How to Use Footnotes in Research Papers
edfuentesg / Getty Images
- An Introduction to Punctuation
- Ph.D., Rhetoric and English, University of Georgia
- M.A., Modern English and American Literature, University of Leicester
- B.A., English, State University of New York
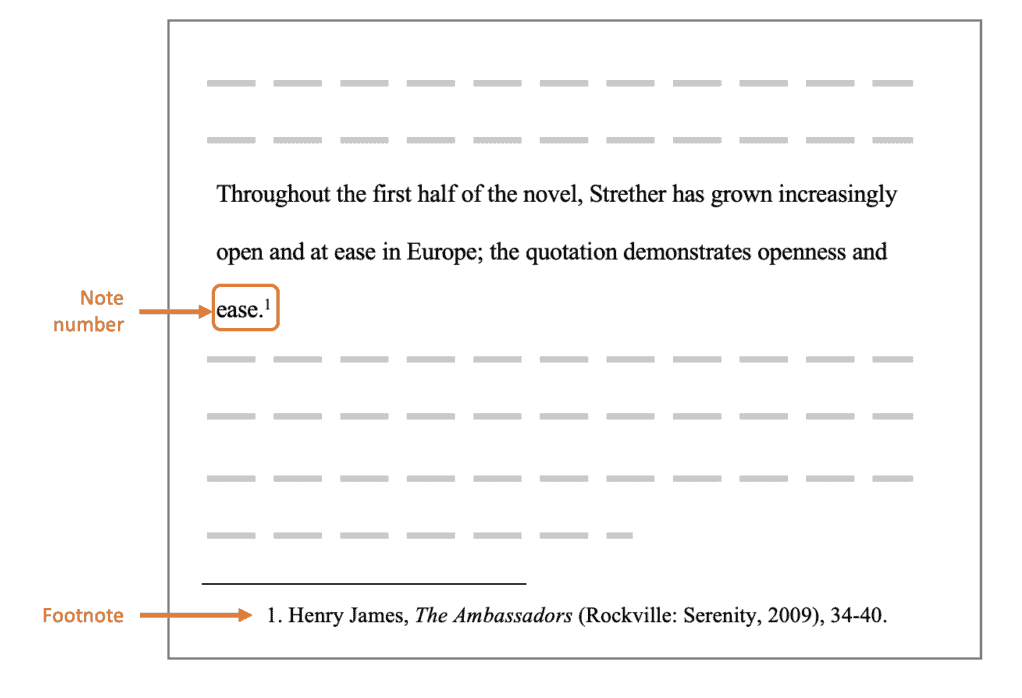
A footnote is a reference, explanation, or comment 1 placed below the main text on a printed page. Footnotes are identified in the text by a numeral or a symbol .
In research papers and reports , footnotes commonly acknowledge the sources of facts and quotations that appear in the text.
" Footnotes are the mark of a scholar," says Bryan A. Garner. "Overabundant, overflowing footnotes are the mark of an insecure scholar — often one who gets lost in the byways of analysis and who wants to show off" ( Garner's Modern American Usage , 2009).

Examples and Observations
- " Footnotes: vices . In a work containing many long footnotes, it may be difficult to fit them onto the pages they pertain to, especially in an illustrated work."
- " Content footnotes supplement or simplify substantive information in the text; they should not include complicated, irrelevant, or nonessential information..." " Copyright permission footnotes acknowledge the source of lengthy quotations, scale and test items, and figures and tables that have been reprinted or adapted."
- Content Footnotes "What, after all, is a content footnote but material that one is either too lazy to integrate into the text or too reverent to discard? Reading a piece of prose that constantly dissolves into extended footnotes is profoundly disheartening. Hence my rule of thumb for footnotes is exactly the same as that for parentheses . One should regard them as symbols of failure. I hardly need to add that in this vale of tears failure is sometimes unavoidable."
- Footnote Forms All notes have the same general form: 1. Adrian Johns. The Nature of the Book: Print and Knowledge in the Making (Chicago: University of Chicago Press, 1998), 623. If you cite the same text again, you can shorten subsequent notes: 5. Johns. Nature of the Book , 384-85.
- The Disadvantages of Footnotes "More than one recent critic has pointed out that footnotes interrupt a narrative . References detract from the illusion of veracity and immediacy . . . . (Noel Coward made the same point more memorably when he remarked that having to read a footnote resembles having to go downstairs to answer the door while in the midst of making love.)"
- Belloc on Footnotes "[L]et a man put his foot-notes in very small print indeed at the end of a volume, and, if necessary, let him give specimens rather than a complete list. For instance, let a man who writes history as it should be written — with all the physical details in evidence, the weather, the dress, colors, everything — write on for the pleasure of his reader and not for his critic. But let him take sections here and there, and in an appendix show the critic how it is being done. Let him keep his notes and challenge criticism. I think he will be secure. He will not be secure from the anger of those who cannot write clearly, let alone vividly, and who have never in their lives been able to resurrect the past, but he will be secure from their destructive effect."
- The Lighter Side of Footnotes "A footnote is like running downstairs to answer the doorbell on your wedding night."
1 "The footnote has figured prominently in the fictions of such leading contemporary novelists as Nicholson Baker 2 , David Foster Wallace 3 , and Dave Eggers. These writers have largely revived the digressive function of the footnote." (L. Douglas and A. George, Sense and Nonsensibility: Lampoons of Learning and Literature . Simon and Schuster, 2004)
2 "[T]he great scholarly or anecdotal footnotes of Lecky, Gibbon, or Boswell, written by the author of the book himself to supplement, or even correct over several later editions, what he says in the primary text, are reassurances that the pursuit of truth doesn't have clear outer boundaries: it doesn't end with the book; restatement and self-disagreement and the enveloping sea of referenced authorities all continue. Footnotes are the finer-suckered surfaces that allow tentacular paragraphs to hold fast to the wider reality of the library." (Nicholson Baker, The Mezzanine . Weidenfeld and Nicholson, 1988)
3 "One of the odd pleasures in reading the work of the late David Foster Wallace is the opportunity to escape from the main text to explore epic footnotes , always rendered at the bottoms of pages in thickets of tiny type." (Roy Peter Clark, The Glamour of Grammar . Little, Brown, 2010)
- Hilaire Belloc, On , 1923
- Chicago Manual of Style , University of Chicago Press, 2003
- Anthony Grafton, The Footnote: A Curious History . Harvard University Press, 1999.
- Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association , 6th ed., 2010.
- Paul Robinson, "The Philosophy of Punctuation." Opera, Sex, and Other Vital Matters . University of Chicago Press, 2002.
- Kate Turabian, A Manual for Writers of Research Papers, Theses, and Dissertations , 7th ed. University of Chicago Press, 2007 .
- What Are Endnotes, Why Are They Needed, and How Are They Used?
- What Is a Style Guide and Which One Do You Need?
- What's the Preferred Way to Write the Abbreviation for United States?
- What Is a Research Paper?
- Justification (Typesetting and Composition)
- Definition and Examples of Asterisks (*)
- Documentation in Reports and Research Papers
- An Introduction to Academic Writing
- What Is a Citation?
- Margin (Composition Format) Definition
- Thesis: Definition and Examples in Composition
- Characteristics of a Formal Prose Style
- How to Use Block Quotations in Writing
- Definition of Appendix in a Book or Written Work
- Cite, Sight, and Site
- Bibliography: Definition and Examples

