- Privacy Policy

Home » What is a Hypothesis – Types, Examples and Writing Guide

What is a Hypothesis – Types, Examples and Writing Guide
Table of Contents
In research, a hypothesis is a clear, testable statement predicting the relationship between variables or the outcome of a study. Hypotheses form the foundation of scientific inquiry, providing a direction for investigation and guiding the data collection and analysis process. Hypotheses are typically used in quantitative research but can also inform some qualitative studies by offering a preliminary assumption about the subject being explored.

A hypothesis is a specific, testable prediction or statement that suggests an expected relationship between variables in a study. It acts as a starting point, guiding researchers to examine whether their predictions hold true based on collected data. For a hypothesis to be useful, it must be clear, concise, and based on prior knowledge or theoretical frameworks.
Key Characteristics of a Hypothesis :
- Testable : Must be possible to evaluate or observe the outcome through experimentation or analysis.
- Specific : Clearly defines variables and the expected relationship or outcome.
- Predictive : States an anticipated effect or association that can be confirmed or refuted.
Example : “Increasing the amount of daily physical exercise will lead to a reduction in stress levels among college students.”
Types of Hypotheses
Hypotheses can be categorized into several types, depending on their structure, purpose, and the type of relationship they suggest. The most common types include null hypothesis , alternative hypothesis , directional hypothesis , and non-directional hypothesis .
1. Null Hypothesis (H₀)
Definition : The null hypothesis states that there is no relationship between the variables being studied or that any observed effect is due to chance. It serves as the default position, which researchers aim to test against to determine if a significant effect or association exists.
Purpose : To provide a baseline that can be statistically tested to verify if a relationship or difference exists.
Example : “There is no difference in academic performance between students who receive additional tutoring and those who do not.”
2. Alternative Hypothesis (H₁ or Hₐ)
Definition : The alternative hypothesis proposes that there is a relationship or effect between variables. This hypothesis contradicts the null hypothesis and suggests that any observed result is not due to chance.
Purpose : To present an expected outcome that researchers aim to support with data.
Example : “Students who receive additional tutoring will perform better academically than those who do not.”
3. Directional Hypothesis
Definition : A directional hypothesis specifies the direction of the expected relationship between variables, predicting either an increase, decrease, positive, or negative effect.
Purpose : To provide a more precise prediction by indicating the expected direction of the relationship.
Example : “Increasing the duration of daily exercise will lead to a decrease in stress levels among adults.”
4. Non-Directional Hypothesis
Definition : A non-directional hypothesis states that there is a relationship between variables but does not specify the direction of the effect.
Purpose : To allow for exploration of the relationship without committing to a particular direction.
Example : “There is a difference in stress levels between adults who exercise regularly and those who do not.”
Examples of Hypotheses in Different Fields
- Null Hypothesis : “There is no difference in anxiety levels between individuals who practice mindfulness and those who do not.”
- Alternative Hypothesis : “Individuals who practice mindfulness will report lower anxiety levels than those who do not.”
- Directional Hypothesis : “Providing feedback will improve students’ motivation to learn.”
- Non-Directional Hypothesis : “There is a difference in motivation levels between students who receive feedback and those who do not.”
- Null Hypothesis : “There is no association between diet and energy levels among teenagers.”
- Alternative Hypothesis : “A balanced diet is associated with higher energy levels among teenagers.”
- Directional Hypothesis : “An increase in employee engagement activities will lead to improved job satisfaction.”
- Non-Directional Hypothesis : “There is a relationship between employee engagement activities and job satisfaction.”
- Null Hypothesis : “The introduction of green spaces does not affect urban air quality.”
- Alternative Hypothesis : “Green spaces improve urban air quality.”
Writing Guide for Hypotheses
Writing a clear, testable hypothesis involves several steps, starting with understanding the research question and selecting variables. Here’s a step-by-step guide to writing an effective hypothesis.
