

Brainstorming Versus Creative Problem-Solving
by Roger Firestien | Jun 13, 2024
Creative Problem-Solving is NOT Brainstorming
It’s a common misconception that brainstorming and Creative Problem-Solving (CPS) are the same.
They are not.
While brainstorming is a technique for generating ideas, CPS is a comprehensive process for solving problems.
A technique is a specific method or approach used to accomplish a particular task or goal.
Brainstorming is a divergent thinking technique. It is designed to help an individual problem solver or a group of people generate many varied and unusual options. Notice the use of the word “options.” Most people associate brainstorming with generating creative solutions. However, brainstorming can also be used to generate questions, criteria to evaluate ideas, and action steps to implement solutions .
A process refers to a series of steps or stages that are followed in a particular order to achieve a desired result.
Processes are more comprehensive and overarching compared to techniques, as they encompass a broader set of activities and often involve the use of multiple techniques.
Creative Problem-Solving (CPS) is a process that involves various techniques, including brainstorming, to develop a solution to a problem. As you proceed through the process, you develop creative questions, generate ideas, refine ideas, and develop a plan to implement solutions. Think of Creative Problem-Solving as imagination applied to problem-solving or imagination applied to your future.
Generating Ideas with Brainstorming
A brainstorming session follows specific guidelines that team members must follow if they are going to effectively generate solutions to a problem. The brainstorming rules for generating ideas are:
- Defer judgment. Don’t judge your ideas while you are generating them.
- Strive for quantity. The more ideas you generate, the greater your chance of getting breakthrough ideas.
- Seek wild and unusual ideas. The reason why you are stymied with this problem is that the usual approaches haven’t worked. Go for unconventional ideas.
- Combine and build on ideas. Let one idea inspire another idea, and inspire another idea.

Generating Creative Questions
Because brainstorming is not limited to generating ideas, below you will find the guidelines for generating creative questions. By generating many creative questions, team members increase the probability of identifying the real problem getting in their way instead of just a symptom.
- Defer judgment. Don’t judge your creative questions while you are generating them.
- Strive for quantity. The more creative questions you generate, the greater your chance of identifying the real problem.
- Seek wild and unusual questions. Go for unconventional questions.
- Combine and build on other questions. Let one creative question inspire another creative question, and inspire another.
Wondering why your brainstorming sessions don’t work?
Don’t Botch Your Next Brainstorming Session!
Alex Osborn, the “O” in the advertising agency BBDO, invented the brainstorming technique in the late 1940s and popularized it in his classic book Applied Imagination . From Osborn’s point of view, he recognized that brainstorming was a technique and nothing more. With that in mind, he collaborated with Sidney J. Parnes to develop the Osborn-Parnes Creative Problem-Solving process. That process has continued to evolve over the years. The latest development in the Creative Problem-Solving process is the 21st Century Creative Problem-Solving process .
The process consists of four steps:
- Clarify the Problem,
- Generate Ideas,
- Develop Solutions,
- and Plan for Action.

The brainstorming technique is used in each stage of the 21st Century Creative Problem-Solving process.
Brainstorming is used to generate creative questions in the Clarify the Problem stage of the process.
Brainstorming is used to generate ideas to solve the “real” problem that was identified in the Clarify the Problem stage.
In the Develop Solutions stage of the CPS process, brainstorming is used to generate ways to overcome any concerns identified in the solution that were identified by the PPCo (Pluses, Potentials, Concerns, Overcome concerns) technique.
In Plan for Action , brainstorming is used to generate all of the potential action steps that might be taken to implement solutions.
To recap…
Techniques are specific methods or tools used within a process, while a process is a more comprehensive framework that guides the overall approach to problem-solving or creativity.
Brainstorming FAQ’s
Although the scope of this article is to make a distinction between the brainstorming technique and the Creative Problem-Solving process, I would like to address some frequently asked questions.
Are there a variety of brainstorming techniques, or are there different types of brainstorming?
Osborn emphasized that brainstorming is not only a group technique. You can brainstorm individually. Just follow the same guidelines as when you are working in a group. It is unlikely that you will come up with the quantity of ideas that a group would generate, but you will come up with many more ideas than if you had not deferred judgment and strived for quantity.
A very popular brainstorming technique is Brainwriting. Brainwriting emphasizes the fourth brainstorming guideline, which is to “combine and build on other ideas.” In a traditional brainstorming session, group members say their ideas out loud. In a Brainwriting session, participants do not have to talk to each other. They work individually to generate ideas. Video number eleven in the Create in a Flash Online Course shows the Brainwriting technique in action.
Are there online brainstorming tools?
I have found the Mural platform especially helpful when it comes to Creative Problem-Solving. In addition to creating a variety of brainstorming templates on Mural we have also developed a number of templates for the entire Creative Problem-Solving.
My Breakthrough Lab has been used to develop ideas for new products, create strategies for international food guidance, plan and execute business transitions, develop methods to improve medical education, and create detailed plans for business expansion.
Creative Problem-Solving is perfect for challenges that are a part of everyday life like raising your children, solving community problems, starting your own business, or creating the life that you love.
The beauty of the Creative Problem-Solving process is that it can be applied to any ill-defined problem that needs creative ideas.
Creative Problem-Solving is a life-giving process. It helps you see possibilities that you could have never imagined.
Want to know more?
About dr. roger firestien.
Dr. Roger Firestien has presented programs on innovation to over 600 organizations around the world including Fortune 500 corporations, government agencies, universities, associations, hospitals, and religious institutions.
Roger has written seven books and hundreds of articles on the creative process . His books include Why didn’t I think of that ? and Create in a Flash . His latest book is Solve the REAL problem . It will be released soon as an audiobook.
Subscribe to Roger’s Email List
Sign up for a dose of creativity tools, stories, and inspiration to ignite innovation, brought to you by Dr. Roger Firestien. Just the good stuff, once per month.
Get in Touch
(716) 631-3564 | [email protected]
How Roger Can Help:
Free live webinar.
Join Roger on Friday, November 15, 2024 from 12:00 to 1:00 Eastern Time for a free interactive live webinar, To Create Breakthroughs Make Connections . Experience how making new connections can create breakthrough solutions. And we will solve a real problem at the same time.
Register Now For Roger’s Course April 23 to 25, 2025
Mastering your creativity: discovering breakthrough solutions fast.
Through a series of structured learning experiences, you will learn to become deliberately creative and build your skills to lead innovation teams in your organization. You will be instructed by Dr. Roger Firestien who has presented programs on innovation to over 600 organizations around the world including Fortune 500 corporations, government agencies, universities, associations and religious institutions.
Breakthrough Labs
Discover the real problems facing your organization and then generate hundreds of ideas for solving those problems with the Breakthrough Lab.
On-Demand Videos
You and your team are now only a click away from Dr. Firestien’s help to find the solution to any challenge with his nine-part video series on the OpenSesame Learning platform. Watch a trailer and learn more.
Related Content

