

How to Write an Essay Introduction (with Examples)

The introduction of an essay plays a critical role in engaging the reader and providing contextual information about the topic. It sets the stage for the rest of the essay, establishes the tone and style, and motivates the reader to continue reading.
Table of Contents
What is an essay introduction , what to include in an essay introduction, how to create an essay structure , step-by-step process for writing an essay introduction , how to write an essay introduction paragraph with paperpal – step -by -step, how to write a hook for your essay , how to include background information , how to write a thesis statement .
- Argumentative Essay Introduction Example:
- Expository Essay Introduction Example
Literary Analysis Essay Introduction Example
Check and revise – checklist for essay introduction , key takeaways , frequently asked questions .
An introduction is the opening section of an essay, paper, or other written work. It introduces the topic and provides background information, context, and an overview of what the reader can expect from the rest of the work. 1 The key is to be concise and to the point, providing enough information to engage the reader without delving into excessive detail.
The essay introduction is crucial as it sets the tone for the entire piece and provides the reader with a roadmap of what to expect. Here are key elements to include in your essay introduction:
- Hook : Start with an attention-grabbing statement or question to engage the reader. This could be a surprising fact, a relevant quote, or a compelling anecdote.
- Background information : Provide context and background information to help the reader understand the topic. This can include historical information, definitions of key terms, or an overview of the current state of affairs related to your topic.
- Thesis statement : Clearly state your main argument or position on the topic. Your thesis should be concise and specific, providing a clear direction for your essay.
Before we get into how to write an essay introduction, we need to know how it is structured. The structure of an essay is crucial for organizing your thoughts and presenting them clearly and logically. It is divided as follows: 2
- Introduction: The introduction should grab the reader’s attention with a hook, provide context, and include a thesis statement that presents the main argument or purpose of the essay.
- Body: The body should consist of focused paragraphs that support your thesis statement using evidence and analysis. Each paragraph should concentrate on a single central idea or argument and provide evidence, examples, or analysis to back it up.
- Conclusion: The conclusion should summarize the main points and restate the thesis differently. End with a final statement that leaves a lasting impression on the reader. Avoid new information or arguments.

Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to write an essay introduction:
- Start with a Hook : Begin your introduction paragraph with an attention-grabbing statement, question, quote, or anecdote related to your topic. The hook should pique the reader’s interest and encourage them to continue reading.
- Provide Background Information : This helps the reader understand the relevance and importance of the topic.
- State Your Thesis Statement : The last sentence is the main argument or point of your essay. It should be clear, concise, and directly address the topic of your essay.
- Preview the Main Points : This gives the reader an idea of what to expect and how you will support your thesis.
- Keep it Concise and Clear : Avoid going into too much detail or including information not directly relevant to your topic.
- Revise : Revise your introduction after you’ve written the rest of your essay to ensure it aligns with your final argument.
Unsure of how to start your essay introduction? Leverage Paperpal’s Generative AI templates to provide a base for your essay introduction. Here’s an example of an essay outline generated by Paperpal.

Use Paperpal’s Preditive AI writing features to maintain your writing flow
This is one of the key steps in how to write an essay introduction. Crafting a compelling hook is vital because it sets the tone for your entire essay and determines whether your readers will stay interested. A good hook draws the reader in and sets the stage for the rest of your essay.
- Avoid Dry Fact : Instead of simply stating a bland fact, try to make it engaging and relevant to your topic. For example, if you’re writing about the benefits of exercise, you could start with a startling statistic like, “Did you know that regular exercise can increase your lifespan by up to seven years?”
- Avoid Using a Dictionary Definition : While definitions can be informative, they’re not always the most captivating way to start an essay. Instead, try to use a quote, anecdote, or provocative question to pique the reader’s interest. For instance, if you’re writing about freedom, you could begin with a quote from a famous freedom fighter or philosopher.
- Do Not Just State a Fact That the Reader Already Knows : This ties back to the first point—your hook should surprise or intrigue the reader. For Here’s an introduction paragraph example, if you’re writing about climate change, you could start with a thought-provoking statement like, “Despite overwhelming evidence, many people still refuse to believe in the reality of climate change.”
Write essays 2x faster with Paperpal. Try for free
Including background information in the introduction section of your essay is important to provide context and establish the relevance of your topic. When writing the background information, you can follow these steps:
- Start with a General Statement: Begin with a general statement about the topic and gradually narrow it down to your specific focus. For example, when discussing the impact of social media, you can begin by making a broad statement about social media and its widespread use in today’s society, as follows: “Social media has become an integral part of modern life, with billions of users worldwide.”
- Define Key Terms : Define any key terms or concepts that may be unfamiliar to your readers but are essential for understanding your argument.
- Provide Relevant Statistics: Use statistics or facts to highlight the significance of the issue you’re discussing. For instance, “According to a report by Statista, the number of social media users is expected to reach 4.41 billion by 2025.”
- Discuss the Evolution: Mention previous research or studies that have been conducted on the topic, especially those that are relevant to your argument. Mention key milestones or developments that have shaped its current impact. You can also outline some of the major effects of social media. For example, you can briefly describe how social media has evolved, including positives such as increased connectivity and issues like cyberbullying and privacy concerns.
- Transition to Your Thesis: Use the background information to lead into your thesis statement, which should clearly state the main argument or purpose of your essay. For example, “Given its pervasive influence, it is crucial to examine the impact of social media on mental health.”

