- Scroll to top
- / Sign Up
- HOW WE HELP CLIENTS
- schedule your conversation

Innovation vs Invention: Definition, Difference & Importance
Published: 17 January, 2024
Social Share:

Table of Contents
The terms “invention” and “innovation” are frequently used interchangeably, which is not only incorrect but also overlooks important nuances in meaning that can significantly impact a conversation. Invention involves the discovery of something new, while innovation entails the utilization of a novel idea or method. Innovation is the act of introducing fresh concepts or approaches to the market and transforming existing inventions into practical products or processes that have real-world utility. Some believe that a successful entrepreneurial journey starts with an invention, and the rest is mere “execution”. However, this perspective overlooks the risks and significant differences involved. In this comparison of innovation vs. invention, we aim to highlight and clarify these distinctions.
Innovation Vs Invention: Definitions
Innovation and invention are two terms often used interchangeably, but they represent distinct concepts in the realm of creativity and progress. Understanding the fundamental differences between innovation and invention is essential for grasping their unique roles in driving advancements across various fields. Let’s delve into clear definitions of these terms to shed light on their nuanced characteristics.
What is an Invention?
Invention refers to the initial creation of a product or the introduction of a process, marking its first occurrence. It is the conception of an idea that holds the innovation potential . Invention addresses a specific problem by utilizing technology, with its technical aspects serving a functional purpose. The patentability of an invention relies on its technical character, which necessitates the application of natural laws to achieve the desired outcome. Invention is often referred to as a “teaching for technical action.”
What is Innovation?
The term “ innovation ” originates from the Latin verb “innovāre” , which means introducing new things, ideas, or ways of doing something. Unlike improvement or transformation, innovation involves doing something entirely different from what is already being done, rather than just doing it better. Innovation has permeated various domains of life, leading to diverse applications in business, politics, society, and science. Its expansive nature reflects the potential for innovation in all areas of life.

Since de facto all areas of life form potential areas of innovation, it is not surprising that the concept of innovation has practically taken on a life of its own in recent years and has accordingly found quite different uses in business, politics, society, and science.
This fact can perhaps also serve as an explanation for the fact that to date there is neither a self-contained innovation theory nor a generally accepted definition of innovation or the concept of it.
Related: Types of Innovation in Business – How to Choose yours?
Innovation Vs Invention
| Invention refers to the occurrence of a completely new idea for a product or process that has never been created before. | Innovation involves the implementation of an idea for a product or process that is being introduced for the first time. | |
| The invention is based on an original idea and its theoretical workings. | Innovation focuses on adding value to something that already exists. | |
| Innovation involves the implementation of an idea for a product or process that is being introduced. | Innovation is characterized by the practical implementation of a new idea. | |
| Invention typically requires scientific skills. | Innovation necessitates a combination of marketing, technical, and strategic skills. | |
| Invention occurs when a new idea strikes a scientist or inventor. | Innovation arises when there is a perceived need for a new product or an improvement to an existing product. | |
| Invention is primarily concerned with a single product or process. | Innovation encompasses the integration of various products and processes. | |
| The invention involves the creation of a fresh product. | Invention activities are often limited to the Research and Development (R&D) department. | Innovation activities are spread across the organization, involving multiple departments and stakeholders. |
Why Innovation Is Not Just The Execution Of An Invention?
The underlying risk of this assumption becomes evident when considering the multitude of inventors who never saw their creations come to practical fruition due to overlooked details or the subsequent success of their inventions being achieved by completely different individuals.
Schumpeter drew a central distinction between these two processes: the invention process and the innovation process . In the realm of “business start-ups,” as Schumpeter contended, it is the innovators who assume the primary role, rather than the inventors.
Related: Digital Business Strategy Definition, Concepts, and Strategies
Furthermore, groundbreaking inventions often require significant time to become market-ready, encounter initial setbacks or lack recognition, and may face public resistance. Consequently, successful entrepreneurs typically emerge as innovators rather than inventors.
These entrepreneurs leverage existing resources, building upon what already exists. This perspective aligns with the observations of Israel M. Kirzner , an esteemed American economist, who underscored the concept of “discovering what already exists.” The core characteristic of an entrepreneur lies in recognizing and rediscovering the significance and potential of existing ideas. Paradoxical as it may seem, there is no need for reinvention when something already exists.
A compelling illustration of this phenomenon is exemplified by the fax machine. Although the invention had been in existence for an extended period, its ultimate utilization and market success were driven by different companies than the original inventors and initial market entrants.
Related: The UNITE Business Model Innovation Patterns
Why Innovation Means More Than Inventing New Products?
In an environment where markets change rapidly, the unique selling proposition of once-innovative products can quickly diminish. Consequently, maintaining a state of permanent innovation becomes an imperative for companies. While it is impossible to predict with certainty which good ideas will successfully evolve into innovations , it is certainly possible to make informed forecasts.
Today’s hyped products can swiftly become tomorrow’s interchangeable commodities, intensifying the struggle for the survival of innovative offerings, technologies, and services even before they ascend to the pinnacle of innovation.
The relentless transformation of markets coupled with unceasing competition compels companies to pursue constant renewal as a matter of necessity. This obligation extends across all areas of business and is particularly accentuated within the realm of service portfolios. The global digitization landscape further amplifies the pressure to innovate.
Related: Digitization vs. Digitalization: Differences, Definitions, and Examples
At the crossroads: Decline or turnaround
Failure to renew leads to the risk of falling into the cost trap, where interchangeable services result in lower profit margins. To achieve growth, companies may resort to cost-cutting measures, which in turn require increased efficiency in standard products. If trapped in this downward spiral, there is limited space for innovation. However, embracing innovation can be the key to initiating a turnaround.
Innovation and Invention Examples that Shaped the Modern World
1. microprocessor.
The microprocessor, credited to Intel’s Ted Hoff and Federico Faggin, is a small electronic device that serves as the brain of a computer.
Innovation:
The microprocessor serves as a prime example to illustrate the difference between innovation and invention. The innovation lies in the development and evolution of microprocessors, enabling the creation of countless electronic devices, advancements in computing power, and the foundation for the digital age.
2. Light Bulb
Thomas Edison’s invention of the practical and commercially viable electric light bulb revolutionized indoor lighting.
The innovation came through the widespread adoption and application of light bulbs, leading to the electrification of cities, the creation of lighting industries, and advancements in lighting technology.
Gideon Sundback’s invention of the zipper was a fastening device used in clothing, bags, and other products.
The innovation lies in the integration of zippers into various products, streamlining fastening processes, and enabling the development of new designs and functionalities.
4. AT&T
AT&T’s Bell Labs contributed to various inventions such as transistor technology and the solar cell.
The innovation stems from the application and commercialization of these inventions by other companies, leading to advancements in electronics, communication systems, and renewable energy technologies.
Xerox’s Palo Alto Research Center (PARC) was responsible for inventions like the computer mouse and graphical user interface (GUI).
The innovation occurred when these inventions were adopted and further developed by companies like Apple, leading to the widespread use of GUIs and user-friendly computing interfaces.
6. Solar Cell
The invention of the solar cell, which converts sunlight into electricity, is credited to Bell Labs’ researchers.
The innovation lies in the application of solar cells for generating renewable energy, leading to advancements in solar technology, photovoltaic systems, and the growth of the solar industry.
7. Computer Mouse
The invention of the computer mouse by Douglas Engelbart, an input device that revolutionized computer interaction.
The innovation came from the integration of computer mice into personal computers and their widespread adoption, transforming the way users interacted with graphical user interfaces and facilitating more intuitive navigation.
8. Graphical User Interface (GUI)
Xerox’s PARC contributed to the development of GUI, a visual interface that allows users to interact with digital devices using icons, menus, and windows.
The innovation came when GUIs were incorporated into personal computers, making computing more user-friendly, visually appealing, and accessible to a broader audience.
9. Telephone
The invention of the telephone by Alexander Graham Bell, enabled voice communication over long distances.
The innovation came through the establishment and expansion of telephone networks, leading to the global telecommunications industry and advancements in communication technology.
10. Penicillin
Alexander Fleming’s discovery of the antibiotic substance produced by Penicillium mold.
The innovation lies in the mass production and widespread use of penicillin as a life-saving antibiotic, revolutionizing medical treatment and significantly reducing the impact of infectious diseases.
11. Printing Press
Johannes Gutenberg’s invention of the printing press revolutionized the mass production of books and printed materials.
The innovation came through the dissemination of knowledge, the democratization of information, and the development of publishing industries, contributing to education, cultural exchange, and the spread of ideas.
12. Steam Engine
The invention of the steam engine, with key contributions from James Watt, revolutionized transportation, industrial processes, and power generation during the Industrial Revolution.
The innovation occurred through the integration of steam engines into various applications, enabling advancements in manufacturing, transportation, and the mechanization of industries.
13. Computer
The invention of the computer, a programmable electronic device, can be attributed to multiple pioneers in computing history.
The innovation lies in the continuous development and evolution of computers, leading to advancements in computing power, data processing, artificial intelligence, and transformative changes in various fields and industries.
14. Internet
The creation of the Internet, a global network of interconnected computer systems, involved the contributions of numerous individuals and organizations.
The innovation came through the utilization of the internet for communication, information sharing, e-commerce, social networking, and the digital transformation of society, revolutionizing how we connect, work, and access information.
The microprocessor serves as a prime example to illustrate the difference between innovation and invention . The innovation lies in the development and evolution of microprocessors, enabling the creation of countless electronic devices, advancements in computing power, and the foundation for the digital age.
Innovative Vs Inventive
Similarly, to innovation vs. invention, we also want to explain the oftentimes confused usage of their adjectives: Inventive vs. innovative. Two words that are also spelled similarly and pronounced similarly. As for innovation and invention, the terms have slightly different meanings:
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Inventive | Refers to someone who demonstrates the ability to design new things and exhibits creativity in thinking and imagination. An inventive individual is skilled at coming up with original concepts and solutions, often starting from scratch and introducing something completely new. |
| Innovative | Describes someone who introduces new things, ideas, or ways of doing something. An innovative person showcases creativity in thinking and imagination, but their focus lies in taking existing concepts or practices to the next level. They excel in advancing and improving upon established ideas or processes, pushing the boundaries of what is currently known or practiced. |
Related: Creativity and Innovation: Differences, Examples & Definitions
Innovation and Invention Importance
Invention and innovation are two crucial components of progress and advancement. They are interconnected and rely on each other to drive positive change. Inventions serve as the foundation, laying the groundwork for innovation to flourish. They represent the initial creation of new concepts, ideas, or products that showcase originality and novelty. Inventions demonstrate the credibility of scientific knowledge and require specialized skills and expertise.
Inventions Importance
- Inventions involve the creation of entirely new concepts or ideas.
- Inventions serve as evidence of the credibility of scientific knowledge.
- Inventions require specific skills and expertise.
- Inventions are characterized by their originality and novelty.
- Inventions often yield unexpected results.
- Inventions serve as the foundation or building blocks for innovation.
- Inventions should be prioritized as they lay the groundwork for further progress
Innovations Importance
- Innovation focuses on improving existing concepts, services, or products.
- Innovation contributes significantly to the growth and success of companies.
- Innovation introduces new ideas or ways of doing things while incorporating changes to existing concepts or patterns.
- Innovation provides a technical or competitive advantage.
- Innovation demands a diverse range of skills and expertise.
- Innovation has the ability to attract top talent and creative minds.
- Innovation emerges when there is a need for change within an organization.
Whereas invention can be described as a fundament, innovation can be referred to as the introduction of new things, ideas, or ways of doing something.

If we would need to answer the question of innovation vs. invention: what is more important then, it could be concluded that both play an important role in creating continuous value for a company.
Industry Standard Approach to Innovation
Since we know that the topic of innovation vs. invention will continue to be of significant importance in the future, we would like to share the following excerpt from our book “How to Create Innovation” with you: “We know – innovation is an epic challenge. Depending on where you are and how you play it, your levels of success and the outcomes you create will be drastically different, so a particular result cannot be guaranteed. But if you do not make a major leap forward leveraging this consolidated body of knowledge, ask yourself what is going wrong, and do let us equally know what you have been struggling with.
Using this proposed industry-standard approach to innovations, organizations can create innovation in a target-oriented way, leverage their strengths, create blue oceans, and overcome luck.
The practices we introduced are mostly well-established, have proven themselves in the trenches, or are deeply rooted practices by Silicon Valley players. In addition, there are numerous reads to take you further.
Our contribution was to identify winning practices, add what is missing consolidate everything in a holistic setting, and adapt it to the realities of large organizations.
In addition to this industry-standard approach to innovation , we have a variety of other ground-breaking tools and models. These are available via our download link .
The UNITE Business Model Framework
How to Create Innovation includes a number of canvases that focus on value creation and finding the right business model to meet your customer segment and customer needs . The framework is built to inspire drastic changes that help you find a competitive advantage. Our hope is that your company grows through business model innovation, and so we again encourage you to look deeper into our website and the book.
Here is a summary of the key ingredients of the framework:

Related Posts
Business level strategy: examples & types for business strategy success.
In strategic management, businesses use a variety of approaches to craft a1
The Four Types of Innovation and Their Impact on Business Success
In business landscape, innovation isn't just a buzzword; it's a strategic imperative1
50 Innovation Examples: Exciting Innovative Ideas in Business
In the Business environment, strategic innovation has taken centre stage as a1
Innovation Strategy: Developing Innovative Strategies in Business
Innovation has become an imperative for organizations worldwide, yet the multitude of1
Recent Posts

Examples and Types of Effective Functional Level Strategy for Business Support
A key objective of any business strategy is to improve operational efficiencies...

The Three Levels of Strategy: Corporate Strategy, Business Strategy, and Functional Strategy
Understanding the intricate levels of strategy is crucial for any organization aiming...

Register For Your FREE Innovation WorkShop Seat Now!
Learn how to overcome the 90% failure rate in innovation from a master innovator and best-selling author.

Expert tactics to boost your innovation odds.
Insights on capturing customer needs for innovation.
Tools that turn your ideas into triumphs.
First name *
Last name *
Professional E-mail *
I want to be kept up-to-date and accept the privacy statement *
By signing up, you agree to receive news and accept the privacy statement (mandatory)
Verify your e-mail address now by entering the 6-digit code we’ve just sent to your inbox
Don't receive Code? Resend code
Last one step
Help us better understand our innovation Show members
Country * Please Select Afghanistan Albania Algeria Andorra Angola Antigua and Barbuda Argentina Armenia Australia Austria Azerbaijan Bahamas Bahrain Bangladesh Barbados Belarus Belgium Belize Benin (Dahomey) Bolivia Bosnia and Herzegovina Botswana Brazil Brunei Brunswick and Lüneburg Bulgaria Burkina Faso (Upper Volta) Burundi Cabo Verde Cambodia Cameroon Canada Cayman Islands Central African Republic Central American Federation Chad Chile China Colombia Comoros Congo Free State Costa Rica Cote d’Ivoire (Ivory Coast) Croatia Cuba Cyprus Czechia Democratic Republic of the Congo Denmark Djibouti Dominica Dominican Republic Ecuador Egypt El Salvador Equatorial Guinea Eritrea Estonia Eswatini Ethiopia Fiji Finland France Gabon Gambia Georgia Germany Ghana Grand Duchy of Tuscany Greece Grenada Guatemala Guinea Guinea-Bissau Guyana Haiti Holy See Honduras Hungary Iceland India Indonesia Iran Iraq Ireland Israel Italy Jamaica Japan Jordan Kazakhstan Kenya Kiribati Korea Kosovo Kuwait Kyrgyzstan Laos Latvia Lebanon Lesotho Liberia Libya Liechtenstein Lithuania Luxembourg Madagascar Malawi Malaysia Maldives Mali Malta Marshall Islands Mauritania Mauritius Mexico Micronesia Moldova Monaco Mongolia Montenegro Morocco Mozambique Namibia Nassau Nauru Nepal Netherlands New Zealand Nicaragua Niger Nigeria North Macedonia Norway Oman Pakistan Palau Panama Papal States Papua New Guinea Paraguay Peru Philippines Piedmont-Sardinia Poland Portugal Qatar Republic of Congo Republic of Korea (South Korea) Republic of the Congo Romania Russia Rwanda Saint Kitts and Nevis Saint Lucia Saint Vincent and the Grenadines Samoa San Marino Sao Tome and Principe Saudi Arabia Schaumburg-Lippe Senegal Serbia Seychelles Sierra Leone Singapore Slovakia Slovenia Solomon Islands Somalia South Africa South Sudan Spain Sri Lanka Sudan Suriname Sweden Switzerland Syria Tajikistan Tanzania Thailand Timor-Leste Togo Tonga Trinidad and Tobago Tunisia Turkey Turkmenistan Tuvalu Uganda Ukraine United Arab Emirates United Kingdom Uruguay Uzbekistan Vanuatu Venezuela Vietnam Württemberg Yemen Zambia Zimbabwe Industry * Please Select Automotive, mobilty & transport Financial Services Chemical & agriculture Construction & Real Estate Consulting Education Energy Banking, insurance & FS FMCG Food Gov / Public Industry Health & lifestyle Logistics, Aero & Shipping Media & Entertainment Natural resources & mining Pharma & Biotech Retail & trade Tech & E-Commerce Telco Tourism design Information technology & services Management consulting Retail Pharmaceuticals International trade & development Professional training & coaching luxury goods & jewelry Automotive Insurance Mechanical or industrial engineering Company Size * XS - 1-10 S - 10-100 M - 100-1000 L - 1000-5000 XL - > 5000
Seniority * Please Select Junior Consultant Senior Consultant Manager Senior Manager Director VP SVP Partner CXO Board Member
Areas of interest * Innovation Digital Transformation Culture & Organization IT Strategy & Bus. Alignment Customer Experience
Discover the largest library of innovation & transformation tools on the entire Internet!
LOG IN VIA E-MAIL
| | |
Forgot password?
New to Digital Leadership? Create your account
Thanks, We’ve Received Your Updated Details

Learn how to overcome the 90% failure rate in innovation from a master innovator & bestselling author!
Your e-mail address: * Your first name: *

One Last Step..
Help us better understand the UNITE community
Free guide to improve your innovation success rate*
Our 35-page comprehensive innovation guide covers the key areas why innovation fails. While it cannot cover all the solutions (that would take books to fill), it provides you with a convenient starting point for your analysis and provides further resources and links to the corresponding UNITE models, ultimately allowing you to work towards a doubling and tripling your chances of success.