After the Creative Slump – What’s Next?

Got a Creative Slump? It may not be what you think it is.
What is Divergent Thinking?

Overcome Your Creative Blocks with Seven Creative “Blockbusters”

Guest Post on thoughtleadersllc.com

Innovation Can’t be “Managed”
Subscribe to innovation espresso ®.
What is brainstorming? Definition, guide, and methods

Start collaborating with Mural today
When you hear the term brainstorming, there are a few images that might come to mind. One is the classic stock photo of a group of colleagues huddled around a whiteboard or a pile of papers, all big smiles and high energy.
But brainstorming sessions don’t always go as smoothly as these images make them seem. Sometimes, there are disagreements between co-workers. Other times, there’s too much agreement with just one person’s ideas. And then there are days when ideas just don’t seem to make their way onto the blank canvas in front of you.
Whether you’re problem-solving, developing a new product, or trying to come up with creative ideas for your business, brainstorming isn't just about gathering your group members together and hoping the innovation sparks fly.
There are proven methods, techniques, and tools that can make effective brainstorming easier than ever.
In this guide, we’ll dive into all of the resources Mural has put together to help managers and their teams run successful brainstorms.
What is brainstorming?
Brainstorming is a method for producing ideas and solving problems by tapping into creative thinking. Brainstorming usually takes place in an informal, relaxed environment, where participants are encouraged to share their thoughts freely, build upon the ideas of others, and explore a wide range of possibilities.
How to get the most out of your next brainstorming session
Running a great brainstorming session encourages your team to use techniques that inspire creative thinking. As a manager, you’ll likely be the one to facilitate these sessions and make sure they run smoothly and produce positive results.
How to run a brainstorming session
As a facilitator, it’s your job to guide your team in the right direction throughout the process, from start to finish. To start, prepare for the session and define your brainstorming topic.
This means setting a clear purpose or goal for the session, deciding on a structure, and dividing your team up into small groups if need be. You’ll also want to define the rules and parameters for your team members.
Next, depending on the brainstorming method you’ve chosen, you may need to keep an eye on the time to give everyone a chance to contribute. Throughout the process, encourage members to voice their opinions. Toward the end, make sure you explain any next steps or action items for your team.
Strategies for better group brainstorming
Group brainstorming can help you generate awesome ideas that one person alone might never come up with. But when you gather a group of people together, it often comes with some challenges. Dominant personalities can hijack a conversation, making the exercise less effective and the rest of the group feel unheard. Groupthink is another potential issue in which too much conformity prevents you from delivering original or creative solutions.
Here are a few things you can do to combat these challenges and have better group brainstorming sessions:
- Establish rules that emphasize the importance of diverse points of view.
- Choose a brainstorming technique that's beneficial for groups, like reverse brainstorming or ‘Crazy 8s.’
- Make sure team members have time to also do some solo thinking.
No matter what techniques you implement, the key is to make sure every participant is on the same page when it comes to rules and expectations.
Structured brainstorming and when to use it
A structured brainstorm helps keep everyone focused on your goals or the task at hand. It’s also a good way to make sure everyone’s opinion is heard. In some cases, participants can also prepare ahead of time, which could be beneficial for the overall success of the activity.
Structured brainstorms are best for remote or distributed teams to efficiently replicate past successes, and for large groups.
Understanding problem framing
Problem framing is a critical step in the brainstorming process that gives context and provides a deeper understanding of the purpose of the brainstorm. It helps provide your team with clarity and a narrow scope so that their ideas aren’t all over the place. It also helps increase the efficiency of the session as you or the facilitator can spend less time re-orienting them back in the right direction.
Here are a few steps for framing a problem:
- Create a problem statement .
- Identify the root of the problem.
- Empathize with customers or stakeholders.
- Frame the problem with prompts or questions that can be used during brainstorming.
Brainstorming questions to generate better ideas
Thought-provoking questions can really help your team thrive during a brainstorming session. They provide participants with a starting point to think up ideas or directions. They can also be used to enhance or refine any suggestions or solutions that have already been produced. Here are a few examples of the types of questions that produce better ideas:
- Information-gathering questions (e.g., “Why did we shift our marketing strategy from traditional advertising to digital platforms?”)
- Problem-solving questions (e.g., “What are the criteria we should use to evaluate potential solutions?”)
- Refining questions (e.g., “How can we ensure the sustainability of the solution over time?”)
Questions can help reduce the overwhelm or blind spots that can happen as you develop ideas. It narrows everyone’s focus and helps you make ideal decisions.
Advice for teams during a brainstorming session
Generating ideas that solve challenges can be a lot of pressure for your team. It can also be discouraging if it feels like they’re not coming up with anything groundbreaking or even viable. Not to mention, there can be a lack of cohesion and beneficial collaboration among group members.
But, knowing the right strategies and rules for effective brainstorming can help turn a stressful activity into a productive and fruitful one.
Ground rules for brainstorming
Ground rules help set expectations, decrease the chance of a conflict, and make participants feel more comfortable throughout the process. Before your team gets started on ideation, they should create a “rules of brainstorming” document that they can refer to throughout the process. You can create this for them or have them make one as a team.
Here are a few examples of significant ground rules that improve the flow of a brainstorming session:
- There are no “bad ideas”; be accepting of all suggestions no matter how crazy and wild. (You can always iterate, refine, or vote on it later.)
- Incorporate a “private” portion of the brainstorm so people can think for themselves.
- Read ideas carefully before commenting, and don’t judge others' ideas at face value.
Following these rules and others relevant to your team’s needs can help ensure a smooth and efficient process.
Avoiding groupthink in teams
Groupthink is when people, consciously or unconsciously, choose to agree with one another rather than challenge each other with conflicting views. This can happen when there’s poor conflict management, a lack of diversity, or psychological safety issues. One way you can tell that your team is under the spell of groupthink is when there's quick and unanimous agreement or a lack of push-back or follow-up questions to others’ ideas.
To reduce the chances of groupthink, consider ways you can remove bias, like using a private mode or voting feature. Participants should encourage each other to express their own ideas, even if that means light conflict when there's a difference of opinion. It’s also important that every team member understands groupthink and how to spot it.
Creating better action items to follow up on
