
- Our Audit Process
- SOC 1 Audits
- SOC 2 Audits
- HIPAA Audits
- HITRUST Certification
- FedRAMP Compliance
- StateRAMP Assessment
- CMMC Compliance Assessment
- Penetration Testing
- ISO/IEC 27001:2022 Certification
- PCI Compliance Audits
- Leadership Team
- What is SOC 2?
- What is a SOC 2 Report?
- What is SOC 1?
- 2022 Trust Services Criteria (TSCs)
- Audit Terms

IT Audits 101: Professional Guidance From an IT Auditor

In the ever-evolving landscape of technology, organizations rely heavily on their information systems and digital infrastructure to operate efficiently and securely. However, with technological advancements come new risks and vulnerabilities. To determine the integrity , availability , and confidentiality of data , organizations turn to Information Technology (IT) audits—a systematic evaluation of their IT systems and controls. In this blog post, we will delve into the world of IT audits, understanding their significance, and exploring the benefits they bring to businesses.
What Is an IT (Information Technology) Audit & What Is Its Purpose?
An IT audit is a comprehensive examination of an organization’s IT systems, infrastructure, and processes. Its primary objective is to evaluate the effectiveness of internal controls and identify any weaknesses or vulnerabilities that could compromise the confidentiality, integrity, or availability of information. IT audits cover a wide range of areas, including data security, network infrastructure, hardware and software assets, IT governance, compliance, and more. Auditing – whether it is internally or by a third-party – helps organizations determine that their IT is functioning as effectively as possible. The purpose of an IT audit is to provide visibility into the effectiveness of your IT systems.
How Does an IT Audit Differ From an Audit?
The key difference between an audit and an IT audit lies in the scope and focus of the examination. An audit, generally referred to as a financial or external audit, is a comprehensive examination of an organization’s financial statements, accounting records, and internal controls.
What Are the Two Types of IT Auditing?
There are two main kinds of IT audits: compliance audits and controls assessments.
- Compliance Audits: These audits focus on how well you’re adhering to regulations, industry best practices, and standards. Popular IT compliance audits are SOC 1 and SOC 2 audits. A SOC 1 audit includes both business process and information technology control objectives and testing. SOC 2 compliance demonstrates that your company has adequate controls in place governing information security in your environment . Both SOC 1 and SOC 2 must be issued by a CPA firm that specializes in auditing IT security and business process controls.
- Controls Assessments: These assessments look at whether your system has been set up in a way that prevents high-risk activities from happening. There are several control frameworks your controls assessments can be tested against. For example, if a hacker wants to break into your systems but can’t because it’s too secure or has been designed in such a way that it won’t let them get through – that’s good! You’ve got strong controls on your side!
See more information on frameworks and examples of IT audits here: HIPAA , HITRUST , NIST 800-53 , NIST 800-171 , NIST CSF , CMMC , FEDRAMP , ISO/IEC 27001:2022 , GDPR , and CCPA .

What Is the IT Audit Process & What Should You Expect?
The IT audit process typically involves the following 6 phases:
- Planning and Preparation: The audit process begins with defining the scope and objectives of the audit. This phase involves understanding the organization’s IT landscape, identifying critical systems and processes, and determining the audit methodology and timeline.
- Risk Assessment: A comprehensive risk assessment is a vital component of any IT audit. It involves identifying potential threats, assessing their impact, and evaluating existing controls to mitigate those risks . This step helps prioritize audit activities and determines a targeted approach.
- Evaluation of Controls: Auditors assess the effectiveness of IT controls in place to protect information assets. These controls encompass various aspects, such as access management , data backups, change management , network security, and incident response. Evaluating controls provides insights into their adequacy and identifies gaps that need to be addressed.
- Compliance Review: Compliance with relevant regulations, industry standards, and internal policies is a critical aspect of IT audits. Auditors review documentation, procedures, and practices to determine alignment with the required standards, thereby minimizing legal and reputational risks.
- Vulnerability Assessment: Auditors perform vulnerability scans and penetration tests to identify weaknesses in the organization’s IT infrastructure. This involves assessing the robustness of firewalls, intrusion detection systems, encryption protocols , and other security mechanisms. The findings help organizations remediate vulnerabilities and strengthen their defenses.
- Reporting: The audit findings are documented in a comprehensive report that outlines identified risks, control deficiencies , and considerations for improvement. This report serves as a roadmap for management to address the identified issues and enhance the security and efficiency of their IT systems.
Who Performs an IT Audit?
An IT audit can be performed internally or externally by a third party.
- The organization’s own IT staff performs internal IT audits . These are often done to evaluate and improve the efficiency of existing systems, or to determine that information security policies and procedures are being followed correctly.
- External IT audits can be performed by a third party who is not affiliated with your company. This type of audit is typically used by companies that want an unbiased opinion on their security measures or other aspects of their technology infrastructure, such as cloud storage solutions used by employees working remotely .
What Do IT Auditors Look For?
IT auditors look for various aspects during an IT audit to assess the effectiveness, reliability, and security of an organization’s IT infrastructure, systems, and processes. Here are some key areas that IT auditors typically focus on:
- Access controls, authentication mechanisms, password policies , network security measures, firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and data encryption techniques.
- Data backup and recovery procedures, data retention policies , data classification frameworks , and privacy controls.
- Change management processes to determine that changes to IT systems, applications, and configurations are properly authorized, documented, tested, and implemented.