Get access to the UNITE Models now!
Discover the largest library of innovation & transformation tools on the internet!
Choose Your Password *
Confirm Your Password *
Already have an account? Log in
Country * Please Select Afghanistan Albania Algeria Andorra Angola Antigua and Barbuda Argentina Armenia Australia Austria Azerbaijan Bahamas Bahrain Bangladesh Barbados Belarus Belgium Belize Benin (Dahomey) Bolivia Bosnia and Herzegovina Botswana Brazil Brunei Brunswick and Lüneburg Bhutan Bulgaria Burkina Faso (Upper Volta) Burundi Cabo Verde Cambodia Cameroon Canada Cayman Islands Central African Republic Central American Federation Chad Chile China Colombia Comoros Congo Free State Costa Rica Cote d’Ivoire (Ivory Coast) Croatia Cuba Cyprus Czechia Democratic Republic of the Congo Denmark Djibouti Dominica Dominican Republic Ecuador Egypt El Salvador Equatorial Guinea Eritrea Estonia Eswatini Ethiopia Fiji Finland France Gabon Gambia Georgia Germany Ghana Grand Duchy of Tuscany Greece Grenada Guatemala Guinea Guinea-Bissau Guyana Haiti Holy See Honduras Hungary Iceland India Indonesia Iran Iraq Ireland Israel Italy Jamaica Japan Jordan Kazakhstan Kenya Kiribati Korea Kosovo Kuwait Kyrgyzstan Laos Latvia Lebanon Lesotho Liberia Libya Liechtenstein Lithuania Luxembourg Madagascar Malawi Malaysia Maldives Mali Malta Marshall Islands Mauritania Mauritius Mexico Micronesia Moldova Monaco Mongolia Montenegro Morocco Mozambique Myanmar Namibia Nassau Nauru Nepal Netherlands New Zealand Nicaragua Niger Nigeria North Macedonia Norway Oman Pakistan Palau Panama Papal States Papua New Guinea Paraguay Peru Philippines Piedmont-Sardinia Poland Portugal Qatar Republic of Congo Republic of Korea (South Korea) Republic of the Congo Romania Russia Rwanda Saint Kitts and Nevis Saint Lucia Saint Vincent and the Grenadines Samoa San Marino Sao Tome and Principe Saudi Arabia Schaumburg-Lippe Senegal Serbia Seychelles Sierra Leone Singapore Slovakia Slovenia Solomon Islands Somalia South Africa South Sudan Spain Sri Lanka Sudan Suriname Sweden Switzerland State of Palestine Syria Tajikistan Tanzania Thailand Timor-Leste Togo Tonga Trinidad and Tobago Tunisia Turkey Turkmenistan Tuvalu Uganda Ukraine United States United Arab Emirates United Kingdom Uruguay Uzbekistan Vanuatu Venezuela Vietnam Württemberg Yemen Zambia Zimbabwe Industry * Please Select Automotive, mobilty & transport Financial Services Chemical & agriculture Construction & Real Estate Consulting Education Energy Banking, insurance & FS FMCG Food Gov / Public Industry Health & lifestyle Logistics, Aero & Shipping Media & Entertainment Natural resources & mining Pharma & Biotech Retail & trade Tech & E-Commerce Telco Tourism design Information technology & services Management consulting Retail Pharmaceuticals International trade & development Professional training & coaching luxury goods & jewelry Automotive Insurance Mechanical or industrial engineering Company Size * XS - 1-10 S - 10-100 M - 100-1000 L - 1000-5000 XL - > 5000
Editable UNITE models (PowerPoint) included
Most of our models and canvases are designed to be applied!
To help you personalize them to your exact business requirements, you can download fully editable versions of the UNITE models available (PowerPoint format)!
They are straightforward to work with, and you can directly incorporate them into your presentations as you need…thus saving countless hours of replication!
PS: did you know that you are also getting hi-res print-ready versions for your workshops?
Monthly live webinars
Each month we host our exclusive, invitation-only webinar series where one of our industry-leading experts updates our members on the latest news, progress and concepts around business strategy, innovation and digital transformation, as well as other related topics.
You will receive the book in PDF and EPUB formats, ideal for your computer, Kindle, Tablet or other eReading device.
Bi-weekly live group Q&A sessions
These sessions are your opportunity to bring any questions or challenges you’re facing and receive expert guidance on the spot.
Come and be a part of engaging discussions where your unique concerns are heard and addressed.
1x personal coaching session / month
If you are occasionally looking for a sparring partner or you need limited support, then this option will be ideal for you. Coaching sessions are 1-2 hours where we can discuss any challenge or opportunity you are currently facing.
If you need a few more hours outside of this provision, then these could be billed transparently.
Unlimited video call support! – it’s like always making the right decision!
We believe support shouldn’t be limited. Because we typically find that the occasional hour just doesn’t cut it – particularly if you and your team are in the midst of a large and complex project.
Your time with Stefan is therefore unlimited (fair usage applies) – in his function as coach and sparring partner. That does mean that you will still have to do the work – we cannot take that off you, unless you hire us as consultants. But you will get valuable strategic insight and direction to make sure you are always focusing your efforts where they will lead to the best results.
One personal coaching session / month + unlimited support via e-mail & WhatsApp
We believe support shouldn’t be limited. If you generally know what you are doing but want a sparring partner to frequently raise questions to, this is the perfect choice!
In addition to your monthly 1-1 live coaching sessions with Stefan, you will also get unlimited support from him via email and WhatsApp messaging (fair usage applies). This not only allows you to get valuable strategic direction in your calls, but also gives you instant access to expert help as you work through your plans each month.
The fact that support is text-based means that we can speed up our responses to you while keeping the overall cost of support down.
Welcome gift of our book “How to Create Innovation” (digital + physical editions)*
As a welcome gift, you will receive the both the digital and physical version of our book “How to Create Innovation”, which covers numerous relevant resources and provides additional deep dives into our UNITE models and concepts.
The print version will be shipped out to you on sign-up. The digital version will be emailed to you, and comes in PDF and EPUB formats, ideal for your computer, Kindle, Tablet or other eReading device.
1x major workshop or 2x smaller workshops / month
1x major or 2x smaller workshops based on the UNITE models.
- Topics covered: almost any challenge under the header of #strategy, #innovation or #transformation, leveraging the UNITE models.
- Hands-On Learning: solve your challenges while learning the practical application of the UNITE models and walk away with concrete plans and tools to take your next steps.
- Industry thought leadership: facilitated by Stefan, the founder of Digital Leadership and the main author of the UNITE models, ensuring top-tier guidance and knowledge sharing.
- Collaborative approach: engage in interactive sessions that foster collaboration, idea exchange, and real-time problem-solving among peers and industry leaders.
- Continuous Improvement: Regular workshops ensure ongoing development in your organization staying ahead of industry trends and customer needs.
Access all of our UNITE models, (incl. editable & print versions)
All of our Professional plans offer full access to the following:
- 6x UNITE model package downloads are included per month, if you need something in addition to these however, please let us know!
- Hi-res, print-ready versions you can use in your workshops
- Fully editable PowerPoint versions where applicable – personalize to your needs.
- Exclusive access to our vault of never-before-published strategic materials. We have much more to share – a lot of our concepts have never been published!
Exclusive access to our private UNITE community (upcoming)
We are currently in the process of launching our brand new community., we are designing our community to specifically help you:.
- Get answers to questions (“How do I …”)
- Share leading practices & knowledge
- Jointly develop new models
- Network amongst a highly qualified group of peers
Please, select the reason
Cancelling your plan will deactivate your plan after the current billing period ends. You will not be charged further, but also won’t be able to access [exclusive features/services].
- Cost-related issues
- Unsatisfied with the service
- Features I need are missing
- Switching to a different service
- Other (Please specify)
Book Your Initial Blueprint Session Now
Simply fill out the below form and book in a time for our initial session that works for you. This initial session is free, no strings attached, and is where we can discuss your Blueprint needs more in-depth before moving forward.

Stefan F. Dieffenbacher
Founder of digital leadership.
Adam D. Wisniewski
Partner for it strategy & business alignment.

Get in touch with Digital Leadership
Speak to our team today to find the best solution for your business to grow and scale.
We are here to support you across the entire lifecycle in all topics related to #digital, #innovation, #transformation and #marketing!

Stefan F. Dieffenbacher Founder of Digital Leadership
Contact Us!
Contact form, contact details, book a call.
Title, first name & last name * Email address * Phone number Please let us know how we can best support you! *
By clicking “Send”, I agree to Terms of Service and Privacy Policy.
Let’s have a conversation!
“Please be invited to reach out! We are happy to help and look forward to a first meeting!”
+41 (0) 44 562 42 24
Schedule Your Call With Our Team
Find a time on our calender that best suits you !

Founder and CEO of Digital Leadership
SCHEDULE YOUR INITIAL CALL
A Quick Survey!
What is the main challenge you're currently facing in your business?
You Want To Drive Change?
Let’s find the best solution for your business to grow and scale sustainably!
Let’s kick start it!
We will uncover your current business situation and goals and provide you with a bespoke solution that helps you drastically grow your business working with us.

Stefan F. Dieffenbacher, M.B.A.
Feedback about our consulting that we are proud of
Read the reviews and make sure that this is not a waste of time, but a super effective tool.
You want to drive change?
Schedule your free business assessment call with our founder.
On this call, we will uncover your current business situation and goals and talk about how to drive change and solve your need.
Choose the meeting type that applies to your needs and schedule a time to meet with someone from our team. We look forward to speaking with you soon!

Schedule Your Free Business Assessment

Schedule Your Free Business Assessment Call With Adam D. Wisniewski
Welcome to our scheduling page.

Let’s Design your Customer Experience Blueprint !
In a uniquely designed 60 or 90 minute session* , we will …
- > identify where to start with near-certainty
- > define what approach it takes to create success in your organization
Based on the Blueprinting session, you will receive a tailored blueprint that aligns with your objectives, vision and goals, ensuring that your initiative is a success from start to finish.

In this session, you will be working together with Patrick Zimmermann, Associate Partner for Customer Experience

Let’s Design your Culture & Org-Change Blueprint !

In this session, you will be working together with Dr. Andreas Rein, Partner at Digital Leadership for Culture & Org Change
Let’s Design your Innovation Blueprint !

In this session, you will be working together with Sascha Martini, Partner at Digital Leadership for Innovation and Digital Transformation
Let’s Design your Transformation Blueprint !

In this session, you will be working together with Stefan F. Dieffenbacher, Founder of Digital Leadership Stefan is a global thought leader in the innovation space
Let’s Design your IT Strategy & Business Alignment Blueprint !

In this session, you will be working together with Adam D. Wisniewski, Partner for IT Strategy & Business Alignment

Patrick Zimmermann

Sascha Martini

Dr. Andreas Rein
Write a personalized review! Log in
Create Review

- Key Differences
Know the Differences & Comparisons
Difference Between Invention and Innovation

At first sight, the two terms sound alike, but if you dig deeper, you will find that there is a fine line of difference between invention and innovation that lies in their connotations. While invention is all about creating or designing something, innovation is the process of turning a creative idea into reality.
Content: Invention Vs Innovation
Comparison chart.
| Basis for Comparison | Invention | Innovation |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | Invention refers to the occurrence of an idea for a product or process that has never been made before. | Innovation implies the implementation of idea for product or process for the very first time. |
| What is it? | Creation of a new product. | Adding value to something already existing. |
| Concept | An original idea and its working in theory. | Practical implementation of new idea. |
| Skills required | Scientific skills | Set of marketing, technical and strategic skills. |
| Occurs when | New idea strikes a scientist. | A need is felt for a product or improvement in existing product. |
| Concerned with | Single product or process. | Combination of various products and process. |
| Activities | Limited to R & D department. | Spread across the organization. |
Definition of Invention
The term ‘invention’, is defined as the act of creating, designing or discovering a device, method, process, that has not existed before. In finer terms, it is a novel scientific idea conceived through research and experimentation that turns into a tangible object. It can be a new process of producing a product or may be an improvement upon a product or a new product.
Inventions can be patented, as it provides security to the inventor, for intellectual property rights, and also identifies it as an actual invention. Further, different countries have different rules for obtaining the patent and the process is also costly. To be patented, the invention must be novel, have value and non-obvious.
Definition of Innovation
The word ‘innovation’ itself signifies its meaning, as the transformation of an idea into reality. In the purest sense, innovation can be described as a change that adds value to the products or services; that fulfills the needs of the customers. It is when something new and effective is introduced to the market, that fulfills the needs of the customers by delivering better products and services.
Innovation can be an introduction or development of new product, process, technology, service or improving/redesigning the existing ones that provide solutions to the current market requirements. All the process that help in the generation of the new idea and translating it into the products demanded by the customers are covered under innovation.
Key Differences Between Invention and Innovation
The significant differences between invention and innovation are classified below:
- The occurrence of an idea for a product or process that has never been made before is called the invention. The implementation of the idea for product or process for the very first time is called innovation.
- The invention is related to the creation of new product. On the other hand, innovation means adding value or making a change in the existing product.
- The invention is coming up with a fresh idea and how it works in theory. As opposed to innovation, is all about practical implementation of the new idea.
- The invention requires scientific skills. Unlike innovation, which requires a broad set of marketing, technical and strategic skills.
- The invention occurs when a new idea strikes a scientist. Conversely, innovation arises when a need realized for a new product or improvisation in the existing product.
- The invention is concerned with a single product or process. As against this, innovation focuses on the combination of various products and services.
- While the invention is limited to research and development department of the organization. Innovation is spread all over the organization.
So, it can be said that innovation is not the same thing as invention, as these are two different concepts. Both the activities requires huge capital investment in the research process. Further, the invention is when something new or novel to the world is discovered, while innovation is about introducing an effective way of using, producing or distributing something.
One important difference between invention and innovation is, an idea when proved workable, it is called as the invention. On the other hand, an innovation is when the idea not only be proved workable but also requires to be economically feasible and fulfill a specific need.
You Might Also Like:

Jonathan Gilbert says
July 26, 2016 at 8:42 pm
Hi Surbhi, I like your articles as I consider your articles as understandable.
August 2, 2017 at 8:12 am
Jessica says
June 24, 2019 at 5:01 am
I love it too .
December 11, 2019 at 5:21 pm
Very detailed and simplistic in explanation.
Lydiah Moraa Machora says
January 5, 2021 at 5:30 pm
Woooow, very detailed explanations, well illustrated. Simple language and understood. Examples given appropriately. I love the content in it. For revision purposes well illustrated. Great work to the team.
Mudit gupta says
March 16, 2021 at 8:39 am
It helped me in the exam Thank you
Sai prasanna says
July 8, 2021 at 9:21 am
Nice, very understanding language and very simple content I love your detailed explanation. Thank you
daishali says
October 26, 2021 at 4:11 am
Thank you, I was looking this up for my tech class thanks so much!
November 21, 2021 at 1:03 am
Waw It’s great to work!! I appreciate you.
March 30, 2022 at 3:43 pm
U clear all my doubts regarding these aforesaid topics… Thank you very much to clear my doubts…
Michelle says
October 23, 2022 at 1:46 pm
Easy, simple, and briefly described. it has helped me in my exams.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Innovation vs. Invention
What's the difference.
Innovation and invention are two closely related concepts that drive progress and change in various fields. While invention refers to the creation of a new product, process, or idea, innovation goes beyond mere creation and involves the implementation and improvement of these inventions to bring about meaningful and practical change. Invention is the initial spark of creativity, while innovation is the process of transforming that invention into something valuable and impactful. Invention is often seen as a singular event, while innovation is an ongoing and iterative process that involves continuous improvement and adaptation. Both invention and innovation are crucial for driving advancements and pushing the boundaries of human knowledge and capabilities.

| Attribute | Innovation | Invention |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The process of creating something new or improving existing ideas, products, or processes. | The act of inventing or creating something entirely new. |
| Focus | Emphasizes on improvement, novelty, and value creation. | Emphasizes on originality and creation of a new idea or product. |
| Outcome | Results in the introduction of new or improved ideas, products, or processes. | Results in the creation of a new idea, product, or process. |
| Process | Iterative and involves continuous improvement and adaptation. | Linear and involves the initial creation or discovery. |
| Application | Can be applied to various fields, industries, and sectors. | Can be applied to various fields, industries, and sectors. |
| Focus on Problem Solving | Places emphasis on identifying and solving problems. | May or may not involve problem-solving, depending on the context. |
| Collaboration | Often involves collaboration and input from multiple stakeholders. | May or may not involve collaboration, depending on the context. |
| Risk | May involve calculated risks to achieve desired outcomes. | May involve risks associated with the creation of something new. |

