
- LEADER AS STORYTELLER
- LEADERS WHO INFLUENCE
- LEADING WITH AUTHENTICITY
- LEADING WITH AGILITY
- LEADER AS COACH
- LEADERSHIP SKILL WORKSHOPS
- TEAM EFFECTIVENESS SOLUTIONS
- STRATEGIC CHANGE PROGRAMS
- OUR CLIENTS
- DIVERSITY AND BELONGING
- OUR PERFORMANCE BREAKTHROUGH BOOK
- OUR APPROACH AND METHODS
- OUR ENSEMBLE
- SOCIAL MISSION

6 Secrets From the Theater (That Anyone Can Use) For Giving Great Presentations

September 11, 2017 By Cathy Salit Comments are Off
Unless you’re a regular on the TED Talk stage, chances are you could improve your presentation performance.
If you need motivation, look no further than billionaire Warren Buffett , who says that learning to speak in public will increase your earning power by 50 percent. And there’s no shortage of advice on how to do it, from learning “ the rules ” to tapping into neuroscience .
As a lifelong stage performer who is also a CEO, author, executive coach, and public speaker, I’ve learned that some of the most important tools for turning all that motivation and advice into effective presentations come from the theatrical side of my background.
So here are my top six ways to harness the tools of the theater to make your next presentation a performance to remember.
1. It’s a monologue, not a soliloquy. In a play, when a character speaks for an extended period of time, it’s either a monologue or a soliloquy. As a presenter, you’re speaking for an extended period of time — and it better not be a soliloquy.
A soliloquy is a character talking to him or herself (think Hamlet intoning “ To be or not to be… ” and then rambling on about death and vengeance for the next 15 minutes). But a monologue is part of the dialogue of the play. It might be to another character, or to the audience, but it’s always a conversation.
As a presenter, don’t talk to yourself — talk to us.
2. Start in the middle. Movies and plays draw us in by starting in the midst of the action and so should you. Skip the long introduction and instead make a bold assertion.
I once asked a financial controller what she wanted her audience to take away from her quarterly results report. “Well,” she said, “we had a surprisingly good quarter.”
I told her to say that first, with no preamble. She tried it, and her audience of fellow workshop participants leaned in. They later reported that they were intrigued, curious, maybe even a little provoked — but they were paying attention.
3. Rehearse more than you think you need. On average, the cast of a play rehearses for more than a month before opening night. You don’t need to go that far, but thorough preparation is one of the most important factors in giving you confidence in front of an audience.
Speak your presentation out loud, a dozen times or more. Use your slides when you practice. This allows you to stop thinking about what comes next and instead focus on connecting with your audience.
4. Talk to people, not “the audience.” Speaking of the audience, remember the late Charlton Heston’s immortal words in Soylent Green : “ It’s made of people! ” In your case, I’m not suggesting that you eat them, but, please — talk to them.
Instead of looking at the audience as a mass, focus on individuals. Speak directly to them, one after another. Watch their reactions — did somebody nod? Great! Move on to someone else. Do they look perplexed? Maybe you should slow down.
Let your audience help you create your performance, as you move through it together.
5. Don’t compete with yourself. There’s a saying in theater: “Find your light.” It means that moving to the spot(s) onstage in which you’re best illuminated makes it easy for the audience to see you. As a presenter, you can do this too, and not just with lighting.
You can make a range of choices that have a big impact on how you come across. Where do you stand — behind a lectern or closer to the audience? How do you relate to your slides — do you try to read from them, and turn around to face away from the audience (please don’t!).
Speaking of slides: Your slides should not be saying what you’re saying. If they are, the audience will watch them and not you. Instead, let them illustrate and augment what you’re saying, with images or summary headlines.
6. Make deliberate choices. When legendary acting teacher Sanford Meisner directed students in class, his constant question was “What are you doing ?” What he meant was that as you work your way through a scene, you have to make deliberate choices about why and how you’re doing what you’re doing at any given moment.
For example, wandering or pacing around the stage (in the theater or in a presentation) looks aimless and distracting. But choosing to cross the stage (for example, to come closer to another part of the audience) looks confident and conveys command of the space.
Being conscious, prepared, and owning your performance in this way will give you a huge surge in confidence — and a much better presentation.
Originally published on Inc.com .
Cathy Salit is a performer and a founder of Performance of a Lifetime. Her book, Performance Breakthrough: A Radical Approach to Success at Work (Hachette Books) is on sale everywhere books are sold.
Follow us on LinkedIn!
Comments are closed.
- Name First Last
- Name This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.

Broadway Educators
Theatre Resources for Students and Educators
Public Speaking and Theatrical Techniques

Many of us assume that powerful public speakers are simply born with a natural talent for effective presenting. While it is true that some people are better oral communicators than others, anyone can draw on theatrical techniques to improve their public speaking. These theatrical techniques will help you stage your speech in a way that uses movement and visual pictures to enhance content.
Upstage and Downstage
Directors block the movements of actors to emphasize dramatic meaning and to maintain clear sightlines. The downstage area, closest to the audience, is a strong position and is the best place to present the
opening, closing, and most important content of your speech. Upstage, away from the audience, is less powerful but can be used effectively for reflective pauses or moments of offhand humor. Moving from upstage to downstage in order to make an important point can be highly effective.
Even in a less formal public speaking situation, these theatrical techniques can be applied. When you are sitting around a conference table for a meeting, leaning forward (downstage), this implies interest in the topic at hand. When you shift your weight back (upstage), you give your audience the impression that you are not as engaged in the subject matter.
Stage Right and Stage Left
In American and British theatre, Stage Right and Stage Left refer to the actor’s – or speaker’s – point of view. The position Downstage Right is perceived by western audiences as having intimacy and importance (probably because we read from left to right). In theatre, love scenes, monologues and narration are usually performed Down Right. Good public speakers use this position for their most important content, or for stories that have a strong emotional effect. Downstage Left traditionally has a conspiratorial feel to it, a place for plots and discussions in the theatre. Humor in a speech is often very effective when delivered from this position.
Think Like an Actor
Actors never “wander” around the stage. Every move is done with purposeful intention to emphasize, draw attention to, or otherwise offer “subtext” to the script or content. When you move from place to place on a stage, it’s called a cross. Crosses should be precise, clear movements from one place to another. Each movement should be done with purpose, at a specific point in your presentation. Wandering, pacing or even unconscious weight shifting draws attention and weakens the impact of your speech.
Think Like a Director
As a public speaker, you should always think about the stage picture from the audience point of view, keeping it balanced and visually interesting. Look carefully at the placement of furniture (lecterns, tables, projection screens) in relation to YOU and where you are in the audience’s view. If you are using a lectern, place it on one side and then move away from it at precise moments in order to make a point. Standing behind a large piece of furniture like a table creates a barrier between you and the audience. Make sure you are not “upstaged” by an unnecessary piece of large furniture, which unconsciously draws audience attention away from you.
If you are teaching public speaking, using these simple theatrical techniques of intentional movement and purposeful stage pictures will help make any of your students more powerful and polished presenters.
Recent Posts
Get in touch with us – here
- About Ginger
- About Leadership
- All programmes and courses
- Purpose-Driven Leadership
- Storytelling Mastery
- 1-2-1 training/coaching
- Elevate your Influence
- Executive Presence
- Present with Influence
- Public Speaking Foundations
- Assertive Communications
- Boosting Visibility and Confidence
- Building Your Personal Brand
- Clear & Concise Communications
- Courageous Communications
- Fearless Feedback
- High-Impact Communications
- Messages that Stand Out From the Crowd
- The Essentials of Storytelling for Business
- Virtually Brilliant for Online Communicators
- hello@gingerleadershipcomms.com
- +44 (0) 207 3888 645
6 of the Best Theatre Techniques for Public Speaking

Confident public speaking is not about putting on an act, but there are many acting techniques that can help you stretch into the full and fearless parts of your inner inspiring speaker. The key to any great performance is about sharing you – just a fuller version of you unleashed on stage. Many would-be speakers worry that they don’t have the chutzpah to entertain an audience. Worry not! Utilize these six theatre techniques for public speaking and you can be bolder, more memorable and more fearless than you ever dreamed possible.
Master your Speaking Anxiety .
Both the actor and the public speaker have to learn how to manage their their stress and anxiety before a performance. . Many people are astonished in finding out that their diaphragm is a very effective anti-stress method. Public speaking and presentation anxiety go hand in hand for many people. Nightmares like forgetting lines, botching powerpoint slides, losing notes, or fumbling over words can wake some folks up in the middle of the night howling.
The truth is, being a fearless public speaker isn’t about getting rid of your fear, nor is it about suppressing it. It’s about transforming that fear into energy and excitement. You can greatly decrease your anxiety with some relaxation techniques or some simple respiration exercises.
Develop your Stage Presence.
Good actors and good speakers don’t act: they don’t pretend. Both of them have to offer their true self to the audience and to be authentic. Managing to be yourself in front of an audience is perceived as charisma and magnetism, what we usually call “presence”. When you present, you need to become comfortable being in the spotlight. It means accepting your central role (and the exposure that comes with it) as a speaker. Some presenters are uncomfortable with that level of scrutiny, and you can tell. But public speaking is performance. If you don’t become comfortable on stage then you won’t be able to share your message to the world!
Use Performance Body Language.
Body language is a crucial element of effective public speaking. But mastering body language is not about learning a list of rules about where to put your arms and feet at which moment. Body language power comes from within… and it starts with your attitude.Winston Churchill said “Attitude is a little thing that makes a big difference.” It’s no big surprise that how you carry yourself whilst public speaking makes a tremendous impact on your audience.
Learn how to use space. Try to decrease the distance between you and your listeners, for instance. And think about how your position in your “performance space” can be linked to your content. — Can your stage position be tied to the item you’re talking about at the moment?
Your Voice is your BFF.
Is your voice fully expressive? It needs to be, if you’re going to convey the subtle meanings of the points you’re making. Too many public speakers fail to realize the power and importance of not speaking at times. Allow the gravity and weight of what has been spoken to settle on your listeners. And for pity’s sake PLEASE stop using the “story teller voice.” It’s false. You tell a story to 10,000 the same way you tell the story to your best friend. You don’t use some dramatic made up voice. It reeks of playing pretend.
Channel Charisma.
Every actor knows the expression “ Find your light .” It means that if you’re in the dark on stage, step into the light source so you can be seen. Audiences find it hard to pay attention to actors they can’t see! Don’t PUSH. (Push is theatre term for over acting) When you push the work feels false and often self-observed.
The word charisma comes from the Greek word “gift”, befitting the notion that allure is something you’re born with, and can’t earn. Is charisma an intangible, magical aura that you either have or you don’t? Can you learn to “work a room” with a sly grin and a smile and being comfortable in your own skin? Charisma simply equals the confidence to be yourself. And I argue yes… charisma is something you can cultivate and use in your public speaking. Here’s how.
Lead the Audience Response.
Focus too much of your attention on your content and you may as well be speaking to an empty room. Develop an awareness of how your audience is responding. Naturally, actors cultivate this attribute until it’s a finely-tuned instrument. But public speakers can benefit from awakening this awareness.
A big part of what we do when we speak publicly is develop a relationship with our audience. A relationship based on trust, respect, information, and interaction! Sure a speech has mostly been defined as one person talking and other people listening. But it always takes two to tango… you know. You AND your audience have a part to play in this engagement.
And when you end… get everything in before the audience claps. Then get off the stage. Standing around on the stage (unless you invite them to share the stage with you afterwards) breaks the theatrical experience. And never never NEVER turn your back to the audience unless it’s intentional to make a point or convey an emotion. When you need to move upstage (that’s toward the back of the stage, away from the audience) you do it backwards while speaking to the audience.
How to be Brilliant at Public Speaking is available in bookstores and on Amazon.com.
It’s time to rip up the rule book and forget what you think you know about the perils of public speaking.
Whatever the occasion, subject or situation, and with the right advice, anyone can be an entertaining, interesting and inspiring public speaker – you just need to know how. Using my expert tips, tricks, tools and techniques you’ll quickly develop the six simple qualities necessary to banish your nerves, feel relaxed, connect with your audience and really wow them.
Whether you want to overcome your fears and take that first step, or if you’ve already had some practice and want to polish your performance, Sarah will help you build your confidence to deliver your next talk naturally and with style and sophistication.
Anyone can speak in public – even you. Here’s how to do it brilliantly.
Buy this amazing book HERE.
Ginger Leadership Communications
This showcase of inspiring female speakers is part of Ginger’s work with game changing leaders.

- Google Slides Presentation Design
- Pitch Deck Design
- Powerpoint Redesign
- Other Design Services

- Design Tips
- Guide & How to's
- Presenting techniques
Presenting is a craft that requires a thoughtful approach. There’s a lot of stuff to include in the good presentation. From quality visuals to a compelling speech, everything matters. Doing a presentation on your own may be quite a challenge especially if it’s your first time experience with the presentations. What can really help though, are the effective presentation techniques. In essence, they are the blueprint for your presentation, that helps you to hit all the right spots. Let’s look into some of those techniques.
Presentation Methods
Before you start thinking of a technique, let’s first understand the presentation methods and how they relate to the audience and the content of your presentation. Among the different presentation methods, the main ones are formal and formal. Their difference is mainly in the style of your delivery and the data presentation methods. The formal presentation is best suited for the business meetings or college level, scientific presentations. The informal methods of presentation can best be used during the smaller meetings with your team to discuss business subjects or, for example, at a Ted-like speech event.
Method 1: Keeping Everything Simple
This is a rather basic technique. Just strip your presentation of all the unnecessary information, leaving only the core statements that you want to address. Simplicity not only helps your audience to understand your points better but even more, this data presentation method lowers the risk of making a mistake, forgetting — and saves you and your audience quite a lot of time! There are different definitions of simplicity — sometimes just a few words are enough, while in other cases several bullet points on the slide may be sufficient. Choose what suits your topic best.
Method 2: Good Start
This method of presentation is all about attention-grabbing. Starting your presentation with a powerful statement, unusual fact or an interesting question will make the audience engage in your presentation instantly. Another great way to start is a joke, though humor can be quite a landmine, especially when you’re presenting in front of strangers, and you are not sure whether your joke would be fun or actually offensive. So, try to think of something neutral, yet funny.
Method 3: Use Visuals in your Presentation
Visuals are a must for any presentation and are able not only to support your speech but also to tell and contribute to the stuff you’re telling about. The pictures, graphs, infographics, and even short videos especially when done by presentation design services are what truly make the presentation, and help you to connect with your audience. A carefully selected visual connects both with your speech and the slide content, making your presentation methods work in complete harmony. What is more, visuals can serve as a great way to help you recall your speech in case you suddenly forgot some of it during the presentation.
Method 4: Rehearse
Don’t rush to tell your presentation just once you’ve made it. Instead, try to first rehearse your presentation in front of a mirror. This presentation technique allows you to spot the mistakes and downfalls in your speech and visual part and improve powerpoint presentation . What is more, it can also make you more confident, as with each time you rehearse you’ll memorize your stuff better and better. Bonus points for starting rehearsing from the random spots in your presentation — using this presentation technique will allow you to become completely familiar with your information.
Method 5: 10/20/30 Presentation Rule
While it may not be applied to all of the presentations, the ones that you are usually dealing with can really benefit from it. 10 20 30 rule is about the time and size of your presentation:
- Your presentation should have no more than 10 slides
- The time needed for the presentation should be no more than 20 minutes
- The font you are using for presentation text (if there is any on slides) is no less than 30 point
Method 6: Storytelling
Telling a story is a powerful presentation technique for keeping the audience interested. In general, people get bored from being fed just straight-up facts and numbers for a long time. However, an interesting story, connected to the subject of your presentation gives that personal touch to it, engaging the audience into what you are talking about. What is more, a good story in the context of the presentation will actually resonate with the audience, causing more approval to you as an expert.
- Tell a personal story .
- Create suspense.
- Bring characters to life.
- Build up to S.T.A.R moment.
Method 7: Presentate with your Voice
Speech is the most common method of presentation . When you are presenting, it’s important not only WHAT you say, but also HOW do you say it. Creating a proper voice for presentations is actually one of the things you need rehearsal for. Your goal is to sound confident and interested in the subject you are telling about. What is more, it is important to not make unnecessary pauses and avoid the “ummm”, “oh” and other similar stuff that slows down your presentation and may put off the audience.
Method 8: Know your Audience
Make sure that the data presentation methods you are using make your data relevant to your audience. The research of your audience is needed to craft a relatable story, as well as to understand what approach in presenting you may want to take. After you’ve done the research, you can just tell the audience what it wants and expects to hear. Such an approach would result in the satisfied and interested audience enjoying your presentation. And in this case your presentation would surely and up being a huge success!
Method 9: Back up plan
Even though you may plan everything in advance, something can always go wrong. The strange ability of the hardware to malfunction right in the middle of your presentation is probably one of the most known presentation-related memes. So, plan at least some of the bad scenarios. For example, have a printed set of slides with you during your presentation. Check everything right before you’ll start presenting. A good idea also is to have your script written out so that in case you have completely forgotten some of its parts, you can easily and quickly look into it and goon with the presentation.
Method 10: Relax
This one is not only a presentation technique , but a great life technique as well. Actually, the most common reason for the mistakes during presentations are the nerves and fear a lot of people feel while presenting. It’s absolutely normal to be a little worried about the presentation, but you have to instill confidence in your knowledge and expertise with the subject among the audience, and it’s hard to do if you feel fear. Try to reason with yourself — you have rehearsed, prepared great visuals, learned about the audience and even have a plan B in case the situation gets worse. There’s nothing to worry about — you have all the right presentation techniques !
- 50 tips on how to improve PowerPoint presentations in 2022-2023 [Updated]
- How to present a research paper in PPT: best practices
- Present financial information visually in PowerPoint to drive results
- Keynote VS PowerPoint