The Importance of IT Audits for Your Organization
IT audits are an important process for enhancing information security, improving operational efficiency, and supporting strategic decision-making. They provide valuable insights to management and help organizations build a robust and resilient IT infrastructure. The following are key areas/processes within an organization that IT audits can be an integral part of.
Risk Management
IT audits play a crucial role in identifying and assessing risks associated with an organization’s IT environment. By conducting regular audits, businesses can proactively address potential vulnerabilities, reduce the likelihood of security breaches or data loss, and mitigate the impact of technological risks on their operations.
Compliance and Regulations
In today’s regulatory landscape, organizations face a multitude of legal and industry-specific requirements regarding the protection of data and IT systems. IT audits help determine compliance with relevant laws and regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) , Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) , Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) , and more.
Internal Control Evaluation
Robust internal controls are vital for safeguarding assets, preventing fraud, and maintaining operational efficiency. IT audits evaluate the design and effectiveness of internal controls related to IT processes, providing insights into potential weaknesses or gaps that need to be addressed.
Data Security and Privacy
With the increasing frequency and sophistication of cyber threats , organizations must prioritize data security and privacy. IT audits assess the organization’s security posture, identify vulnerabilities, and recommend measures to enhance data protection, including encryption, access controls, user authentication, and incident response plans .

Understanding the Benefits of IT Audits
IT audits provide several benefits to organizations. Here are some key benefits of conducting IT audits:
- Enhanced Security: IT audits help organizations identify security gaps and implement appropriate measures to strengthen their defense against cyber threats. This leads to improved data protection, reduced risk of data breaches, and enhanced overall security posture.
- Increased Efficiency: By evaluating IT processes and controls, audits identify areas where operational efficiency can be enhanced. This may involve streamlining workflows, eliminating redundant tasks, optimizing resource allocation, and adopting best practices, ultimately leading to cost savings and improved productivity.
- Regulatory Compliance: Compliance with applicable laws and regulations is essential for maintaining trust with customers, partners, and stakeholders. IT audits determine that organizations meet regulatory requirements and avoid potential penalties or reputational damage.
- Risk Mitigation: Identifying and addressing IT-related risks helps organizations mitigate the potential impact of disruptions, whether caused by security breaches, system failures, or natural disasters. By proactively managing risks , organizations can enhance business continuity and resilience.
What Are the Limitations of IT Audits?
While IT audits provide valuable insights and benefits, they also have certain limitations that organizations should be aware of. Here are some limitations of IT audits:
- Sampling Limitations: Due to the vastness and complexity of IT systems and processes, IT audits often rely on sampling techniques to assess controls and risks. The auditor selects a subset of items or transactions for examination, which may not fully represent the entire population. As a result, there is a risk that the selected sample may not capture all potential issues or vulnerabilities.
- Limited Scope: IT audits typically focus on specific objectives, such as compliance with regulations, information security, or IT governance . While these areas are essential, the audit scope may not cover all aspects of the organization’s IT environment. Some potential risks or control weaknesses may go undetected if they fall outside the audit’s scope.
- Reliance on Information Provided: IT audits rely on the information provided by the organization being audited. The accuracy, completeness, and reliability of the information can affect the audit findings. If the organization provides incomplete or inaccurate information, it may lead to incorrect assessments or missed vulnerabilities.
- Time Sensitivity: IT audits provide a snapshot of the organization’s IT controls and processes at a particular point in time. IT environments are dynamic, with new technologies, vulnerabilities, and threats emerging regularly. Therefore, the audit findings may become outdated relatively quickly. Organizations need to continually monitor and update their controls to address evolving risks.
- Inherent Limitations of Controls Testing : IT audits assess the design and operating effectiveness of controls. However, even with thorough testing, there is always a possibility of control failures or gaps going undetected. Sophisticated attacks or emerging vulnerabilities may not be captured through standard control testing methodologies.
- Limited Assurance: IT audits provide reasonable assurance rather than absolute assurance. They are based on professional judgment, sampling techniques, and risk assessments. While auditors aim to provide reliable and objective assessments, there is still inherent uncertainty in the audit process. Therefore, audit findings should be interpreted in that context.
- Human Factor: IT audits involve interaction with individuals within the organization. The effectiveness of controls and security measures can be influenced by human behavior, including intentional or unintentional actions that may not be captured during an audit. The human factor introduces an additional layer of complexity and risk that may not be fully assessed through the audit process.
Despite these limitations, IT audits remain valuable for organizations in assessing and improving their IT environment. It is important to recognize these limitations and complement audits with other risk management practices, continuous monitoring , and proactive security measures to address potential gaps.

What Are the Best Practices for IT Audits?
To conduct effective and thorough IT audits, it is important to follow best practices. Here are some key best practices to consider when conducting IT audits:
- Establish Clear Objectives : Clearly define the objectives and scope of the IT audit based on the organization’s needs, regulatory requirements, and risk landscape. Establish specific goals to guide the audit process and align them with the organization’s strategic objectives.
- Risk-Based Approach: Take a risk-based approach to prioritize audit focus and resource allocation. Identify and assess the risks associated with the organization’s IT systems, infrastructure, and processes. Tailor the audit procedures to address the highest-risk areas and potential vulnerabilities.
- Maintain Independence and Objectivity: IT auditors should be independent and objective to maintain unbiased assessments. They should not have any conflicts of interest that could compromise their ability to provide impartial recommendations and findings.
- Use Established Audit Frameworks : Utilize established frameworks and standards, such as COBIT (Control Objectives for Information and Related Technologies) or NIST (National Institute of Standards and Technology) Cybersecurity Framework , to guide the audit process. These frameworks provide best practices and control objectives that can help determine comprehensive coverage and consistency.
- Adequate Planning and Preparation: Thoroughly plan and prepare for the audit. Understand the organization’s IT environment, systems, and processes. Develop a detailed audit plan , including timelines, resource requirements, and methodologies. Engage with relevant stakeholders and gather the necessary documentation to facilitate the audit process.
- Conduct Risk Assessment and Control Testing: Perform a comprehensive risk assessment to identify potential vulnerabilities and weaknesses. Evaluate the design and operating effectiveness of controls through testing, including technical assessments, document reviews, interviews, and observation. Use appropriate sampling techniques to determine representative coverage.
- Document Findings and Recommendations: Document audit findings, including control deficiencies, vulnerabilities, and areas of non-compliance. Provide clear and concise recommendations for addressing identified issues. Determine that findings are well-supported by evidence and include appropriate context to facilitate understanding and action by management.
- Communication and Collaboration: Maintain open communication and collaborate with relevant stakeholders throughout the audit process. Engage with management, IT teams, and other relevant departments to gather information, clarify findings, and discuss recommendations. Foster a collaborative environment to facilitate the implementation of audit recommendations.
- Follow-Up and Monitoring: Monitor the implementation of audit recommendations and track progress over time. Conduct follow-up audits to assess the effectiveness of corrective actions taken . Continuously monitor the IT environment for emerging risks and changes that may impact the effectiveness of controls.
- Continuous Learning and Improvement: Engage in continuous learning and professional development (such as security awareness training ) to stay updated with evolving IT risks, technologies, and best practices. Incorporate lessons learned from previous audits into future engagements to improve the effectiveness and efficiency of the audit process.
- Maintaining IT Audit Records: The responsibility for maintaining these records rests with the organization’s internal audit function, IT department, or a dedicated compliance team, depending on the organizational structure and policies in place.
By following these best practices, organizations can conduct robust and value-added IT audits that provide meaningful insights, drive improvements, and support the organization’s overall risk management and governance objectives.
In an era dominated by technology, IT audits have become an indispensable tool for organizations. They provide a comprehensive assessment of an organization’s IT systems, help identify vulnerabilities, and recommend measures to strengthen security, compliance, and operational efficiency. By investing in regular IT audits, businesses can stay ahead of emerging risks, protect their valuable assets, and determine the seamless functioning of their technology infrastructure.
If you’re looking for more information on IT Audits and SOC 2 compliance, check out our website and blog . We have a wealth of articles about this topic, from preparedness tips and why it’s important for startups as well as how to get started if your company needs help meeting these requirements!
If you are interested in engaging our auditing services or have any questions, please feel free to contact us and our team of audit professionals at Linford & Co .

