Faculty Resources
Assignments.

The Human Resources Management course includes a series of openly licensed written assignments and discussions aligned to specific learning outcomes and chapters. If you import this course into your learning management system (Blackboard, Canvas, etc.), all of the assignments and discussions (listed in the table, below,) will automatically be loaded into your LMS assignment and discussion-board tools. They can be used as is, modified, combined with your own assignments, or removed altogether.
The assignments in this course align with the following scenario:
You are a college senior who has been selected to participate in a hybrid internship/onboarding program with an elite HR research and advisory firm. Your training consists of a combination of formal education—specifically, enrollment in this Human Resource Management course—and a rotation in support of the principals of the firm. In your rotations, you will synthesize what you’ve learned in the relevant modules to address firm or client issues, conducting additional research as necessary and developing draft deliverables as instructed by the principal consultant. The quality of your deliverables – that is, your ability to convert learning into practical insight – will largely determine whether, at the end of the internship period, you are offered a position with the firm or simply thanked for your participation.
You can view them below or throughout the course.

Rubric for Assignments
There is also a sample rubric to assist you in grading. Instructors may modify these guidelines or use their own.
Discussions
The following discussion assignments will also be preloaded (into the discussion-board tool) in your learning management system if you import the course. They can be used as is, modified, or removed. You can view them below or throughout the course.
Rubric for Discussion Posts
Answer keys for the discussion posts are available to faculty who adopt Waymaker, OHM, or Candela courses with paid support from Lumen Learning. This approach helps us protect the academic integrity of these materials by ensuring they are shared only with authorized and institution-affiliated faculty and staff.
- Assignments. Provided by : Lumen Learning. License : CC BY: Attribution
- Pencil Cup. Authored by : IconfactoryTeam. Provided by : Noun Project. Located at : https://thenounproject.com/term/pencil-cup/628840/ . License : CC BY: Attribution

11.1 An Introduction to Human Resource Management
- What has been the evolution of human resource management (HRM) over the years, and what is the current value it provides to an organization?
Human resource management over the years has served many purposes within an organization. From its earliest inception as a primarily compliance-type function, it has further expanded and evolved into its current state as a key driver of human capital development. In the book HR From the Outside In (Ulrich, Younger, Brockbank, Younger, 2012), the authors describe the evolution of HR work in “waves”. 1 Wave 1 focused on the administrative work of HR personnel, such as the terms and conditions of work, delivery of HR services, and regulatory compliance. This administrative side still exists in HR today, but it is often accomplished differently via technology and outsourcing solutions. The quality of HR services and HR’s credibility came from the ability to run administrative processes and solve administrative issues effectively. Wave 2 focused on the design of innovative HR practice areas such as compensation, learning, communication, and sourcing. The HR professionals in these practice areas began to interact and share with each other to build a consistent approach to human resource management. The HR credibility in Wave 2 came from the delivery of best-practice HR solutions.
Wave 3 HR, over the last 15–20 years or so, has focused on the integration of HR strategy with the overall business strategy. Human resources appropriately began to look at the business strategy to determine what HR priorities to work on and how to best use resources. HR began to be a true partner to the business, and the credibility of HR was dependent upon HR having a seat at the table when the business was having strategic discussions. In Wave 4, HR continues to be a partner to the business, but has also become a competitive practice for responding to external business conditions. HR looks outside their organizations to customers, investors, and communities to define success—in the form of customer share, investor confidence, and community reputation. HR’s credibility is thus defined in terms of its ability to support and drive these external metrics. Although each “wave” of HR’s evolution is important and must be managed effectively, it is the “outside in” perspective that allows the human resource management function to shine via the external reputation and successes of the organization.
Catching the Entrepreneurial Spirit
Human resources outsourcing—entrepreneurial ventures.
Human resources is a key function within any company, but not all companies are able to afford or justify full-time HR staff. Over the last decade, HR outsourcing has become a good business decision for many small companies whose current staff doesn’t have the bandwidth or expertise to take on the risks of employee relations issues, benefits and payroll, or HR compliance responsibilities. This has led many HR practitioners to try out their entrepreneurial skills in the areas of HR outsourcing and “fractional HR.”
Human resources outsourcing is very commonly used by smaller companies (and often large companies too) to cover such tasks as benefits and payroll management. This is an area that has been outsourced to third parties for many years. More recent is the trend to have “fractional HR” resources to help with the daily/weekly/monthly HR compliance, employee relations, and talent management issues that companies need to address. Fractional HR is a growing industry, and it has become the service offering of many entrepreneurial HR ventures. Fractional HR is essentially as it sounds—it is the offering of HR services to a company on a part-time or intermittent basis when the company may not be able to justify the cost of a full-time HR resource. An HR professional can be available onsite for a specified number of hours or days weekly or monthly, depending on the company’s needs and budget. The HR professional handles everything from HR compliance issues and training to employee issues support. Also, for companies that are keen on development of employees, the HR resource can drive the talent management processes—such as performance management, succession planning, training, and development—for companies who require more than just basic HR compliance services.
How does a business leader decide whether HR outsourcing is needed? There are generally two factors that drive a leader to consider fractional HR or HR outsourcing—time and risk. If a leader is spending too much time on HR issues and employee relations, he may decide that it is a smart tradeoff to outsource these tasks to a professional. In addition, the risk inherent in some HR issues can be very great, so the threat of having a lawsuit or feeling that the company is exposed can lead the company to seek help from a fractional HR professional.
HR entrepreneurs have taken full advantage of this important trend, which many say will likely continue as small companies grow and large companies decide to off-load HR work to third parties. Some HR companies offer fractional HR as part of their stated HR services, in addition to payroll and benefits support, compensation, and other HR programmatic support. Having a fractional HR resource in place will often illuminate the need for other HR services and program builds, which are generally supported by those same companies. Whether you are an individual HR practitioner or have a small company of HR practitioners and consultants, fractional HR and HR outsourcing can be a very viable and financially rewarding business model. It can also be very personally rewarding, as the HR professional enables smaller companies to grow and thrive, knowing that its HR compliance and processes are covered.
- What do you believe is contributing to the growth of the fractional HR and HR outsourcing trend? Do you expect this trend to continue?
- At what point should a company consider bringing on a full-time HR resource instead of using a fractional HR resource? What questions should the company ask itself?
Human resource management provides value to an organization, to a large extent, via its management of the overall employee life cycle that employees follow—from hiring and onboarding, to performance management and talent development, all the way through to transitions such as job change and promotion, to retirement and exit. Human capital is a key competitive advantage to companies, and those who utilize their human resource partners effectively to drive their human capital strategy will reap the benefits.
Human resource management includes the leadership and facilitation of the following key life cycle process areas:
- Human resources compliance
- Employee selection, hiring, and onboarding
- Performance management
- Compensation rewards and benefits
- Talent development and succession planning
Human resources is responsible for driving the strategy and policies in these areas to be in accordance with and in support of the overall business strategy. Each of these areas provides a key benefit to the organization and impacts the organization’s value proposition to its employees.
Concept Check
- How has the function of human resource management evolved over the years?
- In what way do you usually interact with human resources?
As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution License and you must attribute OpenStax.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/principles-management/pages/1-introduction
- Authors: David S. Bright, Anastasia H. Cortes
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: Principles of Management
- Publication date: Mar 20, 2019
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/principles-management/pages/1-introduction
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/principles-management/pages/11-1-an-introduction-to-human-resource-management
© Jan 9, 2024 OpenStax. Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License . The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.
Browse Course Material
Course info, instructors.
- Prof. Diane Burton
- Prof. Paul Osterman
Departments
- Sloan School of Management
As Taught In
- Industrial Relations and Human Resource Management
Learning Resource Types
Strategic hr management, assignments, course schedule.
Session 1: The Strategic Importance of HR Case: Southwest Airlines: Using Human Resources for Competitive Advantage (A), Stanford Case #HR-1.
Reading: Pfeffer, Jeffrey. The Human Equation: Building Profits by Putting People First . Boston, MA: Harvard Business School Press, 1998, chapters 1 and 2.
Assignment Questions
- What is Southwest’s competitive strategy? What are the sources of its success? How does it make money?
- What are the foundations of Southwest’s competitive advantage?
- How are these sources of competitive advantage produced and sustained by what the organization does and how it does it?
- To what extent are Southwest’s sources of advantage difficult to imitate and likely to persist over time?
- To what extent is Southwest’s success based on Herb Kelleher?
- How serious is the competitive threat? To what extent can United and/or Continental duplicate Southwest’s business model? Why or why not?
Session 2: Strategic Execution and Economic Value: Internal and External Alignment Case: Portman Hotel, HBS 9-489-104.
- What is Portman’s strategy for competing successfully in its chosen market?
- What behaviors, skills, and attitudes will it need from its people, particularly the personal valets, to execute its strategy?
- How do Portman’s human resource management practices (recruitment, selection, compensation, training, career development, performance appraisal, staffing and organizational design, management and supervision) help or hinder the development of the skills and behaviors listed in Question 2.
- Is Portman having problems? What are the symptoms? What are the causes of the problems Portman is experiencing?
- What should Portman do?
- How much should Portman be willing to invest to address its difficulties? Or alternatively, what is the successful implementation of Portman’s strategy worth? Some operating figures are given in the case. FYI: the capital costs of the hotel work out to $310,000 per room.
Session 3: Work Systems Cases: New United Motors Manufacturing, Inc (NUMMI), Stanford Case #HR-11.
Optional Reading: Rubinstein, Saul R., and Thomas A. Kochan. Learning from Saturn: Possibilities for Corporate Governance and Employee Relations . Ithaca, NY: Cornell University/ILR Press, 2001.
- What is motivating the workers at NUMMI?
- What are the design elements of the Toyota team-based manufacturing system?
- Why has General Motors had so much trouble learning from NUMMI and Saturn?
- Jamie Hresko is now running one of GM’s largest assembly plants. What advice would you give him for how he might introduce some of the NUMMI methods to this facility?
Session 4: The Role of the HR Function
Reading: Ulrich, Dave. Human Resource Champions: The Next Agenda for Adding Value and Delivering Results . Boston, MA: Harvard Business School Press, 1998, pp. 23-31 and 231-254.
Session 5: Self-Managed Teams Case: Slade Plating Department, HBS #9-496-018
Reading: Wageman, Ruth. “Critical Success Factors for Creating Superb Self-Managing Teams.” Organizational Dynamics . Summer 1997, pp. 49-61.
- How would you describe the culture of the Sarto group? Be specific. How has it evolved? What impact has it had on the effectiveness of the group?
- What are the determinants of social status and influence within the plating department? The Sarto group? The Clark group?
- What do you learn by analyzing the data provided in the exhibits? How does this influence your interpretations of what is going on?
- Why did management previously ignored the illegal “punch-out” system?
- What actions would you take if you were Porter? What are the risks associated with these actions?
Important supplemental information: The 1996 starting salary in the Plating Department was $8.00; Tony Sarto’s hourly wage was $12.00. The average wage for semi-skilled workers in the U.S. was $12.00. Firms similar to Slade in the Michigan area, such as suppliers to the auto industry, paid an average hourly wage of $14.70. United Auto Workers working at the ‘Big Three (General Motors, Chrysler and Ford), had starting salaries around $13.00 an hour and earned on average $19.00 an hour. The minimum wage in 1996 was $4.25, raised to $4.75 on October 1, 1996.
Session 6: Participation and Involvement Film: Breakdown at Eastern Airlines
Reading: Pfeffer, Jeffrey. “Can You Manage With Unions.” Chap. 8 in The Human Equation: Building Profits by Putting People First . 2000, pp. 225-251.
Session 7: Training and Development Case: ServiceMaster Industries, Inc., HBS #9-388-064.
- What role have ServiceMaster’s values and goals played in the firm’s success?
- Why haven’t other companies successfully copied the ServiceMaster approach?
- How important are training and development in the ServiceMaster system? How does ServiceMaster socialize its employees? How does training and development affect the organization’s continued growth?
- Why has ServiceMaster been willing to spend the resources it has on training and development for a set of jobs that many might see as comparatively low-skilled and for positions that typically experience high turnover?
- There have been proposals (particularly by former U.S. Secretary of Labor, Robert Reich) that the U.S. follow the lead of some other countries (e.g., France, Singapore) and mandate a certain level of training–for instance, as a percentage of the firm’s payroll. What do you think of this policy? Why and when might organizations spend less than a socially optimal amount on training? What else might be done if one believes that too little training and skill development are occurring in the economy?
Session 8: Culture Case: Morgan Stanley: Becoming a One-Firm Firm, HBS #9-400-043.
Reading: Kaplan, R. S., and D. P. Norton. “Linking the Balanced Scorecard to Strategy.” California Management Review 39, no.1 (Fall 1996).
- What do you think of Mack’s strategy for increased integration? Is this compelling to you? Why or why not?
- Given his strategy, what do you think of his emphasis on revamping the performance management system? What are the pros and cons of implementing a new system of the type being discussed?
- If Mack is to be successful at changing the strategy and culture at Morgan Stanley, what other actions would you recommend he take? What other HR levers should he be thinking about using?
- Given your answer to question #3, what recommendations do you have for how he should proceed? How should he implement these changes?
Session 9: Performance Appraisal Case: The Firmwide 360 Performance Evaluation Process at Morgan Stanley, HBS #9-498053 and Rob Parson at Morgan Stanley (A), HBS #9-498-054.
- What is your assessment of Parson’s performance? Should he be promoted?
- Using the data in the case, please complete the Evaluation and Development Summary presented in Exhibit 3 of the Rob Parson (A) case.
- If you were Paul Nasr, how would you plan to conduct the performance appraisal conversation? What would your goals be? What issues would you raise and why, and how would you raise them?
- If you were Rob Parson, how would you conduct yourself in the performance evaluation meeting? What are your goals? Be prepared to role-play the appraisal conversation in class as either Nasr or Parson.
Cases to be distributed in class: Rob Parson at Morgan Stanley (B), HBS #9-498-055, (C), HBS #9-498-056, and (D), HBS #9-498-058.
Session 10: Diversity Case: The Case of the Part-time Partner.
Reading: Thomas, David A., and Robin J. Ely. “Making Differences Matter: A New Paradigm for Managing Diversity.” Harvard Business Review (September-October 1996): 80-90.
- Would you vote to make Julie a partner? Why or why not?
- What are the pros and cons from the firm’s viewpoint and from the society’s viewpoint of this decision?
- What is your assessment of how the firm handled the situation?
- How might they have proceeded differently?
Session 11: Information Sharing Case: Jack Stack (A) and (B), HBS #9-993-009 and #9-993-010.
Reading: Case, John. “Opening the Books.” Harvard Business Review (March-April 1997): 118-127. (Reprint 97201)
- What does it take to succeed in the engine remanufacturing business? What are the critical skills and organizational competencies?
- What is it like to work in such a plant?
- What are the major risks of a leveraged buy-out such as this?
- What do you think of Stack’s ideas about management?
- What are the key elements of the program Stack put in place?
- Can this approach be used elsewhere? Under which circumstances would it be more (less) appropriate? How could it be implemented?
Session 12: Benefits Case: The SAS Institute: A Different Approach to Incentives and People Management Practices in the Software Industry, Stanford Case #HR-6.
Reading: Pfeffer, Jeffrey. “Six Dangerous Myths About Pay.” Harvard Business Review (May-June 1998): 109-119.
- What are the complementary elements of the SAS HR system that make the compensation system effective?
- Why has SAS been able to get away with a compensation system that seems to violate industry conventions?
- Could the SAS approach work in other high technology organizations?
- What would happen if VDS tried to emulate the SAS approach? Why?
Session 13: Compensation Systems Case: Visionary Design Systems, HBS #9-495-011.
- What is the basic philosophy and values of VDS?
- How would you characterize the VDS compensation (base, bonus, and stock) system? On what principles is it based?
- Why has VDS had problems with its Product Data Management effort? To what extent do you see incentive issues as important? What other issues are important?
- What should VDS do about the Product Data Management (PDM) problems?
- Would you make any changes to VDS’ compensation systems? What? Why?
Session 14: Pay for Performance Case: Performance Pay at Safelite Autoglass (A) HBS #9-800-291.
- What are the pros and cons of switching from wage rates to piece rate pay?
- Is Safelite a good candidate for switching from wage rates to piece rates?
- Should there be a guaranteed wage? If so, how should it be set?
- What are the likely consequences of a switch from wage to piece rates for turnover, recruitment, productivity, and product quality?
Session 15: Non-Profit Management Case: The John Snow Institute.
- How successful is JSI?
- How effective is their current human resource management system?
- What should Joel Lamstein do?
Session 16: Managing Service Workers Case: Harrah’s Entertainment, Inc.: Rewarding Our People HBS #9-403-008.
- What were the challenges facing Gary Loveman when he took charge?
- What were the key changes he undertook?
- What were the consequences for employees?
Session 17: Alignment and Motivation Case: Nordstrom Department Store. Center for Human Resources, Wharton School of the University of Pennsylvania.
Reading: Simons, Robert. “Control in an Age of Empowerment.” Harvard Business Review . Reprint #95211.
- How effective is Nordstom’s human resource management system? In what ways does it contribute to the firm’s success?
- Do you have any concerns about the practices described in the case?
- Would you change management systems at Nordstrom? Why? Which systems?
Session 18: Review & Wrap-up
Assignment Question
- Reflecting on the companies we have studied in this course, as well as your own work experience, what lessons do you draw about the respective roles that general managers and the HR function in organizations should play in the management of human resources?
Summary of Class Sessions and Assignment Due Dates ( PDF )

