

Developing a Conceptual Framework: A Step-by-Step Guide for Researchers
- July 5, 2024
Dr. Marvin L. Smith
In academic research, conceptual frameworks serve as essential blueprints, guiding scholars through the complex landscape of their studies. This article will explore how to construct powerful conceptual frameworks that elevate research design and execution.
Whether a seasoned researcher or new to academia, you’ll learn to craft frameworks that clarify objectives, map relationships between variables, and provide a solid foundation for data collection and analysis.
Ready to transform your approach to research design?
Let’s explore the critical role of conceptual frameworks in shaping successful research projects!
Table of Contents
Definition of a conceptual framework
A conceptual framework is a structured approach to organizing and presenting the key ideas, theories, and relationships that underpin a research study or academic argument.
It serves as a roadmap for the researcher, guiding the investigation and helping to connect various concepts logically and coherently.
For example, in a study examining the factors influencing student academic performance, a conceptual framework might include concepts such as socioeconomic status, parental involvement, teacher quality, and school resources. The framework would illustrate how these factors are thought to interact and influence the outcome of academic performance.
Developing conceptual framework in research
Developing a conceptual framework is a crucial step in the research process that helps researchers organize their thoughts, identify key variables, and visualize the relationships between different concepts in their study.
This process involves synthesizing existing literature, personal observations, and theoretical knowledge to create a structured representation of the research problem and its potential solutions.
A well-crafted conceptual framework serves as a roadmap for the entire research project, guiding the researcher through data collection, analysis, and interpretation.
It also helps in communicating complex ideas to readers, making the research more accessible and understandable.
By clearly defining the key concepts and their interconnections, researchers can ensure that their study remains focused and coherent throughout its execution.
Developing a conceptual framework is an iterative process that often evolves as the research progresses. It requires critical thinking, creativity, and a deep understanding of the subject matter. Researchers must be prepared to revise and refine their framework as they gain new insights or encounter unexpected findings during their study.
Creating a conceptual framework not only benefits the researcher but also adds credibility to the research by demonstrating a thoughtful and systematic approach to addressing the research question . It helps in identifying potential gaps in existing knowledge and can highlight areas where the study may contribute to the broader field of research.
Here’s a step-by-step guide can create a conceptual framework.
Related reading: How to write a research proposal
Ready to transform your writing experience?
Sign up for Blainy today and start writing your papers with confidence!
Step#1: Select your research question
Selecting a research question is the crucial first step in developing a conceptual framework. This step lays the foundation for your entire research project and guides the development of your conceptual framework.
Here’s a detailed explanation of this step:
The research question is the central inquiry that your study aims to answer. It should be clear, focused, and relevant to your field of study. When selecting your research question:
1. Identify your area of interest:
Begin by considering topics that genuinely interest you within your field. This ensures that you’ll remain motivated throughout the research process.
2. Review existing literature:
Conduct a preliminary literature review to understand what’s already known about your topic and identify gaps in current knowledge.
3. Consider relevance and significance :
Ensure that your question addresses a meaningful issue or problem in your field. It should contribute to existing knowledge or have practical implications .
4. Assess feasibility:
Consider whether you have access to the necessary resources, data, and time to answer the question effectively.
5. Be specific:
Narrow down your question to make it manageable. Avoid overly broad or vague questions that could lead to unfocused research.
6. Formulate the question:
Craft your question using clear, concise language. It should be open-ended enough to allow for in-depth exploration but specific enough to guide your research.
7. Test your question:
Ask yourself if the question can be researched, analyzed, and potentially answered within the scope of your study.
For example, instead of a broad question like “How does social media affect teenagers?”, you might refine it to “How does daily Instagram use impact self-esteem in female high school students aged 14-18 in urban areas?”
Step#2: Select and define your independent and dependent variables
This step is crucial in developing your conceptual framework as it helps clarify the relationships you’ll be exploring in your research. Let’s break down each component:
Independent Variables:
These are the factors you manipulate or control in your study. They are presumed to cause or influence the dependent variable. In your conceptual framework, independent variables are typically positioned on the left or at the beginning of your model.
