Ohio State nav bar
The Ohio State University
- BuckeyeLink
- Find People
- Search Ohio State

Research Questions & Hypotheses
Generally, in quantitative studies, reviewers expect hypotheses rather than research questions. However, both research questions and hypotheses serve different purposes and can be beneficial when used together.
Research Questions
Clarify the research’s aim (farrugia et al., 2010).
- Research often begins with an interest in a topic, but a deep understanding of the subject is crucial to formulate an appropriate research question.
- Descriptive: “What factors most influence the academic achievement of senior high school students?”
- Comparative: “What is the performance difference between teaching methods A and B?”
- Relationship-based: “What is the relationship between self-efficacy and academic achievement?”
- Increasing knowledge about a subject can be achieved through systematic literature reviews, in-depth interviews with patients (and proxies), focus groups, and consultations with field experts.
- Some funding bodies, like the Canadian Institute for Health Research, recommend conducting a systematic review or a pilot study before seeking grants for full trials.
- The presence of multiple research questions in a study can complicate the design, statistical analysis, and feasibility.
- It’s advisable to focus on a single primary research question for the study.
- The primary question, clearly stated at the end of a grant proposal’s introduction, usually specifies the study population, intervention, and other relevant factors.
- The FINER criteria underscore aspects that can enhance the chances of a successful research project, including specifying the population of interest, aligning with scientific and public interest, clinical relevance, and contribution to the field, while complying with ethical and national research standards.
- The P ICOT approach is crucial in developing the study’s framework and protocol, influencing inclusion and exclusion criteria and identifying patient groups for inclusion.
- Defining the specific population, intervention, comparator, and outcome helps in selecting the right outcome measurement tool.
- The more precise the population definition and stricter the inclusion and exclusion criteria, the more significant the impact on the interpretation, applicability, and generalizability of the research findings.
- A restricted study population enhances internal validity but may limit the study’s external validity and generalizability to clinical practice.
- A broadly defined study population may better reflect clinical practice but could increase bias and reduce internal validity.
- An inadequately formulated research question can negatively impact study design, potentially leading to ineffective outcomes and affecting publication prospects.
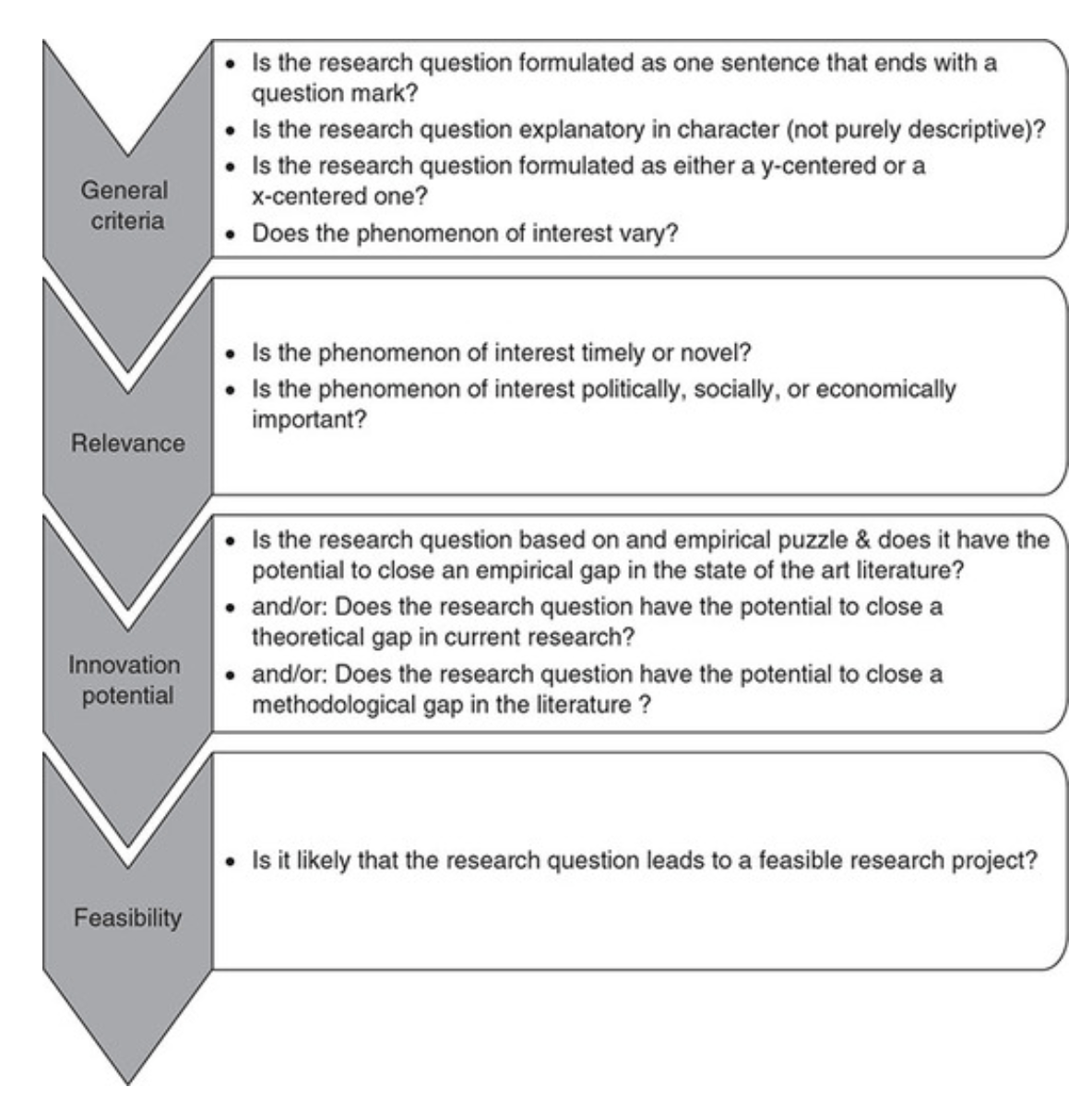
Checklist: Good research questions for social science projects (Panke, 2018)
Research Hypotheses
Present the researcher’s predictions based on specific statements.
- These statements define the research problem or issue and indicate the direction of the researcher’s predictions.