At the end of a brainstorming session, team members should have a list of action items to follow up on. These action items hold everyone accountable and help keep track of progress as you carry out tasks related to the solutions developed during the brainstorming session.
An effective list of action items has the following traits:
- They summarize what needs to be done.
- They explain why each action item or task matters.
- They have a team member assigned to each item with a due date.
You can use a simple to-do list or a project kickoff template , whatever works best for your team!
Tips for brainstorming remotely
Remote brainstorming exercises can be just as successful at idea generation as in-person brainstorming. The main difference between running a regular brainstorm and a virtual one is the tools you use to communicate and collaborate. Group discussions can be done easily through software like Zoom or Microsoft Teams . Plus, online whiteboards like Mural work just as well, if not better than the analog version.
Optimize your virtual brainstorming session
Virtual brainstorms lack some of the face-to-face interaction of an in-person session. This means you’ll need to adapt your processes to fit an online dynamic. For one, it’s crucial to find a collaboration platform where everyone can contribute their ideas in a central location. You’ll also need a facilitator or point person to keep everyone on track and update the shared document or whiteboard accordingly. Brainstorming templates are also extremely useful for creating an efficient and smooth virtual meeting.
Try asynchronous brainstorming
Asynchronous brainstorming is a great option for those who want to prevent groupthink, improve focus, and reduce time constraints — especially for distributed teams. If you have a team that works across different time zones or working hours, individual brainstorming allows them to contribute at a time that works best for them.
Just like a synchronous brainstorming, you still want to establish a clear goal, select a collaborative platform, and outline the rules and expectations. However, a key difference is that for async work, you need to establish a timeframe and set deadlines so that you’re not waiting on any one person to contribute, iterate, or respond to ideas.
Related: 6 essential steps for building an async-first culture
Improve group communication
Whether you’re in-person or remote, effective communication improves collaboration, increases productivity, and promotes problem-solving. But when you’re working on a distributed team, solid group communication is vital. In our busy digital spaces, things can either get lost in translation or literally lost in a pile of emails and Slack messages.
Here are a few helpful things you can do to combat poor online communication:
- Recognize and celebrate healthy behavior and helpful communication examples.
- Foster a supportive culture that invites constructive feedback but not judgemental criticism.
- Build trust through team activities like icebreakers or team check-ins .
- Use tools that make communication easy and efficient.
Working on each of these will help your team get their footing when it comes to communicating and flourishing in remote work environments.
Brainstorming techniques, methods, and templates
There are countless brainstorming methods and techniques you and your team can use to uncover creative solutions. Some involve lateral thinking, while others start with a basic brain dump. Regardless of which you choose, it’s a good idea to try out different ones over time and see which produces the best results for your team. In fact, switching up the brainstorming method could add some novelty by reengaging your team to come up with new ideas each time you’re faced with a challenge.
One thing most brainstorming methods have in common is the idea of quantity over quality. At the beginning of any brainstorming session, the number of ideas you produce is often more valuable than the quality or viability of any one of those ideas. You can always keep workshopping the existing ones until you narrow down and refine the optimal ones.
Rapid ideation
Producing a high quantity of ideas is the name of the game here. There are many brainstorming exercises that incorporate rapid ideation. The key is to be quick and spontaneous so as not to censor or edit any ideas that come to mind.
Brain-netting
Brain-netting is a term used to describe brainstorming via multiple digital tools and spaces, in other words, online brainstorming. Typically, it’s preceded by online brain dumping, and then connecting related ideas and concepts to narrow down the best ones.
Reverse brainstorming
Reverse brainstorming is a counterintuitive technique in which you come up with ideas on how to make a problem worse. Then, you “reverse” those ideas by coming up with applicable solutions to those problems. This process helps you discover some possible ideas for your original challenge.
Round-robin
In round-robins, each participant writes their idea down during a set time limit before the next person gets a turn to contribute. There are a few variations of this: You can compile ideas on sticky notes to return to later, pass them off to the next person to iterate on, or refine the ideas by providing feedback.
Ready to get started? Try the round-robin template from Mural.
Mind mapping
Mind mapping is a visual way to brain-dump ideas onto a blank page and use those existing ideas to spark new ones. You start with one concept in the middle of the whiteboard and add related ideas on branches shooting out from the central topic. Then you keep building on it like a map or family tree.
Get started with the Mind map template .
Rolestorming
During rolestorming, participants role-play as someone else, such as a famous person or customer persona, to embody different perspectives. Taking on that character during the brainstorm can change the way they think and help them produce creative ideas.
Brainwriting
Brainwriting takes advantage of solo brainstorming time. Participants develop their ideas individually before sharing them with the rest of the team. There are different variations of this method, including a rapid ideation version in which six participants need to each generate three ideas in five minutes.
Start generating ideas with the 6-3-5 brainwriting template .
Starbursting
During a starbursting exercise, group members develop questions that begin with “who, what, when, where, why, and how.” These six questions are based on a specific topic or problem statement. The team uses a star graphic, with each point on the star representing one of the six types of questions you come up with during this exercise.
Step-ladder technique
The step-ladder technique begins by selecting two participants in the group to discuss the problem and come up with an idea. Then, you introduce a third team member to the first two, and they present ideas to each other and discuss. Then you add a fourth person, and so on and so forth.
Enhance the collaborative process of brainstorming with the right tools
We use brainstorming activities to help us with creative problem-solving. But without the right tools, it can be difficult to collaborate and record the ideas you’re coming up with together. To make the process more efficient and productive, use tools that make collaboration easier — whether you work in-person, remote, or hybrid.
That’s where Mural can help.
Mural is the visual work platform for all kinds of teams to do better work together — from anywhere. Get team members aligned faster with templates, prompts, and proven methods that guide them to quickly solve any problem. They can gather their ideas and feedback in one spot to see the big picture of any project and act decisively. From online brainstorming , to retrospectives , Mural helps you change how you work, not just where.
That’s what happens when you change not just where, but how you work.
Get started with the free, forever plan with Mural to start collaborating with your team.