How to Format Your Research Paper
- APA 7 Paper Format
- MLA Paper Format
- Chicago Paper Format
How to Create Footnotes
- Hanging Indents
- Ask a Librarian
What Are They
Footnotes are short numbered notes that are placed at the bottom of the page in an essay or article. They are used for a variety of reasons including, citing materials, providing notes on a source or topic, and to acknowledge copyright status.
Although you will find footnotes in many journal articles, they are not typically required in APA or MLA formatted essays. They are most heavily used when applying the CMOS style.
For information on footnotes in the Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association see section 2.13 "Footnotes.". For information on using footnotes with MLA see the " Using Notes in MLA Style " article from the MLA Style Center . For information on footnotes in The Chicago Manual of Style see Chapter 14 "Notes and Bibliography."
Using Google Docs:
- Cómo incorporar notas al calce en Google Docs Vea éste video en español.
Using Microsoft Word:
- Cómo incorporar notas al calce en Microsoft Word Vea éste video en español.
- << Previous: Chicago Paper Format
- Next: Hanging Indents >>
- Last Updated: Jul 19, 2024 3:41 PM
- URL: https://necc.mass.libguides.com/formatting
To cite this LibGuide use the following templates:
APA : Northern Essex Community College Library. (Date updated). Title of page . Title of LibGuide. URL
MLA : Northern Essex Community College Library. "Title of Page." Title of LibGuide, Date updated, URL.
- USC Libraries
- Research Guides
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Reading Research Effectively
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Applying Critical Thinking
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Research Process Video Series
- Executive Summary
- The C.A.R.S. Model
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tiertiary Sources
- Scholarly vs. Popular Publications
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Insiderness
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Writing Concisely
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Further Readings
- Generative AI and Writing
- USC Libraries Tutorials and Other Guides
- Bibliography
Endnote Note citing a particular source or making a brief explanatory comment placed at the end of a research paper and arranged sequentially in relation to where the reference appears in the paper.
Footnote Note citing a particular source or making a brief explanatory comment placed at the bottom of a page corresponding to the item cited in the corresponding text above.
Fiske, Robert Hartwell. To the Point: A Dictionary of Concise Writing . New York: W.W. Norton and Company, 2014.
Structure and Writing Style
Advantages of Using Endnotes
- Endnotes are less distracting to the reader and allows the narrative to flow better.
- Endnotes don't clutter up the page.
- As a separate section of a research paper, endnotes allow the reader to read and contemplate all the notes at once.
Disadvantages of Using Endnotes
- If you want to look at the text of a particular endnote, you have to flip to the end of the research paper to find the information.
- Depending on how they are created [i.e., continuous numbering or numbers that start over for each chapter], you may have to remember the chapter number as well as the endnote number in order to find the correct one.
- Endnotes may carry a negative connotation much like the proverbial "fine print" or hidden disclaimers in advertising. A reader may believe you are trying to hide something by burying it in a hard-to-find endnote.
Advantages of Using Footnotes
- Readers interested in identifying the source or note can quickly glance down the page to find what they are looking for.
- It allows the reader to immediately link the footnote to the subject of the text without having to take the time to find the note at the back of the paper.
- Footnotes are automatically included when printing off specific pages.
Disadvantages of Using Footnotes
- Footnotes can clutter up the page and, thus, negatively impact the overall look of the page.
- If there are multiple columns, charts, or tables below only a small segment of text that includes a footnote, then you must decide where the footnotes should appear.
- If the footnotes are lengthy, there's a risk they could dominate the page, although this issue is considered acceptable in legal scholarship.
- Adding lengthy footnotes after the paper has been completed can alter the page where other sources are located [i.e., a long footnote can push text to the next page].
- It is more difficult learning how to insert footnotes using your word processing program than simply adding endnotes at the end of your paper.
Things to keep in mind when considering using either endnotes or footnotes in your research paper :
1. Footnotes are numbered consecutively throughout a research paper, except for those notes accompanying special material (e.g., figures, tables, charts, etc.). Numbering of footnotes are "superscript"--Arabic numbers typed slightly above the line of text. Do not include periods, parentheses, or slashes. They can follow all punctuation marks except dashes. In general, to avoid interrupting the continuity of the text, footnote numbers are placed at the end of the sentence, clause, or phrase containing the quoted or paraphrased material. 2. Depending on the writing style used in your class, endnotes may take the place of a list of resources cited in your paper or they may represent non-bibliographic items, such as comments or observations, followed by a separate list of references to the sources you cited and arranged alphabetically by the author's last name. If you are unsure about how to use endnotes, consult with your professor. 3. In general, the use of footnotes in most academic writing is now considered a bit outdated and has been replaced by endnotes, which are much easier to place in your paper, even with the advent of word processing programs. However, some disciplines, such as law and history, still predominantly utilize footnotes. Consult with your professor about which form to use and always remember that, whichever style of citation you choose, apply it consistently throughout your paper.
NOTE: Always think critically about the information you place in a footnote or endnote. Ask yourself, is this supplementary or tangential information that would otherwise disrupt the narrative flow of the text or is this essential information that I should integrate into the main text? If you are not sure, it's better to work it into the text. Too many notes implies a disorganized paper.
Cermak, Bonni and Jennifer Troxell. A Guide to Footnotes and Endnotes for NASA History Authors . NASA History Program. History Division; Hale, Ali. Should You Use Footnotes or Endnotes? DailyWritingTips.com; Tables, Appendices, Footnotes and Endnotes. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University; Lunsford, Andrea A. and Robert Connors. The St. Martin's Handbook . New York: St. Martin's Press, 1989; Saller, Carol. “Endnotes or Footnotes? Some Considerations.” The Chronicle of Higher Education 58 (January 6, 2012): http://chronicle.com/blogs/linguafranca/2012/01/06/endnotes-or-footnotes-some-considerations/.
- << Previous: Avoiding Plagiarism
- Next: Further Readings >>
- Last Updated: Aug 21, 2024 8:54 AM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide
Educational resources and simple solutions for your research journey

What are Footnotes and How to Use Them for Research?
The research process is inherently collaborative, involving the analysis of the collective body of knowledge developed over time. It is academically and ethically vital to acknowledge others’ contributions. Footnotes serve as subtle markers of acknowledgment while also providing supplementary details to enhance the reader’s understanding and engagement with your work.
Table of Contents
What are footnotes?
During your research, you’ll encounter inconspicuous superscript numbers at the end of some sentences, which link to corresponding notes at the page’s bottom or ‘foot.’ These notes serve as references to cited works and offer supplementary information to aid the reader’s understanding.
It’s important to note that not all references and supplementary notes are at the bottom of the page; some are placed at the end of the research paper as “endnotes.” This doesn’t lessen their significance; they still offer valuable context and insights.
Footnotes vs Endnotes
Footnotes and endnotes fulfill the same fundamental purpose in scholarly writing. However, the choice between them often reflects an author’s personal preference or aligns with specific style guidelines. Footnotes are frequently utilized for immediate comments or explanations related to the main text. On the other hand, endnotes are commonly reserved for citations of the works referenced within the text.
Let’s examine footnotes and endnotes more closely to understand the distinctions between these two citation methods:
Footnotes are highly effective due to their ease of access and their ability to direct readers to relevant citations or supplementary ideas swiftly. This approach increases the likelihood that readers will engage with the citation or additional information. However, the limited space at the bottom of the page necessitates caution. Overloading it with excessive other text can be overwhelming and potentially distracting for readers.
Endnotes, in contrast, offer the advantage of being located at the end of a paper within a designated section, giving authors the freedom to incorporate supplementary information liberally without the need to use up the limited space on a page. However, endnotes are often overlooked by readers. This oversight can be attributed to a mental justification that if information is not included in the main text, it may not hold significant value.¹²
Footnote Citation Styles
Incorporating footnotes into your research paper is crucial, but it’s equally important to grasp the specific footnote citation style required by your target journal or publication. The format and style of footnote citations can differ significantly based on the citation style guide in use. Below, you’ll find illustrative examples of how to use footnotes in essays according to the central style guides:¹
Chicago Style
The Chicago Style uses footnotes to provide full source details in the form of numbered notes at the bottom of each page. A corresponding bibliography is provided at the end of the research essay or document. Here is an example:
“The Apollo program was designed by men, for men. If we do not acknowledge the gender bias of the early space program, it becomes difficult to move past it.” ¹
1.1 Mary Robinette Kowal, To Make It to the Moon, Women Have to Escape Earth’s Gender Bias (New York Times, 17 July 1969).
In this example, the superscript “1” in the text corresponds to the first footnote, which provides complete source information for an article by Mary Robinette Kowal in The New York Times.
Modern Language Association (MLA) Style
The MLA Style does not typically use footnotes for citations. Instead, it relies on in-text citations with an author-page number format. However, the footnotes might be utilized for explanatory or supplementary information. Example:
“The protagonist’s transformation throughout the novel is central to its theme and character development.” 1
1 This analysis draws on the ideas of literary critic John Smith regarding character evolution in narrative fiction.
In this example, the superscript “1” in the main text points to a footnote that offers additional context and acknowledges the source, i.e., John Smith’s ideas.
American Psychological Association (APA) Style
APA Style typically uses in-text citations rather than footnotes. However, you may use footnotes for clarifications or additional information, not for standard source citations. Here is an example:
“The study’s results revealed a statistically significant correlation between the two variables^1^.”
^1^ Note that the p-value was set at 0.05 as the threshold for statistical significance.
In the example, the superscript “^1^” in the main text indicates a footnote, which is used to provide a brief explanation.
How to add Footnotes in Microsoft Word and Google Docs?
So, how do you make footnotes? Adding footnotes in both Microsoft Word and Google Docs is a straightforward process. Step-by-step instructions are provided below for adding footnotes in both applications:
Microsoft Word
- Position your cursor where you want to insert a footnote in the document.
- Navigate to the “References” tab and click on the “Insert Footnote” button.
- A small superscript number (typically “1”) will appear where you positioned the cursor, and a corresponding footnote area will appear at the bottom of the page. Enter your footnote content in this designated area.
- To insert additional footnotes, repeat the same steps. Microsoft Word will automatically manage the numbering of footnotes. (4)
Google Docs
- Place the cursor at the location where you wish to insert a footnote.
- In the menu bar, click on “Insert” and select “Footnote.”
- A superscript number (usually “1”) will appear where you placed your cursor, and a footnote section will be created at the bottom of the page. Type your footnote content in this section.
- Add more footnotes using the same steps. Google Docs will handle the footnotes numbering. (5)
References:
- Footnotes and Endnotes – Khalifa University
- Footnotes and Endnotes – University of Bristol
- Footnote Referencing Styles – Bibliography.com
- Add footnotes and endnotes – Microsoft Support
- Use headers, footers, page numbers, & footnotes – Google Docs Editors Help
R Discovery is a literature search and research reading app that uses your interests to instantly create personalized reading feeds. Researchers can stay updated on the latest, most relevant content from its continually expanding library of 115M+ research articles sourced from trusted aggregators like CrossRef, Unpaywall, PubMed, PubMed Central, Open Alex as well as prestigious publishing houses like Springer Nature, JAMA, IOP, Taylor & Francis, NEJM, BMJ, Karger, SAGE, Emerald Publishing and more. The top-rated app in its space, R Discovery’s carefully curated features give you the power to choose what, where, and how you read research.
Try the app for free or upgrade to R Discovery Prime, which unlocks unlimited access to app-only features that let you listen to research on the go, read in your language, invite collaborators, auto sync with reference managers and more. It’s like having the world of research at your fingertips! Choose a simpler, smarter way to find and read research – Get R Discovery Prime now at just US$39 a year!
Related Posts

