Home Blog Education How to Present a Lesson Plan

How to Present a Lesson Plan

First days are always exciting, and expectation builds up about the contents of the task ahead, especially if you’re starting a class as a student or professor. This interaction will be significant because it will establish and define the subjects to be covered and the set of expectations flowing from the instructor towards the audience.
Perhaps you are ready to begin your career as a teacher and need some guidance; otherwise, you are a seasoned instructor searching for a refresher in your program. No matter which of the above you represent, the truth of the matter is that you are probably seeking a better way to introduce the subjects you’ll be teaching to your students.
What is a lesson plan?
A lesson plan will be the set of subject matter materials you will be teaching during a specific timeframe. The lesson plan should be an index that students can constantly consult to understand better the parts of the learning journey they will go through during each session.
Teachers and professors should have a lesson plan template that happens in every session. This is different from a syllabus because, in the latter case, the whole curriculum of the program will be laid out; however, for each lesson, there should be one individual lesson plan example to guide the instructor in the set timeframe.
When building the materials for the class or lesson’s attention, it’s always essential to share elements like the purpose or rules that guide the learning process . This article will explore the best way to present a lesson plan and drive a learning session successfully from the instructor or professor’s view.
How to write a lesson plan
Education nowadays guides different sorts of students and target specific learning needs. Therefore, it’s important and relevant to understand how lesson plans can change and be varied to truly implement the best learning path for your students. Once you have this part figured out, the next step is to understand how you will transmit the information and use a PowerPoint Presentation to simplify creating and presenting a lesson plan to your students.
Lesson plans will comprise several different sections that will clarify the first questions students can have: How long will the course be? Will it be an online course ? What will be the main objectives? Which subjects will be discussed along with the class?
1. Introduction
As the lesson begins, it’s essential to place a brief yet descriptive introduction about what the session will cover. A good practice is to create a catchy title for each lesson to have an overall understanding of the information they will be receiving.
Example: Digital Marketing Basics: Industry background, historical review years 1980-2010. In this session, we will cover the birth of digital marketing, including all the touchpoints that shaped today’s industry.
2. Audience
If your class is a one-time-only or recurring session, or even a blended learning journey, it’s essential to explain to your students who this class is for; this will allow them to calibrate their expectations about the matter to be taught ahead.
Example: This lesson is directed to professionals who work in traditional marketing, business owners, or communication specialists seeking to have a profound understanding of how digital marketing came to be.
3. Lesson Objectives
This piece is critical because it will allow the students to assess the intention of each lesson. When thinking about the objectives, it’s vital to consider the acquired skills we expect our students to have at the end of the class. Like any other goals in life or business, each one should be actionable and measurable, meaning after each class, students should be able to use what they have learned and put into action the concepts.
Example : Understand and be able to create a timeline framework of reference to explain the story of the Internet.
4. Materials
Suppose the lesson requires using any specific materials, physical or not, including any software or hardware necessary. In that case, it´s important to list or include within the lesson plan so students can set clear expectations on what they might require. This is particularly important if the session you will be delivering requires them beforehand to bring anything.
Example :
- Computer
- Scratch paper
5. Learning Activities
We´ve covered all the logistics by this point; however, now we need to start sharing the actual activities during the lesson. Ideally, this is a play-by-play of how each activity will guide the lesson towards the already established objectives. To add the list of learning activities that will be helpful for your students, take into account how all of them align with each goal and the requirements students need.
Make sure that you add variety to the activities that you are proposing, go ahead and research trends of how many other teachers or professors, students will appreciate your search to engage them in learning.
Also, consider how much time they will take so that you can note it in the next section.
- Create a timeline on the wall with the most important moments of digital marketing history, including creation of social media, mainstream of email, etc.
Time periods
Pairing each learning activity with a specific timeframe will be useful both for instructors and students. Make sure you calculate a reasonable amount of time for each activity and list it within the lesson plan so everyone can set correct expectations. Assigning time slots for each exercise will also help students and teachers stay on track with the lesson and not waste valuable time invested in learning.
Example : Creation of a timeline – 45 min

How to present a lesson plan
We have now listed the components of the lesson plan structure, everything looks beautiful in the draft, but now we need to start planning how we will present the program to the students. This part is challenging because you have to choose a template that makes sense for you and will be helpful for your students to understand.
A PowerPoint presentation is a great way to showcase all the contents of the lesson plan, however, the trick is to decide how you want to structure it.
Lesson Plan Design
By this point, you’ve structured a lesson plan template that can go through any test. Nevertheless, creating the materials to accompany it can be a key in the commitment generates between the students and the professor.
Design and Style
Before adding any text to your presentation template , think about the requirements you have: Does the academic institution where you work require the use of logos? Do you have to follow any visual guidelines? This might be important for the cohesiveness of your presentation.
It’s essential to think about how you would like to present the lesson plan. You may want to keep it simple and have a 1 pager and talk through it to understand your students fully, or perhaps you need to create one full presentation where every slide will be a relevant piece of information. Let’s explore this a bit further.
One Pager Lesson Plan
If your style is more towards simplicity, this is a great solution: succinct, minimalistic, and straight to the point. You can complete a one-page lesson plan with bullets of the relevant data and send it out to students. A great advantage of this format is that you can either send it as a PDF or even as a single image (JPG or PNG), exporting it directly from PowerPoint.
One significant advantage is that your students will only have to check for one source by choosing this simple format when revising the lesson during the class or afterward.
Several pages lesson plan
Almost like a syllabus, a more extended presentation will include several slides so you can include the information in different formats.
For example, you can use the first slide to include the lesson title; afterward, a new slide can define the purpose or introduction of the lesson. In the upcoming slides, you can include materials, contents, and even ad charts or similar to explain how grades will be affected by each lesson’s assignments on the upcoming slides.
Text in the presentation
It’s always good to follow the reliable practices of presentations and include the necessary information without overwhelming students. Don’t add an excessive amount of text to one slide; actually, make sure that every piece of data is helpful for students to plan their time both during and after class.
However, if you will be sending out the presentation to your students before reviewing it, consider that they will be using it for their reference to follow through with your lesson. So make sure all the information is easy to read and accessible.
Additional elements
Learners of all sorts have become increasingly visual, so don’t be afraid to add infographics, images, photographs, icons or any other elements to make your lesson plan presentation more appealing visually.

Final Words
Remember the lesson plan presentation will be the first approach your students will have with the subject matter. Take your time, enjoy the process, and create comprehensive and attractive lesson plan slides that will inspire your students to have thoughtful and deep learning.
1. 1-Slide Lesson Plan PowerPoint Template

Create a simple and minimalist one-pager lesson plan for your academic uses, course planning, and even as student handouts, with this eye-catching PowerPoint template.
Use This Template
Like this article? Please share
Learning Experience, Learning Styles, Presentation Approaches, Presentation Tips, Presentations Filed under Education
Related Articles

Filed under Design • August 14th, 2024
Creating Custom Themes for PowerPoint and Google Slides
Do you want your slides to go beyond the average result from a template? If so, learn how to create custom themes for presentations with this guide.

Filed under Google Slides Tutorials • August 6th, 2024
How to Use Google Slides Strikethrough Text
Customize your presentation slides by using Google Slides strikethrough and add a factor of humor, emphasize, or track changes in a truly visual method.

Filed under Business • July 24th, 2024
How to Create a Demo Presentation
Discover the secrets behind successful demo presentations and what they should contain with this article. Recommended PPT templates included.
Leave a Reply
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Happiness Hub Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- Happiness Hub
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- Creating Lesson Plans
How to Build a Lesson Plan: Templates, Requirements, and More
Last Updated: April 7, 2024 Fact Checked
Sample Lesson Plans
Constructing a lesson plan, adjusting your lesson plans efficiently, presenting the lesson, expert q&a.
This article was co-authored by César de León, M.Ed. and by wikiHow staff writer, Eric McClure . César de León is an Educational Leadership Consultant and currently serves as an Assistant Principal for the Austin Independent School District in Austin, TX. César specializes in education program development, curriculum improvement, student mentorship, social justice, equity leadership, and family and community engagement. He is passionate about eradicating inequities in schools for all children, especially those who have been historically underserved and marginalized. César holds a Bachelor’s degree in Education and Biology from Texas State University and a Master’s degree in Educational Leadership from The University of Texas at Austin. There are 20 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 3,838,218 times.
As a teacher, developing a thoughtful lesson plan is an essential part of your job. Not only do your lesson plans lay out everything you’ll do in a given class, but they can be shared with subs to complete your lessons when you’re out sick, and administrators can use them to provide feedback and monitor your classroom. While writing a lesson plan may seem like a daunting task at first, take it from a former teacher that they’ll soon become second nature. In this article, we’ll walk you through what you need to include in each lesson plan, show you how to use your lesson plan to make you a better teacher, and walk you through what a class might look like based on your plans.
Things You Should Know
- A lesson plan outlines what you’ll teach in a given lesson and provides justification for why you’re teaching it.
- Every lesson plan needs an objective, relevant standards, a timeline of activities, an overview of the class, assessments, and required instructional materials.
- Overplan in case your lesson ends early and tailor your plans to suit the needs of your students.

- An example of a good objective might be, "Students will be able to analyze nonfiction texts by performing a close reading on a historical document."
- Most teachers will use Bloom’s taxonomy when choosing their objective verb.
- Teachers often abbreviate “Students will be able to” with “SWBAT” on their lesson plans.
- Many teachers start with the objective then work their way out from there, choosing class activities last. This is called “backmapping” and it’s the most widely accepted lesson organization style around today. [2] X Research source

- Our previous objective aligns nicely with the CCSS R.L.8.2, which reads “Determine a theme or central idea of a text and analyze in detail its development over the course of the text…”
- A handful of states, including Florida, Virginia, and Texas, refuse to adopt common core. They have their own state standards.
- If you’re still in school to become a teacher, you may not have specific standards you need to cover just yet.
- Many schools will allow teachers to cover the objectives in whatever order they’d like so far as they cover all of them. Some schools will map out the standards to cover in their curriculum, though.

- For example, if your class is about Shakespeare's Hamlet , your overview might be “Introduction to Hamlet . Historical context, biographical info, and preliminary information. We’ll cover the folio, character list, and assign reading roles. Start Act 1 if time allows.”
- A single overview may get you through multiple classes, so you may find yourself copy and pasting the same overview into multiple plans. That’s totally okay!

- 1:00-1:10: Warm up . Bring class into focus and recap yesterday's discussion on great tragedies; relate it to Hamlet .
- 1:10-1:25: Present information. Discuss Shakespearean history briefly, focusing on his creative period 2 years before and after Hamlet.
- 1:25-1:40: Guided practice . Class discussion regarding major themes in the play.
- 1:40-1:55: Freer practice. Class writes single paragraph describing current event in Shakespearean terms. Individually encourage bright students to write 2 paragraphs, and coach slower students.
- 1:55-2:00: Conclusion. Collect papers, assign homework, dismiss class.

- Formative assessments are instructional tools. They’re anything you use to check if students are learning so you can adjust your lessons. Examples include: class discussions, teacher questions, pop quizzes, group work, surveys, and self-reflections.
- Summative assessments are how you prove a student learned something. They occur at the end of lesson arcs, units, or sections. Examples include: tests, quizzes, essays, presentations, and final projects.
- All summative assessments (outside of tests and quizzes) have rubrics, which are the set of standards you’re judging students on. You do not need to include your rubrics in the lesson plan, but you should be making rubrics.

- You might list textbooks, worksheets, novels, calculators, or whiteboards. If you need to borrow a TV or need a link to a specific YouTube video, include that, too.
- Skip the basic school supplies every student needs. You don’t need to mention pens, pencils, etc.
- Need a worksheet or special materials for a class but don’t want to spend super long making them from scratch? Check out Teachers Pay Teachers . Seasoned educators sell their instructional material to other teachers for cheap!

- Over time, you’ll need to do this less and less. Eventually, you'll be able to go in with practically nothing at all!

- If you find yourself constantly running over your schedule, know what you can and cannot scratch. What must you cover in order for the children to learn most? What is just fluff and time killers?

- Odds are you'll be working with a pile of extroverts and introverts. Some students will benefit more from working alone while others will thrive in pair work or in groups. Knowing this will help you format activities to different interaction preferences. [11] X Research source
- You'll also wind up having a few students that know just about as much as you do on the topic and some that, while smart, look at you like you're from another planet. If you know who these kids are, you can plan accordingly.
Joseph Meyer
Effective teaching strategies consider a student's individual strengths. Tailoring instruction to a student's existing skills and encouraging collaborative activities can improve a student's outcome. Recognizing diverse learning styles allows for a stronger approach, fostering potential in all learners.

- Really, any activity can be manipulated to be done separately, in pairs, or in groups. If you have ideas already mapped out, see if you can revamp them at all to mix it up.

- Every student learns differently. Some need to see the info, some need to hear it, and others need to literally get their hands on it. If you've spent a great while talking, stop and let them talk about it.
- You will likely have some students with IEPs, or Instructional Educational Plans. These are legal documents for students with special needs that require specific instructional adjustments.

- The easiest thing to do is to come up with a quick concluding game or discussion. Throw the students together and have them discuss their opinions or ask questions.

- Avoid using shorthand or acronyms that only you’ll be able to understand.
Eric McClure
"It helps if your backup lesson plans are very easy to find and clearly labeled as substitute plans. If there are any handouts, print those out ahead of time as well. This is the kind of thing that’s easy to overlook early in the year, but trust me—you’ll need a day off at some point and when you do, you won’t want to come in just to drop off lesson plans."

- The warm up can be a simple game (possibly about vocab on the topic to see where their current knowledge lies (or what they remember from last week!). Or, it can be questions, a mingle, or pictures used to start a conversation. Whatever it is, get them talking and thinking about the topic.

- Go over the objective at the beginning of class! Always let your students know why they’re doing what they’re doing.

- This is often explained by teachers as “I do, we do, you do.” In other words, you show them how to do it. Then, the whole class does it together. Finally, the students do it on their own.
- If you have time for two activities, all the better. It's a good idea to test their knowledge on two different levels -- for example, writing and speaking (two very different skills). Try to incorporate different activities for students that have different aptitudes.

- If you've been teaching the same group for a while, odds are you know the students who might struggle with certain concepts. If that's the case, pair them with stronger students to keep the class going.
- You don't want certain students left behind, but you also don't want the class held up, waiting for everyone to get on the same level.

- It all depends on the subject at hand and the skills you want to use. It can be anything from a 20-minute puppet making project to a two-week long dalliance with the oversoul in a heated debate on transcendentalism.

- If you have a group full of kids that can't be paid to raise their hands, turn them amongst themselves. Give them an aspect of the topic to discuss and 5 minutes to converse about it. Then bring the focus to the front of the class and lead a group discussion. Interesting points are bound to pop up!

- Assign and hand out any homework at the end of the class.

- Don’t worry if lesson planning feels really unfulfilling and pointless to you. A lot of new teachers think they feel like busy work at first—especially when classes don’t go as planned. Luckily, once you finish one year of teaching, you’ll have a full year’s worth of lessons to use! [24] X Research source Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0
- Lesson plans typically cover a single class period, although a more complex lesson may require 2-3 days to get through. A single lesson plan may also bleed over into multiple classes if there’s a fire alarm, some behavioral issue that requires attention, or you have to modify your schedule due to a school-wide event. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 1

You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://www.nea.org/professional-excellence/student-engagement/tools-tips/5-tips-improve-your-lesson-plan
- ↑ https://www.calstate.edu/csu-system/why-the-csu-matters/graduation-initiative-2025/co-requisite-mathematics-summit/Handouts/Backmapping_example_and_template.pdf
- ↑ https://drexel.edu/soe/resources/student-teaching/advice/how-to-write-a-lesson-plan/
- ↑ https://iris.peabody.vanderbilt.edu/module/cnm/cresource/q4/p16/
- ↑ https://poorvucenter.yale.edu/Formative-Summative-Assessments
- ↑ https://jan.ucc.nau.edu/~slm/AdjCI/Lessonplan/Elements.html
- ↑ https://awildsurmise.medium.com/improving-teaching-scripting-5950e1d15f54
- ↑ https://assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/511257/Eliminating-unnecessary-workload-around-planning-and-teaching-resources.pdf
- ↑ César de León, M.Ed.. Educational Leadership Consultant. Expert Interview. 11 November 2020.
- ↑ https://onlineprograms.ollusa.edu/ma-in-counseling/resources/learning-styles-of-introverts-and-extroverts
- ↑ http://www.auburn.edu/~nunnath/engl6240/seating.html
- ↑ https://teach.com/what/teachers-know/learning-styles/
- ↑ https://www.ascd.org/el/articles/pacing-lessons-for-optimal-learning
- ↑ https://www.chalk.com/introduction-to-lesson-planning/why-lesson-plan/
- ↑ https://www.edutopia.org/blog/having-an-off-day-josh-stock
- ↑ https://poorvucenter.yale.edu/teaching/teaching-how/chapter-2-teaching-successful-section/running-class
- ↑ https://readingrecovery.clemson.edu/home-2/reading-comprehension/lesson-structure/guided-practice/
- ↑ https://www.teachingenglish.org.uk/professional-development/teachers/knowing-subject/d-h/free-practice
- ↑ https://teaching.cornell.edu/teaching-resources/engaging-students/using-effective-questions
- ↑ https://www.tefl.net/elt/ideas/younglearners/finishing-preschool-english-lessons/
About This Article

If you need to make a lesson plan, start by creating a timeline based on the length of the class or the school day. As you get to know your class throughout the year, try to tailor your lesson plan to their strengths. For instance, some groups might learn better by taking notes during a lecture, while others might benefit more from group discussions or worksheets. Try to include several different activities during each class period so the kids don’t get bored, and also to appeal to the different learning styles in the classroom. Read on for sample lesson plans and more tips on how to budget your time! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Jabulani Simelane
Feb 19, 2020
Did this article help you?

