
Gurukul of Excellence
Classes for Physics, Chemistry and Mathematics by IITians
Join our Telegram Channel for Free PDF Download

Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 10 Light Reflection and Refraction
- Last modified on: 1 year ago
- Reading Time: 10 Minutes
In CBSE Class 10 Science Paper, Students will have to answer some questions based on Assertion and Reason . There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage based as well. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then the MCQ questions based on it will be asked.
Here, we have provided case based/passage based questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 10 Light Reflection and Refraction .
Question 1:
Read the following and answer any four questions from (i) to (v).
The spherical mirror forms different types of images when the object is placed at different locations. When the image is formed on screen, the image is real and when the image does not form on screen, the image is virtual. When the two reflected rays meet actually, the image is real and when they appear to meet, the image is virtual.
A concave mirror always forms a real and inverted image for different positions of the object. But if the object is placed between the focus and pole. the image formed is virtual and erect.
A convex mirror always forms a virtual, erect and diminished image. A concave mirror is used as doctor’s head mirror to focus light on body parts like eyes, ears, nose etc., to be examined because it can form erect and magnified image of the object. The convex mirror is used as a rear view mirrors in automobiles because it can form an small and erect image of an object.
(i) When an object is placed at the centre of curvature of a concave mirror, the image formed is (a) larger than the object (b) smaller than the object (c) same size as that of the object (d) highly enlarged.
(ii) No matter how far you stand from a mirror, your image appears erect. The mirror is likely to be (a) plane (b) concave (c) convex (d) either plane or convex.
(iii) A child is standing in front of a magic mirror. She finds the image of her head bigger, the middle portion of her body of the same size and that of the legs smaller. The following is the order of combinations for the magic mirror from the top. (a) Plane, convex and concave (b) Convex, concave and plane (c) Concave, plane and convex (d) Convex, plane and concave
(iv) To get an image larger than the object, one can use (a) convex mirror but not a concave mirror (b) a concave mirror but not a convex mirror (c) either a convex mirror or a concave mirror (d) a plane mirror.
(v) A convex mirror has wider field of view because (a) the image formed is much smaller than the object and large number of images can be seen. (b) the image formed is much closer to the mirror (c) both (a) and (b) (d) none of these.
Question 2:
The lenses forms different types of images when object placed at different locations. When a ray is incident parallel to the principal axis, then after refraction, it passes through the focus or appears to come from the focus.
When a ray goes through the optical centre of the lens, it passes without any deviation. If the object is placed between focus and optical center of the convex lens, erect and magnified image is formed.
As the object is brought closer to the convex lens from infinity to focus, the image moves away from the convex lens from focus to infinity. Also the size of image goes on increasing and the image is always real and inverted.
A concave lens always gives a virtual, erect and diminished image irrespective to the position of the object.
(i) The location of image formed by a convex lens when the object is placed at infinity is (a) at focus (b) at 2F (c) at optical center (d) between Fand 2F
(ii) When the object is placed at the focus of concave lens, the image formed is (a) real and smaller (b) virtual and inverted (c) virtual and smaller (d) real and erect
(iii) The size of image formed by a convex lens when the object is placed at the focus of convex lens is (a) small (b) point in size (c) highly magnified (d) same as that of object
(iv) When the object is placed at 2F in front of convex lens, the location of image is (a) at F (b) at 2 F on the other side (c) at infinity (d) between F and optical center
(v) At which location of object in front of concave lens, the image between focus and optical centre is formed (a) anywhere between centre and infinity (b) at F (c) at 2F (d) infinity
Related Posts
Category lists (all posts).
All categories of this website are listed below with number of posts in each category for better navigation. Visitors can click on a particular category to see all posts related to that category.
- Full Form (1)
- Biography of Scientists (1)
- Assertion Reason Questions in Biology (37)
- Case Study Questions for Class 12 Biology (14)
- DPP Biology for NEET (12)
- Blog Posts (35)
- Career Guidance (1)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 10 Maths (14)
- Case Study Questions for Class 10 Maths (15)
- Extra Questions for Class 10 Maths (12)
- Maths Formulas for Class 10 (1)
- MCQ Questions for Class 10 Maths (15)
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths (4)
- Quick Revision Notes for Class 10 Maths (14)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 10 Science (16)
- Case Study Questions for Class 10 Science (14)
- Evergreen Science Book Solutions for Class 10 (17)
- Extra Questions for Class 10 Science (23)
- HOTS for Class 10 Science (17)
- Important Questions for Class 10 Science (10)
- Lakhmir Singh Class 10 Biology Solutions (4)
- Lakhmir Singh Class 10 Chemistry Solutions (5)
- Lakhmir Singh Class 10 Physics Solutions (5)
- MCQ Questions for Class 10 Science (20)
- NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 10 Science (16)
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science (15)
- Quick Revision Notes for Class 10 Science (4)
- Study Notes for Class 10 Science (17)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 10 Social Science (14)
- Case Study Questions for Class 10 Social Science (24)
- MCQ Questions for Class 10 Social Science (3)
- Topicwise Notes for Class 10 Social Science (4)
- CBSE CLASS 11 (1)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 11 Chemistry (14)
- Case Study Questions for Class 11 Chemistry (11)
- Free Assignments for Class 11 Chemistry (1)
- MCQ Questions for Class 11 Chemistry (8)
- Very Short Answer Questions for Class 11 Chemistry (7)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 11 Entrepreneurship (8)
- Important Questions for CBSE Class 11 Entrepreneurship (1)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 11 Geography (24)
- Case Study Questions for Class 11 Geography (24)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 11 History (12)
- Case Study Questions for Class 11 History (12)
- Assertion and Reason Questions for Class 11 Maths (16)
- Case Study Questions for Class 11 Maths (16)
- Formulas for Class 11 Maths (6)
- MCQ Questions for Class 11 Maths (17)
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths (8)
- Case Study Questions for Class 11 Physical Education (11)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 11 Physics (15)
- Case Study Questions for Class 11 Physics (12)
- Class 11 Physics Study Notes (5)
- Concept Based Notes for Class 11 Physics (2)
- Conceptual Questions for Class 11 Physics (10)
- Derivations for Class 11 Physics (3)
- Extra Questions for Class 11 Physics (13)
- MCQ Questions for Class 11 Physics (16)
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Physics (16)
- Numerical Problems for Class 11 Physics (4)
- Physics Formulas for Class 11 (7)
- Revision Notes for Class 11 Physics (11)
- Very Short Answer Questions for Class 11 Physics (11)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 11 Political Science (20)
- Case Study Questions for Class 11 Political Science (20)
- CBSE CLASS 12 (8)
- Extra Questions for Class 12 Biology (14)
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 Biology (13)
- Case Studies for CBSE Class 12 Business Studies (13)
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 Business Studies (1)
- Revision Notes for Class 12 Business Studies (10)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 12 Chemistry (15)
- Case Study Based Questions for Class 12 Chemistry (14)
- Extra Questions for Class 12 Chemistry (5)
- Important Questions for Class 12 Chemistry (15)
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 Chemistry (8)
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry (16)
- Revision Notes for Class 12 Chemistry (7)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 12 Economics (9)
- Case Study Questions for Class 12 Economics (9)
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 Economics (1)
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 English (2)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 12 Entrepreneurship (7)
- Case Study Questions for Class 12 Entrepreneurship (7)
