AI ASSISTANTS
Upmetrics AI Your go-to AI-powered business assistant
AI Writing Assist Write, translate, and refine your text with AI
AI Financial Assist Automated forecasts and AI recommendations
AI Research Assist Your go-to AI-powered research assistant
TOP FEATURES
AI Business Plan Generator Create business plans faster with AI
Financial Forecasting Make accurate financial forecasts faster
INTEGRATIONS
QuickBooks Sync and compare with your QuickBooks data
Strategic Planning Develop actionable strategic plans on-the-go
AI Pitch Deck Generator Use AI to generate your investor deck
Xero Sync and compare with your Xero data
See how easy it is to plan your business with Upmetrics: Take a Tour →
AI-powered business planning software
Very useful business plan software connected to AI. Saved a lot of time, money and energy. Their team is highly skilled and always here to help.
- Julien López
BY USE CASE
Secure Funding, Loans, Grants Create plans that get you funded
Starting & Launching a Business Plan your business for launch and success
Validate Your Business Idea Discover the potential of your business idea
E2 Visa Business Plan Create a business plan to support your E2 - Visa
Business Consultant & Advisors Plan with your team members and clients
Incubators & Accelerators Empowering startups for growth
Business Schools & Educators Simplify business plan education for students
Students & Learners Your e-tutor for business planning
- Sample Plans
Plan Writing & Consulting We create a business plan for you
Business Plan Review Get constructive feedback on your plan
Financial Forecasting We create financial projections for you
SBA Lending Assistance We help secure SBA loans for your business
WHY UPMETRICS?
Reviews See why customers love Upmetrics
Blogs Latest business planning tips and strategies
Strategic Planning Templates Ready-to-use strategic plan templates
Business Plan Course A step-by-step business planning course
Customer Success Stories Read our customer success stories
Help Center Help & guides to plan your business
Ebooks & Guides A free resource hub on business planning
Business Tools Free business tools to help you grow

How to Write an Operations Plan Section of your Business Plan
Free Operations Plan Template
- June 26, 2024

An operational plan bridges the gap between high ambitions and actual achievements. This essential integral section helps businesses thrive, achieve their goals, and handle challenges with accuracy and purpose.
But is it challenging for you to write one in a manner that shows a clear picture of your business operations? Drafting the operations plan section can be tricky due to the uncertainties of the business environment and the risks associated with it.
Well, worry not you’re at the right place! Here, we will see how to write an engaging operational plan in a business plan with an example. So let’s get going.
What is an operations plan?
An operations plan of a business plan is an in-depth description of your daily business activities centered on achieving the goals and objectives described in the previous sections of the plan. It outlines various departments’ processes, activities, responsibilities, and execution time frame.
The operations section explains in detail the role of a team or department in the collective accomplishment of your goals. In other words, it’s a strategic allocation of physical, financial, and human resources toward reaching milestones within a specific timeframe.
Key questions your operational plan should address

A successful operational plan section of your business plan should be able to answer the following questions:
- Who is responsible for a specific task or department?
- What are the tasks that need to be completed?
- Where will these operations take place?
- When should the tasks be completed? What are the deadlines?
- How will the tasks be performed? Is there a standard procedure?
- How much is it going to cost to complete these tasks?
Let’s see how to write the operations section that answers all the above questions:
Create winning business plans with our
AI Business Plan Generator
Plans starting from $7/month