What are Experimental Groups in Research

Inductive vs. Deductive Research Approach
Home / Guides / Citation Guides / APA Format / How to do APA footnotes
How to do APA footnotes
Footnotes are a way for the author to provide additional content to their papers without distracting the reader from the text. The information in footnotes is different from the information provided in APA annotated bibliographies . Footnotes can be content based, providing a little more insight on an idea you raise in the text, or they can be used to provide copyright attribution for long quotes and passages.
Properly formatted APA footnotes can be placed at the bottom of the page. Alternatively, you can put them on their own page after the references. This guide on footnotes, end notes, and parentheticals provides information about the differences between these different types of notes. Either way, it’s important to know how to use footnotes properly.
In this guide, students can learn about the different uses for footnotes as well as how to format footnotes according to APA Style. All of the information here comes straight from the 7th edition of the Publication Manual .
Why use footnotes? What information goes into them?
There are two primary reasons why an author would use footnotes:
1. Using a footnote for content
As mentioned above, there are a few different ways to use footnotes. The more common way is when an author wants to provide extra insight on an idea without disrupting the flow of the text. This is called a content footnote.
In this case, you would write a a couple sentences about the extra insight. For example:
______________________
1 This data refers to the situation in 2010, and it includes emissions from industrial processes. Emissions from the latter are released during the physical and chemical transformation of materials like clinker production. Since these industrial production processes are also consumers of energy, here we made the choice to combine them with CO2 emissions from fossil fuel combustion.
2. Using a footnote for copyright attribution
When you are reproducing a portion of a copyrighted work, like an extended passage from a book or journal, it is necessary to provide copyright attribution. This can be done inside a footnote. The footnote is used instead of a parenthetical in-text citation, and you will still need to add the source as an entry in the reference list.
If it is an image or graph you are reproducing, copyright attribution can go in the figure note or table note.
A copyright footnote should start with “ From ” or “ Adapted from ” and the format will change slightly depending on the source.
Here is a template for copyright attribution for a website followed by two examples:
1 From Webpage title , by Group Author OR Author FirstMiddleName Initials. Author Surname. Year Published, Website Name (URL).
*Note: If the Group Author and Website Name are the same, omit the Website Name slot.
2 From First images from the James Webb Space Telescope , by National Aeronautics and Space Administration, 2022 (https://www.nasa.gov/webbfirstimages).
3 From Question of what now for Syria remains as vexed as ever , by M. Chulov. 2022, The Guardian (https://www.theguardian.com/world/2022/jul/19/question-of-what-now-for-syria-remains-as-vexed-as-ever).
Endnotes vs. footnotes: What’s the difference?
According to APA Style, the author may choose to place the footnotes on the bottom of the page on which the callout appears or at the end of the paper on their own page(s).
“Endnotes” is a function on many word processors that inserts callouts and place the notes at the end of the document. While this is the same idea as footnotes, APA calls for a specially-formatted footnotes page.
To place the footnotes at the end of your document, check the preferences of the footnote function. You should be able to select “End of Document” instead of “End of Page.”
How to format APA footnotes
Always use the footnotes function of your word processor to insert footnotes. This will make it much easier to keep track of everything even as page content changes.
How to format footnotes correctly:
- Always use the footnotes function.
- The callout should be in superscript, like this. 1
- The callout should come after the punctuation, like this. 2
- If there’s a dash 3 —the callout comes before the punctuation, not after.
- All callouts should appear in numerical order, like this. 4
APA footnotes example
Now let’s have a look at what properly formatted APA footnotes look like in action.
Here is an example of a concise, relevant, and properly formatted footnote from “The role of renewable energy in the global economy transformation,” published in Energy Strategy Reviews.
. . . A transition away from fossil fuels to low-carbon solutions will play an essential role, as energy-related carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions represent two-thirds of all greenhouse gases (GHG). 1
In this example, the footnotes function automatically created a dividing line at the bottom of the document. It has also reduced the font size by 1pt, which is neither required nor discouraged by APA.
The reason this is a good example, however, is because the footnote provides supplemental information that is both relevant and substantive. The information would have been too distracting to appear in the main text, but it provides helpful insight on the author’s research method.
Published October 28, 2020.
APA Formatting Guide
APA Formatting
- Annotated Bibliography
- Block Quotes
- et al Usage
- In-text Citations
- Multiple Authors
- Paraphrasing
- Page Numbers
- Parenthetical Citations
- Reference Page
- Sample Paper
- APA 7 Updates
- View APA Guide
Citation Examples
- Book Chapter
- Journal Article
- Magazine Article
- Newspaper Article
- Website (no author)
- View all APA Examples
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you!
Let us improve this post!
Tell us how we can improve this post?
You can include more than one footnote on the same page in APA style. There is no restriction on the number of footnotes to be included on a page. Depending upon the number of footnotes on the page, the text area of the page will be automatically adjusted to fit the footnotes.
Footnotes in APA are used to provide the reader some additional information about the idea or the element being discussed. Footnotes are used in all types of publications such as journal articles, book chapters, and conference papers.
Two types of footnotes are used in APA style: content footnotes and copyright attribution footnotes. A content footnote provides additional explanation or information about something mentioned in the text, while a copyright attribution footnote provides copyright information for lengthy content that has been reprinted in the text. For both types, the in-text citation remains the same. Remember the following guidelines when you want to cite a footnote:
- Footnotes (whether content footnotes or copyright attribution footnotes) are numbered consecutively in the order in which they appear in the text.
- Use superscript Arabic numerals (1, 2, 3, etc.) to designate a footnote callout.
- This is a footnote. 1
- In this footnote, 2 the author tries to clarify the idea.
- A footnote callout—unlike in-text reference citation 3 —is simple to add.
- You should not add space before the footnote callout.
- If you want to refer to the same footnote again in the text, do not add any superscript Arabic numeral. Instead, write “see Footnote 3.” In this case, the footnote description need not be given again.
Note that a footnote should have only one idea. If you want to add more information, it is advisable to add the content in the text or create an appendix.
APA Citation Examples
Writing Tools
Citation Generators
Other Citation Styles
Plagiarism Checker
Upload a paper to check for plagiarism against billions of sources and get advanced writing suggestions for clarity and style.
Get Started

- Foundations
- Write Paper
Search form
- Experiments
- Anthropology
- Self-Esteem
- Social Anxiety

- Research Paper >
How to Write Footnotes
Information on how to write footnotes and endnotes. Footnotes, a type of citation format, are most often used for history and philosophy papers. As such, scientists rarely encounter it, but it is still useful to know how to follow the practice.
This article is a part of the guide:
- Outline Examples
- Example of a Paper
- Write a Hypothesis
- Introduction
Browse Full Outline
- 1 Write a Research Paper
- 2 Writing a Paper
- 3.1 Write an Outline
- 3.2 Outline Examples
- 4.1 Thesis Statement
- 4.2 Write a Hypothesis
- 5.2 Abstract
- 5.3 Introduction
- 5.4 Methods
- 5.5 Results
- 5.6 Discussion
- 5.7 Conclusion
- 5.8 Bibliography
- 6.1 Table of Contents
- 6.2 Acknowledgements
- 6.3 Appendix
- 7.1 In Text Citations
- 7.2 Footnotes
- 7.3.1 Floating Blocks
- 7.4 Example of a Paper
- 7.5 Example of a Paper 2
- 7.6.1 Citations
- 7.7.1 Writing Style
- 7.7.2 Citations
- 8.1.1 Sham Peer Review
- 8.1.2 Advantages
- 8.1.3 Disadvantages
- 8.2 Publication Bias
- 8.3.1 Journal Rejection
- 9.1 Article Writing
- 9.2 Ideas for Topics
Many biology journals, for example, prefer footnotes because they allow annotation of the in-text citation on the same page.
Whilst footnotes are a little more cumbersome than the 'author/date' system, they are useful where sources require elaboration and short explanatory notes.