15 Essential Presentation Techniques for Winning Over Any Audience
- The Speaker Lab
- April 13, 2024
Table of Contents
Ever found yourself standing before an audience, your heart racing? That’s the moment when knowing effective presentation techniques can prove to be your unwavering ally. But what are presentation techniques? And what makes them so powerful? In this article, we’re going to answer those questions.
Before we can talk about presentation techniques, though, we first have to talk about good communication. The power of effective communication isn’t just in what you say. It’s how you say it; it’s in those deep breaths that steady nerves, and in maintaining eye contact. It’s about turning a room full of strangers into an engaged audience hanging onto your every word. When it comes to public speaking , real success comes from mastering non-verbal cues to punctuate our words and using visual aids not as crutches but as tools for engagement.
As you hone your communication skills, you will begin to form effective presentation techniques. Expect rough patches as you get the hang of things, but view them as mere footholds propelling you towards your ultimate triumph. Keep pushing forward.
Mastering Presentation Techniques for Impactful Delivery
Presentation techniques are more than just standing in front of a crowd and talking. They’re about making connections, telling stories that resonate, and leaving your audience with something to remember you by.
Elements of an Effective Presentation
For your presentation to resonate, ensure the visuals are straightforward and supportive, rather than distracting. Your message should be concise yet powerful enough to stick. And let’s not forget engagement; keeping your audience on their toes is key.
- Visuals: Keep them simple but impactful.
- Message: Make every word count.
- Engagement: Interact with your audience, ask questions, make them think.
We’ve all seen those slides crammed with text or charts. When you make your slides, don’t cram information, because nobody wants to squint at tiny fonts or decipher complex graphs while trying to listen to you speak. This resource suggests focusing on clarity and simplicity when designing slides—advice worth taking.
Strategies for Delivering a Successful Presentation
To deliver a knockout presentation, start strong. Grab attention from the get-go with an intriguing fact or story related directly back into the topic at hand. Maintain eye contact across the room so everyone feels included in the conversation. Finally, end on a memorable note, either with a call to action or insight gained during the time together. Leave them wanting more information and eager to learn about the subject matter discussed today.
- The opener: Hook your audience with a relevant fact or anecdote.
- Maintain connection: Eyes up, engage everyone around.
- Closing remarks : Last chance for impact–what’s your mic drop?
As author Lilly Walters once said, “The success of your presentation will be judged not by the knowledge you send but by what the listener receives.” This quote reminds us that the true goal of any speech is the understanding achieved between the speaker and the listeners.
Learn How You Could Get Your First (Or Next) Paid Speaking Gig In 90 Days or Less
We receive thousands of applications every day, but we only work with the top 5% of speakers .
Book a FREE call with our team to get started — you’ll learn why the vast majority of our students get a paid speaking gig within 90 days of finishing our program .
Engaging Your Audience with Nonverbal Communication
As the name implies, nonverbal communication denotes all of the ways you communicate without using words. This includes eye contact, body language , and facial expressions. Although nonverbal communication might not be the first presentation technique that comes to mind, it’s nevertheless a very powerful tool to have in your arsenal. Let’s take a look.
The Power of Eye Contact, Body Language, and Facial Expressions
Making eye contact isn’t just about looking someone in the eye; it’s about forging a connection. Aim for brief moments of eye contact across different sections of your audience throughout your presentation. Establishing fleeting eye connections across diverse audience segments fosters a sense of trust and keeps them hooked, all while ensuring no one feels on edge.
Body language is similarly important. Stand tall with good posture; it exudes confidence even when you feel nervous. As you grow more confident, mix up standing still with moving around subtly. This dynamic shift holds attention better than being rooted to one spot or nervous pacing. Use your hands to gesture naturally as you speak—it adds emphasis and keeps things lively.
If there’s one thing people can spot from miles away, it’s insincerity. So let those facial expressions match your words. Smile when you share something amusing, and furrow your brow when diving into serious stuff. After all, it’s not just what you say but how visually engaged and passionate you appear while saying it that counts.
Tying these elements together helps you deliver impactful, memorable talks. When done right, folks will leave feeling more connected, understood, and fired up by your presentation, all thanks to your techniques.
Designing Compelling Presentation Materials
Knowing how to design engaging presentation materials is one technique you can’t do without. Far from mere embellishments, these implements are crafted to hammer your message home. Hence, it’s vital to select these aids with great care and discernment.
Tips for Creating Effective Slides
When it comes to crafting slides, think of each as a billboard advertisement for your idea. You want it clear, impactful, and memorable.
- Keep it simple : One idea per slide keeps confusion at bay and attention locked in.
- Use bullet points : Break down your points so your audience can track.
- Pick a font size : Generally speaking, bigger is better.
- Use color : Harness colors that pop without blinding anyone; contrast is key.
- Use images with purpose : A good picture or chart can help illustrate your point, but keep it relevant and don’t overdo it.
With a few helpful visuals, your presentation can go from good to great. For more on creating slides, check out this link here .
Handling Questions and Interactions Professionally
For some speakers, it’s not the presentation itself that makes them nervous—it’s the Q&A session that follows. This is the moment where you get to shine or stumble based on how well you handle those curveballs from your audience. If you want to round off your presentation well, you’re going to want to learn a few techniques for fielding these questions. Let’s look at a few ways of doing this.
Preparing for Audience Questions and How to Address Them Effectively
Below are six techniques that will help you address audience questions effectively.
- Listen Up : The first rule of thumb is to listen like it’s a superpower. When someone throws a question at you, don’t just hear them out—really listen. Demonstrating this level of attentiveness not only conveys your respect but also affords you a brief moment to collect your ideas.
- Stay Calm : You’ve got this. Even if a question catches you off guard, take a deep breath before diving into your answer. No one expects perfection, but showing confidence matters.
- Practice Beforehand : Before presentation day arrives, think about potential questions folks might ask and prep some responses in advance. Practice makes perfect, after all.
- Vary Your Techniques : Not every question needs an essay as an answer; sometimes short and sweet does the trick. Mix up how detailed or brief your answers are depending on what’s asked.
- Show You Care : If you ever get a question that leaves you stumped, say so honestly—but add that magical line: “Let me find out more and I’ll get back to you.” Then actually do it.
- Appreciate Audience Curiosity : Remember that the reason you audience is asking questions is because they’re interested. So no matter what questions you get, keep engaging with enthusiasm.
Go forth with confidence, knowing not only can these moments boost credibility—they make connections too. So next time when facing down those queries remember to listen hard, stay calm & always engage warmly. With these techniques under your belt, answering audience questions after your presentation will feel much less daunting.
Techniques for a Memorable and Effective Presentation
No matter what topic you cover in your presentation, you can easily add in a story, and more likely than not you can add a little humor too. Together, these two presentation techniques are perfect for making your speech memorable.
Incorporating Storytelling into Your Presentation
One great technique for making your presentation stick is telling stories. Stories have the power to touch people profoundly, especially when they depict relatable experiences. So, when you’re up there presenting, kick things off with a story that ties into your main message. It could be personal, something from history, or even an anecdote that gets your point across. Stories are not just fluff; they’re the glue of your presentation. They make complex ideas digestible and memorable.
Using Humor to Connect with the Audience
Another great way of engaging your audience is by using humor. But here’s the deal—use humor wisely. Keep it tasteful and tied closely to the content at hand so it enhances rather than detracts from your message.
- Pick universal themes everyone can relate to.
- Avoid anything potentially offensive.
- Tie jokes back to your key points to make them relevant.
If humor isn’t your thing, or you’re worried about your comedic timing, it’s perfectly okay to skip the jokes. Especially if you’re new to public speaking, humor can be hard to nail immediately. But as you grow and hone your presentation techniques, consider stretching yourself a bit. By starting small, you can practice using humor to connect with your audience. That is your goal, after all—to leave a positive, memorable impression on your audience.
Find Out Exactly How Much You Could Make As a Paid Speaker
Use The Official Speaker Fee Calculator to tell you what you should charge for your first (or next) speaking gig — virtual or in-person!
Overcoming Public Speaking Anxiety
For some speakers, stepping in front of a crowd to speak causes immediate anxiety. But fear not! Conquering public speaking anxiety is entirely within your grasp.
Techniques to Manage Stage Fright and Boost Confidence
First off, feeling nervous before taking the stage is completely normal. Even Mark Twain admitted, “There are two types of speakers. Those who get nervous and those who are liars.” So take that flutter in your stomach as a sign you care deeply about delivering value to your audience. In addition, consider the following tips as you prepare to hit the stage.
- Breathe Deep: Before stepping up, take some deep breaths. In through the nose, out through the mouth. Feel every muscle relax with each exhale.
- Mind Over Matter: Visualization is key. Picture yourself nailing that presentation, because if you can see it, you can achieve it.
- Keep It Simple: Stick to what you know best; this isn’t the time for surprises or untested waters.
- Pace Yourself: Speak slowly but surely—there’s no rush here.
Believe it or not, acting relaxed often leads to actually being relaxed. Remember when we said mind over matter? Well, it applies here big time. The power pose backstage might just be what turns those nerves into excitement.
So next time you feel stage fright coming on, fight back with these techniques. With these tricks up your sleeve, you’re more than ready. So go ahead, breathe deep, and step onto that stage. You’ve got this.
Using Different Presentation Methods to Engage Your Audience
While learning styles is “ little more than urban myth ,” presenting your material in a variety of ways is a great technique for engaging your audience. By switching it up, you increase your chances of explaining something in a way that clicks with individual audience members. This is especially helpful for more complex topics that might be hard to grasp.
There are three main ways of presenting your material to your audience: through visuals, audio, and hands-on activities.
- Visuals: Use slides packed with images, graphs, and bullet points.
- Audio: Tell stories, play audio clips or engage in discussions.
- Hands-on Activities: Include activities or demonstrations that allow audience members to participate physically.
Making sure everyone gets something from your presentation means considering these techniques when planning content. Not only can incorporating various methods increase audience engagement, but it can also elevate your presentation from decent to memorable.
Essential Tips for First-Time Presenters
Stepping onto the stage or logging into that webinar platform as a first-time presenter can feel nerve-wracking. But fear not! With these tips on how to dress appropriately, arrive early, and make your presentation shine, you’ll be ready to confidently nail that presentation.
Dress Appropriately
Your outfit is your armor. Choose something professional yet comfortable. Whether it’s in-person or online, dressing one notch above what you expect your audience to wear usually hits the sweet spot. Aim for solid colors that won’t distract your audience.
Arriving Early
If possible, arrive at the venue before your audience does. This gives you time to settle in, test any tech gear like microphones or projectors, and take those deep breaths. This extra time also lets you chat with early birds. By connecting with people before taking center stage, you can ease nerves significantly.
Making Presentation Time Count
You only have the audience’s attention for so long. Keep an eye on the clock as you present, but avoid rushing through content. It especially helps to pause after key points, letting information sink in. Your end goal? Leave you’re audience wanting more. You’ll know if you succeeded based on the number of questions you get during the Q&A.
So there you have it—the techniques you need to deliver an engaging presentation. By honing nonverbal communication, like eye contact and posture, you can captivate your audience with your energy. And visual aids? They’re not just ornamental; they help bolster your point and drive it home.
We also learned that tackling audience questions is not an art reserved for the eloquent few but a skill sharpened by preparation and presence. While it takes a little work to nail good storytelling and well-timed humor, the ultimate outcome is worth it.
So while standing before an audience may set your heart racing, know that arming yourself with knowledge and technique can transform not just your presentation, but you yourself. So don’t be afraid to try your hand at these skills; in doing so, you build your own confidence and become a better speaker in the process.
- Last Updated: April 11, 2024

Explore Related Resources
Book a call with our team to get started — you’ll learn why the vast majority of our students get a paid speaking gig within 90 days of finishing our program .
If you’re ready to control your schedule, grow your income, and make an impact in the world – it’s time to take the first step. Book a FREE consulting call and let’s get you Booked and Paid to Speak ® .
About The Speaker Lab
We teach speakers how to consistently get booked and paid to speak. Since 2015, we’ve helped thousands of speakers find clarity, confidence, and a clear path to make an impact.
Get Started
Let's connect.
Copyright ©2023 The Speaker Lab. All rights reserved.
12 Effective Presentation Techniques To Help You Succeed
- By Judhajit Sen
- May 19, 2024
Delivering a good presentation requires more than just good content; it demands careful planning and strategic execution. From mastering your topic to engaging your audience, each element factors in captivating your listeners and making a lasting impact.
Start by thoroughly understanding your topic. Deep research will not only bolster your confidence but also prepare you for any questions that might arise. Organize your points logically with a clear outline, using presentation aids like slides and videos to enhance clarity.
Audience alignment is vital. Customize your content to their needs and interests, using simple language and relatable examples. A well-structured presentation, beginning with a strong, attention-grabbing opening and ending with a memorable conclusion, will keep your audience engaged throughout.
Effective verbal communication further enhances your delivery. Practice speaking clearly and confidently to relate to your audience. Incorporating multimedia and interactive elements such as polls and Q&A sessions are excellent audience engagement strategies .
F ocusing on these presenting techniques can help you give a good presentation.
The following are 12 effective presentation skills to help you succeed.
Key Takeaways
- Thorough Planning: Understanding your topic deeply and organizing your points logically with clear presentation aids sets the stage for a compelling presentation.
- Audience Alignment: Tailor your content to match your audience’s needs, interests, and comprehension level, ensuring maximum engagement and effectiveness.
- Confident Delivery: Master verbal communication, body language, and simplicity to enhance delivery and foster connection with your audience.
- Engagement Techniques: Incorporate storytelling, multimedia, and interactive elements to boost engagement and ensure your message resonates effectively.
Planning: Crafting a Winning Presentation
Behind every successful presentation lies meticulous planning. From understanding your topic to structuring your speech, each step is crucial for a compelling delivery that captivates your audience.
1. Topic Mastery
Begin by diving deep into your presentation topic. Conduct thorough research to bolster your knowledge and confidence. Identify areas where you may need additional preparation, ensuring you’re ready to tackle any questions that come your way.
2. Organized Framework
Map out your slides with an effective presentation outline , arranging the main points in a logical sequence. This blueprint will serve as your roadmap, keeping you focused and ensuring you cover all essential aspects. Consider integrating presentation materials like slides or videos to enhance clarity and engagement.
3. Structural Excellence
Craft a presentation with lasting impact by adhering to a well-defined structure. Start with a captivating introduction, followed by a robust body of content, and conclude with actionable insights. Embrace the 10-20-30 rule as a guide, limiting slides to 10, delivery time to 20 minutes, and font size to a minimum of 30 points.
Effective planning sets the stage to give a killer presentation, empowering you to deliver a compelling narrative that resonates with your audience long after the applause fades.
Audience Alignment: Key to Presentation Success