How do you write an operations plan section?
Writing an operations plan within a business plan involves summarizing the day-to-day tasks necessary to run the business efficiently and meet its goals in both the development and manufacturing phases of the business.
Here’s a step-by-step guide:
1. Development phase
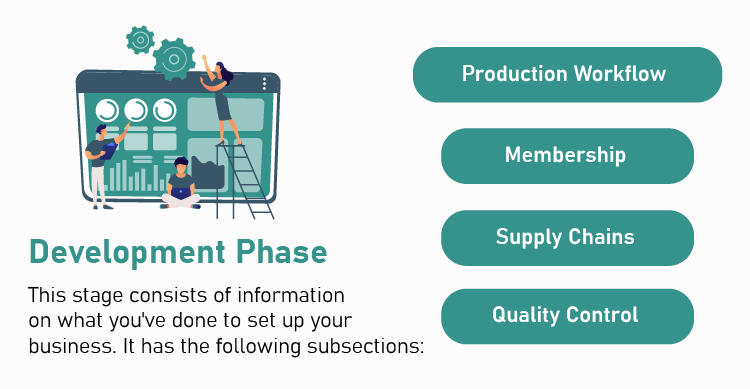
In this stage, you mention what you’ve done to get your business operations up and running. Explain what you aim to change and improvise in the process. These are the elements your development section will contain:
Production workflow
Explain all the steps involved in creating your product. Provide a detailed description of each step, including any inefficiencies and the actions needed to address them. Here, you also mention any inefficiencies that exist and talk about the actions that need to be taken to tackle them.
Write down the risks involved in the production and potential problems you may face later down the line. State the safety measures employees take to avoid any misfortune while working. Explain how you store hazardous material and discard waste.
Mention any industry organizations and associations you’re a part of or plan to join. It’s essential to include this information to convey to the reader that you’re aware of the organizations and associations in your industry.
Supply chains
Here, you mention the vendors you work with to sell your products. Give a quick rundown of the agreements you signed with them. Mention the terms and conditions, prices, and timeframe of the contract. You can also mention if you have any backup suppliers if the existing ones fail to fulfill the requirements.
Quality control
Describe the measures you’re taking to assure and verify the quality of the end product. If you’re working towards getting a product certification, explain the steps you take to meet the set standards.
2. Manufacturing phase
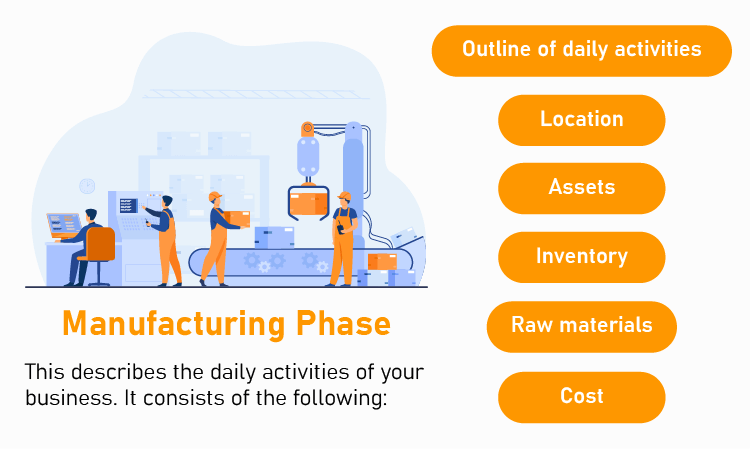
The development stage acquaints the reader with the functioning of your business, while the manufacturing stage describes the day-to-day operation. This includes the following elements:
Outline of daily activities
Create an outline of the day-to-day activities of the production process. This includes the hours of operation, days the business will be open, and whether the business is seasonal or not.
Mention the location of your business , other branches you have, and their locations. If available, include images or drawings of the buildings, lease documents, real estate agreements, and other relevant documents. If you include these in your plan, mention why they’re crucial.
Tools and equipment
Describe the tools and machinery you use. You should also include the cost of the equipment; these will be important to predict financial requirements.
List down all your assets. These include land, buildings, tools, machinery, vehicles, and furniture. Include a legal description and the value of these assets.
Special requirements
If you require any additional facilities like water supply or power requirements, you mention them here. Specify what you need to do or have already done to acquire permissions for these requirements.
Raw materials
Mention your raw material suppliers. If you need any extra materials, you can also include them in your operations plan. Here, you also mention the contracts and agreements with your suppliers.
Productions
Explain the production process and the time required to produce one unit. Include the factors that may disrupt the production flow. Further, mention your strategies to tackle these inefficiencies to avoid delays in manufacturing.
Here, you state the process of storing manufactured products, managing the stock, and the costs of the storage spaces. Stringent management of inventory is essential to maintain product quality and assure customer satisfaction.
Feasibility
To ensure the viability and effectiveness of your product, detail any tests it has undergone. This includes prototype testing to evaluate the design and functionality.
Additionally, highlight product or service testing, such as performance, safety, and user experience assessments. These tests validate your product’s readiness for the market, ensuring it meets customers’ needs and regulatory standards.
Include the pricing strategy for your products or services. You can also include the final prices of your products.
Outline your pricing strategy including which approach you used, for example—cost-plus, value-based, or competitive pricing. Include the final prices of your products or services, providing a breakdown if there are different tiers or packages.
Why do you need an operations plan?
