What is Critical Thinking in Nursing? (With Examples, Importance, & How to Improve)

Successful nursing requires learning several skills used to communicate with patients, families, and healthcare teams. One of the most essential skills nurses must develop is the ability to demonstrate critical thinking. If you are a nurse, perhaps you have asked if there is a way to know how to improve critical thinking in nursing? As you read this article, you will learn what critical thinking in nursing is and why it is important. You will also find 18 simple tips to improve critical thinking in nursing and sample scenarios about how to apply critical thinking in your nursing career.

What Is Critical Thinking In Nursing?
4 reasons why critical thinking is so important in nursing, 1. critical thinking skills will help you anticipate and understand changes in your patient’s condition., 2. with strong critical thinking skills, you can make decisions about patient care that is most favorable for the patient and intended outcomes., 3. strong critical thinking skills in nursing can contribute to innovative improvements and professional development., 4. critical thinking skills in nursing contribute to rational decision-making, which improves patient outcomes., what are the 8 important attributes of excellent critical thinking in nursing, 1. the ability to interpret information:, 2. independent thought:, 3. impartiality:, 4. intuition:, 5. problem solving:, 6. flexibility:, 7. perseverance:, 8. integrity:, examples of poor critical thinking vs excellent critical thinking in nursing, 1. scenario: patient/caregiver interactions, poor critical thinking:, excellent critical thinking:, 2. scenario: improving patient care quality, 3. scenario: interdisciplinary collaboration, 4. scenario: precepting nursing students and other nurses, how to improve critical thinking in nursing, 1. demonstrate open-mindedness., 2. practice self-awareness., 3. avoid judgment., 4. eliminate personal biases., 5. do not be afraid to ask questions., 6. find an experienced mentor., 7. join professional nursing organizations., 8. establish a routine of self-reflection., 9. utilize the chain of command., 10. determine the significance of data and decide if it is sufficient for decision-making., 11. volunteer for leadership positions or opportunities., 12. use previous facts and experiences to help develop stronger critical thinking skills in nursing., 13. establish priorities., 14. trust your knowledge and be confident in your abilities., 15. be curious about everything., 16. practice fair-mindedness., 17. learn the value of intellectual humility., 18. never stop learning., 4 consequences of poor critical thinking in nursing, 1. the most significant risk associated with poor critical thinking in nursing is inadequate patient care., 2. failure to recognize changes in patient status:, 3. lack of effective critical thinking in nursing can impact the cost of healthcare., 4. lack of critical thinking skills in nursing can cause a breakdown in communication within the interdisciplinary team., useful resources to improve critical thinking in nursing, youtube videos, my final thoughts, frequently asked questions answered by our expert, 1. will lack of critical thinking impact my nursing career, 2. usually, how long does it take for a nurse to improve their critical thinking skills, 3. do all types of nurses require excellent critical thinking skills, 4. how can i assess my critical thinking skills in nursing.
• Ask relevant questions • Justify opinions • Address and evaluate multiple points of view • Explain assumptions and reasons related to your choice of patient care options
5. Can I Be a Nurse If I Cannot Think Critically?

The Value of Critical Thinking in Nursing

- How Nurses Use Critical Thinking
- How to Improve Critical Thinking
- Common Mistakes

Some experts describe a person’s ability to question belief systems, test previously held assumptions, and recognize ambiguity as evidence of critical thinking. Others identify specific skills that demonstrate critical thinking, such as the ability to identify problems and biases, infer and draw conclusions, and determine the relevance of information to a situation.
Nicholas McGowan, BSN, RN, CCRN, has been a critical care nurse for 10 years in neurological trauma nursing and cardiovascular and surgical intensive care. He defines critical thinking as “necessary for problem-solving and decision-making by healthcare providers. It is a process where people use a logical process to gather information and take purposeful action based on their evaluation.”
“This cognitive process is vital for excellent patient outcomes because it requires that nurses make clinical decisions utilizing a variety of different lenses, such as fairness, ethics, and evidence-based practice,” he says.
How Do Nurses Use Critical Thinking?
Successful nurses think beyond their assigned tasks to deliver excellent care for their patients. For example, a nurse might be tasked with changing a wound dressing, delivering medications, and monitoring vital signs during a shift. However, it requires critical thinking skills to understand how a difference in the wound may affect blood pressure and temperature and when those changes may require immediate medical intervention.
Nurses care for many patients during their shifts. Strong critical thinking skills are crucial when juggling various tasks so patient safety and care are not compromised.
Jenna Liphart Rhoads, Ph.D., RN, is a nurse educator with a clinical background in surgical-trauma adult critical care, where critical thinking and action were essential to the safety of her patients. She talks about examples of critical thinking in a healthcare environment, saying:
“Nurses must also critically think to determine which patient to see first, which medications to pass first, and the order in which to organize their day caring for patients. Patient conditions and environments are continually in flux, therefore nurses must constantly be evaluating and re-evaluating information they gather (assess) to keep their patients safe.”
The COVID-19 pandemic created hospital care situations where critical thinking was essential. It was expected of the nurses on the general floor and in intensive care units. Crystal Slaughter is an advanced practice nurse in the intensive care unit (ICU) and a nurse educator. She observed critical thinking throughout the pandemic as she watched intensive care nurses test the boundaries of previously held beliefs and master providing excellent care while preserving resources.
“Nurses are at the patient’s bedside and are often the first ones to detect issues. Then, the nurse needs to gather the appropriate subjective and objective data from the patient in order to frame a concise problem statement or question for the physician or advanced practice provider,” she explains.
Top 5 Ways Nurses Can Improve Critical Thinking Skills
We asked our experts for the top five strategies nurses can use to purposefully improve their critical thinking skills.
Case-Based Approach
Slaughter is a fan of the case-based approach to learning critical thinking skills.
In much the same way a detective would approach a mystery, she mentors her students to ask questions about the situation that help determine the information they have and the information they need. “What is going on? What information am I missing? Can I get that information? What does that information mean for the patient? How quickly do I need to act?”
Consider forming a group and working with a mentor who can guide you through case studies. This provides you with a learner-centered environment in which you can analyze data to reach conclusions and develop communication, analytical, and collaborative skills with your colleagues.
Practice Self-Reflection
Rhoads is an advocate for self-reflection. “Nurses should reflect upon what went well or did not go well in their workday and identify areas of improvement or situations in which they should have reached out for help.” Self-reflection is a form of personal analysis to observe and evaluate situations and how you responded.
This gives you the opportunity to discover mistakes you may have made and to establish new behavior patterns that may help you make better decisions. You likely already do this. For example, after a disagreement or contentious meeting, you may go over the conversation in your head and think about ways you could have responded.
It’s important to go through the decisions you made during your day and determine if you should have gotten more information before acting or if you could have asked better questions.
During self-reflection, you may try thinking about the problem in reverse. This may not give you an immediate answer, but can help you see the situation with fresh eyes and a new perspective. How would the outcome of the day be different if you planned the dressing change in reverse with the assumption you would find a wound infection? How does this information change your plan for the next dressing change?
Develop a Questioning Mind
McGowan has learned that “critical thinking is a self-driven process. It isn’t something that can simply be taught. Rather, it is something that you practice and cultivate with experience. To develop critical thinking skills, you have to be curious and inquisitive.”
To gain critical thinking skills, you must undergo a purposeful process of learning strategies and using them consistently so they become a habit. One of those strategies is developing a questioning mind. Meaningful questions lead to useful answers and are at the core of critical thinking .
However, learning to ask insightful questions is a skill you must develop. Faced with staff and nursing shortages , declining patient conditions, and a rising number of tasks to be completed, it may be difficult to do more than finish the task in front of you. Yet, questions drive active learning and train your brain to see the world differently and take nothing for granted.
It is easier to practice questioning in a non-stressful, quiet environment until it becomes a habit. Then, in the moment when your patient’s care depends on your ability to ask the right questions, you can be ready to rise to the occasion.
Practice Self-Awareness in the Moment
Critical thinking in nursing requires self-awareness and being present in the moment. During a hectic shift, it is easy to lose focus as you struggle to finish every task needed for your patients. Passing medication, changing dressings, and hanging intravenous lines all while trying to assess your patient’s mental and emotional status can affect your focus and how you manage stress as a nurse .
Staying present helps you to be proactive in your thinking and anticipate what might happen, such as bringing extra lubricant for a catheterization or extra gloves for a dressing change.
By staying present, you are also better able to practice active listening. This raises your assessment skills and gives you more information as a basis for your interventions and decisions.
Use a Process
As you are developing critical thinking skills, it can be helpful to use a process. For example:
- Ask questions.
- Gather information.
- Implement a strategy.
- Evaluate the results.
- Consider another point of view.
These are the fundamental steps of the nursing process (assess, diagnose, plan, implement, evaluate). The last step will help you overcome one of the common problems of critical thinking in nursing — personal bias.
Common Critical Thinking Pitfalls in Nursing
Your brain uses a set of processes to make inferences about what’s happening around you. In some cases, your unreliable biases can lead you down the wrong path. McGowan places personal biases at the top of his list of common pitfalls to critical thinking in nursing.
“We all form biases based on our own experiences. However, nurses have to learn to separate their own biases from each patient encounter to avoid making false assumptions that may interfere with their care,” he says. Successful critical thinkers accept they have personal biases and learn to look out for them. Awareness of your biases is the first step to understanding if your personal bias is contributing to the wrong decision.
New nurses may be overwhelmed by the transition from academics to clinical practice, leading to a task-oriented mindset and a common new nurse mistake ; this conflicts with critical thinking skills.
“Consider a patient whose blood pressure is low but who also needs to take a blood pressure medication at a scheduled time. A task-oriented nurse may provide the medication without regard for the patient’s blood pressure because medication administration is a task that must be completed,” Slaughter says. “A nurse employing critical thinking skills would address the low blood pressure, review the patient’s blood pressure history and trends, and potentially call the physician to discuss whether medication should be withheld.”
Fear and pride may also stand in the way of developing critical thinking skills. Your belief system and worldview provide comfort and guidance, but this can impede your judgment when you are faced with an individual whose belief system or cultural practices are not the same as yours. Fear or pride may prevent you from pursuing a line of questioning that would benefit the patient. Nurses with strong critical thinking skills exhibit:
- Learn from their mistakes and the mistakes of other nurses
- Look forward to integrating changes that improve patient care
- Treat each patient interaction as a part of a whole
- Evaluate new events based on past knowledge and adjust decision-making as needed
- Solve problems with their colleagues
- Are self-confident
- Acknowledge biases and seek to ensure these do not impact patient care
An Essential Skill for All Nurses
Critical thinking in nursing protects patient health and contributes to professional development and career advancement. Administrative and clinical nursing leaders are required to have strong critical thinking skills to be successful in their positions.
By using the strategies in this guide during your daily life and in your nursing role, you can intentionally improve your critical thinking abilities and be rewarded with better patient outcomes and potential career advancement.
Frequently Asked Questions About Critical Thinking in Nursing
How are critical thinking skills utilized in nursing practice.
Nursing practice utilizes critical thinking skills to provide the best care for patients. Often, the patient’s cause of pain or health issue is not immediately clear. Nursing professionals need to use their knowledge to determine what might be causing distress, collect vital information, and make quick decisions on how best to handle the situation.
How does nursing school develop critical thinking skills?
Nursing school gives students the knowledge professional nurses use to make important healthcare decisions for their patients. Students learn about diseases, anatomy, and physiology, and how to improve the patient’s overall well-being. Learners also participate in supervised clinical experiences, where they practice using their critical thinking skills to make decisions in professional settings.
Do only nurse managers use critical thinking?
Nurse managers certainly use critical thinking skills in their daily duties. But when working in a health setting, anyone giving care to patients uses their critical thinking skills. Everyone — including licensed practical nurses, registered nurses, and advanced nurse practitioners —needs to flex their critical thinking skills to make potentially life-saving decisions.
Meet Our Contributors

Crystal Slaughter, DNP, APRN, ACNS-BC, CNE
Crystal Slaughter is a core faculty member in Walden University’s RN-to-BSN program. She has worked as an advanced practice registered nurse with an intensivist/pulmonary service to provide care to hospitalized ICU patients and in inpatient palliative care. Slaughter’s clinical interests lie in nursing education and evidence-based practice initiatives to promote improving patient care.