- Formulating the research question and hypothesis from existing data (e.g., a database) can lead to multiple statistical comparisons and potentially spurious findings due to chance.
- The research or clinical hypothesis, derived from the research question, shapes the study’s key elements: sampling strategy, intervention, comparison, and outcome variables.
- Hypotheses can express a single outcome or multiple outcomes.
- After statistical testing, the null hypothesis is either rejected or not rejected based on whether the study’s findings are statistically significant.
- Hypothesis testing helps determine if observed findings are due to true differences and not chance.
- Hypotheses can be 1-sided (specific direction of difference) or 2-sided (presence of a difference without specifying direction).
- 2-sided hypotheses are generally preferred unless there’s a strong justification for a 1-sided hypothesis.
- A solid research hypothesis, informed by a good research question, influences the research design and paves the way for defining clear research objectives.
Types of Research Hypothesis
- In a Y-centered research design, the focus is on the dependent variable (DV) which is specified in the research question. Theories are then used to identify independent variables (IV) and explain their causal relationship with the DV.
- Example: “An increase in teacher-led instructional time (IV) is likely to improve student reading comprehension scores (DV), because extensive guided practice under expert supervision enhances learning retention and skill mastery.”
- Hypothesis Explanation: The dependent variable (student reading comprehension scores) is the focus, and the hypothesis explores how changes in the independent variable (teacher-led instructional time) affect it.
- In X-centered research designs, the independent variable is specified in the research question. Theories are used to determine potential dependent variables and the causal mechanisms at play.
- Example: “Implementing technology-based learning tools (IV) is likely to enhance student engagement in the classroom (DV), because interactive and multimedia content increases student interest and participation.”
- Hypothesis Explanation: The independent variable (technology-based learning tools) is the focus, with the hypothesis exploring its impact on a potential dependent variable (student engagement).
- Probabilistic hypotheses suggest that changes in the independent variable are likely to lead to changes in the dependent variable in a predictable manner, but not with absolute certainty.
- Example: “The more teachers engage in professional development programs (IV), the more their teaching effectiveness (DV) is likely to improve, because continuous training updates pedagogical skills and knowledge.”
- Hypothesis Explanation: This hypothesis implies a probable relationship between the extent of professional development (IV) and teaching effectiveness (DV).
- Deterministic hypotheses state that a specific change in the independent variable will lead to a specific change in the dependent variable, implying a more direct and certain relationship.