Understanding your audience is indispensable to delivering the presentation. Tailoring your content to match their needs, interests, and comprehension levels ensures maximum engagement and effectiveness.
1. Know Your Audience
Take the time to learn about your audience’s backgrounds, interests, and concerns. Simplify technical jargon and complex concepts to ensure clarity and comprehension across diverse audiences. By speaking their language, you can foster understanding and avoid confusion.
2. Speak Their Language
Craft your presentation with your target audience in mind. Use strong, concise language and relevant examples to maintain their interest. Avoid using foreign words or clichés that may alienate or confuse your audience. If necessary, provide explanations to ensure clarity.
3. Relevant Data Presentation
Align your data presentation methods with your audience’s preferences. Conduct research to craft a relatable narrative and understand the most effective presentation approach. By addressing their expectations, you can ensure a satisfied and engaged audience.
4. Tailored Content
Identify your audience’s interests and needs to tailor your presentation accordingly. Adjust your language and focus based on whether you’re addressing professionals or a general audience. This personalized approach enhances relevance and engagement.
5. Design for Maximum Impact
Design your presentation around your audience’s needs and interests to deliver maximum value. By aligning your message with their expectations, you enhance comprehension and ensure your message resonates effectively.
By prioritizing audience alignment, you can craft presentations that captivate, inform, and inspire, driving your message home with clarity and impact.
Nailing the Beginning and End of Your Presentation
Starting and ending your presentation with impact is crucial for keeping your audience engaged and leaving a lasting impression. Here’s how to master both:
1. Captivating Start
Start your presentation with a powerful statement, unusual fact, or an interesting question to grab attention instantly. This approach hooks your audience and piques their interest from the get-go. Another method is to share a personal story or use a quote that resonates with your topic. Humor can also be effective, but be cautious with jokes—ensure they are neutral and unlikely to offend.
2. Clear Structure
After your attention-grabbing opening, provide an overview of your presentation’s time and structure. This roadmap helps your audience follow along and understand the flow of your content. Displaying a simplified outline throughout the presentation can keep your audience oriented and focused.
3. Memorable Ending
A strong ending is as important as a strong start. Conclude with a call to action , a memorable quote, or a personal story reinforcing your message. This ensures your audience leaves with a clear understanding of your key points and what you want them to do next. When you end a presentation , don’t forget to thank your audience for their time and attention.
By crafting a compelling beginning and end, you can enhance your presentation’s effectiveness and ensure your message resonates long after you’ve finished speaking.
Streamlined Success: Mastering Simplicity
Simplicity isn’t just a preference; it’s a powerful presentation technique that enhances focus and comprehension. By stripping away excess information and focusing on core messages, you ensure clarity and engagement.
1. Cleanliness
Avoid overwhelming your audience with information overload. Keep slides clean and concise, limiting each to 6-8 lines of text. This not only aids focus but also enhances the appeal of your presentation.
2. Core Focus
Simplicity means distilling your presentation to its essence, stripping away unnecessary details. This minimizes the risk of mistakes or confusion and saves valuable time for you and your audience. Whether a few words or bullet points for presentations suffice, choose a format that suits your topic.
3. Clear Communication
To maximize understanding, keep your presentation simple and straightforward. Use simple language, avoid technical jargon, and emphasize key points. For clarity, incorporate charts or graphs to simplify complex data and break up text with bullet points or subheadings.
By embracing simplicity, you empower your audience to grasp and retain your message effectively, fostering engagement and leaving a lasting impression.
Mastering Verbal Communication in Presentations
How you speak and deliver your message can make or break your presentation. Here’s how to ace it:
1. Speak Clearly and Confidently: Project your voice so everyone can hear. Pause when needed and adapt your language to your audience.
2. Pace Yourself: Don’t rush. Speak slowly and clearly, avoiding both lightning speed and snail pace. Don’t read everything verbatim unless necessary.
3. Mind Your Audience: Remember, they’re hearing this for the first time. Give them time to digest your slides. Master the art of the pause for emphasis and to collect your thoughts.
4. Cut the Fillers: Avoid “um” and “so” – they signal unpreparedness. Keep your speech smooth and confident.
5. Speak, Don’t Read: Engage with your audience. Speak freely, slowly, and clearly. Use note cards if needed, but keep them brief. Memorize the start and end for crucial eye contact.
Mastering verbal communication can turn an okay presentation into a memorable one. Practice, pause, and speak with confidence!
Mastering Presentation Dynamics: The Power of Body Language

Body language is a secret weapon for captivating your audience during presentations. It encompasses posture, expressions, and overall stance in front of the crowd. By harnessing this potential, you can elevate a lackluster presentation into a riveting experience.
1. Establishing Comfort and Connection
Start with a smile! Being pleasant and approachable sets the stage for an engaging presentation. Avoid pacing or making wild gestures that distract from your message. Maintain steady eye contact across the room, from front row to back, and sidestep the trap of fixating on screens or notes.
2. Projection and Poise
Your physical demeanor speaks volumes about your confidence. Stand tall, relax your shoulders, and exude ease. Embrace gestures that underscore your points while avoiding distracting habits like gum chewing or fidgeting. Dressing appropriately adds to your professional image.
3. Engaging Your Audience
Your body stature should mirror your enthusiasm for the topic. Stand confidently, using hand gestures to amplify critical points. Let your facial expressions reflect your passion and commitment to the subject matter.
4. The Power of Eye Contact
Maintaining eye contact fosters a personal connection with each listener, alleviating nerves and enhancing confidence. Start with a friendly face in the crowd, then gradually expand your gaze. Resist the urge to divert attention to screens, floors, or notes.
5. Strategic Positioning
Avoid standing directly in front of your audience, whether on a podium or in an open space, which can subconsciously signal aggression. Instead, position yourself slightly to the side, maintaining fluid movement to keep your audience engaged.
Mastering body language in presentations amplifies your prowess, enabling you to convey confidence, build rapport, and deliver messages that resonate deeply with your audience.
Amplifying Your Message: The Art of Voice Inflection
Your voice is a powerful tool in presentations, shaping comprehension and engagement. Mastering voice inflection enhances clarity, confidence, and audience connection.
1. Projecting with Purpose
Effective projection ensures your audience hears every word clearly, boosting confidence and engagement. Stand tall, breathe deeply, and enunciate each syllable with precision.
2. Emphasizing Key Points
Clarity is key when conveying important ideas. Slow down, articulate, and raise your voice to underscore the significance of your message. Infuse authority, confidence, and enthusiasm into your delivery.
3. Crafting Convincing Speech
In presentations, it’s not just what you say but how you say it that matters. Practice creating a confident and engaging voice. Eliminate unnecessary pauses and filler words like “um” or “oh” to maintain momentum and keep your audience captivated.
By mastering voice inflection, you can elevate your presentations from ordinary to extraordinary, ensuring your message resonates deeply with your audience.
Captivating Narratives: The Power of Storytelling
Storytelling isn’t just for bedtime; it’s a dynamic tool for elevating presentations. By weaving compelling narratives into your speech, you can ignite curiosity, engage your audience, and leave a lasting impression.
1. Breathing Life into Ideas
Embrace storytelling as a potent strategy to animate your subject matter. Don’t shy away from personal anecdotes or moments of suspense; they add depth and intrigue. End on a positive note to drive your message home effectively.
2. Forging Connections
Stories forge connections with your audience, making your message memorable. Use real-life examples, anecdotes, or case studies to illustrate your points and make them relatable. This personal touch resonates with your listeners, fostering a deeper understanding.
3. Sustaining Interest
Break the monotony of facts and figures by infusing your presentation with compelling stories. Engage your audience with narratives that captivate their attention and establish you as an expert. Leverage techniques like creating suspense and bringing characters to life to keep your audience invested.
4. Amplifying Impact
Adopt storytelling to transform your presentation from informative to impactful. Presenting data within a narrative framework ensures better retention and understanding. Start with a problem, introduce statistics, and offer solutions, guiding your audience through a compelling storyline.
Storytelling may seem daunting at first, but its ability to captivate and inspire is worth the effort. With practice, you’ll master the art of storytelling , enriching your presentations and leaving a lasting impression on your audience.
Commanding the Stage: Confidence in Presentations
Confidence is a game-changer in presentations. It keeps your audience engaged and makes your message more compelling. Here’s how to harness confidence to enhance your delivery.
1. Project Presence and Enthusiasm
Infuse your natural demeanor with enthusiasm to project confidence. This will help you connect with your audience, making them more likely to stay engaged. Keep your information interesting, and watch your audience for signs of engagement.
2. Embrace Self-Awareness
Monitoring your emotions and reactions helps you stay personable and handle feedback gracefully. Self-awareness can calm nerves, allowing you to perform more effectively and maintain a confident front.
3. Overcome Nerves
Nervousness is common, but confidence in your knowledge and preparation can counteract it. Practice thoroughly, understand your audience, and have a backup plan. Remind yourself of your readiness to alleviate fear.
4. Exude Self-Confidence
Appear relaxed and avoid showing stress or nervousness. Advanced presenters can step out from behind the podium and move around the room, which exudes confidence and attracts the audience’s attention.
5. Manage Stage Fright
Acknowledge stage fright rather than fighting it. Transform nervous energy into positive enthusiasm. Deep breaths can help soothe your nerves and relax your body.
By projecting confidence, you enhance your stage presence and make your PowerPoint presentation more impactful and engaging.
Perfecting Your Presentation: The Power of Practice

Practicing is crucial for delivering a presentation effectively. Here are some key strategies to help you refine your public speaking and boost your confidence.
1. Rehearse Thoroughly
Practice your presentation multiple times, focusing on delivery and timing. Recording yourself can help you spot areas for improvement. Simulate actual presentation conditions as closely as possible, whether using a microphone or standing, to build comfort and confidence.
2. Mirror Rehearsal
Start by rehearsing in front of a mirror. This technique helps you identify and correct mistakes in your speech. It also enhances your confidence as you become more familiar with your material. Practice from random spots in your presentation to ensure thorough familiarity.
3. Utilize Feedback
Gather feedback from colleagues or mentors to refine your delivery. Practice in front of a small audience to simulate real conditions and get constructive criticism. This feedback loop helps you make necessary adjustments and improves your presentation skills.
4. Self-Monitoring Techniques
Use various self-monitoring techniques to prepare:
– Rehearse in front of an audience.
– Take notes for reference.
– Experiment with different delivery styles.
– Time yourself to stay within limits.
– Record yourself for self-review.
5. Timing and Structure
Adhere to the 10-20-30 rule to keep your presentation concise and engaging. Time your rehearsals to ensure you stay within the desired duration. Well-prepared presentations are more impactful and help you appear more confident and relaxed.
You can improve your presentation skills and ensure a smooth, confident, and impactful delivery by devoting time to practice.
Enhance Your Presentation with Multimedia and Visual Aids
Using presentation tools like multimedia and visual aids can significantly elevate your presentation, making it more engaging and effective. Here’s how to make the most of these tools:
1. Relevant and High-Quality Visuals
Use presentation aids that are relevant to your content and serve as cues for your discussion points. High-quality images and icons can make your slides appealing and professional. Avoid over-reliance on cue cards, as this can create a disconnect with your audience.
2. Embrace Multimedia Trends
Integrate current multimedia trends, such as interactive infographics, short video clips, and animated elements. These tools capture attention and simplify complex concepts. Well-designed graphs and data charts help your audience quickly grasp information without extensive explanations.
3. Diverse Media Formats
Use various media formats to keep your presentation dynamic and engaging. Combine videos, flipcharts, whiteboards, and practical demonstrations. This variety keeps the audience’s attention and prevents monotony.
4. Support and Enhance Your Speech
Visuals should not only support your speech but also contribute to it. Carefully selected images, including pictures, graphs, and infographics, help convey your message more effectively. They also serve as memory aids if you need to recall parts of your speech during the presentation.
By strategically using multimedia in presentations , you can create a more captivating and informative presentation that resonates with your audience.
Boosting Interaction and Engagement in Your Presentations
Engaging your audience is key to keeping them involved in your presentation. Here are some interactive presentation ideas to enhance engagement:
1. Ask Questions
Incorporate questions throughout your presentation to keep your audience attentive. Pose “easy” questions that can be answered readily, encouraging participation and making the audience feel involved. This simple technique helps maintain interest and fosters a connection between you and your listeners.
2. Encourage Participation
Use interactive methods like polls or quizzes to involve your audience actively. These techniques not only make the presentation more dynamic but also provide instant feedback on how well your message is being received. Interactive elements can break the monotony and re-engage attention if it starts to wane.
3. Personalize Interactions
Directly engaging with audience members can make your points clearer and more relatable. Use examples that involve participants by name, referring to their work or experiences. This personal touch can make your presentation more memorable and meaningful.
4. Allocate Time for Q&A
Set aside a significant portion of your presentation time for a Q&A session, allowing your audience to ask questions and express concerns. A good rule of thumb is to spend half your allotted time on the presentation and the other half addressing audience queries. This approach not only clarifies any doubts but also shows that you value their input and are open to dialogue.
By integrating these interaction communication and engagement techniques, you can create a more compelling presentation that resonates with your audience and keeps them involved from start to finish.
Effective Presentation Techniques: Keys to Success
Crafting and delivering an impactful presentation requires a blend of preparation, audience alignment, engaging storytelling, and confident delivery. By mastering these essential elements, you can captivate your audience and leave a lasting impression.
Starting with meticulous planning, understanding your topic inside out lays the foundation for a compelling narrative. Organize your points logically, incorporating aids to enhance clarity. Tailoring your content to your audience’s interests ensures maximum engagement, while a strong opening and memorable conclusion bookend your presentation effectively.
Verbal communication elevates your delivery, fostering connection and rapport with your audience. Simplifying complex ideas and incorporating multimedia elements enhance comprehension and retention.
Storytelling injects life into your presentation, forging a deeper connection with your audience. Confidence, cultivated through thorough practice and self-awareness, is the linchpin of an impactful presentation. Finally, interaction and engagement techniques ensure active participation and maintain interest throughout.
By integrating these types of presentation tips, you can master the art of presentations, delivering messages that resonate deeply and inspire action.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Why is topic mastery essential for presentations?
Mastering your presentation topic through deep research boosts your confidence and enables you to handle any questions from the audience effectively. Thorough understanding ensures you can deliver your points clearly and convincingly.
2. How can I keep my audience engaged throughout my presentation?
Customize your content to your audience’s needs and interests by using simple language and relatable examples. A well-structured presentation with a strong opening and memorable conclusion, coupled with engaging multimedia and interactive elements, ensures maximum engagement.
3. What are some tips for delivering a captivating presentation?
Practice public speaking clearly and confidently, and use gestures to relate to your audience. Incorporating multimedia and interactive elements such as polls and Q&A sessions can boost engagement and make your presentation more memorable.
4. How can I enhance my presentation with multimedia and visual aids?
Choose relevant and high-quality images that support and enhance your speech. Embrace diverse media formats, such as videos, flipcharts, and practical demonstrations, to keep your presentation dynamic and engaging.
Unlock Your Presentation Potential with Prezentium
Mastering presentations isn’t just about what you say but how you say it. From captivating your audience with a solid start to leaving a memorable impression with a powerful conclusion, every step counts. That’s where Prezentium comes in.
With our AI-powered overnight presentations , you can leave the hassle of crafting stellar presentations to us. Just email your requirements by 5:30 pm PST and wake up to a masterpiece in your inbox by 9:30 am PST the next business day.
Need expert guidance to transform ideas into exquisite presentations? Our team of Prezentation Specialists is here to help. We’ll work with you every step of the way to ensure your message shines.
Looking to hone your skills? Dive into our Zenith Learning workshops, where structured problem-solving meets storytelling. Master the 12 presentation skills, from planning to multimedia integration, and watch your presentations soar.
Don’t just deliver presentations; make an impact. Partner with Prezentium today and unlock your presentation potential.
Why wait? Avail a complimentary 1-on-1 session with our presentation expert. See how other enterprise leaders are creating impactful presentations with us.
Best Font for Presentations: Cool Font for PowerPoint Presentation
Make a storyboard creator: 7 tips on how to create a storyboard, understanding the 8 parts of speech in english grammar.
English Studies
This website is dedicated to English Literature, Literary Criticism, Literary Theory, English Language and its teaching and learning.
Theatrical Devices in Plays/Dramas
Theatrical devices, fundamental to the art of stagecraft, comprise a diverse array of techniques employed in theatrical productions to enhance storytelling, evoke emotions, and engage audiences.
Theatrical Devices: Introduction
Table of Contents
Theatrical devices, fundamental to the art of stagecraft, comprise a diverse array of techniques employed in theatrical productions to enhance storytelling, evoke emotions, and engage audiences. These devices encompass multiple facets, including stagecraft elements like set design, props, and costumes that create the visual milieu of a performance. Lighting and sound, with their nuanced interplay of intensity, color, music, and effects, contribute significantly to the creation of mood and atmosphere.
Movement and gesture, coupled with the eloquence of language expressed through dialogue , monologue , and soliloquy , allow actors to embody characters and convey narrative nuances. Symbolism , timing, and narrative techniques, such as foreshadowing and flashbacks , introduce layers of meaning and complexity.
Moreover, special effects, ranging from pyrotechnics to projection, offer the means to achieve visual spectacles and enhance the overall impact. As dynamic components of theatrical artistry, these devices collectively form the rich tapestry that defines the immersive and transformative nature of live performance.
Theatrical Devices: Categories
This table provides a concise overview of various theatrical devices categorized by their functions and impact on theatrical productions.
Theatrical Devices: Significance
- Enhanced Storytelling: Theatrical devices serve as crucial tools for conveying narratives, enriching the storytelling experience with visual, auditory, and symbolic elements.
- Emotional Impact: These devices contribute to the creation of mood, atmosphere, and emotional resonance, eliciting specific reactions and responses from the audience.
- Character Portrayal: Movement, gesture, language, and costumes allow actors to embody characters convincingly, fostering a deeper connection between the audience and the narrative.
- Visual Aesthetics: Stagecraft elements, including set design and props, contribute to the visual appeal of a performance, establishing the visual context for the unfolding story.
- Atmospheric Influence: Lighting and sound, through color, intensity, music, and effects, play a pivotal role in shaping the atmosphere of a scene, influencing the audience’s perception and emotional engagement.
- Symbolic Representation: Symbolism in theatrical devices adds layers of meaning to the narrative, providing a vehicle for conveying abstract concepts or thematic depth.
- Narrative Structure: Timing and narrative techniques contribute to the overall structure of a play, guiding the pacing, suspense, and thematic development.
- Immersive Experience: Special effects, including pyrotechnics and projection, enhance the immersive quality of live performances, creating moments of spectacle and wonder.
- Engagement with Audience: Interactive elements, such as breaking the fourth wall or audience participation, foster a direct and dynamic connection between the performers and the audience.
- Innovation and Creativity: The use of theatrical devices allows for inventive and creative approaches to storytelling, pushing the boundaries of artistic expression in the realm of live performance.
Theatrical Devices: Relevance in Literary Theory
This table illustrates how different theatrical devices align with and contribute to various literary theories, emphasizing their multifaceted significance in the realm of dramatic arts.
Theatrical Devices: Relevant Terms
Theatrical devices: suggested readings.
- Shakespeare, William. The Complete Works of William Shakespeare. Oxford UP, 1988.
- Stanislavski, Konstantin. An Actor Prepares . Bloomsbury Methuen Drama, 2011.
- Aristotle. Poetics. Translated by Malcolm Heath, Penguin Classics, 1996.
- Brecht, Bertolt. Breath of Life: The Early Plays of Bertolt Brecht. Bloomsbury Methuen Drama, 2005.
- Grotowski, Jerzy. Towards a Poor Theatre. Routledge, 2002.
- Artaud, Antonin. The Theater and Its Double. Grove Press, 1958.
- Brockett, Oscar G., and Franklin J. Hildy. History of the Theatre . Pearson, 2010.
- Esslin, Martin. Theatre of the Absurd. Bloomsbury Methuen Drama, 2001.
- Barba, Eugenio, and Nicola Savarese. A Dictionary of Theatre Anthropology: The Secret Art of the Performer. Routledge, 1991.
- Goldberg, RoseLee. Performance Art: From Futurism to the Present. Thames & Hudson, 2011.
Related posts:
- Onomatopoeia: A Literary Device
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.