A thesis statement is a concise summary of the main point or claim of an essay, research paper, or other type of academic writing. It appears near the end of the introduction. Here’s how to write a thesis statement:
- Identify the topic: Start by identifying the topic of your essay. For example, if your essay is about the importance of exercise for overall health, your topic is “exercise.”
- State your position: Next, state your position or claim about the topic. This is the main argument or point you want to make. For example, if you believe that regular exercise is crucial for maintaining good health, your position could be: “Regular exercise is essential for maintaining good health.”
- Support your position: Provide a brief overview of the reasons or evidence that support your position. These will be the main points of your essay. For example, if you’re writing an essay about the importance of exercise, you could mention the physical health benefits, mental health benefits, and the role of exercise in disease prevention.
- Make it specific: Ensure your thesis statement clearly states what you will discuss in your essay. For example, instead of saying, “Exercise is good for you,” you could say, “Regular exercise, including cardiovascular and strength training, can improve overall health and reduce the risk of chronic diseases.”
Examples of essay introduction
Here are examples of essay introductions for different types of essays:
Argumentative Essay Introduction Example:
Topic: Should the voting age be lowered to 16?
“The question of whether the voting age should be lowered to 16 has sparked nationwide debate. While some argue that 16-year-olds lack the requisite maturity and knowledge to make informed decisions, others argue that doing so would imbue young people with agency and give them a voice in shaping their future.”
Expository Essay Introduction Example
Topic: The benefits of regular exercise
“In today’s fast-paced world, the importance of regular exercise cannot be overstated. From improving physical health to boosting mental well-being, the benefits of exercise are numerous and far-reaching. This essay will examine the various advantages of regular exercise and provide tips on incorporating it into your daily routine.”
Text: “To Kill a Mockingbird” by Harper Lee
“Harper Lee’s novel, ‘To Kill a Mockingbird,’ is a timeless classic that explores themes of racism, injustice, and morality in the American South. Through the eyes of young Scout Finch, the reader is taken on a journey that challenges societal norms and forces characters to confront their prejudices. This essay will analyze the novel’s use of symbolism, character development, and narrative structure to uncover its deeper meaning and relevance to contemporary society.”
- Engaging and Relevant First Sentence : The opening sentence captures the reader’s attention and relates directly to the topic.
- Background Information : Enough background information is introduced to provide context for the thesis statement.
- Definition of Important Terms : Key terms or concepts that might be unfamiliar to the audience or are central to the argument are defined.
- Clear Thesis Statement : The thesis statement presents the main point or argument of the essay.
- Relevance to Main Body : Everything in the introduction directly relates to and sets up the discussion in the main body of the essay.
Write strong essays in academic English with Paperpal. Try it for free
Writing a strong introduction is crucial for setting the tone and context of your essay. Here are the key takeaways for how to write essay introduction: 3
- Hook the Reader : Start with an engaging hook to grab the reader’s attention. This could be a compelling question, a surprising fact, a relevant quote, or an anecdote.
- Provide Background : Give a brief overview of the topic, setting the context and stage for the discussion.
- Thesis Statement : State your thesis, which is the main argument or point of your essay. It should be concise, clear, and specific.
- Preview the Structure : Outline the main points or arguments to help the reader understand the organization of your essay.
- Keep it Concise : Avoid including unnecessary details or information not directly related to your thesis.
- Revise and Edit : Revise your introduction to ensure clarity, coherence, and relevance. Check for grammar and spelling errors.
- Seek Feedback : Get feedback from peers or instructors to improve your introduction further.
The purpose of an essay introduction is to give an overview of the topic, context, and main ideas of the essay. It is meant to engage the reader, establish the tone for the rest of the essay, and introduce the thesis statement or central argument.
An essay introduction typically ranges from 5-10% of the total word count. For example, in a 1,000-word essay, the introduction would be roughly 50-100 words. However, the length can vary depending on the complexity of the topic and the overall length of the essay.