An operations plan is like an instruction manual for your business. It helps investors assess your credibility and understand the structure of your operations.
Internally, an operations plan works as a guide, which helps your employees and managers to know their responsibilities. It also helps them understand how to execute their tasks in the desired manner—all while keeping account of deadlines.
The operations plan helps identify and cut the variances between planned & actual performance and makes necessary changes.
It helps you visualize how your operations affect revenue and gives you an idea of when you need to implement new strategies to maximize profits. Some of the advantages of preparing an operations plan include:
Offers clarity
Operational planning makes sure that everyone in the audience and team is aware of the daily, weekly, and monthly work. It improves concentration and productivity.
Contains a roadmap
Operational planning makes it much easier to reach long-term objectives. When members have a clear business strategy to follow—productivity rises, and accountability is maintained.
Set a benchmark
It sets a clear goal for everyone about what is the destination of the company and how to reach it.
Manages resources
It supports you in allocating resources, such as human resources, equipment, and materials, ensuring that nothing is wasted and everything is used optimally.
Helps in decision making
An operations plan helps make smart decisions by showing how the business runs day-to-day. It provides details on resources, wise investments, and effective risk management, ensuring that decisions improve overall business operations.
Operations plan essentials
Now that you have understood the importance of the operations plan, let’s go through the essentials of an operations plan:
Strategic plan
Your operations plan is fundamentally a medium for implementing your strategic plan . Hence, it’s crucial to have a solid plan to write an effective operations plan.
Having clear goals is one of the most important things for an operations plan. For clear goals, you need to think SMART:
- Specific: Clearly define what employees should achieve
- Measurable: Quantify the goal to track progress
- Attainable: Set ambitious but achievable goals
- Timely: Provide a deadline
Different departments will have their objectives, all supporting the main goal. All these strategic objectives are flexible and should align with the company’s long-term goals.
Key performance indicators
It’s essential to choose the right Key Performance Indicators (KPIs). It’s a good practice to involve all your teams while you decide your KPIs. Some of the important KPIs can be revenue growth, customer acquisition cost (CAC), net profit margin, churn rate, etc.
Creating a timeline with milestones is necessary for any business. It keeps everyone focused and helps track efficiency. If some milestones aren’t met in a certain period, then it’s time to re-evaluate them.
Examples of some milestones are:
- Hiring key team members in six months
- Setting checkpoints for different production phases like design, prototype, development, testing, etc.
- Acquiring the first 50 clients in a year
Now you’re all set to write an operations plan section for your business plan. To give you a headstart, we have created an operations plan example.
Operations Plan Example
We know this guide has been helpful for you in drafting a comprehensive operational plan section for your business plan.
If you’re still unsure or need help getting started, consider using business plan software like Upmetrics . It offers step-by-step guidance, so you won’t have to worry about what comes next.
Build your Business Plan Faster
with step-by-step Guidance & AI Assistance.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between a strategic plan and an operational plan.
A strategic plan outlines the long-term vision, mission, and goals of an organization, focusing on growth and direction over several years.
In contrast, an operational plan details the short-term tasks, processes, and resource allocation needed to achieve those strategic goals, emphasizing day-to-day efficiency and productivity.
What role does the operations plan play in securing funding for a business?
The operations plan defines the clear goals of your business and what actions will be taken daily to reach them. So, investors need to know where your business stands and it will prove the viability of the goals helping you in getting funded.
What are the factors affecting the operations plan?
Some of the factors that affect the operations plan are:
- The mission of the company
- Goals to be achieved
- Finance and resources your company will need

