
Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Consumer Motivation and Involvement

15 Involvement Levels
Depending on a consumer’s experience and knowledge, some consumers may be able to make quick purchase decisions and other consumers may need to get information and be more involved in the decision process before making a purchase. The level of involvement reflects how personally important or interested you are in consuming a product and how much information you need to make a decision. The level of involvement in buying decisions may be considered a continuum from decisions that are fairly routine (consumers are not very involved) to decisions that require extensive thought and a high level of involvement. Whether a decision is low, high, or limited, involvement varies by consumer, not by product.
Low Involvement Consumer Decision Making
At some point in your life you may have considered products you want to own (e.g. luxury or novelty items), but like many of us, you probably didn’t do much more than ponder their relevance or suitability to your life. At other times, you’ve probably looked at dozens of products, compared them, and then decided not to purchase any one of them. When you run out of products such as milk or bread that you buy on a regular basis, you may buy the product as soon as you recognize the need because you do not need to search for information or evaluate alternatives . As Nike would put it, you “just do it.” Low-involvement decisions are, however, typically products that are relatively inexpensive and pose a low risk to the buyer if a mistake is made in purchasing them.
Consumers often engage in routine response behaviour when they make low-involvement decisions — that is, they make automatic purchase decisions based on limited information or information they have gathered in the past. For example, if you always order a Diet Coke at lunch, you’re engaging in routine response behaviour. You may not even think about other drink options at lunch because your routine is to order a Diet Coke, and you simply do it. Similarly, if you run out of Diet Coke at home, you may buy more without any information search.
Some low-involvement purchases are made with no planning or previous thought. These buying decisions are called impulse buying . While you’re waiting to check out at the grocery store, perhaps you see a magazine with a notable celebrity on the cover and buy it on the spot simply because you want it. You might see a roll of tape at a check-out stand and remember you need one or you might see a bag of chips and realize you’re hungry or just want them. These are items that are typically low-involvement decisions. Low involvement decisions aren’t necessarily products purchased on impulse, although they can be.
High Involvement Consumer Decision Making
By contrast, high-involvement decisions carry a higher risk to buyers if they fail. These are often more complex purchases that may carry a high price tag, such as a house, a car, or an insurance policy. These items are not purchased often but are relevant and important to the buyer. Buyers don’t engage in routine response behaviour when purchasing high-involvement products. Instead, consumers engage in what’s called extended problem solving where they spend a lot of time comparing different aspects such as the features of the products, prices, and warranties.
High-involvement decisions can cause buyers a great deal of post-purchase dissonance, also known as cognitive dissonance which is a form of anxiety consumers experience if they are unsure about their purchases or if they had a difficult time deciding between two alternatives. Companies that sell high-involvement products are aware that post purchase dissonance can be a problem. Frequently, marketers try to offer consumers a lot of supporting information about their products, including why they are superior to competing brands and why the consumer won’t be disappointed with their purchase afterwards. Salespeople play a critical role in answering consumer questions and providing extensive support during and after the purchasing stage.
Limited Problem Solving
Limited problem solving falls somewhere between low-involvement (routine) and high-involvement (extended problem solving) decisions. Consumers engage in limited problem solving when they already have some information about a good or service but continue to search for a little more information. Assume you need a new backpack for a hiking trip. While you are familiar with backpacks, you know that new features and materials are available since you purchased your last backpack. You’re going to spend some time looking for one that’s decent because you don’t want it to fall apart while you’re traveling and dump everything you’ve packed on a hiking trail. You might do a little research online and come to a decision relatively quickly. You might consider the choices available at your favourite retail outlet but not look at every backpack at every outlet before making a decision. Or you might rely on the advice of a person you know who’s knowledgeable about backpacks. In some way you shorten or limit your involvement and the decision-making process.
Distinguishing Between Low Involvement and High Involvement
Products, such as chewing gum, which may be low-involvement for many consumers often use advertising such as commercials and sales promotions such as coupons to reach many consumers at once. Companies also try to sell products such as gum in as many locations as possible. Many products that are typically high-involvement such as automobiles may use more personal selling to answer consumers’ questions. Brand names can also be very important regardless of the consumer’s level of purchasing involvement. Consider a low-versus high-involvement decision — say, purchasing a tube of toothpaste versus a new car. You might routinely buy your favorite brand of toothpaste, not thinking much about the purchase (engage in routine response behaviour), but not be willing to switch to another brand either. Having a brand you like saves you “search time” and eliminates the evaluation period because you know what you’re getting.
When it comes to the car, you might engage in extensive problem solving but, again, only be willing to consider a certain brand or brands (e.g. your evoke set for automobiles). For example, in the 1970s, American-made cars had such a poor reputation for quality that buyers joked that a car that’s not foreign is “crap.” The quality of American cars is very good today, but you get the picture. If it’s a high-involvement product you’re purchasing, a good brand name is probably going to be very important to you. That’s why the manufacturers of products that are typically high-involvement decisions can’t become complacent about the value of their brands.
Ways to Increase Involvement Levels
Involvement levels – whether they are low, high, or limited – vary by consumer and less so by product. A consumer’s involvement with a particular product will depend on their experience and knowledge, as well as their general approach to gathering information before making purchasing decisions. In a highly competitive marketplace, however, brands are always vying for consumer preference, loyalty, and affirmation. For this reason, many brands will engage in marketing strategies to increase exposure, attention, and relevance; in other words, brands are constantly seeking ways to motivate consumers with the intention to increase consumer involvement with their products and services.
Some of the different ways marketers increase consumer involvement are: customization; engagement; incentives; appealing to hedonic needs; creating purpose; and, representation.
1. Customization

With Share a Coke, Coca-Cola made a global mass customization implementation that worked for them. The company was able to put the labels on millions of bottles in order to get consumers to notice the changes to the coke bottle in the aisle. People also felt a kinship and moment of recognition once they spotted their names or a friend’s name. Simultaneously this personalization also worked because of the printing equipment that could make it happen and there are not that many first names to begin with. These factors lead the brand to be able to roll this out globally ( Mass Customization #12 , 2017).
2. Engagement
Have you ever heard the expression, “content is king”? Without a doubt, engaging, memorable, and unique marketing content has a lasting impact on consumers. The marketing landscape is a noisy one, polluted with an infinite number of brands advertising extensively to consumers, vying for a fraction of our attention. Savvy marketers recognize the importance of sparking just enough consumer interest so they become motivated to take notice and process their marketing messages. Marketers who create content (that isn’t just about sales and promotion) that inspires, delights, and even serves an audience’s needs are unlocking the secret to engagement. And engagement leads to loyalty.
There is no trick to content marketing, but the brands who do it well know that stepping away – far away – from the usual sales and promotion lines is critical. While content marketing is an effective way to increase sales, grow a brand, and create loyalty, authenticity is at its core.
Bodyform and Old Spice are two brands who very cleverly applied just the right amount of self-deprecating humour to their content marketing that not only engaged consumers, but had them begging for more!
Content as a Key Driver to Consumer Engagement
Engaging customers through content might involve a two-way conversation online, or an entire campaign designed around a single customer comment.
In 2012, Richard Neill posted a message to Bodyform’s Facebook page calling out the brand for lying to and deceiving its customers and audiences for years. Richard went on to say that Bodyform’s advertisements failed to truly depict any sense of reality and that in fact he felt set up by the brand to experience a huge fall. Bodyform, or as Richard addressed the company, “you crafty bugger,” is a UK company that produces and sells feminine protection products to menstruating girls and women (Bodyform, n.d.). Little did Richard know that when he posted his humorous rant to Bodyform that the company would respond by creating a video speaking directly at Richard and coming “clean” on all their deceitful attempts to make having period look like fun. When Bodyform’s video went viral, a brand that would have otherwise continued to blend into the background, captured the attention of a global audience.
Xavier Izaguirre says that, “[a]udience involvement is the process and act of actively involving your target audience in your communication mix, in order to increase their engagement with your message as well as advocacy to your brand.” Bodyform gained global recognition by turning one person’s rant into a viral publicity sensation (even though Richard was not the customer in this case).
Despite being a household name, in the years leading up to Old Spice’s infamous “The Man Your Man Should Smell Like” campaign, sales were flat and the brand had failed to strike a chord in a new generation of consumers. Ad experts at Wieden + Kennedy produced a single 30-second ad (featuring a shirtless and self-deprecating Isaiah Mustafa) that played around the time of the 2010 Super Bowl game. While the ad quickly gained notoriety on YouTube, it was the now infamous, “ Response Campaign ” that made the campaign a leader of its time in audience engagement.
3. Incentives

Customer loyalty and reward programs successfully motivate consumers in the decision making process and reinforce purchasing behaviours ( a feature of instrumental conditioning ). The rationale for loyalty and rewards programs is clear: the cost of acquiring a new customer runs five to 25 times more than selling to an existing one and existing customers spend 67 per cent more than new customers (Bernazzani, n.d.). From the customer perspective, simple and practical reward programs such as Beauty Insider – a point-accumulation model used by Sephora – provides strong incentive for customer loyalty (Bernazzani, n.d.).
4. Appealing to Hedonic Needs

A particularly strong way to motivate consumers to increase involvement levels with a product or service is to appeal to their hedonic needs. Consumers seek to satisfy their need for fun, pleasure, and enjoyment through luxurious and rare purchases. In these cases, consumers are less likely to be price sensitive (“it’s a treat”) and more likely to spend greater processing time on the marketing messages they are presented with when a brand appeals to their greatest desires instead of their basic necessities.
5. Creating Purpose
Millennial and Digital Native consumers are profoundly different than those who came before them. Brands, particularly in the consumer goods category, who demonstrate (and uphold) a commitment to sustainability grow at a faster rate (4 per cent) than those who do not (1 per cent) (“Consumer-Goods…”, 2015). In a 2015 poll, 30,000 consumers were asked how much the environment, packaging, price, marketing, and organic or health and wellness claims had on their consumer-goods’ purchase decisions, and to no surprise, 66 per cent said they would be willing to pay more for sustainable brands. (Nielsen, 2015). A rising trend and important factor to consider in evaluating consumer involvement levels and ways to increase them. So while cruelty-free, fair trade, and locally-sourced may all seem like buzz words to some, they are non-negotiable decision-making factors to a large and growing consumer market.
6. Representation

Celebrity endorsement can have a profound impact on consumers’ overall attitude towards a brand. Consumers who might otherwise have a “neutral” attitude towards a brand (neither positive nor negative) may be more noticed to take notice of a brand’s messages and stimuli if a celebrity they admire is the face of the brand.
When sportswear and sneaker brand Puma signed Rihanna on to not just endorse the brand but design an entire collection, sales soared in all the regions and the brand enjoyed a new “revival” in the U.S. where Under Armour and Nike had been making significant gains (“Rihanna Designs…”, 2017). “Rihanna’s relationship with us makes the brand actual and hot again with young consumers,” said chief executive Bjorn Gulden (“Rihanna Designs…”, 2017).
Media Attributions
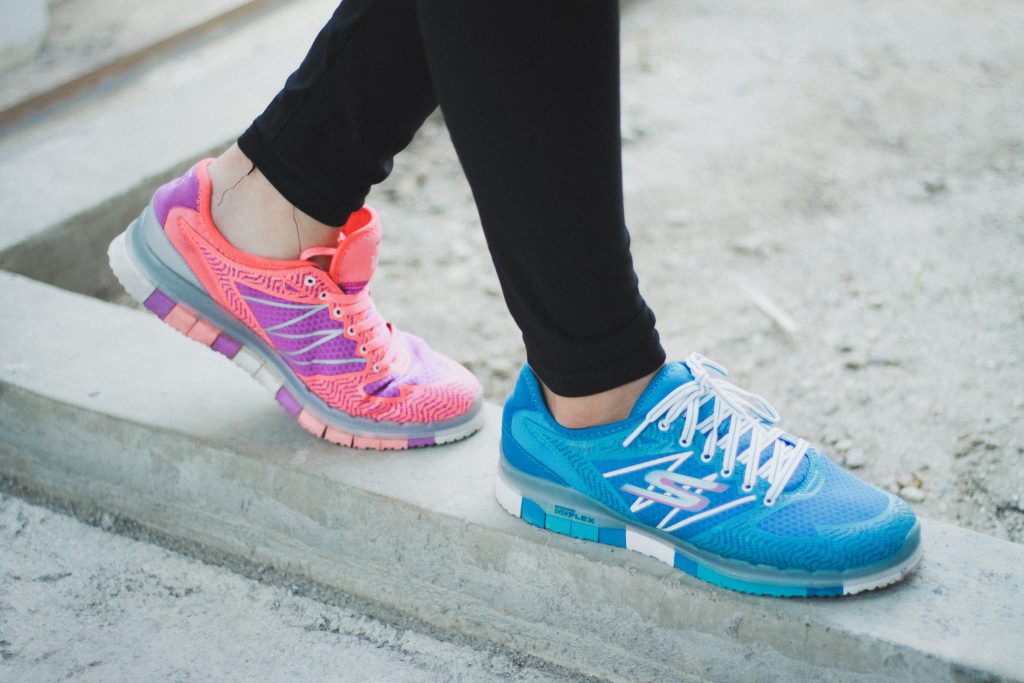
- The image of two different coloured sneakers is by Raka Rachgo on Unsplash .
- The image of a coffee card in a wallet is by Rebecca Aldama on Unsplash .
- The image of an island resort in tropical destination is by Ishan @seefromthesky on Unsplash .
- The image of a stack of glossy magazine covers is by Charisse Kenion on Unsplash .
Text Attributions
- The introductory paragraph; sections on “Low Involvement Consumer Decision Making”, “High Involvement Consumer Decision Making”, and “Limited Problem Solving” are adapted from Principles of Marketing which is licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 3.0.
About Us . (n.d.). Body Form. Retrieved February 2, 2019, from https://www.bodyform.co.uk/about-us/.
Kalamut, A. (2010, August 18). Old Spice Video “Case Study” . YouTube [Video]. https://youtu.be/Kg0booW1uOQ.
Bernazzani, S. (n.d.). Customer Loyalty: The Ultimate Guide [Blog post]. https://blog.hubspot.com/service/customer-loyalty.
Bodyform Channel. (2012, October 16). Bodyform Responds: The Truth . YouTube [Video]. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Bpy75q2DDow&feature=youtu.be.
Consumer-Goods’ Brands That Demonstrate Commitment to Sustainability Outperform Those That Don’t. (2015, October 12). Nielsen [Press Release]. https://www.nielsen.com/us/en/press-room/2015/consumer-goods-brands-that-demonstrate-commitment-to-sustainability-outperform.html.
Curtin, M. (2018, March 30). 73 Per Cent of Millennials are Willing to Spend More Money on This 1 Type of Product . Inc. https://www.inc.com/melanie-curtin/73-percent-of-millennials-are-willing-to-spend-more-money-on-this-1-type-of-product.html.
Izaguirre, X. (2012, October 17). How are brands using audience involvement to increase reach and engagement? EConsultancy. https://econsultancy.com/how-are-brands-using-audience-involvement-to-increase-reach-and-engagement/.
Rihanna Designs Help Lift Puma Sportswear Sales . (2017, October 24). Reuters. https://www.businessoffashion.com/articles/news-analysis/rihanna-designs-help-lift-puma-sportswear-sales.
Tarver, E. (2018, October 20). Why the ‘Share a Coke’ Campaign Is So Successful . Investopedia. https://www.investopedia.com/articles/markets/100715/what-makes-share-coke-campaign-so-successful.asp.
Low involvement decision making typically reflects when a consumer who has a low level of interest and attachment to an item. These items may be relatively inexpensive, pose low risk (can be exchanged, returned, or replaced easily), and not require research or comparison shopping.
This concept describes when consumers make low-involvement decisions that are "automatic" in nature and reflect a limited amount of information the consumer has gathered in the past.
A type of purchase that is made with no previous planning or thought.
High involvement decision making typically reflects when a consumer who has a high degree of interest and attachment to an item. These items may be relatively expensive, pose a high risk to the consumer (can't be exchanged or refunded easily or at all), and require some degree of research or comparison shopping.
Also known as "consumer remorse" or "consumer guilt", this is an unsettling feeling consumers may experience post-purchase if they feel their actions are not aligned with their needs.
Consumers engage in limited problem solving when they have some information about an item, but continue to gather more information to inform their purchasing decision. This falls between "low" and "high" involvement on the involvement continuum.
Introduction to Consumer Behaviour Copyright © by Andrea Niosi is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
6.3 Types of Consumer Decisions
As you read through the stages of the decision making process, did you think “Wait a minute. I do this sometimes but not all the time”? That is indicative of the different levels of involvement within the decision making process. In this section, we will examine this difference in more detail and how it may impact the marketing strategy.
Levels of Involvement in Decision Making
As you have seen, many factors influence a consumer’s behavior. Depending on a consumer’s experience and knowledge, some consumers may be able to make quick purchase decisions and other consumers may need to get information and be more involved in the decision process before making a purchase. The level of involvement reflects how personally important or interested you are in consuming a product and how much information you need to make a decision. The level of involvement in buying decisions may be considered a continuum from decisions that are fairly routine (consumers are not very involved) to decisions that require extensive thought and a high level of involvement. Whether a decision is low, high, or limited, involvement varies by consumer, not by product, although some products such as purchasing a house typically require a high-involvement for all consumers. Consumers with no experience purchasing a product may have more involvement than someone who is replacing a product.
You have probably thought about many products you want or need but never did much more than that. At other times, you’ve probably looked at dozens of products, compared them, and then decided not to purchase any one of them. When you run out of products such as milk or bread that you buy on a regular basis, you may buy the product as soon as you recognize the need because you do not need to search for information or evaluate alternatives. As Nike would put it, you “just do it.” Low-involvement decisions are, however, typically products that are relatively inexpensive and pose a low risk to the buyer if they makes a mistake by purchasing them.
Consumers often engage in routine, or habitual, behavior when they make low-involvement decisions—that is, they make automatic purchase decisions based on limited information or information they have gathered in the past. For example, if you always order a Diet Coke at lunch, you’re engaging in routine response behavior. You may not even think about other drink options at lunch because your routine is to order a Diet Coke, and you simply do it. Similarly, if you run out of Diet Coke at home, you may buy more without any information search.
Some low-involvement purchases are made with no planning or previous thought. These buying decisions are called impulse buying. While you’re waiting to check out at the grocery store, perhaps you see a magazine with the latest celebrity or influencer on the cover and buy it on the spot simply because you want it. You might see a roll of tape at a check-out stand and remember you need one or you might see a bag of chips and realize you’re hungry or just want them.
By contrast, high-involvement decisions carry a higher risk to buyers if they fail, are complex, and/or have high price tags. A car, a house, and an insurance policy are examples. These items are not purchased often but are relevant and important to the buyer. Buyers don’t engage in routine response behavior when purchasing high-involvement products. Instead, consumers engage in what’s called extended problem solving where they spend a lot of time comparing different aspects such as the features of the products, prices, and warranties.
High-involvement decisions can cause buyers a great deal of cognitive (postpurchase) dissonance (anxiety) if they are unsure about their purchases or if they had a difficult time deciding between two alternatives. Companies that sell high-involvement products are aware that dissonance can be a problem. Frequently, they try to offer consumers a lot of information about their products, including why they are superior to competing brands and how they won’t let the consumer down. Salespeople may be utilized to answer questions and do a lot of customer “hand-holding.”

