EnglishComposition.Org
Be a Better Writer

The Five Parts of an Argument

Constructing a persuasive argument is no easy task, but knowing the parts of an argument can structure your thinking as you begin to put one together. Here are the five parts of an argument:
1. Claims 2. Reasons 3. Evidence 4. Warrants 5. Acknowledgment and Response
Your claim is your main point. It should either seek to change how the audience thinks or how the audience acts.
The audience should be able to agree or disagree with your claim, and they should understand the need for the claim. Sometimes a claim can seem more serious and necessary than it actually is. For example, take the claim that the Fourth Amendment should not be repealed. While technically a claim, it isn't a claim that carries much significance because there is no serious debate in the U.S. concerning the repeal of the Fourth Amendment. There is a serious debate, however, concerning the meaning, spirit, and breadth of the Amendment, with serious debates centering on specific issues within the topic of gun control.
It's your job to communicate the exigency, or necessity, of the claim to your audience. They should know what is at stake. Stating your claim clearly and concisely will help, but you must also help the audience understand how your claim responds to a situation that needs a solution.
Good claims are seldom broad; instead, they tend to have a narrow focus and are moderated by qualifiers like “many, “most,” and “often, while avoiding words like “all” and “always.”
Reasons and Evidence
You need reasons and evidence to convince audiences. Reasons and evidence answer the fundamental question: Why are you making this claim?
The evidence should support your reasons, and your reasons should be appropriate to your audience. You should choose the reasons and evidence that are also the most likely to convince your specific readers or listeners. Knowing the general values and priorities of your readers will help you determine what they will count as compelling reasons and evidence.
Evidence should also be reliable and based on authoritative and trustworthy sources. It should be appropriately cited and ample enough to convince, designed to appeal to your target audience's values and priorities .
Here are some useful strategies for using evidence to support your arguments:
- Build on what readers already know.
- Present evidence from general to specific.
- Keep support appropriate and clear.
- Rely on authoritative sources.
- Use diagrams, graphs, and other visuals when appropriate.
- Don’t assume that evidence speaks for itself. Explain its significance to your audience.
Warrants express justifying principles, shared beliefs, or general assumptions. They are the spoken or unspoken logic that connects your reasons to your evidence.
Take, for example, the argument:
I need new shoes because these ones have holes in them and it's the rainy season.
One who accepts this argument is one who likely shares the following warrant (shared belief):
When shoes can no longer protect the feet, they need to be replaced.
To some, this is common sense that justifies the claim for new shoes. But even in cases where your audience shares your warrant, evidence is still needed to connect the warrant with the claim. In other words, the evidence must show that the shoes are indeed in bad condition for the audience to agree.
Sometimes an audience will share the same warrant as you but disagree with the evidence you present. For example, the audience might not believe that the shoes are in as bad of shape as the arguer believes. In that case, the argument is likely to fail for lack of convincing evidence.
Other times, an audience won’t share a warrant with you. For example, a person might not believe in replacing damaged shoes, but rather repairing them. One who has a fix-it-first attitude might respond in the following way: “Who says you need to buy new shoes? I can get those repaired for a fraction of the price.”
As you see, warrants are important for getting an audience to accept specific conclusions. For this reason, warrants may need their own evidence, or backing, to make your audience more likely to accept them. To learn more about warrants, see the post on the Toulmin Model .
Acknowledgment and Response
Acknowledging and responding to opposing viewpoints can help your argument in a few ways:
- It helps you build trust with your audience
- It gives your argument additional context.
- It challenges you to moderate or qualify your claim
- It invites you to find common ground
When stating the opposing viewpoint, it’s important to do so fairly. Misrepresenting the opposing viewpoint is not just unethical, but it will likely cause your audience to lose trust in your argument.
After stating the opposing viewpoint, look for parts of the argument that actually seem right—try to acknowledge valid concerns. Doing so may lead you to make concessions to the other side, which will challenge you to moderate your claim and encourage common ground.
Of course, you also have the opportunity to respond to points you feel are not valid from the opposing viewpoint through refutation and counterpoints. Counterpoints should include their own supporting evidence as well.
Thinking about the five parts of an argument is an important first step toward persuading your audience. Check out the next post for tips on evaluating the quality of your own argument .
License and Attribution

This webpage is a derivative of Three Modules on Clear Writing Style: An Introduction to The Craft of Argument, by Joseph M. Williams and Gregory Colomb by The Cain Project in Engineering and Professional Communication. This webpage includes modification and changes to the arrangement of the original content under a CC BY 2.0 license.
Understanding the Parts of an Argument
Arguments are among the most compelling documents we encounter as we read. Developing a strong argument requires you to take a position on an issue, introduce the issue to your readers in a way that leads then to view your position as reasonable, and develop reasons and provide evidence for your position. In this guide and those associated with it, you'll learn about the parts of an argument as well as the processes that help writers develop effective, well-grounded arguments.
A Clearly Stated Position
By definition, an argument requires the existence of a debatable issue. In other words, for an argument to even take place there must be at least two sides. When two or more arguable positions exist, each constitutes part of the context.
The audience-those to whom your position will be argued-constitute another part of the context. And since it will contain both supporters and detractors, it is essential that your position be clearly stated. It is the foundation upon which each brick of your evidence will be stacked and must be strong enough to bear its own weight as well as the onslaught of opposing arguments.
Types of Positions
Position statements fall into categories and those categories suggest how a claim should be argued. Your position, knowledge and authority on the subject will help you decide which category best suits the argument's purpose.
Before selecting one, however, consider your audience. Which side are they likely to be on or will they be split down the middle? How informed are they? Where lays the largest difference of opinion? Is the issue emotionally charged? If so, how will the audience react?
The answers you come up with will help determine what type of position will be most effective and what to include in the introduction, the type of evidence to be presented and how the presentation should be organized.
Claims of Fact
Claims of fact present verifiable forms of evidence as the supporting foundation for an inferred position statement. In other words, a claim that that which can not be proven by actual facts is, in fact, true or real based on facts that are somewhat pertinent to the issue. For example, the position statement that "grades measure neither intelligence nor achievement," backed with factual evidence like test scores, duplicable research findings and personal testimony.
Claims of fact notwithstanding, the statement can't actually be proven. Intelligence and achievement measurements are, at best, subjective terms that challenge hard definitions. No amount of factual evidence is going to change that.
Nailing down the terms of the position with objective, concrete definitions will strengthen the statement but be advised that an inferred position is poor foundation on which to build an argument.
Claims of Cause and Effect
Claims of cause and effect are propositions based on the concept that one thing influences or causes another. For example, "rap music makes its audience members prone to violence." To prove such a claim your argument must define the terms of both the cause and the effect.
It must define rap, the kinds of rap that lead to violence and the ways in which it does so. It must also define the forms of violence that pertain to rap and conclusively attribute the effect to the cause. Specific incidents of violence must be cited and tied directly back to specific occurrences in which it can be proven that rap played a significant role.
Claims of Value
Claims of value inherently involve a judgment based on comparing and contrasting one position with another and assigning each a value of good or bad, better or worse. For example, "Danielle Steele is the best romance novelist of the last quarter century."
To build an argument on such a claim the criteria by which the judgment will be made as well as the manner in which the person, thing, situation or circumstance being assessed must be established. Elements similar to claims of fact, such as sales figures, publication statistics and awards will come into play.
For Danielle Steele to be judged the best romance novelist of the last quarter century, it has to be proven that she meets the established criteria for a good romance novelist and that she does it better than all other romance novelists from the same time period.
Claims of Policy or Solutions
Claims of policy or solutions propose and promote policies and solutions based on changing an existing policy that is either inadequate for dealing with a bad situation or conducive to its perpetuation. For example, "Football causes too many injuries and ought to be banned."
Arguing such a claim may require arguing a combination of claims and several steps might be involved: A factual claim establishing that a situation exists, a value claim proving the situation is bad, and a cause and effect claim pinning the blame on a policy that, if changed, will improve the situation may all play a role in the overall argument.
Be advised that proposing a solution carries the inherent suggestion that more than one solution may apply. An argument successfully advocating your position must establish the criteria by which all solutions will be measured and prove that yours meets that criteria better than any other.
Identify Your Position
A clearly stated position demands parameters, or boundaries, narrow enough to avoid any tangential digression that might detract from the argument's power. In other words, to be effective, the author must identify a narrow enough position that proving or drawing a conclusion from the argument that follows won't become bogged down in the side-bar arguments a broader statement might stimulate.
The key to identifying a clear position is in the old adage of not biting off more than you can chew. In a courtroom it's called opening the door to testimony previously excluded. A broad position statement invites disaster by opening doors to counter-arguments that you are unprepared for and have no intention of addressing. It muddies the argument.
Following are some examples of position statements that are too broad to be effectively argued.
"True historical analysis lies in everyday experience, not in dates and politics."
This statement is so broad it would take a book, and possibly several, to argue the point. You'd need a wide variety of everyday examples from the lives of those who lived during a significant number of major and minor historical events just to come close to a plausible proof, let alone a conclusive one. The statement bites off more than one can chew.
"Quantitative, college letter-grading systems effectively create a false sense of achievement by equating 'making the grade' with true learning. Having reached adulthood, college students are no longer in need of such incentives and ought to be evaluated more qualitatively, through written evaluations at the end of each semester."
There are two arguments to be made here: (1) as an incentive, letter grades obscure whether true learning occurs, and (2) written evaluations are more valuable and useful than letter grades. Again, the statement constitutes more than a mouthful. Each position could be a paper in itself.
"All grading is problematic because all grades are subjective. Grading objectively, therefore, is impossible."
This is a vague statement based upon an implied assumption that, to be fair, all assessment forms must be objective. To prove this, all forms of assessment would have to be compared and contrasted and their use across all campus curriculums examined. In-class essays, mid-term papers, lab projects, field work, class discussions, multiple-choice and true-false tests would have to be included. Another mouthful too big to chew: A better option would be to select one form of assessment and build an argument constrained within a single curriculum.
Draft Your Position Statement
For all practical purposes, it's useful to view a position statement as a "work-in-progress," a statement that evolves or emerges as your research progresses. It's not necessary that you begin with an ironclad position. A vague idea will do.
As you learn more about your selected-or assigned-issue, you may find your stance changing. Keep an open mind in this regard: It will help you clarify and focus your final position on a narrow and arguable point. Following are some useful tips that will help you in the process.
Don't bore yourself. Choose a topic around which there are issues that interest you and don't worry about defining your position. A good topic is one that arouses passion in others as well as yourself. Consult your course notes and make a list of ideas that appear to have the most potential by answering a few simple questions:
- What questions did your instructor ask the class to think about?
- What topics sparked the most spirited class discussion?
- What question created the greatest disagreement; the most heated debate?
- What topics or questions divide the local, national or global community?
Do some broad preliminary research on your selected topic. Ask your instructor, as well as others in your field of study, for information and guidance. To grasp the complexities and nuances of the issues at hand, select a group of books and articles that approach your topic from different angles and study up on them.
Note your reactions and opinions as they occur and develop or mature. In particular, you will want to note when previously held opinions change as a result of knowledge and insight gained from recent readings or discussion. Hone in on those opinions about which your feel the strongest or interest you the most.
Begin drafting a preliminary statement. Keep in mind that your position must be arguable. When shaping it consider the following questions:
- Is there an ongoing debate regarding the issue? If not, it may be that a consensus of opinion has already been reached. The absence of debate indicates that either 1) there is nothing about which to argue, or 2) the issue is brand new and ripe for argument.
- Has the issue been exhaustively debated? If so, the sides may be so polarized that further argument is pointless. The absence of a consensus of opinion indicates that all positions, both for and against, have been thoroughly argued and there remains nothing substantially new to add.
- Is there something new to add to the debate? If so, for whom; for what audience? Often, a new take on an old issue, arrived at by focusing tightly on one aspect, will rekindle interest in the debate and advance your position.
- Is there a brand new issue ripe for argument? Be on the lookout. New stuff happens all the time. Like ships at sea, new issues pop over the horizon every day. First a grey smudge in the academic fog, and then, one day, a sharp outline closing in on the harbor. The first spyglass to pick the smudge out of the fog gets the gold-first pick among the arguable positions.
Finally, the best advice is to be constantly aware of the arguments you wish not to address and continually refine your preliminary statement so as to exclude having to argue them. In other words, as you move toward completing your research, close and bolt all the doors you don't want the opposition stumbling through.
The Introduction
Getting off to a good start can make or break you, which is why your introduction is so important. It must be both respectful of the audience-not all of whom are going to be on your side-and compelling enough for them to withhold judgment while hearing you out.
Think about throwing a dinner party: Your guests are the audience. You plan a menu and set the table. Before you serve the entrée you serve an appetizer and introduce those who are meeting for the first time. Your introduction should put your guests on common ground-at ease with each other-before the main course, your argument, is served. When dinner is over, your argument made, your guests stay on for coffee and dessert, your conclusion.
Provide Context for the Argument
The introduction establishes an argument's context: it informs the audience of the issue at hand, the prevailing arguments from opposing sides and the position held by the author. It sets the tone for the argument and establishes the disciplinary constraints and boundaries that your particular academic audience will expect.
There are many ways to provide context for an audience but the main thing is to get everyone on an equal footing, a starting point where everyone has equal knowledge of the issue.
One of the best ways to accomplish this is by proposing a common definition of the issue. Another is to begin with a literature review of past work, showing where and how your position has emerged from previous work and how it enters into or contributes to that conversation.
Propose a Common Definition
One way to create a context for your readers and establish common ground is to begin with a definition of the topic that everyone can share and then introduce an issue based on the common definition. For example:
Approximately 10% of U.S. Citizens over the age of 65 are affected by Alzheimer's disease (AD). Furthermore, potentially 50% of individuals over the age of 85 may be at risk (Greene, et al. 461). [A statement of the pervasiveness of the problem] AD is a disease which results in progressive deterioration of mental and eventually physical functions. This progressive decline has been scaled according to the Global Deterioration Scale. The scale ranges from 1 to 7 with "1" designating normal, "4" representing moderate AD, such as inability to perform complex tasks, and a "7" corresponding to severe AD, characterized by loss in the following areas: verbal ability, psychomotor skills such as walking or sitting up, continence of bowel and bladder, and ability to smile and feed oneself (Bennett 95; Greene, et al. 464). [A definition of the disease]
With a continuing growth of the elderly population, this disease presents an extremely difficult problem for the future. How do we treat these individuals with medical costs increasing every year? How will we allocate funds for those whose families cannot afford to pay? The questions are relentless, but I have decided to explore the realm of treatment [an examination of the issues the definition logically brings up] . . .
I feel active euthanasia should be an available choice, via a highly scrutinized selection system, to allow AD patients, as well as family members, to end their suffering, to eliminate the "playing God" factor by hastening the inevitable, and finally, to end an existence which faces a severely reduced quality of life. [A statement of the author's position on one of the issues: her focus in the paper]
Provide a Literature Review
Offering a brief summary of previously published work demonstrates how well versed you are in both your academic discipline and the issue at hand. It also demonstrates how your work adds to, challenges, or offers a different perspective on questions important to others in the same field.
Here are some conventional formulas with which to introduce other authors previously published work.
Although X [insert other scholar's names] argues Y [insert their position] , about Z [insert topic or issue] , they have failed to consider [insert your position] .
X [insert other scholar's names] has already demonstrated Y [insert their position] , however, if we take their work one step further, the next logical issue is Z. [insert your position and the grounds upon which it is justified] .
Although X [insert other scholar's names] argues Y [insert their position] , about Z [insert topic or issue] , the position does not hold up when examined from the perspective of [insert your position] .
Although they appear quite brief, they can vary considerably in length, depending on your argument and the amount of research involved.