Can an operations plan be created for both start-up and established businesses?
Yes, both a startup and a small business need an operations plan to get a better idea of the roadmap they want for their business.
About the Author
Upmetrics Team
Upmetrics is the #1 business planning software that helps entrepreneurs and business owners create investment-ready business plans using AI. We regularly share business planning insights on our blog. Check out the Upmetrics blog for such interesting reads. Read more
Get started with Upmetrics Al
- 400+ sample business plans
- Al-powered financial planning
- Collaborative workspace
Reach Your Goals with Accurate Planning
We use essential cookies to make Venngage work. By clicking “Accept All Cookies”, you agree to the storing of cookies on your device to enhance site navigation, analyze site usage, and assist in our marketing efforts.
Manage Cookies
Cookies and similar technologies collect certain information about how you’re using our website. Some of them are essential, and without them you wouldn’t be able to use Venngage. But others are optional, and you get to choose whether we use them or not.
Strictly Necessary Cookies
These cookies are always on, as they’re essential for making Venngage work, and making it safe. Without these cookies, services you’ve asked for can’t be provided.
Show cookie providers
- Google Login
Functionality Cookies
These cookies help us provide enhanced functionality and personalisation, and remember your settings. They may be set by us or by third party providers.
Performance Cookies
These cookies help us analyze how many people are using Venngage, where they come from and how they're using it. If you opt out of these cookies, we can’t get feedback to make Venngage better for you and all our users.
- Google Analytics
Targeting Cookies
These cookies are set by our advertising partners to track your activity and show you relevant Venngage ads on other sites as you browse the internet.
- Google Tag Manager
- Infographics
- Daily Infographics
- Popular Templates
- Accessibility
- Graphic Design
- Graphs and Charts
- Data Visualization
- Human Resources
- Beginner Guides
Blog Business 10+ Operational Planning Examples to Fulfill your Strategic Goals
10+ Operational Planning Examples to Fulfill your Strategic Goals
Written by: Danesh Ramuthi Oct 25, 2023

