

Intro to Computer Hardware
Jul 26, 2014
220 likes | 659 Views
Intro to Computer Hardware. Digital Basics. Computer Hardware. Hardware – the physical parts of the computer system that you can see and touch. System Unit. The system unit is the box which holds & protects the electronic components of the computer. It is sometimes called the “tower”.
Share Presentation
- electronic components
- hard drives
- largest circuit board
- visual form

Presentation Transcript
Intro to Computer Hardware Digital Basics
Computer Hardware Hardware – the physical parts of the computer system that you can see and touch.
System Unit • The system unit is the box which holds & protects the electronic components of the computer. • It is sometimes called the “tower”. • The system unit is often (incorrectly) called the CPU. As you will see on the following slide, the CPU is only one of the things inside the system unit.
Inside the System Unit • Central Processing Unit (CPU) or microprocessor. It acts as the "brain" of your computer. • Heat sink– a piece of hardware that helps to keep the CPU cool by dissipating the heat.
Inside the System Unit • Motherboard. Computer’s largest circuit board. Everything that has anything to do with the computer is connected in some way to the Motherboard. • Random Access Memory (RAM). It temporarily stores information that the CPU uses while the computer is on. The information stored in RAM is erased when the computer is turned off.
Inside the System Unit • Power Supply - The power supply takes the current that comes from the electrical outlet in the wall and converts it to low voltage, DC current that your computer can use. It also protects the computer from surges in electricity that could damage it.
Inside the System Unit • Expansion Cards - These are circuit boards that can be plugged in to the motherboard. They add functions - like sound cards to operate the computer’s sound or video cards to handle the graphics displayed on your monitor. • Expansion Slots – connections on the motherboard where expansion cards are installed.
Inside the System Unit • Modem – a modem is a special expansion card that allows computers to talk to each other. It has a connection for a cable that is used to connect to the Internet. Some modems are external and in their own cases.
Internal Storage • Hard disk drive – Inside the system unit, your computer's hard disk drive stores information on a hard disk, a rigid platter or stack of platters with a magnetic surface. Because hard disks can hold massive amounts of information, they usually serve as your computer's primary means of storage, holding almost all of your programs and files.
Removable Storage Drives • CD drives use lasers to read (retrieve) data from a CD, and can also write data onto CDs. • DVD drives can do everything that CD drives can, plus read DVDs. If you have a DVD drive, you can watch movies on your computer. Many DVD drives can also record data onto blank DVDs. • Floppy disk drives store information on floppy disks. Compared to CDs and DVDs, floppy disks can store only a small amount of data. They are also slower and more likely to be damage so they are becoming obsolete.
Other Removable Storage • USB (Universal Serial Bus) drives • USB drives are currently the most popular removable storage device. They plug in to USB ports and can hold far more than CDs, DVDs or Floppy Disks yet are small and easy to use. • External Hard Drives • External hard drives also plug in to USB ports and can usually store more than USBs. • They are larger and are usually used to back up hard drive data. • Some external hard drives require their own power. Others are powered through the USB port.
Peripherals • Almost every other part of your computer (monitor, keyboard, mouse, printer, speakers, external hard drives, etc.) connects to the system unit using cables. • The cables plug into specific ports (openings), typically on the back of the system unit. • Hardware that is not part of the system unit is sometimes called a peripheral device.
Monitor • A monitor displays output in visual form, using text and graphics. The portion of the monitor that displays the information is called the screen. Like a television screen, a computer screen can show still or moving pictures. • Newer monitors (LDC - liquid crystal display) are thinner and lighter. Old monitors (like old tv’s) are CRT (cathode ray tube) monitors and are much bigger and heavier.
Keyboard • A keyboard is an input device mainly used for typing text into your computer. It has keys for letters and numbers, but it also has special keys: • The function keys, found on the top row, perform different functions depending on where they are used. • The numeric keypad, located on the right side of most keyboards, allows you to enter numbers quickly. (Don’t forget to turn on the Num Lock!!) • The navigation keys, such as the arrow keys, allow you to move your position within a document or webpage. • You can also use your keyboard to perform many of the same tasks you can perform with a mouse using keyboard shortcuts.
Mouse • A mouse is an input device used to point to and select items on your computer screen. • A mouse usually has two buttons: a primary button (usually the left button) and a secondary button. Many mice also have a wheel between the two buttons, which allows you to scroll smoothly through screens of information. • The pointer's appearance will change depending on where it's positioned on your screenor what you are trying to do. Notice the shapes and how they can be used.
Printers • A printer transfers data from a computer onto paper. It is an output device. • The two main types of printers are: • Inkjet printers: Inkjet printers create images by spraying ink on to paper. They are affordable & can print in color. • Laser printers create images by making toner stick to the paper with heat. They are usually more expensive, but are faster and generally more affordable for heavy use. Color is available but more expensive.
File Size and Storage Capacity • Computers work with digital information – everything is converted to 0’s and 1’s • Each 0 or 1 is a bit • 8 bits = 1 byte • 1 thousand bytes = 1 kilobyte • 1 million bytes = 1 megabyte • 1 billion bytes = 1 gigabyte • 1 trillion bytes = 1 terabyte
Storage Capacity • Floppy disk = 1.44 MB • CD = 650-700 MB • DV = 4.7 GB • USB drives = 32MB – 64 GB or more • Hard drive = measured in GB or TB
Sample File Sizes • single letter (a, b…) = 1 byte (8 bits) • 1 page document = 20-30 kilobytes • 1 (simple) PowerPoint = 1 megabyte • 1 picture = 1 – 4 megabytes • 30 sec. Video (no sound) = 1 megabyte • 90 sec. Video (w/ sound) = 5 megabytes • 1 song = 4 kilobytes
- More by User