For example, in a study on academic performance, independent variables might include:
- Study hours per week
- Teaching methods
Dependent Variables:
These are the outcomes or effects you’re measuring in your study. They are influenced by the independent variables. In your conceptual framework, dependent variables are usually positioned on the right or at the end of your model.
Using the same example, the dependent variable might be:
- Student grades
- Test scores
Moderator Variables:
These are variables that affect the strength or direction of the relationship between independent and dependent variables. They can amplify or diminish the effect of the independent variable on the dependent variable.
For instance, a moderator in our academic performance study could be:
- Student motivation level
Mediator Variables:
These variables explain how or why an independent variable affects the dependent variable. They serve as a link in the causal chain between the independent and dependent variables.
An example of a mediator in our study might be:
- Student engagement level
Moderator vs. Mediator:
The key difference is that moderators affect the strength of the relationship, while mediators explain the process through which the independent variable influences the dependent variable.
Control Variables:
These are variables that you hold constant or control for in your study to ensure that they don’t interfere with the relationship between your main variables of interest. They help isolate the effects of your independent variables on the dependent variables.
In our academic performance example, control variables might include:
- Socioeconomic status
- Prior academic achievement
When selecting and defining these variables:
- Ensure they are related to your research question.
- Choose variables that can be measured or observed.
- Consider how these variables interact with each other.
- Be precise in your definitions to avoid ambiguity.
Related reading: How to find research articles
Step#3: Determine your cause-and-effect relationship
Determining the cause-and-effect relationship is a critical step in developing your conceptual framework. This step involves identifying and clarifying how your independent variables (causes) are expected to influence your dependent variables (effects).
1. Identify potential causal relationships:
Based on your research question and the variables you’ve selected, hypothesize how your independent variables might affect your dependent variables. Consider both direct and indirect relationships.
2. Review existing theories and literature:
Examine established theories and previous research in your field to support your hypothesized relationships. This helps ground your framework in existing knowledge and can provide insights into potential causal mechanisms.
3. Consider the direction of relationships:
Determine whether the relationships are positive (as one variable increases, the other increases) or negative (as one variable increases, the other decreases).
4. Account for complexity:
Recognize that cause-and-effect relationships in social sciences are often complex. Multiple causes might lead to a single effect, or a single cause might have multiple effects.
5. Consider time factors:
Think about whether the effects are immediate or if there’s a time lag between the cause and the effect. This is particularly important in longitudinal studies.
6. Examine potential mediators and moderators:
Consider how mediator variables might explain the mechanism of the cause-effect relationship, and how moderator variables might influence the strength or direction of these relationships.
7. Be aware of spurious relationships:
Consider whether any apparent cause-effect relationships might be due to other, unmeasured variables. This is where your control variables become important.
8. Use logical reasoning:
Ensure that your proposed cause-effect relationships make logical sense and can be explained theoretically.
9. Consider alternative explanations:
Think critically about other possible explanations for the relationships you’re proposing. This helps in developing a more robust framework.
10. Visualize the relationships:
Start sketching out how these cause-and-effect relationships might look in a diagram. This can help you see potential gaps or inconsistencies in your logic.
- In our academic performance study, we might hypothesize that:
- Increased study hours (independent variable) lead to improved grades (dependent variable).
- This relationship might be mediated by an improved understanding of the subject matter.
- The relationship might be moderated by student motivation, where highly motivated students see a stronger effect of study hours on grades.
- Teaching methods (another independent variable) might also influence grades, possibly through increased student engagement.
Remember, at this stage, you’re proposing these relationships based on theory and prior research. Your actual study will test these proposed cause-and-effect relationships. Be prepared to revise your framework if your findings don’t support your initial hypotheses.
Example of a conceptual framework
An example of a conceptual framework can help illustrate how all the elements we’ve discussed come together.
Let’s use our academic performance study to create a sample conceptual framework.
Research Question:
“How do study hours and teaching methods affect high school students’ academic performance, and what role does student motivation play in this relationship?”