Long Example of Reviewing Previously Published Work
As scholars continue to explore how we can best characterize the discursive space of computer discussion technologies currently in use in many classrooms, one thing has become clear: the ways in which power relationships constructed within other contexts (e.g., the classroom, society) play themselves out in this new textual realm is murky at best. [Statement of the issue at hand] The initial excitement about the potential for computer discussion spaces to constitute discourse communities unfettered by the authority of the teacher (e.g., Butler and Kinneavy; Cooper and Selfe) has increasingly become tempered by attempts to characterize the nature of this discursive space. For some, computerized discussion groups create more egalitarian contexts in which marginalized voices can be given equal space (e.g., Selfe; Flores), while for others computerized discussion spaces serve only as reproductions of the ideological, discursive spaces present within society (e.g., Selfe and Selfe; Johnson-Eilola; Hawisher and Selfe). [Establishing common ground that the issue of power is a viable one by direct reference to previously published work] The disparity between these positions is central for feminists concerned with both resisting the patriarchal nature of academic discourse and providing a space for women students to speak and have their experiences validated. The question for feminist teachers becomes, as Pamela Takayoshi puts it, whether computerized communication is "a tool for empowering [women students] and dismantling the 'master's house,' in this case traditional classroom discourse patterns" or whether such modes of communication are "merely new tools that get the same results in a different way" (21). [Restatement of the issue in more specific terms, a focus that again emerges from previously published accounts]
Feminist analyses of computerized discussion spaces, however, are similarly caught up in the conflicting positions of equalization of all voices versus the replication of oppressive ideological positions discussed above. For example, as Janet Carey Eldred and Gail Hawisher point out, much speculation in composition about the nature of computerized discussions, including feminist speculations, relies on the presumption of the "equalization phenomenon," which they summarize as follows: "Because CMC (Computer-Mediated Communication) reduces social context cues, it eliminates social differences and thus results in a forum for more egalitarian participation" (347). From this equalization phenomenon come claims that computerized discussion technologies occlude issues of status and hierarchy usually associated with the visible cue of gender (e.g., Dubrovsky et al.). Yet, as Eldred and Carey note throughout their article, "Researching Electronic Networks," the assumption of reduced social context cues is by no means a proven "fact"; in fact, Eldred and Carey point to studies such as Matheson's which found that "something as subtle as a name dropped, an issue raised, or an image chosen could convey a gender impression" (Eldred and Hawisher 350). Takayoshi's analysis of harassment through e-mail and networked discussions further illustrates how traditional gender hierarchies can resurface in supposedly "egalitarian" spaces. [A summary of the literature on the more focused issue which demonstrates that no one has yet resolved this issue satisfactorily]
What emerges from this admittedly incomplete literature review are directly conflicting views about how power is negotiated in networked discussion groups, particularly regarding the effect of that power on female students and the creation of a space wherein they might resist the more patriarchal discourses found in classroom discourse and academic forms of writing. [Restatement of the unresolved issue] What I'd like to suggest here is that these conflicting views emerge in part from the ways in which the argument has been conducted. In this essay, I hope to open up other possibilities for analysis by suggesting that one of the reasons questions about power, ideological reproduction, and equalization are so difficult to resolve is that our current analyses tend to look at the surface features of the issue without examining the discursive grounds on which these issues of power are constituted. [The writer positions herself as someone who is both "adding to the conversation" and challenging previous work.] Although focusing on the material effects of networked discussions on women's ability to find a speaking space is important work that needs to be done, I want to shift our analytical lens here to an equally important question: the way the textual space of networked discussion groups positions students and the types of voices it allows them to construct. [Poses a different issue that can then be answered in the writer's argument]
Short Example of Reviewing Previously Published Work
As scholars such as Susan McLeod, Anne Herrington and Charles Moran begin to re-think the way writing-across-the-curriculum programs have situated themselves within composition theory, an intriguing disparity has presented itself between writing-to-learn and learning-to-write. As McLeod points out, these two approaches to WAC, which she designates the "cognitive" and the "rhetorical," respectively, exist in most programs simultaneously despite their radically different epistemological assumptions. [Establishes common ground by defining the issue according to previously published work with which the audience is familiar] What I suggest in this paper, however, is that despite the two approaches' seeming epistemological differences, they work toward a similar goal: the accommodation or inscription of (student) subjects into the various disciplinary strands of academic discourse. [Statement of position which addresses the issue formulated in the research]
Establish Credible Authority
Establishing credibility and authority is just as important to you as a student as it is to credentialed experts with years of experience. The only thing different between you and an expert is the length of your résumé. What's not is the importance of convincing your audience that you know what you're talking about.
Demonstrate your Knowledge
Cite relevant sources when generalizing about an issue. This will demonstrate that you are familiar with what others, particularly recognized experts, have already contributed to the conversation. It also demonstrates that you've done your homework, you've read some current literature and that your position is reasonably thoughtful and not based on pure speculation. For example:
Over the past ten years, anthropologists have consistently debated the role the researcher should play when interacting with other cultures (Geertz; Heath; Moss) .
You may also connect your argument to a highly regarded authority by demonstrating that you are taking that person's position or contribution to current thinking one step further.
When James Berlin [the chief authority on social rhetorics] created his taxonomy of composition in Rhetoric and Reality, he defined a key historical moment in the way composition studies imagined the function of writing in culture. By focusing on the effect writing has on reality, Berlin's work helped the field recognize how assumptions about discourse marginalized certain groups of students and reinforced ideological beliefs that helped maintain an inequitable status quo.
Such a "social" perspective on writing and language inarguably had a significant effect on the face of composition studies, making it difficult to discuss writing as anything other than social and the teaching of writing as anything other than political. Yet the similarity in how social rhetorics depict epistemology suggests that the term social can be used to describe a diverse group of theories that share this view of reality.
Although such synonymous usage may be an apt label epistemologically, its use as a blanket term frequently obscures the difference within social rhetorics on issues other than epistemic ones. That difference, I argue here, is focused around questions of identity.
Share your Personal Experience
Consider that the closer you are to an issue the more credible is your authority to speak. Personal experience, from work or travel, for instance, provides your audience with an insider's point of view. A well-told personal story in the introduction demonstrates how the author's interest in an issue emerged and quite often provides an extraordinarily compelling reason to hear an argument out. Here are a couple of examples:
Example One:
As an aide in a nursing home for four years, I was constantly amazed at how little attention the children of elderly patients paid to their aging parents. Over and over again, it became obvious that the home was simply a place to "drop off the folks" so that their concern could be limited to paying the bills. As one woman told me when I called to inform her that her mother really needed a visit soon, "I pay you to take care of her. If I had time on my hands, she wouldn't be there." When did caring become simply a matter of writing a check? What are our obligations to the elderly in this society and how might we better care for them?
Example Two:
With a continuing growth of the elderly population, patients with Alzheimer's disease (AD) present an extremely difficult problem for the future. How do we treat these individuals with medical costs increasing every year? How will we allocate funds for those whose families cannot afford to pay? The questions are relentless, but I have decided to explore the realm of treatment. . . . After observing the lifestyles of these individuals, I feel I have greater insight to the trauma they face versus an individual who has not witnessed their everyday activities. Based on my direct experience with late-stage AD patients and their families , I feel active euthanasia should be an available choice, via a highly scrutinized selection system, to allow AD patients, as well as family members, to end their suffering, to eliminate the "playing God" factor by hastening the inevitable, and to end an existence which faces a severely reduced quality of life.
Speak Convincingly
Write like an authority: Ignore the fact that your audience might know more than you. You may not be an expert, but you are, by no means, ignorant. After plenty of research you've come to know a lot about the issue yourself. Use that knowledge to inform and convince your audience that you know what you're talking about.
Avoid deferential language such as "in my opinion" or "at least I think we should." Try not to be wishy-washy. Don't hedge your bets by arguing "perhaps we should" or "such-and-such might be the way to go." Don't be arrogant, but don't give the audience any reason to think you might not know what you're talking about.
This past year Michael Maren wrote an article for Newsweek, "The Faces of Famine." This article was not what a viewer would have expected to read: the continuation of starving people in Africa because of an apparent lack in economic means. Although most Americans are moved by the pictures of "skeletal" children and hold the belief that the problem stems from a lack in food resources due to drought and severe conditions, according to Maren the general public in the U.S. is misinformed and unaware of the politics involved with this severe famine.
The evidence Maren has compiled informs his audience that providing money donations for relief funds is destructive, not helpful, for those affected. In his essay Maren talks specifically about the situation in Sudan. The root of the famine is from a 15-year-old civil war between the Khartoum Government and the Sudanese People's Liberation Army (SPLA).
Maren has contributed both his personal experiences, living in Africa as an aid worker and journalist for 20 years, and his political knowledge about starvation being used as a weapon for a civil war, as evidence for his argument. His goals are to inform his audience what really is happening in Africa and to begin to assist in saving lives rather than adding fuel to the fire.
One way to establish credibility and authority is to follow both spoken and unspoken rules of research conduct in both your introduction and throughout the argument. Here is a list of guidelines to keep in mind:
- Respect previous research and authority.
- Take all publications seriously, even when you disagree.
- Respect your opposition: No name-calling.
- Cite all sources: No plagiarizing.
- If it's relevant, include it, even when it hurts your case: No sins of omission.
- If it can't be backed up, don't include it: No generalizing.
Compel the Audience to Listen
Your argument must be compelling. What can you say that will convince you audience to hear you out? An important question: It's easy to assume that the answer is obvious and that your audience will "get it" yet, quite often, that's not the case. Don't leave this to chance. Put yourself in the audience's place and think about what they will be asking:
- Why should I care?
Good answers to such questions will help you draw the audience into the body of your argument. Be creative, but don't lose sight of the facts.
Invoke a Truism
Find something everyone in the discipline agrees with and propose it as the reason for your argument. In the example, the writer connects an argument about identity politics to a concern regarding students and how they learn. In this way, a theoretical issue-something many educators find uninteresting-is connected to something about which all educators are interested: their students.
In posing identity constitution as a central question for social rhetoric, I do not…seek to simply point out a theoretical difference in composition studies. Instead, I locate such questions about the discursive construction of identity primarily within a concern for students as writers and citizens. By examining the different assumptions social rhetoric makes about how discourse affects the student writer's construction of identity, I hope to highlight more explicitly the role pedagogy plays in "teaching" students not only how to construct public voices from which to speak of identity politics but also how to construct their identities.
Provide an Eye-Catching Statistic or Quote
Drawn from research, these may be used to highlight the importance of an issue or-if a quote is personal in nature-to appeal to the audience's emotions. In either case, be sure the statistic or quote directly relates to the issue at hand. For example:
In his U.S. News & World Report article, Hey, We're No. 19! , John Leo addresses the results of a recent survey which found that American students, compared to students from 20 other countries, placed well below average on standardized math and science tests. Leo surmises that these results can be blamed on two things: unqualified teachers and "social attitudes that work against achievement" fostered by teachers' colleges.
Leo may or may not have a legitimate point in his essay; it is difficult to tell through all the sarcasm and unsubstantiated opinion. The article is ineffective for two main reasons: the complete lack of evidence and the condescending attitude Leo exhibits toward the very people he aims to convince.
Identify a Common Concern
In this way, you remind an audience that they already care about an issue. In the example, the writer addresses an American audience on the prayer in public schools issue by identifying it with free speech rights: the protection of which everyone is concerned. This provides a compelling reason for the audience to revisit ideas about prayer in schools while keeping the topic within the legal realm. For example:
What would happen if you were fired for criticizing your boss in a bar after work hours? If you were told you could not put a bumper sticker on your car endorsing the Republican candidate because it would offend your Democratic neighbor? Most Americans, in either of these instances, would be justifiably upset at how their right to free speech was being impinged. Yet, mention that students should be allowed to pray in school and, all of a sudden, the issue becomes murky. We are confronted with another legal issue: separation of church and state. Which of these "rights" should win in this battle? In this essay, I argue that neither is more important than the other, yet if we look closely at the issue of prayer in schools, we will see that there is a way to allow prayer, and thus free speech , without violating the separation of church and state.
Tell an Anecdote
Invoke a reader's sympathy with a short narrative of an experience-either your own or one drawn from research-which highlights the personal effect of the issue about which you will be arguing. For example:
Celebrating his acceptance into his fraternity of choice, Benjamin Wynne did something many college students have done at one time or another: he went out and got completely, unabashedly drunk. Wynne, accompanied by other members of Louisiana State University's chapter of Sigma Alpha Epsilon, started off his night of revelry at a party off campus. The group then moved to a local bar before ending up back at the frat house. Though this type of partying may sound typical to many college students, its result was anything but typical: Benjamin Wynne died that night of alcohol poisoning, having consumed the equivalent of 24 drinks (Cohen 54).
His death in early September of last year should serve as a wake-up call to every individual on a college campus in this country, as well as parents of students. Excessive drinking is a widespread, serious problem on many college campuses nationwide, not only for the students who actually do the drinking, but for non-drinking students as well. Students, faculty, administrators, and other individuals on college campuses must admit to themselves that this behavior is not acceptable. We must admit that it is a problem before another student's life is tragically cut short.
Ask Questions
Although this strategy is often overused, asking a few key questions is a good way to introduce your argument. Be cautious, however, of posing any that will not be answered: doing so sets up false expectations. For example:
How many times have you looked at a city street and seen it draped with power lines going in every direction? How many times have you seen housing developments intersected by huge power lines which radiate dangerous levels of high voltage? How many times have you driven the open country only to find miles and miles of steel towers connected by strands of power lines?
If you're like me, you notice these things. To me, they happen to be aesthetically unpleasant. What we don't see is where or how the power within those lines is generated. Chances are it is not good. Over 85% of our current energy source is derived from fossil fuels (RE fact sheet 1). What if our power source wasn't harmful to the earth? What if it was coming from the sun and wind, and didn't harm the people in the neighborhoods who used it?
Promise Something New
Demonstrate how your argument adds to, reframes, redefines, or offers a new solution to an issue with which your audience is already involved. In this example, the writer summarizes current positions in published literature in order to reframe the issue. For example:
In the past twenty years, literacy has become a hot topic among educators and the public alike. For teachers, the issues seem to revolve around the literacy skills students need in order to graduate from high school. The debate ranges from a strong emphasis on critical reading skills (Smith, Jones) to technical literacy skills (Palmquist, Barnes) to writing skills (LeCourt, Thomas). As most teachers know, however, these skills are not separate: writing, for example, can't be taught apart from reading; technical literacy includes both writing and reading.
How, then, should a teacher decide which skills to emphasize in a given high-school curriculum? In this paper, I will argue that the first step to deciding on necessary literacy skills lies in closely examining what students will need to succeed after high school, in college and in the job market. In short, any decision about literacy skills must begin with research into the public sphere. Educators cannot make such decisions in a vacuum, as most theorists (like those cited above) are now doing.
Use an Epigram
A simple block-quote at the beginning of a paper can highlight the importance of an issue or the differences of opinion that surround the debate. Not generally referred to in the argument itself, an epigram serves to set up the context for the argument being introduced. For example:
I agree that students should be able to write well when they leave the University. But I think we don't give them enough credit for how well they can write when they come here. All we need to do is push them a bit more. . . . The University is talking about keeping a writing portfolio for every student: who has the time for that. . . . All this nonsense about WAC is just baloney, just baloney. --Professor of Electrical Engineering
Perhaps I ought not to start my paper with so clear a statement of the disagreement our panel hopes to address. But in some ways, the practical challenge offered by Professor X helps to define a workable theoretical perspective. As other practitioners have discussed, a top-down model of WAC can do nothing in the face of such hostility. At best, proponents of WAC must ignore the faculty who hold such positions. But a model of WAC that focuses largely on students might just side-step this faculty member long enough to convince other faculty and students that WAC has real merits.
Establish Common Ground
What does everyone already know about the issue? One of the best ways to attract the interest of an audience is to locate them on common ground, showing how the issue at hand has been or remains something about which they are already familiar and concerned. There are several ways to do this.
Present a New Angle
Use published material to identify that your issue has already been addressed at length either by experts in the field, or in the broader society. Then demonstrate that your position, one about which your audience already knows quite a bit, is a brand-new take. For example:
Picture in your mind the four women who are closest to you. It may be your sister, your mother, your niece, your aunt, your best friend, your wife, or even yourself. According to at least six of my sources, including the research handbook, Rape and Sexual Assault III edited by Ann Burgess, one of the people pictured in your mind is or will become a sexual assault victim. The research handbook specifically states that one in four female college students will be sexually assaulted during her college career (Burgess, 1991).
Make an Emotional Appeal
Connect your audience emotionally to the issue at hand. Appeal to their sense of compassion: Deliberately pull at the heartstrings. Start at a general enough point where the audience easily recognizes the common ground upon which you and they both stand. Emotionally invested, they will hear you out. For example:
As the video showed a man with violent tremors trying his hardest to speak with some fluency, I thought, "Can't we do any more for people like him?" The man I was watching had Parkinson's, a disease afflicting 1 in 5,000 people (Bennett, lecture). Due to the degeneration of that part of the brain that produces dopamine, a chemical that helps control motor coordination, patients afflicted with Parkinson's disease often suffer muscle rigidity, involuntary tremors and a shuffling gait.
I cannot imagine the frustration a person with Parkinson's disease must feel when tremors prevent them from holding a cup of tea. I cannot imagine the frustration they must feel when walking no longer comes with ease. I cannot imagine the frustration they must feel as they consciously know they are physically deteriorating. And I cannot imagine the frustration family members of Parkinson's patients must feel as they watch their loved one deteriorate and know that there is nothing they can do to help.
In answer to my own question, though, there is more we could be doing to help people with Parkinson's disease. Current research on fetal tissue transplantation shows great promise and could be a great benefit to many people. [The paper goes on to argue in favor of fetal tissue transplantation despite the controversy surrounding such a procedure.]
Present a Solution
Demonstrate that your argument addresses a problem in which everyone in the audience shares or has a legitimate interest. Pull the audience in by explaining its significance to the field of study or connecting it to a larger social issue.
Common ground begins by building the larger picture, one that all audience members recognize, and then whittling it down to a smaller, more focused issue and the one to which your argument provides a solution. Your logic should generally be presented following the pattern of an inverted pyramid. This demonstrates how one problem emerges from another, as in the illustration below.

Clarify or Define a Problem
This is a strategy often found in the social sciences (psychology, sociology, etc.), business and the professional world, though it is not constrained to those disciplines. As part of the context of an issue, a specific problem provides a patch of common ground on which everyone in the audience can stand while you argue the case for a specific solution.
