- Search Search Please fill out this field.

What Is a Marketing Plan?
Understanding marketing plans, how to write a marketing plan, marketing plan vs. business plan.
- Marketing Plan FAQs
The Bottom Line
- Marketing Essentials
What Is a Marketing Plan? Types and How to Write One
James Chen, CMT is an expert trader, investment adviser, and global market strategist.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/photo__james_chen-5bfc26144cedfd0026c00af8.jpeg)
Pete Rathburn is a copy editor and fact-checker with expertise in economics and personal finance and over twenty years of experience in the classroom.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/E7F37E3D-4C78-4BDA-9393-6F3C581602EB-2c2c94499d514e079e915307db536454.jpeg)
- How to Start a Business: A Comprehensive Guide and Essential Steps
- How to Do Market Research, Types, and Example
- Marketing Strategy: What It Is, How It Works, How To Create One
- Marketing in Business: Strategies and Types Explained
- What Is a Marketing Plan? Types and How to Write One CURRENT ARTICLE
- Business Development: Definition, Strategies, Steps & Skills
- Business Plan: What It Is, What's Included, and How to Write One
- Small Business Development Center (SBDC): Meaning, Types, Impact
- How to Write a Business Plan for a Loan
- Business Startup Costs: It’s in the Details
- Startup Capital Definition, Types, and Risks
- Bootstrapping Definition, Strategies, and Pros/Cons
- Crowdfunding: What It Is, How It Works, and Popular Websites
- Starting a Business with No Money: How to Begin
- A Comprehensive Guide to Establishing Business Credit
- Equity Financing: What It Is, How It Works, Pros and Cons
- Best Startup Business Loans
- Sole Proprietorship: What It Is, Pros & Cons, and Differences From an LLC
- Partnership: Definition, How It Works, Taxation, and Types
- What is an LLC? Limited Liability Company Structure and Benefits Defined
- Corporation: What It Is and How to Form One
- Starting a Small Business: Your Complete How-to Guide
- Starting an Online Business: A Step-by-Step Guide
- How to Start Your Own Bookkeeping Business: Essential Tips
- How to Start a Successful Dropshipping Business: A Comprehensive Guide
Investopedia / Zoe Hansen
A marketing plan is an operational document that outlines an advertising strategy that an organization will implement to generate leads and reach its target market . It details the outreach and PR campaigns to be undertaken and for how long, as well as the ways in which the company will measure the effect of these initiatives. It reflects a company’s overall marketing strategy.
Key Takeaways
- The marketing plan details the strategy that a company will use to market its products to customers.
- The plan identifies the target market, value proposition of the brand or product, campaigns to be initiated, and metrics to be used to assess the effectiveness of marketing initiatives.
- The marketing plan should be adjusted on an ongoing basis based on which efforts are having an impact and which are not.
- Digital marketing shows results almost in real time, whereas TV ads require rotation to realize any level of market penetration.
- A marketing plan is part of a business plan, which describes all of the important aspects of a business, such as its goals, values, mission statement, budget, and strategies.
The terms “marketing plan” and “marketing strategy” are often used interchangeably because the former is developed based on an overarching strategic framework. In some cases the strategy and the plan may be incorporated into one document, particularly for smaller companies that may only run one or two major campaigns in a year. The plan outlines marketing activities on a monthly, a quarterly, or an annual basis, while the strategy delineates the overall value proposition .
The components of a marketing plan include:
- Market research – This provides information to support pricing decisions and new market entries.
- Tailored messaging – This involves targeting certain demographics and geographic areas and can include the use of affiliate marketing with third-party publishers who bring customers to the table.
- Platform selection – This looks at the best vehicles for disseminating product information for each advertising campaign: traditional venues such as radio, TV, newspapers, and commercial and trade magazines; digital methods such as websites, online ads, search engine results, informational videos, social media groups (Facebook, YouTube, etc.), email, and text messages; or any mix of these platforms.
- Performance metrics – Metrics accurately assess the results of marketing efforts and their reporting timelines and are crucial to the success of the plan.
The four most important social media networks in 2023 for global marketers were, in descending order, Facebook, Instagram, YouTube, and TikTok.
Types of Marketing Plans
There are a variety of marketing plans that suit different businesses and their needs. These include:
- Product Launch – A product-launch marketing plan outlines how a new product will enter the market, the audience it will target, and the advertising methods used.
- Social Media – A social media marketing plan focuses on the advertising strategies on different social media platforms and how to engage with their users.
- Time Based – Time-based marketing plans, such as those that are executed quarterly or annually, focus on the time of the year, the current condition of the business, and the best strategies in that period.
- Content Based – A content-based marketing plan looks in detail at what kinds of content (blogs, videos, graphics, etc.) will reach the target audience.
- Search Engine Optimization (SEO) – An SEO marketing plan is all about getting the most hits online. It involves keyword research, content optimization, link building, and more, all with the goal of drawing customers to your website.
Mission and Value Proposition
The mission and value proposition is a statement that articulates the value that a product or brand will deliver to a customer. It should appear front and center on the company website and any branding materials.
The value proposition should delineate how a product or brand solves the customer’s problem, the benefits of the product or brand, and why the customer should buy from this company and not another. The marketing plan is based on it.
Set Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Establishing your key performance indicators (KPIs) will allow you to measure the success of your marketing plan in relation to your company’s value proposition. In other words, they track the effectiveness of your marketing strategy. For example, if your goal is to engage with a certain demographic in a certain region, you can track social media impressions and website visits.
There are a number of KPIs that help you measure success including the search engine ranking, click-through rate, cost per click, return on investment (ROI), and conversion rates, which tracks the percentages of visitors to your website that make a specific action such as buying a product or becoming a newsletter subscriber.
In 2023, Facebook and Instagram were tied for having the highest ROI across social media platforms for global marketers, while YouTube fell next in line.
Identify Your Target Market
The marketing plan identifies the target market for a product or brand. Market research is often the basis for a target market and marketing channel decisions. For example, whether the company will advertise via social media, online ads, or regional TV.
Knowing to whom you want to sell and why is an extremely critical component of any business plan. It allows you to focus your business and measure its success. Different demographics have different tastes and needs; knowing your target market will help you market to them.
Strategy and Execution
The marketing plan includes the rationale for these decisions. The plan should focus on the creation, timing, scheduling, and placement of specific campaigns and include the metrics that will measure the outcomes of your marketing efforts. For example, will you advertise on social media or TV? What time will you schedule your marketing if they are through email newsletters? The strategy may include flighting scheduling , which includes the times when you can make the most of your advertising dollars.
Set Your Budget
A marketing plan costs money. Setting a budget will allow you to create a workable plan, prevent runaway costs, and properly allocate your funds.
Adjust Your Plan
A marketing plan can be adjusted at any point based on the results from its metrics. If digital ads are performing better than expected, for example, the budget for a campaign can be adjusted to fund a higher-performing platform, or the company can initiate a new budget. The challenge for marketing leaders is to ensure that every platform has sufficient time to show results.
Without the correct metrics to assess the impact of outreach and marketing efforts, an organization will not know which campaigns to repeat and which to drop. In short, maintaining ineffective initiatives wastes money.
Digital marketing shows results almost immediately, whereas TV ads require rotation to realize any level of market penetration. In the traditional marketing mix model, a marketing plan would fall under the category of “promotion,” which is one of the “ four Ps ,” a term coined by Neil Borden to describe the marketing mix of product, price, promotion, and place.
A business plan is a roadmap that details how a business will operate and function in its entirety. It should cover the goals, missions , values, financials, and strategies that the business will use in day-to-day operations and the achievement of its objectives. Among its many elements are an executive summary, the products and services sold, a marketing analysis, a marketing strategy, financial planning, and a budget .
As mentioned, a business plan should include a marketing plan, which focuses on creating a strategy for creating awareness of the company’s product or service, reaching the target market, and generating sales.
Example of a Marketing Plan
Consider the following marketing plan framework that is designed to help direct marketing objectives:
- Executive Summary: Describes company mission, key executives, and where it is headquartered.
- SWOT Analysis: Describes strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats for the company. This helps you define how to build on your strengths and how to find ways to improve on your weaknesses. It also helps a company analyze their competitors and how they may achieve an advantage based on their unique value proposition.
- Business Initiatives: Outlines the goals of the marketing plan, such as the number of impressions, Google rankings, or email subscribers.
- Customer Analysis: Describes your target market and audience characteristics based on market research. These may include age, pain points, and location, among other variables.
- Competitor Analysis: Outlines the companies providing similar goods or services to your target audience. In addition, it describes their strengths, market share, pricing structure, and most importantly where your company can fill an important gap.
What Is a Marketing Plan Template?
A marketing plan template is a guide for writing a marketing plan. It contains all the important elements needed to create one, including its goals and KPIs, marketing channels, budget, content type, teams involved, and design.
What Is an Executive Summary in a Marketing Plan?
The executive summary is a nutshell description of the marketing plan. It should contain the key findings of the market research, the company’s objectives and marketing goals, an overview of the marketing trends, the description of the product or service being marketed, information on the target market, and the plan budget.
What Is a Top-Down Marketing Strategy?
A top-down marketing strategy is a traditional one, in which a business decides how best to sell its product or brand, and customers are then spurred to take action through advertisements, generally found on radio and/or television. It is usually determined by company executives, which is then communicated with management to delegate to employees. These employees then develop tactics to meet the strategy's objectives.
What Is a Bottom-Up Marketing Strategy?
In comparison to a traditional top-down marketing strategy, a bottom-up strategy begins with employees who formulate marketing tactics based on their analysis of customer preferences and needs. This then may lead to collaboration with other employees to develop a concrete marketing plan, which is sent to executives for review.
Today’s consumer wants to relate to a product or service in a meaningful way, and a bottom-up marketing strategy seeks to achieve this through customer-centric tactics.
How Much Does a Marketing Plan Cost?
The cost of a marketing plan will vary based on the company, the plan’s complexity, and the length of the overall strategy. In 2023, marketing costs made up 10.1% of corporate revenues on average. The consumer packaged goods sector spent the most, at 18.5% of revenues while the mining and construction sector spent the least, at 1% of revenues.
A separate analysis shows that the cost can range anywhere from $10,000 to over $40,000 for a marketing plan.
A marketing plan is the advertising strategy that a business implements to sell its product or service. It determines the target market, how best to reach it, at what price point the product or service should be sold, and how the company will measure its efforts.
Constantly monitoring and adjusting a market plan is an important part of running a business, as it shows the most effective ways to generate sales. As the consumer landscape evolves, it is important for businesses to adapt in order to meet customer needs and better achieve their marketing objectives.
Statista. " Marketing Worldwide – Statistics and Facts ."
American Marketing Association. " What Is a Marketing Plan and How to Write One? [Easy Guide] ."
HubSpot. " The 2024 State of Marketing & Trends Report: Data from 1400+ Global Marketers ."
Deloitte. " The CMO Survey: Managing Marketing Technology, Growth and Sustainability ." Page 16.
Laire. " How Much Does a Marketing Plan Cost? "
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/GettyImages-904536858-c089bc26f4fd4025b23f536345ba73ae.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices
We use essential cookies to make Venngage work. By clicking “Accept All Cookies”, you agree to the storing of cookies on your device to enhance site navigation, analyze site usage, and assist in our marketing efforts.
Manage Cookies
Cookies and similar technologies collect certain information about how you’re using our website. Some of them are essential, and without them you wouldn’t be able to use Venngage. But others are optional, and you get to choose whether we use them or not.
Strictly Necessary Cookies
These cookies are always on, as they’re essential for making Venngage work, and making it safe. Without these cookies, services you’ve asked for can’t be provided.
Show cookie providers
- Google Login
Functionality Cookies
These cookies help us provide enhanced functionality and personalisation, and remember your settings. They may be set by us or by third party providers.
Performance Cookies
These cookies help us analyze how many people are using Venngage, where they come from and how they're using it. If you opt out of these cookies, we can’t get feedback to make Venngage better for you and all our users.
- Google Analytics
Targeting Cookies
These cookies are set by our advertising partners to track your activity and show you relevant Venngage ads on other sites as you browse the internet.
- Google Tag Manager
- Infographics
- Daily Infographics
- Popular Templates
- Accessibility
- Graphic Design
- Graphs and Charts
- Data Visualization
- Human Resources
- Beginner Guides
Blog Marketing What is a Marketing Plan & How to Create One [with Examples]
What is a Marketing Plan & How to Create One [with Examples]
Written by: Sara McGuire Oct 26, 2023