Jenna Liphart Rhoads, Ph.D., RN
Jenna Liphart Rhoads is a nurse educator and freelance author and editor. She earned a BSN from Saint Francis Medical Center College of Nursing and an MS in nursing education from Northern Illinois University. Rhoads earned a Ph.D. in education with a concentration in nursing education from Capella University where she researched the moderation effects of emotional intelligence on the relationship of stress and GPA in military veteran nursing students. Her clinical background includes surgical-trauma adult critical care, interventional radiology procedures, and conscious sedation in adult and pediatric populations.

Nicholas McGowan, BSN, RN, CCRN
Nicholas McGowan is a critical care nurse with 10 years of experience in cardiovascular, surgical intensive care, and neurological trauma nursing. McGowan also has a background in education, leadership, and public speaking. He is an online learner who builds on his foundation of critical care nursing, which he uses directly at the bedside where he still practices. In addition, McGowan hosts an online course at Critical Care Academy where he helps nurses achieve critical care (CCRN) certification.

What is Critical Thinking in Nursing? (Explained W/ Examples)

Last updated on August 23rd, 2023
Critical thinking is a foundational skill applicable across various domains, including education, problem-solving, decision-making, and professional fields such as science, business, healthcare, and more.
It plays a crucial role in promoting logical and rational thinking, fostering informed decision-making, and enabling individuals to navigate complex and rapidly changing environments.
In this article, we will look at what is critical thinking in nursing practice, its importance, and how it enables nurses to excel in their roles while also positively impacting patient outcomes.
What is Critical Thinking?
Critical thinking is a cognitive process that involves analyzing, evaluating, and synthesizing information to make reasoned and informed decisions.
It’s a mental activity that goes beyond simple memorization or acceptance of information at face value.
Critical thinking involves careful, reflective, and logical thinking to understand complex problems, consider various perspectives, and arrive at well-reasoned conclusions or solutions.
Key aspects of critical thinking include:
- Analysis: Critical thinking begins with the thorough examination of information, ideas, or situations. It involves breaking down complex concepts into smaller parts to better understand their components and relationships.
- Evaluation: Critical thinkers assess the quality and reliability of information or arguments. They weigh evidence, identify strengths and weaknesses, and determine the credibility of sources.
- Synthesis: Critical thinking involves combining different pieces of information or ideas to create a new understanding or perspective. This involves connecting the dots between various sources and integrating them into a coherent whole.
- Inference: Critical thinkers draw logical and well-supported conclusions based on the information and evidence available. They use reasoning to make educated guesses about situations where complete information might be lacking.
- Problem-Solving: Critical thinking is essential in solving complex problems. It allows individuals to identify and define problems, generate potential solutions, evaluate the pros and cons of each solution, and choose the most appropriate course of action.
- Creativity: Critical thinking involves thinking outside the box and considering alternative viewpoints or approaches. It encourages the exploration of new ideas and solutions beyond conventional thinking.
- Reflection: Critical thinkers engage in self-assessment and reflection on their thought processes. They consider their own biases, assumptions, and potential errors in reasoning, aiming to improve their thinking skills over time.
- Open-Mindedness: Critical thinkers approach ideas and information with an open mind, willing to consider different viewpoints and perspectives even if they challenge their own beliefs.
- Effective Communication: Critical thinkers can articulate their thoughts and reasoning clearly and persuasively to others. They can express complex ideas in a coherent and understandable manner.
- Continuous Learning: Critical thinking encourages a commitment to ongoing learning and intellectual growth. It involves seeking out new knowledge, refining thinking skills, and staying receptive to new information.
Definition of Critical Thinking
Critical thinking is an intellectual process of analyzing, evaluating, and synthesizing information to make reasoned and informed decisions.
What is Critical Thinking in Nursing?
Critical thinking in nursing is a vital cognitive skill that involves analyzing, evaluating, and making reasoned decisions about patient care.
It’s an essential aspect of a nurse’s professional practice as it enables them to provide safe and effective care to patients.
Critical thinking involves a careful and deliberate thought process to gather and assess information, consider alternative solutions, and make informed decisions based on evidence and sound judgment.
This skill helps nurses to:
- Assess Information: Critical thinking allows nurses to thoroughly assess patient information, including medical history, symptoms, and test results. By analyzing this data, nurses can identify patterns, discrepancies, and potential issues that may require further investigation.
- Diagnose: Nurses use critical thinking to analyze patient data and collaboratively work with other healthcare professionals to formulate accurate nursing diagnoses. This is crucial for developing appropriate care plans that address the unique needs of each patient.
- Plan and Implement Care: Once a nursing diagnosis is established, critical thinking helps nurses develop effective care plans. They consider various interventions and treatment options, considering the patient’s preferences, medical history, and evidence-based practices.
- Evaluate Outcomes: After implementing interventions, critical thinking enables nurses to evaluate the outcomes of their actions. If the desired outcomes are not achieved, nurses can adapt their approach and make necessary changes to the care plan.
- Prioritize Care: In busy healthcare environments, nurses often face situations where they must prioritize patient care. Critical thinking helps them determine which patients require immediate attention and which interventions are most essential.
- Communicate Effectively: Critical thinking skills allow nurses to communicate clearly and confidently with patients, their families, and other members of the healthcare team. They can explain complex medical information and treatment plans in a way that is easily understood by all parties involved.
- Identify Problems: Nurses use critical thinking to identify potential complications or problems in a patient’s condition. This early recognition can lead to timely interventions and prevent further deterioration.
- Collaborate: Healthcare is a collaborative effort involving various professionals. Critical thinking enables nurses to actively participate in interdisciplinary discussions, share their insights, and contribute to holistic patient care.
- Ethical Decision-Making: Critical thinking helps nurses navigate ethical dilemmas that can arise in patient care. They can analyze different perspectives, consider ethical principles, and make morally sound decisions.
- Continual Learning: Critical thinking encourages nurses to seek out new knowledge, stay up-to-date with the latest research and medical advancements, and incorporate evidence-based practices into their care.
In summary, critical thinking is an integral skill for nurses, allowing them to provide high-quality, patient-centered care by analyzing information, making informed decisions, and adapting their approaches as needed.
It’s a dynamic process that enhances clinical reasoning , problem-solving, and overall patient outcomes.
What are the Levels of Critical Thinking in Nursing?
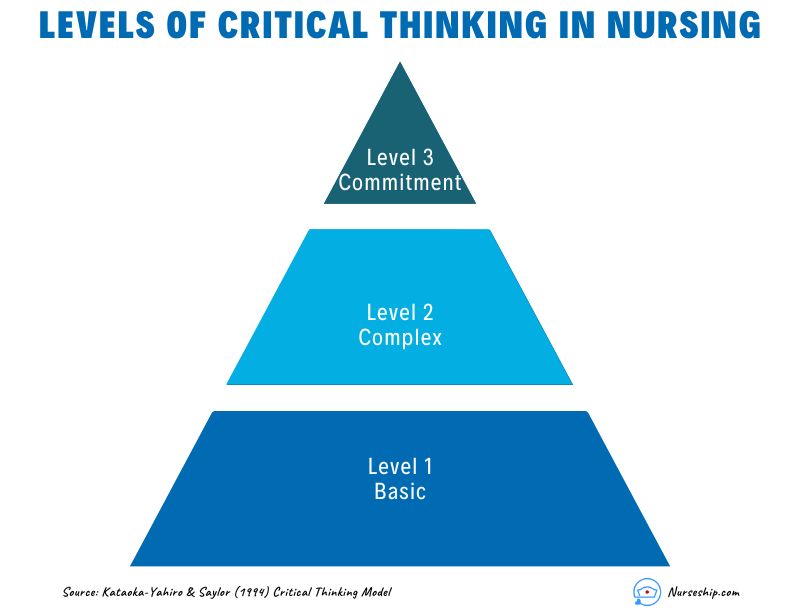
The development of critical thinking in nursing practice involves progressing through three levels: basic, complex, and commitment.
The Kataoka-Yahiro and Saylor model outlines this progression.
1. Basic Critical Thinking:
At this level, learners trust experts for solutions. Thinking is based on rules and principles. For instance, nursing students may strictly follow a procedure manual without personalization, as they lack experience. Answers are seen as right or wrong, and the opinions of experts are accepted.
2. Complex Critical Thinking:
Learners start to analyze choices independently and think creatively. They recognize conflicting solutions and weigh benefits and risks. Thinking becomes innovative, with a willingness to consider various approaches in complex situations.
3. Commitment:
At this level, individuals anticipate decision points without external help and take responsibility for their choices. They choose actions or beliefs based on available alternatives, considering consequences and accountability.
As nurses gain knowledge and experience, their critical thinking evolves from relying on experts to independent analysis and decision-making, ultimately leading to committed and accountable choices in patient care.
Why Critical Thinking is Important in Nursing?
Critical thinking is important in nursing for several crucial reasons:
Patient Safety:
Nursing decisions directly impact patient well-being. Critical thinking helps nurses identify potential risks, make informed choices, and prevent errors.
Clinical Judgment:
Nursing decisions often involve evaluating information from various sources, such as patient history, lab results, and medical literature.
Critical thinking assists nurses in critically appraising this information, distinguishing credible sources, and making rational judgments that align with evidence-based practices.
Enhances Decision-Making:
In nursing, critical thinking allows nurses to gather relevant patient information, assess it objectively, and weigh different options based on evidence and analysis.
This process empowers them to make informed decisions about patient care, treatment plans, and interventions, ultimately leading to better outcomes.
Promotes Problem-Solving:
Nurses encounter complex patient issues that require effective problem-solving.
Critical thinking equips them to break down problems into manageable parts, analyze root causes, and explore creative solutions that consider the unique needs of each patient.
Drives Creativity:
Nursing care is not always straightforward. Critical thinking encourages nurses to think creatively and explore innovative approaches to challenges, especially when standard protocols might not suffice for unique patient situations.
Fosters Effective Communication:
Communication is central to nursing. Critical thinking enables nurses to clearly express their thoughts, provide logical explanations for their decisions, and engage in meaningful dialogues with patients, families, and other healthcare professionals.
Aids Learning:
Nursing is a field of continuous learning. Critical thinking encourages nurses to engage in ongoing self-directed education, seeking out new knowledge, embracing new techniques, and staying current with the latest research and developments.
Improves Relationships:
Open-mindedness and empathy are essential in nursing relationships.
Critical thinking encourages nurses to consider diverse viewpoints, understand patients’ perspectives, and communicate compassionately, leading to stronger therapeutic relationships.
Empowers Independence:
Nursing often requires autonomous decision-making. Critical thinking empowers nurses to analyze situations independently, make judgments without undue influence, and take responsibility for their actions.
Facilitates Adaptability:
Healthcare environments are ever-changing. Critical thinking equips nurses with the ability to quickly assess new information, adjust care plans, and navigate unexpected situations while maintaining patient safety and well-being.
Strengthens Critical Analysis:
In the era of vast information, nurses must discern reliable data from misinformation.
Critical thinking helps them scrutinize sources, question assumptions, and make well-founded choices based on credible information.
How to Apply Critical Thinking in Nursing? (With Examples)
Here are some examples of how nurses can apply critical thinking.
Assess Patient Data:
Critical Thinking Action: Carefully review patient history, symptoms, and test results.
Example: A nurse notices a change in a diabetic patient’s blood sugar levels. Instead of just administering insulin, the nurse considers recent dietary changes, activity levels, and possible medication interactions before adjusting the treatment plan.
Diagnose Patient Needs:
Critical Thinking Action: Analyze patient data to identify potential nursing diagnoses.
Example: After reviewing a patient’s lab results, vital signs, and observations, a nurse identifies “ Risk for Impaired Skin Integrity ” due to the patient’s limited mobility.
Plan and Implement Care:
Critical Thinking Action: Develop a care plan based on patient needs and evidence-based practices.
Example: For a patient at risk of falls, the nurse plans interventions such as hourly rounding, non-slip footwear, and bed alarms to ensure patient safety.
Evaluate Interventions:
Critical Thinking Action: Assess the effectiveness of interventions and modify the care plan as needed.
Example: After administering pain medication, the nurse evaluates its impact on the patient’s comfort level and considers adjusting the dosage or trying an alternative pain management approach.
Prioritize Care:
Critical Thinking Action: Determine the order of interventions based on patient acuity and needs.
Example: In a busy emergency department, the nurse triages patients by considering the severity of their conditions, ensuring that critical cases receive immediate attention.
Collaborate with the Healthcare Team:
Critical Thinking Action: Participate in interdisciplinary discussions and share insights.
Example: During rounds, a nurse provides input on a patient’s response to treatment, which prompts the team to adjust the care plan for better outcomes.
Ethical Decision-Making:
Critical Thinking Action: Analyze ethical dilemmas and make morally sound choices.
Example: When a terminally ill patient expresses a desire to stop treatment, the nurse engages in ethical discussions, respecting the patient’s autonomy and ensuring proper end-of-life care.
Patient Education:
Critical Thinking Action: Tailor patient education to individual needs and comprehension levels.
Example: A nurse uses visual aids and simplified language to explain medication administration to a patient with limited literacy skills.
Adapt to Changes:
Critical Thinking Action: Quickly adjust care plans when patient conditions change.
Example: During post-operative recovery, a nurse notices signs of infection and promptly informs the healthcare team to initiate appropriate treatment adjustments.
Critical Analysis of Information:
Critical Thinking Action: Evaluate information sources for reliability and relevance.
Example: When presented with conflicting research studies, a nurse critically examines the methodologies and sample sizes to determine which study is more credible.
Making Sense of Critical Thinking Skills
What is the purpose of critical thinking in nursing.
The purpose of critical thinking in nursing is to enable nurses to effectively analyze, interpret, and evaluate patient information, make informed clinical judgments, develop appropriate care plans, prioritize interventions, and adapt their approaches as needed, thereby ensuring safe, evidence-based, and patient-centered care.
Why critical thinking is important in nursing?
Critical thinking is important in nursing because it promotes safe decision-making, accurate clinical judgment, problem-solving, evidence-based practice, holistic patient care, ethical reasoning, collaboration, and adapting to dynamic healthcare environments.
Critical thinking skill also enhances patient safety, improves outcomes, and supports nurses’ professional growth.
How is critical thinking used in the nursing process?
Critical thinking is integral to the nursing process as it guides nurses through the systematic approach of assessing, diagnosing, planning, implementing, and evaluating patient care. It involves:
- Assessment: Critical thinking enables nurses to gather and interpret patient data accurately, recognizing relevant patterns and cues.
- Diagnosis: Nurses use critical thinking to analyze patient data, identify nursing diagnoses, and differentiate actual issues from potential complications.
- Planning: Critical thinking helps nurses develop tailored care plans, selecting appropriate interventions based on patient needs and evidence.
- Implementation: Nurses make informed decisions during interventions, considering patient responses and adjusting plans as needed.
- Evaluation: Critical thinking supports the assessment of patient outcomes, determining the effectiveness of intervention, and adapting care accordingly.
Throughout the nursing process , critical thinking ensures comprehensive, patient-centered care and fosters continuous improvement in clinical judgment and decision-making.
What is an example of the critical thinking attitude of independent thinking in nursing practice?
An example of the critical thinking attitude of independent thinking in nursing practice could be:
A nurse is caring for a patient with a complex medical history who is experiencing a new set of symptoms. The nurse carefully reviews the patient’s history, recent test results, and medication list.
While discussing the case with the healthcare team, the nurse realizes that the current treatment plan might not be addressing all aspects of the patient’s condition.
Instead of simply following the established protocol, the nurse independently considers alternative approaches based on their assessment.
The nurse proposes a modification to the treatment plan, citing the rationale and evidence supporting the change.
This demonstrates independent thinking by critically evaluating the situation, challenging assumptions, and advocating for a more personalized and effective patient care approach.
How to use Costa’s level of questioning for critical thinking in nursing?
Costa’s levels of questioning can be applied in nursing to facilitate critical thinking and stimulate a deeper understanding of patient situations. The levels of questioning are as follows:
- 15 Attitudes of Critical Thinking in Nursing (Explained W/ Examples)
- Nursing Concept Map (FREE Template)
- Clinical Reasoning In Nursing (Explained W/ Example)
- 8 Stages Of The Clinical Reasoning Cycle
- How To Improve Critical Thinking Skills In Nursing? 24 Strategies With Examples
- What is the “5 Whys” Technique?
- What Are Socratic Questions?
Critical thinking in nursing is the foundation that underpins safe, effective, and patient-centered care.
Critical thinking skills empower nurses to navigate the complexities of their profession while consistently providing high-quality care to diverse patient populations.
Reading Recommendation
Potter, P.A., Perry, A.G., Stockert, P. and Hall, A. (2013) Fundamentals of Nursing
Comments are closed.
Medical & Legal Disclaimer
All the contents on this site are for entertainment, informational, educational, and example purposes ONLY. These contents are not intended to be used as a substitute for professional medical advice or practice guidelines. However, we aim to publish precise and current information. By using any content on this website, you agree never to hold us legally liable for damages, harm, loss, or misinformation. Read the privacy policy and terms and conditions.
Privacy Policy
Terms & Conditions
© 2024 nurseship.com. All rights reserved.
- Who We Insure
- Insurance Products
- About Berxi
Topics on this page:
The importance of critical thinking in nursing.
Topics on this page