You are leaving MIT OpenCourseWare
I am looking for…
I need support for…
- Login or other general help
- Paycheck Protection Program

Human resource management (HRM)
- Human Capital Management
- Human Resource Management
It’s often said that people are an organization’s greatest resource. Yet, until fairly recently, human resource management was not considered as critical to success as other business operations, like marketing, finance or sales. This notion has been largely altered by new technology, globalized markets and changes in organizational hierarchies. Today, business leaders place great emphasis on hiring the right people and keeping them engaged.
What is human resource management?
Human resource management involves creating personnel policies and procedures that support business objectives and strategic plans. Central to this mission is fostering a culture that reflects core values and empowers employees to be as productive as possible.

What are the functions of human resource management?
HR functions can vary depending on industry, businesses size and the types of workers employed. In most cases, the primary objectives are to acquire and cultivate talent and improve communication and cooperation among workforce members. Other key human resource management functions include:
- Job analysis Determining the skills and experience necessary to perform a job well may make it easier to hire the right people, determine appropriate compensation and create training programs.
- Workforce operations Creating health and safety policies, responding to employee grievances, working with labor unions, etc., can help support regulatory compliance.
- Performance measurement Evaluating performance is important because it not only fosters employee growth through constructive feedback, but also serves as a guide for raises, promotions and dismissals.
- Incentive programs Recognizing achievements and rewarding high performers with bonuses and other perks is a proven way of motivating employees to take ownership of business objectives.
- Professional development From orientation to advanced educational programs, employee training serves to improve productivity, reduce turnover and minimize supervisory needs.

HCM Buyer’s Guide: Evaluating integrated HCM solutions
What are the responsibilities of human resource management.
HR professionals generally are tasked with creating and administering programs that improve workplace efficiency and employer-employee relationships. Within this broad assignment are several different, but critical responsibilities, such as:
- Staffing Staffing a business or an individual department requires a number of key steps. Hiring managers must first determine how many new employees the budget can support, then find and interview qualified candidates, and finally, make selections and negotiate compensation.
- Developing workplace policies If it’s determined that a new or revised policy is needed, HR professionals typically consult with executives and other managers, write the supporting documentation and communicate it to employees. Policies may cover vacations, dress codes, disciplinary actions and other types of workplace protocol.
- Administering pay and benefits In order to attract and retain talent, compensation must meet industry standards and be comparable to what other employees in similar roles are being paid. Creating such a fair pay system requires careful consideration of an employee’s years of service with the business, experience level, education and skills.
- Retaining talent Compensation isn’t the only thing that retains talented employees. HR managers may need to proactively address issues with workplace environments, organizational culture and relationships between employees and supervisors.
- Training employees When employees develop new skills, they tend to be more productive and satisfied with their job. Some of the training programs typically run by HR departments include team-building activities, policy and ethics education, and on-the-job instruction and skills, e.g. how to run a machine or computer program.
- Complying with regulations Laws that affect the workplace – whether they’re related to discrimination, health care or wages and hours – are constantly evolving. HR professionals are required to keep up with these changes and notify the rest of the organization in support of compliance.
- Maintaining safety Safety in the workplace means protecting not just the physical health of employees, but also their private information. To minimize workers’ compensation claims and data breaches, HR must implement security measures and ensure that all federal, state and union standards are met.
Human resource management and small business
While human resource management is important to all businesses, the stakes may be higher for smaller organizations. For example, one incompetent employee in an office of 10 people can be much more detrimental than one in a workforce numbering in the thousands. To improve their people processes, small business owners generally can:
- Assess current operations to determine if new hires are needed or if existing employees and production methods can be utilized more effectively.
- Take an active role in the recruitment process and write job descriptions that match prospective talent to business needs.
- Create an employee handbook or an official document that clearly outlines company policies.
- Provide continuing education opportunities as needed by the particular industry.
- Maintain a work environment where employees are treated fairly and can be productive.
HRM systems and software
Faced with rising numbers of contract-based workers and increasingly complex regulations, HR professionals have turned to HRM software to help them keep pace with changing workforce environments and people management needs. This technology is available with a variety of options to suit businesses of any size. Basic systems may offer recruitment services , payroll and benefits , while more robust solutions tend to include talent management, international compliance support and advanced analytics.
Why use a human resource management system (HRMS)?
HRMS are designed to meet the core needs of HR and turn basic administrative functions into critical enablers of business value. With the aid of these people-centric, data powered solutions, HR managers may be able to:
- Improve their hiring processes
- Manage people more effectively
- Optimize workforce productivity
- Engage and retain employees
- Eliminate costly redundancies
- Make data-driven decisions
- Maintain regulatory compliance
How to choose a human resources management solution
Finding the right solution often requires a strategic evaluation process, such as the following:
- Identify what the organization would like to accomplish, change or improve and how technology can help achieve those goals.
- Ensure that the HRMS can keep pace with the rapidly changing regulatory and statutory requirements in all applicable jurisdictions (local, state, federal, international, etc.).
- Prioritize security and know exactly how sensitive data will be stored, transferred and backed up.
- Look for implementation models with a change management strategy that will get the HRMS up and running efficiently.
- Address stakeholder questions, concerns and objections to drive widespread HRMS support.
- Ask about service plans to manage the hundreds of post-payroll tasks necessary for compliance .
- Inquire into the vendor’s financial history and investments in innovation.
- Get outside-in perspective by looking at peer reviews, industry analyst feedback and product demos.
Examples of HRM software
Business leaders and HR professionals who are looking for software to help them accomplish more with less resources generally have three options available to them:
- Human resource information systems (HRIS) – perform core HR functions , like applicant tracking, payroll and benefits administration
- Human resource management systems (HRMS) – offer the benefits of HRIS, plus talent management services
- Human capital management (HCM) solutions – provide a broad suite of HR capabilities, including global payroll and compliance support and in-depth analytics
Why choose ADP for your human resource management needs?
ADP’s HR management solutions automate and streamline key needs so that HR professionals can focus more time on their people and less on paperwork. We offer basic and customized packages with some of the following features:
- Powerful workforce reporting that turns data into a trusted source of decision-making
- Preconfigured new hire templates for a simplified onboarding process
- Self-service and mobile apps so time-sensitive tasks can be performed quickly
- Industry-recognized security to help safeguard sensitive information
Learn more about ADP Workforce Now® HR Management →
Frequently asked questions about HRM
What is human resource management and its functions.
Human resource management is the strategic approach to nurturing and supporting employees and ensuring a positive workplace environment. Its functions vary across different businesses and industries, but typically include recruitment, compensation and benefits, training and development, and employee relations.
What are the three major roles of human resources management?
The job of an HR manager can be broken out into three major roles:
- Administrator Running payroll , writing job descriptions, creating workplace policies and procuring benefits packages are typical of HR administration.
- Change manager HR professionals must monitor regulations and communicate policy or procedural changes with employees to help support compliance.
- Personnel manager Managing people entails resolving conflicts, overseeing training and development, and fostering employee engagement.
What are the five main areas of HR?
HR professionals perform many activities in the pursuit of employee well-being and organizational stability, but their responsibilities generally lie within five main areas:
- Recruitment and staffing – identifying talent gaps, acquiring applicants, arbitrating contracts, maintaining ethical hiring practices
- Compensation and benefits – determining pay scales, approving raises, negotiating benefits packages
- Training and development – onboarding new hires, making educational opportunities available
- Compliance and safety – monitoring legislative changes, implementing safety measures, processing workers’ compensation claims
- Employee relations – resolving employee conflicts, addressing harassment or abuse allegations, working with union leaders
What are seven functions of HR?
Over the years, HR has evolved from a personnel department engaged largely in administration to a strategic partner that works closely with management teams on organizational development. It’s seven key functions today include:
- Strategic planning
- Recruitment
- Training and development
- Compensation and benefits
- Policy creation
- Employee and labor relations
- Risk management
What is HR compliance?
HR compliance means keeping an organization from violating the growing number of employment laws enacted by federal, state and local governments. This responsibility requires HR professionals to monitor and understand regulatory requirements, enforce policies, classify workers correctly, practice fair hiring practices and provide a safe work environment, among other tasks.
This guide is intended to be used as a starting point in analyzing an employer’s HR obligations and is not a comprehensive resource of requirements. It offers practical information concerning the subject matter and is provided with the understanding that ADP is not rendering legal or tax advice or other professional services.