A marketing plan is a blueprint that outlines your strategies to attract and convert your ideal customers as a part of your customer acquisition strategy. It’s a comprehensive document that details your:
- Target audience: Who you’re trying to reach
- Marketing goals: What you want to achieve
- Strategies and tactics: How you’ll reach your goals
- Budget: Resources you’ll allocate
- Metrics: How you’ll measure success
In this article, I’ll explain everything you need to know about creating a marketing plan . If you need a little extra help, there are professionally designed marketing plan templates that’ll make the process much easier. So, let’s ditch the confusion and get started!
Click to jump ahead:
What is a marketing plan?
How to write a marketing plan , 9 marketing plan examples to inspire your growth strategy.
- Marketing plan v.s. business plan
- Types of marketing plans
Marketing plan FAQs
A marketing plan is a report that outlines your marketing strategy for your products or services, which could be applicable for the coming year, quarter or month.
Watch this quick, 13-minute video for more details on what a marketing plan is and how to make one yourself:
Typically, a marketing plan includes:
- An overview of your business’s marketing and advertising goals
- A description of your business’s current marketing position
- A timeline of when tasks within your strategy will be completed
- Key performance indicators (KPIs) you will be tracking
- A description of your business’s target market and customer needs
- A description of how you will measure marketing plan performance
For example, this marketing plan template provides a high-level overview of the business and competitors before diving deep into specific goals, KPIs and tactics:

Learning how to write a marketing plan forces you to think through the important steps that lead to an effective marketing strategy . And a well-defined plan will help you stay focused on your high-level marketing goals.
With Venngage’s extensive catalog of marketing plan templates, creating your marketing plan isn’t going to be hard or tedious. In fact, Venngage has plenty of helpful communications and design resources for marketers. If you’re ready to get started, sign up for Venngage for Marketers now. It’s free to register and start designing.
Whether you’re a team trying to set smarter marketing goals, a consultant trying to set your client in the right direction, or a one-person team hustling it out, Venngage for Marketers helps you get things done.
As mentioned above, the scope of your marketing plan varies depending on its purpose or the type of organization it’s for.
For example, you could look for performance marketing agency to create a marketing plan that provides an overview of a company’s entire marketing strategy:

A typical outline of a marketing plan includes:
- Executive summary
- Goals and objectives
- User personas
- Competitor analysis/SWOT analysis
- Baseline metrics
- Marketing strategy
- Tracking guidelines
Below you will see in details how to write each section as well as some examples of how you can design each section in a marketing plan.
Let’s look at how to create a successful marketing plan (click to jump ahead):
- Write a simple executive summary
- Set metric-driven marketing goals
- Outline your user personas
- Research all of your competitors
- Set accurate key baselines & metrics
- Create an actionable marketing strategy
- Set tracking or reporting guidelines
1. Write a simple executive summary
Starting your marketing plan off on the right foot is important. You want to pull people into your amazing plan for marketing domination. Not bore them to tears.

One of the best ways to get people excited to read your marketing plan is with a well-written executive summary. An executive summary introduces readers to your company goals, marketing triumphs, future plans, and other important contextual facts.

Basically, you can use the Executive Summary as a primer for the rest of your marketing plan.
Include things like:
- Simple marketing goals
- High-level metrics
- Important company milestones
- Facts about your brand
- Employee anecdotes
- Future goals & plans
Try to keep your executive summary rather brief and to the point. You aren’t writing a novel, so try to keep it under three to four paragraphs.
Take a look at the executive summary in the marketing plan example below:

The executive summary is only two paragraphs long — short but effective.
The executive summary tells readers about the company’s growth, and how they are about to overtake one of their competitors. But there’s no mention of specific metrics or figures. That will be highlighted in the next section of the marketing plan.
An effective executive summary should have enough information to pique the reader’s interest, but not bog them down with specifics yet. That’s what the rest of your marketing plan is for!
The executive summary also sets the tone for your marketing plan. Think about what tone will fit your brand ? Friendly and humorous? Professional and reliable? Inspiring and visionary?
2. Set metric-driven marketing goals
After you perfect your executive summary, it’s time to outline your marketing goals.
(If you’ve never set data-driven goals like this before, it would be worth reading this growth strategy guide ).
This is one of the most important parts of the entire marketing plan, so be sure to take your time and be as clear as possible. Moreover, optimizing your marketing funnel is key. Employing effective funnel software , along with CRO tools , can simplify operations and provide valuable customer insights. It facilitates lead tracking, conversion rate analysis, and efficient marketing optimization .
As a rule of thumb, be as specific as possible. The folks over at VoyMedia advise that you should set goals that impact website traffic, conversions, and customer success — and to use real numbers. Complement your goals with website optimization tools (e.g., A/B testing speed with Nostra – check Nostra AI review to learn more) to further improve conversions.
Avoid outlining vague goals like:
- Get more Twitter followers
- Write more articles
- Create more YouTube videos (like educational or Explainer videos )
- Increase retention rate
- Decrease bounce rate
Instead, identify key performance metrics (KPI) you want to impact and the percentage you want to increase them by.
Take a look at the goals page in the marketing plan example below:

They not only identify a specific metric in each of their goals, but they also set a timeline for when they will be increased.
The same vague goals listed earlier become much clearer when specific numbers and timelines are applied to them:
- Get 100 new Twitter followers per month
- Write 5 more articles per week
- Create 10 YouTube videos each year
- Increase retention rate by 15% by 2020
- Decrease bounce rate by 5% by Q1
- Create an online course and get 1,000 new leads
- Focus more on local SEO strategies
- Conduct a monthly social media report to track progress
You can dive even deeper into your marketing goals if you want (generally, the more specific, the better). Here’s a marketing plan example that shows how to outline your growth goals:

3. Outline your user personas
Now, this may not seem like the most important part of your marketing plan, but I think it holds a ton of value.
Outlining your user personas is an important part of a marketing plan that should not be overlooked.
You should be asking not just how you can get the most visitors to your business, but how you can get the right visitors.
Who are your ideal customers? What are their goals? What are their biggest problems? How does your business solve customer problems?
Answering these questions will take lots of research, but it’s essential information to get.
Some ways to conduct user research are:
- Interviewing your users (either in person or on the phone)
- Conducting focus groups
- Researching other businesses in the same industry
- Surveying your audience
Then, you will need to compile your user data into a user persona guide.
Take a look at how detailed this user persona template is below:

Taking the time to identify specific demographic traits, habits and goals will make it easier for you to cater your marketing plan to them.
Here’s how you can create a user persona guide:
The first thing you should add is a profile picture or icon for each user persona. It can help to put a face to your personas, so they seem more real.
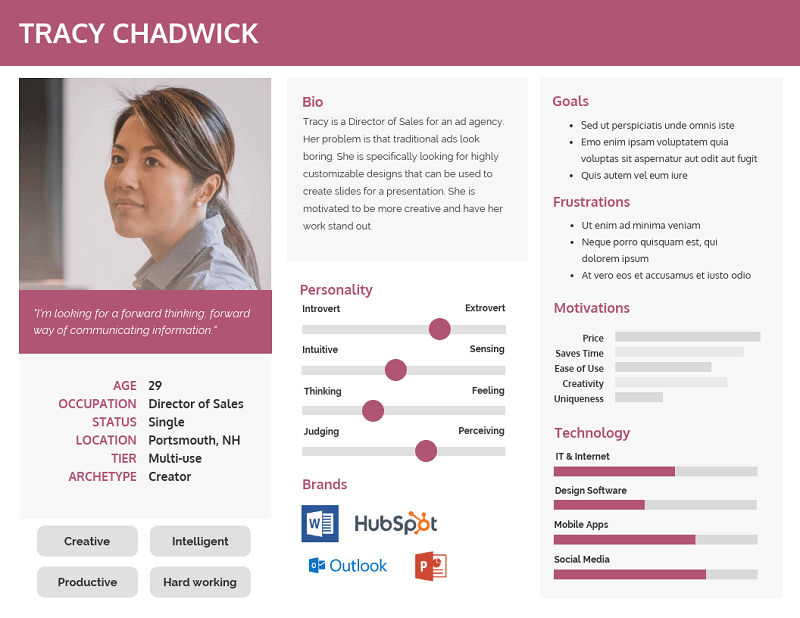
Next, list demographic information like:
- Identifiers
- Activities/Hobbies
The user persona example above uses sliding scales to identify personality traits like introversion vs. extroversion and thinking vs. feeling. Identifying what type of personality your target users tend to have an influence on the messaging you use in your marketing content.
Meanwhile, this user persona guide identifies specific challenges the user faces each day:

But if you don’t want to go into such precise detail, you can stick to basic information, like in this marketing plan example:

Most businesses will have a few different types of target users. That’s why it’s pertinent to identify and create several different user personas . That way, you can better segment your marketing campaigns and set separate goals, if necessary.
Here’s a marketing plan example with a segmented user persona guide:

The important thing is for your team or client to have a clear picture of who their target user is and how they can appeal to their specific problems.
Start creating robust user personas using Venngage’s user persona guide .
4. Conduct an extensive competitor analysis
Next, on the marketing plan checklist, we have the competitor research section. This section will help you identify who your competitors are, what they’re doing, and how you could carve yourself a place alongside them in your niche — and ideally, surpass them. It’s something you can learn to do with rank tracking software .
Competitor research is also incredibly important if you are starting a blog .
Typically, your competitor research should include:
- Who their marketing team is
- Who their leadership team is
- What their marketing strategy and strategic marketing plan are (this will probably revolve some reverse-engineering)
- What their sales strategy is (same deal)
- Social Media strategy (are they using discounting strategies such as coupon marketing to get conversions)
- Their market cap/financials
- Their yearly growth (you will probably need to use a marketing tool like Ahrefs to do this)
- The number of customers they have & their user personas
Also, take as deep a dive as you can into the strategies they use across their:
- Blog/Content marketing
- Social media marketing
- SEO Marketing
- Video marketing
- And any other marketing tactics they use
Research their strengths and weaknesses in all parts of their company, and you will find some great opportunities. Bookmark has a great guide to different marketing strategies for small businesses if you need some more information there.
You can use this simple SWOT analysis worksheet to quickly work through all parts of their strategy as well:

Click the template above to create a SWOT chart . Customize the template to your liking — no design know-how needed.
Since you have already done all the research beforehand, adding this information to your marketing plan shouldn’t be that hard.
In this marketing plan example, some high-level research is outlined for 3 competing brands:

But you could take a deeper dive into different facets of your competitors’ strategies. This marketing plan example analyses a competitor’s inbound marketing strategy :

