
Free Download

Information Technology Business Plan Template
Download this free information technology business plan template, with pre-filled examples, to create your own plan..
Or plan with professional support in LivePlan. Save 50% today
Available formats:
What you get with this template
A complete business plan.
Text and financials are already filled out and ready for you to update.
- SBA-lender approved format
Your plan is formatted the way lenders and investors expect.
Edit to your needs
Download as a Word document and edit your business plan right away.
- Detailed instructions
Features clear and simple instructions from expert business plan writers.
All 100% free. We're here to help you succeed in business, no strings attached.
Get the most out of your business plan example
Follow these tips to quickly develop a working business plan from this sample.
1. Don't worry about finding an exact match
We have over 550 sample business plan templates . So, make sure the plan is a close match, but don't get hung up on the details.
Your business is unique and will differ from any example or template you come across. So, use this example as a starting point and customize it to your needs.
2. Remember it's just an example
Our sample business plans are examples of what one business owner did. That doesn't make them perfect or require you to cram your business idea to fit the plan structure.
Use the information, financials, and formatting for inspiration. It will speed up and guide the plan writing process.
3. Know why you're writing a business plan
To create a plan that fits your needs , you need to know what you intend to do with it.
Are you planning to use your plan to apply for a loan or pitch to investors? Then it's worth following the format from your chosen sample plan to ensure you cover all necessary information.
But, if you don't plan to share your plan with anyone outside of your business—you likely don't need everything.
More business planning resources

Simple Business Plan Outline

How to Start a Business With No Money

Business Plan Template

Industry Business Planning Guides

How to Create a Business Plan Presentation

10 Qualities of a Good Business Plan

How to Write a Business Plan

How to Write a Business Plan for Investors
Download your template now
Need to validate your idea, secure funding, or grow your business this template is for you..
- Fill-in-the-blank simplicity
- Expert tips & tricks
We care about your privacy. See our privacy policy .
Not ready to download right now? We'll email you the link so you can download it whenever you're ready.
Download as Docx
Download as PDF

Finish your business plan with confidence
Step-by-step guidance and world-class support from the #1 business planning software