Allstate’s “You’re in Good Hands” advertisements are designed to convince consumers that the insurance company won’t let them down.
Mike Mozart – Allstate, – CC BY 2.0.
Limited problem solving falls somewhere between low-involvement (routine) and high-involvement (extended problem solving) decisions. Consumers engage in limited problem solving when they already have some information about a good or service but continue to search for a little more information. Assume you need a new backpack for a hiking trip. While you are familiar with backpacks, you know that new features and materials are available since you purchased your last backpack. You’re going to spend some time looking for one that’s decent because you don’t want it to fall apart while you’re traveling and dump everything you’ve packed on a hiking trail. You might do a little research online and come to a decision relatively quickly. You might consider the choices available at your favorite retail outlet but not look at every backpack at every outlet before making a decision. Or you might rely on the advice of a person you know who’s knowledgeable about backpacks. In some way you shorten or limit your involvement and the decision-making process.
Products, such as chewing gum, which may be low-involvement for many consumers, often use advertising such as commercials and sales promotions such as coupons to reach many consumers at once. Companies also try to sell products such as gum in as many locations as possible. Many products that are typically high-involvement such as automobiles may use more personal selling to answer consumers’ questions. Brand names can also be very important regardless of the consumer’s level of purchasing involvement. Consider a low- versus high-involvement decision—say, purchasing a tube of toothpaste versus a new car. You might routinely buy your favorite brand of toothpaste, not thinking much about the purchase (engage in routine response behavior), but not be willing to switch to another brand either. Having a brand you like saves you “search time” and eliminates the evaluation period because you know what you’re getting.
When it comes to the car, you might engage in extensive problem solving but, again, only be willing to consider a certain brand or brands. For example, in the 1970s, American-made cars had such a poor reputation for quality that buyers joked that a car that’s “not Jap [Japanese made] is crap.” The quality of American cars is very good today, but you get the picture. If it’s a high-involvement product you’re purchasing, a good brand name is probably going to be very important to you. That’s why the manufacturers of products that are typically high-involvement decisions can’t become complacent about the value of their brands.
You Try It!
Marketing Copyright © by Kim Donahue is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
3.2 Low-Involvement Versus High-Involvement Buying Decisions and the Consumer’s Decision-Making Process
Learning objectives.
- Distinguish between low-involvement and high-involvement buying decisions.
- Understand what the stages of the buying process are and what happens in each stage.
As you have seen, many factors influence a consumer’s behavior. Depending on a consumer’s experience and knowledge, some consumers may be able to make quick purchase decisions and other consumers may need to get information and be more involved in the decision process before making a purchase. The level of involvement reflects how personally important or interested you are in consuming a product and how much information you need to make a decision. The level of involvement in buying decisions may be considered a continuum from decisions that are fairly routine (consumers are not very involved) to decisions that require extensive thought and a high level of involvement. Whether a decision is low, high, or limited, involvement varies by consumer, not by product, although some products such as purchasing a house typically require a high-involvement for all consumers. Consumers with no experience purchasing a product may have more involvement than someone who is replacing a product.
You have probably thought about many products you want or need but never did much more than that. At other times, you’ve probably looked at dozens of products, compared them, and then decided not to purchase any one of them. When you run out of products such as milk or bread that you buy on a regular basis, you may buy the product as soon as you recognize the need because you do not need to search for information or evaluate alternatives. As Nike would put it, you “just do it.” Low-involvement decisions are, however, typically products that are relatively inexpensive and pose a low risk to the buyer if she makes a mistake by purchasing them.
Consumers often engage in routine response behavior when they make low-involvement decisions—that is, they make automatic purchase decisions based on limited information or information they have gathered in the past. For example, if you always order a Diet Coke at lunch, you’re engaging in routine response behavior. You may not even think about other drink options at lunch because your routine is to order a Diet Coke, and you simply do it. Similarly, if you run out of Diet Coke at home, you may buy more without any information search.
Some low-involvement purchases are made with no planning or previous thought. These buying decisions are called impulse buying . While you’re waiting to check out at the grocery store, perhaps you see a magazine with Angelina Jolie and Brad Pitt on the cover and buy it on the spot simply because you want it. You might see a roll of tape at a check-out stand and remember you need one or you might see a bag of chips and realize you’re hungry or just want them. These are items that are typically low-involvement decisions. Low-involvement decisions aren’t necessarily products purchased on impulse, although they can be.
By contrast, high-involvement decisions carry a higher risk to buyers if they fail, are complex, and/or have high price tags. A car, a house, and an insurance policy are examples. These items are not purchased often but are relevant and important to the buyer. Buyers don’t engage in routine response behavior when purchasing high-involvement products. Instead, consumers engage in what’s called extended problem solving , where they spend a lot of time comparing different aspects such as the features of the products, prices, and warranties.
High-involvement decisions can cause buyers a great deal of postpurchase dissonance (anxiety) if they are unsure about their purchases or if they had a difficult time deciding between two alternatives. Companies that sell high-involvement products are aware that postpurchase dissonance can be a problem. Frequently, they try to offer consumers a lot of information about their products, including why they are superior to competing brands and how they won’t let the consumer down. Salespeople may be utilized to answer questions and do a lot of customer “hand-holding.”

Allstate’s “You’re in Good Hands” advertisements are designed to convince consumers that the insurance company won’t let them down.
Mike Mozart – Allstate, – CC BY 2.0.
Limited problem solving falls somewhere between low-involvement (routine) and high-involvement (extended problem solving) decisions. Consumers engage in limited problem solving when they already have some information about a good or service but continue to search for a little more information. Assume you need a new backpack for a hiking trip. While you are familiar with backpacks, you know that new features and materials are available since you purchased your last backpack. You’re going to spend some time looking for one that’s decent because you don’t want it to fall apart while you’re traveling and dump everything you’ve packed on a hiking trail. You might do a little research online and come to a decision relatively quickly. You might consider the choices available at your favorite retail outlet but not look at every backpack at every outlet before making a decision. Or you might rely on the advice of a person you know who’s knowledgeable about backpacks. In some way you shorten or limit your involvement and the decision-making process.
Products, such as chewing gum, which may be low-involvement for many consumers often use advertising such as commercials and sales promotions such as coupons to reach many consumers at once. Companies also try to sell products such as gum in as many locations as possible. Many products that are typically high-involvement such as automobiles may use more personal selling to answer consumers’ questions. Brand names can also be very important regardless of the consumer’s level of purchasing involvement. Consider a low- versus high-involvement decision—say, purchasing a tube of toothpaste versus a new car. You might routinely buy your favorite brand of toothpaste, not thinking much about the purchase (engage in routine response behavior), but not be willing to switch to another brand either. Having a brand you like saves you “search time” and eliminates the evaluation period because you know what you’re getting.
When it comes to the car, you might engage in extensive problem solving but, again, only be willing to consider a certain brand or brands. For example, in the 1970s, American-made cars had such a poor reputation for quality that buyers joked that a car that’s “not Jap [Japanese made] is crap.” The quality of American cars is very good today, but you get the picture. If it’s a high-involvement product you’re purchasing, a good brand name is probably going to be very important to you. That’s why the manufacturers of products that are typically high-involvement decisions can’t become complacent about the value of their brands.
1970s American Cars
(click to see video)
Today, Lexus is the automotive brand that experiences the most customer loyalty. For a humorous, tongue-in-cheek look at why the brand reputation of American carmakers suffered in the 1970s, check out this clip.
Stages in the Buying Process
Figure 3.9 “Stages in the Consumer’s Purchasing Process” outlines the buying stages consumers go through. At any given time, you’re probably in a buying stage for a product or service. You’re thinking about the different types of things you want or need to eventually buy, how you are going to find the best ones at the best price, and where and how will you buy them. Meanwhile, there are other products you have already purchased that you’re evaluating. Some might be better than others. Will you discard them, and if so, how? Then what will you buy? Where does that process start?
Figure 3.9 Stages in the Consumer’s Purchasing Process
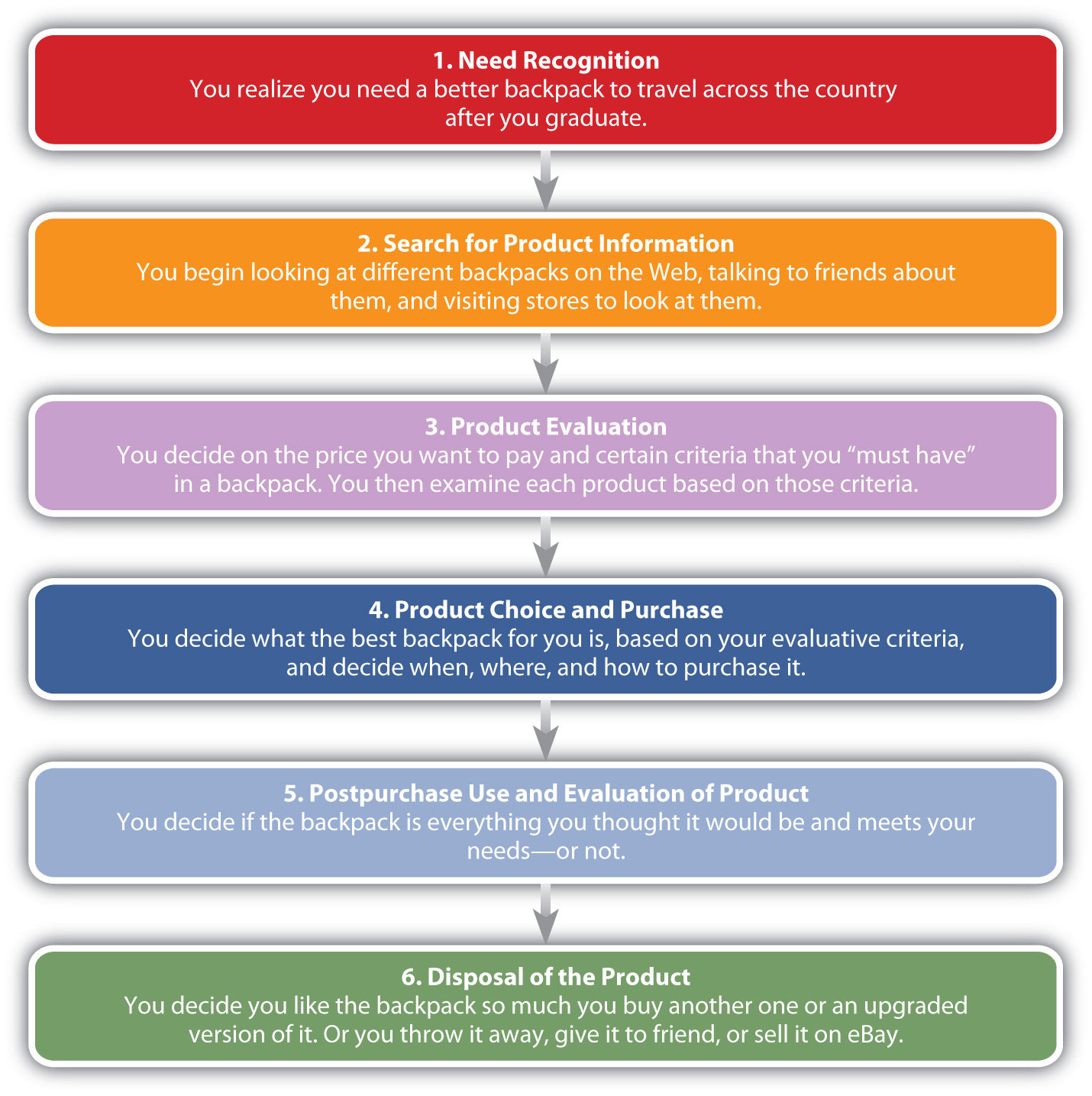
Stage 1. Need Recognition
You plan to backpack around the country after you graduate and don’t have a particularly good backpack. You realize that you must get a new backpack. You may also be thinking about the job you’ve accepted after graduation and know that you must get a vehicle to commute. Recognizing a need may involve something as simple as running out of bread or milk or realizing that you must get a new backpack or a car after you graduate. Marketers try to show consumers how their products and services add value and help satisfy needs and wants. Do you think it’s a coincidence that Gatorade, Powerade, and other beverage makers locate their machines in gymnasiums so you see them after a long, tiring workout? Previews at movie theaters are another example. How many times have you have heard about a movie and had no interest in it—until you saw the preview? Afterward, you felt like you had to see it.
Stage 2. Search for Information
For products such as milk and bread, you may simply recognize the need, go to the store, and buy more. However, if you are purchasing a car for the first time or need a particular type of backpack, you may need to get information on different alternatives. Maybe you have owned several backpacks and know what you like and don’t like about them. Or there might be a particular brand that you’ve purchased in the past that you liked and want to purchase in the future. This is a great position for the company that owns the brand to be in—something firms strive for. Why? Because it often means you will limit your search and simply buy their brand again.
If what you already know about backpacks doesn’t provide you with enough information, you’ll probably continue to gather information from various sources. Frequently people ask friends, family, and neighbors about their experiences with products. Magazines such as Consumer Reports (considered an objective source of information on many consumer products) or Backpacker Magazine might also help you. Similar information sources are available for learning about different makes and models of cars.
Internet shopping sites such as Amazon.com have become a common source of information about products. Epinions.com is an example of consumer-generated review site. The site offers product ratings, buying tips, and price information. Amazon.com also offers product reviews written by consumers. People prefer “independent” sources such as this when they are looking for product information. However, they also often consult non-neutral sources of information, such advertisements, brochures, company Web sites, and salespeople.
Stage 3. Product Evaluation
Obviously, there are hundreds of different backpacks and cars available. It’s not possible for you to examine all of them. In fact, good salespeople and marketing professionals know that providing you with too many choices can be so overwhelming that you might not buy anything at all. Consequently, you may use choice heuristics or rules of thumb that provide mental shortcuts in the decision-making process. You may also develop evaluative criteria to help you narrow down your choices. Backpacks or cars that meet your initial criteria before the consideration will determine the set of brands you’ll consider for purchase.
Evaluative criteria are certain characteristics that are important to you such as the price of the backpack, the size, the number of compartments, and color. Some of these characteristics are more important than others. For example, the size of the backpack and the price might be more important to you than the color—unless, say, the color is hot pink and you hate pink. You must decide what criteria are most important and how well different alternatives meet the criteria.
Figure 3.10

Osprey backpacks are known for their durability. The company has a special design and quality control center, and Osprey’s salespeople annually take a “canyon testing” trip to see how well the company’s products perform.
melanie innis – break – CC BY-NC-ND 2.0.
Companies want to convince you that the evaluative criteria you are considering reflect the strengths of their products. For example, you might not have thought about the weight or durability of the backpack you want to buy. However, a backpack manufacturer such as Osprey might remind you through magazine ads, packaging information, and its Web site that you should pay attention to these features—features that happen to be key selling points of its backpacks. Automobile manufacturers may have similar models, so don’t be afraid to add criteria to help you evaluate cars in your consideration set.
Stage 4. Product Choice and Purchase
With low-involvement purchases, consumers may go from recognizing a need to purchasing the product. However, for backpacks and cars, you decide which one to purchase after you have evaluated different alternatives. In addition to which backpack or which car, you are probably also making other decisions at this stage, including where and how to purchase the backpack (or car) and on what terms. Maybe the backpack was cheaper at one store than another, but the salesperson there was rude. Or maybe you decide to order online because you’re too busy to go to the mall. Other decisions related to the purchase, particularly those related to big-ticket items, are made at this point. For example, if you’re buying a high-definition television, you might look for a store that will offer you credit or a warranty.
Stage 5. Postpurchase Use and Evaluation
At this point in the process you decide whether the backpack you purchased is everything it was cracked up to be. Hopefully it is. If it’s not, you’re likely to suffer what’s called postpurchase dissonance . You might call it buyer’s remorse . Typically, dissonance occurs when a product or service does not meet your expectations. Consumers are more likely to experience dissonance with products that are relatively expensive and that are purchased infrequently.
You want to feel good about your purchase, but you don’t. You begin to wonder whether you should have waited to get a better price, purchased something else, or gathered more information first. Consumers commonly feel this way, which is a problem for sellers. If you don’t feel good about what you’ve purchased from them, you might return the item and never purchase anything from them again. Or, worse yet, you might tell everyone you know how bad the product was.
Companies do various things to try to prevent buyer’s remorse. For smaller items, they might offer a money back guarantee or they might encourage their salespeople to tell you what a great purchase you made. How many times have you heard a salesperson say, “That outfit looks so great on you!” For larger items, companies might offer a warranty, along with instruction booklets, and a toll-free troubleshooting line to call or they might have a salesperson call you to see if you need help with product. Automobile companies may offer loaner cars when you bring your car in for service.
Companies may also try to set expectations in order to satisfy customers. Service companies such as restaurants do this frequently. Think about when the hostess tells you that your table will be ready in 30 minutes. If they seat you in 15 minutes, you are much happier than if they told you that your table would be ready in 15 minutes, but it took 30 minutes to seat you. Similarly, if a store tells you that your pants will be altered in a week and they are ready in three days, you’ll be much more satisfied than if they said your pants would be ready in three days, yet it took a week before they were ready.
Stage 6. Disposal of the Product
There was a time when neither manufacturers nor consumers thought much about how products got disposed of, so long as people bought them. But that’s changed. How products are being disposed of is becoming extremely important to consumers and society in general. Computers and batteries, which leech chemicals into landfills, are a huge problem. Consumers don’t want to degrade the environment if they don’t have to, and companies are becoming more aware of this fact.
Take for example Crystal Light, a water-based beverage that’s sold in grocery stores. You can buy it in a bottle. However, many people buy a concentrated form of it, put it in reusable pitchers or bottles, and add water. That way, they don’t have to buy and dispose of plastic bottle after plastic bottle, damaging the environment in the process. Windex has done something similar with its window cleaner. Instead of buying new bottles of it all the time, you can purchase a concentrate and add water. You have probably noticed that most grocery stores now sell cloth bags consumers can reuse instead of continually using and discarding of new plastic or paper bags.
Figure 3.11

The hike up to Mount Everest used to be pristine. Now it looks more like this. Who’s responsible? Are consumers or companies responsible, or both?
jqpubliq – Recycling Center Pile – CC BY-SA 2.0.
Other companies are less concerned about conservation than they are about planned obsolescence . Planned obsolescence is a deliberate effort by companies to make their products obsolete, or unusable, after a period of time. The goal is to improve a company’s sales by reducing the amount of time between the repeat purchases consumers make of products. When a software developer introduces a new version of product, it is usually designed to be incompatible with older versions of it. For example, not all the formatting features are the same in Microsoft Word 2007 and 2010. Sometimes documents do not translate properly when opened in the newer version. Consequently, you will be more inclined to upgrade to the new version so you can open all Word documents you receive.
Products that are disposable are another way in which firms have managed to reduce the amount of time between purchases. Disposable lighters are an example. Do you know anyone today that owns a nondisposable lighter? Believe it or not, prior to the 1960s, scarcely anyone could have imagined using a cheap disposable lighter. There are many more disposable products today than there were in years past—including everything from bottled water and individually wrapped snacks to single-use eye drops and cell phones.
Figure 3.12

