult to supply money to the carer, and to pick up the child on time. The carer is unhappy about the money situation, and to lesser degree the time problem, and threatens to stop the caring.
Problems to be solved :
This case is about childcare by grandmother. Problem 1 - money, since mother is erratic about providing it.
Problem 2 - time of child collection, since mother is often late.
Problem 3 - carer is unhappy about the money situation, and to a lesser degree the time problem, and threatens to stop the caring.
[You may wish to go one step further and alert the attention of a specific team member by writing Problem 3 as : Problem 3 - ’In my view, the carer may need counselling’ , or ’Carer and mother may need mediation’.]
Expressing client concerns :
Client, grandmother as carer, complained about child’s mother supplying no money and being late. She warned that she could not continue with the childcare unless she was paid.
Lillis, T. (2017). Imagined, prescribed and actual text trajectories: The ‘problem’ with case notes in contemporary social work. Text and Talk, 37 (4), 485–508. http://dx.doi.org/doi:10.1515/text-2017-0013
Government of Northwest Territories Canada. (n.d.). SOAP case notes guide . Retrieved from https://www.hss.gov.nt.ca/professionals/sites/professionals/files/resources/soap-case-notes-guide.pdf
GoodTherapy. (2020). For social workers: Tips for writing case notes . Retrieved from https://www.goodtherapy.org/for-professionals/business-management/private-practices/article/for-social-workers-tips-for-writing-case-notes
Maple, M. (2012). Case notes . Lecture notes, HSSW 100, University of New England, Australia.
Miller, K. (2022). BIRP notes: A complete guide on the BIRP note-taking forma t. Retrieved from https://quenza.com/blog/birp-notes/
Moore, C. (2022a). Writing SOAP notes, step-by-step: Examples + templates . Retrieved from https://quenza.com/blog/soap-note/
Moore, C. (2022b). How to write DAP notes: 5 best templates and examples . Retrieved from https://quenza.com/blog/dap-notes/
Oranga Tamariki (New Zealand Ministry for Children). (2022a). Keeping accurate records – guidance . Retrieved from https://practice.orangatamariki.govt.nz/practice-approach/practice-standards/keep-accurate-records/keep-accurate-records-guidance/
Oranga Tamariki - New Zealand Ministry for Children (2022a) suggests the following general points in providing guidance for social workers when writing case records. Each point below is expanded in the actual document.
Implement the practice standards for each tamaiti (child) in case notes, assessments, plans and reports
Record the process of engaging with, assessing, making decisions and reasons for decisions
Ensure what is recorded is easily understood
Provide adequate support if tamariki (children) want access to records
Keep personal information safe and secure
Document any key decisions made, or actions taken, the rationale for decisions or actions and the next steps.
Records identify the key people with whom engagement has occurred
Document views on relevant people involved in the case and how this has informed decision-making
Develop a chronology of critical key events and changes for te tamaiti (the child) and whanau (family) across their lifespan
Document how tamaiti (child), their whanau (extended family), caregivers or others working with the have responded to social worker decisions
Choose an appropriate communicate approach when communicating with clients
Include in notes how the family responds to decisions made
Document any oversight/approval obtained for key decisions that require it
Record discussions, key points and decisions made during supervision or case consults, including next steps
Review records often to keep the current and accurate
Oranga Tamariki (New Zealand Ministry for Children). (2022b). Case note examples . Retrieved from https://practice.orangatamariki.govt.nz/previous-practice-centre/policy/recording/key-information/case note-examples/
| Date: d/m/y Venue: home address John Last-name (DOB d/m/y) Shirley Last-name (caregiver) Graeme Last-name (caregiver) – not home, at work. Name of social worker (Social Worker)
Ensuring John’s care placement is supported and meeting all his wellbeing needs.