An essay introduction is critical in engaging the reader and providing contextual information about the topic. To ensure its effectiveness, consider incorporating these key elements: a compelling hook, background information, a clear thesis statement, an outline of the essay’s scope, a smooth transition to the body, and optional signposting sentences.
The process of writing an essay introduction is not necessarily straightforward, but there are several strategies that can be employed to achieve this end. When experiencing difficulty initiating the process, consider the following techniques: begin with an anecdote, a quotation, an image, a question, or a startling fact to pique the reader’s interest. It may also be helpful to consider the five W’s of journalism: who, what, when, where, why, and how. For instance, an anecdotal opening could be structured as follows: “As I ascended the stage, momentarily blinded by the intense lights, I could sense the weight of a hundred eyes upon me, anticipating my next move. The topic of discussion was climate change, a subject I was passionate about, and it was my first public speaking event. Little did I know , that pivotal moment would not only alter my perspective but also chart my life’s course.”
Crafting a compelling thesis statement for your introduction paragraph is crucial to grab your reader’s attention. To achieve this, avoid using overused phrases such as “In this paper, I will write about” or “I will focus on” as they lack originality. Instead, strive to engage your reader by substantiating your stance or proposition with a “so what” clause. While writing your thesis statement, aim to be precise, succinct, and clear in conveying your main argument.
To create an effective essay introduction, ensure it is clear, engaging, relevant, and contains a concise thesis statement. It should transition smoothly into the essay and be long enough to cover necessary points but not become overwhelming. Seek feedback from peers or instructors to assess its effectiveness.
References
- Cui, L. (2022). Unit 6 Essay Introduction. Building Academic Writing Skills .
- West, H., Malcolm, G., Keywood, S., & Hill, J. (2019). Writing a successful essay. Journal of Geography in Higher Education , 43 (4), 609-617.
- Beavers, M. E., Thoune, D. L., & McBeth, M. (2023). Bibliographic Essay: Reading, Researching, Teaching, and Writing with Hooks: A Queer Literacy Sponsorship. College English, 85(3), 230-242.
Paperpal is a comprehensive AI writing toolkit that helps students and researchers achieve 2x the writing in half the time. It leverages 21+ years of STM experience and insights from millions of research articles to provide in-depth academic writing, language editing, and submission readiness support to help you write better, faster.
Get accurate academic translations, rewriting support, grammar checks, vocabulary suggestions, and generative AI assistance that delivers human precision at machine speed. Try for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime starting at US$19 a month to access premium features, including consistency, plagiarism, and 30+ submission readiness checks to help you succeed.
Experience the future of academic writing – Sign up to Paperpal and start writing for free!
Related Reads:
- How to Write a Good Hook for Essays, with Examples
- What is an Argumentative Essay? How to Write It (With Examples)
- How Long Should a Chapter Be?
- How to Use Paperpal to Generate Emails & Cover Letters?
Similarity Checks: The Author’s Guide to Plagiarism and Responsible Writing
Types of plagiarism and 6 tips to avoid it in your writing , you may also like, what is the purpose of an abstract why..., what are citation styles which citation style to..., what are the types of literature reviews , abstract vs introduction: what is the difference , mla format: guidelines, template and examples , machine translation vs human translation: which is reliable..., dissertation printing and binding | types & comparison , what is a dissertation preface definition and examples , how to write a research proposal: (with examples..., how to write your research paper in apa....
- Study Documents
- Learning Tools
Writing Guides
- Citation Generator
- Flash Card Generator
- Homework Help
- Essay Examples
- Essay Title Generator
- Essay Topic Generator
- Essay Outline Generator
- Flashcard Generator
- Plagiarism Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Conclusion Generator
- Thesis Statement Generator
- Introduction Generator
- Literature Review Generator
- Hypothesis Generator
- Human Editing Service
- Essay Hook Generator
Writing Guides / How to Write a Strong Essay Introduction with Examples
How to Write a Strong Essay Introduction with Examples

