

Research Writing Process (Book)
Find the following links to be useful in learning about the research writing process., writing a thesis statement, open thesis vs. closed thesis.
Open Thesis vs. Closed Thesis
Implicit Thesis vs. Explicit Thesis
The thesis is a declarative sentence. It is a clear, specific statement, which states the main point of a the paper, thereby limiting the topic and indicating the researcher’s approach to the topic. For this research paper we will be discussing the difference between the open (implicit) thesis approach, and the closed (explicit) thesis. Open (implicit) thesis: Let’s say you are writing a paper on the relationship between the United States criminal court system and the media. You have read on article related to this topic, but you have not yet begun your research. Still, it is possible for you to arrive at a very basic and general opinion without going into detail, secondary topics, or supporting reasons for your assertion. Broad Topic: The United States criminal court system and the media. Example of an open (implicit) thesis statement: The media plays too influential a role in criminal court trials. To assist you in formulating your preliminary thesis, ask basic “W” questions that are related to your topic: who, what, when, where, and why? This will help you determine your particular interests and a possible starting point for your research. Based on the topic above, the following list demonstrates the different kinds of questions that can be generated. *Why is the media involved in court cases? *When did the media start reporting court cases? *What is the media’s role in criminal court cases? *What aspects of the media am I going to write about? *What kind of criminal case is it? *When did the case take place? *Where did the case take place? *Who were the people involved in the case? If you are writing a research paper and you have come up with a long list of random questions, select three or four questions that hold the most interest for you. These questions will narrow your focus and help you to plan your research strategy.
Closed (Explicit) Thesis: If you make an assertion and include the reason or reasons which support your assertion, and it is broad enough in scope, yet specific enough to be unified and to perform as a substantial generalization of your essay, you have written a closed thesis statement. The evidence can take many forms: facts, opinions, anecdotes, statistics, analogies, etc., but the essential relationship between the thesis and the major points of support is one of conclusion to reason: This is believed to be true because… (reasons). Broad Topic: The United States criminal court system and the media. Example of a closed (explicit) thesis: The media plays a very influential role in criminal court trials because of their access to the people, their bias, and because of the special privileges. Based on the topic that YOU have chosen, ask yourself basic “W” questions that are related to YOUR topic to help you plan your research strategy and form a thesis. (Written by Lisa Tolhurst for the Hunter College Reading/Writing Center, 1998) WHY – WHEN – WHAT – WHERE – WHO – HOW – KEEP GOING!.....
Critical Reading
Identifying thesis statements, introduction, learning objectives.
- identify explicit thesis statements in texts
- identify implicit thesis statements in texts
- identify strategies for using thesis statements to predict content of texts
Being able to identify the purpose and thesis of a text, as you’re reading it, takes practice. This section will offer you that practice.
One fun strategy for developing a deeper understanding the material you’re reading is to make a visual “map” of the ideas. Mind maps, whether hand-drawn or done through computer programs, can be fun to make, and help put all the ideas of an essay you’re reading in one easy-to-read format.
Your understanding of what the “central” element of the mind map is might change as you read and re-read. Developing the central idea of your mind map is a great way to help you determine the reading’s thesis.