Argue from a Societal Perspective
One way of presenting a problem is to appeal to your audience as citizens rather than professionals in a given field. Begin with a social problem that might benefit from a disciplinary solution and work towards the disciplinary end. Establishing common knowledge about a societal concern, or problem, usually ties back to a disciplinary issue fairly quickly, however, be advised, that academic audiences expect arguments aimed more directly at their professional concerns rather than their social ones.
As the recent battles over affirmative action, school busing, reactions to separatist movements such as the Million Man March, and the backlash against government control by groups such as the Montana Freemen illustrate, our society is becoming more and more divided on how cultural difference can be maintained while still functioning with a national consciousness. [Statement of a social problem]
In the field of composition, these social tensions translate into issues of identity politics: [An immediate transition to what this social issue means in the disciplinary terms of the field of composition, a sub-field of English studies] how can instruction in academic discourse serve to educate a critical citizenry and yet not infringe upon ethnic, gendered, and sexual identities? How might we prevent the power of academic discourse to rewrite subjectivity without also abandoning the common ground such a discourse provides? [Poses discipline-specific questions related to social issue that define the problem to be answered in the text]
Argue for a New Perspective
Although many arguments focus on a specific problem and its corresponding solution, that's not always the case. Some arguments redefine an issue, arguing for new ways of looking at an old problem.
These types of arguments require a different introduction strategy, typically beginning with a statement of the problem and a brief review of the inadequacies in the solutions offered to date. It's a great approach to presenting a position statement that an existing problem needs to be looked at from a different perspective.
As our readings in class have demonstrated, what constitutes literacy and how it should be defined is a question which encourages lively and active debate. [A brief statement of problem which needs no justification since it was already discussed in the context of the class the paper is being written for] Some scholars (e.g., Hirsch, D'Souza) argue that what it means to be truly "literate" is a mastery of a certain body of knowledge that can provide a common knowledge base for all citizens. Others (e.g., the Bell report) focus on "skills" instead of knowledge, arguing that what students need are basic critical reading and writing skills that then can be applied to whatever context they find themselves in as a adults. More radical educators (e.g., Freire, Giroux) argue that true literacy lies in the ability to be critical about culture: to "read," for example, the media for its insidious cultural messages and act differently upon them. [A brief summary of solutions already offered in the discipline] From this brief summary, it is obvious that what is at stake in this debate is no less than what we think students need to learn to be successful economically and responsible members of a democratic citizenry. [A restatement of the problem in different terms] Yet, ironically enough, although the debate is focused on "what students need to know," rarely is a student's opinion solicited. In this paper, I will examine the literacy debate from my perspective as a college student. When we look at this debate from my perspective, we see that the questions posed about what it means to be literate have little to do with students' concerns and what we think we need to know. [A statement of a new perspective and the challenge it offers to current solutions]
Argue for a New Solution
Rather than arguing for a new perspective, a critique of old solutions can be enough to introduce the argument for a new one. These types of introductions typically recognize the existing problem, briefly review the inadequacy of past solutions and end with a position statement identifying a new solution and a call for its implementation.
As the media coverage of the issue and a variety of polls have demonstrated in the past 10 years, very few members of the national public would dispute the claim that politics has been controlled by too few people for far too long. For example, in a 1994 Guppy Poll, 97% of citizens polled responded that the government was clearly in "grid-lock," although 92% of those polled attributed the grid lock to "career" politicians such as Strom Thurmond and Ted Kennedy (Goldfish Collective, 1994). [A brief statement of a problem immediately recognizable by most citizens] Yet, although the public clearly sees "government by the few" as a serious problem, there is little to no consensus on a solution. [A transition to the argument for inadequacy of solutions]
Various solutions have been posed for this problem, ranging from mandatory term limits to the expansion of the two-party system to "free" television spots for all candidates. [Summary of inadequate solutions] In this paper, however, I will demonstrate that none of these proposed solutions will adequately solve the problem as long as funding for campaigns remains so inequitable. [Overview of argumentative strategy: critiquing other solutions] Instead, I will argue that the "best" solution lies in an option which has received little, if any, attention by the mainstream press: socialized campaigning wherein all campaigns are funded solely by the government and each candidate receives an equal amount of campaign funding. [Statement of thesis: goal of showing inadequacy of other solutions]
The Argument/Presentation of Evidence
The bulk of an argument is given over to supplying and presenting the evidence that supports a particular claim or position, refuting opposing arguments and making appeals to the logical, ethical and emotional sensibilities of the audience.
Acceptable Academic Evidence
Acceptable academic evidence depends a great deal on to whom it is going to be presented, the field in which they work, and the focus and goals of the position being argued. To be convincing it must be founded on fact, well reasoned, logical, and stand up against opposing arguments. Included will be a mix of facts, research findings, quotes, experience and the work of other people.
Logical and textual evidence is generally considered to be more authoritative-stronger and more convincing-than anecdotal evidence or emotional appeals. For it to be academically acceptable, the evidence must meet certain criteria:
- Evidence Must Come from a Reputable Source: Just because someone has written on a topic or issue doesn't mean your audience considers them an authority. Authority is judged by how much experience a source has, the viability of their research methods, and their prior reputation.
- Evidence Must Emerge from Acceptable Research Methods: If you are using any form of quantitative or qualitative research, look closely at the methods. A survey of 5 people is hardly persuasive. A survey of 100 may be acceptable in a sociology class, but not authoritative to an audience of scientists.
- Evidence must be Replicable: If you use an original study, replicating the same conditions and methods should produce the same results. Using the same sources, the same information should be found. Personal experience and observation are hard to replicate, however. The onus to be ethical and honest is on the author.
- Evidence Must be Authoritative and Factual: What counts as factual varies widely from discipline to discipline. Personal experience may be valued in a Women's Studies class, but it won't meet the criteria for a science paper. Your audience must consider all your evidence and sources authoritative.
Acceptable Field-Specific Academic Evidence
Acceptable "field-specific" academic evidence is a bit more complicated. Many disciplines are subdivided into niche fields, each of which may have differing criteria for defining acceptable evidence. For instance, textual evidence will be expected in the Speech Department's Rhetorical History and Theory classes, while the Mass Communications class will expect observational and qualitative research methods.
The best way to judge what constitutes acceptable evidence is by checking the reading assignments in your own class syllabus. Consider what types of evidence your professors use most often when discussing a certain issue or problem. Look at the bibliographies in your textbooks or in articles from other well-known books and journals. You will find many different kinds of evidentiary sources. Here is a list of the most common.
- Surveys are acceptable in many fields, particularly in journalism, communications, business management and sociology where knowing the reaction or feelings of many individuals regarding a specific issue is relevant. They are less acceptable in the biological and physical sciences.
- Observational Research is acceptable in many fields. Descriptive studies of human behavior are especially authoritative in education, anthropology communication, psychology, sociology and many other social sciences. They are less relevant when the object of study is more textual, as in history or literature.
- Case Studies are acceptable in the majority of fields as long as accepted methodologies are followed. Case studies are especially prevalent in the health and human behavior fields, human behavior, education, and business.
- Academic Journals and other reputable publications-including bona fide research studies-are acceptable sources in all academic fields. The key is the status of the publication. Popular magazines, for instance, generally have a lower status than journals, excepting in fields like political science, journalism and sociology where societal issues are often addressed.
- Popular Magazines are acceptable as evidence in fields where public opinion or current events are especially relevant such as political science or journalism. Even here, however, information is expected to be analyzed from an academic perspective unless only facts and events are being cited. Tabloids are seldom acceptable. Note: Depending on your topic, The New York Times might be acceptable.
- Biographical Information is generally not the best form of evidence unless you are actually writing a biographical or an historical paper. In other words, it's only acceptable if it's relevant. In most cases, what a person actually said, did, or discovered will be more useful and relevant.
- Quotes or Summaries of work from established authorities, those with reputations in their fields of study, are more authoritative than that of work from those with little to no experience or publication record on which to judge their expertise.
- Beliefs --defined as opinions or truths based on intuition, faith, or other intangibles-- that can't be backed Back or empirically verified are generally not acceptable in an academic argument. Exceptions may be made, depending on relevancy, for quoting a religious or theological authority.
- Opinions are acceptable only when they have been substantiated through prior examination. Quoting an expert or recognized authority, in other words, after they have already made a convincing argument, can be considered evidentiary. An unsubstantiated opinion from anyone, expert or otherwise, is not acceptable.
- Statistics are accepted in every academic discipline, especially those that rely heavily on quantitative research, like science and engineering. That said: many of the social sciences, like anthropology, psychology and business management, combine both quantitative and qualitative research making statistics just as applicable and acceptable in those fields as well.
- Personal Experience was not considered acceptable in an academic argument until recently. Gaining ground since the 1980's, it is particularly considered credible and acceptable in the humanities and liberal arts. More so, in other words, than in business, social sciences or any of the harder sciences, but that, too, is changing. Check with your professor and read your syllabus closely to find out if and how personal experience can be used as evidence in an argument.
- Interviewing an Authority is acceptable, both in-person and over the telephone, in almost every academic discipline. Their credibility is considered in a similar vein as academic journals and other reputable publications in which field-specific articles are printed.
- Interviewing an Ordinary Citizen can--in the manner of testing which way the wind is blowing--be useful as evidence of public opinion, but it is not acceptable in sBackport of a particular position itself in the same manner as that of an expert or an authority. For example, your roommate's opinion on the environment is not as authoritative as the head of the EPA's.
- Laboratory Research is most acceptable in the hard sciences; however, many of the social sciences (e.g., psychology) view it just as authoritatively. The only fields where laboratory research is less acceptable are in the humanities which rely almost heavily on textual evidence or observational and qualitative research.
- Textual Analysis --analyzing other people's research and drawing logical conclusions or interpreting texts and theory for inferences and evidence--is acceptable in almost every academic field. Highly regarded in the humanities fields, it is of lesser-though still authoritative-importance than any original lab or observational research done in the sciences.
Refuting Opposing Positions
Refuting opposing positions is an important part of building an argument. Not only is it important, it is expected. Addressing the arguments of those who disagree is a way of identifying the opposition and exposing the primary weakness(s) in their argument. Doing so helps establish the contextual parameters, or boundaries, in which your argument will be contained. It's best to start with a summary.
Summarizing the opposing positions demonstrates that you are being fair to the other side. It also allows you to set the table for the claims you are going to be laying out. Here are a few general guidelines for composing a summary:
- Provide only a sentence or two describing the focus of the opposing argument.
- Focus only on the details that will be important to what you are going to present.
- Avoid slanting the summary. It provides grounds for discounting your position.
For example:
George Will's editorial in Newsweek states that the reason "Johnny Can't Write" is the misguided nature of English teachers who focus more on issues of multiculturalism, political correctness, new theories of reading such as deconstruction, and so on, than on the hard and fast rules for paragraph development, grammar, and sentence structure. [Summary: A concise yet fair summary of Will's main argument.] Although Will interviews students and uses sample course descriptions to back up his opinion, he misses the main point: all the "fashionable" theories and approaches he decries have actually been proven to teach writing more effectively than the traditional methods he favors. [Refutation: The beginning of a refutation that will go on to show why Will's judgment is wrong.]
Using a Counter-Example
Using a counter-example, or an instance that flies in the face of the opposition's claim, is one way of refuting an opposing argument. If it can be shown that their research is inadequate, it can be shown that their position is faulty, or at least inconclusive. Casting a shadow of doubt over the opposing argument provides strong evidence that your argument has merit. Be sure to use real instances of how your opponent's position doesn't account for the counter-example.
As Henry Johnson, a vice-president of student services at the University of Michigan explained, "To discuss sexual assault is to send a message to your potential student cohort that it is an unsafe campus, and therefore institutions tend to play that down" (Warshaw, 1994). When deciding which university to attend, prospective students do compare statistics regarding the ratio of males to females, student to faculty and-yes-the incidence of crime. Therefore it is no surprise that more than 60 colleges rejected requests to conduct surveys concerning sexual assault at their schools even though anonymity was guaranteed (Warshaw, 1994). [The writer sets up the opponents' view that information about sexual assault on campus damages universities' reputations.]
Universities fear negative publicity, but at Bates College, a rally of 300 angry college students outside the president's house demanding to know why the college hadn't informed them of a recent series of sexual assaults on campus, did get publicized. This resulted in further negative publicity because it came out that the university, in order to cover-up the occurrence of sexual assaults, punished the assailants without providing fair trials (Gose, 1998). [The counter-example shows that even more negative publicity results from trying to hide sexual assault information.]
Outlining an Opposing Position
Outlining an opposing position, as with a summary, not only refutes or rebuts an argument; it's also a way in which to introduce your position. Explicitly addressing those who disagree provides an opportunity for demonstrating why the opposition is wrong, why a new position is better, where an argument falls short and, quite often, the need for further discussion.
Although there is obviously a strong case for introducing multicultural topics in the English classroom, not all would agree with the argument I've put forth here. One of the most vocal critics of my position is George Will. For example, Will's editorial in Newsweek states that the reason "Johnny Can't Write" is the misguided nature of English teachers who focus more on issues of multiculturalism, political correctness, and new theories of reading such as deconstruction than on the hard and fast rules of paragraph development, grammar, and sentence structure. [Summary: A concise yet fair summary of Will's main argument.]
Yet, as I have shown here, multicultural methods clearly do not interfere with teaching writing. [Refutation #1: Disproves Will's position by referring to research already cited.] Further, Will demonstrates a certain bit of nostalgia in this piece for "older ways" that, although persuasive, has no research, with the exception of Will's childhood memories, to back it up. [Refutation #2: Exposes a flaw in Will's argument.] Although most of us think the way we were taught must be the right way, such is not necessarily the case. We should neither confuse nostalgia with research nor memory with the best curriculum. [Opposing argument: Memory and research are not the same; thus, Will's point is wrong.]
Appealing to the Audience
Appealing to the audience is another important part of building an argument. In an academic argument, logical appeals are the most common, however, depending on your topic, ethical and emotional appeals may be used as well.
Logical Appeals
Logical appeals are a rational presentation of relationships constructed such that an audience will find them hard to refute. In most cases it ties together individual pieces of evidence, uniting the argument in a manner strong enough to persuade the audience to a consensus of opinion. In other cases, logical appeals bolster an argument where the weight of evidence is less dependable, as in the following:
- When tangentially related evidence is tied to the argument at hand because direct evidence is unavailable.
- When the evidence can be interpreted in a variety of ways and the writer needs to focus the audience on his or her version so that they may agree with the conclusion.
- When a connection between widely-accepted evidence and newly argued material needs to be established.
When we appeal to the logical sensibilities of an audience, we often rely on long-established relationships between events and facts. If we can show that one event leads to another, for instance, we are establishing a logical relationship (e.g., cause/effect, deductive reasoning, etc.). Because these relationships are deeply grounded in our thinking and language, they are relatively easy to use. Nonetheless, it will help to review the range of logical appeals available for writing arguments.
Cause and Effect
Cause and effect demonstrates how a given problem leads to effects which are detrimental or how the causes of a problem need to be addressed. In either case, the writer sets up a logical relationship based in causality as a key part of the argument, using other forms of proof to support their analysis of causes or effects.
In a paper arguing for a 35 hour work week for manual laborers, the writer supports her thesis by illustrating the logical effects of the current, 40 hour week on society: (1) more physical ailments, leading to higher health costs; (2) less time spent with family, leading to the further breakdown in the American family; (3) fewer job positions being open, leading to higher unemployment than necessary; (4) diminished quality of life, leading to psychological problems such as anger and depression. For each of the four effects, she must then prove through other forms of evidence that a plausible cause of these problems is the 40-hour work week to make her argument.
Compare and Contrast
Compare and contrast demonstrates how a given argument may be similar to or different from something that they already hold to be true. By logical extension, the similarity between the two gives your argument more persuasive power. Pointing to the differences between something held as fact and something you are arguing can convince the audience of its worthiness and allow you to focus only on the differences.
In a paper arguing that homosexuality should be protected as a civil right and arguing that discrimination based on sexual orientation should be outlawed, the writer demonstrates the similarities between sexual orientation and other "classes of people" protected by civil rights legislation (e.g., women, minorities, religious groups). The writer, then, logically appeals to the audience's belief that discrimination based on gender, race, ethnicity, or religion is wrong and asks that they accept the argument extending the same benefit to homosexuals.
Syllogistic Reasoning
Syllogistic reasoning demonstrates deductive logic and begins from the premise that a fact or opinion is inarguably true. Through a series of steps the writer demonstrates that the position being argued follows logically from that premise; an extension of what is already inarguably true. In another use of this appeal, the writer presents a series of facts from other sources and then draws a logical conclusion based on these facts, showing how each group of facts leads to a premise which the audience can accept as fact, and finally, how these premises, when put together, lead to a certain conclusion.
In a paper arguing for the agreement reached at the World Environmental conference banning the destruction of rain forests and other large forests, the writer attempts to show why the ban is a logical response to global warming. In his paper, the writer presents scientific authorities' descriptions of global warming and its main cause: a lack of oxygen in the atmosphere. He then presents other scientific evidence about how oxygen is produced on earth, through plant life. By syllogistic reasoning, the writer can then draw the conclusion that if global warming is caused by a lack of oxygen [premise #1] , and trees produce the most oxygen on earth as the largest form of plant life [premise #2] , then one way to slow global warming is to protect forests [conclusion] .
