How to Write a Critical Thinking Essay: Steps & Example

Critical thinking is a powerful skill that helps you analyze information and form well-reasoned arguments. As a matter of fact, the human brain uses more energy when critically thinking than when relaxing. This article will guide you through the steps of writing a successful critical thinking essay.
In this article, you will learn:
- How to craft a strong essay
- The importance of these essays
- The structure with an example
- Valuable bonus tips to strengthen your writing
By following these steps and incorporating the provided information, you'll be well on your way to writing impressive essays. If you need further guidance, always count on our fast essay writing service .

What is Critical Thinking Essay
A critical thinking essay is a type of writing where you analyze a topic thoroughly. You'll consider different viewpoints, evaluate evidence from studies or expert opinions, and form your own well-reasoned conclusion. Here, you need to look at an issue from all angles before deciding where you stand. This type of essay goes beyond memorizing facts. It actively engages with information, questions assumptions, and develops your own thoughtful perspective.

Wednesday Addams
Mysterious, dark, and sarcastic
You’re the master of dark humor and love standing out with your unconventional style. Your perfect costume? A modern twist on Wednesday Addams’ gothic look. You’ll own Halloween with your unapologetically eerie vibe. 🖤🕸️
Is Your Essay Giving You a Headache?
Don't call an ambulance; call EssayPro! Let our experts conquer any of your assignments!
Importance of Critical Thinking and Its Use in Writing
Critical thinking is a skill that benefits all types of writing, not just essays. It helps you become a more informed and effective communicator. Here's why it's important:
- Stronger Arguments: Critical thinking helps you build solid arguments. You won't just state your opinion but back it up with evidence and consider opposing viewpoints. This makes your writing more persuasive and convincing.
- Deeper Understanding: When writing a critical thinking essay, you'll analyze information, identify biases, and think about the bigger picture. This leads to a richer understanding of the topic and a more insightful essay.
- Clearer Communication: By organizing your thoughts critically, your writing becomes clearer and more focused. You'll present your ideas in a logical order, making it easier for readers to follow your argument.
- Spotting Fake News: Critical thinking skills help you evaluate the information you encounter online and in the world around you. You'll be better equipped to identify unreliable sources and biased information, making you a more discerning reader and writer.
- Improved Problem-Solving: Critical thinking helps you approach challenges thoughtfully. As you write, you'll learn to analyze complex issues, consider different solutions, and ultimately develop well-reasoned conclusions. This skill extends beyond writing and can be applied to all areas of your life.
For more detailed information on the importance of critical thinking , visit our dedicated article.
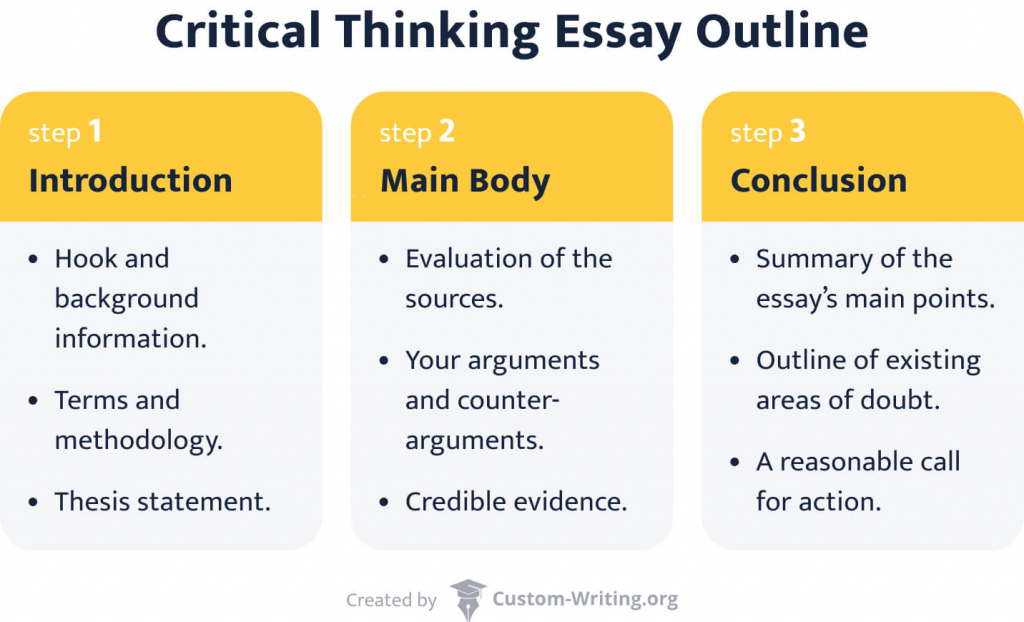
Critical Thinking Essay Format
In a critical thinking essay outline, each piece has its place and contributes to the overall picture. Here's a breakdown of the key components:
Check out our critical analysis example to see how this format comes to life.
Critical Thinking Essay Questions
Now that you understand the structure of this essay, let's get your brain working! Here are some questions to help you generate strong critical thinking essay topics:
- How can you tell if a source of information is reliable?
- What are the potential biases that might influence research or news articles?
- How can you identify logical fallacies in arguments?
- How can you weigh the pros and cons of a complex issue?
- How can your own experiences or background influence your perspective on a topic?
Sample Essay Topics:
- History: Should historical monuments that celebrate controversial figures be removed or repurposed?
- Science: With advancements in gene editing, should we allow parents to choose their children's traits?
- Art & Culture: Does artificial intelligence pose a threat to the creativity and value of human art?
- Space Exploration: Should we prioritize colonizing Mars or focus on solving problems on Earth?
- Business Ethics: Is it ethical for companies to automate jobs and potentially displace workers?
- Education: In a world with readily available information online, is traditional classroom learning still necessary?
- Global Issues: Is focusing solely on national interests hindering efforts to address global challenges like climate change?
Remember, these are just a few ideas to get you started. Choose a topic that interests you and allows you to explore different perspectives critically.
How to Write a Critical Thinking Essay
We've covered the foundation – the structure and key elements of a critical thinking essay. Now, let's dive into the writing process itself! Remember, the steps on how to start a critical thinking essay, such as defining your topic, crafting a thesis, gathering evidence, etc., are all interconnected. As you write, you'll move back and forth between them to refine your argument and build a strong essay.
If you're looking for a hassle-free solution, simply buy cheap argumentative essay from our experts.
.webp)
Understand the Assignment Requirements
Taking some time to understand the assignment from the beginning will save you time and frustration later. Grasping your critical thinking paper instructions ensures you're on the right track and meeting your teacher's expectations. Here's what to focus on:
- The Prompt: This is the core of the assignment, outlining the topic and what you're expected to do. For example, if it asks what critical thinking skills are, Look for keywords like "define," "describe," or "explain." These indicate the type of essay you need to write and the approach you should take.
- Specific Requirements: Pay attention to details like the essay length, formatting style (e.g., MLA, APA), and any specific sources you need to use. Missing these guidelines can lead to point deductions.
- Grading Rubric (if provided): This is a goldmine! The rubric often outlines the criteria your essay will be graded on, like clarity of argument, use of evidence, and proper citation style. Knowing these expectations can help you tailor your writing to excel.
Select a Critical Thinking Topic
Think about the prompt or theme provided by your teacher. Are there any aspects that pique your interest? Perhaps a specific angle you haven't explored much? The best topics are those that spark your curiosity and allow you to engage with the material in a meaningful way.
Here are some tips for selecting a strong critical thinking essay topic:
- Relevance to the Assignment: Make sure your chosen topic directly relates to the prompt and allows you to address the key points. Don't stray too far off course!
- Interest and Engagement: Choose a topic that you find genuinely interesting. Your enthusiasm will show in your writing and make the research and writing process more enjoyable.
- Complexity and Scope: Aim for a topic that's complex enough to provide depth for analysis but not so broad that it becomes overwhelming. You want to be able to explore it thoroughly within the essay's length limitations.
- Availability of Sources: Ensure you have access to credible sources like academic journals, news articles from reputable sources, or books by experts to support your argument.
Remember: Don't be afraid to get creative! While some prompts may seem broad, there's often room to explore a specific angle or sub-topic within the larger theme.
Conduct In-Depth Research
This is where you'll gather the information and evidence when writing a critical thinking essay. However, don't just copy information passively. Critically analyze the sources you find.
- Start with Reliable Sources: Steer clear of unreliable websites or questionable information. Focus on credible sources like academic journals, scholarly articles, reputable news outlets, and books by established experts in the field.
- Use Library Resources: Librarians can guide you towards relevant databases, academic journals, and credible online resources.
- Search Engines Can Be Your Friend: While you shouldn't rely solely on search engines, they can be helpful starting points. Use keywords related to your topic, and be critical of the websites you visit. Look for sites with a clear "About Us" section and reputable affiliations.
- Vary Your Sources: Don't just rely on one type of source. Seek out a variety of perspectives, including research studies, data, historical documents, and even opposing viewpoints. This will give your essay well-roundedness and depth.
Develop a Strong Thesis Statement
Your thesis statement encapsulates your main argument or perspective on the topic. A strong thesis statement tells your readers exactly what your essay will be about and prepares them for the evidence you'll present.
During your critical thinking process, make sure you include these key characteristics:
- Specificity: It goes beyond simply stating the topic and clearly outlines your position on it.
- Focus: It focuses on a single main point that you'll develop throughout the essay.
- Argumentative: It indicates your stance on the issue, not just a neutral observation.
- Clarity: It's clear, concise, and easy for the reader to understand.
For example, here's a weak thesis statement:
Deepfakes are a new technology with both positive and negative implications.
This is too vague and doesn't tell us anything specific about ethics. Here's a stronger version:
While deep lakes have the potential to revolutionize entertainment and education, their ability to create highly convincing misinformation poses a significant threat to democracy and social trust.
This thesis is specific, focused, and clearly states the argument that will be explored in the essay.
Outline the Structure of Your Essay
With a strong thesis statement guiding your way, it's time to create a roadmap for your essay. This outline will serve as a blueprint, ensuring your arguments flow logically and your essay has a clear structure. Here's what a basic outline for a critical thinking essay might look like:
This is a flexible structure, and you may need to adapt it based on your specific topic and the length of your essay. However, having a clear outline will help you stay organized and ensure your essay flows smoothly from point to point.
Write an Engaging Introduction
The introduction should be captivating and give your reader a taste of what's to come. Here are some tips for crafting a strong introduction:
- Start with a Hook: Use an interesting fact, a thought-provoking question, or a relevant anecdote to grab your reader's attention right from the start. This will pique their curiosity and make them want to read more.
- Introduce the Topic: Briefly introduce the topic you'll be exploring and explain its significance. Why is this topic important to discuss?
- Present Your Thesis: Clearly and concisely state your thesis statement. This tells your reader exactly what your essay will argue and prepares them for the evidence you'll present.
For example, Let's say your essay is about the growing popularity of online learning platforms. Here's an introduction that uses a hook, introduces the topic, and presents a thesis statement:
With millions of students enrolled in online courses worldwide, the way we learn is undergoing a dramatic transformation. Traditionally associated with brick-and-mortar classrooms, education is now readily available through virtual platforms, offering flexibility and accessibility. This essay will examine the advantages and challenges of online learning, ultimately arguing that while it offers valuable opportunities, it cannot entirely replace the benefits of a traditional classroom setting.
Construct Analytical Body Paragraphs
The body paragraphs are the heart of your essay, where you develop your argument and convince your reader of your perspective.
- Focus on One Point Per Paragraph: Each paragraph should address a single point that directly relates to your thesis statement. Don't try to cram too much information into one paragraph.
- Start with a Topic Sentence: This sentence introduces the main point of the paragraph and explains how it connects to your thesis.
- Support with Evidence: Back up your claims with credible evidence from your research. This could include facts, statistics, quotes from experts, or relevant examples.
- Analyze and Explain: Don't just list the evidence! Use critical thinking in writing - explain how it supports your argument and analyze its significance. What does this evidence tell you about the issue?
- Consider Counterarguments (Optional): In some cases, it can be effective to acknowledge opposing viewpoints and briefly explain why they're not as strong as your argument. This demonstrates your awareness of the complexity of the issue and strengthens your own position.
For example: Let's revisit the online learning example. Imagine one of your body paragraphs focuses on the flexibility of online learning platforms. Here's a breakdown of how you might structure it:
- Topic Sentence: Online learning platforms offer students unparalleled flexibility in terms of scheduling and pace of learning.
- Evidence: A recent study by the Online Learning Consortium found that 74% of online students reported being able to manage their coursework around their work and personal commitments.
- Analysis: This flexibility allows students who may have work or family obligations to pursue their education without sacrificing other responsibilities. It also empowers students to learn at their own pace, revisiting challenging concepts or accelerating through familiar material.
Craft a Thoughtful Conclusion
The conclusion is your final opportunity to wrap up the story in a satisfying way and leave the audience with something to ponder. Here's how to write a strong conclusion for your critical thinking essay:
- Summarize Key Points: Briefly remind your reader of the main points you've discussed throughout the essay.
- Restate Your Thesis: Restate your thesis statement in a new way, emphasizing its significance.
- Final Thought or Call to Action (Optional): Leave your reader with a final thought that provokes reflection, or consider including a call to action that encourages them to take a particular stance on the issue.
Here's an example conclusion for the online learning essay:
In conclusion, while online learning platforms offer valuable flexibility and accessibility, they cannot entirely replace the benefits of a traditional classroom setting. The social interaction, real-time feedback, and personalized attention offered by in-person learning remain crucial components of a well-rounded educational experience. As technology continues to evolve, future advancements may bridge this gap, but for now, a blended approach that leverages the strengths of both online and traditional learning may be the optimal solution.
Critical Thinking Essay Example
Let's now take a look at a complete critical thinking essay to see how these steps come together. This example will show you how to structure your essay and build a strong argument.
5 Tips on How to Develop Critical Thinking Skills
Critical thinking helps you form well-reasoned arguments and make sound decisions. Here are 5 tips to sharpen your critical thinking skills:
.webp)
- Question Everything (Respectfully): Don't just accept information at face value. Ask questions like "Why is this important?" "What evidence supports this claim?" or "Are there other perspectives to consider?". Develop a healthy skepticism (doubt) but be respectful of others' viewpoints.
- Dig Deeper than Headlines: In today's fast-paced world, headlines can be misleading. Go beyond the surface and seek out credible sources that provide in-depth analysis and evidence. Look for articles from reputable news organizations, academic journals, or books by established experts.
- Embrace Different Viewpoints: Exposing yourself to various perspectives strengthens your critical thinking. Read articles that present opposing viewpoints, watch documentaries that explore different sides of an issue, or engage in respectful discussions with people who hold contrasting opinions.
- Spot Logical Fallacies: Logical fallacies are errors in reasoning that can lead to flawed conclusions. Learn to identify common fallacies like bandwagon appeals (appealing to popularity), ad hominem attacks (attacking the person instead of the argument), or slippery slope arguments (suggesting a small step will lead to a disastrous outcome).
- Practice Makes Progress: Critical thinking is a skill that improves with practice. Engage in activities that encourage analysis and debate. Write persuasive essays, participate in class discussions, or join a debate club. The more you exercise your critical thinking muscles, the stronger they become.
By incorporating these tips into your daily routine, you'll be well on your way to becoming a more critical thinker. Remember, keep questioning things, explore different ideas, and practice your writing!
Drowning in Research and Thesis Statements that Just Don't Click?
Don't waste another minute battling writer's block. EssayPro's expert writers are here to be your research partner!
What is an Example of Critical Thinking?
How do you start writing a critical thinking essay, how to structure a critical thinking essay.

