
More than a Quality Management System: Tools for the entire MedTech Lifecycle.

Featured Capabilities:
Experience the #1 QMS software for medical device companies first-hand. Click through an interactive demo.
Data collection and management designed for MedTech clinical trials.
Get a personalized demo of Greenlight Guru Clinical today.
- By Initiative
- Migrating From Paper
- Managing and Assessing Risk
- Preparing for Regulatory Submissions
- Becoming Audit Ready
- Managing Postmarket Quality
- Managing Clinical Data
- By Org Type
- Post-Market
- By Function
- Product / R&D
- ROI Calculator
- Customer Success
- Resource Hub
- Thought leadership, tips, and tricks for the latest, world-class MedTech Industry Resources.
- View All Resources
- Explore by Type
- Checklist/Template
- True Quality Roadshow
Ultimate Guide to Comparing Quality Management System Solutions
This eBook compares the best QMS software solutions to help medical device companies make an informed decision when investing in a quality management system.
- Quality Pricing
- Clinical Pricing

- Case Studies
- Checklists & Templates
- eBooks & Guides
- Content Hub
- Live & Virtual Events
Medical Device Clinical Trials: Regulatory Pathways & Study Types Explained
.png)
In both the US and the EU, medical devices may be required to undergo a clinical trial before they can be placed on the market. A clinical trial is a systematic assessment of the device’s safety and/or efficacy that uses human participants, and it’s a requirement for certain risk classes:
In the EU, all Class III and Class IIb implantable devices must undergo clinical investigations according to EU MDR.
In the US, all Class III devices are required by FDA to undergo clinical investigations as part of premarket approval (PMA).
With that in mind, let’s take a look at the different stages and designs of medical device clinical trials and the regulations surrounding them.
NOTE: You may see clinical trials referred to as “clinical studies” or, more commonly in the medical device industry, “clinical investigations.” These terms are all synonymous and can be used interchangeably.
BONUS RESOURCE: Click here to download our 15-in-1 clinical investigations content bundle to help you run studies and collect clinical data more efficiently.
How are medical device clinical trials initiated?
Because clinical trials involve human participants, medical device companies must perform preclinical testing and research on their product before even applying for a clinical trial.
Preclinical activities determine whether a device is safe and effective enough for use with human subjects, and include steps like:
Bench testing
Technical testing
Computer simulations
Animal studies
Once the manufacturer believes their device is ready for clinical trials, they must first get approval for their proposed investigation. The processes for getting approval and initiating a clinical trial in the EU and US are different, so let’s take a look at each.
Clinical trial regulatory pathways in the US
In the US, medical device manufacturers that want to pursue a clinical trial must obtain an Investigational Device Exemption (IDE). Only once the IDE has been approved can a device that has not yet received market approval be tested on human subjects.
There are exceptions to the IDE submission, which include certain low-risk diagnostic devices as well as devices that are determined to be non-significant risk (NSR).
If a device is granted an IDE, the clinical investigation must still be reviewed by an Institutional Review Board (IRB). Clinical trials are generally performed within an institution, such as a hospital, and an IRB is an additional layer of scrutiny that the institution provides to ensure the study meets its standards. The study may begin only once the IRB has approved it and FDA has approved the IDE application.
Clinical trial regulatory pathways in the EU
EU MDR has 20 articles outlining the requirements for clinical investigations of medical devices, spanning articles 62 through 82. Within these articles, the regulation lays out three regulatory pathways manufacturers can take:
Article 62 covers investigations that are performed in order to demonstrate conformity and obtain a CE marking. This is the pathway medical device companies will use if their device classification (for Class III or Class IIb implantables ) requires a clinical investigation.
Article 74(1) covers the regulatory pathway for devices that already have a CE marking if the parameters of the investigation are within the device’s intended purpose. In other words, if you are conducting a clinical investigation as part of your Post-Market Clinical Follow-Up (PMCF) , then you will be guided by Article 74(1).
Article 82 covers clinical investigations that are not being performed in order to demonstrate conformity. Additionally, the Member State in which you hold your study may have relevant national provisions for you to follow.
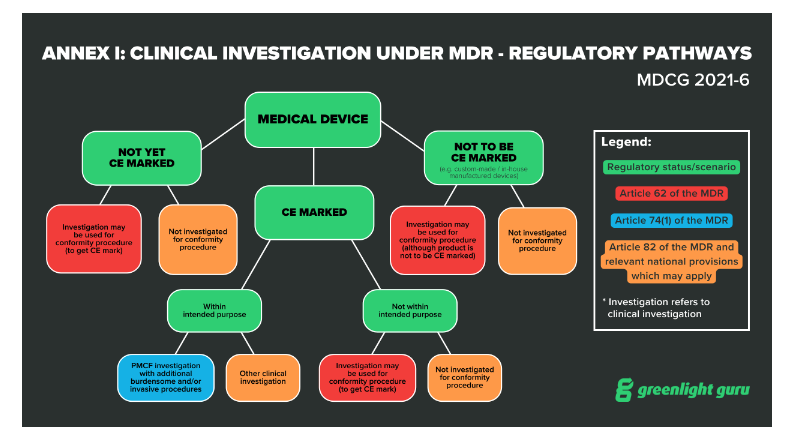
Before initiating a clinical trial in the EU, you’ll also need a CIV-ID and approval from the relevant competent authority. The CIV-ID is an EU specific tracking number that competent authorities in any Member State can use to identify and track your clinical investigation.
Keep in mind that once the EUDAMED database is fully functional, now scheduled for spring of 2024 , the CIV-ID will be replaced by a Single Identification Number tracked through EUDAMED.
What are the different stages and types of medical device clinical trials?