Classification
Classification demonstrates how previous research, the people contributing to a discussion, or the concepts and ideas important to an issue can help shape how an audience thinks about or perceives an issue. It groups people, research and opinions in ways that makes logical sense to your audience and sets up the means by which you can argue either for or against that which a group stands.
In a paper arguing for a certain interpretation of family values, the writer begins by looking at all the groups who profess to be in favor of such values (e.g., the religious right, President Clinton, feminists) and how they define such values differently. Grouping the other people who talk about the issue in this way then allows the writer to ally himself with certain groups and argue against others.
Definition demonstrates how to set the terms or parameters of an argument. Defining issues in terms that support your position frames the argument so that, through syllogistic reasoning, an audience can be lead logically to the conclusion you intend. To argue by definition, then, is to convince the audience that the definitions are reasonable, supportable and logical and, since your argument is based on them, your conclusions are as well.
In an editorial arguing for dismissing a given professor, the writer begins by defining what makes a "good" teacher: knowledge of topic, interest in student learning, a teaching style that holds students' attention, an ability to explain clearly difficult concepts, availability for conferences with students, and fair evaluation methods. Once a good teacher is defined in this way, the author can then demonstrate how Professor X has none of these qualities, proving his judgment with evidence at each point from student evaluations, interviews, etc. Logically, then, if Professor X does not fit the definition of a good teacher, the readers will reach the conclusion that he is a bad one and should be dismissed.
Ethical Appeals
Ethical appeals make use of what an audience values and believes to be good or true. Presented formulaically, it might look something like this:
Values held by audience + connection to your argument = an argument your audience values.
Ethical appeals are acceptable in most forms of academic argument; however, they are not a substitute for evidence or proof. Use them sparingly. Whatever you do, don't assume your ethical positions are shared by your audience as this may differ radically from one to another.
Typically, such appeals appear in the introduction or conclusion to demonstrate how the argument connects to a belief the audience already holds regardless of whether they have ever thought about your position in the same way before.
Arguing from an Ethical Basis
When arguing from an ethical basis, begin by subtly reminding readers of what it is that they are supposed to believe in and then show how your argument is a logical extension of that belief. For example:
Although most people wouldn't call themselves "feminists," it is difficult to find anyone in the 1990s society who doesn't believe women should receive equal pay for equal work. Equal pay, after all, is only fair and makes sense given our belief in justice and equal treatment for all citizens. [First two sentences remind audience what they believe.] However, the fact remains that no matter how commonsensical equal pay seems it is not yet a reality. Addressing the causes of unequal pay, then, is something that goes to the heart of American society, an individual's right to receive fair treatment in the workplace. [Second two sentences illustrate how this ethical belief is being violated, and thus, by logical extension, should be addressed.]
Discipline-Specific Arguments
In discipline-specific arguments, it is best to use an ethic or value shared within that community. For example:
As teachers, we constantly profess the belief that students should be in charge of their own learning. Arguably, a student-centered curriculum is one of the unquestioned values of educational studies. [First two sentences invoke a value within the field of education.] Although seemingly a radical idea, foregoing the teaching of grammar out of workbooks is simply an extension of this value. By working with grammatical mistakes in the context of a student's writing, we are merely gearing the curriculum to a student's needs and helping him/her "take charge" of their own writing. [The last two sentences show how what the author is arguing-teaching grammar in the context of student writing-is a logical extension of this value.]
Arguments for a General Audience
In arguments geared to a more general audience, cultural values may be more appropriate. For Example:
One of America's greatest commodities has been the field of science and medicine. During the four-year governmental ban on fetal tissue research, doctors went to other countries to perform transplants, thus exporting our ideas and innovations in this area to other countries (Donovan, 225). Why shouldn't we continue to be at the forefront of this research? Our technology, especially in medicine, is some of the best in the world, and this research could provide benefits for thousands of people. We need research to continue and to consistently show what exactly needs to be done in this procedure. [Highlights: First sentence invokes an American value-the strength of our medical technology-while the next sentence examines the ethics of exporting such technology without using it on the home front, something most Americans would protest. This sets the stage for the writer to argue for more research into this area.]
Emotional Appeals
Emotional appeals are generally frowned upon in academic circles for the simple reason that they tend to get in the way of logic and reason, the prerequisites of an academic argument. However, under the right circumstances, they can be quite effective. Drawing on our most basic instincts and feelings an emotional appeal can illustrate a truth or depict the reality of a fact in an emotive way far more compelling than a logical or ethical appeal. For example:
Studies show that women earn 80 cents to every dollar earned by a man. What these statistics don't illustrate well is the effect this lesser earning potential has on women's lives. Take Irma as an example. Irma works as a nurse in a major hospital, yet takes home only $250 a week. On this money, she must support her four children whose father abandoned them when the youngest was six months old. With rent at $700 a week, she has only $300 left over for food, clothing, and her own needs. As she describes it, "it's heartbreaking to have to tell my daughter that she has to wear hand-me-downs one more year to begin school or to tell my son that he can't join the baseball league because we can't afford the fee for the uniform. It's even worse when I watch them eat pasta day after day without complaint because our budget doesn't allow for much meat." It's even more frustrating, she explains, when she realizes not all nurses doing the same job are earning the same pay. "Last month, I heard one of the male nurses got a raise because he was supporting a family of four. What makes them think women aren't in the same situation?"
Be cautious using emotional appeals. They have no place in an academic argument if their purpose-as often seen in advertising and politics-is to deceive or distort. When appropriate, use them to introduce an argument that proceeds logically and is supported with acceptable forms of evidence (e.g., statistics, research studies) or, to follow, as a graphic or human illustration of what the evidence suggests.
The Conclusion
There are no hard and fast rules for constructing an argument's conclusion or that mandate what it should contain. Nevertheless, your conclusion should close out the presentation of your evidence in a clear, logical and thoughtful manner and leave the audience with some credible semblance that you have followed through on or fulfilled the promise of your introduction.
If the argument is open-ended, the conclusion should remind the audience of the specifics of the issue being argued, the position you have taken and give them something new to consider. If it is close-ended, it should justify your position. The conclusion is the place to pound home the central points of your argument and persuade the audience that, "given the evidence," your case is indisputable.
Depending on what message you most want to leave your audience with, you may want to conclude using one or more of the following strategies:
- Reflecting Introduction
Summarizing Key Points
Logical synthesis, evaluating the solution, call to action, emotional and ethical appeals, reflecting your introduction.
Reflecting back on your introduction will provide a sense of closure, particularly if you began by asking questions, or proposing a solution to a problem. Having provided the answers or explained the solution in the body of your argument, your concluding remarks provide an opportunity to restate the original questions or problem and show how your argument answered or resolved them. It is also an opportunity to show how your position adds to or changes the context of the issue at hand. For example:
Picture yourself stepping out into a backyard with just enough sturdy turf to be comfortable in a sea of drought-loving flowers such as cosmos, dianthus, columbine, and zinnias. The honeysuckle bushes and juniper hedges are alive with the buzzing of bees and the twittering of birds. At night as you lie down to sleep, you can once again hear crickets through the open window. All this and your mower and hoses have not been out of the shed for weeks!
Summarizing the Key Points of an argument is always a good idea and, in some disciplines, it's considered a standard conclusion. But more often, it is used in conjunction with other concluding remarks and strategies. Be careful not to overdo it: Unless you are presenting a complex argument, or relying on a variety of potentially confusing sub-arguments, a lengthy summary is unnecessary and, in fact, overkill. Be brief. For example:
The current sexual assault reporting rates among students is low because the victim often does not know what resources and options are available. In addition, ignorance, misconceptions and students' false sense of security undermine the sexual assault prevention efforts. The alarming result is that assailants are often unaware that they are assailants and victims unaware that they are victims.
The best way to fight this ignorance is education and, since that is the goal of a university, what better place to begin. Education about sexual assault may be difficult at first but eventually everyone, including the institution, will benefit. It will not only teach students how to succeed in the classroom and office, but how to succeed in life as well.
A logical synthesis of points made summarizes the individual steps taken to arrive at an argument's conclusion and is practically a requirement of an inductively organized presentation. In the body of an argument, each piece of evidence is laid out and examined individually. Synthesizing the logic behind each step pulls all those pieces together and demonstrates how each relates to another. Briefly reminding your audience of all these connections may be the best way to conclude, particularly if your argument is somewhat complicated or difficult to follow. For example:
Some find it easy to adopt a "they're getting what they deserve" attitude toward student binge-drinkers when they suffer the negative effects of their behavior. As long as they are adults making their own choices, and they are the only ones affected, why not let them do as they please? This attitude should not be tolerated for two reasons. First, many of these students are breaking the law by drinking before the age of 21. We cannot ignore this and allow these crimes to go unpunished. Second, they are not the only ones affected. The repercussions of binge-drinkers on non-drinkers living in dorms and Greek houses-the secondhand binge affects-should not be so lightly dismissed.
Wechsler writes, "It is no longer possible to view bingeing as solely the bingers' problem: non-bingeing students are paying too steep a price." On high-binge campuses, for example, that price includes student's sleep or study interrupted (68%), caring for a drunken student (54%), unwanted sexual advances (26%) and personal property damage (15%) (Wechsler 23-60). It is the non-drinking student we must keep especially in mind when we consider whether college binge-drinking is a problem worthy of our attention, or one we can afford to keep on ignoring. Writes Hingson, "Emphasis should be placed on protecting the rights of those [non-drinkers] negatively affected by binge drinkers" (54). All students have the right to be safe and happy at their university, and we cannot continue to allow binge drinkers to infringe upon that right.
Evaluating the Solution to a problem presented in the introduction is also an excellent way to conclude your argument. Since most of an argument focused on solving a problem presents the reasons why a particular solution is best, an evaluation of potential problems and how they might be addressed will leave your audience more convinced of the solution's validity and your objectivity. It provides an opportunity to examine, for the audience's benefit, the strengths and weaknesses of your position one last time before the end of the argument. For example:
A one-credit course would prove that the CSU did take effective steps to help and protect their students and therefore the university would not be found liable for the crime. "Colleges are the last chance that we have to educate young men and women about human relations, living together, competition, and fair play," stated Susan Ervin-Tripp, a psychology professor at the University of California at Berkeley (Warshaw, 1994). This may also be the last chance that society has to give students the tools to prevent unnecessary sexually transmitted diseases, unwanted pregnancies, and lifetimes full of severe emotional stress resulting from sexual assault crimes. [After arguing about the financial and legal liabilities the University might face if they don't institute a required course on preventing sexual assault, the writer moves back to a humane appeal about the long-term personal effects of sexual assault. This emotional appeal builds nicely on the rational appeal to this audience.] Colorado State University can use this chance to offer students a course that will teach them how to protect themselves, aid prevention, and report sexual assault crimes. CSU has a chance to make a huge difference in these students' lives, not only in the classroom but in life. As the U.S. Department of Justice stated so eloquently, "Experiences on campuses will be carried forth to everyday life and will influence future actions. Therefore, every effort to inform students may mean one less victim or one less crime committed" (US Dept. of Justice). Isn't this one student, who was given the tools to avoid a lifetime of shame, doubt, disgust, and depression, enough reward for only a half semester of education?
A call to action work best in deductive arguments that propose solutions to problems (e.g. social problems) or that point out what further research is needed. It takes an argument one step further by addressing what the point of convincing an audience was in the first place. If your goal was advocating some sort of change, and your argument is convincing, your conclusion provides an opportunity to suggest what actions an audience sold on your position can take to actualize that change. For example:
As with any new endeavor, we like to know what we are getting into. We like to know what the advantages and disadvantages are. Exploring every option is something people have been doing for centuries and will continue to do for many more. Fossil fuel studies have shown the world that we have dug much farther into the earth's resources than was probably necessary and that industry has gone too far in tapping the earth of oil and coal. Many scientists believe global climate change has been brought about by pollution resulting from the burning of these fossil fuels.
Maybe we will do something about this problem in the future or, maybe the time to act is right now. Maybe tomorrow is too late for saving the rain-forests. The people who are destroying these trees need an alternative energy source and need to learn more about emerging technologies that will save them from using up all their remaining resources. The sooner we educate ourselves and apply that knowledge toward a sustainable future, the sooner we will be able to offer help to regions of the world which are in dire need.
The sun has tremendous potential for clean, safe and renewable energy and should be exploited in all areas of the world. The future starts right here, right now, with you. It is essential that the simple, yet effective, steps outlined earlier are taken. Write your congressman today. The Solar Forum '97 is taking place this month in Washington. Decisions made there will ultimately affect us all for years to come. Subscribe to a "green" energy program in your area. In Fort Collins it would be the wind program, sponsored by Fort Collins Light and Power. The number to call is 970-221-6704. There are still open slots to fill. Take a look at Home Power Magazine and see how easy it is for renewable energy to fit into your lifestyle. You'll be glad you did. I know I am.
Emotional and ethical appeals prompt your audience to care about an issue on more than an intellectual level. As with introductions, conclusions are an excellent place to do this because it reminds your audience that your position is not merely an academic one, but one that has consequences for real people. Concluding on emotional and ethical grounds provides an opportunity to strengthen the appeal of you position. For example:
The safety of our society is directly influenced by the correct handling of our household hazardous waste. Everyone uses dangerous chemicals every day and the dangers are astounding when they aren't disposed of in a proper and professional manner. In an age of many chemicals, we must be careful not to put each other, our pets, and our environment in harm's way: We do not need sanitation workers losing their lives or are pets poisoned. In a country with a population the size of the United States, it is necessary that every homeowner ensure a healthy environment for everyone-plants and animals included-by taking precautions when disposing of hazardous waste. It is the job of every responsible citizen to ensure that others are not put at risk when disposing of chemicals.
Using evidence, much of which comes from published sources, is an essential part of constructing an argument and proper documentation of those sources is an essential part of convincing your audience that you are credible. All facts and figures, paraphrases, opinions, and quotes from other sources must be cited using specific citation formats such as footnotes, in-text notes, end-notes and bibliographies.
LeCourt, Donna, Kate Kiefer, & Peter Connor. (1996). Understanding the Parts of an Argument. Writing@CSU . Colorado State University. at https://writing.colostate.edu/guides/guide.cfm?guideid=54
ENGL001: English Composition I
Five essential parts of an argument.
Read article on the parts of an argument, especially warrants. How do warrants differ from reasons and evidence?

Why Does Little Red Schoolhouse (LRS) View Writing as Argument?
When we disagree about an issue, care deeply about an outcome, or try to convince others of the validity of our approach, we often resort to argument. Argument as it is depicted on television and experienced in times of stress or conflict carries with it many negative connotations of anger, high emotion, and even irrationality. But each of us also makes arguments every day, and in settings that help us become more rational, better informed, and more clearly understood.
Arguments help us to gather information from our own experience and that of others, to make judgments based on evidence, and to marshal information toward sound conclusions. Argument is appropriate when we seek understanding or agreement, when we want to solve a problem or answer a question, and when we want others to act or think in ways we deem beneficial, suitable, or necessary. Argument also comes in handy when we seek to convince, persuade, or produce change in our audience, and when circumstances require trust, respect, belief in our evidence or agreement with our reasoning.
Argument is everywhere – on television and radio, in politics and publications, and also in our day-to-day decisions about what to have for dinner, when to schedule the next meeting, and who should walk the family dog. As Colomb and Williams point out, the common notion that argument must be combative is built into our very language: opposing sides attack , defend , hold off , triumph , struggle , crush objections and slaughter competitors. On the other hand, in order to use argument as productive and collaborative communication, we must certainly find a way to transcend the vocabulary of argument-as-war. We must negotiate the audience's needs along with the speaker's agenda.
Argument is also about conversation. Although sometimes we forget, the best arguments are a forum for:
- Obtaining and expressing information;
- Airing and sharing assumptions and reasons;
- Establishing common ground;
- Coming to mutual agreement.
Productive argumentation starts with a problem. It makes us realize why we have an interest in seeing that problem solved. It also claims a solution, convincing its audience of the validity of that solution with evidence and reasons that it will accept.
Writing and Argument
The Little Red Schoolhouse (LRS) focus on argumentation raises writers' and readers' awareness of:
- The importance of audience;
- The intersecting languages of information and persuasion; and
- The reading process through which we share the tasks of critical thinking and decision-making.
Argument structure also helps writers to avoid:
- The formulaic "five paragraph essay" that is often assigned in high school ("Scientific progress is good. Here are several reasons why scientific progress is good. In conclusion, scientific progress is good.");
- The default structure of chronological order (First I set up the lab, then I opened my notebook, then performed the first step in my experiment…);
- Simple summary with no so what ; and
- Binary structures where two issues or ideas are described without connection to each other.
Preparing Your Argument
To prepare to make an effective argument you must first:
- Translate your topic into a problem statement ;
- Frame a situation that is debatable or contestable;
- Formulate a question about which reasonable people might disagree; and
- Find a claim your analysis has led you to assert.
Now you can begin to imagine what it will take to convince your audience. What evidence, methods, or models do they expect? What conventions must you follow to win approval?