Charletha Porter
Feb 16, 2020
Xolani Lingela
May 8, 2017
Deborah Amaral
Jan 1, 2020
Dawood Bhaila
Jun 11, 2019

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Don’t miss out! Sign up for
wikiHow’s newsletter
How to Create an Effective Lesson Plan Presentation
Regardless of the subject or content you’re teaching, having a lesson plan in place prepares you for class by offering detailed guidelines for the session. The lesson plan doesn’t have to be lengthy or complex—it just needs to include elements about what you’re teaching, the method of presenting this material, and what objective and goals you wish your students to achieve as part of the curriculum.
Why Lesson Plans Are Important
It’s crucial for teachers to prepare their lessons in advance and implement the best teaching approaches. Attending a session without a lesson plan can be counterproductive for both students and teachers. Without the right preparation beforehand, classes can end up being unproductive or confusing.
Below are a few reasons why you should consider lesson planning:
Lesson Planning is Handy for Classroom Management
Developing the lesson plan from the learning objectives provides flexibility in adapting to different teaching methods and classroom management techniques. For instance, hybrid or online classes require a different delivery approach from the traditional classes, which means making modifications to any existing plans. With the right foresight and plan in place, classes can stay on topic and effective. Such circumstances underscore how crucial lesson plans are in ensuring that the class runs smoothly, regardless of the learning environment.
Lesson Planning Creates Student Success
Various studies have shown that students benefit immensely from and appreciate well-structured lessons. Thus, success is more likely when students engage and show interest in the material being taught. Using a curriculum guide, teachers can develop valuable lesson plans based on specific objectives and goals (what’s intended for students to learn).
Lesson Planning Is Central to Teacher Success
Teachers’ success is, to some extent, pegged on students’ success. Besides that, the documents you develop as part of the lesson planning process are often part of your assessment by school administrators. What’s more, as you advance your teaching career, your lesson plans serve as a repository for your expanding body of knowledge. Thus, the significance of lesson planning cannot be overlooked when it comes to advancing your career as an educator.
Lesson Planning is Vital in Student Assessment
Lastly, lesson plans turn the learning sessions into clear objectives for students and a way to gauge their understanding of the subject matter. One notable benefit of the lesson plan is tailoring the assessment to a particular objective while considering students’ specific needs. You can use common assessment methods such as quizzes, tests, and homework assignments.
How to Write a Lesson Plan
Lesson plans include different sections that clarify questions students might have about the subject on hand. What are the lesson objectives? What subjects will be covered during the session? How long will the course take?
- Introduction – As the lesson commences, it’s good to have a concise yet vivid introduction about what the lesson will cover. The ideal practice is to create a memorable title for every lesson to create a general understanding of the learning material students will be interacting with.
- **Lesson Objectives –**This section is critical as it allows the students to ascertain each lesson. When it comes to objectives, it is crucial to consider the acquired skills you expect the students to gain by the end of the session. Each objective should be measurable and actionable; meaning after every session, students should be able to apply what they’ve learned.
- Learning Activities – This should be a detailed account of how each activity will lead the class to achieve its predetermined goals. To create valuable activities, consider how each learning activity fits each objective, and the requirements students need.
- Practice – Practices are primarily intended to assess students’ comprehension of the material and aid in memorizing what they have learned in class. Therefore, it is crucial to include this in the lesson plan so that assessments can always be done at the appropriate time.
Today, lesson planning has been made less time-consuming and easier, thanks to smart whiteboards for the classroom . A digital whiteboard like the Vibe Board Pro provides unmatched performance that shows you know your craft and are way ahead of the pack.
Download Our New E-book
The Future of Learning
Download Our New E-book The Future of Learning
Read our privacy policy .
We’ve sent you an email with the PDF download link. Enjoy!
Can't wait? Read now
How Smart Whiteboards Simplify Lesson Plan Creation and Presentation
Not only does using a smart whiteboard make learning accessible , it’s also a great way of enhancing and enriching your lesson plans with interactive activities for the class. Smart whiteboards function as a touch screen for all; during class sessions, you and your students can use it as a digital whiteboard to create a space where students’ engagement, knowledge, and teamwork are appreciated.
While the smart whiteboard aids in making your lesson more engaging, interactive, and educational, you as the teacher can still customize your teachings to what you want them to be. This helps in foiling any hitches in your lesson presentation and makes switching from one topic to another seamless.
Below are more specific ways how smart whiteboards make your lesson plan presentation better:
Take Advantage of Built-in Templates
Once you invest in a smart whiteboard, make sure to take advantage of the wide variety of built-in lesson planning templates. You can use these templates to improve lesson plans while leveraging the technology associated with smart whiteboards. Even better, these templates can be easily customized for every lesson plan and cover different subject matters, allowing you to create new lesson plans without always starting from scratch quickly. How cool is that?
Organize and Present Lesson Plans Better
Smart whiteboards combine the power of the traditional whiteboard and a TV/projector into one hub, allowing you to write on the board while concurrently projecting it to the classroom. This allows you to conduct lesson plan presentations on a larger scale while also letting students see what’s going on.
For instance, if you’re presenting on an extensive topic involving multiple subtopics, a smart whiteboard will help you walk students through each subtopic with ease. Begin with the presentation divided into primary or main sections, highlight key definitions, and add infographics and videos to ensure that every student understands the tiniest detail.
Additionally, you can get students involved in the lesson plan presentation by asking questions, polling them on key points, or allowing them to follow along on their tablets or laptops.
Record Lesson Plan Presentations
Another benefit of using smart whiteboards in the classroom is that a lesson plan presentation can be recorded and accessed long after the session is over. This allows your students to access the material on their own time.
Final Words: Creating a Lesson Plan Presentation
Lesson plan presentation offers students the first interaction with the material they will learn. Take your time, appreciate the process, and create an attractive and comprehensive lesson plan that will encourage your students to have deep and thoughtful learning experiences. Even better, all of this can be made easier with smart whiteboard technology. Leave the spiral notebooks and sticky notes at home. A smart whiteboard is all you need.
What is the presentation stage in lesson planning?
Presentation is usually the core of the lesson plan. During this stage, theteacher introduces the topic and the key subject matter the students need to master. Presenting with smart whiteboards is exceedingly easy and less time-consuming.
What are the 5 steps in lesson planning?
The five steps are:
- Objective: A learning concept or objective is introduced.
- Warm-up: Revise the previous lesson
- Presentation: Present the material using suitable tools and techniques.
- Practice: Students try to apply what they have learned.
- Assessment: Evaluate whether the objectives were achieved
How does lesson planning help teachers?
Planning lessons in advance allows teachers to arrive at class each day prepared to introduce new concepts and facilitate engaging discussions rather than improvising as they go. In other words, without a lesson plan, teachers may be left scrambling, making students lose interest in the material to be learned.
Subscribe to get updates on all things at Vibe
- =>Browse all products
- Crèche & Nursery Lesson plans
- Primary Lesson plans
- Junior Secondary Lesson plans
- Senior Secondary Lesson plans
- Primary Lesson Notes
- Junior Secondary Lesson Notes
- Senior Secondary Lesson Notes
- Crèche & Nursery Termly Questions with Answers
- Primary Termly Questions with Answers
- Junior Secondary Termly Questions with Answers
- Senior Secondary Termly Questions with Answers
- Common Entrance Questions with Answers
- BECE Questions with Answers
- WAEC/NECO/GCE Questions with Answers
- Mock/Quiz/Practical Questions with Answers
- JAMB/Post UTME Questions with Answers
- Crèche & Nursery Scheme of Work
- Primary Scheme of Work
- Junior Secondary Scheme of Work
- Senior Secondary Scheme of Work
- Workbooks, Worksheets & Activities
- Study Notes
- Practical Notes
- PowerPoint Slides
- =>Browse all sellers
- =>Return to Homepage
- Buyer: Post request & receive offers
- Seller: View requests & make offers
- Become a Seller
Types of Lesson Plan, Formats and Parts (with Samples)
Teaching is an art, and every masterpiece begins with a plan. For educators in Nigeria and all over the world, that plan is called Lesson Plan . In this guide, we will be looking at the Types of Lesson Plan, the various formats, the parts and sample lesson plans.
Lesson Plans are simply the plan of how teachers plan to deliver their lessons. Lesson plans are not just for formality, they are the backbone of a successful teaching and learning.
Lesson plans are the guiding light for teachers, outlining the objectives of the lesson (what the students need to learn), teaching and learning activities (the teaching methodology), and assessment (what evaluation methods will be used to measure if the objectives of the lesson was achieved or not).
The Importance of Lesson Planning
Teaching without a lesson plan is like trying to find your way around in a new city without a map or city tour guide. It can be so frustrating trying to teach a class unprepared and without a lesson plan. And that is why this article on “Types of Lesson Plan” will not be complete if I fail to mention some of the importance of lesson planning .
Here are some of the reasons why lesson plans are important:
- Guidance: A well-structured lesson plan serves as a guiding roadmap for teachers, providing a clear and organised framework to follow. It acts as a compass that helps in achieving the lesson’s objectives while maintaining a logical flow of content.
- Builds Confidence in Teachers: A well-prepared and detailed lesson plan equips the teacher with understanding of the subject matter, teaching strategies, and potential challenges, fostering a sense of preparedness that directly translates into confidence in the classroom.
- Adequate Preparation: Lesson planning is synonymous with preparation. It prompts teachers to thoroughly research and understand the content they are about to impart. This preparation enhances the overall quality of teaching.
- Creates Anticipatory Mode for Students: A well-structured lesson plan sparks curiosity and engagement in learners making them to anticipate what is going to be taught. Students are more likely to be actively involved in the learning process when they have a clear understanding of the lesson’s direction.
- Time Management: Efficient time management is a crucial aspect of effective teaching. Lesson plans assist teachers in allocating time wisely for each segment of the lesson, preventing overshooting or falling short of time. This ensures that all planned activities are executed within the allocated timeframe.
- Avoids Repetition: Through careful planning, teachers can avoid unnecessary repetition in their teaching.
- Evaluation: Lesson plans serve as a valuable tool for assessing the effectiveness of teaching methods. They enable teachers to reflect on what worked well and what could be improved, fostering continuous professional development.
Key Components of a Lesson Plan
There are different Types of Lesson Plan , various formats and structure, and that is great. However, no matter the type, style or format adopted, every lesson plan should some basic components.
Below are the key components that make a lesson plan effective and impactful.
1. Learning Objectives
The learning objectives is the most important component of the lesson plan. They define the reasons for the lesson and serve as a compass for the teaching and learning activities.
From the lesson plan objectives, one can easy tell what the students are going to learn during the lesson and how learning will be evaluated at the end of the lesson.
Your lesson objectives must be SMART – Specific, Measurable, Attainable, Relevant, and Time-based.
Here are a few examples for Lesson Objectives for SS1 Physics for the topic “Motion in Nature”.
Specific Objectives: By the end of this lesson, students should be able to:
- Define motion and its importance.
- Describe the types of motion, including translational, oscillatory, random, and rotational.
- Explain the concept of relative motion.
2. Subject Matter
The subject matter has to do with the specific topic to be taught and how it aligns with the National Curriculum. Hence it is not just about what to teach, but how to teach it to achieve learning objectives. It includes sources of information and reference materials such as textbooks, lesson notes, websites, or tools for enhancing teaching and learning.
3. Procedure
The procedure is the step-by-step details of how the teacher will deliver the lesson and achieve the stated lesson objectives. The procedure can be arranged in sequential steps or in a tabular form depending on the lesson plan format or style. The procedure includes teacher’s activities, learners’ activities, questions and answers geared towards achieving the learning objects.
4. Evaluation
Assessing student understanding is a pivotal aspect of effective teaching. From multiple-choice questions to formative tests, evaluation helps teachers gauge the effectiveness of their teaching methods and make necessary adjustments.
5. Assignment
The assignment component of Lesson Plan isn’t just about giving the students tasks to do. Assignments are designed to reinforce students’ learning. It includes focused specific questions and exercises that will help reinforce the students’ knowledge of the subject matter.
Types of Lesson Plan: Step Lesson Plan vs. Tabular Lesson Plan
(1) Step Lesson Plan
The Step Lesson Plan is a detailed guide for teachers, ensuring a logical and effective structure for their lessons. Each step serves a specific purpose, contributing to a comprehensive learning experience.
- Introduction: During the introduction, the teacher set the stage for the lesson by introducing the topic and then go ahead to provide background information, and states the learning objectives so as to create anticipation in the students.
- Warm-up: After creating anticipation in students during the lesson introduction, next is to engage the students in short activity or exercise such as game or an interactive session or a quick review of previous lesson, so as to arose their interest and prepare them for learning.
- Presentation: This is the stage where the teacher impart the learners with new information or concepts. Presentation is the heart of the teaching and learning process, and can be achieved using any instructional method such as demonstrations, discussion, storytelling, technology-based or the use of multimedia to pass new information across to the learners.
- Practice: Practice time is set aside to engage the students in applying what they have learnt through individual or group activities and exercises.
- Review: This is a brief recapitulation of the main points covered in the lesson to ensure understanding.
- Conclusion: The final stage where the teacher reviews learning objectives, highlights key takeaways, and may preview the next lesson or assign classwork.
Layout of Step Lesson Plan
| Date: |
| Subject: |
| Period: |
| Duration: |
| Time: |
| Class: |
| Gender: |
| Number of Students In Class: |
| Topic: |
| Sub Topic: |
| Reference Book: |
| Behavioral Objectives: 1. 2. 3. |
| Instructional Materials: |
| Introduction: |
| LESSON CONTENT Step 1: |
| Evaluation: |
| Summary: |
| Assignment: |
| Remark |
(2) Tabular Lesson Plan
The Tabular Lesson Plan offers an organized table format for teachers, streamlining information for efficient lesson delivery. It includes the following elements:
- Subject/Topic of the Lesson: Clearly stating the main subject or topic of the lesson.
- Objectives or Learning Outcomes: Specifying the desired outcomes the lesson aims to achieve.
- Materials or Resources: Listing the instructional materials or resources needed for the lesson.
- Anticipated Problems: Identifying potential challenges and outlining solutions in advance.
- Teaching Strategies: Describing the approaches or methods the teacher will use during the lesson.
- Assessments or Evaluations: Outlining the methods used to assess or evaluate student understanding.
- Time Allocation: Defining the time allocated for each activity or task to ensure efficient use of class time.
Layout of Tabular Lesson Plan
NUMBER OF LEARNERS IN ATTENDANCE:
AVERAGE AGE:
BEHAVIORAL OBJECTIVES:
PRE-REQUISITE KNOWLEDGE:
LEARNING MATERIALS:
REFERENCE MATERIALS:
LESSON DEVELOPMENT
| INTRODUCTION | |||
| PRESENTATION | |||
| STEP 1 | |||
| STEP 2 | |||
| STEP 3 | |||
| STEP 4 | |||
| EVALUATION | |||
| CONCLUSION | |||
| ASSIGNMENT | |||
| Board Summary | |||
Where to Buy and Sell Lesson Plans in Nigeria
I will share a sample each of Step and Tabular Lesson Plan layout with you, but before then, let me introduce you to TermlyPlan. TermlyPlan.com is an online marketplace where teachers and educators like buy and sell lesson plans, question banks and other teaching resources. On the platform, you will find different Types of Lesson Plan across all classes and subjects.
If you have been teaching for years and have your lesson plans in place, you can sell them on TermlyPlan.com and make good money. Or Perhaps you are new to teaching and are struggling with your lesson planning, we’ve got you covered. You can buy the lesson plan you need on TermlyPlan with ease and at an affordable price so you can meet your lesson planning goals and deadlines.
To Buy already-made fixed price Lesson Plans, “ Click Here ”.
However, if you are interested in registering as a seller and to make money selling your own lesson plans, then “ Click Here Now ”.
Alright, back to the article. Let me quickly share two lesson plan samples with you, one for Step Lesson Plan and one for Tabular Lesson Plan.
Samples of Step and Tabular Lesson Plans
(A) Example of Step Lesson Plan: Sample Step Lesson Plan on Family Conflict for JSS2 Home Economics.
LESSON PLAN FOR WEEK TWO ENDING 22ND NOVEMBER, 2023
| 22nd November 2023 Home Economics 7th 40 minutes 12:40 – 1:20 JSS2 Mixed 25 Family Conflict Understanding, Causes, and Resolution Home Economics for Junior Secondary Schools By the end of this lesson, students should be able to: 1. Explain the meaning of family conflict. 2. Identify causes of family conflict. 3. State the negative results of conflict. 4. Enumerate ways of resolving conflicts in the family. 5. Outline some guidelines in conflict resolution. Pictures of people engaged in conflict resolution. To kick off the lesson, I will ask students if they’ve ever experienced conflicts at home with siblings or parents and how those conflicts were resolved. This will set the stage for understanding the relevance of conflict resolution.
A conflict is a struggle between two or more people who disagree. In the context of family, it’s a disagreement among family members over various issues.
1. Becoming aware of the conflict. 2. Setting limits: Identifying points causing the conflict and discussing them. 3. Arguing stage: Bringing disagreements to the surface without personal attacks. 4. Negotiation and compromise: Seeking solutions and arriving at a mutually satisfying agreement. 5. Following up: Ensuring conflicts are fully resolved.
1. Use words, not fists. 2. Decide to resolve conflicts peacefully. 3. Choose a distraction-free environment for discussions. 4. Give everyone a chance to talk. 5. Use active listening and keep an open mind. 6. Show and receive respect. 7. Control your voice. 8. Speak the truth. 9. Control your tongue.
1. What is family conflict? 2. Mention three causes of family conflict. 3. Discuss two negative results of conflict. 4. Outline five ways of resolving conflicts in the family. 5. Outline three guidelines in conflict resolution.
Think of a recent conflict with a friend or family member. Write about: 1. What caused the conflict? 2. How the conflict was resolved. 3. Compare the resolution process with the studied procedures. If different, note the variations.
|
Click here to download the Lesson Plan sample above in pdf format
(B) Example of Tabular Lesson Plan: Sample Tabular Lesson Plan on Family Conflict for JSS2 Home Economics.
LESSON PLAN FOR WEEK TWO ENDING 22 ND NOVEMBER, 2023
- SUBJECT: Home Economics
- THEME: Home Economics
- TOPIC: Family Conflict
- SUB-TOPIC: Understanding Causes and Resolving Issues
- DATE: 22nd November, 2023
- CLASS: JSS2
- NUMBER OF LEARNERS IN ATTENDANCE: 25
- AVERAGE AGE: 13 years
- BEHAVIORAL OBJECTIVES: At the end of the lesson, learners should be able to:
Cognitive:
- define family conflict.
- identify situational causes of family conflict.
- discuss personality differences as contributors to family conflict.
- explain the concept of power struggles in the context of family conflicts.
Affective:
- recognize the negative emotional impact of unresolved family conflicts.
- reflect on personal experiences related to family conflicts.
- value the importance of open communication in conflict resolution within the family.
- appreciate the significance of addressing conflicts to maintain healthy family relationships.
Psychomotor:
- demonstrate effective communication skills during conflict resolution.
- engage in role-playing activities to simulate conflict resolution scenarios.
- apply negotiation and compromise techniques in resolving conflicts.
- exhibit active listening skills when participating in discussions about family conflicts.
- RATIONALE (Why am I teaching the lesson? Why do students need to learn it): (1) To empower learners to comprehend the concept of family conflict, fostering a clear understanding of what constitutes conflicts within the family dynamic. (2) To equip learners with the awareness of the detrimental consequences of unresolved family conflicts, emphasizing the importance of addressing and resolving issues promptly. (3) Recognizing that there are intricate aspects to family relationships and conflicts that learners may not fully grasp, this step encourages students to explore the complexities of their own thoughts and emotions, fostering self-awareness and facilitating effective conflict resolution within the family unit.
- PRE-REQUISITE KNOWLEDGE: Basic understanding of family relationships.
- LEARNING MATERIALS: Pictures of people engaging in conflict resolution.
- REFERENCE MATERIALS: Home Economics for Junior Secondary Schools
| Teacher introduce the lesson by asking the learner’s question based on previous knowledge. | Learner’s respond to teachers questions | Reviewing previous knowledge | |
| Teacher presents the lesson in the following steps: | |||
| Teacher defines conflicts, emphasizing disagreements between family members. | Learners listen actively to the teacher’s explanation. | Definition of family conflicts. | |
| Teacher went further to discuss situational causes of conflicts in the family. | Learners listen to the teachers explanations. | Potential causes of family conflicts. | |
| Teacher explains how personality differences cause conflicts and ask students to discuss how individual behavioural patterns contribute to conflicts. | Learners participate in group discussion on personality differences and share insights gained from activities. | The impact of personality differences and behavioural patterns on family conflicts. | |
| The teacher introduces the concept of power struggles in family conflicts. Explains how conflicts can arise when individuals seek control. | Learners discuss personal experiences related to power struggles. Participate in role-playing activities. | Grasp the significance of power dynamics in conflicts. Understand the potential triggers for family conflicts. | |
| Teacher conducts a quiz to assess understanding of conflict causes. | Learners answer quiz questions individually as well as discuss answers as a class. | Evaluate comprehension of conflict causes. | |
| Teacher recaps the negative results of unresolved conflicts. Emphasize the importance of conflict resolution. | Learners reflect on the potential consequences of conflicts. Engage in a brief class discussion. | Reinforce the need for conflict resolution skills. | |
| Teacher gives the students assignment on conflict reflection. | Learners begin working on the assignment individually. | Apply conflict resolution principles to personal experiences. | |
|
A conflict is a struggle between two or more people who disagree. In the context of family, it’s a disagreement among family members over various issues.
1. Becoming aware of the conflict. 2. Setting limits: Identifying points causing the conflict and discussing them. 3. Arguing stage: Bringing disagreements to the surface without personal attacks. 4. Negotiation and compromise: Seeking solutions and arriving at a mutually satisfying agreement. 5. Following up: Ensuring conflicts are fully resolved.
1. Use words, not fists. 2. Decide to resolve conflicts peacefully. 3. Choose a distraction-free environment for discussions. 4. Give everyone a chance to talk. 5. Use active listening and keep an open mind. 6. Show and receive respect. 7. Control your voice. 8. Speak the truth. 9. Control your tongue. | |||
Lesson Plan Formats: Types of Lesson Plan in Nigeria
Nigeria’s educational landscape boasts various lesson plan formats, each with its unique strengths. Let’s explore some widely used Types of Lesson Plan.
1. SMASE ASEI PDSI Lesson Plan Format
The SMASE ASEI (Activities, Students, Experiments, and Improvisation) PDSI lesson plan format is the current government-approved lesson plan format in Nigeria. This student-centered plan engages learners through activities, critical thinking, and teamwork. The ASEI lesson plan can be presented either in Step or Tabular style (See sample lesson plans above). ASEI lesson plan is based on PDSI practice (Plan, Do, See, Improve). Its advantages include holistic learning and the incorporation of different learning styles.
2. TKT Lesson Plan Format
The Teaching Knowledge Test (TKT) lesson plan format, offered by Cambridge Assessment English, has a basic structure that includes a title, aim, objectives, materials, anticipated problems and solutions, procedure, teaching and learning activities, differentiation, assessment, reflection. It is one of the oldest format of writing lesson plans in Nigeria. However, most school prefer the ASEI format to the TKT format of Lesson Plans.
3. ESSPIN Lesson Plan Format
The ESSPIN (Evaluating Student Skills and Progress in Information and Communication Technology) lesson plan format is a method used for assessing progress students in ICT. ESSPIN Lesson plan includes elements such as a descriptive title, specific and measurable objectives, necessary materials, an introduction, a detailed procedure, evaluation methods, and a conclusive summary.
4. ESL Lesson Plan Format
ESL lesson plan format is designed for teaching English as a Second Language (ESL) to learners. Elements of the lesson plan includes identifying goals, choosing suitable materials, creating an outline, planning for assessment, considering student needs, planning for interaction, and maintaining flexibility.
5. UNESCO Lesson Plan Format
Adaptable to various teaching contexts, UNESCO’s lesson plan format includes essential components like the title, objectives, time allocation, materials, introduction, body, conclusion, evaluation, follow-up, and reflection. Its flexibility makes it suitable for both face-to-face and online teaching.
Buy and Sell Lesson Plans, Question Banks and other Digital Teaching Resources on TermlyPlan.com
TermlyPlan.com is an online marketplace designed to cater to the needs of Nigerian teachers. It’s a platform powered by a community of educators like you. Buy and Sell different Types of Lesson Plans and Teaching Resources on TermlyPlan – Click Here to Get Started today.
There you have it, comprehensive article on the Types of Lesson Plan, Formats and Parts (with Samples). Let me know what you think about this piece in the comment section. I am open to your contributions, suggestions and questions.
PS: Putting Lesson Plans together is not an easy tasks and that is why we created TermlyPlan.com – an online marketplace for buying and selling lesson plans. You can easily order for any lesson plan you need and save yourself from the stress of trying to create one from scratch. Register on TermlyPlan today – it’s easy and completely FREE, “ Click Here ”.
ASEI Lesson Plans – A Comprehensive Guide
Leave a reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
Don't have an account yet? Register
Already have an account? Sign In
Reset Password
Please enter your username or email address, you will receive a link to create a new password via email.
- Grades 6-12
- School Leaders
Get Your Free 21st Century Timeline Poster ✨
30 Lesson Plan Examples for Every Grade Level and Subject
Lots of ways to prepare for top-notch learning.