9 Effective Presentation Techniques You Can Use to Master Public Speaking 6 min read

Sweat drips down the side of your face as you wait quietly backstage, fidgeting.
Your hands are cold and clammy as you fumble through cue cards one last time, trying to recall key points on each card.
Your name gets called and you face the inevitable walk up the stage to deliver what you imagine can be the worst public humiliation of your life.
We have all been there, the uneasy, nauseating feeling of public speaking.
The one thing we fear more than death, so they say.
Unless you make a living from working remotely , speaking in public is a useful, if not an essential tool for educational and professional success .
Why are effective presentation techniques important?
Effective presentation techniques are important because they help you deliver ideas in clear, concise and interesting ways.
Being a good public speaker allows you to demonstrate your knowledge with authority and help you stand out in the workplace.
Therefore, we need to find effective presentation techniques that work for us to put our best selves forward whenever we speak in public.
With numerous resources on improving public speaking written everywhere, here are the best presentation techniques that you can master.
1. Limit your presentation to one core idea
You have so much knowledge you want to share, educate and persuade.
Why limit your speech to just one idea?
Because ideas are complicated.
It takes a pitch to build interests into a desire, a narrative to create empathy, supporting evidence to be persuasive, and a call to action to lead movements.
Instead of squeezing every ounce of your knowledge into the limited time allocated to your speech, you will be most effective by concentrating on just one core idea that your audience can resonate with.
This way, you can be sure your audience can walk away with a clear message after the presentation.
2. Remember that the audience is on your side
Whether you are delivering a business plan in a boardroom or speaking as a keynote speaker at a conference.
Whether you are speaking to a handful of colleagues, or a lecture theatre packed with college seniors.
The audience is there for one reason.

You may imagine the audience is there to watch you make a fool of yourself, but more often than not, they want to be there, be enlightened by your presence, and be inspired by your talk.
3. Gently introduce people to your accents
With all the ethnic diversity in the world, we can all learn from our differences and work towards a greater good.
Despite speaking the same languages, our diverse backgrounds would lead to little nuances in the way we enunciate words and the way we speak phrases.
Intentionally speaking slowly , in the beginning, is not only good practice but a good technique to allow your audience to get used to your accents.
After all, you need your listeners to understand your words before they can understand your ideas.
4. Use language your audience can understand to deliver your idea
Now that your audience can understand the words coming out of your mouth, we can think about how to deliver your idea.
Unless you are speaking to a family member, your audience likely has a different background to yours.
Both geographically and professionally.
This means, the technical jargon and inside jokes that you throw around among your friends and colleagues may not work in a packed conference room.
It’s best to practice explaining your ideas to friends from different backgrounds to get a feel of how effective your presentation is to the public.
5. Spark curiosity in your audience
Listening is hard.
It’s difficult to concentrate on listening to a new idea, even more so if the idea is boring.
Therefore it is your job, as a speaker, to spark curiosity in your audience to make sure both you and your audience enjoy the presentation.

A few common ways to spark interests include humor, storytelling, anecdotes, or even funny cat videos.
6. Present data visually
Not all people perceive numbers and data in the same way.
A simple statistic can mean different ideas to different people.
The best way to control the narrative in numbers and data is to create visual images that tell specific stories.

An effective image can help your audience understand both the meaning and origin of the data to keep people engaged.
7. Your slides are not the centerpiece, you are
It is tempting to use your slide deck as a crutch, and follow it slide by slide, dividing your attention between the presentation slides and your audience.
You will look like a tennis umpire looking back and forth, back and forth.

The audience is here to see you, to listen to what you have to say.
Try to bring your best presence to deliver your speech and only use the slides for images and videos to drive your point home, not to divert attention away from you.
8. Use technology only if necessary
Following the last point, your presentation slides are only used to support your talk, not to take over it.
Use presentation technology with caution, and only in situations where necessary.
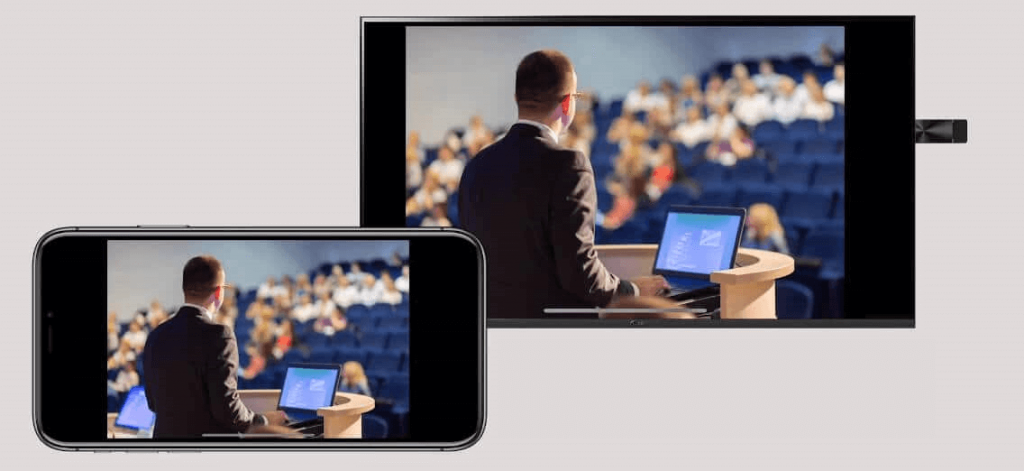

To run your presentation from an iPhone like a pro, there’s always EZCast Pro to help you make wireless presentations in huddle rooms and meeting rooms at work .
9. Practice your presentation over and over again
Now you know all the most effective presentation techniques available, all that’s left for you is to master them through deliberate practice .
Whether you repeat your speech during your daily commute or annunciate key points with purpose in the shower.
Try to memorize your presentation down to every single deliberate pause to make sure you have every detail down pat.
Then you can find a friend or family member to listen to you speak and provide constructive feedback.
Once you iron out the kinks, you will become more effective in presentation and ready for the big time.
在〈 9 Effective Presentation Techniques You Can Use to Master Public Speaking 6 min read 〉中有 3 則留言
Point 3. I think the write meant to write “enunciate” NOT “annunciate”. These 2 words are very different. The 1st one mean to speak clearly and the 2nd one means to announce.
Thank you for the correction Maurice. Just changed it to the correct usage.
Really nice topic. It will helps during presentation.
發佈留言必須填寫的電子郵件地址不會公開。 必填欄位標示為 *
在 瀏覽器 中儲存顯示名稱、電子郵件地址及個人網站網址,以供下次發佈留言時使用。
Privacy Overview
You can see how this popup was set up in our step-by-step guide: https://wppopupmaker.com/guides/auto-opening-announcement-popups/

Interested in wireless conferencing system and would like to talk to our experts?
Contact us now!
The Drama Teacher
Your Go-To Resource for Drama Education
15 Remarkable Acting Techniques for Drama Class
Acting techniques offer a theoretical and practical framework that assists senior drama and theatre students in honing their craft and understanding theatrical performance nuances. This article outlines why studying different acting methods is essential in a senior drama/theatre classroom.
Actors exposed to various acting methods are typically more versatile. Different techniques offer unique approaches to character development, emotional engagement, and stage presence . A well-rounded education in these methods equips students to adapt to different roles and theatrical genres readily.
Studying various acting techniques also invites students to engage in critical analysis and reflection actively. It allows them to compare and contrast various methodologies, discerning the merits and limitations of each. This analytical process cultivates their critical thinking skills, enabling them to make informed choices in their creative endeavours.
Understanding a range of acting methods also assists with differentiation in the senior drama/theatre classroom, as the varying techniques and character exercises will naturally cater for the different learning styles in the classroom.
15 Acting Techniques for Students
Classical technique.
Key Principles The Classical Technique is a foundational pillar in the world of acting methodologies. Rooted in historical traditions, this approach is based on the canons set forth by ancient Greek dramaturges and Elizabethan theatre practitioners. It emphasises rhetorical devices, metrical schemes, and stylised vocal expression. Practices Students undergoing training in Classical Technique are subjected to stringent practices that include mastering the art of elocution, understanding verse structures like iambic pentameter, and developing an acute awareness of gestural language. The rehearsal process might involve reciting Shakespearean soliloquies or delving into Aristophanean comedy, among other classical works. Educational Implications In a pedagogical setting, this technique serves as a gateway to theatre’s rich history. It allows students to comprehend the evolution of acting styles while honing skills integral to a performer’s toolkit, such as voice modulation, posture, and movement.
Stanislavski System
Key Principles Konstantin Stanislavski’s system revolves around the notion of psychological realism. The principal idea is that for an actor to portray a character effectively, belief in the play’s given circumstances is paramount. This involves grasping the objectives, subtext, and emotional undercurrents that drive a character. Practices Training often includes exercises centred around ‘Emotional Memory,’ wherein actors recall personal experiences that mirror their character’s emotional state. This is complemented by techniques that assist in understanding the ‘Objective’ (what the character wants) and the ‘Subtext’ (unspoken thoughts and motives). Educational Implications In a drama education setting, the Stanislavski System offers a structured framework that encourages students to delve deep into the text and their emotional reservoirs. It aids in developing a nuanced understanding of character motivations, thereby enriching performance quality.
Method Acting
Key Principles An offshoot of the Stanislavski System, Method Acting involves a highly immersive approach to characterisation. The actor engrosses themselves in the character’s life to such an extent that the boundaries between performer and role often blur. Practices To achieve this level of immersion, actors may opt for extreme measures like altering their physical attributes or isolating themselves from their usual social settings. This is undertaken to facilitate a visceral connection to the character. Educational Implications While this technique is often best suited for mature performers due to its emotionally demanding nature, it provides invaluable lessons in commitment and the importance of fully realised, three-dimensional characters.

Meisner Technique
Key Principles Developed by Sanford Meisner, this technique is grounded in the axiom that “acting is reacting.” The focus is thus placed on the actor’s responses to external stimuli, primarily from other actors in the scene. Practices Repetition exercises are pivotal in Meisner training. Actors exchange lines or phrases repetitively, altering their emotional tone or physicality each time, thereby learning to react authentically to their scene partners. Educational Implications The Meisner Technique can be particularly effective in teaching students the value of active listening and emotional responsiveness in the classroom. It fosters a sense of spontaneity and adaptability, skills that are crucial both on stage and in life.
Suzuki Method
Key Principles Founded by Tadashi Suzuki, this method from Japan focuses on an actor’s physicality, particularly the lower body. It advocates that the actor’s presence must be commanding, facilitating heightened awareness. Practices Suzuki training typically involves rigorous physical exercises emphasising grounding, breathing, and concentration. The aim is to make the actors aware of their ‘centre’ and teach them how to manipulate their bodies to convey complex emotions and ideas. Educational Implications In an educational context, the Suzuki Method counterbalances Western acting techniques that often focus predominantly on psychological aspects. It allows students to develop strong physical discipline and control, elements crucial for various performance genres.
Chekhov Technique
Key Principles Michael Chekhov’s technique veers towards a more metaphysical realm of acting, focusing on ‘psychological gesture’ and imagination to embody a character. Practices Actors might engage in exercises that involve moving in space with a particular ‘quality’—such as heaviness or lightness—or utilising archetypal gestures to tap into specific emotional states. Educational Implications This technique is particularly useful for students who may struggle with the intense emotional demands of other methods. It provides an alternative route to character development that relies less on personal emotional recall.
Adler Technique
Key Principles Stella Adler’s technique is another variant of the Stanislavski system, but it diverges by emphasising the imagination more than emotional memory. Practices Students are guided to construct a vivid ‘given circumstance’ for their character, leaning heavily on imagination and script analysis rather than personal experiences. Educational Implications The Adler Technique offers a balanced approach to character development, making it accessible to students of varying emotional and imaginative capacities. It lays a strong foundation for script analysis skills, an essential part of theatre education.
Spolin Method
Key Principles Viola Spolin’s methodology is predicated on the power of improvisation and spontaneity. Practices The Spolin Method employs games and theatre sports as educational tools. These are designed to remove inhibitions and unlock creativity, enabling genuine, spontaneous reactions. Educational Implications The improvisational focus of the Spolin Method makes it an excellent introductory technique for younger students or those new to acting. It encourages a free-flowing, instinctual approach to performance and effectively enhances adaptability.
Hagen Technique
Key Principles Uta Hagen’s technique aims for a grounded sense of realism and employs exercises encouraging the actor to draw parallels between the characters’ experiences and their own. Practices Exercises often involve ‘substitution,’ where actors replace the character’s circumstances with comparable situations from their own lives, creating emotional integrity. Educational Implications Hagen’s exercises in a senior drama class can facilitate a deepened emotional connection to the material. These techniques offer practical strategies for developing complex, believable characters.
Practical Aesthetics Technique
Key Principles Formulated by David Mamet and William H. Macy, Practical Aesthetics focuses on serving the narrative over indulging in emotional extravagance. The actor’s primary role is seen as a conduit for the story. Practices The method employs script analysis to deduce a scene’s ‘Literal,’ ‘Want,’ ‘Essential Action,’ and ‘As If’, stripping away unnecessary emotional frills and delivering a nuanced yet straightforward performance. Educational Implications In a pedagogical context, Practical Aesthetics provides students with a structural and analytical approach to acting. This technique can be especially effective in teaching the importance of textual integrity and the actor’s responsibility to the story.
Key Principles Originally developed within dance, Viewpoints considers the two fundamental components of performance: time and space. It divides the actor’s focus into nine categories or ‘viewpoints.’ Practices Training involves exploring spatial relationships, tempo, duration, and kinaesthetic response. The technique is often used in ensemble work to create complex stage pictures and develop a shared vocabulary among performers. Educational Implications In the classroom, Viewpoints can serve as an effective ensemble-building tool. It encourages students to think beyond their roles and consider the collective impact of a performance.

Grotowski Technique
Key Principles Jerzy Grotowski’s technique removes all superfluous elements to focus solely on the interaction between actor and audience. It is theatre stripped to its most fundamental components. Practices Training often involves rigorous physical exercises and ensemble-based activities. The intent is to create a potent, almost spiritual, connection between actor and spectator. Educational Implications For students, the Grotowski method can instil a sense of theatre’s essential elements, pushing them to explore the limits of expression using minimal resources. It offers a radical departure from more commercial forms of theatre, often leading to profound insights into the nature of performance.
Brechtian Technique
Key Principles Bertolt Brecht’s techniques are designed to provoke rational thought rather than emotional involvement. It employs devices like ‘verfremdungseffekt’ to prevent the audience from becoming too immersed in the story. Practices Techniques include direct address, breaking the fourth wall, and using placards or multimedia to separate scenes or ideas. The objective is to encourage critical engagement from the audience. Educational Implications Incorporating Brechtian techniques in a curriculum challenges students to consider the socio-political impact of theatre. It cultivates an awareness of the audience’s intellectual engagement and emotional experience.
Boal Technique
Key Principles Created by Augusto Boal, Theatre of the Oppressed techniques are more than an acting method; they are a tool for social change. These techniques challenge traditional theatre roles by turning the audience into active participants, or ‘spect-actors.’ Practices Various forms like Forum Theatre, Image Theatre, and Invisible Theatre are used to engage the audience actively in the storytelling process, often to explore social issues. Educational Implications Boal’s techniques are particularly effective in fostering an environment of social consciousness and activism within the student community. They provide tools for exploring complex ethical and societal issues through performance.
Laban Movement Analysis
Key Principles Rudolf Laban’s method provides a systematic and comprehensive vocabulary for understanding and describing movement. Practices Actors are trained to break down movement into direction, weight, time, and flow. This allows for a nuanced, expressive physicality in performance. Educational Implications Laban offers a scientific approach to understanding movement, providing students with a structured framework for physical expression. It is often used with other techniques to enrich character development and storytelling.
Physical Theatre Techniques
Key Principles This encompasses a broad spectrum of techniques focusing on physicality, ranging from mime to contemporary dance to clowning. Practices Exercises often involve body awareness, control, and the ability to convey complex ideas and emotions through physical expression alone. Educational Implications The incorporation of physical theatre techniques provides a holistic approach to actor training. It encourages students to explore non-verbal storytelling forms, expanding their range and versatility as performers.
Like what you're reading?
14 effective presentation tips to impress your audience
Get your team on prezi – watch this on demand video.
Anete Ezera July 15, 2022
An effective presentation can communicate key ideas and opinions, save time, and contribute to your overall success as a business, but good presentation skills don’t come naturally to everyone. In this blog post, you’ll find 14 effective presentation tips you can implement in your next presentation to make it a success.
Whether you’re preparing for an important presentation at work or school, or you’re looking for ways to generally improve your presentation skills, you’ll find these presentation tips useful. We’ve gathered a list to help you impress your audience from the get-go. You’ll find tips for creating and presenting your slides, talking in front of an audience, and other effective presentation techniques to help you stand out.