Related blog posts
%2520(1).jpeg)
10 Brainstorming Techniques for Developing New Ideas
%20(1).jpg)
25 Brainstorming Questions to Generate Better Ideas
.jpeg)
How to Facilitate a Brainstorming Session
Related blog posts.

10 activities for team building in the workplace

The complete guide to spaghetti mapping

A guide on Scrum product backlog
- A 2 Z Design Terms
- Web Design Tutorial
- Graphic Design
- User Interface
- User Experience
- Design Principles
- Color Theory
- Color Schemes
- Color Meaning
- Wireframing
- Prototyping
- Responsive Design
- Design Thinking
- Visual Design
- Mobile First Design

What is Brainstorming?
Brainstorming is a creative problem-solving technique where individuals or groups generate a multitude of ideas to address a specific issue or challenge. This method encourages open thinking and the free flow of ideas, promoting innovative solutions and collaboration. Brainstorming sessions can be highly effective in various settings, from business meetings to classroom activities, as they help unlock creativity and allow participants to explore different perspectives. In this article, we will delve into what brainstorming is , its benefits, and how to conduct an effective brainstorming session to maximize productivity and creativity.

Brainstorming is a method used to solve problems and generate innovative ideas through creative thinking. This technique involves bringing together individuals or groups to generate a wide range of solutions or new concepts that can help a brand or project stand out. By encouraging open and unrestricted thinking, brainstorming creates an environment where new and creative ideas can emerge and be explored.
During a brainstorming session , participants are encouraged to think freely and propose any idea that comes to mind, without fear of criticism or judgment. This approach helps in uncovering unique solutions that might not be immediately obvious. Typically, brainstorming is conducted in a team setting to leverage the diverse perspectives and ideas of different participants. However, it can also be effectively done by an individual.
Importance of Brainstorming
Creates unique identity :.
Brainstorming helps brands develop a distinct identity that sets them apart from competitors, giving them a competitive advantage .
Effective Problem-Solving :
When a problem is too challenging for an individual, a team can combine their unique perspectives to find the best solution.
Encourages Diverse Approaches :
The flexibility of brainstorming allows for various approaches and ideas, leading to innovative and unique solutions.
Enhances Team Collaboration :
Fosters teamwork and collective thinking, improving overall team dynamics and productivity.
Promotes Innovation :
Encourages out-of-the-box thinking, driving fresh and creative ideas that can propel the brand forward.
Improves Decision Making :
By considering multiple viewpoints, brainstorming helps in making more informed and well-rounded decisions.
Boosts Engagement :
Engages team members by valuing their input and ideas, leading to higher morale and motivation.
Increases Efficiency :
Rapid idea generation during brainstorming sessions saves time and accelerates the problem-solving process.
How to Use Brainstorming?
To run a successful brainstorming session , follow these steps:
Step 1. Prepare
- Clearly define the problem or topic you're brainstorming about.
- If applicable, gather a diverse group of participants to enhance the variety of ideas.
- Set a comfortable environment to encourage free thinking.
Step 2. Generate Ideas
- Encourage open and unrestricted sharing of ideas, emphasizing quantity over quality .
- Use techniques like free association , mind mapping , or listing to facilitate idea generation.
- Ensure all ideas are recorded visibly for everyone involved to see.
Step 3. Review and Select
- After generating a wide range of ideas, review them to identify the most promising ones .