John took me into his bedroom to show me all his toys and games. We played connect four and then cards. John talked about Jim (Paternal Grandfather) giving him the Sponge Bob cards for Christmas. John had good eye contact and was able to speak freely, chatting and answering questions. His hand eye coordination was great; John showed me how he could make a helicopter which then fired bullets. John talked about Fluffy (cat) and Peaches (dog). John showed me that Peaches will sit down on her blanket when John says “sit”. John talked about how much he loves rugby and can’t wait for the season to begin. John is hoping to have the same coach he had last year (called Wogs) because he really liked him. John said he likes playing touch at lunchtimes at school with his mates Daniel, Ethan, Dante, Jayden and Nikau. If there’s not a touch game on John usually plays basketball or tennis with his mates. John says he is happy seeing his mum. John didn’t expand on this topic.
Shirley had made afternoon tea; we sat at the dining room table together. John stayed in his room playing with his Lego. Shirley said she was “very happy” with how things were going and that John was a “good boy”.
John is playing cricket on Saturday mornings between 10am until 12pm. Graeme takes him to this and watches the games.
John is going well at school however his teacher is a bit concerned about his lack of concentration at times. The teacher said to Shirley that John daydreams a lot and when the teacher asks him what he is thinking about, he says rugby.
John still sees Tracey (mum) every Friday afternoon between 3.30 and 4.30pm at our office. Maggie (resource worker) picks John up from school and takes him to access, then drops him off at Shirley’s afterwards. Tom (Tracey’s partner) sometimes comes along to the visits with Tracey. No issues raised by Shirley.
Finances for John’s rugby subs and a pair of boots; Contact the school teacher to discuss John’s daydreaming, does this impact on his learning? Call Shirley/ Graham by (date), to organise the next home visit. Name Social Worker Office | Met with John and Shirley. John took me into his bedroom to show me all his toys and games. We sat on the floor and played Connect Four and then had a game of snap with some Sponge Bob cards John had got for Christmas from Jim. John then showed me a lego set he had where you can make trucks, cars, motorbikes and even a helicopter. John showed me how he could make the helicopter which then fired bullets. John also showed me Shirley’s cat, Fluffy and Dog, Peaches that he likes. John showed me that Peaches will sit down on her blanket when John says “sit”. Shirley had made afternoon tea, so we then sat at the huge dining room table and had scones with jam and cream and a cup of tea. Shirley said she was very happy with how things were going, and that John was a good boy. He is playing cricket on Saturday mornings at 10am and this goes until 12pm. Graeme takes him to this and watches the games. Shirley wanted to know if we could pay for John’s upcoming rugby subs and a pair of boots. Shirley wants to get John a good pair of Nike boots from Rebel Sport that will last the distance rather than cheap ones from the Warehouse that will fall apart halfway through the season. Shirley also said that John is going well at school however his teacher is a bit concerned about his lack of concentration at times. The teacher at KVPS has said that John daydreams a lot and when the teacher asks him what he is thinking about, he says rugby. John really loves rugby and can’t wait for the season to begin. John wants to have the same coach he had last year; a guy called Wogs who John really liked. John said he likes playing touch at lunchtimes at school with his mates Daniel, Ethan, Dante, Jayden and Nikau. If there’s not a touch game on John usually plays basketball or tennis with his mates. John still sees Tracey every Friday afternoon between 3.30 and 4.30pm at our office. Maggie picks John up from school and takes him to access, then drops him off at Shirley’s afterwards. Tom sometimes comes along to the visits with Tracey. I thanked Shirley for the afternoon tea and told her I’d be back in a couple of months. |
Pacheco, I. (2014). Note taking templates for clinical social work . Retrieved from http://socialworktech.com/2014/06/23/note-taking-templates-for-clinical-social-work/
Social Work Haven. (2021). Sample case notes from social work you can learn from . Retrieved from https://socialworkhaven.com/sample-case-notes-for-social-work/
Case notes cheat sheet
Date and time
Reason for contact or conversation
Capacity to make decisions around subject being discussed if applicable
Views of the person
Views of others
What did you see?
What did you do?
Any risks identified
Did you consult or share information with anyone? If so, why?
Your professional opinion and analysis
Action plan
Somers-Flanagan, J., & Sommers-Flanagan, R. (2009). Intake interviewing and report writing. In J. Sommers-Flanagan & R. Sommers-Flanagan (Eds.). Clinical interviewing (4th ed., 175-212). John Wiley & Sons.