Introduction
An essay introduction establishes tone and sets course. Every journey starts with one—whether you’re getting on a plane, starting out a new school year, joining a new club, or moving to a new neighborhood. The introduction is the welcome mat: it tells a lot about the house you’re about to enter. A warm introduction will make the house seem inviting or the plane ride ahead more pleasurable. A bad introduction is off-putting and makes one want to turn and run away.
In essay writing, the introduction sets the tone and presents the argument, drawing readers in. It engages the reader with a question, an idea, a concept, a fact, a figure, a facet of life to consider.
An effective introduction grabs attention and establishes a connection with the reader. The importance of crafting a strong opening lies in its ability to establish clarity and spur engagement from the start.
What is an Essay Introduction?
An essay introduction is the first paragraph of an essay: it introduces the topic and the main idea of the essay. It may also provide minimal background information to set the stage for the essay body.
Its primary function is to give readers a clear understanding of what the paper will discuss and why it matters. It should lay out for the reader in no uncertain terms why this essay is worth the reader’s time.
In academic writing, the introduction frames the argument and guides the reader through the essay’s structure. It typically includes a hook to catch the reader with an inviting lure, which is then followed by a thesis statement that presents the main argument.
This section also acts as a roadmap, giving readers a sense of what is to come.
The overall point of the introduction is to welcome the reader, get him to want to stay (i.e., read on), give him a map of the house and grounds, and set him on his way. It is a logical way to show the reader upfront all that you are going to allow for his inspection. It is your frame for the picture you are about to unfold. It is your approach to the topic.
Why is the Introduction So Important?
The introduction of an essay is fundamental because it is the first impression the reader gets of your writing. A strong introduction engages readers by providing a point of interest, appropriate context, clarity of purpose, and a well-defined thesis. It pulls the audience in like a tractor beam, slowly but surely. The reader should feel some interest in seeing how the argument unfolds. If the intro doesn’t hold the reader, the essay won’t get read.
Research shows that a captivating introduction often correlates with an overall captivating finished product. In other words, if the essay starts off well, it is likely that the rest of the essay will be polished, too. The polished the parts, the better the odds of getting an A. Better intros equal better essays which equal better academic performance.
That is why we say crafting the essay introduction is like pouring the foundation for the home: you are setting the argument and building the body on that. To pour the foundation properly, you need to dig down a bit—and the same goes for an essay intro. Dig in, dig down, find a nice hard, firm place to set up your thesis and present your argument on the rock you establish.
Of course, this is all easier said than done. No matter what you construct, it is going to take some effort, know-how, skill, and enthusiasm for the project. Many writers struggle with introductions because they are lack something in one or more of those departments.
If you are struggling, the first thing to keep in mind is that the essay introduction must balance capturing attention with clearly presenting the argument. The introduction requires a level of precision that can be challenging to reach—but you can do it by distilling the main message of your essay and presenting it in a few concise words. A successful introduction ultimately frames the essay in a way that makes the reader want to invest in the content.
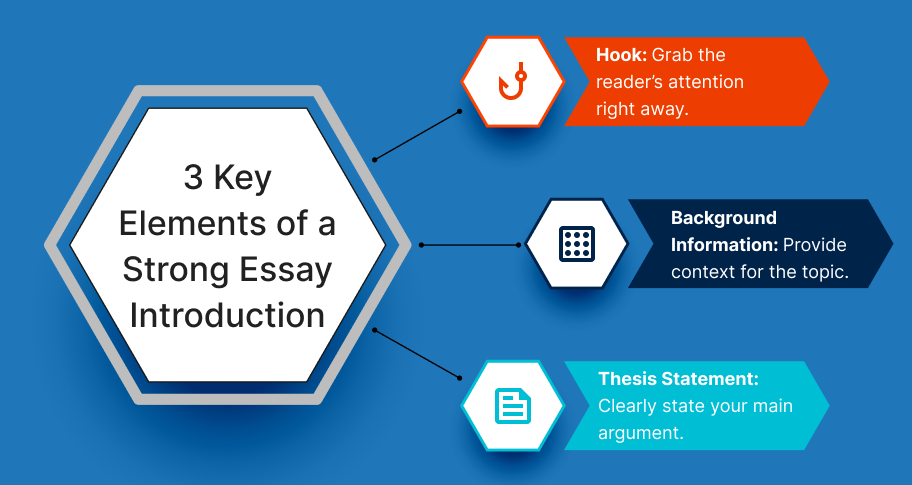
Elements of a Strong Essay Introduction
An effective essay introduction comprises several key components that work together to engage the reader and set the stage for a compelling argument. By carefully constructing each part, writers can create an introduction that is informative, engaging, and clear. Below are the critical elements of a strong essay introduction.
The hook is the first sentence(s) of an essay, and its ultimate function is to grab hold of the reader the way a newsflash bulletin would. A well-crafted hook is like a vortex: it pulls the readers thoughts into the essay, so that he is totally absorbed in the reading. It is essential to writing an intro for your essay because it is the first impression that determines whether the audience will stay engaged or lose interest.
A strong hook is thought-provoking, relevant to the topic, intriguing, and reflective of the essay’s tone and purpose. For example, a fact, anecdote, rhetorical question, or quotation can be used as a hook, depending on the type of essay being written.
Examples of Strong Hooks
- Fact : “According to a recent study, students who write a well-structured introduction score 20% higher on their essays.”
- Anecdote : “I remember the first time I struggled with an essay introduction; it was like trying to build a house without a blueprint.”
- Thought-Provoking Statement : “What if the secret to a great essay isn’t in the body but in the first few lines?”
- Rhetorical Question : “Have you ever wondered why some essays capture your attention instantly while others leave you bored?”
Examples of Weak Hooks
- Generic Statement : “Essays are important in school.”
- Obvious Fact : “People write essays for many reasons.”
- Vague Question : “Do you know how to write an essay?”
The difference between a strong and weak hook lies in the specificity and depth of engagement. Strong essay hooks give readers something to think about or connect to their emotions: they explode in their minds like fireworks and dazzle in the night sky. A weak hook merely states obvious or uninteresting facts: it is bland, boring, like a bowl of porridge, and might as well have gone unsaid in the first place for all the impact it made.