Hand-drawn Mind Map

Locating Explicit and Implicit Thesis Statements
In academic writing, the thesis is often explicit : it is included as a sentence as part of the text. It might be near the beginning of the work, but not always–some types of academic writing leave the thesis until the conclusion.
Journalism and reporting also rely on explicit thesis statements that appear very early in the piece–the first paragraph or even the first sentence.
Works of literature, on the other hand, usually do not contain a specific sentence that sums up the core concept of the writing. However, readers should finish the piece with a good understanding of what the work was trying to convey. This is what’s called an implicit thesis statement: the primary point of the reading is conveyed indirectly, in multiple locations throughout the work. (In literature, this is also referred to as the theme of the work.)
Academic writing sometimes relies on implicit thesis statements, as well.
This video offers excellent guidance in identifying the thesis statement of a work, no matter if it’s explicit or implicit.
Topic Sentences
We’ve learned that a thesis statement conveys the primary message of an entire piece of text. Now, let’s look at the next level of important sentences in a piece of text: topic sentences in each paragraph.
A useful metaphor would be to think of the thesis statement of a text as a general: it controls all the major decisions of the writing. There is only one thesis statement in a text. Topic sentences, in this relationship, serve as captains: they organize and sub-divide the overall goals of a writing into individual components. Each paragraph will have a topic sentence.
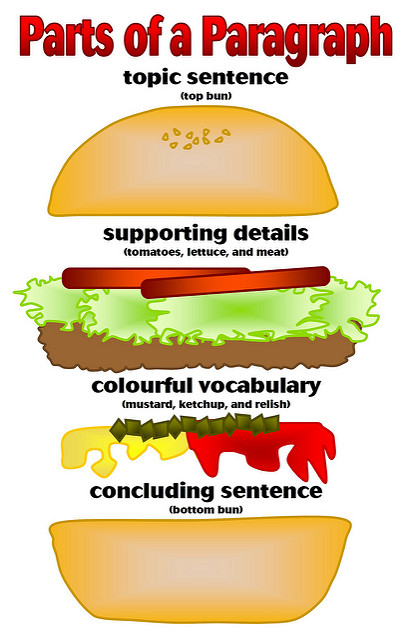
It might be helpful to think of a topic sentence as working in two directions simultaneously. It relates the paragraph to the essay’s thesis, and thereby acts as a signpost for the argument of the paper as a whole, but it also defines the scope of the paragraph itself. For example, consider the following topic sentence:
Many characters in Lorraine Hansberry’s play A Raisin in the Sun have one particular dream in which they are following, though the character Walter pursues his most aggressively.
If this sentence controls the paragraph that follows, then all sentences in the paragraph must relate in some way to Walter and the pursuit of his dream.
Topic sentences often act like tiny thesis statements. Like a thesis statement, a topic sentence makes a claim of some sort. As the thesis statement is the unifying force in the essay, so the topic sentence must be the unifying force in the paragraph. Further, as is the case with the thesis statement, when the topic sentence makes a claim, the paragraph which follows must expand, describe, or prove it in some way. Topic sentences make a point and give reasons or examples to support it.
The topic sentence is often, though not always, the first sentence of a paragraph.
Candela Citations
- Outcome: Thesis. Provided by : Lumen Learning. License : CC BY: Attribution
- Revision and Adaptation of Topic Sentences. Provided by : Lumen Learning. License : CC BY: Attribution
- Image of hand-drawn mind map. Authored by : Aranya. Located at : https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Guru_Mindmap.jpg . License : CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- Topic Sentences. Authored by : Ms. Beardslee. Located at : http://msbeardslee.wikispaces.com/Topic+Sentences?showComments=1 . License : CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- Image of Parts of a Paragraph. Authored by : Enokson. Located at : https://flic.kr/p/ak9H3v . License : CC BY: Attribution
- How to Identify the Thesis Statement. Authored by : Martha Ann Kennedy. Located at : https://youtu.be/di1cQgc1akg . License : All Rights Reserved . License Terms : Standard YouTube License

COMMENTS
Arguments then, can be explicit and implicit, or implied. Explicit arguments contain noticeable and definable thesis statements and lots of specific proofs. Implicit arguments, on the other hand, work by weaving together facts and narratives, logic and emotion, personal experiences and statistics. Unlike explicit arguments, implicit ones do not ...
Implicit Thesis vs. Explicit Thesis. The thesis is a declarative sentence. It is a clear, specific statement, which states the main point of a the paper, thereby limiting the topic and indicating the researcher's approach to the topic. For this research paper we will be discussing the difference between the open (implicit) thesis approach ...
Explicit arguments contain noticeable and definable thesis statements and lots of specific proofs. Implicit arguments, on the other hand, work by weaving together facts and narratives, logic and emotion, personal experiences and statistics. Unlike explicit arguments, implicit ones do not have a one-sentence thesis statement.
In academic writing, the thesis is often explicit: it is included as a sentence as part of the text. It might be near the beginning of the work, but not always-some types of academic writing leave the thesis until the conclusion. Journalism and reporting also rely on explicit thesis statements that appear very early in the piece-the first ...
Unlike explicit arguments, implicit ones do not have a one-sentence thesis statement. Instead, authors of implicit arguments use evidence of many different kinds in effective and creative ways to build and convey their point of view to their audience. Research is essential for creative effective arguments of both kinds.
An implicit thesis statement does not state the main argument or claim of your essay. Such theses can be used in expository (informative) or narrative writing. Example of an implicit thesis statement: The novel "To Kill a Mockingbird" is about a young girl, Scout, who learns about racism and injustice in her small town in Alabama during the ...
This is what's called an implicit thesis statement: the primary point of the reading is conveyed indirectly, in multiple locations throughout the work. (In literature, this is also referred to as the theme of the work.) Academic writing sometimes relies on implicit thesis statements, as well. This video offers excellent guidance in ...
Placement of the thesis statement. Step 1: Start with a question. Step 2: Write your initial answer. Step 3: Develop your answer. Step 4: Refine your thesis statement. Types of thesis statements. Other interesting articles. Frequently asked questions about thesis statements.
Implying Your Thesis. Not all research papers will require an explicitly stated thesis. Some research papers in some fields will simply require a strong focus. You can maintain a strong focus in your essay without an explicitly stated thesis by thinking about an implied thesis for your research paper. With an implied thesis, your point is never ...
Explicit and Implicit Thesis Statements by Elisha Jones and Jacqueline Evans-Bolden Explicit Thesis Statement: ex-plic-it /ik'splisit/: (adjective) 1. state clearly ...