Clinical trials may be carried out during both the premarket and postmarket phases of the device lifecycle. The graphic below includes the many different types of clinical activities, including clinical trials, medical device manufacturers may carry out during the pre-market and post-market phases.
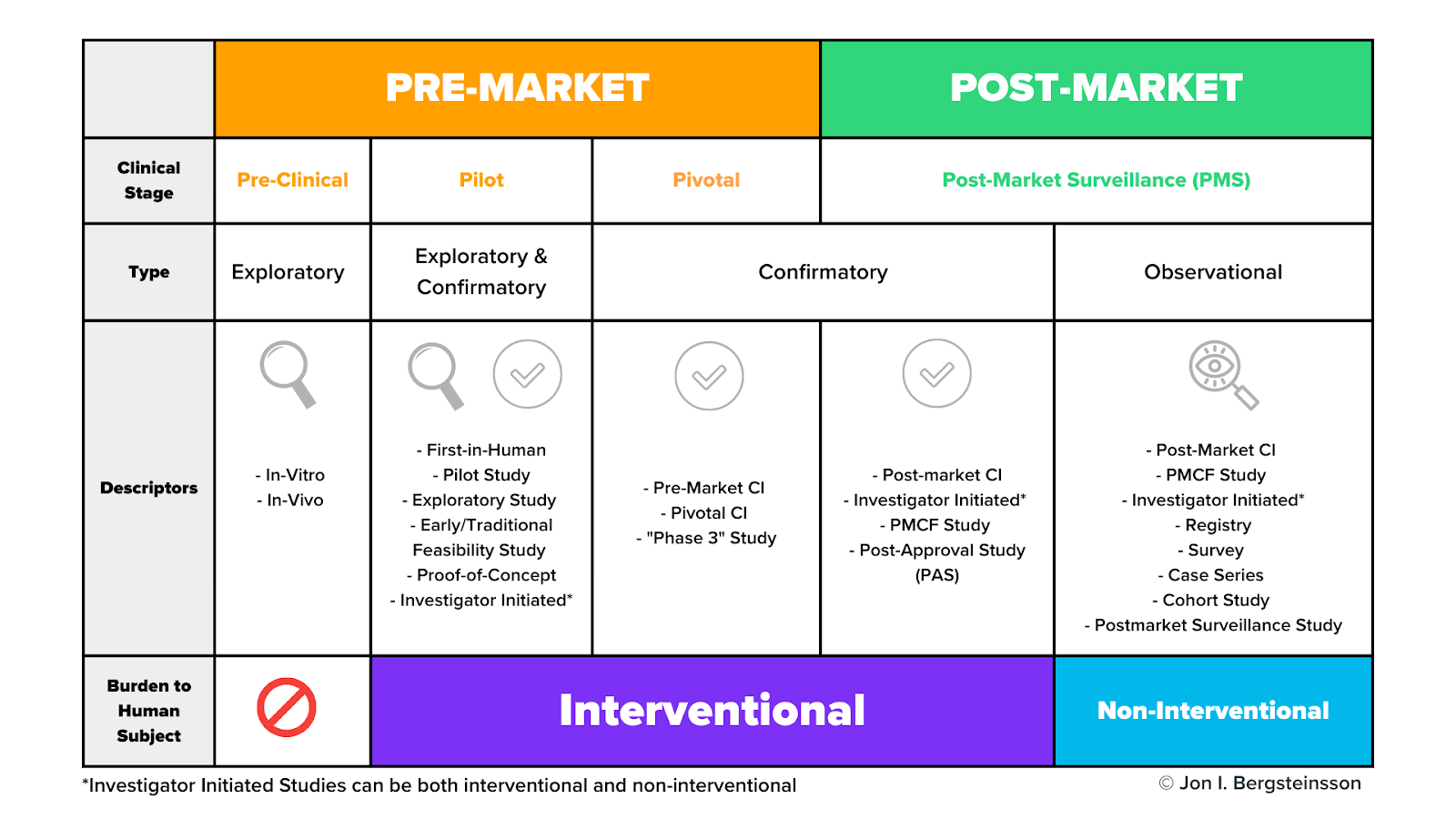
Clinical trials may occur during the pilot stage, the pivotal stage, or during post-market surveillance. As I mentioned earlier, pre-clinical activities do not use human subjects.
As we dig in here, don’t get too hung up on the study descriptors in this graphic. Many of these terms are interchangeable, and different descriptors are often used in different markets to describe the same thing. For now, let’s focus on the general types and stages of studies and their burden to human subjects.
What are pilot studies?
Pilot studies occur early in device development, often before the device design has been finalized. Pilot studies are used when nonclinical testing is unable to provide preliminary information on device functionality and clinical safety. These will be conducted with a very small number of patients—often 10 or fewer.
The purpose of pilot studies is to gain a broad range of information that may be used to:
Identify modifications to the device or procedure
Optimize operator technique
Refine the intended use population
Refine nonclinical test plans or methodologies
Develop subsequent clinical study protocols
The data you gain from a pilot study may then be used to help you design a pivotal study later on.
What are pivotal studies?
A pivotal study is used to gather definitive evidence of the safety and effectiveness of your medical device for a specific intended use. These studies generally use a larger number of subjects than pilot studies, and you’ll use the results of your pivotal study to gain regulatory approval for your device.
Keep in mind, a pivotal study does not necessarily need to be preceded by a pilot study. The types of clinical activities you carry out will depend on your device and the regulatory pathway you’re taking.
Do clinical trials happen during post-market surveillance?
As you can see from the graphic, the post-market surveillance stage includes both confirmatory and observational types of clinical activities.
