Loading, just a moment...

What to Know About Recovery from Gender Affirmation Surgery
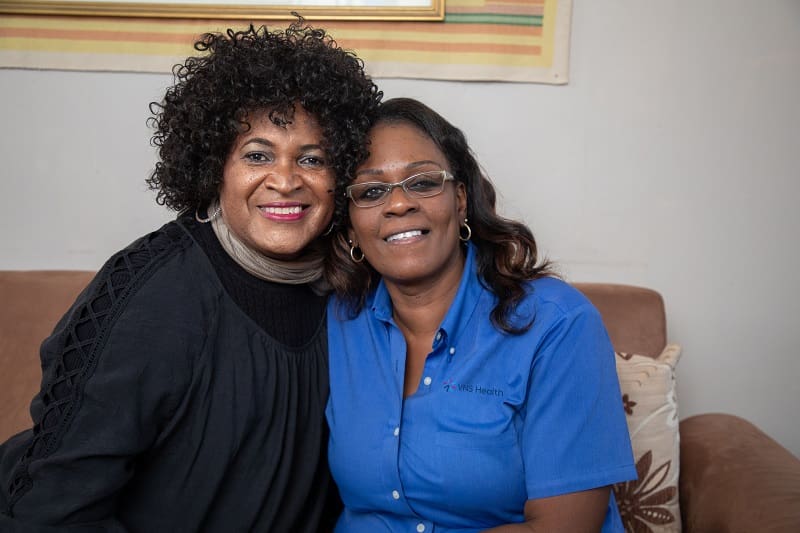

Gender affirmation surgery — like any surgery — includes a recovery period. The time you spend healing is just as important as the surgery itself. But recovery doesn’t happen overnight, and you may need to take some steps now to prepare for the days and weeks following your surgery.
As your surgery date gets close, you may experience a range of emotions. You may have questions about what recovery will look like. Whether you are having top, bottom, or facial surgery, here are some things to keep in mind about your recovery.
Recovery May Take Longer Than You Expect
Preparing for the unknown is always hard, and this can be especially true when planning for gender affirmation surgery. Even if you’ve done your research, your experience may be very different from what you expect. Everyone’s body, surgery, and recovery will be different, and that’s OK.
Your body may not bounce back as fast as you thought it would. Easy tasks may be challenging or even off limits. For example, your doctor may instruct you to avoid lifting your arms after top surgery. And the level of pain and how long it lasts might be more than you expected.
Recovery isn’t a straight line. It will have its ups and downs. If your recovery doesn’t look or feel exactly how you planned, don’t panic. Be gentle with your body — and your expectations — as you heal.
Everyone deserves health care that respects their gender identity. VNS Health supports the unique needs of transgender and nonbinary individuals undergoing and recovering from gender affirmation surgery.
Coordinating Caregiving Is Key
Your recovery should include rest, medication, and following your doctor’s orders, as well as caregiving support.
Caregivers can help as you heal after your surgery. They can prep meals and do chores. Or they can help out with tasks like keeping track of your medicines or monitoring your surgical site. These are big responsibilities, and just because someone is a good friend doesn’t necessarily mean they will be a good caregiver.
Try to plan for at least three caregivers who can help you in shifts and be responsible for different tasks. Having several caregivers also means you will have backup support if you need it. Sometimes, a person may realize that the responsibility is too much for them and may need to step away. This can leave you in a tough spot if you have only one caregiver.
Even if you have loved ones who can care for you, professional home care can be a beneficial part of your recovery. A nurse can provide skilled medical services like emptying drains, supporting with dilation, and changing bandages. They can also answer your questions and reassure you. A nurse can also bring in other professionals, like rehab therapists, social workers, and home health aides. Having an expert team during your recovery can give you extra support and peace of mind.
Your Surgery May Bring Up Big Feelings
Sometimes it’s not so much about the physical recovery from gender affirmation surgery as about how you react to it. After your surgery, you may experience a range of emotions — and they may not be ones you expect.
Before your surgery, you may think that everything will fall into place or that you’ll feel joyful right after your surgery. You might, but you might not — or you might swing from relief to doubt. Feeling sad or scared or angry during your recovery is normal. Your feelings — whatever they may be — are valid.
Feelings and emotions aren’t simple, and they definitely aren’t predictable. It’s all right if you don’t feel happy or joyous after your surgery. It’s okay if you feel regret in the days, weeks, or even months afterwards. Try not to feel guilty about having feelings. Processing such a big experience can take time, and your reactions aren’t wrong — they’re yours. Processing them is part of your recovery, just like physical healing.
Start Preparing for Your Recovery Now
Although many aspects of your healing will be unpredictable, you can take steps to prepare mentally and physically. Prior to gender affirmation surgery, you can:
- Ask your surgeon about your recovery period and discharge instructions, including supplies you will need. Tip: Have the supplies on hand before you come home from the hospital.
- Ask people in your life to provide caregiving support after your surgery, starting with a ride home from the hospital.
- Talk to other people about their gender affirmation surgeries. Online communities like Reddit or a virtual support group may even help you connect with people who have worked with your specific surgeon.
- Prepare your home for your recovery. Make the space comfy, and put commonly used items like your phone charger and the TV remote within reach.
- Secure a gender-affirming therapist prior to surgery. It is recommended that you have access to a licensed mental health professional who can provide the ongoing emotional support you need before your surgery and during and after your recovery.
Your surgeon will order home care services as part of your discharge instructions. Ask specifically about LGBTQ+ focused home care, like the Gender Affirmation Program at VNS Health. By starting your preparation early, you and your loved ones can feel more comfortable and confident in your recovery.
Sign up for VNS Health’s newsletter just for caregivers.

Best Qualities of a Home Health Aide for Someone with Dementia

How to Choose a Home Care Agency That Is LGBTQ+ Friendly

What Is Respite Care? Why Do I Need It?
Choose vns health for your loved one's care..
Road closure on Marquam Hill: Part of S.W. Campus Drive is closed until March 2025.
Transgender Health Program
Gender-affirming surgery.
OHSU surgeons are leaders in gender-diverse care. We provide specialized services tailored to the needs and goals of each patient. We offer:
- Specialists who do hundreds of surgeries a year.
- Plastic surgeons, urologists and other specialists who are leading experts in bottom surgery, top surgery and other gender-affirming options.
- Vocal surgery with a highly trained ear, nose and throat doctor.
- Peer volunteers who can provide support during visits.
- Welcoming care for every patient, every gender and every journey.
Our surgical services
We offer many gender-affirming surgery options for transgender and nonbinary patients, including options within the following types. We also welcome you to request a procedure that isn’t listed on our pages.
Top surgery:
- Gender-affirming mastectomy
- Gender-affirming breast augmentation
Bottom surgery:
- Phalloplasty and metoidioplasty , including vagina-preserving options
- Vaginoplasty and vulvoplasty , including penile-preserving options
Hysterectomy
Nullification surgery, oophorectomy, orchiectomy.
Bottom surgery options also include:
- Scrotectomy
- Scrotoplasty
- Urethroplasty
- Vaginectomy
Additional gender-affirming options:
- Adam’s apple surgery
Vocal surgery
Face and body surgery, preparing for surgery.
Please see our patient guide page to learn about:
- Steps to surgery
- WPATH standards of care
- The letter of support needed for some surgeries
For patients
Request services.
Please fill out an online form:
- I am seeking services for myself.
- I am seeking services for someone else.
Other questions and concerns
Contact us at:
- 503-494-7970
- [email protected]
Refer a patient
- Please complete our Request for Transgender Health Services referral form and fax with relevant medical records to 503-346-6854 .
- Learn more on our For Health Care Professionals page.
At OHSU, our gynecologic surgeon, Dr. Lishiana Shaffer, specializes in hysterectomies (uterus and cervix removal; often combined with oophorectomy, or ovary removal) for gender-diverse patients. She does more than 150 a year.
We also offer a Transgender Gynecology Clinic with a gender-neutral space. Services include surgery. Referrals and appointments are made through the OHSU Center for Women's Health, though the space is not in the center. Call 503-418-4500 to request an appointment.
Some patients choose hysterectomy to:
- More closely align their bodies with their gender identity.
- With ovary removal, to remove a main source of the hormone estrogen.
- To end pain caused by testosterone therapy that shrinks the uterus.
- To end the need for some gynecologic exams, such Pap smears.
Preparation: We usually recommend a year of hormone therapy first, to shrink the uterus. We don’t require a year of social transition.
How hysterectomy is done
Most often, we use a minimally invasive laparoscope and small incisions in the belly. We usually recommend removing fallopian tubes as well, to greatly reduce the risk of ovarian cancer.
Most patients spend one night in the hospital. Recovery typically takes about two weeks. You’re encouraged to walk during that time but to avoid heavy lifting or strenuous exercise.
Considerations and risks
Hysterectomy is usually safe, and we have a low rate of complications. Risks can include blood clots, infection and scar tissue. Because of a possible link between hysterectomy and higher risk of cardiovascular disease, your doctors may recommend regular tests.
Removing the uterus also ends the ability to carry a child. OHSU fertility experts offer options such as egg freezing before treatment, and connecting patients with a surrogacy service.
OHSU offers nullification surgery to create a gender-neutral look in the groin area.
Nullification surgery may include:
- Removing the penis (penectomy)
- Removing the testicles (orchiectomy)
- Reducing or removing the scrotum (scrotectomy)
- Shortening the urethra
- Removing the uterus (hysterectomy)
- Removing the vagina (vaginectomy)
The procedure takes several hours. Patients can expect to spend one to two nights in the hospital. Recovery typically takes six to eight weeks. Patients are asked to limit walking and to stick to light to moderate activity for four weeks. They should wait three months before bicycling or strenuous activity.
Nullification surgery cannot be reversed. Risks can include:
- Changes in sensation
- Dissatisfaction with the final look
- Healing problems
Removing the penis and testicles or the uterus also affects the ability to conceive a child. OHSU fertility experts offer options such as freezing eggs and connecting patients with a surrogacy service.
Having a gynecologic surgeon remove one or both ovaries is often done at the same time as a hysterectomy. We do nearly all these surgeries with a minimally invasive laparoscope and small incisions in the belly.
Most patients spend one night in the hospital and return to their regular routine in about two weeks.
The ovaries produce estrogen, which helps prevent bone loss and the thickening of arteries. After removal, a patient should be monitored long-term for the risk of osteoporosis and cardiovascular disease.
We encourage patients to keep at least one ovary to preserve fertility without egg freezing. This also preserves some hormone production, which can avoid early menopause.
At OHSU, expert urologists do orchiectomies (testicle removal). Patients may choose this option:
- To remove the body’s source of testosterone
- As part of a vaginoplasty or vulvoplasty (surgeries that create a vagina and/or vulva)
- To relieve dysphoria (some patients choose only this surgery)
Removing the testicles usually means a patient can stop taking a testosterone blocker. Patients may also be able to lower estrogen therapy.
How orchiectomy is done
The surgeon makes an incision in the scrotum. The testicles and the spermatic cord, which supplies blood, are removed. Scrotal skin is removed only if the patient specifically requests it. The skin is used if the patient plans a vaginoplasty or vulvoplasty.
You will probably go home the same day. Patients can typically resume normal activities in a week or two.
Reducing testosterone production may increase the risk of bone loss and cardiovascular disease, so we recommend regular tests. Without prior fertility treatment, orchiectomy also ends the ability to produce children. Serious risks are uncommon but include bleeding, infection, nerve damage and scarring.
Adam’s apple reduction (laryngochrondoplasty)
Dr. Joshua Schindler, an ear, nose and throat doctor who does Adam’s apple and vocal surgeries, completed his training at Johns Hopkins University.
Laryngochrondoplasty is also known as Adam’s apple reduction or a tracheal shave (though the trachea, or windpipe, is not affected).
A surgeon removes thyroid cartilage at the front of the throat to give your neck a smoother appearance. This procedure can often be combined with facial surgery.
Thin incision: At OHSU, this procedure can be done by an ear, nose and throat doctor (otolaryngologist) with detailed knowledge of the neck’s anatomy. The surgeon uses a thin incision, tucked into a neck line or fold. It can also be done by one of our plastic surgeons, typically with other facial surgery.
In an office or an operating room: Our team can do a laryngochrondoplasty in either setting, which may limit a patient’s out-of-pocket expenses.
OHSU also offers Adams’ apple enhancement surgery.
Many patients find that hormone therapy and speech therapy help them achieve a voice that reflects their identity. For others, vocal surgery can be added to raise the voice’s pitch.
Voice therapy: Patients have voice and communication therapy before we consider vocal surgery. Your surgeon and your speech therapist will assess your voice with tests such as videostroboscopy (allowing us to see how your vocal cords work) and acoustic voice analysis.
Effective surgery: We use a surgery called a Wendler glottoplasty. It’s done through the mouth under general anesthesia. The surgeon creates a small controlled scar between the two vocal cords, shortening them to increase tension and raise pitch. Unlike techniques that can lose effectiveness over time, this surgery offers permanent results.
Hormone therapy can bring out desired traits, but it can’t change the underlying structure or remove hair follicles. Our highly trained surgeons and other specialists offer options. Patients usually go home the same day or spend one night in a private room.
Face options:
- Browlift (done with the forehead)
- Cheek augmentation
- Chin surgery (genioplasty), including reductive, implants or bone-cut options
- Eyelid surgery
- Face-lift, neck lift
- Forehead lengthening
- Forehead reduction, including Type 3 sinus setback and orbital remodeling
- Hairline advancement (done with the forehead)
- Jawline contouring
- Lip lift and/or augmentation
- Lipofilling (transferring fat using liposuction and filling)
- Nose job (rhinoplasty)
Body options:
Hormone treatment may not result in fat distribution consistent with your gender. We offer liposuction and fat grafting to reshape areas of the body.
- A to Z Guides
What Is Gender Affirmation Surgery?