It can also be helpful to divide your competitors into Primary and Secondary groups. For example, Apple’s primary competitor may be Dell for computers, but its secondary competitor could be a company that makes tablets.
Your most dangerous competitors may not even be in the same industry as you. Like the CEO of Netflix said, “Sleep is our competition.”
5. Set accurate key baselines & metrics
It’s pretty hard to plan for the future if you don’t know where your business stands right now.
Before we do anything at Venngage, we find the baselines so we can compare future results to something. We do it so much it’s almost like second nature now!
Setting baselines will allow you to more accurately track your progress. You will also be able to better analyze what worked and what didn’t work, so you can build a stronger strategy. It will definitely help them clearly understand your goals and strategy as well.
Here’s a marketing plan example where the baselines are visualized:

Another way to include baselines in your plan is with a simple chart, like in the marketing plan example below:

Because data can be intimidating to a lot of people, visualizing your data using charts and infographics will help demystify the information.
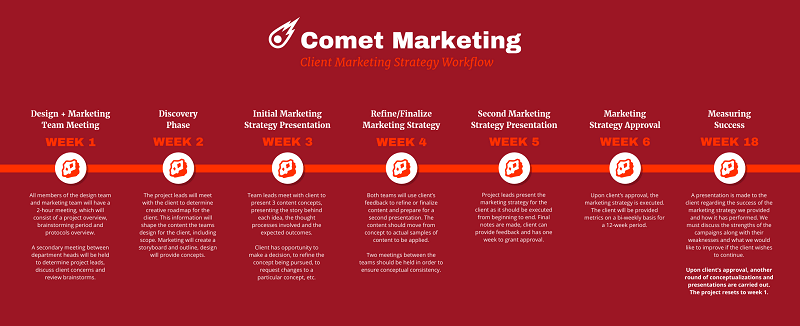
6. Create an actionable marketing strategy
After pulling all the contextual information and relevant metrics into your marketing plan, it’s time to break down your marketing strategy.
Once again, it’s easier to communicate your information to your team or clients using visuals .
Mind maps are an effective way to show how a strategy with many moving parts ties together. For example, this mind map shows how the four main components of a marketing strategy interact together:

You can also use a flow chart to map out your strategy by objectives:

However you choose to visualize your strategy, your team should know exactly what they need to do. This is not the time to keep your cards close to your chest.
Your strategy section may need to take up a few pages to explain, like in the marketing plan example below:

With all of this information, even someone from the development team will understand what the marketing team is working on.
This minimalistic marketing plan example uses color blocks to make the different parts of the strategy easy to scan:

Breaking your strategy down into tasks will make it easier to tackle.
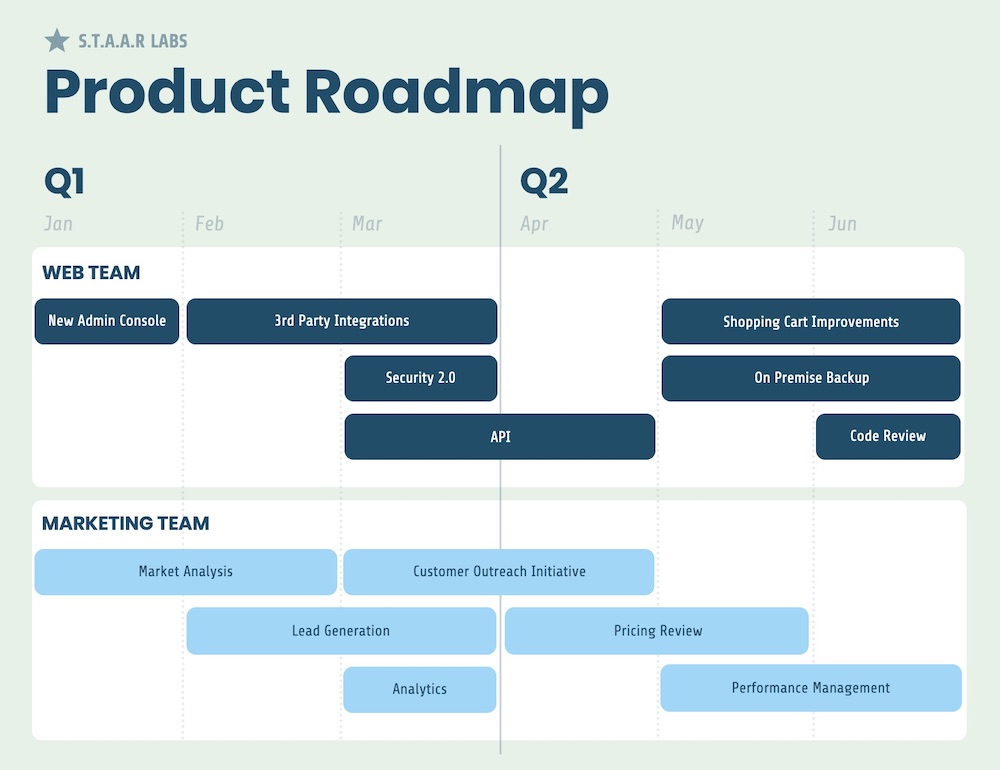
Another important way to visualize your marketing strategy is to create a project roadmap. A project roadmap visualizes the timeline of your product with individual tasks. Our roadmap maker can help you with this.
For example, this project roadmap shows how tasks on both the marketing and web design side run parallel to each other:
A simple timeline can also be used in your marketing plan:
Or a mind map, if you want to include a ton of information in a more organized way:

Even a simple “Next, Now, Later” chart can help visualize your strategy:

7. Set tracking or reporting guidelines
Close your marketing plan with a brief explanation of how you plan to track or measure your results. This will save you a lot of frustration down the line by standardizing how you track results across your team.
Like the other sections of your marketing plan, you can choose how in-depth you want to go. But there need to be some clear guidelines on how to measure the progress and results of your marketing plan.
At the bare minimum, your results tracking guidelines should specify:
- What you plan to track
- How you plan to track results
- How often you plan to measure
But you can more add tracking guidelines to your marketing plan if you see the need to. You may also want to include a template that your team or client can follow, for client reporting , ensure that the right metrics are being tracked.

The marketing plan example below dedicates a whole page to tracking criteria:

Use a task tracker to track tasks and marketing results, and a checklist maker to note down tasks, important life events, or tracking your daily life.
Similarly, the marketing plan example below talks about tracking content marketing instead:

Marketing plan vs. marketing strategy
Although often used interchangeably, the terms “marketing plan” and “marketing strategy” do have some differences.
Simply speaking, a marketing strategy presents what the business will do in order to reach a certain goal. A marketing plan outlines the specific daily, weekly, monthly or yearly activities that the marketing strategy calls for. As a business, you can create a marketing proposal for the marketing strategies defined in your company’s marketing plan. There are various marketing proposal examples that you can look at to help with this.
A company’s extended marketing strategy can be like this:
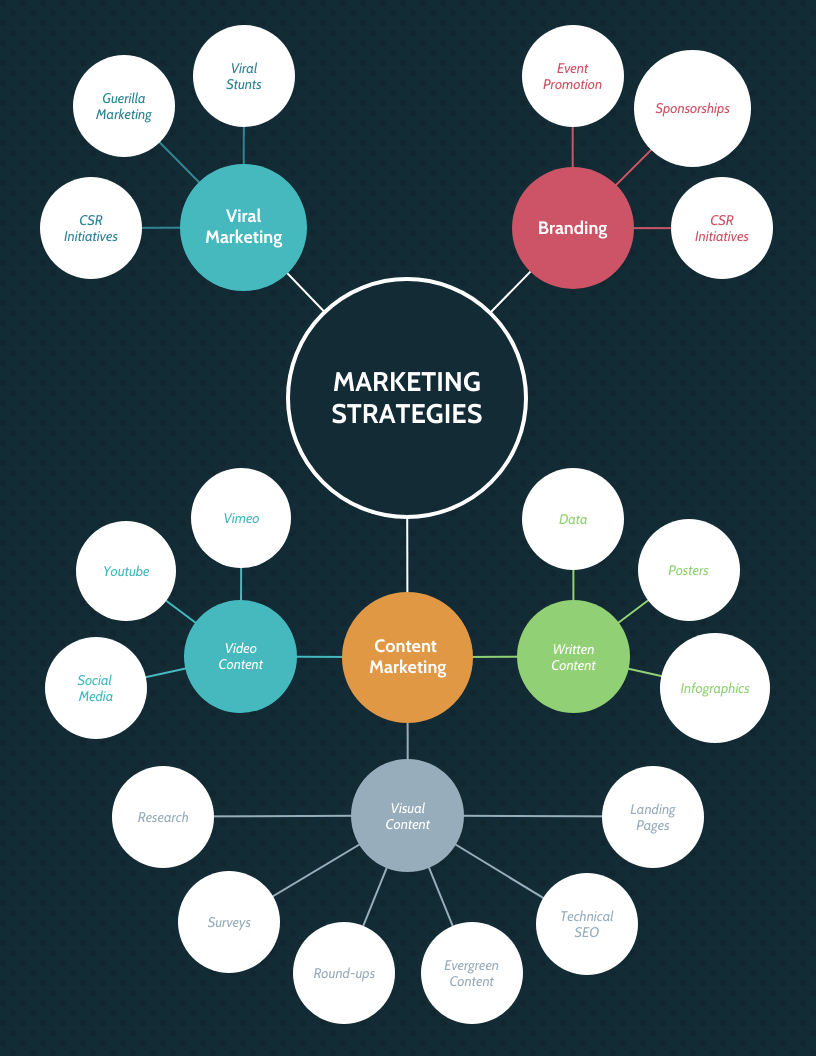
Notice how it’s more general and doesn’t include the actual activities required to complete each strategy or the timeframe those marketing activities will take place. That kind of information is included in a marketing plan, like this marketing plan template which talks about the content strategy in detail:

1. Nonprofit marketing plan
Here’s a free nonprofit marketing plan example that is ideal for organizations with a comprehensive vision to share. It’s a simple plan that is incredibly effective. Not only does the plan outline the core values of the company, it also shares the ideal buyer persona.