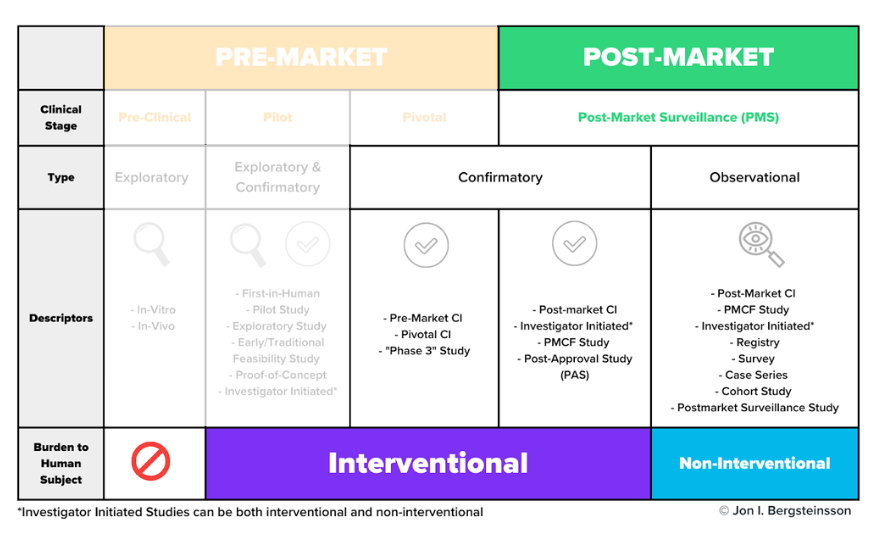
While it may seem odd that you would need to perform a confirmatory study after receiving approval to place your device on the market, this is not an irregular occurrence. For example, EU MDR includes a distinct regulatory pathway—Article 74(1)—for conducting a clinical investigation as part of your PMCF.
These post-market surveillance studies may be conducted for a number of reasons, including to confirm the safety and efficacy of the device once it’s on the market or to answer questions about the long-term safety or performance of the device.
How are observational clinical activities conducted?
Many post-market clinical activities are categorized as “observational” and they use non-interventional methods to collect data.
In interventional studies , such as a pivotal study, someone is actively recruiting participants. For example, a physician may ask a patient who may benefit from a certain device if they would like to volunteer for that study. In other words, they are intervening in the normal clinical pathway the patient would follow.
In non-interventional studies , there is no intervention in the clinical pathway—merely observation. For example, a physician prescribes a treatment they believe the patient needs (the normal clinical pathway), and then asks the patient if they would agree to share the data related to their treatment as part of an observational study.
Remember, some devices may need clinical data from all of these categories, but many will not. For example, low risk devices relying on well-known technology may not require any clinical investigations on your part.
Greenlight Guru Clinical helps you streamline clinical data collection for your medical device
This may seem like a complicated topic, but if you break it down by the stages of the device lifecycle and the type of clinical activity, you have a roadmap for how you’ll obtain the necessary clinical data for your device.
And when it comes time to begin collecting that data, you’ll need a flexible, modern platform that can streamline data collection from any and all of your clinical activities.
Greenlight Guru Clinical is that platform. Whether you’re gathering data in clinical studies, performance studies, PMCF/PMPF studies, surveys, registries, cohorts, or case series, our Electronic Data Capture solution allows you to collect and manage it all with ease. Even better, it comes fully validated out of the box per ISO 14155:2020 .
Ready to learn more? Contact us today for a customized demo →
Jon Bergsteinsson
Jón Ingi Bergsteinsson, M.Sc. in Biomedical Engineering, is the co-founder of Greenlight Guru Clinical (formerly SMART-TRIAL). He was also the technical founder of Greenlight Guru Clinical where he paved the way for the platform’s quality standards, data security, and compliance.
Read More Posts
Quality management consulting: how and when to seek help, decentralized clinical trials: are remote elements right for your next study, building an effective capa program: key steps and common challenges, subscribe to our blog.
Join 200,000+ other medical device professionals outperforming their peers.

Get your free PDF
Change impact analysis checklist.
- Checklists/Templates
- Request a Demo
- Content Title Description
- Research article
- Open access
- Published: 30 May 2013
Case studies of innovative medical device companies from India: barriers and enablers to development
- Szymon Jarosławski 1 &
- Gayatri Saberwal 1
BMC Health Services Research volume 13 , Article number: 199 ( 2013 ) Cite this article
25k Accesses
27 Citations
1 Altmetric
Metrics details
Over 75% of the medical devices used in India are imported. Often, they are costly and maladapted to low-resource settings. We have prepared case studies of six firms in Bangalore that could contribute to solving this problem. They have developed (or are developing) innovative health care products and therefore are pioneers in the Indian health care sector, better known for its reverse engineering skills. We have sought to understand what enablers and barriers they encountered.
Information for the case studies was collected through semi-structured interviews. Initially, over 40 stakeholders of the diagnostics sector in India were interviewed to understand the sector. However the focus here is on the six featured companies. Further information was obtained from company material and other published resources.
In all cases, product innovation has been enabled by close interaction with local medical practitioners, links to global science and technology and global regulatory requirements. The major challenges were the lack of guidance on product specifications from the national regulatory agency, paucity of institutionalized health care payers and lack of transparency and formalized Health Technology Assessment in coverage decision-making. The absence of national evidence-based guidelines and of compulsory continuous education for medical practitioners were key obstacles in accessing the poorly regulated and fragmented private market.
Conclusions
Innovative Indian companies would benefit from a strengthened capacity and interdisciplinary work culture of the national device regulatory body, institutionalized health care payers and medical councils and associations. Continuous medical education and national medical guidelines for medical practitioners would facilitate market access for innovative products.