Lesson planning: Most teachers either love it or hate it. Either way, it’s something every teacher has to spend at least some time doing, so it’s worth learning to do well. Whether you’re a brand-new teacher or an experienced educator looking for some new ideas, these lesson plan examples offer inspiration for every subject and every grade level.
Lesson Plan Sections
Preschool lesson plan examples, elementary school lesson plan examples, middle and high school lesson plan examples.
Many lesson plans include some or all of the following sections.
- Objective : These should be specific and measurable. Often they align with Common Core or other learning standards.
- Materials: List any items you’ll need, including worksheets or handouts, school supplies, etc.
- Activities: This is usually the longest section, where you’ll lay out what the lesson and its activities look like. Some teachers write these in great detail. Others include just an overview to help them plan.
- Assessment : How will you assess your students’ learning? This could be a formal assessment or something simple like an exit ticket.
- Differentiation : Describe how you’ll vary the level of difficulty for students at all levels, including any enrichment for early finishers.
Some people think preschool is just playtime, but pre-K teachers know better! Here are some of the ways preschool teachers plan for their lessons.
Weekly Lesson Plan
Weekly preschool lesson planning helps you plan each day and ensure you’re tackling all the most important skills.
Learn more: Pre-K Weekly Lesson Plan
Pre-K Theme Lesson Plan
If you like to plan by theme, try a template like this. It includes space for a variety of activities that fit your topic.
Learn more: Pre-K Theme Lesson Plan
Alphabet Letter Lesson Plan
If you’re focusing on a new letter of the alphabet each week, try lesson planning like this. You can see the week at a glance, including all the materials and books you’ll need.
Learn more: Alphabet Letter Lesson Plan

Centers Lesson Plan
Your centers need some planning too! Whether you change them out weekly, monthly, or as needed, use plans like these to stay prepared.
Learn more: Centers Lesson Plan

Weekly Unit Lesson Plan
Adding pops of color and a few images can make it easier to locate the lesson plan you’re looking for in a snap.
Learn more: Weekly Weather Unit Lesson Plan
Since elementary teachers tackle multiple subjects every day, their lesson plans might look like a general overview. Or they may prepare more detailed lesson plans for each topic to help them stay on track. The choice is up to you.
Weekly Overview Lesson Plan
Don’t be afraid to write out your lesson plans by hand! A side-by-side setup like this lets you see a whole week at once. We love the use of color to highlight special things like fire drills.
Learn more: Elementary Weekly Overview Lesson Plan
Unit Lesson Plan
Planning out a unit helps ensure you cover all the important topics and meet your learning objectives.
Learn more: Unit Lesson Plan
Yearlong Schedule
Planning a whole year may seem daunting, but it can show you where you’re going to need to stretch a unit and where you can circle back and review. Mrs. D from Mrs. D’s Corner has ideas on how to structure a yearlong lesson plan using Google Sheets.

Guided Math Lesson Plan
This example on adding three numbers together can be altered to fit any math lesson plan.
Learn more: Guided Math Lesson Plan

Art Lesson Plan
While these are elementary art lesson plan examples, you can easily use this style for teaching art at upper levels too.
Learn more: Art Lesson Plans
Special Education Lesson Plans
Lesson planning for special education looks different than general classroom lessons in that the lessons have to cover specific IEP goals and include lots and lots of progress monitoring. The Bender Bunch starts each lesson with independent work (read: IEP practice) and then heads into mini-lessons and group work.
Learn more: Special Education Lesson Plan
Interactive Read-Aloud Plan
Interactive read-alouds take some careful planning. The Colorful Apple explains how to choose a book, get to know it, and get ready to teach it. Once you’re in the book, sticky notes may be the best lesson-planning tool you have for marking questions and vocabulary words you want to point out to students.
Learn more: Interactive Read-Aloud Plan

Social Studies Lesson Plan
Including images of your anchor charts is a great idea! That way, you can pull one out and have it ready to go in advance.
Learn more: Social Studies Lesson Plan
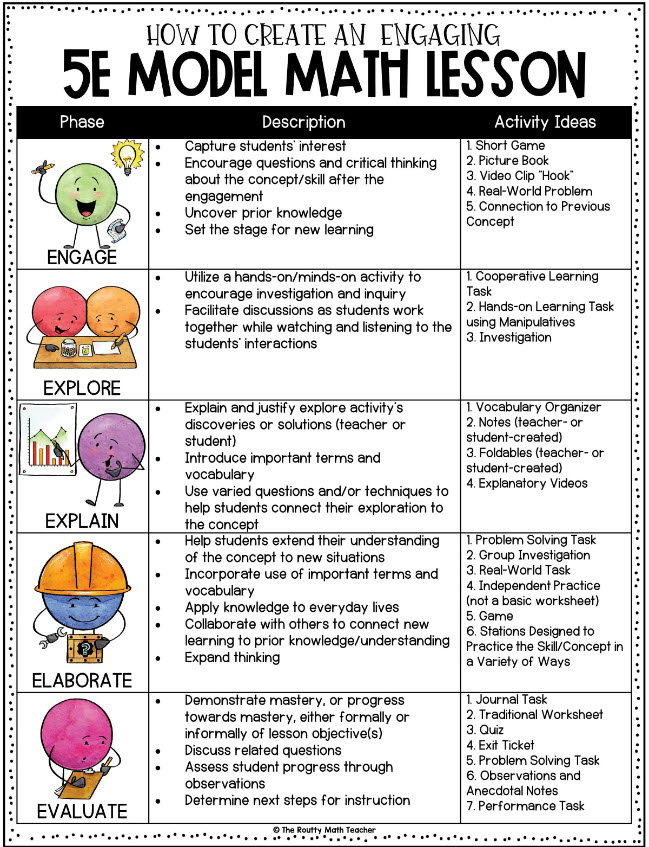
5E Lesson Plan for Elementary School
The 5Es stand for Engagement, Exploration, Explanation, Elaborate, and Evaluate. This type of lesson planning can be helpful for students as they work through each of the 5Es related to the topic you’re studying.
Learn more: 5E Lesson Plan for Elementary Math

Science Lesson Plans
If you like to plan your lessons in more detail, take a look at this elementary science lesson plan example.
Learn more: Science Lesson Plan Template
Reading Group Lesson Plan
Lots of elementary schools have differentiated reading groups. Use a template like this one to plan for each one, all on one page.

P.E. Lesson Plan
Gym teachers will love this lesson plan idea, which includes directions for playing the games.
Learn more: PE Lesson Plan
Music Class Lesson Plan
Plan out the skills and songs you’ll need for a meaningful music class with a lesson plan like this one.
Learn more: Music Class Lesson Plan
At the middle and high school levels, teachers often need more detailed plans for each class, which they may teach multiple times a day. Here are some examples to try.
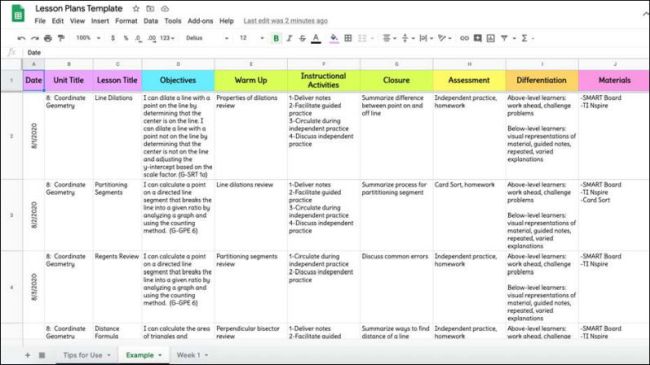
Google Sheets Lesson Plans
Google Sheets (or Excel) is terrific for lesson planning! Create a new tab for each week, unit, or class.
Learn more: Google Sheets Lesson Plan

Handwritten Lesson Plan
Some people really prefer to write things out by hand, highlighting important parts and making notes as they go. You can always convert this kind of plan to a digital format later if you need to.
Learn more: Handwritten Lesson Plan
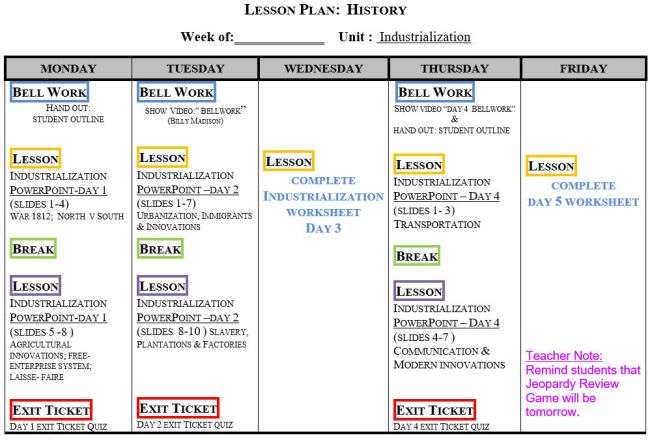
Weekly History Plan
This example shows how you can plan out a week’s worth of lessons at once, and see the entire week all in one spot. This example is for history, but you could use this for math, ELA, or social studies too.
Learn more: Weekly History Plan
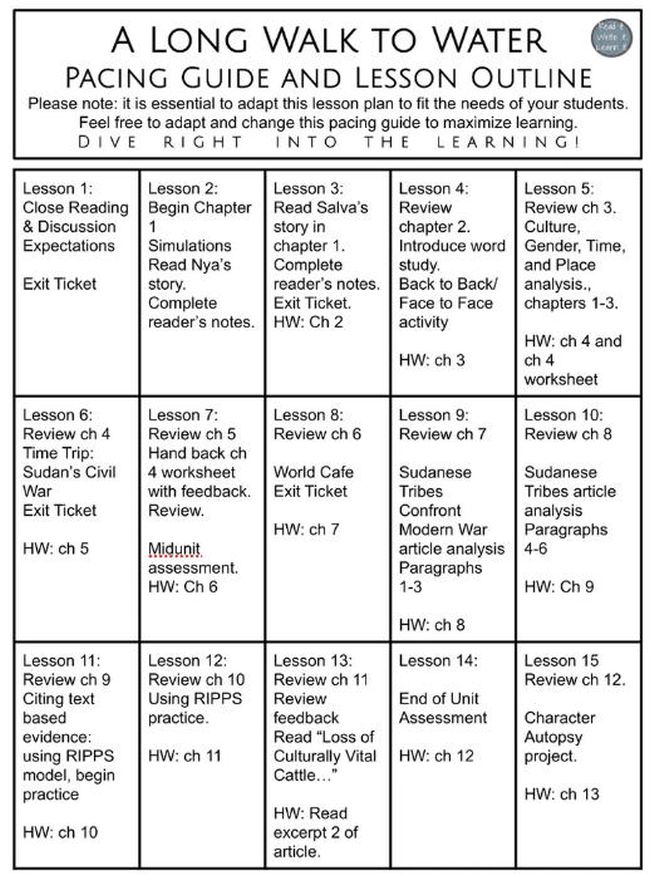
Outline and Pacing Guide Lesson Plan
A pacing guide or outline works for both you and your students. Share it at the beginning of a unit to let them know what’s ahead.
Learn more: Outline and Pacing Guide

5E Lessons in Middle and High School
5E lesson plans (Engagement, Exploration, Explanation, Elaborate, Evaluate) are great for middle and high school as well. This example is for science, but you can use the 5E structure across all lessons.
Learn more: Middle and High School 5E Lesson Plans

Sticky-Note Lesson Plan
At some point, you’ll know what students are doing each day, you’ll just need some reminders for questions to ask and key points to cover. The nice thing about using sticky notes for lesson planning is if you get ahead or behind schedule, you can move the entire sticky-note lesson to another day. ( Find more ways to use sticky notes in the classroom here .)
Learn more: Sticky Note Lesson Plan

Backwards Planning Lesson Plan
If your school uses backwards planning, you’ll be thinking about the outcome first and working back from there (rather than forward from an activity or task). Backwards planning lesson plans are intensive, but they’re also something you can use over and over, modifying them slightly for each group of students you have.
Learn more: Backwards Planning Lesson Plan

Visual Arts Lesson Plan
Detailed lesson plans take longer to prepare, but they make it easier on the day (especially if you wind up needing a sub).
Learn more: Visual Arts Lesson Plan Template

ELL or World Language Lesson Plan
Whether you’re teaching English-language learners (ELL) or a world language to English speakers, this lesson plan style is perfect.
Learn more: ELL/World Language Lesson Plan
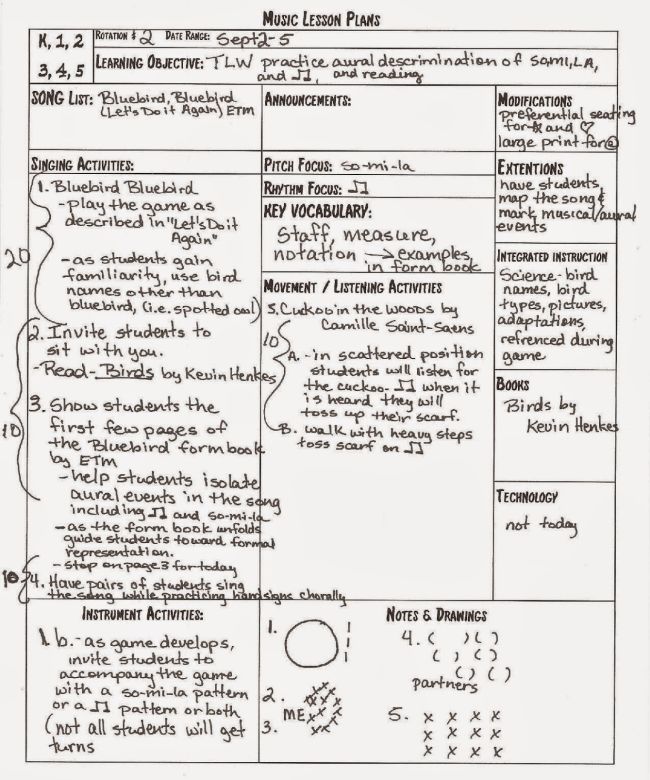
Music Lesson Plan
Use a lesson plan like this for choir, orchestra, band, or individual music lessons.
Learn more: HS Music Lesson Plan
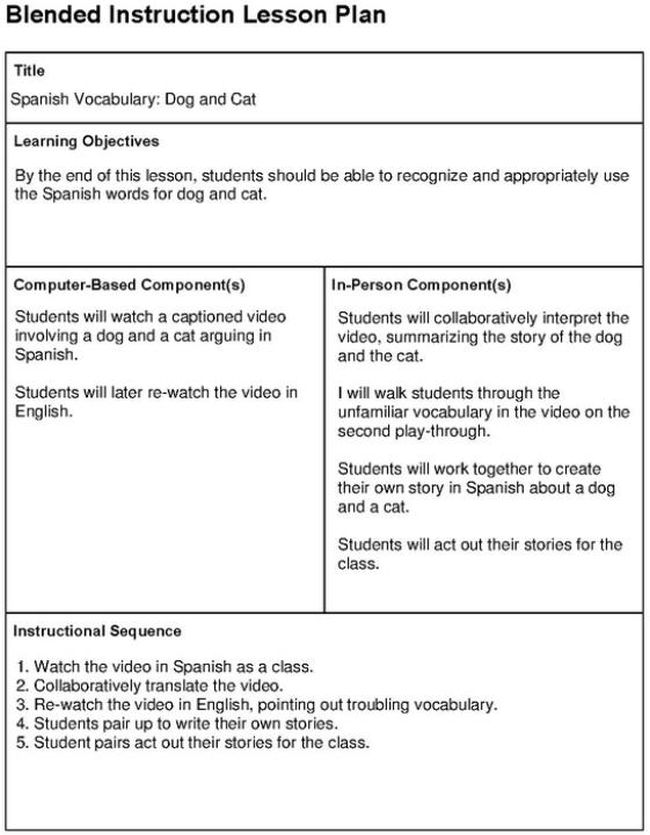
Blended Learning Lesson Plan
If your instruction includes both computer-based and in-person elements, this lesson plan idea might be just what you need.
Learn more: Hot Lunch Tray

One-Sentence Lesson Plan
This kind of lesson planning isn’t for everyone, but the extreme simplicity works well for some. Describe what students will learn, how they will learn it, and how they’ll demonstrate their knowledge.
Learn more: One-Sentence Lesson Plan
Need more help with lesson planning? Come ask for ideas in the We Are Teachers HELPLINE group on Facebook !
Plus, check out ways to make time for more creativity in your lesson plans ..