- Evaluate these based on criteria like feasibility , impact , and resources required .
- Develop an action plan for implementing the selected ideas.
Types of Brainstorming Techniques
Here are some important brainstorming techniques commonly used to generate creative solutions:
1. Random Brainstorming
This method involves using ideas that come up first when the problem is presented. These are spontaneous thoughts that occur without much deliberation. The first words or ideas that come to mind can sometimes lead to unique combinations and optimal solutions .
2. Reverse Brainstorming
In this method, the focus is on the end goal rather than the problem itself. The team considers the outcome and tries to predict future possibilities. This helps identify potential problems and outcomes, allowing the team to avoid specific obstacles and improve the overall process.
3. Rapid Ideation Brainstorming
Here, everyone in the team writes down their first thoughts privately. Unlike random brainstorming, where ideas are spoken aloud, this method ensures that each member has the privacy to jot down their thoughts, leading to more unique and creative solutions. This can provide multiple perspectives on the problem.
4. SCAMPER Brainstorming
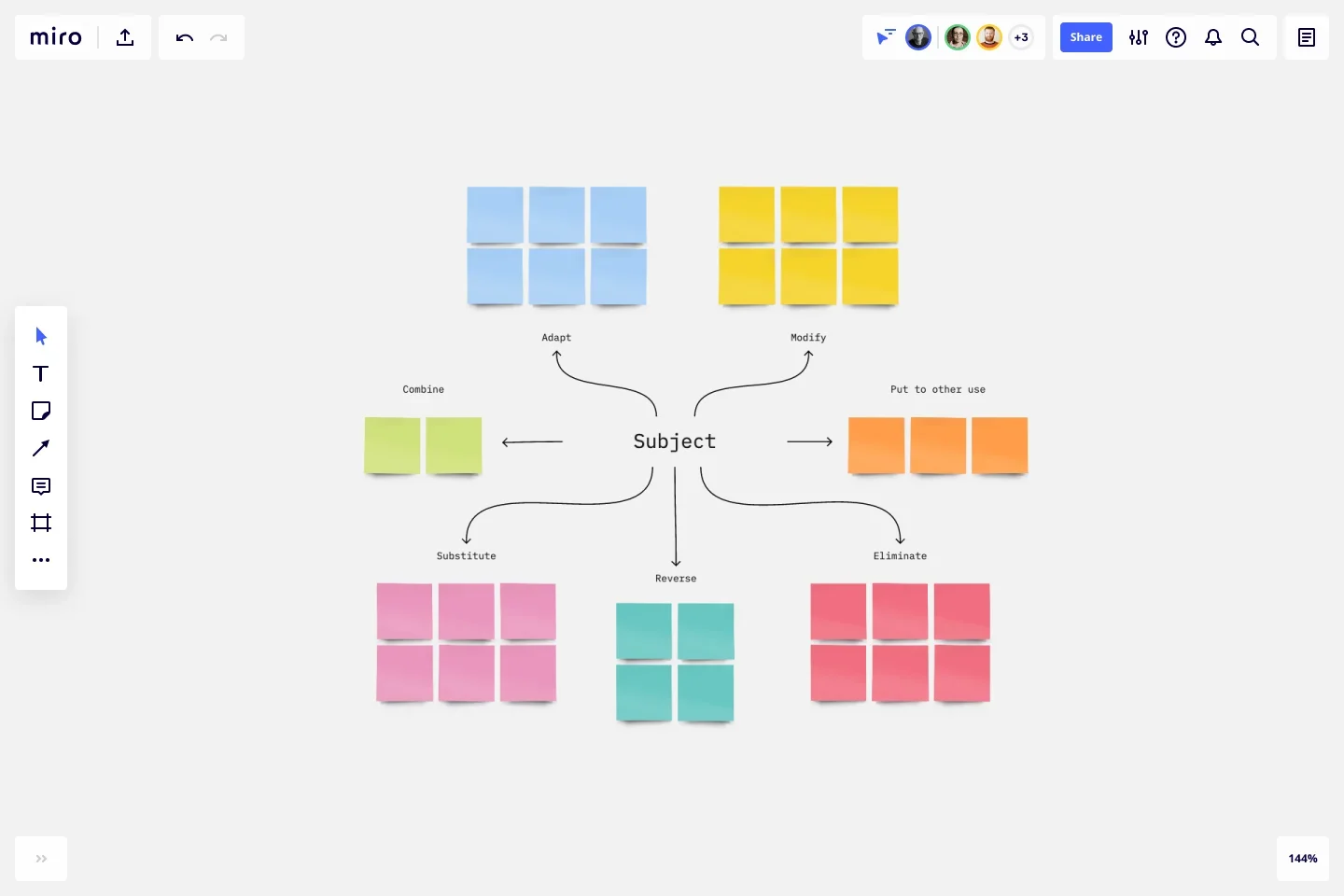
SCAMPER stands for Substitute, Combine, Adapt, Modify, Put to another use, Eliminate, and Reverse . This technique involves looking at a problem from various angles to generate a variety of ideas. Each idea is tested and refined through a series of questions, resulting in a well-rounded solution.
5. Starbursting Brainstorming
In this technique, team members ask questions instead of presenting ideas. This helps in identifying potential issues and exploring different perspectives. By breaking down the problem into multiple questions, it provides a step-by-step solution and a thorough understanding of the problem.
Benefits of Brainstorming
Brainstorming offers numerous advantages, making it a valuable tool for problem-solving and idea generation. Here are some key benefits:
- Different Perspectives : Brainstorming sessions allow team members to provide various viewpoints on a problem. Using different brainstorming techniques can bring in innovative ideas and help the team look at the problem from multiple angles.
- Increases Creativity : Encouraging open and unrestricted idea generation helps bring out creativity in team members. With no predetermined process to follow, each participant can create unique approaches to the problem, fostering a highly creative environment.
- Team Collaboration : Brainstorming promotes collaboration among team members. Working together on a problem helps reveal each member's strengths and weaknesses, improving teamwork and understanding of each other's thinking processes for future sessions.
- Enhanced Problem-Solving : By combining different ideas and approaches, brainstorming leads to more effective problem-solving. The collaborative effort results in well-rounded solutions that might not be achievable individually.
- Boosts Engagement : Brainstorming engages team members by valuing their input and ideas. This leads to higher morale, motivation, and a sense of ownership over the project's outcomes.
- Encourages Risk-Taking : In a brainstorming session, participants feel free to suggest bold and unconventional ideas without fear of criticism. This openness encourages risk-taking and exploration of novel solutions.
- Accelerates Decision Making : By quickly generating a wide range of ideas, brainstorming speeds up the decision-making process. Teams can evaluate and select the best ideas efficiently, saving time in the long run.
- Improves Communication : Brainstorming sessions facilitate better communication among team members. Sharing ideas and discussing potential solutions enhances overall communication skills and fosters a collaborative work environment.