Further Detail
Introduction.
Innovation and invention are two terms often used interchangeably, but they have distinct attributes that set them apart. While both concepts involve the creation of something new, they differ in their focus, process, and impact. Understanding the differences between innovation and invention is crucial for individuals, organizations, and societies to harness their potential for growth and progress. In this article, we will explore the attributes of innovation and invention, highlighting their unique characteristics and the value they bring to various contexts.
Definition and Focus
Invention refers to the creation of a new product, process, or technology that did not previously exist. It involves the discovery or development of a novel idea or solution. Inventions often arise from scientific research, technological advancements, or individual creativity. The focus of invention is primarily on the creation of something new, with an emphasis on the novelty and uniqueness of the idea or product.
In contrast, innovation is the process of implementing new ideas, methods, or practices to bring about positive change. It involves the application of inventions or existing knowledge to improve existing products, processes, or services. Innovation can occur in various domains, including technology, business, healthcare, and social systems. The focus of innovation is on the practical implementation and improvement of existing ideas, with an emphasis on creating value and solving problems.
Process and Approach
The process of invention often begins with a problem or a need for improvement. Inventors engage in research, experimentation, and exploration to develop a solution. They may work individually or collaboratively, using their expertise and creativity to generate new ideas. The process of invention typically involves trial and error, as inventors iterate and refine their concepts until they achieve a viable outcome. Invention is often driven by curiosity, scientific inquiry, and the desire to push the boundaries of knowledge.
Innovation, on the other hand, is a more iterative and collaborative process. It involves identifying opportunities for improvement, gathering insights, and generating ideas. Innovators work closely with stakeholders, such as customers, employees, and partners, to understand their needs and preferences. The process of innovation includes prototyping, testing, and refining ideas based on feedback and data. It requires a multidisciplinary approach, combining technical expertise, market knowledge, and creative problem-solving skills. Innovation is driven by a desire to create value, enhance efficiency, and meet evolving demands.
Impact and Value
Inventions have the potential to disrupt industries, create new markets, and revolutionize the way we live and work. They often represent breakthroughs in science, technology, or engineering that push the boundaries of human knowledge and capabilities. Inventions can lead to the development of new industries, the improvement of existing products, or the creation of entirely new solutions to societal challenges. They have the power to transform societies, improve quality of life, and drive economic growth.
While inventions are undoubtedly valuable, their impact is often realized through innovation. Innovation takes inventions and translates them into practical applications that address real-world problems. By improving existing products, processes, or services, innovation enhances efficiency, productivity, and user experience. It drives competitiveness, fosters growth, and enables organizations to adapt to changing market dynamics. Innovation also plays a crucial role in social progress, as it enables the development of sustainable solutions, promotes inclusivity, and addresses societal challenges.
Examples and Case Studies
To illustrate the attributes of innovation and invention, let's consider a few examples. The invention of the telephone by Alexander Graham Bell in 1876 revolutionized communication, enabling people to connect over long distances. However, it was the innovation of mobile phones and the subsequent development of smartphones that transformed the way we communicate, access information, and conduct business.
Another example is the invention of the light bulb by Thomas Edison in 1879. While the light bulb itself was a groundbreaking invention, it was the innovation of electric power grids and the widespread adoption of electricity that brought about significant societal changes, such as extended working hours, improved safety, and enhanced quality of life.
Furthermore, the invention of the internet in the late 20th century laid the foundation for a digital revolution. However, it was the subsequent innovations in web technologies, e-commerce, social media, and online services that transformed the way we connect, share information, and conduct business in the digital age.
Innovation and invention are both essential drivers of progress and change. While invention focuses on the creation of something new, innovation emphasizes the practical implementation and improvement of existing ideas. Inventions have the potential to disrupt industries and revolutionize societies, but their impact is often realized through innovation. By understanding the attributes of innovation and invention, individuals, organizations, and societies can harness their potential to drive growth, solve complex problems, and create a better future.
Comparisons may contain inaccurate information about people, places, or facts. Please report any issues.
4.2 Creativity, Innovation, and Invention: How They Differ
Learning objectives.
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Distinguish between creativity, innovation, and invention
- Explain the difference between pioneering and incremental innovation, and which processes are best suited to each
One of the key requirements for entrepreneurial success is your ability to develop and offer something unique to the marketplace. Over time, entrepreneurship has become associated with creativity , the ability to develop something original, particularly an idea or a representation of an idea. Innovation requires creativity, but innovation is more specifically the application of creativity. Innovation is the manifestation of creativity into a usable product or service. In the entrepreneurial context, innovation is any new idea, process, or product, or a change to an existing product or process that adds value to that existing product or service.
How is an invention different from an innovation? All inventions contain innovations, but not every innovation rises to the level of a unique invention. For our purposes, an invention is a truly novel product, service, or process. It will be based on previous ideas and products, but it is such a leap that it is not considered an addition to or a variant of an existing product but something unique. Table 4.2 highlights the differences between these three concepts.
| Concept | Description |
|---|---|
| Creativity | ability to develop something original, particularly an idea or a representation of an idea, with an element of aesthetic flair |
| Innovation | change that adds value to an existing product or service |
| Invention | truly novel product, service, or process that, though based on ideas and products that have come before, represents a leap, a creation truly novel and different |
One way we can consider these three concepts is to relate them to design thinking. Design thinking is a method to focus the design and development decisions of a product on the needs of the customer, typically involving an empathy-driven process to define complex problems and create solutions that address those problems. Complexity is key to design thinking. Straightforward problems that can be solved with enough money and force do not require much design thinking. Creative design thinking and planning are about finding new solutions for problems with several tricky variables in play. Designing products for human beings, who are complex and sometimes unpredictable, requires design thinking.
Airbnb has become a widely used service all over the world. That has not always been the case, however. In 2009, the company was near failure. The founders were struggling to find a reason for the lack of interest in their properties until they realized that their listings needed professional, high-quality photographs rather than simple cell-phone photos. Using a design thinking approach, the founders traveled to the properties with a rented camera to take some new photographs. As a result of this experiment, weekly revenue doubled. This approach could not be sustainable in the long term, but it generated the outcome the founders needed to better understand the problem. This creative approach to solving a complex problem proved to be a major turning point for the company. 7
People who are adept at design thinking are creative, innovative, and inventive as they strive to tackle different types of problems. Consider Divya Nag , a millennial biotech and medical device innovation leader, who launched a business after she discovered a creative way to prolong the life of human cells in Petri dishes. Nag’s stem-cell research background and her entrepreneurial experience with her medical investment firm made her a popular choice when Apple hired her to run two programs dedicated to developing health-related apps, a position she reached before turning twenty-four years old. 8
Creativity, innovation, inventiveness, and entrepreneurship can be tightly linked. It is possible for one person to model all these traits to some degree. Additionally, you can develop your creativity skills, sense of innovation, and inventiveness in a variety of ways. In this section, we’ll discuss each of the key terms and how they relate to the entrepreneurial spirit.
Entrepreneurial creativity and artistic creativity are not so different. You can find inspiration in your favorite books, songs, and paintings, and you also can take inspiration from existing products and services. You can find creative inspiration in nature, in conversations with other creative minds, and through formal ideation exercises, for example, brainstorming. Ideation is the purposeful process of opening up your mind to new trains of thought that branch out in all directions from a stated purpose or problem. Brainstorming , the generation of ideas in an environment free of judgment or dissension with the goal of creating solutions, is just one of dozens of methods for coming up with new ideas. 9
You can benefit from setting aside time for ideation. Reserving time to let your mind roam freely as you think about an issue or problem from multiple directions is a necessary component of the process. Ideation takes time and a deliberate effort to move beyond your habitual thought patterns. If you consciously set aside time for creativity, you will broaden your mental horizons and allow yourself to change and grow. 10
Entrepreneurs work with two types of thinking. Linear thinking —sometimes called vertical thinking —involves a logical, step-by-step process. In contrast, creative thinking is more often lateral thinking , free and open thinking in which established patterns of logical thought are purposefully ignored or even challenged. You can ignore logic; anything becomes possible. Linear thinking is crucial in turning your idea into a business. Lateral thinking will allow you to use your creativity to solve problems that arise. Figure 4.5 summarizes linear and lateral thinking.
It is certainly possible for you to be an entrepreneur and focus on linear thinking. Many viable business ventures flow logically and directly from existing products and services. However, for various reasons, creativity and lateral thinking are emphasized in many contemporary contexts in the study of entrepreneurship. Some reasons for this are increased global competition, the speed of technological change, and the complexity of trade and communication systems. 11 These factors help explain not just why creativity is emphasized in entrepreneurial circles but also why creativity should be emphasized. Product developers of the twenty-first century are expected to do more than simply push products and innovations a step further down a planned path. Newer generations of entrepreneurs are expected to be path breakers in new products, services, and processes.
Examples of creativity are all around us. They come in the forms of fine art and writing, or in graffiti and viral videos, or in new products, services, ideas, and processes. In practice, creativity is incredibly broad. It is all around us whenever or wherever people strive to solve a problem, large or small, practical or impractical.
We previously defined innovation as a change that adds value to an existing product or service. According to the management thinker and author Peter Drucker , the key point about innovation is that it is a response to both changes within markets and changes from outside markets. For Drucker, classical entrepreneurship psychology highlights the purposeful nature of innovation. 12 Business firms and other organizations can plan to innovate by applying either lateral or linear thinking methods, or both. In other words, not all innovation is purely creative. If a firm wishes to innovate a current product, what will likely matter more to that firm is the success of the innovation rather than the level of creativity involved. Drucker summarized the sources of innovation into seven categories, as outlined in Table 4.3 . Firms and individuals can innovate by seeking out and developing changes within markets or by focusing on and cultivating creativity. Firms and individuals should be on the lookout for opportunities to innovate. 13
| Source | Description |
|---|---|
| The unexpected | Looking for new opportunities in the market; unexpected product performance; unexpected new products as examples |
| The incongruity | Discrepancies between what you think should be and what is reality |
| Process need | Weaknesses in the organization, product, or service |
| Changes in industry/market | New regulations; new technologies |
| Demographics | Understanding needs and wants of target markets |
| Changes in perceptions | Changes in perceptions of life events and values |
| New knowledge | New technologies; advancements in thinking; new research |
One innovation that demonstrates several of Drucker’s sources is the use of cashier kiosks in fast-food restaurants. McDonald’s was one of the first to launch these self-serve kiosks. Historically, the company has focused on operational efficiencies (doing more/better with less). In response to changes in the market, changes in demographics, and process need, McDonald’s incorporated self-serve cashier stations into their stores. These kiosks address the need of younger generations to interact more with technology and gives customers faster service in most cases. 15
Another leading expert on innovation, Tony Ulwick , focuses on understanding how the customer will judge or evaluate the quality and value of the product. The product development process should be based on the metrics that customers use to judge products, so that innovation can address those metrics and develop the best product for meeting customers’ needs when it hits the market. This process is very similar to Drucker’s contention that innovation comes as a response to changes within and outside of the market. Ulwick insists that focusing on the customer should begin early in the development process. 16
Disruptive innovation is a process that significantly affects the market by making a product or service more affordable and/or accessible, so that it will be available to a much larger audience. Clay Christensen of Harvard University coined this term in the 1990s to emphasize the process nature of innovation. For Christensen, the innovative component is not the actual product or service, but the process that makes that product more available to a larger population of users. He has since published a good deal on the topic of disruptive innovation, focusing on small players in a market. Christensen theorizes that a disruptive innovation from a smaller company can threaten an existing larger business by offering the market new and improved solutions. The smaller company causes the disruption when it captures some of the market share from the larger organization. 17 , 18 One example of a disruptive innovation is Uber and its impact on the taxicab industry. Uber’s innovative service, which targets customers who might otherwise take a cab, has shaped the industry as whole by offering an alternative that some deem superior to the typical cab ride.
One key to innovation within a given market space is to look for pain points, particularly in existing products that fail to work as well as users expect them to. A pain point is a problem that people have with a product or service that might be addressed by creating a modified version that solves the problem more efficiently. 19 For example, you might be interested in whether a local retail store carries a specific item without actually going there to check. Most retailers now have a feature on their websites that allows you to determine whether the product (and often how many units) is available at a specific store. This eliminates the need to go to the location only to find that they are out of your favorite product. Once a pain point is identified in a firm’s own product or in a competitor’s product, the firm can bring creativity to bear in finding and testing solutions that sidestep or eliminate the pain, making the innovation marketable. This is one example of an incremental innovation , an innovation that modifies an existing product or service. 20
In contrast, a pioneering innovation is one based on a new technology, a new advancement in the field, and/or an advancement in a related field that leads to the development of a new product. 21 Firms offering similar products and services can undertake pioneering innovations, but pioneering the new product requires opening up new market space and taking major risks.
Entrepreneur In Action
Pioneering innovation in the personal care industry.
In his ninth-grade biology class, Benjamin Stern came up with an idea to change the personal care industry. He envisioned personal cleaning products (soap, shampoo, etc.) that would contain no harsh chemicals or sulfates, and would also produce no plastic waste from empty bottles. He developed Nohbo Drops , single-use personal cleansing products with water-soluble packaging. Stern was able to borrow money from family and friends, and use some of his college fund to hire a chemist to develop the product. He then appeared on Shark Tank with his innovation in 2016 and secured the backing of investor Mark Cuban . Stern assembled a research team to perfect the product and obtained a patent ( Figure 4.6 ). The products are now available via the company website.
Is a pioneering innovation an invention? A firm makes a pioneering innovation when it creates a product or service arising from what it has done before. Pokémon GO is a great example of pioneering innovation. Nintendo was struggling to keep pace with other gaming-related companies. The company, in keeping with its core business of video games, came up with a new direction for the gaming industry. Pokémon GO is known worldwide and is one of the most successful mobile games launched. 22 It takes creativity to explore a new direction, but not every pioneering innovation creates a distinctly new product or capability for consumers and clients.
Entrepreneurs in the process of developing an innovation usually examine the current products and services their firm offers, investigate new technologies and techniques being introduced in the marketplace or in related marketplaces, watch research and development in universities and in other companies, and pursue new developments that are likely to fit one of two conditions: an innovation that likely fits an existing market better than other products or services being offered; or an innovation that fits a market that so far has been underserved.
An example of an incremental innovation is the trash receptacle you find at fast-food restaurants. For many years, trash cans in fast-food locations were placed in boxes behind swinging doors. The trash cans did one job well: They hid the garbage from sight. But they created other problems: Often, the swinging doors would get ketchup and other waste on them, surely a pain point. Newer trash receptacles in fast-food restaurants have open fronts or open tops that enable people to dispose of their trash more neatly. The downside for restaurants is that users can see and possibly smell the food waste, but if the restaurants change the trash bags frequently, as is a good practice anyway, this innovation works relatively well. You might not think twice about this everyday example of an innovation when you eat at a fast-food restaurant, but even small improvements can matter a lot, particularly if the market they serve is vast.
An invention is a leap in capability beyond innovation. Some inventions combine several innovations into something new. Invention certainly requires creativity, but it goes beyond coming up with new ideas, combinations of thought, or variations on a theme. Inventors build. Developing something users and customers view as an invention could be important to some entrepreneurs, because when a new product or service is viewed as unique, it can create new markets. True inventiveness is often recognized in the marketplace, and it can help build a valuable reputation and help establish market position if the company can build a future-oriented corporate narrative around the invention. 23
Besides establishing a new market position, a true invention can have a social and cultural impact. At the social level, a new invention can influence the ways institutions work. For example, the invention of desktop computing put accounting and word processing into the hands of nearly every office worker. The ripple effects spread to the school systems that educate and train the corporate workforce. Not long after the spread of desktop computing, workers were expected to draft reports, run financial projections, and make appealing presentations. Specializations or aspects of specialized jobs—such as typist, bookkeeper, corporate copywriter—became necessary for almost everyone headed for corporate work. Colleges and eventually high schools saw software training as essential for students of almost all skill levels. These additional capabilities added profitability and efficiencies, but they also have increased job requirements for the average professional.
Some of the most successful inventions contain a mix of familiarity and innovation that is difficult to achieve. With this mix, the rate of adoption can be accelerated because of the familiarity with the concept or certain aspects of the product or service. As an example, the “videophone” was a concept that began to be explored as early as the late 1800s. AT&T began extensive work on videophones during the 1920s. However, the invention was not adopted because of a lack of familiarity with the idea of seeing someone on a screen and communicating back and forth. Other factors included societal norms, size of the machine, and cost. It wasn’t until the early 2000s that the invention started to take hold in the marketplace. 24 The concept of a black box is that activities are performed in a somewhat mysterious and ambiguous manner, with a serendipitous set of actions connecting that result in a surprisingly beneficial manner. An example is Febreeze, a chemical combination that binds molecules to eliminate odors. From a black box perspective, the chemical engineers did not intend to create this product, but as they were working on creating another product, someone noticed that the product they were working on removed odors, thus inadvertently creating a successful new product marketed as Febreeze.
What Can You Do?
Did henry ford invent the assembly line.
Very few products or procedures are actually brand-new ideas. Most new products are alterations or new applications of existing products, with some type of twist in design, function, portability, or use. Henry Ford is usually credited with inventing the moving assembly line Figure 4.7 (a) in 1913. However, some 800 years before Henry Ford, wooden ships were mass produced in the northern Italian city of Venice in a system that anticipated the modern assembly line.
Various components (ropes, sails, and so on) were prefabricated in different parts of the Venetian Arsenal, a huge, complex construction site along one of Venice’s canals. The parts were then delivered to specific assembly points Figure 4.7 (b) . After each stage of construction, the ships were floated down the canal to the next assembly area, where the next sets of workers and parts were waiting. Moving the ships down the waterway and assembling them in stages increased speed and efficiency to the point that long before the Industrial Revolution, the Arsenal could produce one fully functional and completely equipped ship per day . The system was so successful that it was used from the thirteenth century to about 1800.
Henry Ford did not invent anything new—he only applied the 800-year-old process of building wooden ships by hand along a moving waterway to making metal cars by hand on a moving conveyor ( Figure 4.7 ).
Opportunities to bring new products and processes to market are in front of us every day. The key is having the ability to recognize them and implement them. Likewise, the people you need to help you be successful may be right in front of you on a regular basis. The key is having the ability to recognize who they are and making connections to them. Just as those ships and cars moved down an assembly line until they were ready to be put into service, start thinking about moving down the “who I know” line so that you will eventually have a successful business in place.
The process of invention is difficult to codify because not all inventions or inventors follow the same path. Often the path can take multiple directions, involve many people besides the inventor, and encompass many restarts. Inventors and their teams develop their own processes along with their own products, and the field in which an inventor works will greatly influence the modes and pace of invention. Elon Musk is famous for founding four different billion-dollar companies. The development processes for PayPal , Solar City , SpaceX , and Tesla differed widely; however, Musk does outline a six-step decision-making process ( Figure 4.8 ):
- Ask a question.
- Gather as much evidence as possible about it.
- Develop axioms based on the evidence and try to assign a probability of truth to each one.
- Draw a conclusion in order to determine: Are these axioms correct, are they relevant, do they necessarily lead to this conclusion, and with what probability?
- Attempt to disprove the conclusion. Seek refutation from others to further help break your conclusion.
- If nobody can invalidate your conclusion, then you’re probably right, but you’re not certainly right.
In other words, the constant underlying Musk’s decision process is the scientific method. 25 The scientific method , most often associated with the natural sciences, outlines the process of discovering an answer to a question or a problem. “The scientific method is a logical organization of steps that scientists use to make deductions about the world around us.” 26 The steps in the scientific method line up quite nicely with Musk’s decision-making process. Applying the scientific method to invention and innovation makes sense. The scientific method involves becoming aware of a problem, collecting data about it by observing and experimenting, and coming up with suggestions on how to solve it.
Economists argue that processes of invention can be explained by economic forces. But this hasn’t always been the case. Prior to 1940, economic theory focused very little on inventions. After World War II, much of the global economy in the developed world needed to be rebuilt. New technologies were developing rapidly, and research and development investment increased. Inventors and economists alike became aware of consumer demand and realized that demand can influence which inventions take off at a given time. 27 However, inventors are always up against an adoption curve. 28
The Rogers Adoption Curve was popularized through the research and publications of the author and scientist Everett Rogers . 29 He first used it to describe how agricultural innovations diffused (or failed to) in a society. It was later applied to all inventions and innovations. This curve illustrates diffusion of an innovation and when certain people will adopt it. First is the question of who adopts inventions and innovations in society: The main groups are innovators, early adopters, early and late-majority adopters, and “laggards” (Rogers’s own term). 30 The innovators are the ones willing to take a risk on a new product, the consumers who want to try it first. The early adopters are consumers who will adopt new inventions with little to no information. Majority adopters will adopt products after being accepted by the majority. And finally, laggards are often not willing to readily adopt change and are the hardest to convince to try a new invention. 31
Rogers’s second way of looking at the concept is from the point of view of the invention itself. A given population partially or completely adopts an invention or rejects it. If an invention is targeted at the wrong population or the wrong population segment, this can dramatically inhibit its chances of being adopted widely. The most critical point of adoption often occurs at the end of the early adoption phase, before the early majority steps in and truly confirms (or not) the diffusion of an invention. This is called the diffusion chasm (though this process is usually called the diffusion of innovations , for our purposes, it applies quite well to new inventions as we define them here).
The diffusion curve depicts a social process in which the value of an invention is perceived (or not) to be worth the cost ( Figure 4.9 ). Early adopters generally pay more than those who wait, but if the invention gives them a perceived practical, social, or cultural advantage, members of the population, the popularity of the invention itself, and marketing can all drive the invention over the diffusion chasm. Once the early majority adopts an innovation (in very large numbers), we can expect the rest of the majority to adopt it. By the time the late majority and the laggards adopt an innovation, the novelty has worn off, but the practical benefits of the innovation can still be felt.
Inventors are constantly trying to cross the diffusion chasm, often with many products at a time. Crossing the diffusion chasm is a nearly constant concern for business-focused or outcomes-focused inventors. Inventors put many of their resources into an invention during the innovation and early adoption stages. Inventions may not turn a profit for investors or the inventors themselves until they are well into the early majority stage of adoption. Some inventors are pleased to work toward general discovery, but most in today’s social and cultural context are working to develop products and services for markets.
One shortcoming of the diffusion of innovations model is that it treats inventions and innovations as though they are finished and complete, though many are not. Not all inventions are finished products ready for market. Iterative development is more common, particularly in fields with high levels of complexity and in service-oriented ventures. In the iterative development process, inventors and innovators continuously engage with potential customers in order to develop their products and their consumer bases at the same time. This model of business learning, also known as the science of customer development, is essential. 32 Business learning involves testing product-market fit and making changes to an innovation or invention many times over until either investment funding runs out or the product succeeds. Perhaps the most accurate way to summarize this process is to note that many inventions are hit-or-miss prospects that get only a few chances to cross the diffusion chasm. When innovators follow the build-measure-learn model (discussed in detail in Launch for Growth to Success ), they try to work their way across the diffusion chasm rather than making a leap of faith.
Work It Out
The safety razor was an innovation over the straight razor. Safety razor blades are small enough to fit inside a capsule, and the location and type of handle was altered to suit the new orientation of handle to blade ( Figure 4.10 ). Most contemporary razors are themselves innovations on the safety razor, whether they have two, three, four, or more blades. The method of changing razor blades has evolved with each innovation on the safety razor, but the designs are functionally similar.
The electric razor is a related invention. It still uses blades to shave hair off the face or body, but the blades are hidden beneath a foil or foils. Hairs poke through the foils when the razor is pressed against the skin, and blades moving in various directions cut the hairs. Although electric razors use blades as do mechanical razors, the new design and the added technology qualified the electric razor as an invention that offered something new in the shaving industry when Jacob Schick won the patent for a shaving machine in 1930. 33 Still other innovations in the shaving genre include gender-specific razors, beard trimmers, and, more recently, online clubs such as Dollar Shave Club and Harry’s Shave Club .
Think about the conceptual difference between innovation and invention. Is the safety razor a pioneering innovation or an incremental one? What makes the electric razor an invention, as we define it here? What makes it stand out as a leap from previous types of razors? Do you think the electric razor is a “sure thing”? Why or why not? Consider the availability of electricity at the time the first electric razors were being made. Why do you think the electric razor made it over the diffusion chasm between early adopters and early majority adopters? Do you think the electric razor was invented iteratively with small changes to the same product in response to customer preferences? Or did it develop in a series of black box inventions, with each one either diffusing or not?
- 7 “How Design Thinking Transformed Airbnb from Failing Startup to Billion Dollar Business.” First Round Review . n.d. https://firstround.com/review/How-design-thinking-transformed-Airbnb-from-failing-startup-to-billion-dollar-business/
- 8 “Divya Nag, 26.” Fortune . n.d. http://fortune.com/40-under-40/2017/divya-nag-27/
- 9 Rikke Dam and Teo Siang. “Introduction to the Essential Ideation Techniques Which Are the Heart of Design Thinking.” Interaction Design Foundation . April 2019. https://www.interaction-design.org/literature/article/introduction-to-the-essential-ideation-techniques-which-are-the-heart-of-design-thinking
- 10 Dawn Kelly and Terry L. Amburgey. “Organizational Inertia and Momentum: A Dynamic Model of Strategic Change.” Academy of Management Journal 34, no. 3 (1991): 591–612.
- 11 Ian Fillis and Ruth Rentschler. “The Role of Creativity in Entrepreneurship.” Journal of Enterprising Culture 18, no. 1 (2010): 49–81.
- 12 P. F. Drucker. Innovation and Entrepreneurship: Practices and Principles . New York: Harper & Row Publishers, 1986.
- 13 P. F. Drucker. Innovation and Entrepreneurship: Practices and Principles . (New York: Harper & Row Publishers, 1986), 35.
- 14 P. F. Drucker. Innovation and Entrepreneurship: Practices and Principles . New York: Harper & Row Publishers, 1986.
- 15 Blake Morgan. “5 Fresh Examples of Customer Service Innovation.” Forbes . July 17, 2017. https://www.forbes.com/sites/blakemorgan/2017/07/17/5-fresh-examples-of-customer-experience-innovation/#3ae5a46e5c18
- 16 Tony Ulwick. “Reinventing Innovation for 25 Years.” Strategyn . n.d. https://strategyn.com/tony-ulwick/?network=g&matchtype=p&keyword=tony%20ulwick&creative=268244402567&device=c&devicemodel=&placement=&position=1t1&campaignid=1394486829&adgroupid=57939305027&loc_physical_ms=9015694&loc_interest_ms=&gclid=CjwKCAjw29vsBRAuEiwA9s-0B2jD3BYbm-BEiPWHKfd6R6mnW4XCHuhXbX_JhUof76IdXh6joIzlWRoCqJAQAvD_BwE
- 17 Chris Larson. “Disruptive Innovation Theory: What It Is & 4 Key Concepts.” Harvard Business School . November 15, 2016. https://online.hbs.edu/blog/post/4-keys-to-understanding-clayton-christensens-theory-of-disruptive-innovation
- 18 Rosamond Hutt. “What Is Disruptive Innovation?” World Economic Forum . June 25, 2016. https://www.weforum.org/agenda/2016/06/what-is-disruptive-innovation/
- 19 Lloyd Waldo. “What’s a Pain Point? A Guide for Startups.” StartupYard Seed Accelerator . December 1, 2016. https://startupyard.com/whats-pain-point/
- 20 Abdul Ali, Manohar U. Kalwani, and Dan Kovenock. “Selecting Product Development Projects: Pioneering versus Incremental Innovation Strategies.” Management Science 39, no. 3 (1993): 255–274.
- 21 Abdul Ali. “Pioneering versus Incremental Innovation: Review and Research Propositions.” Journal of Product Innovation Management 11, no. 1 (1994): 46–61.
- 22 JV Chamary. “Why ‘Pokémon GO’ Is the World’s Most Important Game.” Forbes . February 10, 2018. https://www.forbes.com/sites/jvchamary/2018/02/10/pokemon-go-science-health-benefits/#2b6f07fd3ab0
- 23 Morten Thanning Vendelø. “Narrating Corporate Reputation: Becoming Legitimate through Storytelling.” International Studies of Management & Organization 28, no. 3 (1998): 120–137.
- 24 Thomas J. Fitzgerald. “For the Deaf: Communication without the Wait.” The New York Times . December 18, 2003. https://www.nytimes.com/2003/12/18/technology/for-the-deaf-communication-without-the-wait.html
- 25 Abby Jackson. “Elon Musk Uses This 6-Step Process to Make Decisions.” Business Insider . November 16, 2017. https://www.inc.com/business-insider/how-elon-musk-makes-decisions-rolling-stone.html
- 26 Joan Whetzel. “Formula for Using the Scientific Method.” Owlcation . February 11, 2017. https://owlcation.com/academia/FormulaForUsingScientificMethod
- 27 N. Rosenberg. “Science, Invention and Economic Growth.” The Economic Journal 84, no. 333 (1974): 90–108.
- 28 Everett M. Rogers. Diffusion of Innovations , 5th ed. New York: Simon and Schuster, 2010.
- 29 John-Pierre Maeli. “The Rogers Adoption Curve & How You Spread New Ideas Throughout Culture.” The Political Informer . May 6, 2016. https://medium.com/the-political-informer/the-rogers-adoption-curve-how-you-spread-new-ideas-throughout-culture-d848462fcd24
- 30 Everett M. Rogers. Diffusion of Innovations , 5th ed. New York: Simon and Schuster, 2010.
- 31 Wayne W. LaMorte. “Diffusion of Innovation Theory.” September 9, 2019. http://sphweb.bumc.bu.edu/otlt/MPH-Modules/SB/BehavioralChangeTheories/BehavioralChangeTheories4.html
- 32 Eric Ries. The Lean Startup: How Today’s Entrepreneurs Use Continuous Innovation to Create Radically Successful Businesses . Largo, Maryland: Crown Books, 2011.
- 33 “Jacob Schick Invents the Electric Razor.” Connecticut History . May 13, 2017. https://connecticuthistory.org/jacob-schick-invents-the-electric-razor/
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution License and you must attribute OpenStax.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/entrepreneurship/pages/1-introduction
- Authors: Michael Laverty, Chris Littel
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: Entrepreneurship
- Publication date: Jan 16, 2020
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/entrepreneurship/pages/1-introduction
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/entrepreneurship/pages/4-2-creativity-innovation-and-invention-how-they-differ
© Jun 26, 2024 OpenStax. Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License . The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.
🔥 Strategically Advance Your Business in 6 Weeks. 🚀 Secure your spot now!
Invention vs Innovation: The Important Difference for Your Organization’s Future Growth