You Might Also Like

Free Lesson Plan Template Bundle (Daily, Weekly, Monthly) + Free Printable
Everything you need to plan the best learning experiences. Continue Reading
Copyright © 2024. All rights reserved. 5335 Gate Parkway, Jacksonville, FL 32256

The Four Main Parts of a Lesson Plan Made Simple

by Brad Melsby – updated January 23, 2024
What is a lesson plan and why do you need one?
The world of education is full of (too) many lesson plan templates and styles. As you develop as a teacher, you’ll naturally grow into a more detailed lesson plan format. Your school or district may require a different format or style of lesson plan. Whatever your situation, it’s most useful for newer teachers to focus on the four main parts of a lesson plan. These four elements are essential to your early success in the classroom.
Your lesson plan is the roadmap for how the class period will be organized. In the lesson plan, you identify what will be taught, how it will be taught, and by what method you plan to see if students learned it. Without a structured lesson plan, a class period can quickly lose focus or direction.
In this article, we’ll focus on the four main parts of a lesson plan.

Lesson Planning Simplified: The Four Main Parts of a Lesson Plan
Lesson component #1: identify the learning objectives.
Ask yourself: What new concepts, knowledge, or skills do I want my students to learn today?
When I chat with new teachers about how their class is going, I sometimes hear them say, “We’re doing the Roman Empire right now” or “We’re doing fractions today.” I get that the word “doing” in this context is just an expression.
But I also remember the realities of being a new teacher. In my first year or two, my goal was to “fill the period” with academic activities. Surely if we are doing something, the kids will learn. Right?
“Doing” does not necessarily equate to learning.
For many new teachers, a major evolution is to focus less on “filling the period” — although unstructured class time is rarely good — and more on your learning objective(s).
Check out the sample learning objectives below. Notice how the addition of learning objectives shifts the focus away from the topic (“We’re doing the Roman Empire”) to the students and their skill acquisition.
Here are a few sample learning objectives:
- At the end of the lesson, students will be able to identify and explain six causes of World War II.
- By the end of the lesson, students will be able to apply the rules of the Order of Operations to evaluate algebraic expressions.
- Students will be able to categorize types of animals into the correct classes with a graphic organizer.
- By the end of the reading lesson, students will be able to identify the rising action, climax, and falling action on a plot diagram.
Learning objectives force the teacher to think strategically. How can you best support the students in achieving the objective? What instructional or learning activities will best fit the objective? Clear learning objectives are arguably the most important part of a lesson.

Lesson Component # 2: The Lesson “Hook”
Ask yourself: How will I introduce the topic? How can I get students interested in the topic?
A lesson introduction should:
- Provide brief context and background information on the topic while engaging interest
- Create excitement or interest. Compel the class to want to know more about the topic
- Explain the relevance of the topic to the larger unit or course
- Provide a clear link between today’s objectives and the student’s prior knowledge
Your students likely possess a wide variety of personal experiences and knowledge. As a result, it’s helpful to use the introduction to gauge prior knowledge or misconceptions about the topic.
A few strategies for introducing the lesson:
Tell a personal story, analyze a relevant image or song, watch a video clip, provide a real-world connection or example, or present a probing challenge or question.

Lesson Component #3 : The Learning Activities
Ask yourself: What will the students do to achieve the lesson objective?
In a general sense, the learning activities can be divided into two parts: Guided Practice and Individual/Group Practice. This is sometimes referred to as the gradual release of responsibility method: I Do, We Do, You Do.
Guided Practice (I Do, We Do): Here, the teacher explains and models the learning activity while answering clarifying questions. Guided practice then allows students to participate in the learning activity under supervision and with direct feedback from the instructor.
From a teacher’s perspective, guided practice is a key form of formative assessment. Teachers use guided practice to determine whether students are ready to complete the activity without scaffolded support.
Individual/Group Practice (You do): Students complete the learning activity. In guided practice, students learn with the steady support of the teacher. Individual/group practice is the time for students to demonstrate proficiency on their own. Independent practice can include homework assignments.

Lesson Component #4 : Assessment and Closure
Ask yourself : How can I know if the students have met the learning objective of the lesson?
Lesson closure gives teachers the chance to briefly conduct one final review of the lesson and check to ensure that the intended student learning has occurred.
Go back to your original lesson objectives. Create questions to ask students that address your learning goals. You can place those questions on a homework assignment, an exit ticket , a quiz, or simply ask the questions in the form of a discussion.
Teachers use the assessment from today’s lesson to inform tomorrow’s lesson plan .
What questions or confusion came up that need clarification? What if anything do I need to reteach? What key concepts from today’s lesson will be useful to build on during tomorrow’s lesson?
Related resource:
Featured articles.

How to Revamp Five Routine Class Activities for High Student Engagement

Three Simple Ways to Boost Engagement in Any Lesson

New Teacher Evaluations: Minor Mistakes vs. “Red Flags”

Three Classroom Policies and Procedures You Need to Consider

Why and How You Should Be Randomly Calling On Your Students

New Teacher Self-Care: A Practical Plan You Can Start Tomorrow

Brad has taught history at the middle and high school levels for 19 years, almost exclusively in American public schools. He holds a master’s in educational technology and is passionate about elevating the status of professional educators.

Set of 70 Pre-Made Exit Tickets and Student Check-Ins
Why we love these:
- They provide a thoughtful and creative way to end class.
- A convenient option if your lesson unexpectedly runs short.
- The prompts are open-ended and accessible for all students.
- Gives you a quick and easy way to tell what your students are thinking or feeling.
Pin It on Pinterest
- https://twitter.com/New_Teach_Coach
- WordPress.org
- Documentation
- Learn WordPress
Create Your Course
How to build a lesson plan (+ templates), share this article.
So you’ve got a great course topic , you’ve built a course outline to help you deliver, and now you’re all set to start your first lesson plan.
When it comes to building an online course that delivers, you need to be strategic about your lessons. Each lesson plan is a building block that ladders up to your overarching course goals.
Let’s talk about how to build a lesson plan that hits home.
Or grab them here for google docs or word!
Skip ahead:
What does a good lesson plan look like?
5 steps for building a lesson plan from scratch .
A well-designed lesson plan has seven key elements:
Class objectives
Objectives, at a basic level, are what the lesson sets out to achieve — think of them as your North Star. Objectives communicate three key things:
- Why students need the lesson
- What they’ll be able to do at the end of the lesson
- How they’ll demonstrate knowledge.
Say one of the lessons in your social media course is “choosing the right channels.” In that case, your objective could be: At the end of this lesson, students will be able to compare different social media channels and choose the one that best aligns with their content goals.
Teaching and learning are more effective when all the stakeholders understand the purpose of the lesson. When anyone veers off the track, they can easily realign themselves with the North Star.
Hook is what grabs the attention of your students. It is usually a statement surfacing the problem they are having — which is why they signed up for your course in the first place. This is your chance to prove that you understand their problem and can solve it.
Back to our previous example, the hook could be a story about a creator who switched channels and finally got traction on social media after trying for many years. Or you could share data around how social channels affect how much money creators make.
Learning activities
Here, you spell out everything the lesson entails — from class activities and instruction time to independent work time and even assessments. Everyone involved needs to know what the lesson covers so they can prepare ahead of time.
Again, referring to our earlier example, the learning activities might look like this:
- Worksheets
- Instructor-led sessions
- One Q and A session at the end of the class
- Independent work time (which doubles as assessment)
- Class discussions
Learn more: Blended learning and scheduled class activities
Timeline shows the duration of each activity in the lesson. More than showing how long the class will take, assign time limits to the different sessions within each lesson, including assessment, main instruction, breaks, and student participation.
Build in a buffer between each session to take care of any unforeseen issues. Say you want to spend 15 minutes on a class presentation; assign 20 minutes to it instead.
Having a realistic lesson timeline helps you stay on track, making sure you have enough time to cover all the key areas of your lesson.
This is where you highlight what students need to make the most of your class — to set them up for success. The last thing you need is for your course to lose credibility because a particular student wasn’t sufficiently equipped for it.
Maybe they need to complete a foundational course first to bring them up to the level of knowledge required for the lesson. Or they need access to certain tools and equipment. Tell them all about it here.
For a social media class, for instance, students must have active accounts and maybe a certain number of followers.
Closure is how you wrap up the class. It typically involves a recap of the key points covered in the lesson and a quick review of the class objectives.
The instructor might ask reflective questions such as “What was the most challenging part of the lesson for you?” or “What would you like to learn more about in this topic?” Or ask students to create a mind map of the key points covered in the lesson.
At this point, students and instructors can reflect on the lesson activities at the end to see if they met their goals. Students can also ask last-minute questions before the final assessment.
Assessment
This is the parameter for measuring how well a student understands what they’ve learned in a particular lesson. It helps the course instructor assess students fairly.
The assessment can take several forms. One might administer a summative test — like an end-of-class quiz. Or conduct a survey with open-ended questions at intervals to gauge students’ knowledge.
Whichever method you choose, make sure you inform students ahead of time so they prepare adequately for it.
Before you begin
Before you dive into lesson planning, start with a few key questions to determine the goal of your lesson. As the topic expert, the breadth of this course content is clear in your head, but your students are still figuring it out as they go along.
Keep a narrow focus for each lesson while keeping the bigger picture in mind – this will help your students build knowledge in context so they can use it independently and remember it forever!
- What do your students already know? This is back to what you’ve covered in previous lessons or what foundational knowledge you expect students to have. Do they have all the definitions they need to understand today’s topic? Are there any gaps you need to close before you dive in? That will be your starting point for this lesson.
- What do they need to learn today? Eyes on the prize here – keep your goal clear, or you’ll get lost along the way! Set yourself a single goal for this lesson: should students understand the formula for a unique value proposition, or should they be able to write a great cover letter? What single concept or skill do you want this lesson to impart to your students? Remember to keep it simple; if it’s too complex, you might want to consider splitting it into smaller lessons to avoid confusing your students with information overload.
- What’s the best way to lock it into place? Now that you’ve locked down the goal for today’s lesson, you can decide on the best way to deliver the information. Is this something best delivered through video, or is it better explained with text and diagrams? Could you represent this as an infographic? What practice activities would help your students lock in their newly acquired skills?
Related: How to do a training needs assessment
It’s not always about downloading your brain onto the page. You need to consider how you explain things so your students fully understand not only the new facts, but the context surrounding them – that’s the key to them being able to apply these new skills independently when the course is over.
With the Thinkific course builder, you have so many teaching tools and resources at your disposal – use them in harmony with one another to give your students a dynamic learning experience .
Now that you’ve got those three guiding principles in mind, let’s put them to work in your lesson plan.
Set the stage
Begin each new lesson by setting the stage for your students. You can do this in three key steps:
- Take a brief moment to look back at what you covered in the last lesson,
- Give a high-level overview of what today’s lesson will entail, and
- Tell students the key skills or takeaways they will have conquered by the end of the lesson.
In particular, consider if any content from previous lessons is applicable to the new lesson. Never miss an opportunity to name-drop or draw examples from old content while introducing new material! It’s a great opportunity to help your students build context between what might feel like a confusing array of new facts. When you build bridges between old and new knowledge, it creates that lightbulb moment for students to see how all the pieces fit together.
This is more than just summarizing or expectation-setting – it’s a strategic educational principle. By reminding students of previous lessons, you help them draw connections between old and new content so they can understand how everything fits together.
When you share the key touchpoints for today’s lesson, you set up a framework for them to contextualize everything that follows. If they know what the final goal is, they will naturally be more attuned to anything you say about those skills from that point onwards. This brief process at the beginning of each lesson provides anchors for students to shape their understanding throughout the rest of the lesson.
Explain new information
This is the main component of any lesson plan. When it’s time to introduce new content, make sure to do so clearly and simply. Explain new concepts in the most straightforward way possible. Consider your weakest student, and explain things with them in mind – even your strongest students will still benefit from that simplicity!
Be sure to use lots of examples to help students develop context with new information. One tip here is to use a mix of examples that draw from general knowledge and subject-specific knowledge. For example, you can and should give concrete examples grounded in the course subject matter; for more abstract concepts, however, it can be helpful to explain things using everyday examples that everyone can relate to.
Related: The Ultimate List of Free Online Course Lesson Plan Templates
Consider using apples and oranges to explain abstract economic concepts, or using nursery rhymes to explain music theory. This doesn’t mean you have to come up with mysterious hypothetical examples like the ones you might have found on a high school math quiz – just look for everyday situations you can use to explain more difficult concepts, so your students can ground their new understanding in something familiar.
Students learn in a myriad of different ways – some through text, others through video, and still others through graphic design or activities like writing by hand. While explaining things clearly in a well-produced video or article is always a great place to start, consider using a variety of methods to make your lesson plan stick.
- Create an infographic to illustrate key points from the lesson
- Provide fill-in-the-blank notes so students can follow along with you and pay attention for key information queues
- Link key words and concepts to external articles or videos to provide students with additional learning resources
- Create a slide deck of key points that students can use as a review tool
- The sky’s the limit – if you can think of an alternative way to present your information, your students will benefit! The Thinkific course builder has a number of different content types to suit your needs, wherever the inspiration leads you.
Learn more about different learning styles and how to teach to them .
Practice makes perfect
After introducing new material to students, it’s vital to give them an opportunity to put their new skills into practice . This is what helps them lock new information into their brains and build contextual links with other skills. It’s also an important tool to help students master the content from this lesson before they move on to the next – as they work through practice activities and find themselves stuck on particular concepts or tasks, it will become clear which aspects of the material they didn’t quite understand. That gives students a targeted opportunity to ask good questions or go back through the course material until they master that skill.
Even in an online course , there are a number of practice activities you can prompt students to use:
- Ask students to define key concepts and use them in a paragraph, so they have an opportunity to put things into their own words
- Suggest students rephrase concepts by converting your notes into questions, like those they might expect to see on a quiz
- If you have a community or online group, ask students to share their summaries or reflections with each other in a dedicated lesson thread
Related: 8 ways to make online classes more interactive
Assessments
Sometimes, you also need to assess student knowledge. While you won’t do this for each and every lesson, it’s a helpful tool to check student understanding at important course milestones.
Thinkific’s course platform makes it easy to deliver student assessments with quizzes, exams, and assignments to put your students to the test, but you should keep future assessments in mind while you plan lessons. As you build a series of lessons, keep these questions in mind for future assessments:
- What facts and skills from this lesson are necessary for a student to succeed in this course?
- Are there any facts in this lesson that students need to be reminded of to make sure they stick?
Keep a running list of these answers as you build your lessons. By the time you reach a course milestone and you’re ready to build an assessment, you’ll already have a list of key questions to use in your quiz or assignment. By drawing questions from across a series of lessons, you help students build contextual links between different batches of information and end up with a more cohesive learning experience.
Get ahead with our free lesson plan template
Building a lesson plan from scratch is challenging and quickly gets complicated if it’s your first time. To help you, we’ve created a customizable template you can tweak to suit your needs fast.
You’re well on your way to building a great course , with solid principles that help you deliver dynamic lessons to your students!
Put your learning into action with Thinkific:
This blog was originally created in August 2020, it has since been updated in August 2023 to become even more useful!
Jenny is a Content Marketer at Thinkific. A lifelong learner, she loves writing about anything from Byron to blockchain. Formerly from Cape Town, she now spends her spare time wandering Vancouver in search of the perfect coffee.
- 10 Instructional Design Models For Creating A Winning Online Course
- 10 Steps To Creating A Wildly Successful Online Course
- 5 Techniques to Create an Effective Online Course
- 5 Ways to Validate Your Online Course Concept
- How To Craft Magnetic & Compelling Learning Outcomes
Related Articles
Jeanine blackwell: how to create a profitable online course.
Learn how to create a profitable, high-impact online course that stands out in the marketplace using Jeanine Blackwell's 5-step Expert Experience Method.
These are the Top Edtech Trends for 2024
How will edtech evolve and change in 2024 and beyond, and what edtech trends do you need to be aware of? Find out here.
Best Free Community Management Software (2024)
Explore the top free community management software options available. Find the perfect tool to effectively manage and engage your online community without breaking the bank.
Try Thinkific for yourself!
Accomplish your course creation and student success goals faster with thinkific..
Download this guide and start building your online program!
It is on its way to your inbox
Lesson Plan Procedures: A Guide for Teachers

| Add to Folder | |
|---|---|
| creative writing | |
| children's book | |
| activities | |
| classroom tools | |
| language arts and writing | |
| vocabulary |
Lesson Plan Procedures
In this article, we will explain how to properly perform a lesson plan in school by diving deeper into lesson plan procedures. We will discuss the three major steps involved in lesson plan procedures and share how teachers can self-evaluate their lesson plan success.
What is a Lesson Plan Procedure?
Lesson plan procedures are the sequence or step-by-step guidelines detailing how a teacher plans to deliver a lesson to students. This includes the activities, methods, materials, and timing necessary to effectively facilitate learning.
Typically, there are three stages of a lesson plan that make up the lesson plan procedure. These stages are the motivational opening, the development of the lesson, and the closing of the lesson. However, there may also be some form of formal or informal periodic assessment. Periodic assessment throughout a lesson will alert you to any misconceptions or misunderstandings students may have long before they conclude the lesson.
Let’s take a closer look at the three major stages of effective lesson planning.