Step 1: Identify the Research Question
Start by defining the primary research question you aim to investigate. This question should be focused, researchable, and specific enough to allow for hypothesis formation.
Example : “Does regular physical exercise improve mental well-being in college students?”
Step 2: Conduct Background Research
Review relevant literature to gain insight into existing theories, studies, and gaps in knowledge. This helps you understand prior findings and guides you in forming a logical hypothesis based on evidence.
Example : Research shows a positive correlation between exercise and mental well-being, which supports forming a hypothesis in this area.
Step 3: Define the Variables
Identify the independent and dependent variables. The independent variable is the factor you manipulate or consider as the cause, while the dependent variable is the outcome or effect you are measuring.
- Independent Variable : Amount of physical exercise
- Dependent Variable : Mental well-being (measured through self-reported stress levels)
Step 4: Choose the Hypothesis Type
Select the hypothesis type based on the research question. If you predict a specific outcome or direction, use a directional hypothesis. If not, a non-directional hypothesis may be suitable.
Example : “Increasing the frequency of physical exercise will reduce stress levels among college students” (directional hypothesis).
Step 5: Write the Hypothesis
Formulate the hypothesis as a clear, concise statement. Ensure it is specific, testable, and focuses on the relationship between the variables.
Example : “College students who exercise at least three times per week will report lower stress levels than those who do not exercise regularly.”
Step 6: Test and Refine (Optional)
In some cases, it may be necessary to refine the hypothesis after conducting a preliminary test or pilot study. This ensures that your hypothesis is realistic and feasible within the study parameters.
Tips for Writing an Effective Hypothesis
- Use Clear Language : Avoid jargon or ambiguous terms to ensure your hypothesis is easily understandable.
- Be Specific : Specify the expected relationship between the variables, and, if possible, include the direction of the effect.
- Ensure Testability : Frame the hypothesis in a way that allows for empirical testing or observation.
- Focus on One Relationship : Avoid complexity by focusing on a single, clear relationship between variables.
- Make It Measurable : Choose variables that can be quantified or observed to simplify data collection and analysis.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Vague Statements : Avoid vague hypotheses that don’t specify a clear relationship or outcome.
- Unmeasurable Variables : Ensure that the variables in your hypothesis can be observed, measured, or quantified.
- Overly Complex Hypotheses : Keep the hypothesis simple and focused, especially for beginner researchers.
- Using Personal Opinions : Avoid subjective or biased language that could impact the neutrality of the hypothesis.
Examples of Well-Written Hypotheses
- Psychology : “Adolescents who spend more than two hours on social media per day will report higher levels of anxiety than those who spend less than one hour.”
- Business : “Increasing customer service training will improve customer satisfaction ratings among retail employees.”
- Health : “Consuming a diet rich in fruits and vegetables is associated with lower cholesterol levels in adults.”
- Education : “Students who participate in active learning techniques will have higher retention rates compared to those in traditional lecture-based classrooms.”
- Environmental Science : “Urban areas with more green spaces will report lower average temperatures than those with minimal green coverage.”
A well-formulated hypothesis is essential to the research process, providing a clear and testable prediction about the relationship between variables. Understanding the different types of hypotheses, following a structured writing approach, and avoiding common pitfalls help researchers create hypotheses that effectively guide data collection, analysis, and conclusions. Whether working in psychology, education, health sciences, or any other field, an effective hypothesis sharpens the focus of a study and enhances the rigor of research.
- Creswell, J. W., & Creswell, J. D. (2018). Research Design: Qualitative, Quantitative, and Mixed Methods Approaches (5th ed.). SAGE Publications.
- Field, A. (2013). Discovering Statistics Using IBM SPSS Statistics (4th ed.). SAGE Publications.
- Trochim, W. M. K. (2006). The Research Methods Knowledge Base (3rd ed.). Atomic Dog Publishing.