Surgery to change the appearance of your body is a common choice for all kinds of people. There are many reasons that people might want to alter their appearance. For transgender or gender nonconforming people, making changes to their bodies is a way of affirming their identity.
A trans person can choose from multiple procedures to make their appearance match their self-identified gender identity. Doctors refer to this as gender "affirmation" surgery.
Trans people might decide to have surgery on their chest, genitals, or face. These surgeries are personal decisions, and each person makes their own choices about what is right for them.
Learn more about gender affirmation surgery and how it helps trans people.
What Does It Mean to Be Transgender or Nonbinary?
Transgender is a word to describe people whose gender identity or gender expression doesn't match the sex they were assigned at birth. Typically, parents and doctors assume a baby's gender based on the appearance of their genitals. But some people grow up and realize that their sense of who they are isn't aligned with how their bodies look. These people are considered transgender.
Trans people may identify as a different gender than what they were assigned at birth. For example, a child assigned male at birth may identify as female. Nonbinary people don't identify as either male or female. They may refer to themselves as "nonbinary" or "genderqueer."
There are many options for trans and nonbinary people to change their appearance so that how they look reflects who they are inside. Many trans people use clothing, hairstyles, or makeup to present a particular look. Some use hormone therapy to refine their secondary sex characteristics. Some people choose surgery that can change their bodies and faces permanently.
Facial Surgery
Facial plastic surgery is popular and accessible for all kinds of people in the U.S. It is not uncommon to have a nose job or a facelift . Cosmetic surgery is great for improving self-esteem and making people feel more like themselves. Trans people can use plastic surgery to adjust the shape of their faces to better reflect their gender identity.
Facial feminization. A person with a masculine face can have surgeries to make their face and neck look more feminine. These can be done in one procedure or through multiple operations. They might ask for:
- Forehead contouring
- Jaw reduction
- Chin surgery
- Hairline advancement
- Cheek augmentation
- Rhinoplasty
- Lip augmentation
- Adam's apple reduction
Facial masculinization. Someone with a feminine face can have surgery to make their face look more masculine. The doctor may do all the procedures at one time or plan multiple surgeries. Doctors usually offer:
- Forehead lengthening
- Jaw reshaping
- Chin contouring
- Adam's apple enhancement
Top Surgery
Breast surgeries are very common in America. The shorthand for breast surgeries is "top surgery." All kinds of people have operations on their breasts , and there are a lot of doctors who can do them. The surgeries that trans people have to change their chests are very similar to typical breast enhancement or breast removal operations.
Transfeminine. When a trans person wants a more feminine bustline, that's called transfeminine top surgery. It involves placing breast implants in a person's chest. It's the same operation that a doctor might do to enlarge someone's breasts or for breast reconstruction .
Transmasculine. Transmasculine top surgery is when a person wants a more masculine chest shape. It is similar to a mastectomy . The doctor removes the breast tissue to flatten the whole chest. The doctor can also contour the skin and reposition the nipples to look more like a typical man's chest.
Bottom Surgery
For people who want to change their genitals, some operations can do that. That is sometimes called bottom surgery. Those are complicated procedures that require doctors with a lot of experience with trans surgeries.
Transmasculine bottom surgery. Some transmasculine people want to remove their uterus and ovaries. They can choose to have a hysterectomy to do that. This reduces the level of female hormones in their bodies and stops their menstrual cycles.
If a person wants to change their external genitals, they can ask for surgery to alter the vaginal opening. A surgeon can also construct a penis for them. There are several techniques for doing this.
Metoidioplasty uses the clitoris and surrounding skin to create a phallus that can become erect and pass urine. A phalloplasty requires grafting skin from another part of the body into the genital region to create a phallus. People can also have surgery to make a scrotum with implants that mimic testicles.
Transfeminine bottom surgery. People who want to reduce the level of male hormones in their bodies may choose to have their testicles removed. This is called an orchiectomy and can be done as an outpatient operation.
Vaginoplasty is an operation to construct a vagina . Doctors use the tissue from the penis and invert it into a person's pelvic area. The follow-up after a vaginoplasty involves using dilators to prevent the new vaginal opening from closing back up.
How Much Does Gender Affirmation Surgery Cost?
Some medical insurance companies will cover some or most parts of your gender-affirming surgery. But many might have certain "exclusions" listed in the plan. They might use language like "services related to sex change" or "sex reassignment surgery." These limitations may vary by state. It's best to reach out to your insurance company by phone or email to confirm the coverage or exclusions.
If your company does cover some costs, they may need a few documents before they approve it.
This can include:
- A gender dysphoria diagnosis in your health records. It's a term used to describe the feeling you have when the sex you're assigned at birth does not match with your gender identity. A doctor can provide a note if it's necessary.
- A letter of support from a mental health professional such as a social worker, psychiatrist , or a therapist.
Gender affirmation surgery can be very expensive. It's best to check with your insurance company to see what type of coverage you have.
If you're planning to pay out-of-pocket, prices may vary depending on the various specialists involved in your case. This can include surgeons, primary care doctors, anesthesiologists, psychiatrists, social workers, and counselors. The procedure costs also vary, and the total bill will include a number of charges, including hospital stay, anesthesia, counseling sessions, medications, and the procedures you elect to have.
Whether you choose facial, top, or bottom or a combination of these procedures, the total bill after your hospital stay can cost anywhere from $5,400 for chin surgery to well over $100,000 for multiple procedures.
Recovery and Mental Health After Gender Affirmation Surgery
Your recovery time may vary. It will depend on the type of surgery you have. But swelling can last anywhere from 2 weeks for facial surgery to up to 4 months or more if you opted for bottom surgery.
Talk to your doctor about when you can get back to your normal day-to-day routine. But in the meantime, make sure to go to your regular follow-up appointments with your doctor. This will help them make sure you're healing well post-surgery.
Most trans and nonbinary people who get gender affirmation surgery report that it improves their overall quality of life. In fact, over 94% of people who opt for surgery say they are satisfied with the results.
Folks who have mental health support before surgery tend to do better, too. One study found that after gender affirmation surgery, a person's need for mental health treatment went down by 8%.
Not all trans and nonbinary people choose to have gender affirmation surgery, or they may only have some of the procedures available. If you are considering surgery, speak with your primary care doctor to discuss what operations might be best for you.
Top doctors in ,
Find more top doctors on, related links.
- Health A-Z News
- Health A-Z Reference
- Health A-Z Slideshows
- Health A-Z Quizzes
- Health A-Z Videos
- WebMDRx Savings Card
- Coronavirus (COVID-19)
- Hepatitis C
- Diabetes Warning Signs
- Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Morning-After Pill
- Breast Cancer Screening
- Psoriatic Arthritis Symptoms
- Heart Failure
- Multiple Myeloma
- Types of Crohn's Disease
- BOOK CONSULTATION
- The Surgical Journey
- Where do I start?
- Am I eligible for surgery?
- Preparing for Surgery
- General Recovery Info
- Risks & Safety
- Top Surgery
- Top Surgery Techniques
- Techniques Beyond the Binary
- Top Surgery Videos
- Breast Augmentation
- Facial Surgery
- Techniques & Incisions
- Body Contouring
- Body Feminization
- Body Masculinization
- Non-Binary Body Contouring
- Bottom Surgery
- “Feminizing” Techniques & Recovery
- “Masculinizing” Techniques & Recovery
- Our Services
- Currently Offered
- Outside Services
- Transition 101
- Introduction to Transitioning
- Support Services: Helpful Links
- Transitioning Later In Life
- Legal Name & Gender Change
- Transmasculine & Pregnancy
- Transgender Healthcare
- Mental Health
- Hormone Therapy
Trans Youth & Adolescents
- Mental Health Support
- Common Questions About Your Child’s Transition
- For Caregivers
- Explaining Your Child’s Identity
- Talking With Schools About Your Child
- Puberty Blockers
- Challenging Topics
- Detransition
- Adolescents
- Gatekeeping vs Empowerment
- Rapid Onset Gender Dysphoria
- Double Incision
- Periareolar
- Inverted T / Aggressive Breast Reduction
- Gynecomastia
- Facial Feminization
- Facial Masculinization
- Labiaplasty
- Vaginoplasty
- Pricing and Financing
- Insurance Approval
- Insurance Denial
- Insurance Accepted
- Referral Letters
- Advocacy Team
- Make a Payment Now
- Our Philosophy
- Meet Our Team
- Office & Facilities
- Testimonials
- Get in Touch
- For Current Patients
- For Providers
Consultation request
- Interpretation Services
- Privacy Policy

Do you have any questions? Check our F.A.Q. section or contact us directly!
Demystifying and Navigating Your Options: Gender Reassignment Surgery

Medically reviewed by Paul Gonzales on March 25, 2024.

