Free PDF Business Plan Templates and Samples
By Joe Weller | September 9, 2020
- Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn
Link copied
We’ve gathered the most useful collection of business plan PDF templates and samples, including options for organizations of any size and type.
On this page, you’ll find free PDF templates for a simple business plan , small business plan , startup business plan , and more.

Simple Business Plan PDF Templates
These simple business plan PDF templates are ready to use and customizable to fit the needs of any organization.
Simple Business Plan Template PDF

This template contains a traditional business plan layout to help you map out each aspect, from a company overview to sales projections and a marketing strategy. This template includes a table of contents, as well as space for financing details that startups looking for funding may need to provide.
Download Simple Business Plan Template - PDF
Lean Business Plan Template PDF

This scannable business plan template allows you to easily identify the most important elements of your plan. Use this template to outline key details pertaining to your business and industry, product or service offerings, target customer segments (and channels to reach them), and to identify sources of revenue. There is also space to include key performance metrics and a timeline of activities.
Download Lean Business Plan Template - PDF
Simple 30-60-90 Day Business Plan Template PDF

This template is designed to help you develop and implement a 90-day business plan by breaking it down into manageable chunks of time. Use the space provided to detail your main goals and deliverables for each timeframe, and then add the steps necessary to achieve your objectives. Assign task ownership and enter deadlines to ensure your plan stays on track every step of the way.
Download Simple 30-60-90 Day Business Plan Template
PDF | Smartsheet
One-Page Business Plan PDF Templates
The following single page business plan templates are designed to help you download your key ideas on paper, and can be used to create a pitch document to gain buy-in from partners, investors, and stakeholders.
One-Page Business Plan Template PDF
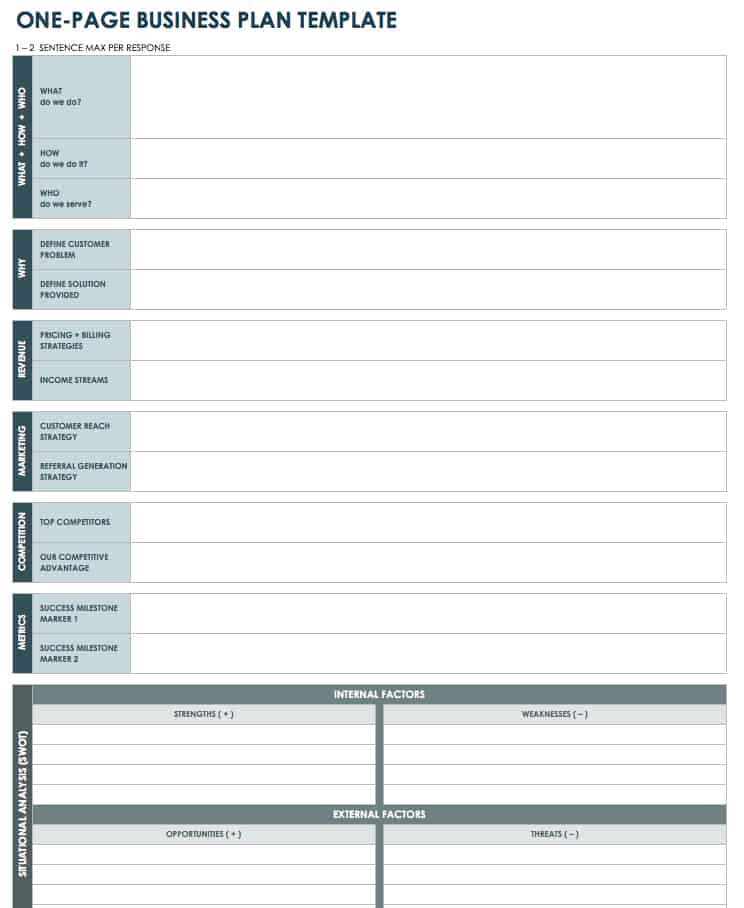
Use this one-page template to summarize each aspect of your business concept in a clear and concise manner. Define the who, what, why, and how of your idea, and use the space at the bottom to create a SWOT analysis (strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats) for your business.
Download One-Page Business Plan Template
If you’re looking for a specific type of analysis, check out our collection of SWOT templates .
One-Page Lean Business Plan PDF

This one-page business plan template employs the Lean management concept, and encourages you to focus on the key assumptions of your business idea. A Lean plan is not stagnant, so update it as goals and objectives change — the visual timeline at the bottom is ideal for detailing milestones.
Download One-Page Lean Business Plan Template - PDF
One-Page 30-60-90 Day Business Plan Template
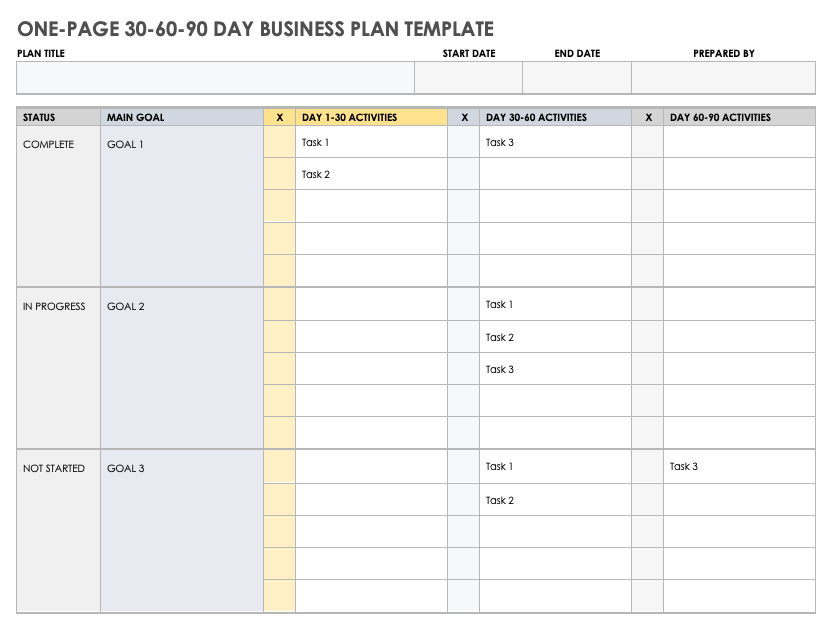
Use this business plan template to identify main goals and outline the necessary activities to achieve those goals in 30, 60, and 90-day increments. Easily customize this template to fit your needs while you track the status of each task and goal to keep your business plan on target.
Download One-Page 30-60-90 Day Business Plan Template
For additional single page plans, including an example of a one-page business plan , visit " One-Page Business Plan Templates with a Quick How-To Guide ."
Small Business Plan PDF Templates
These business plan templates are useful for small businesses that want to map out a way to meet organizational objectives, including how to structure, operate, and expand their business.
Simple Small Business Plan Template PDF
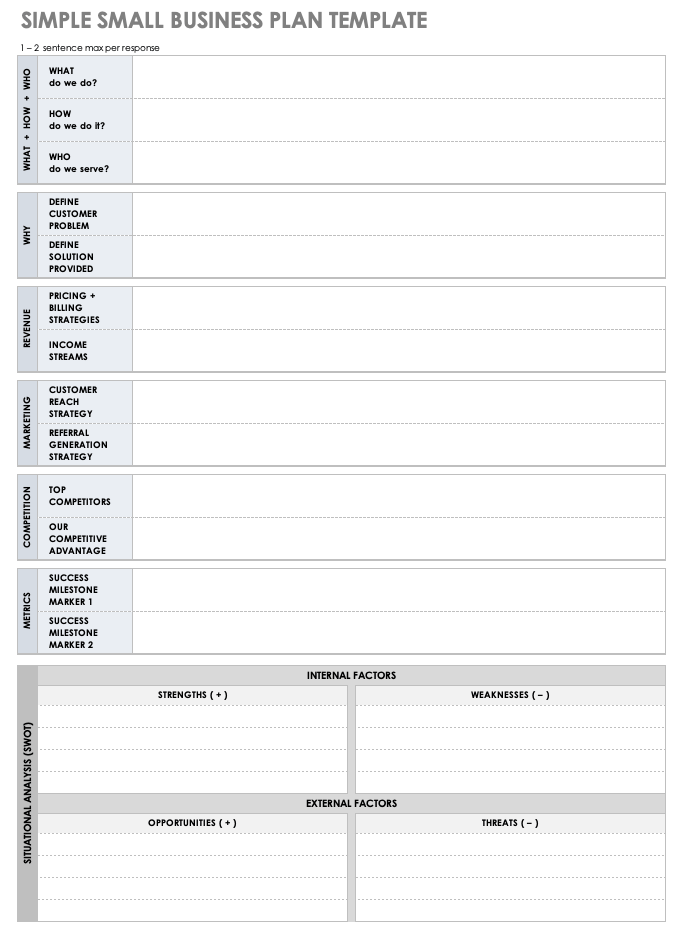
A small business can use this template to outline each critical component of a business plan. There is space to provide details about product or service offerings, target audience, customer reach strategy, competitive advantage, and more. Plus, there is space at the bottom of the document to include a SWOT analysis. Once complete, you can use the template as a basis to build out a more elaborate plan.
Download Simple Small Business Plan Template
Fill-In-the-Blank Small Business Plan Template PDF
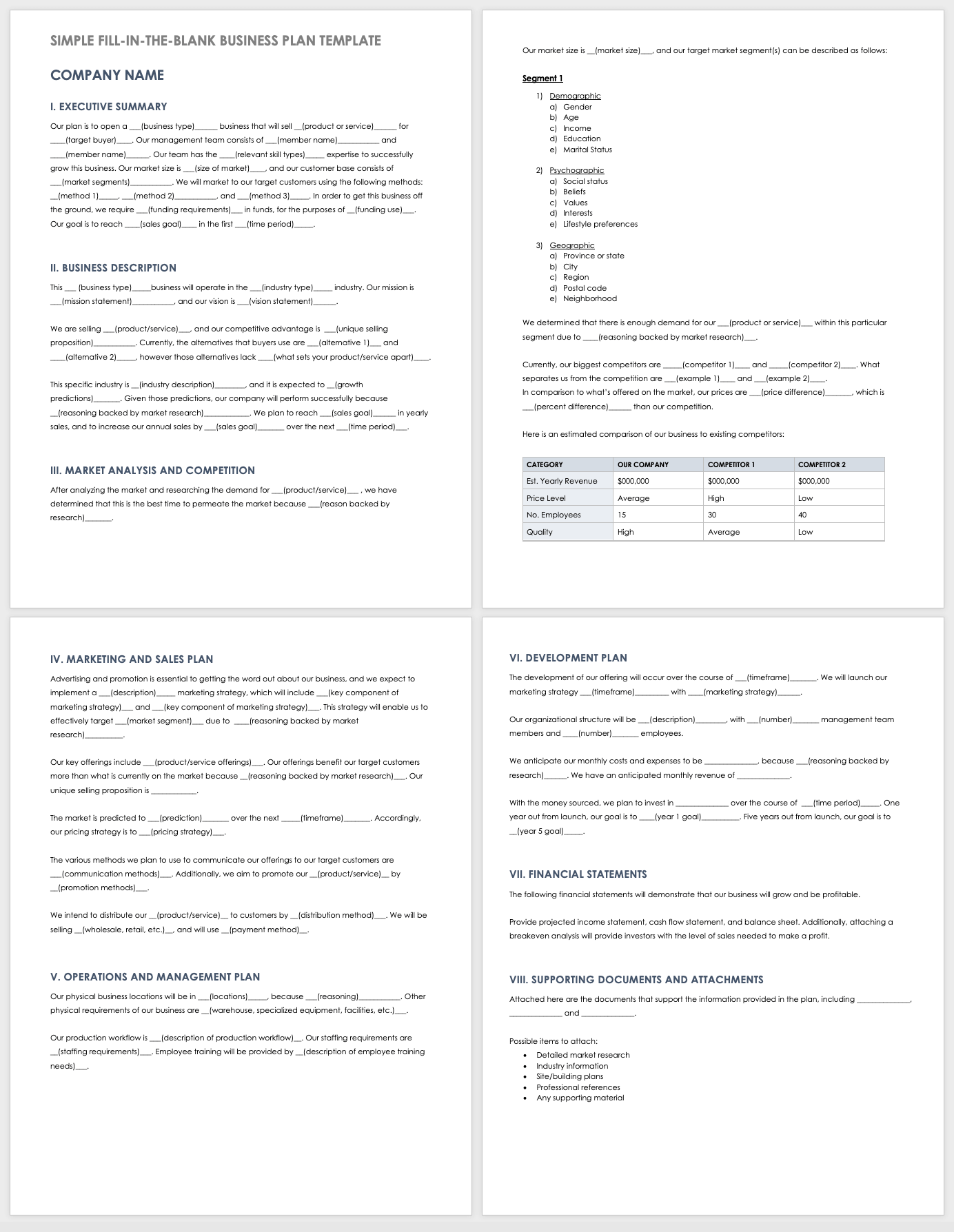
This fill-in-the-blank template walks you through each section of a business plan. Build upon the fill-in-the-blank content provided in each section to add information about your company, business idea, market analysis, implementation plan, timeline of milestones, and much more.
Download Fill-In-the-Blank Small Business Plan Template - PDF
One-Page Small Business Plan Template PDF