Written by The Blue Ocean Team
Includes excerpts from Chan Kim & Renée Mauborgne’s Blue Ocean Strategy (2015) and Blue Ocean Shift (2017) and the case study “ Searching for Value: Value Innovation vs. Technology Innovation “, written by Institute Executive Fellow at the INSEAD Blue Ocean Strategy Institute, Michael Olenick, with Chan Kim & Renée Mauborgne.
Innovation is undoubtedly a major driver of corporate growth. Executives constantly look for ways to innovate to stay ahead of the competition and solve their most pressing problems. Yet, many companies don’t get it right and often confuse innovation with invention .
Although there is a connection between the two terms, innovation and invention are distinct concepts and shouldn’t be used interchangeably. We’ll take a close look and these terms and related concepts to understand the important difference between innovation vs invention , why you should focus on value innovation instead, and what it all means to your company’s future growth strategy. We’ll explore examples of innovation and invention , as well as examples of value innovation to distinguish the concepts.
Before we dive into the differences between invention and innovation, let’s first define what invention is and what innovation is.
The steam engine typically comes to mind when we think of inventions.
What is invention?
Invention is the act of bringing ideas or objects together in a new and unique way to create a device or process that did not exist before. The wheel, paper, steam engine and the internet are typically what come to mind when we think of inventions.
What is innovation?
Innovation is a very broad concept that is based on an original and useful idea regardless of whether that idea is linked to a leap in value that can appeal to the mass of buyers. Corporate graveyards are full of companies that got to market first with innovative offerings not linked to value. Simply creating something original and useful through innovation is not enough to create and capture a new market space, or blue ocean , even if the innovation wins the company accolades.
Innovation vs invention: what’s the difference?
Coming up with new inventions might be personally rewarding but betting your company’s future growth on it is dangerous. The world is filled with new inventions that failed to produce commercial success. Innovation is not invention. So before you run to your research and development department with your new idea, let’s look at some examples to understand the difference between invention and innovation and the results of each.

The Altair computer was a great invention but had limited commercial appeal. Photo © used under license and adapted from the original .
Invention vs innovation examples
Consider the question of who invented the personal computer. Perhaps you think it was Apple under Steve Jobs or maybe IBM? In fact, it was a small company named MITS, whose personal computer was called the Altair. Popular among computer hobbyists, the Altair had limited commercial appeal, which is why you’ve probably never heard of it.
Or take Motorola’s Iridium. Was it great innovation? Sure. It was the first global phone, but did it offer a breakthrough in value that could attract a mass of buyers? The answer is no. The Iridium was an impressive technological feat that worked in remote places like the Gobi Desert, but it did not work in buildings and cars, the precise places that global executives on the move most needed them to work. It failed to create a leap in value for its target mass of buyers.
To understand why some innovations achieve great success while others are commercial failures, we need to understand the difference between value innovation and technology innovation .
What is value innovation?
Value innovation is a concept developed by professors of strategy and world-renowned management thinkers, Chan Kim and Renée Mauborgne in their global bestsellers Blue Ocean Strategy and Blue Ocean Shift .
Value innovation is the cornerstone of blue ocean strategy and places equal emphasis on value and innovation. It is the simultaneous pursuit of differentiation and low cost, creating a leap in value for both buyers and the company.
Value without innovation tends to focus on value creation on an incremental scale, something that improves value but is not sufficient to make you stand out in the marketplace.
Innovations without value tend to be technology-driven , market-pioneering, or futuristic, often shooting beyond what buyers are ready to accept and pay for, as we saw with the Iridium.
When organizations fail to register the difference between value innovation and innovation per se, they all too often end with an innovation that breaks new ground but does not unlock the mass of target buyers, keeping them by and large stuck in the red ocean of competition. Check out Chan Kim and Renée Mauborgne’s blog on the rising importance of value innovation for creating growth for a more in-depth discussion.
Value innovation vs technology innovation – what’s the difference
Technology innovation is the creation of a product or service that focuses on new or improved technology. Often, the technology involved is seen as the differentiating factor and put front and center in the expectation that buyers will find a use for it either now or later.
But when companies mistakenly assume that market creation hinges on breakthrough technologies, their organizations tend to push for products or services that are too “out there,” too complicated, or, like the Segway, lacking a necessary ecosystem.
Read more on the difference between value innovation and technology innovation on the blog: Why technology innovation only counts when linked to buyer value.

Buyers were not impressed with Segway’s technology innovation.
Examples of innovations that failed
Consider the Segway, the two-wheeled self-balancing vehicle that once promised to revolutionize transport. Technologically innovative, the Segway created a massive media buzz on its launch. Buyers, on the other hand, were less impressed. Most people simply did not want to pay US $4000-$5000 for a product that left them wondering where to park it, how to take it in a car, whether it could be brought on a bus or a train, and where it could be used – on sidewalks or roads.
Technology innovation is widely recognized as the key driver of macroeconomic growth, so you would be forgiven for assuming it is the key to unlocking new markets. Certainly, technology exists to enable value. That is, technology is catalytic to value creation but does not, by itself, guarantee commercial success. It is the value to the buyer that is the most important component of innovation.
Many technology innovators fail to create and capture blue oceans by confusing innovation with value innovation.
Google Glass, Motorola’s Iridium, and Segway all suffered by getting this wrong. Google Glass was considered unattractive, nerdish, and expensive, and raised hugely uncomfortable privacy issues. The Iridium satellite phone was a technological feat that worked in the Gobi Desert but not in buildings or cars, where people needed it most.
Although MITS invented the first personal computer, it was Apple and IBM, among others, that dominated the new mass market for PCs by adapting the technology to produce a leap in buyer value – in essence, converting technology innovation into value innovation.
Google Glass is an example of a failed technology innovation. Photo © used under license and adapted from the original .
Example of innovation that succeeded
Zoom – an example of value innovation.
Zoom is a successful value-innovation business that made high-quality, reliable video conferencing easy. Users love Zoom for the simplicity of setup, use, relatively low cost, and quality of the calls.
Zoom didn’t invent the technology – there were other videoconferencing services long before Zoom came along. Videoconferencing was initially developed in the 1950s, and web-based videoconferencing has existed since the 1990s.
Since then, countless web-based videoconferencing companies have emerged but whereas these services could be difficult to set up or suffer substantially lower call quality, Zoom vastly simplified setting up and joining a video call and made sure the calls were clear and seldom or never dropped.
Zoom made the installation and use of this mature technology far easier, allowing a wider group to unlock and realize the utility without the hassle. A click or two are all that is required to start or join a high-quality online video conference. Zoom is a value innovation. For more examples of value innovation, check out Michael Olenick’s case study: Searching for Value: Value Innovation vs Technology Innovation.

Zoom is an example of value innovation.
How to invent something …people want
So how to invent something that people actually want to buy? You might have a great idea for a new product, an improvement of an existing product, or new solutions to existing problems. But how to ensure your organization can make this a commercial success? First, you need to link value to innovation. Second, run your new idea through a Blue Ocean Idea Index to check whether it is a value innovation or an invention that will not be commercially viable.
Link value to innovation
Value innovation, not technological innovation, is what counts when creating new markets. Starbucks, for example, turned the coffee industry on its head by shifting its focus from commodity coffee sales to the emotional atmosphere in which customers enjoy their coffee – an example of value innovation. No new technology was involved.
Or take Google. It didn’t invent the search engine but nevertheless became hugely successful because it offers buyers a huge leap in value. Its search engine is easy to use, fast, and accurate, making people more productive in finding information than most ever imagined possible. Everyone from first graders to senior citizens uses it.
With its search engine, it was Google’s value innovation rather than technology innovation that created new markets by offering a leap in productivity, simplicity, ease of use, convenience, fun, and environmental friendliness.
However, while Google enjoyed extraordinary success with its search engine, another one of its products, Google Glass, became a commercial failure.
Run your new concept through the Blue Ocean Idea Index
Blue ocean strategy offers a robust way to maximize your upside while minimizing risks. A key framework here is the Blue Ocean Idea Index, which lets you test the commercial viability of your new ideas. It poses four questions:
1. Is there a compelling reason for people to buy your offering?
2. Is your offering priced to attract the mass of target buyers so they have a compelling ability to pay for it?
3. Can you produce your offering at the strategic price and still earn a healthy profit from it?
4. What are the adoption hurdles in rolling out your idea and have you addressed these upfront?
The first two questions tackle the revenue side of your business model. They ensure that you create a leap in net buyer value. The third question deals with the profit side of your business model. And the last question encourages you to think about the externalities that could trip up even the best new idea.
Each of these questions comes with tools and frameworks – so you can get systematic about creating your blue oceans.
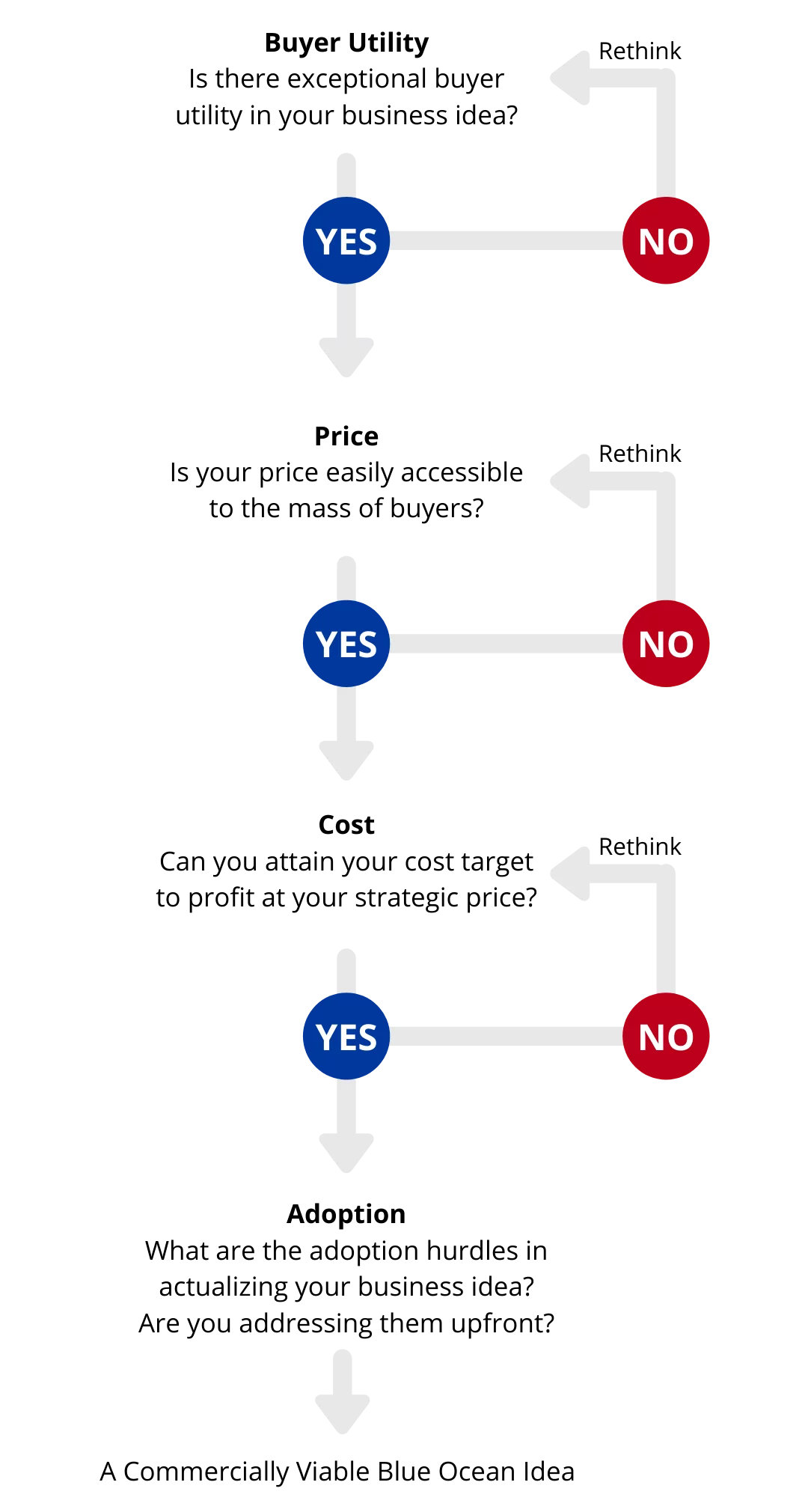
Sequence of creating a blue ocean.
Innovator vs inventor: which one are you?
So are you an innovator or an inventor? Ask yourself: are you pursuing value innovation or simply trying to invent or develop technology that will make a splash without creating new markets?
If you cannot immediately describe the value of the technology to your buyer in terms the buyer can understand, then you need to reconsider your offering.
Remember, value innovation rejects the value-cost trade-off: more cost does not always equate to more value. That’s why value innovation strategic moves often cost less to produce and are often as profitable or more profitable than technology-focused innovation.
Innovation vs improvement
What’s the difference between innovation and improvement.
At this point, it should be noted that innovation is not the same as improvement, which is usually iterative and incremental, coming about through trial and error and getting rid of flaws. Improvement comes after innovation, which involves developing something essentially novel which can then be further improved or optimized.
Simply creating something original and useful through innovation is not enough to create and capture a blue ocean of uncontested market space.
When you fail to register the difference between value innovation and technology innovation or invention, you risk ending up with an innovation that breaks new ground but does not unlock the mass of target buyers.
Remember that while technology innovators may lay extraordinary eggs, they are seldom the ones who ultimately hatch them. The focus of your successful market-creating strategy should not be on how to lay a technology egg per se, but rather on how to hatch the egg for its commercial success.
Check out the Case Studies
If you’re an educator interested in teaching blue ocean strategy to your students, check out these exciting case studies, which come with teaching notes to guide classroom discussion.
Searching for Value: Value Innovation vs. Technology Innovation – Mini Cases & Exercises
Author(s): KIM, W. Chan, MAUBORGNE, Renée, OLENICK, Michael
| | | | |
| | | |