Umar has over 15 years of experience in internal control-based audit, project management, cybersecurity consulting, attestation, and assurance services; 7 of those years were with the “Big Four” accounting firm, KPMG. He has overseen numerous SOC 1 and SOC 2 audits and other IT Compliance audits, including NIST 800-53. He has vast experience implementing comprehensive IT compliance frameworks for clients both in the public and private sectors. Umar is a certified information systems auditor (CISA) and received his Bachelor of Science degree in Business Information Technology from Virginia Tech.
Related Posts:
- SOC for Supply Chain: Professional Guidance for Supply Chain Audits
- How to Maintain Your HITRUST Certification: Professional Guidance
- SOC 2 Considerations for SaaS Providers from an Audit Professional
- Enhancing Your Company’s AI Security Policy - Professional Insights
- Navigating SOC 2 Scope for a Successful Audit - Professional Insights
- Audit Readiness – Professional Tips for a Successful Audit

Due to recent expansions in US sanctions against Russia and Belarus as well as existing country-level sanctions in Iran, North Korea, Syria, Cuba, and the Crimea region (each a “sanctioned country”), Zapier will no longer be able to provide services in any sanctioned country starting September 12, 2024. These sanctions prohibit US companies from offering certain IT and enterprise software services in a sanctioned region.
Starting September 12, 2024, Zapier customers will no longer be able to access Zapier services from a sanctioned country. We understand this may be inconvenient and appreciate your understanding as we navigate these regulatory requirements.
- Contact sales
Start free trial
IT Audit: Definition & Quick Guide (Checklist Included)

If you’re running a business or managing a project, the impact of a cybercriminal on your company can be catastrophic. They can steal customer data and ruin your reputation. It’s something many don’t recover from. And, unlike in the physical world, where bad neighborhoods are more clearly demarcated, IT risks can be like a trojan horse. They can appear friendly, but when your guard is down they ransack your data.
The threat can be internal, too, such as a disgruntled employee sabotaging everything you built for years in seconds. Bottom line: technology is useful, but it’s also vulnerable. That’s why organizations must do an IT audit to make sure their data and network are safe from attack. An IT security audit might be the only thing standing between success and failure.
What Is an IT Audit?
Audits sound bad. Nobody wants to get that letter announcing the IRS is about to open an audit on your financials. But an audit only means an official inspection of one’s accounts. An information technology audit is therefore an official examination of the IT infrastructure, policies and operations of an organization. It also adds an evaluation, to suggest improvements. IT audits have been going on since the mid-1960s and continuously evolved since that point as technology advances. It’s an important part of a good IT project management procedure.
You can think of this as an IT security audit. The point is to see if the IT controls in place are properly protecting the company’s assets, ensuring the integrity of the data, and staying in line with the goals and objectives of the company. This means that everything that involves IT is inspected, from physical security to the overall business and financial concerns.