Background Information
After capturing the reader with a hook, the next step is to give some background information. Background info really depends on the audience: if your audience is not expected to know much at all about the subject, a broad overview can be most beneficial here. If your readership is already considered well-versed, you can segue into your thesis with minimal details and instead focus more on the reasons for which you will be making your argument. In general, definitions, historical context, or a brief overview of the topic can be fair game here. Basically, just give whatever the reader needs to know before diving into the main argument.
The challenge with providing background information is to strike a balance between offering enough context while not overwhelming the reader. Too much information can dilute the introduction and make it seem cluttered, but too little can leave the reader confused. The background should be relevant and directly related to the essay’s topic. Period.
Tips for Providing Background Information:
- Stay focused: Only include information that directly relates to the essay’s argument.
- Be concise: Keep the details brief and to the point, avoiding unnecessary tangents.
- Link to examples: If applicable, reference examples or sources that provide further reading for context, but don’t overload with too many external details.
For instance, in an essay about why Shakespeare’s Hamlet is a tragic figure, a writer might introduce the concept of tragedy as explained by Aristotle. This helps to set the stage and does not require a great deal of extraneous input. Proper context paves the way for the thesis statement, so that the reader is prepared to handle the topic.
The Thesis Statement
The thesis statement is the most essential part of any essay introduction. It is a single sentence (or sometimes two) that clearly states the essay’s main argument or point. The thesis statement gives the reader a sense of what the essay aims to do. It plainly tells the purpose and explains how the content will be structured. Without a clear thesis statement, the essay can seem directionless, and the reader may struggle to understand the writer’s point.
A strong thesis statement is specific, concise, and also debatable. That means it should present a point of view that can be supported by evidence and analysis in the essay’s body but that the reader might not agree with initially.
Examples of Strong Thesis Statements:
- Specific : “The rise of social media has challenged the role of legacy media in delivering news, information, and entertainment by democratizing the way people create and share content.”
- Debatable : “While some hold that standardized curriculum is necessary for national education, the reality is that education should vary from place to place and state to state based on culture, needs, and goals of the people there.”
- Clear : “If authorities want to reduce mass shootings and improve public safety, they need to address the cultural, spiritual and mental health crisis in America—not simply propose more gun laws.”
Examples of Weak Thesis Statements:
- Too Broad : “Social media has had a big impact on society.”
- Vague : “There are many arguments about standardized testing.”
- Obvious : “Gun control is a controversial topic.”
View 120,000+ High Quality Essay Examples
Learn-by-example to improve your academic writing
How to Structure Your Essay Introduction
Here’s how you can structure an introduction effectively, adjust it based on essay type, make sure its length is appropriate, and craft a smooth transition into the main body of your paper.
General Structure
The traditional structure of an essay introduction has three components: a Hook, Background Information, and a Thesis Statement.
- Hook : The hook is the first sentence or few sentences that grab the reader’s attention. It could be an interesting fact, a rhetorical question, a surprising statistic, or a quote. The goal is to engage the reader and spark curiosity about your topic.
- Background Information : After the hook, give some context or background information on the topic you’re writing about. This helps the reader understand the significance of the issue and prepares the reader for the thesis. Depending on the level of knowledge of the audience, the background could be brief or more elaborate.
- Thesis Statement : The thesis is the most important part of your introduction as it clearly states what your essay will be about, how it will proceed, and what your agument or point is. It should be as concise as possible and direct. It can be supported by a brief outline of the main points that will be explored in the essay.
Adjusting the Structure for Different Essay Types
- Argumentative Essay : In an argumentative essay, the introduction should provide a clear thesis that takes a stance on the issue. The background should include opposing viewpoints to set the stage for your argument.
- Expository Essay : For expository essays, the introduction should focus on explaining the topic in a neutral manner, with the thesis outlining what you aim to explain or analyze.
- Narrative Essay : A narrative essay introduction might begin with a personal anecdote or story as the hook, followed by setting the scene, and leading into the thesis or main point of the narrative.
- Descriptive Essay : In a descriptive essay, the hook will rely on vivid imagery that engages the senses, while the background introduces the subject that will be described in detail.
Length of an Introduction
The length of your introduction really depends on the overall length of your essay. As a general rule:
- Short Essays (500-1000 words) : The introduction should be around 50 to 100 words, comprising about 10% of the essay. You can include a brief hook, followed by a concise background and thesis statement.
- Medium-Length Essays (1000-3000 words) : The introduction should be 100-150 words, providing a slightly more detailed background to help the reader grasp the topic’s context.
- Long Essays (3000+ words) : For longer essays, the introduction can span 150-250 words, with a more detailed background and multiple hooks to gradually introduce the thesis.
No matter the length, it’s important to maintain a balance between brevity and clarity, so that your introduction is engaging but not overwhelming.
How to Transition into the Main Body
Transitioning smoothly from your introduction to the main body of the essay is necessary for maintaining flow. A common technique is to end your introduction with a transition sentence that connects the thesis to the first body paragraph.
This transition sentence should hint at the first point or argument you will explore in the essay’s body. Using it allows you to create a logical progression from the general idea presented in your thesis to the specific details in the body paragraphs. For example, if your thesis mentions several factors, your transition sentence can introduce the first factor in more depth. Alternatively, you can use transitional phrases such as “To begin with,” “Firstly,” or “The first aspect to consider” to guide the reader into the next section.
Effective transitions not only keep your writing coherent but also help the reader understand the direction your essay will take from the very start.

