- Privacy Policy

Home » Ethical Considerations – Types, Examples and Writing Guide

Ethical Considerations – Types, Examples and Writing Guide
Table of Contents

Ethical Considerations
Ethical considerations in research refer to the principles and guidelines that researchers must follow to ensure that their studies are conducted in an ethical and responsible manner. These considerations are designed to protect the rights, safety, and well-being of research participants, as well as the integrity and credibility of the research itself
Some of the key ethical considerations in research include:
- Informed consent: Researchers must obtain informed consent from study participants, which means they must inform participants about the study’s purpose, procedures, risks, benefits, and their right to withdraw at any time.
- Privacy and confidentiality : Researchers must ensure that participants’ privacy and confidentiality are protected. This means that personal information should be kept confidential and not shared without the participant’s consent.
- Harm reduction : Researchers must ensure that the study does not harm the participants physically or psychologically. They must take steps to minimize the risks associated with the study.
- Fairness and equity : Researchers must ensure that the study does not discriminate against any particular group or individual. They should treat all participants equally and fairly.
- Use of deception: Researchers must use deception only if it is necessary to achieve the study’s objectives. They must inform participants of the deception as soon as possible.
- Use of vulnerable populations : Researchers must be especially cautious when working with vulnerable populations, such as children, pregnant women, prisoners, and individuals with cognitive or intellectual disabilities.
- Conflict of interest : Researchers must disclose any potential conflicts of interest that may affect the study’s integrity. This includes financial or personal relationships that could influence the study’s results.
- Data manipulation: Researchers must not manipulate data to support a particular hypothesis or agenda. They should report the results of the study objectively, even if the findings are not consistent with their expectations.
- Intellectual property: Researchers must respect intellectual property rights and give credit to previous studies and research.
- Cultural sensitivity : Researchers must be sensitive to the cultural norms and beliefs of the participants. They should avoid imposing their values and beliefs on the participants and should be respectful of their cultural practices.
Types of Ethical Considerations
Types of Ethical Considerations are as follows:
Research Ethics:
This includes ethical principles and guidelines that govern research involving human or animal subjects, ensuring that the research is conducted in an ethical and responsible manner.
Business Ethics :
This refers to ethical principles and standards that guide business practices and decision-making, such as transparency, honesty, fairness, and social responsibility.
Medical Ethics :
This refers to ethical principles and standards that govern the practice of medicine, including the duty to protect patient autonomy, informed consent, confidentiality, and non-maleficence.
Environmental Ethics :
This involves ethical principles and values that guide our interactions with the natural world, including the obligation to protect the environment, minimize harm, and promote sustainability.
Legal Ethics
This involves ethical principles and standards that guide the conduct of legal professionals, including issues such as confidentiality, conflicts of interest, and professional competence.
Social Ethics
This involves ethical principles and values that guide our interactions with other individuals and society as a whole, including issues such as justice, fairness, and human rights.
Information Ethics
This involves ethical principles and values that govern the use and dissemination of information, including issues such as privacy, accuracy, and intellectual property.
Cultural Ethics
This involves ethical principles and values that govern the relationship between different cultures and communities, including issues such as respect for diversity, cultural sensitivity, and inclusivity.
Technological Ethics
This refers to ethical principles and guidelines that govern the development, use, and impact of technology, including issues such as privacy, security, and social responsibility.
Journalism Ethics
This involves ethical principles and standards that guide the practice of journalism, including issues such as accuracy, fairness, and the public interest.
Educational Ethics
This refers to ethical principles and standards that guide the practice of education, including issues such as academic integrity, fairness, and respect for diversity.
Political Ethics
This involves ethical principles and values that guide political decision-making and behavior, including issues such as accountability, transparency, and the protection of civil liberties.
Professional Ethics
This refers to ethical principles and standards that guide the conduct of professionals in various fields, including issues such as honesty, integrity, and competence.
Personal Ethics
This involves ethical principles and values that guide individual behavior and decision-making, including issues such as personal responsibility, honesty, and respect for others.
Global Ethics
This involves ethical principles and values that guide our interactions with other nations and the global community, including issues such as human rights, environmental protection, and social justice.
Applications of Ethical Considerations
Ethical considerations are important in many areas of society, including medicine, business, law, and technology. Here are some specific applications of ethical considerations:
- Medical research : Ethical considerations are crucial in medical research, particularly when human subjects are involved. Researchers must ensure that their studies are conducted in a way that does not harm participants and that participants give informed consent before participating.
- Business practices: Ethical considerations are also important in business, where companies must make decisions that are socially responsible and avoid activities that are harmful to society. For example, companies must ensure that their products are safe for consumers and that they do not engage in exploitative labor practices.
- Environmental protection: Ethical considerations play a crucial role in environmental protection, as companies and governments must weigh the benefits of economic development against the potential harm to the environment. Decisions about land use, resource allocation, and pollution must be made in an ethical manner that takes into account the long-term consequences for the planet and future generations.
- Technology development : As technology continues to advance rapidly, ethical considerations become increasingly important in areas such as artificial intelligence, robotics, and genetic engineering. Developers must ensure that their creations do not harm humans or the environment and that they are developed in a way that is fair and equitable.
- Legal system : The legal system relies on ethical considerations to ensure that justice is served and that individuals are treated fairly. Lawyers and judges must abide by ethical standards to maintain the integrity of the legal system and to protect the rights of all individuals involved.
Examples of Ethical Considerations
Here are a few examples of ethical considerations in different contexts:
- In healthcare : A doctor must ensure that they provide the best possible care to their patients and avoid causing them harm. They must respect the autonomy of their patients, and obtain informed consent before administering any treatment or procedure. They must also ensure that they maintain patient confidentiality and avoid any conflicts of interest.
- In the workplace: An employer must ensure that they treat their employees fairly and with respect, provide them with a safe working environment, and pay them a fair wage. They must also avoid any discrimination based on race, gender, religion, or any other characteristic protected by law.
- In the media : Journalists must ensure that they report the news accurately and without bias. They must respect the privacy of individuals and avoid causing harm or distress. They must also be transparent about their sources and avoid any conflicts of interest.
- In research: Researchers must ensure that they conduct their studies ethically and with integrity. They must obtain informed consent from participants, protect their privacy, and avoid any harm or discomfort. They must also ensure that their findings are reported accurately and without bias.
- In personal relationships : People must ensure that they treat others with respect and kindness, and avoid causing harm or distress. They must respect the autonomy of others and avoid any actions that would be considered unethical, such as lying or cheating. They must also respect the confidentiality of others and maintain their privacy.
How to Write Ethical Considerations
When writing about research involving human subjects or animals, it is essential to include ethical considerations to ensure that the study is conducted in a manner that is morally responsible and in accordance with professional standards. Here are some steps to help you write ethical considerations:
- Describe the ethical principles: Start by explaining the ethical principles that will guide the research. These could include principles such as respect for persons, beneficence, and justice.
- Discuss informed consent : Informed consent is a critical ethical consideration when conducting research. Explain how you will obtain informed consent from participants, including how you will explain the purpose of the study, potential risks and benefits, and how you will protect their privacy.
- Address confidentiality : Describe how you will protect the confidentiality of the participants’ personal information and data, including any measures you will take to ensure that the data is kept secure and confidential.
- Consider potential risks and benefits : Describe any potential risks or harms to participants that could result from the study and how you will minimize those risks. Also, discuss the potential benefits of the study, both to the participants and to society.
- Discuss the use of animals : If the research involves the use of animals, address the ethical considerations related to animal welfare. Explain how you will minimize any potential harm to the animals and ensure that they are treated ethically.
- Mention the ethical approval : Finally, it’s essential to acknowledge that the research has received ethical approval from the relevant institutional review board or ethics committee. State the name of the committee, the date of approval, and any specific conditions or requirements that were imposed.
When to Write Ethical Considerations
Ethical considerations should be written whenever research involves human subjects or has the potential to impact human beings, animals, or the environment in some way. Ethical considerations are also important when research involves sensitive topics, such as mental health, sexuality, or religion.
In general, ethical considerations should be an integral part of any research project, regardless of the field or subject matter. This means that they should be considered at every stage of the research process, from the initial planning and design phase to data collection, analysis, and dissemination.
Ethical considerations should also be written in accordance with the guidelines and standards set by the relevant regulatory bodies and professional associations. These guidelines may vary depending on the discipline, so it is important to be familiar with the specific requirements of your field.
Purpose of Ethical Considerations
Ethical considerations are an essential aspect of many areas of life, including business, healthcare, research, and social interactions. The primary purposes of ethical considerations are:
- Protection of human rights: Ethical considerations help ensure that people’s rights are respected and protected. This includes respecting their autonomy, ensuring their privacy is respected, and ensuring that they are not subjected to harm or exploitation.
- Promoting fairness and justice: Ethical considerations help ensure that people are treated fairly and justly, without discrimination or bias. This includes ensuring that everyone has equal access to resources and opportunities, and that decisions are made based on merit rather than personal biases or prejudices.
- Promoting honesty and transparency : Ethical considerations help ensure that people are truthful and transparent in their actions and decisions. This includes being open and honest about conflicts of interest, disclosing potential risks, and communicating clearly with others.
- Maintaining public trust: Ethical considerations help maintain public trust in institutions and individuals. This is important for building and maintaining relationships with customers, patients, colleagues, and other stakeholders.
- Ensuring responsible conduct: Ethical considerations help ensure that people act responsibly and are accountable for their actions. This includes adhering to professional standards and codes of conduct, following laws and regulations, and avoiding behaviors that could harm others or damage the environment.
Advantages of Ethical Considerations
Here are some of the advantages of ethical considerations:
- Builds Trust : When individuals or organizations follow ethical considerations, it creates a sense of trust among stakeholders, including customers, clients, and employees. This trust can lead to stronger relationships and long-term loyalty.
- Reputation and Brand Image : Ethical considerations are often linked to a company’s brand image and reputation. By following ethical practices, a company can establish a positive image and reputation that can enhance its brand value.
- Avoids Legal Issues: Ethical considerations can help individuals and organizations avoid legal issues and penalties. By adhering to ethical principles, companies can reduce the risk of facing lawsuits, regulatory investigations, and fines.
- Increases Employee Retention and Motivation: Employees tend to be more satisfied and motivated when they work for an organization that values ethics. Companies that prioritize ethical considerations tend to have higher employee retention rates, leading to lower recruitment costs.
- Enhances Decision-making: Ethical considerations help individuals and organizations make better decisions. By considering the ethical implications of their actions, decision-makers can evaluate the potential consequences and choose the best course of action.
- Positive Impact on Society: Ethical considerations have a positive impact on society as a whole. By following ethical practices, companies can contribute to social and environmental causes, leading to a more sustainable and equitable society.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Research Paper Introduction – Writing Guide and...