Use this one-page template to create a scannable business plan that highlights the most essential parts of your organization’s strategy. Provide your business overview and management team details at the top, and then outline the target market, market size, competitive offerings, key objectives and success metrics, financial plan, and more.
Download One-Page Business Plan for Small Business - PDF
Startup Business Plan PDF Templates
Startups can use these business plan templates to check the feasibility of their idea, and articulate their vision to potential investors.
Startup Business Plan Template
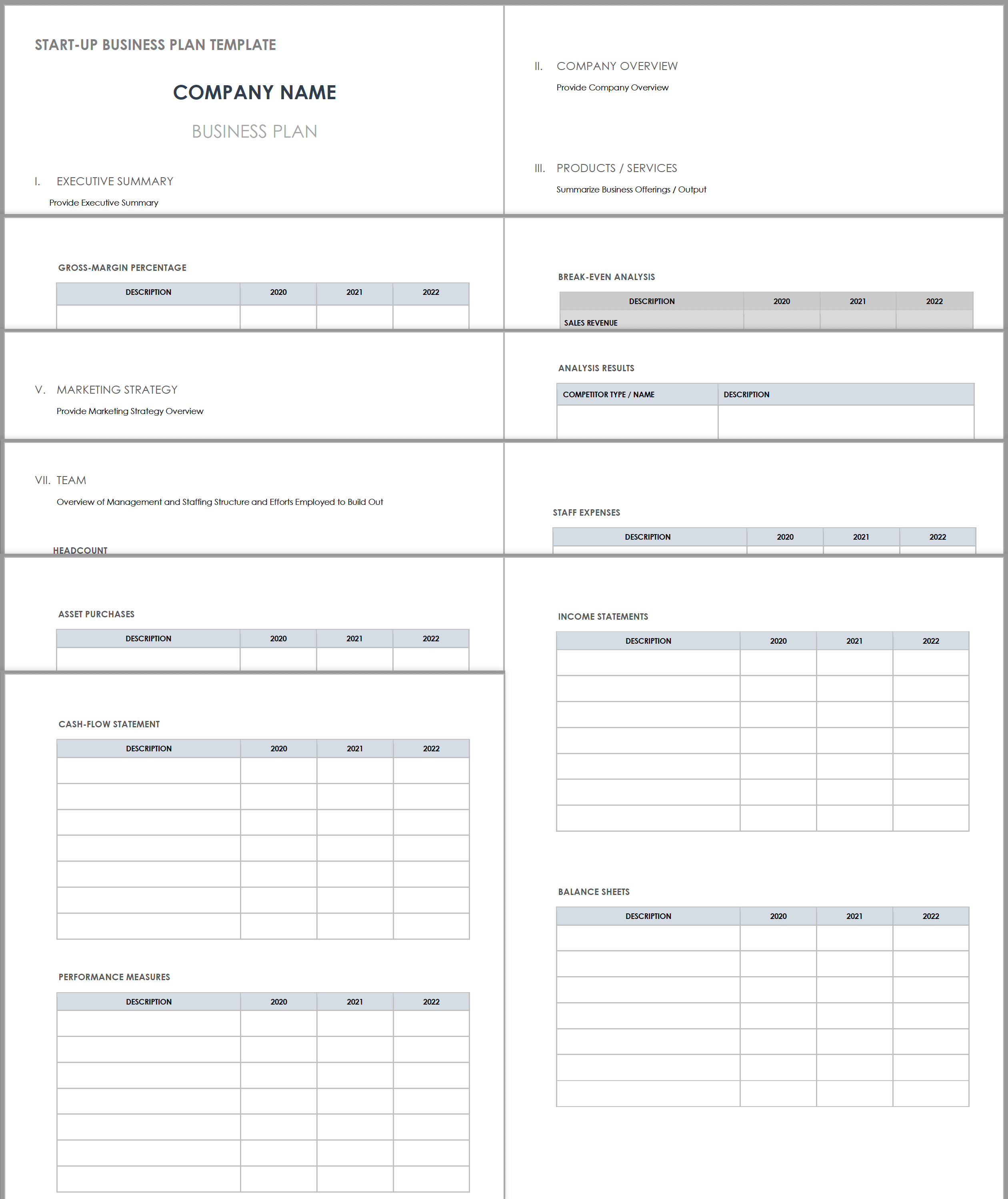
Use this business plan template to organize and prepare each essential component of your startup plan. Outline key details relevant to your concept and organization, including your mission and vision statement, product or services offered, pricing structure, marketing strategy, financial plan, and more.
Download Startup Business Plan Template
Sample 30-60-90 Day Business Plan for Startup
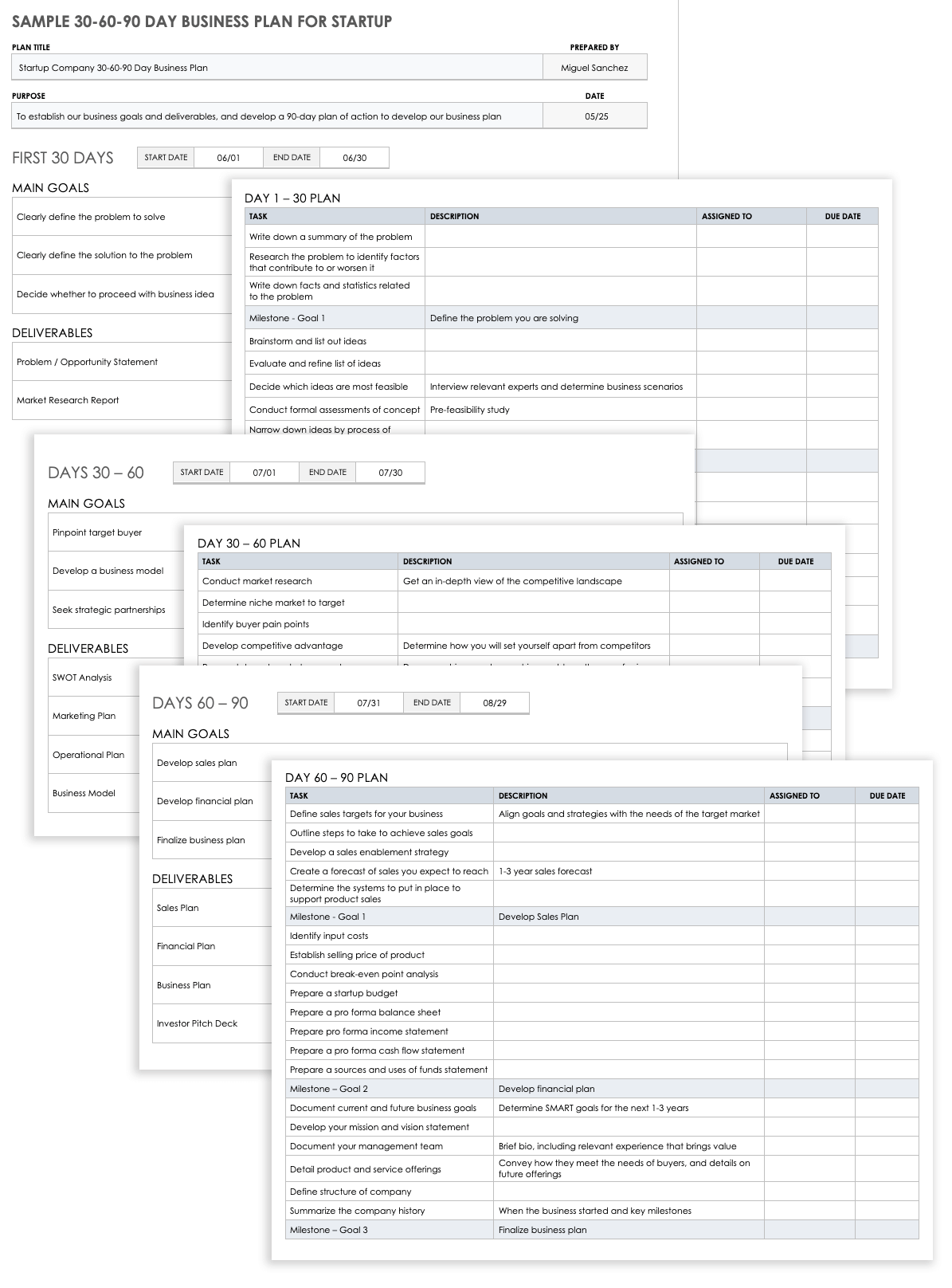
Startups can use this sample 30-60-90 day plan to establish main goals and deliverables spanning a 90-day period. Customize the sample goals, deliverables, and activities provided on this template according to the needs of your business. Then, assign task owners and set due dates to help ensure your 90-day plan stays on track.
Download Sample 30-60-90 Day Business Plan for Startup Template
For additional resources to create your plan, visit “ Free Startup Business Plan Templates and Examples .”
Nonprofit Business Plan PDF Templates
Use these business plan PDF templates to outline your organization’s mission, your plan to make a positive impact in your community, and the steps you will take to achieve your nonprofit’s goals.
Nonprofit Business Plan Template PDF
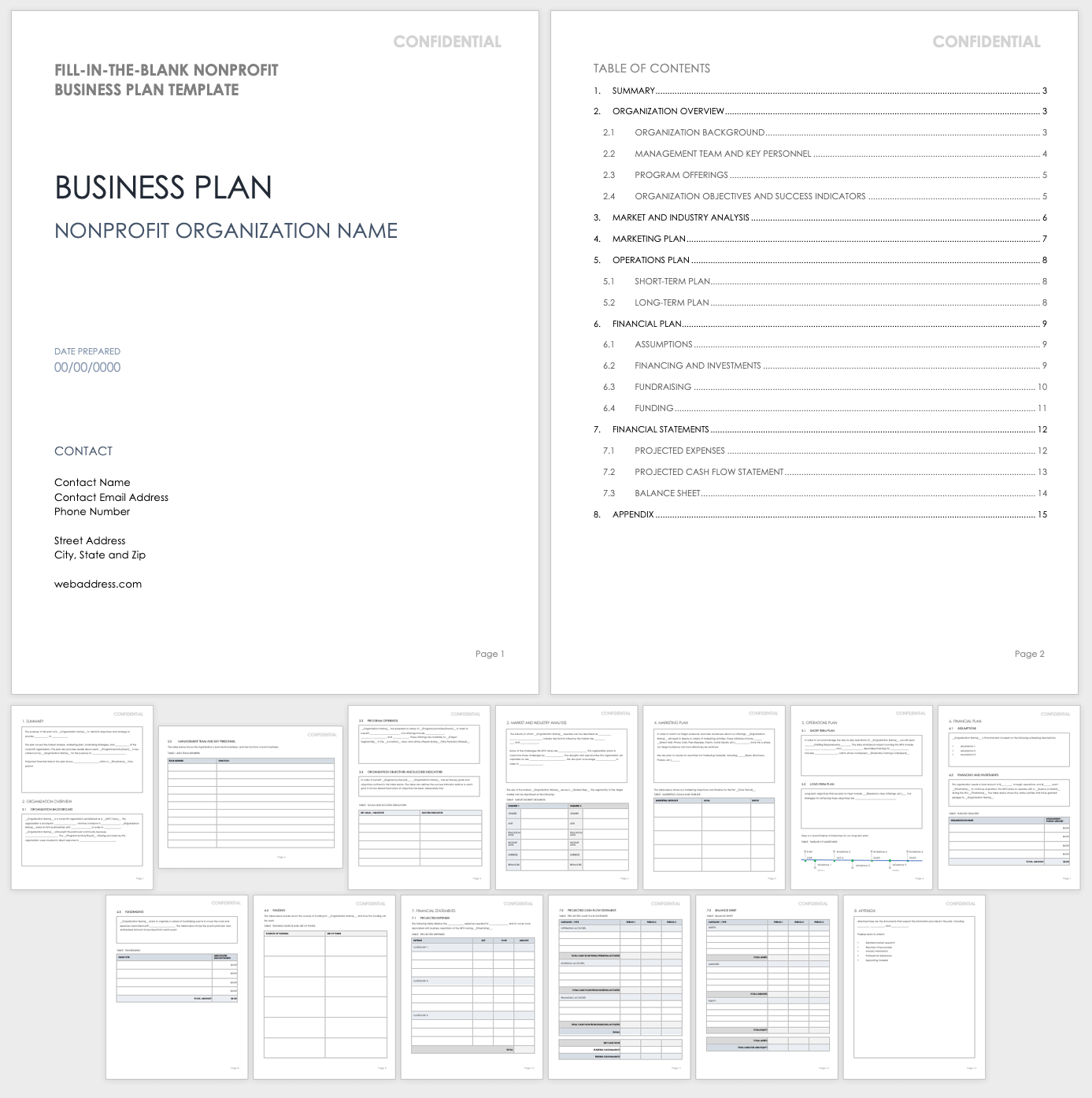
Use this customizable PDF template to develop a plan that details your organization’s purpose, objectives, and strategy. This template features a table of contents, with room to include your nonprofit’s mission and vision, key team and board members, program offerings, a market and industry analysis, promotional plan, financial plan, and more. This template also contains a visual timeline to display historic and future milestones.
Download Nonprofit Business Plan Template - PDF
One-Page Business Plan for Nonprofit Organization PDF
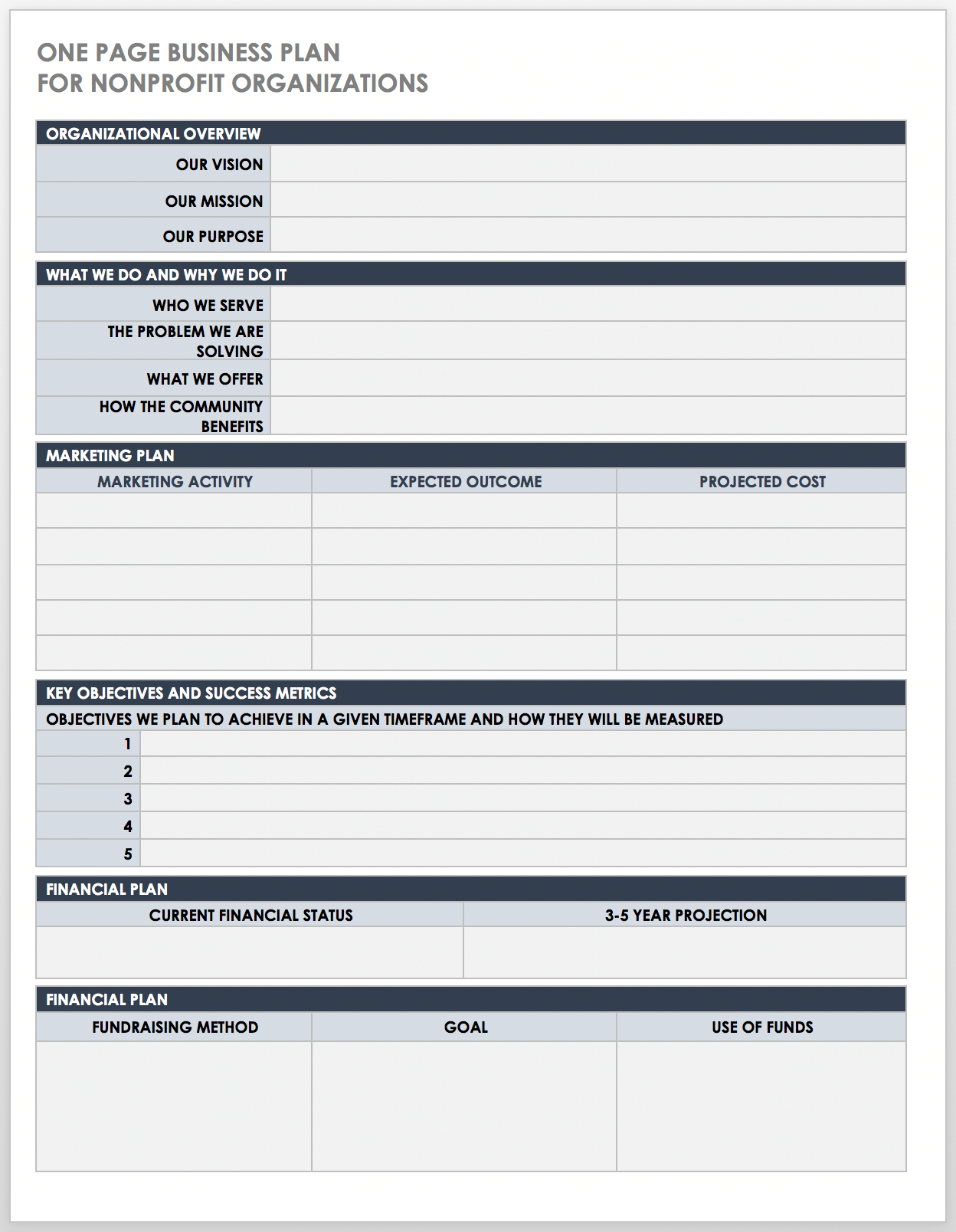
This one-page plan serves as a good starting point for established and startup nonprofit organizations to jot down their fundamental goals and objectives. This template contains all the essential aspects of a business plan in a concise and scannable format, including the organizational overview, purpose, promotional plan, key objectives and success metrics, fundraising goals, and more.
Download One-Page Business Plan for Nonprofit Organization Template - PDF
Fill-In-the-Blank Business Plan PDF Templates
Use these fill-in-the-blank templates as a foundation for creating a comprehensive roadmap that aligns your business strategy with your marketing, sales, and financial goals.
Simple Fill-In-the-Blank Business Plan PDF
The fill-in-the-blank template contains all the vital parts of a business plan, with sample content that you can customize to fit your needs. There is room to include an executive summary, business description, market analysis, marketing plan, operations plan, financial statements, and more.
Download Simple Fill-In-the-Blank Business Plan Template - PDF
Lean Fill-In-the-Blank Business Plan PDF
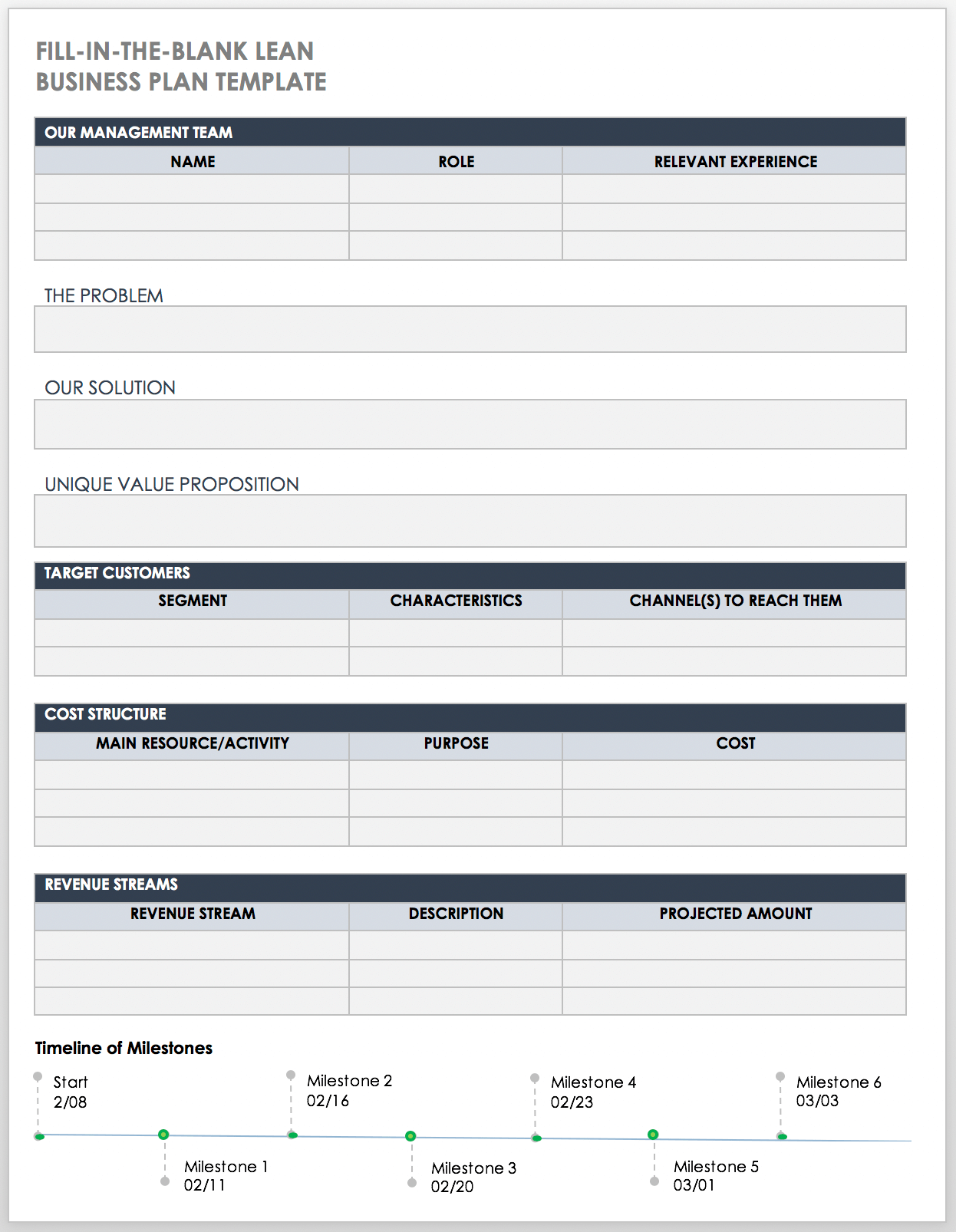
This business plan is designed with a Lean approach that encourages you to clarify and communicate your business idea in a clear and concise manner. This single page fill-in-the-blank template includes space to provide details about your management team, the problem you're solving, the solution, target customers, cost structure, and revenue streams. Use the timeline at the bottom to produce a visual illustration of key milestones.
Download Fill-In-the-Blank Lean Business Plan Template - PDF
For additional resources, take a look at " Free Fill-In-the-Blank Business Plan Templates ."
Sample Business Plan PDF Templates
These sample business plan PDF templates can help you to develop an organized, thorough, and professional business plan.
Business Plan Sample
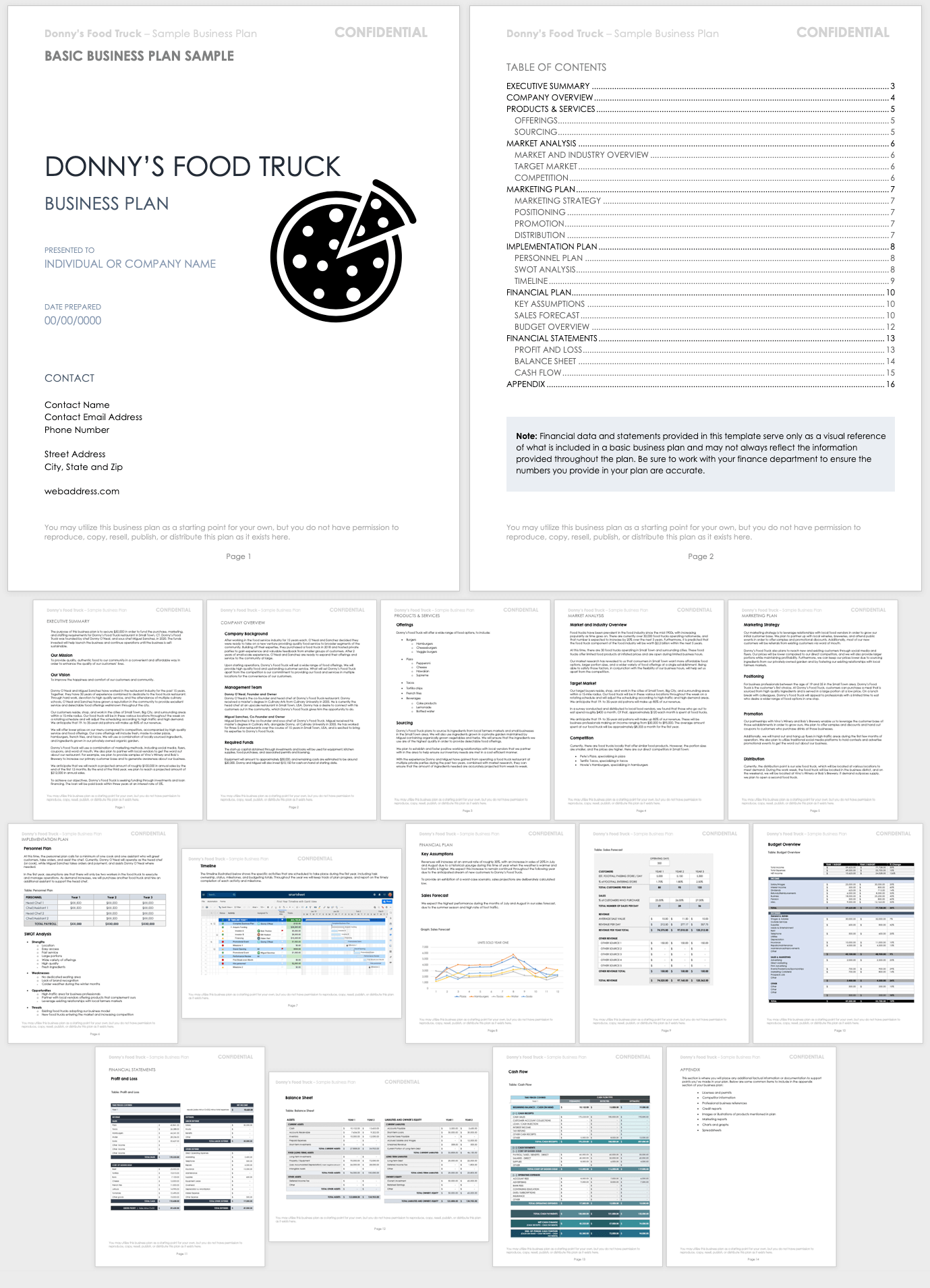
This business plan example demonstrates a plan for a fictional food truck company. The sample includes all of the elements in a traditional business plan, which makes it a useful starting point for developing a plan specific to your business needs.
Download Basic Business Plan Sample - PDF
Sample Business Plan Outline Template

Use this sample outline as a starting point for your business plan. Shorten or expand the outline depending on your organization’s needs, and use it to develop a table of contents for your finalized plan.
Download Sample Business Plan Outline Template - PDF
Sample Business Financial Plan Template
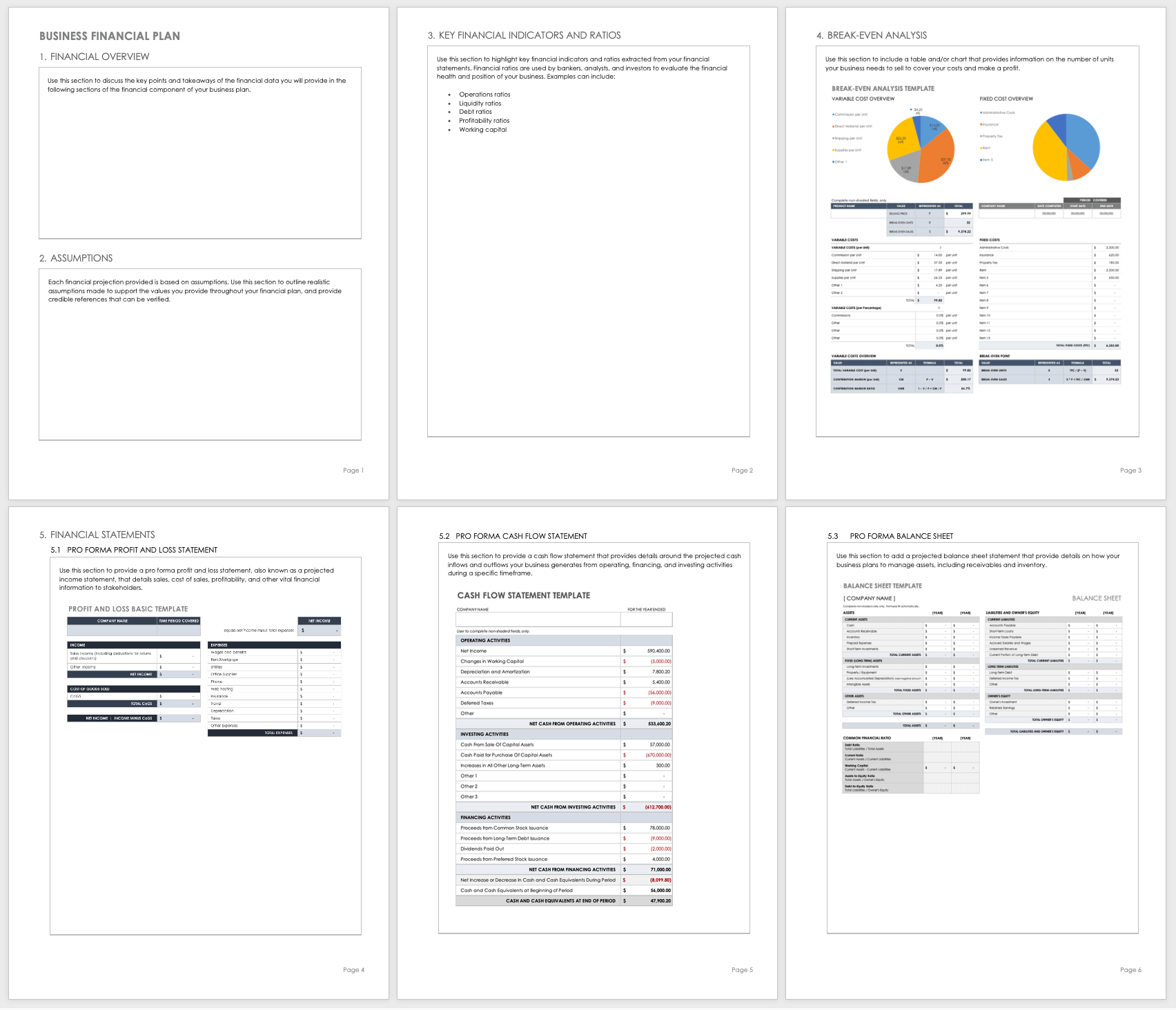
Use this sample template to develop the financial portion of your business plan. The template provides space to include a financial overview, key assumptions, financial indicators, and business ratios. Complete the break-even analysis and add your financial statements to help prove the viability of your organization’s business plan.
Download Business Financial Plan Template
PDF | Smartsheet
For more free, downloadable templates for all aspects of your business, check out “ Free Business Templates for Organizations of All Sizes .”
Improve Business Planning with Real-Time Work Management in Smartsheet
Empower your people to go above and beyond with a flexible platform designed to match the needs of your team — and adapt as those needs change.
The Smartsheet platform makes it easy to plan, capture, manage, and report on work from anywhere, helping your team be more effective and get more done. Report on key metrics and get real-time visibility into work as it happens with roll-up reports, dashboards, and automated workflows built to keep your team connected and informed.
When teams have clarity into the work getting done, there’s no telling how much more they can accomplish in the same amount of time. Try Smartsheet for free, today.
Discover why over 90% of Fortune 100 companies trust Smartsheet to get work done.

- Customer Reviews
- Net 30 Account
- Wise Services
- Steps & Timeline
- Work at a Glance
- Market Research at a Glance
- Business Plan Writing Services
- Bank Business Plan
- Investor Business Plan
- Franchise Business Plan
- Cannabis Business Plan
- Strategic Business Plan
- Corporate Business Plan
- Merge and Acquisition Business Plan (M&A)
- Private Placement Memorandums (PPM)
- Sample Business Plans
- Professional Feasibility Study
- PowerPoint Presentations
- Pitch Deck Presentation Services
- Business Plan Printing
- Market Research
- L-1 Business Plan
- E-2 Business Plan
- EB-5 Business Plan
- EB-5 Regional Centers
- Immigration Attorneys
- Nonprofit Business Plan
- Exit Business Planning
- Business Planning
- Business Formation
- Business License
- Business Website
- Business Branding
- Business Bank Account
- Digital Marketing
- Business Funding Resources
- Small Business Loans
- Venture Capital
- Net 30 Apply

14 Professional Business Plan Samples [Downloadable pdf]
Looking for business plan examples for inspiration? Download or view 14 business plans examples/samples, vetted by our MBA business plan writers. Download in PDF format or read like a book. These real business plan samples would help in writing your own business plan.