Peer Review reports
In the case of drugs, due to its strong reverse engineering skills, India is virtually self-sufficient. In contrast, 75% of the annual purchase of devices and diagnostics comes from imports [ 1 ]. A WHO report on medical devices pointed out that: “almost all devices present in developing countries have been designed for use in industrialized countries” [ 2 ]. Consequently, they are often unaffordable and are maladapted to low resource settings.
Whereas rural health care providers are a documented source of grassroots technical innovation on a micro scale [ 3 ] the private industry world-wide has valuable expertise in the development of medical devices for mass use [ 2 ]. However, the industry has traditionally perceived that developing-world markets are too small to justify the development of new products [ 2 , 4 ]. Thus, over the past decade, a number of push and pull incentives have been proposed by international public health organizations, non-governmental organizations (NGOs) and donors in order to incentivize the western industry to undertake research and development (R&D) addressing the specific needs of the developing world [ 4 , 5 ], although market access challenges of this industry in such markets have been well-documented [ 6 ]. More recent is health technology innovation, largely by young companies located in developing countries, where the companies perceive local markets as the main focus of their R&D strategy [ 7 , 8 ].
Important to health technology innovation is Health Technology Assessment (HTA), defined as the “systematic evaluation of the properties and effects of a health technology, addressing the direct and intended effects of this technology, as well as its indirect and unintended consequences, and aimed mainly at informing decision making regarding health technologies” ( http://htaglossary.net ). In industrialized countries, there is a growing interest in interactions among bodies concerned with HTA, coverage (institutional purchasing or reimbursement), and regulation with whom the industry needs to engage in order to develop novel products that can reach patients [ 9 ]. Improving such interactions is believed “to speed patient access to valuable products” and “to remove unnecessary barriers to successful development and appropriate market access for innovative products” [ 9 ].
In contrast, India doesn’t have a formalized national HTA process and the public financing of new technologies is very limited [ 10 ]. Whereas 60-80% of health care is delivered in the private sector, only 3-5% of the population has health insurance [ 11 ] so coverage decisions by insurers have negligible impact on the market uptake. Further, medical practitioners in the private sector are not obliged to follow any official evidence-based guidelines, and continuous medical education is not mandatory [ 12 – 14 ]. Finally, the regulation of medical devices is minimal: in the case of in-vitro tests, only those for HIV, hepatitis B and C and blood typing are considered 'critical’ by the Indian regulator and only these tests must be clinically validated before receiving a license. In this context, our study aimed to provide qualitative insights into the frugal innovation experience of companies that function in an environment that doesn’t have a tradition of indigenous novel bio-medical product development.
Here we present case studies of six private companies in Bangalore, India, that have developed and launched (four cases) or are expecting to soon launch (two cases) devices for the Indian market. These firms belong to a new wave of intellectual property (IP)-based product ventures in the country. We study (i) the evolution of the firms and their approaches to product development; (ii) their funding and human resource challenges; (iii) their access to global science and technology (S&T); (iv) their use of global regulatory requirements, and finally (v) the market challenges that must be overcome in order to access patients with their products. We believe that insights from this study will be of interest to many young companies, regulators and policy makers in the world.
We adopted a qualitative case study research methodology that has been used by others to study medical innovation in developing countries [ 8 , 15 – 17 ]. The innovative medical device industry in India is only emerging today and a quantitative study would not be feasible with such a small sample size. Further, as explained below, the firms have gone through very different paths since their inception and the case study methodology is better suited to capture this heterogeneity. The study protocol was approved by the Ethics Committee of IBAB. Written informed consent was obtained from participants by asking them to positively reply to an interview invitation e-mail. Initially more than 40 private and government doctors, diagnostic labs, manufacturers and distributors of diagnostic tests, NGOs and academics were interviewed about the diagnostics’ business in India. The interviews concerned local innovation versus imported products, delivery of devices to patients in public and government sectors, regulatory issues and doctors’ prescription behaviour. Informants were chosen by purposeful sampling and were chiefly located in metropolitan cities although their experience extended to rural areas as well. Results of these interviews are not presented here, but served to select the six companies located in Bangalore that were the basis for this study. Additionally, the following sources were used: the BioSpectrum India Life Sciences Resource Guide 2010 which is one of the most comprehensive repositories of information on the Indian life science industry ( http://www.newindigo.eu/biotech/main/index.htm ) and a published review of the Indian biotech industry [ 18 ]. Since none of the firms had achieved significant sales at the time of our research, financial measures such as profit, volumes or return on investment could not be used as criteria for selection. Nor were details of debt or equity available for the (largely) privately held companies. We selected medical device firms located in Bangalore, arguably the most innovative biomedical hub in India, that were developing innovative, IP-based products for the Indian market, and low-resource settings in particular. Finally, in the one situation where two companies with similar profiles were identified (that is, inception or origin, type of product and development path) the company that was further in the product development process was chosen. The company-specific interviews sought to understand the inception of the firm and the origin of the key personnel; the path of product development and target product profiles; sources of funding; issues related to clinical validation; regulatory approval and market access in private and government settings. Interviews were not recorded but detailed notes were made during and immediately after each interview. The analysis presented here is based on multiple interviews with the founders of five of the companies. In the case of GE Healthcare India (GEH) the informant was the senior product manager who led the development of MAC400 and MACi. Consequently, the perspective of his own R&D centre may not fully reflect the history of General Electric (GE) in India. In each case there was one interview at the company, followed by a few more conversations in person, by phone or by e-mail. Further information was obtained from company material and other published interviews of the founders. After all the interviews, the write up on each of the six companies was verified by the concerned firm. However the final manuscript was not submitted to them for their verification. All interviews were semi-structured and were conducted between March and December 2011, inclusive.