HCM evaluation center
Is this the right time to upgrade your HCM system? We have the resources to help guide your decision.
View resources
Related resources

Get pricing specific to your business
Your privacy is assured.

Get 3 months FREE!*
Sign up for payroll with ADP, and get 3 months on us .
Call 800-225-5237 or get pricing now.
Compare Packages
*See terms & conditions

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
2.2 Writing the HRM Plan
Learning objective.
- Describe the steps in the development of an HRM plan.
As addressed in Section 2.1 “Strategic Planning” , the writing of an HRM strategic plan should be based on the strategic plans of the organization and of the department. Once the strategic plan is written, the HR professional can begin work on the HR plan. This is different from the strategic plan in that it is more detailed and more focused on the short term. The six parts described here are addressed in more detail in Chapter 4 “Recruitment” , Chapter 5 “Selection” , Chapter 6 “Compensation and Benefits” , Chapter 7 “Retention and Motivation” , Chapter 8 “Training and Development” , Chapter 9 “Successful Employee Communication” , Chapter 10 “Managing Employee Performance” , and Chapter 11 “Employee Assessment” .
How Would You Handle This?
Compensation Is a Touchy Subject
As the HR manager, you have access to sensitive data, such as pay information. As you are looking at pay for each employee in the marketing department, you notice that two employees with the same job title and performing the same job are earning different amounts of money. As you dig deeper, you notice the employee who has been with the company for the least amount of time is actually getting paid more than the person with longer tenure. A brief look at the performance evaluations shows they are both star performers. You determine that two different managers hired the employees, and one manager is no longer with the organization. How would you handle this?
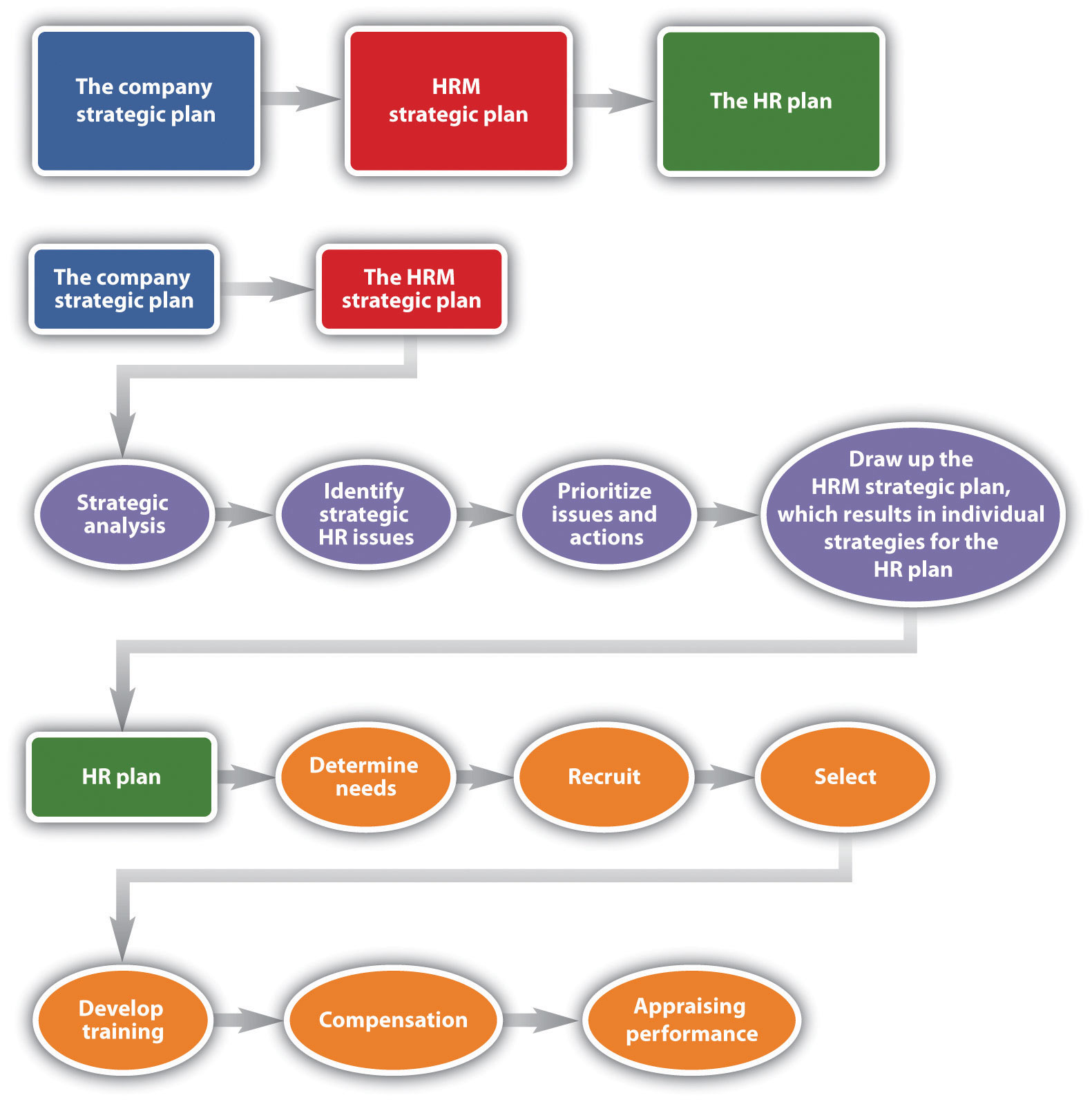
As you can see from this figure, the company strategic plan ties into the HRM strategic plan, and from the HRM strategic plan, the HR plan can be developed.
The six parts of the HRM plan include the following:
- Determine human resource needs. This part is heavily involved with the strategic plan. What growth or decline is expected in the organization? How will this impact your workforce? What is the economic situation? What are your forecasted sales for next year?
- Determine recruiting strategy. Once you have a plan in place, it’s necessary to write down a strategy addressing how you will recruit the right people at the right time.
- Select employees. The selection process consists of the interviewing and hiring process.
- Develop training. Based on the strategic plan, what training needs are arising? Is there new software that everyone must learn? Are there problems in handling conflict? Whatever the training topics are, the HR manager should address plans to offer training in the HRM plan.
- Determine compensation. In this aspect of the HRM plan, the manager must determine pay scales and other compensation such as health care, bonuses, and other perks.
- Appraise performance. Sets of standards need to be developed so you know how to rate the performance of your employees and continue with their development.
Each chapter of this text addresses one area of the HR plan, but the next sections provide some basic knowledge of planning for each area.
Determine Human Resource Needs
The first part of an HR plan will consist of determining how many people are needed. This step involves looking at company operations over the last year and asking a lot of questions:
- Were enough people hired?
- Did you have to scramble to hire people at the last minute?
- What are the skills your current employees possess?
- What skills do your employees need to gain to keep up with technology?
- Who is retiring soon? Do you have someone to replace them?
- What are the sales forecasts? How might this affect your hiring?
These are the questions to answer in this first step of the HR plan process. As you can imagine, this cannot be done alone. Involvement of other departments, managers, and executives should take place to obtain an accurate estimate of staffing needs for now and in the future. We discuss staffing in greater detail in Chapter 4 “Recruitment” .
Many HR managers will prepare an inventory of all current employees, which includes their educational level and abilities. This gives the HR manager the big picture on what current employees can do. It can serve as a tool to develop employees’ skills and abilities, if you know where they are currently in their development. For example, by taking an inventory, you may find out that Richard is going to retire next year, but no one in his department has been identified or trained to take over his role. Keeping the inventory helps you know where gaps might exist and allows you to plan for these gaps. This topic is addressed further in Chapter 4 “Recruitment” .
HR managers will also look closely at all job components and will analyze each job. By doing this analysis, they can get a better picture of what kinds of skills are needed to perform a job successfully. Once the HR manager has performed the needs assessment and knows exactly how many people, and in what positions and time frame they need to be hired, he or she can get to work on recruiting, which is also called a staffing plan . This is addressed further in Chapter 4 “Recruitment” .
Recruitment is an important job of the HR manager. More detail is provided in Chapter 4 “Recruitment” . Knowing how many people to hire, what skills they should possess, and hiring them when the time is right are major challenges in the area of recruiting. Hiring individuals who have not only the skills to do the job but also the attitude, personality, and fit can be the biggest challenge in recruiting. Depending on the type of job you are hiring for, you might place traditional advertisements on the web or use social networking sites as an avenue. Some companies offer bonuses to employees who refer friends. No matter where you decide to recruit, it is important to keep in mind that the recruiting process should be fair and equitable and diversity should be considered. We discuss diversity in greater detail in Chapter 3 “Diversity and Multiculturalism” .
Depending on availability and time, some companies may choose to outsource their recruiting processes. For some types of high-level positions, a head hunter will be used to recruit people nationally and internationally. A head hunter is a person who specializes in matching jobs with people, and they usually work only with high-level positions. Another option is to use an agency that specializes in hiring people for a variety of positions, including temporary and permanent positions. Some companies decide to hire temporary employees because they anticipate only a short-term need, and it can be less expensive to hire someone for only a specified period of time.
No matter how it is done, recruitment is the process of obtaining résumés of people interested in the job. In our next step, we review those résumés, interview, and select the best person for the job.
After you have reviewed résumés for a position, now is the time to work toward selecting the right person for the job. Although we discuss selection in great detail in Chapter 6 “Compensation and Benefits” , it is worth a discussion here as well. Numerous studies have been done, and while they have various results, the majority of studies say it costs an average of $45,000 to hire a new manager (Herman, 1993). While this may seem exaggerated, consider the following items that contribute to the cost:
- Time to review résumés
- Time to interview candidates
- Interview expenses for candidates
- Possible travel expenses for new hire or recruiter
- Possible relocation expenses for new hire
- Additional bookkeeping, payroll, 401(k), and so forth
- Additional record keeping for government agencies
- Increased unemployment insurance costs
- Costs related to lack of productivity while new employee gets up to speed
Because it is so expensive to hire, it is important to do it right. First, résumés are reviewed and people who closely match the right skills are selected for interviews. Many organizations perform phone interviews first so they can further narrow the field. The HR manager is generally responsible for setting up the interviews and determining the interview schedule for a particular candidate. Usually, the more senior the position is, the longer the interview process takes, even up to eight weeks (Crant, 2009). After the interviews are conducted, there may be reference checks, background checks, or testing that will need to be performed before an offer is made to the new employee. HR managers are generally responsible for this aspect. Once the applicant has met all criteria, the HR manager will offer the selected person the position. At this point, salary, benefits, and vacation time may be negotiated. Compensation is the next step in HR management.
Determine Compensation
What you decide to pay people is much more difficult than it seems. This issue is covered in greater detail in Chapter 6 “Compensation and Benefits” . Pay systems must be developed that motivate employees and embody fairness to everyone working at the organization. However, organizations cannot offer every benefit and perk because budgets always have constraints. Even governmental agencies need to be concerned with compensation as part of their HR plan. For example, in 2011, Illinois State University gave salary increases of 3 percent to all faculty, despite state budget cuts in other areas. They reasoned that the pay increase was needed because of the competitive nature of hiring and retaining faculty and staff. The university president said, “Our employees have had a very good year and hopefully this is a good shot in the arm that will keep our morale high” (Pawlowski, 2011).
Determination of compensation systems is a balancing act. Compensation should be high enough to motivate current employees and attract new ones but not so high that it breaks the budget.
Nathan Rupert – Venice Beach Tightrope Walker – CC BY-NC-ND 2.0.
The process in determining the right pay for the right job can have many variables, in addition to keeping morale high. First, as we have already discussed, the organization life cycle can determine the pay strategy for the organization. The supply and demand of those skills in the market, economy, region, or area in which the business is located is a determining factor in compensation strategy. For example, a company operating in Seattle may pay higher for the same job than their division in Missoula, Montana, because the cost of living is higher in Seattle. The HR manager is always researching to ensure the pay is fair and at market value. In Chapter 6 “Compensation and Benefits” , we get into greater detail about the variety of pay systems, perks, and bonuses that can be offered. For many organizations, training is a perk. Employees can develop their skills while getting paid for it. Training is the next step in the HR planning process.
Develop Training
Once we have planned our staffing, recruited people, selected employees, and then compensated them, we want to make sure our new employees are successful. Training is covered in more detail in Chapter 8. One way we can ensure success is by training our employees in three main areas:
- Company culture. A company culture is the organization’s way of doing things. Every company does things a bit differently, and by understanding the corporate culture, the employee will be set up for success. Usually this type of training is performed at an orientation, when an employee is first hired. Topics might include how to request time off, dress codes, and processes.
- Skills needed for the job. If you work for a retail store, your employees need to know how to use the register. If you have sales staff, they need to have product knowledge to do the job. If your company uses particular software, training is needed in this area.
- Human relations skills. These are non-job-specific skills your employees need not only to do their jobs but also to make them all-around successful employees. Skills needed include communication skills and interviewing potential employees.
Perform a Performance Appraisal
The last thing an HR manager should plan is the performance appraisal. While we discuss performance appraisals in greater detail in Chapter 11 “Employee Assessment” , it is definitely worth a mention here, since it is part of the strategic plan. A performance appraisal is a method by which job performance is measured. The performance appraisal can be called many different things, such as the following:
- Employee appraisal
- Performance review
- Career development review
No matter what the name, these appraisals can be very beneficial in motivating and rewarding employees. The performance evaluation includes metrics on which the employee is measured. These metrics should be based on the job description, both of which the HR manager develops. Various types of rating systems can be used, and it’s usually up to the HR manager to develop these as well as employee evaluation forms. The HR manager also usually ensures that every manager in the organization is trained on how to fill out the evaluation forms, but more importantly, how to discuss job performance with the employee. Then the HR manager tracks the due dates of performance appraisals and sends out e-mails to those managers letting them know it is almost time to write an evaluation.
Human Resource Recall
Have you ever been given a performance evaluation? What was the process and the outcome?
Communication Is Key in Performance Evaluations
(click to see video)
Communication is imperative in any workplace, but especially when giving and receiving a performance evaluation.
Key Takeaways
- Human resource planning is a process that is part of the strategic plan. It involves addressing specific needs within the organization, based on the company’s strategic direction.
- The first step in HR planning is determining current and future human resource needs. In this step, current employees, available employees in the market, and future needs are all analyzed and developed.
- In the second step of the process, once we know how many people we will need to hire, we can begin to determine the best methods for recruiting the people we need. Sometimes an organization will use head hunters to find the best person for the job.
- After the recruiting process is finished, the HR manager will begin the selection process. This involves setting up interviews and selecting the right person for the job. This can be an expensive process, so we always want to hire the right person from the beginning.
- HR managers also need to work through compensation plans, including salary, bonus, and other benefits, such as health care. This aspect is important, since most organizations want to use compensation to attract and retain the best employees.
- The HR manager also develops training programs to ensure the people hired have the tools to be able to do their jobs successfully.
- Of the parts of HR planning, which do you think is most difficult, and why? Which would you enjoy the most, and why?
- Why is it important to plan your staffing before you start to hire people?
- What is the significance of training? Why do we need it in organizations?
Crant, J., “How Long Does an Interview Process Take?” Jobsinminneapolis.com, December 2, 2009, accessed October 28, 2010, http://www.jobsinminneapolis.com/articles/title/How-Long-Does-an-Interview-Process-Take/3500/422 .
Herman, S., Hiring Right: A Practical Guide (Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 1993), xv.
Pawlowski, S., “Illinois State University to Get Salary Bump,” WJBC Radio, July 11, 2011, accessed July 11, 2011, http://wjbc.com/illinois-state-university-faculty-to-get-salary-bump .
Human Resource Management Copyright © 2016 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
10 Assignments For Human Resource Managers To Develop Future Skills
- By Simon Carvi
- No Comments