- McLeod, S. A. (2019). What is a Hypothesis? Retrieved from https://www.simplypsychology.org/what-is-a-hypotheses.html
- Walliman, N. (2017). Research Methods: The Basics (2nd ed.). Routledge.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Problem Statement – Writing Guide, Examples and...

Research Questions – Types, Examples and Writing...

Thesis Format – Templates and Samples


Data Verification – Process, Types and Examples

What is Research Topic – Ideas and Examples

Conceptual Framework – Types, Methodology and...
What Are The Steps Of The Scientific Method?
Julia Simkus
Editor at Simply Psychology
BA (Hons) Psychology, Princeton University
Julia Simkus is a graduate of Princeton University with a Bachelor of Arts in Psychology. She is currently studying for a Master's Degree in Counseling for Mental Health and Wellness in September 2023. Julia's research has been published in peer reviewed journals.
Learn about our Editorial Process
Saul McLeod, PhD
Editor-in-Chief for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MRes, PhD, University of Manchester
Saul McLeod, PhD., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years of experience in further and higher education. He has been published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology.
Olivia Guy-Evans, MSc
Associate Editor for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MSc Psychology of Education
Olivia Guy-Evans is a writer and associate editor for Simply Psychology. She has previously worked in healthcare and educational sectors.
On This Page:
Science is not just knowledge. It is also a method for obtaining knowledge. Scientific understanding is organized into theories.
The scientific method is a step-by-step process used by researchers and scientists to determine if there is a relationship between two or more variables. Psychologists use this method to conduct psychological research, gather data, process information, and describe behaviors.
It involves careful observation, asking questions, formulating hypotheses, experimental testing, and refining hypotheses based on experimental findings.
How it is Used
The scientific method can be applied broadly in science across many different fields, such as chemistry, physics, geology, and psychology. In a typical application of this process, a researcher will develop a hypothesis, test this hypothesis, and then modify the hypothesis based on the outcomes of the experiment.
The process is then repeated with the modified hypothesis until the results align with the observed phenomena. Detailed steps of the scientific method are described below.