Conceptual Framework Example:
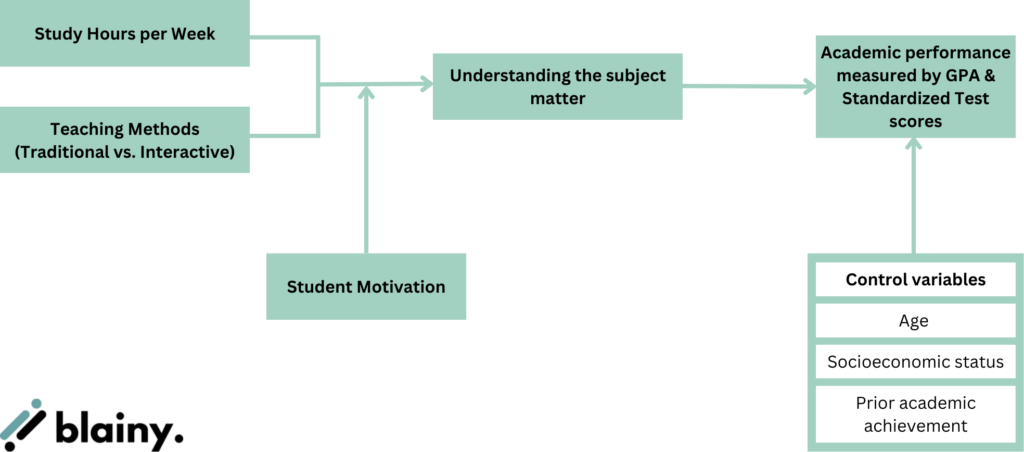
Explanation of the framework:
1. Independent Variables:
- Study Hours per Week
- Teaching Methods (Traditional vs. Interactive)
2. Dependent Variable:
- Academic Performance (measured by GPA and Standardized Test Scores)
3. Mediator:
- Understanding of Subject Matter (explains how study hours and teaching methods affect performance)
4. Moderator:
- Student Motivation (affects the strength of the relationship between independent and dependent variables)
5. Control Variables:
- Socioeconomic Status
- Prior Academic Achievement
Proposed Relationships:
- Increased study hours are expected to lead to better academic performance.
- Interactive teaching methods are hypothesized to result in higher academic performance compared to traditional methods.
- The effect of study hours and teaching methods on academic performance is mediated by the student’s understanding of the subject matter.
- Student motivation moderates these relationships. For highly motivated students, the positive effects of study hours and interactive teaching methods on academic performance are expected to be stronger.
- The control variables are held constant to isolate the effects of the main variables of interest.
This conceptual framework visually represents the hypothesized relationships between variables.
It shows how study hours and teaching methods (independent variables) are expected to influence academic performance (dependent variable), with the understanding of the subject matter as a mediator.
Student motivation serves as a moderator, potentially affecting the strength of these relationships.
The framework also acknowledges the presence of control variables, which are important for the study but not the primary focus of the research question.
Conclusion
Developing a conceptual framework is a critical step in research, providing structure and clarity to complex investigations. This article has outlined key steps in creating robust frameworks, emphasizing variable selection, relationship determination, and visual representation.
A well-constructed framework, as illustrated in our academic performance example, integrates various elements into a comprehensive model.
It’s important to remember that conceptual frameworks are dynamic, evolving with new insights.
Ultimately, they serve as invaluable tools, guiding research processes and effectively communicating ideas, thus forming a solid foundation for knowledge advancement in any field.
Frequently asked questions
What is a conceptual framework in research.
A conceptual framework in research is a structured approach to organizing and presenting the theoretical and conceptual underpinnings of a study. It visually or narratively explains the main variables, concepts, or constructs in a research project and how they are expected to relate to one another. Essentially, it’s a researcher’s map of the territory they plan to explore, showing the anticipated relationships between key elements of their study.
What are the 3 components of conceptual framework in research?
The three main components of a conceptual framework in research are:
- Variables: These include independent variables (factors that influence outcomes), dependent variables (outcomes being studied), and potentially mediating or moderating variables.
- Relationships: This component describes how the variables are expected to interact or influence each other, often based on existing theories or previous research.
- Context: This includes the broader theoretical background, assumptions, and limitations that frame the study and help explain why certain variables and relationships are being examined.
What are the three main types of conceptual frameworks for research?
The three main types of conceptual frameworks in research are:
- Descriptive Frameworks: These aim to identify, define, and describe the key concepts or variables in a study without necessarily proposing specific relationships between them.
- Explanatory Frameworks: These go beyond description to propose and explain relationships between variables, often drawing on existing theories to predict how and why certain factors influence outcomes.
- Predictive Frameworks: These frameworks not only describe and explain relationships but also aim to predict outcomes based on specific conditions or interventions.
What is the difference between theoretical and conceptual frameworks?
Theoretical and conceptual frameworks serve different roles in research. A theoretical framework focuses on existing theories relevant to the research topic , providing a broader context for understanding the problem. It draws from multiple theories to explain phenomena and positions the study within the larger body of knowledge in the field.
A conceptual framework, however , is specific to the particular study being conducted. It identifies and defines the key variables and concepts in the study, showing how these variables are expected to relate to each other. While it often incorporates elements from the theoretical framework, it applies them to the specific research context.
The conceptual framework is more practical, serving as a roadmap for the study by guiding data collection, analysis, and interpretation. It helps researchers visualize relationships between variables and clarify their hypotheses, bridging the gap between broad theories and the practical aspects of the research.
About the Author:

Research Implications 101: A Beginner’s Guide to Writing for Impact

The Significance of Research: Why It Matters

What is a Position Paper? Definition, Purpose & Examples

How to Write a Biographical Essay?

Capstone Projects 101: Definition, Purpose, and More

How to Rephrase a Thesis Statement in 4 Easy Steps

Unlock effortless writing excellence with the world's #1 AI-powered essay and research paper writer. Experience instant research paper perfection and elevate your writing to the next level.
Limited time offers 🎁🎉.
Black Friday Sale
Cyber Monday Sale
Discover More
50+ Free AI Tools
Terms & Condition
Privacy Policy
✉ [email protected]
✆ +971 50 760 0820
📍190 Hackett Inlet, Eastern Region, Dubai, UAE.
Copyright © 2024 Blainy
- Privacy Policy

Home » Conceptual Framework – Types, Methodology and Examples
Conceptual Framework – Types, Methodology and Examples
Table of Contents

Conceptual Framework
Definition:
A conceptual framework is a structured approach to organizing and understanding complex ideas, theories, or concepts. It provides a systematic and coherent way of thinking about a problem or topic, and helps to guide research or analysis in a particular field.
A conceptual framework typically includes a set of assumptions, concepts, and propositions that form a theoretical framework for understanding a particular phenomenon. It can be used to develop hypotheses, guide empirical research, or provide a framework for evaluating and interpreting data.
Conceptual Framework in Research
In research, a conceptual framework is a theoretical structure that provides a framework for understanding a particular phenomenon or problem. It is a key component of any research project and helps to guide the research process from start to finish.
A conceptual framework provides a clear understanding of the variables, relationships, and assumptions that underpin a research study. It outlines the key concepts that the study is investigating and how they are related to each other. It also defines the scope of the study and sets out the research questions or hypotheses.
Types of Conceptual Framework
Types of Conceptual Framework are as follows:

Theoretical Framework
A theoretical framework is an overarching set of concepts, ideas, and assumptions that help to explain and interpret a phenomenon. It provides a theoretical perspective on the phenomenon being studied and helps researchers to identify the relationships between different concepts. For example, a theoretical framework for a study on the impact of social media on mental health might draw on theories of communication, social influence, and psychological well-being.
Conceptual Model
A conceptual model is a visual or written representation of a complex system or phenomenon. It helps to identify the main components of the system and the relationships between them. For example, a conceptual model for a study on the factors that influence employee turnover might include factors such as job satisfaction, salary, work-life balance, and job security, and the relationships between them.
Empirical Framework
An empirical framework is based on empirical data and helps to explain a particular phenomenon. It involves collecting data, analyzing it, and developing a framework to explain the results. For example, an empirical framework for a study on the impact of a new health intervention might involve collecting data on the intervention’s effectiveness, cost, and acceptability to patients.
Descriptive Framework
A descriptive framework is used to describe a particular phenomenon. It helps to identify the main characteristics of the phenomenon and to develop a vocabulary to describe it. For example, a descriptive framework for a study on different types of musical genres might include descriptions of the instruments used, the rhythms and beats, the vocal styles, and the cultural contexts of each genre.
Analytical Framework
An analytical framework is used to analyze a particular phenomenon. It involves breaking down the phenomenon into its constituent parts and analyzing them separately. This type of framework is often used in social science research. For example, an analytical framework for a study on the impact of race on police brutality might involve analyzing the historical and cultural factors that contribute to racial bias, the organizational factors that influence police behavior, and the psychological factors that influence individual officers’ behavior.
Conceptual Framework for Policy Analysis
A conceptual framework for policy analysis is used to guide the development of policies or programs. It helps policymakers to identify the key issues and to develop strategies to address them. For example, a conceptual framework for a policy analysis on climate change might involve identifying the key stakeholders, assessing their interests and concerns, and developing policy options to mitigate the impacts of climate change.
Logical Frameworks
Logical frameworks are used to plan and evaluate projects and programs. They provide a structured approach to identifying project goals, objectives, and outcomes, and help to ensure that all stakeholders are aligned and working towards the same objectives.
Conceptual Frameworks for Program Evaluation
These frameworks are used to evaluate the effectiveness of programs or interventions. They provide a structure for identifying program goals, objectives, and outcomes, and help to measure the impact of the program on its intended beneficiaries.
Conceptual Frameworks for Organizational Analysis
These frameworks are used to analyze and evaluate organizational structures, processes, and performance. They provide a structured approach to understanding the relationships between different departments, functions, and stakeholders within an organization.
Conceptual Frameworks for Strategic Planning
These frameworks are used to develop and implement strategic plans for organizations or businesses. They help to identify the key factors and stakeholders that will impact the success of the plan, and provide a structure for setting goals, developing strategies, and monitoring progress.
Components of Conceptual Framework
The components of a conceptual framework typically include:
- Research question or problem statement : This component defines the problem or question that the conceptual framework seeks to address. It sets the stage for the development of the framework and guides the selection of the relevant concepts and constructs.
- Concepts : These are the general ideas, principles, or categories that are used to describe and explain the phenomenon or problem under investigation. Concepts provide the building blocks of the framework and help to establish a common language for discussing the issue.
- Constructs : Constructs are the specific variables or concepts that are used to operationalize the general concepts. They are measurable or observable and serve as indicators of the underlying concept.
- Propositions or hypotheses : These are statements that describe the relationships between the concepts or constructs in the framework. They provide a basis for testing the validity of the framework and for generating new insights or theories.
- Assumptions : These are the underlying beliefs or values that shape the framework. They may be explicit or implicit and may influence the selection and interpretation of the concepts and constructs.
- Boundaries : These are the limits or scope of the framework. They define the focus of the investigation and help to clarify what is included and excluded from the analysis.
- Context : This component refers to the broader social, cultural, and historical factors that shape the phenomenon or problem under investigation. It helps to situate the framework within a larger theoretical or empirical context and to identify the relevant variables and factors that may affect the phenomenon.
- Relationships and connections: These are the connections and interrelationships between the different components of the conceptual framework. They describe how the concepts and constructs are linked and how they contribute to the overall understanding of the phenomenon or problem.
- Variables : These are the factors that are being measured or observed in the study. They are often operationalized as constructs and are used to test the propositions or hypotheses.
- Methodology : This component describes the research methods and techniques that will be used to collect and analyze data. It includes the sampling strategy, data collection methods, data analysis techniques, and ethical considerations.
- Literature review : This component provides an overview of the existing research and theories related to the phenomenon or problem under investigation. It helps to identify the gaps in the literature and to situate the framework within the broader theoretical and empirical context.