What is a Footnote
The footnote takes the form of a superscripted number, just after a paraphrased piece of information. Subsequently, a cross-reference to this number is inserted at the bottom of the same page.
In fact, for dissertations and theses, many writers use footnotes to keep track of their citations , adding a short note of what exactly each one adds to the paper.
Once the paper is complete, the writer converts them to endnotes at the end or every chapter, or even removes them all together, and uses a standard APA or MLA bibliography instead.

Automatically Inserting Footnotes
The reason that footnotes are still popular in some fields is that most word processing programs now include a function that makes it very easy to include footnotes in any paper.
In Microsoft Word, clicking Insert > Reference > Footnote allows you to insert footnotes automatically, and automatically numbers them. This function is so useful, that even if you cut and paste, and swap information around, it automatically adjusts the footnotes.
This is why it is an excellent resource for keeping track of your sources during the course of a research paper .
How to Write Footnotes - Protocols
If you are using footnotes, the common convention is to insert a full citation, including author, year and the title of the book, followed by the page number. Afterwards, the surname of the author and the page number is sufficient.
Older journals often use the word ibid, to show that a footnote uses the same source as the previous one, but this has become much rarer.
- Psychology 101
- Flags and Countries
- Capitals and Countries
Martyn Shuttleworth (Nov 21, 2009). How to Write Footnotes. Retrieved Aug 21, 2024 from Explorable.com: https://explorable.com/how-to-write-footnotes
You Are Allowed To Copy The Text
The text in this article is licensed under the Creative Commons-License Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) .
This means you're free to copy, share and adapt any parts (or all) of the text in the article, as long as you give appropriate credit and provide a link/reference to this page.
That is it. You don't need our permission to copy the article; just include a link/reference back to this page. You can use it freely (with some kind of link), and we're also okay with people reprinting in publications like books, blogs, newsletters, course-material, papers, wikipedia and presentations (with clear attribution).
Want to stay up to date? Follow us!
Check out the official book.
Learn how to construct, style and format an Academic paper and take your skills to the next level.

(also available as ebook )
Save this course for later
Don't have time for it all now? No problem, save it as a course and come back to it later.
Footer bottom
- Privacy Policy

- Subscribe to our RSS Feed
- Like us on Facebook
- Follow us on Twitter
Footnotes made easy
Why footnotes, where to start, where to get more help, automate the process with reference managers.
- Secondary sources
- Primary sources
- Frequently-asked questions
- Using Zotero at Princeton This link opens in a new window
Librarian for History and African American Studies

The footnotes and bibliography in any scholarly work have two purposes:
- to acknowledge the author's debt to the work of others
- to enable the reader to locate the sources consulted by the author
To do that, your footnotes and bibliography need to include complete and accurate information about your sources, arranged in a consistent way that does not confuse your reader. At this point in your research, you will all have encountered unhelpful footnotes with mysterious abbreviations, incorrect information, or other problems.
There are many ways to arrange the information. This is called "style" and there are several common styles in use. Historians generally prefer the style defined by The Chicago Manual of Style , now in its 16th edition. You may have been asked to use other styles for courses in other departments, for example MLA or APA. Always check with your reader to find out if he/she cares about which style you use. When you write for publication, the publisher or journal editor will tell you which style they want you to use.
Why does it matter? Correct style will make things easier for your reader. And you want the reader to think about your ideas, not the messy punctuation at the bottom of the page.
History department guidelines:
- JP Guidelines
- Thesis Guidelines
The Chicago Manual of Style Online
Chicago Manual of Style (print edition)
- Marquand Library - Reference: Z253 .U69 2017
- Stokes Library (SPIA): Writing Shelf. Z253 .U69 2017
- retrieve print copy from ReCAP
An overview and summary of Chicago style is found at Purdue OWL Research and Citation Resources
- Chicago Manual of Style citations PowerPoint PowerPoint that explains citations according to Chicago Manual of Style
- Citation Generator For certain sources, this website can help formulate citations
- Using Zotero at Princeton Zotero is software that can help organize your references and prepare citations and bibliographies
Need more help? Ask!
- Writing Center
- History Writing Group, led by the undergraduate writing advisor
- your advisor
These products allow you to store your references in a database, then automatically generate citations and bibliographies.
Zotero (see the library's Guide to using Zotero )
And there are others as well
- Next: Secondary sources >>
- Last Updated: Dec 19, 2023 1:33 PM
- URL: https://libguides.princeton.edu/history/footnotes
Footnotes in a Paper: How to Use Them Effectively in Your Writing
Discover the best way to use footnotes in a paper. Get expert tips on how to efficiently and effectively use footnotes in academic papers.
Footnotes in a paper can be a valuable tool in providing a way to supplement our writing with additional information, citations, and explanations without disrupting the flow of the main text. However, many writers may be unsure of when and how to use footnotes effectively. In this article, we will explore the importance and usage of footnotes in academic writing, and provide practical tips for incorporating footnotes into your own writing. Whether you are a seasoned academic writer or just starting out, understanding how to use footnotes can help you increase the clarity and credibility of your writing.
What Are Footnotes?
Footnotes are a useful tool in academic writing that allows for the inclusion of additional information or comments in a document or text. Typically denoted by a small number or symbol in the main text, footnotes in a paper appear at the bottom of the page and can serve a variety of purposes. For example, footnotes can be used to clarify a point, provide background information, or give credit to a source that is not directly quoted or referenced in the main text. They are also helpful in avoiding disruptions to the flow of the main text, particularly when lengthy citations or explanations are required. In short, footnotes provide readers with additional information or references related to specific sections of the text, making them a valuable tool for researchers.
How to Write a Footnote
To write a footnote for a paper, follow these general steps:
- Determine what information needs to be included in the footnote. This may include the author’s name, the title of the source, the publication date, the publisher, and the page number(s) you are referencing.
- Place the footnote number or symbol at the end of the sentence or clause that requires the footnote. The footnote number or symbol should be placed after the punctuation, such as a period or comma.
- Write the footnote itself at the bottom of the page. The first line of the footnote should be indented, and the subsequent lines should be flush with the left margin.
- Format the footnote according to the citation style you are using (e.g. MLA, APA , Chicago). Each citation style has specific rules for how footnotes should be formatted, so consult the appropriate style guide for details.
- If you are using a word processing program, such as Microsoft Word, you can use the “Insert Footnote” function to automatically insert footnotes and format them correctly.
Difference Between Footnotes and Endnotes
The main difference between footnotes and endnotes is their placement within a document. Footnotes appear at the bottom of the page on which they are referenced, while endnotes appear at the end of a document, chapter, or section.
Here are some other differences between footnotes and endnotes:
| Definition | Notes placed at the bottom of the same page as the reference. | Notes placed at the end of the document. |
| Placement | Below the text they reference, usually in smaller font sizes. | At the end of the document, usually in the same font size as the main text. |
| Usage | Used to provide additional information or explanation of a point in the text. | Used to provide additional information, explanation, or citation of a source. |
| Advantages | Easy to locate and read in the of the text. | Keep the text clean and uncluttered. |
| Disadvantages | May clutter the page and distract the reader. | May require the reader to flip back and forth between the text and the endnotes. |
Chicago Style Footnotes
Chicago-style footnotes are a common citation style used in research papers. In this format, footnotes are used to provide information about a source within the text. There are two types of Chicago-style footnotes: short form and long form. Short form citations include only the basic details of a source if a full bibliography is provided, while long form citations include a full citation the first time a source is cited, with subsequent citations using the short form.
Here is an example of a Chicago-style footnote using the short form:
“The concept of social capital has been widely discussed in recent years, with Putnam’s Bowling Alone¹ being one of the most influential works in the field.” At the bottom of the page, the corresponding footnote would appear as: ¹ Putnam, Bowling Alone, 26.
Note that the author’s last name is listed first, followed by the abbreviated title of the work (in this case, “Bowling Alone”), and the page number where the information was found.
Here is a Chicago-style footnote using the short form example:
First reference: John Smith, The History of Chicago (Chicago: University of Chicago Press, 2005), 25. Subsequent reference: Smith, The History of Chicago, 30.
Here is an example of a Chicago footnote in text:
“According to Smith, the notion of human rights can be traced back to ancient Greek philosophy.¹”² Bottom of page: ¹John Smith, The Origins of Human Rights (New York: Oxford University Press, 2021), 15. ²Smith, Origins of Human Rights, 22.
Learn how to make citations in Chicago style in our blog “ Chicago Style Citation Made Easy: Formatting and Examples “.
APA Style Footnotes
APA format generally uses parenthetical in-text citations instead of footnotes. However, there are two exceptions to this rule: content footnotes and copyright attribution. Content footnotes provide additional information on a single topic that does not fit coherently in the text, while copyright attribution footnotes are used when a writer uses a lengthy quotation or other copyrighted material, such as a stock photograph. Footnotes are formatted similarly to Chicago style, with sequential superscript numbers coming after the passage and the corresponding footnote at the bottom of the page.
Here’s an example of an APA-style footnote for supplementary information:
In-text: According to recent studies, the COVID-19 vaccine is highly effective in preventing infection and transmission of the virus.¹ Footnote: ¹For more information on the studies cited, see Smith et al. (2021) and Jones et al. (2022).
Learn how to make citations in APA style in our blog “ How to Make Citations using APA Formatting: A Guide “.