The Covid-19 pandemic has put tremendous pressure on organizations to change the way they operate: from sales and marketing, to finance and customer service. CEOs know that resilience and capacity to innovate are deeply rooted in the company’s human resources.
To kickstart skilling efforts in the organization, what better place to start than to make sure the Human Resources department is properly equipped. Otherwise, who else should you empower to upskill the rest of your organization? As a matter of fact, the HR function is at the forefront of digital disruption. Your ability to build a skilled HR department is instrumental to make your organization future-ready.
Remember that when it comes to training, individual Active Learning (classroom, eLearning, reading, etc.) accounts for roughly 10% of the job only! Around 20% of the learning journey to retain a skill is done through others (mentoring, peer interactions, etc.) and 70% by actually doing things! Of course the right blend depends on you and other parameters, such as your company’s business, industry and individual themselves.
In this short article we will explore 10 SMART ways C-Level and Directors can make sure their HR Managers are being stretched in a good way, exploring projects that will strategically fit the company’s long-term growth and resilience to change.
Let’s get started!
Table of Contents
1. Present a digital transformation strategy to top management
Competency developed: Digital transformation.
Objective: Own the topic of digital transformation within your company.
Explanation: Yes, strategy! Ultimately digital transformation is about people skills and the ability to evolve in a digital environment. HR managers should be at the center of the conversation to understand future needs, analyze current gaps, and design a plan.
Tips: Read the literature on the topic. Collect feedback from experts or peers leading the same topic within their organizations. WORK WITH IT.
2. Create and present new dashboard to CHRO including key metrics and qualitative analysis
Competency developed: People Analytics.
Objective: Analyse your company’s HR performance and contribute to business success.
Explanation: Has your company a clear vision of its HR performance? Take advantage of the latest HR systems and Business Intelligence tools available to connect the dots. Measure actionable indicators and present them to management.
Tips: Collect expectations from CHRO and top management. Does your company already have a dashboard in place? Start collecting feedback from the current dashboard and try to connect new data points to provide new insights Collaborate with IT to learn how to structure and visualize data!
3. Make 5-year manpower plan aligned to business targets and present to top management
Competency developed: Strategic workforce planning.
Objective : Plan the Human side of your company strategy so it can meet its turnover, profitability, or sustainability targets.
Explanation : How workforce will be utilized in the future? How to attract and develop the necessary skills. You’ll need more than one meeting to produce such a plan.
Tips: Make sure you collect the most relevant business targets to get a clear vision of the 5-year objectives and gaps. Meet with business line manager, top management, and collect market data to validate assumptions.
4. Highlight company’s top 5 turnover reasons with action plan to top management.
Competency developed: Business partnering.
Objective: Develop your HR Managers to become real Business partner.
Explanation: From back seat to the front seat. HR managers are not only responsible for collecting data, but also to strategize an action plan.
Tips: This stretch assignment is better utilized during the yearly budgeting period where managers are expected to summarize data and action plans.
5. Ask HR Manager to personally train all managers on how to make Individual development plans
Competency developed: Career development planning .
Objective: Boost your organization career development culture and processes.
Explanation: It is true that HR managers do not own the career development paths of all employees, Line Managers do. On the other hand, HR Managers are responsible for the talent management process , making sure high potential employees are identified and that provided career paths match the organization’s long-term goals. This assignment will boost the HR Manager’s influencing skills while putting employee retention clearly at the center of the conversation.
Tips: This stretch assignment is better implemented with different workshops 5-7 managers maximum. Ultimately, the HR Manager shall control the quality of each Individual Development Plan (IDP) formalized. It is possible to imagine one on one sessions with managers failing to pass the IDP quality control.
6. Rethink your company’s benefit package and implement one innovative benefit in line with the new workplace reality
Competency developed : Compensation & Benefits management.
Objective : Make your company compatible with 2020 new workplace expectations.
Explanation : Disrupted times call for bold measures and flexibility has just become every employee’s number one priority. HR managers must be creative and offer to top management solutions that will guarantee performance while fitting the employee’s expectation of the new normal.
Tips : You do not need to think money when thinking benefit. A good place to start to ensure creativity would be to run a survey. For example, what does work from home implies for your employees, or top management? Try to know more about those changes, and how does the company can help.
7. Apply reverse mentoring within your team during monthly one on one sessions
Competency developed : People Management.
Objective : Become a more balanced leader, get a deeper understanding of the motivations of younger employees and get up-to-date with digital tools.
Explanation : The odds are your HR Manager is a bit older than the team he/she manages. Organize ways to collect constructive feedback about your leadership and use them to improve. Subordinates can offer a wealth of feedback and guidance (digital tools!).
Tips : Reverse mentoring is hard, but the benefits on leadership skills can be huge. Do come with an open mind. During the meeting, let subordinate talk most of the time. Receive their feedback with a smile and spare some time to study their deeper meaning.
8. Redesign performance management system to make it a continuous process.
Competency developed : Continuous performance management.
Objective : Retain and develop talents.
Explanation : Spoiler alert! Feedback is not a “twice-a-year” thing anymore and one should not wait 6 months to get a meaningful conversation about performance with its boss. To cope with new expectations of the workforce, it is critical companies rethink the way they manage and record employee’s performance.
Advice : Implement a culture of feedback by enforcing regular one-on-ones once per month. Turn to automated dashboards to measure competency development progress, KPIs and deviations.