Annie Lambert
specializes in creating authoritative content on marketing, business, and finance, with a versatile ability to handle any essay type and dissertations. With a Master’s degree in Business Administration and a passion for social issues, her writing not only educates but also inspires action. On EssayPro blog, Annie delivers detailed guides and thought-provoking discussions on pressing economic and social topics. When not writing, she’s a guest speaker at various business seminars.

is an expert in nursing and healthcare, with a strong background in history, law, and literature. Holding advanced degrees in nursing and public health, his analytical approach and comprehensive knowledge help students navigate complex topics. On EssayPro blog, Adam provides insightful articles on everything from historical analysis to the intricacies of healthcare policies. In his downtime, he enjoys historical documentaries and volunteering at local clinics.
- Critical thinking and writing . (n.d.). https://studenthub.city.ac.uk/__data/assets/pdf_file/0011/372818/2.-Critical-thinking-guide_FINAL.pdf
- Lane, J. (2023, September 6). Critical thinking for critical writing | SFU Library . Www.lib.sfu.ca . https://www.lib.sfu.ca/about/branches-depts/slc/writing/argumentation/critical-thinking-writing

Developing a Thesis Statement
Many papers you write require developing a thesis statement. In this section you’ll learn what a thesis statement is and how to write one.
Keep in mind that not all papers require thesis statements . If in doubt, please consult your instructor for assistance.
What is a thesis statement?
A thesis statement . . .
- Makes an argumentative assertion about a topic; it states the conclusions that you have reached about your topic.
- Makes a promise to the reader about the scope, purpose, and direction of your paper.
- Is focused and specific enough to be “proven” within the boundaries of your paper.
- Is generally located near the end of the introduction ; sometimes, in a long paper, the thesis will be expressed in several sentences or in an entire paragraph.
- Identifies the relationships between the pieces of evidence that you are using to support your argument.
Not all papers require thesis statements! Ask your instructor if you’re in doubt whether you need one.
Identify a topic
Your topic is the subject about which you will write. Your assignment may suggest several ways of looking at a topic; or it may name a fairly general concept that you will explore or analyze in your paper.
Consider what your assignment asks you to do
Inform yourself about your topic, focus on one aspect of your topic, ask yourself whether your topic is worthy of your efforts, generate a topic from an assignment.
Below are some possible topics based on sample assignments.
Sample assignment 1
Analyze Spain’s neutrality in World War II.
Identified topic
Franco’s role in the diplomatic relationships between the Allies and the Axis
This topic avoids generalities such as “Spain” and “World War II,” addressing instead on Franco’s role (a specific aspect of “Spain”) and the diplomatic relations between the Allies and Axis (a specific aspect of World War II).
Sample assignment 2
Analyze one of Homer’s epic similes in the Iliad.
The relationship between the portrayal of warfare and the epic simile about Simoisius at 4.547-64.
This topic focuses on a single simile and relates it to a single aspect of the Iliad ( warfare being a major theme in that work).
Developing a Thesis Statement–Additional information
Your assignment may suggest several ways of looking at a topic, or it may name a fairly general concept that you will explore or analyze in your paper. You’ll want to read your assignment carefully, looking for key terms that you can use to focus your topic.
Sample assignment: Analyze Spain’s neutrality in World War II Key terms: analyze, Spain’s neutrality, World War II
After you’ve identified the key words in your topic, the next step is to read about them in several sources, or generate as much information as possible through an analysis of your topic. Obviously, the more material or knowledge you have, the more possibilities will be available for a strong argument. For the sample assignment above, you’ll want to look at books and articles on World War II in general, and Spain’s neutrality in particular.
As you consider your options, you must decide to focus on one aspect of your topic. This means that you cannot include everything you’ve learned about your topic, nor should you go off in several directions. If you end up covering too many different aspects of a topic, your paper will sprawl and be unconvincing in its argument, and it most likely will not fulfull the assignment requirements.
For the sample assignment above, both Spain’s neutrality and World War II are topics far too broad to explore in a paper. You may instead decide to focus on Franco’s role in the diplomatic relationships between the Allies and the Axis , which narrows down what aspects of Spain’s neutrality and World War II you want to discuss, as well as establishes a specific link between those two aspects.
Before you go too far, however, ask yourself whether your topic is worthy of your efforts. Try to avoid topics that already have too much written about them (i.e., “eating disorders and body image among adolescent women”) or that simply are not important (i.e. “why I like ice cream”). These topics may lead to a thesis that is either dry fact or a weird claim that cannot be supported. A good thesis falls somewhere between the two extremes. To arrive at this point, ask yourself what is new, interesting, contestable, or controversial about your topic.
As you work on your thesis, remember to keep the rest of your paper in mind at all times . Sometimes your thesis needs to evolve as you develop new insights, find new evidence, or take a different approach to your topic.
Derive a main point from topic
Once you have a topic, you will have to decide what the main point of your paper will be. This point, the “controlling idea,” becomes the core of your argument (thesis statement) and it is the unifying idea to which you will relate all your sub-theses. You can then turn this “controlling idea” into a purpose statement about what you intend to do in your paper.
Look for patterns in your evidence
Compose a purpose statement.
Consult the examples below for suggestions on how to look for patterns in your evidence and construct a purpose statement.
- Franco first tried to negotiate with the Axis
- Franco turned to the Allies when he couldn’t get some concessions that he wanted from the Axis
Possible conclusion:
Spain’s neutrality in WWII occurred for an entirely personal reason: Franco’s desire to preserve his own (and Spain’s) power.
Purpose statement
This paper will analyze Franco’s diplomacy during World War II to see how it contributed to Spain’s neutrality.
- The simile compares Simoisius to a tree, which is a peaceful, natural image.
- The tree in the simile is chopped down to make wheels for a chariot, which is an object used in warfare.
At first, the simile seems to take the reader away from the world of warfare, but we end up back in that world by the end.
This paper will analyze the way the simile about Simoisius at 4.547-64 moves in and out of the world of warfare.
Derive purpose statement from topic
To find out what your “controlling idea” is, you have to examine and evaluate your evidence . As you consider your evidence, you may notice patterns emerging, data repeated in more than one source, or facts that favor one view more than another. These patterns or data may then lead you to some conclusions about your topic and suggest that you can successfully argue for one idea better than another.
For instance, you might find out that Franco first tried to negotiate with the Axis, but when he couldn’t get some concessions that he wanted from them, he turned to the Allies. As you read more about Franco’s decisions, you may conclude that Spain’s neutrality in WWII occurred for an entirely personal reason: his desire to preserve his own (and Spain’s) power. Based on this conclusion, you can then write a trial thesis statement to help you decide what material belongs in your paper.
Sometimes you won’t be able to find a focus or identify your “spin” or specific argument immediately. Like some writers, you might begin with a purpose statement just to get yourself going. A purpose statement is one or more sentences that announce your topic and indicate the structure of the paper but do not state the conclusions you have drawn . Thus, you might begin with something like this:
- This paper will look at modern language to see if it reflects male dominance or female oppression.
- I plan to analyze anger and derision in offensive language to see if they represent a challenge of society’s authority.
At some point, you can turn a purpose statement into a thesis statement. As you think and write about your topic, you can restrict, clarify, and refine your argument, crafting your thesis statement to reflect your thinking.
As you work on your thesis, remember to keep the rest of your paper in mind at all times. Sometimes your thesis needs to evolve as you develop new insights, find new evidence, or take a different approach to your topic.
Compose a draft thesis statement
If you are writing a paper that will have an argumentative thesis and are having trouble getting started, the techniques in the table below may help you develop a temporary or “working” thesis statement.
Begin with a purpose statement that you will later turn into a thesis statement.
Assignment: Discuss the history of the Reform Party and explain its influence on the 1990 presidential and Congressional election.
Purpose Statement: This paper briefly sketches the history of the grassroots, conservative, Perot-led Reform Party and analyzes how it influenced the economic and social ideologies of the two mainstream parties.
Question-to-Assertion
If your assignment asks a specific question(s), turn the question(s) into an assertion and give reasons why it is true or reasons for your opinion.
Assignment : What do Aylmer and Rappaccini have to be proud of? Why aren’t they satisfied with these things? How does pride, as demonstrated in “The Birthmark” and “Rappaccini’s Daughter,” lead to unexpected problems?
Beginning thesis statement: Alymer and Rappaccinni are proud of their great knowledge; however, they are also very greedy and are driven to use their knowledge to alter some aspect of nature as a test of their ability. Evil results when they try to “play God.”
Write a sentence that summarizes the main idea of the essay you plan to write.
Main idea: The reason some toys succeed in the market is that they appeal to the consumers’ sense of the ridiculous and their basic desire to laugh at themselves.
Make a list of the ideas that you want to include; consider the ideas and try to group them.
- nature = peaceful
- war matériel = violent (competes with 1?)
- need for time and space to mourn the dead
- war is inescapable (competes with 3?)
Use a formula to arrive at a working thesis statement (you will revise this later).
- although most readers of _______ have argued that _______, closer examination shows that _______.
- _______ uses _______ and _____ to prove that ________.
- phenomenon x is a result of the combination of __________, __________, and _________.
What to keep in mind as you draft an initial thesis statement
Beginning statements obtained through the methods illustrated above can serve as a framework for planning or drafting your paper, but remember they’re not yet the specific, argumentative thesis you want for the final version of your paper. In fact, in its first stages, a thesis statement usually is ill-formed or rough and serves only as a planning tool.
As you write, you may discover evidence that does not fit your temporary or “working” thesis. Or you may reach deeper insights about your topic as you do more research, and you will find that your thesis statement has to be more complicated to match the evidence that you want to use.
You must be willing to reject or omit some evidence in order to keep your paper cohesive and your reader focused. Or you may have to revise your thesis to match the evidence and insights that you want to discuss. Read your draft carefully, noting the conclusions you have drawn and the major ideas which support or prove those conclusions. These will be the elements of your final thesis statement.
Sometimes you will not be able to identify these elements in your early drafts, but as you consider how your argument is developing and how your evidence supports your main idea, ask yourself, “ What is the main point that I want to prove/discuss? ” and “ How will I convince the reader that this is true? ” When you can answer these questions, then you can begin to refine the thesis statement.
Refine and polish the thesis statement
To get to your final thesis, you’ll need to refine your draft thesis so that it’s specific and arguable.
- Ask if your draft thesis addresses the assignment
- Question each part of your draft thesis
- Clarify vague phrases and assertions
- Investigate alternatives to your draft thesis
Consult the example below for suggestions on how to refine your draft thesis statement.
Sample Assignment
Choose an activity and define it as a symbol of American culture. Your essay should cause the reader to think critically about the society which produces and enjoys that activity.
- Ask The phenomenon of drive-in facilities is an interesting symbol of american culture, and these facilities demonstrate significant characteristics of our society.This statement does not fulfill the assignment because it does not require the reader to think critically about society.
Drive-ins are an interesting symbol of American culture because they represent Americans’ significant creativity and business ingenuity.
Among the types of drive-in facilities familiar during the twentieth century, drive-in movie theaters best represent American creativity, not merely because they were the forerunner of later drive-ins and drive-throughs, but because of their impact on our culture: they changed our relationship to the automobile, changed the way people experienced movies, and changed movie-going into a family activity.
While drive-in facilities such as those at fast-food establishments, banks, pharmacies, and dry cleaners symbolize America’s economic ingenuity, they also have affected our personal standards.
While drive-in facilities such as those at fast- food restaurants, banks, pharmacies, and dry cleaners symbolize (1) Americans’ business ingenuity, they also have contributed (2) to an increasing homogenization of our culture, (3) a willingness to depersonalize relationships with others, and (4) a tendency to sacrifice quality for convenience.
This statement is now specific and fulfills all parts of the assignment. This version, like any good thesis, is not self-evident; its points, 1-4, will have to be proven with evidence in the body of the paper. The numbers in this statement indicate the order in which the points will be presented. Depending on the length of the paper, there could be one paragraph for each numbered item or there could be blocks of paragraph for even pages for each one.
Complete the final thesis statement
The bottom line.
As you move through the process of crafting a thesis, you’ll need to remember four things:
- Context matters! Think about your course materials and lectures. Try to relate your thesis to the ideas your instructor is discussing.
- As you go through the process described in this section, always keep your assignment in mind . You will be more successful when your thesis (and paper) responds to the assignment than if it argues a semi-related idea.
- Your thesis statement should be precise, focused, and contestable ; it should predict the sub-theses or blocks of information that you will use to prove your argument.
- Make sure that you keep the rest of your paper in mind at all times. Change your thesis as your paper evolves, because you do not want your thesis to promise more than your paper actually delivers.
In the beginning, the thesis statement was a tool to help you sharpen your focus, limit material and establish the paper’s purpose. When your paper is finished, however, the thesis statement becomes a tool for your reader. It tells the reader what you have learned about your topic and what evidence led you to your conclusion. It keeps the reader on track–well able to understand and appreciate your argument.