- Case Study Questions for Class 12 Geography (18)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 12 History (8)
- Case Study Questions for Class 12 History (13)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 12 Informatics Practices (13)
- Case Study Questions for Class 12 Informatics Practices (11)
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 Informatics Practices (5)
- Assertion and Reason Questions for Class 12 Maths (14)
- Case Study Questions for Class 12 Maths (13)
- Maths Formulas for Class 12 (5)
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 Maths (14)
- Problems Based on Class 12 Maths (1)
- RD Sharma Solutions for Class 12 Maths (1)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 12 Physical Education (11)
- Case Study Questions for Class 12 Physical Education (11)
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 Physical Education (10)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 12 Physics (16)
- Case Study Based Questions for Class 12 Physics (14)
- Class 12 Physics Conceptual Questions (16)
- Class 12 Physics Discussion Questions (1)
- Class 12 Physics Latest Updates (2)
- Derivations for Class 12 Physics (8)
- Extra Questions for Class 12 Physics (4)
- Important Questions for Class 12 Physics (8)
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 Physics (14)
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Physics (18)
- Numerical Problems Based on Class 12 Physics (16)
- Physics Class 12 Viva Questions (1)
- Revision Notes for Class 12 Physics (7)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 12 Political Science (16)
- Case Study Questions for Class 12 Political Science (16)
- Notes for Class 12 Political Science (1)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 6 Maths (13)
- Case Study Questions for Class 6 Maths (13)
- Extra Questions for Class 6 Maths (1)
- Worksheets for Class 6 Maths (1)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 6 Science (16)
- Case Study Questions for Class 6 Science (16)
- Extra Questions for Class 6 Science (1)
- MCQ Questions for Class 6 Science (9)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 6 Social Science (1)
- Case Study Questions for Class 6 Social Science (26)
- NCERT Exemplar for Class 7 Maths (13)
- NCERT Exemplar for Class 7 Science (19)
- NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 7 Maths (12)
- NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 7 Science (18)
- NCERT Notes for Class 7 Science (18)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 7 Maths (14)
- Case Study Questions for Class 7 Maths (14)
- Extra Questions for Class 7 Maths (5)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 7 Science (18)
- Case Study Questions for Class 7 Science (17)
- Extra Questions for Class 7 Science (19)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 7 Social Science (1)
- Case Study Questions for Class 7 Social Science (30)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 8 Maths (7)
- Case Study Questions for Class 8 Maths (17)
- Extra Questions for Class 8 Maths (1)
- MCQ Questions for Class 8 Maths (6)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 8 Science (16)
- Case Study Questions for Class 8 Science (11)
- Extra Questions for Class 8 Science (2)
- MCQ Questions for Class 8 Science (4)
- Numerical Problems for Class 8 Science (1)
- Revision Notes for Class 8 Science (11)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 8 Social Science (27)
- Case Study Questions for Class 8 Social Science (23)
- CBSE Class 9 English Beehive Notes and Summary (2)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 9 Maths (14)
- Case Study Questions for Class 9 Maths (14)
- MCQ Questions for Class 9 Maths (11)
- NCERT Notes for Class 9 Maths (6)
- NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths (12)
- Revision Notes for Class 9 Maths (3)
- Study Notes for Class 9 Maths (10)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 9 Science (16)
- Case Study Questions for Class 9 Science (15)
- Evergreen Science Book Solutions for Class 9 (15)
- Extra Questions for Class 9 Science (22)
- MCQ Questions for Class 9 Science (11)
- NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science (15)
- Revision Notes for Class 9 Science (1)
- Study Notes for Class 9 Science (15)
- Topic wise MCQ Questions for Class 9 Science (2)
- Topicwise Questions and Answers for Class 9 Science (15)
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 9 Social Science (15)
- Case Study Questions for Class 9 Social Science (19)
- CHEMISTRY (8)
- Chemistry Articles (2)
- Daily Practice Problems (DPP) (3)
- Books for CBSE Class 9 (1)
- Books for ICSE Class 10 (3)
- Editable Study Materials (8)
- Exam Special for CBSE Class 10 (3)
- H. C. Verma (Concepts of Physics) (13)
- Study Materials for ICSE Class 10 Biology (14)
- Extra Questions for ICSE Class 10 Chemistry (1)
- Study Materials for ICSE Class 10 Chemistry (5)
- Study Materials for ICSE Class 10 Maths (16)
- Important Questions for ICSE Class 10 Physics (13)
- MCQ Questions for ICSE Class 10 Physics (4)
- Study Materials for ICSE Class 10 Physics (8)
- Study Materials for ICSE Class 9 Maths (7)
- Study Materials for ICSE Class 9 Physics (10)
- Topicwise Problems for IIT Foundation Mathematics (4)
- Challenging Physics Problems for JEE Advanced (2)
- Topicwise Problems for JEE Physics (1)
- DPP for JEE Main (1)
- Integer Type Questions for JEE Main (1)
- Integer Type Questions for JEE Chemistry (6)
- Chapterwise Questions for JEE Main Physics (1)
- Integer Type Questions for JEE Main Physics (8)
- Physics Revision Notes for JEE Main (4)
- JEE Mock Test Physics (1)
- JEE Study Material (1)
- JEE/NEET Physics (6)
- CBSE Syllabus (1)
- Maths Articles (2)
- NCERT Books for Class 12 Physics (1)
- NEET Chemistry (13)
- Important Questions for NEET Physics (17)
- Topicwise DPP for NEET Physics (5)
- Topicwise MCQs for NEET Physics (32)
- NTSE MAT Questions (1)
- Physics (1)
- Alternating Current (1)
- Electrostatics (6)
- Fluid Mechanics (2)
- PowerPoint Presentations (13)
- Previous Years Question Paper (3)
- Products for CBSE Class 10 (15)
- Products for CBSE Class 11 (10)
- Products for CBSE Class 12 (6)
- Products for CBSE Class 6 (2)
- Products for CBSE Class 7 (5)
- Products for CBSE Class 8 (1)
- Products for CBSE Class 9 (3)
- Products for Commerce (3)
- Products for Foundation Courses (2)
- Products for JEE Main & Advanced (10)
- Products for NEET (6)
- Products for ICSE Class 6 (1)
- Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance (1)
- Topic Wise Study Notes (Physics) (2)
- Topicwise MCQs for Physics (2)
- Uncategorized (138)
Test series for students preparing for Engineering & Medical Entrance Exams are available. We also provide test series for School Level Exams. Tests for students studying in CBSE, ICSE or any state board are available here. Just click on the link and start test.
Download CBSE Books
Exam Special Series:
- Sample Question Paper for CBSE Class 10 Science (for 2024)
- Sample Question Paper for CBSE Class 10 Maths (for 2024)
- CBSE Most Repeated Questions for Class 10 Science Board Exams
- CBSE Important Diagram Based Questions Class 10 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Numericals Class 10 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Practical Based Questions for Class 10 Science Board Exams
- CBSE Important “Differentiate Between” Based Questions Class 10 Social Science
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Physics (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Chemistry (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Maths (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Biology (for 2024)
- CBSE Important Diagrams & Graphs Asked in Board Exams Class 12 Physics
- Master Organic Conversions CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Board Exams
- CBSE Important Numericals Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Definitions Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Laws & Principles Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Physics Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Maths Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Biology Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- ICSE Important Numericals Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams (215 Numericals)
- ICSE Important Figure Based Questions Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams (230 Questions)
- ICSE Mole Concept and Stoichiometry Numericals Class 10 Chemistry (65 Numericals)
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Chemistry BOARD Exams (150 Qs)
- ICSE Important Functions and Locations Based Questions Class 10 Biology
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Biology BOARD Exams (100 Qs)
✨ Join our Online NEET Test Series for 499/- Only for 1 Year
3 thoughts on “ Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 10 Light Reflection and Refraction ”
Thank you so much bruh you are God
- Pingback: CBSE Class 10 Science Case Study Questions – ebookpublisher.in
Leave a Reply Cancel reply