Disposable lighters came into vogue in the United States in the 1960s. You probably don’t own a cool, nondisposable lighter like one of these, but you don’t have to bother refilling it with lighter fluid either.
Europeana staff photographer – A trench art lighter – public domain.
Key Takeaways
Consumer behavior looks at the many reasons why people buy things and later dispose of them. Consumers go through distinct buying phases when they purchase products: (1) realizing the need or wanting something, (2) searching for information about the item, (3) evaluating different products, (4) choosing a product and purchasing it, (5) using and evaluating the product after the purchase, and (6) disposing of the product. A consumer’s level of involvement is how interested he or she is in buying and consuming a product. Low-involvement products are usually inexpensive and pose a low risk to the buyer if he or she makes a mistake by purchasing them. High-involvement products carry a high risk to the buyer if they fail, are complex, or have high price tags. Limited-involvement products fall somewhere in between.
Review Questions
- How do low-involvement decisions differ from high-involvement decisions in terms of relevance, price, frequency, and the risks their buyers face? Name some products in each category that you’ve recently purchased.
- What stages do people go through in the buying process for high-involvement decisions? How do the stages vary for low-involvement decisions?
- What is postpurchase dissonance and what can companies do to reduce it?
Principles of Marketing Copyright © 2015 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
If you still have questions or prefer to get help directly from an agent, please submit a request. We’ll get back to you as soon as possible.
Please fill out the contact form below and we will reply as soon as possible.
- Marketing, Advertising, Sales & PR
- Principles of Marketing
Types of Consumer Decision - Explained
What types of decisions do Consumers Make?
Written by Jason Gordon
Updated at April 17th, 2024
- Marketing, Advertising, Sales & PR Principles of Marketing Sales Advertising Public Relations SEO, Social Media, Direct Marketing
- Accounting, Taxation, and Reporting Managerial & Financial Accounting & Reporting Business Taxation
- Professionalism & Career Development
- Law, Transactions, & Risk Management Government, Legal System, Administrative Law, & Constitutional Law Legal Disputes - Civil & Criminal Law Agency Law HR, Employment, Labor, & Discrimination Business Entities, Corporate Governance & Ownership Business Transactions, Antitrust, & Securities Law Real Estate, Personal, & Intellectual Property Commercial Law: Contract, Payments, Security Interests, & Bankruptcy Consumer Protection Insurance & Risk Management Immigration Law Environmental Protection Law Inheritance, Estates, and Trusts
- Business Management & Operations Operations, Project, & Supply Chain Management Strategy, Entrepreneurship, & Innovation Business Ethics & Social Responsibility Global Business, International Law & Relations Business Communications & Negotiation Management, Leadership, & Organizational Behavior
- Economics, Finance, & Analytics Economic Analysis & Monetary Policy Research, Quantitative Analysis, & Decision Science Investments, Trading, and Financial Markets Banking, Lending, and Credit Industry Business Finance, Personal Finance, and Valuation Principles
What are the types of Consumer Decisions?
Consumer decisions can be categorized into three primary types:
- Routinized Response - This is the kind of decision where you don't really have to think much about it.
- Limited Problem Solving - This type of purchase decision involves a little more thinking or a little more consideration.
- Extensive Problem Solving - This is when we're making a decision to purchase and we are really going to labor over that decision.
Each of these is discussed further below.
What is a Routinized Response?
This is the kind of decision where you don't really have to think much about it. That is, it's a routine. In the context of making a purchase, this is when we make the decision to purchase without going through the consumer decision-making process. Generally, it means we simply follow or repeat a previous course of action. Think of going to the store and buying the same type or brand of grocery item that you buy every week. You do this as a routine, rather than identifying alternatives and comparing them.
What is Limited Problem Solving?
This type of purchase decision involves a little more thinking or a little more consideration. Maybe we consider different products in making our purchase. Maybe we consider how much to buy. Whatever our considerations, we're going to spend more time and effort making this decision or making this purchase.
What is Extensive Problem Solving?
This is when we're making a decision to purchase and we are really going to labor over that decision. That is, we are really going to consider it thoroughly. We may do a great deal of research. We may consult friends or look at customer reviews. We generally use this approach when it is something that we have never bought before, its very technical in nature, or when it is a very expensive item (like a car). Generally, this type of decision involves the most time, information, and effort in the evaluation of alternatives.
Related Articles
- Marketing Mix - Explained
- Captive Pricing - Explained
- Marketing Ethics - Explained
- Publicity - Explained
Module 4: Identifying and Understanding Customer Behavior
Increasing sales with limited problem solving, learning objectives.
- Describe how a retailer can increase sales from customers engaged in limited problem solving
By contrast, consumers with a limited problem solving mindset put in little consideration before arriving at a decision. Because of the minimal time and energy committed to the search, this mindset is most common with the selection and purchase of low-consideration or low-value items. These may also be purchases that have little to no emotional significance. Simply, the consumer is unwilling to over-invest time or effort in a decision that has little importance or where a “bad” decision has no lingering negative effects.
These shoppers don’t need a high level of engagement. Instead, they need to be cued to make a purchase. Thus, advertising, promotion and in-store merchandising can be especially helpful in influencing the decision. Think again about your local grocery store, imagining that you’re walking down the dental care aisle. Each item on-shelf, through its packaging—the images and words, the colors and fonts—is trying to communicate to you a reason to buy. The displays, floor or shelf graphics and special tags are doing the same. And, given the low relative price-point of the items and the low risk of making a mistake in buying the “wrong” product,” shoppers can make purchase decisions with a limited problem solving mindset.
Practice Questions
- Increasing Sales with Limited Problem Solving. Authored by : Patrick Williams. Provided by : Lumen Learning. License : CC BY: Attribution


Four Modes of Consumer Decision Making

Extended problem solving
Extended problem solving customer decision – making mode relates to a situation where customers lack experience in a specific consumption setting, nevertheless, the setting is perceived by them as a highly involving. The products are usually of a high value and they also contribute to an individual’s social status, however, their purchase is often associated with significant amount of risk in terms of making improper purchase decision. Purchasing the first car or the first house can be mentioned as instances for extended problem solving.
Limited problem solving
Customer decision – making mode of limited problem solving , relates to a situation where both, customer experience, as well as, the level of their involvement are low. Considered to be the most common mode of decision – making, it lacks systematic approach in terms of decision – making. Examples for this mode of decision – making might include searching for and purchasing products and services associated with pest control within private properties.
In other words, as Perrey and Spillecke (2011) confirm, limited problem – solving customer decision – making mode relate to situations where customers are attempting to find appropriate solutions to their unpleasant issues. Retailers often attempt to attract such type of customers by employing a range of marketing techniques that include introducing discount vouchers, offering free samples etc.
Habit or variety seeking
Habit or variety seeking is the customer decision – making mode where a decision is not involving, however, there are high amount of repeated purchases from a specific brand. For example, the purchase of a specific brand of a dishwasher gel can be repeated over a long period of time in a habitual manner, without re-considering the value associated with the brand even when there are more valuable alternatives have emerged in the market.
Variety seeking relates to instances where customer moves to another brand within a given product category. At the same time, interestingly, “from one purchase occasion to the next, the individual will switch brands from within this set, just for the sake of variety” (O’Guinn et al, 2011, p.175).
Brand loyalty
Customers with a decision – making mode of brand loyalty practice high level of involvement in decision – making and they also possess high level of experience with a particular brand. Instances of brand loyalty customer decision – making mode include using specific brand of cigarettes for a long period of time.
According to Cant et al (2009), factors effecting customer brand loyalty in retail setting include brand name, the quality of products and services, price and style of products, environment of the store, the level and nature of promotion offered, and the quality of customer services provided. Considerable amount of financial resources are usually invested by leading retailers in order to enhance their brand image and therefore increase their long-term growth prospects.
- Cant, M.C., Strydom, J.W. & Jooste, C.J. (2009) “Marketing Management” Juta Publications
- O’Guinn, T.C., Allen, C.T. & Semenik, R.J. (2011) “Advertising and Integrated Brand Promotion” Cengage Learning
- Perrey, J & Spillecke, D. (2011) “Retail Marketing and Branding: A Definitive Guide to Maximising ROI” John Wiley & Sons

Chapter 3 – Consumer Behaviour: How People Make Buying Decisions
3.3 Low-Involvement Versus High-Involvement Buying Decisions
LEARNING OBJECTIVE
- Distinguish between low and high involvement buying decisions.
One of the ways that the purchase decision process is modified is by consumers’ level of involvement in the decision. Low-involvement decisions usually pose a low risk to the buyer if they make a mistake by purchasing them. High-involvement decisions carry a high risk and limited-involvement products fall somewhere in between. Many factors influence a consumer’s behaviour. Depending on a consumer’s experience and knowledge, some consumers may be able to make quick decisions, and other consumers may need to be more involved before making a purchase.
The level of involvement reflects how important or interested the consumer is in the decision. That changes the amount of information they need to make a decision. The level of involvement may be considered a continuum from decisions that are fairly routine, sometimes called habits, to decisions that require extensive thought and a high level of involvement. Whether a decision is low, high, or limited, involvement typically varies by consumer rather than by the product or service. For example, for most consumers, purchasing a car is high-involvement decision because it doesn’t happen often, it is expensive compared to their income and it is a complex and long term decision. When a consumer is engaged in the purchase process for the car, they might engage in extensive search using word of mouth, online product reviews, and safety ratings.
For high-involvement products, the brand reputation may important to consumers. For example, beginning in the 1970s, American-made cars had such a poor reputation for quality that Japanese car brands were able to enter and dominate the market. Since then, due to government regulation, the quality of American cars has improved (with the exception of Tesla) but American cars continue to have a lower product quality brand image than Japanese cars. In the 2021 Consumer Report’s Annual Report on Car Performance, Reliability, Satisfaction, Safety & Emissions, Mazda, Toyota, and Lexus have consistently been the top three brands ( Consumer Reports, 2021 ). ‡
Consumers do not go through all the stages in the decision process for low involvement products such as bread or rice because they don’t need to search for information or evaluate alternatives. Low-involvement decisions are typically inexpensive (compared to income), purchased regularly and pose low risk to buyers if they make a mistake or there is a problem with them. Not going through all the stages is called routine response behaviour , that is, they make automatic purchase decisions based on limited information or information they have gathered in the past. For example, if you always order bottled water at lunch, you are exhibiting routine response behaviour. You likely don’t think about other drink options because your routine is to order bottled water. Similarly, if you run out of your bottled water at home, you may buy more without going through information search.
Unanticipated low-involvement purchases are made without planning or previous thought. These are called impulse buying . While you’re waiting to check out at the grocery store, perhaps you see a protein bar and buy it simply because you want it. You might see a roll of tape at a check-out stand and remember you need one or you might see a bag of popcorn and realize you’re hungry or just want them.
To reach as many consumers as possible at the moment of decision, low involvement products, such as chocolate bars, often place them in as many locations as possible. Products that are typically high-involvement such as cars may use more personal selling to answer consumers’ questions. Brand names can also be very important regardless of the consumer’s level of purchasing involvement. Consider a low- versus high-involvement decision, for example, purchasing a tube of toothpaste versus a new car. You might routinely buy your favorite brand of toothpaste, not thinking much about the purchase (engage in routine response behaviour), but not be willing to switch to another brand either. Having a brand you like saves you “search time” and eliminates the evaluation period because you know what you’re getting.
By contrast, high-involvement decisions carry a higher risk to buyers if they fail, are complex, and/or have a high price. A car or laptop computer are examples. These items are not purchased often but are relevant and important to the buyer. Buyers don’t engage in routine response behaviour when purchasing high-involvement products. Instead, consumers engage in what’s called extended problem solving , where they may spend time comparing different aspects such as the features of the products, prices, and warranties.
High-involvement decisions can cause buyers a great deal of post-purchase dissonance (anxiety) if they are unsure about their purchases or if they had a difficult time deciding between two alternatives. Companies that sell high-involvement products are aware that post purchase dissonance can be a problem. They offer potential customers lots of information about their products, including why they are superior to competing brands and how well they function post purchase. Real salespeople, either in person or as live chats, or artificial intelligence in the form of chatbots may be used to answer questions and reassure customers. ‡
Limited problem solving falls somewhere between low-involvement (routine) and high-involvement (extended problem solving) decisions. Consumers engage in limited problem solving when they already have some information about a good or service but continue to search for a little more information. Assume you need a new backpack for a hiking trip. While you are familiar with backpacks, you know that new features and materials are available since you purchased your last backpack. You’re going to spend some time looking for one that’s decent because you don’t want it to fall apart while you’re traveling and dump everything you’ve packed on a hiking trail. You might do a little research online and come to a decision relatively quickly. You might consider the choices available at your favorite retail outlet but not look at every backpack at every outlet before making a decision. You might rely on the advice of a person you know who’s knowledgeable about backpacks. In some way, you shorten or limit your involvement and the decision-making process.
Principles of Marketing, 1st Canadian Edition Copyright © by Anthony Francescucci, Joanne McNeish, Nukhet Taylor is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2024 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
Problem-Solving Strategies and Obstacles
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
Sean is a fact-checker and researcher with experience in sociology, field research, and data analytics.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Sean-Blackburn-1000-a8b2229366944421bc4b2f2ba26a1003.jpg)
JGI / Jamie Grill / Getty Images
- Application
- Improvement
From deciding what to eat for dinner to considering whether it's the right time to buy a house, problem-solving is a large part of our daily lives. Learn some of the problem-solving strategies that exist and how to use them in real life, along with ways to overcome obstacles that are making it harder to resolve the issues you face.
What Is Problem-Solving?
In cognitive psychology , the term 'problem-solving' refers to the mental process that people go through to discover, analyze, and solve problems.
A problem exists when there is a goal that we want to achieve but the process by which we will achieve it is not obvious to us. Put another way, there is something that we want to occur in our life, yet we are not immediately certain how to make it happen.
Maybe you want a better relationship with your spouse or another family member but you're not sure how to improve it. Or you want to start a business but are unsure what steps to take. Problem-solving helps you figure out how to achieve these desires.
The problem-solving process involves:
- Discovery of the problem
- Deciding to tackle the issue
- Seeking to understand the problem more fully
- Researching available options or solutions
- Taking action to resolve the issue
Before problem-solving can occur, it is important to first understand the exact nature of the problem itself. If your understanding of the issue is faulty, your attempts to resolve it will also be incorrect or flawed.
Problem-Solving Mental Processes
Several mental processes are at work during problem-solving. Among them are:
- Perceptually recognizing the problem
- Representing the problem in memory
- Considering relevant information that applies to the problem
- Identifying different aspects of the problem
- Labeling and describing the problem
Problem-Solving Strategies
There are many ways to go about solving a problem. Some of these strategies might be used on their own, or you may decide to employ multiple approaches when working to figure out and fix a problem.
An algorithm is a step-by-step procedure that, by following certain "rules" produces a solution. Algorithms are commonly used in mathematics to solve division or multiplication problems. But they can be used in other fields as well.
In psychology, algorithms can be used to help identify individuals with a greater risk of mental health issues. For instance, research suggests that certain algorithms might help us recognize children with an elevated risk of suicide or self-harm.
One benefit of algorithms is that they guarantee an accurate answer. However, they aren't always the best approach to problem-solving, in part because detecting patterns can be incredibly time-consuming.
There are also concerns when machine learning is involved—also known as artificial intelligence (AI)—such as whether they can accurately predict human behaviors.
Heuristics are shortcut strategies that people can use to solve a problem at hand. These "rule of thumb" approaches allow you to simplify complex problems, reducing the total number of possible solutions to a more manageable set.
If you find yourself sitting in a traffic jam, for example, you may quickly consider other routes, taking one to get moving once again. When shopping for a new car, you might think back to a prior experience when negotiating got you a lower price, then employ the same tactics.
While heuristics may be helpful when facing smaller issues, major decisions shouldn't necessarily be made using a shortcut approach. Heuristics also don't guarantee an effective solution, such as when trying to drive around a traffic jam only to find yourself on an equally crowded route.
Trial and Error
A trial-and-error approach to problem-solving involves trying a number of potential solutions to a particular issue, then ruling out those that do not work. If you're not sure whether to buy a shirt in blue or green, for instance, you may try on each before deciding which one to purchase.
This can be a good strategy to use if you have a limited number of solutions available. But if there are many different choices available, narrowing down the possible options using another problem-solving technique can be helpful before attempting trial and error.
In some cases, the solution to a problem can appear as a sudden insight. You are facing an issue in a relationship or your career when, out of nowhere, the solution appears in your mind and you know exactly what to do.
Insight can occur when the problem in front of you is similar to an issue that you've dealt with in the past. Although, you may not recognize what is occurring since the underlying mental processes that lead to insight often happen outside of conscious awareness .
Research indicates that insight is most likely to occur during times when you are alone—such as when going on a walk by yourself, when you're in the shower, or when lying in bed after waking up.
How to Apply Problem-Solving Strategies in Real Life
If you're facing a problem, you can implement one or more of these strategies to find a potential solution. Here's how to use them in real life:
- Create a flow chart . If you have time, you can take advantage of the algorithm approach to problem-solving by sitting down and making a flow chart of each potential solution, its consequences, and what happens next.
- Recall your past experiences . When a problem needs to be solved fairly quickly, heuristics may be a better approach. Think back to when you faced a similar issue, then use your knowledge and experience to choose the best option possible.
- Start trying potential solutions . If your options are limited, start trying them one by one to see which solution is best for achieving your desired goal. If a particular solution doesn't work, move on to the next.
- Take some time alone . Since insight is often achieved when you're alone, carve out time to be by yourself for a while. The answer to your problem may come to you, seemingly out of the blue, if you spend some time away from others.
Obstacles to Problem-Solving
Problem-solving is not a flawless process as there are a number of obstacles that can interfere with our ability to solve a problem quickly and efficiently. These obstacles include:
- Assumptions: When dealing with a problem, people can make assumptions about the constraints and obstacles that prevent certain solutions. Thus, they may not even try some potential options.
- Functional fixedness : This term refers to the tendency to view problems only in their customary manner. Functional fixedness prevents people from fully seeing all of the different options that might be available to find a solution.
- Irrelevant or misleading information: When trying to solve a problem, it's important to distinguish between information that is relevant to the issue and irrelevant data that can lead to faulty solutions. The more complex the problem, the easier it is to focus on misleading or irrelevant information.
- Mental set: A mental set is a tendency to only use solutions that have worked in the past rather than looking for alternative ideas. A mental set can work as a heuristic, making it a useful problem-solving tool. However, mental sets can also lead to inflexibility, making it more difficult to find effective solutions.
How to Improve Your Problem-Solving Skills
In the end, if your goal is to become a better problem-solver, it's helpful to remember that this is a process. Thus, if you want to improve your problem-solving skills, following these steps can help lead you to your solution:
- Recognize that a problem exists . If you are facing a problem, there are generally signs. For instance, if you have a mental illness , you may experience excessive fear or sadness, mood changes, and changes in sleeping or eating habits. Recognizing these signs can help you realize that an issue exists.
- Decide to solve the problem . Make a conscious decision to solve the issue at hand. Commit to yourself that you will go through the steps necessary to find a solution.
- Seek to fully understand the issue . Analyze the problem you face, looking at it from all sides. If your problem is relationship-related, for instance, ask yourself how the other person may be interpreting the issue. You might also consider how your actions might be contributing to the situation.
- Research potential options . Using the problem-solving strategies mentioned, research potential solutions. Make a list of options, then consider each one individually. What are some pros and cons of taking the available routes? What would you need to do to make them happen?
- Take action . Select the best solution possible and take action. Action is one of the steps required for change . So, go through the motions needed to resolve the issue.
- Try another option, if needed . If the solution you chose didn't work, don't give up. Either go through the problem-solving process again or simply try another option.
You can find a way to solve your problems as long as you keep working toward this goal—even if the best solution is simply to let go because no other good solution exists.
Sarathy V. Real world problem-solving . Front Hum Neurosci . 2018;12:261. doi:10.3389/fnhum.2018.00261
Dunbar K. Problem solving . A Companion to Cognitive Science . 2017. doi:10.1002/9781405164535.ch20
Stewart SL, Celebre A, Hirdes JP, Poss JW. Risk of suicide and self-harm in kids: The development of an algorithm to identify high-risk individuals within the children's mental health system . Child Psychiat Human Develop . 2020;51:913-924. doi:10.1007/s10578-020-00968-9
Rosenbusch H, Soldner F, Evans AM, Zeelenberg M. Supervised machine learning methods in psychology: A practical introduction with annotated R code . Soc Personal Psychol Compass . 2021;15(2):e12579. doi:10.1111/spc3.12579
Mishra S. Decision-making under risk: Integrating perspectives from biology, economics, and psychology . Personal Soc Psychol Rev . 2014;18(3):280-307. doi:10.1177/1088868314530517
Csikszentmihalyi M, Sawyer K. Creative insight: The social dimension of a solitary moment . In: The Systems Model of Creativity . 2015:73-98. doi:10.1007/978-94-017-9085-7_7
Chrysikou EG, Motyka K, Nigro C, Yang SI, Thompson-Schill SL. Functional fixedness in creative thinking tasks depends on stimulus modality . Psychol Aesthet Creat Arts . 2016;10(4):425‐435. doi:10.1037/aca0000050
Huang F, Tang S, Hu Z. Unconditional perseveration of the short-term mental set in chunk decomposition . Front Psychol . 2018;9:2568. doi:10.3389/fpsyg.2018.02568
National Alliance on Mental Illness. Warning signs and symptoms .
Mayer RE. Thinking, problem solving, cognition, 2nd ed .
Schooler JW, Ohlsson S, Brooks K. Thoughts beyond words: When language overshadows insight. J Experiment Psychol: General . 1993;122:166-183. doi:10.1037/0096-3445.2.166
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
35 problem-solving techniques and methods for solving complex problems