Note how the branding is consistent throughout this example so there is no doubt which company is presenting this plan. The content plan is an added incentive for anyone viewing the document to go ahead and give the team the green light.
2. Social media marketing plan
Two-page marketing plan samples aren’t very common, but this free template proves how effective they are. There’s a dedicated section for business goals as well as for project planning.
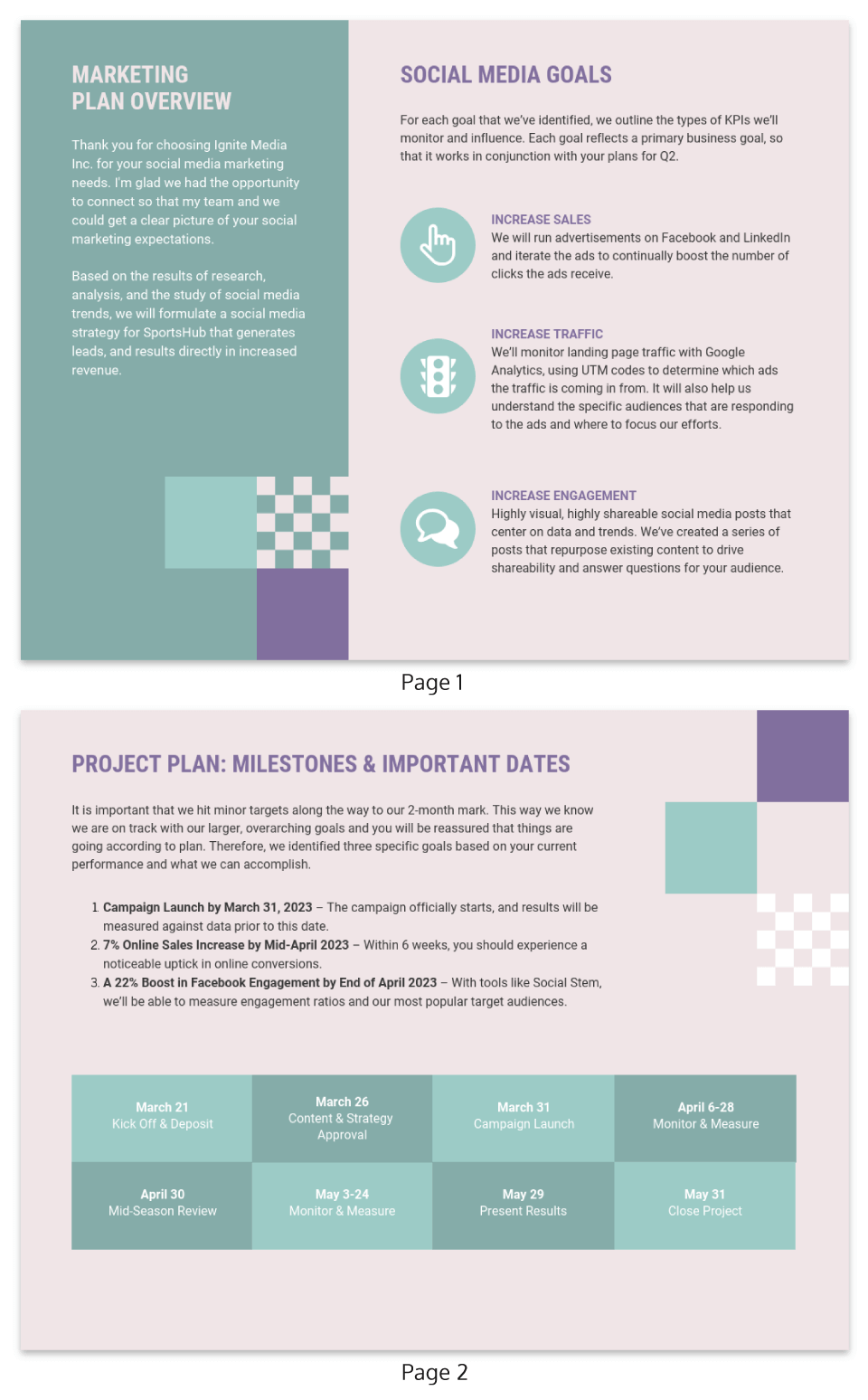
The milestones for the marketing campaign are clearly laid out, which is a great way to show how organized this business strategy is.
3. Small business marketing plan
This marketing plan template is perfect for small businesses who set out to develop an overarching marketing strategy for the whole year:

Notice how this aligns pretty well with the marketing plan outline we discussed in previous sections.
In terms of specific tactics for the company’s marketing strategy, the template only discusses SEO strategy, but you can certainly expand on that section to discuss any other strategies — such as link building , that you would like to build out a complete marketing plan for.
4. Orange simple marketing proposal template
Marketing plans, like the sample below, are a great way to highlight what your business strategy and the proposal you wan to put forward to win potential customers.

5. One-page marketing plan
This one-page marketing plan example is great for showcasing marketing efforts in a persuasive presentation or to print out for an in-person meeting.

Note how the fact sheet breaks down the marketing budget as well as the key metrics for the organization. You can win over clients and partners with a plan like this.
6. Light company business fact sheet template
This one-page sample marketing plan clearly outlines the marketing objectives for the organization. It’s a simple but effective way to share a large amount of information in a short amount of time.

What really works with this example is that includes a mission statement, key contact information alongside all the key metrics.
7. Marketing media press kit template
This press kit marketing plan template is bright and unmistakable as belonging to the Cloud Nine marketing agency . The way the brand colors are used also helps diversify the layouts for each page, making the plan easier to read.

We like the way the marketing department has outlined the important facts about the organization. The bold and large numbers draw the eye and look impressive.
8. Professional marketing proposal template
Start your marketing campaign on a promising note with this marketing plan template. It’s short, sharp and to the point. The table of contents sets out the agenda, and there’s a page for the company overview and mission statement.

9. Social media marketing proposal template
A complete marketing plan example, like the one below, not only breaks down the business goals to be achieved but a whole lot more. Note how the terms and conditions and payment schedule are included, which makes this one of the most comprehensive marketing plans on our list.

Marketing plan vs. business plan
While both marketing plans and business plans are crucial documents for businesses, they serve distinct purposes and have different scopes. Here’s a breakdown of the key differences:
Business plan is a comprehensive document that outlines all aspects of your business, including:
- Mission and vision
- Products or services
- Target market
- Competition
- Management team
- Financial projections
- Marketing strategy (including a marketing plan)
- Operations plan
Marketing plan on the other hand, dives deep into the specific strategies and tactics related to your marketing efforts. It expands on the marketing section of a business plan by detailing:
- Specific marketing goals (e.g., brand awareness, lead generation, sales)
- Target audience analysis (detailed understanding of their needs and behaviors)
- Product: Features, benefits, positioning
- Price: Pricing strategy, discounts
- Place: Distribution channels (online, offline)
- Promotion: Advertising, social media, content marketing, public relations
- Budget allocation for different marketing activities
- Metrics and measurement to track progress and success
In short, business plans paint the entire business picture, while marketing plans zoom in on the specific strategies used to reach your target audience and achieve marketing goals.
Types of marketing plans that can transform your business strategy
Let’s take a look at several types of marketing plans you can create, along with specific examples for each.
1. General marketing strategic plan / Annual marketing plan
This is a good example of a marketing plan that covers the overarching annual marketing strategy for a company:
Another good example would be this Starbucks marketing plan:

This one-page marketing plan example from coffee chain Starbucks has everything at a glance. The bold headers and subheadings make it easier to segment the sections so readers can focus on the area most relevant to them.
What we like about this example is how much it covers. From the ideal buyer persona to actional activities, as well as positioning and metrics, this marketing plan has it all.
Another marketing plan example that caught our eye is this one from Cengage. Although a bit text-heavy and traditional, it explains the various sections well. The clean layout makes this plan easy to read and absorb.

The last marketing plan example we would like to feature in this section is this one from Lush cosmetics.
It is a long one but it’s also very detailed. The plan outlines numerous areas, including the company mission, SWOT analysis , brand positioning, packaging, geographical criteria, and much more.

2. Content marketing plan
A content marketing plan highlights different strategies , campaigns or tactics you can use for your content to help your business reach its goals.
This one-page marketing plan example from Contently outlines a content strategy and workflow using simple colors and blocks. The bullet points detail more information but this plan can easily be understood at a glance, which makes it so effective.

For a more detailed content marketing plan example, take a look at this template which features an editorial calendar you can share with the whole team:

3. SEO marketing plan
Your SEO marketing plan highlights what you plan to do for your SEO marketing strategy . This could include tactics for website on-page optimization , off-page optimization using AI SEO , and link building using an SEO PowerSuite backlink API for quick backlink profile checks. Additionally, incorporating a rank tracker can help monitor keyword performance and track the impact of your optimization efforts.
This SEO marketing plan example discusses in detail the target audience of the business and the SEO plan laid out in different stages:

4. Social media marketing plan
Your social media marketing plan presents what you’ll do to reach your marketing goal through social media. This could include tactics specific to each social media channel that you own, recommendations on developing a new channel, specific campaigns you want to run, and so on, like how B2B channels use Linkedin to generate leads with automation tools and expand their customer base; or like making use of Twitter walls that could display live Twitter feeds from Twitter in real-time on digital screens.
For B2C brands, you can target Facebook and Instagram. Gain Instagram likes to build trust for your brand’s profile and post engaging content on both platforms. Leverage AI social media tools to automate and scale your content plan..
Edit this social media marketing plan example easily with Venngage’s drag-and-drop editor:

5. Demand generation marketing plan
This could cover your paid marketing strategy (which can include search ads, paid social media ads, traditional advertisements, etc.), email marketing strategy and more. Here’s an example:

What should marketing plans include?
Marketing plans should include:
- A detailed analysis of the target market and customer segments.
- Clear and achievable marketing objectives and goals.
- Strategies and tactics for product promotion and distribution.
- Budget allocation for various marketing activities.
- Timelines and milestones for the implementation of marketing strategies.
- Evaluation metrics and methods for tracking the success of the marketing plan.
What is an executive summary in a marketing plan and what is its main goal?
An executive summary in a marketing plan is a brief overview of the entire document, summarizing the key points, goals, and strategies. Its main goal is to provide readers with a quick understanding of the plan’s purpose and to entice them to read further.
What are the results when a marketing plan is effective?
When a marketing plan is effective, businesses can experience increased brand visibility, higher customer engagement , improved sales and revenue, and strengthened customer loyalty.
What is the first section of a marketing plan?
The first section of a marketing plan is typically the “Executive Summary,” which provides a concise overview of the entire plan, including the business’s goals and the strategies to achieve them.
Now that you have the basics for designing your own marketing plan, it’s time to get started:
More marketing design guides and templates:
- Marketing Infographics: The Definitive Guide [Includes Infographic Templates]
- 20+ Business Pitch Deck Templates to Win New Clients and Investors
- 20+ White Paper Examples [Design Guide + White Paper Templates]
- The Evolution of Marketing [Timeline Infographic]
Discover popular designs

Infographic maker

Brochure maker

White paper online

Newsletter creator

Flyer maker

Timeline maker

Letterhead maker

Mind map maker

Ebook maker

- Join the AMA
- Find learning by topic
- Free learning resources for members
- Credentialed Learning
- Training for teams
- Why learn with the AMA?
- Marketing News
- Academic Journals
- Guides & eBooks
- Marketing Job Board
- Academic Job Board
- AMA Foundation
- Diversity, Equity and Inclusion
- Collegiate Resources
- Awards and Scholarships
- Sponsorship Opportunities
- Strategic Partnerships
We noticed that you are using Internet Explorer 11 or older that is not support any longer. Please consider using an alternative such as Microsoft Edge, Chrome, or Firefox.
![What is a Marketing Plan & How To Write One? [Easy Guide] What is a Marketing Plan & How To Write One? [Easy Guide]](https://www.ama.org/wp-content/uploads/2024/03/marketing-plan-2.jpeg?resize=1360%2C550)
What is a Marketing Plan & How To Write One? [Easy Guide]

What is a Marketing Plan?
A marketing plan is a strategic guide that helps businesses map out their advertising and promotional strategies to attract prospective customers and connect with their intended audience. It offers clear and detailed direction on how to achieve business objectives through targeted marketing efforts.
Marketing Plan vs. Business Plan
Understanding the distinction between a marketing plan and a business plan is crucial for any organization aiming to navigate the complexities of strategic planning and resource allocation.
- Marketing Plan: This is a focused document dedicated to the marketing segment of an organization’s strategy. It meticulously outlines the marketing objectives, strategies, and tactics that will be employed to achieve the desired market presence and customer engagement.
- Business Plan: A business plan has a broader scope, encompassing every facet of the company’s operations. While it includes marketing, it also delves into finance, operations, human resources, and more, providing a comprehensive overview of the entire business.
Marketing Strategy vs. Marketing Plan
Differentiating between a marketing strategy and a marketing plan is essential for implementing effective marketing operations within a business. These two elements, while closely related, serve distinct functions in the marketing process.
- Marketing Strategy: This aspect defines the overarching approach and long-term vision for a company’s engagement in the market. Each element of the marketing strategy is designed to align with the company’s top-level goals and contribute to realizing its vision statement. In essence, the marketing strategy answers the “what” and “why” behind a company’s marketing efforts, outlining what the company aims to achieve and why those goals are important.
- Marketing Plan: In contrast, the marketing plan focuses on the “how” of reaching strategic objectives. It is a practical document that outlines specific actions, timelines, and resources required to execute the marketing strategy. It details the campaigns, channels, tools, and tactics that will be used to achieve the strategic goals outlined in the marketing strategy.