Why Is It Important to Conduct an IT Audit?
An IT audit is crucial to guarantee that the IT operations, controls, infrastructure and processes of a company are safe from threats and working as intended. The main objective of an IT audit is to find areas of improvement and vulnerabilities to reduce the chances of IT risks and remain compliant with IT security standards. In addition to this key objective, there are other benefits from conducting regular IT audits, such as:
- Improving existing IT service management policies, guidelines and processes to better adjust to the business objectives of the organization.
- Finding new technologies such as software, hardware or networking that could help companies better store, manage and transfer their business data.
- Obtaining certifications such as SOC 2 allows companies to offer their products and services to new markets.
- Ensure employees across departments understand the IT best practices of the company.
- Avoid regulatory fines or potential business losses due to ineffective IT security practices.
Types of IT Audits
In broad strokes, an IT audit can be broken into two types; general control review and application control review. But, if you want to get more specific, here are five categories of a well-executed audit.
- Systems & applications: This focuses on the systems and applications within an organization. It makes sure they are appropriate, efficient, valid, reliable, timely and secure on all levels of activity.
- Information processing facilities: Verifies that the process is working correctly, timely and accurately, whether in normal or disruptive conditions.
- Systems development: To see if those systems that are under development are being created in compliance with the organization’s standards.
- Management of IT and enterprise architecture: Making sure that IT management is structured and processes in a controlled and efficient manner.
- Client/server, telecommunications, intranets and extranets: This spotlights telecommunication controls, such as a server and network, which is the bridge between clients and servers.All of this can be expedited with the help of IT project management software .
What Is an IT Auditor?
An IT auditor is responsible for inspecting the internal controls and risks associated with an organization’s IT infrastructure. Some of the main responsibilities of an IT auditor are identifying weaknesses, vulnerabilities and threats and suggesting solutions to prevent security breaches.
IT auditors help organizations meet security standards, obtain certifications and improve how data is managed. There are certifications for this skill, such as certified information system auditor (CISA) and certified information systems security professionals (CISSP).
IT Audit Process: How to Do an IT Audit
In a sense, an IT audit is a project and like any project, it involves planning , scheduling, reporting and tracking activities. Here’s a quick overview of each of the steps of the IT audit process.
1. Plan Your IT Audit
An IT audit is a thorough process so you need to plan carefully. Without a solid action plan , your audit might not achieve its key purpose which is to accurately find flaws, inefficiencies and vulnerabilities in the IT environment of your organization. To plan your IT audit there are several steps you and your team should go through. Here are some of the most important of them.
- Select an IT auditor, it could be an in-house internal auditor or an external firm
- Set goals and objectives for your IT audit
- Define the scope of your IT audit
- Decide if your IT audit will be recurrent and if so, how often it will be conducted
- Define a timeframe for your IT audit as well as a detailed schedule to inspect each area of your IT department
- Establish roles and responsibilities for your employees as the audit is executed to make sure they’re on the same page
- Create an IT audit plan to make sure stakeholders understand the IT audit scope, objectives and schedule
2. Execute the IT Audit
Once you have a solid IT audit plan, you can move on to the execution phase of your audit. During this phase, team management is key to making sure your IT department and any other employees and stakeholders involved collaborate with the IT auditor so that everything goes according to plan and the IT audit can be completed on time.
Related: IT project management templates
3. Make IT Audit Reports
As explained above, an IT audit is a process that seeks to find inefficiencies, vulnerabilities, threats and opportunities for improvement for your business’ IT operations, so documenting these findings is key for success. Once the IT audit is complete, it is critical to create a thorough audit report that compiles all the observations and suggestions from the IT auditor. This is one of the most important steps of any audit, as the findings are only useful to the organization if they’re well documented.
4. Follow Up
Ideally, the IT audit report should be an informative document with lots of suggestions to improve how your company manages its IT practices. Now, it’s time to plan how to put the audit findings into practice by taking actions such as training employees, procuring assets and implementing IT risk management frameworks .
IT Audit Checklist
Now that we’ve defined the major steps of the IT auditing process, let’s review some of the key areas that should be inspected during an IT audit.
IT Security Controls
- Antivirus software
- Network firewall
- Passwords encryption
- Two-factor authentication
- Physical security measures
- Unauthorized access alerts
- Employee IT security training
Standards & Procedures
- Employees are required to sign IT security acknowledgment agreements
- IT assets are disposed of safely to avoid data breaches
- Documents with sensitive data are shredded or disposed of safely
- Data backups are done and reviewed frequently
- Data is backed up in multiple locations
- There’s a well-defined IT disaster recovery plan
Documentation & Reporting
- Security protocols are well-documented
- Security protocols are updated as IT infrastructure changes
- IT logs are safely stored and reviewed frequently
- IT incidents are documented thoroughly
Performance Monitoring
- Outage events are recorded
- Hard drive, RAM and cloud storage are monitored
- Network performance is measured consistently
- IT expenses are tracked and minimized
Systems Development
- There are clear guidelines for managing the system design and development process
- System testing protocols are established
- There’s a post-implementation review process in place
While the items outlined above are a good starting point, there are many more variables that you should consider when planning and executing your IT audit so that it adjusts to the particular needs of your organization.