Design your next session with SessionLab
Join the 150,000+ facilitators using SessionLab.
Recommended Articles
A step-by-step guide to planning a workshop, how to create an unforgettable training session in 8 simple steps, 47 useful online tools for workshop planning and meeting facilitation.
All teams and organizations encounter challenges as they grow. There are problems that might occur for teams when it comes to miscommunication or resolving business-critical issues . You may face challenges around growth , design , user engagement, and even team culture and happiness. In short, problem-solving techniques should be part of every team’s skillset.
Problem-solving methods are primarily designed to help a group or team through a process of first identifying problems and challenges , ideating possible solutions , and then evaluating the most suitable .
Finding effective solutions to complex problems isn’t easy, but by using the right process and techniques, you can help your team be more efficient in the process.
So how do you develop strategies that are engaging, and empower your team to solve problems effectively?
In this blog post, we share a series of problem-solving tools you can use in your next workshop or team meeting. You’ll also find some tips for facilitating the process and how to enable others to solve complex problems.
Let’s get started!
How do you identify problems?
How do you identify the right solution.
- Tips for more effective problem-solving
Complete problem-solving methods
- Problem-solving techniques to identify and analyze problems
- Problem-solving techniques for developing solutions
Problem-solving warm-up activities
Closing activities for a problem-solving process.
Before you can move towards finding the right solution for a given problem, you first need to identify and define the problem you wish to solve.
Here, you want to clearly articulate what the problem is and allow your group to do the same. Remember that everyone in a group is likely to have differing perspectives and alignment is necessary in order to help the group move forward.
Identifying a problem accurately also requires that all members of a group are able to contribute their views in an open and safe manner. It can be scary for people to stand up and contribute, especially if the problems or challenges are emotive or personal in nature. Be sure to try and create a psychologically safe space for these kinds of discussions.
Remember that problem analysis and further discussion are also important. Not taking the time to fully analyze and discuss a challenge can result in the development of solutions that are not fit for purpose or do not address the underlying issue.
Successfully identifying and then analyzing a problem means facilitating a group through activities designed to help them clearly and honestly articulate their thoughts and produce usable insight.
With this data, you might then produce a problem statement that clearly describes the problem you wish to be addressed and also state the goal of any process you undertake to tackle this issue.
Finding solutions is the end goal of any process. Complex organizational challenges can only be solved with an appropriate solution but discovering them requires using the right problem-solving tool.
After you’ve explored a problem and discussed ideas, you need to help a team discuss and choose the right solution. Consensus tools and methods such as those below help a group explore possible solutions before then voting for the best. They’re a great way to tap into the collective intelligence of the group for great results!
Remember that the process is often iterative. Great problem solvers often roadtest a viable solution in a measured way to see what works too. While you might not get the right solution on your first try, the methods below help teams land on the most likely to succeed solution while also holding space for improvement.
Every effective problem solving process begins with an agenda . A well-structured workshop is one of the best methods for successfully guiding a group from exploring a problem to implementing a solution.
In SessionLab, it’s easy to go from an idea to a complete agenda . Start by dragging and dropping your core problem solving activities into place . Add timings, breaks and necessary materials before sharing your agenda with your colleagues.
The resulting agenda will be your guide to an effective and productive problem solving session that will also help you stay organized on the day!
Tips for more effective problem solving
Problem-solving activities are only one part of the puzzle. While a great method can help unlock your team’s ability to solve problems, without a thoughtful approach and strong facilitation the solutions may not be fit for purpose.
Let’s take a look at some problem-solving tips you can apply to any process to help it be a success!
Clearly define the problem
Jumping straight to solutions can be tempting, though without first clearly articulating a problem, the solution might not be the right one. Many of the problem-solving activities below include sections where the problem is explored and clearly defined before moving on.
This is a vital part of the problem-solving process and taking the time to fully define an issue can save time and effort later. A clear definition helps identify irrelevant information and it also ensures that your team sets off on the right track.
Don’t jump to conclusions
It’s easy for groups to exhibit cognitive bias or have preconceived ideas about both problems and potential solutions. Be sure to back up any problem statements or potential solutions with facts, research, and adequate forethought.
The best techniques ask participants to be methodical and challenge preconceived notions. Make sure you give the group enough time and space to collect relevant information and consider the problem in a new way. By approaching the process with a clear, rational mindset, you’ll often find that better solutions are more forthcoming.
Try different approaches
Problems come in all shapes and sizes and so too should the methods you use to solve them. If you find that one approach isn’t yielding results and your team isn’t finding different solutions, try mixing it up. You’ll be surprised at how using a new creative activity can unblock your team and generate great solutions.
Don’t take it personally
Depending on the nature of your team or organizational problems, it’s easy for conversations to get heated. While it’s good for participants to be engaged in the discussions, ensure that emotions don’t run too high and that blame isn’t thrown around while finding solutions.
You’re all in it together, and even if your team or area is seeing problems, that isn’t necessarily a disparagement of you personally. Using facilitation skills to manage group dynamics is one effective method of helping conversations be more constructive.
Get the right people in the room
Your problem-solving method is often only as effective as the group using it. Getting the right people on the job and managing the number of people present is important too!
If the group is too small, you may not get enough different perspectives to effectively solve a problem. If the group is too large, you can go round and round during the ideation stages.
Creating the right group makeup is also important in ensuring you have the necessary expertise and skillset to both identify and follow up on potential solutions. Carefully consider who to include at each stage to help ensure your problem-solving method is followed and positioned for success.
Document everything
The best solutions can take refinement, iteration, and reflection to come out. Get into a habit of documenting your process in order to keep all the learnings from the session and to allow ideas to mature and develop. Many of the methods below involve the creation of documents or shared resources. Be sure to keep and share these so everyone can benefit from the work done!
Bring a facilitator
Facilitation is all about making group processes easier. With a subject as potentially emotive and important as problem-solving, having an impartial third party in the form of a facilitator can make all the difference in finding great solutions and keeping the process moving. Consider bringing a facilitator to your problem-solving session to get better results and generate meaningful solutions!
Develop your problem-solving skills
It takes time and practice to be an effective problem solver. While some roles or participants might more naturally gravitate towards problem-solving, it can take development and planning to help everyone create better solutions.
You might develop a training program, run a problem-solving workshop or simply ask your team to practice using the techniques below. Check out our post on problem-solving skills to see how you and your group can develop the right mental process and be more resilient to issues too!
Design a great agenda
Workshops are a great format for solving problems. With the right approach, you can focus a group and help them find the solutions to their own problems. But designing a process can be time-consuming and finding the right activities can be difficult.
Check out our workshop planning guide to level-up your agenda design and start running more effective workshops. Need inspiration? Check out templates designed by expert facilitators to help you kickstart your process!
In this section, we’ll look at in-depth problem-solving methods that provide a complete end-to-end process for developing effective solutions. These will help guide your team from the discovery and definition of a problem through to delivering the right solution.
If you’re looking for an all-encompassing method or problem-solving model, these processes are a great place to start. They’ll ask your team to challenge preconceived ideas and adopt a mindset for solving problems more effectively.
- Six Thinking Hats
- Lightning Decision Jam
- Problem Definition Process
- Discovery & Action Dialogue
Design Sprint 2.0
- Open Space Technology
1. Six Thinking Hats
Individual approaches to solving a problem can be very different based on what team or role an individual holds. It can be easy for existing biases or perspectives to find their way into the mix, or for internal politics to direct a conversation.
Six Thinking Hats is a classic method for identifying the problems that need to be solved and enables your team to consider them from different angles, whether that is by focusing on facts and data, creative solutions, or by considering why a particular solution might not work.
Like all problem-solving frameworks, Six Thinking Hats is effective at helping teams remove roadblocks from a conversation or discussion and come to terms with all the aspects necessary to solve complex problems.
2. Lightning Decision Jam
Featured courtesy of Jonathan Courtney of AJ&Smart Berlin, Lightning Decision Jam is one of those strategies that should be in every facilitation toolbox. Exploring problems and finding solutions is often creative in nature, though as with any creative process, there is the potential to lose focus and get lost.
Unstructured discussions might get you there in the end, but it’s much more effective to use a method that creates a clear process and team focus.
In Lightning Decision Jam, participants are invited to begin by writing challenges, concerns, or mistakes on post-its without discussing them before then being invited by the moderator to present them to the group.
From there, the team vote on which problems to solve and are guided through steps that will allow them to reframe those problems, create solutions and then decide what to execute on.
By deciding the problems that need to be solved as a team before moving on, this group process is great for ensuring the whole team is aligned and can take ownership over the next stages.
Lightning Decision Jam (LDJ) #action #decision making #problem solving #issue analysis #innovation #design #remote-friendly The problem with anything that requires creative thinking is that it’s easy to get lost—lose focus and fall into the trap of having useless, open-ended, unstructured discussions. Here’s the most effective solution I’ve found: Replace all open, unstructured discussion with a clear process. What to use this exercise for: Anything which requires a group of people to make decisions, solve problems or discuss challenges. It’s always good to frame an LDJ session with a broad topic, here are some examples: The conversion flow of our checkout Our internal design process How we organise events Keeping up with our competition Improving sales flow
3. Problem Definition Process
While problems can be complex, the problem-solving methods you use to identify and solve those problems can often be simple in design.
By taking the time to truly identify and define a problem before asking the group to reframe the challenge as an opportunity, this method is a great way to enable change.
Begin by identifying a focus question and exploring the ways in which it manifests before splitting into five teams who will each consider the problem using a different method: escape, reversal, exaggeration, distortion or wishful. Teams develop a problem objective and create ideas in line with their method before then feeding them back to the group.
This method is great for enabling in-depth discussions while also creating space for finding creative solutions too!
Problem Definition #problem solving #idea generation #creativity #online #remote-friendly A problem solving technique to define a problem, challenge or opportunity and to generate ideas.
4. The 5 Whys
Sometimes, a group needs to go further with their strategies and analyze the root cause at the heart of organizational issues. An RCA or root cause analysis is the process of identifying what is at the heart of business problems or recurring challenges.
The 5 Whys is a simple and effective method of helping a group go find the root cause of any problem or challenge and conduct analysis that will deliver results.
By beginning with the creation of a problem statement and going through five stages to refine it, The 5 Whys provides everything you need to truly discover the cause of an issue.
The 5 Whys #hyperisland #innovation This simple and powerful method is useful for getting to the core of a problem or challenge. As the title suggests, the group defines a problems, then asks the question “why” five times, often using the resulting explanation as a starting point for creative problem solving.
5. World Cafe
World Cafe is a simple but powerful facilitation technique to help bigger groups to focus their energy and attention on solving complex problems.
World Cafe enables this approach by creating a relaxed atmosphere where participants are able to self-organize and explore topics relevant and important to them which are themed around a central problem-solving purpose. Create the right atmosphere by modeling your space after a cafe and after guiding the group through the method, let them take the lead!
Making problem-solving a part of your organization’s culture in the long term can be a difficult undertaking. More approachable formats like World Cafe can be especially effective in bringing people unfamiliar with workshops into the fold.
World Cafe #hyperisland #innovation #issue analysis World Café is a simple yet powerful method, originated by Juanita Brown, for enabling meaningful conversations driven completely by participants and the topics that are relevant and important to them. Facilitators create a cafe-style space and provide simple guidelines. Participants then self-organize and explore a set of relevant topics or questions for conversation.
6. Discovery & Action Dialogue (DAD)
One of the best approaches is to create a safe space for a group to share and discover practices and behaviors that can help them find their own solutions.
With DAD, you can help a group choose which problems they wish to solve and which approaches they will take to do so. It’s great at helping remove resistance to change and can help get buy-in at every level too!
This process of enabling frontline ownership is great in ensuring follow-through and is one of the methods you will want in your toolbox as a facilitator.
Discovery & Action Dialogue (DAD) #idea generation #liberating structures #action #issue analysis #remote-friendly DADs make it easy for a group or community to discover practices and behaviors that enable some individuals (without access to special resources and facing the same constraints) to find better solutions than their peers to common problems. These are called positive deviant (PD) behaviors and practices. DADs make it possible for people in the group, unit, or community to discover by themselves these PD practices. DADs also create favorable conditions for stimulating participants’ creativity in spaces where they can feel safe to invent new and more effective practices. Resistance to change evaporates as participants are unleashed to choose freely which practices they will adopt or try and which problems they will tackle. DADs make it possible to achieve frontline ownership of solutions.
7. Design Sprint 2.0
Want to see how a team can solve big problems and move forward with prototyping and testing solutions in a few days? The Design Sprint 2.0 template from Jake Knapp, author of Sprint, is a complete agenda for a with proven results.
Developing the right agenda can involve difficult but necessary planning. Ensuring all the correct steps are followed can also be stressful or time-consuming depending on your level of experience.
Use this complete 4-day workshop template if you are finding there is no obvious solution to your challenge and want to focus your team around a specific problem that might require a shortcut to launching a minimum viable product or waiting for the organization-wide implementation of a solution.
8. Open space technology
Open space technology- developed by Harrison Owen – creates a space where large groups are invited to take ownership of their problem solving and lead individual sessions. Open space technology is a great format when you have a great deal of expertise and insight in the room and want to allow for different takes and approaches on a particular theme or problem you need to be solved.
Start by bringing your participants together to align around a central theme and focus their efforts. Explain the ground rules to help guide the problem-solving process and then invite members to identify any issue connecting to the central theme that they are interested in and are prepared to take responsibility for.
Once participants have decided on their approach to the core theme, they write their issue on a piece of paper, announce it to the group, pick a session time and place, and post the paper on the wall. As the wall fills up with sessions, the group is then invited to join the sessions that interest them the most and which they can contribute to, then you’re ready to begin!
Everyone joins the problem-solving group they’ve signed up to, record the discussion and if appropriate, findings can then be shared with the rest of the group afterward.
Open Space Technology #action plan #idea generation #problem solving #issue analysis #large group #online #remote-friendly Open Space is a methodology for large groups to create their agenda discerning important topics for discussion, suitable for conferences, community gatherings and whole system facilitation
Techniques to identify and analyze problems
Using a problem-solving method to help a team identify and analyze a problem can be a quick and effective addition to any workshop or meeting.
While further actions are always necessary, you can generate momentum and alignment easily, and these activities are a great place to get started.
We’ve put together this list of techniques to help you and your team with problem identification, analysis, and discussion that sets the foundation for developing effective solutions.
Let’s take a look!
- The Creativity Dice
- Fishbone Analysis
- Problem Tree
- SWOT Analysis
- Agreement-Certainty Matrix
- The Journalistic Six
- LEGO Challenge
- What, So What, Now What?
- Journalists
Individual and group perspectives are incredibly important, but what happens if people are set in their minds and need a change of perspective in order to approach a problem more effectively?
Flip It is a method we love because it is both simple to understand and run, and allows groups to understand how their perspectives and biases are formed.
Participants in Flip It are first invited to consider concerns, issues, or problems from a perspective of fear and write them on a flip chart. Then, the group is asked to consider those same issues from a perspective of hope and flip their understanding.
No problem and solution is free from existing bias and by changing perspectives with Flip It, you can then develop a problem solving model quickly and effectively.
Flip It! #gamestorming #problem solving #action Often, a change in a problem or situation comes simply from a change in our perspectives. Flip It! is a quick game designed to show players that perspectives are made, not born.