Most common presentation mistakes
Before we list our top effective presentation tips, let’s explore the most common presentation mistakes. If you’ve made one or more mistakes in this list, you’re not alone. Most people have made at least one mistake. However, what’s important is to be aware of these errors and try avoiding them next time.
#1 A poor start
One of the most common mistakes people make is undermining the importance of the first few minutes or seconds of their presentation.
Let’s say you’ve practiced your key talking points meticulously and gone over your slides a million times, but when you’re in the spotlight and need to say your first line, do you know exactly what to say to wow the audience?
The start of your presentation is crucial. Not only because how you start sets the tone for the rest of your presentation, but also because people generally require around 8 seconds to decide whether they find the subject interesting enough to keep listening. Starting your presentation with a captivating intro is even more important than you think. To ensure you start off right, read our guide on how to start your presentation .
#2 Lack of preparation
Yes, even though it’s clear that you should prepare before giving a presentation, it’s still a common mistake amongst presenters. Preparing content and talking points is an obvious start, but there are other steps that you might be overlooking.
Before you even join a meeting or walk into a room where you’re going to present, consider the technical requirements and get familiar with the equipment. If you’re presenting online, make sure to test-run your presentation and the visual aids you’re going to use. The last thing you want is a broken video link, poor audio, or a weak connection when you’re presenting.
Also, consider the questions your audience might want to ask you about the topic. Think about how you’d answer those questions, or do even further research to really impress the audience with your answers.
Explore other ways to prepare for a presentation to feel even more confident when presenting.

#3 Losing track of time
It’s great to feel passionate about your topic. However, you’ll have to consider your audience’s level of interest and knowledge. Some details might seem fascinating to you, and you’d like to talk about them for hours, but for your audience, too much information will drain their energy and lose their attention.
Therefore, make sure to keep track of time. Also, consider your audience’s interests. A concise presentation is always better than a long one with a ton of information. Plus, you’ll have a higher chance of keeping your audience’s attention throughout the presentation.
Effective presentation tips
Now that we’ve looked at some of the most common presentation mistakes – let’s dive into effective presentation tips that’ll help you excel in future presentations.
#1 Tell a story
Stories connect, inspire, and empower people. Telling a story can entice action, help understand an idea, and make people feel connected to the storyteller. It’s also one of the most effective presentation tips. A study by organizational psychologist Peg Neuhauser found that a well-told story is easier to remember than facts, which makes it a highly effective learning technique.
With that in mind, telling a story when you’re presenting can engage your audience and make it a more memorable experience. You can either share a personal story or a historical event, just make sure to have a clear connection between the story and the topic you’re presenting.
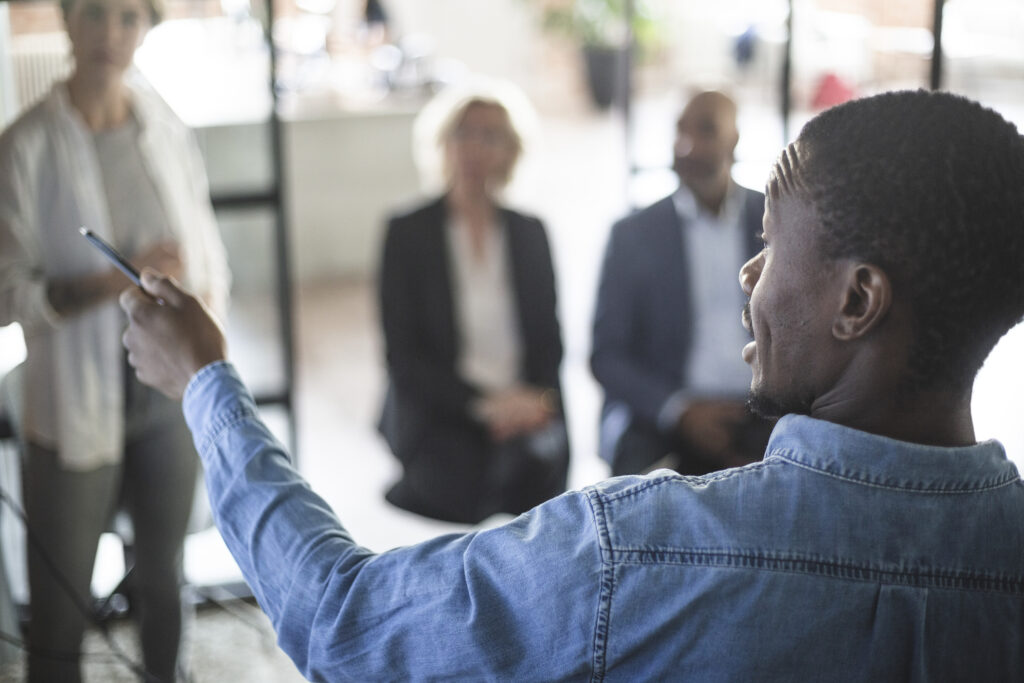

#2 Work on your body language
Body language can make a huge difference in how your presentation is perceived. It’s one of the presentation tips you definitely shouldn’t overlook.
Body language says a lot about a person’s confidence level, emotions, state of mind, and even credibility. For the audience, it’s a way to understand what the person is saying and how interested they are in the topic.
Therefore, work on your body language to better convey the message you’re trying to communicate. Practice in front of a mirror before your presentation and be conscious of your hand gestures and facial expressions.
#3 Understand your audience
Before crafting your presentation, you must know who you’re speaking to. Understanding the interests, demographics, professional background, and other valuable information of your audience is crucial in making your speech successful.

If you’re speaking at an event, contact the organizers to get more information about other speakers and the audience. If you’re presenting at work, you may already know your audience fairly well. Use this information to your advantage and create content you know they’ll resonate with.
#4 Use high-quality visuals
What’s one of the most effective presentation techniques? Use of visuals. They play a crucial role in your presentation. However, only high-quality visuals will make a good impression and effectively communicate your message. Use high-quality visuals like images, videos, graphs, maps, and others to really land your point.
Using visuals is a great way to convey your ideas as they’re easier to process than text. If you’re not sure where to find great visuals, check out our blog post on presentation visuals for five free resources.
P.S. the Prezi library holds a variety of images, videos, GIFs, stickers, and other visuals, including different charts and maps to spice up your presentation. It’s all available in your dashboard .
#5 Use data visualizations
Do you want to showcase statistics or other datasets in your presentation? Use data visualizations to make your data stand out and impress your audience.
There’s nothing more boring than a bunch of data presented in a flat way. If you want to tell a story with your data, use interactive infographics or slides enriched with eye-catching visuals. Showcasing data will make your ideas appear more trustworthy and credible.
Prezi Design offers a range of templates to choose from. You can start creating data visualizations from scratch or choose a template and edit the data there.
#6 Make it engaging with interactive elements
It’s not easy to deliver an engaging presentation. People can easily get distracted or try to multitask, especially in the virtual environment. Sometimes, it’s difficult to focus on the speaker and the written text. Other times, the content just isn’t impressive enough to hold the audience’s attention. But it doesn’t have to be this way.
You can make your presentation more engaging for everyone by including interactive content like graphs and charts. With interactive data visualizations, you’ll make the data discovery process more engaging and exciting for your audience.
Your audience will be able to hover over data points and click on certain icons or datasets to discover information on their own. Interactive visualizations will make the presentation more memorable and impressive.
As you can see in the example below, you can discover different data by engaging with the infographic.
#7 Stay consistent with fonts and color styles
You want your presentation to look visually appealing and highlight essential information. To make that happen, stay consistent with font styles and color schemes throughout your presentation.
Use one or two fonts max to make the text easy to read and understand. Also, use a carefully selected color scheme that’s not too distracting. If you’re using Prezi Design, you can easily copy and paste styles by right-clicking on your data visualizations and selecting “copy styles.” This makes it easier to stay consistent and saves time when picking matching colors.
#8 Structure your presentation properly
Before creating your presentation, think about its structure. What’s the main idea you want to convey? Use that as your starting point, and only include information that adds value to the narrative.
Plan out the first topics carefully to properly introduce your argument. Add the essential information in the middle part of your presentation. Lastly, close your presentation with a summary of the main points and leave your audience with an afterthought. Also, plan when you’re taking questions and for how long.
For more insight, watch this tutorial on how to structure your presentation:
#9 Practice your public speaking skills
Public speaking may not be your forte, but you can get better with practice. Don’t decline a great opportunity to share your ideas with a larger audience just because you feel nervous speaking in front of a group of people.
One of the best ways to improve your public speaking skills is to practice in front of your family or friends – people you feel comfortable with. Also, focus on the topic you’re presenting and get excited about the idea you want to convey. This way you’ll appear more confident and feel less nervous about public speaking.
Explore other public speaking tips from Jessica Chen, the founder, and CEO of Soulcast Media:
#10 Show your slides next to you on-screen
If you’re presenting on Zoom or in a virtual meeting , think twice before you share your screen. The days of hiding behind slides are over. People want to see and connect with other people, not sit through another run-of-the-mill screen share. To do that, use Prezi Video to showcase all your content right next to you in your video feed.
As a result, your presentation will look more engaging than a traditional virtual presentation . Also, your audience will have the chance to read your body language and follow along with what you’re saying even better.
If you already have your slides prepared, don’t worry – you can easily integrate them into Prezi.
See Prezi Video in action and check out our video templates to get started.
#11 Calm down before presenting
Being in front of an audience can feel nerve-racking. However, there are ways to calm down before presenting that will make you feel more centered and confident. The last thing you want is all your hard work to go to waste just because of stress.
Try breathing exercises or a five-minute guided meditation before presenting. The trick is to remove all distractions and focus on the present moment so you’re not overthinking right before starting your presentation. Also, be fully prepared and know exactly what to say and when which will help you feel more collected. If you want to discover other ways to feel and look more confident, read how not to be nervous before a presentation .
#12 Use transitions and animations
Add movement to your slides with transitions and animations. You’ll make your presentation more visually appealing and engaging. However, be careful not to overwhelm your audience with your choice of transitions and animations.
Choose a transition that matches your presentation visually and use it throughout your presentation. Consider what animations will be relevant to your audience and select a few to add to your slides. Don’t overdo it. Keep the focus on the message you’re trying to convey, and use animations to only support that message.
#13 Be enthusiastic
When you’re in a room with a positive and enthusiastic person, you can’t help but feel uplifted as well. High-energy people have this effect on others. Most importantly, a lot of people tend to mimic people’s behavior and mirror their energy when they feel a connection or relate to them. That’s called the chameleon effect .

When you’re presenting, you want your audience to feel curious about what you’re presenting. You may also want to leave your audience feeling uplifted, interested to know more, or inspired. To have that effect on others, try to convey those emotions when presenting. Practice your speech, slow down your narration at times, or take a pause after you’ve delivered a statement, and use different presentation techniques to present your project and really drive your points home.
#14 End your presentation in a memorable way
The first few minutes of your presentation are crucial for captivating your audience’s attention. However, don’t underestimate the importance of ending your presentation as powerfully as you started it.
The way you end your presentation will play a crucial part in how your audience will remember it. You want to make a memorable impression by closing your presentation with a summarizing statement, a rhetorical question, a call to action, or another impactful way. Discover 10 ways you can end your presentation in our guide.

There are a lot of factors to consider when creating and delivering a presentation. You want your slides to look professional and visually appealing while conveying your main points. You also want to look and sound confident even if you’re nervous about public speaking. Whatever your concerns may be, remember that preparation is essential. Practice and dedication are the keys to giving a successful presentation . Make sure to follow these effective presentation tips to excel in your future presentations. If you’re interested in creating a captivating presentation with Prezi, contact us to learn more or try it for free .
Elevating presentations with Prezi AI
Embrace the innovation of Prezi to bring your presentations to life. With its unique platform, Prezi AI offers more than just visually appealing templates; it provides an immersive narrative experience, engaging your audience with a story-driven approach. By integrating Prezi AI , our platform’s capabilities are further enhanced, offering intelligent design suggestions and optimizing content layouts to ensure your presentations are not only beautiful but impactful. This integration is a perfect example of effective presentation techniques in action, using technology to create a more engaging presentation.
Interactive elements: transforming passive listening into active engagement
Prezi revolutionizes the way information is presented by incorporating interactive elements that invite audience participation. With Prezi AI, these features become even more accessible, suggesting ways to make your presentation more engaging through clickable areas, zoomable images, and dynamic visualizations. This level of interaction encourages exploration, making your message more memorable and transforming a standard presentation into an effective presentation.
Adding a personal touch in digital presentation with video
Prezi Video stands out by seamlessly integrating your content alongside your video feed, bridging the gap between traditional presentations and personal engagement. This feature is crucial for those looking to follow presentation tips that emphasize the importance of connecting with your audience on a more personal level. Prezi AI enhances this experience, ensuring your content is displayed in the most effective way possible, making your virtual presentations feel as though you’re directly conversing with your audience.
Mastering presentation artistry with Prezi
The journey to becoming a skilled presenter involves continuously refining your approach and embracing tools that elevate your ability to communicate effectively. Prezi, enriched with Prezi AI, is one such tool that transforms ordinary presentations into captivating experiences. By leveraging these advanced features, you can deliver presentations that are successful, memorable, and truly unforgettable, embodying the essence of tips for presentation mastery.
Whether you’re an experienced speaker or preparing for your first presentation, Prezi equips you with the tools to succeed. Engage your audience, tell compelling stories, and deliver your message with confidence and creativity. Following effective presentation tips and exploring how Prezi AI can transform your next presentation is a step towards mastering the art of impactful communication. Delve into the features and begin your journey to presentation mastery today.

Give your team the tools they need to engage
Like what you’re reading join the mailing list..
- Prezi for Teams
- Top Presentations

Improve your practice.
Enhance your soft skills with a range of award-winning courses.
Complete Guide for Effective Presentations, with Examples
July 9, 2018 - Dom Barnard
During a presentation you aim to look confident, enthusiastic and natural. You’ll need more than good words and content to achieve this – your delivery plays a significant part. In this article, we discuss various techniques that can be used to deliver an effective presentation.
Effective presentations
Think about if you were in the audience, what would:
- Get you to focus and listen
- Make you understand
- Activate your imagination
- Persuade you
Providing the audience with interesting information is not enough to achieve these aims – you need to ensure that the way you present is stimulating and engaging. If it’s not, you’ll lose the audience’s interest and they’ll stop listening.
Tips for an Effective Presentation
Professional public speakers spend hours creating and practicing presentations. These are the delivery techniques they consider:
Keep it simple
You shouldn’t overwhelm your audience with information – ensure that you’re clear, concise and that you get to the point so they can understand your message.
Have a maximum of three main points and state them at the beginning, before you explain them in more depth, and then state them at the end so the audience will at least remember these points.
If some of your content doesn’t contribute to your key message then cut it out. Also avoid using too many statistics and technical terminology.
Connect with your audience
One of the greatest difficulties when delivering a presentation is connecting with the audience. If you don’t connect with them it will seem as though you’re talking to an empty room.
Trying to make contact with the audience makes them feel like they’re part of the presentation which encourages them to listen and it shows that you want to speak to them.