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software

IT Services Business Plan Template
Written by Dave Lavinsky
IT Services Business Plan
Over the past 20+ years, we have helped over 500 entrepreneurs and business owners create business plans to start and grow their IT companies.
If you’re unfamiliar with creating an IT business plan, you may think creating one will be a time-consuming and frustrating process. For most entrepreneurs it is, but for you, it won’t be since we’re here to help. We have the experience, resources, and knowledge to help you create a great business plan.
In this article, you will learn some background information on why business planning is important. Then, you will learn how to write an IT business plan step-by-step so you can create your plan today.
Download our Ultimate Business Plan Template here >
What is an IT Services Business Plan?
A business plan provides a snapshot of your IT business as it stands today, and lays out your growth plan for the next five years. It explains your business goals and your strategies for reaching them. It also includes market research to support your plans.
Why You Need a Business Plan for IT Company
If you’re looking to start an IT business or grow your existing IT company, you need a business plan. A business plan will help you raise funding, if needed, and plan out the growth of your IT business to improve your chances of success. Your IT business plan is a living document that should be updated annually as your company grows and changes.
Sources of Funding for IT Businesses
With regards to funding, the main sources of funding for an IT business are personal savings, credit cards, bank loans, and angel investors. When it comes to bank loans, banks will want to review your business plan and gain confidence that you will be able to repay your loan and interest. To acquire this confidence, the loan officer will not only want to ensure that your financials are reasonable, but they will also want to see a professional plan. Such a plan will give them the confidence that you can successfully and professionally operate a business. Personal savings and bank loans are the most common funding paths for IT companies.
Finish Your Business Plan Today!
How to Write a Business Plan for an IT Services Business
If you want to start an IT business or expand your current one, you need a business plan. The guide below details the necessary information for how to write each essential component of your IT business plan.
Executive Summary
Your executive summary provides an introduction to your business plan, but it is normally the last section you write because it provides a summary of each key section of your plan.
The goal of your executive summary is to quickly engage the reader. Explain to them the kind of IT business you are running and the status. For example, are you a startup, do you have an IT business that you would like to grow, or are you operating a chain of IT businesses?
Next, provide an overview of each of the subsequent sections of your plan.
- Give a brief overview of the IT industry.
- Discuss the type of IT business you are operating.
- Detail your direct competitors. Give an overview of your target customers.
- Provide a snapshot of your marketing strategy. Identify the key members of your team.
- Offer an overview of your financial plan.
Company Overview
In your company overview, you will detail the type of IT business you are operating.
For example, you might specialize in one of the following types of IT businesses:
- Computer repair : This type of IT business provides computer maintenance and repair services.
- Computer training: This type of IT professional specializes in teaching others how to use computers as well as various software and computer programs.
- IT support: This type of IT professional provides services for businesses such as setting up a network, backing up data, and systems management.
- Cloud computing: This type of IT specialist helps individuals and businesses establish cloud platforms and tools, or may help to migrate their information to the cloud.
In addition to explaining the type of IT business you will operate, the company overview needs to provide background on the business.
Include answers to questions such as:
- When and why did you start the business?
- What milestones have you achieved to date? Milestones could include the number of new clients served, the number of repeat clients, reaching $X amount in revenue, etc.
- Your legal business Are you incorporated as an S-Corp? An LLC? A sole proprietorship? Explain your legal structure here.
Industry Analysis
In your industry or market analysis, you need to provide an overview of the IT industry.
While this may seem unnecessary, it serves multiple purposes.
First, researching the IT industry educates you. It helps you understand the market in which you are operating.
Secondly, market research can improve your marketing strategy, particularly if your analysis identifies market trends.
The third reason is to prove to readers that you are an expert in your industry. By conducting the research and presenting it in your plan, you achieve just that.
The following questions should be answered in the industry analysis section of your IT business plan:
- How big is the IT industry (in dollars)?
- Is the market declining or increasing?
- Who are the key competitors in the market?
- Who are the key suppliers in the market?
- What trends are affecting the industry?
- What is the industry’s growth forecast over the next 5 – 10 years?
- What is the relevant market size? That is, how big is the potential target market for your IT business? You can extrapolate such a figure by assessing the size of the market in the entire country and then applying that figure to your local population.
Customer Analysis
The customer analysis section of your IT business plan must detail the customers you serve and/or expect to serve.
The following are examples of customer segments: individuals, schools, families, and corporations.
As you can imagine, the customer segment(s) you choose will have a great impact on the type of IT business you operate. Clearly, individuals would respond to different marketing promotions than corporations, for example.
Try to break out your target customers in terms of their demographic and psychographic profiles. With regards to demographics, including a discussion of the ages, genders, locations, and income levels of the potential customers you seek to serve.
Psychographic profiles explain the wants and needs of your target customers. The more you can recognize and define these needs, the better you will do in attracting and retaining your customers.
Finish Your IT Business Plan in 1 Day!
Don’t you wish there was a faster, easier way to finish your business plan?
With Growthink’s Ultimate Business Plan Template you can finish your plan in just 8 hours or less!
Competitive Analysis
Your competitive analysis should identify the indirect and direct competitors your business faces and then focus on the latter.
Direct competitors are other IT businesses.
Indirect competitors are other options that customers have to purchase from that aren’t directly competing with your product or service. This includes other types of IT consultants, in-house IT support, or do-it-yourself IT tutorials. You need to mention such competition as well.
For each such competitor, provide an overview of their business and document their strengths and weaknesses. Unless you once worked at your competitors’ businesses, it will be impossible to know everything about them. But you should be able to find out key things about them such as
- What types of customers do they serve?
- What type of IT business are they?
- What is their pricing (premium, low, etc.)?
- What are they good at?
- What are their weaknesses?
With regards to the last two questions, think about your answers from the customers’ perspective. And don’t be afraid to ask your competitors’ customers what they like most and least about them.
The final part of your competitive analysis section is to document your areas of competitive advantage. For example:
- Will you make it easier for clients to acquire your product or service?
- Will you offer products or services that your competition doesn’t?
- Will you provide better customer service?
- Will you offer better pricing?
Think about ways you will outperform your competition and document them in this section of your plan.
Marketing Plan
Traditionally, a marketing plan includes the four P’s: Product, Price, Place, and Promotion. For an IT business plan, your marketing strategy should include the following:
Product : In the product section, you should reiterate the type of IT company that you documented in your company overview. Then, detail the specific products or services you will be offering. For example, will you provide cloud computing, data center management, or network setup services?
Price : Document the prices you will offer and how they compare to your competitors. Essentially in the product and price sub-sections of your plan, you are presenting the products and/or services you offer and their prices.
Place : Place refers to the site of your IT company. Document where your company is situated and mention how the site will impact your success. For example, is your IT business located in a busy retail district, a business district, a standalone office, or purely online? Discuss how your site might be the ideal location for your customers.
Promotions : The final part of your IT marketing plan is where you will document how you will drive potential customers to your location(s). The following are some promotional methods you might consider:
- Advertise in local papers, radio stations and/or magazines
- Reach out to websites
- Distribute flyers
- Engage in email marketing
- Advertise on social media platforms
- Improve the SEO (search engine optimization) on your website for targeted keywords
Operations Plan
While the earlier sections of your business plan explained your goals, your operations plan describes how you will meet them. Your operations plan should have two distinct sections as follows.
Everyday short-term processes include all of the tasks involved in running your IT business, including answering calls, meeting with new clients, billing and collecting payments from clients, etc.
Long-term goals are the milestones you hope to achieve. These could include the dates when you expect to acquire your Xth client, or when you hope to reach $X in revenue. It could also be when you expect to expand your IT business to a new city.
Management Team
To demonstrate your IT business’ potential to succeed, a strong management team is essential. Highlight your key players’ backgrounds, emphasizing those skills and experiences that prove their ability to grow a company.
Ideally, you and/or your team members have direct experience in managing IT businesses. If so, highlight this experience and expertise. But also highlight any experience that you think will help your business succeed.
If your team is lacking, consider assembling an advisory board. An advisory board would include 2 to 8 individuals who would act as mentors to your business. They would help answer questions and provide strategic guidance. If needed, look for advisory board members with experience in managing an IT business or successfully running a small IT consulting service.
Financial Plan
Your financial plan should include your 5-year financial statement broken out both monthly or quarterly for the first year and then annually. Your financial statements include your income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statements.
Income Statement
An income statement is more commonly called a Profit and Loss statement or P&L. It shows your revenue and then subtracts your costs to show whether you turned a profit or not.
In developing your income statement, you need to devise assumptions. For example, will you charge your clients an hourly rate of $250 per hour, and will you work 5 hours per day? And will sales grow by 2% or 10% per year? As you can imagine, your choice of assumptions will greatly impact the financial forecasts for your business. As much as possible, conduct research to try to root your assumptions in reality.
Balance Sheets
Balance sheets show your assets and liabilities. While balance sheets can include much information, try to simplify them to the key items you need to know about. For instance, if you spend $50,000 on building out your IT business, this will not give you immediate profits. Rather it is an asset that will hopefully help you generate profits for years to come. Likewise, if a lender writes you a check for $50,000, you don’t need to pay it back immediately. Rather, that is a liability you will pay back over time.
Cash Flow Statement
Your cash flow statement will help determine how much money you need to start or grow your business, and ensure you never run out of money. What most entrepreneurs and business owners don’t realize is that you can turn a profit but run out of money and go bankrupt.
When creating your Income Statement and Balance Sheets be sure to include several of the key costs needed in starting or growing an IT business:
- Cost of equipment and office supplies
- Payroll or salaries paid to staff
- Business insurance
- Other start-up expenses (if you’re a new business) like legal expenses, permits, computer software, and equipment
Attach your full financial projections in the appendix of your plan along with any supporting documents that make your plan more compelling. For example, you might include your office location lease or a list of your IT credentials.
Writing a business plan for your IT business is a worthwhile endeavor. If you follow the template above, by the time you are done, you will truly be an expert on IT business planning. You will understand the IT industry, your competition, and your customers. You will develop a marketing strategy and will understand what it takes to launch and grow a successful IT business.
Don’t you wish there was a faster, easier way to finish your IT business plan?
OR, Let Us Develop Your Plan For You
Since 1999, Growthink has developed business plans for thousands of companies who have gone on to achieve tremendous success. See how Growthink’s business plan services can give you a winning business plan.
Other Helpful Business Plan Articles & Templates