Intro To Computer Graphics
Intro To Computer Graphics Geb Thomas Learning Objectives Learn the differences between image-order, object-order and volume rendering. Learn how the eye perceives color and how monitors present color.
1.08k views • 24 slides

Intro. to Computer Science
Intro. to Computer Science. Course number: CSIE 1000 Classroom: 102 Instructor: 周承復 TA: 謝育璘 @505, [email protected] 何鈺涵 @505, [email protected] http://www.csie.ntu.edu.tw/~ccf [email protected] https://www.csie.ntu.edu.tw/~r03944025/intro2015/.
655 views • 7 slides

Intro to MIS – MGS351 Computer Hardware and Software
Intro to MIS – MGS351 Computer Hardware and Software. Extended Learning Module A. Chapter Overview. History Binary and Digital Communications Hardware CPU, Memory, Storage Devices, Input Devices, Output Devices Software Operating Systems, Application Software, Programming Languages .
490 views • 43 slides
Intro to Computer Forensics
Intro to Computer Forensics. CSC 485/585. Objectives. Understand the roles and responsibilities of a computer forensic examiner. Understand the “Safety Net” concept. What is a Computer Forensic Examiner?.
138 views • 0 slides

Introduction to Computer Hardware
Introduction to Computer Hardware. Dr. Steve Broskoske Misericordia University. 3 Parts of a PC (As Seen from Outside PC). Power Supply. Motherboard (Microprocessor, cards, RAM memory). Storage Devices. 3 Parts of a PC (As Seen from Inside PC). Storage Devices. Motherboard
535 views • 20 slides

Intro to computer (LAB)
Intro to computer (LAB). Introduction To office 2007. Teaching Assistant : Zain - ul -Hassan. COURSE DESCRIPTION:
334 views • 12 slides

Intro to Computer Hardware. Computer Hardware. Hardware – the physical parts of the computer system that you can see and touch. System Unit. The system unit is the box which holds & protects the parts of the computer. It is sometimes called the “tower”.
361 views • 22 slides


Intro. to Computer Network
Intro. to Computer Network. Thu. 9:10am-12:10pm, in CSIE 105 Instructor: Cheng-Fu Chou Email:[email protected] Office hours: by appointments TAs: 康永昌 : fkang2965[at]gmail.com; R506 王挺宇 : robertabcd[at]gmail.com ; R506 Lecture Format: Slides Interactive. Class Resources.
311 views • 18 slides

Intro. to Computer Science. Course number: CSIE 1000 Classroom: 104 Instructor: 周承復 TA: 周家緯 : [email protected] 林煒晧 : [email protected] 曾清陽 : [email protected] http://www.csie.ntu.edu.tw/~ccf [email protected]
332 views • 7 slides
Intro. to Computer Networks
Intro. to Computer Networks. Some Terminology Computer network an interconnected collection of autonomous computers Distributed system a software system built on top of a network Client-server model Use of Computer Network Networks for companies
374 views • 8 slides