Institutional Review Board – Application Sample...

Research Paper Title – Writing Guide and Example

Research Approach – Types Methods and Examples

Thesis Statement – Examples, Writing Guide

APA Table of Contents – Format and Example
- The Open University
- Accessibility hub
- Guest user / Sign out
- Study with The Open University
My OpenLearn Profile
Personalise your OpenLearn profile, save your favourite content and get recognition for your learning

Addressing ethical issues in your research proposal
This article explores the ethical issues that may arise in your proposed study during your doctoral research degree.
What ethical principles apply when planning and conducting research?
Research ethics are the moral principles that govern how researchers conduct their studies (Wellcome Trust, 2014). As there are elements of uncertainty and risk involved in any study, every researcher has to consider how they can uphold these ethical principles and conduct the research in a way that protects the interests and welfare of participants and other stakeholders (such as organisations).
You will need to consider the ethical issues that might arise in your proposed study. Consideration of the fundamental ethical principles that underpin all research will help you to identify the key issues and how these could be addressed. As you are probably a practitioner who wants to undertake research within your workplace, consider how your role as an ‘insider’ influences how you will conduct your study. Think about the ethical issues that might arise when you become an insider researcher (for example, relating to trust, confidentiality and anonymity).
What key ethical principles do you think will be important when planning or conducting your research, particularly as an insider? Principles that come to mind might include autonomy, respect, dignity, privacy, informed consent and confidentiality. You may also have identified principles such as competence, integrity, wellbeing, justice and non-discrimination.
Key ethical issues that you will address as an insider researcher include:
- Gaining trust
- Avoiding coercion when recruiting colleagues or other participants (such as students or service users)
- Practical challenges relating to ensuring the confidentiality and anonymity of organisations and staff or other participants.
(Heslop et al, 2018)
A fuller discussion of ethical principles is available from the British Psychological Society’s Code of Human Research Ethics (BPS, 2021).
You can also refer to guidance from the British Educational Research Association and the British Association for Applied Linguistics .

Ethical principles are essential for protecting the interests of research participants, including maximising the benefits and minimising any risks associated with taking part in a study. These principles describe ethical conduct which reflects the integrity of the researcher, promotes the wellbeing of participants and ensures high-quality research is conducted (Health Research Authority, 2022).
Research ethics is therefore not simply about gaining ethical approval for your study to be conducted. Research ethics relates to your moral conduct as a doctoral researcher and will apply throughout your study from design to dissemination (British Psychological Society, 2021). When you apply to undertake a doctorate, you will need to clearly indicate in your proposal that you understand these ethical principles and are committed to upholding them.
Where can I find ethical guidance and resources?
Professional bodies, learned societies, health and social care authorities, academic publications, Research Ethics Committees and research organisations provide a range of ethical guidance and resources. International codes such as the Universal Declaration of Human Rights underpin ethical frameworks (United Nations, 1948).
You may be aware of key legislation in your own country or the country where you plan to undertake the research, including laws relating to consent, data protection and decision-making capacity, for example, the Data Protection Act, 2018 (UK). If you want to find out more about becoming an ethical researcher, check out this Open University short course: Becoming an ethical researcher: Introduction and guidance: What is a badged course? - OpenLearn - Open University
You should be able to justify the research decisions you make. Utilising these resources will guide your ethical judgements when writing your proposal and ultimately when designing and conducting your research study. The Ethical Guidelines for Educational Research (British Educational Research Association, 2018) identifies the key responsibilities you will have when you conduct your research, including the range of stakeholders that you will have responsibilities to, as follows:
- to your participants (e.g. to appropriately inform them, facilitate their participation and support them)
- clients, stakeholders and sponsors
- the community of educational or health and social care researchers
- for publication and dissemination
- your wellbeing and development
The National Institute for Health and Care Research (no date) has emphasised the need to promote equality, diversity and inclusion when undertaking research, particularly to address long-standing social and health inequalities. Research should be informed by the diversity of people’s experiences and insights, so that it will lead to the development of practice that addresses genuine need. A commitment to equality, diversity and inclusion aims to eradicate prejudice and discrimination on the basis of an individual or group of individuals' protected characteristics such as sex (gender), disability, race, sexual orientation, in line with the Equality Act 2010.
The NIHR has produced guidance for enhancing the inclusion of ‘under-served groups’ when designing a research study (2020). Although the guidance refers to clinical research it is relevant to research more broadly.
You should consider how you will promote equality and diversity in your planned study, including through aspects such as your research topic or question, the methodology you will use, the participants you plan to recruit and how you will analyse and interpret your data.
What ethical issues do I need to consider when writing my research proposal?

You might be planning to undertake research in a health, social care, educational or other setting, including observations and interviews. The following prompts should help you to identify key ethical issues that you need to bear in mind when undertaking research in such settings.
1. Imagine you are a potential participant. Think about the questions and concerns that you might have:
- How would you feel if a researcher sat in your space and took notes, completed a checklist, or made an audio or film recording?
- What harm might a researcher cause by observing or interviewing you and others?
- What would you want to know about the researcher and ask them about the study before giving consent?
- When imagining you are the participant, how could the researcher make you feel more comfortable to be observed or interviewed?
2. Having considered the perspective of your potential participant, how would you take account of concerns such as privacy, consent, wellbeing and power in your research proposal?
[Adapted from OpenLearn course: Becoming an ethical researcher, Week 2 Activity 3: Becoming an ethical researcher - OpenLearn - Open University ]
The ethical issues to be considered will vary depending on your organisational context/role, the types of participants you plan to recruit (for example, children, adults with mental health problems), the research methods you will use, and the types of data you will collect. You will need to decide how to recruit your participants so you do not inappropriately exclude anyone. Consider what methods may be necessary to facilitate their voice and how you can obtain their consent to taking part or ensure that consent is obtained from someone else as necessary, for example, a parent in the case of a child.
You should also think about how to avoid imposing an unnecessary burden or costs on your participants. For example, by minimising the length of time they will have to commit to the study and by providing travel or other expenses. Identify the measures that you will take to store your participants’ data safely and maintain their confidentiality and anonymity when you report your findings. You could do this by storing interview and video recordings in a secure server and anonymising their names and those of their organisations using pseudonyms.
Professional codes such as the Code of Human Research Ethics (BPS, 2021) provide guidance on undertaking research with children. Being an ‘insider’ researching within your own organisation has advantages. However, you should also consider how this might impact on your research, such as power dynamics, consent, potential bias and any conflict of interest between your professional and researcher roles (Sapiro and Matthews, 2020).
How have other researchers addressed any ethical challenges?
The literature provides researchers’ accounts explaining how they addressed ethical challenges when undertaking studies. For example, Turcotte-Tremblay and McSween-Cadieux (2018) discuss strategies for protecting participants’ confidentiality when disseminating findings locally, such as undertaking fieldwork in multiple sites and providing findings in a generalised form. In addition, professional guidance includes case studies illustrating how ethical issues can be addressed, including when researching online forums (British Sociological Association, no date).
Watch the videos below and consider what insights the postgraduate researcher and supervisor provide regarding issues such as being an ‘insider researcher’, power relations, avoiding intrusion, maintaining participant anonymity and complying with research ethics and professional standards. How might their experiences inform the design and conduct of your own study?
Postgraduate researcher and supervisor talk about ethical considerations
Your thoughtful consideration of the ethical issues that might arise and how you would address these should enable you to propose an ethically informed study and conduct it in a responsible, fair and sensitive manner.
British Educational Research Association (2018) Ethical Guidelines for Educational Research. Available at: https://www.bera.ac.uk/publication/ethical-guidelines-for-educational-research-2018 (Accessed: 9 June 2023).
British Psychological Society (2021) Code of Human Research Ethics . Available at: https://cms.bps.org.uk/sites/default/files/2022-06/BPS%20Code%20of%20Human%20Research%20Ethics%20%281%29.pdf (Accessed: 9 June 2023).
British Sociological Association (2016) Researching online forums . Available at: https://www.britsoc.co.uk/media/24834/j000208_researching_online_forums_-cs1-_v3.pdf (Accessed: 9 June 2023).
Health Research Authority (2022) UK Policy Framework for Health and Social Care Research . Available at: https://www.hra.nhs.uk/planning-and-improving-research/policies-standards-legislation/uk-policy-framework-health-social-care-research/uk-policy-framework-health-and-social-care-research/#chiefinvestigators (Accessed: 9 June 2023).
Heslop, C., Burns, S., Lobo, R. (2018) ‘Managing qualitative research as insider-research in small rural communities’, Rural and Remote Health , 18: pp. 4576.
Equality Act 2010, c. 15. Available at: https://www.legislation.gov.uk/ukpga/2010/15/introduction (Accessed: 9 June 2023).
National Institute for Health and Care Research (no date) Equality, Diversity and Inclusion (EDI) . Available at: https://arc-kss.nihr.ac.uk/public-and-community-involvement/pcie-guide/how-to-do-pcie/equality-diversity-and-inclusion-edi (Accessed: 9 June 2023).
National Institute for Health and Care Research (2020) Improving inclusion of under-served groups in clinical research: Guidance from INCLUDE project. Available at: https://www.nihr.ac.uk/documents/improving-inclusion-of-under-served-groups-in-clinical-research-guidance-from-include-project/25435 (Accessed: 9 June 2023).
Sapiro, B. and Matthews, E. (2020) ‘Both Insider and Outsider. On Conducting Social Work Research in Mental Health Settings’, Advances in Social Work , 20(3). Available at: https://doi.org/10.18060/23926
Turcotte-Tremblay, A. and McSween-Cadieux, E. (2018) ‘A reflection on the challenge of protecting confidentiality of participants when disseminating research results locally’, BMC Medical Ethics, 19(supplement 1), no. 45. Available at: https://bmcmedethics.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12910-018-0279-0
United Nations General Assembly (1948) The Universal Declaration of Human Rights . Resolution A/RES/217/A. Available at: https://www.un.org/en/about-us/universal-declaration-of-human-rights#:~:text=Drafted%20by%20representatives%20with%20different,all%20peoples%20and%20all%20nations . (Accessed: 9 June 2023).
Wellcome Trust (2014) Ensuring your research is ethical: A guide for Extended Project Qualification students . Available at: https://wellcome.org/sites/default/files/wtp057673_0.pdf (Accessed: 9 June 2023).
More articles from the research proposal collection