Previously, the term gender reassignment surgery (GRS) referred to genital reconstruction bottom surgeries like vaginoplasty, vulvoplasty, phalloplasty, or metoidioplasty. Individuals who look up this term on a search engine do so looking for information on gender-affirming procedures generally for transgender, non-binary and gender non-conforming people. This detailed guide breaks down everything you need to know about these procedures, their costs, their eligibility requirements, the potential benefits and risks and more. If you are interested in undergoing any gender-affirming or “gender reassignment” surgery, you can schedule a free, virtual consultation with one of our surgeons.
At the Gender Confirmation Center (GCC), we generally avoid using terminology like GRS in a clinical setting out of the recognition that for the vast majority of our patients, surgeries do not “reassign” anyone’s gender. Rather, surgery can help individuals experience greater alignment with their bodies and greater gender euphoria as a result.
Types of Gender “Reassignment” Surgeries: “Female to Male (FTM)”
Female to Male (FTM) is outdated terminology that the GCC does not use in our clinical practice. This abbreviation leaves out the experiences of many trans masculine and non-binary patients who do not identify with being labeled as a “woman becoming a man.”
In the past, “FTM gender confirmation surgery” was used to describe surgical procedures that reverse the effects of an initial estrogenic puberty or procedures that reconstruct a patient’s genitals. We still receive various inquiries about which “FTM” procedures we offer, so below you can find a list of surgeries that have typically been placed under this label.
Please note that patients can seek out any of these procedures regardless of their gender identity. The goal of our practice is not to make our patients “into men,” but to help them feel more comfortable, affirmed, and/or aligned with their bodies.
Chest Surgery or Top Surgery
“FTM” top surgery is an antiquated term that refers to gender-affirming chest reconstruction and/or breast reduction. Practices who use this acronym sometimes have limited experience meeting the unique needs of non-binary patients seeking top surgery . Patients who would like to remove their chest tissue to have a flatter chest can choose from a variety of incision options to reach their desired results around chest tightness, contour and/or scar shape.
Not all patients who pursue top surgery want flat chests. Whether you would like to opt for a breast reduction or a chest reconstruction with some volume left behind, the button buttonhole incision is the most commonly pursued type.
Top surgery patients who would like to maintain an erotic or a high level of sensation in their nipples can ask their surgeon about nerve-preservation techniques . Inversely, many patients who get top surgery choose to have their nipples removed .
Genital Reconstruction or Bottom Surgery
While the following bottom surgery procedures are traditionally put under the “FTM” category, we recognize that not all patients who pursue these procedures identify as men nor are they looking to “masculinize” their genitals.
Two procedures can be used to reconstruct a penis or “neophallus”: metoidioplasty and phalloplasty. Metoidioplasty or “meta” releases the ligaments around the erectile tissue (called a clitoris or penis) to extend it to about 2-4 inches in length. A phalloplasty uses a donor flap (usually from the forearm or thigh) to construct a penis of 4 inches in length or more (depending on availability of tissue). Both procedures can be specialized to allow a patient to maintain erotic sensation in their genitals (nerve preservation) and/or urinate standing up (urethroplasty).
Associated procedures include the removal of the uterus (hysterectomy), the removal of the vaginal canal (vaginectomy), the construction of a scrotum (scrotoplasty), the insertion of penile/testicular implants, and more.
Body Masculinization Surgery (BMS)
Body Masculinization Surgery (BMS) refers to a series of body contouring procedures. Most often, BMS involves liposuction of one or more of the following areas: abdomen, flanks, hips, thighs, buttocks, or arms. BMS can also involve removing unwanted, excess skin from fat loss or liposuction. Occasionally, some patients may opt for silicone pectoral implants alongside or after their top surgery results.
Facial Masculinization Surgery (FMS)
Facial Masculinization Surgery (FMS) refers to a series of procedures that patients can choose from to give their face a more angular, conventionally masculine appearance. In the bottom third of the face, the chin, jaw, or laryngeal prominence (aka Adam’s apple) can be augmented or increased in size. In the middle third of the face, the appearance of the nose and/or cheeks can be altered. In the top third of the face, the hairline’s position can be changed and the forehead can be augmented.
Types of Gender “Reassignment” Surgeries: “Male to Female (MTF)”
Male to Female (MTF) is outdated terminology that we do not use in our clinical practice. This abbreviation leaves out the experiences of many trans feminine and non-binary patients who do not identify with being labeled as a “man becoming a woman.”
In the past, “MTF gender confirmation surgery” was used to describe surgical procedures that reverse the effects of an initial androgenic (testosterone-dominant) puberty and/or reconstruct a patient’s genitals. As a practice, we still get asked by prospective patients about the “MTF” procedures we offer, which is why we have compiled a guide of surgeries that have typically been placed under this category.
Please note that patients can seek out any of these procedures regardless of their gender identity. The goal of our practice is not to make our patients turn “into women,” but to help them feel greater gender congruence with their bodies.
Breast Augmentation or “MTF” Top Surgery
Typically, for trans feminine and non-binary patients who prefer to have more volume on their chest, breast augmentation with saline or silicone implants allows for greater success in their desired outcomes. Fat grafting procedures limit the amount of volume transferred to the chest based on available body fat that can be safely removed.
Genital Reconstruction or Bottom Surgeries
The most common surgeries that are placed under this category are vaginoplasty and vulvoplasty (also called zero-depth vaginoplasty) procedures. The most common vaginoplasty uses a penile-inversion technique to reconstruct a vaginal canal. However, a penile-preserving vaginoplasty is also another option for patients. Lifelong dilation after this procedure is necessary to maintain the depth of the canal so that it can be used for penetrative sex. Labiaplasty revisions are sometimes sought out by patients wishing to adjust the size, shape and symmetry of their labia and/or clitoral hood.
Before a vaginoplasty, patients may opt to remove the testicles ( orchiectomy ). Patients of varying gender identities undergo orchiectomies for many reasons, such as chronic pain or to simplify their hormone therapy. For patients who plan to have a vaginoplasty in the future, it’s best to consider the timing of an orchiectomy procedure since scrotal tissue can be used to construct the labia.
Facial Feminization Surgery (FFS)
FFS refers to a series of procedures that a patient can choose from to give their face a softer, more conventionally feminine appearance. In the bottom third of the face, the laryngeal prominence (or Adam’s apple), chin, or jaw can be reduced in size. In the middle third of the face, the appearance of the nose and/or cheeks can be altered. In the top third of the face, the hairline’s position can be changed and the forehead can be reduced.
Body Feminization Surgery (BFS)
BFS encompasses a series of body contouring procedures. Most often, BFS involves removal of fat through liposuction of one or more of the following areas: the thighs, the abdomen/waist, or the arms. The fat removed from these areas of the body can be transferred to the buttocks and/or hip areas and is commonly referred to as a Brazilian butt lift (BBL). BFS can also involve removing unwanted excess skin from fat loss or liposuction, a procedure often referred to as a tummy tuck or abdominoplasty.
Evaluating Candidacy for Gender Affirmation Surgery
The following guidelines are used to evaluate patient readiness for gender-affirming surgical procedures:
Informed consent
The GCC follows an informed consent model for surgery because it gives patients autonomy over their health. Under this model, adults can consent to procedures if they have received adequate education about their risks, advantages, and potential effects on their health given their unique medical history. Historically, TGD people have had a difficult time accessing quality gender-affirming health care in part because of gatekeeping and discrimination based on requirements set by insurance companies. For example, letters from medical and mental health providers are a part of these requirements. We recognize that therapists and other healthcare providers are invaluable sources of support for patients undergoing a medical gender transition.
Please note that per the WPATH’s SOC 8 Guidelines , patients must present a support letter from a licensed mental health professional to be eligible for bottom surgery, regardless of whether or not you are seeking insurance coverage. However, Dr. Ley does not require that patients present a support letter to undergo a bottom surgery revision procedure. Whether or not you underwent your initial bottom surgery procedure with her, the support letter eligibility requirement will be waived.
Health factors
We recommend our patients get medical clearance from their primary care provider (PCP) before surgery. If you have medical conditions that may affect your surgery, we can work with your PCP or specialist to ensure a safe recovery. Patients should inform their surgeons of any cardiovascular or respiratory issues, history of anorexia, diabetes, or use of immunosuppressant medications.
Different surgeons may consider a patient’s Body Mass Index (BMI) as part of their eligibility for surgery. You can read more about our requirements and recommendations around BMI here .
We require all our patients to stop smoking or consuming any form of nicotine for at least 3 weeks before and 3 weeks after surgery, as this can lead to significant problems with delayed wound healing. Please do not drink alcohol for at least 1 week before and 1 week after surgery or until prescription pain medications are discontinued.
Insurance requirements
Patients who wish to have their insurance cover their gender affirming surgery need to fulfill certain requirements. You will need to get at least one letter of support from a mental health professional to confirm that the procedure is medically necessary. In the case of bottom surgery, most insurance plans require two letters of support. We recognize that the two-letter insurance requirement can be an extra barrier for patients to access medically necessary, gender-affirming care. For this reason, once you have requested a surgical consultation , we can help you through the process of securing additional documentation.
Additionally, if the surgeon is outside of your insurance’s in-network providers, you will need to get a referral letter from your primary care provider (PCP). Additionally, some insurance companies may require that a patient undergo gender-affirming hormone therapy to cover surgery.
Hormone Therapy Considerations
At GCC, we do not require our patients to undergo hormone therapy to access medically necessary, gender-affirming surgeries. That said, undergoing hormones before surgery can help some patients improve the appearance of post-op results.
- Facial surgery: It may take up to 1.5 years on hormone therapy before soft tissue changes can appear on the face so patients should consider waiting to undergo facial surgery until these changes have settled.
- Bottom surgery: Maximal bottom growth may take up to 2 years for patients on a standard dose of testosterone so patients should consider undergoing metoidioplasty until maximal growth is achieved for optimal outcomes.
- Breast augmentation: Maximal breast growth may take up to 1.5 to 2 years for patients on a standard dose of estrogen so patients should consider undergoing breast augmentation until maximal growth is achieved.
- Body contouring: It may take up to 1.5 years on hormone therapy before the fat redistribution process settles so patients should consider waiting until then before undergoing liposuction or fat grafting procedures.
When it comes to age and eligibility for surgery, we are typically asked about 2 populations: adolescents and seniors. The World Professional Association for Transgender Health (WPATH) has outlined in their Standards of Care (SOC), Version 8 , the need for the involvement of caregivers/parents and mental health professionals in the informed consent process for adolescents. If these protocols are followed, the only type of gender-affirming surgery that an adolescent can undergo is top surgery.
As long they are in good health and cleared for surgery, senior patients are eligible for surgery regardless of their age and can achieve good aesthetic outcomes. It’s important to consider what accommodations are necessary to support post-op recovery. You can read more about our eligibility standards here .
Weighing GRS Benefits Against Complications
The decision to undergo “gender reassignment surgery” is a highly personal one. Understanding both the pros and cons provides critical insight.
How GRS Can Transform Lives
The WPATH’s SOC 8 reviews the medical research literature around the long-term effects of gender-affirming surgery on trans and non-binary patients. Gender-affirming procedures report greater satisfaction and lower regret rates compared to similar cosmetic and reconstructive procedures performed in cisgender patients.
- Improved mental health
- Improved body-image, etc.
- Enhanced quality of life
Rates of anxiety, depression, and suicide risk all tend to decrease substantially following surgery for those who need it, which is why these procedures are considered medically necessary for many patients.
Risk Factors and Long-Term Effects
All surgeries carry risks of complications. Generally speaking, patients who optimize their health prior to surgery (e.g., do not smoke tobacco) and manage any pre-existing medical conditions can greatly reduce their risk for complications. Undergoing surgery with a board-certified surgeon who has hospital access privileges can help ensure the integrity of your surgical process. If you have specific questions about surgical complications and how to prevent them, you can consult our content library on this question.
Navigating Emotions
Surgery not only takes a physical, but also an emotional toll on the body. Experiencing pain, inflammation, discomfort and limitations on physical activity occasionally mat result in temporary postoperative depression. Likewise, having to wait weeks or months to have a sense of what your final results from surgery will look like can give some patients temporary feelings of regret during recovery. For this reason, we highly encourage patients to tap into their support networks of friends, (chosen) family and/or mental health professionals during this time. To learn more about the emotional recovery process, click here .
Conclusion: Is Gender Reassignment Surgery the Right Choice?
While gender-affirming surgery has been proven to be positively life-changing for many trans and non-binary individuals. Whether you seek surgery or not, we remain dedicated to your health, empowerment, and right to be your authentic self.
More Articles
Understanding the cost of double incision top surgery: a comprehensive guide, gatekeeping vs. empowerment: accessing gender affirming care, treating gender dysphoria in adolescents, request a free surgical consultation today..
All virtual and in-person consultations with our board-certified surgeons are free. Once you fill out this form, our patient care team will reach out and guide you through every step to get to surgery.
Suite 1010, 450 Sutter St San Francisco, CA 94108 Phone: (415) 780-1515 Fax: ( 628) 867-6510
Gender Journey Resources
- Trans Youth & Adolescents
Before & After
- Top surgery
- Virtual Consultations
Board Certification & Memberships