Intro to Computer Org.
Intro to Computer Org. Instructor: Joshua A. Horton TA: Meizhu Liu. Contact Info. Office hours @ E309 My email: [email protected] TA email: [email protected] Subject line – CDA 3101. Meeting Times. Lecture ( you are here ) MWF 7 th period: 5:00 PM – 6:15 PM Discussion
231 views • 13 slides

Intro to Computer Org. Assembly Programming – An In-Depth Look At Memory. Layout Of Memory. Layout Of Memory. Text segment Holds all instructions of the program. Layout Of Memory. Data Segment Static part
450 views • 32 slides

Intro to Computer Org. MIPS Architecture & Assembly: More Instructions. MIPS Assembly Instructions. All MIPS instructions are one of these three types. R-type All the data is in registers I-type Only way to load from/store to memory Uses registers + hardcoded data J-type
521 views • 32 slides

Intro to Computer Org. MIPS Assembly – Program Implementation. Composition of Programs. As we referenced before, all computer programs are represented as binary data. This data must first be loaded into memory, then jumped to by an operating system in order to execute. Composition of Programs.
517 views • 40 slides

Intro to Computer Math
Intro to Computer Math. Binary – Octal - Hexadecimal. B 1011 0100 1100 0x B 4 C. Binary: What is it???. Electronics: 0,1 is easy numbering system Data is stored as 32 or 64 bits of 0s and 1s: Registers, Memory, Disk, CDs, DVDs, ROM, Data Communications Bit = 1 binary digit: 1 or 0
443 views • 29 slides

Intro. to Computer Science. Course number: CSIE 1000 Classroom: 102 Instructor: 周承復 TA: 王子安 @505 吳政軒 @505 田顏禎 @505 http://www.csie.ntu.edu.tw/~ccf [email protected] http://www.csie.ntu.edu.tw/~r02944034/intro2014/. Intro. to Computer Science. Textbook:
252 views • 7 slides

Intro. to Computer Network. Thu. 9:10am-12:10pm, in CSIE 102 Instructor: Cheng-Fu Chou Email:[email protected] Office hours: by appointments TAs: 康永昌 : fkang2965[at]gmail.com; R505 劉雨鑫 : alex800826 [at]gmail.com ; R505 Lecture Format: Slides Interactive. Class Resources.
334 views • 18 slides

Computer Hardware
Data Representation and Digital Electronics. Section A. CHAPTER 2. Computer Hardware. PARSONS/OJA. Page 58. Chapter 2. Computer Hardware. Chapter PREVIEW. When you complete this chapter, you should be able to: Explain why most computers are digital Describe the role of the ALU
1.17k views • 40 slides

Intro To Computer Graphics. Geb Thomas. Learning Objectives. Learn the differences between image-order, object-order and volume rendering. Learn how the eye perceives color and how monitors present color.
253 views • 24 slides
Intro. to Computer Network. Thu. 9:10am-12:10pm, CSIE 102 Instructor: Cheng-Fu Chou Email:[email protected] Office hours: by appointments TAs: 張庭嘉 : r03922038 [at] ntu.edu.tw Office: 德田館 (CSIE Building)R505 王韋閔 b99902057 [at] ntu.edu.tw Office: 德田館 (CSIE Building)R505
193 views • 17 slides

Intro to Computer Security
Intro to Computer Security. Computer crime is a serious and growing problem In 1994, The Yankee Group estimated that computer security breaches cost businesses based in the USA $5 billion annually! In 1995, this estimate had risen to $10 billion!
233 views • 20 slides

- My presentations
Auth with social network:
Download presentation
We think you have liked this presentation. If you wish to download it, please recommend it to your friends in any social system. Share buttons are a little bit lower. Thank you!
Presentation is loading. Please wait.
Presentation On Computer Hardware & Software. What is Hardware? Hardware is a general term for the physical objects of technology. It may also mean the.
Published by Griselda Knight Modified over 8 years ago
Similar presentations
Presentation on theme: "Presentation On Computer Hardware & Software. What is Hardware? Hardware is a general term for the physical objects of technology. It may also mean the."— Presentation transcript:

Introduction to Computers Lecture By K. Ezirim. What is a Computer? An electronic device –Desktops, Notebooks, Mobile Devices, Calculators etc. Require.