Writing your research proposal
A doctoral research degree is the highest academic qualification that a student can achieve. The guidance provided in these articles will help you apply for one of the two main types of research degree offered by The Open University.
Level: 1 Introductory

Defining your research methodology
Your research methodology is the approach you will take to guide your research process and explain why you use particular methods. This article explains more.

Writing your proposal and preparing for your interview
The final article looks at writing your research proposal - from the introduction through to citations and referencing - as well as preparing for your interview.
Free courses on postgraduate study

Are you ready for postgraduate study?
This free course, Are you ready for postgraduate study, will help you to become familiar with the requirements and demands of postgraduate study and ensure you are ready to develop the skills and confidence to pursue your learning further.

Succeeding in postgraduate study
This free course, Succeeding in postgraduate study, will help you to become familiar with the requirements and demands of postgraduate study and to develop the skills and confidence to pursue your learning further.

Applying to study for a PhD in psychology
This free OpenLearn course is for psychology students and graduates who are interested in PhD study at some future point. Even if you have met PhD students and heard about their projects, it is likely that you have only a vague idea of what PhD study entails. This course is intended to give you more information.
Become an OU student
Ratings & comments, share this free course, copyright information, publication details.
- Originally published: Tuesday, 27 June 2023
- Body text - Creative Commons BY-NC-SA 4.0 : The Open University
- Image 'Pebbles balance on a stone see-saw' - Copyright: Photo 51106733 / Balance © Anatoli Styf | Dreamstime.com
- Image 'Camera equipment set up filming a man talking' - Copyright: Photo 42631221 © Gabriel Robledo | Dreamstime.com
- Image 'Succeeding in postgraduate study' - Copyright: © Everste/Getty Images
- Image 'Applying to study for a PhD in psychology' - Copyright free
- Image 'Writing your research proposal' - Copyright free
- Image 'Defining your research methodology' - Copyright free
- Image 'Writing your proposal and preparing for your interview' - Copyright: Photo 133038259 / Black Student © Fizkes | Dreamstime.com
- Image 'Addressing ethical issues in your research proposal' - Copyright: Photo 50384175 / Children Playing © Lenutaidi | Dreamstime.com
- Image 'Are you ready for postgraduate study?' - Copyright free
Rate and Review
Rate this article, review this article.
Log into OpenLearn to leave reviews and join in the conversation.
Article reviews
For further information, take a look at our frequently asked questions which may give you the support you need.

Research Ethics & Ethical Considerations
A Plain-Language Explainer With Examples
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Reviewers: Dr Eunice Rautenbach | May 2024
Research ethics are one of those “ unsexy but essential ” subjects that you need to fully understand (and apply) to conquer your dissertation, thesis or research paper. In this post, we’ll unpack research ethics using plain language and loads of examples .
Overview: Research Ethics 101
- What are research ethics?
- Why should you care?
- Research ethics principles
- Respect for persons
- Beneficence
- Objectivity
- Key takeaways
What (exactly) are research ethics?
At the simplest level, research ethics are a set of principles that ensure that your study is conducted responsibly, safely, and with integrity. More specifically, research ethics help protect the rights and welfare of your research participants, while also ensuring the credibility of your research findings.
Research ethics are critically important for a number of reasons:
Firstly, they’re a complete non-negotiable when it comes to getting your research proposal approved. Pretty much all universities will have a set of ethical criteria that student projects need to adhere to – and these are typically very strictly enforced. So, if your proposed study doesn’t tick the necessary ethical boxes, it won’t be approved .
Beyond the practical aspect of approval, research ethics are essential as they ensure that your study’s participants (whether human or animal) are properly protected . In turn, this fosters trust between you and your participants – as well as trust between researchers and the public more generally. As you can probably imagine, it wouldn’t be good if the general public had a negative perception of researchers!
Last but not least, research ethics help ensure that your study’s results are valid and reliable . In other words, that you measured the thing you intended to measure – and that other researchers can repeat your study. If you’re not familiar with the concepts of reliability and validity , we’ve got a straightforward explainer video covering that below.
The Core Principles
In practical terms, each university or institution will have its own ethics policy – so, what exactly constitutes “ethical research” will vary somewhat between institutions and countries. Nevertheless, there are a handful of core principles that shape ethics policies. These principles include:
Let’s unpack each of these to make them a little more tangible.
Ethics Principle 1: Respect for persons
As the name suggests, this principle is all about ensuring that your participants are treated fairly and respectfully . In practical terms, this means informed consent – in other words, participants should be fully informed about the nature of the research, as well as any potential risks. Additionally, they should be able to withdraw from the study at any time. This is especially important when you’re dealing with vulnerable populations – for example, children, the elderly or people with cognitive disabilities.
Another dimension of the “respect for persons” principle is confidentiality and data protection . In other words, your participants’ personal information should be kept strictly confidential and secure at all times. Depending on the specifics of your project, this might also involve anonymising or masking people’s identities. As mentioned earlier, the exact requirements will vary between universities, so be sure to thoroughly review your institution’s ethics policy before you start designing your project.
Need a helping hand?
Ethics Principle 2: Beneficence
This principle is a little more opaque, but in simple terms beneficence means that you, as the researcher, should aim to maximise the benefits of your work, while minimising any potential harm to your participants.
In practical terms, benefits could include advancing knowledge, improving health outcomes, or providing educational value. Conversely, potential harms could include:
- Physical harm from accidents or injuries
- Psychological harm, such as stress or embarrassment
- Social harm, such as stigmatisation or loss of reputation
- Economic harm – in other words, financial costs or lost income
Simply put, the beneficence principle means that researchers must always try to identify potential risks and take suitable measures to reduce or eliminate them.

Ethics Principle 3: Objectivity
As you can probably guess, this principle is all about attempting to minimise research bias to the greatest degree possible. In other words, you’ll need to reduce subjectivity and increase objectivity wherever possible.
In practical terms, this principle has the largest impact on the methodology of your study – specifically the data collection and data analysis aspects. For example, you’ll need to ensure that the selection of your participants (in other words, your sampling strategy ) is aligned with your research aims – and that your sample isn’t skewed in a way that supports your presuppositions.
If you’re keen to learn more about research bias and the various ways in which you could unintentionally skew your results, check out the video below.
Ethics Principle 4: Integrity
Again, no surprises here; this principle is all about producing “honest work” . It goes without saying that researchers should always conduct their work honestly and transparently, report their findings accurately, and disclose any potential conflicts of interest upfront.
This is all pretty obvious, but another aspect of the integrity principle that’s sometimes overlooked is respect for intellectual property . In practical terms, this means you need to honour any patents, copyrights, or other forms of intellectual property that you utilise while undertaking your research. Along the same vein, you shouldn’t use any unpublished data, methods, or results without explicit, written permission from the respective owner.
Linked to all of this is the broader issue of plagiarism . Needless to say, if you’re drawing on someone else’s published work, be sure to cite your sources, in the correct format. To make life easier, use a reference manager such as Mendeley or Zotero to ensure that your citations and reference list are perfectly polished.
FAQs: Research Ethics
Research ethics & ethical considertation, what is informed consent.
Informed consent simply means providing your potential participants with all necessary information about the study. This should include information regarding the study’s purpose, procedures, risks, and benefits. This information allows your potential participants to make a voluntary and informed decision about whether to participate.
How should I obtain consent from non-English speaking participants?
What about animals.
When conducting research with animals, ensure you adhere to ethical guidelines for the humane treatment of animals. Again, the exact requirements here will vary between institutions, but typically include minimising pain and distress, using alternatives where possible, and obtaining approval from an animal care and use committee.
What is the role of the ERB or IRB?
An ethics review board (ERB) or institutional review board (IRB) evaluates research proposals to ensure they meet ethical standards. The board reviews study designs, consent forms, and data handling procedures, to protect participants’ welfare and rights.
How can I obtain ethical approval for my project?
This varies between universities, but you will typically need to submit a detailed research proposal to your institution’s ethics committee. This proposal should include your research objectives, methods, and how you plan to address ethical considerations like informed consent, confidentiality, and risk minimisation. You can learn more about how to write a proposal here .
How do I ensure ethical collaboration when working with colleagues?
Collaborative research should be conducted with mutual respect and clear agreements on roles, contributions, and publication credits. Open communication is key to preventing conflicts and misunderstandings. Also, be sure to check whether your university has any specific requirements with regards to collaborative efforts and division of labour.
How should I address ethical concerns relating to my funding source?
Key takeaways: research ethics 101.
Here’s a quick recap of the key points we’ve covered:
- Research ethics are a set of principles that ensure that your study is conducted responsibly.
- It’s essential that you design your study around these principles, or it simply won’t get approved.
- The four ethics principles we looked at are: respect for persons, beneficence, objectivity and integrity
As mentioned, the exact requirements will vary slightly depending on the institution and country, so be sure to thoroughly review your university’s research ethics policy before you start developing your study.