Technology Business Plan Template
Written by Dave Lavinsky
Technology Business Plan
You’ve come to the right place to create your own Technology business plan.
We have helped over 1,000 entrepreneurs and business owners create business plans and many have used them to start or grow their Technology businesses.
Technology Business Plan Example & Template
Below is a Technology business plan template and sample to help you create each section of your own business plan.
Executive Summary
Business overview.
Kearney Tech Inc., located in Houston, Texas is a tech startup that focuses on developing and commercializing new artificial intelligence (AI) technology applications designed for small-to-medium sized businesses. The company has created proprietary technology that helps businesses improve their profitability by using AI to increase customer engagement. We offer multiple products, including AI hardware, marketing AI software, and CRM AI software. Many of our most basic services are free, but the rest can be accessed by paying a subscription fee. By providing flexible and affordable subscription options for our clients, Kearney Tech Inc. aims to be the next big technology company in the AI space for small and medium-sized businesses.
Kearney Tech Inc. was founded and is led by Abigail Kearney. Abigail has been a senior software engineer for nearly 10 years and has extensive experience in artificial intelligence and machine learning. In addition to her experience, she has a bachelor’s degree in computer science and an MBA. Her education and experience are sure to lead Kearney Tech Inc. to success.
Product Offering
Kearney Tech Inc. will showcase a variety of different applications for its AI technology that companies can utilize to increase their customer engagement from day one. Businesses can choose the platform package that works for them, based on a freemium subscription pricing structure.
The following are the services that Kearney Tech Inc. will provide:
- AI Hardware
- Marketing AI Software
- Customer Relationship Management AI Software
- Customer Support AI Software
- Technology Training: Training sessions on how to use our AI solutions and integrate them into their businesses
Customer Focus
Kearney Tech Inc. will serve small to medium-sized businesses within a 30-mile radius of Houston, Texas. Many of the businesses in our target demographic are startups looking to expand their reach and thus would benefit from technology that can increase their customer base.
Management Team
Kearney Tech Inc. will also employ an experienced assistant to work as a business analyst and help with various administrative duties around the office. She will also hire several developers, salesmen, and other administrative staff to assist her.
Success Factors
Kearney Tech Inc. will be able to achieve success by offering the following competitive advantages:
- Management: Abigail Kearney has been extremely successful working in the technology industry and will be able to use her previous experience to provide the best service experience. Her unique qualifications will serve customers in a much more sophisticated manner than Kearney Tech Inc.’s competitors.
- Relationships: Abigail Kearney knows many of the local leaders, business managers, and other influencers within Houston, Texas. With her 10 years of experience and good relationships with business leaders in the area, she will be able to develop an initial client base.
- Proprietary technology : The company has developed proprietary AI technology that will be used to add new data sources, expand on valuable insights, launch advanced features like benchmarking, provide predictive and prescriptive analytics, and ensure self-guided data discovery.
- Client-oriented service: Kearney Tech Inc. will have full-time customer service and sales managers to keep in contact with clients and answer their everyday questions.
Financial Highlights
Kearney Tech Inc. is seeking a total funding of $400,000 of debt capital to open its office. The funding will be dedicated to office design, software development, marketing, and working capital. Specifically, these funds will be used as follows:
- Office design/build: $50,000
- Software development: $150,000
- Three months of overhead expenses (payroll, rent, utilities): $150,000
- Marketing costs: $25,000
- Working capital: $25,000
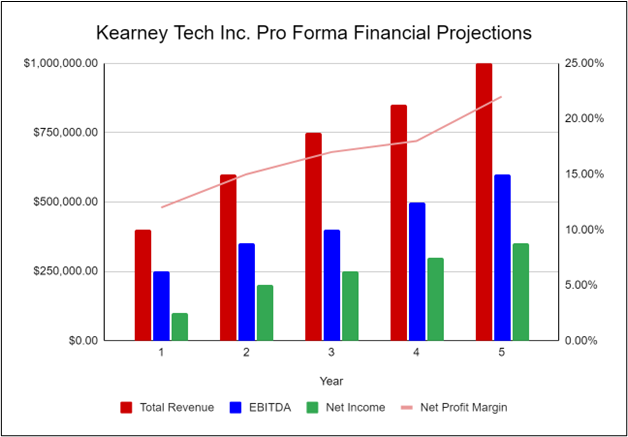
The following graph below outlines the pro forma financial projections for Kearney Tech Inc.:
Company Overview
Who is kearney tech inc..
Abigail began researching what it would take to create her own technology company and did a thorough analysis of the costs, market, demographics, and competition. Abigail has compiled enough information to develop her business plan in order to approach investors.
Kearney Tech Inc.’s History
Once her market analysis was complete, Abigail Kearney began surveying the local vacant office space and located an ideal location to house the technology company. Abigail Kearney incorporated Kearney Tech Inc. as a Limited Liability Corporation in April 2023.
Since incorporation, the company has achieved the following milestones:
- Located available office space for rent
- Developed the company’s name, logo, and website
- Determined equipment and necessary supplies
- Began recruiting key employees
Kearney Tech Inc. Services
Industry analysis.
As of 2021, the global technology industry was valued at approximately $5.2T. Of all countries worldwide, the United States currently has the largest technology market, with 32% of the market share at $1.7T. The technology industry in the U.S. accounts for a large part of the nation’s economy.
The Information Technology market can be segmented by categories such as software, devices, infrastructure IT and business services, emerging technology, and telecom services. In the United States, IT and business services hold the greatest market share (30%), followed by software (20%) and telecom services (20%).
Market drivers include the economy, employment rates, and the digital transformation of daily life for a growing number of people and businesses worldwide. Corporations and organizations are seeking IT service providers that can help improve their software, cybersecurity, data, and infrastructure. Technology companies that can provide products and services that cater to these issues can be competitive in the constantly evolving market.
Technology is an integral part of society. Developments in AI and machine learning are essential to keep society moving forward and make businesses more efficient. Therefore, businesses will always be in need of AI solutions to bring in more customers and streamline their services and products. According to Market Watch, the Technology industry is set to grow at a CAGR of 25.73% from now until 2027. Very few industries see this growth, which shows how much demand there is for technological solutions. Therefore, we expect Kearney Tech Inc. to see great success in our local market.
Customer Analysis
Demographic profile of target market.
Kearney Tech Inc. will serve the small and medium-sized businesses of Houston, Texas, and the surrounding areas.
Many small businesses in the community are startups or established enterprises looking to expand their reach and thus would benefit from technology that can increase their customer engagement.
Customer Segmentation
Kearney Tech Inc. will primarily target the following customer profiles:
- Small businesses
- Medium-sized businesses
Competitive Analysis
Direct and indirect competitors.
Kearney Tech Inc. will face competition from other companies with similar business profiles. A description of each competitor company is below.
Tekuserv has been a reliable technology company in Houston, Texas for more than fifteen years. The company is known for its wide range of technology solutions that serve many small-to-medium-sized businesses. With its large number of experts focused on delivering customer satisfaction, the organization maintains its high standard of developing quality products and providing exceptional customer service. Tekuserv provides business software on a freemium subscription basis. It develops enterprise technology solutions with a focus on customer relationship management.
Prime AI Business Solutions
Prime AI Business Solutions is a technology development company in Houston, Texas. In business for several years, the company has developed highly-rated AI solutions used by many well-known businesses in a variety of industries. Prime AI Business Solutions now offers a range of AI hardware and software products geared toward helping businesses of all sizes increase their customer base. The company has also introduced a “pay-as-you-grow” pricing model that scales to provide users with more support as they scale up.
AICE Developments
AICE stands for Artificial Intelligence for Customer Engagement. AICE Developments is also a local technology company that manufactures and distributes a variety of technology products. AICE Developments was established in 2009 in Houston, Texas, providing integrated AI applications and platform services. Its products include applications and infrastructure offerings delivered through various IT deployment models, including on-premise deployments, cloud-based deployments, and hybrid deployments. The company serves automotive, financial services, healthcare, hospitality, retail, utilities, construction, etc. It provides AI solutions for enterprise marketing and customer engagement.
Competitive Advantage
Kearney Tech Inc. will be able to offer the following advantages over the competition:
- Proprietary technology: The company has developed proprietary AI technology that will be used to add new data sources, expand on valuable insights, launch advanced features like benchmarking, provide predictive and prescriptive analytics, and ensure self-guided data discovery.
Marketing Plan
Brand & value proposition.
Kearney Tech Inc. will offer a unique value proposition to its clientele:
- Service built on long-term relationships
- Big-firm expertise in a small-firm environment
- Thorough knowledge of the clients and their varying needs
- Proprietary technology developed by skilled software engineers
Promotions Strategy
The promotions strategy for Kearney Tech Inc. is as follows:
Kearney Tech Inc. understands that the best promotion comes from satisfied customers. The company will encourage its clients to refer other businesses by providing economic or financial incentives for every new client produced. This strategy will increase in effectiveness after the business has already been established.
Social Media
Kearney Tech Inc. will invest heavily in a social media advertising campaign. The brand manager will create the company’s social media accounts and invest in ads on all social media platforms. It will use targeted marketing to appeal to the target demographics.
Website/SEO
Kearney Tech Inc. will invest heavily in developing a professional website that displays all of the features and benefits of the technology company. It will also invest heavily in SEO so that the brand’s website will appear at the top of search engine results.
Direct Mail
Kearney Tech Inc. will blanket businesses with direct mail pieces. These pieces will provide general information on Kearney Tech Inc., offer discounts, and/or provide other incentives for companies to use the AI platform.
Kearney Tech Inc.’s pricing will be on par with competitors so clients feel they receive great value when purchasing the technology.
Operations Plan
The following will be the operations plan for Kearney Tech Inc.:
Operation Functions:
- Abigail Kearney will be the Owner and CEO of the company. She will oversee all the operations and executive functions of the company. In the beginning, she will also provide customer support and market/sell AI products to potential clients.
- Abigail will employ an experienced assistant to work as a business analyst and help with various administrative duties around the office.
- Abigail will also hire several developers to maintain and develop AI products and services.
- Abigail will also hire a solid sales team to sell our products to potential clients. As the company grows, she will also hire a team that is solely dedicated to customer service.
Milestones:
Kearney Tech Inc. will have the following milestones completed in the next six months.
5/2023 – Finalize lease agreement
6/2023 – Design and build out Kearney Tech Inc.
7/2023 – Hire and train initial staff
8/2023 – Kickoff of promotional campaign
9/2023 – Launch Kearney Tech Inc.
10/2023 – Reach break-even
Financial Plan
Key revenue & costs.
Kearney Tech Inc.’s revenues will come primarily from its technology solution subscription sales. The company will use a freemium subscription model, in which basic functions can be used by any company for free. Additional solutions and support will be available in a tiered package model based on the enterprises’ size and the number of users.
The office lease, equipment, supplies, and labor expenses will be the key cost drivers of Kearney Tech Inc. Ongoing marketing expenditures are also notable cost drivers for Kearney Tech Inc.