Editable Study Materials for Your Institute - CBSE, ICSE, State Boards (Maharashtra & Karnataka), JEE, NEET, FOUNDATION, OLYMPIADS, PPTs
Discover more from Gurukul of Excellence
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading
- Light – Reflection and Refraction Class 10 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 10

Last Updated on August 26, 2024 by XAM CONTENT
Hello students, we are providing case study questions for class 10 science. Case study questions are the new question format that is introduced in CBSE board. The resources for case study questions are very less. So, to help students we have created chapterwise case study questions for class 10 science. In this article, you will find case study questions for cbse class 10 science chapter 10 Light – Reflection and Refraction.
| Light – Reflection and Refraction | |
| Case Study Questions | |
| Competency Based Questions | |
| CBSE | |
| 10 | |
| Science | |
| Class 10 Studying Students | |
| Yes | |
| Mentioned | |

Table of Contents
Case Study Questions on Light – Reflection and Refraction
Question 1:
Read the following and answer the questions given below:
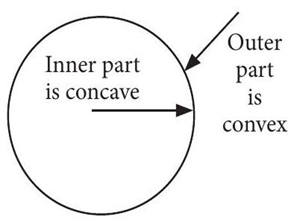
The curved surface of a spoon can be considered as a spherical mirror. A highly smooth polished surface is called mirror. The mirror whose reflecting surface is curved inwards or outwards is called a spherical mirror. Inner part works as a concave mirror and the outer bulging part acts as a convex mirror. The center of the reflecting surface of a spherical mirror is called pole and the radius of the sphere of which the mirror is formed is called radius of curvature.
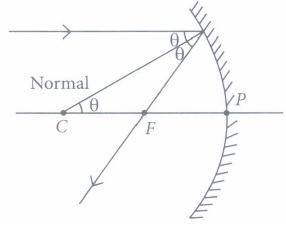
(i) When a concave mirror is held towards the sun and its sharp image is formed on a piece of carbon paper for some time, a hole is burnt in the carbon paper. What is the name given to the distance between the mirror and carbon paper? (a) Radius of curvature (b) Focal length (c) Principal focus (d) Principal axis
Difficulty Level: Medium
Ans. Option (b) is correct. Explanation: The focal length of a concave mirror is the distance between its pole and principal focus.
(ii) The distance between pole and focal point of a spherical mirror is equal to the distance between (a) pole and center of curvature (b) focus point and center of curvature (c) pole and object (d) object and image.
Ans. Option (b) is correct. Explanation: As f=R/2, the distance between pole and focal point of a spherical mirror is equal to the distance between focus point and center of curvature.
(iii) The focal length of a mirror is 15 cm. The radius of curvature is (a) 15 cm (b) 30 cm (c) 45 cm (d) 60 cm
Difficulty Level: Easy
Ans. Option (b) is correct. Explanation: As f=R/2, R=2f = 30 cm
(iv) The normal at any point on the mirror passes through (a) focus (b) pole (c) center of curvature (d) any point
Ans. Option (c) is correct. Explanation: In a spherical mirror, normal drawn at any point passes through the centre of curvature.
(v) In a convex spherical mirror, reflection of light takes place at (a) a flat surface (b) a bent-in surface (c) a bulging-out surface (d) an uneven surface
Ans. Option (c) is correct. Explanation: In a convex spherical mirror, reflection of light takes place at a bulging-out surface.
Question 2:
A lens is a piece of any transparent material bounded by two curved surfaces. There are two types of lenses convex lens and concave lens.
Convex lens is made up of a transparent medium bounded by two spherical surfaces such that thicker at the middle and thinner at the edges. Concave lens is also made up of a transparent medium such that thicker at the edge and thinner at the middle. The mid-point of the lens is called optical centre.
A point on the principal axis, where the incident parallel rays meet or appears to come out after refraction is called focus.
A convex lens converges a parallel beam of light to other side whereas concave lens spreads out.
(i) Which of the following lenses would you prefer to use while reading small letters found in dictionary? (a) A convex lens of focal length 50 cm (b) A concave lens of focal length 50 cm (c) A convex lens of focal length 5 cm (d) A concave lens of focal length 5 cm
Ans. Option (c) is correct. Explanation: Convex lens is used as magnifying glass. For better performance its focal length should be small.
(ii) Which type of lenes are shown in given figure (a) and (b).
(a) Plano concave, concavo convex (b) Plano convex, convexo concave (c) Double concave, concave convex (d) Convexo concave, double convex
Ans. Option (a) is correct. Explanation: Plano convex, convexo concave
(iii) A small bulb is placed at the focal point of a converging lens. When the bulb is switched on, the lens produces (a) a convergent beam of light (b) a divergent beam of light (c) a parallel beam of light (d) a patch of coloured light.
Ans. Option (c) is correct.
(iv) The part of lens through which the refraction takes place is called (a) aperture (b) centre of curvature (c) principal axis (d) focus
Ans. Option (a) is correct. Explanation: Aperture is the area of the lens available for refraction.
(v) A water drop acts as a (a) convex lens (b) concave lens (c) double concave lens (d) none of these
Ans. Option (a) is correct. Explanation: Water droplets behave like a convex lens only as refraction takes place on outer surface.
- Electricity Class 10 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 12
- The Human Eye and the Colourful World Class 10 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 11
- Metals and Non-metals Class 10 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 3
- Life Processes Class 10 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 6
Acids Bases and Salts Class 10 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 2
Chemical reactions and equations class 10 case study questions science chapter 1, topics from which case study questions may be asked.
- Reflection of Light
- Laws of Reflection
- Real and Virtual Image
- Mirror Formula
- Lens Formula
- Convex and Concave Lens
- Magnification
- Refraction of Light
- Laws of Refraction
- Refractive Index
- Power of lens
This chapter deals with the basic understanding of light. In this chapter we study about reflection and refraction of light phenomenon.
Helpful Links for CBSE Class 10 Science Preparation
- Download 125 Important Case Study Questions for CBSE Class 10 Science
- Download 220 Important Assertion Reason Questions for CBSE Class 10 Science
- Download 225 Practical Based Questions for CBSE Class 10 Science
- Download 65 Important Numerical Problems for CBSE Class 10 Physics
- Download 60 Important Diagram Based Questions for CBSE Class 10 Physics
- Download 150 Most Repeated Questions for CBSE Class 10 Science
- Download Chapter Test for CBSE Class 10 Science
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Light – Reflection and Refraction Case Study Questions
Q1: what are case study questions for cbse examinations.
A1: Case study questions in CBSE examinations typically involve scenarios or real-life examples, requiring students to apply their understanding of concepts to solve problems or analyze situations.
Q2: Why are case study questions important for understanding class 10 science chapters?
A2: Case study questions provide a practical context for students to apply theoretical knowledge to real-world situations, fostering deeper understanding and critical thinking skills.
Q3: How should students approach answering case study questions for CBSE?
A3: Students should carefully read the case study, identify the key issues or problems presented, analyze the information provided, apply relevant concepts and principles of chemical reactions and equations, and formulate well-supported solutions or responses.
Q4: Are there any resources available online for students to practice case study questions on class 10 science chapters for CBSE exams?
A4: Yes, several educational websites offer case study questions for CBSE students preparing for science examinations. We also offer a collection of case study questions for all classes and subject on our website. Visit our website to access these questions and enhance your learning experience. If you need more case study questions for your preparation, then you visit Physics Gurukul website.
Q5: How can students effectively prepare for case study questions on Light – Reflection and Refraction for CBSE exams?
A5: Effective preparation strategies include regular revision of concepts, solving practice questions, analyzing case studies from previous exams, seeking clarification on doubts, and consulting with teachers or peers for guidance and support.
Q6: How can teachers incorporate case study questions on Light – Reflection and Refraction class 10 science into classroom teaching?
A6: Teachers can integrate case studies into lesson plans, group discussions, or interactive activities to engage students in active learning, promote problem-solving skills, and facilitate a deeper understanding of Light – Reflection and Refraction.
Q7: Is light a form of energy?
Ans. Yes, light is a form of energy.
Q8: Do the laws of reflection hold good for spherical mirrors?
A8: Yes, laws of reflection hold good for spherical mirrors.
Q9: What do you understand by reflection of light?
A9: The phenomenon of bouncing back of light to the first medium from the surface of separation of two media is called reflection of light.
Q10: Is linear magnification always positive?
A10: No, it can be negative also. If the magnification has a plus sign, then the image is virtual and erect.
Q11: For driving a car, what type of mirror would you prefer to see the traffic at your back?
A11: We prefer convex mirror for observing the traffic behind us because its field of view is much larger than the plane mirror. However, it gives erroneous idea about the speed of the vehicles behind us.
Q12: One reads a newspaper due to the light reflected from it. Why then we do not see even faint image of ourselves in the newspaper?
A12: The newspaper causes scattering of light, which is an irregular and diffused sort of reflection. From each point, light goes in all directions. The image is seen only when there is regular refection of light. It is the homogeneous nature of the surface which causes irregular reflection or scattering of light.
Q13: Which part of the eye is reused when one donates the eye?
A13: The cornea of the donor is removed after the death of the person and transplanted in a blind person whose original cornea is opaque. Thus, the blind person gets sight.
Q14: What is meant by refraction of light?
A14: The bending of a ray of light as it passes from one medium to another is called refraction.

Related Posts

Case Study Questions Class 10 Science Light Reflection and Refraction
Case study questions class 10 science chapter 10 light reflection and refraction, case study:1, case study: 2, case study:3.
While convex mirrors are used as rear view mirror in vehicles to see the traffic behind the person for safe driving. As these mirrors are curved outwards they has wider field of view. In convex mirrors the image formed is always diminished, virtual and erect.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
We have a strong team of experienced teachers who are here to solve all your exam preparation doubts, dav class 5 math solution chapter 7 multiplication and division of decimal numbers, dav class 6 english reader book solution chapter 2 hobbies, up scert solutions class 6 english chapter 8 – gulliver in lilliput, ncert solutions class 6 math ganita prakash.
CBSE Expert
Class 10 Science: Case Study Chapter 10 Light Reflection and Refraction PDF Download
In CBSE Class 10 Science Paper, Students will have to answer some questions based on Assertion and Reason . There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage-based as well. In that, a paragraph will be given.