Writing Process and Structure
This is an accordion element with a series of buttons that open and close related content panels.
Getting Started with Your Paper
Interpreting Writing Assignments from Your Courses
Generating Ideas for
Creating an Argument
Thesis vs. Purpose Statements
Architecture of Arguments
Working with Sources
Quoting and Paraphrasing Sources
Using Literary Quotations
Citing Sources in Your Paper
Drafting Your Paper
Generating Ideas for Your Paper
Introductions
Paragraphing
Developing Strategic Transitions
Conclusions
Revising Your Paper
Peer Reviews
Reverse Outlines
Revising an Argumentative Paper
Revision Strategies for Longer Projects
Finishing Your Paper
Twelve Common Errors: An Editing Checklist
How to Proofread your Paper
Writing Collaboratively
Collaborative and Group Writing

Library Guides
Essay writing: criticality and argumentation.
- Criticality and Argumentation
Critical Thinking and Argumentation
Your essay needs to demonstrate some degree of critical thinking and argumentation. The degree will depend on your education level (on a scale from Foundation to Postgraduate) and on the specific essay brief (for example, some assignments, especially in the natural sciences, may not demand you defend an argument).
This page gives you some tips on how to write critically and argue effectively.
Critical Thinking and Writing
It may happen to receive feedback on your essay stating that your writing is too descriptive, not showing enough criticality: "too descriptive", "not supported by enough evidence", "unbalanced", "not presenting enough critical analysis". How to include more criticality in your writing? How to move from mere description to analysis and evaluation?
Consider the differences between descriptive and critical writing:
- Descriptive writing summarises, reports, lists and outlines information, theories and sources.
- Critical writing looks for links between sources, identifies issues, challenges established ideas and considers alternatives.
Critical thinking entails:
- Being objective
- Assessing the quality of information, e.g. looking for weaknesses in arguments in terms of logic and accuracy
- Looking at an idea or data from different perspectives
- Questioning the topic
- Drawing conclusions
- Using good evidence to support your arguments
Check the guide on Critical Thinking and Writing for more information on writing critically.
Argumentation
Presenting and defending an argument with reasons and evidence is a main expectation (and assessment criterion) of most essays. With argumentation you demonstrate critical thinking as you not only understand a topic, but also draw conclusions and formulate a position on it.
What is an argument?
In academic writing, an argument is the reason or set of reasons that demonstrate the validity of a thesis statement.
What is a thesis statement?
The view/position that you defend is called a thesis statement.
Why arguments?
When writing an essay, you are not expected to identify the 'right' answer to the essay question, but to demonstrate that you are familiar with a range of views and are able to develop and defend your own view.
In fact, there my not be a 'right' answer to to an essay question. This relates to the concept that essays often deal with complex, 'ill-structured problems' , which do not bear a right or wrong solution, but better or worse views. The 'better views' are those that are argued with better reasons, evidence and rhetoric.

The handout below looks at the difference between everyday arguments and arguments in academic writing:
- Academic vs. Everyday Arguments An analysis of the similarities and differences between academic arguments and everyday arguments
Thesis Statements
After you analyse the essay question and undertake reading and research you should develop a general view in relation to the essay question/topic. The view that you defend in your essay is called a thesis statement.
Your thesis statement should be:
- Your position on the essay topic
- Developed through your reading
- Expressed in a single sentence
- Provided in the introduction
- Usually following a brief outline of the problem, or issue, addressed by the essay question
- Specific and relevant to the essay question
- Defended with one or more arguments in the body of the essay
A note on thesis statements:
It can feel scary to commit yourself to a thesis statement because thesis statements seem to speak with tremendous certainty! However, consider that your thesis statement may be nuanced - it doesn't have to present an 'extreme', 'black or white' position.
Examples of Thesis Statements
Essay question: ‘Discuss the claim that mass public schooling provides equal access to high quality education.’
Thesis: This essay will argue that while the introduction of mass public schooling was a great advancement in ensuring equal access to education, the influence of socio-economic status on educational attainment has not yet been overcome.
"This essay will argue" → Signposting phrase to introduce your argument
"while mass public schooling was a great advancement in ensuring equal access to education, the influence of socio-economic status on educational attainment has not yet been overcome" → Clearly indicates your position on the issue
Example 2:
Essay question: To what extent is there a 'participation crisis' in UK politics?
Thesis: If we define 'participation' as xyz, it can be argued that there is not in fact a participation crisis in UK politics.
Video on Thesis Statements
Effective Argumentation
To present an effective argument try to provide the following:
- Thesis statement in the introduction
- Evidence in the form of literature, data, research findings etc
- Logic: the thesis statement must be supported logically by the evidence
- Consideration of counter-arguments
- You can present concessions to counter-arguments, but should reject their key points with your evidence/reasoning.
- Confident whenever possible
- Cautious, qualifying, hedging, when there are uncertainties and limitations
Structuring Your Arguments
In defending your thesis statement, you will likely have to break it down into separate issues, or aspects, which are dealt with separately.
In discussing these separate aspects, you might develop smaller thesis statements, which are related to your larger thesis statement .
This means that your essay will have a "tree structure".
Essay tree structure

An example of a more developed tree structure:
Thesis: Digital technology will lead to greater social mistrust and dysfunctionality rather than greater social cohesion
- << Previous: Structure
- Last Updated: Oct 2, 2024 2:29 PM
- URL: https://libguides.westminster.ac.uk/essaywriting
CONNECT WITH US