- Example: “If the school curriculum changes from traditional lecture-based methods to project-based learning (IV), then student collaboration skills (DV) are expected to improve because project-based learning inherently requires teamwork and peer interaction.”
- Hypothesis Explanation: This hypothesis presumes a direct and definite outcome (improvement in collaboration skills) resulting from a specific change in the teaching method.
- Example : “Students who identify as visual learners will score higher on tests that are presented in a visually rich format compared to tests presented in a text-only format.”
- Explanation : This hypothesis aims to describe the potential difference in test scores between visual learners taking visually rich tests and text-only tests, without implying a direct cause-and-effect relationship.
- Example : “Teaching method A will improve student performance more than method B.”
- Explanation : This hypothesis compares the effectiveness of two different teaching methods, suggesting that one will lead to better student performance than the other. It implies a direct comparison but does not necessarily establish a causal mechanism.
- Example : “Students with higher self-efficacy will show higher levels of academic achievement.”
- Explanation : This hypothesis predicts a relationship between the variable of self-efficacy and academic achievement. Unlike a causal hypothesis, it does not necessarily suggest that one variable causes changes in the other, but rather that they are related in some way.
Tips for developing research questions and hypotheses for research studies
- Perform a systematic literature review (if one has not been done) to increase knowledge and familiarity with the topic and to assist with research development.
- Learn about current trends and technological advances on the topic.
- Seek careful input from experts, mentors, colleagues, and collaborators to refine your research question as this will aid in developing the research question and guide the research study.
- Use the FINER criteria in the development of the research question.
- Ensure that the research question follows PICOT format.
- Develop a research hypothesis from the research question.
- Ensure that the research question and objectives are answerable, feasible, and clinically relevant.
If your research hypotheses are derived from your research questions, particularly when multiple hypotheses address a single question, it’s recommended to use both research questions and hypotheses. However, if this isn’t the case, using hypotheses over research questions is advised. It’s important to note these are general guidelines, not strict rules. If you opt not to use hypotheses, consult with your supervisor for the best approach.
Farrugia, P., Petrisor, B. A., Farrokhyar, F., & Bhandari, M. (2010). Practical tips for surgical research: Research questions, hypotheses and objectives. Canadian journal of surgery. Journal canadien de chirurgie , 53 (4), 278–281.
Hulley, S. B., Cummings, S. R., Browner, W. S., Grady, D., & Newman, T. B. (2007). Designing clinical research. Philadelphia.
Panke, D. (2018). Research design & method selection: Making good choices in the social sciences. Research Design & Method Selection , 1-368.