Here we are providing you with Class 10 Science Chapter 10 Light Reflection and Refraction Case Study Questions, by practicing these Case Study and Passage Based Questions will help you in your Class 10th Board Exam.
Case Study Chapter 10 Light Reflection and Refraction
Here, we have provided case-based/passage-based questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 10 Light Reflection and Refraction
Case Study/Passage-Based Questions
Question 1:
The spherical mirror forms different types of images when the object is placed at different locations. When the image is formed on the screen, the image is real and when the image does not form on-screen, the image is virtual. When the two reflected rays meet actually, the image is real and when they appear to meet, the image is virtual. A concave mirror always forms a real and inverted image for different positions of the object. But if the object is placed between the focus and pole, the image formed is virtual and erect. A convex mirror always forms a virtual, erect, and diminished image. A concave mirror is used as a doctor’s head mirror to focus light on body parts like eyes, ears, nose, etc., to be examined because it can form erect and magnified images of the object. The convex mirror is used as a rear view mirror in automobiles because it can form a small and erect image of an object.
(i) When an object is placed at the center of curvature of a concave mirror, the image formed is
| (a) larger than the object | (b) smaller than the object |
| (c) same size as that of the object | (d) highly enlarged. |
Answer: (c) same size as that of the object
(ii) No matter how far you stand from a mirror, your image appears erect. The mirror is likely to be
| (a) plane | (b) concave |
| (c) convex | (d) either plane or convex. |
Answer: (d): The image is erect in a plane mirror and also in a convex mirror, for all positions of the object.
(iii) A child is standing in front of a magic mirror. She finds the image of her head bigger, the middle portion of her body of the same size and that of the legs smaller. The following is the order of combinations for the magic mirror from the top.
| (a) Plane, convex and concave | (b) Convex, concave and plane |
| (c) Concave, plane and convex | (d) Convex, plane and concave |
Answer: (c) : As the image of head is bigger, the upper portion of magic mirror is concave. The middle portion of the image is of same size, so, middle portion of magic mirror is plane. Now, the image of legs looks smaller, therefore, the lower portion of magic mirror is convex.
(iv) To get an image larger than the object, one can use (a) convex mirror but not a concave mirror (b) a concave mirror but not a convex mirror (c) either a convex mirror or a concave mirror (d) a plane mirror.
Answer: (b) a concave mirror but not a convex mirror
(v) A convex mirror has wider field of view because (a) the image formed is much smaller than the object and large number of images can be seen (b) the image formed is much closer to the mirror (c) both (a) and (b) (d) none of these.
Answer: (c) both (a) and (b)
Question 2:
The lenses form different types of images when objects are placed at different locations. When a ray is incident parallel to the principal axis, then after refraction, it passes through the focus or appears to come from the focus.
When a ray goes through the optical center of the lens, it passes without any deviation. If the object is placed between the focus and the optical center of the convex lens, an erect and magnified image is formed.
As the object is brought closer to the convex lens from infinity to focus, the image moves away from the convex lens from focus to infinity. Also, the size of the image goes on increasing and the image is always real and inverted.
A concave lens always gives a virtual, erect, and diminished image irrespective of the position of the object.
(i) The location of image formed by a convex lens when the object is placed at infinity is (a) at focus (b) at 2F (c) at optical center (d) between Fand 2F
Answer: (a) at focus
(ii) When the object is placed at the focus of concave lens, the image formed is (a) real and smaller (b) virtual and inverted (c) virtual and smaller (d) real and erect
Answer: (b) virtual and inverted
(iii) The size of image formed by a convex lens when the object is placed at the focus of convex lens is (a) small (b) point in size (c) highly magnified (d) same as that of object
Answer: (c) highly magnified
(iv) When the object is placed at 2F in front of convex lens, the location of image is (a) at F (b) at 2 F on the other side (c) at infinity (d) between F and optical center
Answer: (b) at 2 F on the other side
(v) At which location of object in front of concave lens, the image between focus and optical centre is formed (a) anywhere between centre and infinity (b) at F (c) at 2F (d) infinity
Answer: (a) anywhere between centre and infinity
You can also practice Class 10 Science MCQ Questions for Board Exams.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Download India's best Exam Preparation App Now.
Key Features
- Revision Notes
- Important Questions
- Previous Years Questions
- Case-Based Questions
- Assertion and Reason Questions
No thanks, I’m not interested!
CBSE NCERT Solutions
NCERT and CBSE Solutions for free
Case Study Chapter 10 Light Reflection and Refraction
Please refer to Chapter 1 Light Reflection and Refraction Case Study Questions with answers provided below. We have provided Case Study Questions for Class 10 Science for all chapters as per CBSE, NCERT and KVS examination guidelines. These case based questions are expected to come in your exams this year. Please practise these case study based Class 10 Science Questions and answers to get more marks in examinations.
Case Study Questions Chapter 1 Light Reflection and Refraction
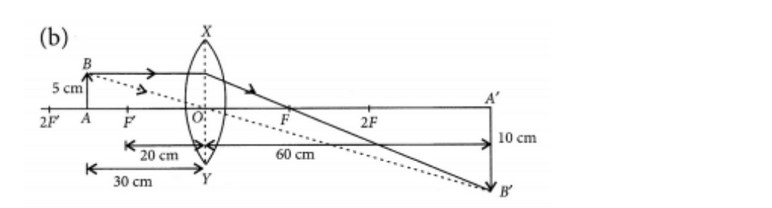
Case/Passage – 1 A 5.0 cm tall object is placed perpendicular to the principal axis of a convex lens of focal length 20 cm. The distance of the object from the lens is 30 cm.
Question: What is the power of the used lens? (a) + 5 D (b) – 5 D (c) + 0.5 D (d) – 0.5 D
Question: What is the distance of image from the pole of lens? (a) v = 60 cm (b) v = – 60 cm (c) v = 30 cm (d) v = –30 cm
Case/Passage – 2
Light travels through a vacuum at a speed c = 3 × 108 m/s. It can also travel through many materials, such as air, water and glass. Atoms in the material absorb, reemit and scatter the light, however. Therefore, light travels through the material at a speed that is less than c, the actual speed depending on the nature of the material. To describe the extent to which the speed of light in a material medium differs from that in a vacuum, we use a parameter called the index of refraction (or refractive index).
Question: Figure shows a ray of light as it travels from medium A to
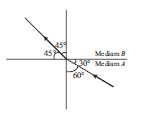
medium B. Retractive index of the medium B relative to medium A is (a) √3/2 (b)√2/3 (c)√1/2 (d) √2
Question:The path of a ray of light coming from air passing through a rectangular glass slab traced by four students shown as A, B, C and D in the figure. Which one of them is correct?

(a) A (b) B (c) C (d) D
Question: A light ray enters from medium A to medium B as shown
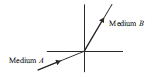
in the figure. The refractive index of medium B relative to A will be (a) greater than unity (b) less than unity (c) equal to unity (d) zero
Question: You are given water, mustard oil, glycerine and kerosene. In which of these media, a ray of light incident obliquely at same angle would bend the most? (a) Kerosene (b) Water (c) Mustard oil (d) Glycerine
Question: A ray of light is incident in medium 1 on a surface that separates medium 1 from medium 2. Let v1 and v2 represent the velocity of light in medium 1 and medium 2 respectively. Also let n12 and n21 represent the refractive index of medium 1 with respect to medium 2 and refractive index of medium 2 with respect to medium 1, respectively. If i and r denote the angle of incidence and angle of refraction, then- (a) sin i/sin r = n 21 V 1 /V 2 (b) sin i/sin r = n 21 V 2 /V 1 (c) sin i/sin r = n 12 V 1 /V 2 (d) sin i/sin r = n 12 V 2 /V 1
Case/Passage – 3 Inside a substance such as glass or water, light travels more slowly than it does in a vacuum. If c denotes the speed of light in a vacuum and v denotes its speed through some other substance, then v = c/n where n is a constant called the index of refraction. To good approximation, a substance’s index of refraction does not depend on the wavelength of light. For instance, when red and blue light waves enter water, they both slow down by about the same amount. More precise measurements, however, reveal that n varies with wavelength. Table presents some indices of refraction of Custon glass, for different wavelengths of visible light. A nanometer (nm) is 10– 9 meters. In a vacuum, light travels as c = 3.0 × 10 8 m/s