Writing to Think: Critical Thinking and the Writing Process
“Writing is thinking on paper.” (Zinsser, 1976, p. vii)
Google the term “critical thinking.” How many hits are there? On the day this tutorial was completed, Google found about 65,100,000 results in 0.56 seconds. That’s an impressive number, and it grows more impressively large every day. That’s because the nation’s educators, business leaders, and political representatives worry about the level of critical thinking skills among today’s students and workers.
What is Critical Thinking?
Simply put, critical thinking is sound thinking. Critical thinkers work to delve beneath the surface of sweeping generalizations, biases, clichés, and other quick observations that characterize ineffective thinking. They are willing to consider points of view different from their own, seek and study evidence and examples, root out sloppy and illogical argument, discern fact from opinion, embrace reason over emotion or preference, and change their minds when confronted with compelling reasons to do so. In sum, critical thinkers are flexible thinkers equipped to become active and effective spouses, parents, friends, consumers, employees, citizens, and leaders. Every area of life, in other words, can be positively affected by strong critical thinking.
Released in January 2011, an important study of college students over four years concluded that by graduation “large numbers [of American undergraduates] didn’t learn the critical thinking, complex reasoning and written communication skills that are widely assumed to be at the core of a college education” (Rimer, 2011, para. 1). The University designs curriculum, creates support programs, and hires faculty to help ensure you won’t be one of the students “[showing]no significant gains in . . . ‘higher order’ thinking skills” (Rimer, 2011, para. 4). One way the University works to help you build those skills is through writing projects.
Writing and Critical Thinking
Say the word “writing” and most people think of a completed publication. But say the word “writing” to writers, and they will likely think of the process of composing. Most writers would agree with novelist E. M. Forster, who wrote, “How can I know what I think until I see what I say?” (Forster, 1927, p. 99). Experienced writers know that the act of writing stimulates thinking.
Inexperienced and experienced writers have very different understandings of composition. Novice writers often make the mistake of believing they have to know what they’re going to write before they can begin writing. They often compose a thesis statement before asking questions or conducting research. In the course of their reading, they might even disregard material that counters their pre-formed ideas. This is not writing; it is recording.
In contrast, experienced writers begin with questions and work to discover many different answers before settling on those that are most convincing. They know that the act of putting words on paper or a computer screen helps them invent thought and content. Rather than trying to express what they already think, they express what the act of writing leads them to think as they put down words. More often than not, in other words, experienced writers write their way into ideas, which they then develop, revise, and refine as they go.
What has this notion of writing to do with critical thinking? Everything.
Consider the steps of the writing process: prewriting, outlining, drafting, revising, editing, seeking feedback, and publishing. These steps are not followed in a determined or strict order; instead, the effective writer knows that as they write, it may be necessary to return to an earlier step. In other words, in the process of revision, a writer may realize that the order of ideas is unclear. A new outline may help that writer re-order details. As they write, the writer considers and reconsiders the effectiveness of the work.
The writing process, then, is not just a mirror image of the thinking process: it is the thinking process. Confronted with a topic, an effective critical thinker/writer
- asks questions
- seeks answers
- evaluates evidence
- questions assumptions
- tests hypotheses
- makes inferences
- employs logic
- draws conclusions
- predicts readers’ responses
- creates order
- drafts content
- seeks others’ responses
- weighs feedback
- criticizes their own work
- revises content and structure
- seeks clarity and coherence
Example of Composition as Critical Thinking
“Good writing is fueled by unanswerable questions” (Lane, 1993, p. 15).
Imagine that you have been asked to write about a hero or heroine from history. You must explain what challenges that individual faced and how they conquered them. Now imagine that you decide to write about Rosa Parks and her role in the modern Civil Rights movement. Take a moment and survey what you already know. She refused to get up out of her seat on a bus so a White man could sit in it. She was arrested. As a result, Blacks in Montgomery protested, influencing the Montgomery Bus Boycott. Martin Luther King, Jr. took up leadership of the cause, and ultimately a movement was born.
Is that really all there is to Rosa Parks’s story? What questions might a thoughtful writer ask? Here a few:
- Why did Rosa Parks refuse to get up on that particular day?
- Was hers a spontaneous or planned act of defiance?
- Did she work? Where? Doing what?
- Had any other Black person refused to get up for a White person?
- What happened to that individual or those individuals?
- Why hadn’t that person or those persons received the publicity Parks did?
- Was Parks active in Civil Rights before that day?
- How did she learn about civil disobedience?
Even just these few questions could lead to potentially rich information.
Factual information would not be enough, however, to satisfy an assignment that asks for an interpretation of that information. The writer’s job for the assignment is to convince the reader that Parks was a heroine; in this way the writer must make an argument and support it. The writer must establish standards of heroic behavior. More questions arise:
- What is heroic action?
- What are the characteristics of someone who is heroic?
- What do heroes value and believe?
- What are the consequences of a hero’s actions?
- Why do they matter?
Now the writer has even more research and more thinking to do.
By the time they have raised questions and answered them, raised more questions and answered them, and so on, they are ready to begin writing. But even then, new ideas will arise in the course of planning and drafting, inevitably leading the writer to more research and thought, to more composition and refinement.
Ultimately, every step of the way over the course of composing a project, the writer is engaged in critical thinking because the effective writer examines the work as they develop it.
Why Writing to Think Matters
Writing practice builds critical thinking, which empowers people to “take charge of [their] own minds” so they “can take charge of [their] own lives . . . and improve them, bringing them under [their] self command and direction” (Foundation for Critical Thinking, 2020, para. 12). Writing is a way of coming to know and understand the self and the changing world, enabling individuals to make decisions that benefit themselves, others, and society at large. Your knowledge alone – of law, medicine, business, or education, for example – will not be enough to meet future challenges. You will be tested by new unexpected circumstances, and when they arise, the open-mindedness, flexibility, reasoning, discipline, and discernment you have learned through writing practice will help you meet those challenges successfully.
Forster, E.M. (1927). Aspects of the novel . Harcourt, Brace & Company.
The Foundation for Critical Thinking. (2020, June 17). Our concept and definition of critical thinking . https://www.criticalthinking.org/pages/our-concept-of-critical-thinking/411
Lane, B. (1993). After the end: Teaching and learning creative revision . Heinemann.
Rimer, S. (2011, January 18). Study: Many college students not learning to think critically . The Hechinger Report. https://www.mcclatchydc.com/news/nation-world/national/article24608056.html
Zinsser, W. (1976). On writing well: The classic guide to writing nonfiction . HarperCollins.
Share this:
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window)
- Click to print (Opens in new window)
Follow Blog via Email
Enter your email address to follow this blog and receive email notifications of new posts.
Email Address
- RSS - Posts
- RSS - Comments
- COLLEGE WRITING
- USING SOURCES & APA STYLE
- EFFECTIVE WRITING PODCASTS
- LEARNING FOR SUCCESS
- PLAGIARISM INFORMATION
- FACULTY RESOURCES
- Student Webinar Calendar
- Academic Success Center
- Writing Center
- About the ASC Tutors
- DIVERSITY TRAINING
- PG Peer Tutors
- PG Student Access
Subscribe to Blog via Email
Enter your email address to subscribe to this blog and receive notifications of new posts by email.
- College Writing
- Using Sources & APA Style
- Learning for Success
- Effective Writing Podcasts
- Plagiarism Information
- Faculty Resources
- Tutor Training
Twitter feed
How to Write a Critical Thinking Essay: Examples & Outline
Critical thinking is the process of evaluating and analyzing information. People who use it in everyday life are open to different opinions. They rely on reason and logic when making conclusions about certain issues.
A critical thinking essay shows how your thoughts change as you research your topic. This type of assignment encourages you to learn rather than prove what you already know. In this article, our custom writing team will:
- explain how to write an excellent critical essay;
- introduce 30 great essay topics;
- provide a critical thinking essay example in MLA format.
- 🤔 Critical Thinking Essay Definition
- 💡 Topics & Questions
- ✅ Step-by-Step Guide
- 📑 Essay Example & Formatting Tips
- ✍️ Bonus Tips
🔍 References
🤔 what is a critical thinking essay.
A critical thinking essay is a paper that analyses an issue and reflects on it in order to develop an action plan. Unlike other essay types, it starts with a question instead of a thesis. It helps you develop a broader perspective on a specific issue. Critical writing aims at improving your analytical skills and encourages asking questions.
Critical Thinking in Writing: Importance
When we talk about critical thinking and writing, the word “critical” doesn’t have any negative connotation. It simply implies thorough investigation, evaluation, and analysis of information. Critical thinking allows students to make objective conclusions and present their ideas logically. It also helps them avoid errors in reasoning.
The Basics: 8 Steps of Critical Thinking Psychology
Did you know that the critical thinking process consists of 8 steps? We’ve listed them below. You can try to implement them in your everyday life:
It’s possible that fallacies will occur during the process of critical thinking. Fallacies are errors in reasoning that fail to provide a reasonable conclusion. Here are some common types of fallacies:
- Generalization . It happens when you apply generally factual statements to a specific case.
- Ambiguity . It occurs when the arguments are not clear and are not supported by evidence.
- Appeal to authority . This mistake happens when you claim the statement is valid only because a respected person made it.
- Appeal to emotion . It occurs when you use highly emotive language to convince the audience. Try to stay sensible and rely on the evidence.
- Bifurcation . This mistake occurs when you choose only between two alternatives when more than two exist.
- False analogy . It happens when the examples are poorly connected.
If you want to avoid these mistakes, do the following:
- try not to draw conclusions too quickly,
- be attentive,
- carefully read through all the sources,
- avoid generalizations.
How to Demonstrate Your Critical Thinking in Writing
Critical thinking encourages you to go beyond what you know and study new perspectives. When it comes to demonstrating your critical thinking skills in writing, you can try these strategies:
- Read . Before you start writing an essay, read everything you can find on the subject you are about to cover. Focus on the critical points of your assignment.
- Research . Look up several scholarly sources and study the information in-depth.
- Evaluate . Analyze the sources and the information you’ve gathered. See whether you can disagree with the authors.
- Prove . Explain why you agree or disagree with the authors’ conclusions. Back it up with evidence.
According to Purdue University, logical essay writing is essential when you deal with academic essays. It helps you demonstrate and prove the arguments. Make sure that your paper reaches a logical conclusion.
There are several main concepts related to logic:
If you want your essay to be logical, it’s better to avoid syllogistic fallacies, which happen with certain invalid deductions. If syllogisms are used carelessly, they can lead to false statements and ruin the credibility of your paper.
💡 Critical Thinking Topics & Questions
An excellent critical thinking essay starts with a question. But how do you formulate it properly? Keep reading to find out.
How to Write Critical Thinking Questions: Examples with Answers
Asking the right questions is at the core of critical thinking. They challenge our beliefs and encourage our interest to learn more.
Here are some examples of model questions that prompt critical thinking:
- What does… mean?
- What would happen if…?
- What are the principles of…?
- Why is… important?
- How does… affect…?
- What do you think causes…?
- How are… and… similar/different?
- How do you explain….?
- What are the implications of…?
- What do we already know about…?
Now, let’s look at some critical thinking questions with the answers. You can use these as a model for your own questions:
Question: What would happen if people with higher income paid more taxes?
- Answer: It would help society to prosper and function better. It would also help people out of poverty. This way, everyone can contribute to the economy.
Question: How does eating healthy benefit you?
- Answer: Healthy eating affects people’s lives in many positive ways. It reduces cancer risk, improves your mood and memory, helps with weight loss and diabetes management, and improves your night sleep.
Critical Thinking Essay Topics
Have you already decided what your essay will be about? If not, feel free to use these essay topic examples as titles for your paper or as inspiration. Make sure to choose a theme that interests you personally:
- What are the reasons for racism in healthcare?
- Why is accepting your appearance important?
- Concepts of critical thinking and logical reasoning .
- Nature and spirit in Ralf Waldo Emerson’s poetry.
- How does technological development affect communication in the modern world?
- Social media effect on adolescents.
- Is the representation of children in popular fiction accurate?
- Domestic violence and its consequences.
- Why is mutual aid important in society?
- How do stereotypes affect the way people think?
- The concept of happiness in different cultures.
- The purpose of environmental art.
- Why do people have the need to be praised?
- How did antibiotics change medicine and its development?
- Is there a way to combat inequality in sports?
- Is gun control an effective way of crime prevention?
- How our understanding of love changes through time.
- The use of social media by the older generation.
- Graffiti as a form of modern art.
- Negative health effects of high sugar consumption.
- Why are reality TV shows so popular?
- Why should we eat healthily?
- How effective and fair is the US judicial system?
- Reasons of Cirque du Soleil phenomenon.
- How can police brutality be stopped?
- Freedom of speech: does it exist?
- The effects of vaccination misconceptions.
- How to eliminate New Brunswick’s demographic deficit: action plan.
- What makes a good movie?
- Critical analysis of your favorite book.
- The connection between fashion and identity.
- Taboo topics and how they are discussed in gothic literature.
- Critical thinking essay on the problem of overpopulation.
- Does our lifestyle affect our mental health?
- The role of self-esteem in preventing eating disorders in children.
- Drug abuse among teenagers.
- Rhetoric on assisted suicide.
- Effects of violent video games on children’s mental health.
- Analyze the effect stress has on the productivity of a team member.
- Discuss the importance of the environmental studies.
- Critical thinking and ethics of happy life.
- The effects of human dignity on the promotion of justice.
- Examine the ethics of advertising the tobacco industry.
- Reasons and possible solutions of research misconduct.
- Implication of parental deployment for children.
- Cultural impact of superheroes on the US culture.
- Examine the positive and negative impact of technology on modern society.
- Critical thinking in literature: examples.
- Analyze the impact of COVID-19 pandemic on economic transformation.
- Benefits and drawbacks of mandatory vaccination.
Haven’t found a suitable essay idea? Try using our topic generator !
✅ How to Write a Critical Thinking Essay Step by Step
Now, let’s focus on planning and writing your critical thinking essay. In this section, you will find an essay outline, examples of thesis statements, and a brief overview of each essay part.

Critical Thinking Essay Outline
In a critical thinking essay, there are two main things to consider: a premise and a conclusion :
- A premise is a statement in the argument that explains the reason or supports a conclusion.
- A conclusion indicates what the argument is trying to prove. Each argument can have only one conclusion.
When it comes to structuring, a critical thinking essay is very similar to any other type of essay. Before you start writing it, make sure you know what to include in it. An outline is very helpful when it comes to structuring a paper.
How to Start a Critical Essay Introduction
An introduction gives readers a general idea of an essay’s contents. When you work on the introduction, imagine that you are drawing a map for the reader. It not only marks the final destination but also explains the route.
An introduction usually has 4 functions:
- It catches the reader’s attention;
- It states the essay’s main argument;
- It provides some general information about the topic;
- It shows the importance of the issue in question.
Here are some strategies that can make the introduction writing easier:
- Give an overview of the essay’s topic.
- Express the main idea.
- Define the main terms.
- Outline the issues that you are going to explore or argue about.
- Explain the methodology and why you used it.
- Write a hook to attract the reader’s attention.
Critical Analysis Thesis Statement & Examples
A thesis statement is an integral part of every essay. It keeps the paper organized and guides both the reader and the writer. A good thesis:
- expresses the conclusion or position on a topic;
- justifies your position or opinion with reasoning;
- conveys one idea;
- serves as the essay’s map.
To have a clearer understanding of what a good thesis is, let’s have a look at these examples.
The statement on the left is too general and doesn’t provide any reasoning. The one on the right narrows down the group of people to office workers and specifies the benefits of exercising.
Critical Thinking Essay Body Paragraphs: How to Write
Body paragraphs are the part of the essay where you discuss all the ideas and arguments. In a critical thinking essay, arguments are especially important. When you develop them, make sure that they:
- reflect the key theme;
- are supported by the sources/citations/examples.
Using counter-arguments is also effective. It shows that you acknowledge different points of view and are not easily persuaded.
In addition to your arguments, it’s essential to present the evidence . Demonstrate your critical thinking skills by analyzing each source and stating whether the author’s position is valid.
To make your essay logically flow, you may use transitions such as:
- Accordingly,
- For instance,
- On the contrary,
- In conclusion,
- Not only… but also,
- Undoubtedly.
How to Write a Critical Thinking Conclusion
In a critical thinking essay, the notion of “conclusion” is tightly connected to the one used in logic. A logical conclusion is a statement that specifies the author’s point of view or what the essay argues about. Each argument can have only one logical conclusion.
Sometimes they can be confused with premises. Remember that premises serve as a support for the conclusion. Unlike the conclusion, there can be several premises in a single argument. You can learn more about these concepts from the article on a logical consequence by Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy.
Keeping this in mind, have a look at these tips for finishing your essay:
- Briefly sum up the main points.
- Provide a final thought on the issue.
- Suggest some results or consequences.
- Finish up with a call for action.
📑 Critical Thinking Essays Examples & Formatting Tips
Formatting is another crucial aspect of every formal paper. MLA and APA are two popular formats when it comes to academic writing. They share some similarities but overall are still two different styles. Here are critical essay format guidelines that you can use as a reference:
Finally, you’re welcome to check out a full critical essay sample in MLA format. Download the PDF file below:
Currently, the importance of critical thinking has grown rapidly because technological progress has led to expanded access to various content-making platforms: websites, online news agencies, and podcasts with, often, low-quality information. Fake news is used to achieve political and financial aims, targeting people with low news literacy. However, individuals can stop spreading fallacies by detecting false agendas with the help of a skeptical attitude.
✍️ Bonus Tips: Critical Thinking and Writing Exercises
Critical thinking is a process different from our regular thinking. When we think in everyday life, we do it automatically. However, when we’re thinking critically, we do it deliberately.
So how do we get better at this type of thinking and make it a habit? These useful tips will help you do it:
- Ask basic questions. Sometimes, while we are doing research, the explanation becomes too complicated. To avoid it, always go back to your topic.
- Question basic assumptions. When thinking through a problem, ask yourself whether your beliefs can be wrong. Keep an open mind while researching your question.
- Think for yourself. Avoid getting carried away in the research and buying into other people’s opinions.
- Reverse things. Sometimes it seems obvious that one thing causes another, but what if it’s the other way around?
- Evaluate existing evidence. If you work with sources, it’s crucial to evaluate and question them.
Another way to improve your reasoning skills is to do critical thinking exercises. Here are some of them:
Thanks for reading through our article! We hope that you found it helpful and learned some new information. If you liked it, feel free to share it with your friends.
Further reading:
- Critical Writing: Examples & Brilliant Tips [2024]
- How to Write a Rhetorical Analysis Essay: Outline, Steps, & Examples
- How to Write an Analysis Essay: Examples + Writing Guide
- How to Write a Critique Paper: Tips + Critique Essay Examples
- How to Write a Literary Analysis Essay Step by Step
- Critical Thinking and Writing: University of Kent
- Steps to Critical Thinking: Rasmussen University
- 3 Simple Habits to Improve Your Critical Thinking: Harvard Business Review
- In-Class Writing Exercises: University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
- Demonstrating Critical Thinking in Writing: University of South Australia
- 15 Questions that Teachers and Parents Can Ask Kids to Encourage Critical Thinking: The Hun School
- Questions to Provoke Critical Thinking: Brown University
- How to Write a College Critical Thinking Essay: Seattle PI
- Introductions: What They Do: Royal Literary Fund
- Thesis Statements: Arizona State University
- Share to Facebook
- Share to LinkedIn
- Share to email