Recent posts

The Benefits of Innovation That Isn’t Disruptive
When it comes to innovation and growth, disruption is not the only path.
Artificial Intelligence on the Runway
How Technology is Transforming Fashion and Inspiring Blue Oceans

What Innovators Who Create New Markets Do Differently
How to excel at nondisruptive creation

A Nondisruptive Approach to the Environment
Companies can help the transition to a greener economy without sacrificing their financial interests.
Five Key Insights for Positive-Sum Innovation
With the right tools, businesses can innovate and achieve growth without negatively impacting society.
Nondisruptive Creation: An Alternative Path to Innovation and Growth?
How leaders can innovate and achieve growth without displacing industries, companies or jobs.

The Economic and Social Impact of Nondisruptive Creation
Where nondisruptive creation breaks from disruption

Kim and Mauborgne Honored as Two of the Four Leading Thinkers in Harvard Business Review’s 100-year Celebration
Recognized for their ground-breaking research journey, which seeks to understand how to go beyond zero-sum, win-lose paradigms to achieve positive-sum outcomes that create a larger economic pie for all.

Reimagining Veterinary Care: The Blue Ocean Strategy of PetWellClinic
How one vet used blue ocean strategy to turnaround his industry and life, creating a national chain of pet care clinics.

Announcing the International Blue Ocean Awards 2023
Celebrating Blue Ocean Strategy, Innovation & Entrepreneurship at the INSEAD Blue Ocean Strategy Institute

You May Also Like…

We’ve all heard the refrain: Disrupt this, disrupt that. Disrupt – or die. Unsurprisingly, many business leaders have...

Excerpts from Chan Kim & Renée Mauborgne’s Beyond Disruption: Innovate and Achieve Growth without Displacing...

Harvard Business Review paid tribute to INSEAD’s Chan Kim and Renée Mauborgne, along with Harvard’s Michael Porter and...
Return to the Blog →

BLUE OCEAN SPRINT
Learn how to leave the competition behind. discover how to create a new market space while lowering your costs, fast..
“LOVED this course. No nonsense, 100% practical tools I can start implementing TODAY in my organisation!” Amalia C., Google
Join thousands of leaders like you who are creating innovative companies, products, and services that stand out from the crowd.
THE BLUE OCEAN STRATEGY PRACTITIONER PROGRAM

Transform your strategic perspective, master blue ocean tools and frameworks, & learn to unlock new growth opportunities
Get started with new market creation with our live, interactive, expert-led program.
ENROLL TODAY

- Onsite training
3,000,000+ delegates
15,000+ clients
1,000+ locations
- KnowledgePass
- Log a ticket
01344203999 Available 24/7

Innovation vs Invention: A Detailed Comparison
Explore the nuances of 'Innovation vs Invention' in this comprehensive blog. Delve into the realms of creativity, development, and impact as we dissect the differences between these two fundamental concepts. Discover how Innovation breathes life into Inventions, reshaping industries and driving progress. Join us on a journey to uncover the true essence of 'Innovation vs Invention.'

Exclusive 40% OFF
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Share this Resource
- Leadership Skills Training
- Employee Dispute Resolution Course
- Social Innovation Course
- Business Model Innovation Training

What is the difference between Innovation vs Invention? This is a question that many people ask, especially in the fields of science, business and technology. To answer this question, we need to understand the definitions and characteristics of both terms. Innovation and Invention are related but different. This blog delves into the nuanced differences and similarities between these concepts, exploring how each contributes to advancing technology and society. We'll uncover the essence of Innovation vs Invention, examining real-world examples and their impacts.
Table of Contents
1) What is an Invention?
a) Importance of Invention
2) What is Innovation?
3) Innovation vs Invention
4) Conclusion

What is an Invention?
An Invention is creating a new product, process, or idea that has never existed. It is the result of original research, experimentation, or discovery. An Invention can be a physical object, such as a machine, a device, a tool, or a non-physical concept, such as a theory, a formula, or a method. An Invention can be patented, giving the inventor the exclusive right to make, use or sell the Invention for a limited time.
Importance of Inventions
Inventions are important because they advance human knowledge and capabilities. They solve problems, improve existing solutions, or create new opportunities. Inventions can significantly impact various aspects of society, such as culture, economy, environment, health, education, and security. Some examples of Inventions that have changed the world are:
a) The wheel, which enabled transportation, agriculture, and industry. The wheel is one of the oldest and most fundamental Inventions, dating back to the Neolithic era. The wheel allowed humans to move heavy loads, plough fields, and build vehicles. The wheel also led to the development of other Inventions, such as gears, clocks, and turbines.
b) The printing press facilitated communication, education, and culture. In the 15th century, Johannes Gutenberg invented the printing press. It made books and other printed materials more accessible and affordable, spreading knowledge and literacy worldwide. The printing press also stimulated the growth of art, science, religion, and politics.
c) The light bulb extended the hours of work and leisure. In the 19th century, Thomas Edison invented the light bulb. It replaced candles and oil lamps, providing a safer and more efficient illumination source. The light bulb enabled people to work and play longer and explore new fields of study, such as photography, cinema, and electricity.
d) The telephone connected people across distances. In the 19th century, Alexander Graham Bell invented the telephone. It allowed people to communicate verbally over long distances, breaking the barriers of time and space. The telephone also paved the way for other Inventions, such as the radio, the television, and the internet.
e) The aeroplane revolutionised travel and trade. In the 20th century, the Wright brothers invented the aeroplane. It made air travel possible, reducing the time and cost of transportation. The aeroplane also opened up new exploration, commerce, and warfare possibilities.
f) The internet enabled information exchange and collaboration. The internet was invented by a network of researchers and engineers in the 20th century. It connected computers and devices worldwide, allowing people to access and share resources, information and services. The internet also fostered Innovation, creativity, and social interaction.
|
|
|
|
| Wheel | Physical and patentable | Enabled transportation, agriculture, and industry |
| Printing press | Physical and patentable | Facilitated communication, education, and culture |
| Light bulb | Physical and patentable | Extended the hours of work and leisure |
| Telephone | Physical and patentable | Connected people across distances |
| Aeroplane | Physical and patentable | Revolutionised travel and trade |
| Internet | Non-physical and non-patentable | Enabled information exchange and collaboration |

What is Innovation?
An Innovation is applying a new or improved product, process, or idea that creates value for customers, users, or society. It is the result of creative thinking, experimentation, or adaptation. An Innovation can be incremental, which means it improves an existing solution, or radical, which creates a new solution. Innovation can be disruptive, which means it changes the market or industry, or sustaining, which means it maintains the market or industry. An Innovation can be commercialised, which means it generates revenue, profit, or social, addressing a social or environmental issue.
Importance of Innovations
Innovations are important because they create value and competitive advantage. They satisfy customer needs, enhance user experience, or improve social welfare. Innovations can positively impact various aspects of society, such as productivity, efficiency, quality, sustainability, and diversity. Some examples of Innovations that have created value are:
a) The smartphone combines multiple functions and features into one device. The smartphone is a radical and disruptive Innovation, as it replaced many other devices, such as cameras, music players, and calculators, and created new markets, such as apps, games, and social media. The smartphone also improved communication, entertainment, and education for millions of users worldwide.
b) E-commerce, which enabled online shopping and delivery. E-commerce is an incremental and sustaining Innovation, as it improves the existing retail industry by offering convenience, variety, and lower prices. E-commerce also expanded the reach and access of customers and sellers and created new opportunities for entrepreneurship and Innovation.
c) The electric car, which reduced emissions and fuel consumption. The electric car is a radical and disruptive Innovation, as it introduced a new way of powering vehicles and challenged the dominance of the oil and gas industry. The electric car also contributed to environmental protection, energy efficiency, and social responsibility.
d) The vaccine prevented and cured diseases. The vaccine is a radical and sustaining Innovation, as it created a new method of preventing and treating infectious diseases, saved millions of lives and improved public health. The vaccine also advanced scientific knowledge, medical research, and biotechnology.
e) Social media enabled online communication and networking. Social media is an incremental and disruptive Innovation, as it enhances the existing internet and media platforms by offering more interactivity, personalisation, and engagement. Social media also transformed how people communicate, socialise, and express themselves and influenced culture, politics, and activism.
f) The blockchain-enabled secure and transparent transactions. The blockchain is a radical and disruptive Innovation, as it created a new system of storing and transferring data and challenged the authority of centralised institutions, such as banks and governments. The blockchain also enabled new applications, such as cryptocurrencies, smart contracts, and decentralised organisations.
|
|
|
|
| Smartphone | Radical and disruptive | Replaced many devices and created new markets |
| E-commerce | Incremental and sustaining | Improved the retail industry by offering convenience, variety, and lower prices |
| Electric car | Radical and disruptive | Introduced a new way of powering vehicles and challenged the oil and gas industry |
| Vaccine | Radical and sustaining | Created a new method of preventing and treating infectious diseases and saved millions of lives |
| Social media | Incremental and disruptive | Enhanced the internet and media platforms by offering more interactivity, personalisation, and engagement |
| Blockchain | Radical and disruptive | Created a new system of storing and transferring data and challenged the authority of centralised institutions |
Empower your Leadership journey: Join our Leadership Skills Training today!
Innovation vs Invention
Innovation and Invention are essential for human progress but have different meanings and implications. Here are some of the main differences between them:
a) Innovation is the application of a new or improved product, process, or idea, while Invention is the creation of a new product, process, or idea. Innovation is finding new ways to use existing knowledge, while Invention creates new knowledge. Innovation is often based on existing Inventions, while Invention is often the basis for future Innovations.
b) Innovation creates value for customers, users, or society, while Invention advances human knowledge and capabilities. Innovation is about meeting the needs, expectations, or desires of the target market or audience, while Invention is about expanding the boundaries of human understanding and potential. Innovation is measured by the value it generates, while Invention is measured by the novelty it produces.
c) Innovation is driven by customer needs, market opportunities, or social issues, while Invention is driven by curiosity, research, or discovery. Innovation is motivated by the external environment's demand, competition, or challenge. In contrast, Invention is motivated by interest, passion, or inspiration in the internal environment. Innovation is often a response to a problem. In contrast, Invention is often a result of a question.
d) Innovation involves creative thinking, experimentation, or adaptation, while Invention involves original research, experimentation, or discovery. Innovation is all about finding new solutions to existing problems, while Invention is about finding new problems to solve. Innovation is about testing and validating ideas, while Invention is about generating and exploring ideas. Innovation is about applying knowledge, while Invention is about acquiring knowledge.
e) Innovation can be incremental or radical, disruptive or sustaining, commercial or social, while Invention can be physical or non-physical, patentable or non-patentable. Innovation can be classified by the degree of change, the impact on the market or industry, or the purpose of the value creation. In contrast, Invention can be classified by the nature of the product, process, or idea or the legal protection of intellectual property. Innovation can be more or less transformative, influential, or beneficial, while Invention can be more or less tangible, exclusive, or original.
|
|
|
| The application of a new or improved product, process, or idea | The creation of a new product, process, or idea |
| Finding new ways to use existing knowledge | Creating new knowledge |
| Often based on existing Inventions | Usually, the basis for future Innovations |
| Creates value for customers, users, or society | Advances human knowledge and capabilities |
| About meeting the needs, expectations, or desires of the target market or audience | About expanding the boundaries of human understanding and potential |
| Measured by the value it generates | Measured by the novelty it produces |
| Driven by customer needs, market opportunities, or social issues | Driven by curiosity, research, or discovery |
| Motivated by the external environment’s demand, competition, or challenge | Motivated by interest, passion, or inspiration in the internal environment |
| Often, a response to a problem | Often, a result of a question |
| Involves creative thinking, experimentation, or adaptation | Involves original research, experimentation, or discovery |
| All about finding new solutions to existing problems | All about finding new problems to solve |
| About testing and validating ideas | About generating and exploring ideas |
| About applying knowledge | About acquiring knowledge |
| Can be incremental or radical, disruptive or sustaining, commercial or social | Can be physical or non-physical, patentable or non-patentable |
| Can be classified by the degree of change, the impact on the market or industry, or the purpose of the value creation | Can be classified by the nature of the product, process, or idea or the legal protection of intellectual property |
| Can be more or less transformative, influential, or beneficial | Can be more or less tangible, exclusive, or original |
Transform ideas into impact: Join our Managing Innovation Training now!
Conclusion
Innovation vs Invention are two terms often used interchangeably, but they have different meanings and implications. Innovation is applying a new or improved product, process, or idea that creates value for customers, users, or society. Invention is creating a new product, process, or idea that has never existed before. Innovation and Invention are essential for human progress but have different goals and processes. They both involve creating something new but have different characteristics and impacts.
Lead with Confidence: Discover Our Leadership Training now!
Frequently Asked Questions
Innovation and Invention are both important and valuable, but they have different purposes and outcomes. Innovation is better when the goal is to create value for customers, users, or society, while Invention is better when the goal is to advance human knowledge and capabilities. Innovation and Invention can also complement each other, as Inventions can inspire Innovations and enable Inventions.
This question has no definitive answer, as Innovation and Invention depend on various factors, such as personality, skills, motivation, environment, and resources. However, some general tips that can help are:
a) Be curious and open-minded and seek new knowledge and experiences.
b) Identify problems, needs, or opportunities and generate ideas or solutions.
c) Experiment, test, or prototype your ideas or solutions and get feedback or validation.
d) Adapt, improve, or iterate your ideas or solutions, and learn from failures or mistakes.
e) Collaborate, network, or partner with others who have different perspectives or expertise.
The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs , videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA .
The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass , a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.
The Knowledge Academy offers various Leadership Training , including Social Innovation Courses, Innovation courses, etc. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights about Innovation in the Innovation Course .
Dive into our Business skills blogs, a trove of resources covering Leadership training. Whether you are a beginner or aiming to enhance your Leadership Skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and insightful blogs are your go-to source.
Upcoming Business Skills Resources Batches & Dates
Fri 11th Oct 2024
Get A Quote
WHO WILL BE FUNDING THE COURSE?
My employer
By submitting your details you agree to be contacted in order to respond to your enquiry
- Business Analysis
- Lean Six Sigma Certification
Share this course
Our biggest summer sale.

We cannot process your enquiry without contacting you, please tick to confirm your consent to us for contacting you about your enquiry.
By submitting your details you agree to be contacted in order to respond to your enquiry.
We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Or select from our popular topics
- ITIL® Certification
- Scrum Certification
- ISO 9001 Certification
- Change Management Certification
- Microsoft Azure Certification
- Microsoft Excel Courses
- Explore more courses
Press esc to close
Fill out your contact details below and our training experts will be in touch.
Fill out your contact details below
Thank you for your enquiry!
One of our training experts will be in touch shortly to go over your training requirements.
Back to Course Information
Fill out your contact details below so we can get in touch with you regarding your training requirements.
* WHO WILL BE FUNDING THE COURSE?
Preferred Contact Method
No preference
Back to course information
Fill out your training details below
Fill out your training details below so we have a better idea of what your training requirements are.
HOW MANY DELEGATES NEED TRAINING?
HOW DO YOU WANT THE COURSE DELIVERED?
Online Instructor-led
Online Self-paced
WHEN WOULD YOU LIKE TO TAKE THIS COURSE?
Next 2 - 4 months
WHAT IS YOUR REASON FOR ENQUIRING?
Looking for some information
Looking for a discount
I want to book but have questions
One of our training experts will be in touch shortly to go overy your training requirements.
Your privacy & cookies!
Like many websites we use cookies. We care about your data and experience, so to give you the best possible experience using our site, we store a very limited amount of your data. Continuing to use this site or clicking “Accept & close” means that you agree to our use of cookies. Learn more about our privacy policy and cookie policy cookie policy .
We use cookies that are essential for our site to work. Please visit our cookie policy for more information. To accept all cookies click 'Accept & close'.
Reference Library
Collections
- See what's new
- All Resources
- Student Resources
- Assessment Resources
- Teaching Resources
- CPD Courses
- Livestreams
Study notes, videos, interactive activities and more!
Economics news, insights and enrichment
Currated collections of free resources
Browse resources by topic
- All Economics Resources
Resource Selections
Currated lists of resources
Study Notes
What is the difference between invention and innovation?
Last updated 4 Sept 2023
- Share on Facebook
- Share on Twitter
- Share by Email
While these terms are often used interchangeably, they actually mean two different things!
Invention and innovation are related concepts, but they refer to different stages and aspects of the process of bringing new ideas, products, or technologies to market.
Here's a breakdown of the key differences between invention and innovation, along with real-world examples to illustrate each concept:
- Definition: Invention refers to the creation of a new idea, concept, method, or product that is entirely original or a significant improvement over existing solutions. It involves coming up with a novel concept or design.
- Focus: Invention is primarily concerned with the generation of new ideas or the development of a new product or technology. It is the initial stage of the creative process.
- Thomas Edison's Light Bulb: Thomas Edison is often credited with inventing the practical incandescent light bulb. His work involved developing a filament that could produce light when an electric current passed through it, which was a significant innovation in lighting technology.
- Alexander Graham Bell's Telephone: Bell is known for inventing the telephone, a device that allowed for voice communication over long distances. His invention was a groundbreaking development in telecommunications.
Innovation:
- Definition: Innovation refers to the process of taking an invention or a new idea and applying it in a way that creates value, often by bringing it to the market, improving upon it, or finding new uses for it. Innovation involves the practical implementation and commercialization of ideas.
- Focus: Innovation is more focused on the practical application of ideas and their impact on society, the economy, or an industry. It is about making an invention useful and marketable.
- Apple's iPhone: While the concept of a touchscreen smartphone existed before the iPhone, Apple innovatively combined various technologies and features to create a user-friendly and highly marketable product. The iPhone transformed the mobile phone industry and how people communicate.
- Netflix's Streaming Service: Netflix started as a DVD rental service but innovated by transitioning into a streaming service, allowing subscribers to watch movies and TV shows online. This innovation revolutionized the entertainment industry and disrupted traditional cable TV.
Key Differences:
- Invention is about creating something new or significantly improving an existing concept, often in a laboratory or research setting. Innovation involves bringing these inventions to the market, adapting them for practical use, and creating value for consumers.
- Invention is the initial creative spark, while innovation is the process of turning that spark into a real-world solution or product.
- Inventions can be purely theoretical or experimental and may not necessarily lead to a marketable product. Innovations, on the other hand, are practical and market-oriented.
- Invention is focused on the "what" (the creation of something new), while innovation is focused on the "how" (the implementation, adaptation, and commercialization of new ideas).
In summary, invention and innovation are complementary processes in the development of new ideas and technologies. Invention generates novel concepts or products, while innovation transforms these concepts into practical and marketable solutions that improve lives and drive economic growth. Both are essential for progress and advancement in various fields.
In a nutshell:
- Invention refers to the creation of a new product or technology, such as the light bulb or the internet.
- Innovation refers to the implementation and adoption of new products or technologies in the market, or the improvement of existing ones. For example, smartphones are an innovation built upon the invention of the mobile phone.
- Innovation can happen without invention, and vice versa, but they often go hand-in-hand!
- Creative Destruction
- Process innovation
- Product innovation
You might also like
Sources of comparative advantage.