Keep in mind that the scientific method does not have to follow this fixed sequence of steps; rather, these steps represent a set of general principles or guidelines.
7 Steps of the Scientific Method
Psychology uses an empirical approach.
Empiricism (founded by John Locke) states that the only source of knowledge comes through our senses – e.g., sight, hearing, touch, etc.
Empirical evidence does not rely on argument or belief. Thus, empiricism is the view that all knowledge is based on or may come from direct observation and experience.
The empiricist approach of gaining knowledge through experience quickly became the scientific approach and greatly influenced the development of physics and chemistry in the 17th and 18th centuries.
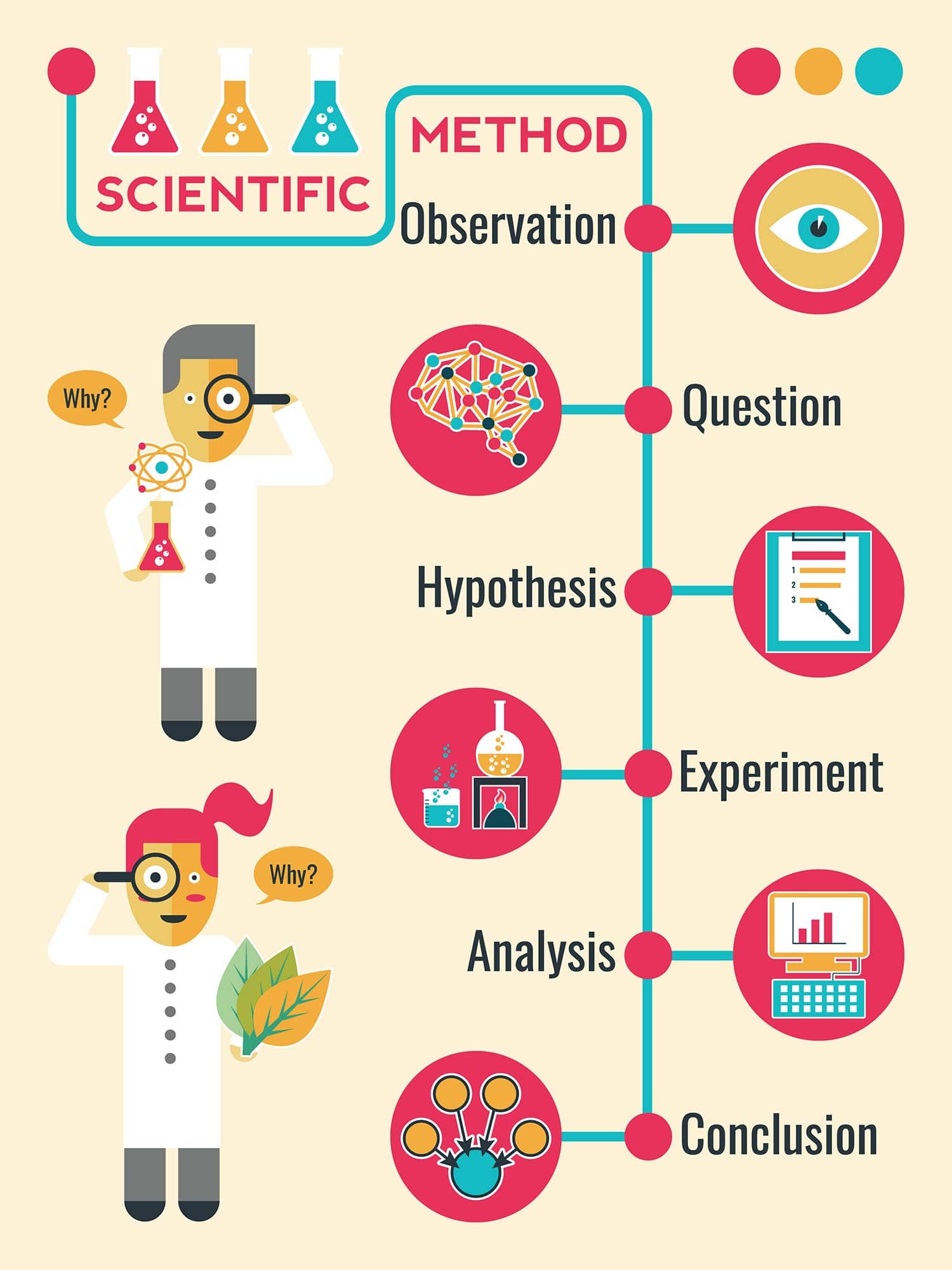
Step 1: Make an Observation (Theory Construction)
Every researcher starts at the very beginning. Before diving in and exploring something, one must first determine what they will study – it seems simple enough!
By making observations, researchers can establish an area of interest. Once this topic of study has been chosen, a researcher should review existing literature to gain insight into what has already been tested and determine what questions remain unanswered.
This assessment will provide helpful information about what has already been comprehended about the specific topic and what questions remain, and if one can go and answer them.
Specifically, a literature review might implicate examining a substantial amount of documented material from academic journals to books dating back decades. The most appropriate information gathered by the researcher will be shown in the introduction section or abstract of the published study results.
The background material and knowledge will help the researcher with the first significant step in conducting a psychology study, which is formulating a research question.
This is the inductive phase of the scientific process. Observations yield information that is used to formulate theories as explanations. A theory is a well-developed set of ideas that propose an explanation for observed phenomena.
Inductive reasoning moves from specific premises to a general conclusion. It starts with observations of phenomena in the natural world and derives a general law.
Step 2: Ask a Question
Once a researcher has made observations and conducted background research, the next step is to ask a scientific question. A scientific question must be defined, testable, and measurable.
A useful approach to develop a scientific question is: “What is the effect of…?” or “How does X affect Y?”
To answer an experimental question, a researcher must identify two variables: the independent and dependent variables.