The companies and their products
The firms profiled are XCyton Diagnostics (XCyton), Bigtec Labs (Bigtec), GEH, ReaMetrix India (ReaMetrix), Embrace Global (Embrace) and Achira Labs (Achira). The companies were founded from 2 to 18 years ago (Table 1 ). Interestingly the founders of these six firms came from six of the nine categories of biotech founders in India, identified previously [ 18 ]. The earlier study had pointed out a low rate of company formation by local academics, and that is reflected here, where none is a scientist from local academia (Additional file 1 ). In terms of the companies’ evolution GEH started as a manufacturing support unit of GE Healthcare Worldwide's Indian manufacturing facility and then evolved into an R&D centre. The remaining ventures started as R&D firms and this has remained unchanged (Additional file 2 ). Most of the firms were able to take their products from concept to clinical validation in two to three years. The exception was Bigtec where the founders operated in a field that was unfamiliar to them, and where – when the product launches later this year – it will have taken 12 years from the firm’s founding.
Each firm wanted its products to be appropriate for use in low-resource settings which constitute the bulk of the Indian market both in volume and in overall value. Thus, each company undertook an independent assessment of the needs of health-care providers in such settings. It went on to construct product profiles according to its own market- and consumer-research without guidance from national health-care payers or regulators. Low-cost was therefore a common criterion, although other specifications varied with the company (Additional file 3 ). Each firm’s route to its product(s) is outlined below.
XCyton develops diagnostic kits for infectious diseases. It has relied on (i) an invention sourced from the local R&D centre of a multinational company (MNC) (one case), or (ii) science sourced from or products developed in collaboration with Indian public or private research institutions (11 cases). These scientific collaborations were enabled by the personal contacts and informal links of the founder to local scientists. They were unofficial collaborations with low administrative burden and great flexibility in negotiation. Initially, XCyton developed ELISA-based kits (CheX) which require a generic reader but are relatively easy to perform even by untrained manpower. Later, the company developed polymerase chain reaction (PCR)-based kits (XCyto Screen) which call for skilled staff and dedicated laboratory facilities. This shift from rapid kits to high-resource technology was partially motivated by fading confidence in the public health-care market.
ReaMetrix started out as a contract research organization (CRO) offering services to Western clients. This led to a gradual build up of its capabilities and capacity. Subsequently the firm changed track and developed a proprietary dried reagent tailored to the needs of the National AIDS Control Organization (NACO) program which covers approximately 50% of the patients on anti-retroviral treatment in India. This reagent is used for a flow-cytometer-based test which monitors the patient’s absolute CD4+ and CD8+ T-cell counts and can replace a more expensive product supplied to NACO by an MNC. Also, it (i) removes the necessity of both cold-chain distribution (storage and transport) and on-bench refrigeration and (ii) reduces the possibility of procedural errors by supplying the pre-weighed reagent in ready-to-use disposable tubes. The company went on to develop a cheaper, simpler and more robust fluorescence reader that can replace the flow-cytometer that was supplied to NACO by the MNC. The company estimates that the currently used instrument costs $20,000–90,000 and it is willing to offer its reader at $15,000–20,000. In resource-limited settings it would offer a reagent rental scheme wherein the cost of ownership of the machine is zero. However, disappointed with the government market, the company is considering re-inventing itself yet again to build advanced R&D instruments for Western markets.
Initially Bigtec worked on a recombinant insulin for the Indian market. Subsequently it shifted to an innovative PCR-based microfluidics platform for the detection of infectious diseases specific to India. Notably, the founders were not microfluidics’ specialists. They were nevertheless attracted to this technology because it offers the automation and short sample processing times necessary in point-of-care settings. The diagnostic device allows sample preparation and mixing, bio-chemical reactions and sample screening and detection to be performed on a single chip. The diagnosis takes 45 minutes rather than several hours, and can be performed in harsh environmental conditions by an untrained person. The technology has been clinically validated for several diseases. Bigtec is planning to price the device below the cost of a real-time PCR machine. The cost of running a test would be similar to that with a currently available in-vitro diagnostic (IVD) kit for the concerned infection.
GEH started as a low cost, off-shored manufacturing unit of the mother MNC. Subsequently, it developed the MAC400 electrocardiogram (ECG) device for emerging markets by removing some features from an existing GE model. It was the first product released for the Brazil, Russia, India and China (BRIC) markets and was priced at $800, compared with GE’s other hospital-class ECG units that had a price tag between $2,000 and $10,000. However, the development of the next ECG device, MACi, was specific to the Indian market. The needs of rural health-care practitioners were surveyed by engineers from several Indian states. This was felt to be a necessity in a country with a multitude of local languages, a range of geographies and wide disparities in income-levels. It featured a fast-charging, long-life battery and was robust and portable. Also, the company realized that the poorly-regulated local market was dominated by very low-cost ECG machines, which was rather unique among BRIC countries. MACi was therefore priced at $500. It was released on the market just one year after product conceptualization. The emergence of GEH as an innovative product development centre capable of the entire design, development and manufacturing of a product was enabled by two key factors: extensive supervision and deliberate technology transfer from GE R&D units located in Germany and the US, as well as the initiative and corporate advocacy of a team at GEH for the development of a product tailored to the Indian market.
Embrace was set up to develop and commercialize a portable and safe warmer for low-birth infants. Although initially based in the US, it relocated to India, where the core R&D team made field trips to rural and urban settings in order to consult with potential end-users. One version of the warmer has been developed for use in hospitals and clinics. In the former setting it facilitates the inter-ward transfers of infants which might take up to 40 minutes. It is available for less than $300 compared to $580–$1900 for currently used radiant warmers. Another version is being developed for use at home and in rural settings. In all settings, Embrace’s warmers would replace potentially dangerous electric radiators which can accidentally catch fire.