10. The Creativity Dice
One of the most useful problem solving skills you can teach your team is of approaching challenges with creativity, flexibility, and openness. Games like The Creativity Dice allow teams to overcome the potential hurdle of too much linear thinking and approach the process with a sense of fun and speed.
In The Creativity Dice, participants are organized around a topic and roll a dice to determine what they will work on for a period of 3 minutes at a time. They might roll a 3 and work on investigating factual information on the chosen topic. They might roll a 1 and work on identifying the specific goals, standards, or criteria for the session.
Encouraging rapid work and iteration while asking participants to be flexible are great skills to cultivate. Having a stage for idea incubation in this game is also important. Moments of pause can help ensure the ideas that are put forward are the most suitable.
The Creativity Dice #creativity #problem solving #thiagi #issue analysis Too much linear thinking is hazardous to creative problem solving. To be creative, you should approach the problem (or the opportunity) from different points of view. You should leave a thought hanging in mid-air and move to another. This skipping around prevents premature closure and lets your brain incubate one line of thought while you consciously pursue another.
11. Fishbone Analysis
Organizational or team challenges are rarely simple, and it’s important to remember that one problem can be an indication of something that goes deeper and may require further consideration to be solved.
Fishbone Analysis helps groups to dig deeper and understand the origins of a problem. It’s a great example of a root cause analysis method that is simple for everyone on a team to get their head around.
Participants in this activity are asked to annotate a diagram of a fish, first adding the problem or issue to be worked on at the head of a fish before then brainstorming the root causes of the problem and adding them as bones on the fish.
Using abstractions such as a diagram of a fish can really help a team break out of their regular thinking and develop a creative approach.
Fishbone Analysis #problem solving ##root cause analysis #decision making #online facilitation A process to help identify and understand the origins of problems, issues or observations.
12. Problem Tree
Encouraging visual thinking can be an essential part of many strategies. By simply reframing and clarifying problems, a group can move towards developing a problem solving model that works for them.
In Problem Tree, groups are asked to first brainstorm a list of problems – these can be design problems, team problems or larger business problems – and then organize them into a hierarchy. The hierarchy could be from most important to least important or abstract to practical, though the key thing with problem solving games that involve this aspect is that your group has some way of managing and sorting all the issues that are raised.
Once you have a list of problems that need to be solved and have organized them accordingly, you’re then well-positioned for the next problem solving steps.
Problem tree #define intentions #create #design #issue analysis A problem tree is a tool to clarify the hierarchy of problems addressed by the team within a design project; it represents high level problems or related sublevel problems.
13. SWOT Analysis
Chances are you’ve heard of the SWOT Analysis before. This problem-solving method focuses on identifying strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats is a tried and tested method for both individuals and teams.
Start by creating a desired end state or outcome and bare this in mind – any process solving model is made more effective by knowing what you are moving towards. Create a quadrant made up of the four categories of a SWOT analysis and ask participants to generate ideas based on each of those quadrants.
Once you have those ideas assembled in their quadrants, cluster them together based on their affinity with other ideas. These clusters are then used to facilitate group conversations and move things forward.
SWOT analysis #gamestorming #problem solving #action #meeting facilitation The SWOT Analysis is a long-standing technique of looking at what we have, with respect to the desired end state, as well as what we could improve on. It gives us an opportunity to gauge approaching opportunities and dangers, and assess the seriousness of the conditions that affect our future. When we understand those conditions, we can influence what comes next.
14. Agreement-Certainty Matrix
Not every problem-solving approach is right for every challenge, and deciding on the right method for the challenge at hand is a key part of being an effective team.
The Agreement Certainty matrix helps teams align on the nature of the challenges facing them. By sorting problems from simple to chaotic, your team can understand what methods are suitable for each problem and what they can do to ensure effective results.
If you are already using Liberating Structures techniques as part of your problem-solving strategy, the Agreement-Certainty Matrix can be an invaluable addition to your process. We’ve found it particularly if you are having issues with recurring problems in your organization and want to go deeper in understanding the root cause.
Agreement-Certainty Matrix #issue analysis #liberating structures #problem solving You can help individuals or groups avoid the frequent mistake of trying to solve a problem with methods that are not adapted to the nature of their challenge. The combination of two questions makes it possible to easily sort challenges into four categories: simple, complicated, complex , and chaotic . A problem is simple when it can be solved reliably with practices that are easy to duplicate. It is complicated when experts are required to devise a sophisticated solution that will yield the desired results predictably. A problem is complex when there are several valid ways to proceed but outcomes are not predictable in detail. Chaotic is when the context is too turbulent to identify a path forward. A loose analogy may be used to describe these differences: simple is like following a recipe, complicated like sending a rocket to the moon, complex like raising a child, and chaotic is like the game “Pin the Tail on the Donkey.” The Liberating Structures Matching Matrix in Chapter 5 can be used as the first step to clarify the nature of a challenge and avoid the mismatches between problems and solutions that are frequently at the root of chronic, recurring problems.
Organizing and charting a team’s progress can be important in ensuring its success. SQUID (Sequential Question and Insight Diagram) is a great model that allows a team to effectively switch between giving questions and answers and develop the skills they need to stay on track throughout the process.
Begin with two different colored sticky notes – one for questions and one for answers – and with your central topic (the head of the squid) on the board. Ask the group to first come up with a series of questions connected to their best guess of how to approach the topic. Ask the group to come up with answers to those questions, fix them to the board and connect them with a line. After some discussion, go back to question mode by responding to the generated answers or other points on the board.
It’s rewarding to see a diagram grow throughout the exercise, and a completed SQUID can provide a visual resource for future effort and as an example for other teams.
SQUID #gamestorming #project planning #issue analysis #problem solving When exploring an information space, it’s important for a group to know where they are at any given time. By using SQUID, a group charts out the territory as they go and can navigate accordingly. SQUID stands for Sequential Question and Insight Diagram.
16. Speed Boat
To continue with our nautical theme, Speed Boat is a short and sweet activity that can help a team quickly identify what employees, clients or service users might have a problem with and analyze what might be standing in the way of achieving a solution.
Methods that allow for a group to make observations, have insights and obtain those eureka moments quickly are invaluable when trying to solve complex problems.
In Speed Boat, the approach is to first consider what anchors and challenges might be holding an organization (or boat) back. Bonus points if you are able to identify any sharks in the water and develop ideas that can also deal with competitors!
Speed Boat #gamestorming #problem solving #action Speedboat is a short and sweet way to identify what your employees or clients don’t like about your product/service or what’s standing in the way of a desired goal.
17. The Journalistic Six
Some of the most effective ways of solving problems is by encouraging teams to be more inclusive and diverse in their thinking.
Based on the six key questions journalism students are taught to answer in articles and news stories, The Journalistic Six helps create teams to see the whole picture. By using who, what, when, where, why, and how to facilitate the conversation and encourage creative thinking, your team can make sure that the problem identification and problem analysis stages of the are covered exhaustively and thoughtfully. Reporter’s notebook and dictaphone optional.
The Journalistic Six – Who What When Where Why How #idea generation #issue analysis #problem solving #online #creative thinking #remote-friendly A questioning method for generating, explaining, investigating ideas.
18. LEGO Challenge
Now for an activity that is a little out of the (toy) box. LEGO Serious Play is a facilitation methodology that can be used to improve creative thinking and problem-solving skills.
The LEGO Challenge includes giving each member of the team an assignment that is hidden from the rest of the group while they create a structure without speaking.
What the LEGO challenge brings to the table is a fun working example of working with stakeholders who might not be on the same page to solve problems. Also, it’s LEGO! Who doesn’t love LEGO!
LEGO Challenge #hyperisland #team A team-building activity in which groups must work together to build a structure out of LEGO, but each individual has a secret “assignment” which makes the collaborative process more challenging. It emphasizes group communication, leadership dynamics, conflict, cooperation, patience and problem solving strategy.
19. What, So What, Now What?
If not carefully managed, the problem identification and problem analysis stages of the problem-solving process can actually create more problems and misunderstandings.
The What, So What, Now What? problem-solving activity is designed to help collect insights and move forward while also eliminating the possibility of disagreement when it comes to identifying, clarifying, and analyzing organizational or work problems.
Facilitation is all about bringing groups together so that might work on a shared goal and the best problem-solving strategies ensure that teams are aligned in purpose, if not initially in opinion or insight.
Throughout the three steps of this game, you give everyone on a team to reflect on a problem by asking what happened, why it is important, and what actions should then be taken.
This can be a great activity for bringing our individual perceptions about a problem or challenge and contextualizing it in a larger group setting. This is one of the most important problem-solving skills you can bring to your organization.
W³ – What, So What, Now What? #issue analysis #innovation #liberating structures You can help groups reflect on a shared experience in a way that builds understanding and spurs coordinated action while avoiding unproductive conflict. It is possible for every voice to be heard while simultaneously sifting for insights and shaping new direction. Progressing in stages makes this practical—from collecting facts about What Happened to making sense of these facts with So What and finally to what actions logically follow with Now What . The shared progression eliminates most of the misunderstandings that otherwise fuel disagreements about what to do. Voila!
20. Journalists
Problem analysis can be one of the most important and decisive stages of all problem-solving tools. Sometimes, a team can become bogged down in the details and are unable to move forward.
Journalists is an activity that can avoid a group from getting stuck in the problem identification or problem analysis stages of the process.
In Journalists, the group is invited to draft the front page of a fictional newspaper and figure out what stories deserve to be on the cover and what headlines those stories will have. By reframing how your problems and challenges are approached, you can help a team move productively through the process and be better prepared for the steps to follow.
Journalists #vision #big picture #issue analysis #remote-friendly This is an exercise to use when the group gets stuck in details and struggles to see the big picture. Also good for defining a vision.
Problem-solving techniques for developing solutions
The success of any problem-solving process can be measured by the solutions it produces. After you’ve defined the issue, explored existing ideas, and ideated, it’s time to narrow down to the correct solution.
Use these problem-solving techniques when you want to help your team find consensus, compare possible solutions, and move towards taking action on a particular problem.
- Improved Solutions
- Four-Step Sketch
- 15% Solutions
- How-Now-Wow matrix
- Impact Effort Matrix
21. Mindspin
Brainstorming is part of the bread and butter of the problem-solving process and all problem-solving strategies benefit from getting ideas out and challenging a team to generate solutions quickly.
With Mindspin, participants are encouraged not only to generate ideas but to do so under time constraints and by slamming down cards and passing them on. By doing multiple rounds, your team can begin with a free generation of possible solutions before moving on to developing those solutions and encouraging further ideation.
This is one of our favorite problem-solving activities and can be great for keeping the energy up throughout the workshop. Remember the importance of helping people become engaged in the process – energizing problem-solving techniques like Mindspin can help ensure your team stays engaged and happy, even when the problems they’re coming together to solve are complex.
MindSpin #teampedia #idea generation #problem solving #action A fast and loud method to enhance brainstorming within a team. Since this activity has more than round ideas that are repetitive can be ruled out leaving more creative and innovative answers to the challenge.
22. Improved Solutions
After a team has successfully identified a problem and come up with a few solutions, it can be tempting to call the work of the problem-solving process complete. That said, the first solution is not necessarily the best, and by including a further review and reflection activity into your problem-solving model, you can ensure your group reaches the best possible result.
One of a number of problem-solving games from Thiagi Group, Improved Solutions helps you go the extra mile and develop suggested solutions with close consideration and peer review. By supporting the discussion of several problems at once and by shifting team roles throughout, this problem-solving technique is a dynamic way of finding the best solution.
Improved Solutions #creativity #thiagi #problem solving #action #team You can improve any solution by objectively reviewing its strengths and weaknesses and making suitable adjustments. In this creativity framegame, you improve the solutions to several problems. To maintain objective detachment, you deal with a different problem during each of six rounds and assume different roles (problem owner, consultant, basher, booster, enhancer, and evaluator) during each round. At the conclusion of the activity, each player ends up with two solutions to her problem.
23. Four Step Sketch
Creative thinking and visual ideation does not need to be confined to the opening stages of your problem-solving strategies. Exercises that include sketching and prototyping on paper can be effective at the solution finding and development stage of the process, and can be great for keeping a team engaged.
By going from simple notes to a crazy 8s round that involves rapidly sketching 8 variations on their ideas before then producing a final solution sketch, the group is able to iterate quickly and visually. Problem-solving techniques like Four-Step Sketch are great if you have a group of different thinkers and want to change things up from a more textual or discussion-based approach.
Four-Step Sketch #design sprint #innovation #idea generation #remote-friendly The four-step sketch is an exercise that helps people to create well-formed concepts through a structured process that includes: Review key information Start design work on paper, Consider multiple variations , Create a detailed solution . This exercise is preceded by a set of other activities allowing the group to clarify the challenge they want to solve. See how the Four Step Sketch exercise fits into a Design Sprint
24. 15% Solutions
Some problems are simpler than others and with the right problem-solving activities, you can empower people to take immediate actions that can help create organizational change.
Part of the liberating structures toolkit, 15% solutions is a problem-solving technique that focuses on finding and implementing solutions quickly. A process of iterating and making small changes quickly can help generate momentum and an appetite for solving complex problems.
Problem-solving strategies can live and die on whether people are onboard. Getting some quick wins is a great way of getting people behind the process.
It can be extremely empowering for a team to realize that problem-solving techniques can be deployed quickly and easily and delineate between things they can positively impact and those things they cannot change.
15% Solutions #action #liberating structures #remote-friendly You can reveal the actions, however small, that everyone can do immediately. At a minimum, these will create momentum, and that may make a BIG difference. 15% Solutions show that there is no reason to wait around, feel powerless, or fearful. They help people pick it up a level. They get individuals and the group to focus on what is within their discretion instead of what they cannot change. With a very simple question, you can flip the conversation to what can be done and find solutions to big problems that are often distributed widely in places not known in advance. Shifting a few grains of sand may trigger a landslide and change the whole landscape.
25. How-Now-Wow Matrix
The problem-solving process is often creative, as complex problems usually require a change of thinking and creative response in order to find the best solutions. While it’s common for the first stages to encourage creative thinking, groups can often gravitate to familiar solutions when it comes to the end of the process.
When selecting solutions, you don’t want to lose your creative energy! The How-Now-Wow Matrix from Gamestorming is a great problem-solving activity that enables a group to stay creative and think out of the box when it comes to selecting the right solution for a given problem.
Problem-solving techniques that encourage creative thinking and the ideation and selection of new solutions can be the most effective in organisational change. Give the How-Now-Wow Matrix a go, and not just for how pleasant it is to say out loud.
How-Now-Wow Matrix #gamestorming #idea generation #remote-friendly When people want to develop new ideas, they most often think out of the box in the brainstorming or divergent phase. However, when it comes to convergence, people often end up picking ideas that are most familiar to them. This is called a ‘creative paradox’ or a ‘creadox’. The How-Now-Wow matrix is an idea selection tool that breaks the creadox by forcing people to weigh each idea on 2 parameters.
26. Impact and Effort Matrix
All problem-solving techniques hope to not only find solutions to a given problem or challenge but to find the best solution. When it comes to finding a solution, groups are invited to put on their decision-making hats and really think about how a proposed idea would work in practice.
The Impact and Effort Matrix is one of the problem-solving techniques that fall into this camp, empowering participants to first generate ideas and then categorize them into a 2×2 matrix based on impact and effort.
Activities that invite critical thinking while remaining simple are invaluable. Use the Impact and Effort Matrix to move from ideation and towards evaluating potential solutions before then committing to them.
Impact and Effort Matrix #gamestorming #decision making #action #remote-friendly In this decision-making exercise, possible actions are mapped based on two factors: effort required to implement and potential impact. Categorizing ideas along these lines is a useful technique in decision making, as it obliges contributors to balance and evaluate suggested actions before committing to them.
27. Dotmocracy
If you’ve followed each of the problem-solving steps with your group successfully, you should move towards the end of your process with heaps of possible solutions developed with a specific problem in mind. But how do you help a group go from ideation to putting a solution into action?
Dotmocracy – or Dot Voting -is a tried and tested method of helping a team in the problem-solving process make decisions and put actions in place with a degree of oversight and consensus.
One of the problem-solving techniques that should be in every facilitator’s toolbox, Dot Voting is fast and effective and can help identify the most popular and best solutions and help bring a group to a decision effectively.
Dotmocracy #action #decision making #group prioritization #hyperisland #remote-friendly Dotmocracy is a simple method for group prioritization or decision-making. It is not an activity on its own, but a method to use in processes where prioritization or decision-making is the aim. The method supports a group to quickly see which options are most popular or relevant. The options or ideas are written on post-its and stuck up on a wall for the whole group to see. Each person votes for the options they think are the strongest, and that information is used to inform a decision.
All facilitators know that warm-ups and icebreakers are useful for any workshop or group process. Problem-solving workshops are no different.
Use these problem-solving techniques to warm up a group and prepare them for the rest of the process. Activating your group by tapping into some of the top problem-solving skills can be one of the best ways to see great outcomes from your session.
- Check-in/Check-out
- Doodling Together
- Show and Tell
- Constellations
- Draw a Tree
28. Check-in / Check-out
Solid processes are planned from beginning to end, and the best facilitators know that setting the tone and establishing a safe, open environment can be integral to a successful problem-solving process.
Check-in / Check-out is a great way to begin and/or bookend a problem-solving workshop. Checking in to a session emphasizes that everyone will be seen, heard, and expected to contribute.
If you are running a series of meetings, setting a consistent pattern of checking in and checking out can really help your team get into a groove. We recommend this opening-closing activity for small to medium-sized groups though it can work with large groups if they’re disciplined!
Check-in / Check-out #team #opening #closing #hyperisland #remote-friendly Either checking-in or checking-out is a simple way for a team to open or close a process, symbolically and in a collaborative way. Checking-in/out invites each member in a group to be present, seen and heard, and to express a reflection or a feeling. Checking-in emphasizes presence, focus and group commitment; checking-out emphasizes reflection and symbolic closure.
29. Doodling Together
Thinking creatively and not being afraid to make suggestions are important problem-solving skills for any group or team, and warming up by encouraging these behaviors is a great way to start.
Doodling Together is one of our favorite creative ice breaker games – it’s quick, effective, and fun and can make all following problem-solving steps easier by encouraging a group to collaborate visually. By passing cards and adding additional items as they go, the workshop group gets into a groove of co-creation and idea development that is crucial to finding solutions to problems.
Doodling Together #collaboration #creativity #teamwork #fun #team #visual methods #energiser #icebreaker #remote-friendly Create wild, weird and often funny postcards together & establish a group’s creative confidence.
30. Show and Tell
You might remember some version of Show and Tell from being a kid in school and it’s a great problem-solving activity to kick off a session.
Asking participants to prepare a little something before a workshop by bringing an object for show and tell can help them warm up before the session has even begun! Games that include a physical object can also help encourage early engagement before moving onto more big-picture thinking.
By asking your participants to tell stories about why they chose to bring a particular item to the group, you can help teams see things from new perspectives and see both differences and similarities in the way they approach a topic. Great groundwork for approaching a problem-solving process as a team!
Show and Tell #gamestorming #action #opening #meeting facilitation Show and Tell taps into the power of metaphors to reveal players’ underlying assumptions and associations around a topic The aim of the game is to get a deeper understanding of stakeholders’ perspectives on anything—a new project, an organizational restructuring, a shift in the company’s vision or team dynamic.
31. Constellations
Who doesn’t love stars? Constellations is a great warm-up activity for any workshop as it gets people up off their feet, energized, and ready to engage in new ways with established topics. It’s also great for showing existing beliefs, biases, and patterns that can come into play as part of your session.
Using warm-up games that help build trust and connection while also allowing for non-verbal responses can be great for easing people into the problem-solving process and encouraging engagement from everyone in the group. Constellations is great in large spaces that allow for movement and is definitely a practical exercise to allow the group to see patterns that are otherwise invisible.
Constellations #trust #connection #opening #coaching #patterns #system Individuals express their response to a statement or idea by standing closer or further from a central object. Used with teams to reveal system, hidden patterns, perspectives.
32. Draw a Tree
Problem-solving games that help raise group awareness through a central, unifying metaphor can be effective ways to warm-up a group in any problem-solving model.
Draw a Tree is a simple warm-up activity you can use in any group and which can provide a quick jolt of energy. Start by asking your participants to draw a tree in just 45 seconds – they can choose whether it will be abstract or realistic.
Once the timer is up, ask the group how many people included the roots of the tree and use this as a means to discuss how we can ignore important parts of any system simply because they are not visible.
All problem-solving strategies are made more effective by thinking of problems critically and by exposing things that may not normally come to light. Warm-up games like Draw a Tree are great in that they quickly demonstrate some key problem-solving skills in an accessible and effective way.
Draw a Tree #thiagi #opening #perspectives #remote-friendly With this game you can raise awarness about being more mindful, and aware of the environment we live in.
Each step of the problem-solving workshop benefits from an intelligent deployment of activities, games, and techniques. Bringing your session to an effective close helps ensure that solutions are followed through on and that you also celebrate what has been achieved.
Here are some problem-solving activities you can use to effectively close a workshop or meeting and ensure the great work you’ve done can continue afterward.
- One Breath Feedback
- Who What When Matrix
- Response Cards
How do I conclude a problem-solving process?
All good things must come to an end. With the bulk of the work done, it can be tempting to conclude your workshop swiftly and without a moment to debrief and align. This can be problematic in that it doesn’t allow your team to fully process the results or reflect on the process.
At the end of an effective session, your team will have gone through a process that, while productive, can be exhausting. It’s important to give your group a moment to take a breath, ensure that they are clear on future actions, and provide short feedback before leaving the space.
The primary purpose of any problem-solving method is to generate solutions and then implement them. Be sure to take the opportunity to ensure everyone is aligned and ready to effectively implement the solutions you produced in the workshop.
Remember that every process can be improved and by giving a short moment to collect feedback in the session, you can further refine your problem-solving methods and see further success in the future too.
33. One Breath Feedback
Maintaining attention and focus during the closing stages of a problem-solving workshop can be tricky and so being concise when giving feedback can be important. It’s easy to incur “death by feedback” should some team members go on for too long sharing their perspectives in a quick feedback round.
One Breath Feedback is a great closing activity for workshops. You give everyone an opportunity to provide feedback on what they’ve done but only in the space of a single breath. This keeps feedback short and to the point and means that everyone is encouraged to provide the most important piece of feedback to them.
One breath feedback #closing #feedback #action This is a feedback round in just one breath that excels in maintaining attention: each participants is able to speak during just one breath … for most people that’s around 20 to 25 seconds … unless of course you’ve been a deep sea diver in which case you’ll be able to do it for longer.
34. Who What When Matrix
Matrices feature as part of many effective problem-solving strategies and with good reason. They are easily recognizable, simple to use, and generate results.
The Who What When Matrix is a great tool to use when closing your problem-solving session by attributing a who, what and when to the actions and solutions you have decided upon. The resulting matrix is a simple, easy-to-follow way of ensuring your team can move forward.
Great solutions can’t be enacted without action and ownership. Your problem-solving process should include a stage for allocating tasks to individuals or teams and creating a realistic timeframe for those solutions to be implemented or checked out. Use this method to keep the solution implementation process clear and simple for all involved.
Who/What/When Matrix #gamestorming #action #project planning With Who/What/When matrix, you can connect people with clear actions they have defined and have committed to.
35. Response cards
Group discussion can comprise the bulk of most problem-solving activities and by the end of the process, you might find that your team is talked out!
Providing a means for your team to give feedback with short written notes can ensure everyone is head and can contribute without the need to stand up and talk. Depending on the needs of the group, giving an alternative can help ensure everyone can contribute to your problem-solving model in the way that makes the most sense for them.
Response Cards is a great way to close a workshop if you are looking for a gentle warm-down and want to get some swift discussion around some of the feedback that is raised.
Response Cards #debriefing #closing #structured sharing #questions and answers #thiagi #action It can be hard to involve everyone during a closing of a session. Some might stay in the background or get unheard because of louder participants. However, with the use of Response Cards, everyone will be involved in providing feedback or clarify questions at the end of a session.
Save time and effort discovering the right solutions
A structured problem solving process is a surefire way of solving tough problems, discovering creative solutions and driving organizational change. But how can you design for successful outcomes?
With SessionLab, it’s easy to design engaging workshops that deliver results. Drag, drop and reorder blocks to build your agenda. When you make changes or update your agenda, your session timing adjusts automatically , saving you time on manual adjustments.
Collaborating with stakeholders or clients? Share your agenda with a single click and collaborate in real-time. No more sending documents back and forth over email.
Explore how to use SessionLab to design effective problem solving workshops or watch this five minute video to see the planner in action!