While not every decision is an immediate life-and-death situation, there are hundreds of decisions nurses must make every day that impact patient care in ways small and large.
“Being able to assess situations and make decisions can lead to life-or-death situations,” said nurse anesthetist Aisha Allen . “Critical thinking is a crucial and essential skill for nurses.”
The National League for Nursing Accreditation Commission (NLNAC) defines critical thinking in nursing this way: “the deliberate nonlinear process of collecting, interpreting, analyzing, drawing conclusions about, presenting, and evaluating information that is both factually and belief-based. This is demonstrated in nursing by clinical judgment, which includes ethical, diagnostic, and therapeutic dimensions and research.”
Why Critical Thinking in Nursing Is Important
An eight-year study by Johns Hopkins reports that 10% of deaths in the U.S. are due to medical error — the third-highest cause of death in the country.
“Diagnostic errors, medical mistakes, and the absence of safety nets could result in someone’s death,” wrote Dr. Martin Makary , professor of surgery at Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine.
Everyone makes mistakes — even doctors. Nurses applying critical thinking skills can help reduce errors.
“Question everything,” said pediatric nurse practitioner Ersilia Pompilio RN, MSN, PNP . “Especially doctor’s orders.” Nurses often spend more time with patients than doctors and may notice slight changes in conditions that may not be obvious. Resolving these observations with treatment plans can help lead to better care.
Key Nursing Critical Thinking Skills
Some of the most important critical thinking skills nurses use daily include interpretation, analysis, evaluation, inference, explanation, and self-regulation.
- Interpretation: Understanding the meaning of information or events.
- Analysis: Investigating a course of action based on objective and subjective data.
- Evaluation: Assessing the value of information and its credibility.
- Inference: Making logical deductions about the impact of care decisions.
- Explanation: Translating complicated and often complex medical information to patients and families in a way they can understand to make decisions about patient care.
- Self-Regulation: Avoiding the impact of unconscious bias with cognitive awareness.
These skills are used in conjunction with clinical reasoning. Based on training and experience, nurses use these skills and then have to make decisions affecting care.
It’s the ultimate test of a nurse’s ability to gather reliable data and solve complex problems. However, critical thinking goes beyond just solving problems. Critical thinking incorporates questioning and critiquing solutions to find the most effective one. For example, treating immediate symptoms may temporarily solve a problem, but determining the underlying cause of the symptoms is the key to effective long-term health.
8 Examples of Critical Thinking in Nursing
Here are some real-life examples of how nurses apply critical thinking on the job every day, as told by nurses themselves.
Example #1: Patient Assessments
“Doing a thorough assessment on your patient can help you detect that something is wrong, even if you're not quite sure what it is,” said Shantay Carter , registered nurse and co-founder of Women of Integrity . “When you notice the change, you have to use your critical thinking skills to decide what's the next step. Critical thinking allows you to provide the best and safest care possible.”
Example #2: First Line of Defense
Often, nurses are the first line of defense for patients.
“One example would be a patient that had an accelerated heart rate,” said nurse educator and adult critical care nurse Dr. Jenna Liphart Rhoads . “As a nurse, it was my job to investigate the cause of the heart rate and implement nursing actions to help decrease the heart rate prior to calling the primary care provider.”
Nurses with poor critical thinking skills may fail to detect a patient in stress or deteriorating condition. This can result in what’s called a “ failure to rescue ,” or FTR, which can lead to adverse conditions following a complication that leads to mortality.
Example #3: Patient Interactions
Nurses are the ones taking initial reports or discussing care with patients.
“We maintain relationships with patients between office visits,” said registered nurse, care coordinator, and ambulatory case manager Amelia Roberts . “So, when there is a concern, we are the first name that comes to mind (and get the call).”
“Several times, a parent called after the child had a high temperature, and the call came in after hours,” Roberts said. “Doing a nursing assessment over the phone is a special skill, yet based on the information gathered related to the child's behavior (and) fluid intake, there were several recommendations I could make.”
Deciding whether it was OK to wait until the morning, page the primary care doctor, or go to the emergency room to be evaluated takes critical thinking.
Example #4: Using Detective Skills
Nurses have to use acute listening skills to discern what patients are really telling them (or not telling them) and whether they are getting the whole story.
“I once had a 5-year-old patient who came in for asthma exacerbation on repeated occasions into my clinic,” said Pompilio. “The mother swore she was giving her child all her medications, but the asthma just kept getting worse.”
Pompilio asked the parent to keep a medication diary.
“It turned out that after a day or so of medication and alleviation in some symptoms, the mother thought the child was getting better and stopped all medications,” she said.
Example #5: Prioritizing
“Critical thinking is present in almost all aspects of nursing, even those that are not in direct action with the patient,” said Rhoads. “During report, nurses decide which patient to see first based on the information gathered, and from there they must prioritize their actions when in a patient’s room. Nurses must be able to scrutinize which medications can be taken together, and which modality would be best to help a patient move from the bed to the chair.”
A critical thinking skill in prioritization is cognitive stacking. Cognitive stacking helps create smooth workflow management to set priorities and help nurses manage their time. It helps establish routines for care while leaving room within schedules for the unplanned events that will inevitably occur. Even experienced nurses can struggle with juggling today’s significant workload, prioritizing responsibilities, and delegating appropriately.
Example #6: Medication & Care Coordination
Another aspect that often falls to nurses is care coordination. A nurse may be the first to notice that a patient is having an issue with medications.
“Based on a report of illness in a patient who has autoimmune challenges, we might recommend that a dose of medicine that interferes with immune response be held until we communicate with their specialty provider,” said Roberts.
Nurses applying critical skills can also help ease treatment concerns for patients.
“We might recommend a patient who gets infusions come in earlier in the day to get routine labs drawn before the infusion to minimize needle sticks and trauma,” Robert said.