Funding Requirements and Use of Funds
Key assumptions.
The following outlines the key assumptions required in order to achieve the revenue and cost numbers in the financials and pay off the startup business loan.
- Average number of clients per month
- Annual rent: $20,000
Financial Projections
Income statement, balance sheet, cash flow statement, technology business plan faqs, what is a technology business plan.
A technology business plan is a plan to start and/or grow your technology business. Among other things, it outlines your business concept, identifies your target customers, presents your marketing plan and details your financial projections. You can easily complete your Technology business plan using our Technology Business Plan Template here .
What are the Main Types of Technology Businesses?
There are a number of different kinds of technology businesses, some examples include: Network technology, Software technology, and Customer relationship technology.
How Do You Get Funding for Your Technology Business Plan?
Technology businesses are often funded through small business loans. Personal savings, credit card financing and angel investors are also popular forms of funding.
What are the Steps To Start a Technology Business?
Starting a technology business can be an exciting endeavor. Having a clear roadmap of the steps to start a business will help you stay focused on your goals and get started faster.
1. Develop A Technology Business Plan - The first step in starting a business is to create a detailed technology business plan that outlines all aspects of the venture. This should include potential market size and target customers, the services or products you will offer, pricing strategies and a detailed financial forecast.
2. Choose Your Legal Structure - It's important to select an appropriate legal entity for your technology business. This could be a limited liability company (LLC), corporation, partnership, or sole proprietorship. Each type has its own benefits and drawbacks so it’s important to do research and choose wisely so that your technology business is in compliance with local laws.
3. Register Your Technology Business - Once you have chosen a legal structure, the next step is to register your technology business with the government or state where you’re operating from. This includes obtaining licenses and permits as required by federal, state, and local laws.
4. Identify Financing Options - It’s likely that you’ll need some capital to start your technology business, so take some time to identify what financing options are available such as bank loans, investor funding, grants, or crowdfunding platforms.
5. Choose a Location - Whether you plan on operating out of a physical location or not, you should always have an idea of where you’ll be based should it become necessary in the future as well as what kind of space would be suitable for your operations.
6. Hire Employees - There are several ways to find qualified employees including job boards like LinkedIn or Indeed as well as hiring agencies if needed – depending on what type of employees you need it might also be more effective to reach out directly through networking events.
7. Acquire Necessary Technology Equipment & Supplies - In order to start your technology business, you'll need to purchase all of the necessary equipment and supplies to run a successful operation.
8. Market & Promote Your Business - Once you have all the necessary pieces in place, it’s time to start promoting and marketing your technology business. This includes creating a website, utilizing social media platforms like Facebook or Twitter, and having an effective Search Engine Optimization (SEO) strategy. You should also consider traditional marketing techniques such as radio or print advertising.
Learn more about how to start a successful Technology business: How to Start a Tech Company
ZenBusinessPlans
Home » Sample Business Plans » Technology
How to Write an IT Tech Startup Business Plan [Sample Template]
Are you about starting an IT tech startup? If YES, here is a detailed sample IT tech startup business plan template & feasibility report you can use for FREE . If you are a software developer or you have a background in the ICT industry and you are looking for An IT business to start, then you need to look far because there are loads of businesses in the industry and one of them is software as a service (or SaaS) company.
Software as a service (or SaaS) is an emerging paradigm business that enables software to be delivered as a service. This is an arrangement that enables companies to expand their network capacity, and run applications directly on a vendor’s network, offer a host of advantages with the most primary being radically lowering IT costs.
The lower budgetary requirements and commitments allow even smaller companies to piece together an IT project without spending on purchasing legacy server, and storage systems. However, due to the technical nature of this business, it would be wise to consult with a business consultant before starting off.
If your business concept is a great one, the business consultant would offer you tips and suggestions on the way forward. Below is a sample IT tech startup company business plan template that can help you successfully write your own with little or no stress.
A Sample IT Tech Startup Business Plan Template
1. industry overview.
An IT technology company (often tech company) is a type of business entity that focuses on the development and manufacturing of technology products, or providing technology as a service. “Technology”, in this context, has come to mean electronics-based technology. This can include businesses relating to digital electronics, software, and internet-related services, such as e-commerce.
For the purpose of this business plan, we will be looking at software development as a service. Software as a service (or SaaS) is part of the Business Analytics and Enterprise Software Publishing industry and players in this industry consist of companies that are into ERP software, bi software, crm software, scm software and other software development and they may decide to strictly adopt the Software as a services (SaaS) Business model.
A recent report published by IBISWorld shows that the Business Analytics and Enterprise Software Publishing industry has grown steadily due to favorable demand conditions caused by high corporate profit and investment. Over the five years to 2018, industry revenue rose at an annualized rate of 7.1 percent, driven by businesses’ increased technological complexity and the eagerness to adopt efficiency-enhancing software.
The report also shows that many industry products, such as customer relationship management and enterprise resource planning software systems, have become basic tools in the management of large companies. In 2018, industry revenue is expected to rise 2.6 percent to $55.4 billion. The world’s largest software companies have spent the past five years acquiring high-performing enterprise software vendors, cloud companies and data.
The report further states that over the past five years, the Business Analytics & Enterprise Software Publishing in the US industry has grown by 7.1 percent to reach revenue of $55bn in 2018. In the same timeframe, the number of businesses has grown by 10.0 percent and the number of employees has grown by 10.2 percent.
The Business Analytics and Enterprise Software Publishing industry is indeed a growing industry and is gaining ground in most countries of the world. Statistics has it that in the united states of America alone, there are about 2,869 registered and licensed business analytics and enterprise software publishing companies (Software as a services (SaaS) business model inclusive) responsible for employing about 139,347 people and the industry rakes $55 billion annually.
The industry is projected to grow at 7.1 percent annual growth within 2013 and 2018. The companies holding the largest market share in the Business Analytics & Enterprise Software Publishing in the US industry include SAP SE, International Business Machines Corporation, Salesforce.com Inc. and Oracle Corporation.
Some of the factors that encourage entrepreneurs to start their own Software as a service (SaaS) business could be the growing recognition of economic and operational benefits and the efficiency of this business model. As companies ease out gradually from the economic uncertainties and financial shackles, widespread adoption of Software as a service is in the offing.