9. Link learning and development activities to OKRs and competencies listed in your performance management system
Objective : Get ROI from learning activities offered to employees.
Explanation : Whether your organization use OKRs (Objectives and Key Results) or KPIs & competencies, make sure learning activities are linked with performance outputs. Follow up implementation on a monthly basis using one on ones.
Advice : Diversify learning and apply the 70/20/10 approach: Active Learning, Social Learning and Stretch assignments.
10. Implement monthly change management committees with top management
Objective : Put HR at the centre of change in your organization.
Explanation : HR Managers will not change organizations by themselves. They must collect voices from business line managers and must proceed to risk analysis before launching propositions.
Advice : Change needs buy-in at the highest level. Get your CEO buy-in and offer him a seat at your committee.
Do you agree with those suggestions? Do they sound challenging enough to develop long-term skills? Or at the contrary too difficult? Are you an HR Manager willing to develop future-proof skills or a CEO that want to impulse change in the organization? Let us know in the comments below. If you want to get more ideas to develop your teams, you can browse different development plans with 70/20/10 activities on Huneety.com . New positions are added every week.
This article has been written by our guest writer Simon Carvi who is an HR expert professional presenting over 7 years of experience gained through roles in Talent Acquisition and Employee Retention globally and in APAC. Simon is passionate about how people learn and the future of work. He helps organizations find practical ways to upskill their workforce as Huneety top learning contributors.
You can reach him on Li n kedIN :
Simon Carvi
Simon Carvi is an HR expert professional presenting over 7 years of experience gained through roles in Talent Acquisition an Employee Retention globally and in APAC. Simon is passionate about how people learn and future of work. He helps organizations find practical ways to upskill their workforce as Huneety top learning contributor.
You must also read

Motivation in the Workplace – Top 13 Simple

Employee Attrition: Everything You Need To Know

Know Everything About New Employee Orientation (Ch
Leave a comment cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Recent Post

24 Interesting Welcome G

9 Best Employer Branding

HR Career Path: Definiti

Dysfunctional Turnover:

12 Ways To Improve Work
- Business Growth
- Case Studies
- Covid-19 Resources
- Human resource
- Leave Management System
- Productivity
- Project Management
- Software Suggestion
- Time Tracker
Featured Articles

- Reward Management
- E-Recruitment
- Time and Attendance
- Diversity and Equality
- Employee Relations
- More >>

- Compensation

Cloud based solution, designed for small and medium scale businesses.

What's CuteHR
Signup for FREE
Share Feedback
Workflow Solutions
Hr Templates
Knowledge Base
FAQ’s
Cookies Policy
Terms & Conditions
CAREER GUIDES
- Strategic Human Resource Management Overview
- Organizational Design
- Leadership Development Plan
- Leadership Competencies
- HR Scorecard
- HR Operations
- HR Policies
- HR Audit Overview
- HR Audit Checklist
- Payroll Tax Holiday
- Human Resources Career Path
- HR Resume Examples
- HR Situational interview Questions
- HR Operations Interview Questions
- HR Operations Skills
- Human Resources Intern Overview
- HR Intern Resume
- How to Become an HR Intern
- HR Intern Job Description
- HR Intern Skills
- HR Intern Interview Questions
- HR Assistant Overview
- HR Assistant Cover Letter
- How to Write an HR Assistant Resume
- HR Assistant Job Description
- HR Assistant Salary
- HR Assistant Interview Questions
- HR Specialist Overview
- How to Write an HR Specialist Resume
- HR Specialist Skills
- HR Specialist Interview Questions
- HR Specialist Salary
- HR Specialist vs. HR Generalist
- HR Specialist Cover Letter
- Human Resources Administrator Overview
- HR Administrator Salary
- HR Administrator Job Description
- HR Administrator Resume
- How to Become an Human Resources Administrator
- Human Resources Administrator Skills
- HR Coordinator Overview
- How to Become an HR Coordinator
- HR Coordinator Interview Questions
- HR Coordinator Skills
- HR Coordinator Job Description
- HR Coordinator Salary
- HR Coordinator Resume
- HR Generalist Overview
- HR Generalist Career Path
- How to Become an HR Generalist
- HR Generalist Salary
- HR Generalist Job Description
- HR Generalist Skills
- HR Generalist Interview Questions
- HR Generalist Resume
- HR Generalist Cover Letter
- HR Generalist vs. HR Administrator
- HR Generalist Behavioral Interview Questions
- HR Manager Overview
- HR Manager Career Path
- How to Become a HR Manager
- HR Manager Interview Questions
- HR Manager Resume
- HR Manager Cover Letter
- HR Manager Skills
- HR Manager Salary
- HR Manager Job Description
- HR Specialist vs. HR Manager
- HR Operations Manager Overview
- HR Operations Manager Salary
- HR Operations Job Description Examples
- HR Operations Specialist Overview
- HR Operations Specialist Salary
- Senior HR Manager Overview
- Senior HR Manager Salary
- Senior HR Manager Job Description
- Onboarding Specialist Overview
- HR Onboarding Specialist Job Description
- Onboarding Specialist Interview Questions
- Onboarding Specialist Salary
- HRIS Analyst Overview
- HR Analyst Career Path
- HRIS Analyst Career Path
- How to Become an HRIS Analyst
- HRIS Analyst Interview Questions
- HR Analyst Job Description
- HR Analyst Salary
- HR Business Overview
- HR Business Partner Career Path
- HR Business Partner Skills
- HR Business Partner Interview Questions
- How to Become an HR Business Partner
- HR Business Partner Salary
- HR Business Partner Job Description
- HR Business Partner Resume
- HR Business Partner Cover Letter
- Google HR Business Partner Interview Questions
- HR Business Partner Behavioral Interview Questions
- HR Business Partner Model
- Senior HR Business Partner Overview
- Senior HR Business Partner Salary
- Senior HR Business Partner Job Description
- Human Resources Director Overview
- How to Become an HR Director
- HR Director Skills
- HR Director Interview Questions
- HR Director Salary
- HR Director vs HR Manager
- HR Director Cover Letter
- HR Director Resume
- Director of People Overview
- How to Become a Director of People
- Director of People Skills
- HR Executive Overview
- HR Executive Skills
- How to Become an HR Executive
- HR Executive Interview Questions
- HR Executive Job Description
- HR Executive Resume
- HR Executive Cover Letter
- VP of HR Overview
- How to Become a VP of HR
- How to Write a VP of HR Resume
- VP of HR Skills
- VP of HR Job Description
- VP of HR Salary
- Change Champion Overview
- Change Manager Overview
- Operational Change Manager Overview
- How to Become a Change Manager
- Change Manager Salary
- Change Management Interview Questions
- Change Manager Skills
- Change Manager Job Description
- Change Manager vs. Project Manager
- HR Consultant Overview
- HR Transformation Consultant Overview
- HR Technology Consultant Overview
- HR Consultant Job Description
- Performance Management Overview
- Employee Performance Metrics
- Performance Improvement Plan
- Onboarding Overview
- Employee Onboarding Checklist
- Talent Management Overview
- 9 Box Talent Review Grid
- Best Behaviorally Anchored Rating Scale
- Skill Matrix
- Job Evaluation Methods
- Full Life Cycle Recruiting
- HRIS Systems
- Performance Management Software
- Employee Onboarding Software
- HCM Software
- HR Analytics Software
- Change Management Software
- Change Management Tools
- HR Analytics Overview
- People Analytics Overview
- HR Metrics Dashboard Examples
- Predictive Analytics in HR
- Employee Turnover Rate
- Employee Engagement Overview
- Employee Appreciation Ideas
- Employee Incentive Programs
- Team Building Activities
- Turnover Rate
- Employee Misconduct
- What is Employee Feedback?
- Positive Employee Feedback
- Employee Exit Interview Questions
- HR Training Overview
- Diversity, Inclusion, and Belonging Overview
- Inclusion vs Diversity
- Diversity and Inclusion Training Programs
- Diversity and Inclusion Mission Statement
- Diversity and Inclusion Discussion Topics
- Diversity and Inclusion Survey Questions
- Diversity and Inclusion Initiatives
- Discrimination Training Programs
- Best Sensitivity Training Programs
- Sexual Harassment Prevention Training Programs
- HR Certifications
- Human Resources Management Certification
- Diversity and Inclusion Certification
- HR Generalist Certification
- HR Business Partner Certification
- Diversity and Inclusion Certification Harvard
- Cornell University Diversity Certification
- SHRM Certification CP and SCP
- Flexible Benefits Overview
- Employee Assistance Programs
- Time Off Request Form
- Bereavement Leave
- Sabbatical Leave
- How to Calculate Fringe Benefits
- Fringe Benefits Examples
- Flexible Benefits Examples
- Disadvantages of Flexible Benefits
- How to Implement Flexible Benefits
- Benefits Specialist Overview
- Benefits Coordinator Overview
- Interview Appointment Letter Templates
- Verification of Employment Letter Templates
- Employee Handbook Templates
- Letter of Recommendation for Employee Template
- Termination Letter Templates
- Incident Report Template
- New Hire Paperwork Templates
- Exit Interview Template Examples
Home › Strategic Human Resources Management › What is Strategic Human Resource Management?
What is Strategic Human Resource Management?
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Strategic human resource management is a process that helps the human resources department maximize the potential of its workforce through strategic planning, talent management, leadership development, organizational design, and performance management.
In the past, strategic HR management was an administrative function. Today, HR managers play a critical role in ensuring that the organization has the right people that help improve business performance and ensure that it delivers on its mission.
It means that HR professionals need to understand its goals and objectives. How they can best help the organization achieve those goals, and what actions will allow them to do so. This article will help you better understand what strategic human resource management is and how a smart plan can bring tremendous value to the organization.
If you’re interested in learning more via video, then watch below. Otherwise, skip ahead.