Brainstorming involves thinking about different solutions which can help in solving problems and coming up with new innovative ideas that can help the brand.
Different Types of Brainstorming methods can be used to tackle a problem which can help to come up with the best and most optimal solution for a problem. It helps build teamwork between members and increase creativity. Different ideas should be considered and worked on.
What is Brainstorming - FAQs
What do you mean by brainstorming.
Brainstorming is a creative problem-solving technique used to generate a large number of ideas or solutions to a particular problem or challenge. It typically involves a group of people gathering together to freely share and explore their thoughts, ideas, and perspectives without judgment or criticism.
What are the 4 methods of Brainstorming?
The 4 methods of Brainstorming are: Traditional Brainstorming Mind Mapping Reverse Brainstorming Brainwriting
What is Brainstorm example?
An example of brainstorming could be a group of marketing professionals gathering to generate ideas for a new advertising campaign. During the brainstorming session, participants might suggest various concepts, slogans, visuals etc. with the idea to generate a diverse range of ideas that can later be evaluated.
Who first used Brainstorming?
Brainstorming was first introduced by Alex Osborn, an advertising executive, in the late 1930s.
Why is it called Brainstorm?
The term "brainstorm" combines "brain" for thinking and "storm" for sudden activity , representing rapid idea generation.
Is Brainstorming a skill?
Yes, Brainstorming is one of the skills included in the general category of critical thinking .
Why is brainstorming hard?
Brainstorming can be challenging due to social dynamics, like fear of judgment or dominance by vocal individuals , and structural issues, such as maintaining focus and effectively managing diverse ideas within a limited time frame.
Similar Reads
- UI UX Design
Please Login to comment...
Improve your coding skills with practice.
What kind of Experience do you want to share?
Table of contents
What is brainstorming?
Definition of brainstorming.
Brainstorming is a creative thinking technique for coming up with new ideas and solving problems. Teams use this ideation method to encourage new ways of thinking and collectively generate solutions. Brainstorming encourages free thinking and allows for all ideas to be voiced without judgment, fostering an open and innovative environment. This process typically involves a group of people, although it can be done individually as well.
This guide will help you get the most out of every creative session. When you're ready to start your next free thinking exercise, jump into Miro’s brainstorming tool to generate ideas and turn them into action.
What is the main purpose of brainstorming?
The primary purpose of a brainstorming session is to generate and document many ideas, no matter how “out there” they might seem. Through this lateral thinking process, inventive ideas are suggested, which sparks creative solutions. By encouraging everyone to think more freely and not be afraid to share their ideas, teams can build on each other’s thoughts to find the best possible solution to a problem. Brainstorming usually takes place in a group setting where people get together to creatively solve problems and come up with ideas. However, it’s also useful for individuals who need to explore novel solutions to a problem. Sitting down by yourself and writing down solutions to potential problems is a great way to brainstorm individually. Focusing your mind on a defined problem allows you to think of many creative ways to get to an answer. While brainstorming normally allows for free-form methods of thinking and doesn’t require many rules, the best results usually stem from controlled sessions. Posing questions and role-playing different scenarios during the brainstorming session is a smart way to pull out unusual ideas and never-before-thought-of solutions.