Why electric cars aren't always greener
26th December 2014

Amazon and Creative Destruction
3rd November 2015
Electric cars threaten oil corporations
19th October 2016
Carbon: From Pollutant to Product
28th December 2017
Barriers to Entry (Quizlet Revision Activity)
Quizzes & Activities

Dynamic efficiency - stickers that make fruit last 2 weeks longer
18th May 2021

Web browser market share - a changing structure
10th August 2022
Our subjects
- › Criminology
- › Economics
- › Geography
- › Health & Social Care
- › Psychology
- › Sociology
- › Teaching & learning resources
- › Student revision workshops
- › Online student courses
- › CPD for teachers
- › Livestreams
- › Teaching jobs
Boston House, 214 High Street, Boston Spa, West Yorkshire, LS23 6AD Tel: 01937 848885
- › Contact us
- › Terms of use
- › Privacy & cookies
© 2002-2024 Tutor2u Limited. Company Reg no: 04489574. VAT reg no 816865400.
What is the Difference Between Innovation and Invention?
Invention is the creation of a concept without confirming its usefulness, while innovation involves commercializing an invention and promoting its widespread adoption. According to a McKinsey survey, 84% of executives think innovation is crucial to growth, but only 6% are pleased with their performance. Invention is creating a new product, while innovation adds benefits or makes a transition to an existing product. Innovation requires communication, technological, and strategic expertise, in contrast to invention's need for scientific knowledge. The difference between invention and innovation impacts strategy, as inventions are greenfield opportunities, while innovations penetrate developed markets and may face competition.
More Innovation Resources:

What We Can Learn from the 8 of the Most Innovative Schools in the World

Business Innovation - 45 Articles to Improve Your Organization's Success
Brainzooming offers a comprehensive list of new business innovation articles from 2010, covering topics such as innovation strategy, whole brain thinking, innovation techniques, market-driven innovation, innovation challenges, and innovation in practice.

How to make innovation training really stick
Innovation training often fails to produce results because the lessons are quickly forgotten or ignored. Here are 8 ways to make innovation training stick and become embedded in the organization.
This Is The Difference Between 'Invention' And 'Innovation'
There's a fundamental difference between an innovator and an inventor, writes digital entrepreneur Tom Grasty in a great column over at MediaShift Idea Lab .
Invention is the "creation of a product or introduction of a process for the first time." Thomas Edison was an inventor.
Innovation happens when someone "improves on or makes a significant contribution" to something that has already been invented. Steve Jobs was an innovator.
Okay, so they're different. What's that mean for entrepreneurs?
You can't just focus on innovation and you can't just focus on invention. That's not what an entrepreneur does. The entrepreneur recognizes the potential early on, then turns it into something big.
Grasty explains it with an analogy :
"If invention is a pebble tossed in the pond, innovation is the rippling effect that pebble causes. Someone has to toss the pebble. That's the inventor. Someone has to recognize the ripple will eventually become a wave. That's the entrepreneur.
"Entrepreneurs don't stop at the water's edge. They watch the ripples and spot the next big wave before it happens. And it's the act of anticipating and riding that "next big wave" that drives the innovative nature in every entrepreneur."
NOW SEE: 11 Groundbreaking Inventions Of 2011 >

- Main content
- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer

Stay Informed Group
Stay informed with opportunities online
Innovation vs Invention: Difference and Comparison
November 6, 2023 by Chukwuemeka Gabriel Leave a Comment
Is there a difference between innovation and invention (innovation vs invention)?
The English dictionary defines the term “innovation” as the act of innovating, or introducing something new. Invention is a noun, something invented by someone with an innovative idea.
Throughout history, men and women have invented things to make life easier for people. From the Medieval era to the Industrial Revolution, the world advanced through innovations.
The early 20 th century was the period aeroplanes were invented and ever since then, new technology has made it possible for us to explore the far edge of the solar system.
In this article, we will be discussing more on the difference between innovation and invention.
What Is Innovation?
According to the English dictionary, the term “innovation” is defined as the act of innovating, the introduction of something new in rites, customs, etc. It’s the transformation of an idea into reality.
Innovation can also be the development or introduction of a new product, service, process, or service. Innovation is a noun that signifies its meaning as the transformation of an idea into reality.
The term “innovation” can be described as a change that typically adds value to the products or services.
Innovation offers new techniques to make things easier for people.
Also Read: Dialogue vs Monologue: Difference and Comparison
What Is Invention?
The term “invention” defines something invented or the act of inventing. Invention is the act of inventing or being creative to invent a device or process that has never been manufactured before.
The idea is to make something unique, a durable and reliable product. The steam engine, the light bulb, computers, and the diesel engine were all invented by people with innovative ideas.
Inventors with their ideas have generally improved areas such as medicine, engineering, construction, entertainment, education, technology, etc.
German automobile engineer, Karl Franklin Benz invented the gasoline automobile in 1886. In the 1890s, another German engineer Rudolf Diesel invented the diesel engine.
Invention is typically a scientific idea conceived through experimentation and extensive research. Through extensive research and experimentation, a result will be achieved to create a tangible product.
Invention can be the new process of manufacturing a product or making an improvement to existing products. It can be patented in order to provide security to the inventor for intellectual property rights and to also acknowledge the invention.
Generally, every country has their specific rules for obtaining a patent and the process can be quite pricey. In order to be patented, the requirement is that the invention must be novel and also have value.
Innovation vs Invention: Key Difference between Innovation and Invention
The term “innovation” is defined as the act of innovating, the introduction of something new in rites, customs, etc. It’s the transformation of an idea into reality.
On the other hand, the term “invention” defines something invented or the act of inventing. Invention is the act of inventing or being creative to invent a device or process that has never existed before.
What are the key differences between innovation vs invention?
The term “innovation” is the act of innovating, the introduction of something new in rites, customs, etc. It’s described as the first time a product or process is put into action.
Invention is the act of inventing or being creative to invent a device or process that has never been manufactured before. Invention involves the creation of a modern product that will accepted by the public.
Innovation is the implementation of ideas for a new product or process, made for the first time. Invention is related to the manufacturing of new products.
Innovation is about adding meaningful value or making a change in the existing product. It improves the overall appearance of a product, adding new features to improve sales.
It often takes place through the development of products, processes, technologies, artworks, services or business models that innovators provide for society, government, and markets.
Innovation is however related to invention, but it’s not the same as invention. Technical innovation usually manifests through an engineering process when the problem solved is more of a technical or scientific nature.
While innovation requires a broad set of marketing, technical, and strategic skills, invention requires scientific skills. An invention is made when new ideas to create something exceptional strike a scientist.
Also Read: Indexes vs Indices: Difference and Comparison
More on Innovation vs Invention
Inventions are said to be often unintended, which we can all agree to.
According to Britannica, in the late 19 th century, American entrepreneur in the field of electric lighting Edward Acheson was working towards inventing artificial diamonds when an electrified mix of coke and clay resulted in producing the ultra-hard abrasive, Carborundum.
Also, during the mid-1800s, British chemist William Perkin attempted to create an artificial quinine. While Perkin was investigating the coal tar, the first artificial dye, Tyrian purple was created instead.
In contrast, innovation is the creation of a new method of doing something. It plays a key role in the development of reliable and sustainable methods- both in production and living.
Innovation plays a major role in business success and in scientific progress.
Also Read: Rigid vs Flexible: Difference and Comparison
Innovation vs Invention: Competitive Strategy
Inventions are considered opportunities to build and create. Inventions create their own market and there will likely be no competition when they are introduced.
For example, a company selling a new product will do everything in their power to prevent its rivals from competing with them.
While invention works towards eliminating competitors in the market, innovation would develop the markets and may encounter direct or indirect competition.
Examples of Innovation vs Invention
What are the examples of innovation and invention?
Examples include;
- OLED and QLED TVs
- iPhone and other Apple products
- Passenger-carrying drone
- Virtual reality (VR)
- Augmented reality (AR)
- Wrinkle-free suits
- Small electric cars
- Almond milk and oat milk
Examples of Invention
- Gasoline automobile engines were invented by Karl Franklin Benz
- Airplanes were invented by the Wright Brothers
- Steam turbines were invented by Charles Parsons
- Diesel engine was invented by Rudolf Diesel
- The computer was invented by Charles Babbage
Innovation vs Invention: Comparison Chart
| Innovation is defined as the act of innovating, the introduction of something new in rites, customs, etc. | The act of inventing or being creative to invent a device or process that has never been manufactured before. | |
| Practical implementation of new ideas | The original idea and its working in theory | |
| Adding value to something already exists | Creation of new products or process | |
| Adding value to something that already exists | Occurs when new ides strike scientists | |
| Set of marketing, technical, and strategic skills | Requires scientific skills to create a device or process that has never been manufactured before. |
Also Read: Practical vs Practicable: Difference and Comparison
Recommendations
- Philippians vs Philippines: Difference and Comparison
- Teal vs Turquoise: Difference and Comparison
- Ivory vs Ecru: Difference and Comparison
- Purple vs Magenta: Difference and Comparison
- Sarape vs Poncho: Difference and Comparison
- KeyDifferences : Difference Between Invention and Innovation
- MITIDINNOVATION : What Is The Difference Between Innovation And Invention?
- DigitalLeardership : Innovation vs Invention: Definition, Difference & Importance
- Britannica : innovation
- Britannica : invention
About Chukwuemeka Gabriel
Gabriel Chukwuemeka is a graduate of Physics; he loves Geography and has in-depth knowledge of Astrophysics. Gabriel is an ardent writer who writes for Stay Informed Group and enjoys looking at the world map when he is not writing.
Reader Interactions
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
10 Morning Meetings Greeting Ideas for Students
What are the 12 ivy league schools in 2024, examples of praying scripture for students, 21 top dental schools for international students 2024, negative effects of technology you should know, do scholarships count as income, 39 best law schools in uk and ranking, woods vs. forest: what is the difference, top 10 marketable careers in the world in 2024, what are the best architecture schools in the us, 15 best psychology schools in the world 2024, what are the best exercise science schools, 10 best medical schools in mexico in 2024, student loan forgiveness: how to obtain a student loan forgiveness, what are the 14 punctuation marks for effective english writing, top rated universities in canada with the highest acceptance rate, reasons why is education important all you need to know, most important languages to learn for more opportunities, top tips for first-year students, 10 tips to choosing an online college, what is the difference between going green and sustainability, how many nickels make a dollar all you need to know, highest paid military in the world in 2024 (top 10 countries), how to record a meeting on microsoft teams, 100 positive affirmations for students, 5 universities in cambridge massachusetts ma, 25 cheapest universities in usa for international students, why you should get your master’s in counselling, 32 best work from home companies that are legit, 15 google meet ideas for teachers, 25 short term courses with high salary, career opportunities for bcom students, how to become a pilot with or without a degree, how to become a home inspector, is a master’s in information technology worth it, how to build a career in digital marketing, is an online associate degree in health science for you, how to become a video game designer, what is a business lawyer, how to capitalize job titles, project management methodologies: definition, types and examples, career development plan: how to create a career plan, what does a film producer do, how to become a medical writer, how to become a music producer without school, 20 high paying part time jobs.
What Is The Difference Between Innovation And Invention?
Definition of innovation and invention.
The actual development of a new concept or theory is known as invention . It is described as the creation of a concept for doing or doing something without first confirming that it works or is commercially useful. Invention is impossible without creativity, but creativity alone is insufficient to successfully create an idea. In the industry, innovation binds everything together. The impacts of having a strongly aligned innovation strategy (with the overall company plan) and a pro-innovation culture on the growth of the enterprise’s value were explored in a Booz & Co. research , which found a 30% improvement over businesses that didn’t have both.
Innovation entails commercialising an invention and promoting its widespread adoption. This is the point at which big ideas, after they’ve been fully created, are presented to the public. But despite all this, according to a survey by McKinsey Global Innovation, 84% of executives think that innovation is critical to their growth plan, just 6% are pleased with their innovation performance.
Difference between Innovation and Invention
Below are the major distinctions between invention and innovation :
- An invention is the phenomenon of a new concept for a device or procedure that has never been produced before. Innovation is described as the first time a product or process concept is put into action.
- I nvention has to do with the creation of a modern product. On the other hand, innovation entails adding benefits to a current product or making a transition to it.
- I nvention entails coming up with a novel concept and demonstrating how it functions in theory. In contrast to innovation , it is more about putting the latest concept into practice.
- I nvention necessitates scientific knowledge. Innovation , on the other hand, necessitates a diverse range of communications, technological, and strategic expertise.
- When a physicist has a new idea, he or she invents something. In contrast, innovation occurs as a need for a new product or an improvement to a current product is identified.
- A single substance or procedure is the subject of the invention . Innovation , on the other hand, is concerned with the synthesis of different goods and services.
- Although the invention is restricted to the organization’s research and development department. The culture of innovation is pervasive in the organisation.
Why does the difference between Innovation and Invention matter?
Despite the fact that they are often used interchangeably, invention and innovation are scientifically distinct. The distinction between invention and innovation is important because it has an effect on strategy. Here’s how it affects strategy:
Competitive strategy
By design, inventions are greenfield opportunities; they build their own markets and will have no competition when they are published. If a company is selling a new product, their competitive approach is focused on preventing rivals from joining. Innovations , on the other hand, would penetrate developed markets and may face direct or indirect competition.
Growth strategy
Whether or not the company’s products are inventions or innovations have a big impact on its success. When the company’s first product is an invention , for example, their development plan becomes based on how to remain competitive by constantly innovating on the product and space they’ve developed.
Examples of Innovation and Invention
Examples of Innovation
- Almond milk and oat milk
- Small electric cars
- iPhones and other gadgets made by Apple Inc.
- LED screens by LG
- Zara’s policy to not spend on advertising
A survey done by BCG showed that companies that have product and policy innovation examples as shown above do better than 77% competitors which is what separates them from the rest.
Examples of Invention
- Airplane by Wright Brothers
- Steam Turbine by Charles Parsons
- Light Bulb by Thomas Edison
- Electricity by Benjamin Franklin
- Alternating current machinery by Nikola Tesla
These are just some of the many great inventions by famous scientists and inventors.
MIT ID Innovation
The MIT Institute of Design was established with the aim of forging stronger ties with industry and society, as well as ensuring excellence in both academic processes and outcomes. The institute’s mission is to build a learning environment that trains today’s young minds to be design pioneers who add value to business and community.
MIT ID focuses on leading the way in terms of innovative and unconventional approaches that help design doers evolve. The institute is able to provide a dynamic and multifaceted learning environment for students by combining a diverse student body with highly experienced staff.
Reference links
- https://www.ineteconomics.org/perspectives/videos/invention-vs-innovation#:~:text=In%20its%20purest%20sense%2C%20%E2%80%9Cinvention,existing%20product%2C%20process%20or%20service.&text=Innovation%20flows%20from%20invention.
Related Posts

Uncategorized
Career Prospects After an MBA in Innovation and Entrepreneurship from MIT ID Innovation

Explore Salary & Growth with an MBA in Innovation Management | MIT ADT Pune

MBA in Innovation Management: The Scope and Impact in Today’s Economy
- Recent Updates
- Weekly Newsletter
- Monthly Newsletter
- Quarterly Newsletter
- AR/VR & Digital twins
- AI & Data Analytics
- IoT & Wearable
- Sensors & Perception
- 3D Printing
- Energy Tech
- Transportation
- Mining & Blue Economy
- Food & Living
- Communication
- Entertainment
- Manufacturing
- Work & Management
- Public Service
- Accelerators
- Death Valley
- Investments
- Exit & IPO
- Valuation & Financing
- Idea & IP
- Academic Research
- Corporate Research
- Public-funded Research
- Economics of Innovation
- Growth Economics
- Publications
- Patents & IP
- Future of Work
- Sustainable Development
- Smart Manufacturing
- Job Transformation
- Industry Transformation
- Competition & Monopoly
- National Response
- Education & Skills
- Social Change
- Venture Capital
- Capital Market
- Philanthropy
- Personality
- Sustainability Goals
- Business Model
- Complementary
- Externality
- Disruptive Innovation
- Incremented Innovation
- Schumpeter’s Creative Destruction
- Redesign for Winning
- Monopolisation
- Porter’s Five Forces
- Business Cycle
- Human Capital
- R&D Management
- Tripple Helix
- Intellectual Property
- Productive Knowledge
- Technology Managment
- Organization Agility
- Innovation Culture
- Infrastructure
- R&D facility
- Great by Choice
- Build to Last
- Good to Great
- Scientific discovery
- Adaptation & Refinement
- Start-up acquisition
- Technology Development
- Innovation Diffusion
- Jobs, Privacy & Security
- Regulation & Law
- Sustainability
- Equity & Inclusiveness
- Climate Change
- Environment
- Individual Preferences
- Planet and Society
- Political Economy
- Market Power & Monopoly
- Globalisation
- Schumpeter’s creative destruction
- Startups & VC
- Human Role in Work
- Value of Natural Resources
- Patents & Ideas for Redesign
- Case Studies
- White Papers
Technology, Society and Policy