What are Strategic HR Management Goals?
Strategic human resource management involves developing and implementing strategies for attracting, retaining, motivating, and managing talented individuals who contribute to the organization’s success. HRM also includes policies and practices designed to ensure fairness in employment relations.
Strategic human resource management aims to achieve a competitive advantage by creating value for customers, shareholders, employees, and other stakeholders. The term “strategy” refers to the organization’s overall plan of action to create value. It is not just one thing; it is a combination of many things, including:
- Actions are taken by the organization to meet customer needs
- Policies and procedures used to manage the organization
- Processes used to produce goods or services
- Marketing activities used to sell products and services
- Financial decisions made to fund operations
- Organizational structure
- The technology used to support business processes
- People-related issues such as recruitment, selection, training, compensation, benefits, and performance management
- Legal requirements and regulations affecting the organization
How Can Businesses Benefit from HR Strategic Planning?
Businesses benefit from strategic human resources management because it allows human resource departments to make better decisions. For example, companies can develop plans to improve productivity, reduce costs, increase profits, and enhance employee satisfaction. The sales and HR departments play a role in determining whether the company should expand into new markets, acquire another company, or merge with another business.
If you want to attract more customers, understand what your target market wants and how you can provide it. It would be best if you also decided which marketing methods would work best.
To retain current customers, you must first find out why they buy from you instead of competitors. Then you must figure out ways to keep them satisfied. You may even wish to consider offering discounts or gifts to reward loyal customers.
You must also think about motivating your employees to perform well and stay productive. If you want to hire more qualified candidates, you must first understand the qualities you are looking for in potential hires. You must also decide if you’re going to use job descriptions or conduct interviews when hiring.
Once you have determined your priorities, you can begin to implement changes to improve results.
Strategic Human Resources Management Benefits
Strategic HR involves careful consideration and analysis. Due to that, here are specific benefits of human resource strategic planning for businesses:
- Identify areas of weakness and strengths
- Develop strategies to address these weaknesses and strengths
- Establish sub-goals and objectives to measure progress toward the end goal
- Make sure there is alignment between business strategy and human resources strategy
- Ensure that all aspects of the organization revolve around the same set of goals and objectives
- Create a culture of continuous improvement
- Evaluate the effectiveness of programs and policies
- Increased job satisfaction
- Employee retention
Check our certified HR courses if you want to learn more about developing and implementing a strategic HR management plan. Master HR management and how to get the best out of your employees.
7 Steps to Creating a Strategic HR Plan
One of the main functions of HR is to provide an effective organization’s workforce management. It includes operational and strategic management and developing a plan that helps employees evolve. To do this, you need to start by determining the purpose of your human resource strategy.
Next, you need to look at the organizational structure of your company. How many levels are there? Do you have a different human resources department within each class? Are some divisions larger than others?
Some of the target outcomes for human resources planning include the following:
- Increase profitability through a strategic HR planning process
- Improve customer service
- Enhance employee morale and motivation
- Provide training and development opportunities
- Reduce turnover rates
- Maintain high-quality standards
Once you have these outcomes in mind, you can follow the following steps in developing a strategic HR department.
1. Define Goals
Defining goals helps you focus on a more strategic human resource management strategy. It gives you direction and provides a framework for measuring success. A goal is an objective you hope to achieve within a specific time frame. It’s something you want to accomplish. A plan is usually quantifiable. For example, you might say, “I want to increase my sales revenue by 20% to achieve a competitive advantage.”
Goals break down into sub-goals. The intermediate goals help you reach the ultimate goal. Additionally, they provide milestones in the strategic HR planning process. For example, if your ultimate goal is to increase sales revenue by 20%, then your intermediate goals can be:
- Achieve a 5% increase in sales revenue over last year.
- Achieve a 10% increase in sales revenue from January to June.
- Achieve a 15% increase in sales revenue during July.
It’s also essential to develop a SWOT analysis when defining your strategic HRM goals. The SWOT analysis helps identify any potential threats or obstacles that may hinder organizational success.
When conducting a SWOT analysis of your HR strategy, consider the following questions:
- What are your strengths?
- What are your weaknesses?
- Where are your opportunities?
- What are your threats?
Answering these questions will help you define business goals and improve business performance.
2. Determine Objectives
Objectives are measurable actions you take to meet your goals. They are how you achieve your goals.
Your objectives should be realistic. They should not be too ambitious. If they are too complicated, you may fail. You also don’t want them to be so easy that you will never succeed.
You should have a working strategic human resource management process to define specific human resource objectives for your business. Some examples include:
- Increase the number of new hires by 50%.
- Increase the average length of employment by three months.
- Reduce the percentage of employees who leave their jobs by 25%.
- Eliminate the use of temporary workers.
- Increase the number and proportion of women in management positions.
- Increase the proportion of senior managers with MBA degrees.
Your HR objectives should align with your overall company objectives. For example, if your company wants to increase its market share, setting up similar goals makes sense. Additionally, you should align all your HR objectives to your company’s financial objectives.
Keep in mind that the more tangible your objectives are, the easier it will be to measure progress.
3. Create Strategies
Strategic human resource management is all about the strategies you intend to use to achieve your objectives. They are the methods you’ll use to get there. There are many different strategies available. However, there are three main types.
- Change Strategy – This involves changing the current status quo or making changes that are already underway.
- Reinforcement Strategy – Involves reinforcing existing practices and policies.
- Innovation Strategy – Introduces new ideas and processes.
Your organization’s strengths and weaknesses are the foundation for your strategic human resource management. There isn’t a single best tactic. Instead, the best strategy depends on the situation.
4. Develop Tactics
Develop HR techniques you’ll use to implement your strategies. There are two kinds of tactics:
- Direct Tactics – These involve implementing your strategies immediately. Examples include hiring additional staff, promoting more people, giving raises to employees, and employee retention strategies.
- Indirect Tactics – These involve using other resources to support your strategies. Examples include advertising, training, outsourcing services, etc.
When developing strategic human resource management tactics, think about the results you expect from each tactic. Do you need immediate results? Or can you wait until later? How much money will you need? How much time do you have before you need to start seeing results?
It would be best to keep in mind that you can only do what you have authority over. So, if you’re trying to promote employees but they report directly to someone else, you won’t be able to do anything about it.
5. Plan Implementation
Planning is determining when, where, and how to execute each tactic. Planning includes deciding whether to act now, wait until later, or do nothing.
While implementing, it’s essential to closely monitor different factors that may affect the composition of a workplace. These factors include:
- Age – Older employees tend to have more significant experience than younger ones. Younger employees are usually less experienced. It can be hard to find good talent among young people.
- Gender – Women typically make up about half of the workforce. Men generally make up the rest. Companies with a higher proportion of female employees tend to have better performance.
- Race – People of color tend to earn lower salaries than white men. In addition, they are less likely to receive promotions.
6. Monitor Performance
Monitoring results is the process of evaluating what has happened after implementation. Monitoring includes measuring performance against pre-determined benchmarks. It also includes assessing the impact of any changes made by strategic HR management to improve effectiveness.
Monitoring performance is an ongoing activity. It requires constant attention. Monitoring helps determine what works and what doesn’t.
There are several tools you can use, including:
- Observation
7. Evaluate Performance
Evaluating performance is critical in any HR department. It is the process of comparing actual results to expected outcomes. Evaluation can be done by analyzing data collected through monitoring and evaluation.
Evaluating your performance is crucial because it lets you know if your strategies are working. If not, then you need to change them. For example, if your HR strategies aren’t producing desired results, you might consider changing your approach, including outsourcing strategic human resource services.
Including strategic human resource management in the overall business strategy help with creating a productive environment, but it also helps with other crucial aspects such as retaining employees.
If the human resource department succeeds in creating an effective strategy, it brings value to the organization.
Take time to create the human resource management strategy. Having the right plan creates a streamlined process that’s easy to follow. Good luck.
If you are new to human resources and are looking to break into an HR role, we recommend taking our HR Certification Courses , where you will learn how to build your skillset in human resources, build your human resources network, craft a great HR resume, and create a successful job search strategy.
We offer a wide variety of programs and courses built on adaptive curriculum and led by leading industry experts.
- Work on projects in a collaborative setting
- Take advantage of our flexible plans and community
- Get access to experts, templates, and exclusive events
Become a Certified HR Manager. The HR Management Certification helps to demonstrate knowledge and skills in best practices for managing employees, handling disciplinary action, and other important aspects of the job.
Become a Certified HR Generalist. After taking this certification course, you'll better understand how to become a great HR Generalist and a letter of certification to showcase to employers and colleagues.
Become a Certified HR Business Partner. The certificate has become a popular credential because it can help individuals seeking advancement within their current organization and those looking to change jobs or industries.
Please check your email for a confirmation message shortly.
Join 5000+ Technical Writers
Get our #1 industry rated weekly technical writing reads newsletter.
Your syllabus has been sent to your email
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