Sample Intake Report Outline
Use the following intake report outline as a guide for writing a thorough intake report. Keep in mind that this outline is lengthy and therefore, in practical clinical situations, you will need to select what to include and what to omit in your client reports.
--------------------------------------------------------------
NAME: DATE OF BIRTH: AGE: DATE OF INTAKE: INTAKE INTERVIEWER: DATE OF REPORT:
I. Identifying Information and Reason for Referral
A. Client name
D. Racial/Ethnic information
E. Marital status
F. Referral source (and telephone number, when possible)
G. Reason for referral '(why has the client been sent to you for a consultation/intake session?)
H. Presenting complaint (use a quote from me client to describe the complaint)
II. Behavioral Observations (and Mental Status Examination)
A. Appearance upon presentation (including comments about contact, body posture, and facial expression)
B. Quality and quantity of speech and responsivity to questioning
C. Client description of mood (use a quote in the report when appropriate)
D. Primary thought content (including presence or absence of suicidal ideation)
E. Level of cooperation with the interview
F. Estimate of adequacy of the data obtained
III. History of the Present Problem (or iIlness)
A. Include one paragraph describing the client's presenting problems and associated current stressors
B. Include one or two paragraphs outlining when the problem initially began and the course or development of symptoms
C. Repeat, as needed, paragraph-long descriptions of additional current problems identified during the intake interview (client problems are usually organized using diagnostic-DSM-groupings, however, suicide ideation, homicide ideation, relationship problems, etc., may be listed)
D. Follow, as appropriate, with relevant negative or rule-out statements (e.g., with a clinically depressed client, it is important to rule out mania: "The client denied any history ofmanic episodes.")
IV. Past Treatment (Psychiatric) History and Family Treatment (Psychiatric) History
A. Include a description of previous clinical problems or episodes not included in the previous section (e.g., if the client is presenting with a problem of clinical anxiety, but also has a history of treatment for an eating disorder, the eating disorder should be noted here)
B. Description of previous treatment received, including hospitalization, medications, psychotherapy or counselling, case management, and so on.
C. Include a description of all psychiatric and substance abuse disorders found in all blood relatives (i.e., at least parents, siblings, grandparents, and children, but also possibly aunts, uncles, and cousins)
D. Also include a list of any significant major medical disorders in blood relatives (e.g., cancer, diabetes, seizure disorders, thyroid disease)
V. Relevant Medical History
A. List and briefly describe past hospitalizations and major medical illnesses (e.g., asthma, mv positive, hypertension)
B. Include a description of the client's current health status (it's good to use a client quote or physician quote here)
C. Current medications and dosages
D. Primary care physician (and/or specialty physician) and telephone numbers
VI. Developmental History (This section is optional and is most appropriate for inclusion in child/adolescent cases.)
VII. Social and Family History
A. Early memories/experiences (including, when appropriate, descriptions of parents and possible abuse or childhood trauma)
B. Educational history
C. Employment history
D. Military history
E. Romantic relationship history
F. Sexual history
G. Aggression/Violence history
H. Alcohol/Drug history (if not previously covered as a primary problem area)
I. Legal history
J. Recreational history
K. Spiritual/Religious history
VIII. Current situation and Functioning
A. A description of typical daily activities
B. Self-perceived strengths and weaknesses
C. Ability to complete normal activities of daily living
IX. Diagnostic Impressions (This section should include a discussion of diagnostic issues or a listing of assigned diagnoses.)
A. Brief discussion of diagnostic issues
B. Multiaxial diagnosis from DSM
X. Case Formulation and Treatment Plan
A. Include a paragraph description of how you conceptualize the case. This description will provide a foundation for how you will work with this per- son. For example, a behaviorist will emphasize reinforcement contingencies that have influenced the client's development of symptoms and that will likely aid in alleviation of client symptoms. Alternatively, a psycho- analytically oriented interviewer will emphasize personality dynamics and historically significant and repeating relationship conflicts.