Invention vs Innovation
Clarity between these two closely related terms is vital for comprehending unfolding dynamics, and engineering the competition strategy..
- Rokon Zaman
- Created: September 20, 2020
- Last updated: January 19, 2022

Invention and Innovation appear to be the same for many of us. We also use these two terminologies interchangeably. However, there is a distinctly visible fine line between them. The clarity of this fine line about invention vs innovation not only makes us more literate about technology innovation. More importantly, it plays a vital role to assess the likely implications of technology invention on both product and Process innovation . We need to take this distinction into consideration in managing technology for driving innovation strategy.
Often, we engage in invention vs innovation discourse. The distinction between them invariably gets blurred . Sometimes, we use invention and innovation interchangeably. However, there is an obvious line between them. Clarity about it reduces the complexity in i nterpreting reality, and also predicts unfolding dynamics. It also leads to more effective and efficient communication. Such clarity is vital in formulating technology and product strategy and also pursuing inventions and innovations for implementation.
For example, the light bulb is an innovation. It came out of the invention of the technology of producing light by heating carbon filament with electricity. It happens to be that Thomas Alpha Edison got credit for both the invention and innovation of electric lighting. He invented or perfected the invention of producing light by passing an electric current through carbon filament. He also innovated the light bulb around that invention. Many types of light bulbs have been innovated around the same technology core for meeting various lighting purposes. Light bulb innovation as car headlights largely varies from light bulbs used in households. However, sometimes, they use the same technology invention. At present, it’s light-emitting diode technology.
Invention vs innovation examples
To bring clarity, let’s look into a number of examples. Let’s go back to the light bulb. We are still using light bulb innovation. However, the present light bulb’s technology core is a light-emitting diode (LED) instead of filament. The invention of LED technology has led to making light bulb innovation far more energy-efficient than ever before. Although the technology core has changed, credit given to Edison for light bulb innovation is still valid, and also in use. However, the modern light bulb no longer usages Edison’s invention —a light-producing filament .
The electronic image sensor is a technological invention. For this invention, two scientists working at the Bell laboratory got Nobel Prize. Their invention was basically limited to demonstrating a technique of producing and collecting electrons in proportionate to the number of incident photons. However, this invention did not serve any practical pursuit until the effort to improve it and innovate digital cameras. Hence, the digital camera is an innovation developed out of the invention of the electronic image sensor. Many different types of cameras have been innovated out of this invention.
Similarly, the internal combustion engine is an invention. This invention is about the technique of producing mechanical motion out of the combustion of gasoline in a closed chamber. The technique of producing rotating mechanical motion out of the flow of steam was an invention. These inventions have been refined and used to innovate all kinds of engines and products around them. The list goes on. For example, Transistor as a solid-state electronic switch is an invention. Numerous already innovated products experienced improvement with this invention. Similarly, some innovative products came out using Transistor as the technology core.
Differences and similarities between invention and innovation
Invention forms the foundation for innovation. It’s like a substrate on which innovation grows. However, the urgency of innovation or making improvements of existing innovations often drives invention. For example, in the 1940s, AT&T was desperate for an invention of a solid-state switch, having a moving component, to replace an electromechanical one. This desperation led to the invention of the Transistor . Subsequently, this invention led to the improvement of existing innovations and innovating new ones.
Innovation vs invention: what is more important?
In innovation vs invention discourse, there is also debate about which is more important. It appears to be a non-conclusive one. In the absence of invention, innovations do not lead to realization. On the other hand, the invention itself does not offer any Utility . Products, innovated out of the invention, offer us means to get jobs done better. We derive benefits from the invention by making usages of innovation. For example, the invention of the Transistor or electronic image sensor was of no use till Sony innovated the pocket radio or digital Camera out of them. However, in absence of those inventions, how would have Sony offered innovations to get our jobs done better? Hence, they are complementary. Their benefits emerge in a collective form.
Effects of the invention on innovation and business strategy
The invention of technologies and their progression leads to business strategy in exploiting innovation potentials. They use them to make an incremental progression of their product and processes. Sometimes, they also take a radical step in changing the technology core of products. For example, Sony changed the technology of the core of the Camera for creating an entry into the imaging industry. Sony’s such attempt also made Kodak bankrupt. The invention of the Transistor is also leading to software-intensive innovation in changing the underlying competition strategy. For example, once word processing used to be a mechanical machine. This mechanical machine’s transformation into software running on personal computers enabled Microsoft to monopolize the global word processing market. Many other products and industries are undergoing such transformation.
Invention and Schumpeter’s Creative destruction
The invention of new technology often leads to changing the technology core of incumbent innovations. The purpose is to offer better substitutes. Despite primitive emergence, often, such substitutes grow as creative destruction to existing products and industries. For example, the internal combustion engine’s invention led to the emergence of automobile innovation, causing creative destruction to horse wagons. Similarly, the electronic image sensor led to digital camera innovation. Technology invention leading to the creative destruction to existing products is at the core of our increasing quality of living standards. However, it poses both challenges and opportunities to firms. Moreover, society goes through a messy transformation to benefit from the creative destruction of innovations , fueled by inventions.
Clayton’s Disruptive innovation gets fuel from technology invention
The change of the technology core with recent inventions leads to the primitive emergence of substitutions of existing innovations. For example, the mobile telephone was primitive in comparison to landline phones in the 1980s. Similarly, PC was highly inferior to minicomputers. Similarly, electric vehicle is inferior to gasoline ones now. Often, customers of existing products around matured inventions are not interested in such primitive emergence. Moreover, the sale of such inferior alternatives also produces loss-making revenue. Such a situation causes a decision-making Dilemma to incumbent firms. Prof. Clayton termed it an innovator’s Dilemma. Sometimes, this decision-making dilemma leads to failure to switch to a new wave of innovation fueled by emerging inventions. Consequentially, failing to switch leads to the disruption of firms –terming it as disruptive innovation.
Invention and innovation have bidirectional links, driving each other. They unfold both opportunities and challenges. On the one hand, invention fuels innovation creating new firms, industries, and markets. It also destroys the existing ones based on mature inventions. In the Market Economy , invention fueling innovation is vital for our prosperity. However, such progress takes place through a messy transformation. Hence, we should have clarity about invention vs innovation concepts. This clarity is vital to drive the progression out of innovations by using inventions as fuel, as opposed to getting marginalized.
Subscribe now to our newsletter
You May Also Like

Technology Readiness for Reinvention–NASA’s TRLs good enough?

Technology Adoption Life Cycle–redefined

Technology Evolution–advancing and transforming society
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Input your search keywords and press Enter.
The Difference Between Invention and Innovation
Many think innovation is simply a fancy new word for invention, wrongly assuming that they are one and the same
Matthew Herbert
Director of Marketing Communications (he/him)
Innovation has become a buzzword in the business world; if you want to compliment a company, calling them “ innovative” is the way to go. This has happened quietly, at the expense of another word that we don’t hear much anymore. Invention has all but dropped out of the business lexicon. It’s easy to miss its absence; after all, many people think innovation is simply a fancy new word for invention, wrongly assuming that they are effectively one and the same.
Admittedly, the two words are closely connected, but they are not synonyms and should never be used interchangeably – innovation and invention are two very different things.
Innovation connects the dots between inventions . Spotting potential for improvement, it cleverly fills a gap in the market and combines inventions into products that will attract customers and generate commercial success.
Not convinced yet? Let’s have a closer look at invention, innovation, and the line between these two buzzwords.
Invention creates something new, innovation creates something that sells
The Cambridge Dictionary defines an invention as “ something that has never been made before, or theprocess ofcreating something that has never been made before”. By definition, it has to be something entirely new, so an invention is something that has never been done before. To invent something is to discover a new thing.
Meanwhile, to innovate means “ to use a newidea ormethod”. To innovate is to introduce something new to the market, to manipulate existing inventions and turn them into a product or process that is of use in the real world.
It’s not difficult to see how tricky it can be to distinguish between these two concepts. After all, “ new” is the keyword for both innovation and invention. But the essential difference is that inventors create something completely original. This could, for example, be a technical idea or a scientific process.
Of course, inventions also have to be proven to work. You can’t simply come up with any new idea – you have to be able to show that you can make it a success. That’s where innovation comes in. Innovators might come up with something that is not new at all. Rather, they operate within the realm of what already exists and is readily available to work with. Innovators use processes or platforms that have already been invented to create a commercially successful product or process that will satisfy a market need and have customers ready to queue. A product or process is inventive if it has never been done before – whether it is innovative depends on whether users will get a real value out of it.
If we think about invention and innovation in a real-life context, we can observe a pattern. Great innovations were not necessarily made by those who first came up with the idea. Instead, they are credited to the innovator who managed to turn the idea into a viable product.
Take for example the telegraph, one of the great innovations of the nineteenth century. The first crude telegraph was invented in Bavaria in 1809 , but Samuel Morse, who also created Morse Code, was the first person to build a commercially successful telegraph communication system. Morse’s telegraph was affordable, efficient, and could reach further than similar efforts made by Sir William Cooke and Charles Wheatstone at the same time in London. Who cared that it wasn’t his idea to begin with? Morse certainly didn’t – he started the Magnetic Telegraph Company and launched the first commercial telegraph line in the US . With its high speed, this innovation revolutionised the face of communication. Morse didn’t invent the first telegraph, but he developed and improved the process, launching the first commercial telegraph and shaping the communication landscape of the early nineteenth century.
There’s a valuable lesson to be learnt here. An original invention won’t get you very far if it’s not innovative enough. If an invention lacks real-life value for the user, it will be overtaken by an innovation that manages to satisfy a need.
James Dyson’s spin on the vacuum cleaner is a more modern example of how innovation can reshape an entire industry. Dyson noticed that a traditional vacuum cleaner loses suction as the bag fills up, and set about developing a more efficient machine. During a visit to a local sawmill, Dyson observed how sawdust was removed from the air by large industrial cyclones, identifying that the technology could be applied to a vacuum cleaner; separating dust by cyclonic action and spinning it out of the airstream, thus eliminating the need for a bag and filter. When finally launched, Dyson’s machine became the biggest selling vacuum cleaner in the UK in just 18 months, evidence that with a little creative thinking, even the most everyday items can be innovated and improved upon.
“ Creative” is another word often bandied around in the same breath as “ innovation” and “ invention”. Let’s examine what creativity really means in the context of invention and innovation, and how it can help us add another layer to our understanding of the two.
The term “ creative” refers to the ability to think and act in novel ways. Invention requires creativity in the sense that it depends on the inventor’s ability to create a vision of what they think they are able to build, and to make something happen that no one else has ever done before. Of course, the inventor’s creative vision is constrained by the framework of reality. They want to figure out how to do something in a novel way, working within the constraints of what is possible through science.
Innovators, meanwhile, take an invention and use it to create a vision of a process or product that will be so useful to its users they will happily pay for it. They ask: what needs to be done to improve a product? What is the missing piece of the puzzle that will make this product an invaluable addition to what is already available? Innovators don’t use their creativity to come up with something new. Instead, they use it to envision a commercial success.
So we’ve established that while invention is about creating something new and original, innovation involves turning that novelty into a commercial product. Innovation might be the business world’s glamorous synonym for success, but at its core will always lay invention.
At CPI , we thrive on innovation. We help our inventor clients from industry and academia take their ideas and develop them into innovative solutions which are capable of commercialisation, using our world class open access facilities and wide ranging technological expertise.
Steve Jobs would never have been able to completely turn the market upside down with Apple if Ted Hoff, an Intel engineer, hadn’t invented the first microprocessor in 1971 . Hoff’s microprocessor, which was as small as a thumbnail, could run computer programs, remember information, and manage data all in one, paving the way for what we know as the personal computer. Few will know Hoff’s name nowadays, but in order to create something that is irresistible to the market, you need to have a brilliant invention to start with.
Innovative creativity is key to the success of a business and has to underlie any viable commercial concept, but while we celebrate the innovators of today, let’s not forget that behind every great innovation there’s an invention that made everything possible in the first place.
Enjoyed this article? Keep reading more expert insights...
What is deep tech .
Arun Harish
Chief Strategy Officer
Cleaning up with wastewater management solutions
Robert Mitchell
Senior Research Scientist - Nanomaterials
The future of the pharma industry can be sustainable
Katie Murray
Technical Director, Medicines Manufacturing Innovation Centre
CPI ensures that great inventions gets the best opportunity to become a successfully marketed product or process. We provide industry-relevant expertise and assets, supporting proof of concept and scale up services for the development of your innovative products and processes.
Stay updated with our insights by signing up to our newsletter
Let’s innovate together.
To find out more about how we can work together, please enter your details below.

Innovation vs. Invention: Will Innovation Beat Invention? 12 min read

A lot of people get confused with the words “invention” and “ innovation “. In the business world, most entrepreneurs use them interchangeably.
While they are closely related, being able to pinpoint what separates them makes a difference.
As most organizations think these terms are the same, what draws the boundaries between them? Which one gets more credit than the other?
In this article, let us discuss how “innovation” differs from “invention”. Once we achieve that part, let’s see which process is more important for your business to focus on.
Let’s start.
Did Thomas Edison invent the lightbulb?
For years, people assumed it was Thomas Edison who invented the lightbulb. Further research , however, says otherwise.
The concept of incandescent lighting began 79 years before Edison patented the first-ever commercially successful lightbulb. What makes this even more interesting is that this idea got into the hands of numerous scientists way before Thomas was able to lay his hands on it.

For the most part, there were at least twenty scientists who made an incandescent lamp before him. Yet many years later, it was Thomas Edison who got the credit of “inventing” it.
From this scenario, we understand that it wasn’t Edison who gave birth to the concept of incandescent lighting, nor was he the first person to create the “bulb” as it is. However, he exceeded its earlier versions and ended up being historically acknowledged for it.
Technically, Edison was able to achieve this because of three things:
- He created a lightbulb with materials that are practical for commercial production.
- He had an efficient design that made power distribution economically viable.
- He achieved a higher vacuum (earlier versions of light bulbs had this to prevent filaments from burning) than others.
In short, he redeveloped light bulbs and enhanced them in a way that others didn’t. His version was the best at that time, and it was something that others found hard to outdo.
What makes “innovation” and “invention” different?
The situation between Edison and the other lightbulb inventors perfectly mirrors the difference between “innovation” and “invention”.
When talking about these terms, people often confuse one with the other. What makes differentiating them even harder is that Oxford Languages, Google’s official English dictionary, names “innovate” as a synonym of the word “invent”.

Seeing how something so widely recognized interchanges these terms, it’s a good thing that Merriam Webster has included a section that distinguishes these two.
In one of the notes listed below its definition of “invention”, Merriam Webster states that invention is a product of one’s imagination. While innovation, on the other hand, is a change made to an existing product or idea.

To explain this even further, it cited the telephone as an invention and the smartphone as an innovation.
This example reiterates the truth that while to invent is to create something new, to innovate means to improve, redevelop, or significantly contribute to a process, product, or service that already exists.
An invention is something that has never occurred in the face of the earth before. It’s something that no one has ever seen. It’s the first of its kind.
Meanwhile, innovation is an invention’s evolution. It’s a better version of something — a repurposing of an existing idea or technology.
Why do they say invention is easy and innovation is genius?
Inventing and innovating are processes that both require one’s full attention and careful study. However, several people say that invention is easy and innovation is genius because of two reasons.
1. Innovation involves more than just a single idea.
Innovation involves knowing what your strategies are, as well as understanding how you can consistently execute them to create a mark in the industry . These strategies come from a constant generation of ideas that are well-defined and carefully studied.
As an organization, you have to be open-minded to changes and choices that will foster growth. You have to consider other people’s insights , particularly that of your employees, and identify whether the things they’re proposing are sustainable.
You have to keep a bank of ideas and continually ideate to:
- Apply cost-cutting
- Participate in trends
- Improve current work
- Ensure business survival
- Achieve economic growth
- Gain competitive advantage
- Discover and undertake opportunities
- Pull off higher business revenue gains
- Improve customer performance and satisfaction
- Enhance employee performance and satisfaction
2. Innovation involves knowing what you want and how to achieve it.
Implementing innovation projects must involve key performance indicators. Aligning these indicators with your business strategies is imperative in securing optimal success and growth.
Establishing metrics requires meticulous planning, tracking, and development. It is vital not only in securing the success of innovation projects but also in understanding what improvements are necessary to make along the way.
They are also essential in setting targets and driving investments in companies. The indicators provide a concrete direction for innovation projects that encourage organizations to focus on areas that matter most. They also influence the kind of strategies and methods to follow.
That is why most of the world’s game-changing products are often innovations rather than inventions.
Most of the world’s greatest innovators are those who have a clear understanding of who they are, what they want, and how to achieve things. They spend their time, energy, and resources on integrating existing inventions with their own ideas and creativity.
You could say they have enhanced and redefined things according to their own interpretation, along with their very own goals and desired features.
Steve Jobs and Innovation
Steve Jobs is one of the many faces of innovation. His iPod instituted Apple as one of the world’s most innovative brands .

But even then, the iPod was still considered as one of the world’s most iconic innovations because it revolutionized the music industry by creating a music player that surpassed all of its predecessors in every feature possible.
Not only was it smaller in size and greater than most MP3 players in terms of storage capacity and battery life. It also had a user-friendly interface, a design that solved compatibility issues, and a system that allowed syncing from computers to MP3 players.
In the end, Apple’s success with the iPod made it a significant game-changer in the tech industry.
Which among invention and innovation should businesses focus more on?
In a business sense, innovation is a part of strategic renewal, along with invention and improvement.
Companies that are on the invention level dedicate a large portion of their resources to a research and development department . They aim to create never-before-seen products and services and eventually label them as the organization’s “intellectual property”.
However, intellectual properties come with a long list of risks that include data theft, divulgence of confidential information, and accidental breaches through corporate emails, messaging apps, or file-sharing tools.
Improvements are projects that refine products, services, and/or processes while already in use. These are low-risk procedures that only require a small investment in time and money. There is almost no research necessary to see that an improvement is worthwhile.
Innovation on the other hand occurs when you introduce something new into your organization that may not be the first of its kind, but is relatively new to your organization and your customers .
Moreover, innovation is a customer-centric process .
Companies aim to create products with elements that are beneficial to both the organization and its customers — not only to strengthen customer relationships and increase sales but also to respond to the needs of the market by solving real-time problems and creating value .
However, this doesn’t mean that the essence of inventing is to be downplayed, nor should inventors be unrecognized in this time and day.
Innovation should be a process pursued by organizations because innovators are the real game-changers. Their innovations made them market leaders by successfully transforming inventions into something that changed people’s way of living.
Why Focus More on Innovation
Innovation combines invention, creativity, consumer behavior, resources, and business models to solve real-time problems and target consumers.
The problem with organizations nowadays is that they focus too much on making groundbreaking products and technologies they often forget to add their customers into the equation .
This is where they forget that the most compelling products and services are those that have integrated existing knowledge and ideas with practical, unique, and creative solutions.
Now that you understand why you need to focus more on innovation, here are five things that you should consider in transforming your business from invention to innovation:
- Customers : You have to know and understand the behavior of your customers to effectively come up with something that they would love to have, particularly something that solves their problems and enhances their way of living.
- Business value : The main objective of innovation is to provide added value to customers and employees. Aside from making sure that your innovation ends up being useful, introduce more features that would make your product, process, or service worth every penny to spend and every effort to implement.
- Competitive advantage : Despite improving existing ideas, incorporate something that would still make your product “your own.” Insert artistry. Make it unique and compelling. Conceptualize what makes it different from the rest. Make it stand out.
- Business alignment : Conceptualize your innovation around the key strategic focus of your business and its objectives.
- Execution : Distinguish processes, risks, resources, suppliers, and entities to partner with. See to it that everyone and everything on board follows and understands the organization’s vision.
Next steps : Innovation beats invention as it celebrates the integration of existing knowledge and ideas with unique, practical, and creative methods. It transforms people’s way of living and promotes a culture of creativity among organizations.
It celebrates the sharing and refinement of ideas to create added value for both the organization and its customers. It encourages collaboration among teams. It implements ideas well and conceptualizes them in a way that no one has ever done before.
Start using innovation platforms like Accept Mission to select the best ideas and create projects that would significantly change the way things are done.
Learn more about what Accept Mission has to offer by going on a feature tour.
Engage Your Circle: Share This Article on
Related posts.