Human Resource Management Assignment

2017, Human Resource Management Assignment
Related Papers
Procter Frank Hamatuli
the paper explores the effectiveness of the Human Resources available to an organisation.
Jon Hairsine
Janice Baltor
Note: upload the soft copy of your assignment in Moodle for plagiarism checks first finalizing your submission Human resource management has never had so much significance in today's dynamic and competitive business environment than in the last decade. It has been acknowledged by
Slobodan Camilovic
Abstract: In the process of organizational adaptation to environmental demands, primarily through the anticipated outputs, human resources play a key role. The procuring of necessary human resources, their working commitment and development, are the basic assignments of the management of human resources. The appliance of a contemporary concept of management of human resources, based on theoretical and practical cognizance of successful organizations, contributes to a successful execution of these and other assignments. In order to develop such a concept it is necessary to provide, in addition to the relevant basics, a whole chain of professional and managerial activities.
Gihan Yatawatte
Review of Professional Management- A Journal of New Delhi Institute of Management
Teena Singh
Md. Ali Ahsan, PhD
James Sample-Marble
AMJAD ALI IKRAM
Dian Damayanti
RELATED TOPICS
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
- Book a Speaker
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Vivamus convallis sem tellus, vitae egestas felis vestibule ut.
Error message details.
Reuse Permissions
Request permission to republish or redistribute SHRM content and materials.
Managing International Assignments
International assignment management is one of the hardest areas for HR professionals to master—and one of the most costly. The expense of a three-year international assignment can cost millions, yet many organizations fail to get it right. Despite their significant investments in international assignments, companies still report a 42 percent failure rate in these assignments. 1
With so much at risk, global organizations must invest in upfront and ongoing programs that will make international assignments successful. Selecting the right person, preparing the expatriate (expat) and the family, measuring the employee's performance from afar, and repatriating the individual at the end of an assignment require a well-planned, well-managed program. Knowing what to expect from start to finish as well as having some tools to work with can help minimize the risk.
Business Case
As more companies expand globally, they are also increasing international assignments and relying on expatriates to manage their global operations. According to KPMG's 2021 Global Assignment Policies and Practices Survey, all responding multinational organizations offered long-term assignments (typically one to five years), 88 percent offered short-term assignments (typically defined as less than 12 months), and 69 percent offered permanent transfer/indefinite length.
Managing tax and tax compliance, cost containment and managing exceptions remain the three principal challenges in long-term assignment management according to a 2020 Mercer report. 2
Identifying the Need for International Assignment
Typical reasons for an international assignment include the following:
- Filling a need in an existing operation.
- Transferring technology or knowledge to a worksite (or to a client's worksite).
- Developing an individual's career through challenging tasks in an international setting.
- Analyzing the market to see whether the company's products or services will attract clients and users.
- Launching a new product or service.
The goal of the international assignment will determine the assignment's length and help identify potential candidates. See Structuring Expatriate Assignments and the Value of Secondment and Develop Future Leaders with Rotational Programs .
Selection Process
Determining the purpose and goals for an international assignment will help guide the selection process. A technical person may be best suited for transferring technology, whereas a sales executive may be most effective launching a new product or service.
Traditionally, organizations have relied on technical, job-related skills as the main criteria for selecting candidates for overseas assignments, but assessing global mindset is equally, if not more, important for successful assignments. This is especially true given that international assignments are increasingly key components of leadership and employee development.
To a great extent, the success of every expatriate in achieving the company's goals in the host country hinges on that person's ability to influence individuals, groups and organizations that have a different cultural perspective.
Interviews with senior executives from various industries, sponsored by the Worldwide ERC Foundation, reveal that in the compressed time frame of an international assignment, expatriates have little opportunity to learn as they go, so they must be prepared before they arrive. Therefore, employers must ensure that the screening process for potential expatriates includes an assessment of their global mindset.
The research points to three major attributes of successful expatriates:
- Intellectual capital. Knowledge, skills, understanding and cognitive complexity.
- Psychological capital. The ability to function successfully in the host country through internal acceptance of different cultures and a strong desire to learn from new experiences.
- Social capital. The ability to build trusting relationships with local stakeholders, whether they are employees, supply chain partners or customers.
According to Global HR Consultant Caroline Kersten, it is generally understood that global leadership differs significantly from domestic leadership and that, as a result, expatriates need to be equipped with competencies that will help them succeed in an international environment. Commonly accepted global leadership competencies, for both male and female global leaders, include cultural awareness, open-mindedness and flexibility.
In particular, expatriates need to possess a number of vital characteristics to perform successfully on assignment. Among the necessary traits are the following:
- Confidence and self-reliance: independence; perseverance; work ethic.
- Flexibility and problem-solving skills: resilience; adaptability; ability to deal with ambiguity.
- Tolerance and interpersonal skills: social sensitivity; observational capability; listening skills; communication skills.
- Skill at handling and initiating change: personal drivers and anchors; willingness to take risks.
Trends in international assignment show an increase in the younger generation's interest and placement in global assignments. Experts also call for a need to increase female expatriates due to the expected leadership shortage and the value employers find in mixed gender leadership teams. See Viewpoint: How to Break Through the 'Mobility Ceiling' .
Employers can elicit relevant information on assignment successes and challenges by means of targeted interview questions with career expatriates, such as the following:
- How many expatriate assignments have you completed?
- What are the main reasons why you chose to accept your previous expatriate assignments?
- What difficulties did you experience adjusting to previous international assignments? How did you overcome them?
- On your last assignment, what factors made your adjustment to the new environment easier?
- What experiences made interacting with the locals easier?
- Please describe what success or failure means to you when referring to an expatriate assignment.
- Was the success or failure of your assignments measured by your employers? If so, how did they measure it?
- During your last international assignment, do you recall when you realized your situation was a success or a failure? How did you come to that determination?
- Why do you wish to be assigned an international position?
Securing Visas
Once an individual is chosen for an assignment, the organization needs to move quickly to secure the necessary visas. Requirements and processing times vary by country. Employers should start by contacting the host country's consulate or embassy for information on visa requirements. See Websites of U.S. Embassies, Consulates, and Diplomatic Missions .
Following is a list of generic visa types that may be required depending on the nature of business to be conducted in a particular country:
- A work permit authorizes paid employment in a country.
- A work visa authorizes entry into a country to take up paid employment.
- A dependent visa permits family members to accompany or join employees in the country of assignment.
- A multiple-entry visa permits multiple entries into a country.
Preparing for the Assignment
An international assignment agreement that outlines the specifics of the assignment and documents agreement by the employer and the expatriate is necessary. Topics typically covered include:
- Location of the assignment.
- Length of the assignment, including renewal and trial periods, if offered.
- Costs paid by the company (e.g., assignment preparation costs, moving costs for household goods, airfare, housing, school costs, transportation costs while in country, home country visits and security).
- Base salary and any incentives or allowances offered.
- Employee's responsibilities and goals.
- Employment taxes.
- Steps to take in the event the assignment is not working for either the employee or the employer.
- Repatriation.
- Safety and security measures (e.g., emergency evacuation procedures, hazards).
Expatriates may find the reality of foreign housing very different from expectations, particularly in host locations considered to be hardship assignments. Expats will find—depending on the degree of difficulty, hardship or danger—that housing options can range from spacious accommodations in a luxury apartment building to company compounds with dogs and armed guards. See Workers Deal with Affordable Housing Shortages in Dubai and Cairo .
Expats may also have to contend with more mundane housing challenges, such as shortages of suitable housing, faulty structures and unreliable utility services. Analyses of local conditions are available from a variety of sources. For example, Mercer produces Location Evaluation Reports, available for a fee, that evaluate levels of hardship for 14 factors, including housing, in more than 135 locations.
Although many employers acknowledge the necessity for thorough preparation, they often associate this element solely with the assignee, forgetting the other key parties involved in an assignment such as the employee's family, work team and manager.
The expatriate
Consider these points in relation to the assignee:
- Does the employee have a solid grasp of the job to be done and the goals established for that position?
- Does the employee understand the compensation and benefits package?
- Has the employee had access to cultural training and language instruction, no matter how similar the host culture may be?
- Is the employee receiving relocation assistance in connection with the physical move?
- Is there a contact person to whom the employee can go not only in an emergency but also to avoid becoming "out of sight, out of mind"?
- If necessary to accomplish the assigned job duties, has the employee undergone training to get up to speed?
- Has the assignee undergone an assessment of readiness?
To help the expatriate succeed, organizations are advised to invest in cross-cultural training before the relocation. The benefits of receiving such training are that it: 3
- Prepares the individual/family mentally for the move.
- Removes some of the unknown.
- Increases self-awareness and cross-cultural understanding.
- Provides the opportunity to address questions and anxieties in a supportive environment.
- Motivates and excites.
- Reduces stress and provides coping strategies.
- Eases the settling-in process.
- Reduces the chances of relocation failure.
See Helping Expatriate Employees Deal with Culture Shock .
As society has shifted from single- to dual-income households, the priorities of potential expatriates have evolved, as have the policies organizations use to entice employees to assignment locations. In the past, from the candidate's point of view, compensation was the most significant component of the expatriate package. Today more emphasis is on enabling an expatriate's spouse to work. Partner dissatisfaction is a significant contributor to assignment failure. See UAE: Expat Husbands Get New Work Opportunities .
When it comes to international relocation, most organizations deal with children as an afterthought. Factoring employees' children into the relocation equation is key to a successful assignment. Studies show that transferee children who have a difficult time adjusting to the assignment contribute to early returns and unsuccessful completion of international assignments, just as maladjusted spouses do. From school selection to training to repatriation, HR can do a number of things to smooth the transition for children.
Both partners and children must be prepared for relocation abroad. Employers should consider the following:
- Have they been included in discussions about the host location and what they can expect? Foreign context and culture may be more difficult for accompanying family because they will not be participating in the "more secure" environment of the worksite. Does the family have suitable personal characteristics to successfully address the rigors of an international life?
- In addition to dual-career issues, other common concerns include aging parents left behind in the home country and special needs for a child's education. Has the company allowed a forum for the family to discuss these concerns?
The work team
Whether the new expatriate will supervise the existing work team, be a peer, replace a local national or fill a newly created position, has the existing work team been briefed? Plans for a formal introduction of the new expatriate should reflect local culture and may require more research and planning as well as input from the local work team.
The manager/team leader
Questions organization need to consider include the following: Does the manager have the employee's file on hand (e.g., regarding increases, performance evaluations, promotions and problems)? Have the manager and employee engaged in in-depth conversations about the job, the manager's expectations and the employee's expectations?
Mentors play an important role in enhancing a high-performing employee's productivity and in guiding his or her career. In a traditional mentoring relationship, a junior executive has ongoing face-to-face meetings with a senior executive at the corporation to learn the ropes, set goals and gain advice on how to better perform his or her job.
Before technological advances, mentoring programs were limited to those leaders who had the time and experience within the organization's walls to impart advice to a few select people worth that investment. Technology has eliminated those constraints. Today, maintaining a long-distance mentoring relationship through e-mail, telephone and videoconferencing is much easier. And that technology means an employer is not confined to its corporate halls when considering mentor-mentee matches.
The organization
If the company is starting to send more employees abroad, it has to reassess its administrative capabilities. Can existing systems handle complicated tasks, such as currency exchanges and split payrolls, not to mention the additional financial burden of paying allowances, incentives and so on? Often, international assignment leads to outsourcing for global expertise. Payroll, tax, employment law, contractual obligations, among others, warrant an investment in sound professional advice.
Employment Laws
Four major U.S. employment laws have some application abroad for U.S. citizens working in U.S.-based multinationals:
- Title VII of the Civil Rights Act.
- The Age Discrimination in Employment Act (ADEA).
- The Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA).
- The Uniformed Services Employment and Reemployment Rights Act (USERRA).
Title VII, the ADEA and the ADA are the more far-reaching among these, covering all U.S. citizens who are either:
- Employed outside the United States by a U.S. firm.
- Employed outside the United States by a company under the control of a U.S. firm.
USERRA's extraterritoriality applies to veterans and reservists working overseas for the federal government or a firm under U.S. control. See Do laws like the Fair Labor Standards Act and the Family and Medical Leave Act apply to U.S. citizens working in several other countries?
Employers must also be certain to comply with both local employment law in the countries in which they manage assignments and requirements for corporate presence in those countries. See Where can I find international employment law and culture information?
Compensation
Companies take one of the following approaches to establish base salaries for expatriates:
- The home-country-based approach. The objective of a home-based compensation program is to equalize the employee to a standard of living enjoyed in his or her home country. Under this commonly used approach, the employee's base salary is broken down into four general categories: taxes, housing, goods and services, and discretionary income.
- The host-country-based approach. With this approach, the expatriate employee's compensation is based on local national rates. Many companies continue to cover the employee in its defined contribution or defined benefit pension schemes and provide housing allowances.
- The headquarters-based approach. This approach assumes that all assignees, regardless of location, are in one country (i.e., a U.S. company pays all assignees a U.S.-based salary, regardless of geography).
- Balance sheet approach. In this scenario, the compensation is calculated using the home-country-based approach with all allowances, deductions and reimbursements. After the net salary has been determined, it is then converted to the host country's currency. Since one of the primary goals of an international compensation management program is to maintain the expatriate's current standard of living, developing an equitable and functional compensation plan that combines balance and flexibility is extremely challenging for multinational companies. To this end, many companies adopt a balance sheet approach. This approach guarantees that employees in international assignments maintain the same standard of living they enjoyed in their home country. A worksheet lists the costs of major expenses in the home and host countries, and any differences are used to increase or decrease the compensation to keep it in balance.
Some companies also allow expatriates to split payment of their salaries between the host country's and the home country's currencies. The expatriate receives money in the host country's currency for expenses but keeps a percentage of it in the home country currency to safeguard against wild currency fluctuations in either country.
As for handling expatriates taxes, organizations usually take one of four approaches:
- The employee is responsible for his or her own taxes.
- The employer determines tax reimbursement on a case-by-case basis.
- The employer pays the difference between taxes paid in the United States and the host country.
- The employer withholds U.S. taxes and pays foreign taxes.
To prevent an expatriate employee from suffering excess taxation of income by both the U.S. and host countries, many multinational companies implement either a tax equalization or a tax reduction policy for employees on international assignments. Additionally, the United States has entered into bilateral international social security agreements with numerous countries, referred to as "totalization agreements," which allow for an exemption of the social security tax in either the home or host country for defined periods of time.
A more thorough discussion of compensation and tax practices for employees on international assignment can be found in SHRM's Designing Global Compensation Systems toolkit.
How do we handle taxes for expatriates?
Can employers pay employees in other countries on the corporate home-country payroll?
Measuring Expatriates' Performance
Failed international assignments can be extremely costly to an organization. There is no universal approach to measuring an expatriate's performance given that specifics related to the job, country, culture and other variables will need to be considered. Employers must identify and communicate clear job expectations and performance indicators very early on in the assignment. A consistent and detailed assessment of an expatriate employee's performance, as well as appraisal of the operation as a whole, is critical to the success of an international assignment. Issues such as the criteria for and timing of performance reviews, raises and bonuses should be discussed and agreed on before the employees are selected and placed on international assignments.
Employees on foreign assignments face a number of issues that domestic employees do not. According to a 2020 Mercer report 4 , difficulty adjusting to the host country, poor candidate selection and spouse or partner's unhappiness are the top three reasons international assignments fail. Obviously, retention of international assignees poses a significant challenge to employers.
Upon completion of an international assignment, retaining the employee in the home country workplace is also challenging. Unfortunately, many employers fail to track retention data of repatriated employees and could benefit from collecting this information and making adjustments to reduce the turnover of employees returning to their home country.
Safety and Security
When faced with accident, injury, sudden illness, a disease outbreak or politically unstable conditions in which personal safety is at risk, expatriate employees and their dependents may require evacuation to the home country or to a third location. To be prepared, HR should have an evacuation plan in place that the expatriate can share with friends, extended family and colleagues both at home and abroad. See Viewpoint: Optimizing Global Mobility's Emergency Response Plans .
Many companies ban travel outside the country in the following circumstances:
- When a travel advisory is issued by the World Health Organization, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, International SOS or a government agency.
- When a widespread outbreak of a specific disease occurs or if the risk is deemed too high for employees and their well-being is in jeopardy.
- If the country is undergoing civil unrest or war or if an act of terrorism has occurred.
- If local management makes the decision.
- If the employee makes the decision.
Once employees are in place, the decision to evacuate assignees and dependents from a host location is contingent on local conditions and input from either internal sources (local managers, headquarters staff, HR and the assignee) or external sources (an external security or medical firm) or both. In some cases, each host country has its own set of evacuation procedures.
Decision-makers should consider all available and credible advice and initially transport dependents and nonessential personnel out of the host country by the most expeditious form of travel.
Navigating International Crises
How can an organization ensure the safety and security of expatriates and other employees in high-risk areas?
The Disaster Assistance Improvement Program (DAIP)
Repatriation
Ideally, the repatriation process begins before the expatriate leaves his or her home country and continues throughout the international assignment by addressing the following issues.
Career planning. Many managers are responsible for resolving difficult problems abroad and expect that a well-done job will result in promotion on return, regardless of whether the employer had made such a promise. This possibly unfounded assumption can be avoided by straightforward career planning that should occur in advance of the employee's accepting the international assignment. Employees need to know what impact the expatriate assignment will have on their overall advancement in the home office and that the international assignment fits in their career path.
Mentoring. The expatriate should be assigned a home-office mentor. Mentors are responsible for keeping expatriates informed on developments within the company, for keeping the expatriates' names in circulation in the office (to help avoid the out-of-sight, out-of-mind phenomenon) and for seeing to it that expatriates are included in important meetings. Mentors can also assist the expatriate in identifying how the overseas experience can best be used on return. Optimum results are achieved when the mentor role is part of the mentor's formal job duties.
Communication. An effective global communication plan will help expatriates feel connected to the home office and will alert them to changes that occur while they are away. The Internet, e-mail and intranets are inexpensive and easy ways to bring expatriates into the loop and virtual meeting software is readily available for all employers to engage with global employees. In addition, organizations should encourage home-office employees to keep in touch with peers on overseas assignments. Employee newsletters that feature global news and expatriate assignments are also encouraged.
Home visits. Most companies provide expatriates with trips home. Although such trips are intended primarily for personal visits, scheduling time for the expatriate to visit the home office is an effective method of increasing the expatriate's visibility. Having expatriates attend a few important meetings or make a presentation on their international assignment is also a good way to keep them informed and connected.
Preparation to return home. The expatriate should receive plenty of advance notice (some experts recommend up to one year) of when the international assignment will end. This notice will allow the employee time to prepare the family and to prepare for a new position in the home office. Once the employee is notified of the assignment's end, the HR department should begin working with the expatriate to identify suitable positions in the home office. The expatriate should provide the HR department with an updated resume that reflects the duties of the overseas assignment. The employee's overall career plan should be included in discussions with the HR professional.
Interviews. In addition to home leave, organizations may need to provide trips for the employee to interview with prospective managers. The face-to-face interview will allow the expatriate to elaborate on skills and responsibilities obtained while overseas and will help the prospective manager determine if the employee is a good fit. Finding the right position for the expatriate is crucial to retaining the employee. Repatriates who feel that their new skills and knowledge are underutilized may grow frustrated and leave the employer.
Ongoing recognition of contributions. An employer can recognize and appreciate the repatriates' efforts in several ways, including the following:
- Hosting a reception for repatriates to help them reconnect and meet new personnel.
- Soliciting repatriates' help in preparing other employees for expatriation.
- Asking repatriates to deliver a presentation or prepare a report on their overseas assignment.
- Including repatriates on a global task force and asking them for a global perspective on business issues.
Measuring ROI on expatriate assignments can be cumbersome and imprecise. The investment costs of international assignments can vary dramatically and can be difficult to determine. The largest expatriate costs include overall remuneration, housing, cost-of-living allowances (which sometimes include private schooling costs for children) and physical relocation (the movement to the host country of the employee, the employee's possessions and, often, the employee's family).
But wide variations exist in housing expenses. For example, housing costs are sky-high in Tokyo and London, whereas Australia's housing costs are moderate. Another significant cost of expatriate assignments involves smoothing out differences in pay and benefits between one country and another. Such cost differences can be steep and can vary based on factors such as exchange rates (which can be quite volatile) and international tax concerns (which can be extremely complex).
Once an organization has determined the costs of a particular assignment, the second part of the ROI challenge is calculating the return. Although it is relatively straightforward to quantify the value of fixing a production line in Puerto Rico or of implementing an enterprise software application in Asia, the challenge of quantifying the value of providing future executives with cross-cultural perspectives and international leadership experience can be intimidating.
Once an organization determines the key drivers of its expatriate program, HR can begin to define objectives and assess return that can be useful in guiding employees and in making decisions about the costs they incur as expatriates. Different objectives require different levels and lengths of tracking. Leadership development involves a much longer-term value proposition and should include a thorough repatriation plan. By contrast, the ROI of an international assignment that plugs a skills gap is not negatively affected if the expatriate bolts after successfully completing the engagement.
Additional Resources
International Assignment Management: Expatriate Policy and Procedure
Introduction to the Global Human Resources Discipline
1Mulkeen, D. (2017, February 20). How to reduce the risk of international assignment failure. Communicaid. Retrieved from https://www.communicaid.com/cross-cultural-training/blog/reducing-risk-international-assignment-failure/
2Mercer. (2020). Worldwide Survey of International Assignment Policies and Practices. Retrieved from https://mobilityexchange.mercer.com/international-assignments-survey .
3Dickmann, M., & Baruch, Y. (2011). Global careers. New York: Routledge.
4Mercer. (2020). Worldwide Survey of International Assignment Policies and Practices. Retrieved from https://mobilityexchange.mercer.com/international-assignments-survey
Related Articles