View Real Business Plan Examples/Samples

As an entrepreneur, effectively pitching your idea to attract investors and secure funding can be a challenge. Moreover, when launching a business, creating a comprehensive business plan is paramount.
To aid you in these crucial tasks, we offer a collection of real-world and sample business plan examples across diverse industries. A well-structured business plan is indispensable in the fast-paced entrepreneurial landscape, as it delineates your goals, strategies, and financial projections, providing a clear roadmap for your venture.
Our aim is to facilitate the creation of an effective business plan by integrating real-life examples to elucidate the key elements involved. Below, you’ll find a range of 14 detailed business plan examples available for download and use.
Important Sections to Include in Business Plan
To create a robust business plan, ensure inclusion of the following key sections:
- Executive Summary: A brief snapshot of your business and the key highlights of your business plan. Read more
- Product and Services: An elaborate description of the offerings you will provide to your customers. Read more
- Marketing and Sales Plan: A strategic roadmap outlining how you intend to promote and market your business before, during, and after its launch. Read more
- Operating Planning: An explanation of the systems, processes, and tools necessary to efficiently run your business behind the scenes. Read more
- Organization and Management: Organization and management in a business plan outline the structure and leadership of the company. Read more
- Financial Plan: A comprehensive plan mapping out your short-term and long-term financial goals and the associated costs of running your business. If you require funding, this section is where you can outline your request and financial needs. Read more
- Key External Drivers: External drivers encompass factors like outsourcing, economic changes, industry competition, and business legislation complexity. Read more
- Startup Summary: The startup summary offers a comprehensive financial overview of , detailing expenses, asset value, and total requirements, crucial for transparency with entrepreneurs and investors. Read more
- Projected Industry Growth : Projected industry growth forecasts the sector’s expansion, offering a 10-year perspective and average annual growth rate, providing clarity to investors. Read more
- Break-even analysis: The break-even analysis visually presents key metrics and a 12-month revenue forecast to help stakeholders grasp the point where the business covers costs and starts generating profit . Read more
- Management Summary: The management summary provides a concise overview of organizational structure, key personnel, their roles, and financial commitments, ensuring stakeholders understand the business’s operational strength and leadership capability. Read more
- Financial Indicators: The financial indicators section evaluates organizational fiscal health, focusing on year-over-year profitability metrics, leverage ratios, liquidity ratios, and additional metrics, providing a comprehensive understanding of the business’s financial performance and efficiency in revenue generation from equity investments. Read more
Practical Business Plan Examples Illustrating Strategies for Startup Success

1. E-commerce Plan Sample or Example
Something Borrowed Something New is a burgeoning e-commerce enterprise specializing in wedding accessories and personalized gifts. Operating on a drop-shipping model, this business has the capability to make a significant impact in the market.
Moreover, leveraging social networking and blogging can be instrumental in generating awareness and capturing interest, thereby creating a robust online marketing strategy for Something Old and Something New.
To enhance their business operations, they are contemplating the integration of a WhatsApp CRM system. This initiative aims to optimize communication with potential customers, ensuring prompt responses to inquiries and fostering a seamless interaction process.

2. Online Marketplace Business Plan Example or Sample
EPlace Solutions will be an innovative online marketplace business portal offering a variety of products to consumers throughout the globe. Founded by Mr. John Jones, a seasoned business visionary with an eye toward profit and achievement, the organization is set to enter the market in 2023.
Online shopping is at an all-time high with new consumer mindsets calling for them to shop for the types of deals and bargains that will be so much a part of the online marketplace business model.

3. Snack Bar Business Plan Sample / Business Plan Example
There is an increasing demand for snack-type fast food to be consumed while window shopping and walking around inside a shopping mall.
Do you plan to start a snack bar business? Then here’s a complete snack bar startup business plan template and feasibility report you can use FREE of charge. It sounds easy to open a snack bar, but in reality, you need well-planned strategies to ensure that your business stands the test of time.
Our snack bar business plan sample includes a detailed description of the products and services offered, as well as a market a nalysis and competitive analysis.
It also includes a financial plan that outlines the startup costs, revenue projections, and break-even analysis. We like this sample plan because it demonstrates how to build a profitable snack bar business by creating a unique menu and offering healthy, high-quality snac ks that meet custome r demand.
Your snack shop business plan can look as polished and professional as the sample plan. It’s fun and easy, with Wise Business Plan. Let’s review the snack shop business plan sample and adjust them according to your audience for the best results.

4. Coffee Shop Business Plan Sample/Business Plan Example PDF
A coffee shop business plan is a document that outlines what your business idea is and how it will be implemented. Its purpose is to answer questions such as what it costs to start a coffee shop, how these costs will be financed, and how much money you can expect to earn from your cafe.
Are you looking for the right business plan for your cafe? Let’s review the Coffee shop business plan sample to find out how cloud-based software can make your day-to-day work more efficient.
Our coffee shop business plan sample includes a detailed description of the products and services offered, as well as a market analysis and competitive analysis.
It also includes a financial plan that outlines the startup costs, revenue projections, and break-even analysis. We like this sample plan because it demonstrates how to build a profitable coffee shop business by creating a unique brand and offering high-quality products a nd customer service.

5. Food Hall Business Plan Sample/Business Plan Example PDF
In the food industry, there is fierce competition. To ensure success, you need to hit the ground running with the right pitch. Our food house business plan is the ideal solution with an attractive design highlighting key information and conveying the right message.
This food business plan example features food images intended to tantalize the taste buds. It captures the theme perfectly and will convey the ultimate message to investors, clients and customers.
It is important to remember that the business plan template can be customized to meet your company’s specific needs and requirements. It will help showcase your business as a leader in the modern industry.
This food business plan template provides key slides to showcase everything from finances to marketing and key competitors. If you prefer, you can alter the content displayed to meet your specific needs, but this is a good starting point.
Ultimately, this food house business plan will be suitable for any business operating in the food industry and keen to get interested from key individuals. It will ensure that you can build up the rep of your company.
We provide a one-of-a-kind sales pitch deck designed to appeal to your prospective audience, as well as a custom presentation tailored to their information requirements.

6. Printing Shop Business Plan Sample/Business Plan Example Plan
When establishing a think tank, you will need to develop a business plan and document it properly. As a mass think tank, you need a special strategy to legalize the think tank as a non-profit organization and to raise funds for your project successfully.
Copy and print businesses offer a variety of services to both businesses and consumers. A copy and print shop can handle everything from single-page printing to large-volume jobs using several types of media.
Our printing shop business plan sample includes a detailed description of the products and services offered, as well as a market analysis and competitive analysis. It also includes a financial plan that outlines the startup costs, revenue projections, and break-even analysis. We like this sample plan because it demonstrates how to build a profitable printing shop business by offering high-quality, customized printing services with a focus on customer s ervice and efficient operations.
Let’s take a look at Printing and Photocopy Business Plan Sample that you can use to inspire your own and easily create one.

7. Acquisition Business Plan Sample/ Example PDF
The acquisition business plan sample is intended for businesses seeking to acquire another company or merge with a competitor. This plan includes an analysis of the target company, a valuation, and a strategy for integrating the acquired business into the existing operations. We like this sample plan because it provides a clear roadmap for the acquisition process and demonstrates the potential benefits of the deal.

8. L-1 Visa Business Plan Example with Sample PDF
At Wisebusinessplans, we understand that obtaining an L1 visa for an executive or manager requires a thorough and compelling business plan.
Our L1 business plan sample includes all the necessary components to satisfy USCIS requirements and demonstrate your qualifications and your company’s viability in the US market.
The L1 business plan sample is a comprehensive plan for a new business seeking L1 visa approval for an executive or manager. This plan focuses on demonstrating the applicant’s qualifications and the company’s viability in the US market.
We like this sample plan because it is specific to the L1 visa process and includes all the necessary components to satisfy USCIS requirements.

9. E-2 Visa Business Plan Sample/ Example PDF
If you’re an entrepreneur seeking E-2 visa approval, Wise Business Plans can help you create a persuasive business plan.
Our E-2 business plan sample outlines your investment, business operations, and financial projections, providing a clear and compelling case for your ability to successfully run a business and make a significant economic impact.
The E-2 business plan sample is designed for entrepreneurs seeking E-2 visa approval, which allows individuals to invest in and manage a business in the United States. This plan outlines the applicant’s investment, business operations, and financial projections. We like this sample plan because it provides a clear and compelling case for the applicant’s ability to successfully run a business and make a significant economic impact.

10. EB-5 Business Plan Sample/ Example PDF
If you’re looking to obtain an EB-5 visa by investing in a new commercial enterprise in the United States, Wise Business Plans can help you create a compelling business plan.
Our EB-5 business plan sample includes a description of your business, a market analysis, and financial projections, providing a detailed and persuasive case for the potential success of your venture.
The EB-5 business plan sample is designed for individuals seeking to obtain an EB-5 visa by investing in a new commercial enterprise in the United States. This plan includes a description of the business, a market analysis, and financial projections. We like this sample plan because it provides a detailed and persuasive case for the potential success of the business, which is crucial for obtaining EB-5 visa approval.

11. Investor Business Plan Sample/ Example PDF
If you’re seeking investment from angel investors, venture capitalists, or other private equity firms, Wise Business Plans can help you create a compelling pitch.
Our investor business plan sample includes a pitch deck, financial projections, and a detailed analysis of the market the potential return on investment and the scalability of your business.
The investor business plan sample is intended for businesses seeking to attract investment from angel investors, venture capitalists, or other private equity firms. This plan includes a pitch deck, financial projections, and a detailed analysis of the market opportunity. We like this sample plan because it emphasizes the potential return on investment and the scalability of the business.

12. Nonprofit Business Plan Sample/ Example PDF
At Wisebusinessplans, we’re committed to helping non-profit organizations achieve their social impact goals.
Our non-profit business plan sample includes a mission statement, programs and services, marketing and outreach strategies, and a financial analysis, providing a clear roadmap for establishing or expanding your organization.
The non-profit business plan sample is designed for organizations seeking to establish or expand a non-profit entity. This plan includes a mission statement, programs and services, marketing and outreach strategies, and a financial analysis. We like this sample plan because it demonstrates a strong commitment to social impact and outlines a clear strategy for achieving the organization’s goals.

13. Bank Business Plan Sample/ Example PDF
Whether you’re seeking financing from a bank or other financial institution, Wise Business Plans can help you create a detailed and persuasive business plan.
Our bank business plan sample includes a thorough financial analysis, market research, and a strategy for achieving profitability, highlighting the key factors that banks consider when evaluating loan applications.
The bank business plan sample is tailored for businesses seeking financing from a bank or other financial institution. This plan includes a detailed financial analysis, market research, and a strategy for achieving profitability. We like this sample plan because it highlights the key factors that banks consider when evaluating loan applications, and provides a strong case for the borrower’s ability to repay the loan.

14. Cannabis Business Plan Sample/ Example PDF
The cannabis industry is rapidly growing, and Wise Business Plans can help you enter it with confidence.
Our cannabis business plan sample includes a market analysis, operational strategy, and regulatory compliance a comprehensive overview of the unique challenges and opportunities in the industry and offering a clear roadmap for success.
The cannabis business plan sample is tailored for entrepreneurs seeking to enter the rapidly growing cannabis industry. This plan includes a market analysis, operational strategy, and regulatory compliance plan. We like this sample plan because it provides a comprehensive overview of the unique challenges and opportunities in the cannabis industry, and offers a clear roadmap for success.
Detailed Overview of Key Components of a Business Plan
1. executive summary.
The executive summary is a concise overview of your business plan, highlighting the key points of each section. It should capture the essence of your business, its mission, and the purpose of the business plan. This section should be written last, but it’s placed at the beginning of the business plan. Here is an example executive summary from our professional business plan written for Eplace Solution , an innovative e-commerce portal.

Tips for Writing Executive Summary
- Keep it brief and focused on key points.
- Clearly define the problem and your solution.
- Highlight market opportunities and growth potential.
- Showcase your team’s qualifications.
- Include financial projections.
- End with a clear call to action.
- Tailor it to your audience.
- Review and update regularly.

2. Company Overview or Description
In this section, provide a detailed description of your company, including its history, legal structure, location, and vision. Explain your mission statement and core values that guide your business decisions. Use real-life examples of successful companies and how their strong company descriptions have contributed to their growth. In addition, you can reuse your company description on your About page, Instagram page, or other properties that ask for a boilerplate description of your business.
This section also allows you to describe how you register your business . Here you must choose whether your business is a corporation, sole proprietorship, LLC , or another type of business .

Tips for Writing Company Description
- Describe your company’s mission and vision.
- Explain what your business does and the problems it solves.
- Mention your target market and customer base.
- Highlight your unique selling points.
- Provide a brief history and background.
3. Market Analysis
A market analysis analyzes how you are positioned in the market, who your target customers are, what your product or service will offer them, and industry trends. It might be useful to do a SWOT analysis to discover your strengths and weaknesses to identify market gaps that you may be able to exploit to build your business.
As part of your market research, you’ll also need to perform a competitive analysis. It will give you an idea of who your competition is and how to differentiate your brand. Here’s an example of a competitive analysis we did for a food business.

Tips for Writing Market Analysis
- Research and understand your industry thoroughly.
- Identify market trends and growth opportunities.
- Analyze your competitors and their strengths and weaknesses.
- Define your target audience and their needs.
- Include data and statistics to support your analysis.

4. Product and Services
Adding products and services to a business plan involves more than listing your company’s offerings. If you intend to gain funding or partner with another business, your products, and services section needs to demonstrate your company’s quality, value, and benefits.
Here’s an example of a product and service section in the business plan we wrote for an e-commerce business that offers wedding accessories.

Tips for Writing Product and Services
- Clearly describe your offerings and their features.
- Explain how your products/services address customer needs.
- Highlight any unique qualities or advantages.
- Discuss your pricing strategy.
- Mention any future product/service development plans.
Here is example of services section of a bank.

5. Marketing and Sales Plan
It is always a good idea to have a marketing plan before launching your business. A potential investor will want to know how you will advertise your business. Therefore, you should create a marketing plan that explains your planned promotion and customer acquisition strategies.
Discuss how you will make a sale. How will you attract customers and maximize their lifetime value? Ensure your marketing and sales forecasts align with your financial forecasts Marketing plans are usually based on the four Ps : product, price, place, and promotion. Breaking it down by marketing channels makes it easier. Discuss how you intend to market your business via blogs, email, social media, and word-of-mouth. Here is an example of marketing strategies we develop for a restaurant business.

Tips for Writing Marketing and Sales Plan
- Define your marketing goals and objectives.
- Outline your marketing strategies, including channels and tactics.
- Explain your sales strategy and target sales goals.
- Include a budget for marketing and sales activities.
- Discuss your sales team and their roles.
- Detail your customer acquisition and retention strategies.
- Mention any partnerships or collaborations for marketing and sales.
Example of marketing and sales plan section of a bank

6. Operation Planning
The operation plan should include all the steps needed to run the business in the long run. The plan should include details about logistics, duties for each department of the company, and responsibilities for the team.
The main aspect of running a business is its costs. Whether it’s machinery or services, each requires capital.
how to write an operation plan in a business plan
Tips for Writing Operational Planning
- Describe your day-to-day business operations.
- Explain your supply chain and production processes.
- Outline your facility and equipment requirements.
- Discuss your quality control and efficiency measures.
- Mention any legal and regulatory compliance considerations.
- Detail your staffing and management structure.
- Include contingency plans for potential disruptions.
7. Organization and Management
In this section, you can describe your current team and the people you need to hire. You will need to highlight your team’s relevant experience if you intend to seek funding. Basically, this is where you demonstrate that this team can be successful in starting and growing the business.

Tips for Writing Organization and Management Summary
- Introduce your leadership team and their roles.
- Highlight their relevant experience and qualifications.
- Explain your organizational structure and hierarchy.
- Discuss key personnel responsibilities and functions.
- Mention any plans for team growth or development.
- Address any advisory boards or external support.
Management summary of coffee shoppe business.

8. Financial Plan
A financial plan should include sales and revenue forecasts, profit and loss statements , cash flow statements , and balance sheets .
Now, if you plan to pitch investors or submit a loan application, you’ll also need a “use of funds” report. Here you outline how you plan to leverage any funding you might acquire for your business.
With our business templates , you can create your own income statement, cash flow statement, and balance sheet.

Tips for Writing Financial Plan
- Include detailed financial projections (income statement, cash flow, balance sheet).
- Explain your funding requirements and sources.
- Discuss your pricing and revenue model.
- Describe your expense management and cost controls.
- Mention any financial risks and mitigation strategies.
- Highlight key financial milestones and goals.
Financial highlights of foodShack business.

9. Key External Drivers
External drivers refer to the external factors or influences that significantly impact the activity and growth of an industry. These drivers include outsourcing of non-core activities, changes in economic activity, competition from other industries, and the complexity of business legislation.
Additionally, external drivers encompass the effects of changes in new business formation, especially among small businesses, which directly affect the demand for services within the industry.

Tips for writing key external drivers
- Identify and analyze current and emerging market trends in your industry.
- Assess potential positive or negative impacts these trends may have on your business.
- Evaluate broader economic conditions, including inflation rates, interest rates, and GDP growth.
- Elucidate how changes in economic conditions could influence consumer behavior, product demand, and overall cost structure.
- Outline key industry regulations and compliance requirements, discussing potential impacts on operations, costs, and market access.
- Highlight relevant technological advancements and explain their potential effects on your product or service offerings, operations, and competitiveness.
- Analyze current and potential future competitors, emphasizing the evolving competitive landscape’s impact on market share, pricing strategy, and overall business strategy.
- Consider social and cultural factors influencing consumer preferences and behaviors, exploring how societal changes can affect product demand.
- Evaluate environmental trends and regulations, discussing potential impacts on operations, supply chain, and customer perceptions.
- Assess political stability, government policies, and geopolitical factors, exploring potential risks and opportunities from political changes.
- Discuss global market conditions, analyzing how global economic trends, trade policies, and currency fluctuations may affect operations and expansion plans.
- Identify and discuss potential risks in the supply chain, such as disruptions, shortages, or geopolitical issues.
- Consider demographic shifts affecting your target market and discuss how changes may impact your customer base and marketing strategies.
- Highlight key legal and regulatory factors affecting the business, discussing potential legal challenges, compliance costs, and regulatory changes.
- Outline comprehensive risk management strategies, including contingency plans and risk mitigation strategies.
- Explain how you will monitor external drivers and emphasize the importance of staying agile and responsive to changes in the external environment.

10. Startup Summary
The startup summary serves as a comprehensive overview of essential financial aspects, encompassing total startup expenses, the overall value of startup assets, and the total requirements, which is the cumulative sum of all expenses and startup investments.
It provides a clear financial snapshot, outlining the costs involved in launching the business, the value of assets acquired, and the overall financial needs for the startup.
This section is crucial for entrepreneurs and potential investors, offering a transparent understanding of the financial foundation required to initiate and sustain the business successfully.
This roadmap ensures a realistic evaluation of the business idea, identifying potential challenges and offering solutions.To write an effective plan, focus on what sets your venture apart from competitors, maintain conciseness, and embrace flexibility as a living document.
Answer fundamental questions about your business, create actionable checklists, execute the plan, and continually revise and update based on experiences and feedback.This iterative process fosters continuous improvement, helping entrepreneurs stay adaptable and enhance their business strategies over time.

Tips for writing Startup Summary
- Clearly state the startup’s name and provide a concise description of its activities.
- Include a succinct mission statement capturing the startup’s purpose and goals, reflecting its core values.
- Specify the founding date and offer brief bios of key founders, highlighting relevant experience.
- Summarize the startup’s concept, explaining offered products or services and key distinguishing features.
- Clearly articulate the problem or need in the market that the startup addresses, defining the target audience.
- State what makes the startup unique, whether it’s a special feature, market gap, or competitive advantage.
- Provide a brief description of the market opportunity, covering target market size, trends, and growth prospects.
- Outline how the startup plans to generate revenue, detailing streams, pricing strategy, and potential partnerships.
- Offer a snapshot of the startup’s current status, highlighting key achievements such as product development or partnerships.
- If seeking funding, clearly state the amount sought and its allocation, covering areas like product development and marketing.
- Include a high-level financial summary with key projections for revenue, expenses, and profitability.
- Briefly outline future aspirations and plans, encompassing areas like expansion, product development, or strategic partnerships.
11. Projected Industry Growth
The projected industry growth is a pivotal aspect that forecasts the expansion of a specific sector over a defined timeframe.
For instance, it could provide an estimate of where that particular business will be standing in the next 10 years, and what will be the average annual growth rate of that industry.
This information provides prospective investors and stakeholders with a clear understanding of the industry’s potential and positions the startup within a dynamic and flourishing market.

Tips for writing Projected Industry Growth
- Emphasize the importance of industry trends and growth to your business.
- Provide a concise overview, including market size, major players, and recent trends.
- Briefly explain how you gathered data on industry growth projections (e.g., market research reports, expert interviews).
- Identify and discuss prevailing trends, such as technological advancements, changes in consumer behavior, and regulatory shifts.
- Summarize the industry’s historical growth, highlighting growth rates, market expansion, and notable milestones.
- Highlight key factors expected to drive industry growth, such as emerging markets, technological innovations, and demographic shifts.
- Discuss specific opportunities within the industry, including gaps in the market, underserved segments, or areas of competitive advantage.
- Acknowledge potential challenges or risks that could impact industry growth, demonstrating a realistic understanding.
- Present projections for future growth rates based on historical data, expert opinions, and your analysis. Include short-term and long-term projections.
- Discuss how key competitors are positioned to leverage industry growth, emphasizing your business’s differentiation strategies.
- Consider the regulatory landscape impacting growth, discussing anticipated changes and their potential effects on the industry.
- Explore international trends and their implications for industry growth, including factors like global economic conditions and geopolitical influences.
Here is example of market analysis section of a bank.

12. Break-even Analysis
The break-even analysis serves as a vital financial tool, offering a detailed estimation of key metrics such as Sales Revenue, Cost of Sales, Gross Profit, Fixed Expenses, and Income Before Tax.
These critical components are visually presented through a bar graph, providing a clear and concise overview of the financial dynamics.
Additionally, the break-even analysis delves into a 12-month forecast, outlining the projected amount of revenue generated and the corresponding fixed costs.
This section is instrumental in helping stakeholders understand the financial threshold at which the business covers its costs and begins to generate profit.

Tips for writing Break-even Analysis
- Define break-even analysis as a financial calculation where total revenue equals total costs.
- Identify constant costs regardless of production or sales levels.
- Enumerate and explain costs changing with production or sales.
- Present the break-even analysis formula, indicating the units needed to cover costs.
- Perform a practical break-even calculation using business-specific fixed costs, selling price, and variable cost per unit.
- Include a break-even chart or graph for a visual understanding of cost-revenue dynamics.
- Conduct a proactive sensitivity analysis to explore how changes in variables impact the break-even point.
- Specify the anticipated timeframe to reach the break-even point in terms of months or units sold.
- Clearly outline assumptions made in the analysis and provide justifications for transparency and credibility.
- Acknowledge potential risks or challenges that may affect the accuracy of the break-even analysis.
- Briefly mention contingency plans for difficulties in reaching the break-even point within the projected timeframe.
13. Management Summary
The management summary within the business plan provides a concise overview of the organizational structure and key personnel.
This includes a count of individuals, specifying the number of founders and operational team members integral to the organization.
The summary delves into the roles and responsibilities of each key figure, offering insights into the leadership dynamics driving the business.
Furthermore, the management summary sheds light on the financial aspect by presenting details about personal wages and payroll allocations for both founders and operational staff.
This comprehensive section ensures a clear understanding of the human resource framework and the financial commitments associated with the management team, crucial for stakeholders evaluating the business’s operational strength and leadership capability.