Process analysis is an explanation of how something works or happens. Want to know more? Read the following article prepared by our custom writing specialists and learn about: So, let’s start digging deeper into this topic! ♻️ What Is Process Analysis? A process analysis describes and explains the succession of...

A visual analysis essay is an academic paper type that history and art students often deal with. It consists of a detailed description of an image or object. It can also include an interpretation or an argument that is supported by visual evidence. In this article, our custom writing experts...

Want to know how to write a reflection paper for college or school? To do that, you need to connect your personal experiences with theoretical knowledge. Usually, students are asked to reflect on a documentary, a text, or their experience. Sometimes one needs to write a paper about a lesson...

A character analysis is an examination of the personalities and actions of protagonists and antagonists that make up a story. It discusses their role in the story, evaluates their traits, and looks at their conflicts and experiences. You might need to write this assignment in school or college. Like any...

Any literary analysis is a challenging task since literature includes many elements that can be interpreted differently. However, a stylistic analysis of all the figurative language the poets use may seem even harder. You may never realize what the author actually meant and how to comment on it! While analyzing...

As a student, you may be asked to write a book review. Unlike an argumentative essay, a book review is an opportunity to convey the central theme of a story while offering a new perspective on the author’s ideas. Knowing how to create a well-organized and coherent review, however, is...

The difference between an argumentative and persuasive essay isn’t always clear. If you’re struggling with either style for your next assignment, don’t worry. The following will clarify everything you need to know so you can write with confidence. First, we define the primary objectives of argumentative vs. persuasive writing. We...

You don’t need to be a nerd to understand the general idea behind cause and effect essays. Let’s see! If you skip a meal, you get hungry. And if you write an essay about it, your goal is achieved! However, following multiple rules of academic writing can be a tough...
![thesis statement and critical thinking How to Write an Argumentative Essay: 101 Guide [+ Examples]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2021/01/young-writer-taking-notes-284x153.jpg)
An argumentative essay is a genre of academic writing that investigates different sides of a particular issue. Its central purpose is to inform the readers rather than expressively persuade them. Thus, it is crucial to differentiate between argumentative and persuasive essays. While composing an argumentative essay, the students have to...
![thesis statement and critical thinking How to Title an Essay: Guide with Creative Examples [2024]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2021/01/close-up-woman-making-greeting-card-new-year-christmas-2021-friends-family-scrap-booking-diy-writing-letter-with-best-wishes-design-her-homemade-card-holidays-celebration-284x153.jpg)
It’s not a secret that the reader notices an essay title first. No catchy hook or colorful examples attract more attention from a quick glance. Composing a creative title for your essay is essential if you strive to succeed, as it: Thus, how you name your paper is of the...

The conclusion is the last paragraph in your paper that draws the ideas and reasoning together. However, its purpose does not end there. A definite essay conclusion accomplishes several goals: Therefore, a conclusion usually consists of: Our experts prepared this guide, where you will find great tips on how to...
![thesis statement and critical thinking How to Write a Good Introduction: Examples & Tips [2024 Upd.]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2021/01/closeup-shot-woman-working-studying-from-home-with-red-coffee-cup-nearby-284x153.jpg)
A five-paragraph essay is one of the most common academic assignments a student may face. It has a well-defined structure: an introduction, three body paragraphs, and a conclusion. Writing an introduction can be the most challenging part of the entire piece. It aims to introduce the main ideas and present...
Welcome to the new OASIS website! We have academic skills, library skills, math and statistics support, and writing resources all together in one new home.

- Walden University
- Faculty Portal
Writing a Paper: Thesis Statements
Basics of thesis statements.
The thesis statement is the brief articulation of your paper's central argument and purpose. You might hear it referred to as simply a "thesis." Every scholarly paper should have a thesis statement, and strong thesis statements are concise, specific, and arguable. Concise means the thesis is short: perhaps one or two sentences for a shorter paper. Specific means the thesis deals with a narrow and focused topic, appropriate to the paper's length. Arguable means that a scholar in your field could disagree (or perhaps already has!).
Strong thesis statements address specific intellectual questions, have clear positions, and use a structure that reflects the overall structure of the paper. Read on to learn more about constructing a strong thesis statement.
Being Specific
This thesis statement has no specific argument:
Needs Improvement: In this essay, I will examine two scholarly articles to find similarities and differences.
This statement is concise, but it is neither specific nor arguable—a reader might wonder, "Which scholarly articles? What is the topic of this paper? What field is the author writing in?" Additionally, the purpose of the paper—to "examine…to find similarities and differences" is not of a scholarly level. Identifying similarities and differences is a good first step, but strong academic argument goes further, analyzing what those similarities and differences might mean or imply.
Better: In this essay, I will argue that Bowler's (2003) autocratic management style, when coupled with Smith's (2007) theory of social cognition, can reduce the expenses associated with employee turnover.
The new revision here is still concise, as well as specific and arguable. We can see that it is specific because the writer is mentioning (a) concrete ideas and (b) exact authors. We can also gather the field (business) and the topic (management and employee turnover). The statement is arguable because the student goes beyond merely comparing; he or she draws conclusions from that comparison ("can reduce the expenses associated with employee turnover").
Making a Unique Argument
This thesis draft repeats the language of the writing prompt without making a unique argument:
Needs Improvement: The purpose of this essay is to monitor, assess, and evaluate an educational program for its strengths and weaknesses. Then, I will provide suggestions for improvement.
You can see here that the student has simply stated the paper's assignment, without articulating specifically how he or she will address it. The student can correct this error simply by phrasing the thesis statement as a specific answer to the assignment prompt.
Better: Through a series of student interviews, I found that Kennedy High School's antibullying program was ineffective. In order to address issues of conflict between students, I argue that Kennedy High School should embrace policies outlined by the California Department of Education (2010).
Words like "ineffective" and "argue" show here that the student has clearly thought through the assignment and analyzed the material; he or she is putting forth a specific and debatable position. The concrete information ("student interviews," "antibullying") further prepares the reader for the body of the paper and demonstrates how the student has addressed the assignment prompt without just restating that language.
Creating a Debate
This thesis statement includes only obvious fact or plot summary instead of argument:
Needs Improvement: Leadership is an important quality in nurse educators.
A good strategy to determine if your thesis statement is too broad (and therefore, not arguable) is to ask yourself, "Would a scholar in my field disagree with this point?" Here, we can see easily that no scholar is likely to argue that leadership is an unimportant quality in nurse educators. The student needs to come up with a more arguable claim, and probably a narrower one; remember that a short paper needs a more focused topic than a dissertation.
Better: Roderick's (2009) theory of participatory leadership is particularly appropriate to nurse educators working within the emergency medicine field, where students benefit most from collegial and kinesthetic learning.
Here, the student has identified a particular type of leadership ("participatory leadership"), narrowing the topic, and has made an arguable claim (this type of leadership is "appropriate" to a specific type of nurse educator). Conceivably, a scholar in the nursing field might disagree with this approach. The student's paper can now proceed, providing specific pieces of evidence to support the arguable central claim.
Choosing the Right Words
This thesis statement uses large or scholarly-sounding words that have no real substance:
Needs Improvement: Scholars should work to seize metacognitive outcomes by harnessing discipline-based networks to empower collaborative infrastructures.
There are many words in this sentence that may be buzzwords in the student's field or key terms taken from other texts, but together they do not communicate a clear, specific meaning. Sometimes students think scholarly writing means constructing complex sentences using special language, but actually it's usually a stronger choice to write clear, simple sentences. When in doubt, remember that your ideas should be complex, not your sentence structure.
Better: Ecologists should work to educate the U.S. public on conservation methods by making use of local and national green organizations to create a widespread communication plan.
Notice in the revision that the field is now clear (ecology), and the language has been made much more field-specific ("conservation methods," "green organizations"), so the reader is able to see concretely the ideas the student is communicating.
Leaving Room for Discussion
This thesis statement is not capable of development or advancement in the paper:
Needs Improvement: There are always alternatives to illegal drug use.
This sample thesis statement makes a claim, but it is not a claim that will sustain extended discussion. This claim is the type of claim that might be appropriate for the conclusion of a paper, but in the beginning of the paper, the student is left with nowhere to go. What further points can be made? If there are "always alternatives" to the problem the student is identifying, then why bother developing a paper around that claim? Ideally, a thesis statement should be complex enough to explore over the length of the entire paper.
Better: The most effective treatment plan for methamphetamine addiction may be a combination of pharmacological and cognitive therapy, as argued by Baker (2008), Smith (2009), and Xavier (2011).
In the revised thesis, you can see the student make a specific, debatable claim that has the potential to generate several pages' worth of discussion. When drafting a thesis statement, think about the questions your thesis statement will generate: What follow-up inquiries might a reader have? In the first example, there are almost no additional questions implied, but the revised example allows for a good deal more exploration.
Thesis Mad Libs
If you are having trouble getting started, try using the models below to generate a rough model of a thesis statement! These models are intended for drafting purposes only and should not appear in your final work.
- In this essay, I argue ____, using ______ to assert _____.
- While scholars have often argued ______, I argue______, because_______.
- Through an analysis of ______, I argue ______, which is important because_______.
Words to Avoid and to Embrace
When drafting your thesis statement, avoid words like explore, investigate, learn, compile, summarize , and explain to describe the main purpose of your paper. These words imply a paper that summarizes or "reports," rather than synthesizing and analyzing.
Instead of the terms above, try words like argue, critique, question , and interrogate . These more analytical words may help you begin strongly, by articulating a specific, critical, scholarly position.
Read Kayla's blog post for tips on taking a stand in a well-crafted thesis statement.
Related Resources
Didn't find what you need? Email us at [email protected] .
- Previous Page: Introductions
- Next Page: Conclusions
- Office of Student Disability Services
Walden Resources
Departments.
- Academic Residencies
- Academic Skills
- Career Planning and Development
- Customer Care Team
- Field Experience
- Military Services
- Student Success Advising
- Writing Skills
Centers and Offices
- Center for Social Change
- Office of Academic Support and Instructional Services
- Office of Degree Acceleration
- Office of Research and Doctoral Services
- Office of Student Affairs
Student Resources
- Doctoral Writing Assessment
- Form & Style Review
- Quick Answers
- ScholarWorks
- SKIL Courses and Workshops
- Walden Bookstore
- Walden Catalog & Student Handbook
- Student Safety/Title IX
- Legal & Consumer Information
- Website Terms and Conditions
- Cookie Policy
- Accessibility
- Accreditation
- State Authorization
- Net Price Calculator
- Cost of Attendance
- Contact Walden
Walden University is a member of Adtalem Global Education, Inc. www.adtalem.com Walden University is certified to operate by SCHEV © 2024 Walden University LLC. All rights reserved.
25 Thesis Statement Examples