An operational plan is a comprehensive, action-driven document that maps out how daily activities within an organization fuel the journey towards achieving strategic objectives.
Essentially acting as the nexus between high-level strategy and practical execution, this plan ensures that every department, from human resources to specific departments, operates in synchrony, aligning their day-to-day activities with the broader strategic goals.
By streamlining processes, it fosters cohesive efforts amongst diverse cross-functional teams, ensuring that both individual team members and entire departments work together harmoniously towards the company goals.
Ready to sculpt your organization’s future? Start your journey with venngage business plan maker and leverage their expertly crafted operational plan templates .
Click to jump ahead:
Why is an operational plan important?
10 operational plan examples, what should an operational plan include, how to write an operational plan.
- Strategic plan vs operational plan: What is the difference?
In summary
An operational plan is crucial because it serves as a bridge between a company’s high-level strategic planning and its day-to-day activities, ensuring that the business operations align with the strategic goals.
While a strategic plan provides a long-term vision, outlining the company’s objectives and goals to gain competitive advantages in the business environment, the operational plan outlines the specific actions, key elements and resource allocation required to achieve those objectives.
For example, while the strategic plan might set a goal for revenue growth over the fiscal year, the operational plan provides a detailed roadmap, breaking down major projects, assigning responsibilities to individual team members or specific departments and setting key performance indicators to monitor progress and ensure the entire organization works together effectively.
Operational planning, in essence, transforms the strategic objectives into actionable plans, ensuring that the entire team, from department heads to diverse cross-functional teams, is aligned and works in tandem to support revenue growth, increase productivity, and achieve the desired outcomes.
Operational plans, through a well-structured operational planning process, also provide a clear understanding of the day-to-day activities, allowing team members to know their roles, leading to better collaboration and synergy.
Moreover, by having clear operational plan examples or templates, businesses can ensure realistic expectations, manage their operating budget effectively and track progress through key performance metrics, thus ensuring that the company stays on course to realize its long-term vision.
Operational plans play a pivotal role in the business landscape, bridging the gap between strategic vision and tangible actions. They translate the overarching goals of an organization into detailed procedures, ensuring that daily operations are in line with the desired strategic outcomes.
In the section below, I will explore a few operational plan examples, shedding light on their structure and importance.
Business operational plan example
A business operational plan is a comprehensive document that elucidates the specific day-to-day activities of a company. It presents a detailed overview of the company’s organizational structure, management team, products or services and the underlying marketing and sales strategies.
For businesses, irrespective of their size, an operational plan can prove invaluable. By laying down the business goals and objectives, it acts as a blueprint, guiding entrepreneurs through the creation and implementation of strategies and action plans. The planning process also incorporates mechanisms to track progress and performance.
Additionally, for startups or companies looking to scale, a meticulously crafted operational plan can be pivotal in securing funds from potential investors and lenders.