Tips for Writing Management Summary
- Highlighting the critical role the management team plays in the business’s success, the introduction emphasizes their significance.
- Listing each key member with names, positions, and brief role summaries introduces the core of the management team.
- Providing brief biographies for each team member underscores their relevant experience, skills, achievements, and industry-specific expertise.
- Clearly outlining roles and responsibilities emphasizes how each team member’s skills contribute to the overall success of the business.
- Sharing the team’s vision and strategy involves discussing key strategic goals and outlining the plans to achieve them.
- Highlighting notable achievements or milestones showcases the team members’ successful ventures, industry recognition, or career accomplishments.
- Discussing team dynamics emphasizes collaboration and the complementary nature of their skills in driving the business forward.
- Introducing advisory board members, if applicable, underscores the additional guidance and expertise they bring to the business.
- Discussing how the team plans to contribute to future growth and development includes strategies for talent acquisition, leadership development, and succession planning.
- Touching on the team’s culture and values emphasizes their role in shaping the overall ethos of the business.
- If seeking investment, briefly mentioning how the management team plans to use funding for business growth and development provides insight into their financial strategy.
Here is example of marketing and sales plan section of a bank.

14. Financial Indicators
The financial indicators section within the business plan helps in evaluating the fiscal health and performance of the organization.
Year-after-year profitability estimates take center stage, encompassing key metrics such as gross margin, net profit margin, and EBITDA to revenue.
These indicators provide a comprehensive understanding of the business’s ability to generate profit relative to its revenue.
Furthermore, the financial indicators extend to leverage ratios, including the critical Debt to Equity ratio, Debt to Assets ratio, and Interest Coverage ratio.
These metrics illuminate the organization’s capital structure, debt management, and its capacity to meet interest obligations.
Liquidity ratios includes the Current Ratio and Current Debt to Total Asset Ratio.
These ratios provide insights into the company’s short-term financial health and its ability to meet immediate obligations.
The financial indicator toolbox is enriched with additional metrics, notably the Revenue to Equity ratio, which sheds light on the efficiency of generating revenue from equity investments.

Tips For Writing Financial Indicators
- Detailed revenue forecasts for the next 3-5 years. Breakdown by product/service and geographical regions.
- Detailed breakdown of anticipated expenses. Include fixed and variable costs, operational expenses, and other relevant expenditures.
- Historical P&L statements if available. Projected future profits and losses based on revenue and expense projections.
- Outline of expected cash inflows and outflows. Emphasis on the ability to meet short-term obligations.
- Snapshot of the company’s financial position. Includes assets, liabilities, and equity.
- Calculation and presentation of key financial ratios (liquidity, solvency, profitability). Discussion on the significance of these ratios.
- Identification and explanation of relevant KPIs. Highlighting alignment with the overall business strategy.
- Discussion of potential financial risks. Mitigation strategies and addressing uncertainties.
- Clear statement of the amount and purpose of funds required.
- Outline of key assumptions underlying financial projections. Rationale for these assumptions.
- Summary of industry financial trends and business positioning. Outlook on future financial prospects considering market dynamics.

Discover Business Plan Formats and Free Templates
Looking For The Right Business Plan Format?
These sample business plans will provide you with a complete structure and format for your business plan, which will give you a head start on developing your document, so you won’t be stuck seeing an empty page and wondering what to write.
Simply going through the process of writing a business plan is one of its key benefits. If you sit down to write, you’ll naturally think about your startup costs, your target market , and any market analysis or research you’ll need to conduct. In addition to defining your position among your competitors, you will establish your goals and milestones.
You can see what should be included in a sample financial plan, but It is wrong to assume that a sample company’s financial projections will fit your own. If you need more resources to get you started, we recommend this guide on how to write a business plan .
In addition, you can download our 40+ free business plan templates covering a range of industries.
Business Plan Examples For Students PDF
Common types of business plan, 1. one page business plan.
One-page business plans are short, compact, and to the point and are designed to make the plan easy to read at a glance. Make sure to include all of the sections, but truncate and summarize them
2. Start-up business plan
Start-up business plans are for businesses that are just getting started. They are usually developed to secure outside funding. In this regard, financials are of increased importance, as well as other sections that determine whether your business idea is viable, such as market research.
3. Strategic business plan
A strategic business plan lays out a company’s goals and how it will achieve them at a high level. It is a foundational document for the company as a whole. A strategic business plan allows all levels of the business to see the big picture, inspiring employees to work together to reach the company’s goals.
4. Feasibility business plan
Developing a feasibility plan answers two primary questions about a business venture: who would purchase the service or product the company wants to sell, and if the venture is profitable.
5. Internal business plan
Internal Business plans are geared to a specific audience within a company to keep your team on the same page and focused on the same goals.
Conclusion
In conclusion, whether you’re venturing into a traditional business or creating an innovative startup, the significance of a well-crafted business plan cannot be overstated. Different types of business plans cater to specific needs, from internal alignment to strategic expansion. Employing a template in MS Word ensures a polished presentation. The process of writing an executive summary, creating a plan, and defining the components of your business plan is essential.
Recognizing the need for a comprehensive and standard business plan can help guide your endeavors. Whether you choose to write a full business plan or opt for a one-page business overview, leveraging templates in MS Word can simplify the process. In essence, understanding the types of business plans and utilizing an executive summary template provides a structured approach to showcase your business overview.
Take inspiration from example business plans to tailor your strategy, ensuring a roadmap for success in the dynamic world of entrepreneurship. Always remember, a meticulously crafted business plan not only communicates your vision effectively but also serves as a valuable resource that can help secure investments and guide your business’s growth trajectory.
Frequently Asked Questions
Begin with an executive summary, delve into market analysis, outline your strategies, create financial projections, and use available business plan examples as templates to guide your writing.
A comprehensive business plan template should encompass key sections such as an executive summary, business description, market analysis, marketing strategy, organizational structure, and financial projections. Seek templates online that cover these elements.
Tailor your business plan to the scale of your small business. Define your objectives clearly, outline cost-effective strategies, and emphasize agility in adapting to market changes.
Explore well-crafted business plan examples you can visit our website wisebusinessplan.
The fundamental components include an executive summary, business description, market analysis, marketing and sales strategy, organizational structure, product/service description, and financial projections.
Investors focus on growth potential, detailed financial projections, market analysis, competition analysis, and the qualifications and experience of your management team when reviewing a business plan.
To find a business plan example for a tech startup,you can visit our visit wisebusinessplan .
A business plan provides a comprehensive overview of your entire business, including strategies, operations, and financials. In contrast, a business proposal typically focuses on a specific project or offer, outlining the details and benefits to a potential client.
Craft an engaging executive summary by summarizing your business’s mission, highlighting the market opportunity, showcasing your product or service, and providing a concise overview of your financial projections.
Seek tailored business plan examples for nonprofit organizations you can visit wisebusinessplan .
Download Pack of 14 Business Plan Examples
These business plans are written by MBA writers. Real-world use cases were used in these plans.
Are you looking for Top Business Plan Writer?
Get our business plan writing and consultation service.
Quick Links

- Investor Business Plans
- M&A Business Plan
- Private Placement
- Feasibility Study
- Hire a Business Plan Writer
- Business Valuation Calculator
- Business Plan Examples
- Real Estate Business Plan
- Business Plan Template
- Business Plan Pricing Guide
- Business Plan Makeover
- SBA Loans, Bank Funding & Business Credit
- Finding & Qualifying for Business Grants
- Leadership for the New Manager
- Content Marketing for Beginners
- All About Crowdfunding
- EB-5 Regional Centers, A Step-By-Step Guide
- Logo Designer
- Landing Page
- PPC Advertising

- Business Entity
- Business Licensing
- Virtual Assistant
- Business Phone
- Business Address
- E-1 Visa Business Plan
- EB1-A Visa Business Plan
- EB1-C Visa Business Plan
- EB2-NIW Business Plan
- H1B Visa Business Plan
- O1 Visa Business Plan
- Business Brokers
- Merger & Acquisition Advisors
- Franchisors
Proud Sponsor of
- 1-800-496-1056

- (613) 800-0227

- +44 (1549) 409190

- +61 (2) 72510077

Download 14 Professional Business Plan Samples
Your Full Name
| You might be using an unsupported or outdated browser. To get the best possible experience please use the latest version of Chrome, Firefox, Safari, or Microsoft Edge to view this website. |
How To Write A Business Plan (2024 Guide)

Updated: Apr 17, 2024, 11:59am

Table of Contents
Brainstorm an executive summary, create a company description, brainstorm your business goals, describe your services or products, conduct market research, create financial plans, bottom line, frequently asked questions.
Every business starts with a vision, which is distilled and communicated through a business plan. In addition to your high-level hopes and dreams, a strong business plan outlines short-term and long-term goals, budget and whatever else you might need to get started. In this guide, we’ll walk you through how to write a business plan that you can stick to and help guide your operations as you get started.
Featured Partners
ZenBusiness
$0 + State Fees
Varies By State & Package

On ZenBusiness' Website

On LegalZoom's Website
Northwest Registered Agent
$39 + State Fees

On Northwest Registered Agent's Website
$0 + State Fee
On Formations' Website
Drafting the Summary
An executive summary is an extremely important first step in your business. You have to be able to put the basic facts of your business in an elevator pitch-style sentence to grab investors’ attention and keep their interest. This should communicate your business’s name, what the products or services you’re selling are and what marketplace you’re entering.
Ask for Help
When drafting the executive summary, you should have a few different options. Enlist a few thought partners to review your executive summary possibilities to determine which one is best.
After you have the executive summary in place, you can work on the company description, which contains more specific information. In the description, you’ll need to include your business’s registered name , your business address and any key employees involved in the business.
The business description should also include the structure of your business, such as sole proprietorship , limited liability company (LLC) , partnership or corporation. This is the time to specify how much of an ownership stake everyone has in the company. Finally, include a section that outlines the history of the company and how it has evolved over time.
Wherever you are on the business journey, you return to your goals and assess where you are in meeting your in-progress targets and setting new goals to work toward.
Numbers-based Goals
Goals can cover a variety of sections of your business. Financial and profit goals are a given for when you’re establishing your business, but there are other goals to take into account as well with regard to brand awareness and growth. For example, you might want to hit a certain number of followers across social channels or raise your engagement rates.
Another goal could be to attract new investors or find grants if you’re a nonprofit business. If you’re looking to grow, you’ll want to set revenue targets to make that happen as well.
Intangible Goals
Goals unrelated to traceable numbers are important as well. These can include seeing your business’s advertisement reach the general public or receiving a terrific client review. These goals are important for the direction you take your business and the direction you want it to go in the future.
The business plan should have a section that explains the services or products that you’re offering. This is the part where you can also describe how they fit in the current market or are providing something necessary or entirely new. If you have any patents or trademarks, this is where you can include those too.
If you have any visual aids, they should be included here as well. This would also be a good place to include pricing strategy and explain your materials.
This is the part of the business plan where you can explain your expertise and different approach in greater depth. Show how what you’re offering is vital to the market and fills an important gap.
You can also situate your business in your industry and compare it to other ones and how you have a competitive advantage in the marketplace.
Other than financial goals, you want to have a budget and set your planned weekly, monthly and annual spending. There are several different costs to consider, such as operational costs.
Business Operations Costs
Rent for your business is the first big cost to factor into your budget. If your business is remote, the cost that replaces rent will be the software that maintains your virtual operations.
Marketing and sales costs should be next on your list. Devoting money to making sure people know about your business is as important as making sure it functions.
Other Costs
Although you can’t anticipate disasters, there are likely to be unanticipated costs that come up at some point in your business’s existence. It’s important to factor these possible costs into your financial plans so you’re not caught totally unaware.
Business plans are important for businesses of all sizes so that you can define where your business is and where you want it to go. Growing your business requires a vision, and giving yourself a roadmap in the form of a business plan will set you up for success.
How do I write a simple business plan?
When you’re working on a business plan, make sure you have as much information as possible so that you can simplify it to the most relevant information. A simple business plan still needs all of the parts included in this article, but you can be very clear and direct.
What are some common mistakes in a business plan?
The most common mistakes in a business plan are common writing issues like grammar errors or misspellings. It’s important to be clear in your sentence structure and proofread your business plan before sending it to any investors or partners.
What basic items should be included in a business plan?
When writing out a business plan, you want to make sure that you cover everything related to your concept for the business, an analysis of the industry―including potential customers and an overview of the market for your goods or services―how you plan to execute your vision for the business, how you plan to grow the business if it becomes successful and all financial data around the business, including current cash on hand, potential investors and budget plans for the next few years.
- Best VPN Services
- Best Project Management Software
- Best Web Hosting Services
- Best Antivirus Software
- Best LLC Services
- Best POS Systems
- Best Business VOIP Services
- Best Credit Card Processing Companies
- Best CRM Software for Small Business
- Best Fleet Management Software
- Best Business Credit Cards
- Best Business Loans
- Best Business Software
- Best Business Apps
- Best Free Software For Business
- How to Start a Business
- How To Make A Small Business Website
- How To Trademark A Name
- What Is An LLC?
- How To Set Up An LLC In 7 Steps
- What is Project Management?
- How To Write An Effective Business Proposal

What Is SNMP? Simple Network Management Protocol Explained
What Is A Single-Member LLC? Definition, Pros And Cons
What Is Penetration Testing? Definition & Best Practices
What Is Network Access Control (NAC)?
What Is Network Segmentation?

How To Start A Business In Louisiana (2024 Guide)
Julia is a writer in New York and started covering tech and business during the pandemic. She also covers books and the publishing industry.
Create, share, and e-sign documents in minutes using Jotform Sign.

- Integrations
- Legality Guide
- Signature Creator
- Real Estate
- See all solutions
Automatically create polished, designed documents

- PDF Templates
- Fillable PDF Forms
- Sign Up for Free
Simple Business Plan Templates

Strategic Plan Template
Focus on the future and keep your company moving forward with Jotform’s Strategic Plan Template. Simply fill in the attached form with your company overview, delve deeper with a SWOT analysis, and finish off by determining your strategic goals, actions, and financial plans. Our fully-customizable template converts submitted information into polished PDFs, which you can download, print, or share instantly.

Single Page Business Plan
Get down to business with a customizable Single-Page Business Plan template from Jotform. Customize your plan in minutes. No coding. Drag and drop to build.
Operational Plan Template
This Operational Plan Sample is structured with important details for your organization. It comes ready to print, but you can simply edit the fields by putting your own organization information.

Marketing Brief Template
Managing a marketing campaign or promotion is a challenging task. You need to have a marketing plan in order to execute the campaign smoothly with the time and budget provided. Creating a Marketing Brief is very beneficial because it summarizes the marketing strategy for a specific campaign.If you are in the advertising agency or part of the marketing department, then this Marketing Creative Brief Template is for you. This well-designed template contains the client information, project information, and the marketing materials that will be used. The project details explain the project title, description, objectives, target audience, budget overview, advertising guidelines, and competitors.

Glamping Business Plan Template
Grab the attention of the investors by using this Glamping Business Plan Template. This business plan is simple yet effective because it contains all the necessary details when building a successful business.

SOP Template
Create a process to organize your employees in managing specific cases or scenarios by using this SOP Template. This template is commonly used in any organization whether it is a small, medium, or large group.

Lean Business Model Canvas Template
See your business from a new perspective with Jotform’s Lean Business Model Canvas Template. Simply fill in a short form with problems your business could solve, how they are currently being solved in the market, and how your company can uniquely work to solve these problems. Our template instantly converts the information into polished PDFs you can download or print for your next big meeting.Our Lean Business Model Canvas Template already looks professional, but you can personalize it further to match your business. Jotform PDF Editor lets you rearrange form fields or add your company logo at the touch of a button! By instantly converting your business model into an accessible PDF format, our Lean Business Model Canvas Template can help you see the bigger picture and determine how to take your business to the next level.

Creative Brief Template
A Creative Brief is used in advertising, branding, and marketing industries. In order to have a strong and outstanding creative campaign, you need to have a game plan to follow. This serves as a guideline that will help in making decisions related to the campaign.This Creative Brief Template PDF discusses the project details like the project name, due date, and project description. The marketing materials that will be used are listed in the document which includes its specifications like the dimension size, the medium that will be used, and the quantity. This is the best Creative Brief Template you can use for your next creative marketing campaign.

Business Model Canvas Template
Our Business Model Canvas Template includes nine segments which are key partners, key activities, value proposition, customer relations, customer segments, key resources, channels, cost structure, and pricing model.

Blog Post Outline Template
Use this Blog Post Outline Template for your blog content in order to get more visitors, followers, shares, and impressions. This template will definitely help your ranking in search engines.

Gym Business Plan Template
Be successful in the gym business that you're building by securing funding or a loan with the help of this Gym Business Plan Template. This PDF can be printed and given to investors or loan applications.

Meeting Minutes Template
Set goals, plan your actions, and update your team members by tracking the team meetings by using this Meeting Minutes Template. This PDF template will surely help the team in terms of planning and productivity.

Pressure Washing Estimate Template
Create estimates for pressure washing services with the use of web tools. Use this Pressure Washing Estimate PDF template and create instant estimates in PDF format without the trouble of hiring programmers.

Business Hours Template
Announce and let the customers know if your business is open and not by using this Business Hours Template. This PDF template can be customized and personalized by using the PDF Editor.

Memorandum of Understanding Template
Build a harmonious relationship between two or more parties by using this Memorandum of Understanding Template. This template is easy to use and can be customized via the PDF Editor.

Scope of Work Template
Establish the responsibilities of the service provider by using this Scope of Work Template. This document will show the list of work and tasks that should be performed by the service provider.
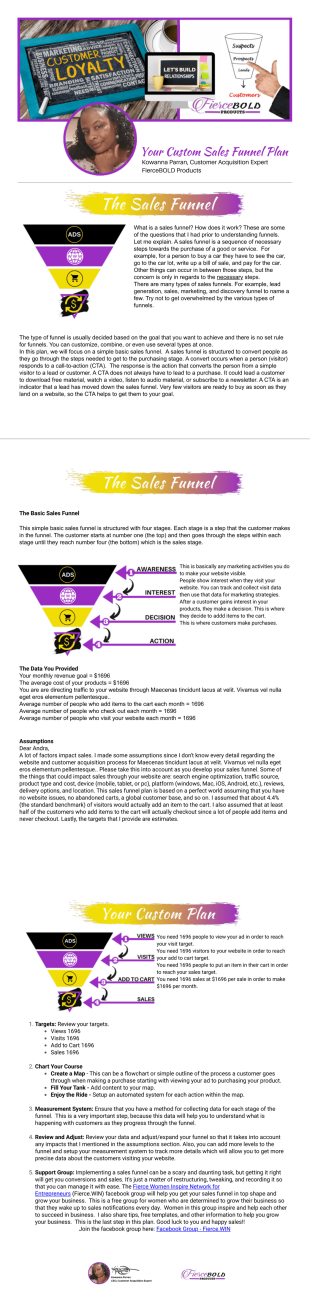
Custom Sales Funnel Plan

Curriculum Vitae
Curriculum Vitae Template will provide you with all the necessary information that you need for your recruitment procedure and automate the job application process of your business.

Preliminary Notice Template
Notify the parties involved like the property owner, hiring party, notifying party, and contractor about the construction project by using this Preliminary Notice Template. This PDF template can be customized if needed via the PDF Editor.
Credit Analysis

Retainer Agreement
Create retainer agreements online. Free, easy-to-customize template. Fill out on any device. Collect e-signatures. Save time with automation tools.
Business Plan Financial Template
Create a business plan financial template with Jotform Sign. Drag and drop to customize. Fill out and e-sign from any smartphone, tablet, or desktop.

Transaction Summary

Employee Code of Conduct Template
Create a professional code of conduct to send to your employees. Can be signed from any smartphone, tablet, or computer. Easy to customize and share. No coding.
About Simple Business Plan Templates
Plans, strategies, roadmaps – Businesses rely on these things to gain perspective on what’s about to happen. Milestones laid down in strategic and careful planning for growth and expansion, visions of where the company’s headed 10 years from now, goals that should meet timelines, all these require a smart, prudent and calculated planning.
Whether you’re a startup, an SMB, or close to a Fortune 500, a solid business plan is crucial. And of course, writing business plans is a huge task. But, what if you needed something that requires input from others though? Say, an online form or a PDF template where responses from your colleagues and managers matter? Well, here’s a collection of PDF templates for business planning.
These are beautifully designed templates, specifically tailored for businesses and companies who don’t know where to start. The hard part was already done and that’s designing the template. These will serve as boilerplates for whatever milestone your business needs. You won’t need to worry on building something from scratch, you just need to focus on the content. Some of these templates will contain or collect executive summaries, opportunities, expectations, execution, financial plans, forecasts, the whole nine yards.
Business plan templates help give a clear vision of what lies ahead. They help you get things organized, planned out, and help you check off items from your to-do list more efficiently.
Frequently Asked Questions
1) what are the seven parts of a business plan.
- Executive summary. This is an overview of your business plan. The executive summary should include your company’s offerings, mission, goals, and projections. Think of it as the elevator pitch for your business plan. If you can’t get investors interested here, it’s unlikely they’ll want to keep reading.
- Company description and history. Describe your business’s legal structure and history in addition to what you do. If you just started this business, you may replace company history with your leadership team’s experience. The purpose of this section is to explain the company structure and build confidence in the people running the company.
- Products and services. Talk about what your company offers, whether that’s products, services, or a combination of the two. Describe your products and services in detail. Explain what makes your offering unique, what your profit margins are, what kind of demand you’re seeing for it, etc.
- Market and competitor research. Investors want to know if there’s demand for your offering. Describe the target market and how your product or service benefits potential customers. Include projections of where the industry is headed over the next few years. Additionally, detail your competitors and how saturated the market is.
- Sales and marketing strategy. This part of the business plan explains how you’ll promote your product. Outline elements such as your ideal customer profile (ICP) as well as your marketing channels, budget, and methods.
- Operations and logistics. Explain how you’ll source materials if you sell products as well as the technology you need to deliver such products and services. Also, provide details about your team, like how many people you’ll need and how you’ll manage employees.
- Financial plan and projections. It’s crucial to prove that your business will be financially viable. For this, you’ll need revenue and expense projections. Many investors want to see sample account statements, balance sheets, and cash flow projections.
2) How do you write a business plan?
Your business plan should be a realistic roadmap that helps you build a successful company. When writing it, take a balanced approach so that you’re not blind to the potential pitfalls and risks. You’ll draft each of the seven sections previously discussed.
Tackling these sections can be overwhelming, so some people like to start with a one-page business plan that includes short paragraphs for each element. Another way to give yourself a head start is by working from a business plan template. Once you have a good start, you can expand each section to make a compelling case for your business.
3) Can I write a business plan myself?
Yes, you can. However, depending on your writing experience and goals, you may want outside help. If the business plan is for internal use with the purpose of improving business functions, you’ll likely be OK tackling it alone. But if you’re trying to secure funding from a bank or investors, a professional business plan writer can give you a leg up.
Even if you decide to do it yourself, have a trusted friend or business mentor review your plan and provide feedback. An objective point of view will help you refine your work.
4) What are the four types of business plans?
- One-page or mini business plan. The one-page option is a great way to improve the focus of your business plan and highlight the essential elements. It can be an effective way to workshop your company’s plan or quickly give others a rundown of your entire business.
- Traditional business plan. The traditional business plan is more in-depth than its one-page counterpart and will be more thorough in each section (often, plans exceed 40 pages). For example, it may contain detailed financials, branding samples, and competitive research documents.
- Business model canvas (BMC). The business model canvas is a more visual representation of your business architecture. It includes sections for infrastructure, offering, customers, finances, etc. Many businesses find the BMC appealing since it can be summarized in a single page.
- Strategic business plan. The strategic business plan can have different purposes, like proving feasibility, discussing planning operations, or projecting growth. It will outline the company’s goals, its strategy for reaching them, and the company structure. The main difference between this and the traditional plan is its focus on specific strategic initiatives.
5) What are the common mistakes in business plans?
- Poor writing. Sloppy writing may suggest that you’re not serious about your business or you lack the needed professionalism.
- Unrealistic expectations. While you should be optimistic about your business, if your financial projections reflect your hopes more than reality, people may hesitate to back your business.
- Lack of supporting documentation. People reviewing your business plan want to see how you back up your claims. You can include research docs, sample financials, and estimates to make your case.
- Failing to define the target audience. For a successful marketing plan, you need to define your target audience. Investors and financial institutions need to see if you’re confident about who you’re selling to.
- Unbalanced. It’s important to lay out the risks and potential upsides. This analysis shows investors that you’re considering the whole picture regarding your business.
These templates are suggested forms only. If you're using a form as a contract, or to gather personal (or personal health) info, or for some other purpose with legal implications, we recommend that you do your homework to ensure you are complying with applicable laws and that you consult an attorney before relying on any particular form.
Access our library of 130 Business Templates
Wow you’ve unlocked access to our library of 130 business templates.
Get started by checking out some of our top business templates:
Featured business templates

Weekly Schedule Template
Tracking employees’ work time and wages is easy with this free weekly schedule template.