Common Mistakes in Writing Essay Introductions
Many writers fall into common traps that can undermine the effectiveness of their opening. Avoiding these mistakes will keep your introduction clear, engaging, and purposeful.
Being Too Vague
One of the most common mistakes in writing an essay introduction is being too vague or general. A vague introduction will lose the reader’s interest because it will seem that the essay has no apparent point. When the introduction lacks focus, the reader assumes the rest of the essay does as well.
For example, starting with a broad statement like “Many people write essays” doesn’t tell the reader much about the specific argument or issue you plan to address. Instead, your introduction should immediately indicate the relevance of your topic and narrow down to your main point. Engage the reader with a clear, focused hook and relevant context to gain and maintain their interest. Remember, readers want to know what your essay is about right from the start, so avoid being overly general or vague.

Overloading with Background Information
Another common mistake is including too much background information in the introduction. While some context is necessary to set up the thesis, overloading your introduction with excessive details can exhaust the reader’s patience. Introductions that turn into a history lessons or a detailed expositions rob the main argument of its impact.
For instance, if you’re writing an argumentative essay on the Civil War, there’s no need to bring up the Federalist Papers—unless, of course, it relates directly to your thesis. Nonetheless, the intro should focus on the most relevant background information needed to understand the thesis. The rest of the essay is where you can go into details. Keep the introduction concise. Background information only needs to be a bridge to the thesis.
Forgetting the Thesis Statement
A big but common mistake in writing introductions is forgetting to include the thesis statement. Most writers do this simply because they themselves don’t know what their point is. Take time to consider it. The thesis is the end goal of your essay—the point it is all about. Without it, the introduction and the essay overall will lack direction and will leave the reader uncertain about the essay’s purpose.
A strong thesis should clearly state your position or the points you’ll discuss in the essay. Omitting it would be like inviting your friends to a dinner and then forgetting to cook the food.

Examples of Effective Essay Introductions
Here are some examples of essay introductions to help you see how they can be crafted.
Argumentative Essay Introduction
Topic: Should the Death Penalty Be Abolished? “The debate surrounding the death penalty has been ongoing for decades, with proponents claiming it deters crime and serves justice, while opponents argue that it violates fundamental human rights. As we move further into the 21st century, questions about the morality, fairness, and effectiveness of capital punishment have become more pressing. This essay will argue that the death penalty should be abolished, not only because of its failure as a deterrent but also due to the irreversible nature of wrongful executions and the disproportionate impact on marginalized communities.”
Why It Works: This introduction hooks the reader by presenting the ongoing debate, then clearly states the position the essay will argue, making it easy to follow and engage with.
Expository Essay Introduction
Topic: The Invention of the Printing Press “The invention of the printing press in 1440 by Johannes Gutenberg was a turning point in European history. For the first time, books could be mass-produced, leading to the spread of ideas, the democratization of knowledge, and significant social, religious, and cultural shifts. This essay will explore the impact of Gutenberg’s invention on society, including its role in the Protestant Reformation and the broader intellectual awakening known as the Renaissance.”
Why It Works: The introduction provides relevant historical context, establishes the importance of the topic, and outlines what the essay will cover, making it easy for readers to understand the scope of the discussion.
Narrative Essay Introduction
Topic: A Lesson Learned from Failure “I’ll never forget the moment I heard my name announced as the runner-up in the statewide debate competition. It wasn’t the disappointment of losing that stuck with me, but the realization that my failure was entirely my own doing. In the weeks leading up to the event, I had neglected to properly prepare, overconfident in my abilities. This experience taught me the value of hard work and humility, and it forever changed the way I approach challenges in life.”
Why It Works: This introduction draws the reader into a personal story, immediately engaging them with a relatable experience. It sets up the main theme of the essay—personal growth through failure.
Descriptive Essay Introduction
Topic: A Childhood Memory “The scent of freshly baked cookies always transports me back to my grandmother’s kitchen. The warm, sugary aroma combined with the gentle hum of the oven and the soft clink of the cookie sheet against the countertop brings a wave of nostalgia. The kitchen, bathed in soft afternoon light, was my childhood haven, a place of safety, love, and the simple joy of baking. This essay will take you through that cherished memory, capturing the sights, sounds, and smells that made it so unforgettable.”
Why It Works: The use of vivid sensory details immediately creates a strong image in the reader’s mind, engaging their senses and emotions. It sets the stage for a descriptive exploration of a meaningful memory.
Hopefully, these essay introduction examples have given you an idea of what works, why, and how. Let’s recap what we’ve learned!
Essay Introductions FAQ
- This varies based on the overall length of the essay. For shorter essays (500–1000 words), the introduction should be about 10% of the total word count, while for longer essays, you may need a more detailed introduction, especially if complex background information is required. If the essay is 3000 words or more, try to keep the introduction somewhere around 200-250 words.
- Yes, starting with a rhetorical question can be a powerful hook, as long as it engages the reader and relates to the essay’s topic. Make sure it fits the tone of the essay and doesn’t sound too informal or out of place in academic writing. Also make sure it is relevant to your essay’s thesis.
- A hook is meant to grab the reader’s attention in the first sentence, while a thesis statement presents the central argument or purpose of the essay, typically at the end of the introduction. The two should relate somehow, though—usually the hook reflects some aspect of the thesis that you will be defending.
- Yes, using a relevant quote can be an effective hook, but make sure it directly ties into your essay’s topic. Avoid overused or clichéd quotes that don’t add value to your argument. And always cite the source if you do use a quote.
Mastering your essay introduction involves carefully balancing three key elements: the hook, background information, and thesis statement. The hook grabs the reader’s attention, the background provides needed context (but doesn’t overwhelm with too many details), and the thesis clearly outlines the main argument and direction of the essay. Avoid common pitfalls like being too vague, overloading the introduction with unnecessary information, or forgetting the thesis.
Strong introductions set the tone for a well-structured essay and guide the reader effortlessly into the main body. The more you practice writing introductions, the better you’ll become at creating clear, engaging, and effective openings. Continuously refining these skills will not only strengthen your essays but also ensure your readers are hooked from the very start. Remember, a powerful introduction lays the foundation for a compelling essay!
Make sure you download our essay introduction worksheet , to help get you started.
Take the first step to becoming a better academic writer.
Writing tools.
- How to write a research proposal 2021 guide
- Guide to citing in MLA
- Guide to citing in APA format
- Chicago style citation guide
- Harvard referencing and citing guide
- How to complete an informative essay outline