Benefits of brainstorming
Why is brainstorming such a popular approach to solving problems and generating ideas? Here are some of its many advantages:
Encourages creativity
Brainstorming sessions are meant to be free of judgment. Everyone involved is meant to feel safe and confident enough to speak their minds. There will be some good and some bad ideas, but this doesn’t matter as long as the final outcome is one that can solve the problem. This kind of free-thinking environment, along with a few essential brainstorming rules, encourage creativity in the workplace.
Fosters collaboration and team building
Brainstorming is not only good for problem-solving. It also allows employees and team members to understand how the people around them think. It helps the team get to know each other’s strengths and weaknesses and helps build a more inclusive and close-knit workforce.
Generates innovative, revolutionary ideas
Brainstorming is the perfect mix between a free-thinking, creative environment and one that is governed by rules. Being faced with a defined problem or asking questions like “What do we do in X scenario?” forces everyone in the room to come up with ideas and solutions. No two people think alike. So, combining the good parts of everyone’s answers will result in holistic and revolutionary solutions.
Establishes different perspectives
One of the major benefits of brainstorming is that it allows and encourages all members of the session to freely propose ideas. This type of environment fosters courage in people who may not usually offer their perspective on a problem. Garnering a range of different perspectives can lead to a never-before-thought-of solution.
Introduces many ideas quickly
The beauty of brainstorming is that it encourages teams to come up with many ideas in a relatively short period of time. Ideas are thrown around, and every train of thought is documented. Different perspectives give different answers, and sifting through a few good answers in quick succession may lead to the perfect solution in no time.
Types of brainstorming techniques
There are plenty of creative brainstorming techniques to choose from. Here are some of the most popular ones:
Reverse brainstorming
In a typical brainstorming session, the group is asked to consider solutions to a problem. This means that they will spend time thinking about the outcome — the end goal — rather than the root of the problem — the starting point. Reverse brainstorming is simply the opposite: teams are asked to ideate on the problem instead of the solution. This type of brainstorming is done before the start of an important project, as it helps teams anticipate any future obstacles that might arise. To help frame this way of thinking, use a Reverse Brainstorming Template to get the team started.
Random word brainstorming
One of the main goals of a brainstorming session is to come up with new ideas. One of the best ways to do this is to say the first words that come to mind when a specific topic or subject is mentioned. Random word brainstorming allows for exactly that. The team is given a problem, and they need to shout out the first words that they think of, regardless of what they are. These words are then written down and later put into interesting combinations to see if they will lead to a usable solution. This brainstorming method is extremely fast and usually very efficient at solving a defined problem. The Random Words Brainstorming Template can help get you started.
The 5 Whys Method
Like the reverse brainstorming method, the 5 Whys method aims to look at the root causes of a problem to stop that same issue from arising again. This method attempts to curb the problem before it can reoccur by asking the question “why?” over and over until it can no longer be answered. Once you reach this stage, you have arrived at the root cause of the issue.
SCAMPER model
Developed by Bob Earle, an author of creativity books for kids, the SCAMPER model was originally a game aimed at imagination development in adolescents. It has, however, become popular in the corporate world as a means of improving and encouraging creativity in team members when dealing with complex, defined problems. Using this model, your team will view a problem through 7 filters: substitute, combine, adapt, modify, put to another use, eliminate, and reverse.
Rapid ideation
Rapid ideation brainstorming is almost the exact same thinking model as random word brainstorming. In this method, however, everyone writes down the solutions they are thinking of instead of shouting them out. This gives participants a bit more privacy with their immediate thoughts — possibly leading to even more creative and revolutionary outcomes.
Starbursting
Once again, brainstorming can change based on the team’s perspective and each session’s expected outcome. Starburst brainstorming focuses on getting the team to ask questions instead of coming up with answers.
How to hold a brainstorming workshop
Ready to harness the power of a well-run brainstorming session? Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to organize a successful brainstorming workshop:
1. Assign a facilitator
When done as a group, a brainstorming session needs to have boundaries. You need to choose someone who will facilitate the session and provide guidelines for the thinking exercises that the group will partake in. This is so the session doesn’t get too scattered and stays on the right track. The facilitator should pose questions and guide the group from start to finish.
2. Establish context and ensure group understanding
A brainstorming session cannot be properly carried out without context. The group must understand why they are meeting and what the end goal of the session is. Everyone should also understand the meaning of brainstorming and what to expect from the brainstorming process. The brainstorming method that will be used should also be established (see point 5) and explained at the outset.
3. Define an objective
While brainstorming is often looked at as a form of free-thinking creativity, it is best to try to stay within certain rules. It’s essential that you define a clear objective and use the session to reach your predetermined goal.