The successful adoption of this technology concept will pave the way for mass enterprise adoption of Software as a service in the upcoming years. The transition of enterprises from virtual machines to the cloud will additionally extend the impetus required for strong growth of Software as a service (SaaS).
Poised to score the maximum gains will be end-to end cloud-computing solutions that offer complete functionalities ranging from integration of internal and external clouds, automation of business-critical tasks, and streamlining of business processes and workflow, among others.
Over and above, starting a software as a services (SaaS) company requires professionalism and good grasp of how the ICT industry works. Besides, you would need to get the required certifications and license and also meet the standard security expected for players in the industry in the United States.
2. Executive Summary
Joel Rogers® Technologies, Inc. is an IT tech startup that will specialize in offering software as a service (SaaS). The business will be based in Overland Park – Kansas and we were able to secure a well – positioned and standard office facility.
Joel Rogers® Technologies, Inc. is a client – focused and result driven IT tech startup company that is into ERP software, bi software, crm software, scm software and other software development. We will provide broad – based software development services at an affordable fee that won’t in any way put a hole in the pocket of our clients. We will offer standard and professional services to all to our clients.
At Joel Rogers® Technologies, Inc., our client’s best interest would always come first, and everything we do is guided by our values and professional ethics. We will ensure that we hire professionals who are experienced in the business analytics and enterprise software publishing industry in general.
Joel Rogers® Technologies, Inc. will at all times demonstrate her commitment to sustainability, both individually and as a firm, by actively participating in our communities and integrating sustainable business practices wherever possible. We will ensure that we hold ourselves accountable to the highest standards by meeting our client’s needs precisely and completely.
Our plan is to position the business to become the leading brand in software as a service (SaaS) business in the whole of Overland Park – Kansas, and also to be amongst the top 10 IT tech startup companies in the United States of America within the first 10 years of operation. This might look too tall a dream but we are optimistic that this will surely be realized.
Joel Rogers® Technologies, Inc. will be owned and managed by Joel Rogers. He has a Bachelor of Technology. He is a certified SOC 2 – Trust (SOC 2 is designed specifically for SaaS operations) and has over 10 years’ experience working in related industry as a senior software engineer prior to starting Joel Rogers® Technologies, Inc.
3. Our Products and Services
Joel Rogers® Technologies, Inc. is going to offer varieties of services within the scope of the business analytics and enterprise software publishing industry in the United States of America. We are well prepared to make profits from the industry and we will do all that is permitted by the law in the United States to achieve our business goals, aim and ambition.
Our business offerings are listed below;
- ERP software development
- BI software development
- CRM software development
- SCM software development
- Other software development
4. Our Mission and Vision Statement
- Our vision is to build an IT tech startup company that will be among the forerunners when it comes to offering software as a service (SaaS) in the world.
- Our mission is as an IT tech startup with bias in software as a services (SaaS) is to help a wide range of clients develop customized software that will help them simplify their businesses and operations.
Our Business Structure
Ordinarily we would have settled for two or three staff members, but as part of our plan to build a standard IT tech startup company in Overland Park – Kansas, we have perfected plans to get it right from the beginning which is why we are going to ensure that we have competent, honest and hardworking employees to occupy all the available positions in our firm.
The kind of IT tech startup company we intend building and the business goals we want to achieve is what informed the amount we are ready to pay for the best hands available in and around Overland Park – Kansas as long as they are willing and ready to work with us.
Below is the business structure that we will build Joel Rogers® Technologies, Inc. on;
- Chief Executive Officer
- Programmers and Software Developers
Admin and HR Manager
- Digital Marketers (Marketing and Sales Executive)
- Customer Care Executive / Front Desk Officer
5. Job Roles and Responsibilities
Chief Executive Office:
- Increases management’s effectiveness by recruiting, selecting, orienting, training, coaching, counseling, and disciplining managers; communicating values, strategies, and objectives; assigning accountabilities; planning, monitoring, and appraising job results
- Creating, communicating, and implementing the organization’s vision, mission, and overall direction – i.e. leading the development and implementation of the overall organization’s strategy.
- Responsible for fixing prices and signing business deals
- Responsible for providing direction for the business
- Responsible for signing checks and documents on behalf of the company
- Evaluates the success of the organization
Programmers and Software Developer
- Responsible for designing, installing, testing and maintenance of software systems for the organization
- Identifying areas for modification in existing programs and subsequently developing these modifications
- Writing and implementing efficient code
- Determining operational practicality
- Developing quality assurance procedures
- Training users
- Working closely with other developers, UX designers, business and systems analysts
- Presenting ideas for system improvements, including cost proposals
- Working closely with analysts, designers and staff
- Producing detailed specifications and writing the programme codes
- Maintaining and upgrading existing systems once they are up and running
- Responsible for overseeing the smooth running of HR and administrative tasks for the organization
- Regularly hold meetings with key stakeholders to review the effectiveness of HR Policies, Procedures and Processes
- Maintains office supplies by checking stocks; placing and expediting orders; evaluating new products.
- Ensures operation of equipment by completing preventive maintenance requirements; calling for repairs.
- Defining job positions for recruitment and managing interviewing process
- Carrying out induction for new team members
- Responsible for training, evaluation and assessment of employees
- Responsible for arranging travel, meetings and appointments
- Oversee the smooth running of the daily office activities.
Marketing and Sales Executive
- Identify, prioritize, and reach out to new partners, and business opportunities et al
- Identifies development opportunities; follows up on development leads and contacts
- Writing winning proposal documents, negotiate fees and rates in line with company policy
- Responsible for handling business research, marker surveys and feasibility studies for clients
- Responsible for supervising implementation, advocate for the customer’s needs, and communicate with clients
- Document all customer contact and information
- Represent the company in strategic meetings
- Help increase sales and growth for the company
- Responsible for preparing financial reports, budgets, and financial statements for the organization
- create reports from the information concerning the financial transactions as recorded
- Prepare the income statement and balance sheet using the trial balance and ledgers
- Provides managements with financial analyses, development budgets, and accounting reports
- Responsible for financial forecasting and risks analysis.
- Performs cash management, general ledger accounting, and financial reporting for one or more properties.
- Responsible for developing and managing financial systems and policies
- Responsible for administering payrolls
- Ensuring compliance with taxation legislation
- Handles all financial transactions for the company
- Serves as internal auditor for the company
Technical Help Desk Officer