- Terms of Use
Copyright © 2023 Gender Confirmation Center. All Rights Reserved.
- Type 2 Diabetes
- Heart Disease
- Digestive Health
- Multiple Sclerosis
- Diet & Nutrition
- Health Insurance
- Public Health
- Patient Rights
- Caregivers & Loved Ones
- End of Life Concerns
- Health News
- Thyroid Test Analyzer
- Doctor Discussion Guides
- Hemoglobin A1c Test Analyzer
- Lipid Test Analyzer
- Complete Blood Count (CBC) Analyzer
- What to Buy
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Medical Expert Board
Gender Confirmation Surgery (GCS)
What is Gender Confirmation Surgery?
- Transfeminine Tr
Transmasculine Transition
- Traveling Abroad
Choosing a Surgeon
Gender confirmation surgery (GCS), known clinically as genitoplasty, are procedures that surgically confirm a person's gender by altering the genitalia and other physical features to align with their desired physical characteristics. Gender confirmation surgeries are also called gender affirmation procedures. These are both respectful terms.
Gender dysphoria , an experience of misalignment between gender and sex, is becoming more widely diagnosed. People diagnosed with gender dysphoria are often referred to as "transgender," though one does not necessarily need to experience gender dysphoria to be a member of the transgender community. It is important to note there is controversy around the gender dysphoria diagnosis. Many disapprove of it, noting that the diagnosis suggests that being transgender is an illness.
Ellen Lindner / Verywell
Transfeminine Transition
Transfeminine is a term inclusive of trans women and non-binary trans people assigned male at birth.
Gender confirmation procedures that a transfeminine person may undergo include:
- Penectomy is the surgical removal of external male genitalia.
- Orchiectomy is the surgical removal of the testes.
- Vaginoplasty is the surgical creation of a vagina.
- Feminizing genitoplasty creates internal female genitalia.
- Breast implants create breasts.
- Gluteoplasty increases buttock volume.
- Chondrolaryngoplasty is a procedure on the throat that can minimize the appearance of Adam's apple .
Feminizing hormones are commonly used for at least 12 months prior to breast augmentation to maximize breast growth and achieve a better surgical outcome. They are also often used for approximately 12 months prior to feminizing genital surgeries.
Facial feminization surgery (FFS) is often done to soften the lines of the face. FFS can include softening the brow line, rhinoplasty (nose job), smoothing the jaw and forehead, and altering the cheekbones. Each person is unique and the procedures that are done are based on the individual's need and budget,
Transmasculine is a term inclusive of trans men and non-binary trans people assigned female at birth.
Gender confirmation procedures that a transmasculine person may undergo include:
- Masculinizing genitoplasty is the surgical creation of external genitalia. This procedure uses the tissue of the labia to create a penis.
- Phalloplasty is the surgical construction of a penis using a skin graft from the forearm, thigh, or upper back.
- Metoidioplasty is the creation of a penis from the hormonally enlarged clitoris.
- Scrotoplasty is the creation of a scrotum.
Procedures that change the genitalia are performed with other procedures, which may be extensive.
The change to a masculine appearance may also include hormone therapy with testosterone, a mastectomy (surgical removal of the breasts), hysterectomy (surgical removal of the uterus), and perhaps additional cosmetic procedures intended to masculinize the appearance.
Paying For Gender Confirmation Surgery
Medicare and some health insurance providers in the United States may cover a portion of the cost of gender confirmation surgery.
It is unlawful to discriminate or withhold healthcare based on sex or gender. However, many plans do have exclusions.
For most transgender individuals, the burden of financing the procedure(s) is the main difficulty in obtaining treatment. The cost of transitioning can often exceed $100,000 in the United States, depending upon the procedures needed.
A typical genitoplasty alone averages about $18,000. Rhinoplasty, or a nose job, averaged $5,409 in 2019.
Traveling Abroad for GCS
Some patients seek gender confirmation surgery overseas, as the procedures can be less expensive in some other countries. It is important to remember that traveling to a foreign country for surgery, also known as surgery tourism, can be very risky.
Regardless of where the surgery will be performed, it is essential that your surgeon is skilled in the procedure being performed and that your surgery will be performed in a reputable facility that offers high-quality care.
When choosing a surgeon , it is important to do your research, whether the surgery is performed in the U.S. or elsewhere. Talk to people who have already had the procedure and ask about their experience and their surgeon.
Before and after photos don't tell the whole story, and can easily be altered, so consider asking for a patient reference with whom you can speak.
It is important to remember that surgeons have specialties and to stick with your surgeon's specialty. For example, you may choose to have one surgeon perform a genitoplasty, but another to perform facial surgeries. This may result in more expenses, but it can result in a better outcome.
A Word From Verywell
Gender confirmation surgery is very complex, and the procedures that one person needs to achieve their desired result can be very different from what another person wants.
Each individual's goals for their appearance will be different. For example, one individual may feel strongly that breast implants are essential to having a desirable and feminine appearance, while a different person may not feel that breast size is a concern. A personalized approach is essential to satisfaction because personal appearance is so highly individualized.
Davy Z, Toze M. What is gender dysphoria? A critical systematic narrative review . Transgend Health . 2018;3(1):159-169. doi:10.1089/trgh.2018.0014
Morrison SD, Vyas KS, Motakef S, et al. Facial Feminization: Systematic Review of the Literature . Plast Reconstr Surg. 2016;137(6):1759-70. doi:10.1097/PRS.0000000000002171
Hadj-moussa M, Agarwal S, Ohl DA, Kuzon WM. Masculinizing Genital Gender Confirmation Surgery . Sex Med Rev . 2019;7(1):141-155. doi:10.1016/j.sxmr.2018.06.004
Dowshen NL, Christensen J, Gruschow SM. Health Insurance Coverage of Recommended Gender-Affirming Health Care Services for Transgender Youth: Shopping Online for Coverage Information . Transgend Health . 2019;4(1):131-135. doi:10.1089/trgh.2018.0055
American Society of Plastic Surgeons. Rhinoplasty nose surgery .
Rights Group: More U.S. Companies Covering Cost of Gender Reassignment Surgery. CNS News. http://cnsnews.com/news/article/rights-group-more-us-companies-covering-cost-gender-reassignment-surgery
The Sex Change Capital of the US. CBS News. http://www.cbsnews.com/2100-3445_162-4423154.html
By Jennifer Whitlock, RN, MSN, FN Jennifer Whitlock, RN, MSN, FNP-C, is a board-certified family nurse practitioner. She has experience in primary care and hospital medicine.
Masks Strongly Recommended but Not Required in Maryland, Starting Immediately
Due to the downward trend in respiratory viruses in Maryland, masking is no longer required but remains strongly recommended in Johns Hopkins Medicine clinical locations in Maryland. Read more .
- Vaccines
- Masking Guidelines
- Visitor Guidelines

Phalloplasty for Gender Affirmation
Featured Expert:

Fan Liang, M.D.
Phalloplasty is surgery for masculinizing gender affirmation. Phalloplasty is a multistaged process that may include a variety of procedures, including:
- Creating the penis
- Lengthening the urethra so you are able to stand to urinate
- Creating the tip (glans) of the penis
- Creating the scrotum
- Removing the vagina, uterus and ovaries
- Placing erectile and testicular implants
- Skin grafting from the donor tissue site
Gender affirmation surgery is customized to each individual. Your surgical plan may include more or fewer of these steps and procedures. Fan Liang, M.D. , medical director of the Center for Transgender and Gender Expansive Health at Johns Hopkins, explains what you should know.