Home » Education » Difference Between Hypothesis and Research Question
Difference Between Hypothesis and Research Question
Main difference – hypothesis vs research question.
Research question and hypothesis are the foundations of a research study. Formulating the research question or developing the hypothesis can help you to decide on the approach of the research. A research question is the question the research study sets out to answer. Hypothesis is the statement the research study sets out to prove or disprove. The main difference between hypothesis and research question is that hypothesis is predictive in nature whereas research question is inquisitive in nature.
In this article, we’ll discuss,
1. What is a Hypothesis? – Meaning, Features, Characteristics, and Usage
2. What is a Research Question? – Meaning, Features, Characteristics, and Usage

What is a Hypothesis
A hypothesis is a prediction about the relationship between two or more variables. It can be described as an educated guess about what happens in an experiment. Researchers usually tend to use hypotheses when significant knowledge is already available on the subject. The hypothesis is based on this existing knowledge. After the hypothesis is developed, the researcher can develop data, analyze and use them to support or negate the hypothesis.
Not all studies have hypotheses. They are usually used in experimental quantitative research studies. They are useful in testing a specific theory or model. A complete hypothesis always includes the variables, population and the predicted relationship between the variables. The main disadvantage of hypotheses is that their tendency to blind a researcher to unexpected results.

What is a Research Question
A research question is the question a research study sets to answer. However, a research study can have more than one research question. The research methodologies , tools used to collect data, etc. all depend on the research question.
Research questions are often used in qualitative research, which seek to answer open-ended questions . But they can also be used in quantitative studies. Research questions can be used instead of hypotheses when there is little previous research on the subject. Research questions allow the researcher to conduct more open-ended queries, and a wide range of results can be reported.
A properly constructed research question should always be clear and concise. It should include the variables, population and the topic being studied.
Hypothesis is a tentative prediction about the relationship between two or more variables.
Research Question is the question a research study sets to answer.
Hypothesis is predictive in nature.
Research Question is inquisitive in nature.
Existing Research
Hypothesis can be used if there is significant knowledge or previous research on this subject.
Research Question can be used if there is little previous research on the subject.
Quantitative vs Qualitative
Hypothesis is mainly used in experimental quantitative studies.
Research Question can be used in both quantitative and qualitative studies.
Hypothesis doesn’t allow a wide range of outcomes.
Research Question allows a wide range of outcomes.
Image Courtesy:
“Research: Mediterranean Center of Medical Sciences” by McmScience Mediterranean Center of Medical Sciences (CC BY 2.0) via Flickr
About the Author: Hasa
Hasanthi is a seasoned content writer and editor with over 8 years of experience. Armed with a BA degree in English and a knack for digital marketing, she explores her passions for literature, history, culture, and food through her engaging and informative writing.
You May Also Like These

Research Hypothesis vs. Research Question: What's the Difference?
Key Differences
Comparison chart, formulation, directionality, relationship to research process, research hypothesis and research question definitions, research hypothesis, research question, what is a research hypothesis, what is a research question, why is a research hypothesis important, how does a research hypothesis differ from a research question, can a study have both a research hypothesis and a research question, what types of research questions are there, what makes a good research question, how do you formulate a research hypothesis, what is a null research hypothesis, how specific should a research hypothesis be, why is a research question important, can a research hypothesis be proven, how broad can a research question be, how do research questions evolve during a study, how do you formulate a research question, how does a research hypothesis guide experimental design, how does a research question influence literature review, what role does a research question play in qualitative research, can a research hypothesis be modified, what happens if a research hypothesis is refuted.

Trending Comparisons

Popular Comparisons

New Comparisons

- Translators
- Graphic Designers
Please enter the email address you used for your account. Your sign in information will be sent to your email address after it has been verified.
How Does a Hypothesis Differ From a Research Question?