- Provide technical assistance and support for incoming queries and issues related to our software
- Identifies problems and issues by performing relevant research using the appropriate tools and by following established procedures.
- Through interaction with clients on the phone, uses every opportunity to build client’s interest in the company’s services
- Consistently stays abreast of any new information on the company’s promotional campaigns etc. to ensure accurate and helpful information is supplied to clients
6. SWOT Analysis
Joel Rogers® Technologies, Inc. engaged the services of a professional in the area of business consulting and structuring to assist the firm in building a well – structured IT tech startup company that can favorably compete in the highly competitive business analytics and enterprise software publishing industry.
Part of what the business consultant did was to work with the management of our organization in conducting a SWOT analysis for Joel Rogers® Technologies, Inc. Here is a summary from the result of the SWOT analysis that was conducted on behalf of Joel Rogers® Technologies, Inc.;
We can boast of a competent technical team that has analytical and critical thinking skills that can help them find creative solutions for our clients. Aside from the synergy that exists in our carefully selected workforce, we have a very strong online presence and we are well positioned to attract loads of clients from the first day we open our doors for business.
One of the weaknesses that is obvious to us is the lack of capacity and inability to compete with big players in the industry especially as it relates to economy of scales.
- Opportunities:
The opportunities in the business analytics and enterprise software publishing industry is massive considering the fact that the world is going the way of technology, and software as a service (SaaS) is indispensable in the value chain of the info tech industry.
Some of the threats that we are likely going to face as an IT tech startup business operating in the United States are hosting issues, installation or upkeep troubles, piracy, unfavorable government policies , and global economic downturn which usually affects purchasing/spending power.
7. MARKET ANALYSIS
- Market Trends
The advancement we are enjoying in our world today can be attributed to the advancement of technology. Technology has indeed given leverage to all aspects of human endeavor. To start with, it is the advancement of technology that landed man in the moon.
It is the advancement of technology that made communication either via the telephone or computer easier and faster. It is the advancement of technology that made transportation faster and perhaps cheaper. It is the advancement of technology that made the manufacturing of goods faster and cheaper, etc.
The technology industry is so wide and vibrant and there is still room large enough for those who are interested in the industry to come in and create their own impact. One thing is certain, the world will always celebrate any inventor who is able to invent machines or devices that can ease the process of doing things.
8. Our Target Market
We are aware that the nature of our business is geared to words serving B2B clients, hence Joel Rogers® Technologies, Inc. will initially serve small to medium sized business, from new ventures to well established businesses and individual clients, but that does not in any way stop us from growing to compete with the leading IT tech startup companies that offer software as a services (SaaS) in the United States.
As a standard and licensed IT tech startup company that offers software as a service (SaaS), Joel Rogers® Technologies, Inc. will develop software apps for the following clients;
- Financial services providers
- Insurance companies
- Businesses in the health sector
- Supply chain businesses
- Other related businesses that may need software as a services (SaaS) technology
Our competitive advantage
The level of competition in the business analytics and enterprise software publishing industry does not in any way depend on the location of the business since most companies that offer software as a service (SaaS), can operate from any part of the world and still effectively compete in the industry.
We are quite aware that to be highly competitive in the business analytics and enterprise software publishing industry means that we should be able to develop software apps that will help simplify business and operation process for clients.
Joel Rogers® Technologies, Inc. might be a new entrant into the industry in the United States of America, but the management staff are considered gurus. They are highly qualified software programmers and developers in the United States. These are part of what will count as a competitive advantage for us.
Lastly, our employees will be well taken care of, and their welfare package will be among the best within our category in the industry meaning that they will be more than willing to build the business with us and help deliver our set goals and achieve all our aims and objectives.
9. SALES AND MARKETING STRATEGY
We are mindful of the fact that there is fast – growing competition amongst IT tech startup companies and other players in the business analytics and enterprise software publishing industry in the United States of America and around the globe; hence we have been able to hire some of the best business developer cum digital marketers to handle our sales and marketing.
Our sales and marketing team will be recruited base on their vast experience in the industry and they will be trained on a regular basis so as to be well equipped to meet their targets and the overall goal of the organization. We will also ensure that our excellent job deliveries speak for us in the market place; we want to build a standard IT tech startup company that offer software as a services (SaaS), that will leverage on word of mouth advertisement from satisfied clients.
Joel Rogers® Technologies, Inc. is set to make use of the following marketing and sales strategies to attract clients;
- Introduce our business by sending introductory letters alongside our brochure to all the companies, institutions and organizations within and outside the United States
- Promptness in bidding for software as a service (SaaS) contracts from companies, and organizations within and outside the United States
- Advertise our business in relevant programming magazines, radio and TV stations
- List our business on local directories/yellow pages
- Attend international software as a services (SaaS) developers related, seminars, and business fairs et al
- Create different packages for different category of clients in order to work with their budgets
- Leverage on the internet to promote our business
- Join related associations around us with the main aim of networking and marketing our services; we are likely going to get referrals from such networks.
Sources of Income
Joel Rogers® Technologies, Inc. is established with the aim of maximizing profits in the business analytics and enterprise software publishing industry and we are going to ensure that we do all it takes to attract clients on a regular basis.
Joel Rogers® Technologies, Inc. will generate income by offering the following services and products
10. Sales Forecast
We are well positioned to take on the available market in Overland Park – Kansas and in the cyberspace and we are quite optimistic that we will meet our set target of generating enough income / profits from the first six months of operation and grow the business and our clientele base beyond Overland Park to other cities in the United States of America and in the cyberspace.
We have been able to examine the business analytics and enterprise software publishing market, we have analyzed our chances in the industry and we have been able to come up with the following sales forecast. Below are the sales projections for Joel Rogers® Technologies, Inc., it is based on the location of our business and the services we will be offering;
- First Fiscal Year (FY1): $300,000
- Second Fiscal Year (FY2): $550,000
- Third Fiscal Year (FY3): $1.5 million
N.B : This projection was done based on what is obtainable in the industry and with the assumption that there won’t be any major economic meltdown and internet shutdown within the period stated above. Please note that the above projection might be lower and at the same time it might be higher.
11. Publicity and Advertising Strategy