IT Audit Best Practices
The process of conducting an IT audit is complex and touches on all aspects of your information system. There are overreaching general management issues and policies to consider. There’s also security architecture and design, systems and networks, authentication and authorization and even physical security. It involves continuity planning and disaster recovery , like any good risk management.
There are, too, some overriding best practices that can steer you through the maze, so you start and finish effectively. These five tips will help you conduct an IT security audit properly.
- Scope: By knowing the scope of the audit ahead of time, you’re more likely to have an audit that runs without problems. For one thing, you’ll want to involve all relevant stakeholders when planning. Speak to those who are working in the IT environment. They can help you understand what risks you’re looking to identify and understand the current capabilities of the system. This way you’ll have a better idea if there’s a need to adopt new technologies or not. Also, know the applicable laws and regulations to make sure you’re compliant.
- Outside resources: You might have a team assembled in-house who are able to run the IT security audit themselves or you might need to seek outside contractors to help with parts or the whole thing. This must be determined beforehand. You might have an IT audit manager or need to hire a consultant, who can then train the team on what to keep an eye out for in-between IT audits.
- Implementation: Know the inventory you have and put these systems down in a list organized by priority. Know industry standards, methods and procedures to make sure you’re keeping up with the most current practices. Evaluate your audit to see if assets are protected and risks mitigated.
- Feedback: IT audit reports can feel like they’re in a different language if you’re not an IT professional. For the audit to be effective, the audit must be clear to those who are decision-makers. The IT auditor should give the report in person and field any questions so that when done there is no question about the work and whatever vulnerabilities were discovered.
- Repeat: An IT audit isn’t a one-time event, of course, but in between audits there is still work to do. That includes offering recommendations going forward and using IT software that can automatically monitor systems, users and assets. It’s a good idea to have a plan set up to review applicable laws, regulations and new developments quarterly, as the technology space is notoriously fast-moving.
How ProjectManager Facilitates the IT Audit Process
When doing an IT audit, there are many tasks that probably require a team to execute. Sounds like a project. While there are software packages that are designed to monitor IT security, an audit is a different animal and can benefit from a project management software to control it effectively.
Every audit can be broken down into a series of tasks, just as you use a work breakdown structure (WBS) to take a large project and break it up into smaller, more manageable pieces. A task list can be prioritized and then that spreadsheet uploaded into ProjectManager, where it’s transformed from a static sheet to a dynamic tool.
Visualize the Workflow With Kanban Boards
Once imported, the task list can be viewed in a variety of ways. There is the kanban view to manage workflows. The various tasks are individual cards, which are organized by columns that state whether the work is to be started, in progress or done. These cards can be assigned to one or more team members, who can comment directly on them to collaborate. Files and images can also be attached.
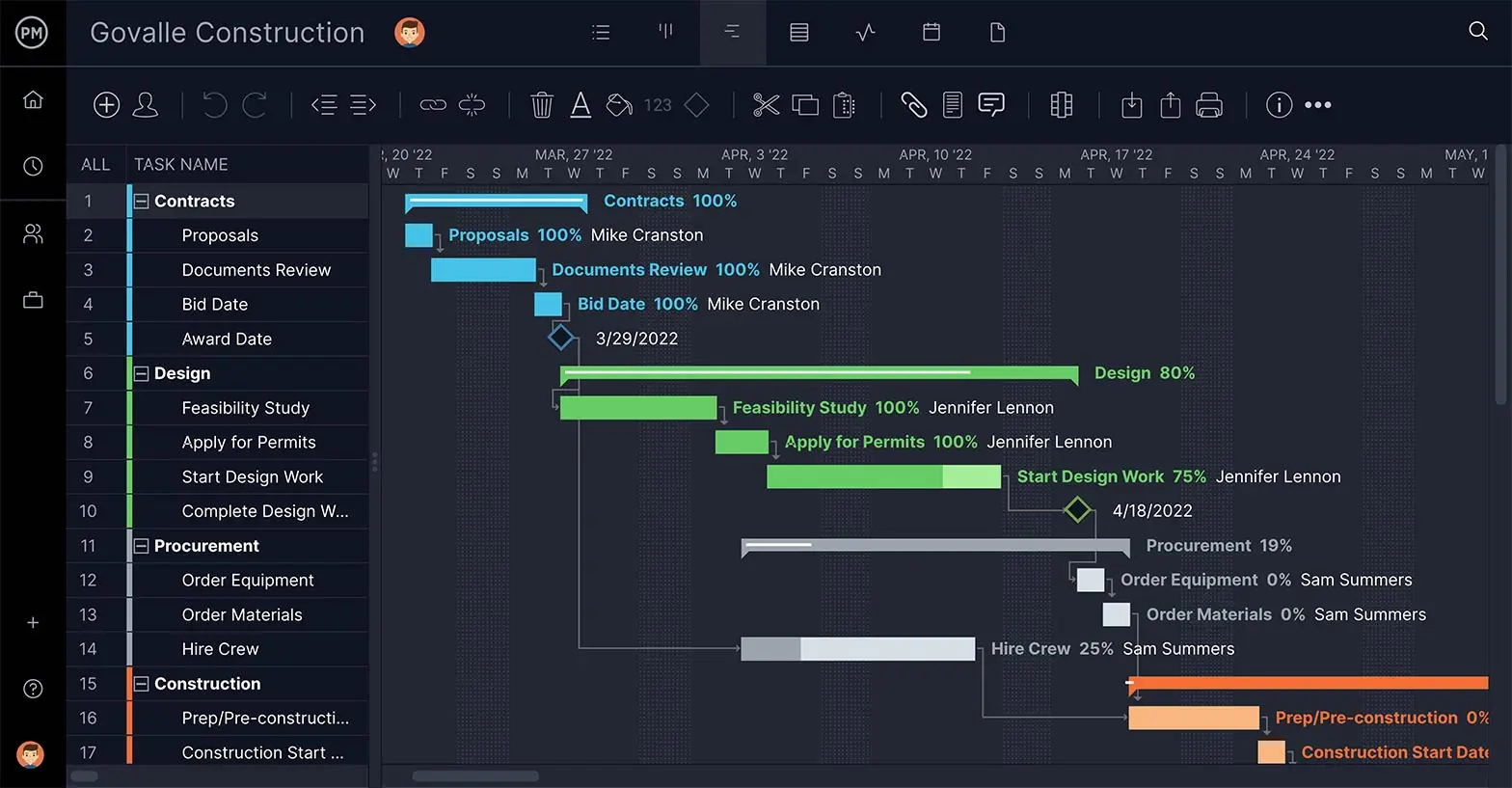
Make an Audit Schedule With Gantt Charts
Another view is the Gantt chart . This shows your task list to the left and populates those tasks across a timeline to the right. The tasks can again be assigned, collaborated on and tracked. ProjectManager is a cloud-based software, so all status updates are instantly reflected. Task dependencies can be linked to avoid blocking team members and if deadlines need to change that can be done with a simple drag and drop of the task timeline.
Project Dashboards for Monitoring the Audit
In terms of monitoring the progress of the IT security audit and reporting back to management, ProjectManager has a real-time dashboard . It keeps the project leader abreast of what’s going to and crunches the numbers automatically, displaying project metrics in clear and colorful graphs and charts. These can then be filtered to reflect the data you want and shared or printed out for a presentation.

ProjectManager also has many free templates to assist with various phases of any project. Our IT risk assessment template is a great place to start when doing an IT audit.
Information technology is part of almost every organization. The benefits are great, but so are the risks. ProjectManager is a cloud-based project management software that helps IT professionals manage the complex tasks involved in an IT audit. Try it free today with this 30-day trial.

Deliver your projects on time and on budget
Start planning your projects.