Sketch Your Approach
- What do you want to show?
- Why should readers agree?
- Based on what evidence?
- What are some possible alternatives or objections?
- What conclusion will you offer, and why should your readers accept it as valuable?
The Five Parts of Argument
The questions that lead to your topic, broadly conceived, also steer you toward what The Craft of Argument formalizes in the five parts of argument .
- Acknowledgement and Response.
These Correspond to the Williams' and Colomb's Five Questions of Argument:
- What are you claiming?
- What reasons do you have for believing your claim?
- What evidence do you base those reasons on?
- What principle connects or makes your reasons relevant to your claims?
- What about such-and-such potential disagreement/difficulty?
Constructing Claims
We learn that, at bottom, an argument is just a claim and its support:
Reason therefore Claim
Claim because of Reason .
Your claim is your main point. It should either be clearly conceptual (seeking to change how we think) or clearly pragmatic (seeking to change how we act). Claims should, by definition, require good reasons. Audiences should be able to disagree with your claim and, by extension, to be convinced and converted by your evidence.
More about Claims
- Make sure your readers can recognize why your claim is significant.
- Ensure that your claim is clear and concise. Readers should be able to tell what is at stake and what principles you intend to use to argue your point.
- Confirm that the claim accurately describes the main tenets of the argument to follow.
- Moderate your claim with appropriate qualifiers like "many", "most", "often", in place of "all", "always", etc.
Evaluating Good Claims
- Your solution is possible.
- Your solution is ethical (moral, legal, fair, etc.).
- Your solution is prudent – it takes into consideration both the problem you seek to resolve and the possible ramifications of your proposal.
Reasons and Evidence
Most arguers know from experience that reasons and evidence help to convince audiences. In the simplest terms, reasons answer the question: "Why are you making that claim?" Evidence offers tangible support for reasons.
When stating reasons, always be aware of your audience. You will need to choose the reasons that support your evidence that are also the most likely to convince your specific readers or listeners. Knowing the general values and priorities of your readers will help you to determine what they will count as compelling reasons.
Knowing what kind of arguments and evidence they will expect from you will guide you in choosing reasons that meet those expectations.
Tailor your appeal to the specific needs and acknowledged concerns of your reading community, because arguments are always audience specific.
Evidence should be reliable and based upon authoritative and trustworthy research and sources. It should be appropriately cited, and ample enough to convince. Evidence should also be designed to appeal to your target audience's values and priorities.
When Arguing through Evidence
- Present evidence from general to specific.
- Build on what readers know.
- Do not rehearse your own work process; instead, support your conclusions.
- Use diagrams, graphs, and other visuals.
- Keep support appropriate and simple.
- Make sure data is authoritative/expert.
- Help the audience to know what is important.
The words reason and evidence are much more familiar to most students of written and oral argument than the term warrant . But reasons and evidence are most powerful when they are utilized within the structure of argument we have been discussing.
To be convincing, the reasons and evidence you present in support of your claim need to be connected through warrants. Warrants express a general belief or principle in a way that influences or explains our judgments in specific cases.
Take, for example, the old saying: "Measure twice, cut once".
Expressing as it does a general belief or principle – that when you take the time to do a thing properly, you don't make mistakes – the saying provides a viable warrant for an argument like:
"It is never a good idea to hurry a task. [Reason] [Connected by the beliefs and assumptions expressed by the warrant to the supporting evidence that] Careless mistakes take longer to fix than it would to do things right the first time." [Evidence]
Warrants express justifying principles, shared beliefs, or general assumptions. They are the spoken or unspoken logic that connects your reasons to your evidence. Warrants take many forms, but Williams and Colomb emphasize that they always have or imply two parts:
- One articulating a general belief or circumstance.
- One stating a conclusion we can infer from applying that circumstance to a specific situation.
Warrants often take the form: Whenever X, then Y. For example, take the commonly held belief expressed by the old saying "When it rains, it pours". The same sentiment and set of assumptions could be described by the general truism "If one thing goes wrong, everything goes wrong". Whether implied or explicit, and whether it takes the form of a general observation or a cultural belief, a warrant states a broader principle that can be applied in a particular case to justify the thinking behind an argument.
More on Clear Warrants
Warrants connect your reasons to your claim in logical ways. Whether a warrant is assumed or implied, it is still crucial that the audience be able to recognize your warrant and be able to determine that they agree with or accept your warrant.
Questions for Determining Good Warrants
- Do readers know the warrant already?
- Will all readers think it is true?
- Will they see its connection to this circumstance or situation?
- If they think it is both valid and appropriate, will they think it applies to their family, corporation, or community?
Warranting: A Specific Case
Consider a case when an audience might not accept your argument unless it first accepts your warrant. Take, for example, the following discussion between a mother and her child.
Child (to mother): "I need new shoes."
Mother: "But why, what are your reasons?"
Child: "Because all the other kids have them." X
Child: "Because red is 'in' this season and my shoes are blue." X
Mother: "Sorry, but I don't accept your argument that you need new shoes."
Above all, warrants require common ground. In the example above, the success of the child's argument depends upon his mother's sharing the values and assumptions upon which the argument for new shoes is based.
Productive argument will require that the child find, and address, some common belief or assumption about what constitutes "need". While his mother might not be influenced by peer pressure or style trends, she probably does share a set of values that would ultimately lead to agreement (Common Ground).
Consider a situation in which the child's previous reasons had not convinced his mother to accept his argument, and we can see how compelling reasons and evidence can be developed alongside shared warrants.
Child: "I need new shoes because these ones have holes in them and it's the rainy season." √
Mother: "Well why didn't you say so?! I agree that you shouldn't be walking around with wet feet!"
We are most likely to accept an argument when we share a warrant. In this case, it is unstated, but implied:
Warrant = When shoes no longer protect the feet from stones and weather, it is time to buy new ones.
There is another way to look at warrants that don't necessarily fit a certain mold. If you believe in a general principle stated about general circumstances (for example, "People who fall asleep at work probably aren't getting enough sleep at home".), then you are likely to link a specific instance (of nodding off at your computer) with a specific conclusion (that you haven't gotten adequate rest). Warrants here can be defined as general truths that lead us to accepted conclusions.
Acknowledgement and Response
Acknowledgement and response can be included in your argument in order to:
- Produce trust;
- Mediate or moderate objections;
- Limit the scope of your claim;
- Demonstrate experience or immersion in a wider field or discipline.
Brainstorm useful concessions to potential dissenters by thinking about the difficulties or questions your argument is likely to produce. Within your argument, acknowledgements and responses often begin with: To be sure , admittedly , some have claimed , etc.
Concessions allow the writer to predict problems that might weaken an argument and respond with rebuttals and reassessments. Acknowledgement and response frequently employs terms like but , however , on the other hand , etc.
Using the Five Parts of Argument
After you have sketched out your full argument, and even after you have drafted the entire piece of writing, you should revisit your claim. Ask yourself: Does the claim still introduce and frame the discussion that follows? Are there elements of the claim that need to be revised? Built upon? Eliminated? Explained?
- Is your claim clear and concise?
- Is it contestable?
- Is there good evidence for your solution?
- Will your audience agree?
Evaluate and Revise Reasons
Consider the specific needs and perspectives of your audience and select reasons that will connect to their priorities and motivations. Make sure that you provide ample reasons for each claim or subclaim you assert. Order your reasons in a way that is logical and compelling: Depending on your argument, you may want to lead with your best reason or save your strongest reason for last. Finally, ask yourself whether any essential evidence is missing from your discussion of the problem.
- Do your reasons make a strong case for the validity of your claim?
- Can you imagine other reasons that would appeal more strongly to your audience?
Assess and Improve Evidence
If there are authorities to appeal to, experts who agree, or compelling facts that support your argument, make sure you have included them in full. Whether you are speaking from experience, research, or reading, make sure to situate yourself firmly in your field. Create confidence in your authority and establish the trustworthiness of your account.
- Have you consulted reputable sources?
- Have you conducted your research and formatted your findings according to accepted standards?
- What does your audience need to know to appreciate the solution you propose?
- What makes it easy or difficult to accept?
- What further support might you offer?
Scrutinize Your Warrants
If you can't articulate the connection between what you claim and why you believe the audience should accept your assertion, your readers probably can't either! Good warrants often take the form of assumptions shared by individuals, communities or organizations. They stem from a shared culture, experience, or perspective. If understanding your claim means sharing a particular set of beliefs or establishing common ground with your reader, make sure your argument takes time to do so.
- Can your audience easily connect your claim to your reasons?
- Are your warrants shared? Explicit? Implied?
- What unspoken agreements do your conclusions depend upon?
Concede and Explain
Gracefully acknowledge potential objections when it can produce trust and reinforce the fairness and authority of your perspective. Try to anticipate the difficulties that different types of readers might have with your evidence or reasoning
- Where are my readers most likely to object or feel unsettled?
- How can I concede potential problems while still advancing the authority of my claim?
Assessing and Revising Your Argument
By way of conclusion, we can revisit the issue of method. Little Red Schoolhouse (LRS) encourages thinking about the parts of argument in order to produce logic that is
- Easy to understand, and
- Easy to acknowledge or accept.
Argument structures comprehension by giving readers a framework within which to understand a given discussion. Argument supplies criteria for judgment, and connects reasons with claims through implicit or explicit warrants. Sometimes, crafting a good argument is as simple as asking yourself three basic questions:
- What do you want to say?
- Why should readers care?
When you set about answering these questions using the five parts of argument, you will hone introductions and thesis statements to make clear and precise claims, make relevant costs and benefits explicit, and connect reasons and evidence through shared and compelling warrants.
Examples taken or adapted from:
- Williams, J. (2005). Style: Ten Lessons in Clarity and Grace. (8th ed.). New York: Pearson.
- Williams, J., Colomb, G. (200 3). The Craft of Argument. ( Concise ed.). New York: Addison Wesley Longman, Inc.


Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
10 Developing Strong Arguments
Josh miller, university of wisconsin-milwaukee, learning objectives.
- Understand the principles of argumentation.
- Identify the parts of an argument.
- Understand the different types of arguments, and how to make an effective argument.
- Explain the techniques for creating and the benefits of having counter arguments.
When you think of the word argument, you might also think of intense shouting matches where one person attempts to yell louder than the other person. You might imagine someone’s feelings getting hurt or relationships falling apart. Or, perhaps a scene emerges in your mind where one friend decides to stop speaking with another friend after an altercation. You might even think of physical violence. In general, people tend to have a negative impression about arguing, thinking that arguments are destructive and harmful. We want to avoid arguments. This chapter, however, takes a different approach to argument. As you will learn in this chapter, effective public speeches develop around arguments, and arguments do not need to be considered harmful things to be avoided. Instead, someone engaged in an argument gives logical reasons to other people—reasons that might enable those people to change their own minds about a particular topic or issue.
This chapter will first equip you with some basic principles for understanding the importance of arguments in public speaking. Based on those principles, you will learn why speeches must have arguments and how to determine the success of an argument. Then, you will learn about the basic structure of an argument, so you have the tools to develop compelling arguments. The chapter will also discuss several types of arguments that you can make, and it will warn you several types of argumentative strategies that you will want to avoid. You will also learn about the significance of knowing what other people might think about your topic and why it is important to address other people’s potential concerns with your topic in your speech itself.
Principles of Argumentation
Before we examine the structure of an argument, it might be helpful to first cover some essential principles of argumentation. These principles help us to be better equipped to answer the following questions: why do we argue? What is argumentation and what is an argument? How do I know that I have made a successful argument? There are four principles in total: (1) argumentation solves problems, (2) argumentation involves uncertainty, (3) arguments are a process and a product, and (4) success is determined by the audience.
Principle #1: Argumentation as Solutions to Problems
Why do we make arguments and why do we engage in argumentation? At the most basic level, we engage in arguments to solve problems. In your local community, you might believe that the roads are littered with too many potholes, so you decide to convince your neighbors and your local city council to raise taxes to fix all of those potholes. To convince your neighbors and city council members to make the change, you need to engage in argumentation. In other words, you need to give your audience, members of your local city council and neighbors, good reasons as to why they should make a change and taxes should be increased. What distinguishes argumentation from other ways to solve problems is that arguers will use evidence and logical reasoning to convince others that there is a problem and that they know the best way to fix the problem. [i] In public speaking, argumentation is not a zero-sum game where there is a clear winner and loser because the goal of argumentation is connection and problem-solving. In short, arguments are used to inspire action and solutions to fix problems.
Principle #2: Argumentation involves Uncertainty
Arguments are necessary when there is uncertainty about what people can do or should do at some point in the future. Arguments work to reduce that uncertainty. When we face a problem in our daily lives, in our communities, or as a nation, we have many different options about what we can do. Some might not even recognize or believe that a problem is occurring and thus believe that we do not need to do anything. Some people might believe that one possible solution is better than the other solutions, and some might disagree with that assessment. Moreover, we generally need to decide how to respond to the problem with limited information, and we can never be certain what the proper course of action entails. If the solution were obvious, we would not need to make arguments to convince others of the best course of action. When we face problems, we can try to agree on the best course of action by giving each other reasons why we should prefer one action over another. Because of the uncertainty inherent in argumentation, arguments require people to take “inferential leaps” or leaps of faith. People make these leaps of faith because they believe that a strong rationale exists for believing in one point of view over another. [ii]
Principle #3: Arguments as Products/Process
We can understand arguments as being both a product and a process. To view an argument as a product is to understand that an argument is something that is made and has a structure. As a public speaker, you will make an argument to convince someone to agree with your point of view. You will give evidence and use that evidence to make an argument about why your point of view is correct. However, arguments are something that you will also have with other people. Arguments do not occur in a vacuum. So, to view argument as a process means to understand that arguments happen in interactions with others. Through that process, you might tell your audience why you believe your evidence justifies a particular position over another, but your audience members might also tell you why they think their point of view is superior to others. Throughout that interaction and exchange of ideas and evidence, hopefully, you and your fellow arguers will arrive and agree upon the best course of action.
In order for the process of argumentation to work, both you and your audience members have to be open to persuasion. This openness is known as the principle of reciprocity . True argumentation can only occur if both you and your audience are open to being persuaded and willing to admit that you may be wrong. [iii] You and your audience members have to be willing to examine the evidence and be willing to compromise. That is, engagement with others is necessary for productive argumentation. [iv] Otherwise, even though you might be exchanging points of view and evidence supporting those points of view, both you and your audience members will not be able to arrive at a collective course of action that will solve the problems you face. In short, arguments are things that we make (produce), but arguments are also things that we do with others (process).
The principle of reciprocity is when both you and your audience members are open to persuasion.
Principle #4: Success is Determine by Your Audience
Being correct is not the same thing as having a strong or successful argument. Success is based on earning agreement of your audience. When we argue, it is because we want others to share our point of view and act with us to solve a problem. Ultimately, it is up to our audience to decide if they want to agree with our point of view and act collectively with us. So, even if we are confident that we are correct in what we believe, we cannot consider our arguments to be successful until we convince others to agree with our point of view. The process of earning agreement from your audience can be long and difficult. However, merely repeating what you believe to be correct will not foster a successful argument. It is not until you realize that your audience determines whether or not your argument is correct that you can begin to work to earn that agreement. As such, creating a successful argument often takes time, effort, research, and a willingness to engage with ideas and beliefs with which you disagree.
Now that we have covered some of the basic principles of argumentation, let us examine the parts of an argument. Knowing the parts of every argument will help you recognize whether or not you are crafting an effective argument for your speech.
The Parts of an Argument
A well-structured argument contains at least three parts: the claim, the data, and the reasoning. The claim is the initial statement with which you would like your audience to agree. The data is the supporting material and evidence that you present to your audience that you believe shows that your claim is accurate. The reasoning is the logical connection between your data and claim. In other words, the reasoning shows your audience why your data supports your claim. [i] For example, if you are attempting to convince your friend to go eat lunch with you at a local burger place, you might say “we should go to that burger place for lunch today.” You want your friend to agree with that statement, and it is thus your claim. Your friend might ask “why?” And, you might respond by stating “it has the best fries.” This statement is your data because it is the supporting material that you provided to your friend to prove that your claim (“we should go to the burger place”) is correct. Your reasoning is the logical connection between your claim and the data. In this case, your reasoning might be that “restaurants that have the best fries are the best places to eat.” This statement connects your data (that the burger place has the best fries) to your claim (that you should eat at the burger place). Thus, your complete argument: “Places that have the best fries are the best places to eat lunch. So, we should eat at the burger place, because they have the best fries.” This statement includes your claim, data, and reasoning.
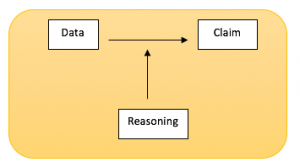
In everyday conversation, speakers do not always explicitly state the reasoning of the argument. When you talk to your friends about where to eat lunch, you might only say “we should eat at the burger place, because they have great fries.” If you ever said this statement, you would have only explicitly stated the claim and data. The reasoning is implied, and you would have assumed that your friends would understand the logical connection between having good fries and going to a place to eat. Based on this example, we might infer that not everyone will explicitly state their reasoning. However, for your argument to be effective, your audience needs to understand and agree with the logical connection between your claim and data. As such, if you do not state the reasoning explicitly, you must be confident that the logical connection is obvious enough that your audience will understand what it is. To be on the safe side, you should be as explicit as possible about how your data supports your claim in your speech, especially if your argument is complex or new to your audience. Remember that without a clear connection between your data and claim your argument will fall flat.