3 Hours | 25 Modules | Beginner
Modern Marketing: Strategy and Execution
Learn from Inc. Magazine’s prize-winning editorial content about the basic concepts of digital marketing, including targeting, value proposition, and more.
Types of Marketing Plans
Marketing plans vary depending on their focus, scope, and objectives. Understanding the different types of plans is crucial for businesses aiming to target their marketing efforts and resources effectively. Here are some of the key types:
- Go-to-market/Product Launch: This plan is specifically designed to introduce a new product. It outlines the target audience, market entry strategy, and advertising tactics to be employed.
- Social Media : A social media plan is tailored to the unique dynamics of social media platforms. It details the advertising strategies to be used on these platforms, focusing on engaging with users and leveraging specific features to maximize reach and impact.
- General Marketing Strategic Plan / Annual Marketing Plan: This comprehensive plan covers a company’s overall marketing activities for the entire year. It encompasses various marketing efforts and campaigns, outlining a cohesive strategy that supports the company’s annual goals.
- Content Marketing Plan : Focused on content creation and distribution, this plan outlines the strategies, campaigns, and tactics for using content to achieve business objectives. It details how different types of content (blog posts, videos, infographics) will be used to attract and engage the target audience.
- SEO Marketing Plan: Dedicated to search engine optimization, this plan outlines the strategies and actions to improve a website’s visibility in search engine results pages (SERPs). It focuses on keyword research, content optimization, link building, and other tactics to drive organic traffic to the website.
Benefits of a Marketing Plan
Having a structured plan is invaluable. It acts as a strategic roadmap, guiding businesses toward achieving their goals through well-organized and monitored marketing activities.
Here are five important benefits of creating a marketing plan:
- Goal Setting: It allows your business to define clear marketing objectives and set measurable targets. This facilitates focused efforts toward lead generation, sales increase, market share expansion, brand awareness, and customer acquisition.
- Strategic Direction: The plan provides a detailed outline of your promotional strategy, helping identify the target audience, their preferences, and the best methods to reach and engage them effectively.
- Competitive Advantage: A plan helps you articulate and leverage your unique selling proposition (USP), ensuring you stand out in the market and secure a competitive edge.
- Consistency and Integration: The plan fosters consistency and integration in marketing efforts, ensuring a unified brand message and customer experience across all marketing channels and touchpoints,
- Long-term Sustainability: A comprehensive plan not only focuses on immediate goals but also lays the groundwork for sustained growth and adaptability to market evolution, customer demands, and emerging trends.
How To Write a Marketing Plan
- Create a mission statement
The foundation of any effective marketing plan begins with a clear and concise mission statement. This crucial step sets the stage for all subsequent planning by articulating the core purpose and direction of your company’s marketing efforts. A mission statement serves as a compass, guiding your marketing strategies and ensuring they align with your organization’s broader goals.
Developing a mission statement is more than just a formality; it’s a strategic exercise that clarifies your marketing vision and sets a purposeful path for your team. With a compelling mission statement in place, you can craft a plan that resonates with your audience and drives your business toward its long-term objectives.
- Set your goals/KPIs
Establishing clear goals and key performance indicators (KPIs) is a pivotal step in crafting a marketing plan that aligns with your company’s value proposition and ensures measurable success. This stage involves setting financial and non-financial objectives to guide your marketing efforts and evaluate their effectiveness.
Marketers who set specific goals are significantly more likely to report success. By defining financial and non-financial objectives, you create a comprehensive framework for guiding your marketing strategies. This dual focus not only drives economic value but also fosters qualitative improvements in your marketing efforts, ensuring a balanced approach to achieving your company’s vision.
- Identify Your Target Market
Pinpointing your target market is a crucial step in any marketing plan. Understanding who your product or service is for and why forms the backbone of your marketing efforts and influences decisions on marketing channels, content creation, and overall outreach strategies.
A key outcome of market research is the development of buyer personas. These semi-fictional representations of your ideal customers are crafted based on real data and insights about your existing clientele. Buyer personas detail your target market’s characteristics, needs, and motivations, offering a detailed profile that guides your marketing strategies.
- Conduct Competitive Analysis
Conducting a competitive analysis is integral to crafting a robust marketing plan. This process involves identifying your main competitors, understanding their strategies, and evaluating how your business can establish a distinctive and superior position in your niche. Through this analysis, you’ll gain insights into the competitive landscape, helping you to leverage your own strengths and identify areas for improvement.
Understanding both the internal and external factors that influence your market positioning is crucial. They include:
- Internal factors: Examine what could impact your competitive advantage, such as your team’s expertise, proprietary technology, or customer service practices.
- External factors: Look beyond your immediate competitive environment to broader market conditions that could affect your position. This includes economic trends, regulatory changes, and technological advancements.
- Economic considerations: Assess how the current economic climate might influence consumer purchasing behavior and, consequently, your market strategy.
- Sociological trends: Understand shifting societal values, lifestyles, and consumer behaviors and how they offer new market opportunities.
- Industry trends: Keep an eye on overarching trends within your industry, including emerging technologies, shifts in consumer preferences, and new regulatory frameworks.
- Set Your Budget
Your marketing budget is the planned amount of money you’ll spend to achieve your marketing goal. Knowing the financial resources you have available for marketing activities allows you to craft a plan that maximizes impact while maintaining fiscal responsibility. This financial foresight prevents overspending and ensures that every dollar spent contributes to achieving your marketing objectives.
This overview should include all sources of funding and any constraints or stipulations attached to them. Having a comprehensive understanding of your financial resources sets the groundwork for all subsequent planning and decision-making.
- Execute your Plan
Execution involves the detailed scheduling of marketing activities, assigning responsibilities to team members, and setting deadlines that align with the marketing plan’s timelines. It’s about bringing the plan to life through a series of coordinated efforts, from launching advertising campaigns to engaging with customers on social media platforms. This phase is where the theoretical aspects of the plan, such as target audience engagement and brand messaging, are put into practice through concrete actions like content creation, digital marketing, and promotional events.
In conclusion, a well-crafted marketing plan is the linchpin of successful marketing efforts, offering a strategic blueprint that guides businesses through the intricate landscape of market engagement and customer interaction. From the initial stages of understanding the marketing plan’s scope and its relationship with the overarching business strategy to the detailed planning and execution of marketing activities, each step is vital in steering an organization toward its desired market position.
By continuing to use this site, you accept the use of cookies, pixels and other technology that allows us to understand our users better and offer you tailored content. You can learn more about our privacy policy here
What is a Marketing Plan & How to Write One [+ Examples]
Updated: August 07, 2024
Published: June 12, 2018
One of my favorite ways to break through writer’s block, whether the assignment is a marketing plan or a short story, is simply reading more examples. (I also recommend taking a long walk; you’d be surprised.)

I can’t take you on a walk, but I can give you some examples, some inspiration, and some guidelines to get your creativity humming.
If you don’t know where to start, we’ve curated lists of marketing plans and marketing strategies to help you write a concrete plan that will produce results.
Let’s start by understanding the differences between the two.
Featured Resource: Free Marketing Plan Template

Looking to develop a marketing plan for your business? Click here to download HubSpot's free Marketing Plan Template to get started .
Table of Contents
Marketing Strategy Examples
What is a marketing plan, marketing plan vs. business plan, how to write a marketing plan, types of marketing plans, marketing plan examples, marketing plan faqs, sample marketing plan.

Free Marketing Plan Template
Outline your company's marketing strategy in one simple, coherent plan.
- Pre-Sectioned Template
- Completely Customizable
- Example Prompts
- Professionally Designed
Download Free
All fields are required.
You're all set!
Click this link to access this resource at any time.
A marketing plan is a strategic road map that businesses use to organize, execute, and track their marketing strategy over a given period. Marketing plans can include different marketing strategies for various marketing teams across the company, all working toward the same business goals.
The purpose of a marketing plan is to write down strategies in an organized manner. This will help keep you on track and measure the success of your campaigns.
Your marketing plan lays out each campaign‘s mission, buyer personas, budget, tactics, and deliverables. With all this information in one place, you’ll have an easier time staying on track with a campaign, and you can figure out what works and what doesn’t.
To learn more about creating your marketing plan, keep reading or jump to the relevant section:

A marketing plan is a strategic document that outlines marketing objectives, strategies, and tactics.
A business plan is also a strategic document. But this plan covers all aspects of a company's operations, including finance, operations, and more. It can also help your business decide how to distribute resources and make decisions as your business grows.
A marketing plan is a subset of a business plan; it shows how marketing strategies and objectives can support overall business goals. And if you need an assist executing a marketing plan, might I recommend HubSpot’s marketing hub ?
Marketing Strategy vs. Marketing Plan
A marketing strategy is the part of your marketing plan that describes how a business will accomplish a particular goal or mission.
This includes which campaigns, content, channels, and marketing software you’ll use to execute that mission and track its success.
A marketing plan contains one or more marketing strategies. It's the framework from which all your marketing strategies are created, and it helps you connect each strategy to a larger marketing operation and business goal.
For example, suppose your company is launching a new software product, and it wants customers to sign up. The marketing department needs to develop a marketing plan that'll help introduce this product to the industry and drive the desired sign-ups.
The department decides to launch a topical blog, debut a YouTube series to establish expertise, and create new X and Instagram accounts to join the conversation around this subject. All this serves to attract an audience and convert this audience into software users.
To summarize, a business' marketing plan is dedicated to introducing a new software product to the marketplace and driving sign-ups for that product. The business will execute that plan with three marketing strategies : a new industry blog, a YouTube video series, and an X account.
Of course, the business might consider these three things as one giant marketing strategy, each with its own specific content strategies. How granular you want your marketing plan to get is up to you. Nonetheless, every marketing plan goes through a particular set of steps in its creation.
- State your business' mission.
- Determine the KPIs for this mission.
- Identify your buyer personas.
- Describe your content initiatives and strategies.
- Clearly define your plan's omissions.
- Define your marketing budget.
- Identify your competition.
- Outline your plan's contributors and their responsibilities.
1. State your business' mission.
Your first step in writing a marketing plan is to state your mission. Although this mission is specific to your marketing department, it should serve as your business' main mission statement.
In my experience, you want to be specific, but not too specific. You have plenty of space left in this marketing plan to elaborate on how you'll acquire new customers and accomplish this mission.
For those of you running startups or small businesses, HubSpot’s starter bundle is a great all-in-one solution — it can help you find and win customers, execute content marketing plans, and more.
If your business' mission is “to make booking travel a delightful experience,” your marketing mission might be “to attract an audience of travelers, educate them on the tourism industry, and convert them into users of our bookings platform.”
Need help building your mission statement? Download this guide for examples and templates and write the ideal mission statement.
2. Determine the KPIs for this mission.
Every good marketing plan describes how the department will track its mission‘s progress. To do so, you need to decide on your key performance indicators (KPIs) .
KPIs are individual metrics that measure the various elements of a marketing campaign. These units help you establish short-term goals within your mission and communicate your progress to business leaders.
Let's take our example of a marketing mission from the above step. If part of our mission is “to attract an audience of travelers,” we might track website visits using organic page views. In this case, “organic page views” is one KPI, and we can see our number of page views grow over time.
Also, make sure to check whether your current reporting software facilitates the KPIs you need. Some reporting tools can only measure a set of pre-defined metrics, which can cause massive headaches in particular marketing campaigns.
However, other tools, like HubSpot’s analytics software , can offer full flexibility over the KPIs you wish to track.
You can generate custom reports that reveal average website engagement rates, page visits, email, social media traffic, and more.
These KPIs will come into the conversation again in step 4.
3. Identify your buyer personas.
A buyer persona is a description of who you want to attract. This can include age, sex, location, family size, and job title.
Each buyer persona should directly reflect your business' current and potential customers. All business leaders must agree on your buyer personas.
4. Describe your content initiatives and strategies.
Here‘s where you’ll include the main points of your marketing and content strategy.
Because there‘s a laundry list of content types and channels available today, you must choose wisely and explain how you’ll use your content and channels in this section of your marketing plan.
When I write this section, I like to stipulate:
- What types of content I'll create. These might include blog posts, YouTube videos, infographics, and ebooks.
- How much I'll create. I typically describe content volume in daily, weekly, monthly, or even quarterly intervals. It all depends on my workflow and the short-term goals for my content.
- The goals (and KPIs) I'll use to track each type. KPIs can include organic traffic, social media traffic, email traffic, and referral traffic. Your goals should also include which pages you want to drive that traffic to, such as product pages, blog pages, or landing pages.
- The channels on which I'll distribute my content. Popular channels include Facebook, X, LinkedIn, YouTube, Pinterest, and Instagram.
- Any paid advertising that will take place on these channels.
5. Clearly define your plan's omissions.
A marketing plan explains the marketing team's focus. It also explains what the marketing team will not focus on.
If there are other aspects of your business that you aren‘t serving in this particular plan, include them in this section. These omissions help to justify your mission, buyer personas, KPIs, and content.
You can’t please everyone in a single marketing campaign, and if your team isn’t on the hook for something, you need to make it known.
In my experience, this section is particularly important for stakeholders to help them understand why certain decisions were made.
6. Define your marketing budget.
Whether it's freelance fees, sponsorships, or a new full-time marketing hire, use these costs to develop a marketing budget and outline each expense in this section of your marketing plan.
You can establish your marketing budget with these 8 free marketing budget templates .
7. Identify your competition.
Part of marketing is knowing your competition. Research the key players in your industry and consider profiling each one.
Keep in mind that not every competitor will pose the same challenges to your business. For example, while one competitor might rank highly on search engines for keywords that you’re also chasing, another competitor might have a heavy footprint on a social network where you plan to launch an account.
Easily track and analyze your competitors with this collection of 10 free competitive analysis templates .
8. Outline your plan's contributors and their responsibilities.
With your marketing plan fully fleshed out, it‘s time to explain who’s doing what.
I don’t like to delve too deeply into my employees’ day-to-day projects, but I know which teams and team leaders are in charge of specific content types, channels, KPIs, and more.
Now that you know why you need to build an effective marketing plan, it’s time to get to work.
Starting a plan from scratch can be overwhelming if you haven't done it before.
That’s why there are many helpful resources that can support your first steps. We’ll share some of the best guides and templates to help you build effective results-driven plans for your marketing strategies.
Ready to make your own marketing plan? Get started with this free template.
The kind of marketing plan you create will depend on your company, your industry, and your business goals. We compiled different samples to suit your needs:
1. Quarterly or Annual Marketing Plans