Monthly Report
Provide a professional, concise summary of project activities with this monthly report template.

One Page Business Plan
Need to write a business plan but don’t know where to begin? Download our free 1-page business plan ...
6 Free Business Plans | PDF Templates & Examples
All business plans | pdf business templates..
Showing 1 - 6 of 6
.png)
Business Case

Executive Summary Template

Simple Business Plan Template

Startup Business Plan Template

Strategic Planning
Explore template collections.

Customer Service

Spreadsheets

Get all Business Plans | PDF templates and more.
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
How to Write a Great Business Plan
- William A. Sahlman

Every seasoned investor knows that detailed financial projections for a new company are an act of imagination. Nevertheless, most business plans pour far too much ink on the numbers–and far too little on the information that really matters. Why? William Sahlman suggests that a great business plan is one that focuses on a series of questions. These questions relate to the four factors critical to the success of every new venture: the people, the opportunity, the context, and the possibilities for both risk and reward. The questions about people revolve around three issues: What do they know? Whom do they know? and How well are they known? As for opportunity, the plan should focus on two questions: Is the market for the venture’s product or service large or rapidly growing (or preferably both)? and Is the industry structurally attractive? Then, in addition to demonstrating an understanding of the context in which their venture will operate, entrepreneurs should make clear how they will respond when that context inevitably changes. Finally, the plan should look unflinchingly at the risks the new venture faces, giving would-be backers a realistic idea of what magnitude of reward they can expect and when they can expect it. A great business plan is not easy to compose, Sahlman acknowledges, largely because most entrepreneurs are wild-eyed optimists. But one that asks the right questions is a powerful tool. A better deal, not to mention a better shot at success, awaits entrepreneurs who use it.
Which information belongs—and which doesn’t—may surprise you.
Few areas of business attract as much attention as new ventures, and few aspects of new-venture creation attract as much attention as the business plan. Countless books and articles in the popular press dissect the topic. A growing number of annual business-plan contests are springing up across the United States and, increasingly, in other countries. Both graduate and undergraduate schools devote entire courses to the subject. Indeed, judging by all the hoopla surrounding business plans, you would think that the only things standing between a would-be entrepreneur and spectacular success are glossy five-color charts, a bundle of meticulous-looking spreadsheets, and a decade of month-by-month financial projections.
- William A. Sahlman is the Dimitri V. D’Arbeloff-MBA Class of 1955 Professor of Business Administration at the Harvard Business School.