Are there different types of phalloplasty?
Phalloplasty involves using skin flaps, which are areas of skin moved from one area of the body to another. The skin flap is then reshaped, contoured and reattached to the groin to create the penis. There are three approaches the surgeon may use to construct the penis, using skin from the arm (radial forearm free flap), leg (anterolateral thigh flap) or side (latissimus dorsi flap).
There are pros and cons to each approach. Factors for choosing skin flap locations include the patient’s health and fat distribution, nerve function, blood flow and desired surgical outcomes.
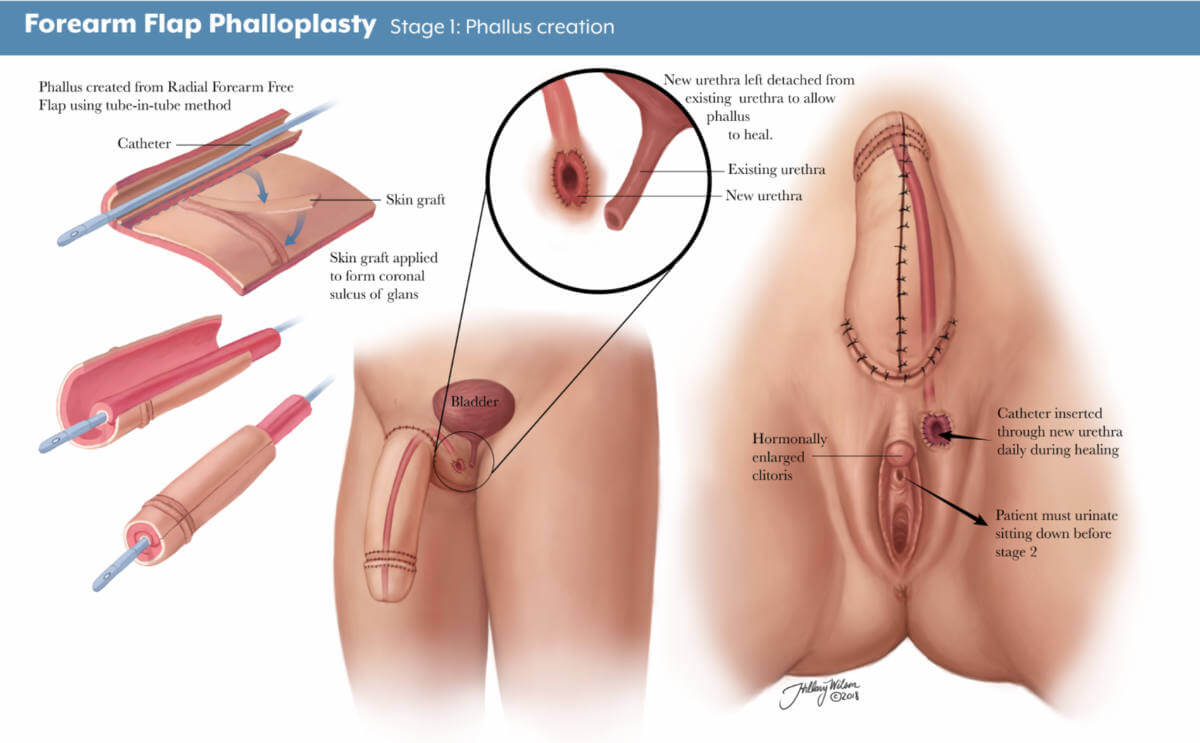
What is a radial forearm free flap?
A radial forearm free flap (RFFF) involves taking the skin, fat, nerves, arteries and veins from your wrist to about halfway up your forearm to create the penis. Typically, the surgeon will use your nondominant hand so it is easier for you to recover and return to your day-to-day activities.
During your surgical consultation, the doctor will check the blood flow to your arm and hand noninvasively. This involves temporarily putting pressure on arteries then releasing the pressure to test blood distribution in the arm and hand.
There are three stages to this procedure.
- Stage 1: The first stage of an RFFF approach is creating the penis using tissue from the forearm. The area where the forearm tissue is taken will require a skin graft. This may occur at the time of the initial phalloplasty surgery, or it may occur three to five weeks afterward. If it occurs later, patients will have a temporary skin covering over the forearm to help it heal.
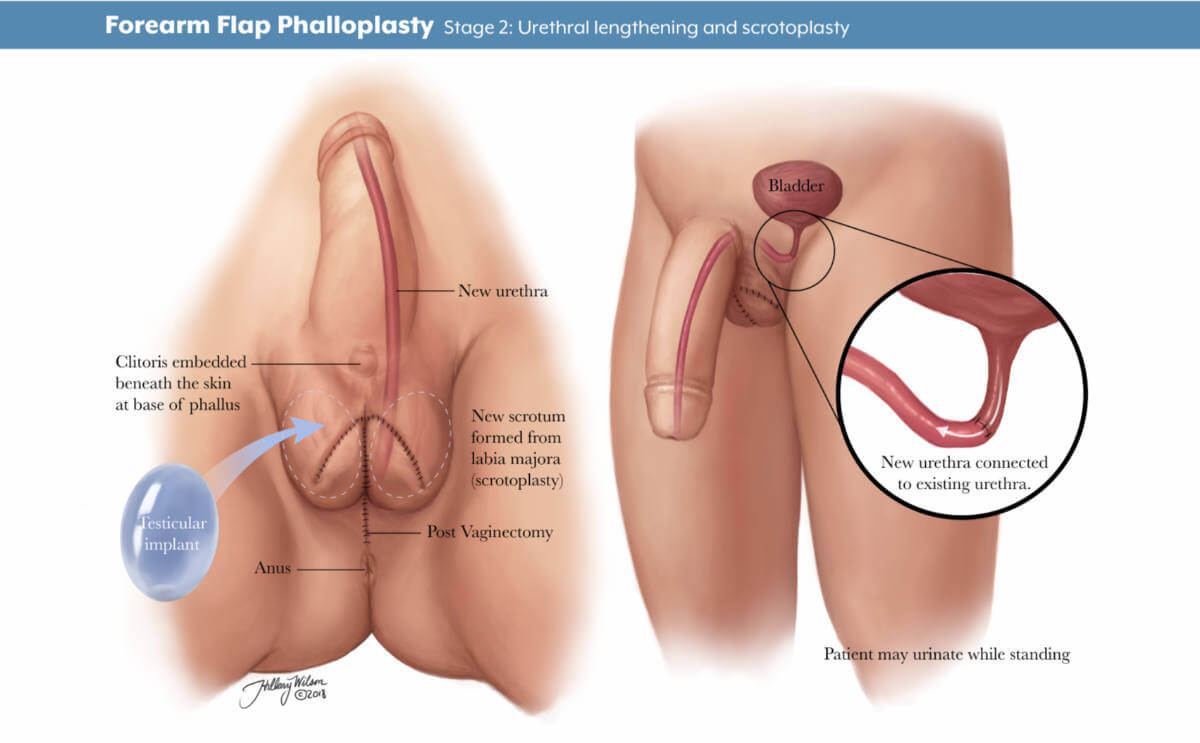
- Stage 2: The second stage, scheduled about five to six months later, may include lengthening the urethra to allow for urination out of the tip of the penis, creating the scrotum and removing the vagina, and other procedures depending on the patient’s individualized plan.
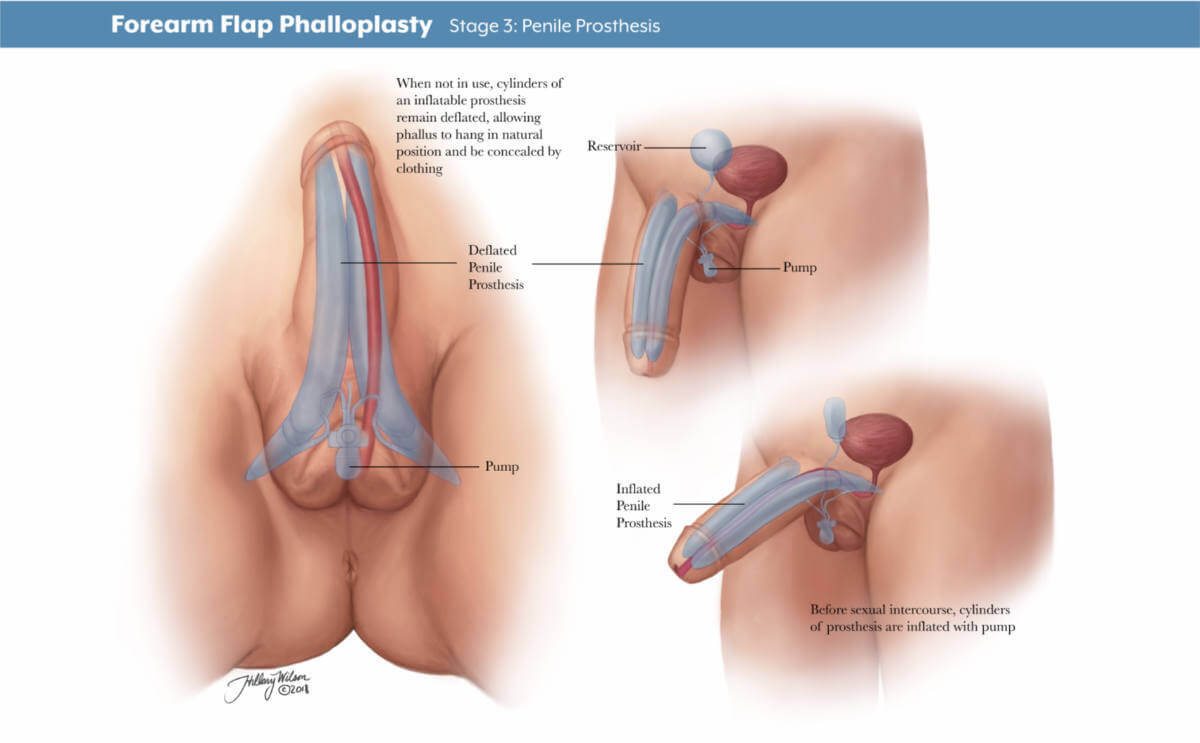
- Stage 3: The third stage of surgery involves putting in place testicle implants and an erectile device to help the patient achieve an erection. The third stage typically takes place 12 months after the second.
Will I have a say in how the phalloplasty is staged and the surgical plan?
Your gender affirmation surgery is highly personalized. Depending on what is most important to you, your surgery team will work with you on a customized plan beforehand. You and your surgeon will discuss your priorities and decide which procedures are right for you. Each stage will be scheduled to ensure your health and safety and provide the best chance of good results.
How long will I be in the hospital?
After your stage 1 surgery, you will stay as an inpatient for four to five days. Your surgical team will frequently monitor the blood supply to the tissue that has been used to create your new penis and ensure you are able to use the bathroom and walk around after surgery. Procedures for stages 2 and 3 do not require a hospital stay.
Will I need a catheter?
During your inpatient stay for stage 1 surgery, you will have a suprapubic tube that goes directly into your bladder and another catheter in your native urethra for at least five days. It is typically removed in the hospital before you go home.
If you decide not to have urethral lengthening as part of stage 2, you will have a Foley catheter placed in the operating room and removed before you leave the hospital. If you decide to have urethral lengthening, you will go home with a Foley catheter in the new urethra and a suprapubic tube. A clamp ensures that the urethra does not leak urine.
What is a suprapubic tube?
A suprapubic tube (SPT) allows urine to drain from your bladder. It is placed in the lower part of your abdomen, below the belly button. The SPT stays in for four to five weeks, depending on your healing and recovery.
When will my SPT be removed?
Before the SPT is removed, around four weeks after surgery, a urologist will perform a retrograde urethrogram. This involves putting dye into the bladder through the new urethra. An X-ray tracks the dye to see if the new urethra is open and ready for urination. If so, the doctor will clamp the SPT and you will be allowed to urinate from your new urethra. If everything looks good after a few days, the SPT is removed.
Forearm Flap Phalloplasty
Stage 1: phallus creation. Enlarged image .
Stage 2: urethral lengthening and scrotoplasty. Enlarged image .
Stage 3: penile prosthesis. Enlarged image .
Other Skin Flaps Used in Phalloplasty
What is an anterolateral thigh flap.
An anterolateral thigh flap (ALT) uses skin, fat, nerves, arteries and veins from the leg to create a penis. A special vascular CT scan can help the surgeon examine the blood supply of each leg to determine which leg will be better for creating the skin flap.
The stage of the ALT phalloplasty are similar to the RFFF. The area where the thigh tissue is taken will also require a skin graft. The resulting scar on the thigh can be covered with shorts.
What is a musculocutaneous latissimus dorsi flap?
A musculocutaneous latissimus dorsi skin flap (MLD) involves the skin, fat, nerves, arteries and veins from the side of your back to create a penis. The surgeon may order a special CT scan to look at the blood flow throughout the donor site area.
The stages of the MLD phalloplasty are similar to the RFFF and ALT. However, the area from which the back tissue is taken usually does not require a skin graft and can be closed in a straight line. The scar can be covered with a shirt. Patients may experience some initial weakness raising their arm, but this improves with time.
How is penis size determined?
Penis size depends on patient preferences and the skin flap harvested from your body. Thinner patients with less fat on the skin flap will have a penis with less girth. Alternatively, patients with a greater amount of fat will have a thicker penis.
The length of the penis depends on the patient’s donor site, but typically it is about 5–6 inches. After the first stage, the penis may decrease in size as postoperative swelling decreases and the tissue settles into its new location.
What determines scrotum size?
Scrotum size is specific to the patient and depends on the amount of skin that is present in the genital area before phalloplasty. The more genital tissue there is, the larger the scrotum and the testicular implants can be.
There are different ways to create the scrotum, including a procedure called V-Y scrotoplasty, a technique that creates a pouch to hold testicular implants. AART silicone round carving blocks have been approved by the FDA to be used as implants.
Procedures to Discuss with Your Physician Before Phalloplasty
Each individual undergoing gender confirmation surgery is different. Your surgeon will work with you to discuss which procedures, and their timing, are best for you and your goals.
Should I have a hysterectomy before phalloplasty surgery?
For those interested in this procedure, hysterectomies are typically done before phalloplasty and do not require a vaginectomy.
Urethral Lengthening Before Phalloplasty
If you choose to have urethral lengthening, this procedure involves lengthening your existing urethra so that you are able to urinate out of the tip of the penis. It involves connecting your current urethra to the new urethra created in the shaft of the penis.
Not all patients choose to have urethral lengthening; however, this will be a necessary step if you want to stand when you urinate. It is also important to know that if you decide not to have urethral lengthening in stage 1 of your phalloplasty, it will not be possible to have the lengthening procedure later.
Complications of Urethral Lengthening
The most common complications for urethral lengthening include urethral strictures (narrowed areas of the urethra), fistula (creation of a passageway between the urethra and another location) and diverticula (formation of a pouch in the urethra). This may require an additional surgical procedure to fix.
What is a metoidioplasty?
A metoidioplasty is a surgical procedure to achieve masculine-appearing genitalia with fewer steps than a phalloplasty. The skin of the labia and around the clitoris is lengthened to achieve the appearance of a penis. Some people prefer to undergo a metoidioplasty if they do not want to use tissue from their arms or legs to create a penis or if they prefer a shorter, more straightforward surgery.
A metoidioplasty procedure has a quicker recovery and fewer complications. Surgeons can discuss metoidioplasty with patients and help them decide if this option is right for them.
Will I need to have hair removal?
Yes, before surgery, after you consult with the surgical team and choose a skin flap site, you will get a template for hair removal that you can give to your hair removal professional.
What if I have a tattoo on my preferred donor site?
As long as there is good blood flow and nerve function, donor sites — even those with a tattoo — can be used.
Penile Function and Sensation After Phalloplasty
What can i do with a reconstructed penis.
Penis function is determined by what you and your surgery team agree on for your surgical plan. If it is important for you to urinate out of the tip of your penis, then urethral lengthening may be a good choice for you. If sensation is most important, your team will focus on a donor site with good nerve innervation. If penetrative sex is most important, and you would like to maintain an erection, then implanting an erectile prosthetic can be part of your surgery plan.
Can I get an erection after phalloplasty?
In stage 3 phalloplasty, a urologist can place a prosthetic erectile device which will allow you to maintain an erection. As of September 2022, no implantable prosthetic devices have been FDA-approved for phalloplasty. Instead, the surgeon can use a device intended for patients with erectile dysfunction to allow transmasculine patients to achieve an erection. There is a risk of infection and implant rejection with an erectile implant . If this happens, it may take six months before another device can be placed into the penis.
What kind of sensation and feeling can I expect?
Sensation recovery varies by patient. Nerve regeneration can begin as early as three weeks after surgery, but it can take longer in some patients. Sometimes sensation can take up to a year or longer. Return of nerve sensation is not guaranteed. As nerves regenerate and strengthen connections, you might experience shooting pain, tingling or electrical sensations. As time goes on, the tingling feeling begins to subside.
What is nerve hookup during phalloplasty?
Nerve hookup involves taking existing nerves from the donor site, such as the arm, and connecting them to nerves located in the pelvis. This allows you to have sensation in the reconstructed penis.
What is clitoral burying during phalloplasty surgery?
Clitoral burying involves moving the clitoris into the base of the penis to increase sensation. This is typically done at stage 2.
Is orgasm possible after phalloplasty?
Orgasm is possible after phalloplasty, especially if your surgery plan emphasizes preserving sensation. It is important to note that your penis will not ejaculate with semen at the time of orgasm.
Find a Doctor
Specializing In:
- Gender Affirmation Surgery
- Transgender Health
Find a Treatment Center
- Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery
- Center for Transgender and Gender Expansive Health
Find Additional Treatment Centers at:
- Howard County Medical Center
- Sibley Memorial Hospital
- Suburban Hospital