The Three Stages of Lesson Plan Procedures
Step 1: the motivational opening.
The first stage of a lesson plan is critical! It’s how you’ll stimulate students’ interest in the topic.
Start by asking students a thought-provoking question, such as, “How would you like to sleep for four months every year?” or “Did you know we can measure any tree on the playground without climbing it?”Other attention-grabbing openers can include the use of models, maps, apparatus, or a demonstration.
When starting a lesson, don’t make the mistake of assuming what students know. For example, just because students studied American history in elementary school, had a basic history course in middle school, and are now in your high school history class, don't assume they know all there is to know about American history. Take the time to find out. Bottom line: Always know what your students know!
Step 2: The Development of the Lesson
The development of a lesson plan is the heart of any lesson. It’s the portion where you teach and students learn.
This vital stage is when students will obtain valuable information, manipulate data, and engage in active discovery through total involvement. Include some of the following elements in this stage:
- Lesson methodologies. Not only is it important to give some thought as to what you're going to teach, it is equally significant that you consider the methods of presentation as well. I'm sure you've been in a class where the only method of instruction was dry, stale lectures. You undoubtedly found the class boring and wearying. The same fate awaits your students if you provide them with an overabundance of one type of teaching methodology to the exclusion of others. (These are addressed in Lesson Methodologies )
- Problem-solving. As I discuss in another article , problem-solving is an inherent part of any lesson. Providing students with the opportunities to solve their own problems in their own way is a valuable motivational technique.
- Creative thinking. Learning is much more than the memorization of facts. Any lesson must allow students opportunities to manipulate data in new and unusual ways.
- Hands-on activities. It's critical that students have sufficient opportunities to create products based on what they learn. These might include but are not limited to posters, dioramas, charts, graphs , mobiles, notebooks, portfolios , and models.
- Students critique the directions or set up for a presentation or demonstration.
- Students verbalize the steps they're taking during the completion of an activity.
- Students manipulate objects or devices and verbalize their feelings about their actions.
- Students work in small groups to share information learned and how it relates to prior knowledge.
- Students graph or illustrate significant points on the chalkboard for class critique.
Teaching Tip! When creating lesson plans, consider both short-term and long-term projects for students. This will keep the learning experience interesting as you switch up styles.

Step 3: The Closing of the Lesson
The closing of the lesson is a vital stage where you recap key points and help students consolidate their learning. It’s an opportunity to review the lesson's objectives and assess whether they have been met. This can be done through summary discussions, quizzes, or reflective activities.
It's also important to provide an outlook for the next lesson, thus creating a seamless transition and maintaining students' interest.
Teaching Tip! To keep your students engaged, try ending the lesson on a cliffhanger. This can be by proposing a question or telling them an enticing bit of information (e.g.“, Tomorrow I'll bring in a creature with eight eyes. You won't want to miss it!”).
Lastly, it’s good practice to end the lesson on a positive note to boost students' confidence and encourage them to look forward to the next session.
Self-Evaluation in Creating Lesson Plan Procedures
As you write lessons, include a brief section at the end that allows you to self-evaluate. This will be important when and if you decide to teach the lesson again. It will also provide you with some important insights relative to your perceived level of success.
You might consider some of these self-evaluative questions:
- “How was my pacing?”
- “Did students understand the content?”
- “Did students understand the important concepts?”
- “Did I use my time appropriately?”
- “What changes should I make the next time I teach this lesson?”
- “Were students engaged and involved?”
- “What new activities or procedures could I include?”
- “Did I present the lesson well?”
Featured High School Resources

Related Resources

About the author

Digital Content Manager & Editor
About haley.


Meet the Team
Customer Success
Conferences
What Makes A Great Lesson Plan: 9 Things To Consider
A great lesson plan provides a clear overview for learning, regardless of the material or subject you're teaching. Your lesson plans don't have to be complicated or lengthy; they should only include information on what you're preparing, how you'll teach it, and what you want your students to achieve as part of the curriculum. Quality lessons tie prior knowledge and understanding and flow easily, connecting ideas and concepts.
Factors That Make a Great Lesson Plan
- Lesson objectives
Every lesson plan must begin with determining what students will need to learn or be able to do after the session. The most exemplary objectives are action-oriented and concentrate on the class' most significant and critical learning demands. They should be quantifiable so that instructors can keep track of students' progress, verify that new ideas are grasped before moving on, and be realistic in time constraints.
2. Find related requirements
Teachers might incorporate larger objectives that expand beyond a particular session, such as critical writing or depth of understanding, in addition to the lesson's objectives. This makes it easier to connect learning to other criteria such as grade-level expectations .
In some situations school administration may establish specific expectations while in others, instructors may be required to make these determinations. In either scenario, ensure the lesson plan is in line with the school's requirements.
- Describe the general structure of a tale, including how the beginning of the narrative initiates the action as well as how the finale brings the action to a close.
- When conducting tests, collecting measurements, or completing technical activities, follow a multistep method to the letter.
- Know how to solve real-world and quantitative issues using the volume formulas for cones, cylindrical, and hemispheres.
3. Pre-assessment: Determine the needs of your students
Are you teaching new content or revisiting what you presented in a previous session with this lesson? A quality lesson plan includes an assessment of your students, so you understand what the students need to be successful. Some of your pupils may have less background knowledge and need additional support while others have previously mastered the content and are ready for enrichment.
A preassessment can be a formal pretest but can also be a planned activity that allows students to explore the learning objectives while you gather information about their mastery levels. It is helpful to conduct your pre-assessment prior to beginning the lesson, so you have the time to plan instruction based upon current student understanding.
4. Be prepared - list the resources you need for instruction
Tools and resources that you may require during the lesson should be arranged and gathered ahead of time. Make a list of all the things you'll need to present a lesson such as paper and notebooks. Technological resources, such as laptops and integrated learning apps or webpages, should be listed as well and tested in advance to ensure smooth performance during instruction.
5. Dynamic opening
Engage your students in the lesson from the beginning of the learning. Create an experience that creates excitement in the content and makes the learning relevant for students. After all, if the students aren't invested, they will not learn at a high level. Creating enthusiasm for the learning through the use of novelty, humor, or cognitive dissonance will help launch your lesson. Helping the students find relevance about the learning will also increase engagement. Tying the learning to a student’s future goals or to current events can increase relevance. Your dynamic openings should align tightly to the learning objectives. Providing a clear statement of the learning objective often can be part of the dynamic opening.

6. Learning activities
The step-by-step overview of the session is the true essence of a lesson plan. Teachers need to divide the lesson into discrete learning activities. For example, the methods by which they will teach the material and explain what will transpire in the classroom throughout each part.
Consider the following factors to help you choose the activities for each lesson.
- How they relate to the learning objectives as well as any additional requirements or standards that students must satisfy
- Whether it's an engaging and relevant approach for pupils
- The timeframe required to complete the task
As activities account for most of the learning time, it's critical to include a range of them in a single lesson plan. Giving students new methods to explore and opportunities to apply what they've studied helps them retain what they learned while providing valuable experiences they may apply to other aspects of their lives.
7. Perform regular assessment
Is the lesson accomplishing its goals? Teachers can find out by incorporating some type of evaluation, such as checking for understanding over each chapter studied in the class. If the goal is for pupils to comprehend a subject, the instructor might have them do an activity that involves discussing or applying that idea.
If the goal is to learn a new skill or perhaps enrich an existing one, the evaluation might ask pupils to demonstrate their mastery of that talent. This phase is made easier if the goal is one that can be measured.
- In-class assignments and activities
- Group presentations and discussion
8. Close the lesson
At the end of the lesson, it is important to provide closure. There are innumerable ways to effectively close a lesson. Closure can be a short and simple statement or include a brief formative assessment. The critical attribute of closure is providing affirmation of the learning objective and clarifying any misunderstandings.
9. Evaluation and reflection
After the lecture, teachers can pause for a moment and jot down some observations from the class as well as their own opinions on the subject. Including reflection in the process provides opportunity for ongoing development, to recognize barriers to learning, and develop more effective lessons in the future.
- What worked well, and what didn't?
- In what areas did students require the greatest assistance?
- Were the pupils able to achieve their goals? Could they set their own goals?

Final Thoughts
A lesson plan is the instructor's road map for what students should learn and how they will learn it effectively throughout the class. You must first determine the instructional outcomes before you can design your lesson. Then you may create relevant learning activities and ways for getting feedback on student progress.
Good lesson preparation is critical to teaching and student learning. A well-prepared instructor increases the likelihood of a successful lesson for all learners. Creating relevant lessons takes time and commitment, but the end result can make a world of difference in a student’s education and life.

Staff Evaluation Software
Document every step of the staff evaluation process, including walk-throughs, self-evaluations, supporting evidence, reporting and performance analytics. Get Started →
More Great Content
We know you'll love

Essential Accommodations in Education To Empower Student Success

What Is Equity in Education? Strategies for Schools and Teachers in 2024

College Career Military Readiness (CCMR): Empowering Students for Future Success

Modification vs. Accommodation in Education: Fostering Equity and Inclusivity
Stay in the know.
Subscribe to our newsletter today!
What is a Lesson Plan?: A Teacher’s Guide for Impactful Lesson Plans!
- July 23, 2024
Table of Content
A lesson plan is more than just a checklist – it’s a dynamic blueprint that guides teachers to create engaging and effective learning experiences. Think of it as a carefully crafted roadmap that navigates students through different stages of learning a subject or topic. A lesson plan is an essential tool that outlines clear learning goals, selects appropriate activities, and ensures student understanding is measured effectively.
A well-structured lesson plan is the cornerstone of successful teaching. It provides a clear framework for teachers, ensuring that every class period is purposeful and aligned with broader learning objectives. By carefully considering student needs and learning styles, educators can create lessons that are both stimulating and informative. Moreover, a thoughtfully designed lesson plan helps teachers manage their time efficiently, allowing for smooth transitions between activities and maximizing instructional time. Ultimately, a lesson plan serves as a valuable tool for reflection and improvement, enabling teachers to refine their practice over time.
Let’s get into understanding what is a lesson plan, why is it important and uncover how to create impactful lessons!
What is a Lesson Plan?
A lesson plan is a teacher’s blueprint for a class. It outlines what students will learn, how they will learn it, and how their learning will be assessed. Its purpose is to ensure organized and focused instruction, maximizing class time efficiency.
For instance, a math lesson plan on multiplication might detail objectives (students multiply single-digit numbers), activities (using manipulatives, solving problems), and assessment (a short quiz), thereby aligning teaching with learning goals and evaluating student understanding.
Digital Lesson Plans for Online Classes
Digital lesson plans are instructional blueprints designed specifically for online learning. They leverage technology to deliver content, engage students, and facilitate interaction. These plans are crucial for online educators as they provide a structured framework for virtual classrooms. By utilizing digital tools, teachers can create dynamic learning experiences, track student progress, and foster collaboration. Digital lesson plans ensure consistency, accessibility, and flexibility in online education, ultimately enhancing student outcomes.
Why are they important?
Digital lesson plans are essential for online educators because they –
- Structure the online classroom: They provide a clear framework for online sessions, ensuring smooth flow and coverage of learning objectives.
- Embrace technology: They leverage digital tools like multimedia content, online platforms, and interactive activities to create dynamic and engaging learning experiences.
- Facilitate interaction: Digital lesson plans can promote communication and collaboration between students and teachers, even in a virtual space.
Do you want to take your business online? Inquire by providing your contact number below and experts at Classplus will contact you to kickstart your business online!
Essential Components of a Good Lesson Plan
A lesson plan is a teacher’s daily guide for what students need to learn, how it will be taught, and how learning will be measured. Good Lesson plans for teachers must include specification of lectures, measurable content, assignments and homework, related requirements, and time bound learning goals. A good lesson plan reflects the capability of a great teacher, by the way he designs a lesson plan, as he should make it according to the needs and requirements of the student. The most effective lesson plans have the following six parts –
- Lesson Plan Objectives: These are the specific, measurable goals that students should achieve by the end of the lesson. What knowledge and skills will students gain from this lesson? Are the objectives clear and concise? Can students understand what they are expected to learn?
| |
When writing objectives, consider the following questions –
- Are the action verbs appropriate for the content (define, identify, calculate etc)?
- Are objectives tailored to the prior knowledge and skills of students?
- Will achieving the objectives advance students towards mastering the overall course/unit goals?
Know How to Define Learning Goals for Online Classes? in detail.
- Related Requirements These are any standards or benchmarks that the lesson plan needs to address. Are there specific learning objectives outlined by your school district or curriculum that this lesson plan needs to cover?
- Lesson Materials: This is a list of all of the materials that will be needed for the lesson, such as textbooks, handouts, manipulatives, technology, and any other resources. Are the materials engaging and appropriate for the age and learning level of the students? Do they align with the lesson objectives?
- Lesson Procedure: This is a step-by-step outline of how the lesson will be conducted. It should include time allotments for each activity. How will you introduce the new concept? What are the different activities that students will participate in? How will you check for understanding throughout the lesson?
- Assessment Method: This is how you will measure student learning to see if they have met the objectives of the lesson. Assessment can take many forms, such as quizzes, homework assignments, class discussions, observations, or exit tickets. How will you know if students have learned what you taught?
- Lesson Reflection: After the lesson is complete, it is important for teachers to take some time to reflect on how it went. What went well? What could have been improved? How will you adjust your lesson plan for future use?
Also read – Types of Lesson Plans
Why are Lesson Plans Important for Teachers?
Lesson Plans are like a blueprint for effective classes. As a teacher, you create lesson plans to identify what needs to be taught and how. It empowers teachers to make learning effective and engaging for students. A lesson plan is important for teachers for the following reasons –
1. To Guide the Teachers
Experience plays an important role in every field, so it is important for beginners to learn and educate and know the importance of lesson plans. New teachers will become more confident by practicing at home and then presenting it in front of the students. Lesson plans for teachers are really helpful as they can cover the whole lecture in that lesson with perfect timing and materials. Teachers can engage themselves in online teaching and practice making sample lesson plans for online teaching through online platforms.
One such online teaching application is Classplus, where a teacher can make their app on various subjects. For example, a language tutor can practice sample lesson plans for English teaching where he can establish a vocabulary and content for himself so that he can become more confident in it and later can teach students with complete control over that language.

2. To Make Teaching Systematic & Organized
Everything that is categorized and well organized is more effective than unorganized lessons and classes. How to plan lessons for new teachers is a big question as this is a very important step that will make them look out of the box. Learning skills are different for every student but observing every student is what a teacher is known for.
3. To Avoid Unnecessary Repetition of Content
The fact is that planning and managing the content helps teachers in the unnecessary repetition of content and delivering it to students in a better way. How to write a lesson plan? The answer to this question must include content related to the syllabus and beneficial information. Making a lesson plan is very laborious and hardworking, but by getting in touch with Classplus, one can make their lesson plans with ease and comfort as it helps you in making your app and selling your content.
4. To Boost Teacher’s Confidence
One of the most beneficial and key features of a lesson plan for a new teacher is to gain confidence. The importance of a lesson plan for a new teacher comes from well organized and structured lesson planning. This allows them to be confident and well-prepared before each lecture.
Not only for teachers, but a well-organized lesson plan is very helpful for students. Also, students by following a lesson plan can build a routine that will help them grow and manage their time in which they can take their time to enjoy and work on their health too. By setting the format and template of the lesson, teachers can improve teaching skills as well as communication in the online classroom, while students can learn and practice time management and language skills indeed.
Find out Top 5 Lesson Planning Resources for Teachers to enhance your lesson plans.
How to Write a Lesson Plan in 7 Steps?
A well-crafted lesson plan is a teacher’s roadmap to effective instruction. It is a detailed blueprint outlining learning objectives, teaching strategies, and assessment methods. By following a structured approach, educators can create engaging and purposeful lessons that cater to diverse learners and maximize classroom time.
Let’s find out the seven essential steps to make a winning lesson plan below –
Step 1 – Determine Learning Objectives
Clearly articulate what students should know, understand, or be able to do by the end of the lesson. These objectives should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART).
Step 2 – Plan Activities
Select a variety of activities that align with your learning objectives and cater to different learning styles. Incorporate hands-on experiences, group work, and technology to enhance student engagement. Choose activities that actively engage students. Think beyond lectures! Incorporate a variety of instructional methods to cater to different learning styles. Consider the following –
- Hands-on activities: Simulations, experiments, projects (e.g., building a model of the solar system)
- Group work: Collaborative problem-solving fosters communication and reinforces concepts.
- Technology integration: Use interactive websites, simulations, or educational games.
- Discussions and debates: Encourage critical thinking and deeper understanding.
Step 3 – Gather Learning Materials
List all the resources you’ll need to bring your activities to life. This includes –
- Textbooks, handouts, worksheets tailored to the lesson’s focus.
- Manipulatives, physical objects, or technology tools to support activities (e.g., globes, models, online simulations).
- Visuals like charts, diagrams, images to enhance understanding.
Double-check! Ensure materials are readily available and appropriate for the age and abilities of your students.
Also read – Types of Teaching Aids & Their Importance
Step 4 – Create a Detailed Lesson Procedure on Paper
Outline the sequence of instructional activities, including estimated time for each. Clearly describe how you will introduce the topic, present new information, guide practice, and provide opportunities for independent work. Writing out your lesson plan on paper will help you visualize any gaps or improvements. Also, do not forget to plan smooth transitions between activities to avoid time wastage and maintain focus.
Step 5 – Organize Lesson Plan for Presentation
Your lesson plan will need constant refining and reviewing based on the students’ response and understanding of the lessons. Therefore, as a next step in making lesson plans, be sure to organize each lesson plan in a binder or folder to avoid loose papers, clutter and confusion. Design your lesson plan according to lecture timelines, so you only have to flip through one sheet after the next to refer to the lesson plan. Organizing lesson plans for presentation will also ensure that there is no repetition of content and will highlight any time delays or any modifications required for improved student outcomes.
Step 6 – Plan Assessment Strategies
How will you determine if students have achieved the learning objectives? An effective lesson plan needs to outline various types of evaluation methods that will determine how you will measure student learning and understanding. Choose appropriate assessment methods such as quizzes, projects, observations, or performance tasks. Align assessments with your learning objectives.
Integrate a variety of assessment methods for a holistic understanding. For example, Exit Tickets which are quick tasks or prompts to gauge student understanding at the end of a lesson. Provide timely and constructive feedback to students to help them improve their learning.
Step 7 – Assign Homework & Assess Progress
Reinforce learning beyond the classroom. For this, it is essential to assign homework that aligns with the lesson’s objectives and provides opportunities for practice. Assess student progress through homework assignments to get valuable insights into students’ understanding. This allows you to adjust your teaching strategies if needed. After teaching the lesson, take time to reflect on its effectiveness. What went well? What are the areas of improvement? Use this feedback to refine the lesson plan for future use.
Also read – Tips for Teachers to Create Effective Lessons
Let’s Sum It Up
To make lesson plans more interesting, teachers can make their app, can make sample lesson plans for online teaching , and further make a perfect lesson plan for students. Students will also enjoy the online lesson plans with digital visuals. There are a lot of platforms that helps teachers in getting their applications and provide plans to the students, and one such application is Classplus which helps teachers in making their app and selling their content and giving the teachers full credit for their efforts and hard work.
It is really important to practice in nets if you want to hit maximums on the match day, which means lesson plans are really important for new teachers as well as their students and online lesson plans are more preferred. Classplus helps you to create your custom app where you can teach anything online, from Digital Marketing and Yoga to Makeup, Cooking, Music, etc.
Lesson Plan for Teachers FAQs
A lesson plan is a document which teachers create to list the key components of a single class. It aims to be a guide for teachers to refer to for each lesson session.
The purpose of a lesson plan is to help teachers stay organized and on track during class. It helps ensure educational goals and standards are covered effectively and the class runs smoothly.
A good lesson plan is well-structured, includes all necessary elements like objectives, procedures and assessments, is tailored to student needs and provides clear instructions for the teacher or substitute.
Common elements included in most lesson plans are – objectives, materials required, motivation/opening, presentation of content, guided/independent practice, assessment and closure.
An effective lesson plan is concise yet detailed. It can range from 1-3 pages depending on the grade level and subject being taught. The key is to include all relevant details in a clear, organized manner using simple language.
[Classplus Official Demo] How to Teach Online+Offline Together?
Shivangi Bhatia
- Growth Tips From Experts
- Online Teaching
- 13 minute read
25 Best Education Influencers on Instagram in India Trending in 2024
- August 20, 2024
- 4 minute read
7 Tips To Make Digital Lesson Plan For Maths!
- July 24, 2024
- Online Classroom
- 10 minute read
Different Types of Lesson Plan & Ideas for Effective Lesson Planning!
- July 22, 2024
- Classroom Management
Barriers to Inclusive Education: Meaning, Types & Ways to Overcome!
- July 17, 2024
We use essential cookies to make Venngage work. By clicking “Accept All Cookies”, you agree to the storing of cookies on your device to enhance site navigation, analyze site usage, and assist in our marketing efforts.
Manage Cookies
Cookies and similar technologies collect certain information about how you’re using our website. Some of them are essential, and without them you wouldn’t be able to use Venngage. But others are optional, and you get to choose whether we use them or not.
Strictly Necessary Cookies
These cookies are always on, as they’re essential for making Venngage work, and making it safe. Without these cookies, services you’ve asked for can’t be provided.
Show cookie providers
- Google Login
Functionality Cookies
These cookies help us provide enhanced functionality and personalisation, and remember your settings. They may be set by us or by third party providers.
Performance Cookies
These cookies help us analyze how many people are using Venngage, where they come from and how they're using it. If you opt out of these cookies, we can’t get feedback to make Venngage better for you and all our users.
- Google Analytics
Targeting Cookies
These cookies are set by our advertising partners to track your activity and show you relevant Venngage ads on other sites as you browse the internet.
- Google Tag Manager
- Infographics
- Daily Infographics
- Popular Templates
- Accessibility
- Graphic Design
- Graphs and Charts
- Data Visualization
- Human Resources
- Beginner Guides
Blog Education 27+ Easy-to-Edit Lesson Plan Examples [+ Writing Tips]
27+ Easy-to-Edit Lesson Plan Examples [+ Writing Tips]
Written by: Alice Corner Dec 07, 2023