The independent variable is the variable manipulated (the cause), and the dependent variable is the variable being measured (the effect).
An example of a research question could be, “Is handwriting or typing more effective for retaining information?” Answering the research question and proposing a relationship between the two variables is discussed in the next step.
Step 3: Form a Hypothesis (Make Predictions)
A hypothesis is an educated guess about the relationship between two or more variables. A hypothesis is an attempt to answer your research question based on prior observation and background research. Theories tend to be too complex to be tested all at once; instead, researchers create hypotheses to test specific aspects of a theory.
For example, a researcher might ask about the connection between sleep and educational performance. Do students who get less sleep perform worse on tests at school?
It is crucial to think about different questions one might have about a particular topic to formulate a reasonable hypothesis. It would help if one also considered how one could investigate the causalities.
It is important that the hypothesis is both testable against reality and falsifiable. This means that it can be tested through an experiment and can be proven wrong.
The falsification principle, proposed by Karl Popper , is a way of demarcating science from non-science. It suggests that for a theory to be considered scientific, it must be able to be tested and conceivably proven false.
To test a hypothesis, we first assume that there is no difference between the populations from which the samples were taken. This is known as the null hypothesis and predicts that the independent variable will not influence the dependent variable.
Examples of “if…then…” Hypotheses:
- If one gets less than 6 hours of sleep, then one will do worse on tests than if one obtains more rest.
- If one drinks lots of water before going to bed, one will have to use the bathroom often at night.
- If one practices exercising and lighting weights, then one’s body will begin to build muscle.
The research hypothesis is often called the alternative hypothesis and predicts what change(s) will occur in the dependent variable when the independent variable is manipulated.
It states that the results are not due to chance and that they are significant in terms of supporting the theory being investigated.
Although one could state and write a scientific hypothesis in many ways, hypotheses are usually built like “if…then…” statements.
Step 4: Run an Experiment (Gather Data)
The next step in the scientific method is to test your hypothesis and collect data. A researcher will design an experiment to test the hypothesis and gather data that will either support or refute the hypothesis.
The exact research methods used to examine a hypothesis depend on what is being studied. A psychologist might utilize two primary forms of research, experimental research, and descriptive research.
The scientific method is objective in that researchers do not let preconceived ideas or biases influence the collection of data and is systematic in that experiments are conducted in a logical way.
Experimental Research
Experimental research is used to investigate cause-and-effect associations between two or more variables. This type of research systematically controls an independent variable and measures its effect on a specified dependent variable.
Experimental research involves manipulating an independent variable and measuring the effect(s) on the dependent variable. Repeating the experiment multiple times is important to confirm that your results are accurate and consistent.
One of the significant advantages of this method is that it permits researchers to determine if changes in one variable cause shifts in each other.
While experiments in psychology typically have many moving parts (and can be relatively complex), an easy investigation is rather fundamental. Still, it does allow researchers to specify cause-and-effect associations between variables.
Most simple experiments use a control group, which involves those who do not receive the treatment, and an experimental group, which involves those who do receive the treatment.
An example of experimental research would be when a pharmaceutical company wants to test a new drug. They give one group a placebo (control group) and the other the actual pill (experimental group).
Descriptive Research
Descriptive research is generally used when it is challenging or even impossible to control the variables in question. Examples of descriptive analysis include naturalistic observation, case studies , and correlation studies .
One example of descriptive research includes phone surveys that marketers often use. While they typically do not allow researchers to identify cause and effect, correlational studies are quite common in psychology research. They make it possible to spot associations between distinct variables and measure the solidity of those relationships.
Step 5: Analyze the Data and Draw Conclusions
Once a researcher has designed and done the investigation and collected sufficient data, it is time to inspect this gathered information and judge what has been found. Researchers can summarize the data, interpret the results, and draw conclusions based on this evidence using analyses and statistics.
Upon completion of the experiment, you can collect your measurements and analyze the data using statistics. Based on the outcomes, you will either reject or confirm your hypothesis.