To understand the difference between a hypothesis and a research question , we must first define the exact nature of scientific inquiry . Essentially, scientific inquiry represents a structured and systematic approach to exploration and discovery, grounded in empirical evidence and guided by the principles of logical reasoning and critical analysis. At the heart of scientific inquiry lies a fundamental commitment to unbiased observation and the rigorous assessment of information, a process that seeks to generate verifiable knowledge based on well-founded theories and methodological robustness.
A pivotal facet of successful scientific investigation is the appropriate framing of research, which serves to delineate the scope and direction of the scholarly endeavor. The meticulous articulation of research parameters not only guides investigators in the methodical exploration of a particular phenomenon but also ensures the reliability and validity of the findings derived from it. Correctly framing a research endeavor equips scholars with a clear framework, thereby preventing research ambiguities and facilitating a coherent and purposeful investigative journey.
Central to the framing of research are two interrelated yet distinct elements: the research question and the hypothesis. While the research question generally articulates the primary inquiry or set of inquiries to be addressed in a study, offering a focal point for the exploration, a hypothesis presents a tentative, testable prediction regarding the expected outcomes of the research. It is grounded in the existing literature and theoretical frameworks, serving as a provisional answer to the research question that is subject to empirical verification.
In essence, a research question seeks to identify and explore potential relationships, patterns, or trends, fostering a deep understanding of the underlying phenomena. In contrast, a hypothesis endeavors to affirm or refute predetermined assumptions through methodical testing and validation, aiming to substantiate or discredit specific theoretical postulates.
To correctly formulate and differentiate between research questions and hypotheses, let us investigate each one in further detail.
Understanding hypotheses
Crafting a well-defined hypothesis is a pivotal step in scholarly research. This task necessitates a profound grasp of the subject matter alongside a comprehensive awareness of existing scholarly dialogues and theories relevant to the topic. The hypothesis acts as a foundational pillar that directs the analytical pathways of the investigation, anchoring the exploration with grounded expectations based on existing knowledge.
In the formulation of a hypothesis, researchers must adhere to vital principles to ensure the creation of a substantial and verifiable statement. A robust hypothesis is delineated by several attributes, including precision, testability, and a congruent alignment with established research and theories. Moreover, it is formulated to facilitate empirical substantiation, aiming to either confirm or refute the established propositions through systematic investigation.
To deepen our comprehension of a hypothesis, let us examine some examples in different research contexts, illustrating how a hypothesis can shape and steer a study:
- Individuals between the ages of 40 and 60 who engage in regular physical activity are less likely to develop heart diseases than those who do not.
- Adolescents who experience traumatic events during the COVID-19 pandemic have a higher prevalence of mental health issues than those who do not.
- Remote learning hampers the development of social skills in elementary school students more than traditional classroom learning does.
- Implementing multicultural education strategies diminishes the achievement gap in multicultural classrooms.
- Marine ecosystems that experience high levels of plastic pollution exhibit a substantial reduction in biodiversity.
- Urbanization leads to a significant decrease in biodiversity in metropolitan areas due to habitat loss.
- Voting behavior in urban communities is significantly influenced by the socioeconomic status of the individuals.
- The prevalent use of social media significantly influences the formation of societal norms and behaviors in contemporary society.
- The integration of artificial intelligence in manufacturing elevates efficiency and productivity.
- An increased dependence on digital platforms compromises personal privacy and heightens the risk of data security breaches.
Each of these hypothesis examples is constructed to offer focused and testable propositions, rooted in contemporary concerns, creating a pathway for empirical verification and the generation of data-driven insights.
Understanding research questions
A critical first step in any research endeavor is the formulation of a research question, a task that requires a deep understanding of both the topic at hand and the existing scholarly landscape surrounding it. The research question serves as the beacon that guides the trajectory of the investigation, providing a focal point that centers the research activities and objectives.
In constructing a research question, scholars must be guided by certain key principles to ensure that their inquiry is both meaningful and fruitful. A well-framed research question is characterized by clarity, specificity, and a sensible alignment with existing research, which aids in building upon established foundations to foster novel insights within its scholarly domain.
To further understand the concept of research questions, let us consider some concrete examples from various fields that illustrate how a well-articulated research question can guide a research project:
- How does lifestyle affect the risk of heart disease in adults aged 40-60?
- What impact has the COVID-19 pandemic had on mental health outcomes in adolescents?
- How does remote learning impact the academic performance and social skills of elementary school students?