Eye contact and smile
Avoiding eye contact is uncomfortable because it make you look insecure. When you maintain eye contact the audience feels like you’re speaking to them personally. If this is something you struggle with, try looking at people’s foreheads as it gives the impression of making eye contact.
Try to cover all sections of the audience and don’t move on to the next person too quickly as you will look nervous.
Smiling also helps with rapport and it reduces your nerves because you’ll feel less like you’re talking to group of faceless people. Make sure you don’t turn the lights down too much before your presentation so you can all clearly see each other.
Body language
Be aware of your body language and use it to connect:
- Keep your arms uncrossed so your body language is more open .
- Match your facial expressions with what you’re saying.
- Avoid fidgeting and displaying nervous habits, such as, rocking on your feet.
- You may need to glance at the computer slide or a visual aid but make sure you predominantly face the audience.
- Emphasise points by using hand gestures but use them sparingly – too little and they’ll awkwardly sit at your side, too much and you’ll be distracting and look nervous.
- Vary your gestures so you don’t look robotic.
- Maintain a straight posture.
- Be aware of cultural differences .
Move around
Avoid standing behind the lectern or computer because you need to reduce the distance and barriers between yourself and the audience. Use movement to increase the audience’s interest and make it easier to follow your presentation.
A common technique for incorporating movement into your presentation is to:
- Start your introduction by standing in the centre of the stage.
- For your first point you stand on the left side of the stage.
- You discuss your second point from the centre again.
- You stand on the right side of the stage for your third point.
- The conclusion occurs in the centre.
Watch 3 examples of good and bad movement while presenting
Example: Movement while presenting
Your movement at the front of the class and amongst the listeners can help with engagement. Think about which of these three speakers maintains the attention of their audience for longer, and what they are doing differently to each other.
Speak with the audience
You can conduct polls using your audience or ask questions to make them think and feel invested in your presentation. There are three different types of questions:
Direct questions require an answer: “What would you do in this situation?” These are mentally stimulating for the audience. You can pass a microphone around and let the audience come to your desired solution.
Rhetorical questions do not require answers, they are often used to emphasises an idea or point: “Is the Pope catholic?
Loaded questions contain an unjustified assumption made to prompt the audience into providing a particular answer which you can then correct to support your point: You may ask “Why does your wonderful company have such a low incidence of mental health problems?” The audience will generally answer that they’re happy.
After receiving the answers you could then say “Actually it’s because people are still unwilling and too embarrassed to seek help for mental health issues at work etc.”

Be specific with your language
Make the audience feel as though you are speaking to each member individually by using “you” and “your.”
For example: asking “Do you want to lose weight without feeling hungry?” would be more effective than asking “Does anyone here want to lost weight without feeling hungry?” when delivering your presentation. You can also increase solidarity by using “we”, “us” etc – it makes the audience think “we’re in this together”.
Be flexible
Be prepared to adapt to the situation at the time, for example, if the audience seems bored you can omit details and go through the material faster, if they are confused then you will need to come up with more examples on the spot for clarification. This doesn’t mean that you weren’t prepared because you can’t predict everything.
Vocal variety
How you say something is just as is important as the content of your speech – arguably, more so.
For example, if an individual presented on a topic very enthusiastically the audience would probably enjoy this compared to someone who covered more points but mumbled into their notes.
- Adapt your voice depending on what are you’re saying – if you want to highlight something then raise your voice or lower it for intensity. Communicate emotion by using your voice.
- Avoid speaking in monotone as you will look uninterested and the audience will lose interest.
- Take time to pronounce every word carefully.
- Raise your pitch when asking questions and lower it when you want to sound severe.
- Sound enthusiastic – the more you sound like you care about the topic, the more the audience will listen. Smiling and pace can help with this.
- Speak loudly and clearly – think about projecting your voice to the back of the room.
- Speak at a pace that’s easy to follow . If you’re too fast or too slow it will be difficult for the audience to understand what you’re saying and it’s also frustrating. Subtly fasten the pace to show enthusiasm and slow down for emphasis, thoughtfulness or caution.
Prior to the presentation, ensure that you prepare your vocal chords :
- You could read aloud a book that requires vocal variety, such as, a children’s book.
- Avoid dairy and eating or drinking anything too sugary beforehand as mucus can build-up leading to frequent throat clearing.
- Don’t drink anything too cold before you present as this can constrict your throat which affects vocal quality.
- Some people suggest a warm cup of tea beforehand to relax the throat.
Practice Presentation Skills
Improve your public speaking and presentation skills by practicing them in realistic environments, with automated feedback on performance. Learn More
Pause to breathe
When you’re anxious your breathing will become quick and shallow which will affect the control you have on your voice. This can consequently make you feel more nervous. You want to breathe steadily and deeply so before you start speaking take some deep breaths or implement controlled breathing.
Controlled breathing is a common technique that helps slow down your breathing to normal thus reducing your anxiety. If you think this may be useful practice with these steps:
- Sit down in an upright position as it easier for your lungs to fill with air
- Breathe in through your nose and into your abdomen for four seconds
- Hold this breathe for two seconds
- Breathe out through your nose for six seconds
- Wait a few seconds before inhaling and repeating the cycle
It takes practice to master this technique but once you get used to it you may want to implement it directly before your presentation.
Completely filling your lungs during a pause will ensure you reach a greater vocal range.
During the presentation delivery, if you notice that you’re speaking too quickly then pause and breathe. This won’t look strange – it will appear as though you’re giving thought to what you’re saying. You can also strategically plan some of your pauses, such as after questions and at the end of sections, because this will give you a chance to calm down and it will also give the audience an opportunity to think and reflect.
Pausing will also help you avoid filler words , such as, “um” as well which can make you sound unsure.
- 10 Effective Ways to use Pauses in your Speech
Strong opening
The first five minutes are vital to engage the audience and get them listening to you. You could start with a story to highlight why your topic is significant.
For example, if the topic is on the benefits of pets on physical and psychological health, you could present a story or a study about an individual whose quality of life significantly improved after being given a dog. The audience is more likely to respond better to this and remember this story than a list of facts.
Example: Which presentation intro keeps you engaged?
Watch 5 different presentation introductions, from both virtual and in-person events. Notice how it can only take a few seconds to decide if you want to keep listening or switch off. For the good introductions, what about them keeps you engaged?
More experienced and confident public speakers use humour in their presentations. The audience will be incredibly engaged if you make them laugh but caution must be exercised when using humour because a joke can be misinterpreted and even offend the audience.
Only use jokes if you’re confident with this technique, it has been successful in the past and it’s suitable for the situation.
Stories and anecdotes
Use stories whenever you can and judge whether you can tell a story about yourself because the audience are even more interested in seeing the human side of you.
Consider telling a story about a mistake you made, for example, perhaps you froze up during an important presentation when you were 25, or maybe life wasn’t going well for you in the past – if relevant to your presentation’s aim. People will relate to this as we have all experienced mistakes and failures. The more the audience relates to you, the more likely they will remain engaged.
These stories can also be told in a humorous way if it makes you feel more comfortable and because you’re disclosing a personal story there is less chance of misinterpretation compared to telling a joke.
Anecdotes are especially valuable for your introduction and between different sections of the presentation because they engage the audience. Ensure that you plan the stories thoroughly beforehand and that they are not too long.
Focus on the audience’s needs
Even though your aim is to persuade the audience, they must also get something helpful from the presentation. Provide the audience with value by giving them useful information, tactics, tips etc. They’re more likely to warm to you and trust you if you’re sharing valuable information with them.
You could also highlight their pain point. For example, you might ask “Have you found it difficult to stick to a healthy diet?” The audience will now want to remain engaged because they want to know the solution and the opportunities that you’re offering.
Use visual aids
Visual aids are items of a visual manner, such as graphs, photographs, video clips etc used in addition to spoken information. Visual aids are chosen depending on their purpose, for example, you may want to:
- Summarise information.
- Reduce the amount of spoken words, for example, you may show a graph of your results rather than reading them out.
- Clarify and show examples.
- Create more of an impact. You must consider what type of impact you want to make beforehand – do you want the audience to be sad, happy, angry etc?
- Emphasise what you’re saying.
- Make a point memorable.
- Enhance your credibility.
- Engage the audience and maintain their interest.
- Make something easier for the audience to understand.

Some general tips for using visual aids :
- Think about how can a visual aid can support your message. What do you want the audience to do?
- Ensure that your visual aid follows what you’re saying or this will confuse the audience.
- Avoid cluttering the image as it may look messy and unclear.
- Visual aids must be clear, concise and of a high quality.
- Keep the style consistent, such as, the same font, colours, positions etc
- Use graphs and charts to present data.
- The audience should not be trying to read and listen at the same time – use visual aids to highlight your points.
- One message per visual aid, for example, on a slide there should only be one key point.
- Use visual aids in moderation – they are additions meant to emphasise and support main points.
- Ensure that your presentation still works without your visual aids in case of technical problems.
10-20-30 slideshow rule
Slideshows are widely used for presentations because it’s easy to create attractive and professional presentations using them. Guy Kawasaki, an entrepreneur and author, suggests that slideshows should follow a 10-20-30 rule :
- There should be a maximum of 10 slides – people rarely remember more than one concept afterwards so there’s no point overwhelming them with unnecessary information.
- The presentation should last no longer than 20 minutes as this will leave time for questions and discussion.
- The font size should be a minimum of 30pt because the audience reads faster than you talk so less information on the slides means that there is less chance of the audience being distracted.
If you want to give the audience more information you can provide them with partially completed handouts or give them the handouts after you’ve delivered the presentation.
Keep a drink nearby
Have something to drink when you’re on stage, preferably water at room temperature. This will help maintain your vocal quality and having a sip is a subtle way of introducing pauses.
Practice, practice, practice
If you are very familiar with the content of your presentation, your audience will perceive you as confident and you’ll be more persuasive.
- Don’t just read the presentation through – practice everything, including your transitions and using your visual aids.
- Stand up and speak it aloud, in an engaging manner, as though you were presenting to an audience.
- Ensure that you practice your body language and gesturing.
- Use VR to practice in a realistic environment .
- Practice in front of others and get their feedback.
- Freely improvise so you’ll sound more natural on the day. Don’t learn your presentation verbatim because you will sound uninterested and if you lose focus then you may forget everything.
- Create cards to use as cues – one card should be used for one key idea. Write down brief notes or key words and ensure that the cards are physically connected so the order cannot be lost. Visual prompts can also be used as cues.
This video shows how you can practice presentations in virtual reality. See our VR training courses .
Two courses where you can practice your presentations in interactive exercises:
- Essential Public Speaking
- How to Present over Video
Try these different presentation delivery methods to see which ones you prefer and which need to be improved. The most important factor is to feel comfortable during the presentation as the delivery is likely to be better.
Remember that the audience are generally on your side – they want you to do well so present with confidence.

9 Dramatic Conventions: A Beginner’s Guide
Dramatic conventions are the building blocks of theatrical storytelling, imbuing performances with depth, meaning, and a unique sense of style. These conventions, rooted in specific dramatic forms and styles, are essential tools for actors, playwrights, and directors to craft compelling narratives and engage audiences. In this beginner’s guide, we will explore nine significant dramatic conventions in the world of theatre, shedding light on their roles and contributions to the art of performance.
1. Soliloquy
Soliloquy is a powerful dramatic convention where a character speaks their innermost thoughts and emotions aloud, often while alone on stage. This convention provides insights into a character’s psyche and allows the audience to intimately understand their motivations and dilemmas.
An aside is a brief remark made by a character directly to the audience or to another character, usually while other characters on stage are unaware of it. It serves to provide additional information, reveal hidden intentions, or offer comedic relief.
3. Narration
Narration is a convention where a character or narrator explicitly recounts events or provides background information to the audience. It can be a vital tool for setting the stage and clarifying complex plot points.
4. Direct Address to Audience
Breaking the fourth wall, direct address to the audience occurs when a character acknowledges the audience’s presence, bridging the gap between the fictional world and reality. This convention creates a unique connection between the actors and the audience, often used for humorous or reflective purposes.
5. Multiple Roles
Multiple roles involve actors portraying more than one character within the same production. This convention challenges actors to showcase their versatility, bringing distinct personalities to life within a single performance.
Incorporating a mask into a performance allows actors to transform into different characters, often in stylized or symbolic productions. Masks can convey emotions and identities in a visually striking manner.
7. Lyrical Voice
Lyrical voice is a convention that emphasizes poetic and musical elements in dialogue or monologues. It infuses language with rhythm, creating a vivid and emotional connection between the character and the audience.
8. Slapstick
Slapstick is a physical comedy convention characterized by exaggerated and humorous physical actions, such as pratfalls, pie throwing, and slapstick violence. It aims to entertain through slapstick humor and physicality.
9. Fourth Wall
The concept of the fourth wall is the imaginary boundary that separates the stage from the audience. Breaking this wall, as mentioned earlier with direct address, invites the audience into the world of the play and can create unique theatrical experiences.
Understanding these dramatic conventions is a crucial step in appreciating the complexity and artistry of theatre. As you explore the world of drama, whether as an actor, playwright, or theatregoer, keep these conventions in mind, for they are the tools that breathe life into the stories that captivate and inspire us on the stage.
Related Articles

Dramatic Forms vs. Styles: A Beginner’s Guide
In this beginner’s guide, we’ll explore dramatic forms and styles, understanding how dramatic forms structure the content and how dramatic styles express the essence of a performance.
The Favourites of Team Haus: A Musical Playlist
There is something truly special about the moment the theatre lights dim and the curtain rises before a performance. The excitement one feels as they…
Soliloquy in Theatre: A Powerful Tool for Storytelling
Soliloquies are a powerful tool for storytelling in theatre, allowing us to get inside the heads of characters and understand their motivations and thought processes.
There was a problem reporting this post.
Block Member?
Please confirm you want to block this member.
You will no longer be able to:
- See blocked member's posts
- Mention this member in posts
- Invite this member to groups
- Add this member as a connection
Please note: This action will also remove this member from your connections and send a report to the site admin. Please allow a few minutes for this process to complete.
Effective Presentation Techniques – The Top 10