Question: Inside Custon glass (a) Orange light travels faster than yellow light (b) Yellow light travels faster than orange light (c) Orange and Yellow light travels equally fast (d) We cannot determine which color of light travels faster
Question: Which of the following phenomena happens because n varies with wavelength (a) A lens focuses light (b) A prism breaks sunlight into different colors (c) Total internal reflections ensures that light travels down a fiber optic cable (d) Light rays entering a pond change direction at the pond’s surface
Question: For blue-green of wavelength 520 nm, the index of refraction of Custon glass is probably closest to (a) 1.49 (b) 1.50 (c) 1.51 (d) 1.52

Related Posts

CBSE Class 10 English Fog Summary

Minerals and Energy Resources Class 10 Social Science Notes and Questions

Manufacturing Industries Class 10 Social Science Notes and Questions
- New QB365-SLMS
- 12th Standard Materials
- 11th Standard Materials
- 10th Standard Materials
- 9th Standard Materials
- 8th Standard Materials
- 7th Standard Materials
- 6th Standard Materials
- 12th Standard CBSE Materials
- 11th Standard CBSE Materials
- 10th Standard CBSE Materials
- 9th Standard CBSE Materials
- 8th Standard CBSE Materials
- 7th Standard CBSE Materials
- 6th Standard CBSE Materials
- Tamilnadu Stateboard
- Scholarship Exams
- Scholarships

CBSE 10th Standard Science Subject Light Reflection and Refraction Chapter Case Study Questions With Solution 2021
By QB365 on 21 May, 2021
QB365 Provides the updated CASE Study Questions for Class 10 , and also provide the detail solution for each and every case study questions . Case study questions are latest updated question pattern from NCERT, QB365 will helps to get more marks in Exams
QB365 - Question Bank Software
Cbse 10th standard science subject light reflection and refraction case study questions with solution 2021.
10th Standard CBSE
Final Semester - June 2015
The curved surface of a spoon can be considered as a spherical mirror. A highly smooth polished surface is called mirror. The mirror whose reflecting surface is curved inwards or outwards is called a spherical mirror. Inner part works as a concave mirror and the outer bulging part acts as a convex mirror. The center of the reflecting surface of a mirror is called pole and the radius of the sphere of which the mirror is formed is called radius of curvature. (i) When a concave mirror is held towards the sun and its sharp image is formed on a piece of carbon paper for some time, a hole is burnt in the carbon paper. What is the name given to the distance between the mirror and carbon paper?
(ii) The distance between pole and focal point of a spherical mirror is equal to the distance between
(iii) The focal length of a mirror is 15 cm. The radius of curvature is
(iv) The normal at any point on the mirror passes through
(v) In a convex spherical mirror, reflection of light takes place at
The spherical mirror forms different types of images when the object is placed at different locations. When the image is formed on screen, the image is real and when the image does not form on screen, the image is virtual. When the two reflected rays meet actually, the image is real and when they appear to meet, the image is virtual. A concave mirror always forms a real and inverted image for different positions of the object. But if the object is placed between the focus and pole, the image formed is virtual and erect. A convex mirror always forms a virtual, erect and diminished image. A concave mirror is used as doctor's head mirror to focus light on body parts like eyes, ears, nose etc., to be examined because it can form erect and magnified image of the object. The convex mirror is used as a rear view mirrors in automobiles because it can form an small and erect image of an object. (i) When an object is placed at the centre of curvature of a concave mirror, the image formed is
(ii) No matter how far you stand from a mirror, your image appears erect. The mirror is likely to be
(iii) A child is standing in front of a magic mirror. She finds the image of her head bigger, the middle portion of her body of the same size and that of the legs smaller. The following is the order of combinations for the magic mirror from the top.
(iv) To get an image larger than the object, one can use (a) convex mirror but not a concave mirror (b) a concave mirror but not a convex mirror (c) either a convex mirror or a concave mirror (d) a plane mirror. (v) A convex mirror has wider field of view because (a) the image formed is much smaller than the object and large number of images can be seen (b) the image formed is much closer to the mirror (c) both (a) and (b) (d) none of these.
The relation between distance of an object from the mirror (u), distance of image from the mirror (v) and the focal length (F) is called mirror formula. This formula is valid in all situations for all spherical mirrors for all positions of the object. The size of image formed by a spherical mirror depends on the position of the object from the mirror. The image formed by a spherical mirror can be bigger than the object, equal to the object or smaller than the object. The size of the image relative to the object is given by the linear magnification (m). Thus, the magnification is given by the ratio of height of image to the height of object. If magnification is negative, image is real and if it is positive, image is virtual. (i) What is the position of an image when an object is placed at a distance of 20 em from a concave mirror of focal length 20 cm?
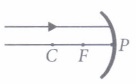
(iii) If the magnification of an image is -2, the characteristic of image will be
(iv) The mirror formula holds for
(v) A parallel beam of light is made to fall on a concave mirror. An image is formed at a distance of7.5 from the mirror. The focal length of the mirror is
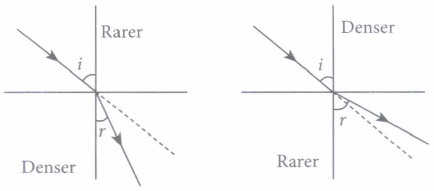
(ii) A ray of light passes from a medium A to another medium B. No bending of light occurs if the ray of light hits the boundary of medium B at an angle of
(iii) When light passes from one medium to another, the frequency of light
(iv) When light passes from glass to water, the speed of light
(v) The bottom of pool filled with water appears to be ______ due to refraction of light
*****************************************
Cbse 10th standard science subject light reflection and refraction case study questions with solution 2021 answer keys.
(i) (d) : When an object is placed at the focus of a concave mirror, the..image is formed at infinity. (ii) (d) : When a light ray parallel to the principal axis is incident on a concave mirror, it passes through the principal focus after reflection. Therefore, figure D is correct. (iii) (a) : If m is negative, the image will be real and inverted. (iv) (d) (v) (b): The distance of object from mirror = \(\infty\) Using, \(\frac{1}{v}+\frac{1}{u}=\frac{1}{f}\) \(\frac{1}{\infty}-\left(-\frac{1}{7.5}\right)=\frac{1}{f}\) f = 7.5 cm
(i) (a): When, a ray of light travels from air to glass, it bends towards the normal. (ii) (c): No bending of light occurs when light is incident normally or perpendicularly on a boundary of two media since angle of incidence and angle of refraction both are zero. (iii) (c): When light goes from one medium to other medium, its frequency does not change (iv) (a): The speed to light increases when light passes from glass to water as water is optically rarer medium. (v) (a): The bottom of a pool of water appears to be less deep than it actually is due to refraction.
Related 10th Standard CBSE Science Materials
10th standard cbse syllabus & materials, cbse 10th maths probability chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths statistics chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths surface areas and volumes chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths areas related to circles chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths circles chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths some applications of trigonometry chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths introduction to trigonometry chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths coordinate geometry chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths triangles chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths arithmetic progressions chapter case study questions with answers, cbse 10th maths quadratic equations chapter case study questions with answers, cbse 10th social science the making of a global world chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th social science nationalism in india chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th social science the rise of nationalism in europe chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th maths pair of linear equation in two variables chapter case study question with answers.

Class VI to XII
Tn state board / cbse, 3000+ q&a's per subject, score high marks.

10th Standard CBSE Study Materials

10th Standard CBSE Subjects

Case Study Questions Class 10 Science Chapter 10 Light Reflection and Refraction
- Post author: studyrate
- Post published:
- Post category: class 10th
- Post comments: 0 Comments
CBSE Board Exam is on the way, so you must practice some good Case Study Questions Class 10 Science to boost your preparation to score 95+% on Boards. In this post, you will get Case Study and Passage Based Questions that will come in CBSE Class 10 Science Board Exams .
Join our Telegram Channel, there you will get various e-books for CBSE 2024 Boards exams for Class 9th, 10th, 11th, and 12th.