A 4-Day Workweek? AI-Fueled Efficiencies Could Make It Happen
The proliferation of artificial intelligence in the workplace, and the ensuing expected increase in productivity and efficiency, could help usher in the four-day workweek, some experts predict.

How One Company Uses Digital Tools to Boost Employee Well-Being
Learn how Marsh McLennan successfully boosts staff well-being with digital tools, improving productivity and work satisfaction for more than 20,000 employees.

Employers Want New Grads with AI Experience, Knowledge
A vast majority of U.S. professionals say students entering the workforce should have experience using AI and be prepared to use it in the workplace, and they expect higher education to play a critical role in that preparation.
HR Daily Newsletter
New, trends and analysis, as well as breaking news alerts, to help HR professionals do their jobs better each business day.
Success title
Success caption
- Using Global Human Resources
Examples of Multiple Managers for an Assignment
You must define at least one line manager for an assignment. Optionally, you can add other manager types. Line managers see the line-manager version of a person's spotlight and other restricted worker information.
Other manager types can also see restricted worker information if their roles have the required security access.
Let's see some examples of assignments that need multiple managers.
Matrix Management in an Engineering Company
An engineering company uses a matrix management structure. An engineer reports to the lead engineer for everyday functional guidance and to the operational manager for project assignment and tracking.
In this example, you define the lead engineer as the line manager and the operational manager as the project manager. This is because the lead engineer interacts with the team members every day and evaluates their progress. The project manager's role is restricted to assigning projects and tracking project completion.
Temporary Project Managers in a Service Company
A service company assigns workers to third parties to deliver contracted services. Each worker has a manager whose primary task is to help the worker find their next assignment. The manager is common for all of the worker's assignments. You define this manager as a line manager.
The worker also has a temporary project manager who manages a particular assignment but may not manage all of the worker's assignments. You define the project manager as an additional manager (for example, as a project manager) in relevant assignments.
Managers in a Global Company
A global company is organized functionally and workers report to a functional manager who may be in a different time zone. You define the functional manager as the line manager for the assignment.
For day-to-day administrative purposes, such as approving leave or absence, each worker also has an administrative manager. You define this administrative manager as an additional manager for the assignment.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Module Alignment. Assignment: Becoming a Changemaker. Module 1: The Role of Human Resources and Module 2: Human Resources Strategy and Planning. Assignment: Develop a Diversity Allies Program. Module 3: People Analytics & Human Capital Trends and Module 4: Promoting a Diverse Workforce. Assignment: Job Description Research and Development.
Human resource management includes the leadership and facilitation of the following key life cycle process areas: Human resources compliance. Employee selection, hiring, and onboarding. Performance management. Compensation rewards and benefits. Talent development and succession planning. Human resources is responsible for driving the strategy ...
SHORT WRITING ASSIGNMENTS There are three (3) writing assignments the correspond to the lecture topics. These assignments should be a minimum of 1 page single-spaced and a maximum of 3 pages single-spaced. The details for these assignments are posted on the course Canvas site. Each assignment is worth a maximum of 50 points,
The specialization begins with a that considers alternative approaches to managing human resources, provides a background to the U.S. legal context in which employees are hired, fired, rewarded, and managed, and outlines the different reasons that people are motivated to work. The remaining tackle three core areas that all managers should ...
UCDE PROGRAM ADVISOR. Crystal Babowal [email protected] 530-757-8629. Visit our website for detailed description and quarterly schedule. 1333 Research Park Drive, Davis, CA 95618 (800) 752-0881 [email protected]. cpe.ucdavis.edu.
Human resource management is organizing, coordinating, and managing an organization's current employees to carry out an organization's mission, vision, and goals. This includes recruiting, hiring, training, compensating, retaining, and motivating employees. HRM staff also develops and enforces policies and procedures that help ensure employee ...
United Auto Workers working at the 'Big Three (General Motors, Chrysler and Ford), had starting salaries around $13.00 an hour and earned on average $19.00 an hour. The minimum wage in 1996 was $4.25, raised to $4.75 on October 1, 1996. Session 6: Participation and Involvement. Film: Breakdown at Eastern Airlines.
Other. Date. Rating. year. Ratings. Show 3 more documents. Show all 11 documents... Studying HRMN 300 Human Resource Management at University of Maryland Global Campus? On Studocu you will find 120 assignments, 43 coursework, 15 lecture notes and.
This course is part of the Human Resource Management: HR for People Managers Specialization. When you enroll in this course, you'll also be enrolled in this Specialization. Learn new concepts from industry experts. Gain a foundational understanding of a subject or tool. Develop job-relevant skills with hands-on projects.
Human Resource Management (HRM) is a collective term for all the formal systems created to help in managing employees and other stakeholders within a company. Human resource management is tasked with three main functions, namely, the recruitment and compensation of employees, and designating work. Ideally, the role of HRM is to find the best ...
Human resource information systems (HRIS) - perform core HR functions, like applicant tracking, payroll and benefits administration. Human resource management systems (HRMS) - offer the benefits of HRIS, plus talent management services. Human capital management (HCM) solutions - provide a broad suite of HR capabilities, including global ...
Business 306 - Assignment 1: HR Consultation ... Human Resource Management Around the... Ch 14. Human Resource Metrics &... Ch 15. Required Assignments for Business 306.
Describe the steps in the development of an HRM plan. As addressed in Section 2.1 "Strategic Planning", the writing of an HRM strategic plan should be based on the strategic plans of the organization and of the department. Once the strategic plan is written, the HR professional can begin work on the HR plan. This is different from the ...
Meet with business line manager, top management, and collect market data to validate assumptions. 4. Highlight company's top 5 turnover reasons with action plan to top management. Competency developed: Business partnering. Objective: Develop your HR Managers to become real Business partner. Explanation: From back seat to the front seat.
Human resource management (HRM or HR) is the strategic and coherent approach to the effective and efficient management of people in a company or organization such that they help their business gain a competitive advantage.It is designed to maximize employee performance in service of an employer's strategic objectives. [need quotation to verify] Human resource management is primarily concerned ...
Conclusion. Strategic human resource management is a process that helps the human resources department maximize the potential of its workforce through strategic planning, talent management, leadership development, organizational design, and performance management. In the past, strategic HR management was an administrative function.
Mandatory assignments 100% (2) 7. LRM 1501 - A practice assignment that might be useful. Practice materials None. 22. HRM1501 (Lesson 08) - textbook. Lecture notes None. 12. HRM1501, Semester 1 2020, Assignment 3 - Stuvia.
Human Resource Management Assignment 1: Individual Essay James Goh Wei Li 101221297. Human resource management (HRM) is recruiting, hiring, deploying, and managing employees in a business. A corporation's or organization's human resources department is typically in charge of establishing, implementing, and overseeing regulations that govern ...
Human Resource Management and Organizational Effectiveness Organizational effectiveness is influenced by some factors including the attraction and selection of the right people for the right job assignment. Human resource management is tasked with the Cornelius Willem van der Westhuizen Unit A/615/2727 - Human Resource Management 4 process of ...
Overview. International assignment management is one of the hardest areas for HR professionals to master—and one of the most costly. The expense of a three-year international assignment can cost ...
oum bussiness school semester year 2018 bbpb 2103 human resources management matriculation no: 920510055012001 identity card no. :920510055012 telephone no. Skip to document. University; High School ... FULL SET OF Assignment- Human Resource Management. Course: Human Resources Management. 103 Documents. Students shared 103 documents in this ...
human resource management individual assignment 2 | p a g e btec hnd diploma in business (level 5) assignment coversheet 2014 unit title & code unit 1: human resource management unit code: k/601/1264 level 4 student name credits 15 assesor student id assessment assignment i.v by: assignment issue date assignment submission date
Let's see some examples of assignments that need multiple managers. Matrix Management in an Engineering Company. An engineering company uses a matrix management structure. An engineer reports to the lead engineer for everyday functional guidance and to the operational manager for project assignment and tracking.