Over to you
The problem-solving process can often be as complicated and multifaceted as the problems they are set-up to solve. With the right problem-solving techniques and a mix of creative exercises designed to guide discussion and generate purposeful ideas, we hope we’ve given you the tools to find the best solutions as simply and easily as possible.
Is there a problem-solving technique that you are missing here? Do you have a favorite activity or method you use when facilitating? Let us know in the comments below, we’d love to hear from you!
thank you very much for these excellent techniques
Certainly wonderful article, very detailed. Shared!
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

Going from a mere idea to a workshop that delivers results for your clients can feel like a daunting task. In this piece, we will shine a light on all the work behind the scenes and help you learn how to plan a workshop from start to finish. On a good day, facilitation can feel like effortless magic, but that is mostly the result of backstage work, foresight, and a lot of careful planning. Read on to learn a step-by-step approach to breaking the process of planning a workshop into small, manageable chunks. The flow starts with the first meeting with a client to define the purposes of a workshop.…

How does learning work? A clever 9-year-old once told me: “I know I am learning something new when I am surprised.” The science of adult learning tells us that, in order to learn new skills (which, unsurprisingly, is harder for adults to do than kids) grown-ups need to first get into a specific headspace. In a business, this approach is often employed in a training session where employees learn new skills or work on professional development. But how do you ensure your training is effective? In this guide, we'll explore how to create an effective training session plan and run engaging training sessions. As team leader, project manager, or consultant,…

Effective online tools are a necessity for smooth and engaging virtual workshops and meetings. But how do you choose the right ones? Do you sometimes feel that the good old pen and paper or MS Office toolkit and email leaves you struggling to stay on top of managing and delivering your workshop? Fortunately, there are plenty of online tools to make your life easier when you need to facilitate a meeting and lead workshops. In this post, we’ll share our favorite online tools you can use to make your job as a facilitator easier. In fact, there are plenty of free online workshop tools and meeting facilitation software you can…
Design your next workshop with SessionLab
Join the 150,000 facilitators using SessionLab
Sign up for free
BUS602: Marketing Management
The Consumer's Decision Making Process
Read these sections on the consumer purchase decision process. Consider the degree of involvement in a purchase, and how this would apply to some, but not all purchasing decisions.
Low-Involvement Versus High-Involvement Buying Decisions and the Consumer's Decision-Making Process
Learning objectives.
- Distinguish between low-involvement and high-involvement buying decisions.
- Understand what the stages of the buying process are and what happens in each stage.
As you have seen, many factors influence a consumer's behavior. Depending on a consumer's experience and knowledge, some consumers may be able to make quick purchase decisions and other consumers may need to get information and be more involved in the decision process before making a purchase. The level of involvement reflects how personally important or interested you are in consuming a product and how much information you need to make a decision. The level of involvement in buying decisions may be considered a continuum from decisions that are fairly routine (consumers are not very involved) to decisions that require extensive thought and a high level of involvement. Whether a decision is low, high, or limited, involvement varies by consumer, not by product, although some products such as purchasing a house typically require a high-involvement for all consumers. Consumers with no experience purchasing a product may have more involvement than someone who is replacing a product. You have probably thought about many products you want or need but never did much more than that. At other times, you've probably looked at dozens of products, compared them, and then decided not to purchase any one of them. When you run out of products such as milk or bread that you buy on a regular basis, you may buy the product as soon as you recognize the need because you do not need to search for information or evaluate alternatives. As Nike would put it, you "just do it". Low-involvement decisions are, however, typically products that are relatively inexpensive and pose a low risk to the buyer if she makes a mistake by purchasing them. Consumers often engage in routine response behavior when they make low-involvement decisions - that is, they make automatic purchase decisions based on limited information or information they have gathered in the past. For example, if you always order a Diet Coke at lunch, you're engaging in routine response behavior. You may not even think about other drink options at lunch because your routine is to order a Diet Coke, and you simply do it. Similarly, if you run out of Diet Coke at home, you may buy more without any information search. Some low-involvement purchases are made with no planning or previous thought. These buying decisions are called impulse buying . While you're waiting to check out at the grocery store, perhaps you see a magazine with Angelina Jolie and Brad Pitt on the cover and buy it on the spot simply because you want it. You might see a roll of tape at a check-out stand and remember you need one or you might see a bag of chips and realize you're hungry or just want them. These are items that are typically low-involvement decisions. Low-involvement decisions aren't necessarily products purchased on impulse, although they can be. By contrast, high-involvement decisions carry a higher risk to buyers if they fail, are complex, and/or have high price tags. A car, a house, and an insurance policy are examples. These items are not purchased often but are relevant and important to the buyer. Buyers don't engage in routine response behavior when purchasing high-involvement products. Instead, consumers engage in what's called extended problem solving , where they spend a lot of time comparing different aspects such as the features of the products, prices, and warranties. High-involvement decisions can cause buyers a great deal of postpurchase dissonance (anxiety) if they are unsure about their purchases or if they had a difficult time deciding between two alternatives. Companies that sell high-involvement products are aware that postpurchase dissonance can be a problem. Frequently, they try to offer consumers a lot of information about their products, including why they are superior to competing brands and how they won't let the consumer down. Salespeople may be utilized to answer questions and do a lot of customer "hand-holding". Figure 3.8

Allstate's "You're in Good Hands" advertisements are designed to convince consumers that the insurance company won't let them down. Limited problem solving falls somewhere between low-involvement (routine) and high-involvement (extended problem solving) decisions. Consumers engage in limited problem solving when they already have some information about a good or service but continue to search for a little more information. Assume you need a new backpack for a hiking trip. While you are familiar with backpacks, you know that new features and materials are available since you purchased your last backpack. You're going to spend some time looking for one that's decent because you don't want it to fall apart while you're traveling and dump everything you've packed on a hiking trail. You might do a little research online and come to a decision relatively quickly. You might consider the choices available at your favorite retail outlet but not look at every backpack at every outlet before making a decision. Or you might rely on the advice of a person you know who's knowledgeable about backpacks. In some way you shorten or limit your involvement and the decision-making process. Products, such as chewing gum, which may be low-involvement for many consumers often use advertising such as commercials and sales promotions such as coupons to reach many consumers at once. Companies also try to sell products such as gum in as many locations as possible. Many products that are typically high-involvement such as automobiles may use more personal selling to answer consumers' questions. Brand names can also be very important regardless of the consumer's level of purchasing involvement. Consider a low- versus high-involvement decision - say, purchasing a tube of toothpaste versus a new car. You might routinely buy your favorite brand of toothpaste, not thinking much about the purchase (engage in routine response behavior), but not be willing to switch to another brand either. Having a brand you like saves you "search time" and eliminates the evaluation period because you know what you're getting. When it comes to the car, you might engage in extensive problem solving but, again, only be willing to consider a certain brand or brands. For example, in the 1970s, American-made cars had such a poor reputation for quality that buyers joked that a car that's "not Jap [Japanese made] is crap". The quality of American cars is very good today, but you get the picture. If it's a high-involvement product you're purchasing, a good brand name is probably going to be very important to you. That's why the manufacturers of products that are typically high-involvement decisions can't become complacent about the value of their brands.
1970s American Cars
Today, Lexus is the automotive brand that experiences the most customer loyalty. For a humorous, tongue-in-cheek look at why the brand reputation of American carmakers suffered in the 1970s, check out this clip.
Stages in the Buying Process
Figure 3.9 "Stages in the Consumer's Purchasing Process" outlines the buying stages consumers go through. At any given time, you're probably in a buying stage for a product or service. You're thinking about the different types of things you want or need to eventually buy, how you are going to find the best ones at the best price, and where and how you will buy them. Meanwhile, there are other products you have already purchased that you're evaluating. Some might be better than others. Will you discard them, and if so, how? Then what will you buy? Where does that process start? Figure 3.9 Stages in the Consumer's Purchasing Process

Stage 1. Need Recognition
You plan to backpack around the country after you graduate and don't have a particularly good backpack. You realize that you must get a new backpack. You may also be thinking about the job you've accepted after graduation and know that you must get a vehicle to commute. Recognizing a need may involve something as simple as running out of bread or milk or realizing that you must get a new backpack or a car after you graduate. Marketers try to show consumers how their products and services add value and help satisfy needs and wants. Do you think it's a coincidence that Gatorade, Powerade, and other beverage makers locate their machines in gymnasiums so you see them after a long, tiring workout? Previews at movie theaters are another example. How many times have you heard about a movie and had no interest in it - until you saw the preview? Afterward, you felt like you had to see it.
Stage 2. Search for Information
For products such as milk and bread, you may simply recognize the need, go to the store, and buy more. However, if you are purchasing a car for the first time or need a particular type of backpack, you may need to get information on different alternatives. Maybe you have owned several backpacks and know what you like and don't like about them. Or there might be a particular brand that you've purchased in the past that you liked and want to purchase in the future. This is a great position for the company that owns the brand to be in - something firms strive for. Why? Because it often means you will limit your search and simply buy their brand again. If what you already know about backpacks doesn't provide you with enough information, you'll probably continue to gather information from various sources. Frequently people ask friends, family, and neighbors about their experiences with products. Magazines such as Consumer Reports (considered an objective source of information on many consumer products) or Backpacker Magazine might also help you. Similar information sources are available for learning about different makes and models of cars. Internet shopping sites such as Amazon.com have become a common source of information about products. Epinions.com is an example of a consumer-generated review site. The site offers product ratings, buying tips, and price information. Amazon.com also offers product reviews written by consumers. People prefer "independent" sources such as this when they are looking for product information. However, they also often consult non-neutral sources of information, such advertisements, brochures, company websites, and salespeople.
Stage 3. Product Evaluation
Obviously, there are hundreds of different backpacks and cars available. It's not possible for you to examine all of them. In fact, good salespeople and marketing professionals know that providing you with too many choices can be so overwhelming that you might not buy anything at all. Consequently, you may use choice heuristics or rules of thumb that provide mental shortcuts in the decision-making process. You may also develop evaluative criteria to help you narrow down your choices. Backpacks or cars that meet your initial criteria before the consideration will determine the set of brands you'll consider for purchase. Evaluative criteria are certain characteristics that are important to you such as the price of the backpack, the size, the number of compartments, and color. Some of these characteristics are more important than others. For example, the size of the backpack and the price might be more important to you than the color - unless, say, the color is hot pink and you hate pink. You must decide what criteria are most important and how well different alternatives meet the criteria. Figure 3.10

Osprey backpacks are known for their durability. The company has a special design and quality control center, and Osprey's salespeople annually take a "canyon testing" trip to see how well the company's products perform. Companies want to convince you that the evaluative criteria you are considering reflect the strengths of their products. For example, you might not have thought about the weight or durability of the backpack you want to buy. However, a backpack manufacturer such as Osprey might remind you through magazine ads, packaging information, and its Web site that you should pay attention to these features - features that happen to be key selling points of its backpacks. Automobile manufacturers may have similar models, so don't be afraid to add criteria to help you evaluate cars in your consideration set.
Stage 4. Product Choice and Purchase
With low-involvement purchases, consumers may go from recognizing a need to purchasing the product. However, for backpacks and cars, you decide which one to purchase after you have evaluated different alternatives. In addition to which backpack or which car, you are probably also making other decisions at this stage, including where and how to purchase the backpack (or car) and on what terms. Maybe the backpack was cheaper at one store than another, but the salesperson there was rude. Or maybe you decide to order online because you're too busy to go to the mall. Other decisions related to the purchase, particularly those related to big-ticket items, are made at this point. For example, if you're buying a high-definition television, you might look for a store that will offer you credit or a warranty.
Stage 5. Postpurchase Use and Evaluation
At this point in the process you decide whether the backpack you purchased is everything it was cracked up to be. Hopefully it is. If it's not, you're likely to suffer what's called postpurchase dissonance . You might call it buyer's remorse. Typically, dissonance occurs when a product or service does not meet your expectations. Consumers are more likely to experience dissonance with products that are relatively expensive and that are purchased infrequently. You want to feel good about your purchase, but you don't. You begin to wonder whether you should have waited to get a better price, purchased something else, or gathered more information first. Consumers commonly feel this way, which is a problem for sellers. If you don't feel good about what you've purchased from them, you might return the item and never purchase anything from them again. Or, worse yet, you might tell everyone you know how bad the product was. Companies do various things to try to prevent buyer's remorse. For smaller items, they might offer a money back guarantee or they might encourage their salespeople to tell you what a great purchase you made. How many times have you heard a salesperson say, "That outfit looks so great on you!" For larger items, companies might offer a warranty, along with instruction booklets, and a toll-free troubleshooting line to call or they might have a salesperson call you to see if you need help with product. Automobile companies may offer loaner cars when you bring your car in for service. Companies may also try to set expectations in order to satisfy customers. Service companies such as restaurants do this frequently. Think about when the hostess tells you that your table will be ready in 30 minutes. If they seat you in 15 minutes, you are much happier than if they told you that your table would be ready in 15 minutes, but it took 30 minutes to seat you. Similarly, if a store tells you that your pants will be altered in a week and they are ready in three days, you'll be much more satisfied than if they said your pants would be ready in three days, yet it took a week before they were ready.
Stage 6. Disposal of the Product
There was a time when neither manufacturers nor consumers thought much about how products got disposed of, so long as people bought them. But that's changed. How products are being disposed of is becoming extremely important to consumers and society in general. Computers and batteries, which leech chemicals into landfills, are a huge problem. Consumers don't want to degrade the environment if they don't have to, and companies are becoming more aware of this fact. Take for example Crystal Light, a water-based beverage that's sold in grocery stores. You can buy it in a bottle. However, many people buy a concentrated form of it, put it in reusable pitchers or bottles, and add water. That way, they don't have to buy and dispose of plastic bottle after plastic bottle, damaging the environment in the process. Windex has done something similar with its window cleaner. Instead of buying new bottles of it all the time, you can purchase a concentrate and add water. You have probably noticed that most grocery stores now sell cloth bags consumers can reuse instead of continually using and discarding of new plastic or paper bags. Figure 3.11

The hike up to Mount Everest used to be pristine. Now it looks more like this. Who's responsible? Are consumers or companies responsible, or both? Other companies are less concerned about conservation than they are about planned obsolescence. Planned obsolescence is a deliberate effort by companies to make their products obsolete, or unusable, after a period of time. The goal is to improve a company's sales by reducing the amount of time between the repeat purchases consumers make of products. When a software developer introduces a new version of product, it is usually designed to be incompatible with older versions of it. For example, not all the formatting features are the same in Microsoft Word 2007 and 2010. Sometimes documents do not translate properly when opened in the newer version. Consequently, you will be more inclined to upgrade to the new version so you can open all Word documents you receive. Products that are disposable are another way in which firms have managed to reduce the amount of time between purchases. Disposable lighters are an example. Do you know anyone today that owns a nondisposable lighter? Believe it or not, prior to the 1960s, scarcely anyone could have imagined using a cheap disposable lighter. There are many more disposable products today than there were in years past - including everything from bottled water and individually wrapped snacks to single-use eye drops and cell phones. Figure 3.12

Disposable lighters came into vogue in the United States in the 1960s. You probably don't own a cool, nondisposable lighter like one of these, but you don't have to bother refilling it with lighter fluid either.
Key Takeaways
Consumer behavior looks at the many reasons why people buy things and later dispose of them. Consumers go through distinct buying phases when they purchase products: (1) realizing the need or wanting something, (2) searching for information about the item, (3) evaluating different products, (4) choosing a product and purchasing it, (5) using and evaluating the product after the purchase, and (6) disposing of the product. A consumer's level of involvement is how interested he or she is in buying and consuming a product. Low-involvement products are usually inexpensive and pose a low risk to the buyer if he or she makes a mistake by purchasing them. High-involvement products carry a high risk to the buyer if they fail, are complex, or have high price tags. Limited-involvement products fall somewhere in between.
Review Questions
- How do low-involvement decisions differ from high-involvement decisions in terms of relevance, price, frequency, and the risks their buyers face? Name some products in each category that you've recently purchased.
- What stages do people go through in the buying process for high-involvement decisions? How do the stages vary for low-involvement decisions?
- What is postpurchase dissonance and what can companies do to reduce it?

An illustration of constrained decision-making in problem solving
- Dorin Grigoras
- 12 minutes read
- Correction policy