We have condensed all of the presentation techniques down to the most effective. Here are the Top 10 effective presentation techniques.
1. Use visual aids
Using pictures in your presentations instead of words can double the chances of meeting your objectives.
2. Keep it short and sweet
There is an old adage that said – “No one ever complained of a presentation being too short.” Nothing kills a presentation more than going on too long.
There are some college professors who will penalise a short presentation (most lecturers see no problem in droning on) , but for most people a shorter presentation is better. Keep your presentation to under 22 minutes if you can.
3. Use the rule of three
A simple technique is that people tend to only remember three things. Work out what the three messages that you want your audience to take away and structure your presentation around them. Use a maximum of three points on a slide.
4. Rehearse
Practice makes for perfect performance. Many experts say that rehearsal is the biggest single thing that you can do to improve your performance. Perform your presentation out loud at least four times. One of these should be in front of a real scary audience. Family, friends or colleagues. Even the dog is better than nothing.
5. Tell stories
All presentations are a type of theatre. Tell stories and anecdotes to help illustrate points. It all helps to make your presentation more effective and memorable.
6. Lose the bullet points – don’t put your speaker notes up on the screen
Bullet points are the kiss of death for most presentations. Most people use bullet points as a form of speaker notes. To make your presentation more effective put your speaker notes in your notes and not up on the screen.
7. Video yourself
Set up a video camera and video yourself presenting. You will see all sorts of mistakes that you are making, from how you are standing, if you are jangling keys, to how well your presentation is structured.
8 . Know what slide is coming next
You should always know when presenting which slide is coming up next. It sounds very powerful when you say “On the next slide [Click] you will see…”, rather than than a period of confusion when the next slide appears.
9. Have a back-up plan
Murphy’s law normally applies during a presentation. Technology not working, power cuts, projector blowing a bulb, spilling coffee on your front, not enough power leads, no loudspeakers, presentation displays strangely on the laptop – all of these are things that have happened in presentations that I have given.
Have a back-up plan. Take with you the following items – a printed out set of slides – (you can hold these up to the audience if you need to), a CD or data stick of your presentation, a laptop with your slides on it. Just in case it goes wrong.
Guess what? When you have back-ups – you seldom need to use them.
10. Check out the presentation room
Arrive early and check out the presentation room. If you can make sure that you see your slides loaded onto the PC and working on the screen. Work out where you will need to stand.
Do you agree or disagree with any of these effective presentation techniques? Have you have any experiences like this? Add it in to the comments box below.
Related posts:
- Attention Grabbers or Ice Breakers
- Seven deadly sins of presentations
- Seven Great Ways to Begin Your Presentation
- Six of the best rehearsal tips for your presentation
Recommended Pages
thanxxx alott for the informationn they r very usful…
They are truly powerful which everyone should apply to make his/her presentation a complete success.
Thank you! Really interesting and important material.
thank you for the top 10 effective presentation techniques
Simple yet very powerful
One thing to add to point 6 Indeed, speaker notes should not be on the slides. Nothing is more boring when sombebody reads exactly what is on the slides, I’d better take a copy home and read it in quietness then.
well….i thought i wouldn’t be lucky but im just da luckiest person in the world who know these different presentation techniques…. but well done i will use these tips while preparing my presentation for accounting… thank you … Nice day…
thts really an amazing to have these presentation techniques.i’ll do my best to follow it while delivering my presentation.
i shall teach these techniques to my students when insha Allah i will be an instructor of spoken English.
Great! Anything on stage fright?
A speaker should keep an eye contact with all the people in the room while giving the presentation .
Rest the tips are useful .Thank u
i think all the technique are excellent
Its really helpful.
Thanks & Regards Shiva.
this is corny
very interesting for me, when you prepare a presentation
According to me you have missed the most vital thing “Know your audience”
Nothing has been said about the element of interaction. It’s clear that a presentation is being made, but, if the audience is engaged, there might be greater attention to the entire presentation.
This is just my take, views may vary.
I am a facilitator in community forestry.these points are powerful materials. However I would like if you can explain more about the number 6. What to use instead of bullets. I have in my mind that slides are the guide of my presentation so I have to use bullets?. On the other side, could you please send me a short presentation prepared with these techiniques and observe the application. at least, one slide I can to observe how is a slide well prepared.
Thanks a million from Colombia
Thank for this 10 points!
I have been training and I feel these are the 10 most important points as well
I find these techniques quite useful, I have to do a presentation on Vending Machines to my head teacher – and you made very strong and strategic points. I’m only in Year 7…
This is highly informative and without doubt, very effective
very good and effective…use this techniques to have a successful presention
I was just making a presentation & I have come to know that my presentation is simply boring & killing. Any way, very effective & informative points.
Life changing, thank you.
I am going to be facilitating a parenting course in a few weeks and loved the idea of of the rule of three to present my message.
tanks fot the info is so important to my life
thankx 2 you for providing me such an informative material. . .
but u forget to mention about dressing of a presenter and can u plzzzzzzzzzzz send me a slide which is one of d perfect one’s. . .
thanks alot……… you khnow i will try to do all these tips in my presentations….
[…] a site which has the top ten effective presentation techniques and they make sense to […]
Like mpz I also think there should be a section/point on knowing your audience.
Roughly (and shortly) speaking there are three styles of learning that each might influence an otherwise excellent presentation: Visual, auditory and sensitive.
The visual learners prefer imagery (Seeing is believing) and requires few words to every slide. Use images, diagrams, tables and such.
The auditory prefers verbal explanations and responses. Encourage questions during the presentation and be prepared to go outside the presentation if it is appropriate. Watch your tone, pitch and volume of voice. Don’t drone 😉
The sensitive learners needs to be connected to you. Use brief statements and demonstrations immediately followed by Q&A. Don’t focus on logic and external elements. Share personal values and experiences. Show empathy and understanding.
Just a short remark 😉
Thanks a lot. Its really very helpful for update and improving my life.
these are realy good tips for presentation.i think there should be some more easy tips which can make our presentation more effective.
It is really nice and helpful
Thank you, it was really helpful, I used to put bullets in my slides, now not anymore, thanks again!
thank u.. that’s really powerful
Guess this is really useful..as we say nothing is perfect but this can go to a great extent forming base, helping individual to build further on these lines!!
i hope my presentation would go well
Thanks a lot, really helpful!
Very good points the 10 ones; also Know the subject, know your audience, be confident when you present your concise presentation which might be effective if you add spice to it (related stories / jockes…) and wake up calls (sudden questions at randomly picked up person from the audience), and for better memorisation, make your objectives clear at beggining and summarise the essential points at the end(using primacy and recency effects at work)… I mostly liked the Murphy’s law, the worst sure happens to the one who does not have a back up plan. Thanks a million… From Ethiopia
Brilliant trigger points. How can I overcome shyness in students who have the Knowledge but can’t present? It is so frustrating.
thanks to you, i won my pitch for the new coca cola commercials they are releasing over here in the states! i make that about $4.5 million U.S i owe you for these tips:)!
Congratulations for your tips on effective teaching presentation! However , how can a teacher in a remote area of Burundi or Malawi get access to some of the materials you have earlier mentioned such as CD, Laptop,… Fine ! May you please suggest what may replace those HITechs that are not available to most of Third World School? May God bless you! Nayingunge from Burundi.
thank you, i believe that with practice i will get better.
thanks to providing perfect informatiom about presentation techniques ,they are really so usefull while preparing any kind of ppt or presentation,its everything
Experience… Great
Very nice Techniq Great Jobs
very well instructions
thanks ..tomorrow is my presentation I’ll apply all the points.IT REALLY BOOST ME UP!!!!!! thanks again
good presentation advice
AWESOME ADVICE & IT REALY WORKS
thank you, i believe that with practice i will get best of the best.
thanks for the information, now i know how to make a good presentation ..
THANK YOU VERY MUCH FOR SHARING YOUR KNOWLEDGE!!!GODBLESS YOU AND YOUR LOVE ONES:)
thank you for the information ,its really helpful.
wow they r really helpfulx
thank you from Saudi Arabia
very awesome that is
thanks it was very useful to me
yes….. very nice because i fully unaware about these techniques …. bye the way i am MBA student ….therefor it is very usefull for me….
Great advice. Thanks
Thanks… Good Tips.
Its was great list of advice about presentation. Thanks.
It’s really useful to have these 10 points when doing presentations. I’m a teacher and this will help me to present things well.
Thanks a lot
Regards Nimal
this has been really helpful 4 me i mean this step is very good it help me out at my presentation and i got all mos 90% on my presentation. i think more people should take time reading this 10 tip
THNKS MUCH 4 BRIEF SUMMARY ON PRESENTATION TECHNIQUE,MAY U INCLUDE ATLEAST DRESSING CODE
thanks for the info regarding presentation techniques,,,it help me out for my presentation some day.
thank u alot realy it is an important material!
Thank yo verry much for all the4 informtions which i enjoyed-am practicing..However at one point where you state that “Keep your presentation to under 22 minutes if you can.” As a technical trainer in my organisation(a tire industry in India)where I have a 5 day sessions (9.00-5.30 p.m)this 22 mts. concept is hard to follow. But inadvertently I don’t dwell on a single topic/concept more than 20 mts, Is it O.K. Thangarajan.P.K.
its really nice for understanding
nice presentation skills
This is just brilliant
This is good stuff. I was a trainer in Zimbabwe so to the gentleman from Burundi I would say that you don’t need fancy aids to make an effective presentation. Pre-prepare a series of flip chart pages with your main points on and use a separate blank flip chart for points made by your audience. Also on visual aids I find that so often every slide looks the same – same font, background, company logo in the corner and so on. For the bits you want them to remember, change the slide completely so it stands out.
gostei muito das técnicas
I LIKE THE THECNIQUES,THANK YOU
Nice techniques……..
thanksfor thes points
This was very helpful… not only for our Philosophy class, but for all college courses. All 10 recommendations were very good. However, the 2 that seemed the most useful of all were to (1) video record yourself to find out how you look… and (2) have a back-up plan ready.
Hey, Hatts off to you man, they are very useful for a layman going for his / her first presentation.
wonderfull stuff!!!
these tips maked me to know more about presentation
tanks .it is very useful in my life
Thanks for the advice… 🙂
this website is amazing thanks so much xx
Ya , friend ….. My Father also likes Powrpoint preaentations & doing commentary …… He & I both likes this two tasks ….. & he is expert explaining ppt presentation in public .. I too wanted to become like him & the tips u had given r the same as what my father always follows ……… So , Thanks
its good 4 me
thank you very much this was very helpful
Thanks a lot for wonderful ideas. I do hope it will be very helpful in my upcoming presentation. May God bless you!
I’ll try to do this for my report on Monday. Thank you.
When using beamer or slides please also look from audience side! As the outside sun might blind them.
dont be over confident be confident
Highly appreciated your tips on business presentation.they will be of my great help in my agribusiness forum next week. Regards
rely great!
Really useful tips, looking forward to have these kinds of tips in future.
Superb info… Tqz
very helpful and valuable points
Very useful info….
these are very informative tips.any perhaps very effective ones
Thanks , very useful
tell stories really helped
The rule of three is something which Id like to try. I would do presentations using bullets as keys — just learned that it’s not advisable to do it.
Thank you very much it has greatly helped.Blessed all the content is useful and with this i hope to get better
Wonderful, l suggest you need to talk like a thought leader as well.
I’m so grateful for this opportunity of visiting this site. I find them so interesting, all the points outlined in this writing. I so much like the self-videoing part of it. This gives you the clear picture of how bad or good your presentation style is. And also gives you the chance to know if your recent pattern is better than the former or not.
From Nigeria
All the points are valid, but particularly like point # 5 which talks about stories. Stories bring life and authenticity to your presentation. Great job!

- All Templates
- Persuasive Speech Topics
- Informative
- Architecture
- Celebration
- Educational
- Engineering
- Food and Drink
- Subtle Waves Template
- Business world map
- Filmstrip with Countdown
- Blue Bubbles
- Corporate 2
- Vector flowers template
- Editable PowerPoint newspapers
- Hands Template
- Red blood cells slide
- Circles Template on white
- Maps of America
- Light Streaks Business Template
- Zen stones template
- Heartbeat Template
- Web icons template

Choose Your Test
- Search Blogs By Category
- College Admissions
- AP and IB Exams
- GPA and Coursework
The 31 Literary Devices You Must Know
General Education

Need to analyze The Scarlet Letter or To Kill a Mockingbird for English class, but fumbling for the right vocabulary and concepts for literary devices? You've come to the right place. To successfully interpret and analyze literary texts, you'll first need to have a solid foundation in literary terms and their definitions.
In this article, we'll help you get familiar with most commonly used literary devices in prose and poetry. We'll give you a clear definition of each of the terms we discuss along with examples of literary elements and the context in which they most often appear (comedic writing, drama, or other).
Before we get to the list of literary devices, however, we have a quick refresher on what literary devices are and how understanding them will help you analyze works of literature.
What Are Literary Devices and Why Should You Know Them?
Literary devices are techniques that writers use to create a special and pointed effect in their writing, to convey information, or to help readers understand their writing on a deeper level.
Often, literary devices are used in writing for emphasis or clarity. Authors will also use literary devices to get readers to connect more strongly with either a story as a whole or specific characters or themes.
So why is it important to know different literary devices and terms? Aside from helping you get good grades on your literary analysis homework, there are several benefits to knowing the techniques authors commonly use.
Being able to identify when different literary techniques are being used helps you understand the motivation behind the author's choices. For example, being able to identify symbols in a story can help you figure out why the author might have chosen to insert these focal points and what these might suggest in regard to her attitude toward certain characters, plot points, and events.
In addition, being able to identify literary devices can make a written work's overall meaning or purpose clearer to you. For instance, let's say you're planning to read (or re-read) The Lion, the Witch, and the Wardrobe by C.S. Lewis. By knowing that this particular book is a religious allegory with references to Christ (represented by the character Aslan) and Judas (represented by Edmund), it will be clearer to you why Lewis uses certain language to describe certain characters and why certain events happen the way they do.
Finally, literary techniques are important to know because they make texts more interesting and more fun to read. If you were to read a novel without knowing any literary devices, chances are you wouldn't be able to detect many of the layers of meaning interwoven into the story via different techniques.
Now that we've gone over why you should spend some time learning literary devices, let's take a look at some of the most important literary elements to know.
List of Literary Devices: 31 Literary Terms You Should Know
Below is a list of literary devices, most of which you'll often come across in both prose and poetry. We explain what each literary term is and give you an example of how it's used. This literary elements list is arranged in alphabetical order.
An allegory is a story that is used to represent a more general message about real-life (historical) issues and/or events. It is typically an entire book, novel, play, etc.
Example: George Orwell's dystopian book Animal Farm is an allegory for the events preceding the Russian Revolution and the Stalinist era in early 20th century Russia. In the story, animals on a farm practice animalism, which is essentially communism. Many characters correspond to actual historical figures: Old Major represents both the founder of communism Karl Marx and the Russian communist leader Vladimir Lenin; the farmer, Mr. Jones, is the Russian Czar; the boar Napoleon stands for Joseph Stalin; and the pig Snowball represents Leon Trotsky.
Alliteration
Alliteration is a series of words or phrases that all (or almost all) start with the same sound. These sounds are typically consonants to give more stress to that syllable. You'll often come across alliteration in poetry, titles of books and poems ( Jane Austen is a fan of this device, for example—just look at Pride and Prejudice and Sense and Sensibility ), and tongue twisters.
Example: "Peter Piper picked a peck of pickled peppers." In this tongue twister, the "p" sound is repeated at the beginning of all major words.
Allusion is when an author makes an indirect reference to a figure, place, event, or idea originating from outside the text. Many allusions make reference to previous works of literature or art.
Example: "Stop acting so smart—it's not like you're Einstein or something." This is an allusion to the famous real-life theoretical physicist Albert Einstein.
Anachronism
An anachronism occurs when there is an (intentional) error in the chronology or timeline of a text. This could be a character who appears in a different time period than when he actually lived, or a technology that appears before it was invented. Anachronisms are often used for comedic effect.
Example: A Renaissance king who says, "That's dope, dude!" would be an anachronism, since this type of language is very modern and not actually from the Renaissance period.
Anaphora is when a word or phrase is repeated at the beginning of multiple sentences throughout a piece of writing. It's used to emphasize the repeated phrase and evoke strong feelings in the audience.
Example: A famous example of anaphora is Winston Churchill's "We Shall Fight on the Beaches" speech. Throughout this speech, he repeats the phrase "we shall fight" while listing numerous places where the British army will continue battling during WWII. He did this to rally both troops and the British people and to give them confidence that they would still win the war.
Anthropomorphism
An anthropomorphism occurs when something nonhuman, such as an animal, place, or inanimate object, behaves in a human-like way.
Example: Children's cartoons have many examples of anthropomorphism. For example, Mickey and Minnie Mouse can speak, wear clothes, sing, dance, drive cars, etc. Real mice can't do any of these things, but the two mouse characters behave much more like humans than mice.
Asyndeton is when the writer leaves out conjunctions (such as "and," "or," "but," and "for") in a group of words or phrases so that the meaning of the phrase or sentence is emphasized. It is often used for speeches since sentences containing asyndeton can have a powerful, memorable rhythm.
Example: Abraham Lincoln ends the Gettysburg Address with the phrase "...and that government of the people, by the people, for the people shall not perish from the Earth." By leaving out certain conjunctions, he ends the speech on a more powerful, melodic note.
Colloquialism
Colloquialism is the use of informal language and slang. It's often used by authors to lend a sense of realism to their characters and dialogue. Forms of colloquialism include words, phrases, and contractions that aren't real words (such as "gonna" and "ain't").
Example: "Hey, what's up, man?" This piece of dialogue is an example of a colloquialism, since it uses common everyday words and phrases, namely "what's up" and "man."
An epigraph is when an author inserts a famous quotation, poem, song, or other short passage or text at the beginning of a larger text (e.g., a book, chapter, etc.). An epigraph is typically written by a different writer (with credit given) and used as a way to introduce overarching themes or messages in the work. Some pieces of literature, such as Herman Melville's 1851 novel Moby-Dick , incorporate multiple epigraphs throughout.
Example: At the beginning of Ernest Hemingway's book The Sun Also Rises is an epigraph that consists of a quotation from poet Gertrude Stein, which reads, "You are all a lost generation," and a passage from the Bible.
Epistrophe is similar to anaphora, but in this case, the repeated word or phrase appears at the end of successive statements. Like anaphora, it is used to evoke an emotional response from the audience.
Example: In Lyndon B. Johnson's speech, "The American Promise," he repeats the word "problem" in a use of epistrophe: "There is no Negro problem. There is no Southern problem. There is no Northern problem. There is only an American problem."

A euphemism is when a more mild or indirect word or expression is used in place of another word or phrase that is considered harsh, blunt, vulgar, or unpleasant.
Example: "I'm so sorry, but he didn't make it." The phrase "didn't make it" is a more polite and less blunt way of saying that someone has died.
A flashback is an interruption in a narrative that depicts events that have already occurred, either before the present time or before the time at which the narration takes place. This device is often used to give the reader more background information and details about specific characters, events, plot points, and so on.
Example: Most of the novel Wuthering Heights by Emily Brontë is a flashback from the point of view of the housekeeper, Nelly Dean, as she engages in a conversation with a visitor named Lockwood. In this story, Nelly narrates Catherine Earnshaw's and Heathcliff's childhoods, the pair's budding romance, and their tragic demise.
Foreshadowing
Foreshadowing is when an author indirectly hints at—through things such as dialogue, description, or characters' actions—what's to come later on in the story. This device is often used to introduce tension to a narrative.
Example: Say you're reading a fictionalized account of Amelia Earhart. Before she embarks on her (what we know to be unfortunate) plane ride, a friend says to her, "Be safe. Wouldn't want you getting lost—or worse." This line would be an example of foreshadowing because it implies that something bad ("or worse") will happen to Earhart.
Hyperbole is an exaggerated statement that's not meant to be taken literally by the reader. It is often used for comedic effect and/or emphasis.
Example: "I'm so hungry I could eat a horse." The speaker will not literally eat an entire horse (and most likely couldn't ), but this hyperbole emphasizes how starved the speaker feels.
Imagery is when an author describes a scene, thing, or idea so that it appeals to our senses (taste, smell, sight, touch, or hearing). This device is often used to help the reader clearly visualize parts of the story by creating a strong mental picture.
Example: Here's an example of imagery taken from William Wordsworth's famous poem "I Wandered Lonely as a Cloud":
When all at once I saw a crowd, A host of golden Daffodils; Beside the Lake, beneath the trees, Fluttering and dancing in the breeze.
Irony is when a statement is used to express an opposite meaning than the one literally expressed by it. There are three types of irony in literature:
- Verbal irony: When someone says something but means the opposite (similar to sarcasm).
- Situational irony: When something happens that's the opposite of what was expected or intended to happen.
- Dramatic irony: When the audience is aware of the true intentions or outcomes, while the characters are not . As a result, certain actions and/or events take on different meanings for the audience than they do for the characters involved.
- Verbal irony: One example of this type of irony can be found in Edgar Allan Poe's "The Cask of Amontillado." In this short story, a man named Montresor plans to get revenge on another man named Fortunato. As they toast, Montresor says, "And I, Fortunato—I drink to your long life." This statement is ironic because we the readers already know by this point that Montresor plans to kill Fortunato.
- Situational irony: A girl wakes up late for school and quickly rushes to get there. As soon as she arrives, though, she realizes that it's Saturday and there is no school.
- Dramatic irony: In William Shakespeare's Romeo and Juliet , Romeo commits suicide in order to be with Juliet; however, the audience (unlike poor Romeo) knows that Juliet is not actually dead—just asleep.