Layered on this are details about the company’s organizational structure, its products or services and its marketing and sales strategies.
The document also delineates the roles and responsibilities of each team member, especially the management and key personnel. Given the dynamic nature of the business environment, it is imperative to revisit and update the operational plan regularly.
Related: 15+ Business Plan Templates for Strategic Planning
Simple operational plan example
A simple operational plan, often used by startups or smaller enterprises, emphasizes the basics, ensuring that the fundamental aspects of the business operations are captured succinctly. While it might not delve into the intricacies of every operation, it provides an overview of day-to-day activities, highlighting the goals and objectives the business aims to achieve in the short term.

In essence, this plan revolves around core elements like the company’s main objectives for the fiscal year, key responsibilities assigned to individual team members and basic resource allocation. A straightforward market analysis might also be included, offering insights into customer needs and competitive advantages the business hopes to leverage.

Though simple, this operational plan example remains pivotal for the organization. It provides a roadmap, guiding team members through their daily responsibilities while ensuring that everyone is working together towards shared goals. It becomes especially essential for diverse cross-functional teams, where clarity of roles can lead to increased productivity.

Modern operational plan example
In today’s fast-paced business environment, the emphasis on efficiency and innovative processes is paramount. The modern operational plan example caters precisely to this demand. Ideal for organizations aiming to streamline processes and highlight workflow, this type of operational plan emphasizes a more dynamic approach to planning.

It not only reflects the evolving nature of business operations but also provides a modern backdrop for content, ensuring that the presentation resonates with the current trends and technological advancements. The use of modern tools and platforms within this plan enables diverse cross-functional teams to work together seamlessly, ensuring that day-to-day activities are synchronized with the company’s long-term vision.

Furthermore, such an operational plan helps the entire organization stay agile, adapting rapidly to changes in the business environment and ensuring alignment with strategic goals.
Minimalist operational plan example
The minimalist operational plan example champions simplicity and clarity. By focusing on clear and concise business strategies, it eliminates any potential ambiguity, ensuring that team members and stakeholders have an unclouded understanding of the company’s objectives and goals.

The minimalist design not only promotes easy comprehension but also aligns with the modern trend of decluttering, ensuring that only the most vital components of the operational planning process are highlighted.
This approach leaves no room for confusion, streamlining the planning process and making sure that individual team members and departments are aligned with the business’s key objectives.

Moreover, the flexibility offered by a minimalist design allows businesses to craft an operational plan template that is not only functional but also accurately reflects their brand image and core values, ensuring cohesion across all aspects of the business strategy.

Clean operational plan example
The clean operational plan example stands as a testament to this principle. Ideal for businesses that prioritize clarity and directness, this format seeks to convey goals and strategies without overwhelming stakeholders.
While maintaining a neat and organized layout, it ensures that tasks are managed effectively, helping team members grasp their roles and responsibilities without getting lost in excessive details.