We have been able to work with our brand and publicity consultants to help us map out publicity and advertising strategies that will help us walk our way into the heart of our target market. We are set to take the software as a services (SaaS) industry by storm which is why we have made provisions for effective publicity and advertisement of our IT tech startup company.
Below are the platforms we intend to leverage on to promote and advertise Joel Rogers® Technologies, Inc.;
- Place adverts on both print (community – based newspapers and magazines) and electronic media platforms
- Sponsor relevant community – based events/programs
- Leverage on the internet and social media platforms like; Instagram, Facebook, twitter, YouTube, Google + et al to promote our brand
- Install our billboards in strategic locations all around Overland Park
- Ensure that all our workers wear our branded shirts and all our vehicles are well branded with our company’s logo et al.
12. Our Pricing Strategy
At Joel Rogers® Technologies, Inc. we will keep our product and service fees a little bit below the average market rate by keeping our overhead low and by collecting payment in advance. In addition, we will also offer special discounted rates to startups, nonprofits, cooperatives, and small social enterprises who want to develop software apps for their business.
- Payment Options
The payment policy adopted by Joel Rogers® Technologies, Inc. is all inclusive because we are quite aware that different customers prefer different payment options as it suits them but at the same time, we will ensure that we abide by the financial rules and regulation of the United States of America.
Here are the payment options that Joel Rogers® Technologies, Inc. will make available to her clients;
- Payment via bank transfer
- Payment with cash
- Payment via online bank transfer
- Payment via mobile money
- Payment via Point of Sales Machines (POS Machines)
- Payment via check
In view of the above, we have chosen banking platforms that will enable our client make payment without any stress on their part.
13. Startup Expenditure (Budget)
These are the areas we are looking towards spending our startup capital on;
- The total fee for incorporating the Business in the United States of America – $750.
- Legal expenses for obtaining licenses and permits as well as the accounting services P.O.S machines – $3,300.
- The total cost for payment of insurance policy covers (general liability, workers’ compensation and property casualty) coverage at a total premium – $9,400.
- The amount needed to acquire a suitable Office facility in a business district for 6 months (Re – Construction of the facility inclusive) – $40,000.
- Marketing expenses for the grand opening of Joel Rogers® Technologies, Inc. in the amount of $3,500 and as well as flyer printing (2,000 flyers at $0.04 per copy) for the total amount of $3,580.
- The total cost for hiring Business Consultant – $2,500
- The cost for equipping the office (computers, software apps and hardware such as Application-specific integrated circuit (ASIC) machines, internet server, printers, fax machines, furniture, telephones, filing cabins, safety gadgets and electronics et al) – $25,000
- The cost of launching our official website – $800
- Budget for paying at least two employees for 3 months and utility bills – $75,000
- Additional expenditure (Business cards, Signage, Adverts and Promotions et al) – $2,500
- Miscellaneous – $10,000
Going by the report from the research and feasibility studies, we will need about Two Hundred and Fifty Thousand US Dollars ($250,000) to set up a small scale but standard IT tech startup company in the United States of America.
Generating Funds/Startup Capital for Joel Rogers® Technologies, Inc.
Joel Rogers® Technologies, Inc. is owned and managed by Joel Rogers. He may likely welcome partners later which is why he has decided to restrict the sourcing of the startup capital for the business to just three major sources.
- Generate part of the startup capital from personal savings
- Source for soft loans from family members and friends
- Apply for loan from the bank
N.B: We have been able to generate about $50,000 (Personal savings $40,000 and soft loan from family members $10,000) and we are at the final stages of obtaining a loan facility of $200,000 from our bank. All the papers and documents have been duly signed and submitted, the loan has been approved and any moment from now our account will be credited.
14. Sustainability and Expansion Strategy
The future of a business lies in the number of loyal customers that they have, the capacity and competence of their employees, their investment strategy and the business structure. If all of these factors are missing from a business (company), then it won’t be too long before the business closes shop.
One of our major goals of starting Joel Rogers® Technologies, Inc. is to build a business that will survive off its own cash flow without injecting finance from external sources once the business is officially running. We know that one of the ways of gaining approval and winning customers over is to offer our software as a services (SaaS) a little bit cheaper than what is obtainable in the market and we are prepared to survive on lower profit margin for a while.
Joel Rogers® Technologies, Inc. will make sure that the right foundation, structures and processes are put in place to ensure that our staff welfare are well taken of. Our company’s corporate culture is designed to drive our business to greater heights and training and retraining of our workforce is at the top burner of our business strategy.
As a matter of fact, profit-sharing arrangement will be made available to all our management staff and it will be based on their performance for a period of three years or more as determined by the board of the organization. We know that if that is put in place, we will be able to successfully hire and retain the best hands we can get in the industry; they will be more committed to help us build the business of our dreams.
Check List/Milestone
- Business Name Availability Check : Completed
- Business Incorporation: Completed
- Opening of Corporate Bank Accounts: Completed
- Opening Online Payment Platforms: Completed
- Application and Obtaining Tax Payer’s ID: In Progress
- Application for business license and permit: Completed
- Purchase of Insurance for the Business: Completed
- Conducting Feasibility Studies: Completed
- Leasing a standard and well positioned office facility in the heart of Overland Park – Kansas: Completed
- Generating part of the start up capital from the founder: Completed
- Applications for Loan from our Bankers: In Progress
- Writing of Business Plan: Completed
- Drafting of Employee’s Handbook: Completed
- Drafting of Contract Documents: In Progress
- Design of The Company’s Logo: Completed
- Printing of Promotional Materials: Completed
- Recruitment of employees: In Progress
- Purchase of the needed software applications, internet server, furniture, office equipment, electronic appliances and facility facelift: In progress
- Creating Official Website for the Company: In Progress
- Creating Awareness for the business (Business PR): In Progress
- Health and Safety and Fire Safety Arrangement: In Progress
- Establishing business relationship with vendors and key players in the industry: In Progress.
More on Technology
- Paragraph Generator
- Cover Letter
- Authorization Letter
- Application Letter
- Letter of Intent
- Letter of Recommendation
- Business Plan
- Incident Report
- Reference Letter
- Minutes of Meeting
- Letter of Resignation
- Excuse Letter
- Research Proposal
- Job Application
- Acknowledgement
- Employment Letter
- Promissory Note
- Business Proposal
- Statement of Purpose
- Offer Letter
- Deed of Sale
- Letter of Interest
- Power of Attorney
- Solicitation Letter
25+ Sample IT Business Plan in PDF | Google Docs | MS Word | Apple Pages
It business plan | google docs | ms word | apple pages, 25+ sample it business plan, understanding the business context, market analysis, designing the it infrastructure, project management, human resources and team formation, budgeting and financial projections, risk management, operational strategy, marketing and outreach, legal and compliance aspects, sustainability in it, evaluating success metrics, feedback mechanism, why is an it business plan important, how often should i update my it business plan, how do i assess market trends for my it business plan, can i use an it business plan for investor pitches, is an exit strategy necessary for my it business plan.