Juxtaposition
Juxtaposition is the comparing and contrasting of two or more different (usually opposite) ideas, characters, objects, etc. This literary device is often used to help create a clearer picture of the characteristics of one object or idea by comparing it with those of another.
Example: One of the most famous literary examples of juxtaposition is the opening passage from Charles Dickens' novel A Tale of Two Cities :
"It was the best of times, it was the worst of times, it was the age of wisdom, it was the age of foolishness, it was the epoch of belief, it was the epoch of incredulity, it was the season of Light, it was the season of Darkness, it was the spring of hope, it was the winter of despair …"
Malapropism
Malapropism happens when an incorrect word is used in place of a word that has a similar sound. This misuse of the word typically results in a statement that is both nonsensical and humorous; as a result, this device is commonly used in comedic writing.
Example: "I just can't wait to dance the flamingo!" Here, a character has accidentally called the flamenco (a type of dance) the flamingo (an animal).
Metaphor/Simile
Metaphors are when ideas, actions, or objects are described in non-literal terms. In short, it's when an author compares one thing to another. The two things being described usually share something in common but are unalike in all other respects.
A simile is a type of metaphor in which an object, idea, character, action, etc., is compared to another thing using the words "as" or "like."
Both metaphors and similes are often used in writing for clarity or emphasis.
"What light through yonder window breaks? It is the east, and Juliet is the sun." In this line from Romeo and Juliet , Romeo compares Juliet to the sun. However, because Romeo doesn't use the words "as" or "like," it is not a simile—just a metaphor.
"She is as vicious as a lion." Since this statement uses the word "as" to make a comparison between "she" and "a lion," it is a simile.
A metonym is when a related word or phrase is substituted for the actual thing to which it's referring. This device is usually used for poetic or rhetorical effect .
Example: "The pen is mightier than the sword." This statement, which was coined by Edward Bulwer-Lytton in 1839, contains two examples of metonymy: "the pen" refers to "the written word," and "the sword" refers to "military force/violence."
Mood is the general feeling the writer wants the audience to have. The writer can achieve this through description, setting, dialogue, and word choice .
Example: Here's a passage from J.R.R. Tolkien's The Hobbit: "It had a perfectly round door like a porthole, painted green, with a shiny yellow brass knob in the exact middle. The door opened on to a tube-shaped hall like a tunnel: a very comfortable tunnel without smoke, with panelled walls, and floors tiled and carpeted, provided with polished chairs, and lots and lots of pegs for hats and coats -- the hobbit was fond of visitors." In this passage, Tolkien uses detailed description to set create a cozy, comforting mood. From the writing, you can see that the hobbit's home is well-cared for and designed to provide comfort.
Onomatopoeia
Onomatopoeia is a word (or group of words) that represents a sound and actually resembles or imitates the sound it stands for. It is often used for dramatic, realistic, or poetic effect.
Examples: Buzz, boom, chirp, creak, sizzle, zoom, etc.
An oxymoron is a combination of two words that, together, express a contradictory meaning. This device is often used for emphasis, for humor, to create tension, or to illustrate a paradox (see next entry for more information on paradoxes).
Examples: Deafening silence, organized chaos, cruelly kind, insanely logical, etc.
A paradox is a statement that appears illogical or self-contradictory but, upon investigation, might actually be true or plausible.
Note that a paradox is different from an oxymoron: a paradox is an entire phrase or sentence, whereas an oxymoron is a combination of just two words.
Example: Here's a famous paradoxical sentence: "This statement is false." If the statement is true, then it isn't actually false (as it suggests). But if it's false, then the statement is true! Thus, this statement is a paradox because it is both true and false at the same time.
Personification
Personification is when a nonhuman figure or other abstract concept or element is described as having human-like qualities or characteristics. (Unlike anthropomorphism where non-human figures become human-like characters, with personification, the object/figure is simply described as being human-like.) Personification is used to help the reader create a clearer mental picture of the scene or object being described.
Example: "The wind moaned, beckoning me to come outside." In this example, the wind—a nonhuman element—is being described as if it is human (it "moans" and "beckons").
Repetition is when a word or phrase is written multiple times, usually for the purpose of emphasis. It is often used in poetry (for purposes of rhythm as well).
Example: When Lin-Manuel Miranda, who wrote the score for the hit musical Hamilton, gave his speech at the 2016 Tony's, he recited a poem he'd written that included the following line:
And love is love is love is love is love is love is love is love cannot be killed or swept aside.
Satire is genre of writing that criticizes something , such as a person, behavior, belief, government, or society. Satire often employs irony, humor, and hyperbole to make its point.
Example: The Onion is a satirical newspaper and digital media company. It uses satire to parody common news features such as opinion columns, editorial cartoons, and click bait headlines.
A type of monologue that's often used in dramas, a soliloquy is when a character speaks aloud to himself (and to the audience), thereby revealing his inner thoughts and feelings.
Example: In Romeo and Juliet , Juliet's speech on the balcony that begins with, "O Romeo, Romeo! Wherefore art thou Romeo?" is a soliloquy, as she is speaking aloud to herself (remember that she doesn't realize Romeo's there listening!).
Symbolism refers to the use of an object, figure, event, situation, or other idea in a written work to represent something else— typically a broader message or deeper meaning that differs from its literal meaning.
The things used for symbolism are called "symbols," and they'll often appear multiple times throughout a text, sometimes changing in meaning as the plot progresses.
Example: In F. Scott Fitzgerald's 1925 novel The Great Gatsby , the green light that sits across from Gatsby's mansion symbolizes Gatsby's hopes and dreams .
A synecdoche is a literary device in which part of something is used to represent the whole, or vice versa. It's similar to a metonym (see above); however, a metonym doesn't have to represent the whole—just something associated with the word used.
Example: "Help me out, I need some hands!" In this case, "hands" is being used to refer to people (the whole human, essentially).
While mood is what the audience is supposed to feel, tone is the writer or narrator's attitude towards a subject . A good writer will always want the audience to feel the mood they're trying to evoke, but the audience may not always agree with the narrator's tone, especially if the narrator is an unsympathetic character or has viewpoints that differ from those of the reader.
Example: In an essay disdaining Americans and some of the sites they visit as tourists, Rudyard Kipling begins with the line, "Today I am in the Yellowstone Park, and I wish I were dead." If you enjoy Yellowstone and/or national parks, you may not agree with the author's tone in this piece.

How to Identify and Analyze Literary Devices: 4 Tips
In order to fully interpret pieces of literature, you have to understand a lot about literary devices in the texts you read. Here are our top tips for identifying and analyzing different literary techniques:
Tip 1: Read Closely and Carefully
First off, you'll need to make sure that you're reading very carefully. Resist the temptation to skim or skip any sections of the text. If you do this, you might miss some literary devices being used and, as a result, will be unable to accurately interpret the text.
If there are any passages in the work that make you feel especially emotional, curious, intrigued, or just plain interested, check that area again for any literary devices at play.
It's also a good idea to reread any parts you thought were confusing or that you didn't totally understand on a first read-through. Doing this ensures that you have a solid grasp of the passage (and text as a whole) and will be able to analyze it appropriately.
Tip 2: Memorize Common Literary Terms
You won't be able to identify literary elements in texts if you don't know what they are or how they're used, so spend some time memorizing the literary elements list above. Knowing these (and how they look in writing) will allow you to more easily pinpoint these techniques in various types of written works.
Tip 3: Know the Author's Intended Audience
Knowing what kind of audience an author intended her work to have can help you figure out what types of literary devices might be at play.
For example, if you were trying to analyze a children's book, you'd want to be on the lookout for child-appropriate devices, such as repetition and alliteration.
Tip 4: Take Notes and Bookmark Key Passages and Pages
This is one of the most important tips to know, especially if you're reading and analyzing works for English class. As you read, take notes on the work in a notebook or on a computer. Write down any passages, paragraphs, conversations, descriptions, etc., that jump out at you or that contain a literary device you were able to identify.
You can also take notes directly in the book, if possible (but don't do this if you're borrowing a book from the library!). I recommend circling keywords and important phrases, as well as starring interesting or particularly effective passages and paragraphs.
Lastly, use sticky notes or post-its to bookmark pages that are interesting to you or that have some kind of notable literary device. This will help you go back to them later should you need to revisit some of what you've found for a paper you plan to write.
What's Next?
Looking for more in-depth explorations and examples of literary devices? Join us as we delve into imagery , personification , rhetorical devices , tone words and mood , and different points of view in literature, as well as some more poetry-specific terms like assonance and iambic pentameter .
Reading The Great Gatsby for class or even just for fun? Then you'll definitely want to check out our expert guides on the biggest themes in this classic book, from love and relationships to money and materialism .
Got questions about Arthur Miller's The Crucible ? Read our in-depth articles to learn about the most important themes in this play and get a complete rundown of all the characters .
For more information on your favorite works of literature, take a look at our collection of high-quality book guides and our guide to the 9 literary elements that appear in every story !

These recommendations are based solely on our knowledge and experience. If you purchase an item through one of our links, PrepScholar may receive a commission.
Trending Now
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
ACT vs. SAT: Which Test Should You Take?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Get Your Free

Find Your Target SAT Score
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
How to Get a Perfect SAT Score, by an Expert Full Scorer
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading and Writing
How to Improve Your Low SAT Score
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading and Writing
Find Your Target ACT Score
Complete Official Free ACT Practice Tests
How to Get a Perfect ACT Score, by a 36 Full Scorer
Get a 36 on ACT English
Get a 36 on ACT Math
Get a 36 on ACT Reading
Get a 36 on ACT Science
How to Improve Your Low ACT Score
Get a 24 on ACT English
Get a 24 on ACT Math
Get a 24 on ACT Reading
Get a 24 on ACT Science
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!

Hannah received her MA in Japanese Studies from the University of Michigan and holds a bachelor's degree from the University of Southern California. From 2013 to 2015, she taught English in Japan via the JET Program. She is passionate about education, writing, and travel.
Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
Responder: O genótipo do primeiro casal é homozigoto recessivo.
Para determinar o genótipo do primeiro casal, é necessário analisar o heredograma fornecido. O genótipo é a combinação de alelos presentes em um organismo. No caso do primeiro casal, é possível determinar o genótipo dos indivíduos através da análise dos genótipos dos descendentes.
Se todos os descendentes são afetados por uma determinada condição genética, isso indica que ambos os pais são portadores do alelo causador dessa condição. Portanto, o genótipo do primeiro casal deve ser homozigoto recessivo para a condição em questão.
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
What It Takes to Give a Great Presentation
- Carmine Gallo

Five tips to set yourself apart.
Never underestimate the power of great communication. It can help you land the job of your dreams, attract investors to back your idea, or elevate your stature within your organization. But while there are plenty of good speakers in the world, you can set yourself apart out by being the person who can deliver something great over and over. Here are a few tips for business professionals who want to move from being good speakers to great ones: be concise (the fewer words, the better); never use bullet points (photos and images paired together are more memorable); don’t underestimate the power of your voice (raise and lower it for emphasis); give your audience something extra (unexpected moments will grab their attention); rehearse (the best speakers are the best because they practice — a lot).
I was sitting across the table from a Silicon Valley CEO who had pioneered a technology that touches many of our lives — the flash memory that stores data on smartphones, digital cameras, and computers. He was a frequent guest on CNBC and had been delivering business presentations for at least 20 years before we met. And yet, the CEO wanted to sharpen his public speaking skills.
- Carmine Gallo is a Harvard University instructor, keynote speaker, and author of 10 books translated into 40 languages. Gallo is the author of The Bezos Blueprint: Communication Secrets of the World’s Greatest Salesman (St. Martin’s Press).
Partner Center

COMMENTS
So here are my top six ways to harness the tools of the theater to make your next presentation a performance to remember. 1. It's a monologue, not a soliloquy. In a play, when a character speaks for an extended period of time, it's either a monologue or a soliloquy.
Even in a less formal public speaking situation, these theatrical techniques can be applied. When you are sitting around a conference table for a meeting, leaning forward (downstage), this implies interest in the topic at hand. When you shift your weight back (upstage), you give your audience the impression that you are not as engaged in the ...
A relationship based on trust, respect, information, and interaction! Sure a speech has mostly been defined as one person talking and other people listening. But it always takes two to tango… you know. You AND your audience have a part to play in this engagement. And when you end… get everything in before the audience claps. Then get off ...
Theatre technique is part of the playwright's creative writing of drama, as a kind of mimesis rather than mere illusion or imitation of life, in that the playwright is able to present a reality to the audience that is different, yet recognisable to that which they usually identify with in their everyday lives.. Another aspect of this is that of creating the kind of dialogue that makes the ...
Method 10: Relax. This one is not only a presentation technique, but a great life technique as well. Actually, the most common reason for the mistakes during presentations are the nerves and fear a lot of people feel while presenting. It's absolutely normal to be a little worried about the presentation, but you have to instill confidence in ...
Keep it simple: One idea per slide keeps confusion at bay and attention locked in. Use bullet points: Break down your points so your audience can track. Pick a font size: Generally speaking, bigger is better. Use color: Harness colors that pop without blinding anyone; contrast is key.
Craft your presentation with your target audience in mind. Use strong, concise language and relevant examples to maintain their interest. Avoid using foreign words or clichés that may alienate or confuse your audience. If necessary, provide explanations to ensure clarity. 3.
Enhanced Storytelling: Theatrical devices serve as crucial tools for conveying narratives, enriching the storytelling experience with visual, auditory, and symbolic elements. Emotional Impact: These devices contribute to the creation of mood, atmosphere, and emotional resonance, eliciting specific reactions and responses from the audience.
Playwriting Techniques. Playwrights work in different ways. Some need isolation and silence, and others prefer to be surrounded by noise and commotion. Some begin with an outline that they ...
The best way to control the narrative in numbers and data is to create visual images that tell specific stories. Visualize data to tell a story. An effective image can help your audience understand both the meaning and origin of the data to keep people engaged. 7. Your slides are not the centerpiece, you are.
Different techniques offer unique approaches to character development, emotional engagement, and stage presence. A well-rounded education in these methods equips students to adapt to different roles and theatrical genres readily. Studying various acting techniques also invites students to engage in critical analysis and reflection actively.
Large, exaggerated "stage acting" can look awkward and silly on screen. Choose a short scene or monologue, and perform it twice-once for "stage" and once for "screen.". For the stage version, use large, exaggerated gestures to reach the back row audience members. For the screen version, use small, controlled expressions.
#4 Use high-quality visuals. What's one of the most effective presentation techniques? Use of visuals. They play a crucial role in your presentation. However, only high-quality visuals will make a good impression and effectively communicate your message. Use high-quality visuals like images, videos, graphs, maps, and others to really land ...
During a presentation you aim to look confident, enthusiastic and natural. You'll need more than good words and content to achieve this - your delivery plays a significant part. In this article, we discuss various techniques that can be used to deliver an effective presentation. Effective presentations
Masks can convey emotions and identities in a visually striking manner. 7. Lyrical Voice. Lyrical voice is a convention that emphasizes poetic and musical elements in dialogue or monologues. It infuses language with rhythm, creating a vivid and emotional connection between the character and the audience. 8. Slapstick.
Here are the Top 10 effective presentation techniques. 1. Use visual aids. Using pictures in your presentations instead of words can double the chances of meeting your objectives. 2. Keep it short and sweet. There is an old adage that said - "No one ever complained of a presentation being too short.". Nothing kills a presentation more ...
Verbal irony: When someone says something but means the opposite (similar to sarcasm). Situational irony: When something happens that's the opposite of what was expected or intended to happen. Dramatic irony: When the audience is aware of the true intentions or outcomes, while the characters are not.
The two presentation techniques used in plays are Representational and Presentational. These terms refer to the actor-audience relationship in a theatrical performance. Representational acting involves the actor ignoring the audience and remaining absorbed in the dramatic action, treating the audience as 'peeping tom' voyeurs.
Here are a few tips for business professionals who want to move from being good speakers to great ones: be concise (the fewer words, the better); never use bullet points (photos and images paired ...