4. New Product Launch Marketing Plan
This will be a road map for the strategies and tactics you‘ll implement to promote a new product. If you’re searching for an example, look no further than Chief Outsiders' Go-To-Market Plan for a New Product :

This marketing plan by Visit Oxnard, a convention and visitors bureau, is packed with information: target markets, key performance indicators, selling points, personas, marketing tactics by channel, and much more.
It also articulates the organization’s strategic plans for the upcoming fiscal year, especially as it grapples with the aftereffects of the pandemic.
Lastly, it has impeccable visual appeal, with color-coded sections and strong branding elements.
- It states clear and actionable goals for the coming year.
- It includes data and other research that shows how the team made its decisions.
- It outlines how the team will measure the plan’s success.
4. Safe Haven Family Shelter

This marketing plan by a nonprofit organization is an excellent example to follow if your plan will be presented to internal stakeholders at all levels of your organization.
It includes SMART marketing goals , deadlines, action steps, long-term objectives, target audiences, core marketing messages , and metrics.
The plan is detailed yet scannable. By the end of it, one can walk away with a strong understanding of the organization’s strategic direction for its upcoming marketing efforts.
- It confirms ongoing marketing strategies and objectives while introducing new initiatives.
- It uses colors, fonts, and formatting to emphasize key parts.
- It closes with long-term goals, key themes, and other overarching topics to set the stage for the future.
5. Wright County Economic Development

- “Going viral” isn’t a goal; it’s an outcome.
- Be surprising. Subvert expectations.
- Be weird and niche if you want to be weird and niche, but establishing a shared cultural understanding might result in a bigger audience.
Pridemore Properties’ Instagram smash hit is unexpected, to say the least. You think you’re getting a home tour that takes your figurative breath away; you get a home tour that takes the agent’s literal breath away.

Verizon’s toe-tapping, hip-shaking Totalmente (aka Total by Verizon, a contractless phone plan) ad debuted during Univision’s Spanish-language broadcast of Super Bowl LVIII. The ad reinvents the 1998 Elvis Crespo song “Suavemente,” an earworm if I’ve ever heard one, replacing the lyrics with Total by Verizon features.
Verizon Value’s CMO and VP of Marketing, Cheryl Gresham, has admitted that she didn’t know much about marketing to a majority-Latinx audience.
In an interview with Campaign Live , she said she didn’t think the idea would have gotten off the ground “if it had just been me and a lot of other people that had a background like myself in that room.”
CampaignLive wrote, “Gresham says the team opted for a creative concept that spoke to all the Latinos in the room — despite Gresham herself not understanding the connection.”
Gresham’s marketing strategy hinged on knowing her audience and, just as importantly, trusting her fellow marketers who knew how to reach that audience.
Strategic Takeaways for Demographic Marketing
- Know what you don’t know.
- Foster diversity in marketing leadership and staff.
- Know your audience.
The catchy tune and the great storytelling certainly don’t hurt.
But more than that, Ogilvy and Verizon dug deep into Latinx culture — more than 25 years deep — to craft an ad that doesn’t feel like it’s just responding to the latest trend. They also tapped Venezuelan American comedian, musician, and producer Fred Armisen to direct the spot.
6. Chappell Roan

AI Target Audience: What I Learned [+ Tools to Try]
![business plan marketing meaning Holistic Marketing Works — Here's How You Can Apply It to Your Campaigns [+ Expert Tips]](https://knowledge.hubspot.com/hubfs/holistic-marketing-1-20241114-5175552.webp)
Holistic Marketing Works — Here's How You Can Apply It to Your Campaigns [+ Expert Tips]

What's Below the Line Marketing Anyway? I Dove Deep Into BTL Marketing to Find Out
![business plan marketing meaning What Is D2C Marketing? Here Are 11 Tips I Found For Doing It Right [+ Examples]](https://www.hubspot.com/hubfs/d2c-marketing-featured.png)
What Is D2C Marketing? Here Are 11 Tips I Found For Doing It Right [+ Examples]

5 Marketing Strategies Polymarket Is Using to Be Everywhere at Once

I Used AI to Create a Marketing Plan 2 Ways — Here’s How You Can Too

What is Marketing, and What's Its Purpose?

The 9 Best Marketing Frameworks You Need to Know
![business plan marketing meaning Sustainable Marketing: Key Principles & How to Leverage It [+ Examples]](https://www.hubspot.com/hubfs/sustainable-marketing-1-20241014-8761093.webp)
Sustainable Marketing: Key Principles & How to Leverage It [+ Examples]
![business plan marketing meaning How to Create a Complete Marketing Strategy in 2025 [Data + Expert Tips]](https://www.hubspot.com/hubfs/marketing-strategy.webp)
How to Create a Complete Marketing Strategy in 2025 [Data + Expert Tips]
The weekly email to help take your career to the next level. No fluff, only first-hand expert advice & useful marketing trends.
Must enter a valid email
We're committed to your privacy. HubSpot uses the information you provide to us to contact you about our relevant content, products, and services. You may unsubscribe from these communications at any time. For more information, check out our privacy policy .
This form is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
You've been subscribed

What is a Marketing Plan and How Do You Create One?

Free Website Traffic Checker
Discover your competitors' strengths and leverage them to achieve your own success
Let’s face it, it’s a bit of a jungle out there when it comes to marketing.
We’re constantly asking ourselves (or being asked) all the ‘who, what, when, where, why, and how’ questions, and guess what?
Developing a thorough marketing plan is the main ingredient to answering all those questions – and to make it thorough, you need good data to contextualize it, optimize it and strategize it.
In this post, we’ll cover the basics, including how to write a marketing plan… and the mistakes to avoid.
What is a marketing plan?
A marketing plan is a roadmap that outlines your marketing strategy and defines how you will attract and convert (and often, retain) customers. In your marketing plan, you’ll spell out your target audience, your goals, your marketing tactics to achieve those goals, and how you’ll measure its success.
We’ll talk more about how to write a marketing plan further down.
5 types of marketing plans
Marketing plans come in all shapes and sizes, depending on your goals, timeframe and team working on it. Here are some of the common types of marketing plans:
- Business marketing plan : The big-picture marketing plan that looks into how marketing can (and will) support your business goals over an extended period of time.
- Digital marketing plan : Focusing on the digital side of marketing, consider how you can leverage online channels (website, social media and email) to reach your target audience and achieve your marketing goals.
- Campaign marketing plan : More of a specific marketing push, a campaign marketing plan outlines the tactics and executions of a single campaign eg. a product launch or building brand awareness for a seasonal event.
- Content marketing plan : A content plan that will outline the different content types you will use to reach and resonate with your target audience, to hit your ultimate marketing goals.
- Social media marketing plan : Defining which social media platforms you’ll use, the content you will push on it, and how to make sure you’re getting engagement from the *right* audience.
How to write a marketing plan
1) understand your company marketing okrs.
Before you get started on actually writing your marketing plan, you need to have a good understanding of what your company marketing OKRs are.
OKRs = objective and key results and together, they’ll look something like:
[Insert your objective here], as measured by [insert key results].
Without marketing OKRs like this, there is no real marketing strategy – let alone a marketing plan – to drive forward to your business’ chosen ‘destination’.
Top tip : Your business doesn’t operate in a vacuum – you will need to benchmark your marketing goals, efforts and performance against others in your industry before committing to your standalone goals to ensure they’re realistic in your competitive landscape .
For more insight into marketing benchmarking, download our recent report covering how the biggest industries use marketing channels to their advantage (and sometimes, disadvantage).
2) Choose marketing activities to support OKRs
To support and achieve these OKRs, your marketing plan will need to define the marketing activities that you’ll focus on to get you there.
This is where you might split your strategy into different marketing channels and assign them to the specific team, or – if you have a smaller marketing team – you will segment your strategy into different focus areas.
For example, say you’re looking to achieve more visibility on search. The marketing activities to support this would look something like:
- SEO : Optimizing existing content, as well as new content produced
- PPC : Creating a series of ads for business-critical keywords
- Content marketing : Creating a series of SEO content and thought leadership
But of course, the marketing channels you use will vary depending on your goal – and so will how much time you spend on each, particularly if you’re working solo or in a smaller marketing team.
3) Set KPIs to measure success
- Overall marketing goals: ✅
- Marketing activities to support these goals: ✅
- Tracking your progress: Pending
Now you’ve got a vague plan of action in place, you hitting those marketing goals is on the horizon. But to make sure you’re heading in the right direction and at the right pace, it’s important to set your team (or teams) KPIs.
Not only is this important to making sure everything’s on track, but it’s also important for motivation.
Here are just a few examples of marketing KPIs, across the different marketing teams:
- Pipeline contribution
- Traffic to MQL
- Click-through rate
- Engagement rate (likes, comments, shares and views)
- Number of subscribers
- Amount of content published
- SERP rankings
- Conversion rate
- Traffic distribution
- Impressions and reach
- Customer acquisition cost (CAC)
Don’t forget to use your market and competitor research to set your team achievable KPIs that make sense for the industry you’re in and the target audience you’re going after.