- What strategies can be employed to reduce the achievement gap in multicultural classrooms?
- What are the effects of plastic waste on marine ecosystems?
- How does urbanization impact biodiversity in metropolitan regions?
- How do socioeconomic factors influence voting behavior in urban communities?
- What role does social media play in shaping contemporary societal norms and behaviors?
- How does the implementation of artificial intelligence in manufacturing enhance efficiency and productivity?
- What are the implications of increasing reliance on digital platforms for personal privacy and data security?
Each of these research question examples not only maintains a clear focus on a specific topic but also stands grounded in current concerns, thereby paving the way for empirical exploration and data-driven conclusions.
Key differences between a hypothesis and a research question
In scholarly research, it is imperative to differentiate clearly between a hypothesis and a research question. The following table delineates the comparative aspects of both concepts:
When to use which
The decision to use a hypothesis or a research question largely hinges on the nature and objectives of the study. Essentially, researchers delineate between exploratory and confirmatory research . The former seeks to explore new phenomena and generate new insights, while the latter aims to verify existing theories and hypotheses. Understanding the correct circumstance for employing either a research question or a hypothesis can significantly streamline the research process, directing it towards more targeted conclusions. Let's delve into the specific situations where one may be more appropriate over the other.
Situations where a hypothesis is more appropriate
- Confirmatory Research: When the research is grounded in existing theories and seeks to validate or invalidate a specific claim or relationship.
- Quantitative Studies: In research designs that predominantly involve statistical analysis of numerical data to address the research problem.
- Experimental Research: Where controlled experiments are conducted to explore the causal relationships between different variables.
- Deductive Approaches: When the research follows a deductive approach , deriving a specific prediction from a general theory.
Situations where a research question is more appropriate
- Exploratory Research: In studies aiming to explore a new field or topic without much existing literature or established theories.
- Qualitative Research: When the study involves analyzing non-numerical data such as texts, interviews, or observational data to garner insights.
- Pilot Studies: Preliminary studies that aim to identify potential issues and refine research tools before a large-scale study.
- Inductive Approaches: Research approaches that work from specific observations to broader generalizations, aiming to develop new theories.
The interrelation between hypotheses and research questions
Understanding how a research question can give rise to hypotheses.
In scholarly inquiries, the formation of a hypothesis often finds its genesis in a well-articulated research question. This dynamic represents a pivotal juncture in research methodology, facilitating a transition from questioning to hypothesizing and setting the stage for focused analytical scrutiny. Leveraging the exploratory nature of research questions can foster the formulation of grounded hypotheses, guiding the investigative trajectory towards evidence-based conclusions.
Indeed, a well-structured research question can give rise to a series of hypotheses, each presenting a plausible answer to the research question and serving as a focal point for systematic investigation. This correlation facilitates a scaffolded approach to exploration, where researchers can build a layered understanding through a structured inquiry process.
Can a hypothesis transform into a research question?
This iterative process we have described can be envisioned as a cyclic pathway rather than a linear trajectory, wherein hypotheses, once tested and analyzed, can refine or even reformulate the initial research questions. This reflexive relationship fosters a deepened understanding and a more nuanced exploration of the research topic at hand.
To illustrate, consider a research question in the field of healthcare: "What are the primary factors influencing sleep quality in adults?" From this question, a researcher might derive several hypotheses, such as "Adults who engage in regular physical activity experience better sleep quality than those who do not." Once this hypothesis is tested, the findings could lead to further questions, fine-tuning the initial research query to delve into specific age groups, lifestyle factors, or physiological aspects, thereby perpetuating a cycle of inquiry that propels the research into deeper and more focused directions.
Research questions serve as the launchpad for scientific exploration, fostering a direction and scope that steer investigations towards relevant and focused pathways. Conversely, hypotheses act as tentative answers to these research questions, laying a grounded foundation for systematic investigations and guiding the trajectory towards evidence-based conclusions.
Selecting the right approach—whether formulating a hypothesis or crafting a research question—is not merely a procedural choice; it is a strategic decision that significantly influences the outcome of the investigation. Recognizing the interdependent and reflexive relationship between the two can foster a more robust and nuanced approach to scientific inquiry.
By embracing the cyclic pathway that intertwines questioning with hypothesizing, researchers can unlock deeper levels of understanding, paving the way for profound discoveries enriched with insight. Remember, the quality of the answers we obtain is invariably linked to the quality of the questions we ask and the hypotheses we formulate.
Header image by Luke Tanis .

IMAGES
VIDEO