One of the primary advantages of a clean operational plan is its ability to eliminate distractions and focus solely on the critical aspects of operational planning.
Such a design aids in making sure that diverse cross-functional teams can work together harmoniously ensuring that day-to-day activities align seamlessly with the company’s long-term vision.
The simplicity of the clean operational plan not only supports revenue growth by ensuring efficiency but also reinforces the company’s strategic goals, making it an excellent tool in the arsenal of businesses that believe in clear communication and precise execution.
An effective operational plan acts as a roadmap, directing how resources should be allocated and tasks should be performed to meet the company’s objectives. Here’s what a comprehensive operational plan should encompass:
- Goals and objectives : Whether short-term or long-term, the operational plan should define clear goals and objectives that align with the company’s strategic plan. This gives direction to the entire organization, ensuring everyone is working towards a common aim.
- Clear responsibilities for team members : It’s essential that team members understand their roles within the operational plan. By outlining who is responsible for what, the plan ensures that there are no overlaps or gaps in duties and that everyone has clarity on their day-to-day activities.
- Assigned tasks: Alongside responsibilities, specific tasks need to be allocated to individual team members or specific departments. This granularity in assignment ensures that every aspect of the operational plan is covered.
- Timeline: This provides a clear schedule for when each task or objective should start and finish. A well-defined timeline assists in monitoring progress and ensures that the plan stays on track.
- Budget and resources : Every operational plan needs to factor in the budget and resources available. This includes everything from the operating budget to human resources, ensuring that the business has everything it needs to execute the plan effectively.
Read Also: 6 Steps to Create a Strategic HR Plan [With Templates]
As businesses evolve, it’s essential to have a comprehensive and adaptive operational plan in place to navigate the complexities of the business environment. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you craft an effective operational plan:
Step 1: Define your goals and objectives
Begin with a clear understanding of your strategic goals and objectives. This will act as a foundation for your operational plan. Ensure that these goals are in alignment with your company’s strategic plan and provide both short-term and long-term visions for the business.
Step 2: Determine roles and responsibilities
Identify the key stakeholders, department heads and team members who will play pivotal roles in executing the plan. Assign responsibilities to ensure that everyone knows their part in the planning process and day-to-day activities.
Step 3: Develop a timeline and milestones
Establish a clear timeline that breaks down the operational planning process. Include key milestones to track progress and ensure the plan remains on target.
Step 4: Allocate budget and resources
Determine the resources required to achieve your goals and objectives. This includes estimating the operating budget, identifying human resources needs and other resource allocations, ensuring you have everything in place to support revenue growth and other business needs.
Step 5: Outline day-to-day operations
Detail the day activities that are integral to the business operations. This will provide clarity on how different tasks and functions work together, ensuring efficiency across diverse cross-functional teams.
Step 6: Monitor and measure performance
Integrate key performance metrics and indicators to regularly monitor progress. Using both leading and lagging indicators will provide a comprehensive view of how well the operational plan is being executed and where improvements can be made.
Step 7: Review and adjust regularly
The business environment is dynamic and as such, your operational plan should be adaptable. Regularly review the plan, comparing actual outcomes with desired outcomes and adjust as necessary to account for changes in the business environment or company goals.
Step 8: Document and communicate
Create an operational plan document, potentially using operational plan examples or an operational plan template for guidance. Ensure that the entire team, from individual team members to the entire organization, is informed and aligned with the plan.
Related: 7 Best Business Plan Software for 2023
Strategic plan vs operational plan: What is the difference?
When running an organization, both strategic and operational planning play pivotal roles in ensuring success. However, each has a distinct purpose, time horizon and scope. Here’s a breakdown of the differences between these two essential business plans:
- Strategic plan : This plan sets the course for the organization’s future. It embodies the long-term vision and mission, detailing the objectives necessary to achieve it. The essence is how everyone, from C-suite executives to individual team members, collaborates towards realizing this vision.
- Operational plan : This is the roadmap for the day-to-day activities of the organization. While the strategic plan looks at the bigger picture, the operational plan hones in on the tactics and execution. It is crafted to support organizational goals with a focus on short-term activities specific to departments or functions.
Time horizon :
- Strategic plan : Long-term in nature, usually spanning three to five years.
- Operational plan : Concentrates on the short-term, with plans laid out yearly, quarterly, or even monthly.
Modification and updates :
- Strategic plan : This evolves over longer intervals, typically three to five years. There might be minor adjustments year over year based on changing business needs and the external business environment.
- Operational plan : Due to its short-term focus, it requires frequent assessments. Plans might be adjusted yearly, quarterly or even monthly to ensure alignment with the strategic objectives and current business environment.
Created by :
- Strategic plan : Crafted by the upper echelons of management – think CEO, CFO and other C-suite members.
- Operational plan : These plans come to life through mid-level management and department heads, ensuring alignment with the broader strategic vision while catering to specific departmental needs.
- Strategic plan : Broad in its outlook, it takes into account external factors like market trends, competition, customer needs and technological innovations.
- Operational plan : This narrows down the focus to the internal workings of the organization. It revolves around technology in use, key performance indicators, budgeting, projects, tasks and the allocation of responsibilities among team members.
As we’ve traversed through the importance of operational planning to various operational plan examples, it becomes evident that having a detailed and efficient operational plan is pivotal.
From the business-centric to the minimalist approach, every operational plan serves as the backbone, guiding team members and ensuring that day-to-day activities align with the long-term vision and strategic goals.
By knowing what should be included in these plans and how to craft them, businesses can navigate the complexities of their operational environment with greater confidence.
For those looking to refine their planning process or start from scratch, the world of digital tools has made it significantly easier. Venngage offers business plan maker and operational plan templates designed to simplify the process.
Whether you need to create an operational plan or draft a business strategy, their intuitive platform can guide you every step of the way.
Discover popular designs