Example #7: Critical Decisions
During the middle of an operation, the anesthesia breathing machine Allen was using malfunctioned.
“I had to critically think about whether or not I could fix this machine or abandon that mode of delivering nursing anesthesia care safely,” she said. “I chose to disconnect my patient from the malfunctioning machine and retrieve tools and medications to resume medication administration so that the surgery could go on.”
Nurses are also called on to do rapid assessments of patient conditions and make split-second decisions in the operating room.
“When blood pressure drops, it is my responsibility to decide which medication and how much medication will fix the issue,” Allen said. “I must work alongside the surgeons and the operating room team to determine the best plan of care for that patient's surgery.”
“On some days, it seems like you are in the movie ‘The Matrix,’” said Pompilio. “There's lots of chaos happening around you. Your patient might be decompensating. You have to literally stop time and take yourself out of the situation and make a decision.”
Example #8: Fast & Flexible Decisions
Allen said she thinks electronics are great, but she can remember a time when technology failed her.
“The hospital monitor that gives us vitals stopped correlating with real-time values,” she said. “So I had to rely on basic nursing skills to make sure my patient was safe. (Pulse check, visual assessments, etc.)”
In such cases, there may not be enough time to think through every possible outcome. Critical thinking combined with experience gives nurses the ability to think quickly and make the right decisions.
Improving the Quality of Patient Care
Nurses who think critically are in a position to significantly increase the quality of patient care and avoid adverse outcomes.
“Critical thinking allows you to ensure patient safety,” said Carter. “It’s essential to being a good nurse.”
Nurses must be able to recognize a change in a patient’s condition, conduct independent interventions, anticipate patients and provider needs, and prioritize. Such actions require critical thinking ability and advanced problem-solving skills.
“Nurses are the eyes and ears for patients, and critical thinking allows us to be their advocates,” said Allen.
Image courtesy of iStock.com/ davidf
Last updated on Jan 05, 2024 .
Originally published on Aug 25, 2021 .
The views expressed in this article are those of the author and do not necessarily reflect those of Berxi™ or Berkshire Hathaway Specialty Insurance Company. This article (subject to change without notice) is for informational purposes only, and does not constitute professional advice. Click here to read our full disclaimer
Delegation in Nursing: Steps, Skills, & Solutions for Creating Balance at Work
The 7 Most Common Nursing Mistakes (And What You Can Do If You Make One)
Resource topics.
- Pre-Nursing
- Nursing School
- After Graduation
How to Apply Critical Thinking in Nursing

Harnessing the power of critical thinking can be the key to becoming a successful and competent nurse.
Developing and refining your critical thinking skills is crucial as you embark on your nursing journey. By doing so, you’ll enhance your ability to provide high-quality care, advance your professional growth, and contribute to the ever-evolving nursing field.
What is critical thinking in nursing?
Critical thinking is an essential cognitive process that enables nurses to analyze, evaluate, and synthesize information to make informed decisions. In the context of nursing, it involves observing, interpreting, and responding to patient needs effectively.
Critical thinking allows nurses to go beyond memorized facts and apply logical reasoning to address patient problems holistically.
As a nurse, you’ll encounter multifaceted healthcare scenarios, each presenting its unique challenges. Critical thinking enables you to approach these situations systematically, evaluate the available data, identify relevant factors, and understand the patient’s condition comprehensively.
By employing critical thinking skills, you can differentiate between urgent and non-urgent issues, prioritize care, anticipate potential complications, and adapt your interventions accordingly. This analytical approach helps minimize errors, promote patient safety, and achieve positive patient outcomes.
Why is critical thinking important in nursing?
Critical thinking serves as the backbone of nursing practice. You’ll encounter various uncertainties, changing conditions, and ethical dilemmas as a nurse. Developing critical thinking abilities empowers you to navigate these challenges confidently and provide optimal patient care.
In nursing, critical thinking is crucial for the following reasons:
- Enhanced Clinical Judgment: Critical thinking enables assessing complex situations, analyzing available information, and drawing logical conclusions. It enhances your clinical judgment, allowing you to make informed decisions based on the best available evidence and expert consensus.
- Effective Problem Solving: Nursing involves encountering problems and finding effective solutions. Critical thinking equips you with the tools to identify underlying issues, explore alternative options, and implement interventions that address the root cause of the problem.
- Patient Advocacy: Critical thinking empowers you to advocate for your patients’ needs. By actively engaging in critical inquiry, you can challenge assumptions, question policies, and promote patient-centered care.
- Adapting to Changing Environments: Healthcare is constantly evolving, with new research findings, technologies, and treatments emerging regularly. Developing critical thinking skills helps you adapt to these changes, ensuring you stay updated and deliver evidence-based care.
Examples of Critical Thinking in Nursing
Let’s dive into some real-life examples that highlight how critical thinking plays a crucial role in nursing practice:
- Prioritization: Imagine working in an emergency department where multiple patients arrive simultaneously with varying degrees of severity. Utilizing critical thinking, you can assess each patient’s condition, prioritize care based on the urgency of their needs, and allocate resources effectively.
- Medication Administration: When administering medication, critical thinking prompts you to cross-check the prescribed dose, assess potential drug interactions or allergies, and evaluate the patient’s response to the medication. This proactive approach ensures patient safety and minimizes medication errors.
- Ethical Dilemmas: Critical thinking helps you navigate complex ethical dilemmas by analyzing the values at stake, considering legal and ethical principles, and collaborating with the healthcare team to make decisions that align with the patient’s best interests.
Supplement Your Nursing Studies and Boost Your Grades
At SimpleNursing , we understand the significance of critical thinking in nursing education. Our comprehensive digital study tools are designed to enhance your critical thinking abilities, providing you with interactive case studies, practice questions, and simulated patient scenarios.
Boost your confidence and excel in your nursing studies with SimpleNursing’s innovative study resources.
Sign up for a free trial and take your nursing study skills to new heights.
Want to ace Nursing School Exams & the NCLEX?
Make topics click with easy-to-understand videos & more. We've helped over 1,000,000 students & we can help you too.
Share this post
Nursing students trust simplenursing.

SimpleNursing Student Testimonial
Most recent posts.

Anatomy of the Hand and Wrist
Raise your hand and take a closer look at it. Do you know how many…

Adolescent Growth Development
When you reflect on your preteen or teenage years, you may remember experiencing many physical,…

Trousseau’s Sign of Latent Tetany
As a nursing student, understanding clinical signs like Trousseau’s sign of latent tetany is crucial…

Comprehensive Overview of the Brachialis Muscle Anatomy
When it comes to muscle anatomy, the brachialis muscle often lies in the shadow of…
Find what you are interested in
- Practice Test
- Fundamentals of Nursing
- Anatomy and Physiology
- Medical and Surgical Nursing
- Perioperative Nursing
- Psychiatric Mental Health Nursing
- Maternal & Child Nursing
- Community Health Nursing
- Pathophysiology
- Nursing Research
- Study Guide and Strategies
- Nursing Videos
- Work for Us!
- Privacy Policy

- Journals and Essays
Thinking Like a Nurse: The Critical Thinking Skills in the Nursing Practice

Thinking how to nurse is thinking like a nurse. Florence Nightingale (1860) wrote on her notes that women who have charge of the other’s health—to which the application of her integrated experiences must teach herself to think how to nurse, a self-learning acquired from “hints”.
Perhaps, Nightingale referred “hints” as the use of critical thinking skills in patient’s care. The ability to think critically was the foundation of nursing practice started from historic times and is becoming one of the key performance indicators for both students and nursing professionals nowadays.
Educational system continues to evolve and progresses heeding to the needs of the society, and parallel to the changing educational structure and methodology. However, Haber (2020) reported that only 75% of employers claim that the students they hire who underwent 12 or more years of formal education lack of critical thinking and problem-solving abilities despite the progress in the educational system.
What is Critical Thinking?
Critical thinking skills, a fundamental skill that plays a pivotal role in our daily survival. In general terms, the skill will not stop in memorization, the process goes beyond connecting the dots from one to concept to another, problem-solving techniques, think creatively, and apply the learned knowledge in new ways (Walden University, 2020). Kaminske (2019), defines critical thinking skills as a domain-specific skill on the ability to solve problems and make effective decisions that require expertise to be applied in a range of situations and scenarios.
In the nursing practice, Critical thinking skill works in assimilation with critical reasoning as a practice-based discipline of decision-making to the health care professionals. Critical thinking is the process of the intentional higher level of thinking to identify patient’s health care needs and appraise evidence-based practice to make choices in the delivery of care.