Achira was set-up to capitalize on the founder’s academic expertise in microfluidics. Although it started out intending to provide such services to large global pharmaceutical companies, it soon shifted focus to developing a lab-on-chip platform for low-resource health-care providers in India. Achira is developing two immunoassay-based platforms: (i) microfluidic chips with a dedicated fluorescence reader for quantitative assays and (ii) device-free silk fibre-based chips for qualitative assays, which can be read by the naked eye. The former technology generates results in less than 30 minutes and can be used with minimal technical training. It has been internally validated by the company and external validation is planned. The latter technology is currently being optimized. It is superior to the currently available lateral-flow technology because multiple types of tests can be performed on a single chip. Its large-scale manufacture requires only low-cost physical infrastructure and therefore it will be sold at a lower price than the first platform.
In order to protect their inventions, all the firms filed patents, in India and in other countries. There was a general tendency to first file the applications in India and then in the US and Europe. However, we formed the impression that the young companies did not have an established IP policy.
Human resources
The Indian medical industry has traditionally been based on reverse-engineering, and therefore many skills required for the development of entirely novel products are rare in the country today [ 19 ]. Consequently the companies faced a few challenges related to the recruitment and retention of appropriately skilled personnel. (i) Indians returning from Western nations, with postgraduate academic degrees or industry experience, played an important role in most of the firms (Additional file 1 ). The process has been accelerated by both the recent economic growth in urban India and the economic stagnation of Western economies. (ii) All the firms have found that neither candidates with experience in the local pharmaceutical industry nor graduates of local academic institutions have the right skill sets to work on the design and marketing of innovative products. Whereas senior scientific staff in the companies are able to train new employees in technical skills, finding experienced candidates for market access activities has been a key challenge. (iii) XCyton and Achira, which employ Indian biologists with postgraduate experience, have found that there are cultural issues related to retaining their staff for long periods. As elsewhere, many biologists in India are women, and there is high attrition due to the relocation of those who follow their spouses to other cities. This churn has serious costs for young firms, in terms of both time and money.

Funding of the companies
The studied companies managed to engage with both local and international investors to fund their R&D programs, without having to forgo majority equity. It turns out that half of the firms were primarily funded from Indian sources and the other half from foreign ones, as detailed below (more details in Additional file 4 ).
Primarily Indian sources
Among the indigenous start-ups, XCyton and Bigtec benefitted from soft loans and small grants for young R&D firms from the Government of India, and this funding was vital. Both companies have had difficulty finding investors who would be willing to fund marketing and distribution activities without taking a majority share. They perceive such offers as unfair since their products have already been clinically validated and therefore the investment would carry relatively low risk. However, XCyton has very recently obtained an equity investment from a US-based entity which will be used mainly for marketing its XCyto Screen services and also to establish new laboratories across the country. Interestingly, this forced the company to discontinue the two approved CheX tests (for HIV and hepatitis C). This was necessary to avoid being classified as a pharmaceutical company under Indian law and it enabled XCyton to finalize the foreign investment deal without government pre-approval.
Primarily Western sources
In contrast to the cases above, ReaMetrix was almost entirely dependent on the private money of the founder who has been a serial entrepreneur in the US, and on international private investors. Although GEH is a division of a global corporation, funds for the development of an ECG for the local market were not granted automatically. After the India-based team of engineers took the initiative, their ideas received financial support first from global headquarters and later from a locally created budget. Finally, Embrace was established as a social enterprise and was funded by US-based donors. The founders are now planning to split the enterprise into a non-profit and a for-profit entity, the latter in order to secure the substantial international investment necessary to enable large-scale manufacturing and global marketing.
Overall, the firms’ major struggle was in raising substantial funds for marketing as well as scaling-up manufacture. Apart from Bigtec which formed a product marketing joint-venture with a major Indian diagnostics manufacturer, the companies needed to rely on foreign investment to finance such activities. Some of the firms fear that an investment by an MNC would result in a loss of control of the pricing strategy, and force them to price their products higher than they would wish even in low-resource settings.
Globalization of science and technology
Overall, the companies value being located in India. It has allowed them to organize frequent field surveys, construct meaningful product specifications and experiment with market access strategies, all with respect to low resource settings. Notably, however, each firm's ability to develop such appropriate technologies was enabled by the founders’ or other key persons’ experience in Western academia or industry (Table 2 and Additional file 1 ). Contact with global S&T occurred in the local divisions of MNCs (XCyton and GEH) or through returning Indians (the other firms). Also, for some of the firms, pre-existing international links were instrumental in accessing Western clients and/or funding sources, which were essential in the early days (Table 2 ). Since the availability of manufacturers and suppliers of advanced services and components in India is limited, this posed a challenge to several of the companies. Being a division of an MNC, GEH has an international network of accredited providers which facilitated sourcing of specific components. However other companies had to establish partnerships with industry located in Europe or the US. These were often initiated during global charity or industry meetings or through international academic collaborations (Additional file 5 ). Thus, medical technology innovation in a developing country can require outsourcing to the West due to the lack of local facilities or expertise.
Experience with international regulatory authorities
The companies’ international reach concerns not only S&T but also regulatory approval for their products. This is mainly because the regulation of medical devices in India is rudimentary. Further, the regulatory body is not accustomed to licensing innovative products that have not been approved in a developed country. Some firms were dissatisfied with the limited regulation in the country primarily for two reasons: (a) the lack of dialogue and guidance on what specifications a product should meet and (b) unfair competition from manufacturers offering sub-standard and cheaper versions of their innovative products.