Request an Appointment

Vaginoplasty for Gender Affirmation

Top Surgery

Metoidioplasty for Gender Affirming Care
Related Topics
- LGBTQ Health
- Gender Affirmation
- Search Close Search submit
ISAPS Olympiad Word Congress 2025, Singapore: submit your abstract by October 18, 2024
Procedure: Male to Female Gender Reassignment Surgery (MTF GRS)
Male-to-female gender reassignment surgery (MTF GRS) is a complex and irreversible genital surgery for male transsexual who is diagnosed with gender identity disorder and has a strong desire to live as female. The procedure is to remove all male genital organs including the penis and testes with the construction of female genitalia composed of labia major/minor, clitoris and neovagina simultaneously.
The patient who is fit for this surgery must strictly follow the standard of care set by the World Professional Association of Transgender Healthcare (WPATH) or equivalent criteria; Express desire or live in another gender role (Male gender) long enough, under hormonal replacement therapy, evaluated and approved by a psychiatrist or other qualified professional gender therapist.
Apart from genital surgery, the patient would seek other procedures to allow them to live as female smoothly such as breast aesthetic surgery, facial feminization surgery, body contouring, hair removal, voice change surgery, etc.
Interested in having this procedure?
Useful Information
Ensure you consider all aspects of a procedure. You can speak to your surgeon about these areas of the surgery in more detail during a consultation.
The surgery is quite complicated and only a handful of surgeons are able to perform this procedure. It can be completed in one stage or more stages depending on techniques and surgeons. The average surgical time ranges between 5-8 hours. There are several options of neovaginal construction depending on the type of tissue, single or in combination, such as penile skin, scrotal skin, large intestine, small intestine, or peritoneum.
The procedure is done under general anesthesia and might be combined with spinal anesthesia for faster recovery by reducing the usage of anesthetic gas.
Inpatient/Outpatient
The patient will be hospitalized as an in-patient for between 5-14 days depending on the technique and surgeon. The patient will have a urinary catheter at all times in the hospital.
Additional Information
What is the recovery process.
During hospitalization, the patient must be restricted in bed continuously or intermittently for several days between 3-5 days. After release from the hospital, the patient can return to their normal lives but not have to do physical exercise during the first 2 months after surgery. The patient has to do vaginal dilation continuously for 6 months to maintain the neovagina canal until completely healed and is ready for sexual intimacy.
What are the results?
With the good surgical technique, the result is very satisfying with an improved quality of life. The patient is able to live in a female role completely and happily either on their own or with their male or female partners.
What are the risks?
The most frequent complication of MTF GRS is bleeding, wound infection, skin flap or graft necrosis, urinary stenosis, neovaginal contracture, unsightly scar or deformed genitalia, vaginal fistula, etc. The revision procedures to improve external appearance are composed of secondary labiaplasty/ urethroplasty/ perineoplasty/ and vulvaplasty. The other revision procedure is secondary vaginoplasty to help the patient able to have sexual intimacy with the partner.
- Patient Information
- Global Statistics
- Media Centre
- Global Sponsors
- Privacy Policy
19 Mantua Road, Mount Royal, NJ 08061 United States
Registration number: 0330131
US Office: +1-603-643-2325
UK Office: +44 20 7038 7812
© 2022 International Society of Aesthetic Plastic Surgery. All Rights Reserved.
- Create an account
Log into My ISAPS
Forgot your password? Reset it here
Join the ISAPS Community
All members will continue to receive information relevant to their membership and ISAPS events.
I confirm by clicking below I would like to receive information about:
Welcome to the ISAPS community
By creating an account, you can:.
- Register for events
- Update your personal details
- Gain access to ISAPS publications and video library
- Become a member (explore our memberships here)
ISAPS Members can also:
- Access your member benefits
- Secure discounted member rates for events
- Read the Aesthetic Plastic Surgery Journal
- Gain full access to the video library
- View the Members Directory
- Update your 'Find a Surgeon' profile details
- Renew/Upgrade your Membership
The first step to becoming a part of the community is creating an account, so join us!
Jump to content
Updated visitor policies
Other michigan medicine sites.
- About Michigan Medicine
- UofMHealth.org
- Medical School
- Find a Clinical Trial

Michigan Medicine
Federated search page form block, quick links.
- Patient Portal Login
- For Health Providers
- Maps & Directions
Gender Confirmation Surgery
The University of Michigan Health System offers procedures for surgical gender transition. Working together, the surgical team of the Comprehensive Gender Services Program, which includes specialists in plastic surgery, urology and gynecology, bring expertise, experience and safety to procedures for our transgender patients.
Access to gender-related surgical procedures for patients is made through the University of Michigan Health System Comprehensive Gender Services Program .
The Comprehensive Gender Services Program adheres to the WPATH Standards of Care , including the requirement for a second-opinion prior to genital sex reassignment.
Available surgeries:
Male-to-Female: Tracheal Shave Breast Augmentation Facial Feminization Male-to-Female genital sex reassignment
Female-to-Male: Hysterectomy, oophorectomy, vaginectomy Chest Reconstruction Female-to-male genital sex reassignment
Sex Reassignment Surgeries (SRS)
At the University of Michigan Health System, we are dedicated to offering the safest proven surgical options for sex reassignment (SRS.) Because sex reassignment surgery is just one step for transitioning people, the Comprehensive Gender Services Program has access to providers for mental health services, hormone therapy, pelvic floor physiotherapy, and speech therapy. Surgical procedures are done by a team that includes, as appropriate, gynecologists, urologists, pelvic pain specialists and a reconstructive plastic surgeon. A multi-disciplinary team helps to best protect the health of the patient.
For patients receiving mental health and medical services within the University of Michigan Health System, the UMHS-CGSP will coordinate all care including surgical referrals. For patients who have prepared for surgery elsewhere, the UMHS-CGSP will help organize the needed records, meet WPATH standards, and coordinate surgical referrals. Surgical referrals are made through Sara Wiener the Comprehensive Gender Services Program Director.
Male-to-female sex reassignment surgery
At the University of Michigan, participants of the Comprehensive Gender Services Program who are ready for a male-to-female sex reassignment surgery will be offered a penile inversion vaginoplasty with a neurovascular neoclitoris.
During this procedure, a surgeon makes “like become like,” using parts of the original penis to create a sensate neo-vagina. The testicles are removed, a procedure called orchiectomy. The skin from the scrotum is used to make the labia. The erectile tissue of the penis is used to make the neoclitoris. The urethra is preserved and functional.
This procedure provides for aesthetic and functional female genitalia in one 4-5 hour operation. The details of the procedure, the course of recovery, the expected outcomes, and the possible complications will be covered in detail during your surgical consultation. What to Expect: Vaginoplasty at Michigan Medicine .
Female-to-male sex reassignment
At the University of Michigan, participants of the Comprehensive Gender Services Program who are ready for a female-to-male sex reassignment surgery will be offered a phalloplasty, generally using the radial forearm flap method.
This procedure, which can be done at the same time as a hysterectomy/vaginectomy, creates an aesthetically appropriate phallus and creates a urethera for standing urination. Construction of a scrotum with testicular implants is done as a second stage. The details of the procedure, the course of recovery, the expected outcomes, and the possible complications will be covered in detail during your surgical consultation.
Individuals who desire surgical procedures who have not been part of the Comprehensive Gender Services Program should contact the program office at (734) 998-2150 or email [email protected] . W e will assist you in obtaining what you need to qualify for surgery.