B. Include a paragraph description (or list) of recommended treatment approaches.
TheraNest. (2020). Elements of effective case notes for social wor k. Retrieved from https://theranest.com/blog/elements-of-effective-case-notes-for-social-work/
The guiding principle for writing effective case notes is to include content relevant to the service(s) or support provided. The specific content will vary based on your specific situation, but AASW broadly recommends the following:
The biopsychosocial, environmental and systemic factors impacting the client, including the client’s culture, religion/spirituality
Facts, theory or research underpinning an assessment
A record of all discussions and interactions with the client and persons/services involved in the provision of support including referral information, telephone and email correspondence
A record of non-attendance (by either you or your client) at scheduled and agreed meetings or activities
Evidence that you and your client have discussed your respective legal and ethical responsibilities — such as client rights and responsibilities, informed consent, confidentiality and privacy, professional boundaries, freedom of information, etc.
In addition to these broad guidelines, experts also recommend including the following specific pieces of information in each case note:
Topics discussed during the session
How the session related to the treatment plan
How the treatment plan goals and objectives are being met
Interventions and techniques used during the session and their effectiveness
Clinical observations
Progress or setbacks
Signs, symptoms and any increase or decrease in the severity of behaviors as they relate to any diagnosis used
Homework assigned, results and compliance
The client’s current strengths and challenges
Additionally, the following have to be included in case notes:
Demographic information
Prognosis and treatment plan
Progress to date
Dates of service
Who attended the sessions
Financial issues (billing, costs, payments, etc.)
This may seem like a lot of information to present, but case notes with this data will help document not only what took place in the session, but also your decision-making process and how you implemented treatment and intervention
Recent Posts
An Everyday Social Work Approach
Bio-Psychosocial-Spiritual Assessment
Home — Essay Samples — Education — Case Study — Challenges Facing Human Services Case Study
Challenges Facing Human Services Case Study
- Categories: Case Study
About this sample

Words: 662 |
Published: Mar 14, 2024
Words: 662 | Page: 1 | 4 min read

Cite this Essay
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing style below:
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Dr. Heisenberg
Verified writer
- Expert in: Education

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
1 pages / 644 words
4 pages / 1752 words
3 pages / 1390 words
1 pages / 476 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online
Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Case Study
The murder case of Jimmy Wayne Glens is a tragic and complex story that has captivated the public's interest for many years. This essay will delve into the details of the case, exploring its history, debates, and ultimate [...]
Cesare Lombroso, an Italian criminologist in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, formulated the theory of atavism, which posits that criminals are primitive or sub-evolved humans. Lombroso believed that certain physical [...]
Social work case studies provide valuable insights into the challenges faced by social workers in their daily practice. By examining real-life scenarios, these case studies allow us to understand the complex nature of social [...]
Community colleges play a pivotal role in the higher education landscape by offering accessible and affordable education to a diverse student population. Guilford Technical Community College (GTCC), located in North Carolina, [...]
The Injaka Bridge project was in a small town called Bushbuckridge in South Africa. It was proposed to be a seven-span 300m steel structure. In July 1998 it was being constructed using the incremental launching method when [...]
Competency Statement 5 is designed to ensure that early childhood educators are able to effectively observe and document children's development and learning. In a case study scenario, this involves carefully observing a child's [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
These cases were designed for use in all levels of social work education and training. Additionally, each of the cases was reviewed by a consultant with expertise in child welfare case development for the purpose of social work education. Learn more about how to use the Case Studies (PDF). Aaron and Amber (PDF)
Case Studies The following case studies were included to highlight different ways that social workers can assess and intervene with issues of social isolation. These cases are free to you to use, modify, and incorporate into your teaching. They include: The case of George, which demonstrates the need to examine our cases with
%PDF-1.5 %µµµµ 1 0 obj >>> endobj 2 0 obj > endobj 3 0 obj >/ExtGState >/XObject >/ProcSet[/PDF/Text/ImageB/ImageC/ImageI] >>/MediaBox[ 0 0 612 792] /Contents 4 0 ...
Case Studies topics. Case Study 1: Eve; Case Study 2: Josef; Case Study 3: Susan; Case Study 4: Anne; Case Study 5: Michelle and Joel; Overarching resources. Top tips for practice; Law and policy; Social work standards; General resources about caring; General resources for social work with carers; Practice Evidence: an overview; Project ...