Psst... there’s more!
This post was based on one of our popular Research Bootcamps . If you're working on a research project, you'll definitely want to check this out ...
Great piece!!!
Looking forward to know more about ethics in research.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly


What Are the Ethical Considerations in Research Design?
When I began my work on the thesis I was always focused on my research. However, once I began to make my way through research, I realized that research ethics is a core aspect of the research work and the foundation of research design.
Research ethics play a crucial role in ensuring the responsible conduct of research. Here are some key reasons why research ethics matter:

Let us look into some of the major ethical considerations in research design.
Ethical Issues in Research
There are many organizations, like the Committee on Publication Ethics , dedicated to promoting ethics in scientific research. These organizations agree that ethics is not an afterthought or side note to the research study. It is an integral aspect of research that needs to remain at the forefront of our work.
The research design must address specific research questions. Hence, the conclusions of the study must correlate to the questions posed and the results. Also, research ethics demands that the methods used must relate specifically to the research questions.
Voluntary Participation and Consent
An individual should at no point feel any coercion to participate in a study. This includes any type of persuasion or deception in attempting to gain an individual’s trust.
Informed consent states that an individual must give their explicit consent to participate in the study. You can think of consent form as an agreement of trust between the researcher and the participants.
Sampling is the first step in research design . You will need to explain why you want a particular group of participants. You will have to explain why you left out certain people or groups. In addition, if your sample includes children or special needs individuals, you will have additional requirements to address like parental permission.
Confidentiality
The third ethics principle of the Economic and Social Research Council (ESRC) states that: “The confidentiality of the information supplied by research subjects and the anonymity of respondents must be respected.” However, sometimes confidentiality is limited. For example, if a participant is at risk of harm, we must protect them. This might require releasing confidential information.
Risk of Harm
We should do everything in our power to protect study participants. For this, we should focus on the risk to benefit ratio. If possible risks outweigh the benefits, then we should abandon or redesign the study. Risk of harm also requires us to measure the risk to benefit ratio as the study progresses.
Research Methods
We know there are numerous research methods. However, when it comes to ethical considerations, some key questions can help us find the right approach for our studies.
i. Which methods most effectively fit the aims of your research?
ii. What are the strengths and restrictions of a particular method?
iii. Are there potential risks when using a particular research method?
For more guidance, you can refer to the ESRC Framework for Research Ethics .
Ethical issues in research can arise at various stages of the research process and involve different aspects of the study. Here are some common examples of ethical issues in research:
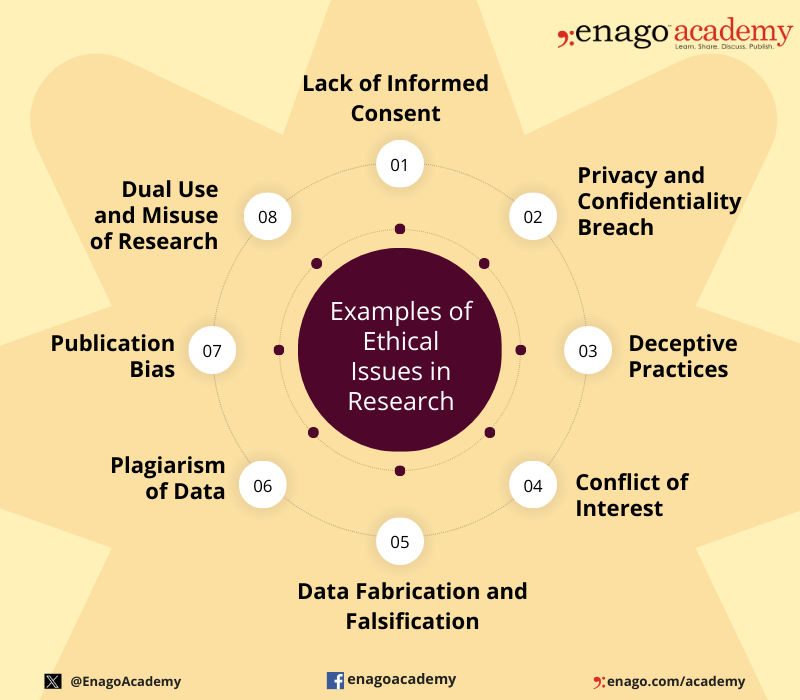
Institutional Review Boards
The importance of ethics in research cannot be understated. Following ethical guidelines will ensure your study’s validity and promote its contribution to scientific study. On a personal level, you will strengthen your research and increase your opportunities to gain funding.
To address the need for ethical considerations, most institutions have their own Institutional Review Board (IRB). An IRB secures the safety of human participants and prevents violation of human rights. It reviews the research aims and methodologies to ensure ethical practices are followed. If a research design does not follow the set ethical guidelines, then the researcher will have to amend their study.
Applying for Ethical Approval
Applications for ethical approval will differ across institutions. Regardless, they focus on the benefits of your research and the risk to benefit ratio concerning participants. Therefore, you need to effectively address both in order to get ethical clearence.
Participants
It is vital that you make it clear that individuals are provided with sufficient information in order to make an informed decision on their participation. In addition, you need to demonstrate that the ethical issues of consent, risk of harm, and confidentiality are clearly defined.
Benefits of the Study
You need to prove to the panel that your work is essential and will yield results that contribute to the scientific community. For this, you should demonstrate the following:
i. The conduct of research guarantees the quality and integrity of results.
ii. The research will be properly distributed.
iii. The aims of the research are clear and the methodology is appropriate.
Integrity and transparency are vital in the research. Ethics committees expect you to share any actual or potential conflicts of interest that could affect your work. In addition, you have to be honest and transparent throughout the approval process and the research process.
The Dangers of Unethical Practices
There is a reason to follow ethical guidelines. Without these guidelines, our research will suffer. Moreover, more importantly, people could suffer.
The following are just two examples of infamous cases of unethical research practices that demonstrate the importance of adhering to ethical standards:
- The Stanford Prison Experiment (1971) aimed to investigate the psychological effects of power using the relationship between prisoners and prison officers. Those assigned the role of “prison officers” embraced measures that exposed “prisoners” to psychological and physical harm. In this case, there was voluntary participation. However, there was disregard for welfare of the participants.
- Recently, Chinese scientist He Jiankui announced his work on genetically edited babies . Over 100 Chinese scientists denounced this research, calling it “crazy” and “shocking and unacceptable.” This research shows a troubling attitude of “do first, debate later” and a disregard for the ethical concerns of manipulating the human body Wang Yuedan, a professor of immunology at Peking University, calls this “an ethics disaster for the world” and demands strict punishments for this type of ethics violation.
What are your experiences with research ethics? How have you developed an ethical approach to research design? Please share your thoughts with us in the comments section below.
I love the articulation of reasoning and practical examples of unethical research
Rate this article Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published.