- Outcomes and implications: These are the expected outcomes or implications of the study. They describe the potential contributions of the study to the theoretical and empirical knowledge in the field and the practical implications for policy and practice.
Conceptual Framework Methodology
Conceptual Framework Methodology is a research method that is commonly used in academic and scientific research to develop a theoretical framework for a study. It is a systematic approach that helps researchers to organize their thoughts and ideas, identify the variables that are relevant to their study, and establish the relationships between these variables.
Here are the steps involved in the conceptual framework methodology:
Identify the Research Problem
The first step is to identify the research problem or question that the study aims to answer. This involves identifying the gaps in the existing literature and determining what specific issue the study aims to address.
Conduct a Literature Review
The second step involves conducting a thorough literature review to identify the existing theories, models, and frameworks that are relevant to the research question. This will help the researcher to identify the key concepts and variables that need to be considered in the study.
Define key Concepts and Variables
The next step is to define the key concepts and variables that are relevant to the study. This involves clearly defining the terms used in the study, and identifying the factors that will be measured or observed in the study.
Develop a Theoretical Framework
Once the key concepts and variables have been identified, the researcher can develop a theoretical framework. This involves establishing the relationships between the key concepts and variables, and creating a visual representation of these relationships.
Test the Framework
The final step is to test the theoretical framework using empirical data. This involves collecting and analyzing data to determine whether the relationships between the key concepts and variables that were identified in the framework are accurate and valid.
Examples of Conceptual Framework
Some realtime Examples of Conceptual Framework are as follows:
- In economics , the concept of supply and demand is a well-known conceptual framework. It provides a structure for understanding how prices are set in a market, based on the interplay of the quantity of goods supplied by producers and the quantity of goods demanded by consumers.
- In psychology , the cognitive-behavioral framework is a widely used conceptual framework for understanding mental health and illness. It emphasizes the role of thoughts and behaviors in shaping emotions and the importance of cognitive restructuring and behavior change in treatment.
- In sociology , the social determinants of health framework provides a way of understanding how social and economic factors such as income, education, and race influence health outcomes. This framework is widely used in public health research and policy.
- In environmental science , the ecosystem services framework is a way of understanding the benefits that humans derive from natural ecosystems, such as clean air and water, pollination, and carbon storage. This framework is used to guide conservation and land-use decisions.
- In education, the constructivist framework is a way of understanding how learners construct knowledge through active engagement with their environment. This framework is used to guide instructional design and teaching strategies.
Applications of Conceptual Framework
Some of the applications of Conceptual Frameworks are as follows:
- Research : Conceptual frameworks are used in research to guide the design, implementation, and interpretation of studies. Researchers use conceptual frameworks to develop hypotheses, identify research questions, and select appropriate methods for collecting and analyzing data.
- Policy: Conceptual frameworks are used in policy-making to guide the development of policies and programs. Policymakers use conceptual frameworks to identify key factors that influence a particular problem or issue, and to develop strategies for addressing them.
- Education : Conceptual frameworks are used in education to guide the design and implementation of instructional strategies and curriculum. Educators use conceptual frameworks to identify learning objectives, select appropriate teaching methods, and assess student learning.
- Management : Conceptual frameworks are used in management to guide decision-making and strategy development. Managers use conceptual frameworks to understand the internal and external factors that influence their organizations, and to develop strategies for achieving their goals.
- Evaluation : Conceptual frameworks are used in evaluation to guide the development of evaluation plans and to interpret evaluation results. Evaluators use conceptual frameworks to identify key outcomes, indicators, and measures, and to develop a logic model for their evaluation.
Purpose of Conceptual Framework
The purpose of a conceptual framework is to provide a theoretical foundation for understanding and analyzing complex phenomena. Conceptual frameworks help to:
- Guide research : Conceptual frameworks provide a framework for researchers to develop hypotheses, identify research questions, and select appropriate methods for collecting and analyzing data. By providing a theoretical foundation for research, conceptual frameworks help to ensure that research is rigorous, systematic, and valid.
- Provide clarity: Conceptual frameworks help to provide clarity and structure to complex phenomena by identifying key concepts, relationships, and processes. By providing a clear and systematic understanding of a phenomenon, conceptual frameworks help to ensure that researchers, policymakers, and practitioners are all on the same page when it comes to understanding the issue at hand.
- Inform decision-making : Conceptual frameworks can be used to inform decision-making and strategy development by identifying key factors that influence a particular problem or issue. By understanding the complex interplay of factors that contribute to a particular issue, decision-makers can develop more effective strategies for addressing the problem.
- Facilitate communication : Conceptual frameworks provide a common language and conceptual framework for researchers, policymakers, and practitioners to communicate and collaborate on complex issues. By providing a shared understanding of a phenomenon, conceptual frameworks help to ensure that everyone is working towards the same goal.