How to Choose the Best Essay Topics

AI Text Detection Services

Unlock Your Writing Potential with Our AI Essay Writing Assistant

The Negative Impacts of Artificial Intelligence on Tactile Learning

Writing an Informative Essay
Informative essays engage readers with new, interesting, and often surprising facts and details about a subject. Informative essays are educational; readers expect to learn something new from them. In fact, much of the reading and writing done in college and the workplace is informative. From textbooks to reports to tutorials like this one, informative writing imparts important and useful information about a topic.
This tutorial refers to the sample informative outline and final essay written by fictional student Paige Turner.
Reasons to Write Informatively
Your purpose for writing and the audience for whom you are writing will impact the depth and breadth of information you provide, but all informative writing aims to present a subject without opinions or bias. Some common reasons to write informatively are to
- report findings that an audience would find interesting,
- present facts that an audience would find useful, and
- communicate information about a person, place, event, issue, or change that would improve an audience’s understanding.
Characteristics of Informative Essays
Informative essays present factual information and do not attempt to sway readers’ opinions about it. Other types of academic and workplace writing do try to influence readers’ opinions:
- Expository essays aim to expose a truth about an issue in order to influence how readers view the issue.
- Persuasive essays aim to influence readers’ opinions, so they will adopt a particular position or take a certain course of action.
Expository and persuasive essays make “arguments.” The only argument an informative essay makes is that something exists, did exist, is happening, or has happened, and the point of the essay is not to convince readers of this but to tell them about it.
- Informative essays seek to enlighten and educate readers, so they can make their own educated opinions and decisions about what to think and how to act.
Strategies for Writing Informatively
Informative essays provide useful information such as facts, examples, and evidence from research in order to help readers understand a topic or see it more clearly. While informative writing does not aim to appeal emotionally to readers in order to change their opinions or behaviors, informative writing should still be engaging to read. Factual information is not necessarily dry or boring. Sometimes facts can be more alarming than fiction!
Writers use various strategies to engage and educate readers. Some strategies include
- introducing the topic with an alarming fact or arresting image;
- asserting what is true or so about the subject in a clear thesis statement;
- organizing the paragraphs logically by grouping related information;
- unifying each paragraph with a topic sentence and controlling idea;
- developing cohesive paragraphs with transition sentences;
- using precise language and terminology appropriate for the topic, purpose, and audience; and
- concluding with a final idea or example that captures the essay’s purpose and leaves a lasting impression.
Five Steps for Getting Started
1. Brainstorm and choose a topic.
- Sample topic : The opioid epidemic in the United States.
- The opiod epidemic or even opiod addiction would would be considered too broad for a single essay, so the next steps aim to narrow this topic down.
2. Next, write a question about the topic that you would like to answer through research.
- Sample question : What major events caused the opioid crisis in the United States?
- This question aims to narrow the topic down to causes of the epidemic in the US.
3. Now go to the Purdue Global Library to find the answers to your research question.
As you begin reading and collecting sources, write down the themes that emerge as common answers. Later, in step four, use the most common answers (or the ones you are most interested in writing and discussing) to construct a thesis statement.
- Sample answers: aggressive marketing, loopholes in prescription drug provider programs, and economic downturn.
4. Next, provide purpose to your paper by creating a thesis statement.
The thesis attempts to frame your research question. The sample thesis below incorporates three of the more common answers for the research question from step two: What caused the opioid crisis in the United States?
- Thesis Statement : Aggressive marketing, loopholes in prescription drug provider programs, and economic downturn contributed to the current opioid crisis in the United States.
- Writing Tip : For additional help with thesis statements, please visit our Writing a Thesis Statement article. For help with writing in 3rd person, see our article on Formal Vs. Informal Writing .
5. Now follow each numbered step in the “Suggested Outline Format and Sample” below.
Sample answers have been provided for “I. Introduction” and “II. First Cause.” A complete sample outline can be seen here. A complete sample informative essay can be seen here.
Suggested Outline Format and Sample
I. INTRODUCTION
A. First provide a topic sentence that introduces the main topic: Sample topic sentence : There is a current prescription pain medication addiction and abuse epidemic possibly caused by an excessive over prescription of these medications.