Enago Academy's Most Popular Articles

- AI in Academia
- Trending Now
6 Leading AI Detection Tools for Academic Writing — A comparative analysis
The advent of AI content generators, exemplified by advanced models like ChatGPT, Claude AI, and…

- Reporting Research
Choosing the Right Analytical Approach: Thematic analysis vs. content analysis for data interpretation
In research, choosing the right approach to understand data is crucial for deriving meaningful insights.…

- Industry News
China’s Ministry of Education Spearheads Efforts to Uphold Academic Integrity
In response to the increase in retractions of research papers submitted by Chinese scholars to…

Comparing Cross Sectional and Longitudinal Studies: 5 steps for choosing the right approach
The process of choosing the right research design can put ourselves at the crossroads of…

- Publishing Research
- Understanding Ethics
Understanding the Difference Between Research Ethics and Compliance
Ethics refers to the principles, values, and moral guidelines that guide individual or group behavior…
Unlocking the Power of Networking in Academic Conferences
Avoiding the AI Trap: Pitfalls of relying on ChatGPT for PhD applications
10 Ways to Help Students Restore Focus on Learning
Switching Your Major As a Researcher: Things to Consider Before Making the Decision

Sign-up to read more
Subscribe for free to get unrestricted access to all our resources on research writing and academic publishing including:
- 2000+ blog articles
- 50+ Webinars
- 10+ Expert podcasts
- 50+ Infographics
- 10+ Checklists
- Research Guides
We hate spam too. We promise to protect your privacy and never spam you.
- Promoting Research
- Career Corner
- Diversity and Inclusion
- Infographics
- Expert Video Library
- Other Resources
- Enago Learn
- Upcoming & On-Demand Webinars
- Open Access Week 2024
- Peer Review Week 2024
- Conference Videos
- Enago Report
- Journal Finder
- Enago Plagiarism & AI Grammar Check
- Editing Services
- Publication Support Services
- Research Impact
- Translation Services
- Publication solutions
- AI-Based Solutions
- Thought Leadership
- Call for Articles
- Call for Speakers
- Author Training
- Edit Profile
I am looking for Editing/ Proofreading services for my manuscript Tentative date of next journal submission:

What factors would influence the future of open access (OA) publishing?
A guide to ethical considerations in research
Last updated
12 March 2023
Reviewed by
Miroslav Damyanov
Whether you are conducting a survey, running focus groups , doing field research, or holding interviews, the chances are participants will be a part of the process.
Taking ethical considerations into account and following all obligations are essential when people are involved in your research. Upholding academic integrity is another crucial ethical concern in all research types.
So, how can you protect your participants and ensure that your research is ethical? Let’s take a closer look at the ethical considerations in research and the best practices to follow.
Make research less tedious
Dovetail streamlines research to help you uncover and share actionable insights
- The importance of ethical research
Research ethics are integral to all forms of research. They help protect participants’ rights, ensure that the research is valid and accurate, and help minimize any risk of harm during the process.
When people are involved in your research, it’s particularly important to consider whether your planned research method follows ethical practices.
You might ask questions such as:
Will our participants be protected?
Is there a risk of any harm?
Are we doing all we can to protect the personal data and information we collect?
Does our study include any bias?
How can we ensure that the results will be accurate and valid?
Will our research impact public safety?
Is there a more ethical way to complete the research?
Conducting research unethically and not protecting participants’ rights can have serious consequences. It can discredit the entire study. Human rights, dignity, and research integrity should all be front of mind when you are conducting research.
- How to conduct ethical research
Before kicking off any project, the entire team must be familiar with ethical best practices. These include the considerations below.
Voluntary participation
In an ethical study, all participants have chosen to be part of the research. They must have voluntarily opted in without any pressure or coercion to do so. They must be aware that they are part of a research study. Their information must not be used against their will.
To ensure voluntary participation, make it clear at the outset that the person is opting into the process.
While participants may agree to be part of a study for a certain duration, they are allowed to change their minds. Participants must be free to leave or withdraw from the study at any time. They don’t need to give a reason.
Informed consent
Before kicking off any research, it’s also important to gain consent from all participants. This ensures participants are clear that they are part of a research study and understand all of the information related to it.
Gaining informed consent usually involves a written consent form—physical or digital—that participants can sign.
Best practice informed consent generally includes the following:
An explanation of what the study is
The duration of the study
The expectations of participants
Any potential risks
An explanation that participants are free to withdraw at any time
Contact information for the research supervisor
When obtaining informed consent, you should ensure that all parties truly understand what they are signing and their obligations as a participant. There should never be any coercion to sign.
Anonymity is key to ensuring that participants cannot be identified through their data. Personal information includes things like participants’ names, addresses, emails, phone numbers, characteristics, and photos.
However, making information truly anonymous can be challenging, especially if personal information is a necessary part of the research.
To maintain a degree of anonymity, avoid gathering any information you don’t need. This will minimize the risk of participants being identified.
Another useful tool is data pseudonymization, which makes it harder to directly link information to a real person. Data pseudonymization means giving participants fake names or mock information to protect their identity. You could, for example, replace participants’ names with codes.
Confidentiality
Keeping data confidential is a critical aspect of all forms of research. You should communicate to all participants that their information will be protected and then take active steps to ensure that happens.
Data protection has become a serious topic in recent years and should be taken seriously. The more information you gather, the more important it is to heavily protect that data.
There are many ways to protect data, including the following:
Restricted access: Information should only be accessible to the researchers involved in the project to limit the risk of breaches.
Password protection : Information should not be accessible without access via a password that complies with secure password guidelines.
Encrypted data: In this day and age, password protection isn’t usually sufficient. Encrypting the data can help ensure its security.
Data retention: All organizations should uphold a data retention policy whereby data gathered should only be held for a certain period of time. This minimizes the risk of breaches further down the line.
In research where participants are grouped together (such as in focus groups), ask participants not to pass on what has been discussed. This helps maintain the group’s privacy.
Data falsification
Regardless of what your study is about or whether it involves humans, it’s always unethical to falsify data or information. That means editing or changing any data that has been gathered or gathering data in ways that skew the results.
Bias in research is highly problematic and can significantly impact research integrity. Data falsification or misrepresentation can have serious consequences.
Take the case of Korean researcher Hwang Woo-suk, for example. Woo-suk, once considered a scientific leader in stem-cell research, was found guilty of fabricating experiments in the field and making ethical violations. Once discovered, he was fired from his role and sentenced to two years in prison.
All conflicts of interest should be declared at the outset to avoid any bias or risk of fabrication in the research process. Data must be collected and recorded accurately, and analysis must be completed impartially.
If conflicts do arise during the study, researchers may need to step back to maintain the study’s integrity. Outsourcing research to neutral third parties is necessary in some cases.
Potential for harm
Another consideration is the potential for harm. When completing research, it’s important to ensure that your participants will be safe throughout the study’s duration.
Harm during research could occur in many forms.
Physical harm may occur if your participants are asked to perform a physical activity, or if they are involved in a medical study.
Psychological harm can occur if questions or activities involve triggering or sensitive topics, or if participants are asked to complete potentially embarrassing tasks.
Harm can be caused through a data breach or privacy concern.
A study can cause harm if the participants don’t feel comfortable with the study expectations or their supervisors.
Maintaining the physical and mental well-being of all participants throughout studies is an essential aspect of ethical research.
- Gaining ethical approval
Gaining ethical approval may be necessary before conducting some types of research.
The US Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) and the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) advise that approval is likely required for studies involving people.
To gain approval, it’s necessary to submit a proposal to an Institutional Review Board (IRB). The board will check the proposal and ensure that the research aligns with ethical practices. It will allow the project to proceed if it meets requirements.
Not gaining appropriate approval could invalidate your study, so it’s essential to pay attention to all local guidelines and laws.
- The dangers of unethical practices
Not maintaining ethical standards in research isn’t just questionable—it can be dangerous too. Many historical cases show just how widespread the ramifications can be.
The case of Korean researcher Hwang Woo-suk shows just how critical it is to obtain information ethically and accurately represent findings.
A case in 1998, which involved fraudulent data reporting, further proves this point.
The study, now debunked, was completed by Andrew Wakefield. It suggested there may be a link between the measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR) vaccine and autism in children. It was later found that the data was manipulated to show a causal link when there wasn’t one. Wakefield’s medical license was removed as a result, but the fraudulent study was still widely cited and continues to cause vaccine hesitancy among many parents.
Large organizational bodies have also been a part of unethical research. The alcohol industry, for example, was found to be highly influential in a major public health study in an attempt to prove that moderate alcohol consumption had health benefits. Five major alcohol companies pledged approximately $66 million to fund the study.
However, the World Health Organization (WHO) is clear that research shows there is no safe level of alcohol consumption. After pressure from many organizations, the study was eventually pulled due to biasing by the alcohol industry. Despite this, the idea that moderate alcohol consumption is better than abstaining may still appear in public discourse.
In more extreme cases, unethical research has led to medical studies being completed on people without their knowledge and against their will. The atrocities committed in Nazi Germany during World War II are an example.
Unethical practices in research are not just problematic or in conflict with academic integrity; they can seriously harm public health and safety.
- The ethical way to research
Considering ethical concerns and adopting best practices throughout studies is essential when conducting research.
When people are involved in studies, it’s important to consider their rights. They must not be coerced into participating, and they should be protected throughout the process.
Accurate reporting, unbiased results, and a genuine interest in answering questions rather than confirming assumptions are all essential aspects of ethical research.
Ethical research ultimately means producing true and valuable results for the benefit of everyone impacted by your study.
What are ethical considerations in research?
Ethical research involves a series of guidelines and considerations to ensure that the information gathered is valid and reliable. These guidelines ensure that:
People are not harmed during research
Participants have data protection and anonymity
Academic integrity is upheld
Not maintaining ethics in research can have serious consequences for those involved in the studies, the broader public, and policymakers.
What are the most common ethical considerations?
To maintain integrity and validity in research, all biases must be removed, data should be reported accurately, and studies must be clearly represented.
Some of the most common ethical guidelines when it comes to humans in research include avoiding harm, data protection, anonymity, informed consent, and confidentiality.
What are the ethical issues in secondary research?
Using secondary data is generally considered an ethical practice. That’s because the use of secondary data minimizes the impact on participants, reduces the need for additional funding, and maximizes the value of the data collection.
However, secondary research still has risks. For example, the risk of data breaches increases as more parties gain access to the information.
To minimize the risk, researchers should consider anonymity or data pseudonymization before the data is passed on. Furthermore, using the data should not cause any harm or distress to participants.
Should you be using a customer insights hub?
Do you want to discover previous research faster?
Do you share your research findings with others?
Do you analyze research data?
Start for free today, add your research, and get to key insights faster
Editor’s picks
Last updated: 24 October 2024
Last updated: 11 January 2024
Last updated: 17 January 2024
Last updated: 12 December 2023
Last updated: 30 April 2024
Last updated: 4 July 2024
Last updated: 12 October 2023
Last updated: 5 March 2024
Last updated: 6 March 2024
Last updated: 31 January 2024
Last updated: 23 January 2024
Last updated: 13 May 2024
Last updated: 20 December 2023
Latest articles
Related topics, decide what to build next, log in or sign up.
Get started for free