MLA Style Footnotes
MLA (Modern Language Association) style does not typically use footnotes. Instead, in-text citations are used to indicate the source of information or quotations. However, if footnotes are required for a specific publication or assignment, the following guidelines can be followed:
Placement: Footnotes should be placed at the bottom of the page on which the reference appears.
Numbering: Footnotes should be numbered consecutively throughout the paper using Arabic numerals. The number should be placed after any punctuation marks, such as periods or commas.
Formatting: Footnotes should be single-spaced and in a smaller font size than the main text.
Content: Footnotes should include bibliographic information for the source being cited, as well as any additional information necessary to clarify the reference. For example, a footnote for a book might include the author, title, publisher, and year of publication, while a footnote for a website might include the URL and date of access.
Example of MLA Style Footnote for a book:
John Doe, The History of Art (New York: Penguin Books, 2000), 24. Example of MLA Style Footnote for a website: “The Benefits of Exercise,” National Institutes of Health, accessed May 15, 2023, https://www.nih.gov/health-information/benefits-exercise .
A MLA Style footnote text example:
Text: According to a recent study, the use of social media can have negative effects on mental health (Johnson 36).² Footnote citation: ² Johnson, Sarah. “The Impact of Social Media on Mental Health.” Journal of Health Psychology, vol. 22, no. 1, 2018, pp. 35-44.
Learn how to make citations in MLA style in our blog “ A Writer’s Guide to MLA Format: How to Get It Right “.
Improve your papers’ impact and visibility through quality visual communication
Mind the Graph is an innovative platform that provides a wide range of tools to help scientists improve their papers’ impact and visibility through quality visual communication . With Mind the Graph , scientists can easily create graphical abstracts, posters, and other visual aids that can effectively communicate their research findings to a wider audience.
Related Articles

Subscribe to our newsletter
Exclusive high quality content about effective visual communication in science.
Sign Up for Free
Try the best infographic maker and promote your research with scientifically-accurate beautiful figures
no credit card required
Content tags
- Translation
How to use Footnotes and Endnotes in academic papers
By charlesworth author services.
- Charlesworth Author Services
- 28 January, 2022
How to use and write Footnotes and Endnotes in academic papers
Research papers and reports often include adjuncts such as charts and graphs, tables , diagrams, a hierarchy of headings, citations and references etc. Notes – whether footnotes or endnotes – are an important adjunct. They primarily serve the role of supplying additional information , which, if weaved into the main text, may reduce its ease of readability .
Footnotes vs. endnotes
- Location : By definition, footnotes appear at the foot of a page on which appears the text they support. Endnotes are placed at the end of a paper, a chapter or a book.
- Space : Footnotes, being located at the bottom of each individual page, are constrained by the amount of space available, whereas endnotes, located right at the end of the text, are afforded much more ample room.
- Amount of information (and flow) : The above point (space) is a useful distinction that tells readers what to expect. Footnotes offer small bits of information that you can choose to take in without breaking stride. You could take a quick look and return to the main text on the same page. On the other hand, endnotes may sometimes contain sizeable amounts of information, but you do not have to interrupt your reading of the main text. You can choose to read them once you have reached the end of the document.
Footnotes: Examples
As discussed, footnotes comprise small bits of information short enough to take in at a glance. Here are a couple of examples to illustrate the function of footnotes.
- A text may mention the name of an organisation and use a footnote to explain that the organisation had a different name in the past.
- A text may mention a certain sum of money in Korean Won, and the corresponding footnotes will indicate the equivalent sum in US dollars.
Endnotes: Examples
As discussed too, endnotes can comprise much longer parcels of information. Here too are a couple of examples to illustrate the use of endnotes.
- While you may describe a certain method in your main text, you might use an endnote to outline in more detail some other tangential studies , perhaps from a slightly different field, which used that same method , the results they produced and why this may be of interest.
- You might cite an important quotation within the main body of your text and then include in a related endnote the full paragraph or section from which that quotation was taken, thus enabling interested readers to explore the wider context and additional insights if they wish.
Usage in academic papers and digital documents
As an author of an academic paper, you can choose between footnotes and endnotes depending on how much additional information you want to give. Be aware, however, that footnotes and endnotes, especially endnotes, are virtually never used in research papers in the physical and biological sciences . They may sometimes be used in the social sciences and are more commonly seen in the humanities .
In digital documents, the distinction between footnotes and endnotes and their placement is less important, because the additional information can be connected to the main text with hyperlinks .
Writing footnotes and endnotes
- Superscripts and symbols : Within the main text, both footnotes and endnotes are typically signalled, or announced, using superscript numbers, although, for footnotes, other symbols such as a star or an asterisk (*), a dagger or obelisk (†), a double dagger or diesis (‡), a section mark (§), a pilcrow or blind p (¶), and so on are also employed, usually in that order. Do note that these symbols are never used with endnotes .
- Numbers : With numbered footnotes, the sequence either begins afresh on each page or can be continued throughout within a paper, a chapter (e.g. if the book has chapters by different contributors) or a book. Endnotes are always numbered and the sequence is always continuous .
- Heading for endnotes : Note that the heading for endnotes, when all of them are gathered at the end, is simply ‘Notes’ and not ‘Endnotes’.
- Footnotes for tables : Table titles, column or row headings, or specific cells within a table can all carry footnotes. Those footnotes are explained at the foot of the table in question and not at the foot of a page on which the table appears.
As a scholar, try to familiarise yourself with the idea of notes and their related mechanics as early on in your writing process as possible. These details can seem numerous at first, but once you master them, you will be able to spontaneously incorporate them into your writing.
Maximise your publication success with Charlesworth Author Services.
Charlesworth Author Services, a trusted brand supporting the world’s leading academic publishers, institutions and authors since 1928.
To know more about our services, visit: Our Services
Share with your colleagues
Scientific Editing Services
Sign up – stay updated.
We use cookies to offer you a personalized experience. By continuing to use this website, you consent to the use of cookies in accordance with our Cookie Policy.
- University of Michigan Library
- Research Guides
Microsoft Word for Dissertations
- Footnotes, Endnotes, & Citations
- Introduction, Template, & Resources
- Formatting for All Readers
- Applying a Style
- Modifying a Style
- Setting up a Heading 1 Example
- Images, Charts, Other Objects
- Cross-References
- Appendix Figures & Tables
- Table of Contents
- List of Figures/Tables
- Chapter and Section Numbering
- Page Numbers
- Landscape Pages
- Combining Chapter Files
- Commenting and Reviewing
- Tips & Tricks
- The Two-inch Top Margin
- Troubleshooting
- Finalizing Without Styles
- Preparing Your Final Document
- Take a break
Footnotes and Endnotes
To use Word's built-in footnote/endnote tool:
- Put your cursor where you want to insert your new footnote or endnote.
- In the References tab, click Insert Footnote or Insert Endnote .

- Remember, too, that you can format the Style of your endnote/footnote as discussed in the Modifying a Style section. Unsurprisingly, footnotes use the "Footnote Text" style, and endnotes use the "Endnote Text" style. You may need to open the Styles Pane and set it to show "All Styles" to find and modify those styles.
Viewing All Your Footnotes in One Place
If you'd like to see all of your footnotes (or endnotes) in one place, here's how to do it:
- Go to the View tab and select Draft view (located near the left side of the ribbon)
- Go to the References tab and select Show Notes
That will open a view of all your notes so you can easily edit, remove extra paragraph/return characters, and make paragraph or indent spacing changes. Just avoid trying to globally change font sizes here -- if you "Select All" and change the font size, that will change the font size for the note text AND the superscript number. Instead, remember that those two things are controlled by Styles -- Footnote Text (for the text) and Footnote Reference (for the footnote number). Modify those styles instead.
Microsoft Word has built-in tools for managing/formatting citations. They work fine for more modestly sized documents, but for a dissertation, it's likely that you'll need greater control and flexibility than Word provides.
We encourage you to take advantage of a dedicated citation/source management tool like EndNote, Zotero, or Mendeley. These citation management applications allow you to store your sources and easily insert properly-formatted citations into Word. They will automatically format both in-text citations and a bibliography.
You can learn more by visiting our Guide to Managing Citations with Zotero, Mendeley, and EndNote
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Happiness Hub Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- Happiness Hub
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Writing
How to Do Footnotes
Last Updated: February 9, 2024 Fact Checked
Sample Footnotes
Placing citations, supplementing text, expert interview, expert q&a.
This article was co-authored by Noah Taxis and by wikiHow staff writer, Jennifer Mueller, JD . Noah Taxis is an English Teacher based in San Francisco, California. He has taught as a credentialed teacher for over four years: first at Mountain View High School as a 9th- and 11th-grade English Teacher, then at UISA (Ukiah Independent Study Academy) as a Middle School Independent Study Teacher. He is now a high school English teacher at St. Ignatius College Preparatory School in San Francisco. He received an MA in Secondary Education and Teaching from Stanford University’s Graduate School of Education. He also received an MA in Comparative and World Literature from the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign and a BA in International Literary & Visual Studies and English from Tufts University. There are 9 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 1,376,568 times.
Footnotes are used generally in academic and professional writing to cite sources or add supplemental information to the main text of a paper. Academic citation styles, such as the Modern Language Association (MLA) and the American Psychological Association (APA), discourage the use of extensive footnotes. Others, such as Chicago style, require them. [1] X Research source

Tip: Footnotes are typically a smaller font size than the main text of your paper. Typically, you won't need to change the default size on the word processing app you're using to write your paper – it will do this automatically when you create a footnote.