Case studies and real-life stories can be a powerful tool for teaching and learning about child welfare issues and practice applications. This guide provides access to a variety of sources of social work case studies and scenarios, with a specific focus on child welfare and child welfare organizations.
Real Cases Project: The Anne M. Case Study 2 Integrating Child Welfare Practice Across the Social Work Curriculum Current Investigation In the morning of 7/17 child protective service (CPS) worker left phone messages for both Mr. and Ms M. stating her name, contact number, agency, and need to schedule ...
13-16 Introduction to the Case Studies, Brenda McGowan 17-18 Overview of the Case Studies, Tatyana Gimein 19-26 Andrea R. Case Study 27-34 Anne M. Case Study 35-42 Mary S. Case Study TEACHING GUIDES 43-58 Social Work Research, Michael Phillips 59-68 Human Behavior in the Social Environment, Rozetta Wilmore-Schaeffer
This brief summarizes case study findings from nine sites across the U.S. that integrate human services with a prevention lens. It includes how case study sites integrated services; what helped and challenged sites during the ongoing implementation of their integrated prevention initiatives; and ideas and strategies for improving implementation ...
Facilitating Learning in Context: Refugee Resettlement Case Management Pedagogy in a Human Services Course Cinzia Pica This article examines a community engagement course for aspiring human service professionals in which we prioritize critical and systemic perspectives in refugee resettlement case management.
Case Study Examples by Key Takeaway The following examples from the case studies help illustrate a subset of the above key takeaways at the ground-level (see the individual case studies for more detail): Upfront Relationship -Building Health Care for High-Risk LGBTQ Youth. In moving to a fully integrated primary and behavioral health
Collaborating to Reduce Hospital Readmissions for Older Adults with Complex Needs: Eastern Virginia Care Transitions Partnership - This case study features a collaborative in Virginia including more than 80 health care and social services organizations, which is designed to reduce hospital readmissions and improve quality of care by using ...
The sample Requests for Information (RFIs) and case studies below provide leading examples that can be employed by other governments to solicit feedback from human services providers and community stakeholders as a way to increase collaboration, enhance competition, and prioritize evidence-based programs.
Colorado as a Case Study for Policymakers 7 As an initial step in offering policymakers a model for human services agencies seeking to drive 2Gen systems change at the state level, Ascend presents a case study on Colorado, a state with significant 2Gen momentum and one in which Ascend has invested deeply since 2012.
This case study focuses on Solution's 1,000-day program, Solutions University, which includes transitional and permanent housing; intensive case management; unpaid work experience; classes about life skills, parenting, and employment readiness; on-site mental health services; and recovery support services for individuals with substance use ...
Case Studies in Supporting Prevention through Human Services Program Integration. October 1, 2024. The Office of the Assistant Secretary for Planning and Evaluation in the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services has been working with researchers, human services agency leaders, and persons with lived experience to visualize, describe, and ...
Lillis (2017) elaborates: case notes could include reference to or inclusion of other documents, e.g. a care plan, a purchase order and a review summary. For Lillis, case notes are a combination of documents that successfully describe the situation, needs and actual services provided.
The Journal of Human Services (JHS) is the official journal of the National Organization for Human Services. Skip to main content. ISSN: 2689-7040 . Journal of Human Services . Menu; Articles. Back; Articles; Book Reviews; Brief Notes; ... Case Studies . October 17, 2023 EDT. Nurturing Success: Empowering Human Services Students to Lead a ...
Evidence Snapshot: Case management, OPRE Report #2023-163, Washington, DC: Office of Planning, Research, and Evaluation, Administration for Children and Families, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. Glossary. Case Management: Meeting, typically one-on-one, with an employment specialist or counselor who helps assess needs and refers ...
with the families. In summary, each of the three family case studies can be integrated throughout this course on social work values and ethics. The following course outline illustrates how the three case studies can be integrated throughout a course on values and ethics. I. Overview of the course A. Use of case studies B. Value base of social work
In today's complex and rapidly changing world, the field of human services faces a myriad of challenges that require innovative solutions and thoughtful... read full [Essay Sample] for free