Lesson plans are the best way to deliver an effective and engaging lesson. Lesson plans also help keep you on track to ensure that your learners hit their goals and targets, in line with your course curriculum.
But sometimes in the high-pressure world of education, it can be difficult to find the time to create inspiring lesson plans on your own. This is the time to enlist the help of a lesson plan maker and lesson plan templates .
I’ve gathered together 28 of the best lesson plan examples for all grade levels that you can use to ensure your lessons are insightful and inspiring.
Click to jump ahead :
What is a lesson plan?
- What are lesson plan sections
How to write a lesson plan?
English lesson plan examples, history lesson plan examples, middle school lesson plan examples, kindergarten lesson plan examples, high school lesson plan examples, preschool lesson plan examples, math lesson plan examples, elementary lesson plan examples, art lesson plan examples.
- Science lesson plan examples
Simple lesson plan examples
Elearning lesson plan examples.
- Simple lesson plan format
How to present the lesson plan
A lesson plan is a document that outlines the content of your lesson step-by-step. It’s a list of tasks that your students will undertake, to help guide your teaching.
Lesson plans are usually printed or saved as PDFs for teachers to use. You can make your own with a lesson plan template .

What are lesson plan sections?
Lesson plans primarily include a schedule of activities that you will deliver in the lesson. Some lesson plans also include additional sections for more thorough planning.
A general format of a lesson plan can be like this :
- Lesson activities
- Lesson materials
- Lesson objectives
- Lesson goals
- Lesson feedback
1. Objectives: know your destination
When writing a lesson plan, start by outlining the learning objectives—what you want your students to take from the session and work backward. Having clear and specific goals helps you plan activities for a successful lesson.
2. Welcome to the hook: make ’em want to learn
Start with an engaging “hook” to capture your students’ attention and make them eager to learn more. This could be a thought-provoking question, an interesting fact, or a surprising tidbit.
Apply a top-down method: plan on a course level the lessons you’re going to include and then go deeper and think about the activities you would like to include in each lesson.
3. Step-by-step: outlining the activities
Now that your students are hooked, it’s time to get down to business. Work on exercises or projects you would like your students to take on. These should serve two important purposes: allowing your students to apply the knowledge they learn in class and allowing you, the teacher, to assess students’ understanding of the materials.
This might include direct instruction (i.e., when you teach the material), guided practice (working together as a class), independent practice (students work on their own) and group activities. Think about the best way to engage students and make sure you include a variety of these activities besides just tests or exams, like quizzes, group discussions, group projects and so on.
Example: If your objective is teaching persuasive writing, your steps might look like this:
- Explanation of persuasive writing techniques and purpose
- Guided practice: analyzing persuasive texts as a class
- Independent practice: having students create a persuasive argument on a given topic
- Group activity: Debating the different arguments in teams
Remember the old adage: “Tell me, and I forget. Teach me, and I remember. Involve me, and I learn.”
4. Check for understanding: keep ’em on track
It’s not uncommon for students to zone out (we’ve all been there), so it’s crucial to regularly check if they’re on track. This means asking questions throughout the lesson and encouraging your students to reflect on the material.
Once you’ve got all these noted down, you can start arranging all the lessons and activities in a meaningful and logical order as well. This applies to the activities within a single lesson too. Answer these questions:
- How much time do you have for the whole lesson?
- What do you plan to start and end the lesson with?
- How much time do you have for each activity?
- If you still have time after all the activities are done, what are you planning to do?
- If you run out of time, what activities are you planning to drop?
As you plan your lesson, keep in mind that not all students learn at the same pace and in the same way. Tailor your activities and materials to accommodate different learning styles, skill levels and interests. This could mean offering choice in assignments, providing extra support for struggling learners, or challenging high-achievers with extended tasks.
Creating an English lesson plan is the best way to keep track of all the learning strands and activities that are needed for learning success.
Imagination, drama, romance and tragedy. English lessons have it all. But they can also be complicated to teach, with many moving parts to any one lesson.
Like you’ll see in the English lesson plan examples below, creating engaging activities to a strict time schedule is perfectly possible with enough planning.
Use your lesson plan to schedule each activity by the minute
Any teacher will know the feeling of reaching the end of your material with 10 minutes left in the lesson.
Avoid running short (or running over!) in your lessons by planning down to the minute. The English lesson plan example below measures out timings for each activity so you finish perfectly on time.
You can use a timer on your interactive whiteboard , or get students to time themselves. Scheduling is a great skill to incorporate into any lesson plan.

Creating a history lesson plan is essential for a successful session no matter if you’re teaching the near past or the ancient history.
Using common teaching resources such as timeline infographics , or imaginative play and learning are exciting ways to make your History lesson plans exciting.
Prepare for history lessons with a history timeline infographic
Teaching history effectively and engagingly relies on the teacher’s ability to bring the past back to life. For some students, mentally visualizing history can be difficult. A timeline infographic is a great way to teach historical events.
When planning your history lesson, make sure you have all of your timelines sorted. You can either prepare your history timelines in advance or get the students to create their own history timeline as part of the lesson activity.
Venngage has a whole range of timeline infographic templates that are easy to customize.

Want to learn more about how to create a timeline infographic ? Check out the video below:
Use themes and historical events to enrich your lesson planning
When planning your history lessons, look for topical themes or historical events that you can anchor your lesson plan around.
In the lesson plan example below, the teacher is using Black History Month as an anchor point for their students’ learning.

Teaching the historical significance of Black History Month and engaging students in related learning activities throughout February is a great way to contextualize current affairs. There are plenty of resources online to help create your Black History Month lesson plans.
Related Reading: Looking for other global holidays and events to theme your lessons on? Check this Ultimate List of Holidays .
When creating middle school lesson plans, like in the templates and examples below, it’s important to focus on success and simplicity.
Middle school is a time for make or break for many learners. Skills that they learn in middle school carry them through life and it can be a huge weight to carry. But teaching middle school can also be incredibly rewarding. Here are some tips to help you create an effective middle school lesson plan:
Make note of what success looks like in your lesson plan
In teaching, quite often the end goal is not for the students to just arrive at the correct answer, but to understand the process of getting there. Having this mentality in your mind whilst lesson planning is an excellent way to ensure your students are learning effectively and that you are maximizing your teaching impact.
Add a section to your lesson plans as to what success looks like for you and your students like in the Middle School lesson plan template:

Color code your lesson plan for ease of use
Colors can be a great differentiator in content and color-coding your lesson plans is a great way to make information pop. In this lesson plan example, each day has a different color which makes planning and evaluating much easier.

Related Reading: What Disney Villains Can Tell Us About Color Psychology
Creating a kindergarten lesson plan involves similar principles to those used for preschoolers but with a bit more structure and focus on foundational academic skills.
We all know that meme “teaching kindergarten is like using a blender without a lid”. Staying organized is super important and having thorough easy-to-follow kindergarten lesson plans is one way to make sure your teaching stays on track.
Use themes to help plan your Kindergarten lessons
Help your kindergarteners embrace learning by using themes to plan their education. Themes are a great way to work through lots of different learning activities under one thematic umbrella.
This kindergarten lesson plan example uses St Patrick’s Day as its thematic anchor and bases Math, Art, Science and more off of one common theme.
Make your lesson plans easy to skim
We’ve all been in a spot when our mind goes blank and we need to quickly refer back to our lesson plan. Especially if you’re interviewing or teaching in front of others.
By making your lesson plans easy to skim, you can quickly regain your train of thought and continue conducting a successful lesson.
In the sample lesson plan below the teacher has used simple blocks, checklists and icons to help ensure their lesson plan is easy to understand at a glance.

Creating a high school lesson plan involves a more structured approach, as students at this level are typically engaged in more advanced academic subjects.
Ensuring that your High School lesson plans account for success and reinforcing skills is one way to deliver the best education for your learners.
Include indicators of skill in your high school lesson plans
In high school, lesson plans tend to be more advanced. In the high school lesson plan example below, the teacher has included a section for indicators of skill.
Indicators of skill are a great way to measure your students’ understanding of a topic and can be used to help inform your planning and teaching. Add two or three skill indicators into your lesson plans to ensure you know how to identify which students may need additional support from you in teaching.

You can also scroll back to the Math lesson plans section for more ideas on high school lesson plan templates.
Remember how I mentioned you should include timelines in your lesson plan? Well, for a high school lesson plan, you can include a timeline template like this one to make sure your students understand all the dates required for their school project:

Creating a preschool lesson plan involves careful consideration of the developmental needs and interests of young children. Shaping young minds is a rewarding experience, but it can sometimes feel like juggling too many balls at once.
With so many different essential key skills to teach, using a thorough Preschool lesson plan is important for making sure that your learners progress stays on track.
Break your Preschool lesson plans into learning sections
Preschool curriculums can be complex, covering multiple areas of crucial childhood development.
Help visualize each of these areas in their own right by creating a preschool lesson plan that takes a broad overview.
By breaking your lesson plan into learning sections, like this Preschool lesson plan example, you can get a glance at all elements of your students learning at once.
Get an overview of your week with a weekly lesson plan
A weekly lesson plan works great for preschool education planning, as it helps you identify and build lessons around common themes or goals. In the lesson plan template below, weeks have been broken down into different areas of focus.

Use icons in your Preschool lesson plan
Using icons is a great way to communicate visually. Icons are easy to understand, especially when you’re skimming a document.
Take this lesson plan template for example, not only do the icons help communicate the lesson themes, they also make the lesson plan example super engaging and fun.
Using icons can also be a great way to help students who struggle with non-visual learning. For more ways to improve your lesson accessibility, check out this guide to creating a Color Blind Friendly Palette .
Creating a math lesson plan involves careful planning and consideration of various elements to ensure effective teaching and learning. Check out these lesson plan ideas for math tutors for writing the best math lesson plan, as well as some templates you can edit.
Use pops of color in your lesson plans
Just because your lesson plan tackles a complex subject doesn’t mean it has to be boring. In this lesson plan example a mint green color has been used to help break up the design. You could color code different subjects or units if you have multiple classes to teach.

Break your lesson plan into sections to make it easy to follow
Being properly prepared for any eventuality in your lesson starts with good planning. By using sections, like in the lesson plan example below, you can cover all of your bases.
When lesson planning, consider the following:
- Lesson discussion questions
- Activity options for multiple group sizes
- Lesson notes or feedback
In this math lesson plan activity, the teacher has thought through all of the needs of their class.

Think outside the box when lesson planning
When lesson planning, the world, or at least the internet, is your Oyster. Instead of just teaching vocabulary, use scavenger hunts, word searches, or story activities.
Try picking a new activity and building your lesson around that. In the lesson activity example below, Merriam-Webster has a dictionary scavenger hunt that will keep students engaged and entertained throughout your English lesson.

Highlight your lesson objectives at the top of your lesson plan
Your learning objectives should guide your lesson planning, not the other way around.
In this sample lesson plan that focuses on analyzing a film for an English class, the learning objectives are housed within the same section as the lesson plan overview, right on the first page:

If you want to learn how to write an actional learning objective , check out this post on learning objective examples .
When creating Elementary school lesson plans, you need to make sure that you’re keeping a good overview of many different subjects at once.
Having a clear, easy to understand Elementary lesson plan, like in the examples below, is really important for making sure that all your learning objectives are being met.
Break your elementary lesson plans into day and subject sections
Elementary students will often be studying various topics and subjects at once and keeping an overview of this can be difficult. By creating a weekly lesson plan you can make sure that your students stay on track.
In this lesson plan template, subjects and activity have been split across the days, with simple summaries of each section within the lesson plan.

Include notes sections in your lesson plans
Planning a lesson is important, but reflecting on a lesson is essential. Adding notes sections to your lesson plans, like in this weekly lesson plan example, is a great way to remind yourself to evaluate as you go.
Evaluating yourself and your lessons can be a daunting task. Applying various evaluation strategies, such as a SWOT Analysis , is an easy way to give your evaluations focus.
When creating art lesson plans, use bright colors, patterns, icons and graphics to create a truly engaging visual art lesson plan, like in the examples below.
Art lessons lend themselves to creative and visual learning , so your Art lesson plans should be creative and visual as well.
Incorporate learning examples in your art lesson plans
Art lesson plans can be one of the most fun to create. Art as a visual medium lends itself to an exciting and decorative lesson plan.
In the art lesson plan example below, the teacher has inserted visual examples to use during the lesson directly into their lesson plan. Collecting all of this information in one place means that you can quickly refer back to your lesson plan mid teaching.

Be creative with your art lesson plan design
If you’re creating an art course, you’re probably a creative person. Why not let that creativity shine in your lesson plan templates?
Fun illustrations and patterns have been used in the lesson plan sample below to create a visually appealing lesson plan design.

When picking colors for your lesson plan design, some schools will need to be aware of color connotations. Certain colors should be avoided due to gang or rivalry associations. Some schools will also want to ensure that all materials produced fit within your school colors.
Use colors and patterns in your art lesson plan designs
As well as colors, patterns can be used, like in this art lesson plan example, to create interest in your lesson plan design.
Picking a patterned but simple background is an easy way to add depth to any lesson plan design.

Science l esson plan examples
Planning a science lesson can mean anything from experiments to monitoring or diagramming and labelling.
Following a template, like in the science lesson plan examples below, can help make sure that your science lessons run smoothly.
Provide a space for reflection in your science lesson plan
Whilst a lesson plan is a place to schedule your activities, it can also be a great document to refer back to when planning future sessions. Adding a reflection section in your science lesson plan can be a great way to add notes about what worked and what didn’t within your lesson, for future reference.

Break projects down into sections of deliverables
If you’re conducting a difficult lesson, such as a hands-on science project, it can be handy to help yourself and your students by outlining expectations. A checklist can be a great way to make your science lesson plan as effective as possible.
In this lesson plan example, the deliverables have been broken into easy-to-follow checklists.

Use illustrations to bring your lesson plan templates to life
Your lesson plans should inspire you, not bore you! Using illustrations is a great way to bring your lesson plans to life.
In this sample lesson plan, the teacher has used colorful and playful illustrations to reflect the content of the lessons.

Creating simple lesson plans involves breaking down the content into manageable components and incorporating straightforward activities.
Sometimes simple is best—especially when it comes to lesson planning. When you’re panicked mid-teaching, having a simple and straightforward lesson plan that you can take a quick glance at it can be invaluable.
Keep your lesson plan simple for stressful situations
When performing under pressure, staying simple is usually the best option. Using a clean and modern lesson plan design is one way to ensure that you can stay focused on what matters: teaching.
Simple doesn’t have to mean boring, though. Using good design principles and following one or two graphic design trends means that your simple lesson plan template can still look smart.

Use an icon to help differentiate different subject lesson plans
Icons are an easy way to differentiate your lesson plans by subject or topic. In the lesson plan example below, a large book icon has been used at the top of the page so that you can quickly see that this is an English lesson plan.
You could use an icon for each subject you teach, or use icons to tell a story . You could even replace the icon with a photo of your lesson materials!

Use an action plan approach in your lesson planning
In the simple lesson plan example, the tasks in the lesson plan have been labeled as an “action plan” . By keeping the lesson plan design simple, the focus is really on the content of the lesson plan.
Creating an action plan when teaching your lessons is a great mindset for creating engaging lessons and proactive teaching.

When creating eLearning , distance learning, remote learning, digital learning lesson plans—basically, anything outside the usual classroom setup—always be ready for its own set of unique challenges.
Engaging learners from behind a screen, or creating lessons that can exist outside of a traditional classroom environment can be difficult. But proper eLearning lesson plans can help you navigate non-traditional learning environments.
Break your eLearning lesson plan into activities or subjects
With so many people shifting to remote or digital learning keeping track of all of your separate subjects can be difficult. Creating an eLearning lesson plan that is broken into smaller chunks, with space for each topic, is an easy way to keep learning on track.
In this eLearning lesson plan example subjects are color coded and broken into small blocks.

For more examples of eLearning lesson plans, check out this post on course design templates .
Looking for more eLearning resources?
- 7 Ways to use eLearning Infographics
- Digital Learning Communication Resources
- What is an Infographic?
- 10 Types of Visual Aids for Learning
Use a daily schedule when learning remotely
Learning remotely can be a big change for both teachers and students. One way to keep your learning on track is with an easy-to-follow daily schedule. Using a daily schedule as a lesson plan, like in the example below, is one way to maintain a routine during difficult times.