Partner Center

300+ Business Plan Examples

With over two decades of experience, Growthink has assisted more than 1 million companies in developing effective business plans to launch and expand their businesses. Trust in our expertise to guide you through developing a business plan that drives your success. In addition to our sample plans, below you’ll learn the answers to key business plan questions and gain insightful tips on writing your business plan.
Quick Links to Sections On this Page:
- Sample Business Plans By Business Category
Answers to Key Sample Business Plan Questions
Shoutmouth business plan example, business plan examples by business category.
Clothing & Fashion Business Plan Templates & Samples
Clothing Store Business Plan
Embroidery Business Plan
Fashion Business Plan
Jewelry Business Plan
Construction, Interior Design & Home Services Business Plan Templates & Samples
|
|
|
Consumer Services Business Plan Templates & Samples
|
|
|
Business Services Business Plan Templates & Samples
|
|
|
Events Business Plan Templates & Samples
Banquet Hall Business Plan
Event Planning Business Plan
Event Venue Business Plan
Sample Event Venue Business Plan
Party Rental Business Plan
Photo Booth Business Plan
Table and Chair Rental Business Plan
Wedding Planning Business Plan
Farm Business Plan Templates & Samples
|
|
|
Financial Services Business Plan Templates & Samples
|
|
|
Fitness & Beauty Business Plan Templates & Samples
|
|
|
Food & Beverage Business Plan Templates & Samples
|
|
|
Medical & Health Business Plan Templates & Samples
|
|
|
Music & Entertainment Business Plan Templates & Samples
Music Business Plan
Party Bus Business Plan
Podcast Business Plan
Production Company Business Plan
Record Label Business Plan
Recording Studio Business Plan
Nonprofit Business Plan Templates & Samples
Sample Non-Profit Business Plan
Charity Business Plan
Sample Nonprofit Business Plan PDF
Social Enterprise Business Plan
Real Estate Business Plan Templates & Samples
Sample Airbnb Business Plan
House Flipping Business Plan
Property Development Business Plan
Property Management Business Plan
Real Estate Business Plan
Real Estate Agent Business Plan
Real Estate Business Plan PDF
Real Estate Development Business Plan
Real Estate Investment Business Plan
Retail & Ecommerce Business Plan Templates & Samples
|
|
|
Technology Business Plan Templates & Samples
Biodiesel Business Plan
Blogging Business Plan
Clean Tech Business Plan
Mobile App Business Plan
Saas Business Plan
Software Company Business Plan
Technology Business Plan
Transportation Business Plan Templates & Samples
|
|
|
Travel and Lodging Business Plan Templates & Samples
Bed and Breakfast Business Plan
Campground Business Plan
Glamping Business Plan
Hotel Business Plan
Mobile Home Park Business Plan
Resort Business Plan
RV Park Business Plan
Travel Agency Business Plan
1. Why is utilizing an example business plan a good idea?
Sample business plans can help you quickly and easily write a business plan for your own business. Business plans are an important tool for any business, but they can be challenging to create. A sample business plan will help you understand the business plan format , the benefit of market research, and how to write a compelling executive summary. It can also serve as a guide for creating your own business plan, outlining the key sections and providing examples of successful plans. Utilizing the best business plan template can save you time and ensure that your plan is well-structured and comprehensive.
Business plan examples may even help you with the different sections of a plan, including market analysis, business description, cash flow statements/business financial statements, and more. Business plans can also show you how a quality plan in your exact business plan category is organized and shows you the appropriate business communications style to use when writing your business plan.
2. Who would benefit from using an example business plan?
Any entrepreneur or business owner who has never written a business plan before can benefit from an example or sample plan. New business owners often start with business plan templates , which are helpful but are sometimes more useful after reviewing other sample business plans.
A good sample plan can be a step-by-step guide as you work on your business planning and business idea. Once you have a sense for the flow, specs, and details, etc. that business plans have, utilizing a business plan template will help you pull everything together, helping you create a plan investors and other stakeholders will value. A solid business plan will also help you if you need a bank loan, which may require a startup business plan. Download our free business plan template to help you get started on your own business plan.
Free Download : Free Business Plan Template PDF
3. How do you get started with a sample business plan and maximize its benefit?
First you should read the business plan thoroughly. Study both the type of information provided in key sections like the executive summary, target market analysis, summary, etc., as well as the format and style of the plan. As you read, you may find yourself thinking through things such as improving or evaluating your business planning process, your business idea, or reconsidering who you want to write your business plan for. This is OK and part of the process. In fact, when you start writing a business plan for the first time, it will be much easier because you’ve gone through this process.
After this initial read, outline your business plan and copy in from the sample plan sections that apply to your business. For instance, if the sample plan included public relations in their marketing strategy and sales plan, and you will also use this tactic, you can copy it into your plan and edit it as appropriate. Finally, answer the other questions answered in the sample plan in ways that reflect your unique business and target customers.
Writing a business plan can seem daunting. Starting your business plan writing process by reviewing a plan that’s already been created can remove a lot of mental and emotional barriers while helping you craft the best plan you can.
4. When should you not use a sample business plan?
If your business is unlike any other, using a sample business plan will not be as effective. In this situation, writing a business plan from scratch utilizing a business plan template is probably your best path forward.
As an example, Facebook’s early business plan was unlike others since it was paving a new path and way of doing business. But, groundbreaking new businesses like Facebook are not the norm, and the vast majority of companies will benefit from utilizing sample business plans.
5. How do you choose the right type of business plan for your venture?
Selecting the appropriate type of business plan depends on your business’s stage, needs, and goals. Let’s explore the different types of business plans and how to determine which business plan format is right for you.
- Startup Business Plan : This type of plan is for businesses just starting out and seeking funding or investment. It typically includes a detailed analysis of the market, target audience, competition, and financial projections.
- Traditional Business Plan : Traditional business plans are the most common type of business plan, used by established businesses to outline their goals and strategies. It includes all the key sections such as market analysis, company description, and financial statements.
- Internal Business Plan : Internal business plans are used for internal purposes, to guide the day-to-day operations and decision making of the business. It may not be as detailed as a traditional business plan, but still includes important information such as company mission, objectives, and key performance indicators.
- Feasibility Business Plan : A feasibility business plan is used to assess the viability of a new product or service in the market. It includes detailed research and analysis to determine if the business idea is feasible and profitable.
- One-Page Business Plan : As the name suggests, this type of business plan is condensed into one page and includes the most critical information about the business. It can be a useful tool for pitching to potential investors or partners.
- Strategic Business Plan : A strategic plan looks at the big picture and long-term business goals of a company. It may include the company’s mission statement, core values, and overarching strategies for achieving success.
Ultimately, the type of business plan you choose will depend on your business’s specific needs and goals. It may also be beneficial to combine elements from different types of plans to create a customized plan that best fits your business. Carefully consider your objectives and resources before deciding on the right type of plan for your venture.
Finish Your Business Plan in 1 Day!
Don’t you wish there was a faster, easier way to finish your business plan?
With Growthink’s Ultimate Business Plan Template you can finish your plan in just 8 hours or less!
The business plan example below is for Shoutmouth, a company that enjoyed much success in the early 2000’s and which was able to raise funding. While the plan’s premise (social networking) is not as unique now as it was then, the format and structure of this business plan still holds.
I. Executive Summary
Business Overview
Launched in late February 2007, Shoutmouth.com is the most comprehensive music news website on the Internet .
Music is one of the most searched and accessed interests on the Internet. Top music artists like Akon receive over 3 million searches each month. In addition, over 500 music artists each receive over 25,000 searches a month.
However, music fans are largely unsatisfied when it comes to the news and information they seek on the artists they love. This is because most music websites (e.g., RollingStone.com, MTV.com, Billboard.com, etc.) cover only the top eight to ten music stories each day – the stories with mass appeal. This type of generic coverage does not satisfy the needs of serious music fans. Music fans generally listen to many different artists and genres of music. By publishing over 100 music stories each day, Shoutmouth enables these fans to read news on all their favorite artists.
In addition to publishing comprehensive music news on over 1200 music artists, Shoutmouth is a social network that allows fans to meet and communicate with other fans about music, and allows them to:
- Create personal profiles
- Interact with other members
- Provide comments on news stories and music videos
- Submit news stories and videos
- Recommend new music artists to add to the community
- Receive customized news and email alerts on their favorite artists
Success Factors
Shoutmouth is uniquely qualified to succeed due to the following reasons:
- Entrepreneurial track record : Shoutmouth’s CEO and team have helped launch numerous successful ventures.
- Affiliate marketing track record : Online affiliate marketing expertise has been cited as one of MySpace’s key success factors. Over the past two years, Shoutmouth’s founders have run one of the most successful online affiliate marketing programs, having sold products to over 500,000 music customers online.
- Key milestones completed : Shoutmouth’s founders have invested $500,000 to-date to staff the company (we currently have an 11-person full-time team), build the core technology, and launch the site. We have succeeded in gaining initial customer traction with 50,000 unique visitors in March, 100,000 unique visitors in April, and 200,000 unique visitors in May 2007.
Unique Investment Metrics
The Shoutmouth investment opportunity is very exciting due to the metrics of the business.
To begin, over the past two years, over twenty social networks have been acquired. The value in these networks is their relationships with large numbers of customers, which allow acquirers to effectively sell to this audience.
The sales price of these social networks has ranged from $25 to $137 per member. Shoutmouth has the ability to enroll members at less than $1 each, thus providing an extraordinary return on marketing expenditures. In fact, during an April 2007 test, we were able to sign-up 2,000 members to artist-specific Shoutmouth newsletters at a cost of only 43 cents per member.
While we are building Shoutmouth to last, potential acquirers include many types of companies that seek relationships with music fans such as music media/publishing (e.g., MTV, Rolling Stone), ticketing (e.g., Ticketmaster, LiveNation) and digital music sales firms (e.g., iTunes, The Orchard).
Financial Strategy, Needs and Exit Strategy
While Shoutmouth’s technological, marketing and operational infrastructure has been developed, we currently require $3 million to execute on our marketing and technology plan over the next 24 months until we hit profitability.
Shoutmouth will primarily generate revenues from selling advertising space. As technologies evolve that allow us to seamlessly integrate music sampling and purchasing on our site, sales of downloadable music are also expected to become a significant revenue source. To a lesser extent, we may sell other music-related items such as ringtones, concert tickets, and apparel.
Topline projections over the next three years are as follows:
| 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | |
| Shoutmouth Members | 626,876 | 4,289,580 | 9,577,020 |
| Unique Visitors | 2,348,050 | 8,390,187 | 18,633,659 |
| Total Page Views (Millions) | 20.7 | 273.5 | 781.0 |
| Revenues | $165,431 | $2,461,127 | $7,810,354 |
| Expenses | $1,407,958 | $2,591,978 | $2,838,423 |
| EBITDA | ($1,242,527) | ($130,851) | $4,971,931 |
II. Shoutmouth Overview
What is Shoutmouth?
Shoutmouth is an operating company of The Kisco Group Inc. (TKG). Since 2003, TKG has capitalized on web-based marketing opportunities via launching targeted websites and generating web-based leads. TKG revenues in 2005 exceeded $1.3 million and grew to $3.5 million in 2006. Shoutmouth is currently the sole focus of TKG; all other TKG business units have been divested.
Development of Shoutmouth began in August 2006 and the site officially launched on February 21, 2007. Shoutmouth (located at www.shoutmouth.com) is the most comprehensive music news community on the Internet. The website covers 1,200 popular bands and music artists and offers more than 100 new music articles each day. In addition to providing news, Shoutmouth is a web community. That is, Shoutmouth members can actively participate on the site, by doing things such as commenting on news stories and submitting their own stories.
The Market Size and Need for Shoutmouth
The music market is clearly vast. According to IFPI, which represents the recording industry worldwide, global music sales were $33.5 billion in 2005, with the U.S. accounting for $12.3 billion of that amount. Importantly, digitally music sales are seeing substantial growth, with IFPI reporting sales of $400 million in 2004, $1.1 billion in 2005 and $2 billion in 2006.
Online, music is the one of the most frequently searched and accessed interests. For example, according to Wordtracker, the music artist Eminem received over 1.7 million web searches in December 2006, while band Green Day received 534,000 searches.
To put these figures in perspective, top celebrities in other entertainment fields receive but a fraction of this search volume. For example, December 2006 search volumes for select sports stars and actors were as follows: Kobe Bryant, 122K; Tiger Woods, 88K; Cameron Diaz, 332K; and Tom Cruise, 82K.
Conversely, 225 music artists received over 100,000 searches in December 2006, and over 500 music artists received over 25,000 searches.
This data is corroborated by Nielsen BuzzMetrics which plots the most popular topics bloggers are posting about. The chart to the right plots September 25, 2006 to March 25, 2007 and shows how music dominates other entertainment sectors online.
When searching for music artists online, fans, which are primarily between the ages of 13 and 35, are looking for news, pictures, lyrics, videos and audio files. In addition, fans enjoy publicly voicing their opinions about music and interacting with other fans.
There is currently no website besides Shoutmouth that provides comprehensive music news. Currently, to get the latest news on their favorite artists, fans must visit the official websites or fan websites of each of the artists they like . Even then, it is unlikely that the fan will get all the news that has occurred. To solve this problem, Shoutmouth scours the web and uncovers news from thousands of web sites.
What Shoutmouth Does and Will Offer
As of May 2007, the site covers the 1,200 most popular music artists (popularity primarily based on the number of web searches over the past 12 months for each artist).
Shoutmouth currently offers members the ability to:
- Read over 500 new music articles each week
- Read special features such as album reviews, interviews, new album release dates, top quotes of the week and other special reports
- Watch and rate music videos
- Listen to select music audio clips
- Comment on news stories and music videos
- Submit news stories that they see/hear of elsewhere
- Suggest new music artists to add to the site
- View articles by music artist or by genre (current genres include Rock, Pop, Rap, R&B, Country, and Electronic)
- Create a user profile that includes their favorite music artists, Shoutmouth friends, news stories submitted to Shoutmouth, and comments made. Members have the ability to find other members based on their favorite artists and via our search functions.
- Receive customized news and email alerts. Members can customize their “My News” page to include only artists they specify. Likewise, they can choose to receive email alerts whenever there is a new story on one of their favorite artists.
While establishing itself as the premier music news community, Shoutmouth will embark on the more aggressive goal of becoming the premier music community online . To accomplish this, Shoutmouth will begin to offer additional content (more videos, audio, pictures, lyrics, etc.) and additional functionality (music compatibility testing (e.g., if you like this, you’ll like this), voting capabilities, member-to-member messaging, etc.). We have already begun mapping out our content and technology growths plans to achieve this goal upon financing.
Importantly, Shoutmouth expects to be able to add massive amounts of relevant content (e.g., lyrics, reviews, pictures, video files, audio files, etc.) via member submissions and moderation. This is the same way that YouTube has been able to quickly add millions of videos and Wikipedia has been able to add millions of articles. Importantly, since established music websites (e.g., MTV, RollingStone.com, Billboard.com, etc.) are not community based, they would have to hire thousands of staff members to rival the content that Shoutmouth will have.
How We Get and Publish Our News
Currently, news stories that appear on Shoutmouth are gathered from numerous online sources. Shoutmouth’s staff writers find these stories by using RSS and News feeds that cover thousands of websites. In addition, Shoutmouth community members have the ability to submit stories they find elsewhere.
Typical stories include factual information plus the insight of the author. Shoutmouth editors ensure that all stories are properly classified by artist and genre, and that duplicate articles are filtered out.
Over the past three months, Shoutmouth has developed a solid infrastructure, which we consider a core competitive advantage, that that allows us to provide comprehensive music news . This infrastructure includes:
- Setting up hundreds of RSS feeds based on comprehensive research regarding sites from which to receive feeds
- Training our editorial team regarding identifying a story and weeding out duplicates
- Assigning music artists among our five-person editorial team to better manage work flow and avoid duplicate articles
We are working on a system to ensure that member-submitted articles are automatically routed to the appropriate member of Shoutmouth’s editorial team to improve our efficiencies further.
Shoutmouth’s Goal to Break News First
The majority (approximately 90%) of Shoutmouth’s articles are currently developed by our in-house editorial team, while the balance is submitted by members. In addition, virtually all of our articles are based on information gleaned from other websites. As such, we are generally not the first to publish news; however we are the first and only site to publish all the news in one easily-accessible place. The one current exception is news which is published on bands’ official MySpace pages; Shoutmouth generally publishes articles on this news 24 to 48 hours before it is reported by other news or music sites (due to our efficiencies in finding news).
Shoutmouth realizes that it will gain a key competitive advantage, and will generate significant market buzz, if it is able to report on music news stories before other media sources . To accomplish this, we have begun contacting publicity departments at record labels to gain direct access to music news. We expect these contacts to enable us to gain immediate and sometimes exclusive access to news which will help further establish Shoutmouth as the canonical source for music news. We also plan to more aggressively solicit member submissions of new, buzzworthy news events and will consider offering rewards for unique substantiated news (much the way paparazzi are compensated).
III. Competition in the Online Music Market
This section of the business plan provides a competitive analysis, which is an overview of the competitive landscape, discusses both indirect and direct competitors and then details Shoutmouth’s competitive advantages.
Because consumer demand for music on the Internet is so great, there are a vast number of music websites. In summary, we consider most sectors of the online music market (which are discussed below) to be indirect competitors and potentially partners, rather than direct competitors, because none of them focus on music news.
The reason we believe that no one focuses on music news is that it is very difficult to do. Because news is very important to music fans, most music websites offer news. However, they primarily get their news from organizations such as CNN, Reuters, the Associated Press and BBC. These large organizations only write about the music stories that have mass appeal, which traditionally amounts to 8-10 music news stories per day. However, since music fans are often zealots when it comes to their favorite artists, they are not merely interested in cover stories. For instance, a U2 fan cares about any U2 news, particularly news that a non-U2 fan might consider insignificant.
In fact, because Shoutmouth is the sole one-stop shop for getting comprehensive music news, there might be an opportunity to license our content to other music websites.
Sectors of the Online Music Market
Shoutmouth specifically comPs in the community-based music news market. While players in this market represent direct competitors, Shoutmouth faces indirect competitors in the following markets:
- Community-Based Sites
- Community-Based News Sites
- Community-Based Music Sites
- Traditional Music Websites
- Official Artist and Fan Sites
Each of these markets is described below.
A. Community-Based Sites
Community-based sites, also known as social networking sites, are websites in which members can create profiles, leave comments throughout the site, and communicate with other members among other features.
A June 2006 report by Piper Jaffray entitled “Silk Road: Social Networking is Here to Stay” effectively sums up the power and longevity of social networking:
“We believe social networking sites have become a permanent part of the fabric of web applications and are rapidly becoming one of the most popular activities online, potentially impacting how other popular services such as email, IM, and maybe even search are accessed.
As a clear indication of the growth rate and scale of social networking, consider this: MySpace monthly page views have now surpassed MSN or AOL in the U.S. and are nearly 75% of the size of Yahoo!. Social networking has filled a gap that was left by all the existing portals and web services and it is fulfilling a very important and basic function for millions of users: allowing them to express themselves and connect with their friends, with the two functions tightly integrated.
The leading sites such as MySpace (News Corp), Facebook, and others are amassing significant power in the new landscape of the Internet and the existing Internet companies are likely to have to work with these newcomers as they may yield material control on the flow of traffic to other applications.”
Social networking sites such as MySpace.com, Facebook.com, Tagged.com, and TagWorld.com have educated consumers regarding the value of these sites and how to use them. Their success has spurred genre-specific social networks such as community-based/social networking news sites and music sites, which are discussed below.
Shoutmouth doesn’t view established social networking sites as competitors since these sites have a general focus. That is, members talk about all aspects of life, from dating to music to movies, etc. Conversely, Shoutmouth is solely focused on music.
B. Community-Based News Sites
Community-based news sites are sites in which members decide what’s newsworthy and what’s not. For instance, on Digg.com, the most prominent community-based news site, members “Digg” stories that they feel are most newsworthy. The stories that the community feels are most important rise to Digg’s homepage, while less important stories get little attention.
Digg’s one million members can submit stories, “digg” stories, and comment on stories. Digg focuses on general news with a slant towards technology, gaming and unique/sensational news. While Digg does have a Music area within its Entertainment section, this receives little focus. In fact, at the time of the writing of this plan, Digg’s music home page only includes one article submitted within the past 48 hours. Furthermore, Digg doesn’t pare down the music category into sub-categories such as Rock and individual music artists. Conversely, these sub-categories are the entire focus of Shoutmouth.
Other sites that are similar to Digg include Newsvine.com, Spotback.com and Gabbr.com. Of most relevance is the Digg-like site for music, Noisetap.com, which was launched by Ticketmaster in January 2007.
Like Digg, Noisetap.com allows members to submit and vote for music stories. Noisetap.com is organized by music genre and not by music artist. This most likely will not satisfy the needs of many music fans since they don’t have the ability to find news on the specific artists they care most about. Likewise, without a full-time staff actively researching and publishing news stories at the artist-level, Noisetap.com will never be able to offer the comprehensive news that Shoutmouth does.
While Shoutmouth is currently similar to community-based news sites in that members can submit stories and comment on the news they find most interesting, no established player in the market provides a comprehensive focus on music. In addition, Shoutmouth sees these sites as marketing partners as we have and will continue to submit our stories on them to increase our readership.
C. Community-Based Music Sites
There are many community-based music websites, although none focuses on music news such as Shoutmouth. Conversely, these sites generally give members the ability to create and listen to song play lists. The community acts to help individual members find new music and new friends based on similarities in their music tastes. Prominent sites in this genre include Last.fm, Finetune, Pandora, RadioBlogClub, MyStrands, iLike[1] and iJigg.
Last.fm is the most prominent community-based music site and is a good model with which to compare Shoutmouth. Likewise, we will benchmark our performance against Last.fm as we reach of goal of becoming the premier music news community and focus on becoming the premier music community.
According to Alexa, Last.fm is the 359th most visited site on the Internet. While Last.fm focuses on allowing members to create customized Internet stations based on their music tastes, the site has much additional content and social networking features. For instance, for each artist, Last.fm includes pictures, a bio, concert dates, discography, fans on Last.fm, and similar artists. Fans are also able to create journals and communicate with other fans. Key features that Last.fm doesn’t currently focus on include news and video.
D. Traditional Music Websites
Traditional music websites such as MTV.com, RollingStone.com, Billboard.com, NME.com, AOL Music, and Yahoo! Music tend to have many features such as news, reviews, pictures, videos and audio. While these sites are generally very well done and extremely popular, they are under-serving visitors in two core areas: music news and community .
These sites’ lack of music news stems from the difficulty in creating this news, specifically that it requires filtering through thousands of articles and websites to find relevant stories. Likewise, as discussed, these firms might wish to license our news content in the future.
Regarding community , none of the top music sites are thriving communities. Rather, either these sites offer no community features or they recently began offering select features (e.g., submitting reviews or commenting on articles). Even when available, the community features on these sites are afterthoughts and are not engrained within the core fabric of the sites.
While they haven’t been able to transform their current sites into communities, top music websites clearly understand the power of online music communities and have an appetite for them. For example, in January 2007, MTV invested in social networking website TagWorld. MTV also acquired RateMyProfessors.com and Quizilla.com (teen social network) in January 2007 and October 2006 respectively.
As mentioned previously, our vision is to build and incorporate additional technologies, and use our “army” of members to publish vast amounts of music content on Shoutmouth, in order to fully satisfy music fans and leapfrog traditional music sites in terms of their music content.
E. Official Artist and Fan Sites
Shoutmouth com’s with official music artist websites and fan websites. These sites often include news about the specific artist as well as pictures, videos and other relevant information.
On one hand, official music artist and fan websites are direct competitors to Shoutmouth. This is because some of these sites offer comprehensive news on the specific artist they cover. In addition, many offer forums, discussion boards or other ways to communicate with other fans.
However, two factors separate Shoutmouth from these types of sites: 1) breadth and 2) sophistication.
- Breadth : Most music fans love more than one artist. As such, in order to get the news they want, they would have to visit/join multiple fan or artist websites rather than getting all of their news from Shoutmouth.
- Sophistication : While some official music artist websites are technologically sophisticated, offering forums, networking and other worthwhile features, the majority of artist and fan websites have limited usability, functionality and networking ability. In fact, this deficiency has lead to the success of MusicToday, which provides front and back-end technology to power artist websites.
Specifically, MusicToday offers web design and hosting, develops sophisticated online stores, builds online fan clubs and offers web ticketing among other services to select top music artists such as Dave Matthews Band, Christina Aguilera, Kenny Chesney, Britney Spears and Usher. While offering sophisticated tools for select music artist websites, MusicToday offers little to no music news nor advanced social networking functions. For instance, the official Dave Matthews Band website offers less than one news story per month.
F. Direct Competitors: Community-Based Music News Sites
Shoutmouth’s direct competitors are other music news websites that have social or community features that allow users to join the site, submit articles, comment on articles, create public profiles and/or communicate with other members. Shoutmouth has identified one significant player who offers this service, AbsolutePunk.net.
AbsolutePunk.net has done a good job of building a user base (the site claims 125,000+ registered members and nearly 500,000 un-registered members). In addition, the user base is very active — the average story on their site receives approximately 20 comments. AbsolutePunk.net offers music news, reviews, pictures and interviews among other features.
On the negative side, AbsolutePunk.net’s articles are generally posted by one staff writer (as opposed to Shoutmouth’s five writers), most articles are simply one sentence posts rather than full articles, and no attempt seems to have been made to cover all news stories. In addition, the site only covers the punk music genre. Although “punk” is broadly defined on the site, the site doesn’t cater to genres such as R&B, rap and country among others, failing to satisfy the broader market.
AbsolutePunk.net is owned by Indieclick, a Los Angeles-based media company. According to the AbsolutePunk.net website, the site:
- Has developed a loyal (72% return rate) reader base
- 5,182,147 Posts
- 163,535 Threads
- 126,448 Members
- 1,711 Artist Profiles
- 20,774 Multimedia Files
- Approx 76,000 visits per day.
- Approx 276,000 pageviews per day.
Shoutmouth’s Competitive Advantage
In addition to being the first to fill the untapped market void for comprehensive music news, Shoutmouth’s competitive advantage in the market primarily includes the following:
Online Marketing Sophistication
Content Development Experience and Expertise
Shoutmouth’s team, primarily team members DL and PF, has operated an affiliate marketing business focusing on music for the past four years. Affiliate marketing is defined as a system of revenue sharing between one site (the affiliate) which features an ad or content designed to drive traffic to another site (the merchant). The affiliate receives a fee based on traffic to the merchant which converts to sales.
Our affiliate business has focused on connecting music fans, primarily aged 13 to 30, with music offers such as iPods and ringtones. Over the past two years, we have successful sold affiliated offers to over 500,000 customers. We have become a significant online advertiser, receiving Google’s “over 1 million leads” award, and are recognized as a major player among the top affiliate networks.
It is important to note that affiliate marketing success has been credited with part of MySpace’s success. This is because effective affiliate marketers understand how to drive and convert on Internet traffic.
Shoutmouth will employ its affiliate marketing techniques to drive traffic to Shoutmouth.com and enroll members. We will utilize technologies and proprietary techniques that allow us to monitor multiple metrics such as the cost per visitor, cost per member sign-up, etc., so that we can set and maintain profitable metrics.
Another venture that Shoutmouth team members, primarily PK and DL, launched was the development of over 3,000 niche websites. To create the content for these websites, we employed a virtual work force of over 90 researchers in India and 30 writers and editors in the US.
This experience taught us how to manage a large workforce, train writers to improve content quality and motivate a large group of people. These skill sets will be critical in allowing Shoutmouth to grow the content of the site, as developed by both staff and members, while maintaining quality standards.
IV. Marketing Plan
Shoutmouth’s marketing plan includes the following:
Online Advertising : Shoutmouth will initiate pay-per-click advertising campaigns on Google and Yahoo! in order to inexpensively drive traffic to the site. Specifically, Shoutmouth believes it can drive qualified traffic to the site for 20 cents per visitor and achieve a 20% member conversion rate, thus generating members at a cost of $1.00 per member.
Keys to Shoutmouth’s success in achieving this metric include:
- Conducting thorough keyword research and advertising on appropriate keywords and keyword groups
- Creating advertising text that maximizes click through rates
- Creating landing pages that maximize conversions while maintaining the highest Google AdWords quality score possible
- Closely monitoring conversions to quickly stop and/or modify unprofitable campaigns
- Getting individuals to enter their email address to join the newsletter is much easier than getting them to join a site where they have to create a username, select a password, etc. As such, step one will be to get visitors to sign up for artist-specific newsletters.
- Once on the newsletter distribution list, members will constantly receive messages (embedded in their daily newsletter) regarding the benefits of participating more on Shoutmouth.
- Active Shoutmouth Membership: the constant reminders regarding Shoutmouth’s value proposition in the daily newsletters will influence members to participate more actively on the site (e.g., customize their profile, visit the site more often, etc.).
Invite-A-Friend : Shoutmouth is in the process of creating an aggressive invite-a-friend/member referral program. In doing so, we are following the lead of social movie community, Flixster, which grew to 5 million members within 10 months. It did this by encouraging members, during their initial registration process, to upload and send an invitation to multiple contacts in their email address books. The technology to develop this process is fairly complex and we expect to be completed with and to rollout this program in June 2007.
Direct Email Marketing : Shoutmouth will directly contact bloggers and prominent music fans we find online to tell them about Shoutmouth, encourage them to join, and encourage them to write about Shoutmouth on their blogs and online journals .
Creating/Distributing Buzzworthy/Viral Content : Shoutmouth plans to have several buzzworthy/viral articles (i.e., content that people would want to email to their friends since it is funny, interesting, etc.) on the site each day. With a single click, visitors will be able to send these articles to social bookmarking sites such as Digg.com or Fark.com, where these articles could receive widespread attention. In addition to our traditional news stories, Shoutmouth will also periodically create special reports/features in order to satisfy our members and visitors and to try to get widespread exposure.
An example of the power of such buzzworthy content, Shoutmouth has already succeeded in having two stories accepted by Fark and Digg, which have brought in over 50,000 unique visitors.
Super Fans/Street Team Development : Shoutmouth also plans to recruit “super fans.” Super fans are individuals who are passionate about a certain music artist/band and actively contribute articles and/or comments on Shoutmouth. We will recruit these fans, reward them with status (e.g., adding a gold Shoutmouth headphones image to their profile page) and encourage them to more aggressively promote the site by:
- Submitting more news to Shoutmouth
- Commenting on more articles on Shoutmouth
- Growing the Shoutmouth community around their favorite artist(s) by actively recruiting new members to join the site (such as actively posting Shoutmouth-related comments on their MySpace pages, on other music forums, etc.)
Public Relations : Upon financing, Shoutmouth will hire a public relations firm to help us get mentions in media sources ranging from magazines, newspapers, radio, television and blogs. To date, we have developed and issued press releases via Billboard Publicity Wire which have been syndicated throughout the web. An effective PR firm will enable Shoutmouth to quickly reach a wide audience.
Widgets : Shoutmouth will create artist-specific and genre-specific music news widgets. For example, our U2 widget (see example on right) would include all of the recent U2 articles published on Shoutmouth. The widget can easily be placed on MySpace pages, blogs, etc. Each story title in the widget links to the full article on Shoutmouth.
Shoutmouth has great expectations for our widget. To begin, no such widget currently exists as there is no one place to get comprehensive news for specific music artists. Secondly, each time someone places a Shoutmouth widget on their blog or social networking page, it will effectively market Shoutmouth to a wide audience at zero cost to us.
V. Technology/Site Development Plan
This section provides a brief roadmap of the initial and future functionality of Shoutmouth.
Initial Site Functionality
The initial Shoutmouth website will include the following features:
- Ability to submit and comment on news stories
- Ability to suggest new music artists to add to the site
- Ability to create user profiles
- Ability to receive customized news and email alerts
- Articles categorized by artist and core genre (e.g., Rock, Rap, Pop, etc.)
- Music artist sections which includes News, Bio and Fans
Future Site Functionality
Shoutmouth will use news and basic functionality as the platform though which we will build a thriving music community. After initial launch, the Shoutmouth technology team will work on incorporating additional features such as:
- Ability to message other members via the site (e.g., members will have an Inbox on the site)
- Event calendars: members will receive online calendars. With the click of a button, the member will be able to add tour dates of their favorite artists/bands to their calendar.
- Articles also categorized by sub-genre (e.g., Alternative Rock, West Coast Rap, etc.)
- Music artist sections to also include videos, audio files, photo galleries, reviews and event calendars to which members can upload files and vote on top content.
- Forums and member blogs
- Music compatibility testing (suggestions on song/artists members might like)
- Trivia quizzes
- Music playlists
VI. Financial Plan
Revenue Model
During the first six months, Shoutmouth will not generate any revenues as it will not sell advertising space nor offer products for sale. This decision has been made to spur the growth of the Shoutmouth community. By initially positioning Shoutmouth more as a non-profit, for-the-people-by-the-people venture, members will be more prone to promote the site and invite their friends than if the site looks too commercial.
Starting in September 2007, Shoutmouth will primarily generate revenues from selling advertising space. As technologies (such as the Snocap music widget) evolve that allow us to seamlessly integrate music sampling and purchasing on our site, sales of downloadable music are also expected to be a significant revenue source. To a lesser extent, we may sell other music-related items such as ringtones, concert tickets, and apparel.
Funding To Date
To date, Shoutmouth’s founders have invested $500,000 in Shoutmouth, with which we have accomplished the following:
- Built the site’s core technology
- Hired and trained our core staff (we currently maintain an 11-person full-time team)
- Populated the website with content (over 10,000 articles and 1,200 artist bios)
- Generated brand awareness among music fans, including driving 50,000 unique visitors in March, 100,000 unique visitors in April, and 200,000 unique visitors in May 2007.
Funding Requirements/Use of Funds
Shoutmouth is currently seeking $3 million to provide funding for the next 24 months. At this point, the site will be profitable and can grow organically, or additional capital may be sought to more aggressively expand our member base.
The capital will be used as follows:
- Execution of Marketing plan : in order for Shoutmouth to grow its visitor and member base, we need to invest dollars in online advertising and public relations. With regards to online advertising, we are confident that we can enroll members at a cost of $1 per member, which is a fraction of the value of the members to an acquirer (minimum $25 per member), thus providing a significant return on our marketing investments.
- Execution of Technology plan : in order to build a thriving community, Shoutmouth needs to offer its visitors a “stickier” website and enhanced features. We currently maintain a vast “wish list” of features, such as members uploading and rating pictures and videos, trivia quizzes, and member-to-member messaging, that will significantly improve the site’s functionality and value proposition.
- Staffing : In order to reach our goals, we will have to hire additional technical and operations personnel.
Financial Projections
Below is an overview of Shoutmouth’s Financial Projections for the next three years. Please see the Appendix for the full financial projections and key assumptions.
Exit Strategy / Valuation Metric
Shoutmouth’s most likely exit strategy is to be acquired by a traditional music website or property (e.g., Viacom/MTV, Ticketmaster, Rolling Stone), an entertainment/media conglomerate (e.g., Yahoo!, IAC/InterActiveCorp, NBC), or a large social networking site (e.g., News Corp/MySpace).
This strategy is supported by the significant M&A activity in the social networking market, which includes the following transactions over the past 24 months:
| Del.icio.us | social bookmarking | 12/05 | $30-$35 million | Yahoo! |
| eCrush Inc. | teen social network | 01/07 | Undisclosed | Hearst Magazines Digital Media |
| FanNation | sports social networking | 01/07 | $20+ million | Sports Illustrated |
| Five Across Inc. | social networking | 02/07 | Undisclosed | Cisco Systems Inc. |
| Flickr | photo uploading and sharing community | 03/05 | $15-35 million (rumored) | Yahoo! |
| Grouper | video creating, uploading and sharing community | 08/06 | $65 million | Sony Pictures |
| Jumpcut | video creating, uploading and sharing community | 09/06 | $15 million (rumored) | Yahoo! |
| KiwiBox.com | teen social network | 02/07 | Undisclosed | Magnitude Information Systems, Inc. |
| MyBlogLog | blog community tool | 01/07 | $10 million (rumored) | Yahoo! |
| MySpace | social networking | 07/05 | $580 million | News Corp. |
| Quizilla.com | teen social network | 10/06 | Undisclosed | Viacom/MTV Networks |
| RateMyProfessors.com | community focused on rating college professors | 01/07 | Undisclosed | Viacom/MTV Networks |
| social news site | 10/06 | Undisclosed | Conde Nast/ Wired Digital | |
| Sconex.com | social network for high school students | 03/06 | $6.1 million | Alloy Inc. |
| TelevisionWithoutPity.com | TV fan site | 03/07 | Undisclosed | Bravo |
| Weblogs Inc. | blogging network | 10/05 | $25 million (rumored) | AOL |
| YouTube | video community | 10/06 | $1.65 billion | Google Inc. |
Regarding valuation, below are the estimated valuations of social networking companies on a per member basis upon exit:
- Del.icio.us: $50 – $100 per member
- MySpace: $25 per member
- Xing (business social network): $137 per member at IPO in 10/06
- Flickr: $56 – $130 per member
- Grouper: $130 per member
Based on this data, not only are social networking sites a promising investment, but sites that can acquire members for less than $25 each (a conservative valuation estimate based on the figures above), should earn a solid return on investment. As discussed above, Shoutmouth’s goal is to acquire members for no more than $1 each.
In addition, per the membership projections above, Shoutmouth’s valuation at the end of 2009, at a $25 valuation per member, is expected to be $239 million. A more conservative, using a 24.4 time EBITDA multiple (the average multiple of tech M&A deals in 2006 according to The M&A Advisor), yields a $121 million valuation in 2009.
Shoutmouth’s founding team includes entrepreneurs and managers with a track record of success and a history of successfully working together.
Management Team
DL, Co-Founder and CEO
D has a history of successfully launching and growing businesses of all sizes. As president and co-founder of an entrepreneurial services firm., D has personally assisted in the launch and development of over 100 ventures.
Over the past three years, D founded and has managed The Kisco Group which includes an affiliate marketing division (2006 revenues exceeded $3 million), a search engine optimization business which includes a network of 3,000 websites (2006 revenues exceeded $500,000) and an e-commerce business (which includes TopPayingKeywords.com and ShowerHeadsEtc.com).
D earned his Bachelors degree from the University of South Carolina.
PK, Co-Founder and Vice President of Operations
For the past two years, P has managed The Kisco Group’s search engine optimization business where he hired, trained and managed nearly 100 employees and a dozen outside firms. During this time, P has honed his management skills with regards to content development, marketing and operations.
P has had a passion for music since childhood and has been a semi-professional drummer for the past 15 years.
P earned his Bachelors of Arts degree, magna cum laude, from Clemson University.
PF, Co-Founder and Vice President of Technology
For the past year, P has managed The Kisco Group’s affiliate marketing business. In addition to setting up and managing widespread marketing campaigns, P has developed sophisticated analytic techniques to precisely analyze web traffic in order to optimize profitability.
Since August 2006, P has shifted his efforts and leveraged his technology skills in developing the Shoutmouth website. P has been instrumental in selecting the Content Management Platform upon which Shoutmouth is built, and finding and managing the technology team.
P earned his Bachelor of Arts degree from Swarthmore College.
AB, Marketing Manager
A’s background in music includes being a singer, songwriter, guitarist and producer. He has also worked on the marketing side of music, having marketed Veritas Records through the development and distribution of promotional materials.
A’s career also includes psychological research and administration, having served as a Research Assistant with the Interpersonal Perception And Communication Laboratory in Cambridge, MA.
A earned his Bachelor of Arts degree in Psychology from Ohio State University.
M, Lead Technology Developer
M is an experienced web programmer with expertise in web design, application development and database development among others.
M’s work experience includes serving as a Senior Developer at Spheres. M has also engaged in multiple, long term freelance projects including serving as a Database Developer Consultant with The Penn Group and a Web Developer Consultant with Volution Media Group and Allied Online Consulting Group.
M earned his Bachelors degree in Computer Science with a minor in Cognitive Science from Rutgers University.
Content Development Team
Shoutmouth’s writing team, managed by PK, includes the following members:
- JS, Editorial Manager: former content manager and copywriter for Scholastic Inc. and Promotions.com.
- TZ: former music intern (Virgin Records and WRRV) and author of the blog, The Tom Z Show .
- ML: former assistant editor for Adventure Publishing; author of the blog Certified Gangsta ; and former editor-in-chief of Fordham University’s newspaper The Paper .
- SB: former staff writer for Paste Magazine , The Clarion Ledger , and Nightclub and Bar Magazine among others.
- CSJ: former editorial intern for Rolling Stone and Editorial Assistant for Psychology Today .
Outsourced Technology Team
Shoutmouth works very closely with 2skies, a technology firm based in Australia with staff in Australia and the United States. 2skies is run by JDN, one of the co-founding developers of XE, the platform upon which Shoutmouth is built.
XE is an extensible, Open Source web application framework written in PHP and licensed under the GNU General Public License. XE delivers the requisite infrastructure and tools to create custom web applications that include fully dynamic multi-platform Content Management Solutions (CMS).
VIII. Appendix: Shoutmouth Financial Projections 3-Year Income Statement
| Total Page Views (MILLIONS) | |||
| Revenues | $165,431 | $2,461,127 | $7,810,354 |
| Staffing | $891,058 | $1,328,078 | $1,522,923 |
| Outsourced Technology | $115,000 | $60,000 | $60,000 |
| Office Space | $26,400 | $90,000 | $90,000 |
| Advertising | $254,000 | $900,000 | $900,000 |
| Other Marketing/Public Relations | $72,000 | $120,000 | $150,000 |
| Web Hosting | $11,500 | $33,900 | $55,500 |
| Other | $38,000 | $60,000 | $60,000 |
| $1,407,958 | $2,591,978 | $2,838,423 | |
| ($1,242,527) | ($130,851) | $4,971,931 | |
| Depreciation | $1,600 | $4,200 | $5,800 |
| ($1,244,127) | ($135,051) | $4,966,131 | |
| Income Taxes @ (40%) | ($497,651) | ($54,020) | $1,986,452 |
| Income Taxes Paid | $0 | $0 | $1,434,781 |
| Income Tax Credit | ($497,651) | ($551,671) | $0 |
| ($1,244,127) | ($135,051) | $3,531,350 |
3-Year Balance Sheet
As of December 31
| Cash | $1,845,206 | $1,614,336 | $4,726,360 |
| Accounts Receivable (30 days) | $13,597 | $202,284 | $641,947 |
| Inventory | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Current Assets | $1,858,803 | $1,816,620 | $5,368,307 |
| Other Assets | |||
| Equipment (Computer systems, office equipment, etc.) | $16,000 | $26,000 | $32,000 |
| Accumulated Depreciation | ($1,600) | ($5,800) | ($11,600) |
| Total Long-Term Assets | $14,400 | $20,200 | $20,400 |
| $1,873,203 | $1,836,820 | $5,388,707 | |
| Accounts Payable (30 days) | $117,330 | $215,998 | $236,535 |
| Total Current Liabilities | $117,330 | $215,998 | $236,535 |
| Long Term Debt | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Paid In Capital | $3,000,000 | $3,000,000 | $3,000,000 |
| Retained Earnings | ($1,244,127) | ($1,379,178) | $2,152,172 |
| Total Equity | $1,755,873 | $1,620,822 | $5,152,172 |
| $1,873,203 | $1,836,820 | $5,388,707 |
3-Year Cash Flow Statement
| Net Income/Loss | ($1,244,127) | ($135,051) | $3,531,350 |
| Depreciation | $1,600 | $4,200 | $5,800 |
| Minus Increase in Accounts Receivable | ($13,597) | ($188,687) | ($439,663) |
| Plus Change in Current Liabilities | $117,330 | $98,668 | $20,537 |
| Net Cash Flow from Operating | ($1,138,794) | ($220,870) | $3,118,024 |
| Purchases of Property & Equipment | ($16,000) | ($10,000) | ($6,000) |
| Net Cash Flow from Investing | ($16,000) | ($10,000) | ($6,000) |
| Cash Received from Investors | $3,000,000 | $0 | $0 |
| Net Cash Flow from Financing | $3,000,000 | $0 | $0 |
| $1,845,206 | ($230,870) | $3,112,024 | |
| $1,845,206 | $1,614,336 | $4,726,360 |