Analyze the Data
So, how does a researcher determine what the results of their study mean? Statistical analysis can either support or refute a researcher’s hypothesis and can also be used to determine if the conclusions are statistically significant.
When outcomes are said to be “statistically significant,” it is improbable that these results are due to luck or chance. Based on these observations, investigators must then determine what the results mean.
An experiment will support a hypothesis in some circumstances, but sometimes it fails to be truthful in other cases.
What occurs if the developments of a psychology investigation do not endorse the researcher’s hypothesis? It does mean that the study was worthless. Simply because the findings fail to defend the researcher’s hypothesis does not mean that the examination is not helpful or instructive.
This kind of research plays a vital role in supporting scientists in developing unexplored questions and hypotheses to investigate in the future. After decisions have been made, the next step is to communicate the results with the rest of the scientific community.
This is an integral part of the process because it contributes to the general knowledge base and can assist other scientists in finding new research routes to explore.
If the hypothesis is not supported, a researcher should acknowledge the experiment’s results, formulate a new hypothesis, and develop a new experiment.
We must avoid any reference to results proving a theory as this implies 100% certainty, and there is always a chance that evidence may exist that could refute a theory.
Draw Conclusions and Interpret the Data
When the empirical observations disagree with the hypothesis, a number of possibilities must be considered. It might be that the theory is incorrect, in which case it needs altering, so it fully explains the data.
Alternatively, it might be that the hypothesis was poorly derived from the original theory, in which case the scientists were expecting the wrong thing to happen.
It might also be that the research was poorly conducted, or used an inappropriate method, or there were factors in play that the researchers did not consider. This will begin the process of the scientific method again.
If the hypothesis is supported, the researcher can find more evidence to support their hypothesis or look for counter-evidence to strengthen their hypothesis further.
In either scenario, the researcher should share their results with the greater scientific community.
Step 6: Share Your Results
One of the final stages of the research cycle involves the publication of the research. Once the report is written, the researcher(s) may submit the work for publication in an appropriate journal.
Usually, this is done by writing up a study description and publishing the article in a professional or academic journal. The studies and conclusions of psychological work can be seen in peer-reviewed journals such as Developmental Psychology , Psychological Bulletin, the Journal of Social Psychology, and numerous others.
Scientists should report their findings by writing up a description of their study and any subsequent findings. This enables other researchers to build upon the present research or replicate the results.
As outlined by the American Psychological Association (APA), there is a typical structure of a journal article that follows a specified format. In these articles, researchers:
- Supply a brief narrative and background on previous research
- Give their hypothesis
- Specify who participated in the study and how they were chosen
- Provide operational definitions for each variable
- Explain the measures and methods used to collect data
- Describe how the data collected was interpreted
- Discuss what the outcomes mean
A detailed record of psychological studies and all scientific studies is vital to clearly explain the steps and procedures used throughout the study. So that other researchers can try this experiment too and replicate the results.
The editorial process utilized by academic and professional journals guarantees that each submitted article undergoes a thorough peer review to help assure that the study is scientifically sound. Once published, the investigation becomes another piece of the current puzzle of our knowledge “base” on that subject.
This last step is important because all results, whether they supported or did not support the hypothesis, can contribute to the scientific community. Publication of empirical observations leads to more ideas that are tested against the real world, and so on. In this sense, the scientific process is circular.
The editorial process utilized by academic and professional journals guarantees that each submitted article undergoes a thorough peer review to help assure that the study is scientifically sound.
Once published, the investigation becomes another piece of the current puzzle of our knowledge “base” on that subject.
By replicating studies, psychologists can reduce errors, validate theories, and gain a stronger understanding of a particular topic.
Step 7: Repeat the Scientific Method (Iteration)
Now, if one’s hypothesis turns out to be accurate, find more evidence or find counter-evidence. If one’s hypothesis is false, create a new hypothesis or try again.