Research Proposal Ethics Statement Example
In the world of academic and professional research, ethical considerations are paramount. Whether you’re studying human behavior, testing new technologies, or analyzing historical data, your research must adhere to strict ethical standards. This is where an ethics statement comes into play. It’s a crucial component of any research proposal, demonstrating your commitment to conducting responsible, respectful, and rigorous research.
This comprehensive guide will walk you through the process of creating an ethics statement for your research proposal. We’ll explore each component in detail, provide examples, and offer insights to help you navigate potential ethical challenges.
By the end of this guide, you’ll have a clear understanding of how to craft an ethics statement that not only meets institutional requirements but also upholds the highest standards of ethical research.
What You'll Learn
What is an Ethics Statement?
An ethics statement, also known as an ethical considerations section or ethical framework, is a detailed document within your research proposal that outlines how you plan to address ethical issues throughout your study. It serves as a roadmap for conducting ethical research, demonstrating your awareness of potential ethical challenges and your strategies for managing them.
Key Purposes of an Ethics Statement:
- Participant Protection : It outlines measures to ensure the safety, privacy, and well-being of research participants.
- Ethical Compliance : It shows that your research adheres to established ethical guidelines and regulations.
- Transparency : It provides a clear overview of your research methods and potential impacts.
- Risk Management : It identifies potential ethical risks and outlines strategies to mitigate them.
- Quality Assurance : It helps maintain the integrity and credibility of your research.
Why is an Ethics Statement Important?
The importance of an ethics statement extends far beyond simply fulfilling a requirement. Let’s delve deeper into why this document is crucial for your research:
1. Protects Participants
The primary purpose of an ethics statement is to ensure the safety, rights, and well-being of your research participants. This includes:
- Physical safety: Minimizing any potential for harm or discomfort.
- Psychological well-being: Addressing potential emotional or mental stress.
- Privacy: Protecting personal information and maintaining confidentiality.
- Autonomy: Respecting participants’ right to make informed decisions about their involvement.
2. Builds Trust
An ethics statement demonstrates your commitment to ethical research practices, which helps to:
- Build credibility with participants, making them more likely to engage honestly.
- Establish trust with your institution, funding bodies, and the wider research community.
- Enhance the reputation of your research and your professional standing.
3. Meets Requirements
Many institutions and funding bodies require an ethics statement as part of the research proposal. It’s often a key factor in:
- Obtaining approval from ethics committees or institutional review boards.
- Securing funding for your research project.
- Getting permission to publish your findings in academic journals.
4. Improves Research Quality
Considering ethical implications often leads to better research design:
- It encourages you to think critically about your methodology.
- It helps identify potential biases or limitations in your approach.
- It can lead to more robust data collection and analysis procedures.
5. Promotes Responsible Science
An ethics statement contributes to the broader goal of promoting responsible scientific practices:
- It helps prevent misconduct and unethical behavior in research.
- It encourages transparency and reproducibility in scientific studies.
- It supports the overall integrity of the scientific process.
Key Components of an Ethics Statement
A comprehensive ethics statement typically includes the following components:
- Informed Consent
- Confidentiality and Privacy
- Risk Assessment and Management
- Data Storage and Protection
- Conflicts of Interest
- Vulnerable Populations (if applicable)
- Cultural Sensitivity
- Deception (if applicable)
- Ethical Approval Process
Let’s examine each of these components in detail, providing explanations, examples, and best practices for addressing them in your ethics statement.
1. Informed Consent
What it is:.
Informed consent is the process by which potential research participants are given all the information they need to make an educated decision about whether to participate in a study. It’s a fundamental ethical principle that respects individuals’ autonomy and right to self-determination.
Why it matters:
Informed consent ensures that participants understand what they’re agreeing to, including any potential risks or benefits. It protects participants from exploitation and helps maintain the integrity of the research process.
How to address it:
Explain in detail how you’ll obtain informed consent from participants. This typically involves:
- Providing an information sheet that clearly explains the study’s purpose, procedures, duration, potential risks and benefits, and participants’ rights.
- Using language that is easy to understand, avoiding jargon or complex terms.
- Allowing time for potential participants to ask questions and consider their decision.
- Obtaining written consent through a signed form or digital agreement for online studies.
- For ongoing studies, implementing a process for continuous consent, allowing participants to withdraw at any time.
“All potential participants will receive a comprehensive information sheet detailing the study’s objectives, methods, expected duration, and potential risks and benefits. This information will be presented in clear, jargon-free language and will be available in multiple languages to accommodate our diverse participant pool. Potential participants will have a minimum of 48 hours to review this information and ask any questions before being asked to sign a consent form. The consent form will clearly state that participation is voluntary and that they have the right to withdraw from the study at any time without penalty. For our online surveys, we will use a digital consent form that must be completed before accessing the survey questions. In the case of our longitudinal study component, we will implement a process of continuous consent, reconfirming participants’ willingness to continue at each stage of data collection.”
2. Confidentiality and Privacy
Confidentiality refers to the protection of participants’ personal information and the data they provide during the research. Privacy relates to participants’ right to control information about themselves and decide what information is shared and with whom.
Maintaining confidentiality and privacy is crucial for several reasons:
- It protects participants from potential harm or embarrassment that could result from their information being disclosed.
- It encourages honest and open responses, improving the quality of your data.
- It’s often a legal requirement, particularly when dealing with sensitive personal information.
Describe in detail the measures you’ll take to ensure confidentiality and protect participants’ privacy. This may include:
- Anonymization or pseudonymization of data
- Secure storage of identifying information
- Limited access to raw data
- Confidentiality agreements for research team members
- Plans for secure destruction of data after the retention period
“To ensure the highest level of confidentiality and privacy, we will implement a multi-layered approach:
- Data Anonymization: All collected data will be immediately anonymized. Each participant will be assigned a unique identifier, and any personally identifiable information will be removed from the dataset.
- Secure Data Storage: All research data will be stored on encrypted, password-protected servers. Physical documents will be kept in a locked cabinet in a secure office accessible only to authorized research team members.
- Limited Access: Only essential members of the research team will have access to the raw data. All team members will sign confidentiality agreements before being granted access.
- Separation of Identifying Information: Any documents linking participant identities to their unique identifiers will be stored separately from the research data, with access restricted to the principal investigator.
- Secure Data Transmission: When transferring data between researchers or institutions, we will use secure, encrypted file transfer protocols.
- Publication Safeguards: In all publications and presentations, we will ensure that no individual participant can be identified. We will use aggregate data and, where necessary, alter non-essential details to protect privacy.
- Data Retention and Destruction: We will retain the anonymized data for five years after the study’s completion, as required by our institution. After this period, electronic data will be securely erased using data destruction software, and physical documents will be shredded and disposed of securely.
- Participant Control: Participants will be informed of their right to request access to their personal data or to have it deleted at any time during the study.”
3. Risk Assessment and Management
Risk assessment involves identifying and evaluating potential risks to participants, researchers, or others involved in the study. Risk management is the process of developing strategies to minimize these risks.
Thorough risk assessment and management are crucial for:
- Protecting the physical and psychological well-being of participants and researchers
- Maintaining the ethical integrity of your research
- Complying with legal and institutional requirements
- Anticipating and preventing potential problems that could compromise your study
Provide a comprehensive overview of potential risks associated with your study and detailed plans for managing each risk. Consider:
- Physical risks
- Psychological risks
- Social risks
- Economic risks
- Legal risks
For each identified risk, explain:
- The nature and likelihood of the risk
- The potential impact if the risk occurs
- Strategies to prevent or minimize the risk
- Plans for addressing the risk if it does occur
“Our study on workplace stress involves both online surveys and in-person interviews. We have identified the following potential risks and developed corresponding management strategies:
- Risk: Participants may experience emotional distress when discussing stressful work experiences.
- Management: a) We will clearly warn participants about potentially distressing topics in the informed consent process. b) Participants will be reminded that they can skip questions or stop the interview at any time. c) We will provide contact information for free counseling services to all participants. d) Interviewers will be trained to recognize signs of distress and respond appropriately.
- Risk: Unauthorized access to sensitive personal and professional information.
- Management: a) Implementation of robust data security measures as outlined in our confidentiality section. b) Regular security audits of our data storage systems. c) Minimal collection of identifying information. d) Development of a data breach response plan, including prompt notification to affected participants.
- Risk: Participants may fear negative consequences at work if their responses become known to employers.
- Management: a) Strict confidentiality measures as detailed earlier. b) Clear communication to participants about how their data will be used and protected. c) Option for participants to review and approve any potentially identifying quotes before publication.
- Risk: Minimal risk of physical discomfort during lengthy interviews.
- Management: a) Interviews will be limited to 90 minutes with optional breaks. b) Interview locations will be chosen for comfort and accessibility. c) Participants will be encouraged to inform the interviewer if they need to pause or stop for any reason.
- Risk: Participation may be time-consuming, potentially causing stress or inconvenience.
- Management: a) Clear communication of expected time commitment in the informed consent process. b) Flexibility in scheduling interviews to accommodate participants’ preferences. c) Option to complete the survey in multiple sessions if needed.
In the unlikely event that any unanticipated risks emerge during the study, we will immediately halt data collection, assess the situation, and consult with our institutional ethics committee before proceeding.”
4. Data Storage and Protection
Data storage and protection refer to the methods and systems used to securely store, manage, and eventually dispose of research data. This includes both physical (e.g., paper documents) and digital data.
Proper data storage and protection are essential for:
- Maintaining participant confidentiality and privacy
- Ensuring the integrity and reliability of your research data
- Complying with data protection laws and regulations (e.g., GDPR in the EU)
- Preventing unauthorized access, data loss, or data breaches
Provide a detailed plan for how you will handle data throughout the research process. Include information on:
- Where and how data will be stored
- Who will have access to the data
- How long data will be retained
- How data will be securely destroyed after the retention period
- Measures to protect against data breaches or loss
“Our data storage and protection plan encompasses the entire data lifecycle, from collection to destruction:
- Online surveys will be conducted using Qualtrics, a GDPR-compliant platform with robust security features.
- Interview recordings will be made using encrypted digital recorders.
- All data transfers will occur over secure, encrypted connections.
- Physical transfer of data (e.g., from interview sites) will use encrypted portable devices.
- Digital data will be stored on a secure, access-controlled server maintained by our university’s IT department. This server is backed up daily and protected by enterprise-level firewalls.
- Any physical documents will be stored in a locked filing cabinet in a secure office accessible only to authorized research team members.
- Access to raw data will be limited to essential research team members, each of whom will have unique login credentials.
- A log will be maintained of all data access events.
- Data analysis will be conducted on secure, password-protected computers in a designated research area.
- When working remotely, researchers will use a secure VPN connection to access data.
- We will retain research data for five years after the completion of the study, as per our institution’s policy.
- During this time, data will be regularly reviewed to ensure it remains necessary for the purposes for which it is being retained.
- After the retention period, digital data will be securely erased using certified data destruction software that overwrites the data multiple times.
- Physical documents will be shredded using a cross-cut shredder and disposed of securely.
- In the event of a suspected data breach, we will immediately: a) Isolate affected systems to prevent further unauthorized access. b) Notify our institution’s data protection officer and IT security team. c) Conduct a thorough investigation to determine the extent of the breach. d) Notify affected participants and relevant authorities as required by law. e) Implement necessary measures to prevent similar breaches in the future.
- Our data protection measures will be reviewed and updated regularly to ensure they remain effective and comply with current best practices and regulations.”
5. Conflicts of Interest
A conflict of interest in research occurs when professional judgment concerning a primary interest (such as research validity) may be influenced by a secondary interest (such as financial gain or personal relationship).
Addressing conflicts of interest is crucial for:
- Maintaining the integrity and credibility of your research
- Ensuring unbiased data collection and analysis
- Complying with ethical guidelines and institutional policies
- Building trust with participants, peers, and the public
Provide a clear disclosure of any potential conflicts of interest related to your research. This should include:
- Financial interests (e.g., funding sources, personal investments)
- Personal relationships (e.g., familial ties to participants or stakeholders)
- Professional relationships (e.g., consulting work, board memberships)
- Intellectual property interests
For each potential conflict, explain how you plan to manage it to minimize its impact on your research.
“In the interest of full transparency, we disclose the following potential conflicts of interest and our plans to manage them:
- Potential Conflict: This study is partially funded by TechCorp, a major player in the industry we’re researching.
- Management Plan: a) The funding agreement explicitly states that TechCorp has no influence over the study design, data collection, analysis, or publication of results. b) We will clearly acknowledge TechCorp’s funding in all publications and presentations. c) All raw data and analysis procedures will be made available for independent verification.
- Potential Conflict: The lead researcher’s spouse is an employee of one of the companies included in our study.
- Management Plan: a) The lead researcher will not be involved in data collection or initial analysis for this specific company. b) An independent researcher will be brought in to oversee the data collection and analysis for this company. c) This relationship will be disclosed in all publications resulting from this research.
- Potential Conflict: One of our co-investigators has previously done consulting work for several companies in the industry we’re studying.