IT Business Marketing Plan

IT Support Business Plan

IT Startup Business Plan

IT Consulting Business Plan

IT Security Business Plan

IT Business Market Plan

IT Business Strategic Plan
IT Business Proposal Plan

IT Business Project Plan

Simple IT Business Plan
IT Business Plan Outline

Sample IT Business Plan

IT Business Summary Plan

IT Business Plan Layout

Printable IT Business Plan
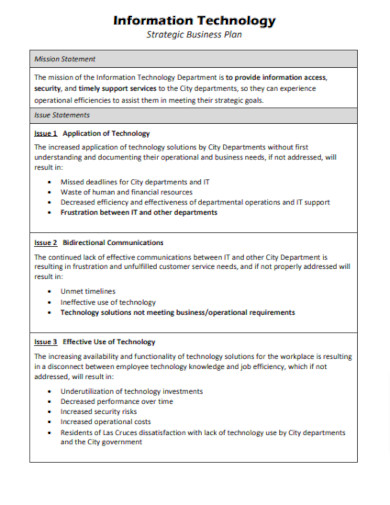
IT Business Plan Format

IT Business Budget Plan

IT Business Financial Plan
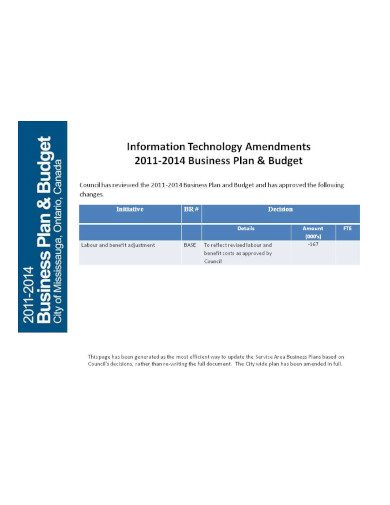
IT Business Approved Plan
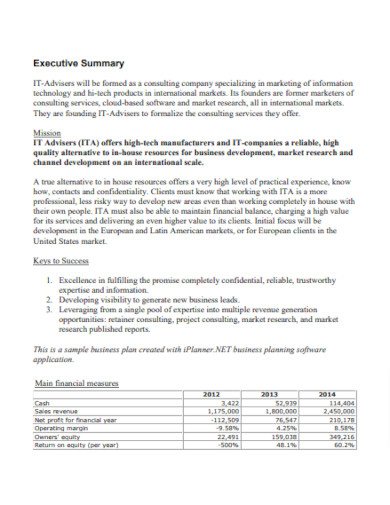
IT Business Executive Plan

IT Business Plan Presentation

Professional IT Business Plan

IT Business Final Plan

IT Business Strategic Implementation Plan

IT Business Department Plan

IT Business Plan in PDF
- Importance of a Clear Vision: A cohesive vision is the rudder that steers the organizational ship, ensuring alignment and purpose in all endeavors.
- Defining Objectives and Scope: Tangible, measurable objectives serve as milestones, ensuring that businesses stay on track and make effective use of resources.
- Assessing Current IT Trends: Staying abreast of evolving trends ensures that businesses remain relevant and proactive in addressing market needs.
- Identifying Market Gaps: Pinpointing unmet needs and market inefficiencies can unveil lucrative opportunities.
- Competitor Analysis: Understanding competitors’ strengths and weaknesses helps in carving out a distinctive market position.
- Hardware and Software Considerations: Infrastructure underpins IT operations report . Choosing the right tools and platforms is pivotal for efficiency and scalability.
- Cloud versus On-Premises Decision-making: Both modalities have their merits. The decision hinges on factors like cost, control, and business size.
- Selecting the Right Methodologies: Whether it’s Agile, Waterfall, or Scrum, the chosen methodology should resonate with the team’s workflow and the project’s complexity.
- Importance of Regular Monitoring: Periodic checks ensure that projects remain on track, preempting potential derailments
- Identifying Key Roles: A clear delineation of roles ensures seamless operations and accountability.
- Skillsets and Training: Continual upskilling keeps the team adept and attuned to the latest industry standards.
- Cost Estimation Techniques: Accurate budgeting preempts financial pitfalls, ensuring the business’s sustainability and profitability.
- Return on Investment (ROI) Analysis: This metric gauges the efficacy of investments, guiding decisions and ensuring that funds yield optimal returns.
- Identifying Potential Threats: Foreseeing challenges allows businesses to preemptively devise countermeasures.
- Mitigation Strategies: From cybersecurity threats to market fluctuations, having a mitigation strategy in place ensures business continuity.
- Day-to-Day Management: Efficient daily operations are the linchpin of a successful IT business.
- Maintenance and Upgrades: Regular system checks and updates ensure optimal performance and security.
- Building Brand Identity in IT: A robust brand identity differentiates businesses in a crowded market.
- Strategies for Customer Acquisition: Effective marketing strategies attract potential clients and foster long-term relationships.
- Navigating IT Regulations: Adherence to legal mandates ensures that businesses remain compliant and sidestep potential legal quagmires.
- Data Privacy Considerations: With data breaches becoming prevalent, safeguarding client information is paramount.
- Environmental Concerns: Green IT practices not only benefit the environment but also enhance a firm’s image.
- Long-Term Viability: Sustainable practices ensure that businesses remain viable and resilient in the long run.
- Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): These quantifiable metrics offer insights into a business’s performance, illuminating areas of improvement.
- Periodic Review and Revisions: Regular audits ensure that the business plan remains relevant and effective.
- Customer Feedback: Constructive feedback is invaluable in refining offerings and enhancing customer satisfaction.
- Continuous Improvement: A commitment to perpetual betterment ensures business evolution and growth.
Share This Post on Your Network
You may also like these articles, school business plan.

A school business plan is a comprehensive document outlining the objectives, strategies, and operational framework for establishing or managing a school. It details the vision, target audience, financial projections,…
Boutique Business Plan

A boutique business plan is a comprehensive roadmap tailored to the unique needs of boutique owners. It outlines the business's goals, market strategies, and financial projections while capturing the…
browse by categories
- Questionnaire
- Description
- Reconciliation
- Certificate
- Spreadsheet
Information
- privacy policy
- Terms & Conditions

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
2.2 Start-up Summary. Our start-up costs will be $1M, which includes $450,000 for the acquisition of the Maui and Hilo operations of Servco Integrated Office Technology. The remainder of the funds will be used for: Initial Inventory: $200,000. Initial Capitalization: $225,000.
1. Don't worry about finding an exact match. We have over 550 sample business plan templates. So, make sure the plan is a close match, but don't get hung up on the details. Your business is unique and will differ from any example or template you come across. So, use this example as a starting point and customize it to your needs.
Marketing Plan. Traditionally, a marketing plan includes the four P’s: Product, Price, Place, and Promotion. For an IT business plan, your marketing strategy should include the following: Product: In the product section, you should reiterate the type of IT company that you documented in your company overview.
Specifically, these funds will be used as follows: Office design/build: $50,000. Software development: $150,000. Three months of overhead expenses (payroll, rent, utilities): $150,000. Marketing costs: $25,000. Working capital: $25,000. Easily complete your Technology business plan! Download the technology business plan template (including a ...
A Sample IT Tech Startup Business Plan Template. 1. Industry Overview. An IT technology company (often tech company) is a type of business entity that focuses on the development and manufacturing of technology products, or providing technology as a service. “Technology”, in this context, has come to mean electronics-based technology.
An IT business plan provides a roadmap for the company’s future, ensuring that all efforts align with the firm’s overarching goals. It aids in securing funding, navigating challenges, identifying opportunities, and serving as a benchmark to measure progress and success.