400+ Business Plan Examples to Launch Your Business

Select your Business Category

IT, Staffing & Customer Service (16)

Construction, Architecture & Engineering (17)

Food, Beverage & Restaurant (57)

Real Estate & Rentals (16)

Mobile Apps & Software (6)

Education & Training (14)

Beauty Salon & Fitness (19)

Medical & Health Care (39)

Retail, Consumers & E-commerce (80)

Entertainment & Media (43)

Transportation, Logistics & Travel (26)

Agriculture, Farm & Food Production (18)

Nonprofit & Community (9)
Manufacturing & Wholesale (33)

Services (213)

Clothing & Fashion (12)

Children & Pets (16)

Fine Art & Crafts (5)

Cleaning, Maintenance & Repair (22)

Hotel & Lodging (9)

Finance & Investing (13)

Consulting, Advertising & Marketing (22)

Accounting, Insurance & Compliance (5)
Didn't find what you are looking for.
Writing a business plan from scratch seems like an uphill climb? We get that, but hold tight—you’re not alone. Even business plan writers often feel the same way while writing from scratch. That’s where a little content reference or inspiration can help—just like these business plan examples .
Reading such real-life sample business plans can be incredibly helpful while drafting your very first business plan with zero clue about business plan writing.
As you read and explore these industry-specific examples, you learn more about what you should and should not include in your business plan, ensuring sustainable and long-term growth.
So, let’s explore these 400+ business plan examples to help you quickly write a business plan—hassle-free.
Why you should refer a business plan example?

A Business plan example will provide you with the complete format and structure for your document, giving you a head start on developing your document so you’re not stuck seeing an empty page working to find out where to start.
Also, it gives you the overall layout of a professional business plan so you understand what goes where and you’re not leaving out anything.
Here are some of the key benefits of using sample business plans:
- Guidance on what to include in each section. If you’ve never attended business school, you might never have created a SWOT analysis or a balance sheet before. Business templates that give guidance — in plain language — about what to include and how to fill in each section and create a complete and effective plan.
- A business plan is vital to get an investment. If you’re seeking investment for your business, you’ll need to convince banks and investors why they should invest in your business. Lenders and investors will only risk their time and money if they’re certain that your business will be successful and profitable and they will get a great return on their investment.
- A business plan can help you prioritize. A complete, well-balanced business plan is one of the most valuable tools in assisting you to reach your long-term goals. It gives your business direction, defines your goals, outlines out strategies to reach your goals, and helps you to manage possible bumps in the way.
Creating a business plan will help you define the business goals you want to achieve, and define the strategies to achieve them. This means you can focus your resources and energy on what is important, rather than wasting time on unimportant things.
If you’re working with a team in your company then having a regular brainstorming session is the best way to keep your business on track and your business plan assures you’re all on the same page.
Make your plan in half the time & twice the impact with Upmetrics.

Sample business plan format
Following is the standard business plan format you must consider while drafting a comprehensive business plan.
- Executive Summary : A high-level overview of your business plan.
- Company Overview : An in-depth and detailed description of your small business, its fundamental elements, and future goals.
- Market Analysis : A detailed description of your industry with the target market, competitors, and growth potential.
- Products and Services : Description of the products or services you intend to exchange for money.
- Sales and Marketing Strategies : Promotional strategies you will use to attract and retain customers.
- Operations Plan : Business processes and procedures that ensure seamless business operations.
- Management Team : Introduction to your founders, key management, and their compensation plan.
- Financial Plan : A breakdown of your financial projections and financing needs.
- Appendix : A supplementary final section that includes additional documents to support your plan.
This was about the outline. Now let’s break down and understand how to write each section, step by step, with real-life examples.
1. Executive Summary
Executive Summary is the first section of your business plan, providing a high-level overview of your entire plan and summarizing it for a quick understanding of your business.
Considering it as an introductory section of your plan, it must be clear, concise, and written to grab readers’ attention and persuade them to take action.
As business plans can be 10-20 to a hundred-page long, an executive summary remains your sole chance to gain a quick extra point.
Here are a few key components your Executive Summary must include:
- Business concept
- Company’s mission
- Company History
- Market Opportunity
- Management Team
- Financial Projections
Remember, you are bound to cover these topics in detail moving forward in your business plan, so make sure your executive summary is brief, covering only the key takeaways.
2. Company Overview
As the name suggests, the Company Overview section of your plan provides an overview of your small business, including your business concept, objectives, future goals, and what customers your business serves.
Since you will provide a brief company description in the executive summary, this section will expand on it—providing an in-depth understanding of your business.
Remember, this section is a platform for introducing and positioning your business as an ideal solution for your target market to your reader. So, make sure it’s short and succinct but impactful enough to help them understand what it does, who your potential customers are, and how you can make a difference.
Here are a few key components your business overview must include:
- Company Description
- Mission Statement
- Business Objectives
- Business History
- Future Goals
3. Market Analysis
Market Analysis is a study of your external business environment, providing a complete overview of your industry and its dynamics. This section provides valuable insights into the market, like what’s working.
When smartly researched, utilized, and written, this section can help you discover and identify untapped areas in the market and strategize to stand out from your competitors.
Remember, this section helps your readers and potential investors understand your target market, market size, and growth potential, so make sure you play your cards right.
Here are a few key components your market analysis section must include:
- Target Market
- Market Size and Growth Potential
- Competitive Analysis
- Market or Industry Trends
- Regulatory Environment
Unlike other sections of your business plan , Market Analysis requires deep research and analytical work. However, using an industry-specific example business plan can save hours of research work.
4. Products And Services
The products and services section is where you will mention and elaborate on your product or service range, description, pricing strategies, and more.
Since your business success solely depends on your products or services, your entire plan revolves around this particular section.
This section can be a crucial component of your plan while searching for an investor or partner, as a well-articulated products and services section can help you persuade them.
Here are a few key elements your products and services section must include:
- Product Description
- Product Comparison
- Pricing Strategy
- Order Management
- Quality Measures
5. Sales And Marketing Strategies
A business’s sales and marketing strategies determine how your product is displayed and reaches your target audience.
A well-designed sales and marketing plan can help you streamline your marketing efforts and create impactful and effective marketing campaigns while keeping track of the marketing budget and maximizing return on investment.
In short, this section will discuss how you’ll acquire new customers using your sales and marketing strategy. You might consider including the following information in your sales and marketing plan:
- Your target audience and brand positioning
- Your business’ UVP
- Marketing channels and distribution tactics you plan to use
- Sales goals and performance measurement
- Your customer retention strategies
- Your sales and marketing goals
6. Operations Plan
The operations plan section outlines the daily business processes and activities centered on achieving business goals and objectives described in the previous sections of your plan.
A detail-oriented logistics and operations plan helps you and your team define your responsibilities, daily tasks, and short-term goals you need to achieve, keeping track of your long-term objective.
Remember, your logistics and operations plan won’t be static but a living document. You may adjust and update it as time goes on.
Here are a few key elements your operations plan section must include:
- Staffing and training
- Tools and equipment
- Inventory management
- Supply chain management
- Operational process
7. Management Team
Your management team plays a crucial role in the ultimate success of your business. And this section introduces your owners and management team, along with their qualifications, industry experience, roles and responsibilities, and compensation plan.
A strong management team section can be critical to weigh authority and help investors be confident about your business idea and vision.
Make sure to include the educational background, accomplishments, work experience, and area of expertise for each individual, part of your management.
You might consider including the following information in the management team section:
- Business owner/founders
- Key management
- Organization structure
- Compensation plan
- Advisors/consultants
8. Financial Plan
It’s no secret that the financial plan is the most crucial yet nerve-wracking aspect of business planning. In fact, it’s one of the deciding factors when it comes to convincing potential investors and banks to invest or lend money.
This section of your plan details your business’s financial information and how it will reach its financial goals. The information may include balance sheet, income, and cash flow statements.
Here are a few key components and financial statements you must include or provide while creating a financial plan:
- Profit and loss statements
- Operating costs
- Income statement
- Cash flow statement
- Balance sheet
- Break-even point
- Financing needs
9. Appendix
While an Appendix isn’t a required element of your business plan, it can be pretty helpful in adding legal notes, charts, tables, or any other critical information to support your business document.
It generally includes financial statements, information, and documents that didn’t naturally fit into your plan but can be considered critical enough to add.
In addition, it helps readers navigate through the entire business plan and easily find specific information or documents.

Need a way out from manual editing and business plan writing work?
Get Upmetrics’ business plan template, import data directly into the editor, and start editing using Upmetrics AI Assistant.
Start Planning Now
Since we are finished discussing the sections of a business, let’s learn more about how you can put an example business plan to use while writing your own.
How to use an Example of a Business Plan to write your own?
Having real-life and industry-specific business plan examples by your side can be incredibly resourceful to help you write a business plan from scratch.
A well-planned structure helps you outline your plan, while content inspiration helps you set the tone for your business document.
Let’s dive deep and understand how to use these examples effectively to write your business plan.
1. Understanding the Structure
Traditional business plans generally follow a similar structure.
It starts with an executive summary followed by a company description, market analysis, product and services, sales and marketing strategies, operational plan, management team, financial plan, and appendix.
Using an example business plan is the best way to understand the structure and outline your plan.
2. Gaining Inspiration
Reading industry-specific business plan examples can help you gain inspiration for your plan. You can gain insights on presenting your business idea, vision, mission, and values and persuade investors to invest in your idea.
3. Learning Industry-Specific Language
There’s no universal template for business planning that fits all. An industry-specific template can help you learn and understand the business language for your industry and the best way to communicate your message to your investors.
4. Identifying Key Elements
Reading business plan examples of similar businesses can help you identify the key elements and information to include in your plan. You can keep note of these and ensure everything necessary for investors to consider is present in your final draft.
5. Crafting Financial Projections
A financial plan is a critical component of your business plan, and a good business plan example can help you better understand how they project their financials which can be incredibly helpful while forecasting yours.
6. Refining Your Executive Summary
As mentioned earlier, your executive summary is a key factor influencing potential investors and lenders to invest or lend you money. Analyzing free business plan templates can help you optimize your executive summary to make it more brief, persuasive, and attention-grabbing.
7. Realizing what works and what doesn’t
Analyzing industry-specific and real-life examples can help you determine what works best and what doesn’t within your industry. Understanding these factors can help you avoid many significant pitfalls.
While business plan examples can be incredibly helpful in writing a plan from scratch, ensure your plan is customized for your business and sends out a unique message. Your business plan must reflect its unique idea, vision, and target market.
Download business plan examples for:
- Business Plan Template for Startups
- Business Plan Template for Small Business
- Business Plan Example for Non Profits
- Business Plan Example for Students
Download a free sample business plan template
Ready to kick-start your business plan writing process? Not sure where to start? Here you go, download our free sample business plan, import data directly into the editor, and start planning.
This intuitive, modern, and investment-ready template is designed specifically for startups and small businesses. In fact, this format has helped 110K+ entrepreneurs create business plans to secure funding, business grants, and loans. It includes a business planning course and step-by-step instructions to write each section.
Business plan types: choose the suitable template
Well, there are a few types of business plans. Though they cover similar categories, they all have different formats intended for different purposes or industries.
Here are a few common business plan types to help you choose the most suitable one for your business:
1. One-page business plan
One page business plan can be considered a one-page version of a standard business plan. It’s mainly used to present a quick overview of small businesses to your vendors, employees, investors, or stakeholders.
Considering its shorter length, creating a one page business plan can be a lot easier and less time-consuming compared to a standard business plan using a business plan software like Upmetrics.
2. Lean business plan
A lean business plan is a summarized version of a standard business plan that is longer than a one-page one. It’s mainly used to track finances and emphasize achieving short-term milestones.
This business plan type is best suitable if you are unsure about the business planning process. Moreover, drafting a lean business plan is also a lot easier and faster than a standard one.
3. Traditional business plan
A traditional business plan is the standard plan entrepreneurs have been using for years to outline marketing strategies, project financials, and draw investors. A traditional business plan can be a few dozen to a hundred-page long, depending on its purpose and your business specifications.
A traditional plan is a must-have business document for business owners aiming to achieve long-term business success.
4. Internal business plan
As the name suggests, an internal business plan is a document designed for internal management and team members to ensure everyone’s on the same page. The primary focus of these plans is to set primary goals and outline processes aiming to achieve them—ultimately streamlining business operations.
Start writing your business plan
There’s no denying—creating a business plan that draws investors in needs some serious work; it’s no stroll in the park. But you must take the first step to stay ahead in the cut-throat competition; there is no way around it.
So, what are you waiting for? Understand your business and the value it offers to its customers, find a suitable template from our library, and start planning.

Simplifying Business Planning through AI-Powered Insights.

Founder, CEO & Lead Scientist at Nanolyse Technologies
After trying Upmetrics, I wish to highly recommend this app to anyone who needs to write a business plan flexibly and to a high standard.
Frequently Asked Questions
How can i write my own business plan.
Follow this step-by-step process to write your business plan on your own.
- Choose a format that best suits your business requirements
- Create a business plan outline
- Create a company description section
- Conduct market research
- Conduct a competitive analysis
- Describe your product and services
- Outline sales and marketing strategies
- Create a logistics and operations plan
- Introduce management team
- Project financials
- Summarize your plan with an executive summary
- Complete your plan with an appendix
Where can I find business plan examples?
Upmetrics is an incredible business planning solution providing 400+ business plan samples and examples. You can easily create a good business plan using these industry-specific templates.
What is a business plan template?
A business plan template is a pre-formatted business plan, usually written for a fictional company. These industry-specific templates can help entrepreneurs understand a business plan’s structure and other key components. These templates are used mainly by entrepreneurs planning to launch a new startup or expand an existing business.
Should I hire someone to write my business plan for me?
Concept, contents, and cashflow are the 3Cs of a business plan that can be defined as follows:
- Concept: Your concept should explain the purpose of your business, summarizing what you plan to accomplish with this very business.
- Contents: Your content should reflect your concept, product and services, target market, and competition.
- Cashflow: Your cash flow section must detail your cash in-and-out flows, including capital investment, operations costs, and revenue projections.
Why Is It Beneficial to Use a Sample Business Plan as a Guide?
Let’s face it—writing a 40-50 page business plan from scratch can be too intimidating; you may soon give up and won’t even finish it.
Instead, using a sample business plan as a guide can help you understand its structure, gain inspiration and ideas for content, plan marketing strategies, and project financials. In short, using business template examples is the best way to write a business plan.
When should you not follow a business plan example?
We’ve always been saying this, using an example of a business plan is the best way to write one. However, it’s also critical to understand when not to follow a template. Here’s when:
- The format does not align with your business model or industry.
- Include outdated templates and information.
- Offer poorly written content.
- Include misleading and poorly done financials.
- There’s a lack of expertise.
These are a few red flags in a template you must consider looking at while choosing one.
Are these examples suited for business plan beginners?
Absolutely. In fact, these examples are specially designed, keeping common issues faced by beginners while drafting a plan in mind to serve them best. So, if you are a new or an established business with no planning experience, you have to check out these templates.
Looking for a faster way to finish your business plan?
Updating a Classic: Writing a Great Business Plan
- A business plan can't be a tightly crafted prediction of the future but rather a depiction of how events might unfold and a road map for change.
- The people making the forecasts are more important than the numbers themselves.
- What matters is having all the required ingredients (or a road map for getting them), not the exact form of communication.
- The best money comes from customers, not external investors.
Sean Silverthorne: " How to Write a Great Business Plan " has been one of the most downloaded articles on Harvard Business Publishing since you wrote it in 1997. Why do you think you hit a nerve?
Bill Sahlman: Writing a business plan is a seminal moment in the life of a new venture. Doing so entails committing to paper a vision of the factors that will affect the success or failure of the enterprise. People take the exercise very seriously and get emotionally invested in what they produce.
In that context, the article was written to give insights into how to think about the role of a business plan and its relation to new venture formation. I tried to explain that a business plan can't be a tightly crafted prediction of the future but rather a depiction of how events might unfold and a road map for change. I emphasized the notion that successful entrepreneurs constantly seek the right mixture of people, opportunity, context, and deal. They anticipate what can go wrong, what can go right, and they try to balance risk and reward.
Over the years, I have received many e-mails from folks trying to craft a business plan. They want feedback. Actually, they really want me to say that they are on the right track. I explain that I would need to get to know them and their opportunity much better than what is possible in an e-mail and that the written document is not as important as the people writing it. It's not science—it's art and craft.
Q: In the decade since the original article came out, business conditions have changed. If you were writing this piece today, would you change it much?
A: I don't think the world has changed materially. Successful ventures still have competent people pursuing sensible opportunities, using resources that help, in a favorable context. Yes, the context is very challenging today. But challenges create opportunities.
If gaining access to capital is hard, sometimes that means there will be fewer competitors. This period is almost the antithesis of the Internet bubble when everyone could raise money and start a company regardless of how lamebrained the idea. Also, we have difficult factor markets like energy, but that simply means that there are great opportunities for people with ideas for alternative energy.
Were I rewriting the article today, I might emphasize the importance of controlling your destiny by being conservative about access to capital. Many great ventures in the Internet era (pre-1999) ended up failing because they assumed they would have continued access to cheap capital. Many of those businesses failed, though the underlying idea was sensible. Similarly, we have seen a period when capital markets got ugly, which has a negative effect on all ventures, sensible and nonsensical.
I would also reinforce the idea that entrepreneurship is critical around the world. We are confronted with many crises from health care to the environment to global poverty. Solutions are likely to come from talented private sector and social entrepreneurs.
Q: You wrote in the original article that most business plans "waste too much ink on numbers and devote too little to the information that really matters to intelligent investors." Still true today? What really matters to investors?
A: When there is great uncertainty in the market, investors become quite risk averse. They will only back proven entrepreneurs with truly compelling ideas. People make the numbers, not conversely. So, I still think the people making the forecasts are more important than the numbers themselves.
Q: More and more entrepreneurial ventures are "born global": They seek to address a global market and attract funding from global investors. Should a business plan be tailored in some way for a global audience?
A: We live in a world of democratized access to ideas, human capital, and money. There are fabulous global ventures being started in every corner of the globe. These ventures can raise money locally or globally. They can disperse talent in many countries.
Take a company like Skype. When I visited Skype several years ago, it had 125 employees from 23 countries. The development team was in Estonia, and its headquarters in Europe. Skype had raised seed capital in Europe and in the United States. That's the new model.
Q: On the technology front, software applications such as Microsoft Word, Excel, and PowerPoint have added many charting, graphing, and visualizing capabilities. Some business plans are even written as Web pages. Should entrepreneurs avail themselves of these tools for business plans, or do they clutter the message too much?
A: On the first floor of the Rock Center at HBS there is a copy of the original business plan that Arthur Rock wrote for Intel some 40 years ago. It's only a few pages long, but it describes an outstanding team pursuing a new technology. I have seen compelling business plans in the form of a few PowerPoint slides, a couple of scribbled pages, and a brief video. What matters is having all the required ingredients (or a road map for getting them), not the exact form of communication.
Q: If you were to update your "Glossary of Business Plan Terms" and what they really mean ("We seek a value-added investor" really means "We are looking for a passive, dumb-as-rocks investor"), what current terms would you include?
A: The glossary holds today. I think entrepreneurs, investors, and employees need to be suitably skeptical about what they read in business plans. I have read perhaps 5,000 plans and have only seen three companies really meet their plan. That sounds like a pattern to me. If anyone makes a bet based on the company doing exactly as written, he or she will be sadly disappointed.
At the same time, every player has to be somewhat optimistic about the possibility of overcoming inevitable setbacks. I think of ventures as roller coasters, not rocket ships.
Q: Any general advice to entrepreneurs seeking funding in the uncertain capital markets of today?
A: The best money comes from customers, not external investors. I think entrepreneurs need ideas that are so compelling they can get early money from customers. I also believe that great teams with great ideas can continue to access capital on quite attractive terms from outstanding investors. If the short term looks unsettled, that often means that focusing on the long term has a big potential payoff.
- 25 Jun 2024
- Research & Ideas
Rapport: The Hidden Advantage That Women Managers Bring to Teams
- 11 Jun 2024
- In Practice
The Harvard Business School Faculty Summer Reader 2024
How transparency sped innovation in a $13 billion wireless sector.
- 24 Jan 2024
Why Boeing’s Problems with the 737 MAX Began More Than 25 Years Ago
- 27 Jun 2016
These Management Practices, Like Certain Technologies, Boost Company Performance
- Entrepreneurship
- Business Model
- Risk and Uncertainty
- Business Strategy
- Business Plan
- Forecasting and Prediction
Sign up for our weekly newsletter

550+ Business Plan Examples to Launch Your Business

Need help writing your business plan? Explore over 550 industry-specific business plan examples for inspiration.
Find your business plan example

Accounting, Insurance & Compliance Business Plans
- View All 25

Children & Pets Business Plans
- Children's Education & Recreation
- View All 33

Cleaning, Repairs & Maintenance Business Plans
- Auto Detail & Repair
- Cleaning Products
- View All 39

Clothing & Fashion Brand Business Plans
- Clothing & Fashion Design
- View All 26

Construction, Architecture & Engineering Business Plans
- Architecture
- Construction
- View All 46

Consulting, Advertising & Marketing Business Plans
- Advertising
- View All 54

Education Business Plans
- Education Consulting
- Education Products
Business plan template: There's an easier way to get your business plan done.