What is an example of limited problem solving decision making? Limited problem-solving decision making is when we make decisions based on a quick evaluation or limited information. An example of this is when we choose a snack at a convenience store based on the packaging or brand name, instead of researching the ingredients or nutrition facts.
Understanding limited problem-solving decision making is important because it can help us identify areas where we may need to take more time and gather more information before making a decision.
In this post, I'll cover some common situations where limited problem-solving decision making occurs, and offer some tips for making more informed choices.
You won't regret watching this Youtube video:
Did you learn anything new from this YouTube video?
Understanding Limited Problem-Solving Decision Making
Limited problem-solving decision making refers to the process of making decisions based on minimum effort and information. In this case, the consumer may have some experience with the product or service, but they do not have enough knowledge to make an informed decision. An example of limited problem-solving decision making is when a person decides to purchase a new brand of shampoo simply because they like the packaging or the smell.
Why did the tomato turn red? Because it saw the salad dressing!
Definition of Limited Problem-Solving Decision Making
Limited problem-solving decision making involves making decisions based on minimal effort and information. Consumers who use this type of decision-making process may have some prior experience with the product or service, but they lack complete knowledge. Therefore, they rely on heuristics or shortcuts to make decisions quickly.
When is Limited Problem-Solving Decision Making Used?
Limited problem-solving decision making is often used in situations where time and effort are limited. Consumers may use this type of decision making for low-risk purchases or when they have a moderate interest in a product or service. Some examples include purchasing snacks at a gas station or selecting a new brand of toothpaste.
Difference between Limited Problem-Solving and Extensive Problem-Solving
The primary difference between limited problem-solving and extensive problem-solving is the amount of effort and information used to make a decision. Limited problem-solving requires minimal effort and information, while extensive problem-solving requires a high level of effort and information. Consumers who use extensive problem-solving may research products, read reviews, and compare prices before making a decision. This type of decision making is often used for high-risk purchases or when a consumer has a significant interest in a product or service.
In conclusion, limited problem-solving decision making is a common type of decision making that consumers use when they have minimal time and information. While it may seem like an irrational way of making decisions, it is often used for low-risk purchases and can be an effective way of making quick decisions.
→ What steps lead to a career as a mobile developer?
Examples of Limited Problem-Solving Decision Making
Limited problem-solving decision making is a type of decision making that occurs when consumers are buying low-cost items that require a small amount of search and decision-making effort. An example of this type of decision making is when a consumer is buying toothpaste. They may ask themselves a few basic questions such as “Do I want fluoride or non-fluoride? ” or “Do I want a whitening toothpaste or not? ” Based on their answers, they will choose a toothpaste that meets their basic needs.
Another example of limited problem-solving decision making is when a consumer is buying a pack of gum. They may quickly scan the options available at the checkout counter and choose a brand they are familiar with or one that catches their eye. This type of decision making is often based on habit or impulse rather than an extensive search for information.
Why did the chewing gum cross the road? To get stuck on the other side!
Buying Groceries:
When buying groceries, limited problem-solving decision making often occurs. Consumers may make quick decisions based on factors such as price, brand loyalty, or habit. For example, a consumer may quickly choose a brand of cereal they are familiar with or opt for a cheaper store-brand option. However, some consumers may engage in extended problem-solving decision making when buying groceries, such as when they are trying a new recipe or have dietary restrictions.
Choosing a Restaurant for a Quick Lunch:
When choosing a restaurant for a quick lunch, consumers may engage in limited problem-solving decision making. Factors such as proximity, price, and menu options may play a role in the decision-making process. For example, a consumer may choose a fast-food chain they are familiar with or opt for a restaurant with a lunch special. However, if a consumer is looking for a specific type of cuisine or has dietary restrictions, they may engage in extended problem-solving decision making.
Selecting a New Brand of Shampoo:
When selecting a new brand of shampoo, consumers may engage in limited problem-solving decision making. Factors such as price, scent, and brand reputation may influence their decision. For example, a consumer may choose a brand they are familiar with or opt for a cheaper store-brand option. However, if a consumer has specific hair care needs or concerns, they may engage in extended problem-solving decision making and research different brands and products to find the best fit.
Q: What is limited problem-solving decision making? A: Limited problem-solving decision making is a type of decision making that occurs when consumers are buying low-cost items that require a small amount of search and decision-making effort.
Q: What are some examples of limited problem-solving decision making? A: Examples of limited problem-solving decision making include buying groceries, choosing a restaurant for a quick lunch, and selecting a new brand of shampoo.
Q: What factors influence limited problem-solving decision making? A: Factors such as price, brand loyalty, habit, and proximity often influence limited problem-solving decision making.
💡 When engaging in limited problem-solving decision making, it can be helpful to set basic criteria for the decision and prioritize those factors that are most important to you. This can help simplify the decision-making process and lead to a quicker decision.
→ What are the steps to build a website with HTML?
Practical Steps for Making Limited Problem-Solving Decisions
Limited problem-solving decision making requires a more straightforward process than extensive decision making. This process involves identifying the problem, gathering information, evaluating alternatives, making a decision, and evaluating the decision.
When identifying the problem, it is essential to understand the issue that needs to be solved to make the appropriate decision. This step is crucial because it sets the foundation for the rest of the decision-making process. Once the problem is identified, gathering information is vital to knowing all the information to consider when making a decision.
Evaluating alternatives involves weighing the pros and cons of each solution, considering how it aligns with the objectives of the decision, and the impact it will have on all stakeholders. Make a decision by choosing the alternative that best solves the problem and aligns with the objectives. Finally, evaluate the decision by reflecting on whether it solved the problem and met the objectives.
As John C. Maxwell said, "A leader is one who knows the way, goes the way, and shows the way". It is essential to keep in mind these practical steps when making limited problem-solving decisions.
"If you don't make mistakes, you aren't really trying." - Coleman Hawkins
Identify the problem: Identifying the problem is the foundation of the decision-making process. Without a clear understanding of the problem, it is impossible to make an informed decision. When identifying the problem, it is essential to look at it from different perspectives to get a complete understanding of the issue.
Gather information: Gathering information is the next step in making a limited problem-solving decision. The information collected needs to be relevant, accurate, and reliable to ensure that the decision is well-informed. Consider the source of the information and its reliability before making the decision.
Evaluate alternatives: Evaluating alternatives is another critical step in the decision-making process. It is essential to consider all available options and weigh their pros and cons against the objectives of the decision. Evaluating alternatives helps in making the best decision that aligns with the objectives.
Make a decision: Once all the alternatives have been evaluated, it is time to make a decision. Choose the alternative that best solves the problem and aligns with the objectives. Ensure that the decision is communicated effectively to all stakeholders.
Evaluate the decision: After making the decision, it is essential to evaluate its effectiveness. Reflect on whether it solved the problem and met the objectives. If the decision did not meet the objectives, identify the areas that need improvement to make better decisions in the future.
In conclusion, making limited problem-solving decisions is a straightforward process that involves identifying the problem, gathering information, evaluating alternatives, making a decision, and evaluating the decision. These practical steps are essential in making informed decisions that align with the objectives of the decision. Remember, making mistakes is a part of the process, but it is essential to learn from them to make better decisions in the future.
→ Simple steps to integrate a script on your website
Benefits and Advantages of Limited Problem-Solving Decision Making
Benefits and Advantages of Limited Problem-Solving Decision Making in What is an Example of Limited Problem-Solving Decision Making?
Limited problem-solving decision making is a method of decision making that is commonly used when making low-risk decisions that do not require a lot of research or information. This type of decision making is often used in situations where there are only a few choices to choose from and time is limited. There are several benefits and advantages of using limited problem-solving decision making.
One of the main benefits of limited problem-solving decision making is that it saves time. Since there is no need for extensive research or information gathering, decisions can be made quickly and efficiently. This can be especially helpful in fast-paced environments where decisions need to be made quickly.
Another advantage of limited problem-solving decision making is that it saves money. Since there is no need for extensive research or information gathering, there are fewer resources needed to make a decision. This can be especially helpful for businesses that are looking to cut costs.
Limited problem-solving decision making is also less stressful than other methods of decision making. Since there is no need for extensive research or information gathering, decision makers can feel more confident in their decision making abilities. This can be especially helpful in high-pressure situations where there is little time to make a decision.
Finally, limited problem-solving decision making can help to reduce information overload. Since there is no need for extensive research or information gathering, decision makers can focus on the most important information and make a decision quickly. This can help to reduce the amount of information that needs to be processed and can help to improve decision making abilities.
In conclusion, limited problem-solving decision making is a useful method of decision making that can help to save time, money, and reduce stress. By focusing on the most important information and making decisions quickly, decision makers can make informed decisions without having to spend a lot of time or resources on research and information gathering.
Disadvantages of Limited Problem-Solving Decision Making
Limited problem-solving decision making is a type of decision making that occurs when a person is faced with a low-risk decision, has a moderate level of involvement, and has limited time and information to make a decision. Unfortunately, this type of decision making can have some significant disadvantages.
One of the biggest disadvantages of limited problem-solving decision making is the limited options available. Since the decision maker has limited information and time, they may not be aware of all the possible options available to them. This can lead to them making a decision based on incomplete information, which can ultimately lead to poor results.
Another disadvantage of limited problem-solving decision making is that it is not suitable for complex problems. Since the decision maker has limited time and information, they may not be able to fully understand the complexity of the problem they are facing. This can lead to them making a decision that does not fully address the underlying issues.
Finally, limited problem-solving decision making may lead to regret. Since the decision maker has limited information and time, they may not fully consider the potential consequences of their decision. This can lead to them regretting their decision later on when they realize the full impact of their actions.
Overall, while limited problem-solving decision making can be a quick and easy way to make low-risk decisions, it is not without its disadvantages. Decision makers should be aware of these disadvantages and take steps to mitigate them whenever possible.
Recommendations for Successful Limited Problem-Solving Decision Making
Limited problem-solving decision making is a type of decision making that is used when the stakes are low and the decision being made is not too complex. It is a quick and efficient way to make a decision without spending too much time or resources. However, there are certain recommendations that can make this process even more successful.
One of the most important things to know about limited problem-solving is when to use it. This type of decision making is best used for small, everyday decisions that do not require a lot of thought or consideration. For example, choosing what to wear in the morning or what to have for lunch are both good examples of decisions that can be made using limited problem-solving.
Another key recommendation for successful limited problem-solving decision making is to keep it simple. Avoid overthinking the decision and stick to the basics. This can help you avoid unnecessary stress and confusion.
Trusting your gut is another important aspect of limited problem-solving. Sometimes, the best decisions are the ones that come from your instincts. If you feel strongly about a certain choice, go with it.
Finally, learning from past decisions is a crucial part of successful limited problem-solving. Take note of what has worked in the past and what hasn't, and use that knowledge to inform your decision making going forward.
By following these recommendations, you can make the most of limited problem-solving decision making and make quick, efficient decisions with ease.
In light of this information
In conclusion, limited problem-solving decision making is a common type of decision-making that we encounter daily. An example of limited problem-solving decision making can be seen when we have to choose a new restaurant to eat at or decide what outfit to wear to a party.
Understanding limited problem-solving decision making is important because it allows us to make informed decisions in a timely manner. To be successful in this type of decision-making, it is essential to practice and experiment with different approaches. Remember to consider the alternatives, gather information, and evaluate the pros and cons before making a decision.
Ultimately, developing a careful and thoughtful approach to limited problem-solving decision making will lead to more positive outcomes and fewer regrets.
Sharing this article with your friends also helps us survive and continue. Thanks!
Join now our growing comunity!
Related articles
The Art of Closing the Sale: Tips and Strategies for Success
Winning Tips for Gamers: From Console Games to Mobile Games
Elevate Your Life and Business: Strategies for a Prosperous 2024
Elevate Your Business and Lifestyle: Master the Art of Professional and Personal Upgrades
How to Make Smart Decisions in Complex Times: A Guide to Navigating Your Personal and Professional Life
Mastering Life’s Transitions: From Business Strategies to Personal Health
Discover Stress-Free Living: Master the Art of Home, Health, and Happiness!
Simple Ways to Make $40 a Day Working from Home
Ensuring Year-Round Comfort and Safety: A Comprehensive Guide
Unveiling the Secrets of Precision: Mastering the Art of Measurement
Effective Strategy for Enhancing PPC Ads
Discover the Innovative Intersection of Technology and Comfort in Your Lifestyle and Business


- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

4.22: Increasing Sales with Limited Problem Solving
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 75603
Learning Objectives
- Describe how a retailer can increase sales from customers engaged in limited problem solving
By contrast, consumers with a limited problem solving mindset put in little consideration before arriving at a decision. Because of the minimal time and energy committed to the search, this mindset is most common with the selection and purchase of low-consideration or low-value items. These may also be purchases that have little to no emotional significance. Simply, the consumer is unwilling to over-invest time or effort in a decision that has little importance or where a “bad” decision has no lingering negative effects.
These shoppers don’t need a high level of engagement. Instead, they need to be cued to make a purchase. Thus, advertising, promotion and in-store merchandising can be especially helpful in influencing the decision. Think again about your local grocery store, imagining that you’re walking down the dental care aisle. Each item on-shelf, through its packaging—the images and words, the colors and fonts—is trying to communicate to you a reason to buy. The displays, floor or shelf graphics and special tags are doing the same. And, given the low relative price-point of the items and the low risk of making a mistake in buying the “wrong” product,” shoppers can make purchase decisions with a limited problem solving mindset.
Practice Questions
https://assessments.lumenlearning.co...sessments/9169
Contributors and Attributions
- Increasing Sales with Limited Problem Solving. Authored by : Patrick Williams. Provided by : Lumen Learning. License : CC BY: Attribution
Artificial Intelligence
Not Even Artificial Intelligence Can Make Central Planning Work
Revolutionary ai technologies can't solve the 'wicked problems' facing policy makers..
Arnold Kling | From the June 2024 issue
The term wicked problem has become a standard way for policy analysts to describe a social issue whose solution is inherently elusive. Wicked problems have many causal factors, complex interdependencies, and no ability to test all of the possible combinations of plausible interventions. Often, the problem itself cannot be articulated in a straightforward, agreed-upon way. Classic examples of wicked problems include climate change, substance abuse, international relations, health care systems, education systems, and economic performance. No matter how far computer science advances, some social problems will remain wicked.
The latest developments in artificial intelligence represent an enormous advance in computer science. Could that technological advance give bureaucrats the tool they have been missing to allow them to plan a more efficient economy? Many advocates of central planning seem to think so. Their line of thinking appears to be:
- Chatbots have absorbed an enormous amount of data.
- Large amounts of data produce knowledge.
- Knowledge will enable computers to plan the economy.
These assumptions are wrong. Chatbots have been trained to speak using large volumes of text, but they have not absorbed the knowledge contained in the text. Even if they had, there is knowledge that is critical for economic operations that is not available to a central planner or a computer.
The Promise of Pattern Matching
The new chatbots are trained on an enormous amount of text. But they have not absorbed this data in the sense of understanding the meaning of the text. Instead, they have found patterns in the data that enable them to write coherent paragraphs in response to queries.
Loosely speaking, there are two approaches to embedding skills and knowledge into computer software. One approach is to hard-code the sort of heuristics that a human being is able to articulate. In chess, this would mean explicitly coding formulas that reflect how people would weigh various factors in order to choose a move. In loan underwriting, it would mean spelling out how an experienced loan officer would regard a borrower's history of late credit-card payments in order to decide whether to make a new loan.
The other approach is pattern matching. In chess, that would mean giving the computer a large database of games that have been played, so that it can identify and distinguish positions that tend to result in wins. When the computer then plays the game, it would select moves that create positions that fit a winning pattern. In loan underwriting, pattern matching would mean looking at a large historic sample of approved loans to find characteristics that distinguish the borrowers who subsequently repaid the money from those who subsequently defaulted. It would then recommend approving loans where the credit report resembles the pattern of a borrower who is likely to repay.
Human beings use both pattern matching and explicit heuristics. An experienced chess player will not try to calculate the advantages and disadvantages of every single possible move in a position. Instead, the player will immediately recognize a pattern in the position, and this will intuitively suggest a few possible moves. The player will then make a more careful analysis to choose from among those moves. In speed chess, a player relies more on pattern recognition and less on heuristics and careful thought.
If you are on a hike, you may instinctively flinch when you see something that resembles the pattern of a snake. But then you will stop and reason about what you see. If it is not moving, you may conclude that it is merely a stick.
In American football, the quarterback may call a play based on careful reasoning about what the defense is likely to do in a situation. But once the play starts, the quarterback has to make instantaneous decisions based on what his instinct tells him about what the defense is doing. For these decisions, the quarterback is pattern matching.
We tend to pride ourselves on our ability to use heuristics and careful reasoning. When we examine our own thought processes, we do not think of ourselves as mere pattern matchers. But the latest advances in computer science rely heavily on pattern matching. ChatGPT has studied an enormous corpus of text in order to find patterns in how words are used in relation to one another, without having been given any instruction about what the words mean. Many experts, who assumed computers would have to be programmed to know the meaning of words, are surprised that this pattern matching works as well as it does. When you type a comment or a question into ChatGPT, not only will it respond by putting words in proper order; the response is usually meaningful, relevant, and appropriate.
It is almost mysterious how this happens. To a chatbot, a word is a mere "token," like a tiny square of cloth with a particular color. All it knows is which squares of cloth tend to appear near each other in the patterns that are in its training dataset. One at a time, it places squares of cloth in a sequence, and when the sequence is read as words it makes sense to a human reader.
Pattern matching also works with images. You can give a computer a prompt to draw an image; based on the patterns it finds, it will produce an image that follows the instructions in the prompt. The same pattern-matching technique can be applied to working with computer code, sounds, and video.
A Natural Language Revolution
These new tools revolutionize the way that people and computers communicate, because now computers can respond to our language. Before, we had to learn the computer's language. The first computers only understood "machine language," consisting of sets of zeroes and ones. An improvement was provided by "assembly language." Beyond assembly language were "programming languages," such as COBOL, FORTRAN, and BASIC.
About 40 years ago, most of us began communicating via the "user interface." We learned to manipulate a cursor and click on a mouse. Later we learned to use gestures on a phone.
With ChatGPT, we can communicate with a computer using "natural language." We type something in English, and we get a response in English. This is a superpower, and we are just starting to learn how to take advantage of it.
I wanted to be able to judge essays based on how well they address differing points of view. Can a computer do this for me? If I had to design, code, and test a program to do so, it would take months of work. But after spending a few hours experimenting with and refining prompts, I can get ChatGPT to perform this essay-grading task.
Pattern matching also lets computers respond to and mimic the emotional content of human writing. Chatbots do not merely retrieve information—for that purpose they may actually be less reliable than a Google search. They respond in paragraphs, using human phrasing and tone.
Because they communicate in natural language, ChatGPT and its relatives can do impersonations. Economist and public intellectual Tyler Cowen used a chatbot to conduct an "interview" with Jonathan Swift, the early 18th century satirist. Prompted to impersonate Swift, the chatbot responded to questions from Cowen. For example, Cowen asked about Swift's attitude toward the Church of Ireland. The chatbot responded, in part: " Ah, dear reader, it is indeed true that I, Jonathan Swift, harbored a certain degree of skepticism towards religious doctrine. Yet, one must not confuse this skepticism with a lack of faith or an aversion to the church altogether. Indeed, I was ordained a priest in the Church of Ireland, and throughout my life, I served in various capacities within its structure.
"Now, you may wonder how a man of my disposition could reconcile these seemingly contradictory stances," it continued. "The answer, I daresay, lies in the understanding that the church and the state must work in concert to maintain order and stability within society. The Church of Ireland, as an established state church, served as an important institution that promoted social cohesion and provided moral guidance to the people. "
Chatbots can impersonate celebrities, therapists, companions, and romantic partners. They are able to connect to us emotionally to an extent that far exceeds any previous computer programs. The implications of this advance may be profound.
A few decades ago, math teacher Jaime Escalante became famous for motivating teenagers in a high-poverty school to learn calculus at an Advanced Placement level. His demanding, confrontational style and striking accomplishments were immortalized in a film, Stand and Deliver . Imagine being able to clone Escalante and put him in classrooms across the country.
Or consider the problem of training a robot. Today that involves working in computer code, but within a few years we should be able to communicate with robots using natural language.
Customer support calls are another area with obvious potential. All of us have experienced the frustration of menu systems ("If you are calling about , press 1"). Thankfully, those systems may soon be obsolete. Instead, a chatbot can quickly catch on to the customer's question or respond sympathetically to the customer's complaint.
Some enthusiasts see chatbots becoming lifelong companions. Futurist Peter Diamandis has predicted that "you'll ultimately give your personal AI assistant access to your phone calls, emails, conversations, cameras…every aspect, of every moment, of your day. Our personal AIs will serve (and we may become dependent upon them) as our cognitive collaborators, our on-demand researcher, our consigliere, our coaches…giving us advice on any and all topics that require unbiased wisdom."
Venture capitalist Marc Andreessen has argued similarly that within a few years every child will grow up with a personal chatbot as a lifelong partner. Your personal chatbot would have the ability to understand your abilities and desires. It would be able to motivate you, coach you, train you, and serve you.
It is too early to know which of these forecasts will actually pan out and which will fail to materialize, let alone what unexpected uses will appear out of nowhere. This is reminiscent of the World Wide Web circa 1995, when many of us anticipated rapid disruptions in education or the real estate market that have yet to occur. Meanwhile, nobody was predicting real-time driving directions or podcasting.
Limited Knowledge
Chatbots use pattern matching to provide coherent, relevant responses. But that does not mean that they have encyclopedic knowledge. The answers that a chatbot gives are not necessarily wise. They are not even necessarily true.
I have written several papers on the 2008 financial crisis, in which I make a case for what I believe were the most important causal factors. But when I asked ChatGPT to summarize my views on the crisis, it included explanations that are favored by other economists but not me. That is because the chatbot is trained to identify word patterns without knowing what the words mean.
Some knowledge is not available in any corpus of data. For example, we cannot predict how an innovation will play out.
As of this writing, Apple has introduced a revolutionary product it calls the Vision Pro. No one knows exactly how this product will be used, or whether it will be successful. This knowledge will emerge over time, with the market providing the ultimate judgment. As economist Friedrich Hayek wrote, market competition is a discovery procedure. Even if a computer possessed all of present knowledge, it could not replace this discovery procedure.
Central Planning Still Won't Work
Economic organization is a wicked problem. Your intuition might be that the best approach would be for a department of experts to determine what goods and services get produced and how they are distributed. This is known as central planning, and it has not worked well in reality. The Soviet Union fell in part because its centrally planned economy could not keep up with the West.
Some advocates of central planning have claimed that computers could provide the solution. In a 2017 Financial Times article headlined "The Big Data revolution can revive the planned economy," columnist John Thornhill cited entrepreneur Jack Ma, among others, claiming that eventually a planned economy will be possible. Those with this viewpoint see central planning as an information-processing problem, and computers are now capable of handling much more information than are individual human beings. Might they have a point?
F.A. Hayek made a compelling counterargument. In a famous paper called "The Use of Knowledge in Society," first published in 1945, Hayek argued that some information is tacit, meaning that it will never be articulated in a form that can be input to a computer. He also argued that some information is dispersed, meaning that it is known only in small part to any one person. Given the decentralized character of information, a market system generates prices, which in turn generate the knowledge necessary to efficiently organize an economy.
A central computer is not going to know how you as an individual would trade off between two goods. You may not be able to articulate your preferences yourself, until you are confronted with a choice at market prices. The computer is not going to know how consumers will respond to a new product or service, and it is not going to know how a new invention might change production patterns. The trial-and-error process of markets, using prices, profits, and losses, addresses these challenges.
Economists have a saying that "all costs are opportunity costs." That is, the cost of any good is the cost of what you have to forgo in order to obtain it. In other words, cost is not inherent in the nature of the good itself or how it is produced. It is impossible to know the cost of a good until it is traded in the market. If central planners do away with the market, then they will not have the information needed to calculate costs and make good decisions. Forced to use guesswork, planners will inevitably misallocate resources.
In a market system, bad decisions result in losses for firms, forcing them to adapt. Without the signals provided by prices, profits, and losses, a central planner's computer will not even be aware of the mistakes that it makes.
Learning From Simulations
The problem of organizing an economy is too wicked to be solved by computers, whether they use pattern matching or other methods. But that does not mean that advances in computer science will be of no help in improving economic policy.
New software tools can be used to create complex simulations. The tools that gave us chatbots could be used to create thousands of synthetic economic "characters." We could have them interact according to rules and heuristics designed to mimic various economic policies and institutions, and we could compare how different economic policies affect the outcomes of these simulations.
Among economists, this technique is known as "agent-based modeling." So far, it has been of only limited value, because it is difficult to create agents that vary along multiple dimensions. But it may be improved if we can use the latest tools to create a richer set of economic characters than what modelers have used in the past. Still, this improvement would be incremental, not revolutionary. They will not permit us to hand off the resource allocation problem to a central computer.
The latest techniques for using large datasets and pattern matching offer new and exciting capabilities. But these techniques alone will not enable us to solve society's wicked problems.
This article originally appeared in print under the headline "Wicked Problems Remain."
The Case of the AI-Generated Giant Rat Penis
Ronald Bailey | From the June 2024 issue
AI Regulators Are More Likely To Run Amok Than Is AI
Ronald Bailey | 5.3.2024 4:45 PM
Trump Promises To Give Police 'Immunity From Prosecution'
Billy Binion | 5.3.2024 4:15 PM
The New York Case Against Trump Relies on a 'Twisty' Legal Theory That Reeks of Desperation
Jacob Sullum | 5.3.2024 4:10 PM