Introduction to Computer Programming CSC 1401: Introduction to Programming with Java Lecture 2 Wanda M. Kunkle.

WkTOPIC(S) 1 Overview of computer system 2 Data and Information 3 Computing Device I (pre computer age to 19 th century) 4 Computing Device I (pre computer.

A “Java Fun For Everyone” Interactive Quiz

Application Software CSC151.

CS 0008 Day 2 1. Today Hardware and Software How computers store data How a program works Operators, types, input Print function Running the debugger.
Types of software. Sonam Dema..

TC2-Computer Literacy Mr. Sencer February 8, 2010.

Computer Software Zaffar Ahmed Shaikh.

COMPUTER MAIN PARTS Hardware Software. HARDWARE Definition: The set of hardware components that make up the material part (physical) of a computer, unlike.

CS101: Introduction to Computing Instructors: Badre Munir, Usman Adeel, Zahid Irfan & Maria Riaz Faculty of Computer Science and Engineering GIK Institute.
Topics Introduction Hardware and Software How Computers Store Data
Configuration.

Brief overview Basic Concepts of Computer. What is a computer? A computer is a tool to process data Data Alphabet/Numeric Graphic Sound.

Outcome 2 – Computer Software The Range of Software Available The Different Categories of Software System Software Programming Languages Applications Software.
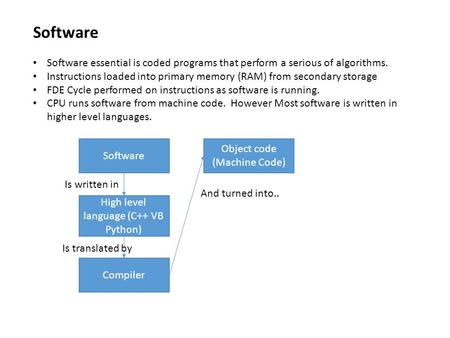
Software Software essential is coded programs that perform a serious of algorithms. Instructions loaded into primary memory (RAM) from secondary storage.

Computer Software Computer Technology Day 5. Software Provides step-by-step instructions that tell the computer how to perform Categories System.

Introduction OF Enterprise Application Development.

Lecture #10 COMPUTER SOFTWARE By Shahid Naseem (Lecturer)

CHAPTER FOUR COMPUTER SOFTWARE.
About project
© 2024 SlidePlayer.com Inc. All rights reserved.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
This document summarizes computer hardware components. It divides hardware into three main groups: input devices, output devices, and the system unit. Input devices like keyboards and mice are used to enter data, while output devices like monitors and printers display or print data.
Understand the history and evolution of computer hardware. Identify the major types and uses of microcomputer, midrange, and mainframe computer systems. Outline the major technologies and uses of computer peripherals for input, output, and storage.
Computer hardware refers to the physical components that make up a computer system. It includes processing components like the CPU and memory, as well as input devices, output devices, and storage devices.
In these lectures, we begin our three-lecture exploration of Computer Hardware. We start by looking at the different types of computer components and how they interact during basic computer operations. Next, we focus specifically on the CPU (Central Processing Unit).
Introduction to computer hardware. This document provides an overview of the basic hardware components of a personal computer, including input devices, the processing unit, storage devices, and output devices.
Hardware represents the physical and tangible components of a computer i.e. the components that can be seen and touched. Examples: Input devices -- keyboard, mouse etc. Output devices -- printer, monitor etc. Secondary storage devices -- Hard disk, CD, DVD etc. Internal components -- CPU, motherboard, RAM etc. Nehal Patel (I.T. Dept.)
Computer Hardware Components • Contents: • The five stage computer model • CPU • Memory on chips and memory on magnetic media, how do they differ? • What do you look for when comparing memory devices?
Intro to Computer Hardware Digital Basics. Computer Hardware Hardware – the physical parts of the computer system that you can see and touch. System Unit • The system unit is the box which holds & protects the electronic components of the computer. • It is sometimes called the “tower”.
A presentation on the basic components and functions of a personal computer system, such as the power supply, motherboard, CPU, bus, peripherals, and software. Learn the definitions, examples, and categories of hardware and software devices, and how they communicate with each other.
Computer hardware consists of the components that can be physically handled. The function of these components are typically divided into three main categories: Input devices, Output devices and Storage Devices.