QUINN JACKSON, MD, MPH, NICOLE T. YEDLINSKY, MD, AND MEREDITH GRAY, MD
Am Fam Physician. 2024;109(6):560-565
Published online May 14, 2024.
Author disclosure: No relevant financial relationships.
Gender-affirming surgery includes a range of procedures that help align a transgender or gender diverse person's body with their gender identity. As rates of gender-affirming surgery increase, family physicians will need to have the knowledge and skills to provide lifelong health care to this population. Physicians should conduct an anatomic survey or organ inventory with patients to determine what health screenings are applicable. Health care maintenance should follow accepted guidelines for the body parts that are present. Patients do not require routine breast cancer screening after mastectomy; however, because there is residual breast tissue, symptoms of breast cancer warrant workup. After masculinizing genital surgery, patients should have lifelong follow-up with a urologist familiar with gender-affirming surgery. If a prostate examination is indicated after vaginoplasty, it should be performed vaginally. If a pelvic examination is indicated after vaginoplasty, it should be performed with a Pederson speculum or anoscope. After gonadectomy, patients require hormone therapy to prevent long-term morbidity associated with hypogonadism, including osteoporosis. The risk of sexually transmitted infections may change after genital surgery depending on the tissue used for the procedure. Patients should be offered the same testing and treatment for sexually transmitted infections as cisgender populations, with site-specific testing based on sexual history. If bowel tissue is used in vaginoplasty, vaginal bleeding may be caused by adenocarcinoma or inflammatory bowel disease. ( Am Fam Physician . 2024;109(6):560-565. Copyright © 2024 American Academy of Family Physicians.)
- Immediate, unlimited access to all AFP content
- More than 130 CME credits/year
- AAFP app access
- Print delivery available
Issue Access
- Immediate, unlimited access to this issue's content
- CME credits
Article Only
- Immediate, unlimited access to just this article
Nolan IT, Dy GW, Levitt N. Considerations in gender-affirming surgery: demographic trends. Urol Clin North Am. 2019;46(4):459-465.
Meerwijk EL, Sevelius JM. Transgender population size in the United States: a meta-regression of population-based probability samples. Am J Public Health. 2017;107(2):e1-e8.
Canner JK, Harfouch O, Kodadek LM, et al. Temporal trends in gender-affirming surgery among transgender patients in the United States. JAMA Surg. 2018;153(7):609-616.
Coleman E, Radix AE, Bouman WP, et al. Standards of care for the health of transgender and gender diverse people, version 8. Int J Transgend Health. 2022;23(suppl 1):S1-S259.
James SE, Herman JL. Rankin S, et al. The report of the 2015 U.S. transgender survey. National Center for Transgender Equality; 2016. Accessed August 3, 2023. https://transequality.org/sites/default/files/docs/usts/USTS-Full-Report-Dec17.pdf
Safer JD, Coleman E, Feldman J, et al. Barriers to healthcare for transgender individuals. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 2016;23(2):168-171.
van Heesewijk J, Kent A, van de Grift TC, et al. Transgender health content in medical education: a theory-guided systematic review of current training practices and implementation barriers & facilitators. Adv Health Sci Educ Theory Pract. 2022;27(3):817-846.
Thawanyarat K, Johnstone T, Rowley M, et al. Travel distance and national access to gender-affirming care. J Am Coll Surg. 2022;235(5):S212.
Grasso C, Goldhammer H, Thompson J, et al. Optimizing gender-affirming medical care through anatomical inventories, clinical decision support, and population health management in electronic health record systems. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2021;28(11):2531-2535.
Deutsch MB. Guidelines for the primary and gender-affirming care of transgender and gender nonbinary people, 2nd ed. University of California–San Francisco, June 17, 2016. Accessed August 3, 2023. https://transcare.ucsf.edu/guidelines
Schrager S, Lyon SM, Poore SO. Breast implants: common questions and answers. Am Fam Physician. 2021;104(5):500-508.
Klein DA, Paradise SL, Goodwin ET. Caring for transgender and gender-diverse persons: what clinicians should know. Am Fam Physician. 2018;98(11):645-653.
Dakkak M, Kriegel DL, Tauches K. Caring for transgender and gender-diverse people: guidelines from WPATH. Am Fam Physician. 2023;108(6):626-629.
Oles N, Darrach H, Landford W, et al. Gender affirming surgery: a comprehensive, systematic review of all peer-reviewed literature and methods of assessing patient-centered outcomes (part 1: breast/chest, face, and voice). Ann Surg. 2022;275(1):e52-e66.
Frederick MJ, Berhanu AE, Bartlett R. Chest surgery in female to male transgender individuals. Ann Plast Surg. 2017;78(3):249-253.
Wolter A, Scholz T, Pluto N, et al. Subcutaneous mastectomy in female-to-male transsexuals: optimizing perioperative and operative management in 8 years clinical experience. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2018;71(3):344-352.
Gooren LJ, van Trotsenburg MAA, Giltay EJ, et al. Breast cancer development in transsexual subjects receiving cross-sex hormone treatment. J Sex Med. 2013;10(12):3129-3134.
Burcombe RJ, Makris A, Pittam M, et al. Breast cancer after bilateral subcutaneous mastectomy in a female-to-male trans-sexual. Breast. 2003;12(4):290-293.
Nikolic DV, Djordjevic ML, Granic M, et al. Importance of revealing a rare case of breast cancer in a female to male transsexual after bilateral mastectomy. World J Surg Oncol. 2012;10:280.
Katayama Y, Motoki T, Watanabe S, et al. A very rare case of breast cancer in a female-to-male transsexual. Breast Cancer. 2016;23(6):939-944.
Brown A, Lourenco AP, Niell BL, et al.; Expert Panel on Breast Imaging. ACR Appropriateness Criteria® transgender breast cancer screening. J Am Coll Radiol. 2021;18(11S):S502-S515.
Ruddy KJ, Winer EP. Male breast cancer: risk factors, biology, diagnosis, treatment, and survivorship. Ann Oncol. 2013;24(6):1434-1443.
Patel DP, Goodwin IA, Acar O, et al. Masculinizing gender-affirming surgery for trans men and non-binary individuals: what you should know. Fertil Steril. 2021;116(4):924-930.
Jolly D, Wu CA, Boskey ER, et al. Is clitoral release another term for metoidioplasty? A systematic review and meta-analysis of metoidioplasty surgical technique and outcomes. Sex Med. 2021;9(1):100294.
Boczar D, Huayllani MT, Saleem HY, et al. Surgical techniques of phalloplasty in transgender patients: a systematic review. Ann Transl Med. 2021;9(7):607.
Heston AL, Esmonde NO, Dugi DD, et al. Phalloplasty: techniques and outcomes. Transl Androl Urol. 2019;8(3):254-265.
Rooker SA, Vyas KS, DiFilippo EC, et al. The rise of the neophallus: a systematic review of penile prosthetic outcomes and complications in gender-affirming surgery. J Sex Med. 2019;16(5):661-672.
Schardein JN, Zhao LC, Nikolavsky D. Management of vaginoplasty and phalloplasty complications. Urol Clin North Am. 2019;46(4):605-618.
Kovar A, Choi S, Iorio ML. Donor site morbidity in phalloplasty reconstructions: outcomes of the radial forearm free flap. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2019;7(9):e2442.
Workowski KA, Bachmann LH, Chan PA, et al. Sexually transmitted infections treatment guidelines, 2021. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2021;70(4):1-187.
Perkins RB, Guido RS, Castle PE, et al. 2019 ASCCP risk-based management consensus guidelines for abnormal cervical cancer screening tests and cancer precursors [published correction appears in J Low Genit Tract Dis . 2020; 24(4): 427]. J Low Genit Tract Dis. 2020;24(2):102-131.
Reisner SL, Deutsch MB, Peitzmeier SM, et al. Test performance and acceptability of self-versus provider-collected swabs for high-risk HPV DNA testing in female-to-male trans masculine patients. PLoS One. 2018;13(3):e0190172.
Hembree WC, Cohen-Kettenis PT, Gooren L, et al. Endocrine treatment of gender-dysphoric/gender-incongruent persons: an Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline [published corrections appear in J Clin Endocrinol Metab . 2018; 103(2): 699, and J Clin Endocrinol Metab . 2018; 103(7): 2758–2759]. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2017;102(11):3869-3903.
van der Sluis WB, Steensma TD, Bouman MB. Orchiectomy in transgender individuals: a motivation analysis and report of surgical outcomes. Int J Transgend Health. 2020;21(2):176-181.
Hontscharuk R, Alba B, Hamidian Jahromi A, et al. Penile inversion vaginoplasty outcomes: complications and satisfaction. Andrology. 2021;9(6):1732-1743.
Krempasky C, Grimstad FW, Harris M, et al. Feminizing gender-affirming surgery. J Gynecol Surg. 2021;37(4):283-290.
Grimstad F, McLaren H, Gray M. The gynecologic examination of the transfeminine person after penile inversion vaginoplasty. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2021;224(3):266-273.
Ferrando CA. Vaginoplasty complications. Clin Plast Surg. 2018;45(3):361-368.
van der Sluis WB, de Haseth KB, Elfering L, et al. Neovaginal discharge in transgender women after vaginoplasty: a diagnostic and treatment algorithm. Int J Transgend Health. 2020;21(4):367-372.
Radix AE, Harris AB, Belkind U, et al. Chlamydia trachomatis infection of the neovagina in transgender women. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2019;6(11):ofz470.
Bodsworth NJ, Price R, Davies SC. Gonococcal infection of the neovagina in a male-to-female transsexual. Sex Transm Dis. 1994;21(4):211-212.
Elfering L, van der Sluis WB, Mermans JF, et al. Herpes neolabialis: herpes simplex virus type 1 infection of the neolabia in a transgender woman. Int J STD AIDS. 2017;28(8):841-843.
Hoebeke P, Selvaggi G, Ceulemans P, et al. Impact of sex reassignment surgery on lower urinary tract function. Eur Urol. 2005;47(3):398-402.
Kronawitter D, Gooren LJ, Zollver H, et al. Effects of transdermal testosterone or oral dydrogesterone on hypoactive sexual desire disorder in transsexual women: results of a pilot study. Eur J Endocrinol. 2009;161(2):363-368.
Cocchetti C, Ristori J, Mazzoli F, et al. Management of hypoactive sexual desire disorder in transgender women: a guide for clinicians. Int J Impot Res. 2020;33(7):703-709.
Jiang DD, Gallagher S, Burchill L, et al. Implementation of a pelvic floor physical therapy program for transgender women undergoing gender-affirming vaginoplasty. Obstet Gynecol. 2019;133(5):1003-1011.
Heller DS. Lesions of the neovagina—a review. J Low Genit Tract Dis. 2015;19(3):267-270.
Yamada K, Shida D, Kato T, et al. Adenocarcinoma arising in sigmoid colon neovagina 53 years after construction. World J Surg Oncol. 2018;16(1):88.
Hiroi H, Yasugi T, Matsumoto K, et al. Mucinous adenocarcinoma arising in a neovagina using the sigmoid colon thirty years after operation: a case report. J Surg Oncol. 2001;77(1):61-64.
Continue Reading

More in AFP
More in pubmed.
Copyright © 2024 by the American Academy of Family Physicians.
This content is owned by the AAFP. A person viewing it online may make one printout of the material and may use that printout only for his or her personal, non-commercial reference. This material may not otherwise be downloaded, copied, printed, stored, transmitted or reproduced in any medium, whether now known or later invented, except as authorized in writing by the AAFP. See permissions for copyright questions and/or permission requests.
Copyright © 2024 American Academy of Family Physicians. All Rights Reserved.
EWTN News, Inc. is the world’s largest Catholic news organization, comprised of television, radio, print and digital media outlets, dedicated to reporting the truth in light of the Gospel and the Catholic Church.
- National Catholic Register
- News Agencies
- Catholic News Agency
- CNA Deutsch
- ACI Afrique
- ACI Digital
- Digital Media
- ChurchPOP Español
- ChurchPOP Italiano
- ChurchPOP Português
- EWTN News Indepth
- EWTN News Nightly
- EWTN Noticias
- EWTN Pro-life Weekly
- Register Radio
Get HALF OFF the Register!
National Catholic Register News https://www.ncregister.com/cna/plastic-surgery-expert-expounds-on-insufficient-evidence-to-justify-trans-surgeries-for-minors

- Synod on Synodality
- Most Popular
- Publisher’s Note
- College Guide
- Commentaries
- Culture of Life
- Arts & Entertainment
- Publisher's Note
- Letters to the Editor
- Support the Register
- Print subscriptions
- E-Newsletter Sign-up
- EWTN Religious Catalogue
Plastic Surgery Expert Expounds on Insufficient Evidence to Justify Trans Surgeries for Minors
At least seven ASPS members are being sued by detransitioners, according to Manhattan Institute fellow and pediatric gender medicine expert Leor Sapir.