- You'll typically only have one footnote per sentence. If you need more than one footnote, place the other footnote at the end of the sentence clause it relates to, outside the closing punctuation. The only exception is if the sentence is broken up by a long dash, in which case, the superscript number goes before the beginning of the dash. [4] X Trustworthy Source Purdue Online Writing Lab Trusted resource for writing and citation guidelines Go to source
Footnote Number in Line with Text: It is well known that patients who suffer from Crohn's and Colitis can have many debilitating symptoms. 1.
Superscripted Footnote Number: It is well known that patients who suffer from Crohn's and Colitis can have many debilitating symptoms. 1

- For some longer papers, such as doctoral theses, footnote numbers may start over with each chapter. If you're unsure if this is appropriate for your project, discuss it with your editor or advisor.
- Most word processing apps will maintain sequential numbering for you, provided you use the app's function for inserting footnotes, rather than trying to type the numbers manually.

- You typically have formatting options that allow you to choose numbers, letters, or other symbols to indicate footnotes. You can also change the size or placement of footnotes, although the default option is usually appropriate.

- For most style guides, the use of footnotes does not replace the need for a list of references at the end of your paper. Even if a full list of references isn't strictly required, it can help place your paper in context.

- For example, suppose you've paraphrased information from a book by Reginald Daily, titled Timeless wikiHow Examples: Through the Ages. If you were using Chicago style, your footnote citation would look something like this: Reginald Daily, Timeless wikiHow Examples: Through the Ages (Minneapolis: St. Olaf Press, 2010), 115.

- For example, suppose later on in your paper you need to cite Reginald Daily's wikiHow book again. Your shortened citation might look something like this: Daily, wikiHow Examples , 130.
Tip: Some citation styles recommend using the abbreviation "id." or "ibid." if you cite to the same source in footnotes immediately following. Others, notably the Chicago Manual of Style, require the use of a shortened citation instead.

- For example, suppose you have a sentence in your text comparing the conclusions in Reginald Daily's book with the observations in another book on the same topic. Your footnote might look something like this: Reginald Daily, Timeless wikiHow Examples: Through the Ages (Minneapolis: St. Olaf Press, 2010), 115; Mary Beth Miller, The wiki Revolution (New York: New Tech Press, 2018), 48.

- For example, if Miller's work reached a conclusion that was contrary to the conclusion Daily reached, your footnote might look something like this: Reginald Daily, Timeless wikiHow Examples: Through the Ages (Minneapolis: St. Olaf Press, 2010), 115; but see Mary Beth Miller, The wiki Revolution (New York: New Tech Press, 2018), 48.
- If you believe it would be helpful to your readers, you can add a brief parenthetical comment after the second source that explains why you included it.

- For example, suppose you want to include a brief explanation as to why you're citing Daily's book, despite the fact that it was published in 2010. Your footnote might look something like this: Reginald Daily, Timeless wikiHow Examples: Through the Ages (Minneapolis: St. Olaf Press, 2010), 115. Although published in 2010, Daily's work provides a jumping-off point for research in this area.

- For example, there may be a basic concept that is beyond the scope of your paper, but important for your readers to understand. You could add a footnote that says "For an explanation of the theory of relativity, see generally" followed by a source or list of sources.
- Typically, these types of footnotes provide your reader with information on something that is tangential to your paper but could be important to help your readers understand the topic as a whole or place your paper in context.

- Some style guides, such as MLA and APA, instruct that parenthetical statements should be included in the main text of your paper, rather than in footnotes. [15] X Trustworthy Source Purdue Online Writing Lab Trusted resource for writing and citation guidelines Go to source
Tip: Keep your footnotes as brief as possible, especially with supplemental footnotes. Don't stray too far off topic or go into a tangent that is only marginally related to the topic of your paper.

- These types of footnotes frequently accompany a quote from a source and may include a citation to the source. For example, if you quoted a source that discussed wikiHow, and you wanted to clarify, you might add a footnote that says "wikiHow examples are used to clarify text in situations where it would be helpful to have a visual cue. Reginald Daily, Timeless wikiHow Examples: Through the Ages (Minneapolis: St. Olaf Press, 2010), 115."

- For example, suppose you are writing a paper about the use of wikiHow articles as sources, and you include a study finding that wikiHow articles are more accurate than articles on major news sites about similar topics. You might add a footnote that says "Despite this fact, the vast majority of professors at public universities in the US do not accept wikiHow articles as sources for research papers."
- You can also use footnotes to make a witty remark, which can add humor and lightheartedness to your paper. However, these types of footnotes should be used extremely rarely, and only when appropriate to the subject matter.

- Before writing, confirm with your professor or organization what style guide you should be using to write your paper. Make sure your use of footnotes follows the rules for that style. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0
- If a footnote includes both a citation and supplemental information, the citation usually comes first. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0

You Might Also Like

Thanks for reading our article! If you’d like to learn more about academic writing, check out our in-depth interview with Noah Taxis .
- ↑ https://www.plagiarism.org/article/what-are-footnotes
- ↑ https://stpauls-mb.libguides.com/citations/footnotes
- ↑ https://www.library.georgetown.edu/tutorials/research-guides/turabian-footnote-guide
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/mla_style/mla_formatting_and_style_guide/mla_endnotes_and_footnotes.html
- ↑ https://libguides.stonehill.edu/c.php?g=884839&p=6358739
- ↑ https://www.law.cornell.edu/citation/6-300
- ↑ https://libguides.utep.edu/c.php?g=429690&p=2930768
- ↑ https://jle.aals.org/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1243&context=home
- ↑ https://libguides.liberty.edu/c.php?g=864199&p=6197236
About This Article

To use footnotes as citations, find a sentence you want to cite and insert a "1" at the end of it using the footnote setting in your word processor. Then, insert your citation next to the corresponding "1" at the bottom of the page, like "Reginald Daily, Timeless wikiHow Examples: Through the Ages (Minneapolis: St. Olaf Press, 2010), 115." When you're finished, move onto the next sentence you need to cite and repeat the process. To learn how to use footnotes to clarify information in your paper, read the article! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Ntando Malandela
Aug 29, 2017
Did this article help you?
Kevin Nesbit
Mar 24, 2017
Violet Black
May 21, 2017
Brandi Bumgardner
Dec 9, 2017

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Don’t miss out! Sign up for
wikiHow’s newsletter