The claim is the intial statement with which you would like your audience to agree.
The data is the supporting material and evidence that you present to your audience that you believe shows that your claim is accurate.
The reasoning is the logical connection between your data and claim.
The basic structure of an argument includes a claim, data, and reasoning. To know how to develop as many diverse arguments as possible, it is helpful to know about the many different ways the reasoning process works in an argument. Let’s examine the different types of argument.
Try It: “Because” Test
Strong data is critical to developing strong arguments. To ensure that you include evidence in every argument, use the “because” test. The word because usually signals that a clause in your sentence will contain data supporting the other clause in the sentence. As such, one way to identify your claim and data is to add the word “because.” Examine the topic sentence of each paragraph (or main point) of your speech. If those sentences do not contain the word “because,” try to rewrite them to include the word “because.” If you cannot, then it is likely that your sentence needs data to support your claim and be a complete argument. Think of the burger place example once again. In this hypothetical, if your sentence was only “we should go to the burger place,” you will notice that you cannot rewrite this sentence to include the word “because.” As such, this sentence is only the claim. However, if your statement was “The burger place has great fries. We should go to it.” You can rewrite that statement as “we should go to the burger place because it has great fries.” This statement includes both the claim (“we should go to the burger place”) and data (“it has great fries”); the “because” in the sentence signals a connection between the claim and data.
Types of Arguments
Understanding different reasoning patterns can help you construct better arguments. We will examine six ways you might reason as you develop and articulate an argument: (1) arguments by induction, (2) arguments from deduction, (3) arguments of cause, (4) arguments by analogy, (5) arguments by sign, and (6) arguments from authority.
Arguments from Induction
When arguing by induction , speakers take specific instances of an occurrence and generalize to a general principle based on their observation of those specific instances. [i] This process of going from specific instances and information to generalizing is also called developing an argument from example. During election seasons, pollsters use reasoning by example to make arguments about which candidate the general population prefers or wants to vote for at a given time. Pollsters ask a sample number of people to determine what they are thinking about the election. Based on the results from that sample, pollsters generalize and draw conclusions about what the general population thinks about the election and the candidates.
When developing an argument from example, your data is a specific instance of a larger phenomenon. You might use your personal experience to make your generalization. For example, if you are giving a speech about the need for public libraries, you can use your personal experience of using the public library to use the internet, check out a book, or have a quiet place to work. Based on your personal experience (your data) of needing to use the library, you generalize (your reasoning) to make the argument that libraries are an essential facet of your community (your claim). Other types of data that might be relevant to an argument from example include testimonies of other and statistics. For instance, if you want to argue that the economy of your state is doing poorly, you might find statistics that three of the largest cities in the state have growing unemployment and have a shrinking economy. Based on those three statistics (your data), you generalize (your reasoning) to conclude that the economy in the entire state is likely weaker than it should be (your claim).
If you decide to use inductive reasoning in your speech, you should ask yourself the following questions: (1) Do I have enough examples to support the generalization? (2) Will my audience members find my examples typical and representative? [ii] Your argument from example may not be persuasive without enough examples to support your conclusion. For instance, if you are giving a speech about funding for libraries and you tell your audience that you use the libraries, your audience will not accept your generalization that the library is important because many people use it. Instead, you could provide your audience with a statistic stating the total number of people that use the libraries to generalize that many people use them. Arguments from example also fail when the examples are outliers or isolated instances. You may not like chocolate cake, but that does not mean that we can then conclude that most people dislike chocolate cake.
Arguments from Deduction
Whereas reasoning by example involves moving from specific instances to a general principle, when using deductive reasoning , speakers take a general principle and apply that principle to a specific case. For example, if you have evidence proving that in general students who attend a preschool do better in their K-12 education than students who do not, you might make an argument that your child should attend preschool so they can do better in their K-12 education. In this example, your claim would be that “my child should attend preschool.” Your data is the study you found saying, attending preschool correlates with more success in K-12 education. The reasoning that connects the data and claim is the belief that what is generally true for other children will be true for your child. When you make an argument that starts with a general principle and then apply that principle to a specific example, you are reasoning by deduction.
Data that supports an argument from deduction can include both facts and values derived from expert testimony, statistics, and revered documents. For example, when Martin Luther King Jr. delivered his “I Have a Dream” speech, he cited two revered documents: the Constitution and the Declaration of Independence. On that hot summer’s day in 1963, King exclaimed:
When the architects of our republic wrote the magnificent words of the Constitution and the Declaration of Independence, they were signing a promissory note to which every American was to fall heir. This note was a promise that all men, yes, black men as well as white men, would be guaranteed the “unalienable Rights” of “Life, Liberty and the pursuit of Happiness.” It is obvious today that America has defaulted on this promissory note, insofar as her citizens of color are concerned. Instead of honoring this sacred obligation, America has given the Negro people a bad check, a check which has come back marked “insufficient funds.” [iii]
The argument that King develops in this passage is one based on deduction. King starts with the data that the Declaration of Independence proclaims that all people are created equal. King then applies the general value principle established by the Declaration of Independence to the issue of racial segregation. When he does that, he can conclude that all races should be treated equally under the law and granted the guarantee of life, liberty, and the pursuit of happiness. Because the Declaration of Independence generally concludes that all people are created equal (data), King argues that in the specific instance (reasoning) of racial segregation that the law should treat all races equally (claim).
When developing an argument from deduction, you need to be confident that the general principle on which you base your argument is accurate and that your audience will believe that it is accurate. If you do not believe that your audience will agree with the general principle, then you would want to include additional evidence justifying that the general principle is accurate before you apply that general principle to a specific situation.
Arguments of Cause
Arguments based on causal reasoning attempt to establish a cause and effect relationship between two items. So, based on an assumption about a relationship between the two items, your argument predicts that something will occur based on the data that you have. That is, you believe that one of the items influences the other items in some way. For instance, if a friend noticed you studying three hours a day for a whole week, that friend might make the following prediction: “you are going to do well on your exam because you have been putting in so many hours of studying.” In this example, your friend’s claim is that you will do well on the exam. The data is your friend’s observation of all of the studying that you have been doing. The reasoning in this argument is that a cause and effect relationship exists between studying and doing well on an exam. When speakers and audiences believe that one thing causes the other thing, they assume that the observation of one of the things allows us to predict that the other thing will occur.
Another example of reasoning by cause would be the argument that “you should stop smoking, so you do not develop lung disease.” In this argument, the claim would be “you should stop smoking.” The speaker making this argument would be using causal reasoning because the argument assumes that a causal relationship between smoking and lung disease exists. The argument assumes that smoking does cause lung disease. To strengthen arguments by cause, you should clearly articulate evidence that supports the cause and effect relationship between the two items. In the instance of the smoking example, citing evidence that establishes the connection between smoking and lung cancer would make the causal argument stronger. Moreover, strong arguments by cause usually include an explanation about how one item influences the other item. For instance, in the example about smoking, saying that smoking damages lung cells which increases the likelihood of lung disease explains to the audience how smoking and lung disease are connected.
Causal arguments fail when they are based on correlation rather than causation. Correlation means that two things tend to happen at the same time—they have a connection. However, in a correlation one thing does not cause the other thing. For example, we may notice that college debt is increasing in the United States, and we may also notice that over the same period of time smoking has been decreasing in the United States. However, we cannot conclude that if more people smoked cigarettes, college debt would decrease. When two things happen at the same time, it does not prove that one causes the other.
Arguments by Analogy
Arguments by analogy assume that if two items are alike in some respects, then they will be alike in other respects. As such, reasoning by analogy connects evidence to the claim by comparing to items. [iv] Take the following argument for example: “Sweden’s health care system dramatically reduced health care costs in five years. Thus, the United States should follow Sweden’s lead and adopt a similar healthcare system.” In this example, the claim is that the United States should adopt a health care system that is similar to Sweden’s. The data is a report that Sweden’s health care costs were reduced in five years. The reasoning connects the claim and data together. In this case, the reasoning is that because the United States and Sweden are comparable countries, what worked in Sweden should work in the United States. This type of reasoning relies on the belief that the two items (in this example, Sweden and the United States) are actually comparable in ways that are relevant to the argument. If members of the audience think that one cannot make a comparison between the two countries, then the reasoning process (and the argument) fails.
Remember that when you reason by analogy, the two objects that you are comparing need to be similar and your audience needs to understand their similarities. The similarities also need to be relevant to your argument. If the two objects that you are comparing seem dissimilar, then it will be more difficult for you to convince your audience to take the “leap of faith” and accept your claim.
Arguments by Sign
When a speaker makes an argument that uses reasoning by sign , the speaker assumes that the observation of one item shows that another item is occurring. Reasoning by sign then allows us to infer the presence of something, even if that thing cannot be physically observed. One of the most common arguments based on sign is the following: “I see smoke. There must be a fire.” Even though the speaker does not see fire, the speaker reasons that the presence of smoke must mean that there is a fire. If we were to break that argument into its parts, we would say the claim is that there is fire. The data is the physical observation of smoke. The reasoning process would be that “smoke is a sign of fire.”
Reasoning by sign is distinct from reasoning by cause because reasoning by sign does not attempt to show a causal relationship between the two things. That is, when you are reasoning by sign, you are not saying that “smoke causes fire” but that “from our observation of smoke, we can assume the presence of fire.” If we were to use reasoning by cause, we might state that: “because fire causes smoke, if I start a fire, there will also be smoke.” In the example of reasoning by cause, we infer something will happen based on the occurrence of something else. In the example of reasoning by sign, we infer something is happening based on our observation of something else.
When reasoning by sign, you want to be careful to take into account alternative explanations of what might be happening. For example, if you walk outside in the morning and see a large puddle of water, you might assume that it recently rained. This assumption would be reasoning by sign because you assume that your observation of the puddle enables you to infer that rain occurred. However, other explanations might exist for why there is a large pool of water. For example, a fire hydrant might be broke nearby that is gushing water everywhere, or someone might have left on their garden hose. So, when you reason by sign, you need to take other possibilities into account and determine if your explanation is the best possible explanation for what occurred. [v]
Arguments from Authority
An argument from authority uses the expertise of someone as data to justify a claim as correct. This type of argument is one of the reasons it is important to cite qualified sources in your speech. The expertise of your sources justifies the arguments that you are making. Take the following argument: “Climate change is a real phenomenon because a vast majority of scientists indicate that it is real. In fact, in a peer-reviewed study, Doctor John Cook and his research team compiled scientific studies about climate change and found over 90% of scientists agree that the phenomenon is real.” [vi] In this argument, the claim is that climate change is real. The data is a study conducted by experts in the field stating that scientific consensus exists around the issue of climate change. The reasoning that connects the claim with the data is that what experts in their field indicate as true is likely to be true. When you reason by authority, you can either quote the authority figure or summarize the authority figure’s arguments. Regardless, you must also tell your audience who the authority figure is and why they are qualified to speak about the topic of your speech.
When developing an argument from authority, remember the following: first, you need to make sure that the person you are citing is an expert in the topic of your speech. Someone might have a doctorate in literature, but that does not mean that their testimony on a scientific process is authoritative. Conversely, someone who has a doctorate in chemistry might not have the most authoritative voice when it comes to a speech involving books that have historically been banned from public schools. Second, the strongest arguments from authority generally do not rely on only one person’s authority. Instead, they rely on the testimony of multiple sources all of which are qualified to speak on the matter of your speech. For example, if you want to make a claim about the effect of increased carbon dioxide emission on plant life, a stronger argument would cite multiple independent qualified sources rather than just one source. Lastly, always remember to cite your sources out loud in your speech. Because your argument relies on the credibility of the people you are citing, you need to make sure you tell your audience your sources’ qualifications.
Arguments and Multiple Types of Reasoning
Not every member of your audience will be persuaded by the same argument. Some people connect better with a clear example. Some people are more trusting of authority figures than others. Because of this, you will want to include several types of arguments in your speech. For example, if you wanted to convince your neighbors to increase taxes to reduce potholes, you might want to both include personal testimonies of people who say that they damaged their cars (reasoning by example) and evidence from car mechanics that detail how potholes can damage cars (reasoning by authority). When you include a few types of reasoning in your speech, the chance that at least one of your arguments will convince your audience of your thesis will increase. To strengthen your argument, you might use multiple pieces of evidence and reason in different ways to justify the same claim.
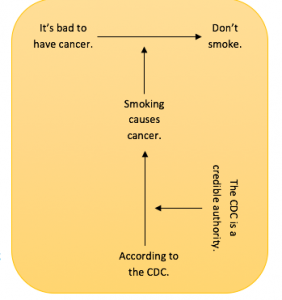
Additionally, you might cite evidence to support the reasoning process of an argument in your speech. Recall the example above about convincing someone to quit smoking. If you said, “you should quit smoking because you do not want to get cancer,” you would be reasoning by cause. Your claim is the person should quit smoking. The data is that it is bad to get cancer. The argument assumes a causal relationship between smoking and cancer. Thus, the argument reasons by cause. Now, imagine that you made the following argument: “you should quit smoking because you do not want to get cancer. According to a report released by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), smoking leads to lung cancer.” [vii] In this statement, you have provided evidence supporting the reasoning of your argument. Think of the second sentence “according to a report released by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), smoking leads to lung cancer” as a new argument. In this argument, the claim is that smoking leads to lung cancer which is the reasoning from the first sentence of the argument. The data for the second sentence is the CDC’s report. The reasoning that connects the claim and data is reasoning by authority because the argument assumes that what experts state as true is likely to be true. So, when you are constructing your arguments for your speech, if you ever think that the reasoning of your argument is unclear or might not convince others, you should find additional evidence to support the logical connection between your claim and data.
Inductive reasoning is when a speaker takes specific instances of occurrence and generalizes to a general principle based on their observation of those specific instances.
Deductive reasoning is when speakers take a general principle and apply that principle to a specific case.
Arguments based on causal reasoning attempt to establish a cause and effect relationship between two items.
Arguments by analogy assume that if two items are alike in some respects, then they will be alike in other respects.
When reasoning by sign , the speaker assumes that the observation of one item shows that another item is occurring.
An argument that reasons from authority uses the expertise of someone as data to justify a claim as correct.
Counter Arguments
Effective speakers recognize that their audience members’ points of view often differ from their own. As a speaker, you will, of course, attempt to prove that your point of view is the one that your audience should adopt. However, because audience members have their own points of view and beliefs about many issues, it is vital for you to brainstorm what those other beliefs and views about your topic might be and how you might address those beliefs in your speech. It might be easy to ignore divergent points of view, but doing so does a disservice to both your speech and your audience. As a speaker, you need to take other points of view into account as you develop your speech.
To ensure that you are considering other points of view, your speech should address potential counter arguments. Counter arguments are positions with which your audience might hold that contradict or oppose your arguments. [i] For example, if you were to give a speech in which you argue that taxes should be increased to maintain public libraries in your hometown, someone else might think “why would we do that? No one uses libraries anymore.” The belief that no one uses libraries anymore may challenge the main argument of your speech. Thus, it is a counter-argument to your speech.
It is important for you to remember that at least one counter argument will exist whenever you give a speech. If there are no counter arguments and everyone in the audience already agrees with your thesis, you would have no reason to deliver the speech. The best speakers, knowing there are likely to be counter arguments present whenever they speak, anticipate and respond to potential beliefs or positions that run contrary to their thesis. For instance, if you were delivering the speech mentioned above about increasing funding for libraries, you would want to tailor your speech to highlight why people might use libraries and provide data to support your claim. You might find reports that show people use libraries for internet access if they do not have internet at home, or you might also find newspaper articles that discuss summer reading program that libraries hold for children. You can then incorporate those pieces of evidence into your speech to address the counter-argument that people do not use libraries anymore. For instance, you might say something like this: “Some of you might think that not enough people use our public libraries to justify the increased expenditures, but a recent Pew Research Institute poll found that people still frequently use public libraries to check out books, take classes about how to use new technology, and use the internet to find jobs.” [ii] If you had delivered this statement, you would have referenced an opposing viewpoint (“not enough people use our public libraries to justify increased expenditures”), showing your audience that you are aware of potential positions that contradict your own. You also would have responded to the opposing position with evidence that shows your audience members why they do not need to be concerned about lack of library use.