On the other hand, clinical reasoning as integrated to clinical thinking in application to clinical situation works as a cognitive process to utilized thinking strategies to gather and critically analyze the data concerning the health care needs of the patient, organized the information according to its prioritization, and formulate efficient nursing care plans to improve patient’s outcomes (Berman, et al., 2016).
“Critical thinking is the intellectually disciplined process of actively and skillfully conceptualizing, applying, analyzing, synthesizing, and/or evaluating information gathered from, or generated by, observation, experience, reflection, reasoning, or communication, as a guide to belief and action”, a precise definition presented by Michael Scriven and Richard Paul at the Eighth Annual International Conference on Critical Thinking and Education Reform during the summer of 1987 (Lakhanigam, 2017).
Lakhanigam added the definition published by the Journal of Nursing Education in 2010 that describes critical thinking as the process involving interpretation and analysis of the problem, reasoning to find a solution, applying, and finally evaluation of the outcomes”. Regis College (2020), emphasized the use of deductive reasoning in observation, analyzing information, formulate conclusions, and performing appropriate actions in a self-directed process.
Theories on the Physiology of Thinking
From the ancient theory of “tabula rasa”, as describes in Wikipedia (2020) that humans are born without built-in mental content, and all knowledge is collected by the brain from experiences and perceptions. In this computer age, a neurologist discovered neurological pathways on how to re-program or reformat our brains like computers by analyzing how the brain appears to process, recognize, remember and transfer information at the level of neural circuits, synapses and neurotransmitters. Willis (2012) discussed the brain’s neuroplastic response to stimulation called neuroplasticity. The information is processed in the reflective and cognitive functions of prefrontal cortex wherein learning incorporated into networks of longterm conceptual memory.
Neuroplasticity is greatly affected by stress, boredom and frustration as seen in the neuroimaging scans of students showed that active metabolic states block the processing in the prefrontal cortex. In response to stress, the amygdala as the switching station became hyperactive resulting to switches of input and output away from the prefrontal cortex down to the control of the lower reactive brain, this response is called fight/flight/freeze (act out/zone out). In this situation, the lower brain’s reactive behaviours are in control. This will result in the loss of information access to the prefrontal cortex and new learning is not retained.
Elseways, Knowles (1984) four principles of andragogy of adult learning included (a.) experiences from mistakes that provide the basis for the learning activities; and (b.) the importance of problems and crisis, as adult learning is problem-centred rather than content-oriented; as well as (c.) involvement in the planning and evaluation of learning; and lastly, (d.) that adults are most interested in a subject that is relevant to their job and personal life.
Learning and thinking as applied in a higher-level context, Ausubel’s assimilation theory may recount the theories on critical thinking. In this theory, Ausubel claimed that learning occurs as a result of the interaction between the acquired learning and the cognitive structure in application to practice (Seel, 2012). Moreover, critical analysis and differentiation of interrelationships between concepts called concept mapping refines the knowledge into a more organized, precise, specific, and integrated learning.
In different circumstances, nursing as a professional working in a toxic environment of the sick, pained, hopeless, weak, and dying patients; bullying, queen bee syndrome, and seniority egoism of colleagues; and backbreaking workloads—have reported cases of work-related boredom and stress. The application of the three theories may improve mentoring-learning strategies in meaningful nursing education and training.
Theories on learning acquisition from the collection of information, physiologic processing on cognitive-reflective functions of the brain, concept mapping, and internal/external utilization of knowledge in application to critical thinking are the frameworks of a skilled critical thinker.
Characteristics of a Skilled Critical-Thinker
Health care system can go a long way, achieving a considerable success having employees that possess the ability to think critically thus decreasing errors in clinical judgments. For this purpose, every nurse is required to obtain the characteristics of an excellent skilled critical thinker.
The study of Scheffer and Rubenfeld revealed the common qualities among internationally diverse expert nurses from nine different countries supporting the idea of critical thinking in nursing that encompasses logic and reasoning (Berman, et. Al., 2016), and that includes:
11 Affective Components of a Skilled Critical-Thinker Nurse:
- Perseverance
- Open-mindedness
- Flexibility
- Inquisitiveness
- Intellectual integrity
- Perspective
7 Cognitive Skills of a Skilled Critical-Thinker Nurse:
- Information seeking
- Discriminating
- Transforming knowledge
- Applying standards
- Logical reasoning
Critical Thinking Beyond Exigency and Expediency
Undeniably, nurses with critical thinking ability diversified with effective problem-solving and efficient decision-making skills are the most in-demand and highly valued in the field of the health care industry and academe.
As a nurse striding in the most complicated, stressful and multi-tasking job, you are responsible for making life-changing decisions under the pressure of time and emotions. These reasons as to why critical thinking skills in nursing practice plays a vital role in the care of the patient. Luna (2020), cited seven importance of critical thinking skills in the practice of nursing, such as:
- Nurses’ Critical Thinking Heavily Impacts Patient Care
- It’s Vital to Recognizing Shifts in Patient Status
- It’s Integral to an Honest and Open Exchange of Ideas
- It Allows You to Ensure Patient Safety
- It Helps Nurses Find Quick Fixes and Troubleshooting
- Critical Thinking can Lead to Innovative Improvements
- It Plays a Role in Rational Decision Making
Critical thinking skill is needed in problems identification and implementation of interventions resulting in improved patients outcomes, as well as development in nursing practice by providing new insights on the learned knowledge. Feedback and reflections provide interconnections between nursing research , critical thinking and the nursing practice (Berman, et. Al., 2016).
Critical Thinking Skills: The Mastery, Update and Upgrade
Critical thinking skill is an ability beyond thinking rationally and clearly. It is a process of thinking independently and working at your own feet in formulating own opinions or new theory by utilizing critical analysis on the interrelationship of two or more ideas and delineating conclusions without external control (Wabisabi Learning, 2020).
Modified Wabisabi Learning’s 12 Solid Strategies for Teaching Critical Thinking Skills, and its Application to Nursing Education, Training and Practice:
1. Practice on Eloquence in Question and Answer (Solution Fluency)
Mastery requires ample amount of practice to become highly skilled in critical thinking. Accustom to deliberate open discussions encouraging brainstorming on issues affecting the practice and daily living by using explicit open-ended questions and comprehensive instructions for problem-solving may provide opportunities to apply knowledge into practice as well as encouraging the transfer of ideas between domains (Haber, 2020). Brainstorming is an excellent learning tool to exercise critical thinking (Walden University, 2020) particularly if applied in a situational crisis or a hospital scenario.
2. Create a Foundation
From the theory of back to basic, mastery of low-level skills is a requirement in preparatory to the application of critical thinking skills (Kaminske, 2019).
Learning experiences from theoretical and experiential knowledge are good foundations to start critical thinking. Moreover, practicing thinking skills obtained from theoretical and experiential undertakings improve intellectual ability (Berman, et. al., 2016). Practical understanding and specialization on a particular focus may excel you more in thinking critically. The competence and skills acquired from clinical experience are the most essential learning in developing clinical judgment.
3. Consult the Classics
Nursing theorists and their work are the best examples of consulting the classics. In critical thinking, nurses identify claims based on facts, conclusions, judgment/opinions and evidence-based practice. Exploring nursing theorists and their works are like exploring great minds, acquiring lessons on character motivation, refuting theories or formulating a new theory from existing theory. Case studies and in-depth objective critiques of nursing theories may not only promote critical thinking but act as a leverage to bridge the gap between theory and practice.
4. Create an Environment for Open Communication
During clinical rounds, nurses and/or students with a clinical instructor are engaged into thinking process by providing the opportunity to communicate assessment data, collaborate ideas, formulate nursing care plan, and discuss the various context of the situation from different perspectives (Di Vito-Thomas, 2005).
5. Use Information Fluency
Information fluency is mastering the proper use of information and to the ability to intuitively analyze and interpret it in unearthing knowledge and appropriate facts useful in solving a problem (Wabisabi Learning, 2020).
Knowledge of medical conditions, procedures and its connections to patient’s care are important in building critical thinking. Learning from available resources like medical journals, surfing the internet, and meaningful dialogue with colleagues can increase your medical know-how (Jillings, 2020).
6. Utilize Peer Groups
Peer groups, particularly well experienced and highly skilled colleagues are an excellent source of information, questions, and problem-solving techniques as it expands thinking and viewpoints. It also develops interpersonal skills like teamwork and resolving conflicts (Berman, et. Al., 2016).
7. Try One Sentence of Reflections at a time
Reflections will teach the learner to apply their knowledge, logic and reasoning by explaining themselves in a low-pressure setting. It provides an opportunity to explore situations with a different approach and better solutions for future use (Jillings, 2020).
The mastery of metacognition helps the learner to use reflection in defining clinical experiences and explore ways on how to improve it. Recollecting facts and events in patient’s care may integrate the learner into different concepts by connecting different ideas from one another (Di Vito-Thomas, 2005).
8. Problem-solving with Reasoning
Understanding rationale, the sets of reasons or logical basis for a course of action assist the learners to gain a broad knowledge of the topic and promotes a higher level of understanding. Problem-solving guided by rationale is a technique to the use of deductive and inductive reasoning in the thinking process (Di Vito-Thomas, 2005).
9. Roleplaying and Return Demonstration
Role-playing is a self-directed activity that encourages analytic and creative thinking. It helps the learner to internalize empathy while compromising in portraying a role or another persona creating a wider chance for memory retention.
Practice and repetition of observed procedures during return demonstration creates an avenue for re-thinking ways on how to do a task properly with ease in your own phase as you implement it by yourself.
10. Thinking and Speaking With Sketch (Concept Mapping)
Incorporating a concept with multiple perspectives and connecting complex ideas in a structured way to search for potential solutions. These processes create an abstract concept that encourages logical arguments used in critical thinking (Kaminske, 2019).
Interactive activities such as case study with a panel discussion, observing clinical dynamics during in-depth arguments, making a multidisciplinary joint care plan for patient promotes an environment for critical thinking thus facilitating the development of clinical judgment (Di Vito-Thomas, 2005).
11. Do Some Prioritizing and Decision-making
Make critical thinking as a culture and not just an activity by encouraging decision-making. Prioritizing through analyzing information, applying knowledge, and evaluating a prospected solution are the cornerstones of decision-making. This will allows the learner to apply learned theories to a different scenario by weighing the advantages and disadvantages of different solutions and option in deciding best practices.
12. Correct Misconceptions and Personal Bias
Personal beliefs greatly influence one’s ability to think critically as people always seek out ideas that conform to their own beliefs (Kaminske (2019). Several factors that act as the pitfalls in critical thinking are misconceptions, personal bias, and assumptions—which can bring a learner into a wrong direction. A discussion with colleagues who have mastery in evidence-based practice and conducting more in-depth investigations can give ideas and extends point of view (Jillings, 2020).
Conclusion and Suggestions:
Analytical skills through keen observation, understanding important data, and identifying a pattern of recognition; problem-solving capacity by connecting relationship of phenomena, data interpretation guided by significance and rationale; and use of reflection and evaluation abilities in formulating conclusion are the important factors in clinical judgment and decision-making.
Critical thinking is a learned skill resulted from a rolled-up innate curiosity in the application of strong theoretical and experiential foundations in solving clinical problems that direct to the best care decision, which produce positive patient outcomes and improve patient care services.
In this era of technological advancement where machine replaces almost of everything, critical thinking still plays an important role in the nursing practice. Nurses who can manipulate complex clinical situations with efficient skills on critical/analytical thinking, problem-solving and decision-making are often in the front line to compete for the position with greater autonomy and higher chances for opportunities.
- Nightingale, F. (1860). Notes on Nursing: What it Is, and what it is Not. London: Harrisons & Sons.
- Haber, J. (2020). It’s Time to Get Serious About Teaching Critical Thinking. Inside Higher Ed. Retrieved on 24 October 2020 from https://www.insidehighered.com/views/2020/03/02/teaching-students-think-critically-opinion
- Walden University. (2020). 7 Ways to Teach Critical Thinking in Elementary Education. Retrieved on 24 October 2020 from https://www.waldenu.edu/online-bachelors-programs/bs-in-elementary-education/resource/seven-ways-to-teach-critical-thinking-in-elementary-education
- Kaminske, A.N. (2019). Can We Teach Critical Thinking?. The Learning Scientists. Retrieved on 24 October 2020 from https://www.learningscientists.org/blog/2019/2/28/can-we-teach-critical-thinking#:~:text=beliefs%20(3).-,Can%20we%20teach%20critical%20thinking%3F,happens%20to%20enjoy%20science%20fiction
- Berman, A., Snyder, S.J. & Frandsen, G. (2016). Kozier & Erb’s Fundamentals of Nursing: Concepts, Process, and Practice, 10 th New Jersey: Pearson Education, Inc.
- Lakhanigam, S. (2017). Critical Thinking: A Vital Trait for Nurses. Minority Nurse. Retrieved on 24 October 2020 from https://minoritynurse.com/critical-thinking-vital-trait-nurses/
- Regis College (2020). How to Leverage Critical Thinking in Nursing Practice. Retrieved on 24 October 2020 from https://online.regiscollege.edu/blog/how-to-leverage-critical-thinking-in-nursing-practice/
- (2020). Tabula Rasa. Retrieved on 24 October 2020 from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tabula_rasa
- Willis, J. (2012). A Neurologist Makes the Case for Teaching Teachers About the Brain. George Lucas Educational Foundation. Retrieved on 24 October 2020 from https://www.edutopia.org/blog/neuroscience-higher-ed-judy-willis
- Knowles, M. (1984). The Adult Learner: A Neglected Species, 3 rd Houston, TX: Gulf Publishing.
- Seel, N.M. (2012). Assimilation Theory of Learning. In: Seel N.M. (eds) Encyclopedia of the Sciences of Learning. Springer, Boston, MA. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4419-1428-6_358
- Luna, A. (2020). 7 Reasons Critical Thinking In Nursing Is Important. AMN Healthcare Company. Retrieved on 24 October 2002 from https://www.onwardhealthcare.com/nursing-resources/seven-reasons-critical-thinking-in-nursing-is-important/
- Wabisabi Learning. (2020). 12 Solid Strategies for Teaching Critical Thinking Skills. Retrieved on 24 October 2020 from https://wabisabilearning.com/blogs/critical-thinking/teaching-critical-thinking-skills
- Di Vito-Thomas, P. (2005). Nursing Student Stories on Learning How to Think Like a Nurse. Nurse Educator, 30(3), pp. 133-136.
- Jillings, B. (2020). Critical Thinking in Nursing: Why It’s Important and How to Improve. AMN Healthcare Company. Retrieved on 24 October 2020 from https://www.americanmobile.com/mobile/NZArticle/?articleId=3346
RELATED ARTICLES MORE FROM AUTHOR
Autism: a comprehensive guide to raising and supporting a child with autism, methylprednisolone: a vital tool in the healthcare toolbox, adult adhd management, treatment and strategies, the most common types of eating disorder, health risks linked to obesity, 120+ fresh nursing essay topics (with faqs and essay writing tips), leave a reply cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Critical Thinking in Nursing
- First Online: 02 January 2023
Cite this chapter