In the absence of local regulation, the companies pursued WHO pre-qualification, US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval or the CE mark (Additional file 4 ). It was considered necessary to engage with foreign regulatory agencies not only for their guidance and to distinguish the companies’ innovative products from substandard ones, but also for accessing global markets, including those of low-income countries. Surprisingly, as exemplified by the struggle of XCyton, even WHO pre-qualification involves mobilizing significant resources. Thus, whereas the company’s HIV CheX test was compliant with WHO guidelines, pre-qualification came only after a two-year effort to attract the attention of the relevant officer who was based in Geneva. Notably, this contract gave XCyton global visibility. Subsequently, international organizations have helped the firm obtain accreditation abroad for other tests.
The firms have also pursued international certifications due to the high uncertainty related to the Indian public market, that is discussed further below. The companies that have tried to sell to the Indian government have failed to do so. Therefore, the companies have accessed, or have considered accessing, the local market via funding from foreign donor organizations. For this, international accreditation of their products would be required.
Accessing the market
Health-care providers in India range from high-end private hospitals manned by highly qualified personnel and equipped with the latest technologies, to public and private rural health-care centres lacking trained staff and with serious shortcomings in basic facilities such as the availability of uninterrupted power and water. This has large implications for the product planning process since there is significant uncertainty regarding the kind of end users and their sample throughput needs, as well as the target price range. The companies’ perception is that whereas high-end settings require high throughput capacity of an instrument and national or international accreditation, other settings primarily require (i) low capital investment and maintenance costs, (ii) low costs to the patient, (iii) resistance to adverse operating conditions and (iv) the equipment should be explicitly designed to facilitate task shifting to lower cadres of workers. Consequently, the companies have found that reaching such complex markets requires more time than product R&D. Notably, the experience of GEH in marketing to high-resource settings in India proved insufficient to access low-resource settings with the MACi. Thus, for the Indian market, the key obstacles to reaching the customer have been: (a) an underfunded and non-transparent government health-care market and (b) a highly fragmented and poorly regulated for-profit private market. In the case of diagnostics, soaring competition among diagnostic labs has increased the occurrence of referral fees that are paid to doctors on a per patient basis. It is also complex and costly to access African countries, even via the WHO purchasing process. XCyton and Embrace said that the largest funding rounds in their existence would be used in large part for marketing and distribution. These obstacles are discussed in Additional file 6 .
Five of the six companies discussed here took their products from concept to validation in two to three years. This compares well to the average product lifecycle of 18–24 months estimated by Eucomed, the medical technology industry body in Europe ( http://www.eucomed.org ). However, the availability of both funding and the human resources necessary to access the market with finished products has been one of the major impediments to the companies. Whereas advanced technological knowledge could be accessed via links to global academic and industry communities, the lack of local regulatory guidance posed a major challenge for product development. Although FDA, CE and WHO certifications are an alternative, the interviewed companies assert that the high cost of such procedures and/or distant location of these agencies are serious obstacles and result in delays. Whereas there is scarcity of literature on the innovative health care industry in India, some of these issues have been reported previously [ 17 , 20 ]. Further, the paucity of institutional health care payers, the fragmentation of private health-care providers and the lack of national consensus guidelines meant that the companies had to use their own resources to educate the doctors and laboratories about their technologies. Notably, the for-profit nature of the private sector demands that when pricing their products, firms must consider both the affordability for the patient and the provider’s desire to generate profits from the provision of a technology [ 12 , 21 – 23 ]. This market complexity implies that the commercial success and survival of such companies will depend on their ability to develop ground-breaking strategies in the post-R&D phase also.
We believe that the future of India’s innovative biomedical industry will depend on the upgradation of several national policies. Whereas this study was not designed to inform such policies, and tools such as stakeholder analysis are better suited for this purpose than the case study method adopted here, we would like to make three recommendations for the development of an innovative medical device sector in India: First, the national regulatory bodies need to offer guidance to industry about product development as the FDA, European Medicines Agency and WHO do. Currently, the scientific capabilities of the relevant agencies are inadequate to do this. Second, government procurement of innovative devices needs to be increased. Also, the process to do so should be made more transparent through the incorporation of explicit evidence-based decision making. The UK’s National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence and similar government agencies in many other European and some Asian countries, such as Japan, Singapore and Malaysia, appraise medical technologies and advise on their financing from public sources. Third, the private healthcare sector requires more regulation. This implies tackling the issue of referral fees and the production of national guidelines for diagnosis and treatment. In many countries that have nationalised health systems this is achieved through close collaboration between the HTA bodies, medical councils that control doctors’ practice and the national health funds or insurers that directly employ most health care professionals. However, it remains to be seen whether such centralized control can or should be achieved in a large and diverse country such as India, that has a health care sector that is highly fragmented and largely private.
Abbreviations
Achira labs
Bigtec labs
Brazil Russia, India and China
Contract research organization
Electrocardiogram device
Embrace global
General electric
GE Healthcare India
Health technology assessment
In-vitro diagnostic
Multinational company
National AIDS Control Organization
Non-governmental organization
Polymerase chain reaction
ReaMetrix India
Science and technology
XCyton Diagnostics
Intellectual property
Research and development.