Here, you can see the website engagement metrics of asos.com and its competitors.
4) Identify buyer personas
… to make sure your KPIs make sense for the target audience you’re going after, you also kinda need to know who your target audience actually is .
You might be working with one buyer persona or you might be working with multiple buyer personas – either way, it pays to have this detailed in a buyer persona template.
This will make sure your team is aligned on who you’re targeting, including things like:
- Buyer behaviors
- Hobbies and interests
- Pain points
- Motivations
- Brand affiliations
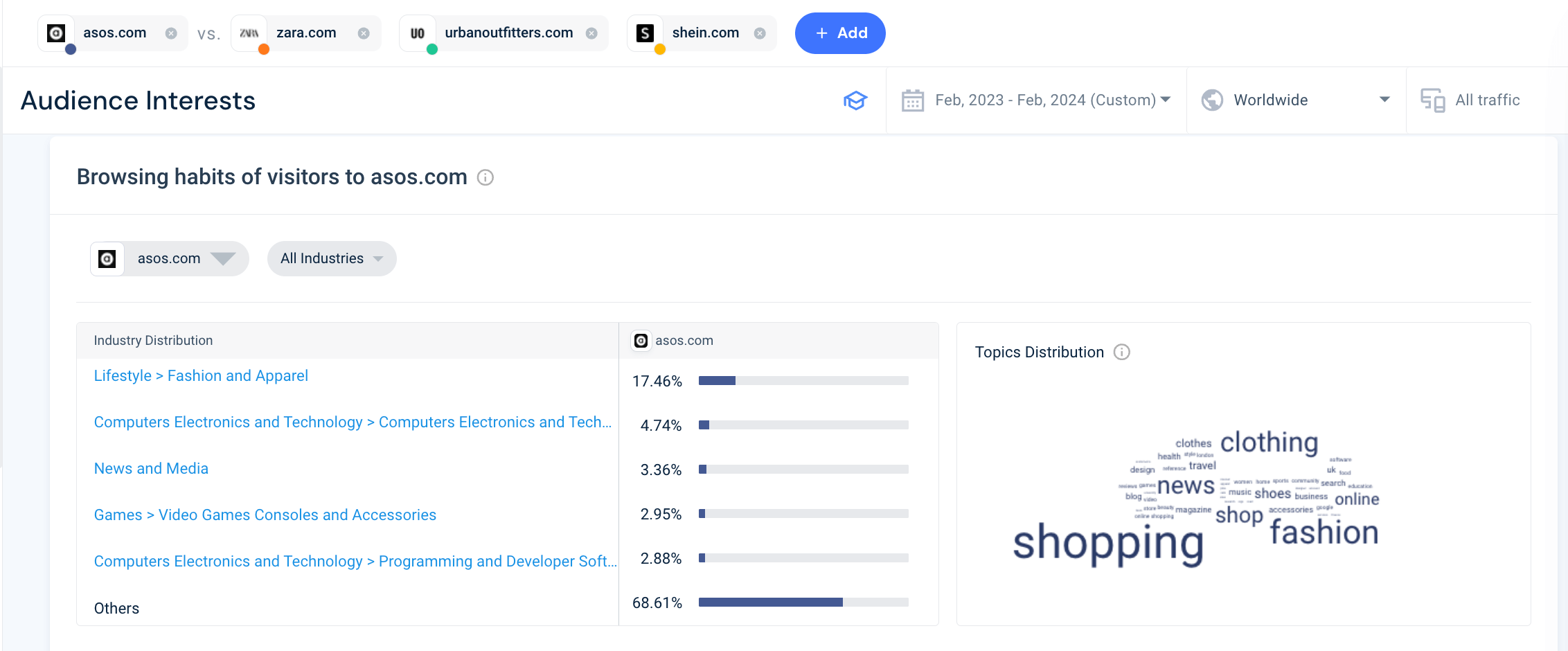
By aligning on buyer personas or the “who” your marketing is targeted at (admittedly, being a little bit stereotypical), your team can then mold the ‘what, when, why, and how’ of their marketing too. This will make sure your marketing efforts resonate with the right audience, and get you the engagement you’re after – for example, choosing the right marketing channel for the persona.

If your product or strategy doesn’t change too much, you can leave this step out when it comes to a new planning cycle.
5) Define your budget
First, you need to define the budget you have to achieve this marketing plan of yours. Then, you’ll need to allocate the budget across each of the teams working toward the ultimate goal.
It’s likely that this allocation will require some research (and often, some compromise), for example, your PPC team will want to determine the average cost-per-click for the target keywords you’re going after to get the best ROI.
With the right kind of data, you can even spy on how much your competitors are spending on their pay-per-click advertising.

6) Identify your competitors
In order to make your marketing plan competitive, you’ve got to understand your competitive landscape – that includes who you’re up against, and what they’re up to.
So, here are two words we talk about constantly: Competitor + analysis .
A competitive analysis tool like Similarweb (which – may we add, is an all-in-one tool) can provide you with all the data you need to run a thorough competitive analysis .
So thorough in fact, that it can reveal your competitors’ complete marketing strategies and how your marketing performance compares – which is great for inspiration, and even better for gaining the competitive edge in your industry.
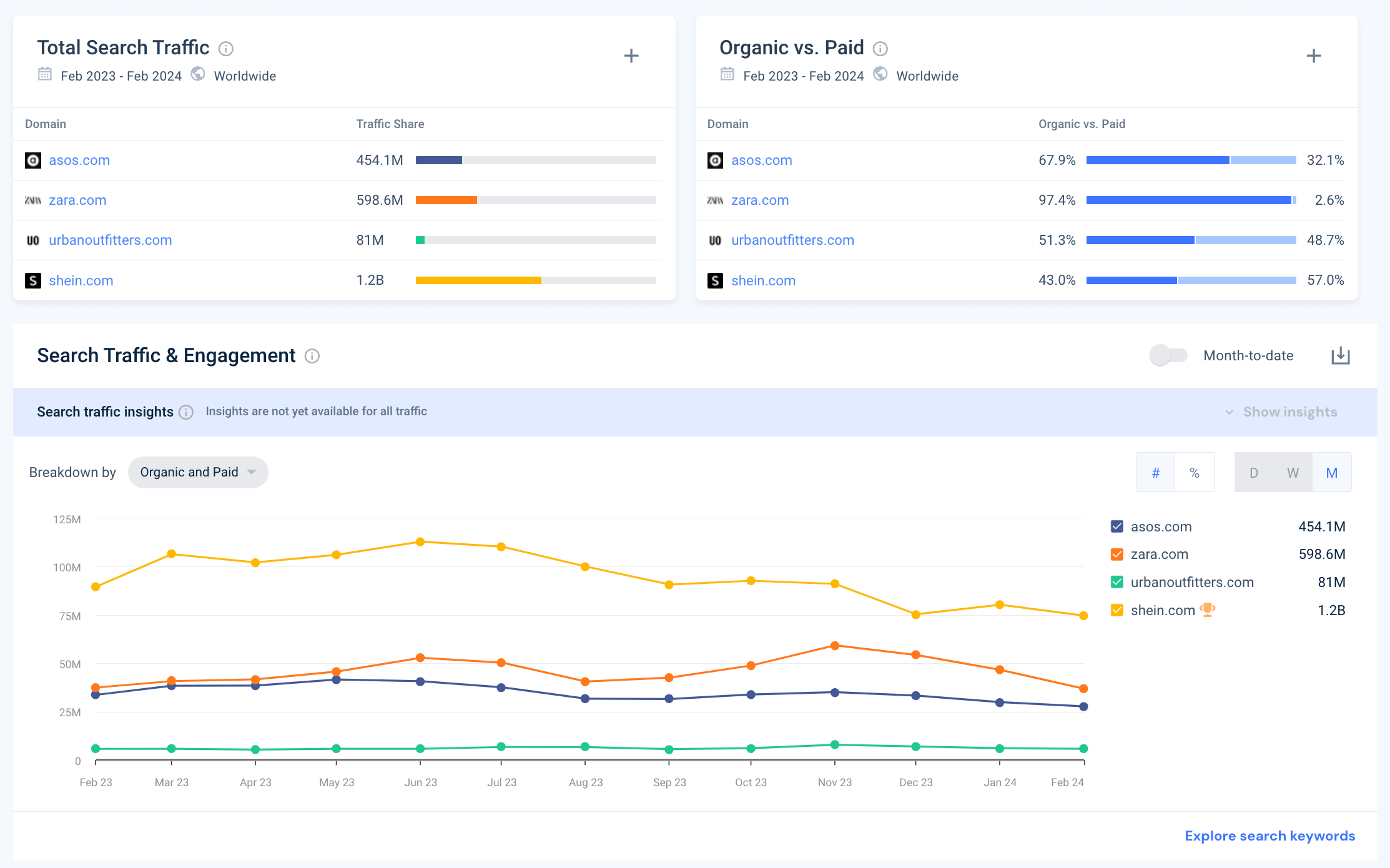
You can even set up a Competitor Tracker to make sure you never miss a beat on your competitors’ next moves. See it all on an interactive dashboard, and get emails sent straight to your inbox.
7) Outline your plan
Now you’ve got everything you need to outline your plan of action and get started.
With good data, you have all the keyword research and competitor research you need to dominate the market. Plus, you have all the information you need to brief each of your teams (eg. PPC, SEO and content) to make sure they’re aligned and going in the right direction, at the right time.
Similarweb can help you with all of that, and more. The thing is, with a marketing plan, the world around us never stays still – the digital world included. With real-time and real-user data – like Similarweb – you can ensure your marketing plan still adapts with the landscape.
6 mistakes to avoid when creating a marketing plan
When creating or writing up your marketing plan, there are a few common mistakes you want to avoid, including:
- Not conducting thorough market research
- Not benchmarking effectively and setting unrealistic goals
- Not having a clear definition of your target audience
- Underestimating your competition and the competitive landscape
- Failing to allocate resources (and budget) effectively
- Not regularly reviewing and updating your marketing plan
What’s the difference: Marketing plan vs. Business plan
When you’re in a marketing team, the business plan and marketing plan may feel very similar – and they certainly do touch. In reality, you can’t have one without the other.
A business plan should be considered as the “big picture”, whereas the marketing plan is the roadmap; the map – or sat nav – towards that big picture.
The marketing plan or marketing map zooms in on how you’ll reach and engage your target audience, which requires knowing your ideal customer profile and buyer personas, as well as the best channels and tactics to get their attention.
That attention from your target audience is crucial to the bigger business plan, which will outline your company’s:
- Mission and vision
- Financial goals
- Competitive landscape
What’s the difference: Marketing plan vs. Marketing strategy
A very common question for marketing generalists: what’s the difference between a marketing plan and marketing strategy?
While your marketing plan acts as your roadmap that gives your team direction and a clear plan of action (often with timelines, deliverables, and budgets in tow), your marketing strategy is the “why” behind your marketing efforts.
For example, your marketing strategy is to double your website traffic in a year and improve your engagement rates as an online business. Your marketing plan here might be to improve your SEO across your existing pages to get your content ranking higher on search, as well as investing in PPC for some more short-term impact into your brand awareness.
Smarter planning, smarter marketing, smarter reporting
… you want all that? You need smarter data.
A marketing plan isn’t a good marketing plan without the right kind of data – and Similarweb can give you that data.
With Similarweb, you can make sure your marketing plan and strategy is up to scratch – that means fully optimized and efficiently prioritized.
If that sounds good to you, try the platform for free today and watch it transform your marketing strategy.
It’s time to nail your digital marketing strategy
Get the freshest, most accurate competitive data now.
A marketing plan is a comprehensive document that outlines a company’s marketing objectives and strategies for achieving them. It typically includes an analysis of the target market, competitive landscape, marketing goals, tactics, and budget allocation.
Why is a marketing plan important?
A marketing plan provides a roadmap for achieving marketing objectives and helps ensure that marketing efforts are aligned with overall business goals. It helps in allocating resources efficiently, measuring progress, and adapting strategies based on market changes.
What should be included in a marketing plan?
A marketing plan should include an executive summary, a situational or competitor analysis, clear marketing objectives, target audience identification, marketing strategies and tactics, budget allocation, timeline, and metrics for measuring success.
How often should a marketing plan be updated?
Ideally, a marketing plan should be reviewed and updated regularly to reflect changes in the market, consumer behavior , and business goals. Quarterly or annually are common intervals for updates, but it ultimately depends on the pace of change in your industry.
How do you measure the success of a marketing plan?
The success of a marketing plan can be measured using various metrics, including sales revenue, customer acquisition and retention rates, website traffic, social media engagement, brand awareness, and return on investment (ROI) for marketing activities.