As well as scheduling within your lesson plan, you can also create a calendar to help keep your students on track.
Allow time for creativity and fun in your lesson plans
One of the biggest benefits of eLearning, Remote Learning and Digital Learning is that you can stray from the confines of a traditional classroom.
Giving students the opportunity to explore topics creatively can be one way to engage your learners in difficult times. Every student will have a different learning style and by scheduling structured creative learning activities you can ensure that your entire class has the opportunity to thrive.
Simple lesson plan format you can use
Though there are a several lesson plan types and no one format can be used for all lessons, the basic lesson format is always a good starting point.
This format covers the basics of teaching – say a little bit, do a little bit . The important part here is to provide input in a way that enables learners to see the structure and sequence.
You should format it this way:
- Lesson purpose: What you want students to learn or know about?
- Input : Specific information you want students to know.
- Activity : Used to get students to manipulate information from input.
Informing students on what they’ll be learning or doing keeps them more engaged and on track. So, it’s always a good idea to share your lesson plan by writing a brief agenda on the board or telling students explicitly what they will be learning and doing in class.
By doing this, you help students not only retain knowledge better but understand the rationale behind in-class activities.
To sum up: Use a lesson plan template to write an actionable and easy-to-follow lesson plan
Writing a lesson plan from scratch can be difficult, which is why Venngage has created tons of lesson plan templates you can edit easily. You can also draw inspiration from the different lesson plan examples in this post to customize your lesson plan template.
Simply create a Venngage account, pick the template you want and begin editing. It’s free to get started.
Discover popular designs

Infographic maker

Brochure maker

White paper online

Newsletter creator

Flyer maker

Timeline maker

Letterhead maker

Mind map maker

Ebook maker
Top 10 Teacher Lesson Plan presentation templates

Having a Teacher Lesson Plan template is crucial for educators as it provides a structured and organized approach to delivering lessons. Teachers, tutors, and instructors across various educational levels and subjects benefit from using these templates. Utilizing a presentation template, like the examples below, streamlines the process of creating visually appealing and engaging content, allowing educators to focus on the quality of their instruction and save valuable time.
What makes a good Teacher Lesson Plan?
- Clear objectives: Clearly outline the goals and learning outcomes for the lesson, ensuring that students understand what they are expected to achieve by the end of the session.
- Engaging visuals: Incorporate relevant images, graphics, and multimedia elements to capture students' attention and enhance their understanding of the subject matter.
- Logical structure: Organize the content in a coherent and easy-to-follow manner, breaking down complex topics into smaller, manageable sections for better comprehension.
- Interactive activities: Include opportunities for students to actively participate in the learning process through group discussions, hands-on exercises, or problem-solving tasks.
- Assessment methods: Provide a variety of assessment tools, such as quizzes, assignments, or projects, to evaluate students' progress and understanding of the lesson content.
1. Tome's Teacher Lesson Plan Template

Easily organize and execute educational lessons with the Tome's Teacher Lesson Plan Template , perfect for educators aiming to structure their sessions effectively. This template is ideal when preparing detailed lesson plans that align with course objectives, facilitating student engagement and learning.
- Slides: Guides for lesson structuring, engaging questions, and student involvement.
- Format: Available online via Tome app, exportable in PDF or PowerPoint format.
- Pricing: Free to use on the Tome.app.
2. Space Illustrative Lesson Plan for High School PowerPoint and Google Slides Template

The Space Illustrative Lesson Plan for High School Template captures the vastness of space in an educational format, perfect for high school and college astronomy units. Use it when the lesson's aim is to explore celestial phenomena and foster scientific curiosity.
- Slides: Engaging and themed visuals to complement space-related lessons.
- Format: Available in PowerPoint and Google Slides formats.
- Pricing: Free to download.
3. STEM Elective Subject for Middle School - 7th Grade: Principles of IT, Cybersecurity and Engineering Template

STEM Elective Subject for Middle School Template is ideal for introducing students to the basics of IT, cybersecurity, and engineering, best used in middle school STEM curricula.
- Slides: Includes 3D illustrations and various educational resources.
- Format: Available in Google Slides format.
4. Global Education PowerPoint Template Template

Global Education PowerPoint Template is suited for presenting global educational concepts and multicultural learning experiences, great for broadening students' worldviews.
- Slides: Features vibrant colors and interactive design elements.
- Format: Compatible with PowerPoint.
- Pricing: Specific pricing information is not publicly available. Users may buy the template through a subscription at SlideModel.
5. Kimok Science Doodles Style Lesson Template - Daily Learning: STEM Infographics

Kimok Science Doodles Style Lesson Template makes science subjects approachable and fun, ideal for daily STEM lessons that encourage interactive learning and creativity.
- Slides: Doodle-style graphics and STEM-focused infographics.
6. 1-Slide Lesson Plan PowerPoint Template

The 1-Slide Lesson Plan PowerPoint Template simplifies the educational planning process, ideal for teachers needing a quick overview of daily or weekly educational objectives.
- Slides: A single slide for a concise lesson summary.
- Format: Available in PowerPoint format.
7. Math lesson PowerPoint and Google Slides Template

Math Lesson PowerPoint and Google Slides Template offers a vibrant and engaging approach to math lessons, perfect for educators looking to make math fun and accessible for students.
- Slides: Colorful and math-themed design to enhance learning.
- Format: Available in both PowerPoint and Google Slides formats.
8. Lesson Roadmap Presentation Template

Lesson Roadmap Presentation Template is great for outlining the journey of a lesson or unit, helping educators plan and communicate the path of learning effectively.
- Slides: Customizable for different educational needs.
- Format: Available for Google Slides, PowerPoint, and Canva.
9. Biology Subject for High School: Stem Cells Presentation Template

Biology Subject for High School: Stem Cells Presentation Template is designed for high school biology lessons, especially effective for topics on stem cells and advanced biological concepts.
- Slides: Rich in scientific illustrations and content.
10. Simple 5-Step Timeline Concept for PowerPoint Template

The Simple 5-Step Timeline Concept for PowerPoint Template is perfect for educators and professionals needing to outline processes or timelines clearly and concisely.
- Slides: Features a straightforward 5-step timeline design.
Create the best presentations with Tome!
As an educator, you're always looking for ways to create engaging and interactive lesson plans that capture your students' attention. With Tome , you can effortlessly craft polished presentations that not only look great on any screen but also incorporate AI tools to help you express your ideas quickly and effectively. Our platform is designed to assist you in developing structured starting points for compelling presentations, integrating web references, and ensuring your finished output is both captivating and clear.
Whether you're teaching a science class or a history lesson, Tome's versatility allows you to create immersive and interactive experiences for your students. By transforming your existing documents into polished presentations, you can elevate your lesson plans and make learning more enjoyable for your students.
Ready to see how Tome can enhance your lesson plans? Sign up for free and start shaping your ideas with Tome today.

Flirtify is an AI-powered tool designed to generate pickup lines based on user-provided information about a person they're interested in.

In this article, we will share the main uses of Playground AI, its pricing, reviews, and some alternatives to it.

In this article, we will share the main uses of Poe AI, its pricing, reviews, and some alternatives to it.

In this article, we will share the main uses of ElevenLabs.io, its pricing, reviews, and some alternatives to it.

In this article, we will share the main uses of Namelix, its pricing, reviews, and some alternatives to it.

In this article, we will share the main uses of Runway AI, its pricing, reviews, and some alternatives to it.
Here's What You Need to Know About Lesson Plans
The best teachers use a simple, seven-step format.
Janelle Cox
- Assessments & Tests
- Becoming A Teacher
- Elementary Education
- Secondary Education
- Special Education
- Homeschooling
- M.S., Education, Buffalo State College
- B.S., Education, Buffalo State College
A lesson plan is a detailed step-by-step guide that outlines the teacher's objectives for what the students will accomplish during the course of the lesson and how they will learn it. Creating a lesson plan involves setting goals , developing activities, and determining the materials that you will use.
All good lesson plans contain specific components or steps, and all essentially derive from the seven-step method developed by Madeline Hunter , a UCLA professor and education author. The Hunter Method , as it came to be called, includes these elements: objective/purpose, anticipatory set, input modeling/modeled practice, check for understanding, guided practice, independent practice, and closure.
Regardless of the grade level you teach, Hunter's model has been adopted and used in various forms for decades by teachers across the nation and at every grade level. Follow the steps in this method, and you'll have a classic lesson plan that will be effective at any grade level. It doesn't have to be a rigid formula; consider it a general guideline that will help any teacher cover the necessary parts of a successful lesson.
Objective/Purpose
Students learn best when they know what they are expected learn and why, says the U.S. Department of Education . The agency uses an eight-step version of Hunter's lesson plan, and its detailed explanations are well worth reading. The agency notes:
"The purpose or objective of the lesson includes why students need to learn the objective, what they will be able to do once they have met the criterion, (and) how they will demonstrate learning....The formula for the behavioral objective is: The learner will do what + with what + how well."
For example, a high school history lesson might focus on first-century Rome , so the teacher would explain to students that they are expected to learn the salient facts about the empire's government, its population, daily life, and culture.
Anticipatory Set
The anticipatory set involves the teacher working to get students excited about the upcoming lesson. For that reason, some lesson plan formats actually put this step first. Creating an anticipatory set "means doing something that creates a sense of anticipation and expectancy in the students," says Leslie Owen Wilson, Ed.D. in " The Second Principle ." This can include an activity, a game, a focused discussion, viewing a film or video clip, a field trip, or reflective exercise.
For example, for a second-grade lesson on animals, the class might take a field trip to a local zoo or watch a nature video. By contrast, in a high school class getting ready to study William Shakespeare 's play, " Romeo and Juliet ," students might write a short, reflective essay on a love they lost, such as a former boyfriend or girlfriend.
Input Modeling/Modeled Practice
This step—sometimes called direct instruction — takes place when the educator actually teaches the lesson. In a high school algebra class, for example, you might write an appropriate math problem on the board, and then show how to solve the problem in a relaxed, leisurely pace. If it's a first-grade lesson on important sight words to know, you might write the words on the board and explain what each word means. This step should be very visual, as the DOE explains:
"It is important for the students to 'see' what they are learning. It helps them when the teacher demonstrates what is to be learned."
Modeled practice, which some lesson plan templates list as a separate step, involves walking the students through a math problem or two as a class. You might write a problem on the board and then call on students to help you solve it, as they also write the problem, the steps to solve it, and then the answer. Similarly, you might have first-grade students copy the sight words as you spell each out verbally as a class.
Check for Understanding
You need to make sure students understand what you have taught. One easy way to do this is to ask questions. If you're teaching a lesson on simple geometry to seventh-graders, have students practice with the information you just taught, says the ASCD (formerly the Association for Supervision and Curriculum Development) . And, be sure to guide the learning. If students don't seem to grasp the concepts you've just taught, stop and review. For the seventh-graders learning geometry, you may need to repeat the previous step by showing more geometry problems—and how to solve them—on the board.
Guided and Independent Practice
If you're feeling like the lesson plan involves a lot of guidance, you're right. At the heart, that's what teachers do. Guided practice provides each student a chance to demonstrate her grasp of new learning by working through an activity or exercise under the teacher’s direct supervision. During this step, you might move around the room to determine your students' level of mastery and provide individual help as needed. You may need to pause to show students how to successfully work through problems if they are still struggling.
Independent practice , by contrast, can include homework or seatwork assignments, which you give to the students to complete successfully without the need for supervision or intervention.
In this important step, the teacher wraps things up. Think of this phase as a concluding section in an essay. Just as a writer wouldn't leave her readers dangling without a conclusion, so too, the teacher should review all key points of the lesson. Go over any areas where students might still be struggling. And, always, asked focused questions: If students can answer specific questions about the lesson, they likely have learned the material. If not, you may need to revisit the lesson tomorrow.
Tips and Hints
Always gather all needed supplies ahead of time, and have them ready and available at the front of the room. If you'll be conducting a high school math lesson and all students will need are their textbooks, lined paper, and calculators, that makes your job easier. Do have extra pencils, textbooks, calculators, and paper available, though, in case any students have forgotten these items.
If you're conducting a science experiment lesson, make sure you have all of the ingredients needed so that all students can complete the experiment. You don't want to give a science lesson on creating a volcano and find out once students are gathered and ready that you've forgotten a key ingredient like baking soda.
To ease your job in creating a lesson plan, use a template . The basic lesson plan format has been around for decades, so there's no need to start from scratch. Once you figure out what kind of lesson plan you will be writing, then you can determine the best way to use the format to fit your needs.
- Substitute Folders
- What Does a Great Lesson Look Like on the Outside?
- Emergency Lesson Plan Ideas
- Thanksgiving Acrostic Poem Lesson Plan
- Christmas Acrostic Poem Lesson Plan
- Valentines Day Acrostic Poem Lesson
- Memorial Day Lesson Plans and Quick Last-Minute Craft Ideas
- Mini-Lesson Plans: Template for Writers Workshop
- Map Skills Thematic Unit Plan for First Grade
- Easter Acrostic Poem Lesson Plan
- Cooperative Learning Sample Lesson
- Investigating Healthy Snacks Lesson Plan
- Elementary School Summer Session Activities by Subject
- Second Grade Map Project Ideas
- Thematic Unit Definition and How to Create One
- Plan Like a Pro: The Teacher’s Ultimate Guide to Lesson Planning »
Plan Like a Pro: The Teacher’s Ultimate Guide to Lesson Planning

Lesson plans are written outlines that education professionals use to map out their courses for students. These plans act as a guide for instructors, covering their teaching goals and the learning activities planned to achieve them. By following a lesson plan, students gain a clearer picture of the course structure and upcoming material.
This article will explain what lesson plans are, explore different types, offer tips for writing one, and break down the main elements of a strong lesson plan.
Quick Links
What is a Lesson Plan?
Think of a lesson plan as a teacher’s roadmap for a class session. As mentioned earlier, it outlines what students will learn (the goal) and how they’ll learn it (the activities). The plan also helps check how well students understood the material (through assignments or tests). It basically brings together the teacher’s goals for the students’ learning and the methods to achieve them. This involves deciding what to teach, why it’s important, and the best way to present it. Lesson plans typically include learning objectives, activities for students, and ways to assess their understanding. Every lesson plan is unique, depending on the topic and students’ needs.

Types of Lesson Plans
Here are five common ways to structure lesson plans:
Daily Lesson Plan
Weekly lesson plan, whole unit lesson plan, subject-specific lesson plan, grade-specific lesson plans, impact of lesson planning on students.
Lesson plans aren’t just helpful for teachers; they play an important role in student learning as well. Without a clear roadmap, a lesson can feel confusing and disorganised for students. Lesson plans benefit students in several ways:
Clear Learning Goals
A well-defined lesson plan helps students understand what they’ll be learning and how they’ll participate in the process. This mental preparation can improve their focus and engagement in activities and lectures.
Simplified Learning
Students often struggle with topics they find difficult. Lesson plans can help by breaking down complex concepts into smaller, more manageable pieces. Bullet points or timelines can make the information easier to understand and connect, creating a clear learning path for students.
Stronger Learning Outcomes
A well-designed lesson plan ensures clear explanations for each topic, catering to all students. Visual aids like videos, flowcharts, and presentations can be incorporated to enhance understanding for complex concepts, ultimately leading to improved learning outcomes .
Inclusive Learning Environment
Students have diverse learning styles . A well-structured lesson plan helps address these differences by incorporating a variety of teaching methods. This creates a more inclusive learning environment where each student has the opportunity to benefit from the education.
Personalised Learning
Lesson plans help teachers identify areas where students might need additional explanation or support. If a particular concept seems difficult for the class, the teacher can adjust the plan to address those challenges. This allows for a more personalised learning experience for each student.
Steps for Lesson Planning
Before class, identify learning objectives, plan learning activities, gather your learning materials, set up a realistic timeline.
Having a clear timeline is essential for a successful lesson. Here are some tips to ensure your timeline realistic:
Keep Your Work Organised
Plan an effective lesson wrap-up, benefits for instructors.
- Check for understanding : This allows you to adjust your teaching for the next lesson based on student needs.
- Emphasise Key Information : Briefly revisit important concepts to ensure they stick in students’ minds.
- Clear up Misunderstandings : Address any confusion students might have before moving on.
- Preview Upcoming Topics : Briefly introduce what students will learn next to create a smooth transition.
Benefits for Students
- Review and Demonstrate Understanding : Closure activities allow students to summarise what they learned, showcase their knowledge, and identify areas needing further clarification.
- Connect Ideas : Provides opportunities to connect lesson ideas to broader concepts and prior knowledge.
- Transfer Learning : Closure can help students see how they can apply their knowledge in new situations.
Strategies for Lesson Closure
Here are a few ways to effectively close your lesson:
- Summarise Important Points Yourself : Briefly recap the main ideas of the lesson.
- Student-led summary : Have a student volunteer to summarise the lesson.
- Written review : Have students write down the main points they learned.
During the Class
After the class (evaluate and reflect), enhance your teaching with extramarks.
Extramarks can be your ultimate tool for better teaching. We offer features to streamline your entire workflow, from planning to assessment.
Here’s how Extramarks can help:
Let’s transform your teaching journey together. Join us today!
Closing Thoughts
Lesson plans are more than just outlines; they’re powerful tools that benefit both educators and students. A well-structured lesson plan acts as a roadmap, guiding students through the learning process. This clarity helps to boost engagement and understanding, ultimately leading to better achievement. We explored various lesson plan formats, offered steps for crafting effective plans, and emphasised the importance of adapting them based on student needs. Remember, a well-designed lesson plan acts as a guide for successful learning. By taking this approach, educators can create engaging and effective lessons that empower students to learn.
Last Updated on August 22, 2024
About the author

Mrinai Gulhane
Mrinai is the Brand & Content Marketing Lead at Extramarks, driving strategies that enhance brand identity and build a connect with audiences. With over a decade of experience and passion for storytelling, Mrinai seamlessly combines brand vision with content expertise, using innovative approaches in content strategy, social media, and SEO to elevate brand presence and achieve marketing goals.
More Recent Blogs

Beyond Lectures: How Visual Learning Can Help Students...
Many students develop their own preferred methods for studying. Some rely on taking detailed notes, […]

Everything You Need to Know About Immersive Learning
As technology advances, the traditional approach of having a teacher or lecturer instruct a class […]

How Professional Development For Teachers Improves Learning Outcomes
This National Technology Day, let us reiterate the importance of professional development for teachers. In […]
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Found the blog insightful?
Get such ed tech insights delivered weekly to your inbox, for free. Subscribe to our newsletter.
- Teaching App
- Live Classes
- Learning App
- School Solutions
- STAR Program
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11
- Solved Board Paper CBSE
- Solved Board Paper ICSE
- CBSE Class 12
- CBSE Class 11
- CBSE Class 10
- ICSE Class 12
- Sample Paper CBSE
- Exam Weightage CBSE
- CBSE Class 12 Solution
- Terms of Use