When to use Conceptual Framework
There are several situations when it is appropriate to use a conceptual framework:
- To guide the research : A conceptual framework can be used to guide the research process by providing a clear roadmap for the research project. It can help researchers identify key variables and relationships, and develop hypotheses or research questions.
- To clarify concepts : A conceptual framework can be used to clarify and define key concepts and terms used in a research project. It can help ensure that all researchers are using the same language and have a shared understanding of the concepts being studied.
- To provide a theoretical basis: A conceptual framework can provide a theoretical basis for a research project by linking it to existing theories or conceptual models. This can help researchers build on previous research and contribute to the development of a field.
- To identify gaps in knowledge : A conceptual framework can help identify gaps in existing knowledge by highlighting areas that require further research or investigation.
- To communicate findings : A conceptual framework can be used to communicate research findings by providing a clear and concise summary of the key variables, relationships, and assumptions that underpin the research project.
Characteristics of Conceptual Framework
key characteristics of a conceptual framework are:
- Clear definition of key concepts : A conceptual framework should clearly define the key concepts and terms being used in a research project. This ensures that all researchers have a shared understanding of the concepts being studied.
- Identification of key variables: A conceptual framework should identify the key variables that are being studied and how they are related to each other. This helps to organize the research project and provides a clear focus for the study.
- Logical structure: A conceptual framework should have a logical structure that connects the key concepts and variables being studied. This helps to ensure that the research project is coherent and consistent.
- Based on existing theory : A conceptual framework should be based on existing theory or conceptual models. This helps to ensure that the research project is grounded in existing knowledge and builds on previous research.
- Testable hypotheses or research questions: A conceptual framework should include testable hypotheses or research questions that can be answered through empirical research. This helps to ensure that the research project is rigorous and scientifically valid.
- Flexibility : A conceptual framework should be flexible enough to allow for modifications as new information is gathered during the research process. This helps to ensure that the research project is responsive to new findings and is able to adapt to changing circumstances.
Advantages of Conceptual Framework
Advantages of the Conceptual Framework are as follows:
- Clarity : A conceptual framework provides clarity to researchers by outlining the key concepts and variables that are relevant to the research project. This clarity helps researchers to focus on the most important aspects of the research problem and develop a clear plan for investigating it.
- Direction : A conceptual framework provides direction to researchers by helping them to develop hypotheses or research questions that are grounded in existing theory or conceptual models. This direction ensures that the research project is relevant and contributes to the development of the field.
- Efficiency : A conceptual framework can increase efficiency in the research process by providing a structure for organizing ideas and data. This structure can help researchers to avoid redundancies and inconsistencies in their work, saving time and effort.
- Rigor : A conceptual framework can help to ensure the rigor of a research project by providing a theoretical basis for the investigation. This rigor is essential for ensuring that the research project is scientifically valid and produces meaningful results.
- Communication : A conceptual framework can facilitate communication between researchers by providing a shared language and understanding of the key concepts and variables being studied. This communication is essential for collaboration and the advancement of knowledge in the field.
- Generalization : A conceptual framework can help to generalize research findings beyond the specific study by providing a theoretical basis for the investigation. This generalization is essential for the development of knowledge in the field and for informing future research.
Limitations of Conceptual Framework
Limitations of Conceptual Framework are as follows:
- Limited applicability: Conceptual frameworks are often based on existing theory or conceptual models, which may not be applicable to all research problems or contexts. This can limit the usefulness of a conceptual framework in certain situations.
- Lack of empirical support : While a conceptual framework can provide a theoretical basis for a research project, it may not be supported by empirical evidence. This can limit the usefulness of a conceptual framework in guiding empirical research.
- Narrow focus: A conceptual framework can provide a clear focus for a research project, but it may also limit the scope of the investigation. This can make it difficult to address broader research questions or to consider alternative perspectives.
- Over-simplification: A conceptual framework can help to organize and structure research ideas, but it may also over-simplify complex phenomena. This can limit the depth of the investigation and the richness of the data collected.
- Inflexibility : A conceptual framework can provide a structure for organizing research ideas, but it may also be inflexible in the face of new data or unexpected findings. This can limit the ability of researchers to adapt their research project to new information or changing circumstances.
- Difficulty in development : Developing a conceptual framework can be a challenging and time-consuming process. It requires a thorough understanding of existing theory or conceptual models, and may require collaboration with other researchers.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Research Project – Definition, Writing Guide and...

Scope of the Research – Writing Guide and...

Purpose of Research – Objectives and Applications

Institutional Review Board – Application Sample...

Research Recommendations – Examples and Writing...

Data Analysis – Process, Methods and Types

IMAGES
VIDEO