by Leah Messenger
Senior Content Marketing Manager
Leah is a Senior Content Marketing Manager with a passion for turning complex topics into engaging, educational content.
Related Posts

7 Proven Strategies to Convert Website Traffic into More Sales
Fake Web Traffic: How to Spot and Stop It for Real Results

What Is Website Analytics: Top Tools You Can Use

How To Create Better Competitive Analysis Reports

11 Benefits of Market Research + Free Templates

Competition-Based Pricing: Strategies, Benefits, and Drawbacks
Your full marketing toolkit for a winning strategy.
The ultimate solution to help you build the best digital strategy
US and International: +1-306-955-5512 | UK and EU: 0121 512 0304
Community Support

Local Impact Awards
Marketing Plan
Aug 28, 2023 | Business & Strategy , glossary
Related articles or contents
Youtube advertising, zero click search, zip code targeting, website speed, white hat seo, what is a marketing plan definition & examples.
For a marketing agency, a marketing plan is an invaluable tool for helping clients reach their goals. It can provide a roadmap for the agency to follow, ensuring that all marketing efforts are focused on the right objectives. It can also help the agency identify potential opportunities and develop strategies to capitalize on them. By creating a comprehensive marketing plan, a marketing agency can ensure that its clients are getting the most out of their marketing efforts.
Table of Contents
Introduction to marketing plans, identifying goals and objectives, developing strategies and tactics, implementing the plan.
- Measuring Results
Key Takeaways
- Understand the purpose of a marketing plan and its components
- Identify goals and objectives for the plan
- Develop strategies and tactics to achieve the goals
- Implement the plan and measure the results
A marketing plan is a critical component of any successful marketing strategy . It provides a clear roadmap for the agency to follow, ensuring that all marketing efforts are focused on the right objectives. It also helps the agency identify potential opportunities and develop strategies to capitalize on them.
When creating a marketing plan, there are several key elements to consider. These include:
- Defining the target audience : Identifying the target audience is essential for any marketing plan. It helps the agency determine which strategies and tactics will be most effective in reaching the desired audience.
- Setting objectives : Establishing clear objectives is essential for any marketing plan. It helps the agency focus its efforts on the right goals and measure progress towards them.
- Developing strategies : Once the target audience and objectives have been identified, the agency can develop strategies to reach them. This includes selecting the right channels, creating content, and developing campaigns.
- Tracking progress : Tracking progress is essential for any marketing plan. It helps the agency measure the success of its efforts and make adjustments as needed.
By creating a comprehensive marketing plan, a marketing agency can ensure that its clients are getting the most out of their marketing efforts. It can provide a roadmap for the agency to follow, ensuring that all marketing efforts are focused on the right objectives. It can also help the agency identify potential opportunities and develop strategies to capitalize on them.
Once the target audience and objectives have been identified, the next step is to develop strategies to reach them. This includes selecting the right channels, creating content, and developing campaigns. It is important to ensure that the strategies are aligned with the objectives and target audience. This will help the agency maximize its efforts and ensure that the desired results are achieved.
When developing strategies, the agency should consider the following:
- Budget: Establishing a budget is essential for any marketing plan. It helps the agency determine how much it can spend on each strategy and ensure that it is within the client’s budget.
- Timing: Timing is key when it comes to marketing. The agency should consider when the best time is to launch a campaign or create content.
- Channels: Selecting the right channels is essential for any marketing plan. The agency should consider which channels are most effective for reaching the target audience.
- Content: Creating content that resonates with the target audience is essential for any marketing plan. The agency should consider what type of content will be most effective in reaching the desired audience.
- Measurement: Measuring the success of the strategies is essential for any marketing plan. The agency should consider which metrics to track and how to measure progress.
By identifying goals and objectives, and developing strategies to reach them, a marketing agency can ensure that its clients are getting the most out of their marketing efforts. It can provide a roadmap for the agency to follow, ensuring that all marketing efforts are focused on the right objectives. It can also help the agency identify potential opportunities and develop strategies to capitalize on them.
Once the strategies have been developed, the next step is to develop tactics to implement them. Tactics are the specific actions that the agency will take to reach the target audience and achieve the desired objectives. Tactics should be tailored to the specific strategies and objectives.
When developing tactics, the agency should consider the following:
- Advertising: Advertising is a great way to reach a large audience. The agency should consider which platforms and channels are best for reaching the target audience.
- Social Media: Social media is a powerful tool for reaching a target audience. The agency should consider which platforms are best for reaching the target audience and creating content that resonates with them.
- Events: Events can be a great way to reach a target audience. The agency should consider which events are best for reaching the target audience and creating content that resonates with them.
- Public Relations: Public relations can be a great way to reach a target audience. The agency should consider which channels are best for reaching the target audience and creating content that resonates with them.
- Content Marketing : Content marketing is a great way to reach a target audience. The agency should consider which platforms are best for reaching the target audience and creating content that resonates with them.
By developing strategies and tactics, a marketing agency can ensure that its clients are getting the most out of their marketing efforts. It can provide a roadmap for the agency to follow, ensuring that all marketing efforts are focused on the right objectives. It can also help the agency identify potential opportunities and develop strategies to capitalize on them.
Once the strategies and tactics have been developed, the next step is to implement them. This involves taking the necessary steps to ensure that the strategies and tactics are executed effectively. The agency should consider the following when implementing the plan:
- Timing: Timing is key when implementing a plan. The agency should consider when the best time is to launch the plan and ensure that all elements are in place.
- Resources: The agency should consider the resources that are needed to implement the plan. This includes personnel, budget, and other resources.
- Measurement: The agency should consider how it will measure the success of the plan. This includes setting key performance indicators and tracking progress.
- Communication: The agency should consider how it will communicate the plan to the target audience. This includes developing a communication plan and ensuring that all stakeholders are informed.
By taking the necessary steps to implement the plan, the agency can ensure that the strategies and tactics are executed effectively. This will help the agency achieve its desired objectives and ensure that the client is getting the most out of their marketing efforts.
What is the purpose of a marketing plan?
The purpose of a marketing plan is to outline the strategies and tactics that will be used to reach a company”s marketing goals and objectives. It is a document that outlines the steps that need to be taken in order to achieve the desired results.
What are the components of a marketing plan?
The components of a marketing plan typically include an introduction, identifying goals and objectives, developing strategies and tactics, implementing the plan, measuring results, and a conclusion.
How often should a marketing plan be updated?
A marketing plan should be updated regularly, as the market and the company”s goals and objectives may change over time. It is important to review the plan regularly to ensure that it is still relevant and effective.
What are the benefits of having a marketing plan?
Having a marketing plan can help a company to focus its efforts and resources on the most effective strategies and tactics. It can also help to ensure that the company is working towards its goals and objectives in an organized and efficient manner.
- Accounting & invoicing (3)
- Advertising & Promotion (54)
- Agencies (41)
- Branding (1)
- Bulletins (15)
- Business & Strategy (32)
- Calendar & scheduling (1)
- Case Studies (53)
- Chat bots & messaging (2)
- Communication & PR (6)
- Content Creation (1)
- Content Distribution (1)
- Content Marketing (2)
- Customer support (1)
- Data & Analytics (59)
- Digital Marketing (8)
- Email marketing (1)
- Franchises (1)
- glossary (305)
- In The News (50)
- Inbound Marketing (1)
- Integration (28)
- Integration platforms (3)
- Local Business (3)
- MSP/IT Services (3)
- Newsroom (153)
- Project & Operations Management (20)
- Search Engine Optimization (SEO) (46)
- Social Media & Online Presence (17)
- Specialized Markets & Services (2)
- Task management (3)
- Technology & Development (55)
- Uncategorized (1)
- Web forms & surveys (1)
Recent Posts
- Vendasta Honored as a Top Growing Company in Canada for Innovation and Performance
- Vendasta Welcomes Sanjay Manchanda as New Chief Marketing Officer
- Forbes Spotlights Vendasta CEO Brendan King’s Leadership in Trusted AI Innovation.
- MatchCraft Wins Prestigious Microsoft Advertising Rising Star of the Year Award for 2023
- Vendasta Expands Presence in Chennai’s Thriving Tech Hub

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A marketing plan is part of a business plan, which describes all of the important aspects of a business, such as its goals, values, mission statement, budget, and strategies. Understanding ...
Marketing plan vs. business plan. While both marketing plans and business plans are crucial documents for businesses, they serve distinct purposes and have different scopes. Here’s a breakdown of the key differences: Business plan is a comprehensive document that outlines all aspects of your business, including: Mission and vision; Products ...
Marketing Plan: This is a focused document dedicated to the marketing segment of an organization’s strategy. It meticulously outlines the marketing objectives, strategies, and tactics that will be employed to achieve the desired market presence and customer engagement. Business Plan: A business plan has a broader scope, encompassing every ...
A marketing plan is a strategic document that outlines marketing objectives, strategies, and tactics. A business plan is also a strategic document. But this plan covers all aspects of a company's operations, including finance, operations, and more. It can also help your business decide how to distribute resources and make decisions as your ...
Marketing plan vs. business plan. A business plan paints a bigger picture of how you plan to run your business. It includes a mission statement, products you’ll launch, and market research. A marketing plan, on the other hand, is a specific document that details how you plan to achieve these wider goals through marketing.
The purpose of a marketing plan includes the following: To clearly define the marketing objectives of the business that align with the corporate mission and vision of the organization. The marketing objectives indicate where the organization wishes to be at any specific period in the future. The marketing plan usually assists in the growth of ...
Creating a marketing plan is a step-by-step process. Make sure you take your time with each step before moving on to the next one. 1. Create an Executive Summary. An executive summary is a ...
A marketing plan is a roadmap that outlines your marketing strategy and defines how you will attract and convert (and often, retain) customers. In your marketing plan, you’ll spell out your target audience, your goals, your marketing tactics to achieve those goals, and how you’ll measure its success. We’ll talk more about how to write a ...
Definition & Examples. A marketing plan is a comprehensive document or blueprint that outlines a business”s overall marketing efforts. It details the goals that the business hopes to achieve through various marketing strategies and tactics, and provides a step-by-step guide for how it will reach those goals.
Strategy: Segmentation, Targeting and Positoning (STP) and the tactics forming the 7Ps of the marketing mix. Action: Budget, resourcing including team and tools and marketing technology (Martech) and 90-day action plans. As a marketer, every activity will fall into either an opportunity, strategy, or action.