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
Learn about our Editorial Process
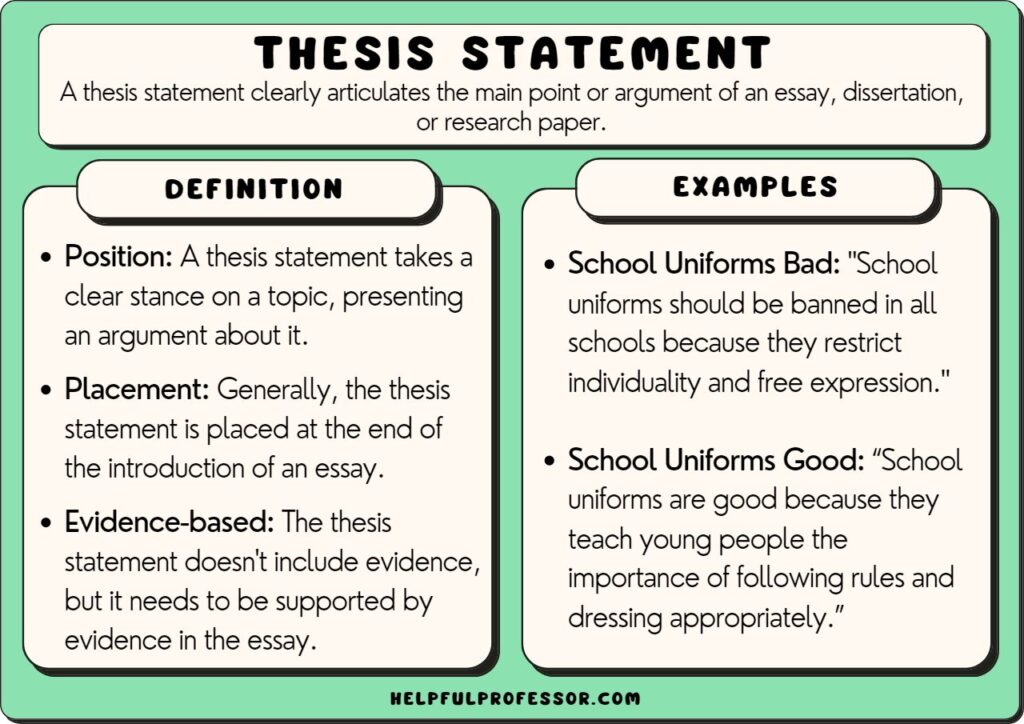
A thesis statement is needed in an essay or dissertation . There are multiple types of thesis statements – but generally we can divide them into expository and argumentative. An expository statement is a statement of fact (common in expository essays and process essays) while an argumentative statement is a statement of opinion (common in argumentative essays and dissertations). Below are examples of each.
Strong Thesis Statement Examples

1. School Uniforms
“Mandatory school uniforms should be implemented in educational institutions as they promote a sense of equality, reduce distractions, and foster a focused and professional learning environment.”
Best For: Argumentative Essay or Debate
Read More: School Uniforms Pros and Cons

2. Nature vs Nurture
“This essay will explore how both genetic inheritance and environmental factors equally contribute to shaping human behavior and personality.”
Best For: Compare and Contrast Essay
Read More: Nature vs Nurture Debate

3. American Dream
“The American Dream, a symbol of opportunity and success, is increasingly elusive in today’s socio-economic landscape, revealing deeper inequalities in society.”
Best For: Persuasive Essay
Read More: What is the American Dream?

4. Social Media
“Social media has revolutionized communication and societal interactions, but it also presents significant challenges related to privacy, mental health, and misinformation.”
Best For: Expository Essay
Read More: The Pros and Cons of Social Media

5. Globalization
“Globalization has created a world more interconnected than ever before, yet it also amplifies economic disparities and cultural homogenization.”
Read More: Globalization Pros and Cons

6. Urbanization
“Urbanization drives economic growth and social development, but it also poses unique challenges in sustainability and quality of life.”
Read More: Learn about Urbanization

7. Immigration
“Immigration enriches receiving countries culturally and economically, outweighing any perceived social or economic burdens.”
Read More: Immigration Pros and Cons

8. Cultural Identity
“In a globalized world, maintaining distinct cultural identities is crucial for preserving cultural diversity and fostering global understanding, despite the challenges of assimilation and homogenization.”
Best For: Argumentative Essay
Read More: Learn about Cultural Identity

9. Technology
“Medical technologies in care institutions in Toronto has increased subjcetive outcomes for patients with chronic pain.”
Best For: Research Paper

10. Capitalism vs Socialism
“The debate between capitalism and socialism centers on balancing economic freedom and inequality, each presenting distinct approaches to resource distribution and social welfare.”

11. Cultural Heritage
“The preservation of cultural heritage is essential, not only for cultural identity but also for educating future generations, outweighing the arguments for modernization and commercialization.”
12. Pseudoscience
“Pseudoscience, characterized by a lack of empirical support, continues to influence public perception and decision-making, often at the expense of scientific credibility.”
Read More: Examples of Pseudoscience

13. Free Will
“The concept of free will is largely an illusion, with human behavior and decisions predominantly determined by biological and environmental factors.”
Read More: Do we have Free Will?

14. Gender Roles
“Traditional gender roles are outdated and harmful, restricting individual freedoms and perpetuating gender inequalities in modern society.”
Read More: What are Traditional Gender Roles?

15. Work-Life Ballance
“The trend to online and distance work in the 2020s led to improved subjective feelings of work-life balance but simultaneously increased self-reported loneliness.”
Read More: Work-Life Balance Examples
16. Universal Healthcare
“Universal healthcare is a fundamental human right and the most effective system for ensuring health equity and societal well-being, outweighing concerns about government involvement and costs.”
Read More: The Pros and Cons of Universal Healthcare

17. Minimum Wage
“The implementation of a fair minimum wage is vital for reducing economic inequality, yet it is often contentious due to its potential impact on businesses and employment rates.”
Read More: The Pros and Cons of Raising the Minimum Wage

18. Homework
“The homework provided throughout this semester has enabled me to achieve greater self-reflection, identify gaps in my knowledge, and reinforce those gaps through spaced repetition.”
Best For: Reflective Essay
Read More: Reasons Homework Should be Banned

19. Charter Schools
“Charter schools offer alternatives to traditional public education, promising innovation and choice but also raising questions about accountability and educational equity.”
Read More: The Pros and Cons of Charter Schools

20. Effects of the Internet
“The Internet has drastically reshaped human communication, access to information, and societal dynamics, generally with a net positive effect on society.”
Read More: The Pros and Cons of the Internet

21. Affirmative Action
“Affirmative action is essential for rectifying historical injustices and achieving true meritocracy in education and employment, contrary to claims of reverse discrimination.”
Best For: Essay
Read More: Affirmative Action Pros and Cons

22. Soft Skills
“Soft skills, such as communication and empathy, are increasingly recognized as essential for success in the modern workforce, and therefore should be a strong focus at school and university level.”
Read More: Soft Skills Examples

23. Moral Panic
“Moral panic, often fueled by media and cultural anxieties, can lead to exaggerated societal responses that sometimes overlook rational analysis and evidence.”
Read More: Moral Panic Examples

24. Freedom of the Press
“Freedom of the press is critical for democracy and informed citizenship, yet it faces challenges from censorship, media bias, and the proliferation of misinformation.”
Read More: Freedom of the Press Examples

25. Mass Media
“Mass media shapes public opinion and cultural norms, but its concentration of ownership and commercial interests raise concerns about bias and the quality of information.”
Best For: Critical Analysis
Read More: Mass Media Examples
Checklist: How to use your Thesis Statement
✅ Position: If your statement is for an argumentative or persuasive essay, or a dissertation, ensure it takes a clear stance on the topic. ✅ Specificity: It addresses a specific aspect of the topic, providing focus for the essay. ✅ Conciseness: Typically, a thesis statement is one to two sentences long. It should be concise, clear, and easily identifiable. ✅ Direction: The thesis statement guides the direction of the essay, providing a roadmap for the argument, narrative, or explanation. ✅ Evidence-based: While the thesis statement itself doesn’t include evidence, it sets up an argument that can be supported with evidence in the body of the essay. ✅ Placement: Generally, the thesis statement is placed at the end of the introduction of an essay.
Try These AI Prompts – Thesis Statement Generator!
One way to brainstorm thesis statements is to get AI to brainstorm some for you! Try this AI prompt:
💡 AI PROMPT FOR EXPOSITORY THESIS STATEMENT I am writing an essay on [TOPIC] and these are the instructions my teacher gave me: [INSTUCTIONS]. I want you to create an expository thesis statement that doesn’t argue a position, but demonstrates depth of knowledge about the topic.
💡 AI PROMPT FOR ARGUMENTATIVE THESIS STATEMENT I am writing an essay on [TOPIC] and these are the instructions my teacher gave me: [INSTRUCTIONS]. I want you to create an argumentative thesis statement that clearly takes a position on this issue.
💡 AI PROMPT FOR COMPARE AND CONTRAST THESIS STATEMENT I am writing a compare and contrast essay that compares [Concept 1] and [Concept2]. Give me 5 potential single-sentence thesis statements that remain objective.

- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 10 Reasons you’re Perpetually Single
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 20 Montessori Toddler Bedrooms (Design Inspiration)
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 21 Montessori Homeschool Setups
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 101 Hidden Talents Examples
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Developing Strong Thesis Statements

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
The thesis statement or main claim must be debatable
An argumentative or persuasive piece of writing must begin with a debatable thesis or claim. In other words, the thesis must be something that people could reasonably have differing opinions on. If your thesis is something that is generally agreed upon or accepted as fact then there is no reason to try to persuade people.
Example of a non-debatable thesis statement:
This thesis statement is not debatable. First, the word pollution implies that something is bad or negative in some way. Furthermore, all studies agree that pollution is a problem; they simply disagree on the impact it will have or the scope of the problem. No one could reasonably argue that pollution is unambiguously good.
Example of a debatable thesis statement:
This is an example of a debatable thesis because reasonable people could disagree with it. Some people might think that this is how we should spend the nation's money. Others might feel that we should be spending more money on education. Still others could argue that corporations, not the government, should be paying to limit pollution.
Another example of a debatable thesis statement:
In this example there is also room for disagreement between rational individuals. Some citizens might think focusing on recycling programs rather than private automobiles is the most effective strategy.
The thesis needs to be narrow
Although the scope of your paper might seem overwhelming at the start, generally the narrower the thesis the more effective your argument will be. Your thesis or claim must be supported by evidence. The broader your claim is, the more evidence you will need to convince readers that your position is right.
Example of a thesis that is too broad:
There are several reasons this statement is too broad to argue. First, what is included in the category "drugs"? Is the author talking about illegal drug use, recreational drug use (which might include alcohol and cigarettes), or all uses of medication in general? Second, in what ways are drugs detrimental? Is drug use causing deaths (and is the author equating deaths from overdoses and deaths from drug related violence)? Is drug use changing the moral climate or causing the economy to decline? Finally, what does the author mean by "society"? Is the author referring only to America or to the global population? Does the author make any distinction between the effects on children and adults? There are just too many questions that the claim leaves open. The author could not cover all of the topics listed above, yet the generality of the claim leaves all of these possibilities open to debate.
Example of a narrow or focused thesis:
In this example the topic of drugs has been narrowed down to illegal drugs and the detriment has been narrowed down to gang violence. This is a much more manageable topic.
We could narrow each debatable thesis from the previous examples in the following way:
Narrowed debatable thesis 1:
This thesis narrows the scope of the argument by specifying not just the amount of money used but also how the money could actually help to control pollution.
Narrowed debatable thesis 2:
This thesis narrows the scope of the argument by specifying not just what the focus of a national anti-pollution campaign should be but also why this is the appropriate focus.
Qualifiers such as " typically ," " generally ," " usually ," or " on average " also help to limit the scope of your claim by allowing for the almost inevitable exception to the rule.
Types of claims
Claims typically fall into one of four categories. Thinking about how you want to approach your topic, or, in other words, what type of claim you want to make, is one way to focus your thesis on one particular aspect of your broader topic.
Claims of fact or definition: These claims argue about what the definition of something is or whether something is a settled fact. Example:
Claims of cause and effect: These claims argue that one person, thing, or event caused another thing or event to occur. Example:
Claims about value: These are claims made of what something is worth, whether we value it or not, how we would rate or categorize something. Example:
Claims about solutions or policies: These are claims that argue for or against a certain solution or policy approach to a problem. Example:
Which type of claim is right for your argument? Which type of thesis or claim you use for your argument will depend on your position and knowledge of the topic, your audience, and the context of your paper. You might want to think about where you imagine your audience to be on this topic and pinpoint where you think the biggest difference in viewpoints might be. Even if you start with one type of claim you probably will be using several within the paper. Regardless of the type of claim you choose to utilize it is key to identify the controversy or debate you are addressing and to define your position early on in the paper.
Critical Thinking Essay: A Complete Student Guide
- Icon Calendar 30 June 2024
- Icon Page 4044 words
- Icon Clock 19 min read
Essay writing is an integral academic exercise for students in higher educational institutions. As an example of different paper types, a critical thinking essay requires people to employ analytical and reflective writing skills. In essence, these skills underscore essential features of such an essay: analysis of information, reflection on key findings, a review of information’s relevance, and an identification of any conclusions made by an author(s) or other scholars. Hence, a critical thinking paper is a specific type of writing that requires learners to read documents and make interpretations from their points of view. In turn, people need to learn how to write these essays to master their analytical, creative, and reflective skills.
General Guidelines
Critical thinking is an essential skill, particularly for students who need to analyze and interpret data. In turn, a real essence of such a skill is that learners confront issues every day that require them to make prompt decisions. Moreover, it is a unique mechanism by which individuals arrive at these decisions. Therefore, a critical thinking essay is a document that allows students to address an issue holistically. Then, it means addressing issues in an essay format by using critical thinking skills from different perspectives, highlighting possible alternatives, and making well-thought-out decisions. To a target audience, such a text makes it easy to understand a writer’s message and either agree or disagree with it. Besides, a particular decision to agree or disagree is based on a writer’s information regarding an issue in question. Hence, this is why authors of such essays need to provide details that make their arguments stronger and more palatable to an intended audience.
What Is a Critical Thinking Essay and Its Purpose
According to its definition, a critical thinking essay is an academic writing form that challenges students to analyze, evaluate, and synthesize information to form a reasoned argument or perspective. The main purpose of writing a critical thinking essay is to encourage a deeper understanding and engagement with a topic at hand and allow students to question assumptions, recognize different viewpoints, and articulate their own reasoned conclusions (Atkins & Carver, 2022). Further on, learners enhance their ability to think logically and argue persuasively, skills that are valuable not only in academic contexts but also in everyday decision-making and problem-solving. Moreover, common elements of critical thinking include analysis, evaluation, explanation, and logical conclusion (Thurman & Gary, 2020). As a result, such a composition shapes a reflective and analytical mindset, preparing people for complex real-world and problem-solving situations. In terms of pages and words, a typical length of writing a critical thinking essay depends on an academic level, course, professor, and specific assignment criteria, while general guidelines are:
High School:
- Length: 2-4 pages
- Word Count: 500-1,000 words
- Length: 3-5 pages
- Word Count: 750-1,250 words
University (Undergraduate):
- Length: 5-8 pages
- Word Count: 1,250-2,000 words
Master’s:
- Length: 8-12 pages
- Word Count: 2,000-3,000 words
- Length: 15-20 pages
- Word Count: 3,750-5,000 words