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
3.2 Low-Involvement Versus High-Involvement Buying Decisions and the Consumer’s Decision-Making Process
Learning objectives.
- Distinguish between low-involvement and high-involvement buying decisions.
- Understand what the stages of the buying process are and what happens in each stage.
As you have seen, many factors influence a consumer’s behavior. Depending on a consumer’s experience and knowledge, some consumers may be able to make quick purchase decisions and other consumers may need to get information and be more involved in the decision process before making a purchase. The level of involvement reflects how personally important or interested you are in consuming a product and how much information you need to make a decision. The level of involvement in buying decisions may be considered a continuum from decisions that are fairly routine (consumers are not very involved) to decisions that require extensive thought and a high level of involvement. Whether a decision is low, high, or limited, involvement varies by consumer, not by product, although some products such as purchasing a house typically require a high-involvement for all consumers. Consumers with no experience purchasing a product may have more involvement than someone who is replacing a product.
You have probably thought about many products you want or need but never did much more than that. At other times, you’ve probably looked at dozens of products, compared them, and then decided not to purchase any one of them. When you run out of products such as milk or bread that you buy on a regular basis, you may buy the product as soon as you recognize the need because you do not need to search for information or evaluate alternatives. As Nike would put it, you “just do it.” Low-involvement decisions are, however, typically products that are relatively inexpensive and pose a low risk to the buyer if she makes a mistake by purchasing them.
Consumers often engage in routine response behavior when they make low-involvement decisions—that is, they make automatic purchase decisions based on limited information or information they have gathered in the past. For example, if you always order a Diet Coke at lunch, you’re engaging in routine response behavior. You may not even think about other drink options at lunch because your routine is to order a Diet Coke, and you simply do it. Similarly, if you run out of Diet Coke at home, you may buy more without any information search.
Some low-involvement purchases are made with no planning or previous thought. These buying decisions are called impulse buying . While you’re waiting to check out at the grocery store, perhaps you see a magazine with Angelina Jolie and Brad Pitt on the cover and buy it on the spot simply because you want it. You might see a roll of tape at a check-out stand and remember you need one or you might see a bag of chips and realize you’re hungry or just want them. These are items that are typically low-involvement decisions. Low-involvement decisions aren’t necessarily products purchased on impulse, although they can be.
By contrast, high-involvement decisions carry a higher risk to buyers if they fail, are complex, and/or have high price tags. A car, a house, and an insurance policy are examples. These items are not purchased often but are relevant and important to the buyer. Buyers don’t engage in routine response behavior when purchasing high-involvement products. Instead, consumers engage in what’s called extended problem solving , where they spend a lot of time comparing different aspects such as the features of the products, prices, and warranties.
High-involvement decisions can cause buyers a great deal of postpurchase dissonance (anxiety) if they are unsure about their purchases or if they had a difficult time deciding between two alternatives. Companies that sell high-involvement products are aware that postpurchase dissonance can be a problem. Frequently, they try to offer consumers a lot of information about their products, including why they are superior to competing brands and how they won’t let the consumer down. Salespeople may be utilized to answer questions and do a lot of customer “hand-holding.”
Allstate’s “You’re in Good Hands” advertisements are designed to convince consumers that the insurance company won’t let them down.
Mike Mozart – Allstate, – CC BY 2.0.
Limited problem solving falls somewhere between low-involvement (routine) and high-involvement (extended problem solving) decisions. Consumers engage in limited problem solving when they already have some information about a good or service but continue to search for a little more information. Assume you need a new backpack for a hiking trip. While you are familiar with backpacks, you know that new features and materials are available since you purchased your last backpack. You’re going to spend some time looking for one that’s decent because you don’t want it to fall apart while you’re traveling and dump everything you’ve packed on a hiking trail. You might do a little research online and come to a decision relatively quickly. You might consider the choices available at your favorite retail outlet but not look at every backpack at every outlet before making a decision. Or you might rely on the advice of a person you know who’s knowledgeable about backpacks. In some way you shorten or limit your involvement and the decision-making process.
Products, such as chewing gum, which may be low-involvement for many consumers often use advertising such as commercials and sales promotions such as coupons to reach many consumers at once. Companies also try to sell products such as gum in as many locations as possible. Many products that are typically high-involvement such as automobiles may use more personal selling to answer consumers’ questions. Brand names can also be very important regardless of the consumer’s level of purchasing involvement. Consider a low- versus high-involvement decision—say, purchasing a tube of toothpaste versus a new car. You might routinely buy your favorite brand of toothpaste, not thinking much about the purchase (engage in routine response behavior), but not be willing to switch to another brand either. Having a brand you like saves you “search time” and eliminates the evaluation period because you know what you’re getting.
When it comes to the car, you might engage in extensive problem solving but, again, only be willing to consider a certain brand or brands. For example, in the 1970s, American-made cars had such a poor reputation for quality that buyers joked that a car that’s “not Jap [Japanese made] is crap.” The quality of American cars is very good today, but you get the picture. If it’s a high-involvement product you’re purchasing, a good brand name is probably going to be very important to you. That’s why the manufacturers of products that are typically high-involvement decisions can’t become complacent about the value of their brands.
1970s American Cars
<a target=”_blank” href=”http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pjzpx_jUUA0″(Link to American Cars video)
Today, Lexus is the automotive brand that experiences the most customer loyalty. For a humorous, tongue-in-cheek look at why the brand reputation of American carmakers suffered in the 1970s, check out this clip.
Stages in the Buying Process
Figure 3.9 “Stages in the Consumer’s Purchasing Process” outlines the buying stages consumers go through. At any given time, you’re probably in a buying stage for a product or service. You’re thinking about the different types of things you want or need to eventually buy, how you are going to find the best ones at the best price, and where and how will you buy them. Meanwhile, there are other products you have already purchased that you’re evaluating. Some might be better than others. Will you discard them, and if so, how? Then what will you buy? Where does that process start?
Figure 3.9 Stages in the Consumer’s Purchasing Process
Stage 1. Need Recognition
You plan to backpack around the country after you graduate and don’t have a particularly good backpack. You realize that you must get a new backpack. You may also be thinking about the job you’ve accepted after graduation and know that you must get a vehicle to commute. Recognizing a need may involve something as simple as running out of bread or milk or realizing that you must get a new backpack or a car after you graduate. Marketers try to show consumers how their products and services add value and help satisfy needs and wants. Do you think it’s a coincidence that Gatorade, Powerade, and other beverage makers locate their machines in gymnasiums so you see them after a long, tiring workout? Previews at movie theaters are another example. How many times have you have heard about a movie and had no interest in it—until you saw the preview? Afterward, you felt like you had to see it.
Stage 2. Search for Information
For products such as milk and bread, you may simply recognize the need, go to the store, and buy more. However, if you are purchasing a car for the first time or need a particular type of backpack, you may need to get information on different alternatives. Maybe you have owned several backpacks and know what you like and don’t like about them. Or there might be a particular brand that you’ve purchased in the past that you liked and want to purchase in the future. This is a great position for the company that owns the brand to be in—something firms strive for. Why? Because it often means you will limit your search and simply buy their brand again.
If what you already know about backpacks doesn’t provide you with enough information, you’ll probably continue to gather information from various sources. Frequently people ask friends, family, and neighbors about their experiences with products. Magazines such as Consumer Reports (considered an objective source of information on many consumer products) or Backpacker Magazine might also help you. Similar information sources are available for learning about different makes and models of cars.
Internet shopping sites such as Amazon.com have become a common source of information about products. Epinions.com is an example of consumer-generated review site. The site offers product ratings, buying tips, and price information. Amazon.com also offers product reviews written by consumers. People prefer “independent” sources such as this when they are looking for product information. However, they also often consult non-neutral sources of information, such advertisements, brochures, company Web sites, and salespeople.
Stage 3. Product Evaluation
Obviously, there are hundreds of different backpacks and cars available. It’s not possible for you to examine all of them. In fact, good salespeople and marketing professionals know that providing you with too many choices can be so overwhelming that you might not buy anything at all. Consequently, you may use choice heuristics or rules of thumb that provide mental shortcuts in the decision-making process. You may also develop evaluative criteria to help you narrow down your choices. Backpacks or cars that meet your initial criteria before the consideration will determine the set of brands you’ll consider for purchase.
Evaluative criteria are certain characteristics that are important to you such as the price of the backpack, the size, the number of compartments, and color. Some of these characteristics are more important than others. For example, the size of the backpack and the price might be more important to you than the color—unless, say, the color is hot pink and you hate pink. You must decide what criteria are most important and how well different alternatives meet the criteria.
Figure 3.10
Osprey backpacks are known for their durability. The company has a special design and quality control center, and Osprey’s salespeople annually take a “canyon testing” trip to see how well the company’s products perform.
melanie innis – break – CC BY-NC-ND 2.0.
Companies want to convince you that the evaluative criteria you are considering reflect the strengths of their products. For example, you might not have thought about the weight or durability of the backpack you want to buy. However, a backpack manufacturer such as Osprey might remind you through magazine ads, packaging information, and its Web site that you should pay attention to these features—features that happen to be key selling points of its backpacks. Automobile manufacturers may have similar models, so don’t be afraid to add criteria to help you evaluate cars in your consideration set.
Stage 4. Product Choice and Purchase
With low-involvement purchases, consumers may go from recognizing a need to purchasing the product. However, for backpacks and cars, you decide which one to purchase after you have evaluated different alternatives. In addition to which backpack or which car, you are probably also making other decisions at this stage, including where and how to purchase the backpack (or car) and on what terms. Maybe the backpack was cheaper at one store than another, but the salesperson there was rude. Or maybe you decide to order online because you’re too busy to go to the mall. Other decisions related to the purchase, particularly those related to big-ticket items, are made at this point. For example, if you’re buying a high-definition television, you might look for a store that will offer you credit or a warranty.
Stage 5. Postpurchase Use and Evaluation
At this point in the process you decide whether the backpack you purchased is everything it was cracked up to be. Hopefully it is. If it’s not, you’re likely to suffer what’s called postpurchase dissonance . You might call it buyer’s remorse . Typically, dissonance occurs when a product or service does not meet your expectations. Consumers are more likely to experience dissonance with products that are relatively expensive and that are purchased infrequently.
You want to feel good about your purchase, but you don’t. You begin to wonder whether you should have waited to get a better price, purchased something else, or gathered more information first. Consumers commonly feel this way, which is a problem for sellers. If you don’t feel good about what you’ve purchased from them, you might return the item and never purchase anything from them again. Or, worse yet, you might tell everyone you know how bad the product was.
Companies do various things to try to prevent buyer’s remorse. For smaller items, they might offer a money back guarantee or they might encourage their salespeople to tell you what a great purchase you made. How many times have you heard a salesperson say, “That outfit looks so great on you!” For larger items, companies might offer a warranty, along with instruction booklets, and a toll-free troubleshooting line to call or they might have a salesperson call you to see if you need help with product. Automobile companies may offer loaner cars when you bring your car in for service.
Companies may also try to set expectations in order to satisfy customers. Service companies such as restaurants do this frequently. Think about when the hostess tells you that your table will be ready in 30 minutes. If they seat you in 15 minutes, you are much happier than if they told you that your table would be ready in 15 minutes, but it took 30 minutes to seat you. Similarly, if a store tells you that your pants will be altered in a week and they are ready in three days, you’ll be much more satisfied than if they said your pants would be ready in three days, yet it took a week before they were ready.
Stage 6. Disposal of the Product
There was a time when neither manufacturers nor consumers thought much about how products got disposed of, so long as people bought them. But that’s changed. How products are being disposed of is becoming extremely important to consumers and society in general. Computers and batteries, which leech chemicals into landfills, are a huge problem. Consumers don’t want to degrade the environment if they don’t have to, and companies are becoming more aware of this fact.
Take for example Crystal Light, a water-based beverage that’s sold in grocery stores. You can buy it in a bottle. However, many people buy a concentrated form of it, put it in reusable pitchers or bottles, and add water. That way, they don’t have to buy and dispose of plastic bottle after plastic bottle, damaging the environment in the process. Windex has done something similar with its window cleaner. Instead of buying new bottles of it all the time, you can purchase a concentrate and add water. You have probably noticed that most grocery stores now sell cloth bags consumers can reuse instead of continually using and discarding of new plastic or paper bags.
Figure 3.11
The hike up to Mount Everest used to be pristine. Now it looks more like this. Who’s responsible? Are consumers or companies responsible, or both?
jqpubliq – Recycling Center Pile – CC BY-SA 2.0.
Other companies are less concerned about conservation than they are about planned obsolescence . Planned obsolescence is a deliberate effort by companies to make their products obsolete, or unusable, after a period of time. The goal is to improve a company’s sales by reducing the amount of time between the repeat purchases consumers make of products. When a software developer introduces a new version of product, it is usually designed to be incompatible with older versions of it. For example, not all the formatting features are the same in Microsoft Word 2007 and 2010. Sometimes documents do not translate properly when opened in the newer version. Consequently, you will be more inclined to upgrade to the new version so you can open all Word documents you receive.
Products that are disposable are another way in which firms have managed to reduce the amount of time between purchases. Disposable lighters are an example. Do you know anyone today that owns a nondisposable lighter? Believe it or not, prior to the 1960s, scarcely anyone could have imagined using a cheap disposable lighter. There are many more disposable products today than there were in years past—including everything from bottled water and individually wrapped snacks to single-use eye drops and cell phones.
Figure 3.12
Disposable lighters came into vogue in the United States in the 1960s. You probably don’t own a cool, nondisposable lighter like one of these, but you don’t have to bother refilling it with lighter fluid either.
Europeana staff photographer – A trench art lighter – public domain.
Key Takeaways
Consumer behavior looks at the many reasons why people buy things and later dispose of them. Consumers go through distinct buying phases when they purchase products: (1) realizing the need or wanting something, (2) searching for information about the item, (3) evaluating different products, (4) choosing a product and purchasing it, (5) using and evaluating the product after the purchase, and (6) disposing of the product. A consumer’s level of involvement is how interested he or she is in buying and consuming a product. Low-involvement products are usually inexpensive and pose a low risk to the buyer if he or she makes a mistake by purchasing them. High-involvement products carry a high risk to the buyer if they fail, are complex, or have high price tags. Limited-involvement products fall somewhere in between.
Review Questions
- How do low-involvement decisions differ from high-involvement decisions in terms of relevance, price, frequency, and the risks their buyers face? Name some products in each category that you’ve recently purchased.
- What stages do people go through in the buying process for high-involvement decisions? How do the stages vary for low-involvement decisions?
- What is postpurchase dissonance and what can companies do to reduce it?
3.2 Low-Involvement Versus High-Involvement Buying Decisions and the Consumer’s Decision-Making Process Copyright © 2015 by University of Minnesota. All Rights Reserved.
Share This Book

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Limited Problem Solving. Limited problem solving falls somewhere between low-involvement (routine) and high-involvement (extended problem solving) decisions. Consumers engage in limited problem solving when they already have some information about a good or service but continue to search for a little more information. Assume you need a new ...
Limited problem solving falls somewhere between low-involvement (routine) and high-involvement (extended problem solving) decisions. Consumers engage in limited problem solving when they already have some information about a good or service but continue to search for a little more information. Assume you need a new backpack for a hiking trip.
Limited problem solving falls somewhere between low-involvement (routine) and high-involvement (extended problem solving) decisions. Consumers engage in limited problem solving when they already have some information about a good or service but continue to search for a little more information. Assume you need a new backpack for a hiking trip.
Consumer decisions can be categorized into three primary types: Routinized Response - This is the kind of decision where you don't really have to think much about it. Limited Problem Solving - This type of purchase decision involves a little more thinking or a little more consideration. Extensive Problem Solving - This is when we're making a ...
Describe how a retailer can increase sales from customers engaged in limited problem solving. By contrast, consumers with a limited problem solving mindset put in little consideration before arriving at a decision. Because of the minimal time and energy committed to the search, this mindset is most common with the selection and purchase of low ...
Learning Objectives. Describe how a retailer can increase sales from customers engaged in limited problem solving. By contrast, consumers with a limited problem solving mindset put in little consideration before arriving at a decision. Because of the minimal time and energy committed to the search, this mindset is most common with the selection ...
Limited problem solving. Customer decision - making mode of limited problem solving, relates to a situation where both, customer experience, as well as, the level of their involvement are low. Considered to be the most common mode of decision - making, it lacks systematic approach in terms of decision - making. Examples for this mode of ...
Limited Problem Solving. buying situations in which a purchaser has had some previous experience but is unfamiliar with suppliers, product options, prices, etc. Also referred to as Limited Decision Making. See: Extensive Problem Solving.
A marketer's goal with routine problem solving is to reinforce the purchase habits of existing customers and change the habits of non-existing customers. Limited problem-solving—In a limited problem-solving situation, a consumer is familiar with the product class and the major brands in the product class and knows the attributes and ...
Limited problem solving falls somewhere between low-involvement (routine) and high-involvement (extended problem solving) decisions. Consumers engage in limited problem solving when they already have some information about a good or service but continue to search for a little more information. Assume you need a new backpack for a hiking trip.
The McKinsey guide to problem solving. Become a better problem solver with insights and advice from leaders around the world on topics including developing a problem-solving mindset, solving problems in uncertain times, problem solving with AI, and much more.
Problem-solving involves taking certain steps and using psychological strategies. Learn problem-solving techniques and how to overcome obstacles to solving problems. ... This can be a good strategy to use if you have a limited number of solutions available. But if there are many different choices available, narrowing down the possible options ...
Limited problem solving falls somewhere between low-involvement (routine) and high-involvement (extended problem solving) decisions. Consumers engage in limited problem solving when they already have some information about a good or service but continue to search for a little more information. Assume you need a new backpack for a hiking trip.
Limited decision making is consumer decision making that is used when purchasing products that require a moderate amount of time and effort to compare models and brands before making a choice. The ...
Marketing 210 - Ch. 7. Consumer Problem Solving Process. Click the card to flip 👆. 3 kinds: Consumer Specific -A)Routinized Response Behavior, B) Limited Problem Solving, Product Specific - C) Extended Problem Solving. Click the card to flip 👆. 1 / 24.
6. Discovery & Action Dialogue (DAD) One of the best approaches is to create a safe space for a group to share and discover practices and behaviors that can help them find their own solutions. With DAD, you can help a group choose which problems they wish to solve and which approaches they will take to do so.
Limited problem solving is used A. when consumers put much effort into deciding how to satisfy a need. B. for purchases that have little importance or relevance for the customer. C. by consumers when some effort is required in deciding the best way to satisfy a need. D. when consumers regularly select a particular way of satisfying a need when ...
Limited problem solving falls somewhere between low-involvement (routine) and high-involvement (extended problem solving) decisions. Consumers engage in limited problem solving when they already have some information about a good or service but continue to search for a little more information. Assume you need a new backpack for a hiking trip.
Limited problem-solving decision making is a method of decision making that is commonly used when making low-risk decisions that do not require a lot of research or information. This type of decision making is often used in situations where there are only a few choices to choose from and time is limited.
Learning Objectives. Describe how a retailer can increase sales from customers engaged in limited problem solving. By contrast, consumers with a limited problem solving mindset put in little consideration before arriving at a decision. Because of the minimal time and energy committed to the search, this mindset is most common with the selection ...
Limited problem solving is used when purchasing frequently bought, low-priced items needing very little decision effort. True or False? Here's the best way to solve it. Limited problem solving is used for products purchased occasionally or when buyers need to acquire information ….
The problem of organizing an economy is too wicked to be solved by artificial intelligence. Revolutionary AI technologies can't solve the 'wicked problems' facing policy makers. ... Limited Knowledge.
Limited problem solving falls somewhere between low-involvement (routine) and high-involvement (extended problem solving) decisions. Consumers engage in limited problem solving when they already have some information about a good or service but continue to search for a little more information. Assume you need a new backpack for a hiking trip.