Entertainment & Recreation Business Plans
- Entertainment
- Film & Television
- View All 60

Events Business Plans
- Event Planning
- View All 17

Farm & Agriculture Business Plans
- Agri-tourism
- Agriculture Consulting
- View All 16

Finance & Investing Business Plans
- Financial Planning
- View All 10

Fine Art & Crafts Business Plans

Fitness & Beauty Business Plans
- Salon & Spa
- View All 36

Food and Beverage Business Plans
- Bar & Brewery
- View All 77

Hotel & Lodging Business Plans
- Bed and Breakfast
Brought to you by
Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy

IT, Staffing & Customer Service Business Plans
- Administrative Services
- Customer Service
- View All 22

Manufacturing & Wholesale Business Plans
- Cleaning & Cosmetics Manufacturing
- View All 68

Medical & Health Business Plans
- Dental Practice
- Health Administration
- View All 41

Nonprofit Business Plans
- Co-op Nonprofit
- Food & Housing Nonprofit
- View All 13

Real Estate & Rentals Business Plans
- Equipment Rental

Retail & Ecommerce Business Plans
- Car Dealership
- View All 116

Technology Business Plans
- Apps & Software
- Communication Technology

Transportation, Travel & Logistics Business Plans
- Airline, Taxi & Shuttle
- View All 62
View all sample business plans
Example business plan format
Before you start exploring our library of business plan examples, it's worth taking the time to understand the traditional business plan format . You'll find that the business plan samples in this library and most investor-approved business plans will include the following sections:
Executive summary
The executive summary is an overview of your business and your plans. It comes first in your business plan and is ideally only one to two pages. You should also plan to write this section last after you've written your full business plan.
Your executive summary should include a summary of the problem you are solving, a description of your product or service, an overview of your target market, a brief description of your team, a summary of your financials, and your funding requirements (if you are raising money).
Products & services
The products & services chapter of your business plan is where the real meat of your plan lives. It includes information about the problem that you're solving, your solution, and any traction that proves that it truly meets the need you identified.
This is your chance to explain why you're in business and that people care about what you offer. It needs to go beyond a simple product or service description and get to the heart of why your business works and benefits your customers.
Market analysis
Conducting a market analysis ensures that you fully understand the market that you're entering and who you'll be selling to. This section is where you will showcase all of the information about your potential customers. You'll cover your target market as well as information about the growth of your market and your industry. Focus on outlining why the market you're entering is viable and creating a realistic persona for your ideal customer base.
Competition
Part of defining your opportunity is determining what your competitive advantage may be. To do this effectively you need to get to know your competitors just as well as your target customers. Every business will have competition, if you don't then you're either in a very young industry or there's a good reason no one is pursuing this specific venture.
To succeed, you want to be sure you know who your competitors are, how they operate, necessary financial benchmarks, and how your business will be positioned. Start by identifying who your competitors are or will be during your market research. Then leverage competitive analysis tools like the competitive matrix and positioning map to solidify where your business stands in relation to the competition.
Marketing & sales
The marketing and sales plan section of your business plan details how you plan to reach your target market segments. You'll address how you plan on selling to those target markets, what your pricing plan is, and what types of activities and partnerships you need to make your business a success.
The operations section in our business plan examples covers the day-to-day workflows for your business to deliver your product or service. What's included here fully depends on the type of business. Typically you can expect to add details on your business location, sourcing and fulfillment, use of technology, and any partnerships or agreements that are in place.
Milestones & metrics
The milestones section is where you lay out strategic milestones to reach your business goals.
A good milestone clearly lays out the parameters of the task at hand and sets expectations for its execution. You'll want to include a description of the task, a proposed due date, who is responsible, and eventually a budget that's attached. You don't need extensive project planning in this section, just key milestones that you want to hit and when you plan to hit them.
You should also discuss key metrics, which are the numbers you will track to determine your success. Some common data points worth tracking include conversion rates, customer acquisition costs, profit, etc.
Company & team
Use this section of your business plan to describe your current team and who you need to hire. If you intend to pursue funding, you'll need to highlight the relevant experience of your team members. Basically, this is where you prove that this is the right team to successfully start and grow the business. You will also need to provide a quick overview of your legal structure and history if you're already up and running.
Financial projections
Your financial plan should include a sales and revenue forecast, profit and loss statement, cash flow statement, and a balance sheet. You may not have established financials of any kind at this stage. Not to worry, rather than getting all of the details ironed out, focus on making projections and strategic forecasts for your business. You can always update your financial statements as you begin operations and start bringing in actual accounting data.
Now, if you intend to pitch to investors or submit a loan application, you'll also need a "use of funds" report in this business plan section. This outlines how you intend to leverage any funding for your business and how much you're looking to acquire. Like the rest of your financials, this can always be updated later on.
The appendix isn't a required element of your business plan. However, it is a useful place to add any charts, tables, definitions, legal notes, or other critical information that supports your business plan. These are often lengthier or out-of-place information that simply didn't work naturally into the structure of your plan. You'll notice that in these business plan examples, the appendix mainly includes extended financial statements.
Types of business plans explained
While all business plans cover similar categories, the style and function fully depend on how you intend to use your plan. To get the most out of your business plan, it's best to find a format that suits your needs. Here are a few common business plan types worth considering.
Traditional business plan
The tried-and-true traditional business plan is a formal document meant to be used for external purposes. Typically this is the type of plan you'll need when applying for funding or pitching to investors. It can also be used when training or hiring employees, working with vendors, or in any other situation where the full details of your business must be understood by another individual.
Business model canvas
The business model canvas is a one-page template designed to demystify the business planning process. It removes the need for a traditional, copy-heavy business plan, in favor of a single-page outline that can help you and outside parties better explore your business idea.
The structure ditches a linear format in favor of a cell-based template. It encourages you to build connections between every element of your business. It's faster to write out and update, and much easier for you, your team, and anyone else to visualize your business operations.
One-page business plan
The true middle ground between the business model canvas and a traditional business plan is the one-page business plan . This format is a simplified version of the traditional plan that focuses on the core aspects of your business.
By starting with a one-page plan , you give yourself a minimal document to build from. You'll typically stick with bullet points and single sentences making it much easier to elaborate or expand sections into a longer-form business plan.
Growth planning
Growth planning is more than a specific type of business plan. It's a methodology. It takes the simplicity and styling of the one-page business plan and turns it into a process for you to continuously plan, forecast, review, and refine based on your performance.
It holds all of the benefits of the single-page plan, including the potential to complete it in as little as 27 minutes . However, it's even easier to convert into a more detailed business plan thanks to how heavily it's tied to your financials. The overall goal of growth planning isn't to just produce documents that you use once and shelve. Instead, the growth planning process helps you build a healthier company that thrives in times of growth and remains stable through times of crisis.
It's faster, keeps your plan concise, and ensures that your business plan is always up-to-date.
Download a free sample business plan template
Ready to start writing your own business plan but aren't sure where to start? Download our free business plan template that's been updated for 2024.
This simple, modern, investor-approved business plan sample is designed to make planning easy. It's a proven format that has helped over 1 million businesses write business plans for bank loans, funding pitches, business expansion, and even business sales. It includes additional instructions for how to write each section and is formatted to be SBA-lender approved. All you need to do is fill in the blanks.
How to use an example business plan to help you write your own

How do you know what elements need to be included in your business plan, especially if you've never written one before? Looking at business plan examples can help you visualize what a full, traditional plan looks like, so you know what you're aiming for before you get started. Here's how to get the most out of a business plan sample.
Choose a business plan example from a similar type of company
You don't need to find an example of a business plan that's an exact fit for your business. Your business location, target market, and even your particular product or service may not match up exactly with the business plans in our gallery. But, you don't need an exact match for it to be helpful. Instead, look for a business plan sample that's related to the type of business you're starting.
For example, if you want to start a vegetarian restaurant, a plan for a steakhouse can be a great match. While the specifics of your actual startup will differ, the elements you'd want to include in your restaurant's business plan are likely to be very similar.
Use a business plan example as a guide
Every startup and small business is unique, so you'll want to avoid copying an example of a business plan word for word. It just won't be as helpful, since each business is unique. You want your business plan to be a useful tool for starting a business —and getting funding if you need it.
One of the key benefits of writing a business plan is simply going through the process. When you sit down to write, you'll naturally think through important pieces, like your startup costs, your target market , and any market analysis or research you'll need to do to be successful.
You'll also look at where you stand among your competition (and everyone has competition), and lay out your goals and the milestones you'll need to meet. Looking at an example of a business plan's financials section can be helpful because you can see what should be included, but take them with a grain of salt. Don't assume that financial projections for a sample company will fit your own small business.
If you're looking for more resources to help you get started, our business planning guide is a good place to start. You can also download our free business plan template .
Think of business planning as a process, instead of a document
Think about business planning as something you do often , rather than a document you create once and never look at again. If you take the time to write a plan that really fits your own company, it will be a better, more useful tool to grow your business. It should also make it easier to share your vision and strategy so everyone on your team is on the same page.
Adjust your business plan regularly to use it as a business management tool
Keep in mind that businesses that use their business plan as a management tool to help run their business grow 30 percent faster than those businesses that don't. For that to be true for your company, you'll think of a part of your business planning process as tracking your actual results against your financial forecast on a regular basis.
If things are going well, your business plan will help you think about how you can re-invest in your business. If you find that you're not meeting goals, you might need to adjust your budgets or your sales forecast. Either way, tracking your progress compared to your plan can help you adjust quickly when you identify challenges and opportunities—it's one of the most powerful things you can do to grow your business.
Prepare to pitch your business
If you're planning to pitch your business to investors or seek out any funding, you'll need a pitch deck to accompany your business plan. A pitch deck is designed to inform people about your business. You want your pitch deck to be short and easy to follow, so it's best to keep your presentation under 20 slides.
Your pitch deck and pitch presentation are likely some of the first things that an investor will see to learn more about your company. So, you need to be informative and pique their interest. Luckily we have a round-up of real-world pitch deck examples used by successful startups that you can review and reference as you build your pitch.
For more resources, check out our full Business Pitch Guide .
Ready to get started?
Now that you know how to use an example of a business plan to help you write a plan for your business, it's time to find the right one.
Use the search bar below to get started and find the right business plan example for your business idea.

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
What Is a Business Plan?
Understanding business plans, how to write a business plan, common elements of a business plan, the bottom line, business plan: what it is, what's included, and how to write one.
Adam Hayes, Ph.D., CFA, is a financial writer with 15+ years Wall Street experience as a derivatives trader. Besides his extensive derivative trading expertise, Adam is an expert in economics and behavioral finance. Adam received his master's in economics from The New School for Social Research and his Ph.D. from the University of Wisconsin-Madison in sociology. He is a CFA charterholder as well as holding FINRA Series 7, 55 & 63 licenses. He currently researches and teaches economic sociology and the social studies of finance at the Hebrew University in Jerusalem.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/adam_hayes-5bfc262a46e0fb005118b414.jpg)
- How to Start a Business: A Comprehensive Guide and Essential Steps
- How to Do Market Research, Types, and Example
- Marketing Strategy: What It Is, How It Works, How To Create One
- Marketing in Business: Strategies and Types Explained
- What Is a Marketing Plan? Types and How to Write One
- Business Development: Definition, Strategies, Steps & Skills
- Business Plan: What It Is, What's Included, and How to Write One CURRENT ARTICLE
- Small Business Development Center (SBDC): Meaning, Types, Impact
- How to Write a Business Plan for a Loan
- Business Startup Costs: It’s in the Details
- Startup Capital Definition, Types, and Risks
- Bootstrapping Definition, Strategies, and Pros/Cons
- Crowdfunding: What It Is, How It Works, and Popular Websites
- Starting a Business with No Money: How to Begin
- A Comprehensive Guide to Establishing Business Credit
- Equity Financing: What It Is, How It Works, Pros and Cons
- Best Startup Business Loans
- Sole Proprietorship: What It Is, Pros & Cons, and Differences From an LLC
- Partnership: Definition, How It Works, Taxation, and Types
- What is an LLC? Limited Liability Company Structure and Benefits Defined
- Corporation: What It Is and How to Form One
- Starting a Small Business: Your Complete How-to Guide
- Starting an Online Business: A Step-by-Step Guide
- How to Start Your Own Bookkeeping Business: Essential Tips
- How to Start a Successful Dropshipping Business: A Comprehensive Guide
A business plan is a document that outlines a company's goals and the strategies to achieve them. It's valuable for both startups and established companies. For startups, a well-crafted business plan is crucial for attracting potential lenders and investors. Established businesses use business plans to stay on track and aligned with their growth objectives. This article will explain the key components of an effective business plan and guidance on how to write one.
Key Takeaways
- A business plan is a document detailing a company's business activities and strategies for achieving its goals.
- Startup companies use business plans to launch their venture and to attract outside investors.
- For established companies, a business plan helps keep the executive team focused on short- and long-term objectives.
- There's no single required format for a business plan, but certain key elements are essential for most companies.
Investopedia / Ryan Oakley
Any new business should have a business plan in place before beginning operations. Banks and venture capital firms often want to see a business plan before considering making a loan or providing capital to new businesses.
Even if a company doesn't need additional funding, having a business plan helps it stay focused on its goals. Research from the University of Oregon shows that businesses with a plan are significantly more likely to secure funding than those without one. Moreover, companies with a business plan grow 30% faster than those that don't plan. According to a Harvard Business Review article, entrepreneurs who write formal plans are 16% more likely to achieve viability than those who don't.
A business plan should ideally be reviewed and updated periodically to reflect achieved goals or changes in direction. An established business moving in a new direction might even create an entirely new plan.
There are numerous benefits to creating (and sticking to) a well-conceived business plan. It allows for careful consideration of ideas before significant investment, highlights potential obstacles to success, and provides a tool for seeking objective feedback from trusted outsiders. A business plan may also help ensure that a company’s executive team remains aligned on strategic action items and priorities.
While business plans vary widely, even among competitors in the same industry, they often share basic elements detailed below.
A well-crafted business plan is essential for attracting investors and guiding a company's strategic growth. It should address market needs and investor requirements and provide clear financial projections.
While there are any number of templates that you can use to write a business plan, it's best to try to avoid producing a generic-looking one. Let your plan reflect the unique personality of your business.
Many business plans use some combination of the sections below, with varying levels of detail, depending on the company.
The length of a business plan can vary greatly from business to business. Regardless, gathering the basic information into a 15- to 25-page document is best. Any additional crucial elements, such as patent applications, can be referenced in the main document and included as appendices.
Common elements in many business plans include:
- Executive summary : This section introduces the company and includes its mission statement along with relevant information about the company's leadership, employees, operations, and locations.
- Products and services : Describe the products and services the company offers or plans to introduce. Include details on pricing, product lifespan, and unique consumer benefits. Mention production and manufacturing processes, relevant patents , proprietary technology , and research and development (R&D) information.
- Market analysis : Explain the current state of the industry and the competition. Detail where the company fits in, the types of customers it plans to target, and how it plans to capture market share from competitors.
- Marketing strategy : Outline the company's plans to attract and retain customers, including anticipated advertising and marketing campaigns. Describe the distribution channels that will be used to deliver products or services to consumers.
- Financial plans and projections : Established businesses should include financial statements, balance sheets, and other relevant financial information. New businesses should provide financial targets and estimates for the first few years. This section may also include any funding requests.
Investors want to see a clear exit strategy, expected returns, and a timeline for cashing out. It's likely a good idea to provide five-year profitability forecasts and realistic financial estimates.
2 Types of Business Plans
Business plans can vary in format, often categorized into traditional and lean startup plans. According to the U.S. Small Business Administration (SBA) , the traditional business plan is the more common of the two.
- Traditional business plans : These are detailed and lengthy, requiring more effort to create but offering comprehensive information that can be persuasive to potential investors.
- Lean startup business plans : These are concise, sometimes just one page, and focus on key elements. While they save time, companies should be ready to provide additional details if requested by investors or lenders.
Why Do Business Plans Fail?
A business plan isn't a surefire recipe for success. The plan may have been unrealistic in its assumptions and projections. Markets and the economy might change in ways that couldn't have been foreseen. A competitor might introduce a revolutionary new product or service. All this calls for building flexibility into your plan, so you can pivot to a new course if needed.
How Often Should a Business Plan Be Updated?
How frequently a business plan needs to be revised will depend on its nature. Updating your business plan is crucial due to changes in external factors (market trends, competition, and regulations) and internal developments (like employee growth and new products). While a well-established business might want to review its plan once a year and make changes if necessary, a new or fast-growing business in a fiercely competitive market might want to revise it more often, such as quarterly.
What Does a Lean Startup Business Plan Include?
The lean startup business plan is ideal for quickly explaining a business, especially for new companies that don't have much information yet. Key sections may include a value proposition , major activities and advantages, resources (staff, intellectual property, and capital), partnerships, customer segments, and revenue sources.
A well-crafted business plan is crucial for any company, whether it's a startup looking for investment or an established business wanting to stay on course. It outlines goals and strategies, boosting a company's chances of securing funding and achieving growth.
As your business and the market change, update your business plan regularly. This keeps it relevant and aligned with your current goals and conditions. Think of your business plan as a living document that evolves with your company, not something carved in stone.
University of Oregon Department of Economics. " Evaluation of the Effectiveness of Business Planning Using Palo Alto's Business Plan Pro ." Eason Ding & Tim Hursey.
Bplans. " Do You Need a Business Plan? Scientific Research Says Yes ."
Harvard Business Review. " Research: Writing a Business Plan Makes Your Startup More Likely to Succeed ."
Harvard Business Review. " How to Write a Winning Business Plan ."
U.S. Small Business Administration. " Write Your Business Plan ."
SCORE. " When and Why Should You Review Your Business Plan? "
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/marketing-plan-ff4bce0e2c52493f909e631039c8f4ca.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Lean Business Plan Template PDF. This scannable business plan template allows you to easily identify the most important elements of your plan. Use this template to outline key details pertaining to your business and industry, product or service offerings, target customer segments (and channels to reach them), and to identify sources of revenue.
Download or view 14 business plans examples/samples, vetted by our MBA business plan writers. Download in PDF format or read like a book. These real business plan samples would help in writing your own business plan. Download Pack of 14 Business Plan Examples FREE.
Start with a cogent and concise one sentence statement of the business idea. A sentence that is so clear and appealing that the reader can immediately visualise or 'see' the business. You can then go on to describe: The market at which you are aiming. The specific benefits offered by your product or service.
The rest, while still useful, go a bit lighter on guidance in favor of tailoring the plan to a specific industry. Explore: PandaDoc's business plan template library. 5. Canva — Pitch with your plan. Canva is a great option for building a visually stunning business plan that can be used as a pitch tool.
A good business plan guides you through each stage of starting and managing your business. You'll use your business plan as a roadmap for how to structure, run, and grow your new business. It's a way to think through the key elements of your business. Business plans can help you get funding or bring on new business partners.
Describe Your Services or Products. The business plan should have a section that explains the services or products that you're offering. This is the part where you can also describe how they fit ...
What You'll Get: A complete business plan Unlike other blank templates, our business plan examples are complete business plans with all of the text and financial forecasts already filled out. Edit the text to make the plan your own and save hundreds of hours. A professional business plan template All 550 of our business plans are in the SBA-approved format that's proven to raise money from ...
Download a free business plan template in Google Doc, Microsoft Word, and PDF formats. Includes expert guidance to help fill out each section. ... While not required, this last section of your business plan is a great place to drop in additional documents that support and strengthen the rest of your plan.
Using a predefined business plan PDF template will effectively lessen the time and effort required in designing. ... One-page or mini business plan. The one-page option is a great way to improve the focus of your business plan and highlight the essential elements. It can be an effective way to workshop your company's plan or quickly give ...
Content marketing software. Free and premium plans. Operations Hub. Operations software. Free and premium plans. Commerce Hub. B2B commerce software. Free and premium plans. A collection of professionally designed Business Plans templates available for PDF. Download, customize, and send in minutes.
A great business plan is not easy to compose, Sahlman acknowledges, largely because most entrepreneurs are wild-eyed optimists. But one that asks the right questions is a powerful tool.
Set out the structure and key skills of your management team and staf. Identify any skill shortages, such as IT skills and your plans to cover these. Past financial performance. Set out the historical financial information on your business for the last three to five years (if applicable). Break the sales figures down.
company, having the right business plan is crucial. We are thrilled to present this "How To Write A Business Plan Step-By-Step" document to you in a convenient PDF format, to help transform your entrepreneurial vision into a reality. It includes both details on how to write a business plan, plus a template with the questions you must answer.
One-Page Business Plan: As the name suggests, this type of business plan is condensed into one page and includes the most critical information about the business. It can be a useful tool for pitching to potential investors or partners. Strategic Business Plan: A strategic plan looks at the big picture and long-term business goals of a company ...
Most business plans also include financial forecasts for the future. These set sales goals, budget for expenses, and predict profits and cash flow. A good business plan is much more than just a document that you write once and forget about. It's also a guide that helps you outline and achieve your goals. After completing your plan, you can ...
William Sahlman suggests that a great business plan is one that focuses on a series of questions. These questions relate to the four factors critical to the success of every new venture: the people, the opportunity, the context, and the possibilities for both risk and reward. A great business plan is not easy to compose, Sahlman acknowledges ...
Sample business plan format Following is the standard business plan format you must consider while drafting a comprehensive business plan. Executive Summary: A high-level overview of your business plan.; Company Overview: An in-depth and detailed description of your small business, its fundamental elements, and future goals.; Market Analysis: A detailed description of your industry with the ...
Judging by all the hoopla surrounding business plans, you'd think the only things standing between would-be entrepreneurs and spectacular success are glossy five-color charts, bundles of meticulous-looking spreadsheets, and decades of month-by-month financial projections. Yet nothing could be further from the truth. In fact, often the more elaborately crafted a business plan, the more likely ...
Bill Sahlman: Writing a business plan is a seminal moment in the life of a new venture. Doing so entails committing to paper a vision of the factors that will affect the success or failure of the enterprise. People take the exercise very seriously and get emotionally invested in what they produce. In that context, the article was written to ...
A well-crafted plan will continue to serve you throughout the life of your business. Expect to update your document regularly to ensure the information is current and aligns with the overall goals and growth of your organization. Instructions: Use this workbook to solidify and document the core components of your business plan.
The business model canvas is a one-page template designed to demystify the business planning process. It removes the need for a traditional, copy-heavy business plan, in favor of a single-page outline that can help you and outside parties better explore your business idea. The structure ditches a linear format in favor of a cell-based template.
Business Plan: A business plan is a written document that describes in detail how a business, usually a new one, is going to achieve its goals. A business plan lays out a written plan from a ...