How to Build a Business Case Presentation for Buying SaaS Innovation Software

Practical Use Cases Generative AI for Innovation

Why an innovation pilot is always a good idea to execute

How to stay updated on the latest trends and opportunities in innovation

Innovation Management vs Change Management

How to Measure and Improve Your Innovation Performance with Dashboard and Reports

What is an Innovation Dashboard and Why You Need One for Your Business

Blue Sky Thinking: How to Boost Your Innovation Success

How to Make Better Decisions with Group Decision Making
In this article.
- ¿Thomas Edison inventó la bombilla?
- ¿Qué diferencia a la “innovación” de la “invención”?
- 1. La innovación implica más que una sola idea.
- 2. La innovación implica saber qué se quiere y cómo conseguirlo.
- Steve Jobs y la innovación
- ¿En cuál de las invenciones y la innovación deberían centrarse más las empresas?
- Por qué centrarse más en la innovación
Idea & Innovation Management Software
"Empower innovators in the most fun way"

Free downloads
"Downloads to empower Innovators"
Sign up for our mailing list!
Accept Mission is the next-generation idea & Innovation Management Software for organizations who want to boost innovation success
Accept Mission
Latest articles, the power of digital idea collection: spontaneous ideas vs. idea campaigns.
2024-08-04T20:25:18+02:00 August 4th, 2024 |
Unlocking Innovation: A Comprehensive Guide to Innovation Canvases
2024-07-23T12:26:23+02:00 July 23rd, 2024 |
Engaging Employees with Company Strategy Using Innovation Software
2024-07-01T22:44:47+02:00 July 1st, 2024 |
2024-06-23T17:32:02+02:00 June 23rd, 2024 |
Quick Links

Copyright ©2024, Accept Mission® is a registered trademark. All Rights Reserved.

FREE DOWNLOAD Innovation E-Book

We take your digital experience seriously, and to ensure it’s top-notch, we use technology like cookies to store and/or access information. By consenting, you’re allowing us to process data such as your browsing activity or unique IDs on this site. If you’re not on board, or decide to change your mind later, it’s okay, but some features might not function at their best. It’s all about giving you the control to enhance your visit.
Essay Service Examples Science Invention
Difference Between Invention And Innovation
Table of contents
Introduction, definition of innovation, definition of invention.
- Proper editing and formatting
- Free revision, title page, and bibliography
- Flexible prices and money-back guarantee

Our writers will provide you with an essay sample written from scratch: any topic, any deadline, any instructions.
Cite this paper
Related essay topics.
Get your paper done in as fast as 3 hours, 24/7.
Related articles

Most popular essays
- Engineering
A man comes home from work after solving complex mathematical equations. He then dreams of the day...
The modern vision of science is similar to the ways science is practiced today with an overall...
- Religious Beliefs
The book helps to understand the difference between faith with science. It does not give us much...
- Mechanical Engineering
To tackle this topic, we first must understand what the term Science and Technology means and in...
- Middle Ages
Medival engineers created marvellous machines, some of which were capable of immense destructive...
During ancient times, not a lot of Arabs were educated enough to know how to perform simple...
For decades’ people have been influenced by the entertainment industry. Movies and television has...
- Electronics
“Science extends and enriches our lives, expands our imagination and liberates us from the bonds...
The Civil War was during a time period that saw many new methods and inventions being used for the...
Join our 150k of happy users
- Get original paper written according to your instructions
- Save time for what matters most
Fair Use Policy
EduBirdie considers academic integrity to be the essential part of the learning process and does not support any violation of the academic standards. Should you have any questions regarding our Fair Use Policy or become aware of any violations, please do not hesitate to contact us via [email protected].
We are here 24/7 to write your paper in as fast as 3 hours.
Provide your email, and we'll send you this sample!
By providing your email, you agree to our Terms & Conditions and Privacy Policy .
Say goodbye to copy-pasting!
Get custom-crafted papers for you.
Enter your email, and we'll promptly send you the full essay. No need to copy piece by piece. It's in your inbox!
More From Forbes
Invention vs. innovation: what is best for your organization.
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to Linkedin
Garry coaches business owners, executives and high-performance teams as CEO and Managing Director of Compass Business Coaching .
Many entrepreneurs, business owners and CEOs are regularly attempting to reinvent themselves and their businesses to gain market share and a competitive advantage with varying levels of success. The size or market share of the business is not limited to small or mid-sized companies, either. We know the world looked different in 2020 and will continue to look different for the foreseeable future, but is reinventing the best path for success?
The attempt to replace Coca-Cola with a reinvented version became a case study for business schools for decades. In 1985 , Coca-Cola had been losing market share to diet colas and other products for many years. In taste studies, it was discovered that consumers preferred the sweeter taste of Pepsi-Cola. Executives decided to reinvent the formulation of its product to try to meet the demands of the consumer. The backlash from loyal customers was truly seismic. Three short months later, the original formulation, Cocoa-Cola Classic, was back, and "New Coke" was gone. The lesson? Coca-Cola was a well-established brand that could have been improved upon, but reinventing it completely was a mistake.
I was on a Zoom call recently with Ron Klein. The overwhelming majority of people are familiar with some of Ron's products but wouldn't recognize his name. Probably the most widely used was one he received the patent for in 1966 . Credit cards had existed since the early 1950s but had not become the widespread tool they are today until Ron convinced credit card companies to use the magnetic strip on the back of the card. Rather than inventing something new, Ron was an innovator. He improved on existing products to make them easier to use. This is a subtle but incredibly important distinction. How many times has your organization decided to reinvent a process or product causing a revolution when an evolution would have been the best choice?
Some of the companies that dramatically impact how we lived today did so out of innovation rather than invention. Steve Jobs, who is uniformly recognized as having a tremendous impact on how we function in our everyday lives, took items that had already existed and made them better. There was the Blackberry before the iPhone and the Walkman before the iPod. There were tablets before the iPad (including Apple's own Newton more than 15 years earlier during Jobs's absence from the helm of Apple). The Fitbit was before the Apple Watch. Apple products improved the existing product offerings. The same could be said for Henry Ford and the production assembly line of the automobile, or Jeff Bezos, who basically took the catalog business model (like the Sears Roebuck Catalog from the 1890s) and created a faster, more responsive and personalized way to buy products that are delivered to your doorstep.
Many businesses focus on creating the latest and greatest goods or services and lose sight of what is truly important to their customers. While companies often focus on what can be produced or created, customers really care about how they solve their problems and can make their lives simpler. The difference between an average company and a truly outstanding organization is their commitment to operational excellence. I believe the constant focus on operational excellence is created by innovation, not invention. It could be said that inventing can interfere with operational excellence by completely interrupting process improvement with process substitution. When referring to operational excellence, I am not referring to just improvement in the manufacturing of products but to improving every step of the process that delivers the ultimate customer experience.
Innovation isn't as glamorous as creating something completely new, but it is the constant vehicle of improvement that can be your competitive advantage. We can actually confuse innovation with invention because it can literally change entire industries or, in the case of Apple or Amazon (as well as many others), change the landscape of the world.
When you look at your business today, what three innovations could your team focus their attention on that would significantly impact your customer's experience and your operational excellence? If, as an organization, you consistently focus on three innovations to improve operational excellence, over a period of time, some of your customers will believe that you have reinvented your company, but all it really took was innovation.
Forbes Business Council is the foremost growth and networking organization for business owners and leaders. Do I qualify?

- Editorial Standards
- Reprints & Permissions

Essay on Invention
Students are often asked to write an essay on Invention in their schools and colleges. And if you’re also looking for the same, we have created 100-word, 250-word, and 500-word essays on the topic.
Let’s take a look…
100 Words Essay on Invention
The magic of inventions.
Inventions are the creations of brilliant minds. They are new devices, methods, or processes made from innovative ideas. Inventions have shaped our world, making life easier and more interesting.
Types of Inventions
Inventions can be physical, like the telephone, or conceptual, like mathematical formulas. They can also be improvements of existing things, like the smartphone.
Impact of Inventions
Inventions have a great impact. They can change how we live, work, and play. For instance, the internet has transformed communication and information access.
Inventing the Future
Inventing is about solving problems and imagining new ways to do things. It’s a key part of progress and the future of our world.
250 Words Essay on Invention
The genesis of invention, the role of necessity.
The axiom “necessity is the mother of invention” holds true. The need to solve problems or improve existing conditions often sparks the flame of invention. For instance, the invention of the wheel was driven by the need for easier transportation, while the development of the internet was a response to the need for global connectivity.
The Power of Curiosity
However, necessity alone can’t fuel invention. It’s the marriage of necessity and curiosity that truly births invention. Curiosity pushes us to question the status quo, to seek answers, and to venture into the unknown. It’s this curiosity that led to inventions like the telescope, which expanded our understanding of the cosmos.
The Impact of Invention
Inventions have a profound impact on society. They revolutionize industries, transform lifestyles, and redefine societal norms. The printing press democratized knowledge, the steam engine propelled the Industrial Revolution, and digital technology is reshaping our world today.
Conclusion: The Continuum of Invention
Invention is a continuum, a never-ending journey of discovery and improvement. Every invention is a stepping stone to the next, creating a chain reaction of progress. As we stand on the brink of a new era of innovation, the power of invention promises to continue shaping our collective destiny.
500 Words Essay on Invention
Introduction to invention.
Invention is a creative process that has been the cornerstone of human progress. It is the act of bringing ideas or objects together in a novel way to create something that did not exist before. Inventions have shaped and reshaped our world, influencing every aspect of our lives, from communication and transportation to healthcare and entertainment.
The Essence of Invention
Invention and society.
Inventions have profound impacts on society. They can stimulate economic growth, improve living standards, and even redefine societal norms. The invention of the printing press, for instance, revolutionized information dissemination, fostering literacy and the spread of new ideas. Similarly, the invention of the internet transformed the way we communicate, access information, and conduct business.
Invention and Technological Advancement
Technological advancements are often the result of inventions. For instance, the invention of the transistor led to the development of the digital computer, which has since revolutionized many fields, from data processing to artificial intelligence. Technological inventions, in turn, often spur further inventions, creating a cycle of innovation.
The Role of Invention in Scientific Discovery
Challenges and ethical considerations in invention.
However, invention is not without its challenges and ethical considerations. The process of invention often requires significant resources, and there is always the risk of failure. Moreover, some inventions can be used for harmful purposes or have unintended negative consequences. For example, the invention of nuclear technology has brought both the potential for clean energy and the threat of nuclear weapons. Therefore, it is crucial to consider the ethical implications of inventions and to strive for responsible innovation.
In conclusion, invention is a powerful force that drives human progress. It is a process of creative problem-solving that leads to new products, technologies, and scientific discoveries, with far-reaching impacts on society. However, it also brings challenges and ethical considerations that need to be carefully managed. As we continue to invent and innovate, we must strive to do so in a way that benefits society and minimizes potential harm.
Apart from these, you can look at all the essays by clicking here .
Happy studying!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
- Personal Finance
- Today's Paper
- Partner Content
- Web Stories
- Entertainment
- Social Viral
Chevron corp to invest Rs 8,300 cr in Karnataka, says minister Patil
The investment was announced during a high-profile meeting attended by the karnataka minister for large and medium industries and infrastructure development, m b patil and others.
)
The minister noted that Bengaluru is already home to more than 500 Global Competence Centres (GCCs). | Soruce: Official website of Chevron
Listen to This Article
More from this section.
)
MPCB accuses Mercedes-Benz of non-compliance with environmental standards
)
Abrupt CEO change prompted by growth concerns, says Nestle Chairman
)
Hindustan Zinc to organise half-marathon in Udaipur to fight against hunger
)
Zydus Lifesciences to acquire 50% stake in Sterling Biotech
)
Auto parts maker Carraro India files papers with Sebi for Rs 1812 crore IPO
(Only the headline and picture of this report may have been reworked by the Business Standard staff; the rest of the content is auto-generated from a syndicated feed.)
)
Chevron to set up engineering & innovation center with $1bn investment
)
LIVE: We believe we will be able to free India from left wing extremism by March 2026, says Shah
)
Premier League 2024-25 LIVE UPDATES: BHA beat MUN 2-1, MCI vs IPS next, ARS in action later
)
IAF plane departs for India with bodies of 25 pilgrims killed in Nepal
)
2,144 pages chargesheet filed against Prajwal Revanna in sexual abuse case
Don't miss the most important news and views of the day. Get them on our Telegram channel
First Published: Aug 24 2024 | 7:18 PM IST
Explore News
- Suzlon Energy Share Price Adani Enterprises Share Price Adani Power Share Price IRFC Share Price Tata Motors Share Price Tata Steel Share Price Yes Bank Share Price Infosys Share Price SBI Share Price Tata Power Share Price
- Latest News Company News Market News India News Politics News Cricket News Personal Finance Technology News World News Industry News Education News Opinion Shows Economy News Lifestyle News Health News
- Today's Paper About Us T&C Privacy Policy Cookie Policy Disclaimer Investor Communication GST registration number List Compliance Contact Us Advertise with Us Sitemap Subscribe Careers BS Apps
- ICC T20 World Cup 2024 Budget 2024 Olympics 2024 Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP)

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Innovation has the ability to attract top talent and creative minds. Innovation emerges when there is a need for change within an organization. Whereas invention can be described as a fundament, innovation can be referred to as the introduction of new things, ideas, or ways of doing something. INVENTION AND INNOVATION.
The invention is related to the creation of new product. On the other hand, innovation means adding value or making a change in the existing product. The invention is coming up with a fresh idea and how it works in theory. As opposed to innovation, is all about practical implementation of the new idea. The invention requires scientific skills.
While invention refers to the creation of a new product, process, or idea, innovation goes beyond mere creation and involves the implementation and improvement of these inventions to bring about meaningful and practical change. Invention is the initial spark of creativity, while innovation is the process of transforming that invention into ...
All inventions contain innovations, but not every innovation rises to the level of a unique invention. For our purposes, an invention is a truly novel product, service, or process. It will be based on previous ideas and products, but it is such a leap that it is not considered an addition to or a variant of an existing product but something unique.
Coming up with new inventions might be personally rewarding but betting your company's future growth on it is dangerous. The world is filled with new inventions that failed to produce commercial success. Innovation is not invention. So before you run to your research and development department with your new idea, let's look at some examples ...
Innovation vs Invention . Innovation and Invention are essential for human progress but have different meanings and implications. Here are some of the main differences between them: a) Innovation is the application of a new or improved product, process, or idea, while Invention is the creation of a new product, process, or idea.
In a nutshell: Invention refers to the creation of a new product or technology, such as the light bulb or the internet. Innovation refers to the implementation and adoption of new products or technologies in the market, or the improvement of existing ones. For example, smartphones are an innovation built upon the invention of the mobile phone.
Invention is the creation of a concept without confirming its usefulness, while innovation involves commercializing an invention and promoting its widespread adoption. According to a McKinsey survey, 84% of executives think innovation is crucial to growth, but only 6% are pleased with their performance. Invention is creating a new product ...
Invention is the "creation of a product or introduction of a process for the first time." Thomas Edison was an inventor. Innovation happens when someone "improves on or makes a significant ...
Invention involves the creation of a modern product that will accepted by the public. Innovation is the implementation of ideas for a new product or process, made for the first time. Invention is related to the manufacturing of new products. Innovation is about adding meaningful value or making a change in the existing product.
An invention is the phenomenon of a new concept for a device or procedure that has never been produced before. Innovation is described as the first time a product or process concept is put into action. I nvention has to do with the creation of a modern product. On the other hand, innovation entails adding benefits to a current product or making ...
The incorporation of an invention into the yolk may also be viewed as convention moving in the direction of the invention. That is, the new idea stays more or less in one location, while convention catches up with it. Today's conventional idea is yesterday's unconventional idea. 9 Innovation involves the implementation and adoption of an invention.
This desperation led to the invention of the Transistor. Subsequently, this invention led to the improvement of existing innovations and innovating new ones. Innovation vs invention: what is more important? In innovation vs invention discourse, there is also debate about which is more important. It appears to be a non-conclusive one. In the ...
To invent something is to discover a new thing. Meanwhile, to innovate means " to use a new idea or method". To innovate is to introduce something new to the market, to manipulate existing inventions and turn them into a product or process that is of use in the real world. It's not difficult to see how tricky it can be to distinguish ...
In its purest sense, "invention" can be defined as the creation of a product or introduction of a process for the first time. "Innovation," on the other hand, occurs if someone improves on or makes a significant contribution to an existing product, process or service. In other words, they are, as Andrew Wyckoff, Director of the OECD's ...
Economics, 5(2), 87-109. Joshi, M. 2017. Invention, Innovation and Innovative practices: a reason to study in a VUCA pe r-. spective. 88. Introduction. Rogers (1983) defines innovation as an ...
In one of the notes listed below its definition of "invention", Merriam Webster states that invention is a product of one's imagination. While innovation, on the other hand, is a change made to an existing product or idea. To explain this even further, it cited the telephone as an invention and the smartphone as an innovation.
Definition of invention. We have covered one of the words regarding what is the difference between an invention and an innovation. So, let us see what an invention is. It means a new product has been created that varies from any object that has been present before. It required tremendous brains to create any such product.
Innovation isn't as glamorous as creating something completely new, but it is the constant vehicle of improvement that can be your competitive advantage. We can actually confuse innovation with ...
Innovation vs Invention Examples 1. Inventions Leading to Innovation. Many innovations can trace their roots back to a groundbreaking invention. For instance, consider the advent of the Internet, which began as a revolutionary invention that fundamentally changed communication and information-sharing. Over time, innovators found new ways to ...
Invention is a continuum, a never-ending journey of discovery and improvement. Every invention is a stepping stone to the next, creating a chain reaction of progress. As we stand on the brink of a new era of innovation, the power of invention promises to continue shaping our collective destiny. 500 Words Essay on Invention Introduction to Invention
Essay on Innovation And Invention. There is no question in my mind that with appropriate management, we can improve the levels of innovation and creativity within organizations. There is no magic here. Innovative people are no more 'born' than Olympic gold medallists or virtuoso musicians. Yes, some of us are gifted with more initial ...
The state government is committed to promoting innovation, economic growth and job creation," he said. ... Auto parts maker Carraro India files papers with Sebi for Rs 1812 crore IPO. Patil explained the Chevron team that will be operating here will execute complex global operations and energy projects in collaboration with international ...