4. Set a time limit
Setting a defined time limit before the session starts is important to the success of your brainstorming session. No doubt your team could come up with countless ideas, but there has to be a limit on how long the session can run. Knowing that you need to solve a problem within one hour, for instance, will help the team focus on the job at hand and come up with ideas faster. It will also keep everyone thinking about the same problem.
5. Decide on the brainstorming technique
The brainstorming technique that will be used must be decided on before the session begins. The best way to do this is to look at the problem at hand. If you’re looking to prevent obstacles from arising in the future, try the “5 Whys” technique. If you’re looking to come up with new marketing ideas or get creative with workplace conflicts, try the rapid ideation technique.
6. Set some ground rules
As stated above, the best and most productive brainstorming sessions are those that allow for free thinking and creativity within preset boundaries. Brainstorming ground rules are essential to to the success of the session, as they keep everyone focused on the topic at hand and ensure that no one goes off track.
7. Capture all ideas
The entire point of a brainstorming session is to come up with as many ideas as possible, regardless of whether the standalone suggestion will lead to success. This means that you need to use the right tools to document the ideas being suggested. Miro has a host of idea-capturing tools, including a simple-to-use visual platform for remote brainstorming sessions and digital sticky notes .
8. Discuss and vote on ideas
After all the ideas have been captured, it’s time to discuss them. The team needs to be productive in choosing a creative idea that suits the problem, or they can try combining a few ideas to come up with a holistic solution. To make decisions as a group and come to an agreement, teams can use the dot voting method . This technique reveals group priorities and helps everyone reach a consensus on the direction to take.
9. Turn ideas into action
Once the final idea has been chosen, it’s time to create a plan of action and a deadline for the idea to be put in place. Transform your ideas into detailed, tangible steps with the Action Plan Template . This will help with coordination between team members and ensures that nothing is missed.
Tips for your brainstorming activities
While all brainstorming sessions look a little different, here are some best practices to get the most out of yours:
Record all ideas
If you want to have a successful and productive brainstorming session, it’s important that you capture every idea suggested, good and bad. An idea might seem silly when first brought up, but it might become an invaluable idea as the session moves on. Capture everything, and right at the end, work out which ideas best suit the problem.
Ensure that everyone’s ideas are heard
When brainstorming is done as a group activity, everyone needs to feel comfortable and confident to propose ideas. The best way to make sure the environment fosters these feelings is to make the session feel like a conversation, not a presentation. Create a safe and open environment that gives everyone equal opportunity to voice their opinions and ideas.
Focus on quantity
People often like to say, "Focus on quality, not quantity," but it’s the opposite when brainstorming. In a brainstorming session, you should focus on getting as many ideas on the board as possible, even if they're only one-word ideas. These can all be used to come to a holistic solution at the end of the session. Each suggestion could be invaluable if you're coming up with a combined idea.
Brainstorming should be a fun and creative endeavor. You shouldn’t be too rigid — though some ground rules are important. If your team has weekly brainstorming sessions, try new brainstorming techniques and activities each time you meet. This will keep your team members on their toes and help make them excited about the next meeting. It will also encourage out-of-the-box thinking, which is essential to any successful brainstorming session.
Avoid criticism
We’ll say it again: there are no bad ideas in a brainstorming session. This is the attitude that all team members must adopt when entering the session. No one should be criticized for the ideas that they propose. The best way to foster an environment that is devoid of criticism and encourages creativity is to maintain a relaxed approach. This will make everyone feel comfortable and happy to contribute their ideas.
Discover more
Guide to collaborative brainstorming, when to use brainstorming (and which techniques are best), what is brainwriting, what is reverse brainstorming, how to conduct a brainstorming session, get on board in seconds, plans and pricing.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Brainstorming is a powerful tool for generating creative ideas and engaging teams in collaborative problem-solving. By encouraging spontaneous idea sharing and carefully managing the process, individuals and teams can explore new possibilities and develop …
As nouns the difference between brainstorming and brainstorm is that brainstorming is a method of problem solving in which members of a group contribute ideas spontaneously …
Brainstorming is a method for producing ideas and solving problems by tapping into creative thinking. Brainstorming usually takes place in an informal, relaxed environment, where participants are encouraged to share …
What are the main differences between brainstorming and mind mapping? Brainstorming is focused on generating new ideas, while mind mapping is focused on creating relationships between ideas. Brainstorming …
Brainstorming is a creative problem-solving technique where individuals or groups generate a multitude of ideas to address a specific issue or challenge. This method encourages open thinking and the free flow of ideas, …
Brainstorming is not only good for problem-solving. It also allows employees and team members to understand how the people around them think. It helps the team get to know each other’s strengths and weaknesses and helps build a …