- Şefika Dilek Güven 3
Part of the book series: Integrated Science ((IS,volume 12))
1098 Accesses
Critical thinking is an integral part of nursing, especially in terms of professionalization and independent clinical decision-making. It is necessary to think critically to provide adequate, creative, and effective nursing care when making the right decisions for practices and care in the clinical setting and solving various ethical issues encountered. Nurses should develop their critical thinking skills so that they can analyze the problems of the current century, keep up with new developments and changes, cope with nursing problems they encounter, identify more complex patient care needs, provide more systematic care, give the most appropriate patient care in line with the education they have received, and make clinical decisions. The present chapter briefly examines critical thinking, how it relates to nursing, and which skills nurses need to develop as critical thinkers.
Graphical Abstract/Art Performance

Critical thinking in nursing.
This painting shows a nurse and how she is thinking critically. On the right side are the stages of critical thinking and on the left side, there are challenges that a nurse might face. The entire background is also painted in several colors to represent a kind of intellectual puzzle. It is made using colored pencils and markers.
(Adapted with permission from the Association of Science and Art (ASA), Universal Scientific Education and Research Network (USERN); Painting by Mahshad Naserpour).
Unless the individuals of a nation thinkers, the masses can be drawn in any direction. Mustafa Kemal Atatürk
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
- Durable hardcover edition
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Bilgiç Ş, Kurtuluş Tosun Z (2016) Birinci ve son sınıf hemşirelik öğrencilerinde eleştirel düşünme ve etkileyen faktörler. Sağlık Bilimleri ve Meslekleri Dergisi 3(1):39–47
Article Google Scholar
Kantek F, Yıldırım N (2019) The effects of nursing education on critical thinking of students: a meta-analysis. Florence Nightingale Hemşirelik Dergisi 27(1):17–25
Ennis R (1996) Critical thinking dispositions: their nature and assessability. Informal Logic 18(2):165–182
Riddell T (2007) Critical assumptions: thinking critically about critical thinking. J Nurs Educ 46(3):121–126
Cüceloğlu D (2001) İyi düşün doğru karar ver. Remzi Kitabevi, pp 242–284
Google Scholar
Kurnaz A (2019) Eleştirel düşünme öğretimi etkinlikleri Planlama-Uygulama ve Değerlendirme. Eğitim yayın evi, p 27
Doğanay A, Ünal F (2006) Eleştirel düşünmenin öğretimi. In: İçerik Türlerine Dayalı Öğretim. Ankara Nobel Yayınevi, pp 209–261
Scheffer B-K, Rubenfeld M-G (2000) A consensus statement on critical thinking in nursing. J Nurs Educ 39(8):352–359
Article CAS Google Scholar
Rubenfeld M-G, Scheffer B (2014) Critical thinking tactics for nurses. Jones & Bartlett Publishers, pp 5–6, 7, 19–20
Gobet F (2005) Chunking models of expertise: implications for education. Appl Cogn Psychol 19:183–204
Ay F-A (2008) Mesleki temel kavramlar. In: Temel hemşirelik: Kavramlar, ilkeler, uygulamalar. İstanbul Medikal Yayıncılık, pp 205–220
Birol L (2010) Hemşirelik bakımında sistematik yaklaşım. In: Hemşirelik süreci. Berke Ofset Matbaacılık, pp 35–45
Twibell R, Ryan M, Hermiz M (2005) Faculty perceptions of critical thinking in student clinical experiences. J Nurs Educ 44(2):71–79
The Importance of Critical Thinking in Nursing. 19 November 2018 by Carson-Newman University Online. https://onlinenursing.cn.edu/news/value-critical-thinking-nursing
Suzanne C, Smeltzer Brenda G, Bare Janice L, Cheever HK (2010) Definition of critical thinking, critical thinking process. Medical surgical nursing. Lippincott, Williams & Wilkins, pp 27–28
Profetto-McGrath J (2003) The relationship of critical thinking skills and critical thinking dispositions of baccalaureate nursing students. J Adv Nurs 43(6):569–577
Elaine S, Mary C (2002) Critical thinking in nursing education: literature review. Int J Nurs Pract 8(2):89–98
Brunt B-A (2005) Critical thinking in nursing: an integrated review. J Continuing Educ Nurs 36(2):60–67
Carter L-M, Rukholm E (2008) A study of critical thinking, teacher–student interaction, and discipline-specific writing in an online educational setting for registered nurses. J Continuing Educ Nurs 39(3):133–138
Daly W-M (2001) The development of an alternative method in the assessment of critical thinking as an outcome of nursing education. J Adv Nurs 36(1):120–130
Edwards S-L (2007) Critical thinking: a two-phase framework. Nurse Educ Pract 7(5):303–314
Rogal S-M, Young J (2008) Exploring critical thinking in critical care nursing education: a pilot study. J Continuing Educ Nurs 39(1):28–33
Worrell J-A, Profetto-McGrath J (2007) Critical thinking as an outcome of context-based learning among post RN students: a literature review. Nurse Educ Today 27(5):420–426
Morrall P, Goodman B (2013) Critical thinking, nurse education and universities: some thoughts on current issues and implications for nursing practice. Nurse Educ Today 33(9):935–937
Raymond-Seniuk C, Profetto-McGrath J (2011) Can one learn to think critically?—a philosophical exploration. Open Nurs J 5:45–51
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Nevşehir Hacı Bektaş Veli University, Semra ve Vefa Küçük, Faculty of Health Sciences, Nursing Department, 2000 Evler Mah. Damat İbrahim Paşa Yerleşkesi, Nevşehir, Turkey
Şefika Dilek Güven
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Şefika Dilek Güven .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Universal Scientific Education and Research Network (USERN), Stockholm, Sweden
Nima Rezaei
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Güven, Ş.D. (2023). Critical Thinking in Nursing. In: Rezaei, N. (eds) Brain, Decision Making and Mental Health. Integrated Science, vol 12. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-15959-6_10
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-15959-6_10
Published : 02 January 2023
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-031-15958-9
Online ISBN : 978-3-031-15959-6
eBook Packages : Behavioral Science and Psychology Behavioral Science and Psychology (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research

Two Examples of How I Used Critical Thinking to Care for my Patient (Real Life Nursing Stories) | NURSING.com

What are you struggling with in nursing school?
NURSING.com is the BEST place to learn nursing. With over 2,000+ clear, concise, and visual lessons, there is something for you!
Critical Thinking on the Nursing Floor
Critical thinking can seem like such an abstract term that you don’t practically use. However, this could not be farther from the truth. Critical thinking is frequently used in nursing. Let me give you a few examples from my career in which critical thinking helped me take better care of my patient.
The truth is, that as nurses we can’t escape critical thinking . . . I know you hate the word . . . but let me show you how it actually works!
Critical Thinking in Nursing: Example 1
I had a patient that was scheduled to go to get a pacemaker placed at 0900. The physician wanted the patient to get 2 units of blood before going downstairs for the procedure. I administered it per protocol. About 30 minutes after that second unit got started, I noticed his oxygen went from 95% down to 92% down to 90%. I put 2L of O2 on him and it came up to 91%. But it just sort of hung around the low 90s on oxygen.
I stopped. And thought. What the heck is going on?
I looked at his history. Congestive heart failure.
I looked at his intake and output. He was positive 1.5 liters.
I thought about how he’s got extra fluid in general, and because of his CHF, he can’t really pump out the fluid he already has, let alone this additional fluid. Maybe I should listen to his lungs..
His lungs were clear earlier. I heard crackles throughout both lungs.
OK, so he’s got extra fluid that he can’t get out of his body. What do I know that will get rid of extra fluid and make him pee? Maybe some Lasix?
I ran over my thought process with a coworker before calling the doc. They agreed. I called the doc and before I could suggest anything, he said “Give him 20 mg IV Lasix one time, and I’ll put the order in.” CLICK.
I gave the Lasix. He peed like a racehorse (and was NOT happy with me for making that happen!). And he was off of oxygen before he went down to get his pacemaker.
Badda Bing Bada Boom!
Critical Thinking in Nursing: Example 2
My patient just had her right leg amputated above her knee. She was on a Dilaudid PCA and still complaining of awful pain. She maxed it out every time, still saying she was in horrible pain. She told the doctor when he rounded that morning that the meds weren’t doing anything. He added some oral opioids as well and wrote an order that it was okay for me to give both the oral and PCA dosings, with the goal of weaning off PCA.
“How am I going to do that?” I thought. She kept requiring more and more meds and I’m supposed to someone wean her off?
I asked her to describe her pain. She said it felt like nerve pain. Deep burning and tingling. She said the pain meds would just knock her out and she’d sleep for a little while but wake up in even worse pain. She was at the end of her rope.
I thought about nerve pain. I thought about other patients that report similar pain. Diabetics with neuropathy would talk about similar pain… “What did they do for it? ” I thought. Then I remembered that many of my patients with diabetic neuropathy were taking gabapentin daily for pain.
“So if this works for their nerve pain, could it work for a patient who has had an amputation?” I thought.
I called the PA for the surgeon and asked them what they thought about trying something like gabapentin for her pain after I described my patient’s type of pain and thought process.
“That’s a really good idea, Kati. I’ll write for it and we’ll see if we can get her off the opioids sooner. ”
She wrote for it. I gave it. It takes a few days to really kick in and once it did, the patient’s pain and discomfort were significantly reduced. She said to get rid of those other pain meds because they “didn’t do a damn thing,” and to “just give her that nerve pain pill because it’s the only thing that works”.
And that we did!
She was able to work with therapy more because her pain was tolerable and was finally able to get rest.
What the HELL is Critical Thinking . . . and Why Should I Care?
What your nursing professor won’t tell you about critical thinking .
by Ashely Adkins RN BSN
When I started nursing school, I remember thinking, “how in the world am I going to remember all of this information, let alone be able to apply it and critically think?” You are not alone if you feel like your critical thinking skills need a little bit of polishing.
Let’s step back for a moment, and take a walk down memory lane. It was my first semester of nursing school and I was sitting in my Fundamentals of Nursing course. We were learning about vital signs, assessments, labs, etc. Feeling overwhelmed with all of this new information (when are you not overwhelmed in nursing school?), I let my mind wonder to a low place…
Am I really cut out for this? Can I really do this? How can I possibly retain all of this information? Do they really expect me to remember everything AND critically think at the same time?
One of my first-semester nursing professors said something to me that has stuck with me throughout my nursing years. It went a little something like this:
“Critical thinking does not develop overnight . It takes time. You don’t learn to talk overnight or walk overnight. You don’t learn to critically think overnight .”
My professor was absolutely right.
As my journey throughout nursing school, and eventually on to being a “real nurse” continued, my critical thinking skills began to BLOSSOM. With every class, lecture, clinical shift, lab, and simulation, my critical thinking skills grew.
You may ask…how?
Well, let me tell you…
- Questioning
These are the key ingredients to growing your critical thinking skills.
Time. Critical thinking takes time. As I mentioned before, you do not learn how to critically think overnight. It is important to set realistic expectations for yourself both in nursing school and in other aspects of your life.
Exposure. It is next to impossible to critically think if you have never been exposed to something. How would you ever learn to talk if no one ever talked to you? The same thing applies to nursing and critical thinking.
Over time, your exposure to new materials and situations will cause you to think and ask yourself, “why?”
This leads me to my next point. Questioning. Do not be afraid to ask yourself…
“Why is this happening?”
“Why do I take a blood pressure and heart rate before I give a beta-blocker?”
“Why is it important to listen to a patient’s lung sounds before and after they receive a blood transfusion?”
It is important to constantly question yourself. Let your mind process your questions, and discover answers.
Confidence. We always hear the phrase, “confidence is key!” And as cheesy as that phrase may be, it really holds true. So many times, we often times sell ourselves short.
YOU KNOW MORE THAN YOU THINK YOU KNOW.
In case you did not catch it the first time…
Be confident in your knowledge, because trust me, it is there. It may be hiding in one single neuron in the back of your brain, but it is there.
It is impossible to know everything. Even experienced nurses do not know everything.
And if they tell you that they do…they are wrong!
The key to critical thinking is not about knowing everything ; It is about how you respond when you do not know something .
How do you reason through a problem you do not know the answer to? Do you give up? Or do you persevere until you discover the answer?
If you are a nursing student preparing for the NCLEX, you know that the NCLEX loves critical thinking questions. NRSNG has some great tips and advice on critical thinking when it comes to taking the NCLEX .
There are so many pieces to the puzzle when it comes to nursing, and it is normal to feel overwhelmed. The beauty of nursing is when all of those puzzle pieces come together to form a beautiful picture.
That is critical thinking.
Critical thinking is something you’ll do every day as a nurse and honestly, you probably do it in your regular non-nurse life as well. It’s basically stopping, looking at a situation, identifying a solution, and trying it out. Critical thinking in nursing is just that but in a clinical setting.
We’ve written a MASSIVE lesson on Care Plans and Critical Thinking :
Mastering The COPD Nursing Care Plan in Just 10 Minutes!
Renal Failure Pt Care
4 "real world" examples of using clinical judgement to figure out what to do first as a nurse | nursing.com, 12 study tips for how to study for pharmacology in nursing school | nursing.com, similar blog posts.