One may wish to revise their first hypothesis to make a more niche experiment to design or a different specific question to test.
The amazingness of the scientific method is that it is a comprehensive and straightforward process that scientists, and everyone, can utilize over and over again.
So, draw conclusions and repeat because the scientific method is never-ending, and no result is ever considered perfect.
The scientific method is a process of:
- Making an observation.
- Forming a hypothesis.
- Making a prediction.
- Experimenting to test the hypothesis.
The procedure of repeating the scientific method is crucial to science and all fields of human knowledge.
Further Information
- Karl Popper – Falsification
- Thomas – Kuhn Paradigm Shift
- Positivism in Sociology: Definition, Theory & Examples
- Is Psychology a Science?
- Psychology as a Science (PDF)
List the 6 steps of the scientific methods in order
- Make an observation (theory construction)
- Ask a question. A scientific question must be defined, testable, and measurable.
- Form a hypothesis (make predictions)
- Run an experiment to test the hypothesis (gather data)
- Analyze the data and draw conclusions
- Share your results so that other researchers can make new hypotheses
What is the first step of the scientific method?
The first step of the scientific method is making an observation. This involves noticing and describing a phenomenon or group of phenomena that one finds interesting and wishes to explain.
Observations can occur in a natural setting or within the confines of a laboratory. The key point is that the observation provides the initial question or problem that the rest of the scientific method seeks to answer or solve.
What is the scientific method?
The scientific method is a step-by-step process that investigators can follow to determine if there is a causal connection between two or more variables.
Psychologists and other scientists regularly suggest motivations for human behavior. On a more casual level, people judge other people’s intentions, incentives, and actions daily.
While our standard assessments of human behavior are subjective and anecdotal, researchers use the scientific method to study psychology objectively and systematically.
All utilize a scientific method to study distinct aspects of people’s thinking and behavior. This process allows scientists to analyze and understand various psychological phenomena, but it also provides investigators and others a way to disseminate and debate the results of their studies.
The outcomes of these studies are often noted in popular media, which leads numerous to think about how or why researchers came to the findings they did.
Why Use the Six Steps of the Scientific Method
The goal of scientists is to understand better the world that surrounds us. Scientific research is the most critical tool for navigating and learning about our complex world.
Without it, we would be compelled to rely solely on intuition, other people’s power, and luck. We can eliminate our preconceived concepts and superstitions through methodical scientific research and gain an objective sense of ourselves and our world.
All psychological studies aim to explain, predict, and even control or impact mental behaviors or processes. So, psychologists use and repeat the scientific method (and its six steps) to perform and record essential psychological research.
So, psychologists focus on understanding behavior and the cognitive (mental) and physiological (body) processes underlying behavior.
In the real world, people use to understand the behavior of others, such as intuition and personal experience. The hallmark of scientific research is evidence to support a claim.
Scientific knowledge is empirical, meaning it is grounded in objective, tangible evidence that can be observed repeatedly, regardless of who is watching.
The scientific method is crucial because it minimizes the impact of bias or prejudice on the experimenter. Regardless of how hard one tries, even the best-intentioned scientists can’t escape discrimination. can’t
It stems from personal opinions and cultural beliefs, meaning any mortal filters data based on one’s experience. Sadly, this “filtering” process can cause a scientist to favor one outcome over another.
For an everyday person trying to solve a minor issue at home or work, succumbing to these biases is not such a big deal; in fact, most times, it is important.
But in the scientific community, where results must be inspected and reproduced, bias or discrimination must be avoided.
When to Use the Six Steps of the Scientific Method ?
One can use the scientific method anytime, anywhere! From the smallest conundrum to solving global problems, it is a process that can be applied to any science and any investigation.
Even if you are not considered a “scientist,” you will be surprised to know that people of all disciplines use it for all kinds of dilemmas.
Try to catch yourself next time you come by a question and see how you subconsciously or consciously use the scientific method.

IMAGES
VIDEO