Headnotes or Footnotes? A Quick Guide on Organizing Your Research Paper
In academic writing, footnotes, endnotes, and headnotes provide additional information on a particular topic. They are placed in the document as a supplement to the main text. These notes can be inserted into the document as a footer or at the end of a chapter.
The notes should be kept as brief as possible. The objective is to provide more information without distracting the reader. We discuss the different types of notes, how to use them, and their pros and cons.
What Are They and Why Use Them?
A footnote is a reference placed at the bottom of a page or footer. They are referenced in the text in the same way as a citation i.e. the referenced text is followed by a superscript numeral ( 1 ), which corresponds to the numbered footnote at the bottom of the page. When writing your research paper , you would use a footnote for two major reasons:
- To cite sources of facts or quotations
- Provide additional information
The two types of footnotes are:
- Content : Supplements or simplifies substantive information; not detailed.
- Copyright permission : Cites quoted text and any reprinted materials used in the text.
The format of footnotes is fairly standard (see below for specific rules) and is the same as that for references as follows:
Adrian Johns. The Nature of the Book: Print and Knowledge in the Making (Chicago: University of Chicago Press, 1998), 623.
When citing the same reference again, the footnote can be shortened as follows:
Johns. Nature of the Book , 384–85.
Some older journals use “ ibid ” instead of a shortened version of the reference. Ibid is short for the Latin “ ibidem” , which means “in the same place.” This format was previously used in most printed text but rarely used now.
Endnotes are much the same as footnotes except that they are placed at the end your research paper instead of at the bottom of a page. In books, they can be placed after each chapter or at the end of the book.
In many cases, the book publisher decides the best placement. Endnotes, as footnotes, are numerically noted in superscript. The format is the same as that for footnotes.
Headnotes are used as introductions in legal documents or as summaries of the text that follows them. In academic writing, headnotes are explanatory notes included with tables and figures. They are placed below the table itself or just below the figure title and typed in a font size that is smaller than the main text (e.g., 8- or 10-point font). Headnotes are used to define acronyms used, units of measure, significance, etc. Because tables and figures should be able to “stand alone” without the main text, headnotes should always be used.
Format for Footnotes, Endnotes, and Headnotes
Although the format for footnotes and endnotes is almost similar, there are specific rules depending on the journal where the paper is submitted. Most scientific journals use specific reference formats; however, some style guides do not allow footnotes and endnotes.
For example, the Modern Language Association (MLA), which deals specifically with disciplines in the humanities allows limited use of footnotes. These are to provide the reader with other sources for more information on the subject covered. The MLA style for these notes is shown in the example below and the number corresponds to the superscript number noted in the referenced text:
See [name of author], especially chapters 3 and 4, for an insightful analysis of this trend.
MLA suggests using “content” footnotes when necessary to avoid interrupting the text with an explanation or other details.
In contrast, the American Psychological Association (APA), the style for the behavioral and social sciences, does not usually allow footnotes. Your particular journal guidelines will provide that information.
A third style guide, the American Medical Association (AMA) , is used mostly with papers in the biological and medical sciences. AMA also discourages the use of footnotes but allows them on the title page. The information on the title page would include the authors’ names and affiliations, corresponding author, members of affiliated groups, etc.
Pros and Cons
Scientific papers do not usually include footnotes. Endnotes may be used sometimes, but sparingly. Other disciplines, such as law and history, still use them regularly . There are pros and cons to each.
The advantages of using footnotes are that they provide the reader with a fast reference and link to additional information. They are easy to insert and will automatically print. The advantage of using endnotes instead of footnotes is that their placement is less distracting. They also provide the reader with an easy reference list in one place.
According to the Chicago Manual of Style (CMOS), endnotes are preferred to footnotes simply because they don’t clutter up a page. CMOS does caution that it can seem disconcerting to a reader to see pages of notes at the end of a chapter or book, so use them sparingly.
Again, another disadvantage to footnotes is that they tend to interrupt the flow of the text. The reader might feel that he must stop and look at the note before moving on, which can be very distracting. Some disadvantages to endnotes are that the reader must turn to the end of the text or chapter to find the additional information. In books with several chapters, this can be tedious, especially if the endnotes are renumbered in each chapter.
As for headnotes, there are really no drawbacks to using them in tables and figures. They offer the reader helpful information that is readily available as they read the data or interpret a figure.
Bottom Line
The style to which you conform when writing your paper will ultimately depend on the journal’s guidelines. Pay careful attention to its protocols for citations and references and whether it will allow footnotes and endnotes. If allowed, be mindful of the disadvantages of both and consider either greatly limiting them or eliminating them altogether.
Rate this article Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published.

Enago Academy's Most Popular Articles

- Industry News
- Trending Now
ICMJE Updates Guidelines for Medical Journal Publication, Emphasizes on Inclusivity and AI Transparency
The International Committee of Medical Journal Editors (ICMJE) recently updated its recommendations for best practices…

- AI in Academia
- Infographic
- Manuscripts & Grants
- Reporting Research
Can AI Tools Prepare a Research Manuscript From Scratch? — A comprehensive guide
As technology continues to advance, the question of whether artificial intelligence (AI) tools can prepare…

- Manuscript Preparation
- Publishing Research
How to Choose Best Research Methodology for Your Study
Successful research conduction requires proper planning and execution. While there are multiple reasons and aspects…

- Journal Guidelines
How to Use CSE Style While Drafting Scientific Manuscripts
What is CSE Style Guide? CSE stands for Council of Science Editors. Originated in the…

How to Create Publication-ready Manuscripts Using AIP Style Guide
What is AIP Style Guide? The AIP style guide refers to a specific citation format…
What Are the Unique Characteristics of the AMA Style Guide?

Sign-up to read more
Subscribe for free to get unrestricted access to all our resources on research writing and academic publishing including:
- 2000+ blog articles
- 50+ Webinars
- 10+ Expert podcasts
- 50+ Infographics
- 10+ Checklists
- Research Guides
We hate spam too. We promise to protect your privacy and never spam you.
- Promoting Research
- Career Corner
- Diversity and Inclusion
- Infographics
- Expert Video Library
- Other Resources
- Enago Learn
- Upcoming & On-Demand Webinars
- Peer-Review Week 2023
- Open Access Week 2023
- Conference Videos
- Enago Report
- Journal Finder
- Enago Plagiarism & AI Grammar Check
- Editing Services
- Publication Support Services
- Research Impact
- Translation Services
- Publication solutions
- AI-Based Solutions
- Thought Leadership
- Call for Articles
- Call for Speakers
- Author Training
- Edit Profile
I am looking for Editing/ Proofreading services for my manuscript Tentative date of next journal submission:

In your opinion, what is the most effective way to improve integrity in the peer review process?
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Footnotes and Endnotes

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
Note: This page reflects APA 6, which is now out of date. It will remain online until 2021, but will not be updated. The equivalent APA 7 page can be found here .
APA does not recommend the use of footnotes and endnotes because they are often expensive for publishers to reproduce. However, if explanatory notes still prove necessary to your document, APA details the use of two types of footnotes: content and copyright.
When using either type of footnote, insert a number formatted in superscript following almost any punctuation mark. Footnote numbers should not follow dashes ( — ), and if they appear in a sentence in parentheses, the footnote number should be inserted within the parentheses.
When using the footnote function in a word-processing program like Microsoft Word, place all footnotes at the bottom of the page on which they appear. Footnotes may also appear on the final page of your document (usually this is after the References page). Center the word “Footnotes” at the top of the page. Indent five spaces on the first line of each footnote. Then, follow normal paragraph spacing rules. Double-space throughout.
Content Notes
Content notes provide supplemental information to your readers. When providing content notes, be brief and focus on only one subject. Try to limit your comments to one small paragraph.
Content notes can also point readers to information that is available in more detail elsewhere.
Copyright Permission Notes
If you quote more than 500 words of published material or think you may be in violation of “Fair Use” copyright laws, you must get the formal permission of the author(s). All other sources simply appear in the reference list.
Follow the same formatting rules as with content notes for noting copyright permissions. Then attach a copy of the permission letter to the document.
If you are reproducing a graphic, chart, or table, from some other source, you must provide a special note at the bottom of the item that includes copyright information. You should also submit written permission along with your work. Begin the citation with “ Note .”
Note . From “Title of the article,” by W. Jones and R. Smith, 2007, Journal Title , 21, p. 122. Copyright 2007 by Copyright Holder. Reprinted with permission.
Generate accurate MLA citations for free
- Knowledge Base
- MLA footnotes and endnotes
MLA Footnotes & Endnotes | Format & Examples
Published on August 23, 2019 by Shona McCombes . Revised on March 5, 2024 by Jack Caulfield.
MLA style requires you to cite sources using MLA in-text citations , not notes. However, you can still use footnotes or endnotes in MLA style for other purposes:
Citing a lot of sources at once
- Providing any extra explanation needed about your citation or translation practice
- Elaborating on ideas
- Providing additional examples that don’t fit into the main text
Footnotes appear at the bottom of the relevant page, while endnotes appear at the end of the paper, just before the Works Cited list. MLA allows the use of either type, but stick to one or the other.
Any sources you cite in your footnotes or endnotes must also be included in your Works Cited list , just like sources in the main text. Scribbr’s free MLA Citation Generator can help you create accurate MLA citations.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Formatting footnotes and endnotes in mla, explaining citation or translation practice, using notes to elaborate on ideas, providing more examples in notes, frequently asked questions about mla notes.
Both footnotes and endnotes are indicated by superscript numbers. The number usually appears at the end of a sentence, after the period.
If you need to use a note in the middle of a sentence to avoid ambiguity, place the number directly after a punctuation mark (with the exception of the dash , where the number comes before).
Four main factors have been determined as possible characteristics of any successful fictional work: 6 popularity, enduring fame, commercial success and scholarly appeal. Each of the case studies must possess at least one of these. 7
The note itself begins with the corresponding number, again in superscript, followed by a space, and then the content of the note. Notes should be in the same font as the rest of your document, but a smaller font size; the first line of each note is slightly indented.
Your word processing program should allow you to automatically insert footnotes .
Formatting the endnotes page
If you are using endnotes, list them on a separate page directly before the Works Cited list. The title (“Notes” or “Endnotes”) appears centered at the top of the page. Like the rest of an MLA format paper , the endnotes should be double-spaced.

Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
When you have a lot of sources to cite at once, you can save space in your text by placing them in a note instead. These can be sources for a statement you made in the text, or sources providing supplementary information relevant to the discussion.
Note that you don’t need to use parentheses around the page numbers when the note just consists of a list of sources.
When there’s any important information that might not be immediately obvious from your citations, you can explain it in a note at the first point where it comes up.
For example, you might use your own translations for some texts but not others, or you might cite different editions of a text in different ways. These details can be clarified in notes where relevant.
When you mention something in passing but think more information may be useful to the reader, you can add the extra information, as well as related sources if relevant, in a note.
Bear in mind that long notes with superfluous information can be distracting for readers. Use notes of this kind sparingly, and keep them brief. If a piece of information is essential to your point, you should usually include it in the main text.
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
Sometimes you have more examples than you can smoothly fit into your text. In those cases, it can be worth placing further examples in a note, if you think they add something to your point. You might also provide a counterexample to acknowledge the limitations of your argument.
No, you should use parenthetical MLA in-text citations to cite sources. Footnotes or endnotes can be used to add extra information that doesn’t fit into your main text, but they’re not needed for citations.
If you need to cite a lot of sources at the same point in the text, though, placing these citations in a note can be a good way to avoid cluttering your text.
In MLA style , footnotes or endnotes can be used to provide additional information that would interrupt the flow of your text.
This can be further examples or developments of ideas you only briefly discuss in the text. You can also use notes to provide additional sources or explain your citation practice.
You don’t have to use any notes at all; only use them to provide relevant information that complements your arguments or helps the reader to understand them.
Footnotes appear at the bottom of the relevant page. Endnotes appear in a list at the end of the text, just before the reference list or bibliography. Don’t mix footnotes and endnotes in the same document: choose one or the other and use them consistently.
In Chicago notes and bibliography style , you can use either footnotes or endnotes, and citations follow the same format in either case.
In APA and MLA style , footnotes or endnotes are not used for citations, but they can be used to provide additional information.
Some source types, such as books and journal articles , may contain footnotes (or endnotes) with additional information. The following rules apply when citing information from a note in an MLA in-text citation :
- To cite information from a single numbered note, write “n” after the page number, and then write the note number, e.g. (Smith 105n2)
- To cite information from multiple numbered notes, write “nn” and include a range, e.g. (Smith 77nn1–2)
- To cite information from an unnumbered note, write “un” after the page number, with a space in between, e.g. (Jones 250 un)
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2024, March 05). MLA Footnotes & Endnotes | Format & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved August 21, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/mla/footnotes-and-endnotes/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to format your mla works cited page, a complete guide to mla in-text citations, mla format for academic papers and essays, what is your plagiarism score.

COMMENTS
APA footnotes use superscript numbers and should appear in numerical order. You can place footnotes at the bottom of the relevant pages, or on a separate footnotes page at the end: For footnotes at the bottom of the page, you can use your word processor to automatically insert footnotes.; For footnotes at the end of the text in APA, place them on a separate page entitled "Footnotes," after ...
Footnotes should be placed at the bottom of the page on which the corresponding callout is referenced. Alternatively, a footnotes page could be created to follow the reference page. When formatting footnotes in the latter manner, center and bold the label "Footnotes" then record each footnote as a double-spaced and indented paragraph.
A footnote is a reference, explanation, or comment 1 placed below the main text on a printed page. Footnotes are identified in the text by a numeral or a symbol . In research papers and reports, footnotes commonly acknowledge the sources of facts and quotations that appear in the text. " Footnotes are the mark of a scholar," says Bryan A. Garner.
For information on footnotes in the Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association see section 2.13 "Footnotes.". For information on using footnotes with MLA see the "Using Notes in MLA Style" article from the MLA Style Center. For information on footnotes in The Chicago Manual of Style see Chapter 14 "Notes and Bibliography."
How to write a footnote. Within the text, place a footnote signal directly after the passage that the footnote relates to. Footnote signals should come after punctuation and at the end of sentences when possible. The only exception is the dash (—), in which case the footnote signal comes before, not after. At the bottom of the page, that same ...
Published on March 28, 2022 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on June 7, 2022. Footnotes are notes placed at the bottom of the page in a piece of academic writing and indicated in the text with superscript numbers (or sometimes letters or other symbols). You can insert footnotes automatically in Word or Google Docs.
Things to keep in mind when considering using either endnotes or footnotes in your research paper:. 1. Footnotes are numbered consecutively throughout a research paper, except for those notes accompanying special material (e.g., figures, tables, charts, etc.). Numbering of footnotes are "superscript"--Arabic numbers typed slightly above the line of text.
Short note example. 2. Woolf, "Modern Fiction," 11. The guidelines for use of short and full notes can vary across different fields and institutions. Sometimes you might be required to use a full note for every citation, or to use a short note every time as long as all sources appear in the Chicago style bibliography.
Navigate to the "References" tab and click on the "Insert Footnote" button. A small superscript number (typically "1") will appear where you positioned the cursor, and a corresponding footnote area will appear at the bottom of the page. Enter your footnote content in this designated area. To insert additional footnotes, repeat the ...
MLA (Modern Language Association) style is most commonly used to write papers and cite sources within the liberal arts and humanities. This resource, updated to reflect the MLA Handbook (9th ed.), offers examples for the general format of MLA research papers, in-text citations, endnotes/footnotes, and the Works Cited page.
Footnotes are a way for the author to provide additional content to their papers without distracting the reader from the text. The information in footnotes is different from the information provided in APA annotated bibliographies.Footnotes can be content based, providing a little more insight on an idea you raise in the text, or they can be used to provide copyright attribution for long ...
Automatically Inserting Footnotes. The reason that footnotes are still popular in some fields is that most word processing programs now include a function that makes it very easy to include footnotes in any paper. In Microsoft Word, clicking Insert > Reference > Footnote allows you to insert footnotes automatically, and automatically numbers them.
With APA 7 style, you should use footnotes only when you absolutely must. Ask your instructor for clarification. The purpose of footnotes is to add to or clarify a point. Footnotes are also used to add copyright information. Types of APA Footnotes. There are two types of footnotes used in APA format: content footnotes and copyright footnotes.
How to Write a Footnote Citation in MLA. Place footnotes at the bottom of the page in their own special section. Follow the same numerical order on the page. Firstly, start each note with the superscript number that corresponds with the in-text citation. Then, remember that bibliographical notes provide citations similar to the works cited and ...
The footnotes and bibliography in any scholarly work have two purposes: ... A Manual for Writers of Research Papers, Theses, and Dissertations has been fully revised to meet the needs of today's writers and researchers. The Manual retains its familiar three-part structure, beginning with an overview of the steps in the research and writing ...
Footnotes are a useful tool in academic writing that allows for the inclusion of additional information or comments in a document or text. Typically denoted by a small number or symbol in the main text, footnotes in a paper appear at the bottom of the page and can serve a variety of purposes. For example, footnotes can be used to clarify a ...
Footnotes vs. endnotes. Location: By definition, footnotes appear at the foot of a page on which appears the text they support. Endnotes are placed at the end of a paper, a chapter or a book. Space: Footnotes, being located at the bottom of each individual page, are constrained by the amount of space available, whereas endnotes, located right ...
To use Word's built-in footnote/endnote tool: Put your cursor where you want to insert your new footnote or endnote. In the References tab, click Insert Footnote or Insert Endnote.; To adjust the settings of your footnote, including the numbering style, when to start and stop the numbering of your notes, where to place the note, etc..., right-click on any footnote/endnote and select Footnote...
1. Use the same font for footnotes as the rest of the paper. Generally, you should use the same font for your entire paper rather than using several different fonts. The default font on your word processing app is usually fine. [2] Tip: Footnotes are typically a smaller font size than the main text of your paper.
In academic writing, footnotes, endnotes, and headnotes provide additional information on a particular topic. They are placed in the document as a supplement to the main text. These notes can be inserted into the document as a footer or at the end of a chapter. The notes should be kept as brief as possible.
APA (American Psychological Association) style is most commonly used to cite sources within the social sciences. This resource, revised according to the 6th edition, second printing of the APA manual, offers examples for the general format of APA research papers, in-text citations, endnotes/footnotes, and the reference page. For more information, please consult the Publication Manual of the ...
Elaborating on ideas. Providing additional examples that don't fit into the main text. Footnotes appear at the bottom of the relevant page, while endnotes appear at the end of the paper, just before the Works Cited list. MLA allows the use of either type, but stick to one or the other. Any sources you cite in your footnotes or endnotes must ...
Copy the exact words from the original source. 2. Place quotation marks (") at the beginning and end of the quoted text. 3. Insert the superscript number at the end of the sentence containing the quote. If more than one author is quoted within a sentence, insert a footnote next to each author's name.