Infographic maker

Brochure maker

White paper online

Newsletter creator

Flyer maker

Timeline maker

Letterhead maker

Mind map maker

Ebook maker

How To Write the Operations Plan Section of Your Business Plan + Example
Written by Dave Lavinsky

Operational plans are important for any effective business plan . They provide a roadmap for how your company will operate on a day-to-day basis, and specifically detail the specific strategies and actions you will take to accomplish your company’s goals.
What is the Operations Plan in the Business Plan?
The Operations Plan is one of the critical business plan components to include in your plan as it presents your company’s action plan for executing its long-term vision. Your business operations plan must detail:
- The processes that are performed to serve customers every day (short-term processes) and
- The overall business milestones that the company must attain to be successful (long-term processes).
Why Your Operations Plan is Important
Anyone can have lofty goals (e.g., we will reach $X million in revenue in year X). The Operations Plan proves to the reader that you have thought through and devised a plan to achieve your goals.
What to Include in Your Operations Plan
The operations section of your business plan has two sub-sections: Key Operational Processes and Business Milestones.
Key Operational Processes (Short-Term Processes)
Every company has processes to provide its customers with products and services. For instance, Wal-Mart has a unique distribution system to effectively move products from its warehouses to its stores, and finally to its customers’ homes. Technology product manufacturers have processes to convert raw materials into finished products. And service-oriented businesses have processes to serve clients, to identify prospective new clients, to continually update service features, etc.
Below are key operational functions that your organization may need to fulfill. In your plan, identify each of these areas that are relevant to your company and what the role of that function is. For example, our customer service team will ensure our customers are satisfied. We will provide 24/7 customer service and post product updates on social media each week.
- Product Development
- Customer Service
- Manufacturing
- Administration
- Accounting/Payroll
- Human Resources
The processes that a company uses to serve its customers are what transform a business plan from concept to reality. Anyone can have a concept. Importantly, investors do not invest in concepts; rather, they invest in reality. Reality is proving that your management team can execute the concept better than anyone else, and the Operations Plan is where the plan proves this by detailing key operational processes.
Business Milestones (Long-Term Processes)
The second part of your Operations Plan is showing your team’s expected timeline to achieving key milestones. This is best presented in a chart. On the left side, there should be a list of the key milestones the company must reach, and on the right, the target date for achieving them. Sample operational milestones include expected dates when:
- New products and services will be introduced
- New stores will open
- Revenue milestones will be achieved (date when sales exceed $X, when sales exceed $Y, etc.)
- Key partnerships will be executed
- Key customer contracts will be secured
- Key financial events (future funding rounds, IPO, etc.) will occur
- Key employee hires will happen
Additional text should be used, where necessary, to support the projections laid out in the chart.
The milestone projections presented in the Operations Plan must be consistent with the projections in your Financial Plan. In both sections, it is important to be aggressive but credible. Presenting a plan in which the company grows too quickly will show the naivete of the management team while presenting too conservative a growth plan will often fail to excite the potential investor or lender.
By including your Operation Strategy in your business plan you a) show investors/lenders you have a real plan for executing your vision upon funding and b) have a roadmap to follow to ensure your long-term success.
Operations Plan in Business Plan Example
The following operational plan example outlines a hypothetical plan for a small consulting firm, XYZ Company. The plan details the resources required, key operational processes, performance indicators, and milestones to guide the company’s growth and success. This example can be adapted to fit the specific needs and goals of various businesses.
Resource Requirements:
- Physical Space: 1,000 square feet of office space
- Equipment: $10,000 for office furniture and equipment
- 3 full-time employees
- 2 part-time employees
- 1 contractor
Key Operational Processes:
- Client Acquisition and Onboarding:
- Process: All new client inquiries will be responded to within 24 hours. Initial consultations will be scheduled within 48 hours of contact. Proposals will be presented within 10 days of the initial consultation.
- Team: John Smith (full-time) and Jane Doe (full-time)
- Project Management and Execution:
- Process: Work will begin within 2 weeks of proposal acceptance. Projects will be managed collaboratively by John Smith and Jane Doe.
- Support Functions:
- Process: Contractor Joe Johnson will provide support as needed.
- Team: Joe Johnson (contractor)
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs):
- Client Acquisition: Number of new clients acquired per month
- Client Satisfaction: Customer satisfaction ratings (e.g., Net Promoter Score)
- Project Completion: Percentage of projects completed on time and within budget
- Operational Efficiency: Average time to complete projects
Milestones:
- Month 1: Secure office space and equipment
- Month 2: Hire key personnel
- Month 3: Launch initial marketing campaign
- Month 6: Acquire first 10 clients
- Year 1: Achieve $X in revenue
Tracking Key Performance Indicators with Operational Planning
As a business owner, it’s important to track your progress against your company goals. This is where KPIs come in. KPIs, or key performance indicators, are an important part of your company’s strategic plan, and help you track progress and identify areas of improvement. You should document your KPIs in the operations plan of your business plan.
Here are a few things to keep in mind when choosing KPIs for your business:
- Make sure that the KPIs you choose are relevant to your company’s goals.
- Choose KPIs that can be easily measured.
- Avoid choosing too many KPIs, as this can be overwhelming. Stick to a few key ones that will give you the most insights into your business’s progress.
- Set realistic targets for each KPI. This will help you track your progress and identify areas of improvement.
- Review your KPIs regularly to ensure that they are still relevant and accurate, while also being in line with strategic plans.
Examples of KPIs that You Could Track with an Operational Plan
Some examples of KPIs that you could track are:
- Sales growth
- Delivery times
- Customer satisfaction ratings
- Product quality
- Production processes
- Employee retention
- Operational costs
Creating an operational plan with KPIs will help you track your progress, identify areas of improvement, improve strategic planning, and make necessary changes to reach your company’s strategic objectives.
Key Takeaways
A few key things to remember when writing your operations plan:
- Describe the resources that will be required to run your business
- Detail the processes and procedures that will be used to get work done
- Identify the people who will be responsible for carrying out various tasks
Following these tips will help you create a comprehensive and effective operations plan for your business.
How to Finish Your Business Plan Template in 1 Day!
Don’t you wish there was a faster, easier way to finish your business plan template?
With Growthink’s Ultimate Business Plan Template you can finish your plan in just 8 hours or less!


IMAGES