Anonymous: Medical technology industry in India: riding the growth curve. 2010, Deloitte
Google Scholar
WHO: Medical devices: managing the mismatch. An outcome of the Priority Medical Devices project. 2011, World Health Organization
Sahayog JS: Impressions from a rural laboratory. MFC Bull. 2006, 316-317. April-June:1–4
Anonymous: Incentives and innovative financing for global health product development. 2010, The Global Health Technologies Coalition
Anonymous: Innovative financing mechanisms for global health: overview and considerations for U.S. government participation. 2011, The Henry J. Kaiser Family Foundation
Frost L, Reich M: ACCESS: how do good health technologies get to poor people in poor countries?. 2008, Cambridge, Massachusetts: Harvard Center for Population and Development Studies
Moran M, Henderson K, Ropars AL, McDonald A, McSherry L, Wu L, Illmer A, Sturm T, Zmudzki F: G-FINDER. Neglected disease research and development: new times, new trends. 2009, Sydney, Australia: The George Institute for International Health
Frew SE, Kettler HE, Singer PA: The Indian and Chinese health biotechnology industries: potential champions of global health?. Health Aff (Millwood). 2008, 27: 1029-1041. 10.1377/hlthaff.27.4.1029.
Article Google Scholar
Henshall C, Mardhani-Bayne L, Fronsdal KB, Klemp M: Interactions between health technology assessment, coverage, and regulatory processes: emerging issues, goals, and opportunities. Int J Technol Assess Health Care. 2011, 27: 253-260. 10.1017/S0266462311000262.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Thatte U, Hussain S, de Rosas-Valera M, Malik MA: Evidence-based decision on medical technologies in Asia Pacific: experiences from India, Malaysia, Philippines, and Pakistan. Value Health. 2009, 12 (Suppl 3): S18-S25.
Anonymous: Eleventh Five Year Plan 2007–12. 2008, Planning Commission, Government of India
Nandraj S: Beyond the law and the Lord: Quality of private health care. Econ Pol Wkly. 1994, 29: 1680-1685.
Das J, Hammer J: Money for nothing: The dire straits of medical practice in Delhi, India. J Development Economics. 2007, 83: 1-36. 10.1016/j.jdeveco.2006.05.004.
Das J, Hammer J, Leonard K: The quality of medical advice in low-income countries. J Econ Perspect. 2008, 22: 93-114.
Kamunyori S, Al-Bader S, Sewankambo N, Singer PA, Daar AS: Science-based health innovation in Uganda: creative strategies for applying research to development. BMC Int Health Hum Rights. 2010, S5-10 Suppl 1
Chakma J, Masum H, Perampaladas K, Heys J, Singer PA: Case study: India’s billion dollar biotech. Nat Biotechnol. 2010, 28: 783-10.1038/nbt0810-783.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Frew SE, Rezaie R, Sammut SM, Ray M, Daar AS, Singer PA: India’s health biotech sector at a crossroads. Nat Biotechnol. 2007, 25: 403-417. 10.1038/nbt0407-403.
Saberwal G: New pharma-biotech company formation in India. Nat Biotechnol. 2006, 24: 499-501.
Saberwal G: Seeding a skilled workforce. Nat Biotechnol. 2009, 27: 773-775. 10.1038/nbt0809-773.
Engel N, Kenneth J, Pai M: TB diagnostics in India: creating an ecosystem for innovation. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 12: 21-24.
Jarosławski S, Pai M: Why are inaccurate tuberculosis serological tests widely used in the Indian private healthcare sector? A root-cause analysis. J Epidemiol Global Health. 2012, 2: 39-50. 10.1016/j.jegh.2011.12.001. Available online 31 January 2012
Bajaj R: It is time to wash the linen. The Natl Med J India. 2007, 20 (3): 147-149.
PubMed Google Scholar
Rajagopalan A: Misuse of diagnostic tests. Indian J Med Ethics. 2008, 5: 121-122.
Pre-publication history
The pre-publication history for this paper can be accessed here: http://www.biomedcentral.com/1472-6963/13/199/prepub
Download references
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to all the interviewees from the studied companies who generously contributed their time. We are also very grateful to the Institut Merieux (IM), Lyon, which funded this study as part of support to several of GS’s projects. SJ is supported financially by France Volontaires, Ivry-sur-Seine.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Institute of Bioinformatics and Applied Biotechnology, Biotech Park, Electronics City Phase I, Bangalore, India
Szymon Jarosławski & Gayatri Saberwal
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Gayatri Saberwal .
Additional information
Competing interests.
GS’s research is funded by Institut Merieux (IM) which has financial interests in the medical technology industry. However IM did not play any role in designing this study, or in any other aspect related to it other than general funding, as indicated below.
Authors’ contributions
GS proposed the study. SJ performed and analysed the interviews. SJ and GS wrote the manuscript. Both authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Electronic supplementary material
Additional file 1: detailed profiles and origins of the founders and key people in the studied companies.(doc 38 kb), additional file 2: key events in the evolution of each company and sources of innovation.(doc 34 kb), 12913_2012_2626_moesm3_esm.doc.
Additional file 3: Key criteria considered by the companies when constructing product profiles for their devices and other issues of product development.(DOC 36 KB)
Additional file 4: Sources of funding for the studied companies.(DOC 33 KB)
12913_2012_2626_moesm5_esm.doc.
Additional file 5: Details of the six companies’ pursuit of global (i) science and technology and (ii) regulatory requirements.(DOC 34 KB)
12913_2012_2626_MOESM6_ESM.doc
Additional file 6: Challenges faced by each company in accessing the Government and private markets in India or other developing countries.(DOC 36 KB)
Rights and permissions
This article is published under license to BioMed Central Ltd. This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0 ), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Jarosławski, S., Saberwal, G. Case studies of innovative medical device companies from India: barriers and enablers to development. BMC Health Serv Res 13 , 199 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1186/1472-6963-13-199
Download citation
Received : 08 August 2012
Accepted : 15 May 2013
Published : 30 May 2013
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/1472-6963-13-199
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Health Technology Assessment
- Continuous Medical Education
- Market Access
- Innovative Product
- Indian Market
BMC Health Services Research
ISSN: 1472-6963
- General enquiries: [email protected]