Conducting An IT System Audit
Auditing your IT system is essential in ensuring the security and efficiency of your business operations. However, the process can be complex and overwhelming. This guide will provide a comprehensive overview of conducting an IT system audit, including tips for streamlining the process and identifying potential security risks.
Define the scope and objectives of the audit.
Before beginning an IT system audit, it’s essential to define the scope and objectives of the audit. This will help you determine what areas of your IT system need to be audited and what specific goals you want to achieve. Some common objectives of an IT system audit include identifying security vulnerabilities, assessing system performance, and ensuring compliance with industry regulations. Once you have a clear understanding of the scope and objectives of the audit, you can begin to plan and execute the audit process.
Identify all hardware and software assets.
The first step in an IT system audit is identifying your organization’s hardware and software assets. This includes servers, workstations, laptops, mobile devices, printers, routers, switches, and other devices connected to your network. You should also identify all software applications and systems used within your organization, including operating systems, databases, and business applications. This information will help you understand the scope of your IT system and ensure that all assets are accounted for during the audit process.
Assess the security of your systems.
Once you have identified all hardware and software assets within your organization, the next step is to assess the security of your systems. This includes evaluating the effectiveness of your current security measures, such as firewalls, antivirus software, and intrusion detection systems. You should also review your organization’s security policies and procedures to ensure they are up-to-date and effective. You are identifying any vulnerabilities or weaknesses in your systems and addressing them before cybercriminals can exploit them. Regular security assessments are critical to maintaining the security of your IT systems and protecting your organization from cyber threats.
Evaluate the effectiveness of your backup and disaster recovery plans.
One crucial aspect of conducting an IT system audit is evaluating the effectiveness of your backup and disaster recovery plans. This includes reviewing your backup procedures, such as how often backups are performed and where they are stored, and testing your disaster recovery plan to ensure it can effectively restore your systems during a disruption. Identifying gaps or weaknesses in your backup and disaster recovery plans and addressing them is essential to minimize the impact of any potential data loss or system downtime.
Review your IT policies and procedures.
Another critical aspect of an IT system audit is reviewing your organization’s IT policies and procedures. This includes evaluating your security policies, such as password requirements and access controls, as well as your data retention and disposal policies. Ensuring that your policies and procedures are up-to-date and aligned with industry best practices is essential to minimize the risk of security breaches and data loss. Additionally, reviewing your policies and procedures can help identify areas where employee training may be necessary to ensure compliance and reduce the risk of human error.
A Comprehensive Guide to Conducting an Effective IT System Audit
In today’s fast-paced and technology-driven world, conducting regular audits of your IT systems is more critical than ever. But where do you start? How do you ensure that your audit is practical and comprehensive? This guide will take you through the step-by-step process of conducting an IT system audit, giving you the tools and knowledge you need to assess the health and security of your systems.
Whether you are a small business or a large enterprise, understanding the intricacies of your IT infrastructure is vital for optimization and risk management. From evaluating hardware and software to analyzing network security, this guide will help you gain a holistic view of your IT systems and identify areas for improvement.
Following the best practices outlined in this comprehensive guide can uncover potential vulnerabilities, streamline operations, and ensure compliance with industry standards. Conducting an effective IT system audit is essential for any organization serious about protecting its digital assets and staying ahead in an increasingly competitive landscape.
Don’t wait for a security breach or data loss to take action. Dive into this guide and equip yourself with the knowledge to conduct an effective IT system audit today .
Steps involved in conducting an IT system audit
Ensuring the health and security of your IT systems should be a top priority for any organization. Conducting regular IT system audits plays a crucial role in achieving this goal. By performing audits, you can identify potential vulnerabilities, assess the effectiveness of your security measures, and make informed decisions to improve your IT infrastructure. Here are some key reasons why conducting IT system audits is so important:
1. Identifying vulnerabilities: IT systems are constantly exposed to various threats, such as cyberattacks, system failures, and data breaches. By conducting audits, you can identify and proactively address vulnerabilities before they become significant issues.
2. Optimizing performance: Auditing your IT systems allows you to evaluate their performance and identify areas for optimization. Reviewing hardware, software, and network components can identify bottlenecks, streamline operations, and improve efficiency.
3. Ensuring compliance: Compliance with industry and regulatory standards is essential for organizations of all sizes. Conducting IT system audits helps ensure that your systems align with the required standards, reducing the risk of penalties, legal issues, and reputational damage.
4. Enhancing data security: Data breaches can have severe financial and reputation consequences. Auditing your IT systems enables you to assess the effectiveness of your security measures, identify potential weaknesses, and implement appropriate safeguards to protect sensitive data.
5. Planning for the future: By conducting regular IT system audits, you can develop a roadmap for the future. Audits provide valuable insights into the current state of your IT infrastructure, allowing you to plan for upgrades, expansions, and technology advancements.
Now that we understand the importance of conducting IT system audits let’s examine the step-by-step process of completing an effective audit.
Assessing IT infrastructure and network security
Conducting an IT system audit may seem daunting, but breaking it down into manageable steps can simplify the process. Here is a step-by-step guide to help you achieve an effective IT system audit:
Step 1: Assessing IT Infrastructure and Network Security
The first step in conducting an IT system audit is to assess your organization’s IT infrastructure and network security. This involves evaluating the hardware, software, and network components that make up your IT systems. Here are some key areas to focus on during this assessment:
1. Hardware evaluation: Assess the condition, performance, and capacity of your servers, workstations, routers, switches, and other hardware components. Identify any outdated or underperforming equipment that may need to be upgraded or replaced.
2. Software evaluation: Evaluate your organization’s software applications and operating systems. Check for outdated versions, security patches, and compatibility issues. Ensure that all software is licensed correctly and up to date.
3. Network security assessment: Analyze your network infrastructure for potential vulnerabilities. Review firewall configurations, intrusion detection systems, access controls, and encryption protocols. Identify any security gaps and implement appropriate measures to mitigate risks.
Step 2: Evaluating IT Asset Management Processes
Effective IT asset management is crucial for organizations to optimize resources, control costs, and ensure compliance. During the audit, evaluate your IT asset management processes to ensure they are efficient and effective. Here are some key aspects to consider:
1. Inventory management: Maintain an accurate inventory of all hardware and software assets. Check if the inventory is current, including information such as asset location, ownership, and lifecycle status. Implement automated tools to streamline asset tracking.
2. License management: Ensure all software licenses are appropriately documented and comply with licensing agreements. Verify that the number of permits matches the actual usage. Identify any unauthorized software installations and take appropriate action.
3. Asset disposal: Establish a process for properly disposing of retired or obsolete IT assets. Ensure that data is securely erased from storage devices and that hardware is disposed of in an environmentally friendly manner. Maintain records of asset disposal.
Step 3: Reviewing Data Backup and Disaster Recovery Plans
Data loss can have catastrophic consequences for organizations. Therefore, reviewing your data backup and disaster recovery plans during the IT system audit is crucial. Here are some key aspects to consider:
1. Data backup procedures: Evaluate your data backup procedures to ensure that critical data is regularly and securely backed up. Check the backup frequency, storage locations, and recovery procedures. Test the data restoration process periodically.
2. Disaster recovery plans: Assess your organization’s plans to ensure they are comprehensive and current. Determine if the plans include procedures for data recovery, system restoration, and alternative infrastructure options in case of a disaster.
3. Business continuity: Review your business continuity plans to ensure they align with your IT systems. Identify critical systems and processes that need to be prioritized during a disruption. Test the effectiveness of your business continuity plans regularly.
Step 4: Analyzing IT System Vulnerabilities and Risks
Identifying vulnerabilities and risks is a crucial part of an IT system audit. By conducting vulnerability assessments and risk analyses, you can understand the potential threats and take appropriate measures to mitigate them. Here are some critical steps to follow:
1. Vulnerability scanning: Use automated vulnerability scanning tools to identify potential weaknesses in your systems. Scan your network, servers, and applications for known vulnerabilities. Regularly update and patch software to address any identified vulnerabilities.
2. Risk assessment: Evaluate the impact and likelihood of potential risks to your IT systems. Identify threats such as unauthorized access, data breaches, malware attacks, and system failures. Prioritize risks based on their severity and likelihood of occurrence.
3. Risk mitigation: Develop and implement strategies based on the identified vulnerabilities and risks. This may involve implementing additional security measures, updating policies and procedures, or enhancing employee training programs.
Step 5: Conducting Software and Hardware Inventory Audits
Maintaining an accurate inventory of software and hardware assets is crucial for effective IT system management. As part of the audit, conduct software and hardware inventory audits to ensure that all assets are properly documented and accounted for. Here are some critical steps to follow:
1. Software inventory audit: Create a comprehensive list of all software applications used within your organization. Verify the licensing information, version numbers, and installation locations. Identify any unauthorized or unlicensed software.
2. Hardware inventory audit: Document all hardware assets, including servers, workstations, laptops, and peripherals. Record information such as make, model, serial numbers, and location. Identify any missing or unaccounted-for hardware.
3. Asset reconciliation: Compare the software and hardware inventories with the purchases, licenses, and warranties records. Resolve any discrepancies and update the inventory records accordingly. Implement procedures to ensure the inventory’s ongoing accuracy.
Step 6: Assessing IT Governance and Compliance
Effective IT governance and compliance are essential for organizations to ensure the alignment of IT initiatives with business objectives and regulatory requirements. During the audit, assess your organization’s IT governance and compliance practices. Here are some key aspects to consider:
1. Policy and procedure review: Evaluate the effectiveness of your IT policies and procedures. Ensure they are current, comprehensive, and aligned with industry best practices and regulatory requirements.
2. Compliance assessment: Determine if your organization complies with relevant laws, regulations, and industry standards. Conduct internal audits to identify any compliance gaps and take appropriate remedial actions.
3. Risk management: Evaluate the effectiveness of your organization’s risk management practices. Ensure that risks are identified, assessed, and mitigated systematically. Implement risk management frameworks and processes as needed.
Evaluating IT asset management processes
An effective IT system audit is critical for organizations of all sizes. By following the step-by-step process outlined in this guide, you can assess the health and security of your IT systems, identify areas for improvement, and mitigate potential risks. Regular audits are essential to stay ahead in a rapidly evolving technology landscape.
Investing time and resources in conducting IT system audits is a proactive approach to protecting your digital assets, optimizing performance, and ensuring compliance. Don’t wait for a security breach or data loss to take action. Start conducting regular IT system audits today and safeguard your organization’s future.
Now that you have a comprehensive guide to conducting an effective IT system audit, it’s time to put this knowledge into practice. Continuous improvement is critical, so regularly revisit and update your audit processes to adapt to new technologies and emerging threats. Stay proactive, stay secure, and stay ahead!
Reviewing data backup and disaster recovery plans
Evaluating your organization’s IT asset management processes is crucial when conducting an IT system audit. This involves assessing how assets are acquired, tracked, and disposed of throughout their lifecycle. Effective asset management ensures that your organization clearly understands the hardware and software it owns, its locations and its maintenance schedules.
To start the evaluation, gather information about your existing asset management policies and procedures. Review documentation such as purchase orders, invoices, and asset registers. Identify any gaps or inconsistencies in the data.
Next, assess your asset tracking system. Determine whether it provides accurate and up-to-date information about your assets. Evaluate the effectiveness of your inventory management practices, including how assets are assigned to employees and how they are retired or replaced.
Lastly, review your disposal procedures. Ensure that assets are adequately decommissioned and sensitive data is securely wiped before disposal. By evaluating your IT asset management processes, you can identify areas for improvement and ensure that your organization’s assets are effectively tracked and managed.
Analyzing IT system vulnerabilities and risks
Data loss can have severe consequences for any organization. That’s why reviewing your data backup and disaster recovery plans is essential to an IT system audit. A robust backup strategy ensures that critical data is regularly backed up and can be restored during a data loss incident.
Start by assessing your current backup procedures. Evaluate the frequency of backups, the types of data being backed up, and the storage locations. Determine whether backups are automated and if they are tested regularly to ensure their integrity.
Next, review your disaster recovery plans. Assess the procedures in place for restoring systems and data during a disaster. Evaluate the recovery time objectives (RTOs) and recovery point objectives (RPOs) to ensure they align with your organization’s needs.
Finally, test your backups and disaster recovery plans. Conduct simulated disaster scenarios to evaluate their effectiveness. Identify any weaknesses or bottlenecks in the process and make the necessary improvements.
By reviewing and updating your data backup and disaster recovery plans, you can minimize the risk of data loss and ensure that your organization can quickly recover from any unexpected events.
Conducting software and hardware inventory audits
Assessing IT system vulnerabilities and risks is critical in conducting an effective IT system audit . Vulnerabilities can leave your organization open to cyber-attacks and data breaches, while risks can impact the availability and reliability of your systems.
Start by conducting a vulnerability assessment. Use automated tools or engage the services of a cybersecurity expert to scan your systems for potential weaknesses . Identify vulnerabilities such as outdated software, misconfigured devices, or insecure network connections.
Next, prioritize and remediate the identified vulnerabilities. Develop a plan to address each vulnerability, considering the potential impact and the resources required for remediation. Implement security patches, update software, and configure devices to reduce the risk of exploitation.
Once vulnerabilities are addressed, analyze your organization’s risks. Assess the potential impact of hazards such as hardware failures, power outages, or human errors. Identify the controls and safeguards in place to mitigate these risks.
By analyzing vulnerabilities and risks, you can proactively address security weaknesses and develop strategies to protect your IT systems from potential threats.
Assessing IT governance and compliance
To manage your IT systems effectively, it’s crucial to understand your organization’s software and hardware assets clearly. Conducting software and hardware inventory audits helps you identify outdated or unauthorized software, track license compliance, and ensure that your hardware is properly maintained.
Start by gathering information about your software and hardware assets. Create an inventory list including software versions, license keys, hardware specifications, and purchase dates. Use automated tools to scan your systems and collect accurate data.
Next, compare your inventory list with the actual assets in your organization. Identify any discrepancies, such as unauthorized software installations or unaccounted-for hardware. Determine the root cause of these discrepancies and take appropriate actions to resolve them.
Additionally, review your software license agreements. Ensure you comply with the terms and conditions of your licenses. Identify any unused licenses or opportunities for cost savings through license optimization.
You can maintain control over your IT assets by conducting software and hardware inventory audits , ensuring compliance with licensing requirements, and optimizing your software and hardware investments.
Conclusion and final thoughts
IT governance and compliance are essential for organizations to operate effectively and meet industry standards and regulations. Assessing IT governance helps evaluate the effectiveness of decision-making processes, while compliance ensures adherence to legal and regulatory requirements.
Start by reviewing your organization’s IT governance framework. Evaluate the roles and responsibilities of key stakeholders involved in IT decision-making. Assess the processes for prioritizing IT initiatives, managing risks, and ensuring alignment with business objectives.
Next, assess your organization’s compliance with relevant regulations and standards. Identify the specific requirements applicable to your industry, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) or the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS). Review your organization’s policies and procedures to ensure they meet these requirements.
Additionally, evaluate the effectiveness of your organization’s IT controls. Assess the implementation of security measures, such as access controls, encryption, and monitoring tools. Identify any gaps in your control environment and develop plans to address them.
By assessing IT governance and compliance, you can ensure that your organization’s IT practices align with industry standards, mitigate risks, and maintain the trust of your stakeholders.