Writing Format
Note: Some sections in a critical thinking essay can be added, deleted, or combined with each other. In turn, its typical structure in writing includes an introduction with a thesis statement, body paragraphs with evidence, explanation, and analysis, counterarguments with refutations, and a conclusion that summarizes key points and restates a thesis.
Characteristics
When writing a critical thinking essay, people should address several essential features. Firstly, authors need to reflect on what they have read, meaning taking time to consider specific information’s relevance (Larsson, 2019). In essence, such an attitude helps them to make strong arguments in defense of their points of view. Secondly, learners need to analyze how this information is presented and state whether it is sufficient or needs improvement. Thirdly, they need to review observed information based on previous knowledge (Southworth, 2022). Here, they should say whether this information advances a concept or theory or contradicts existing knowledge. Finally, scholars need to identify a final conclusion reached by an author(s) of reviewed information and support or challenge it. In turn, some examples of sentence starters for beginning a critical thinking essay are:
- In recent discussions about [topic/theme], a current controversial issue involves whether [specific aspect], with various scholars arguing both for and against this perspective based on differing evidence and interpretations.
- The phenomenon of [topic] raises important questions about [related issue], prompting a need to critically examine the underlying causes and broader implications for [field or society].
- As [author/expert] argues in [source’s title], the implications of [topic] require a deeper analysis of possible factors that contribute to an ongoing debate on [related aspect].
- A primary purpose of this essay is to examine the impact of [topic] on [specific group or field] and explore how different viewpoints and evidence shape a current understanding of [issue].
- In addressing the complexities of [topic], it is essential to consider a historical context, key arguments, and counterarguments to fully appreciate that [theme] is a solution to a current discourse.
- Understanding [topic] requires more analysis of underlying factors, such as [factor 1], [factor 2], and [factor 3], each of which plays a crucial role in shaping a current discussion.
- A particular debate surrounding [topic] often centers on an issue of [specific aspect], with proponents and opponents offering contrasting perspectives that cannot be used as a single solution.
- A critical aspect of [topic] that warrants further analysis is [specific aspect], as it reveals significant implications for [related issue].
- To fully grasp an actual significance of [topic], one must first explore historical developments and key arguments that have shaped a current understanding and ongoing debates on [issue].
- In light of recent developments in [field], a hot discussion of [topic] has become increasingly relevant because it highlights a current importance of an issue and a need for a critical examination of its broader impact on [aspect].
How to Identify
Based on essential features described above, students can tell whether an essay they are writing is a critical thinking paper. Ideally, learners can know their papers are critical thinking essays if prompt requirements require them to read and analyze a text. Basically, an analysis process includes reflecting on an assigned text, commenting on how information is presented and its relation to previous knowledge, and supporting or challenging a final conclusion made (Butler, 2024). In principle, these requirements reflect defining features of such essays. A a result, to think critically, people systematically question assumptions, evaluate evidence, consider multiple perspectives, and reason logically to formulate well-supported conclusions.
A critical thinking paper differs fundamentally from other types of essays because it requires a student to read a text, such as a book or a poem, and analyze it using a writer’s perspective. Moreover, some instructions need people to analyze a film. In other words, writing a critical thinking essay emphasizes a learner’s understanding of information with a specific meaning of what a person has read, watched, or heard (Nosich, 2022). Indeed, it is a central point of difference from other types of papers that require people to refrain from personal viewpoints. Then, this feature means instructors grade such papers based on a writer’s ability to develop a coherent argument and use essential writing skills. As such, one can argue a critical thinking essay is a form of an argumentative essay.
Prompt Examples for Critical Thinking
Identify Communication Differences Between Men and Women
Under this prompt example, a student’s task is to read texts that talk about how men and women communicate and identify the differences. Hence, writers should analyze what they have read and summarize it via concise statements or arguments.
Discuss Drug Use in Sports
Under this prompt example, a student’s task is to research texts, such as research journal articles and government reports, that address a particular problem of drug use in sports and summarize their findings.
Explore an Anti-Meth Campaign
Under this prompt example, a student’s task is to read widely about anti-meth campaigns and provide an in-depth analysis of their impacts. By reading an essay, a target audience should understand whether specific campaigns have been effective or ineffective.
Describe Homelessness and Its Social Impacts
Under this prompt example, a student’s task is to read texts about homelessness, such as journal articles and reports by governments and other humanitarian organizations, and explain root causes and social implications of homelessness.
Analyze a History of College Football in the United States
Under this prompt example, a student’s task is to read documents, such as books and media articles, narrating college football history in the United States. After writing a whole essay, a target audience should identify specific challenges that college football has faced in its development in a country.
Define Health Effects of Obesity
Under this prompt example, a student’s task is to read research studies and medical reports discussing obesity. In turn, an essay should explain specific causes of obesity and corresponding risks that obese individuals face.
Review a Significance of Street Art and Graffiti
Under this prompt example, a student’s task is to read texts discussing an entire evolution of street art and graffiti and make compelling arguments as to why they are essential features of modern art.
Sports on Television: Is It Necessary?
Under this prompt example, a student’s task is to explain why television has become an essential platform for sports and how it undermines or helps advance its social and cultural significance.
What Is an Essence of Multicultural Identity?
Under this prompt example, a student’s task is to explore a phenomenon of multiculturalism that has become notable and acceptable in modern society and explain its significance.
Examine a Relevance of Body Size in Modeling
Under this prompt example, a student’s task is to explore a modeling profession and explain why body size matters. In other words, a complete essay should make a case as to why a model should have a particular body size.
Write About Understanding Multicultural Families
Under this prompt example, a student’s task is to explore multicultural families by reading texts that address a unique issue from a research or commentary perspective and summarize its leading arguments.
Changing Gender Roles: What It Means for Traditionalists?
Under this prompt example, a student’s task is to explore gender roles from a historical and present perspective and discuss how they threaten or cement traditional views about common roles of men and women.
What Is Ethnic Music, and Does It Matter in a Multicultural Society?
Under this prompt example, a student’s task is to study multiculturalism and identify how ethnic music is a significant characteristic.
Explain American Society and Latino’s Influence
Under this prompt example, a student’s task is to study contemporary American society’s characteristics and indicate a specific extent to which Latinos and their culture (Latin American) have become a significant part of an American identity.
Discuss Challenges of Single-Parent Households
Under this prompt example, a student’s task is to read research studies on single parenthood and identify its challenges.
What Are Unique Features of a Good Movie?
Under this prompt example, a student’s task is to watch movies they consider “good” and provide an analysis of what makes them so.
Interpret a Poem With a First-Person Point of View
Under this prompt example, a student’s task is to select a poem, examine it, and describe its outstanding features, such as literary devices.
Illustrate a Dynamics of Adoption in a Multicultural Society
Under this prompt example, a student’s task is to examine a particular aspect of adoption within a specific context of a multicultural society.
What Store Strategies Influence Consumers?
Under this prompt example, a student’s task is to study a phenomenon of retail stores and give an analysis of specific factors that lead to their growth or shutdown.
Euthanasia: Questions of Ethics, Morals, and Legality
Under this prompt example, a student’s task is to examine a controversial aspect of euthanasia (mercy or assisted killing) and give an opinion on whether society should address it from some perspectives of ethics, morals, or law.
Need to Think Critically by Looking at a Topic
When it comes to essay writing, educational department’s requirements provide direction about a debatable topic. By reading such a topic, people get an idea of what kind of paper they are supposed to write. Regarding such a document, a topic should require them to research a specific theme, reflect on what they have read, and comment on a way how an author has presented information, its relevance to existing knowledge, and its actual significance for a person’s conclusion (Nosich, 2022). In turn, these five tasks underscore essential features of such a composition. As a result, to start a critical thinking essay, writers begin with an engaging introduction that provides context, introduces the topic, and clearly states their thesis statements.
When it comes to an essay structure, a critical thinking paper comprises three main sections: introduction, body, and conclusion. When writing each of these sections, students should capture essential features. Firstly, an introduction should provide a hook to capture a reader’s attention and formulate a thesis statement to guide paper’s main arguments and ideas (Atkins & Carver, 2022). In a body section, writers should use topic sentences to introduce paragraphs. Besides, learners should follow a sandwich rule, where they make a claim, provide supporting facts, and explain a significance of cited evidence to a paper’s thesis (Thurman & Gary, 2020). In a conclusion part, authors should restate a thesis statement, summarize main body points, and make a concluding remark. Finally, other essential features that people should use in their text’s paragraphs are transitions to give an entire paper a natural and logical flow of ideas and arguments.
Steps on How to Write a Critical Thinking Essay
To write a critical thinking essay, people usually start by clearly defining their topics and thesis statements, gathering and analyzing credible evidence, considering multiple perspectives, including counterarguments, and presenting a reasoned and coherent argument supported by thorough analysis and logical reasoning. In turn, some steps for writing a good critical thinking essay include:
- Understand an Assignment: Carefully read and comprehend an essay prompt or question to know exactly what is required.
- Choose a Topic: Select a relevant and engaging topic that allows for deep analysis and corresponding thinking.
- Conduct Research: Gather reliable and relevant sources to provide evidence and support for key arguments.
- Develop a Thesis Statement: Formulate a clear thesis statement that presents a main argument, claim, or perspective.
- Create an Outline: Organize central ideas and structure an essay by creating an outline with main points and subpoints.
- Write an Introduction: Develop an engaging introduction that provides context and states a central thesis.
- Develop Body Paragraphs: Write detailed body paragraphs, each focusing on a single point, connecting to a thesis, and using evidence, explanation, and analysis.
- Address Counterarguments: Identify and refute potential opposing views to strengthen a main argument.
- Write a Conclusion: Summarize central points, restate a thesis in light of the evidence, and end with a strong concluding thought.
- Revise and Edit: Review a critical thinking essay for clarity, coherence, and logical flow, and correct any grammatical or typographical errors.
Sample Outline Template
I. Introduction
A. Start with a hook sentence that makes an essay interesting. B. Cover brief information about a theme discussed in body paragraphs. C. End with a thesis statement.
A. Background Information:
- introduce an issue for readers;
- provide examples that support this issue;
- explain how examples correlate with a theme;
- finish with defining an issue for readers.
B. Argument on an Issue
- begin with an argument on an issue;
- covers examples to support this argument;
- explain how examples and argument are related;
- conclude how an argument on this theme is relevant.
C. Importance of an Issue
- state why this issue is important;
- support this statement with examples from credible sources;
- explain how these examples underline the importance of an issue;
- end with a concluding sentence that supports this importance.
III. Conclusion
A. Restate a thesis claim. B. Cover the key points discussed in body paragraphs. C. Provide a final thought on an issue.
Example of a Critical Thinking Essay
Topic: Roles of Critical Thinking Skills
Introduction Sample
Critical thinking is a requirement in higher education because it reflects the level of mental preparedness of students intending to join the labor industry. In this case, essay writing is one of the strategies that higher education institutions use to develop these critical thinking skills in students. Writing argumentative essays has profoundly shaped my critical thinking skills and made me more reflective and analytical in my texts.
Examples of Body Paragraphs
Background Information of an Issue
The advent of the Internet opened a new world of research as scholars found a platform to publish research findings. Besides scholars, public and private entities have turned to online platforms to spread information they perceive as critical and needful. Over time, I have come to see the Internet as a crucial reservoir of knowledge, and I always turn to it for personal enrichment. Moreover, Gilster (1997) perceives critical thinking as a critical skill for individuals who use online platforms for academic purposes. In this case, the author demonstrates that, since the Internet is full of falsehoods and incomplete and obsolete information, it is critical for those who depend on this technology to employ critical thinking. Hence, such thinking helps users distinguish between essential, relevant information and what appears to be irrelevant and nonessential.
Argument on an Issue
On the issue of critical thinking, examining and analyzing content are fundamental exercises. In essence, critical thinking entails reading a text and interpreting it by using an analytical lens. For example, when students read novels, they can use their critical thinking skills to analyze the plot and characters and provide arguments that indicate an in-depth understanding of both (Gilster, 1997). In most cases, such ideas go beyond what is written in the novel to include the student’s interpretation of events. In my case, I use the Internet to find research and media articles on different topics, such as homelessness, substance abuse, crime, and police and law enforcement. Moreover, I use these articles to reflect on the dynamics that shape life in contemporary society, using my critical thinking skills to relate the past, present, and future. Therefore, I can state confidently that this habit has made me a strong debater on contemporary issues.
Importance of an Issue
By using critical thinking skills, readers make deductions, thereby showcasing their understanding levels. As the literature suggests, critical thinking serves as a basis for knowledge accumulation and advancement (Ku & Ho, 2010). In my academic journey, I have employed critical thinking to gain insight into several issues. Furthermore, one of these issues is the significance of politics to the lives of ordinary citizens. Then, many documents I have read about politics have made me conclude that politicians are selfish by default and only develop consensus when their interests are accommodated. Hence, this understanding has made me have minimal expectations from local and national political figures.
Conclusion Sample
Critical thinking is a key skill that helps individuals to analyze and reflect on information from diverse sources. Over the years, I have used critical thinking to analyze research and media articles published on online platforms and make logical deductions. Moreover, these deductions point to my ability to take information, analyze it, and interpret it. Thus, I can confidently state that my critical thinking skills have made me aware of human weaknesses and the risk of putting too much trust in people vulnerable to shortcomings.
List of References
Gilster, P. (1997). Digital literacy: The thinking and survival skills new users need to make the Internet personally and professionally meaningful . New York, NY: Wiley.
Ku, K. Y., & Ho, I. T. (2010). Metacognitive strategies that enhance critical thinking. Metacognition and Learning , 5 (3), 251-267.
What to Include
Common mistakes.
- Lack of a Thesis: Failing to present a specific and arguable thesis that guides an essay.
- Insufficient Evidence: Relying on writing personal opinions without providing credible and relevant sources to support arguments.
- Ignoring Counterarguments: Not addressing opposing viewpoints or failing to refute them effectively.
- Poor Structure: Writing an essay without a logical flow or clear organization, making it difficult for readers to follow a central argument.
- Overgeneralization: Making general statements without sufficient evidence to back them up.
- Questionable Analysis: Offering unclear interpretations or analysis of evidence rather than engaging in a deep and well-reasoned examination.
- Repetition: Repeating same points or ideas without adding new insights or evidence.
- Weak Conclusions: Ending a paper without effectively summarizing main points and restating a thesis.
- Ignoring Formatting and Citation Guidelines: Failing to properly format an essay or cite sources according to a required academic style (e.g., APA, MLA, Chicago/Turabian, Harvard, etc.).
- Grammatical and Typographical Errors: Submitting a document with numerous grammatical mistakes and typographical errors, which can distract from its content and weaken its main argument.
A critical thinking essay is a document that reflects a student’s ability to use analytical and reflective skills in studying an issue. Although writing such a composition assumes following a basic structure of a standard essay, it has features that distinguish it from other papers. When writing this type of essay, people should master the following tips:
- Read and analyze information.
- Reflect on study findings.
- Review an actual relevance of observed information within a context of existing knowledge.
- Identify any conclusions made by authors or other scholars and their significance.
Atkins, H. S., & Carver, L. (2022). Writing is thinking: Strategies for all content areas . Rowman & Littlefield.
Butler, H. A. (2024). Predicting everyday critical thinking: A review of critical thinking assessments. Journal of Intelligence , 12 (2), 1–12. https://doi.org/10.3390/jintelligence12020016
Larsson, K. (2019). Using essay responses as a basis for teaching critical thinking – A variation theory approach. Scandinavian Journal of Educational Research , 65 (1), 21–35. https://doi.org/10.1080/00313831.2019.1650824
Nosich, G. M. (2022). Critical writing: A guide to writing a paper using the concepts and processes of critical thinking . Rowman & Littlefield.
Southworth, J. (2022). Bridging critical thinking and transformative learning: The role of perspective-taking. Theory and Research in Education , 20 (1), 44–63. https://doi.org/10.1177/14778785221090853
Thurman, S. S., & Gary, W. L. (2020). Critical literacy: Integrating critical thinking, reading, and writing . Cognella Academic Publishing.
To Learn More, Read Relevant Articles