- Management Plan: a) The co-investigator will not be involved in data collection from any companies they’ve consulted for in the past five years. b) We will maintain a log of which team members are involved in data collection and analysis for each company to ensure no conflicts. c) This past consulting work will be disclosed in our methodology section and any resulting publications.
- Potential Conflict: Our research may lead to patentable innovations in workplace stress management tools.
- Management Plan: a) We have established a clear agreement with our institution regarding the ownership and potential commercialization of any intellectual property resulting from this research. b) Any patents filed as a result of this research will be disclosed this in future related academic work.
- Potential Conflict: The principal investigator has publicly expressed strong views on workplace stress management policies.
- Management Plan: a) We will implement a structured, objective data collection and analysis protocol to minimize potential bias. b) An independent researcher will review our analysis and conclusions to ensure objectivity. c) We will explicitly address how we’ve managed this potential bias in our methodology section.
We are committed to managing these conflicts of interest transparently and ethically. We will promptly disclose any additional conflicts that may arise during the course of the research and develop appropriate management strategies in consultation with our institutional ethics committee.”
6. Vulnerable Populations (if applicable)
Vulnerable populations are groups that require special ethical considerations due to their increased susceptibility to harm or exploitation in research contexts. These may include children, elderly individuals, prisoners, individuals with cognitive impairments, or socially or economically disadvantaged groups.
Extra care must be taken when working with vulnerable populations to:
- Protect their rights and well-being
- Ensure they are not exploited or unfairly burdened by research
- Address unique ethical challenges that may arise
- Comply with specific regulations governing research with these groups
If your research involves vulnerable populations, provide a detailed explanation of:
- Why the inclusion of this population is necessary for your research
- The specific vulnerabilities of this group in the context of your study
- Extra precautions you’ll take to protect their rights and well-being
- How you’ll obtain informed consent (including from guardians if applicable)
- Any special accommodations you’ll make in your research procedures
“Our study on the effects of social media use on mental health includes adolescents aged 13-17, who are considered a vulnerable population. We address this as follows:
- Justification for Inclusion: Adolescents are primary users of social media, and understanding its impact on their mental health is crucial for developing appropriate interventions and policies.
- Limited capacity to assess long-term risks and benefits
- Susceptibility to peer influence
- Ongoing cognitive and emotional development
- Potential for parental influence on participation decision
- We will obtain written consent from a parent or legal guardian for all participants under 18.
- We will also obtain assent from the adolescents themselves, using an age-appropriate assent form.
- Both parents and adolescents will be informed that the adolescent can withdraw at any time, regardless of parental consent.
- All study materials, including information sheets and survey questions, will be written in clear, simple language appropriate for the youngest participants.
- We will pilot test these materials with a small group of adolescents to ensure comprehension.
- Extra measures will be taken to protect adolescents’ privacy, including conducting online surveys that can be completed privately.
- We will clearly explain to both parents and adolescents what information will and will not be shared with parents.
- Our study is designed to pose no more than minimal risk to participants.
- Questions about sensitive topics (e.g., cyberbullying) will be carefully worded and optional.
- We will provide all participants with information about mental health resources, including helplines and online support specifically for adolescents.
- All researchers interacting with adolescent participants will undergo specialized training in working with this age group.
- We will establish a process for ongoing monitoring of participant well-being throughout the study.
- We will clearly explain our legal obligations to report any disclosures of abuse or serious self-harm, both in the consent/assent process and at the beginning of data collection.
By implementing these measures, we aim to conduct our research ethically and responsibly while gathering valuable data on this important topic.”
7. Cultural Sensitivity
Cultural sensitivity in research involves recognizing, respecting, and appropriately responding to the diversity of cultural backgrounds, beliefs, and practices among your research participants.
Cultural sensitivity is crucial for:
- Ensuring equitable treatment of all participants
- Avoiding misunderstandings or offense that could compromise your research
- Collecting more accurate and meaningful data
- Building trust with diverse communities
- Producing research results that are applicable across different cultural contexts
Explain how you’ll ensure cultural sensitivity throughout your research process. Consider:
- Language and communication
- Customs and traditions
- Religious beliefs and practices
- Gender roles and norms
- Socioeconomic factors
“Our research on global workplace practices involves participants from diverse cultural backgrounds. We will ensure cultural sensitivity through the following measures:
- All research materials (information sheets, consent forms, surveys, interview scripts) will be professionally translated into the primary languages of our participant groups.
- Bilingual researchers or interpreters will be available for interviews and focus groups.
- We will consult with cultural experts or community leaders from each major cultural group represented in our study to review our research materials and protocols.
- These consultations will help us identify and address potential cultural sensitivities or misunderstandings.
- Our research team includes members from various cultural backgrounds, providing diverse perspectives in study design and data interpretation.
- Team members will undergo cultural competency training specific to the cultures represented in our study.
- We will accommodate different cultural and religious observances when scheduling interviews and focus groups.
- Participants will be asked about any timing considerations during the recruitment process.
- In cultures where it may be inappropriate for men to interview women (or vice versa), we will match the gender of interviewers and participants as needed.
- We will be mindful of gender dynamics in mixed-gender focus groups and adjust our facilitation accordingly.
- We will consult with local contacts to ensure that any incentives or compensation offered are culturally appropriate and do not inadvertently cause offense or undue influence.
- In cultures where it’s important to obtain approval from community leaders or elders before conducting research, we will follow appropriate protocols to seek this approval.
- We will be mindful of culturally sensitive topics and approach them carefully in our questions.
- Participants will always have the option to decline answering any questions they’re uncomfortable with.
- We will be cautious about imposing Western frameworks on data interpretation and will consider cultural contexts in our analysis.
- Where appropriate, we will involve participants or cultural consultants in reviewing our interpretations.
- We will make efforts to disseminate our research findings in culturally appropriate ways, including providing summaries in local languages.
- We will be mindful of any cultural sensitivities in how we present our findings.
By implementing these measures, we aim to conduct our research in a way that respects and values the cultural diversity of our participants, leading to more valid and ethically sound results.”
8. Deception (if applicable)
Deception in research involves deliberately withholding information from or misleading participants about the true nature or purpose of a study.
While sometimes necessary for certain types of research (e.g., some psychology studies), deception raises significant ethical concerns:
- It can violate the principle of informed consent
- It may cause distress to participants when the deception is revealed
- It can potentially damage trust in researchers and the scientific process
If your research involves any form of deception, you must:
- Provide a strong justification for why deception is necessary
- Explain why alternative methods without deception are not feasible
- Describe the nature and extent of the deception
- Detail how and when participants will be debriefed
- Explain how you’ll mitigate potential negative effects of the deception
“Our study on decision-making under pressure involves a minor element of deception. We address this as follows:
- Justification for Deception: The study aims to measure natural responses to unexpected time pressure. If participants know in advance that they will face sudden time constraints, it would likely alter their behavior and invalidate our results.
- Nature of Deception: Participants will be told they have 30 minutes to complete a series of decision-making tasks. However, at a random point between 10-15 minutes into the session, they will be informed that due to a “scheduling error,” they must complete the tasks in the next 5 minutes.
- Alternatives Considered: We considered informing participants that time pressure might be introduced but concluded this would still likely alter their approach to the tasks. We also considered using naturally occurring time pressure situations but found we couldn’t control for important variables in such settings.
- The deception is minor and short-lived.
- No false information is given about the nature of the tasks themselves.
- The time pressure, while unexpected, is not extreme and poses minimal risk of distress.
- Immediately after completing the tasks, participants will be fully debriefed about the deception.
- We will explain the true purpose of the study and the reason for the deception.
- Participants will have the opportunity to ask questions and discuss their experience.
- We will assess whether the deception caused any distress and provide appropriate support if needed.
- During the debriefing, participants will be given the option to withdraw their data if they are uncomfortable with the deception used.
- This will be a genuine option with no penalty, and we will make it clear that withdrawing will not affect any compensation they were promised.
- This use of deception has been reviewed and approved by our institutional ethics committee.
- We will report any unanticipated negative reactions to the committee and adjust our protocols if necessary.
By carefully limiting and managing this minor deception, we aim to balance the scientific need for valid data with our ethical obligation to treat participants with respect and minimize potential harm.”
9. Debriefing
Debriefing is the process of providing participants with full information about the study after their participation is complete. It’s particularly important in studies involving deception but is valuable in all types of research.
Debriefing serves several important purposes:
- It fulfills the ethical obligation to inform participants about the true nature of the research they participated in
- It provides an opportunity to assess and mitigate any negative effects of participation
- It can be an educational opportunity for participants to learn about the research process
- It allows researchers to gather valuable feedback from participants
Explain your debriefing process, including:
- When and how debriefing will occur
- What information will be provided during debriefing
- How you’ll address any questions or concerns raised by participants
- What support will be available if participants experience any distress
“Our debriefing process is designed to ensure that all participants leave the study fully informed and with a positive research experience:
- Debriefing will occur immediately after the completion of each participant’s involvement in the study.
- For in-person studies, this will be a face-to-face conversation. For online studies, we will provide a detailed written debriefing followed by the option for a phone or video call with a researcher.
- We will explain the full purpose of the study, including any elements that were not disclosed at the outset.
- We’ll describe how the data will be used and what we hope to learn from the study.
- If any deception was used, we’ll explain why it was necessary and give participants the option to withdraw their data.
- We’ll invite participants to share their experience of the study and any thoughts or feelings it brought up.
- This feedback will be recorded (with permission) to help us improve our research processes.
- Participants will be encouraged to ask any questions they have about the study.
- We’ll provide honest, clear answers and take the time to ensure participants fully understand.
- We’ll ask participants if they experienced any discomfort or distress during the study.
- If any negative impacts are identified, we’ll discuss these with the participant and offer appropriate support.
- All participants will receive a handout with contact information for the research team and relevant support services.
- For studies dealing with sensitive topics, we’ll have a trained counselor available during debriefing sessions.
- Participants will be given the option to receive a summary of the study results when available.
- We’ll provide our contact information and encourage participants to reach out if they have any questions or concerns in the future.
- We’ll remind participants about our confidentiality procedures and how their data will be protected.
- We’ll express our sincere thanks for their participation and explain how their contribution helps advance knowledge in the field.
By conducting thorough, thoughtful debriefings, we aim to ensure that participation in our research is a positive, educational experience and that participants feel respected and valued for their contribution.”
10. Ethical Approval Process
The ethical approval process involves submitting your research proposal, including your ethics statement, to an Institutional Review Board (IRB) or Ethics Committee for review and approval before beginning your research.
Obtaining ethical approval is crucial because it:
- Ensures your research meets established ethical standards
- Protects the rights and well-being of your participants
- Helps identify and address potential ethical issues before they arise
- Is often required for publication and funding
- Provides legal and institutional protection for researchers
Outline the steps you’ll take to obtain ethical approval, including:
- Which ethics committee or IRB you’ll submit to
- What documents you’ll include in your submission
- Your timeline for obtaining approval
- How you’ll address any feedback or concerns from the committee
- Your plan for ongoing ethical oversight throughout the research process
Related Articles
How to Critically Appraise a Research Article
How to Write a Psychology Research Proposal
Addressing ethical issues in your research proposal
“We are committed to conducting our research in full compliance with ethical standards. Our ethical approval process will proceed as follows:
- Detailed research proposal
- This ethics statement
- All research instruments (surveys, interview guides, etc.)
- Informed consent forms
- Recruitment materials
- Data management plan
- CVs of key research personnel
- Before submission, our application will be reviewed by senior colleagues in our department to identify any potential issues.
- We will submit our application to the University of [Name] Institutional Review Board (IRB).
- Submission will occur at least two months before our planned start date to allow time for review and any necessary revisions.
- We will promptly address any questions or concerns raised by the IRB.
- If major changes are required, we will consult with our research team and advisors to ensure we maintain the integrity of our study while meeting ethical requirements.
- We will not begin any recruitment or data collection until we have received written approval from the IRB.
- Once approved, we will keep a copy of the approval letter on file and available for review if needed.
- We will adhere strictly to the approved protocol throughout the study.
- Any proposed changes to the research design or procedures will be submitted to the IRB for review and approval before implementation.
- We will promptly report any unanticipated problems or adverse events to the IRB.
- For studies lasting more than one year, we will submit an annual progress report to the IRB for continuing review and approval.
- Upon completion of the study, we will submit a final report to the IRB, including a summary of results and any ethical issues encountered.
- We will include a statement about ethical approval in all publications and presentations resulting from this research.
By following this rigorous ethical approval process, we aim to ensure that our research meets the highest ethical standards and respects the rights and well-being of all participants.”
Start by filling this short order form order.studyinghq.com
And then follow the progressive flow.
Having an issue, chat with us here
Cathy, CS.
New Concept ? Let a subject expert write your paper for You
Post navigation
Previous post.
📕 Studying HQ
Typically replies within minutes
Hey! 👋 Need help with an assignment?
🟢 Online | Privacy policy
WhatsApp us