You can also address counter arguments is by establishing a value hierarchy. A value hierarchy prioritizes certain values and beliefs over others while still affirming all of those values and beliefs. For example, imagine that you are involved in a debate with another person about whether or not the United States should adopt a counter-terrorism measure and increase surveillance on its citizens. One side might argue, “No, we should not increase surveillance because that undermines our freedom and right to privacy.” The other side might argue, “Yes, we should increase surveillance because that will make us safer from terror attacks.” Both sides have constructed their argument based on the need for preserving a particular value. One side wants to preserve freedom, and the other side wants to preserve safety. Both positions can establish a value hierarchy to respond to the other side’s argument. For example, the person who opposes the counter-terrorism measure might say, “Although our safety is important, we must remember that we are fighting to protect the principles and rights on which our country was founded, including the right to privacy. Give me liberty or give me death.” In this statement, the speaker values the opposing side’s safety concerns but also indicates that the right to privacy is more important than safety. So, although the speaker agrees that safety is important, the speaker concludes that the counter-terror measure should not be adopted based on another more important value. Yet, the speaker who supports the counter-terror measure might also attempt to establish a value hierarchy. That speaker might say, “You are correct that privacy is important. However, to truly enjoy the benefits of living in a free society, we must all feel that we are safe. Without a feeling of security, we will never benefit from the freedoms we have.” This speaker establishes a value hierarchy by suggesting the safety is necessary for freedom, which takes counter-argument of needing to preserve freedom into account and addresses it. Therefore, when you are constructing your speech, one way you can address counter-arguments is by considering related values and developing a value hierarchy.
In general, acknowledging counter arguments and responding to them makes you appear more credible to your audience members than if you simply ignored counter-argument. The first reason that this is the case is that addressing counter arguments makes you appear more knowledgeable about the topic and less biased. Explaining potential reasons that someone might disagree with your speech shows your audience that you did your research and tried to understand all sides of the issue as you developed your speech. Your knowledge enhances your credibility on a particular topic. Then, when you address the various sides of the issue, you show your audience that you took the time to consider other viewpoints and why your position is still the correct one. What this does is show your audience that you care about finding the correct solution to a problem, making you seem more trustworthy.
The second reason that you should address counter arguments is that audience members who agree with the counter argument will view you with skepticism if you fail to address their concerns. For example, if you attempt to get a vegetarian or someone who wants to eat healthy to join you for lunch at your local burger place, they are unlikely to be convinced by your argument that the burger place has really juicy burgers. The vegetarian would probably think “but I don’t eat meat. What is in it for me?” And, the person trying to eat healthily might think, “but don’t those have a thousand calories?” Neither one of these people would be convinced by your argument because you have not addressed the counter-arguments. Just stating the burger place has great burgers may make these members of your audience feel that you did not care about their beliefs and values or, in another sense, whether or not you actually convinced them to go to the burger place. Without taking into account your audience’s beliefs, it can be difficult for you to establish a connection with your audience. Remember, a connection is necessary for you to persuade your audience to accept your point of view.
Counter arguments are positions with which your audience might hold that contradict or oppose your arguments.
A value hierarchy holds certain values and beliefs over others while still affirming all of those values and beliefs.
Logical Fallacies: Weaknesses in Reasoning
Many potential pitfalls exist when you are creating arguments. These pitfalls, known as logical fallacies, are weaknesses in reasoning. As you read earlier in the chapter, every argument contains a claim, data, and reasoning that logically connects your data to your claim. In other words, when you craft an argument, a clear reason as to why your data supports and justifies your claim must exist. Without that clear connection, your argument will not make sense. Saying, for example, it will rain today because my finger itches does not make sense because there is not a clear connection between an itchy finger and rain. Logical fallacies are arguments in which there is not a clear connection between the claim and evidence, or there appears to be a connection between the two, but that connection is flawed. In other words, logical fallacies are weakness or flaws in the logic and reasoning of particular arguments.
Logical fallacies are fairly common. They can occur in political speeches, in arguments with friends and parents, commercials, and advertisements. An important part of being a critical listener is being able to notice the weaknesses in arguments. And, an important part of being an effective speaker is being able to avoid logical fallacies and develop the strongest arguments possible. As such, learning to identify logical fallacies will enhance your critical listening skills as well as your ability to be an effective speaker.
The Strawperson Fallacy
The strawperson fallacy exaggerates or misrepresents someone else’s argument to make that argument easier to refute. Recall the example from earlier in the chapter about giving a speech where you argued that taxes should be increased in order to pay for fixing potholes. Now, imagine that someone said, “all tax and spend liberals want is to take all your money and increase the size of government.” This statement is an example of the strawperson fallacy because your argument is not that the government should take all of the local townsfolk’s money. This person is exaggerating your argument to make it sound ridiculous and weaker than it is. The strawperson fallacy is a dishonest argumentative strategy because it fails to tell the audience the actual argument that needs to be refuted. It might be easier to “beat” a position if you misrepresent it, but doing so is unethical. Audience members who are familiar with the actual argument that you are refuting will know that you are exaggerating the argument and will view you with skepticism.
False Cause
The false cause fallacy assumes that if an actual or perceived relationship exists between two things, then one must be the cause of the other. That is, this fallacy assumes that correlation is causation. Thus, the false cause fallacy is committed when an argument is based on the mistaken belief that a causal relationship exists between two variables when no support for that relationship exists. When the false cause fallacy occurs in a speech, it is likely that causal relationship between the two variables has not been established or cannot be established. A Buzzfeed article posted in 2013 by Ky Harlin exhibits several interesting correlations and why you should not assume that one variable causes another based on a simple correlation. For example, Harlin’s article shows that there is a correlation between the amount of ice cream sold in a month and the number of murders that occur in a month. An argument using a false cause fallacy may claim that buying ice cream causes murder. Another example in Harlin’s article is a correlation exists between M. Night Shyamalan’s movie score on Rotten Tomatoes and total newspaper ad sales. [i] Assuming that people failing to buy newspaper ads makes M. Night Shyamalan worse at making movies would be a false cause fallacy. For each of these examples, other explanations likely exist for changes to each variable. In the case of ice cream and murder, perhaps the reason that both ice cream buying and murder increases in the summer is due to the weather or another variable entirely.
Post Hoc Ergo Propter Hoc
Meaning “after this, therefore because of this,” post hoc ergo propter hoc is a subset of the false cause fallacy. This fallacy assumes that if Event A happened before Event B, then Event A was the cause of Event B. If you ever hear people make the argument that their itchy fingers mean it is about to rain, they are likely committing this fallacy. Imagine that your finger started itching and then ten minutes later it started to rain. If you conclude that your itchy finger made it rain, then you would be assuming that an event happened first and thus caused the second event to occur. Logically, there is not a connection between the two events unless you are able to prove that connection to your audience. In other words, pointing out that two things happened in chronological order is not proof that one is connected to the other. Your audience will likely see the two things as independent of each other unless you can provide an explanation of why they are connected.
Red Herring
The red herring fallacy occurs when someone introduces irrelevant information or topics into a discussion in order to distract from the topic or debate at hand. This action is an attempt to “win” a debate by starting a discussion of another topic or by distracting those you are engaged with in an argument. For example, if you were at a local city council meeting where the topic of discussion was the road quality and potholes, someone giving a speech about the prevalence of local corruption in politics would probably distract people’s attention from the question about how to best fix the roads in the city. Red Herring is a fallacy because changing the discussion to another topic does not prove that you are correct about the previous topic. Asking yourself “does the claim that I am making clearly connect to the issue I am discussing?” will help you avoid making the red herring fallacy. [ii]
Meaning “to the person,” this logical fallacy is when someone attacks their opponent and does not respond to the opponent’s argument. Ad hominem is an attack on a person’s character, personality, or traits. For example, if you are trying to convince someone that college campuses should be tuition-free and that person responds by saying “you are stupid and have bad breath,” then that person has committed the ad hominem fallacy. This fallacy is a poor argumentative strategy because it distances the arguer from the audience. People generally avoid interacting with and listening to people who call them names or attack their character. Moreover, proving that someone else has bad character traits does not demonstrate to your audience that you are correct about a particular issue. So, instead of attempting to demean other points of view, use your speech to establish why you are correct about the topic to which you are speaking.
Either-Or Fallacy
Also called the forced dilemma fallacy, the either-or fallacy happens when someone presents two competing possibilities as the only two possibilities in a given situation. This presentation is a fallacy because it is likely that more than two possibilities exist. An example of this fallacy would be if a speaker argued for funding a new college by saying “either we fund this new college or it will close and our kids will never be able to attend college.” In that statement, the speaker only articulates two possibilities for what can happen. However, as you can probably tell, there are many other options for what could occur. Those kids could go to a different college, or funding for the new college could come from somewhere else. Using the either-or fallacy is a flawed argumentative strategy because members of your audience will recognize that other options exist. When members of your audience think of other options, you will lose credibility as a speaker because your audience will be able to tell that you did not take all other opinions and options about the issue into consideration as you developed your speech. Many issues are complex. Do not attempt to make them appear overly simplistic. Doing so does a disservice to yourself as a speaker and to your audience members.
Hasty Generalization
The hasty generalization fallacy is when a speaker reasons using examples but then jumps to a general conclusion without a sufficient number of examples. That is, the speaker uses examples to establish a general claim but uses too few examples to support that generalization. Moreover, the speaker might use examples that do not relate to the general claim that the speaker is attempting to make. Often stereotypes can arise because people reason using the hasty generalization fallacy. For instance, if someone made the argument that “one time I met a man wearing a red hat and he was really rude, therefore all men who wear red hats are rude,” that person would be using a hasty generalization to stereotype people with red hats. The hasty generalization is a weak argument strategy because members of an audience can often think of counter-examples that disprove the general claim. When making arguments based on examples, make sure that you have enough examples to demonstrate that your generalization is accurate.
The bandwagon fallacy occurs when someone assumes that something is true just because many people believe it to be true. Thus, appealing to the popularity of an idea as its primary support is the bandwagon fallacy. For example, if you wanted to convince your audience to avoid skydiving and argued that everyone knows that skydiving causes death, you have substituted actual evidence for the assertion that everyone knows you are correct. Just because people believe something is true does not mean that it is the case. Remember that a lot of people used to believe that the earth is flat and that leeches effectively cured diseases. Do not rely on the popularity of an idea to demonstrate that the idea is correct.
Logical fallacies arguments in which there is not a clear connection between the claim and evidence, or there appears to be a connection between the two, but that connection is flawed.
The strawperson fallacy exaggerates or misrepresents someone else’s argument to make that argument easier to refute.
The false cause fallacy assumes that if an actual or perceived relationship exists between two things, then one must be the cause of the other.
Post hoc ergo propter hoc , meaning “after this, therefore because of this,” is a subset of the false cause fallacy. This fallacy assumes that if Event A happened before Event B, then Event A was the cause of Event B.
The red herring fallacy occurs when someone introduces irrelevant information or topics into a discussion in order to distract from the topic or debate at hand.
Ad hominem is an attack on a person’s character, personality, or traits.
The either-or fallacy, or forced dilemma fallacy, happens when someone presents two competing possibilities as the only two possibilities in a given situation.
The hasty generalization fallacy is when a speaker reasons using examples but then jumps to a general conclusion without a sufficient number of examples.
The bandwagon fallacy occurs when someone assumes that something is true just because many people believe it to be true.
In this chapter, you learned several principles of argumentation. As you now know, arguments are about trying to solve collective problems. When we need to argue, it is because there is something needs to be changed or improved. We argue to convince people that there is a problem and that we can solve it. This mindset creates conditions where people might actually work to change and fix an issue. Moreover, arguments occur when there is uncertainty about what should happen in the future. We argue in an attempt to create more certainty by highlighting which options for the future are the best options. Finally, you learned that the success of an argument is based on whether or not it earns agreement from the audience.
This chapter also detailed the parts of the argument. Arguments contain these three parts: (1) the claim, (2) the data, and (3) the reasoning. The reasoning is the logical connection that shows why a particular piece of data supports the claim that a speaker is attempting to make. In addition, this chapter described six types of arguments that you might make in a speech: (1) arguments from examples, (2) arguments from deduction, (3) arguments of cause, (4) arguments by analogy, (5) arguments by sign, and (6) arguments from authority. It remains important to remember that your speech should develop several types of arguments in support of your thesis because certain types of arguments might be more persuasive than others. This chapter also defined and illustrated several types of weaknesses in arguments. These logical fallacies should be avoided when you develop a speech.
Whenever you need to develop an argument, other people might have different points of view on the issue. Rather than ignoring other people’s points of view, engage them and explain to your audience why they should prefer your point of view. Also, be willing to change your mind. Argumentation is not about who can yell the loudest. Instead, it is about giving your audience good reasons to believe in your point of view and engage ideas with which you may disagree. You cannot force someone to change their mind, but you can give good reasons as to why they should change their mind. That is the purpose of argumentation.
Stand up, Speak out Copyright © 2017 by Josh Miller; Marnie Lawler-Mcdonough; Megan Orcholski; Kristin Woodward; Lisa Roth; and Emily Mueller is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

Arguments and Information
Learning Objectives
- Define and explore brainstorming for argument selection
- Write a specific purpose statement
- Write effective thesis statements
When you’re preparing to speak, finding an argument, perspective, or topic can feel overwhelming. “Where should I start?” “What do I care about?” “Why should the audience care?” are all questions that you’ll likely encounter.
These are important queries, and we don’t want to downplay the difficulty in selecting an argument and formulating an idea that is worthwhile to the audience. Finding an argument that fits the context, is timely, well-reasoned, and interesting can be difficult. Oftentimes, when we sit down to think about ideas, brainstorm, and jot down some insights, our page feels oddly blank. “What should we talk about?” “Where do we start?” are common questions that race through our minds. You might experience this, too, and feel confused about how to begin selecting an argument or sorting through information to locate an interesting idea.
When you begin searching for an argument, you aren’t alone; you have tons of informational avenues that can direct you to different topics that are relevant in the world.
In fact, you’re experiencing interesting information all the time! You are constantly absorbing, sorting, and curating information and ideas. Think about your social media accounts. If you’re like us, you likely scroll through and click on articles that seem unique or insightful; you “like” or comment in response to posts that draw you in. There’s a constant flow of information (and potential speech topics).
In this chapter, we explore how to select and formulate the main argument for a speech. It’s often uncommon to snap our fingers and know exactly what our argument will be, and that’s OK! This chapter works to funnel you through brainstorming and searching toward writing a clear and narrow argument that is specific to your public speaking context. It’s our goal to encourage curiosity, and we hope that you’ll accept the challenge.
By the end of this chapter, you will have deeper critical thinking skills that lead you from broad topic ideas to specific arguments and thesis statements. Before brainstorming a topic can begin, however, you must zero in on the context.
Context is Key
Your context should always guide your preparatory process, including selecting an argument to present. The context defines why you’re there, how long you’re there for, when, and with whom.
By answering the “why” – i.e. “Why am I here?” – you can determine your general purpose for speaking: informing, persuading, or entertaining. While arguments can often be adapted to fit many purposes, it’s always important to begin any project by knowing the parameters and overarching goals – in this case, why am I speaking? For example, are you trying to:
- Solve a problem
- Reduce uncertainty
- Increase awareness
- Honor someone
Selecting a final topic before considering the context means “placing the cart before the horse,” so to speak. Your context will inform the general purpose which will guide your specific argument.
It’s important, too, to stay appraised of the other contextual factors, particularly the time. How much time you have to speak will influence how broad or narrow your argument can be. If you have 3 minutes, for example, you must have a specific and focused take-away for the audience within that short amount of time. Alternatively, a 20-minute speech provides more flexibility. There may be some ideas or arguments that aren’t feasible within certain time constraints.
As you’ll remember from Chapter 1, “context” also refers to the broader historical and cultural context. Being aware of larger cultural conversations and dialogues can assist in selecting arguments that are timely and relevant for your audience. In other words, it allows you to find information that is having an impact on your community/communities right now, and that information becomes significant to share.
If you aren’t sure how to locate such arguments, stay tuned! Below, we tackle brainstorming as a mechanism to locate potential arguments.
Brainstorming
Brainstorming is the process and practice of searching to find ideas or information. When you brainstorm, you are generating ideas to overcome a barrier or confront a problem. The problem you’re confronting is,

“What can I talk about that will sustain the audience’s attention and have an impact?” For speeches, brainstorming assists in locating and narrowing information to an accurate idea that supports the development of a well-reasoned argument.
Like we mentioned in the introduction, you are already sorting through vast amounts of information daily. We are confronted with so many ideas, research findings, memes, tweets, advertisements, and podcasts (to name a few); we develop personal strategies to find information that is meaningful and worthwhile to us.
Brainstorming is a practice that formalizes that sorting process. It asks you to make those choices more deliberately and consciously. The key to successful brainstorming is openness – you must be open to finding, locating, and narrowing down information.
Arguments are Advocacies
Topic selection and argument construction are key parts of formulating an advocacy. Speeches are meaningful and impactful communication acts. When you speak, you are supporting an idea, cause, or policy. You should approach brainstorming purposefully and intentionally with a framework in mind that “What I select matters.” Because what you select matters.
In addition, your advocacy may begin broadly, but your goal is to tailor that advocacy down to a workable argument. It’s helpful to think about your topics as orbiting an advocacy. For example, you may be interested in environmental advocacy, where environmentalism is a large and broad topic. But “environmentalism” isn’t a workable speech argument – it’s way too big! With research, critical thinking, and expertise, you’ll narrow that broad advocacy umbrella down to a workable argument – a thesis statement – and craft the remainder of your speech with that specific argument in mind.
We suggest two broad brainstorming strategies, and let’s start with the first: exploratory research.