How to Cite a TED Talk in APA 7 With Tips and Examples
- Icon Calendar 29 September 2020
- Icon Page 1498 words

Common Grammar, Punctuation, and Spelling Mistakes With Examples
- Icon Calendar 27 September 2020
- Icon Page 5628 words
Pasco-Hernando State College
Proving the Thesis/Critical Thinking
- The Writing Process
- Paragraphs and Essays
- Unity and Coherence in Essays
- Proving the Thesis - General Principles
- Proving the Thesis - Logic
- Proving the Thesis - Logical Fallacies and Appeals
- Proving the Thesis - Rhetorical Mode
- Appropriate Language
Good writing is not just about presenting information in an organized way such as an essay or research paper with an introduction, body paragraphs, and a concluding paragraph. It is about persuading your reader that you are right. In the case of an academic paper, the body paragraphs each must have a proof point (a topic sentence), and the content of each of the body paragraphs must include information that shows that the proof point is accurate. There are several ways to achieve this goal.
This section covers how to critically evaluate your writing with some general information in Proving the Thesis - General Principles and then goes on to explain logical thinking in Proving the Thesis - Logic and problems with logic in Proving the Thesis - Logical Fallacies and Appeals. Rhetorical modes such as description, definition, cause and/or effect, and compare/contrast can be used to help prove the thesis.
The same principles are applied when you're evaluating someone else's presentation whether it is a potential source for a paper or simply reading a news article. Even what is called a documentary - which presumably is the truth - should be critically evaluated.
- Printer-friendly version


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Develop a Strong Thesis Statement. Your thesis statement encapsulates your main argument or perspective on the topic. A strong thesis statement tells your readers exactly what your essay will be about and prepares them for the evidence you'll present. During your critical thinking process, make sure you include these key characteristics:
Placement of the thesis statement. Step 1: Start with a question. Step 2: Write your initial answer. Step 3: Develop your answer. Step 4: Refine your thesis statement. Types of thesis statements. Other interesting articles. Frequently asked questions about thesis statements.
A thesis statement: tells the reader how you will interpret the significance of the subject matter under discussion. is a road map for the paper; in other words, it tells the reader what to expect from the rest of the paper. directly answers the question asked of you. A thesis is an interpretation of a question or subject, not the subject itself.
A thesis statement . . . Makes an argumentative assertion about a topic; it states the conclusions that you have reached about your topic. Makes a promise to the reader about the scope, purpose, and direction of your paper. Is focused and specific enough to be "proven" within the boundaries of your paper. Is generally located near the end ...
Critical writing looks for links between sources, identifies issues, challenges established ideas and considers alternatives. Critical thinking entails: Being objective. Assessing the quality of information, e.g. looking for weaknesses in arguments in terms of logic and accuracy. Looking at an idea or data from different perspectives.
It serves as a foundation for a strong thesis statement, which articulates the main argument of a piece of writing. A well-crafted arguable claim invites discussion, encourages critical thinking, and allows for multiple perspectives.
Critical Thinking Lab CRITICAL THINKING LAB HANDOUT A BRIEF GUIDE TO CONSTRUCTING THESIS STATEMENTS AND INTRODUCTIONS I. WHAT IS A THESIS STATEMENT? (3) A thesis statement is a sentence, within an introduction, that asserts your position on a given topic. It is the central claim that you will be arguing for in your paper. HOW DO I CONSTRUCT A ...
They often compose a thesis statement before asking questions or conducting research. In the course of their reading, they might even disregard material that counters their pre-formed ideas. ... Writing practice builds critical thinking, which empowers people to "take charge of [their] own minds" so they "can take charge of [their] own ...
Thesis Statements What this handout is about This handout describes what a thesis statement is, how thesis statements work in your writing, ... A thesis is the result of a lengthy thinking process. Formulating a thesis is not the first thing you do after reading an essay assignment. Before you develop an argument on any topic, you
Thesis Statements - Defining ... Effective thesis statements are the product of good critical thinking. Rarely do they emerge fully formed in an early draft of a paper. Rather, they are the ...
Write a draft of a whole paper to see how you express ideas on paper. Outline your essay to structure the ideas you have. Set a timer and write a draft within a set amount of time. Analyze your draft at the sentence level and see if your paper makes sense. Highlight the main point of your paper.
Critical thinking is the ability to effectively analyze information and form a judgment. To think critically, you must be aware of your own biases and assumptions when encountering information, and apply consistent standards when evaluating sources. Critical thinking skills help you to: Identify credible sources. Evaluate and respond to arguments.
When drafting your thesis statement, avoid words like explore, investigate, learn, compile, summarize, and explain to describe the main purpose of your paper. These words imply a paper that summarizes or "reports," rather than synthesizing and analyzing. Instead of the terms above, try words like argue, critique, question, and interrogate.
A thesis statement is a one- to two-sentence statement that presents the main idea and makes an assertion about your issue. You may have a longer thesis for much longer essays, but one to two sentences is a good general guideline. And, remember, in an argumentative essay, the assertion you present in your thesis is going to be particularly ...
Strong Thesis Statement Examples. 1. School Uniforms. "Mandatory school uniforms should be implemented in educational institutions as they promote a sense of equality, reduce distractions, and foster a focused and professional learning environment.". Best For: Argumentative Essay or Debate. Read More: School Uniforms Pros and Cons.
This thesis statement is not debatable. First, the word pollution implies that something is bad or negative in some way. Furthermore, all studies agree that pollution is a problem; they simply disagree on the impact it will have or the scope of the problem. No one could reasonably argue that pollution is unambiguously good.
A thesis is an in-depth research study that identifies a particular topic of inquiry and presents a clear argument or perspective about that topic using evidence and logic. Writing a thesis showcases your ability of critical thinking, gathering evidence, and making a compelling argument. Integral to these competencies is thorough research ...
Note: Some sections in a critical thinking essay can be added, deleted, or combined with each other. In turn, its typical structure in writing includes an introduction with a thesis statement, body paragraphs with evidence, explanation, and analysis, counterarguments with refutations, and a conclusion that summarizes key points and restates a thesis.
Proving the Thesis/Critical Thinking. Good writing is not just about presenting information in an organized way such as an essay or research paper with an introduction, body paragraphs, and a concluding paragraph. It is about persuading your reader that you are right. In the case of an academic paper, the body paragraphs each must have a proof ...
A virtue epistemic approach to critical thinking [Doctoral thesis, Bond University]. Bond University Research Portal. ... Facione, P. A. (1990). Critical thinking: A statement of expert consensus for purposes of educational assessment and instruction. Research Findings and Recommendations Prepared for the Committee on Pre-College Philosophy of ...