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Ethical considerations in research are a set of principles that guide your research designs and practices. These principles include voluntary participation, informed consent, anonymity, confidentiality, potential for harm, and results communication.
Some of the key ethical considerations in research include: Informed consent: Researchers must obtain informed consent from study participants, which means they must inform participants about the study’s purpose, procedures, risks, benefits, and their right to withdraw at any time.
You will need to consider the ethical issues that might arise in your proposed study. Consideration of the fundamental ethical principles that underpin all research will help you to identify the key issues and how these could be addressed.
This proposal should include your research objectives, methods, and how you plan to address ethical considerations like informed consent, confidentiality, and risk minimisation. You can learn more about how to write a proposal here .
Explore key ethical considerations in research, from informed consent to fair compensation. Learn how to conduct responsible studies that protect participants.
Research ethics protect the rights and well-being of participants, uphold the integrity of research findings, and contribute to the positive impact of research on individuals and society. Let us look into some of the major ethical considerations in research design.
Ensuring that your research is conducted ethically is essential to protecting the welfare of your participants and the validity of your data. Learn more about ethical considerations in research.
The inclusion of validating findings, ethical considerations (to be addressed shortly), the need for preliminary results, and early evidence of practical significance focus a reader’s attention on key elements often overlooked in discussions about proposed projects.
Ethical considerations in research: a framework for practice. We conduct research to validate and improve our professional practice and to obtain generalizable knowledge. Through research we strive to better under-stand the natural history of diseases, human behavior, and outcomes of interventions.
Research Proposal Ethics Statement Example. Rachel R.N. July 9, 2024. In the world of academic and professional research, ethical considerations are paramount. Whether you’re studying human behavior, testing new technologies, or analyzing historical data, your research must adhere to strict ethical standards.