In CBSE Class 10 Science Paper, Students will have to answer some questions based on Assertion and Re a son . There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage-based as well. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then the MCQ questions based on it will be asked.
Light Reflection and Refraction Case Study Questions With Answers
Here, we have provided case-based/passage-based questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 10 Light Reflection and Refraction
Case Study/Passage-Based Questions
Question 1:
The spherical mirror forms different types of images when the object is placed at different locations. When the image is formed on the screen, the image is real and when the image does not form on-screen, the image is virtual. When the two reflected rays meet actually, the image is real and when they appear to meet, the image is virtual. A concave mirror always forms a real and inverted image for different positions of the object. But if the object is placed between the focus and pole, the image formed is virtual and erect. A convex mirror always forms a virtual, erect, and diminished image. A concave mirror is used as a doctor’s head mirror to focus light on body parts like eyes, ears, nose, etc., to be examined because it can form erect and magnified images of the object. The convex mirror is used as a rear view mirror in automobiles because it can form a small and erect image of an object.
(i) When an object is placed at the center of curvature of a concave mirror, the image formed is
| (a) larger than the object | (b) smaller than the object |
| (c) same size as that of the object | (d) highly enlarged. |
Answer: (c) same size as that of the object
(ii) No matter how far you stand from a mirror, your image appears erect. The mirror is likely to be
| (a) plane | (b) concave |
| (c) convex | (d) either plane or convex. |
Answer: (d): The image is erect in a plane mirror and also in a convex mirror, for all positions of the object.
(iii) A child is standing in front of a magic mirror. She finds the image of her head bigger, the middle portion of her body of the same size and that of the legs smaller. The following is the order of combinations for the magic mirror from the top.
| (a) Plane, convex and concave | (b) Convex, concave and plane |
| (c) Concave, plane and convex | (d) Convex, plane and concave |
Answer: (c) : As the image of head is bigger, the upper portion of magic mirror is concave. The middle portion of the image is of same size, so, middle portion of magic mirror is plane. Now, the image of legs looks smaller, therefore, the lower portion of magic mirror is convex.
(iv) To get an image larger than the object, one can use (a) convex mirror but not a concave mirror (b) a concave mirror but not a convex mirror (c) either a convex mirror or a concave mirror (d) a plane mirror.
Answer: (b) a concave mirror but not a convex mirror
(v) A convex mirror has wider field of view because (a) the image formed is much smaller than the object and large number of images can be seen (b) the image formed is much closer to the mirror (c) both (a) and (b) (d) none of these.
Answer: (c) both (a) and (b)
Question 2:
The lenses form different types of images when objects are placed at different locations. When a ray is incident parallel to the principal axis, then after refraction, it passes through the focus or appears to come from the focus.
When a ray goes through the optical center of the lens, it passes without any deviation. If the object is placed between the focus and the optical center of the convex lens, an erect and magnified image is formed.
As the object is brought closer to the convex lens from infinity to focus, the image moves away from the convex lens from focus to infinity. Also, the size of the image goes on increasing and the image is always real and inverted.
A concave lens always gives a virtual, erect, and diminished image irrespective of the position of the object.
(i) The location of image formed by a convex lens when the object is placed at infinity is (a) at focus (b) at 2F (c) at optical center (d) between Fand 2F
Answer: (a) at focus
(ii) When the object is placed at the focus of concave lens, the image formed is (a) real and smaller (b) virtual and inverted (c) virtual and smaller (d) real and erect
Answer: (b) virtual and inverted
(iii) The size of image formed by a convex lens when the object is placed at the focus of convex lens is (a) small (b) point in size (c) highly magnified (d) same as that of object
Answer: (c) highly magnified
(iv) When the object is placed at 2F in front of convex lens, the location of image is (a) at F (b) at 2 F on the other side (c) at infinity (d) between F and optical center
Answer: (b) at 2 F on the other side
(v) At which location of object in front of concave lens, the image between focus and optical centre is formed (a) anywhere between centre and infinity (b) at F (c) at 2F (d) infinity
Answer: (a) anywhere between centre and infinity
Case Study 3: Light reflection and refraction are fundamental phenomena that occur when light interacts with surfaces and passes through different mediums. Reflection is the bouncing back of light when it strikes a surface. The laws of reflection state that the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection, and the incident ray, reflected ray, and normal at the point of incidence lie in the same plane. Refraction, on the other hand, is the bending of light as it passes from one medium to another with a different optical density. The bending of light is governed by Snell’s law, which states that the ratio of the sine of the angle of incidence to the sine of the angle of refraction is constant for a given pair of media. The concepts of reflection and refraction help us understand various optical phenomena, such as the formation of images by mirrors and lenses, the dispersion of light, and the phenomenon of total internal reflection.
What is reflection? a) The bending of light as it passes from one medium to another b) The bouncing back of light when it strikes a surface c) The formation of images by mirrors and lenses d) The dispersion of light Answer: b) The bouncing back of light when it strikes a surface
What do the laws of reflection state? a) The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection b) The incident ray, reflected ray, and normal lie in the same plane c) The angle of incidence, angle of reflection, and normal form a right triangle d) All of the above Answer: d) All of the above
What is refraction? a) The bending of light as it passes from one medium to another b) The bouncing back of light when it strikes a surface c) The formation of images by mirrors and lenses d) The dispersion of light Answer: a) The bending of light as it passes from one medium to another
What law governs the bending of light during refraction? a) Law of reflection b) Snell’s law c) Newton’s law d) Coulomb’s law Answer: b) Snell’s law
What optical phenomena can be explained using the concepts of reflection and refraction? a) Formation of images by mirrors and lenses b) Dispersion of light c) Total internal reflection d) All of the above Answer: d) All of the above
Hope the information shed above regarding Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 10 Light Reflection and Refraction with Answers Pdf free download has been useful to an extent. If you have any other queries about CBSE Class 10 Science Light Reflection and Refraction Case Study and Passage Based Questions with Answers, feel free to comment below so that we can revert back to us at the earliest possible. By Team Study Rate
You Might Also Like

NTSE Syllabus 2024 | DPP Class 10 NTSE Exam 2024
Extra questions of class 10 maths chapter 13 surface areas and volumes pdf download, assertion reason questions class 10 science chapter 7 control and coordination, leave a reply cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- CBSE Class 10
CBSE Class 10 Physics Chapter 10 Important Questions and Answers for 2023
Cbse class 10 physics chapter 10 important questions and answers : get the important questions with answers for cbse class 10 science chapter 10 light reflection and refraction. use these along with other cbse resources to score good marks..