- Instructional Guide
Lesson Plan: Presentation
Oral communication is a highly valuable skill that is becoming lost in a world of emails, texts, and tweets. There is a new generation of youngsters and young adults for whom speaking-discussion, or a group presentation is frightening. If it is true that “practice makes perfect,” then it is no wonder that students may find themselves dreading speaking in a formal setting, there are fewer and fewer opportunities to practice. Effective presentation skills foster student learning by establishing clear communication and helping students to engage in the learning process. While it might begin for a presentation, practicing public speaking will carry over to important life experiences and help students build self-confidence, poise, and learn to communicate effectively in a variety of settings.
The student will be able to select a topic, create a presentation that will provide information on that topic, and deliver the presentation to others in an interesting, informative and engaging way.
Objectives:
Academic Content:
(This will be provided in the curriculum of the section that you are teaching.)
- Select an appropriate topic.
- Narrow the topic so that it can be comfortably delivered in the allotted time.
- Create an outline of the important points to be covered.
- Create visual aids, when appropriate, to enhance the understanding of the topic.
- Present the information clearly.
- Check for understanding.
Presentation Skills:
- Identify the elements that will be used to deliver the information including, demonstration, visual aids, technology, etc.
- Identify a plan for connecting with the audience including the use of questions, anecdotes, humor, etc.
- Practice speaking clearly and loudly enough to be heard by everyone.
- Engage the audience with opportunities to interact and provide feedback.
- Consider a variety of elements of delivery including, making eye contact, speaking with enthusiasm and relating subject matter to life experiences.
Lesson Sequence:
A successful presentation begins with identifying an appropriate topic and carefully planning the content and delivery of the presentation.
- Select a topic. While it is possible to assign topics, students will be more engaged and enthusiastic about the presentation when they have had an opportunity to identify the topic they would like to present.
- Narrow the topic. Select the information that will be presented in order to effectively communicate the essential information in the time frame provided.
- Identify what listeners will learn from the content of this presentation.
- Create an outline for presenting the information. The outline should have enough detail that the ideas are clear but should consists of words and phrases that cannot be used as a script, but rather guide the explanation.
- Select and design appropriate supporting materials that most effectively enhance the topic.
- Practice the delivery of the presentation until a comfort level is established and delivery is smooth and relaxed.
- Build in opportunities to interact with the audience including time for comments, questions and feedback.
- Create a feedback form for the audience that will provide them with an opportunity to explain what they learned from the presentation. How does this compare with what was identified as intended learning?
A successful presentation is characterized by engaging the listeners in both the content and the delivery of the information. The audience should provide feedback in terms of what they learned from the presentation and suggestions for improvement.
With each presentation it is anticipated that the presenter will improve both content identification skills and delivery skills. This feedback can be reflected by teacher observation, audience participation, and self- reflection.
Assessment:
In presentation development, both content and process are considered. Students should demonstrate improvement in topic selection, identification of appropriate supporting details and visual aids, and organization of the introduction, body, and summary of the presentation. The process of delivery should improve in voice, clarity, tone, eye contact, and movement.
When considering the evaluation of presentation skills, it is as important to assess the presentation itself relative to the improvement of skills over time and with practice. Teacher input, student feedback, and self-reflection are key in developing a comfort level with oral communication skills.
Like what you're reading?
Creating engaging teacher presentations: tips, ideas, and tools
Get your team on prezi – watch this on demand video.
Anete Ezera August 21, 2024
Teacher presentations should effectively convey information, engage students, and enrich the learning process. While business presentations often focus on sales or data analysis, educational presentations aim to foster comprehension and spark curiosity. This article delves into the differences between teacher presentations and other presentation types, provides practical tips for educators, and shares design strategies for creating engaging teacher presentations. Additionally, we’ll highlight Prezi , a tool known for its format that offers a refreshing take on educational presentations.

Understanding teacher presentations
Purpose and audience.
The main objective of a teacher presentation is to educate. Whether the presentations are used to introduce new ideas, revisit old topics, or help students understand complex concepts, the main aim is to make the content easy to understand and interesting. In contrast, business presentations usually seek to convince or update stakeholders. A teacher presentation is tailored for the student audience. Ultimately, it should accommodate learning preferences, keep students engaged, and promote participation.
Design and structure
When preparing a teacher presentation, it’s crucial to maintain simplicity. Steer clear of overcrowding slides with information or incorporating flashy visuals that could divert attention from the main message. Opt for a balanced layout that leverages visuals to complement the delivery rather than overshadowing it. Using Prezi , with its non-linear format, empowers teachers to create compelling presentations that flow seamlessly and engage students effectively.
Tips for creating effective teacher presentations
1. know your audience.
Knowing the age, background knowledge, and learning preferences of your students is essential when creating a teacher presentation. Customize your material to suit their requirements, making sure it strikes a balance between being overly complicated and overly simplistic. When presenting to students, make sure to include plenty of visuals and interactive features, and focus on providing in-depth explanations and fostering discussions.
2. Focus on clarity and simplicity
Avoid cluttering your presentation with too much text or too many graphics. Use bullet points to break down information and keep the slides clean. Remember, presentation is a tool to support your teaching, not to replace your voice. The content on your slides should be clear, concise, and directly related to your lesson objectives.
3. Use engaging visuals and media
Using aids like pictures, videos, and diagrams can help improve comprehension and memory of information. Prezi enables you to design captivating presentations with zoom features that assist students in engagingly exploring the material. In contrast to slide decks, Prezi’s canvas offers a natural progression of content, simplifying the task of emphasizing relationships between ideas.
4. Encourage interaction
Incorporate interactive elements into your presentation to keep students engaged. Ask questions, use polls, or include discussion points that require student participation. Prezi’s format supports this by allowing teachers to zoom in on specific points for discussion, making the presentation feel more like a conversation than a lecture.
5. Rehearse and time your presentation
Practicing your presentation ensures that you can deliver it smoothly and confidently. Time your presentation to fit within the class period, leaving room for questions and discussions. A well-timed teacher presentation keeps students engaged and allows for a natural flow of information.
Things to keep in mind when creating a teacher presentation
When preparing a teacher presentation, it’s important to concentrate on developing a useful resource that improves student’s understanding. Here are some dos and don’ts to consider, especially when incorporating images and text, and designing the layout:
Teacher presentation dos:
Use high-quality visuals: Include clear, high-resolution images and graphics that support your lesson content. Visual aids can significantly improve understanding, especially for visual learners. Infographics, charts, and diagrams can be powerful tools to illustrate complex concepts.
Keep text minimal: When creating slides, opt for bullet points and concise phrases. Ensure that your slide content supports your spoken presentation rather than duplicating it. Also, highlight the points that students should keep in mind.
Incorporate multimedia: Use videos, audio clips, and animations where appropriate. These elements can help bring your lesson to life and maintain student interest. However, ensure that any multimedia used directly relates to and enhances the lesson.
Ensure consistent design: Maintain a consistent design throughout your presentation. Use the same font, color scheme, and layout style across all slides. Consistency helps create a professional look and makes the presentation easier to follow.
Use contrasting colors: Choose colors that contrast well, especially between text and background. This ensures that your content is easily readable, even from the back of the classroom. For example, dark text on a light background works well, as does light text on a dark background.

Teacher presentation don’ts:
Avoid overloading slides with information: Avoid overcrowding a slide with information. Too much content on one slide can be daunting for students, and it may distract from the key messages you intend to communicate. Strive for a clear design instead.
Don’t use distracting fonts or colors: Avoid using fonts or colors that clash. Opt for fonts and colors that improve visibility without taking attention from the content. Limit yourself to two or three fonts, and avoid using more than four colors in your presentation.
Don’t overuse animations or transitions: Avoid using too many animations or transitions when switching between slides. Although these elements can make the presentation engaging, excessive movement might become a distraction and take away from the educational material. It’s best to use them with intent.
Avoid irrelevant visuals: Avoid adding any pictures or illustrations that aren’t closely tied to the lesson. Even though visuals can improve a presentation, unrelated ones might perplex students and lessen the significance of your points.
Don’t neglect accessibility: Remember to take into account the learning requirements of students. Make sure your presentation is easy for all students to access by using clear fonts, including text for images, and providing transcripts for any video or audio materials.
By following these guidelines, you can create a teacher presentation that not only looks good but also effectively conveys your lesson material. Keep in mind that the aim is to leverage visuals and design features to enrich learning rather than detract from the information.
Exploring teacher presentation tools: spotlight on Prezi
When it comes to creating captivating teacher presentations, selecting the right tool is key. Although PowerPoint and Google Slides are commonly used, Prezi presents an option that can revolutionize the way educators deliver information.
What makes Prezi stand out?
Prezi’s unique presentation style allows educators to deliver information in a more captivating manner. Rather than following a slide progression, Prezi empowers teachers to explore various aspects of their presentations by zooming in and out, creating a storytelling experience rather than a traditional lecture. This method can engage students effectively and simplify subjects by visually emphasizing the relationships among concepts.

According to research from Prezi, this format is more engaging and memorable compared to traditional slide-based presentations. The study found that Prezi presentations are 25% more effective in keeping audience attention and 20% more effective in making content memorable.
Examples of engaging teacher presentations using Prezi
To illustrate how Prezi can be used effectively in the classroom, here are a few teacher presentation ideas that stand out:
Literacy Genres Prezi Video : This presentation gives a look at types of literary genres using Prezi’s zoom function to delve into each genre extensively. It serves as a method to familiarize students with ideas in an interactive and visually captivating way.
Board Game Lesson Plan Template : This template uses the concept of a board game to structure the lesson, making learning feel like an adventure. It’s perfect for gamifying lessons and keeping students excited about the material.
The Civil Rights Movement VOR : This presentation explores the background of the Civil Rights Movement, showcasing Prezi features to zoom in on events and individuals. It illustrates how Prezi can animate narratives effectively.
Back to School Template VOR : Ideal for the first day of school, this presentation helps teachers introduce themselves and outline class expectations in a fun and engaging way. It’s a great alternative to a traditional teacher introduction PowerPoint.
Light Book Report Template VOR : This is a creative template that inspires students to showcase their book reports, encouraging them to analyze and share their opinions thoughtfully.
For more inspiration, teachers can explore the Prezi Gallery’s Teacher Picks , which offers a variety of templates and examples designed specifically for educational purposes.
Additional teacher presentation ideas
Teacher introduction presentation.
At the start of the year, teachers have a chance to introduce themselves to their students. Using platforms like Prezi, educators can create a narrative that showcases their personality, teaching style, and what learners can expect in the course. Incorporating anecdotes and engaging elements helps in building a rapport with students from the beginning.
Interactive lesson recaps
To enrich learning, think about using Prezi for making summaries of lessons. When wrapping up a unit or lesson, a recap presentation can go over aspects, pose queries, and even incorporate a quiz to improve comprehension. This method strengthens the content and maintains student interest and active participation in their educational journey.
Virtual field trips
The increasing use of tools in education has made virtual field trips more popular as a means to explore the world without leaving the classroom. Teachers can now create tours using platforms such as Prezi, giving students a look at different locations and providing them with an engaging learning experience that improves their knowledge of geography, history, and science subjects.

Try Prezi for your next teacher presentation
In summary, preparing a teacher presentation entails capturing the needs of your audience, emphasizing clarity, promoting interaction, and sharpening your delivery skills. Through platforms such as Prezi, educators can enhance their presentations to captivate students with engaging content. Whether you’re introducing yourself at the beginning of the year, revisiting topics, or guiding students through a virtual excursion, a thoughtfully prepared presentation can enrich the learning experience and leave a lasting impact on your teaching.

Give your team the tools they need to engage
Like what you’re reading join the mailing list..
- Prezi for Teams
- Top Presentations
- International
- Education Jobs
- Schools directory
- Resources Education Jobs Schools directory News Search

Describing Clothes (Celebrities) (Vocabulary-Listening-Speaking) PPT Lesson
Subject: English
Age range: 11-14
Resource type: Lesson (complete)
Last updated
17 August 2024
- Share through email
- Share through twitter
- Share through linkedin
- Share through facebook
- Share through pinterest

In this lesson, students can expand their vocabulary on clothing and fashion and enhance their understanding through engaging speaking and listening activities.
Vocabulary in this lesson: Sparkly - Lacy - Cotton - Baggy - Leather - Furry - Gold/Golden.
Remember: You can add more vocabulary if you think it’s necessary.
Tes paid licence How can I reuse this?
Your rating is required to reflect your happiness.
It's good to leave some feedback.
Something went wrong, please try again later.
This resource hasn't been reviewed yet
To ensure quality for our reviews, only customers who have purchased this resource can review it
Report this resource to let us know if it violates our terms and conditions. Our customer service team will review your report and will be in touch.
Not quite what you were looking for? Search by keyword to find the right resource:
- Work & Careers
- Life & Arts
How this Yimby was taught a lesson
To read this article for free, register for ft edit now.
Once registered, you can: • Read this article and many more, free for 30 days with no card details required • Enjoy 8 thought-provoking articles a day chosen for you by senior editors • Download the award-winning FT Edit app to access audio, saved articles and more
Explore more offers.
Then $75 per month. Complete digital access to quality FT journalism. Cancel anytime during your trial.
Standard Digital
Essential digital access to quality FT journalism on any device. Pay a year upfront and save 20%.
- Global news & analysis
- Expert opinion
- FT App on Android & iOS
- FT Edit app
- FirstFT: the day's biggest stories
- 20+ curated newsletters
- Follow topics & set alerts with myFT
- FT Videos & Podcasts
Premium Digital
Complete digital access to quality FT journalism with expert analysis from industry leaders. Pay a year upfront and save 20%.
- 20 monthly gift articles to share
- Lex: FT's flagship investment column
- 15+ Premium newsletters by leading experts
- FT Digital Edition: our digitised print edition
Terms & Conditions apply
Explore our full range of subscriptions.
Why the ft.
See why over a million readers pay to read the Financial Times.

IMAGES
COMMENTS
A lesson plan will be the set of subject matter materials you will be teaching during a specific timeframe. The lesson plan should be an index that students can constantly consult to understand better the parts of the learning journey they will go through during each session. Teachers and professors should have a lesson plan template that ...
1. Warm your students up with a bell ringer activity. At the beginning of every class, the students' brains aren't primed yet for the content. Ease your students into every lesson with a little warm up known as a bell ringer. These are 3- to 5-minute quick activities that serve as introductions to your lesson.
Begin with the presentation divided into primary or main sections, highlight key definitions, and add infographics and videos to ensure that every student understands the tiniest detail. Additionally, you can get students involved in the lesson plan presentation by asking questions, polling them on key points, or allowing them to follow along ...
1. SMASE ASEI PDSI Lesson Plan Format. The SMASE ASEI (Activities, Students, Experiments, and Improvisation) PDSI lesson plan format is the current government-approved lesson plan format in Nigeria. This student-centered plan engages learners through activities, critical thinking, and teamwork.
5E Lessons in Middle and High School. 5E lesson plans (Engagement, Exploration, Explanation, Elaborate, Evaluate) are great for middle and high school as well. This example is for science, but you can use the 5E structure across all lessons. Learn more: Middle and High School 5E Lesson Plans. The Wise and Witty Teacher.
1. Determine the Learning Outcome. Begin with the end in mind. The learning outcome, sometimes called a learning target or objective, communicates what students should know and be able to do by the end of the lesson. Further, all resources, tasks, and activities should be aligned to the learning outcome. These objectives should be attainable ...
Step 2: Include Any Relevant Resource Materials for the Lesson. Integrating relevant and interesting learning tools into the classroom helps improve learning and participation. These might include things such as presentations, handouts, online videos, pages from a book, etc. . Step 3: Cite Lesson Plan Procedures.
A lesson introduction should: Provide brief context and background information on the topic while engaging interest. Create excitement or interest. Compel the class to want to know more about the topic. Explain the relevance of the topic to the larger unit or course. Provide a clear link between today's objectives and the student's prior ...
A good lesson plan might include the following: An objective for the lesson. Time requirements for each aspect of the lesson. Specific activities that will be done. Materials that will be used. How the lesson will be differentiated. The method in which you will assess students' progress. Standards that the lesson will address.
Build in a buffer between each session to take care of any unforeseen issues. Say you want to spend 15 minutes on a class presentation; assign 20 minutes to it instead. Having a realistic lesson timeline helps you stay on track, making sure you have enough time to cover all the key areas of your lesson.
When drafting your lesson plan, keep these nine elements in mind. 1. Grade Level/Subject. The grade level and subject of the lesson you're going to teach are some of the first sections of a ...
Lesson plan procedures are the sequence or step-by-step guidelines detailing how a teacher plans to deliver a lesson to students. This includes the activities, methods, materials, and timing necessary to effectively facilitate learning. Typically, there are three stages of a lesson plan that make up the lesson plan procedure.
Make a list of all the things you'll need to present a lesson such as paper and notebooks. Technological resources, such as laptops and integrated learning apps or webpages, should be listed as well and tested in advance to ensure smooth performance during instruction. 5. Dynamic opening. Engage your students in the lesson from the beginning of ...
Out of the three types of lesson plans, detailed and semi-detailed plans are the ones that can be broken down into five parts. The five parts of a lesson plan differ across websites and even across primary schools, as there are many variants, but the most common ways of dividing lessons are listed below: 1. Objectives.
A basic format for a student teacher lesson plan structure includes: The title of the unit and the content area and grade-level for whom the lesson is written. State Standards and Common Core Standards addressed in the lesson. An overview of how the individual lesson falls under the umbrella of the essential questions in the unit.
Step 1 - Determine Learning Objectives. Step 2 - Plan Activities. Step 3 - Gather Learning Materials. Step 4 - Create a Detailed Lesson Procedure on Paper. Step 5 - Organize Lesson Plan for Presentation. Step 6 - Plan Assessment Strategies. Step 7 - Assign Homework & Assess Progress. Let's Sum It Up.
Objectives: know your destination. When writing a lesson plan, start by outlining the learning objectives—what you want your students to take from the session and work backward. Having clear and specific goals helps you plan activities for a successful lesson. 2. Welcome to the hook: make 'em want to learn.
The Space Illustrative Lesson Plan for High School Template captures the vastness of space in an educational format, perfect for high school and college astronomy units. Use it when the lesson's aim is to explore celestial phenomena and foster scientific curiosity. Slides: Engaging and themed visuals to complement space-related lessons. Format: Available in PowerPoint and Google Slides formats.
Updated on January 14, 2019. A lesson plan is a detailed step-by-step guide that outlines the teacher's objectives for what the students will accomplish during the course of the lesson and how they will learn it. Creating a lesson plan involves setting goals, developing activities, and determining the materials that you will use.
Lesson plans can help by breaking down complex concepts into smaller, more manageable pieces. Bullet points or timelines can make the information easier to understand and connect, creating a clear learning path for students. Stronger Learning Outcomes. A well-designed lesson plan ensures clear explanations for each topic, catering to all students.
Lesson Plan: Presentation; Lesson Plan: Presentation. Rationale: Oral communication is a highly valuable skill that is becoming lost in a world of emails, texts, and tweets. There is a new generation of youngsters and young adults for whom speaking-discussion, or a group presentation is frightening. If it is true that "practice makes perfect ...
Board Game Lesson Plan Template: This template uses the concept of a board game to structure the lesson, making learning feel like an adventure. It's perfect for gamifying lessons and keeping students excited about the material. ... When wrapping up a unit or lesson, a recap presentation can go over aspects, pose queries, and even incorporate ...
In this lesson, students can expand their vocabulary on clothing and fashion and enhance their understanding through engaging speaking and listening activities. Vocabulary in this lesson: Sparkly - Lacy - Cotton - Baggy - Leather - Furry - Gold/Golden. Remember: You can add more vocabulary if you think it's necessary.
Like our new prime minister Sir Keir Starmer, I would like to think of myself as a Yimby not a Nimby. When it comes to house building, my slogan is, "Yes In My Backyard".