Exploratory Research
Exploratory research encompasses brainstorming strategies that spark curiosity. When you explore, you are going on an adventure, and exploratory research is similar. You are sorting information to find broad topics or ideas (that you’ll narrow down later). Conducting a personal inventory and exploring online are two great exploratory brainstorming strategies.
Personal Inventory
An old adage states, “Write about what you know.”
To write what you know, begin by conducting a personal inventory – a process of tracking ideas, insights, or topics that you have experience with or interest in . Retail stores do regular inventories to know what is actually stocked in the business. You have much more going on in your brain and background than you can be conscious of at any one time. Being asked the right kinds of prompts can help you find ideas. Look over Table 3.1 for some prompting questions when conducting a persona inventory.
This may not be an inventory that you complete in one sitting. In fact, it’s worthwhile to jot down a few things that catch your attention throughout the day or for a series of days. Once complete, the inventory may seem long and intrusive, but digging a little deeper may help you find ideas and directions that are unique to you. Generating your list based on these questions and prompts will get you excited about your topic and talking about it to your audience.
Let’s work through a hypothetical application of the personal inventory. Imagine brainstorming for a speech, and you write the following in response to Table 3.1:
Major: Economics (for now) Goals : Complete my degree with honors; travel to Brazil Barriers to achieving those goals : Procrastination, assigned class schedules, expensive college and fees, problems with gaining a visa
As you look over these broad ideas, your next step is to highlight topics that pique your interest or are a priority. You might highlight “expensive college” as a barrier that could prohibit you from completing your economics degree on time. After all, if you are unable to afford college (or are worried about loans), you may take a semester break or drop out. Also, as an economics major, you become more interested in exploring college affordability.
As the personal inventory implies, good speech topic ideas often begin with the speaker. After all, if a speaker is intrigued by an idea, that passion is more likely to translate to an audience. But it doesn’t end there. Remember, we are just brainstorming! It’s still necessary to research and read about a topic or problem from multiple viewpoints and sources. If we only begin from ourselves, we often fail to see or learn about different perspectives, other important areas, or problems. Exploring online can help in narrowing your topic and deciding if it’s a relevant argument for your audience and community.
Explore Online
A second brainstorming technique is online exploration—searching digital information with an open mind. You can use your personal inventory as guidance or, if you’re stuck, you can read information online for ideas that spark curiosity. There are ample online locations to find an array of information, from Google News to Twitter.
When you search, look far and wide. It’s common to search and seek out information that we’re looking for, but brainstorming isn’t about finding what you already know; It’s about finding what you don’t. Use different search engines and social media platforms for help.
As you search, skim. Remember that this is an exploratory phase (we’ll talk more about searching in-depth in Chapter 4), so you don’t need to read every article that pops up on a search engine. Write down words. Write down phrases. Ask yourself questions about those words and phrases to determine how relevant and interesting they could be.
For example, if you continued brainstorming about “expensive college” – an idea on your hypothetical personal inventory—you might find a series of posts, articles, and insights that a) help you learn more and b) help narrow down the topic. You’d learn that, under the broad category of college affordability, there are a range of topics that influence students, including: student loan interest rates, textbook cost, private loans, and the depletion of Pell grants. You could attack any of these issues, of course, but some are more complicated than others. Textbooks seem like they could be a potential topic. Perhaps you recently experienced purchasing expensive college textbooks. Perhaps you loaned a friend money after their textbook bill made it difficult to pay rent. After reflecting, books seem ripe for advocacy.
Whenever you are exploring a topic online, it is important to remember that if you have one good source, you probably have several. The trick is being able to use that one good article to track down multiple sources. For example, a Vox article about textbooks, titled “The High Cost of College Textbooks, Explained,” provides opportunities for more online exploration. Below is a list of ideas or concepts to click on or research in other tabs. Look for these in every article as you brainstorm. Pretty soon, you will probably have a dozen or more tabs open, meaning you will have much more expertise and a deeper understanding of your topic.
- Hyperlinks : journalists do not cite their sources with footnotes, endnotes, or internal citations like you do for class. Instead, they hyperlink their sources to make it easier for you to track down their evidence.
- Big I deas : You can easily Google main topics of an article to see how other people are talking about it. This will allow you to see more than one perspective on a topic and to cross-check your original article against other writers.
- People : From the author to the people they talked to or about, look up people to read their credentials and determine if they are qualified to write or talk about the relevant topic.
- Jargon: If you find any words that are unfamiliar, look them up. This will help you understand the argument better and make certain the author actually knows what they are writing about. Plus, it will give you some words to use for mind-mapping.
Before we move further into narrowing and mapping our topic, let’s conclude this section by busting a few myths about online information.
Myth # 1: Wikipedia is bad. You’ve likely heard that “you can absolutely not cite Wikipedia [in a formal essay or speech].” While, yes, Wikipedia is a collaborative encyclopedia, meaning that anyone can technically add to its content, its pages can be useful for brainstorming. We recommend using Wikipedia in two ways.
First, search Wikipedia for their internally-cited material. If you’ve used Wikipedia recently, you know that the content includes references to other sources that validate the findings. Use those! The references are helpful in locating (often) credible sources for your own research on a topic.
Second, use Wikipedia to clarify complex ideas. Because Wikipedia is a community-based and collaborative encyclopedia, technical language is commonly translated to allow better comprehension. If you aren’t sure about an idea, search Wikipedia for help (but verify the information through other sources, too).
While we don’t recommend using Wikipedia as the source, their content can direct you toward reputable research and clarify difficult concepts.
Myth #2 : Information is neutral. It’s easy to believe that, because something is published online, it’s a neutral and reputable source. Sadly, that’s not the case. In our digital information age, virtually anyone can be an author, and that’s great! But it also reduces the reliability of information that’s being posted.
You’ve likely heard about “fake news,” but we’ll use the term propaganda – biased or misleading information that promotes a particular agenda. Propaganda is junk science, and it can’t be trusted as reliable. For example, you might notice a meme that posts a Harriett Tubman quote in support of strict immigration reform. Digging deeper, you’d likely find that the quote was misrepresented or made up to support an anti-immigrant agenda.
Advertising more subtly influences information. That’s because many information sorting sites, including Google, use an algorithm that’s specific to you. If you and a friend search the same thing, your search results may differ, especially after the first page.
Does that mean you can’t use Google? Of course not. We do! But you should be aware that targeted sites may be rising to the top, and when you search, dig deep and search multiple pages.
Using a Mind Map
After conducting exploratory research to dig a little deeper, a mind map is a second brainstorming strategy to narrow and isolate a topic. A mind map is a visual tool that allows you to chart and expand key topic ideas or concepts.
As you mind map, use the following tips:
- Start with a big idea.
- Break this big concept down into smaller ideas until you can’t break them down anymore.
- Look up synonyms or like words.
- Write down any words you find during your research to tap into the larger conversation.
Figure 3.2 is an example of a mind map based on “college affordability.” You can see how the topic narrowed from college affordability to textbook costs. The mind map also includes words that were used in the Vox article, such as “open textbooks.” Jotting down ideas and language that are used in source information will provide insight into common wording used by topic experts. Keep in mind, if you do not like mind maps, make a list or develop some alternative method, but make certain to keep track of everything.
You can create a mind map using a program like Popplet , Powerpoint, Word, or Google Docs. We usually just grab a blank sheet of paper and a pencil, though.
As you expand topics through a mind map, the narrower that your argument becomes. Instead of a broad approach to “college affordability,” you now have options to explore textbook costs, open textbooks, or open educational resources.
We promise this will not be a waste of your time. Writing down your ideas and thoughts will help you identify keywords for further searching, so you won’t have to come up with words on the fly. As you search, you can easily scratch off words that fail to get you any information, mark the words that seem to get you exactly what you need, or jot down new words you stumble across as you search. All of this will save you time in the long run because it won’t leave you searching for just the right word or trying the wrong word over and over.
Formulating a Specific Purpose Statement
After identifying your general purpose (to inform, to persuade, or to entertain) and brainstorming key topic ideas, you can start to move in the direction of the specific purpose.
A specific purpose statement builds on your general purpose (such as to inform) and makes it more specific (as the name suggests). So, if you’re giving a persuasive speech, your general purpose will be to persuade your audience about, for example, the rising cost of textbooks. Written together, your specific purpose would read, “to persuade my audience to support campus solutions to rising textbook costs.”
Your general purpose and audience will influence how to write your specific purpose statement (see Table 3.3.)
Table 3.3. (Stand Up, Speak Out).
Table 3.3 demonstrates how to move from the general purpose to the specific purpose while keeping your audience in mind.
So far, so good, right? Before moving to your thesis, be aware these common pitfalls for writing specific purpose statements.
Being Too Broad
Specific purpose statements sometimes try to cover far too much and are too broad. You are funneling a broad topic to a specific argument, so don’t stop at the topic. Instead, ask, “am I trying to do too much?”
Consider this specific purpose statement: To explain to my classmates the history of ballet.
This subject could result in a three-hour lecture, maybe even a whole course. You will probably find that your first attempt at a specific purpose statement will need refining.
These examples are much more specific and much more manageable given the limited amount of time you will have:
To explain to my classmates how ballet came to be performed and studied in the U.S. To explain to my classmates the difference between Russian and French ballet. To explain to my classmates how ballet originated as an art form in the Renaissance. To explain to my classmates the origin of the ballet dancers’ clot h ing.
Often, broadness is signaled by the use of “and,” where a specific statement is making two arguments.
These examples cover two different topics:
To explain to my audience how to swing a golf club and choose the best golf shoes. To persuade my classmates to be involved in the Special Olympics and vote to fund better classes for the intellectually disabled.
Too Specialized
The second problem with specific purpose statements is the opposite of being too broad, in that some specific purposes statements are so focused that they might only be appropriate for people who are already extremely interested in the topic or experts in a field. For example:
To inform my classmates of the life cycle of a new species of lima bean (botanists, agriculturalists). To inform my classmates about the Yellow 5 ingredient in Mountain Dew (chemists, nutritionists). To persuade my classmates that JIF Peanut Butter is better than Peter Pan. (organizational chefs in large institutions) .
Formulating a Thesis
While you will not actually say your specific purpose statement during your speech, you will need to clearly state what your focus and main points are going to be. Your specific purpose is still not your main argument. It’s part of the funnel as you move to your main argument, or thesis statement. A thesis statement is a single, declarative statement that outlines the purpose of your speech.
The point of your thesis statement is to reveal and clarify the main argument of your speech.
This part of the process is important because it’s where your topic becomes an argument. Like we mentioned in the introduction, you will funnel your advocacy down to a specific argument that fits the context and goals of your speech.
However, as you are processing your ideas and approach, you may still be working on them. Sometimes those main points will not be clear to you immediately. As much as we would like these writing processes to be straightforward, sometimes we find that we have to revise our original approach. This is why preparing a speech the night before you are giving it is a really, really bad idea. You need lots of time for the preparation and then the practice.
Sometimes you will hear the writing process referred to as “ iterative.” This word means, among other things, that a speech or document is not always written in the same order as the audience finally experiences it. You may have noticed that we have not said anything about the introduction of your speech yet. Even though that is the first thing the audience hears, it may be one of the last parts you actually compose. It is best to consider your speech flexible as you work on it, and to be willing to edit and revise. If your instructor asks you to turn the outline in before the speech, you should be clear on how much you can revise after that. Otherwise, it helps to know that you can keep editing your speech until you deliver it, especially while you practice.
Here are some examples that pair the general purpose, specific purpose statements and thesis statements.
General Purpose: To inform Specific Purpose: To demonstrate to my audience the correct method for cleaning a computer keyboard. Thesis : Your computer keyboard needs regular cleaning to function well, and you can achieve that in four easy steps.
General Purpose : To persuade Specific Purpose: To persuade my political science class that labor unions are no longer a vital political force in the U.S. Thesis : Although for decades in the twentieth century labor unions influenced local and national elections, in this speech I will point to how their influence has declined in the last thirty years.
General Purpose : To persuade Specific Purpose: To motivate my audience to oppose the policy of drug testing welfare recipients. Thesis : Many voices are calling for welfare recipients to have to go through mandatory, regular drug testing, but this pol-icy is unjust, impractical, and costly, and fair-minded Americans should actively oppose it.
General Purpose : To inform Specific Purpose: To explain to my fellow civic club members why I admire Representative John Lewis. Thesis : John Lewis has my admiration for his sacrifices during the Civil Rights movement and his service to Georgia as a leader and U.S. Representative.
Notice that in all of the above examples that neither the specific purpose nor the central idea ever exceeds one sentence. You may divide your central idea and the preview of main points into two sentences or three sentences, depending on what your instructor directs. If your central idea consists of more than three sentences, then you probably are including too much information and taking up time that is needed for the body of the speech.
For thesis statements, remember the following few guidelines:
- Do not write the statement as a question.
- Use concrete language (“I admire Beyoncé for being a talented performer and businesswoman”), and avoid subjective terms (“My speech is about why I think Beyoncé is the bomb”) or jargon and acronyms (“PLA is better than CBE for adult learners.”)
Remember that your thesis statement cements your main argument – it’s the foundation to building the speech. A clear and focused thesis statement define the speech, and we’ll continue building the research and content around your argument.
Case Studies in Specific Purposes and Thesis Statements
Case Study One : Mitchell is taking a Fundamentals of Speech course in his second year of college. As a member of the college’s tennis team, he wants to speak on his favorite subject, tennis. He is assigned an informative speech that should be seven minutes long and use four external sources (other than his own experience). He realizes off the bat that he knows a great deal about the subject as far as how to play and be good at it, but not much about the history or origins or the international impact of the sport. He brainstorms a list of topics: 1. Famous tennis players 2. Rules of tennis 3. How to start playing tennis 4. How to buy or choose equipment for tennis 5. Why tennis is a great sport 6. Tennis organizations 7. Where tennis came from 8. Dealing with tennis injuries 9. Tennis and the Olympics 10. Famous tennis tournaments—grand slam events
However, he also wants to be sure that his audience is not bored or confused. His instructor gives him a chance to get in a small group and have four of his classmates give him some ideas about the topics. He finds out no one in his group has ever played tennis but they do have questions. He knows that everyone in his class is 18-24 years old, single, no children, enrolled in college, and all have part-time jobs.
Critique Mitch’s brainstorm topics based on what you know. What should he do? Can you come up with a good starting specific purpose?
Case Study Two : Bonita is required to give a 5- to 6-minute presentation as part of a job interview. The interview is for a position as public relations and social media director of a nonprofit organization that focuses on nutrition in a five-county region near her home. There will be five people in her audience: the president of the organization, two board members, the office manager (who is also the Human Resources director), and a volunteer. She has never met these people. Bonita has a college degree in public relations, so she knows her subject. She does as much research on the organization as she can and finds out about their use of social media and the Internet for publicity, marketing, and public relations. It does have a Facebook page but is not utilizing it well. It does not have any other social media accounts.
What would you suggest for Bonita? Here are some questions to consider. Should she be persuasive, informative, or inspiring? (General purpose) What should be her specific content area? How can she answer the two questions of the value of her topic to the audience and why would the audience think she is credible?
In this chapter, we discussed best practices for brainstorming topics that funnel to an argument. Argument selection is exciting, and use these tips alongside your other creative information gathering skills. Next up: research!
Speak Out, Call In: Public Speaking as Advocacy Copyright © 2019 by Meggie Mapes is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
In this article, we explain what an argument is, list the different parts of an argument, explore the steps you should take when crafting an argument and provide some examples of effective parts of an argument.
There are two main parts to an argument: premises and conclusions. A premise is a statement of evidence or support that justifies or leads to a conclusion. A conclusion is any statement for which evidence or support has been offered.
Constructing a persuasive argument is no easy task, but knowing the parts of an argument can structure your thinking as you begin to put one together. Here are the five parts of an argument: 1. Claims 2. Reasons 3. Evidence 4. Warrants 5. Acknowledgment and Response
The bulk of an argument is given over to supplying and presenting the evidence that supports a particular claim or position, refuting opposing arguments and making appeals to the logical, ethical and emotional sensibilities of the audience.
6.8: Basic Structure and Content of Argument. When you are tasked with crafting an argumentative essay, it is likely that you will be expected to craft your argument based upon a given number of sources–all of which should support your topic in some way.
Five Essential Parts of an Argument. Read article on the parts of an argument, especially warrants. How do warrants differ from reasons and evidence? Why Does Little Red Schoolhouse (LRS) View Writing as Argument?
We will examine six ways you might reason as you develop and articulate an argument: (1) arguments by induction, (2) arguments from deduction, (3) arguments of cause, (4) arguments by analogy, (5) arguments by sign, and (6) arguments from authority.
Topic selection and argument construction are key parts of formulating an advocacy. Speeches are meaningful and impactful communication acts. When you speak, you are supporting an idea, cause, or policy.
Knowledge Base. Essay. How to write an argumentative essay | Examples & tips. How to Write an Argumentative Essay | Examples & Tips. Published on July 24, 2020 by Jack Caulfield. Revised on July 23, 2023. An argumentative essay expresses an extended argument for a particular thesis statement.
One part of an argument. Premise —a reason behind a conclusion. The other part of an argument. Most conclusions have more than one premise. Statement —a declarative sentence that can be evaluated as true or false. The parts of an argument, premises and the conclusion, should be statements.