CBSE Class 10 Physics Chapter 10 Important Questions and Answers: In this article we are going to cover the Multiple Choice Questions, Very Short Answer Questions, Short Answer Questions, Case Study Questions, Long Answer Questions and even Assertion Reason questions that are important for CBSE Class 10 Science Board Examination 2023. These questions are from the tenth chapter of the third unit of the syllabus - Natural Phenomena.
The answers to the questions are also available. Scroll down to the end of the questions to check your answers.
Important Questions for CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 10 Light Reflection and Refraction
Multiple choice questions.
Q.1. Rays from the sun converge at a point 15 cm in front of a concave mirror. Where should an object be placed so that the size of its image is equal to the size of the object?
(a) 15 cm in front of the mirror
(b) 30 cm in front of the mirror
(c) between 15 cm and 30 cm in front of the mirror
(d) more than 30 cm in front of the mirror
Q.2. No matter how far you stand from a mirror, your image appears erect. The mirror islikely to be
(a) Plane
(b) Concave
(c) Convex
(d) Either plane or convex
Q.3. You are given water, mustard oil, glycerine and kerosene. In which of these media, a ray of light incident obliquely at same angle would bend the most?
(a) Kerosene
(b) Water
(c) Mustard oil
(d) Glycerine
Q.4. As light travels from a rarer to a denser medium it will have
(a) Increased velocity
(b) Decreased velocity
(c) Decreased wavelength
(d) both (b) and (c)
Q.5. How will the image formed by a convex lens be affected if the upper half of the lens is wrapped with a black paper?
(a) The size of the image is reduced to one-half.
(b) The upper half of the image will be absent.
(c) The brightness of the image is reduced.
(d) There will be no effect
Q.6. The velocity of light is maximum in a medium of
(a) glass
(b) water
(c) vacuum
(d) diamond
Q.7. A full length image of a distant tall building can definitely be seen by using:
(a) a concave mirror
(b) a convex mirror
(c) a plane mirror
(d) both concave as well as plane mirror
8. A student conducts an activity using a flask of height 15 cm and a concave mirror. He finds that the image formed is 45 cm in height. What is the magnification of the image?
(a) 45 times
(b) 1/ 45 times
(c) 1/ 3 times
(d) 3 times
Q.9. A student determines the focal length of a device 'X' by focusing the image of a distant object on a screen placed 20 cm from the device on the same side as the object. The device 'X' is
(a) Concave lens of focal length 10 cm
(b) Convex lens of focal length 20 cm
(c) Concave mirror of focal length 10 cm
(d) Concave mirror of focal length 20 cm
Q.10.. A student conducts an experiment using a convex lens of focal length 20 cm and an object of height 15 cm. He placed the object at 25 cm from the lens. Can the image be formed on a screen?
(a) yes, because a real image will be formed
(b) no, because a virtual image will be formed
(c) yes, because an erect image will be formed
ASSERTION AND REASON
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of assertion (A) is followed by a
statement of reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
(a) If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion
(b) If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion
(c) If assertion is true but reason is false.
(d) If both assertion and reason are false.
Q.1. Assertion: A ray incident along normal to the mirror retraces its path.
Reason: In reflection, angle of incidence is always equal to angle of reflection.
2. Assertion: A convex lens is made of two different materials. A point object is placed on the principal axis. The number of images formed by the lens will be two.
Reason :The image formed by convex lens is always virtual.
Q.3. Assertion: When a concave mirror is held in water, its focal length will decrease.
Reason: The focal length of a concave mirror depends on the density the medium in Which it is placed.
Q.4. Assertion: Full length image of a distant object, such as a tall building, can be seen in a convex mirror.
Reason: A convex mirror has a greater focal length than a concave mirror of the same aperture.
Q.5. Assertion: Higher is the refractive index of the medium, lesser is the velocity of light in that medium.
Case Study Based Questions
Q.1. Light is a form of energy which induces sensation of vision to our eyes. It becomes visible when it bounces off on surfaces and hits our eyes. The phenomenon of bouncing back of light rays in the same medium on striking a smooth surface is called reflection of light. If parallel beam of incident rays remains parallel even after reflection and goes only in one direction is known as regular reflection. It takes place mostly in plane mirrors or highly polished metal surfaces. The mirror outside the driver side of a vehicle is usually a spherical mirror and printed on such a mirror is usually the warning "vehicles in this mirror are closer than they appear."
a) Plane mirror
(b) Concave mirror
(c) Convex mirror
(d) Magic mirror
(ii) No matter how far you stand from a mirror, your image appears erect. The mirror can be
(b) Concave
(c) convex
(iv) If an object is placed at 10 cm from a convex mirror of radius of curvature 60 cm, then find the position of image.
(a) 4 cm
(c) 10 cm
(d) 12.5 cm
(v) The focal length of mirror is 12 cm. The radius of curvature is
(a) 12 cm
(c) 20 cm
Q.2. We know that lenses form different types of images when objects are kept at varying positions. When a ray is incident parallel to the principal axis, then after refraction, it passes through the focus or appears to come from the focus.When a ray goes through the optical centre of the lens, it passes without any deviation. If the objectis placed between the focus and optical center of the convex lens, erect and magnified image is formed. As the object is brought closer to the convex lens from infinity to focus, the image moves away from the convex lens from focus to infinity. Also the sizeof the image goes on increasing and the image is always real and inverted. A concave lens always gives a virtual, erect and diminished image irrespective of the position of the object.
i. The location of image formed by a convex lens when the object is placed at infinity is
(a) at focus
(b) at 2F
(c) at optical center
(d) betweenFand 2F
ii. When the object is placed at the focus of concave lens, the image formed is
(a)real and smaller
(b) virtual and smaller
(c) virtual and inverted
(d) real and erect
iii. The size of image formed by a convex lens when the object is placed at the focus of convex lens is
(a) highly magnified
(b) point in size
(c) small
(d) same as that of object
iv. When the object is placed at 2F in front of convex lens, the location of image is
(a) at F
(b) between F and optical center
(c) at infinity
(d) none of the above
Q.3. The refractive index of a medium with respect to vacuum is called the absolute refractive index of the medium. It is given by, μ = sin i/sinr
i) How is absolute refractive index related to speed of light?
(a)μ = C/vm
(c)μ=Vm
(ii) In which of the materials given in the above table, light travels fastest?
(a) A
(c) C
(iii) The speed of light in air is 3x108 ms-1 and that in medium A is 2.5 x 10 ms-1. The refractive index of A will be
(a) 1.2
(c)4.5
(iv) When light travels from air to glass,
(a) angle of incidence > angle of refraction
(b) angle of incidence < angle of refraction
(c) angle of incidence = angle of refraction
(d) Can't say
(v) The refractive index of P with respect to Qis 2. Find the refractive index of Q with respect to P.
(a) 0.5
(c) 2
VERY SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS (2 marks)
Q.1. If the image formed by a spherical mirror for all positions of the object placed in front of it is always erect and diminished, what type of mirror is it?
Draw a labelled ray diagram to support your answer.
Q.2. State the two laws of reflection of light.
Q.3. State the laws of refraction of light. Explain the term absolute refractive index of a medium’ and write an expression to relate it with the speed of light in vacuum.
Q.4. A fish under water is viewing obliquely a fisherman standing on the bank of lake.Does the man look taller or shorter?
Q.5. Which phenomenon occurs when light falls on
(a) highly polished surface
SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS (3 MARKS)
Q.1. A concave mirror has a focal length of 20 cm. At what distance from the mirror should a 4 cm tall object be placed so that it forms an image at a distance of 30 cm from the mirror? Also calculate the size of the image formed.
Q.2. (a) Water has refractive index 1.33 and alcohol has refractive index 1.36. Which of the two medium is optically denser? Give reason for your answer.
(b) Draw a ray diagram to show the path of a ray of light passing obliquely from water to alcohol.
(c) State the relationship between angle of incidence and angle of refraction in the above case.
Q.3. Three mirrors, one plane, one concave and one convex are lying on the table. identify them without touching them or using any other apparatus or device?
Q.4. A convex lens of focal length 25 cm and a concave lens of focal length 10 cm are placed in closed contact with each other. Calculate the lens power of the combination.
Q.5. An object is placed at a distance of 12 cm in front of a concave mirror of radius ofcurvature 30 cm. List four characteristics of the image formed by the mirror
Q.6. A convex lens of focal length 2.0 m can produce a magnified virtual as well as real image. Is this a correct statement? If yes, where shall the object be placed in each case for obtaining these images?
LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS (4 MARKS)
Q.1. (i) A doctor has prescribed a corrective lens of power +1.5 D. Find the focal length of the lens. Is the prescribed lens diverging or converging?
(ii) A concave lens of focal length 15 cm forms an image 10 cm from the lens. How far is the object placed from the lens? Draw the ray diagram.
Q.2. (a) A 5 cm tall object is placed perpendicular to the principal axis of a convex lens of focal length 20 cm. The distance of the object from the lens is 30 cm. Find the position, nature and size of the image formed.
Answers to Important Questions for CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 10 Light Reflection and Refraction
Unit III: Natural Phenomena
Answer- (b) 30 cm in front of the mirror
Answer- (d) Either plane or convex
Answer- (d) Glycerine
Answer- (b) Decreased velocity
Answer- (c) The brightness of the image is reduced.
Answer- (c) vacuum
Answer- (b) a convex mirror
Answer- (d) 3 times
Answer- (d) Concave mirror of focal length 20 cm
(d)No because the image is
Answer- (a)
Answer- (c)
Answer- (d)
Reason: Refractive index of a medium is inversely proportional to the velocity of light.
Case Study Based Questions:
(i) Which type of mirror is used outside the driver's side of a vehicle?
(iii) If an object is placed at 10 cm from a convex mirror of radius of curvature 60 cm, then find the position of image.
(iv) The focal length of the mirror is 12 cm. The radius of curvature is
Q.2. We know that lenses form different types of images when objects are kept at varying positions. When a ray is incident parallel to the principal axis, then after refraction, it passes through the focus or appears to come from the focus.When a ray goes through the optical centre of the lens, it passes without any deviation. If the object is placed between the focus and optical center of the convex lens, erect and magnified image is formed. As the object is brought closer to the convex lens from infinity to focus, the image moves away from the convex lens from focus to infinity. Also the sizeof the image goes on increasing and the image is always real and inverted. A concave lens always gives a virtual, erect and diminished image irrespective of the position of the object.
i The location of image formed by a convex lens when the object is placed at infinity is
(d) between Fand 2F
ii When the object is placed at the focus of concave lens, the image formed is
iii The size of image formed by a convex lens when the object is placed at the focus of convex lens is
iv When the object is placed at 2F in front of convex lens, the location of image is
(a)at F
Answer- If the image formed by a spherical mirror is always erect and diminished then it is convex mirror.
Laws of reflection of light states that
(i) The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection.
(ii) The incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal to the mirror at the point of incidence all lie in the same plane.
Q.3. State the laws of refraction of light. Explain the term absolute refractive index of a
medium’ and write an expression to relate it with the speed of light in vacuum.
Answer- (a) Laws of refraction of light:
(i) The incident ray, the refracted ray and the normal to the interface of two transparent media at the point of incidence, all lie in the same plane.
(ii) The ratio of sine of angle of incidence to the sine of the angle of refraction is constant, for the light of a given colour and for the given pair of media.
This law is also known as Snell’s law of refraction.
sini/sinr = constant,
where i is the angle of incidence and r is the angle of refraction.
This constant value is called refractive index of the second medium with respect to the first when the light travels from first medium to second medium.
⇒ constant = n21 = v1/v2 ∴sini/sinr = v1/v2
If n is the absolute refractive index of the medium, c is the velocity of light in vacuum and v is the speed of light in a given medium, then n = c/v.
Ans. As light travels from rarer to denser medium, it bends towards normal and appears to come from greater height. Therefore, to fish under water, man looks taller.
(b) a transparent medium?
Ans. (a) Reflection of light.
Answer- Given f = -20 cm v = -30 cm, u = ?
Using 1/v + 1/u = 1/f
1/u = 1/f – 1/v = 1/(−20) – /(−30) = (−3+2)/60
⇒ u = -60 cm
∴ Object placed at 60 cm from the mirror.
Also magnification, m = h′/h = −v/u
⇒ h’ = −(−30)/−60 × 4 = -2 cm
∴ The size of the image is 2 cm.
Answer- (a) Here, alcohol is optically denser medium as its refractive index is higher than that of water. When we compare the two media, the one with larger refractive index is called the optically denser medium than the other as the speed of light is lower in this medium.
(b) Since light is travelling from water (rarer medium) to alcohol (denser medium), it slows down and bends towards the normal.
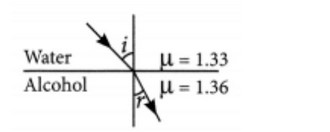
where i = angle of incidence and r = angle of refraction.
(c) According to Snell’s law,
sini/sinr=μalcohol /μwater =1.36/1.33 = 1.0225
∴ sin i = 1.0225 × sin r
Ans. Plane mirror produces the image of same size. Concave mirror produced the magnified image while the convex mirror will produce a diminished image
f1=25cm=0.25 m
f2= -10cm= - 0.1m
Power of convex lens, P1 = 1/f1=1/0.25=+4D
Power of concave lens, P2 = 1/f2=1/ - 0.1m=-10D
power of combination, P = P1 +P2 = 4D – 10D = -6D
Ans: Radius of curvature (R) = 30 cm, object distance is 12 cm in front of the mirror.Thus we can say that object is placed between focus and pole. Four characteristics of the image formed by die given concave mirror when object is placed between pole and focus are:
(i) Virtual
(iii) Enlarged
(iv) Image is formed behind the mirror
Ans: Yes, it is correct. If the object is placed within 2.0 m from the lens in the it forms magnified virtuaL image Between 2 m and 4 m it will form a real inverted and magnified image.
Q.7. “The magnification produced by a spherical mirror is -3”. List all information youobtain from this statement about the mirror/ image.
LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS

(b) Draw a labelled ray diagram showing object distance, image distance and focal length in the above case.
Answer- (a) Given, h = 5 cm, f = 20 cm, u = -30 cm
Using lens formula, 1/v – 1/u = 1/f
1/v=1/u+1/f=1/(−30)+1/20=(−2+3)/60=1/60
⇒ v = 60 cm
Now, magnification, m = h′/h = v/u
⇒ h’ = v/u × h = 60/(−30) × 5 = -10 cm
Hence, the image formed at 60 cm, which is real and magnified.
|
|
Get here latest School , CBSE and Govt Jobs notification and articles in English and Hindi for Sarkari Naukari , Sarkari Result and Exam Preparation . Download the Jagran Josh Sarkari Naukri App .
- India Post GDS Merit List 2024
- NDA Question Paper 2024
- RBI Grade B Admit Card 2024
- UP Police Constable Admit Card 2024
- SSC CGL Admit Card 2024
- UP Police Constable Question Paper 2024 PDF
- CDS Question Paper 2024
- RRB NTPC Recruitment 2024
- Teachers Day Speech
- Teachers Day Gift
- CBSE Class 10 QnA
- Education News
- CBSE Class 10 Study Material
Latest Education News
RPSC RAS Recruitment 2024: Applications Invited For 733 Various Posts, Check eligibility and application process
Rajasthan Police Constable Result 2024 Out at police.rajasthan.gov.in: Direct Link to Download Result PDF Here
Paris Paralympics 2024 India Medals list: किन भारतीयों ने जीते मेडल,पढ़ें सबके नाम
उत्तर प्रदेश के 8 रेलवे स्टेशनों को मिले नए नाम, यहां देखें नई लिस्ट
Jasdeep Singh Gill Story: कौन हैं जसदीप सिंह गिल? केमिकल इंजीनियर से धार्मिक गुरु बनने तक की कहानी
बिना पासपोर्ट और वीजा के विदेश की सैर, बस यह डॉक्यूमेंट रखें साथ
Brain Teaser: This High IQ Logic Puzzle Will Separate the Smart From the Smarter
Teacher’s Day 2024: डॉ. सर्वपल्ली राधाकृष्णन, जो राष्ट्रपति के रूप में दान कर देते थे आधे से अधिक वेतन
Picture Puzzle IQ Test: Find the mistake in the picture in 5 seconds!
Maharashtra Police SRPF Result 2022-23 OUT at mahapolice.gov.in, Download Here
Kerala SET Result 2024 OUT at lbsedp.lbscentre.in: Download KSET Marks Link
UP Scholarship 2024: Direct Link to Apply Online for Pre-Matric and Post-Matric Scheme, Check Eligibility, Other Details
Dr MGR Medical University Result 2024 OUT at tnmgrmu.ac.in; Direct Link to Download UG and PG Marksheet
Teachers Day 2024: How Dr. Sarvepalli Radhakrishnan's Birthday Became Teachers' Day in India? Details Here
MGSU Result 2024 OUT at mgsubikaner.ac.in, Direct Link to Download UG and PG Marksheet PDF
SSC CGL Admit Card 2024 Out at ssc.gov.in: Direct Link to Download Region Wise Tier 1 Hall Ticket PDF Here
Delhi Home Guard Admit Card 2024 OUT at dghgenrollment.in: Download Link Here
SSC CGL Reasoning Questions With Solution, Download PDF Here
Synonyms and Antonyms: 100+ Synonyms and Antonyms List with Examples and Meaning for SSC; Download PDF
SSC CGL Previous Year Question Paper PDF Download, Tier 1 & 2 PDFs with Solutions

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Here, we have provided case based/passage based questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 10 Light Reflection and Refraction. Question 1: Read the following and answer any four questions from (i) to (v).
Q6: How can teachers incorporate case study questions on Light – Reflection and Refraction class 10 science into classroom teaching? Q7: Is light a form of energy? Q8: Do the laws of reflection hold good for spherical mirrors?
Important Case Study Questions for Class 10 Board Exam Students. Here we have arranged some Important Case Base Questions for students who are searching for Paragraph Based Questions Light Reflection and Refraction.
Here we are providing you with Class 10 Science Chapter 10 Light Reflection and Refraction Case Study Questions, by practicing these Case Study and Passage Based Questions will help you in your Class 10th Board Exam.
Find case study questions with answers for Class 10 Science Chapter 1 on light reflection and refraction. Learn about the concepts, formulas, examples and applications of light in different media.
CBSE 10th Standard Science Subject Light Reflection and Refraction Chapter Case Study Questions With Solution 2021. By QB365 on 21 May, 2021. QB365 Provides the updated CASE Study Questions for Class 10 , and also provide the detail solution for each and every case study questions .
Here, we have provided case-based/passage-based questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 10 Light Reflection and Refraction. Case Study/Passage-Based Questions. Question 1: The spherical mirror forms different types of images when the object is placed at different locations.
When the rays of light travels from one transparent medium to another, the path of light is deviated. "Ihis phenomena is called refraction of light. The bending of light depends on the optical density of medium through which the light pass. Denser The speed of light varies from medium to medium.
Get CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter Wise Important Case Study Questions with Solution here to prepare for CBSE Class 120 Science board exam 2024.
Important Questions for CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 10 Light Reflection and Refraction. MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS. Q.1. Rays from the sun converge at a point 15 cm in front of a...