Critical Thinking and Nursing Care Plans Go Together Like Chicken and Waffles | NURSING.com

Patients We Will Never Forget | NURSING.com
The Ultimate Guide to Creating an ICU Report Sheet (for new Critical Care Nurses and RN Students) | NURSING.com
- Nursing School
Critical Thinking Nursing Interview Questions

Critical thinking nursing interview questions feature prominently in any interview. They aren’t supposed to trip you up, but they will do just that if you aren’t ready.
Along with your nursing school application cover letter and your nursing school letter of intent , your nursing school interview questions give you an opportunity to show an admissions board, in your own words, how perfect you are for nursing school.
This article will show you how to take that opportunity and maximally utilize it to your advantage. We will go through what exactly a critical thinking question is, why they are being asked, and what types of responses you can give. Finally, we will cover several sample answers so that you can prepare your own answers for your upcoming interview.
>> Want us to help you get accepted? Schedule a free strategy call here . <<
Article Contents 7 min read
Why are critical thinking questions asked.
While critical thinking questions may relate to aspects of healthcare and nursing, including patient care, working as part of a team, and response to emergencies, they may also deal with dilemmas that have nothing to do with healthcare. For example, you may be faced with a conflict of interest scenario, or an ethical dilemma with a close friend.
Essentially, you’re being tested on your decision-making processes and how you solve problems, whether they are healthcare related or not. Your interviewer is trying to find out if you think logically, quickly, and in ways that provide good solutions in real-world scenarios.
Critical thinking is important to any job, but is of particular importance to nursing. Any healthcare professional deals with immense challenges on a daily basis. These challenges come up with little warning and require clearheaded responses.
Because the question is looking for your decision-making processes, you need to make sure that your responses put those processes in the limelight. Therefore, your answers should focus on the steps of how you made your decision and the why behind those steps: in other words, how you arrived at that response. You should show off how you evaluate situations and respond, but also how you concluded that your response was the most logical course of action.
Even if the question you are asked is hypothetical or situational, as we like to call it, you can definitely use your personal experiences to answer. Make sure to demonstrate non-judgmental attitude and objectivity when making your decision.
With nursing school interview questions, expert responses are required.
Let’s look at a sample critical thinking question and an expert response.
Prompt: Describe the most stressful event of your life. Why was it stressful, and how did you handle the situation?
Example: I\u2019m not saying it was easy, but that organization made things much more straightforward, and it helped to keep my mind calm and disciplined in all that chaos. I learned how to not only balance all of these disparate elements of my life, but that I could use the very act of balancing as a calming influence. "}]">
Nurses often have to deal with hostile patients. Can you recall a time you had to deal with hostility? What did you do and what were the results?
Sample answer:
I was working in a supporting role at a psychiatric institution, and one of the patients was a very angry person. He had a very quick temper and would often be physically violent, in addition to uncooperative or verbally abusive. The nurses said that giving meds felt like playing Russian roulette.
So, I would always make sure that I was around for that patient’s med time, ready to call security if he became violent.
He didn’t like taking his pills, either. One day, I was speaking with him and I discovered that his anger over medication was coming from a lack of understanding; he didn’t fully know what the pills did. So, I talked to his nurse about it, and she went over the reasons for his particular drugs and their side-effects. I also let his physician know about his concerns so that the doctor could have a conversation about it at her next visit in.
Once those issues had been dealt with, medication was much easier to distribute. It didn’t solve all the problems, but it helped make his days a lot smoother.
Critical thinking questions can be daunting and difficult, but they can also show some of your best talents and establish your abilities in a very concrete way. These aren’t abstract. These are demonstrations of actual actions taken. Use these questions to show off your impressive side with a committee.
The focus is the main difference, and with a critical thinking question, that focus is on how you use problem-solving and decision-making in different scenarios. They are to get a sense of how you deal with challenges and obstacles on a day-to-day basis.
Contrast this to more open-ended questions like “Tell us a little bit about yourself,” or “ Why do you want to be a nurse? ”
Fairly compact; you should answer in less than a minute.
Use just enough language to set up the problem you faced, your thought processes on how to deal with those problems, the actions you took, and the outcomes that those actions produced. This can be done in a fairly swift amount of time.
That doesn’t mean you should skimp on detail. While the interviewers don’t need every small thing that happened, they shouldn’t be confused or feel like they’re missing anything. Remember to showcase your abilities – don't brush past them: highlight!
Use mock interviews as part of your nursing school interview preparation to hone your answers for time and detail.
The most important reason is that you will wind up sounding robotic and insincere.
Additionally, the critical thinking questions might be slight variants, so a memorized answer could (or will) end up not quite fitting the question.
Better to memorize scenarios than words so that you can apply those examples to any question that comes up.
You can, and sometimes are directly asked to provide an example of failure.
If an interviewer asks you to describe a time you failed at implementing critical thinking, of course you must supply them with something, and should prepare for such questions in their own right.
Remember that they are looking for your decision-making processes and skills, so the outcome might have been bad, but if your processes were excellent, the interviewer will make note of that. Sometimes even good decisions lead to negative outcomes – sometimes that’s inevitable.
If you failed to apply good critical thinking in a situation, you can highlight what you learned from the experience and how it has improved subsequent actions and decision-making processes.
Failure is only truly failure if no lessons were learned.
You can take a short pause to think, and give yourself enough time to recall an appropriate event or incident. It’s important to research the different types of nursing school interview questions and prepare a relevant story for a variety of scenarios.
While it is unlikely that you will be asked about something that you can’t relate to at all (most of the questions are broad enough to allow some sort of connection) it might happen that you just haven’t had a given experience yet.
You can’t just say, “That’s never happened to me,” and leave it at that.
However, you might want to acknowledge this by saying, “That exact thing has never happened to me, but I have had a similar experience,” and speak of the closest thing you have to what was asked. Perhaps it wasn’t a work or healthcare setting, but maybe something that happened with family members or friends in a social setting, for instance – that will do.
Get as close as you can to the question, acknowledge the discrepancy, and answer to the best of your ability.
Expect anything, because depending on the interview, almost anything can be covered.
Even the type of interview can change, depending on the school. Some will use a traditional panel-style interview, but others will use the multiple mini-interview (MMI) format. If the latter, you might want to learn more about how to prepare for your multiple mini interview .
What exactly is in the interview depends on the school and panel, so be ready for anything.
Want more free tips? Subscribe to our channels for more free and useful content!
Apple Podcasts
Like our blog? Write for us ! >>
Have a question ask our admissions experts below and we'll answer your questions, get started now.
Talk to one of our admissions experts
Our site uses cookies. By using our website, you agree with our cookie policy .
FREE Training Webclass:
How to improve your nursing school interview practice score by 27% , using the proven strategies they don’t want you to know.
Critical thinking definition

Critical thinking, as described by Oxford Languages, is the objective analysis and evaluation of an issue in order to form a judgement.
Active and skillful approach, evaluation, assessment, synthesis, and/or evaluation of information obtained from, or made by, observation, knowledge, reflection, acumen or conversation, as a guide to belief and action, requires the critical thinking process, which is why it's often used in education and academics.
Some even may view it as a backbone of modern thought.
However, it's a skill, and skills must be trained and encouraged to be used at its full potential.
People turn up to various approaches in improving their critical thinking, like:
- Developing technical and problem-solving skills
- Engaging in more active listening
- Actively questioning their assumptions and beliefs
- Seeking out more diversity of thought
- Opening up their curiosity in an intellectual way etc.
Is critical thinking useful in writing?
Critical thinking can help in planning your paper and making it more concise, but it's not obvious at first. We carefully pinpointed some the questions you should ask yourself when boosting critical thinking in writing:
- What information should be included?
- Which information resources should the author look to?
- What degree of technical knowledge should the report assume its audience has?
- What is the most effective way to show information?
- How should the report be organized?
- How should it be designed?
- What tone and level of language difficulty should the document have?
Usage of critical thinking comes down not only to the outline of your paper, it also begs the question: How can we use critical thinking solving problems in our writing's topic?
Let's say, you have a Powerpoint on how critical thinking can reduce poverty in the United States. You'll primarily have to define critical thinking for the viewers, as well as use a lot of critical thinking questions and synonyms to get them to be familiar with your methods and start the thinking process behind it.
Are there any services that can help me use more critical thinking?
We understand that it's difficult to learn how to use critical thinking more effectively in just one article, but our service is here to help.
We are a team specializing in writing essays and other assignments for college students and all other types of customers who need a helping hand in its making. We cover a great range of topics, offer perfect quality work, always deliver on time and aim to leave our customers completely satisfied with what they ordered.
The ordering process is fully online, and it goes as follows:
- Select the topic and the deadline of your essay.
- Provide us with any details, requirements, statements that should be emphasized or particular parts of the essay writing process you struggle with.
- Leave the email address, where your completed order will be sent to.
- Select your prefered payment type, sit back and relax!
With lots of experience on the market, professionally degreed essay writers , online 24/7 customer support and incredibly low prices, you won't find a service offering a better deal than ours.
Nursing students in teams use simulators to…
Share this:.
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on X (Opens in new window)
- Click to print (Opens in new window)
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window)
- Entertainment
- Immigration
- Sports Betting
Post-Tribune
Nursing students in teams use simulators to compete in real-world scenarios, ‘everybody is kind of thinking together’.