B. Now provide a couple sentences with evidence to support the main topic: Sample sentence one with evidence to support the main topic : According to Dr. Nora Volkow, Director of National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA), in testimony before the 115th Congress, “In 2016, over 11 million Americans misused prescription opioids … and 2.1 million had an opioid use disorder due to prescription opioids” (Federal Efforts to Combat the Opioid Crisis, 2017, p. 2).
C. Sample sentence two with evidence to support the main topic : Volkow indicated “more than 300,000 Americans have died of an opioid overdose” since 2013 (Federal Efforts to Combat the Opioid Crisis, 2017, p.2).
D. Sample sentence three with evidence to support the main topic : According to Perez-Pena (2017), the Center for Disease Control and Prevention reported more than 25,000 people in the United States died in 2015 from overdosing on opioids Fentanyl, Oxycodone, and Hydrocodone.
E. Toward the end of the introduction, include your thesis statement written in the 3rd-person point-of-view: Sample thesis statement : Potential solutions to the growing opioid epidemic may be illuminated by examining how opioid addiction is triggered through aggressive pharmaceutical marketing, how opioid addiction manifests among prescribed patients, and how economic downturns play a role in the increase of opioid addiction.
F. Write down the library sources you can use in this introductory paragraph to help support the main topic.
- Federal Efforts to Combat the Opioid Crisis, 2017
- Perez-Pena, 2017
- Writing Tip : For more help writing an introduction, please refer to this article on introductions and conclusions .
II. FIRST CAUSE
A. First provide a topic sentence that introduces the first cause of the opioid epidemic: Sample topic sentence that introduces the first cause : One issue that helped contribute to the opioid epidemic is aggressive marketing by pharmaceutical manufacturers.
B. Now provide sentences with evidence to support the first cause: Sample sentence one with evidence that supports the first cause : Perez-Pena (2017) concluded that while the healthcare industry was attempting to effectively and efficiently treat patients with chronic pain, pharmaceutical companies were providing funding to prominent doctors, medical societies, and patient advocacy groups in order to win support for a particular drug’s adoption and usage.
C. Sample sentence two with evidence to support the first cause : In fact, pharmaceutical companies continue to spend millions on promotional activities and materials that deny or trivialize any risks of opioid use while at the same time overstating each drug’s benefit (Perez-Pina, 2017).
D. Next, add more information or provide concluding or transitional sentences that foreshadows the upcoming second cause: Sample concluding and transitional sentence that foreshadow the second cause : Although aggressive marketing by pharmaceutical companies played a large role in opioid addiction, patients are to blame too, as many take advantage of holes in the healthcare provider system in order to remedy their addiction.
E. Write down the library sources you can use in this body paragraph to help support the first cause:
- Writing Tip : For more assistance working with sources, please visit the Using Sources page here.
III. SECOND CAUSE
A. First provide a topic sentence that introduces the second cause.
B. Now provide sentences with evidence to support the second cause.
C. Next, add more information or provide concluding or transitional sentences that foreshadows the upcoming third cause.
D. Write down the library sources you can use in this body paragraph to help support the second cause:
- Writing Tip : Listen to Writing Powerful Sentences for information and features of effective writing.
IV. THIRD CAUSE
A. First provide a topic sentence that introduces the third cause.
B. Now provide sentences with evidence to support the third cause.
C. Next, add more information or provide a concluding sentence or two.
D. Write down the library sources you can use in this body paragraph to help support the third cause:
V. CONCLUSION: Summary of key points and evidence discussed.
- Writing Tip : For more help writing a conclusion, refer to this podcast on endings .
- Writing Tip : Have a question? Leave a comment below or Purdue Global students, click here to access the Purdue Global Writing Center tutoring platform and available staff.
- Writing Tip : Ready to have someone look at your paper? Purdue Global students, click here to submit your assignment for feedback through our video paper review service.
See a Sample Informative Essay Outline here .
See a sample informative essay here., share this:.
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window)
- Click to print (Opens in new window)
2 Responses
- Pingbacks 0
dang bro i got an A
Having faith with all this mentioned, that i will pass my english class at a college. Thank you for posting.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Follow Blog via Email
Enter your email address to follow this blog and receive email notifications of new posts.
Email Address
- RSS - Posts
- RSS - Comments
- COLLEGE WRITING
- USING SOURCES & APA STYLE
- EFFECTIVE WRITING PODCASTS
- LEARNING FOR SUCCESS
- PLAGIARISM INFORMATION
- FACULTY RESOURCES
- Student Webinar Calendar
- Academic Success Center
- Writing Center
- About the ASC Tutors
- DIVERSITY TRAINING
- PG Peer Tutors
- PG Student Access
Subscribe to Blog via Email
Enter your email address to subscribe to this blog and receive notifications of new posts by email.
- College Writing
- Using Sources & APA Style
- Learning for Success
- Effective Writing Podcasts
- Plagiarism Information
- Faculty Resources
- Tutor Training
Twitter feed

IMAGES
VIDEO