The president of the Plastic Surgery Foundation, the research arm of the American Society of Plastic Surgeons (ASPS) told “EWTN News Nightly” that as of now, the research on chest and genital surgery for adolescents with gender dysphoria “simply isn't strong enough to support any definitive recommendations” for such surgeries.
The ASPS recently made headlines for breaking with a perceived medical consensus, as many leading U.S. medical organizations continue to support both hormonal treatments and surgeries for minors with gender dysphoria.
“As members of the multidisciplinary care team, plastic surgeons prioritize evidence-based medicine,” Dr. Scott Bradley Glasburg , president of the Plastic Surgery Foundation, told EWTN News Nightly anchor Catherine Hadro on Tuesday.
“We have a responsibility to provide comprehensive education and maintain a robust and evidence-based informed consent process,” he continued. “Currently, the research on chest and genital surgeries for adolescents with gender dysphoria simply isn't strong enough to support any definitive recommendations from our society,” he stated.
When asked if the professional association experienced any political pressure to arrive at a particular decision, Glasburg responded that “plastic surgery is a specialty guided by evidence, and we're not influenced by external sources or by politics.”
“We believe that more high-quality research in this rapidly evolving area of health care is what's needed, and our priority remains focused on patient safety and informed decision-making,” he added.
At least seven ASPS members are being sued by detransitioners, according to Manhattan Institute fellow and pediatric gender medicine expert Leor Sapir, who first published the statement from ASPS on the lack of evidence for justifying “transgender” surgeries.
For instance Kayla Lovdahl, 18, sued an ASPS doctor and two other physicians last year for allegedly pressuring her into sex-change surgeries when she was a child. ASPS member Winnie Tong and two other doctors performed a double mastectomy on Lovdahl when she was 13 years old and gave her puberty blockers when she was 12, according to her legal complaint .
Lovdahl “detransitioned” shortly after, at age 17, and received psychotherapy treatment for her mental health symptoms.
When asked about the ASPS’s recent statement on the quality of referenced evidence, Glasburg further explained: “We believe that the level of evidence in these studies are of low quality. What that means is every study has strengths and limitations that can tell us something interesting. But it's important to take a step back and look at the effects that we see and analyze the larger body of evidence that accumulates over time.”
Uncertainty Over Long-Term Efficacy
“When we say there‘s uncertainty as to long-term efficacy for the use of certain surgical interventions for the treatment of adolescents with gender dysphoria, we mean that there’s uncertainty at many different levels,” Glasburg continued. “We're unclear, really, what the outcomes [and] data show, what the long-term effects of these treatments might be or could be.”
“We feel a responsibility to remain committed to that evidence-based approach and seeing out the research necessary for the society to make any firm recommendations or come up with any guidance or guidelines” he said.
Glasburg explained that ASPS will be following the evidence closely in the future, focusing on “patient safety” and “the clinical evidence available.”
“It‘s all about the evidence for us,” he said. “Again, we’re separate from politics. We're separate from outside forces.”
“We are committed to being a scientific organization of surgeons who want to do right by our patients and want to provide the education necessary to our members to make the right choices that are in the best interests of our patients and that of patient safety,” Glasburg noted.
Catholic Bioethical Take
In a separate interview with EWTN News, Catholic bioethicist Dr. Joseph Meaney, president of the National Catholic Bioethics Center, also weighed in on the issue.
“Particularly with young people, that these irreversible changes should not be done to young persons who don't really understand the lifelong consequences,” Meaney explained. “I think American medical societies are more and more going to realize this.”
“I think also that they are going to be aware of the legal liability that doing this to children could come back in the form of lawsuits later on saying, ‘Wait a second, I did not have proper informed consent as to how life-transforming this would be, and I regret that decision,’” he noted.
The American College of Pediatricians in June called on all medical institutions to stop gender transition medication and surgeries for minors, urging organizations to treat mental health instead.
- transgenderism
- Related Stories
- Latest News

Elon Musk Moves Companies From California, Blasts Law That Hides Gender Transition From Parents
Musk announced Tuesday that X headquarters would move to Austin and SpaceX would relocate to a town near Brownsville, Texas.

Catholic Counselors Sue Michigan Over Therapy Restrictions for Trans-Identifying Kids
Catholic counselor Emily McJones and several local Catholic Charities affiliates argue in the suit that the law, passed in July of last year, 'harms vulnerable children.'

MIT Academics Answer the Question: ‘Is Sex Binary?’
COMMENTARY: The erosion of our understanding of biological sex is a result of straying from the teachings of the ancient Faith regarding the representation of the relationship between Christ and the Church in the two sexes.

Judge Blocks Biden Administration’s Inclusion of ‘Gender Identity’ in Title IX Regulations
The regulation, which is set to go into effect Aug. 1, would reinterpret Title IX’s prohibition on sex discrimination to include a new prohibition on discriminating against a person’s ‘gender identity.’

Democrats for Life Leader Says Party Has Left Them
Kristen Day and her colleagues want convention delegates to know that a pro-abortion Democratic Party doesn’t speak for them.

Holy Toledo! City Tries Novel Legal Move to Stop Historic Church’s Demo
Bishop Daniel Thomas says city’s ordinance violates religious freedom.

Sainthood Cause Advances for Eileen O’Connor, Lay Woman and Mystic
She could become Australia’s second saint.

Princess Saints: A Great Picture Book for Your Own Little Princess
Young girls especially will enjoy the stories of Sts. Joan of Arc, Josephine Bakhita, Kateri Tekakwitha, Narcisa de Jesús, Lucy Yi Zhenmei and Thérèse of Lisieux.

We Have Two Choices in Times Like These: Follow Christ Boldly, or Perish
The Catholic Church challenges us to step out of our comfort zone to rediscover the spirit of risk and adventure.

Confession Is Not Enough, 12 Unknown Sorrows of Mary, Healthiest Diet Is Fasting, and More Great Links!
The Best In Catholic Blogging

As a Culture, We Must Remember the Joy of Children
There is no career, hobby or overall focus that could be more important and transformative than having children.
UPDATE: Cardinal Cupich Invocation at DNC Stirs Disappointment Among Pro-Life Activists
Akita’s fatima connection: our lady’s messages to sister agnes sasagawa, 2024 democratic platform: what catholics need to know, how gender ideology is forcing christian families out of foster care, faith and fiction: 4 novels that inspire priests in their ministry, baltimore orioles host first-ever ‘faith night’; players share ‘what god has done’, when was baseball’s golden age, st. bernard of clairvaux: monastic reformer and adviser to popes, pope francis: living the fruits of the holy spirit helps us spread holiness, subscription options.

Subscriber Service Center Already a subscriber? Renew or manage your subscription here .
Subscribe and Save HALF OFF! Start your Register subscription today.
Give a Gift Subscription Bless friends, family or clergy with a gift of the Register.
Order Bulk Subscriptions Get a discount on 6 or more copies sent to your parish, organization or school.
Sign-up for E-Newsletter Get Register Updates sent daily or weeklyto your inbox.

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Recovery time from these surgeries depends on the type of surgery you have and your body's response to surgery and healing. The best time to develop your recovery plan is well in advance of surgery. About 4 to 6 weeks before surgery is a good time to finalize details with work, school, and your caregivers.
Gender affirming surgery can be used to create a vulva and vagina. It involves removing the penis, testicles and scrotum. During a vaginoplasty procedure, tissue in the genital area is rearranged to create a vaginal canal (or opening) and vulva (external genitalia), including the labia. A version of vaginoplasty called vulvoplasty can create a ...
Top surgery is surgery that removes or augments breast tissue and reshapes the chest to create a more masculine or feminine appearance for transgender and nonbinary people. Facial gender surgery: While hormone replacement therapy can help achieve gender affirming changes to the face, surgery may help. Facial gender surgery can include a variety ...
Gender affirmation surgery, also known as gender confirmation surgery, is performed to align or transition individuals with gender dysphoria to their true gender. A transgender woman, man, or non-binary person may choose to undergo gender affirmation surgery. The term "transexual" was previously used by the medical community to describe people ...
Request an Appointment. 410-955-5000 Maryland. 855-695-4872 Outside of Maryland. +1-410-502-7683 International. To help provide guidance for those considering gender affirmation surgery, two experts from the Johns Hopkins Center for Transgender Health answer questions about what to expect before and after your surgery.
Prior to gender affirmation surgery, you can: Ask your surgeon about your recovery period and discharge instructions, including supplies you will need. Tip: Have the supplies on hand before you come home from the hospital. Ask people in your life to provide caregiving support after your surgery, starting with a ride home from the hospital.
She does more than 150 a year. We also offer a Transgender Gynecology Clinic with a gender-neutral space. Services include surgery. Referrals and appointments are made through the OHSU Center for Women's Health, though the space is not in the center. Call 503-418-4500 to request an appointment.
A trans person can choose from multiple procedures to make their appearance match their self-identified gender identity. Doctors refer to this as gender "affirmation" surgery. Trans people might ...
Gender-affirming surgeries can be split into a few overarching categories: top surgeries and bottom surgeries, feminization and masculinization. If you are transitioning from male to female, surgeries include: Facial feminization surgery, such as forehead and browbone reduction, jaw and neck feminization, rhinoplasty and Adam's apple reduction.
Recovering from bottom surgery. Three to six days of hospitalization is required, followed by another 7-10 days of close outpatient supervision. After your procedure, expect to refrain from work ...
The WPATH's SOC 8 reviews the medical research literature around the long-term effects of gender-affirming surgery on trans and non-binary patients. Gender-affirming procedures report greater satisfaction and lower regret rates compared to similar cosmetic and reconstructive procedures performed in cisgender patients. Improved mental health.
Risks and complications. There are always risks associated with surgery, but vaginoplasty complications are rare. Infections can usually be cleared up with antibiotics. Some immediate postsurgical ...
The cost of transitioning can often exceed $100,000 in the United States, depending upon the procedures needed. A typical genitoplasty alone averages about $18,000. Rhinoplasty, or a nose job, averaged $5,409 in 2019. Insurance Coverage for Sex Reassignment Surgery.
Gender reassignment surgery: what is it, how it works, recovery, cost. Many transgender individuals choose to align their bodies with their true gender identities through gender reassignment surgery. These surgeries can help relieve psychological distress and are often considered medically necessary. Many surgeries are available, and treatment ...
Featured Expert: Fan Liang, M.D. Phalloplasty is surgery for masculinizing gender affirmation. Phalloplasty is a multistaged process that may include a variety of procedures, including: Creating the penis. Lengthening the urethra so you are able to stand to urinate. Creating the tip (glans) of the penis. Creating the scrotum.
Gender affirming surgery, also known as sex reassignment surgery (SRS) or confirmation surgery, is the surgical procedure (s) by which a transgender or non-binary person's physical appearance and functional abilities are changed to align with the gender they know themselves to be.
Procedure: Male to Female Gender Reassignment Surgery (MTF GRS) Male-to-female gender reassignment surgery (MTF GRS) is a complex and irreversible genital surgery for male transsexual who is diagnosed with gender identity disorder and has a strong desire to live as female. The procedure is to remove all male genital organs including the penis ...
Individuals who desire surgical procedures who have not been part of the Comprehensive Gender Services Program should contact the program office at (734) 998-2150 or email [email protected]. We will assist you in obtaining what you need to qualify for surgery. University of Michigan Comprehensive Gender Services Program brings ...
Consensus guidelines and expert opinion from transgender health and breast radiology experts in the absence of clinical trials. After masculinizing genital surgery, patients should have lifelong ...
Please tell your medical provider the words you use to describe your body. Vaginoplasty is a gender-affirming, feminizing, lower surgery (transgender surgery; gender reassignemnt surgery; sex change surgery) to create a vagina and vulva (including mons, labia, clitoris, and urethral opening) and remove the penis, scrotal sac and testes.
Zsa Zsa Padilla extended her gratitude to those who prayed for her quick recovery following her ureter surgery. The singer underwent Robotic Left Ureteric Reimplantation and insertion of left DJ Stent in Singapore.
The president of the Plastic Surgery Foundation, the research arm of the American Society of Plastic Surgeons (ASPS) told "EWTN News Nightly" that as of now, the research on chest and genital ...