They gathered by the hospital bed on the stage at Bergland Auditorium in teams of three to test their nursing skills in a timed round-robin competition as part of the annual SIM Wars, a simulation competition that highlights what the students have learned in the week leading up to finals week.
Four teams each consisting of a senior, junior and sophomore nursing student appeared on stage one at a time to tackle the scenario and resolve the patient’s concerns. The teams were selected in advance, Crystal Shannon, dean of the College of Health and Human Services and director of nursing, said. Students did not know what scenario they would be tasked with handling.
“These are patient care scenes,” Shannon said. SIM Wars are a fun way to let students demonstrate what they have learned in a friendly competition outside of the regular classroom. It builds what she described as “an active robust (nursing) simulation program.”
In the first round, a med-surg scenario is described to the team members, who must determine what is happening with the resources they would find in a typical hospital room interaction.
“They don’t tell us what they are going to do, they are showing us,” Shannon said.

If they are successful treating the condition the patient is presenting with, the simulation ends. A countdown clock on a large screen behind the mock hospital room ticking down from 15 minutes provides the backdrop for students competing and watching.
All four teams were able to master the scenario before the time ran out, with the two top-performing teams moving on to a more challenging simulation. The top-performing team in that scenario wins SIM Wars.
During the break between each group, the atmosphere remained festive and competitive as everyone participated in a Jeopardy-style game about nursing. Each grade level competed to gain the title, answering questions in categories including assessment, perfusion and oxygenation, and nursing processes among others.
Shannon said before SIM Wars, instructors recruited the 12 challenge participants. Most of the 200 students in the nursing program attend the event, which is a run-up to finals week beginning Monday.

Junior Marrin Brandt of Valparaiso, sophomore Jackson Mielczarek of Lowell and senior Dylan Rouhselang of Valparaiso were on one team, while senior Latoya David of Griffith, sophomore Valerie Mendoza of Hammond and senior Kayla Cheeks of Portage were another of the four teams participating.
“We paused a lot,” Mielczarek said critiquing his team’s performance. “I was kind of nervous.”
“You couldn’t think about the crowd,” Rouhselang said. Overall they said things went pretty well once they got past their nerves.
“I think we did good,” Mielczarek said.
Mendoza said the competition helped participants act quickly and think critically.
The simulations also help teach students to look at the small things that they may not think are the problem, Cheeks said.

David said her teammates did well during the competition and thought of things that she on her own did not.
“It’s better having a team. Everybody is kind of thinking together,” she said.
Brandt said the simulations were helpful, but she wished the challenge was in the middle of the semester and not the week before finals.
“I like the simulations. I think they are super helpful,” Brandt said.
More in Post-Tribune

Post-Tribune Sports | Michael Osipoff’s baseball rankings and player of the week for Northwest Indiana

Dunn testifies man held gun to his head before he killed him

Post-Tribune | Monday candlelight vigil planned to remember Dakota Levi Stevens
![Being a fast-growing city, Crown Point is currently building the ranks of its police force, offering a variety of incentives to bring in top candidates. The perks start with a take-home police car, a $1,400 annual clothing allowance, double-time-and-a-half holiday pay, and a two-month rotation from days to nights with every other weekend off. Patrolman starting pay is $63,850, but that jumps to $72,972 after successful completion of a 90-day training and probationary period. And retired police officers can count on annual compensation of $84,364. Mayor Pete Land, who previously served as the city’s police chief, said that Crown Point […] Being a fast-growing city, Crown Point is currently building the ranks of its police force, offering a variety of incentives to bring in top candidates. The perks start with a take-home police car, a $1,400 annual clothing allowance, double-time-and-a-half holiday pay, and a two-month rotation from days to nights with every other weekend off. Patrolman starting pay is $63,850, but that jumps to $72,972 after successful completion of a 90-day training and probationary period. And retired police officers can count on annual compensation of $84,364. Mayor Pete Land, who previously served as the city’s police chief, said that Crown Point […]](https://www.chicagotribune.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/05/PTB-L-CP-POLICE-0503-01.jpg?w=467)
Post-Tribune | Crown Point’s growth extends to its police department
Trending nationally.
- Trump says ‘a lot of people like it’ when he floats the idea of being a dictator
- Ousted ABC News meteorologist Rob Marciano fired after ‘screaming match’: report
- 4.1-magnitude quake centered near Corona jolts Southern California
- Biologists believe a TikTok-famous monkey was taken from a South Florida colony. His owner says he was rescued from a lab
- Private boarding school to receive $100 million gift. It’s one of the largest ever made

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The following are examples of attributes of excellent critical thinking skills in nursing. 1. The ability to interpret information: In nursing, the interpretation of patient data is an essential part of critical thinking. Nurses must determine the significance of vital signs, lab values, and data associated with physical assessment.
How to Develop and Apply Critical-Thinking Skills in Nursing. Critical-thinking skills develop as you gain experience and advance in your career. The ability to predict and respond to nursing challenges increases as you expand your knowledge and encounter real-life patient care scenarios outside of what you learned from a textbook.
Critical thinking in nursing requires self-awareness and being present in the moment. During a hectic shift, it is easy to lose focus as you struggle to finish every task needed for your patients. Passing medication, changing dressings, and hanging intravenous lines all while trying to assess your patient's mental and emotional status can ...
In summary, critical thinking is an integral skill for nurses, allowing them to provide high-quality, patient-centered care by analyzing information, making informed decisions, and adapting their approaches as needed. It's a dynamic process that enhances clinical reasoning, problem-solving, and overall patient outcomes.
Critical thinking in nursing is an essential component of professional accountability and quality nursing care. Critical thinkers in nursing exhibit these habits of the mind: confidence, contextual perspective, creativity, flexibility, inquisitiveness, intellectual integrity, intuition, openmindedness, perseverance, and reflection.
Some of the most important critical thinking skills nurses use daily include interpretation, analysis, evaluation, inference, explanation, and self-regulation. Interpretation: Understanding the meaning of information or events. Analysis: Investigating a course of action based on objective and subjective data. Evaluation: Assessing the value of ...
Critical thinking is an essential cognitive process that enables nurses to analyze, evaluate, and synthesize information to make informed decisions. In the context of nursing, it involves observing, interpreting, and responding to patient needs effectively. Critical thinking allows nurses to go beyond memorized facts and apply logical reasoning ...
Critical thinking is applied by nurses in the process of solving problems of patients and decision-making process with creativity to enhance the effect. It is an essential process for a safe, efficient and skillful nursing intervention. Critical thinking according to Scriven and Paul is the mental active process and subtle perception, analysis ...
Kaminske (2019), defines critical thinking skills as a domain-specific skill on the ability to solve problems and make effective decisions that require expertise to be applied in a range of situations and scenarios. In the nursing practice, Critical thinking skill works in assimilation with critical reasoning as a practice-based discipline of ...
Critical thinking is an integral part of nursing, especially in terms of professionalization and independent clinical decision-making. It is necessary to think critically to provide adequate, creative, and effective nursing care when making the right decisions for practices and care in the clinical setting and solving various ethical issues encountered.
Critical thinking skills that will be utilized in nursing are based on the following cognitive skills: Observation. Analysis. Interpretation. Reflection. Recognition. Questioning. Information ...
Chang el al 19 examined the relationship between critical thinking and nursing competence, using the Watson-Glaser Critical Thinking Appraisal and the Nursing Competence Scale. A total of 570 clinical nurses participated in the study. ... The Performance Based Development System, a scenario-based tool, was used in a study to identify critical ...
Critical Thinking in Nursing: Example 1. I had a patient that was scheduled to go to get a pacemaker placed at 0900. The physician wanted the patient to get 2 units of blood before going downstairs for the procedure. I administered it per protocol. About 30 minutes after that second unit got started, I noticed his oxygen went from 95% down to ...
Introduction to Critical Thinking and Clinical Reasoning for Nursing Students. In the dynamic and demanding field of healthcare, nurses play a pivotal role in ensuring the well-being and recovery of patients. To excel in this profession, nurses must possess a crucial skill set, and at the core of that skill set lies critical thinking. In this ...
6 Steps to Replace Clinical Using Case Studies. 1. Watch the intro video as a group. Gather the entire class together and view the intro video. This video lays out the scenario for the given case study and helps them begin to consider the disease process. 2.
Scenarios were developed from actual patient situations as well as from calls to the rapid response team. Nurses were given the opportunity to practice assessment, critical thinking, and communication skills. ... Nursing education for critical thinking: An integrative review. Journal of Nursing Education, 38(3), 111-119. > Link Google Scholar ...
Simulation helps to develop different scenarios requiring the use of both clinical skills and critical thinking skills by nurses, in order to solve problems. In addition, according to Savarese ( 31 ) there is a trend towards replacing the clinical experience of the hospital with simulation programmes, even by fifty per cent, in the curricula of ...
While critical thinking questions may relate to aspects of healthcare and nursing, including patient care, working as part of a team, and response to emergencies, they may also deal with dilemmas that have nothing to do with healthcare. For example, you may be faced with a conflict of interest scenario, or an ethical dilemma with a close friend.
Critical thinking is defined as: Clear, rational thinking involving critique. Its details vary amongst those who define it. According to Barry K. Beyer (1995), critical thinking means making clear, reasoned judgments. During the process of critical thinking, ideas should be reasoned, well thought out, and judged.
Clinical reasoning and critical thinking have been identified as competency deficient in many new graduate nurses (Herron, 2018; Theisen & Sandau, 2013). As a result enhancing critical thinking in undergraduate nursing education is a significant focus of contemporary nursing education research internationally (Alfaro-LeFevre, 2019; Carvalho et al., 2017; Levett-Jones, 2017).
There is an imperative need for nursing faculty to teach clinical judgment, critical thinking skills, and clinical reasoning on medication administration safety, specifically administering the correct medication, dose, and reason to the right patient or accurately holding the medication to prevent medication administration errors.
The following inclusion criteria were examined: (a) clinical reasoning, clinical judgment, and critical thinking in nursing students as a primary study aim; (b) articles published for the last eleven years; (c) research conducted between January 2012 and September 2023; (d) articles published only in English and Spanish; and (e) Randomised ...
Share via: Critical thinking, as described by Oxford Languages, is the objective analysis and evaluation of an issue in order to form a judgement. Active and skillful approach, evaluation, assessment, synthesis, and/or evaluation of information obtained from, or made by, observation, knowledge, reflection, acumen or conversation, as a guide to ...
Most of the 200 students in the nursing program attend the event, which is a run-up to finals week beginning Monday. Indiana University School of Nursing students surround a dummy with a simulated ...