IMAGES
COMMENTS
What Is the IT Audit Process & What Should You Expect? The IT audit process typically involves the following 6 phases: Planning and Preparation: The audit process begins with defining the scope and objectives of the audit. This phase involves understanding the organization's IT landscape, identifying critical systems and processes, and determining the audit methodology and timeline.
Audit steps performed and audit evidence gathered; Whether services of other auditors and experts were used and their contributions; Audit findings, conclusions and recommendations; Audit documentation relation with document identification and dates (your cross-reference of evidence to audit step) A copy of the report issued as a result of the ...
The IT checklist above divides common audit tasks into five typical IT buckets we'll explore in the next section in more detail: system security, standards and procedures, documentation and reporting, performance monitoring, and systems development. Keep in mind that a checklist, while essential, isn't sufficient internal documentation for an ...
IT audit is the examination and evaluation of an organization's information technology infrastructure, policies and operations. IT audit can be considered the process of collecting and evaluating evidence to determine whether a computer system safeguards assets,
internal audit to provide assurance over project milestones. the caE should assess the level of skills and knowledge required to perform it audit work and assign appropriate resources. in some cases, external subject matter expertise is needed to properly staff such engagements. necessary steps are discussed in more detail in GTAG 12: Auditing IT
Performance standards (1200 series)—Deal with the conduct of the assignment, such as planning and supervision, scoping, risk and materiality, resource mobilization, supervision and assignment management, audit and assurance evidence, and the exercising of professional judgment and due care.
Project Dashboards for Monitoring the Audit. In terms of monitoring the progress of the IT security audit and reporting back to management, ProjectManager has a real-time dashboard.It keeps the project leader abreast of what's going to and crunches the numbers automatically, displaying project metrics in clear and colorful graphs and charts.
Auditing your IT systems enables you to assess the effectiveness of your security measures, identify potential weaknesses, and implement appropriate safeguards to protect sensitive data. 5. Planning for the future: By conducting regular IT system audits, you can develop a roadmap for the future. Audits provide valuable insights into the current ...
Launch the audit. Brief the IT department team on audit discovery processes, expectations, timeframes, evidence types and interview schedules. Prepare work papers. These may be interview notes, computer screenshots, policy documents, procedures, various reports, prior audit reports and other relevant materials. Prepare and deliver the audit report.
IT Audit Framework (ITAF), 4th Edition. Get the guidance and techniques that will lend consistency and effectiveness to your audits. The new 4th edition of IT Audit Framework (ITAF) outlines standards and best practices aligned with the sequence of the audit process (risk assessment, planning and field work) to guide you in assessing the operational effectiveness of an enterprise and in ...