28 Questionnaire Examples, Questions, & Templates to Survey Your Clients
Published: May 15, 2023
The adage "the customer is always right" has received some pushback in recent years, but when it comes to conducting surveys , the phrase is worth a deeper look. In the past, representatives were tasked with solving client problems as they happened. Now, they have to be proactive by solving problems before they come up.

Salesforce found that 63% of customers expect companies to anticipate their needs before they ask for help. But how can a customer service team recognize these customer needs in advance and effectively solve them on a day-to-day basis?
![example of a research survey questionnaire → Free Download: 5 Customer Survey Templates [Access Now]](https://no-cache.hubspot.com/cta/default/53/9d36416b-3b0d-470c-a707-269296bb8683.png)
A customer questionnaire is a tried-and-true method for collecting survey data to inform your customer service strategy . By hearing directly from the customer, you'll capture first-hand data about how well your service team meets their needs. In this article, you'll get free questionnaire templates and best practices on how to administer them for the most honest responses.
Table of Contents:

Questionnaire Definition
Survey vs. questionnaire, questionnaire templates.
- Questionnaire Examples
Questionnaire Design
Survey question examples.
- Examples of Good Survey Questions
How to Make a Questionnaire
.webp)
5 Free Customer Satisfaction Survey Templates
Easily measure customer satisfaction and begin to improve your customer experience.
- Net Promoter Score
- Customer Effort Score
Download Free
All fields are required.
You're all set!
Click this link to access this resource at any time.
A questionnaire is a research tool used to conduct surveys. It includes specific questions with the goal to understand a topic from the respondents' point of view. Questionnaires typically have closed-ended, open-ended, short-form, and long-form questions.
The questions should always stay as unbiased as possible. For instance, it's unwise to ask for feedback on a specific product or service that’s still in the ideation phase. To complete the questionnaire, the customer would have to imagine how they might experience the product or service rather than sharing their opinion about their actual experience with it.
Ask broad questions about the kinds of qualities and features your customers enjoy in your products or services and incorporate that feedback into new offerings your team is developing.
What makes a good questionnaire?
Define the goal, make it short and simple, use a mix of question types, proofread carefully, keep it consistent.
A good questionnaire should find what you need versus what you want. It should be valuable and give you a chance to understand the respondent’s point of view.
Make the purpose of your questionnaire clear. While it's tempting to ask a range of questions simultaneously, you'll get more valuable results if you stay specific to a set topic.
According to HubSpot research , 47% of those surveyed say their top reason for abandoning a survey is the time it takes to complete.
So, questionnaires should be concise and easy to finish. If you're looking for a respondent’s experience with your business, focus on the most important questions.
5 Customer Survey Templates
Featured resource.
Your questionnaire should include a combination of question types, like open-ended, long-form, or short-ended questions.
Open-ended questions give users a chance to share their own answers. But closed-ended questions are more efficient and easy to quantify, with specific answer choices.
If you're not sure which question types are best, read here for more survey question examples .
While it's important to check spelling and grammar, there are two other things you'll want to check for a great questionnaire.
First, edit for clarity. Jargon, technical terms, and brand-specific language can be confusing for respondents. Next, check for leading questions. These questions can produce biased results that will be less useful to your team.
Consistency makes it easier for respondents to quickly complete your questionnaire. This is because it makes the questions less confusing. It can also reduce bias.
Being consistent is also helpful for analyzing questionnaire data because it makes it easier to compare results. With this in mind, keep response scales, question types, and formatting consistent.
In-Depth Interviews vs. Questionnaire
Questionnaires can be a more feasible and efficient research method than in-depth interviews. They are a lot cheaper to conduct. That’s because in-depth interviews can require you to compensate the interviewees for their time and give accommodations and travel reimbursement.
Questionnaires also save time for both parties. Customers can quickly complete them on their own time, and employees of your company don't have to spend time conducting the interviews. They can capture a larger audience than in-depth interviews, making them much more cost-effective.
It would be impossible for a large company to interview tens of thousands of customers in person. The same company could potentially get feedback from its entire customer base using an online questionnaire.
When considering your current products and services (as well as ideas for new products and services), it's essential to get the feedback of existing and potential customers. They are the ones who have a say in purchasing decisions.
A questionnaire is a tool that’s used to conduct a survey. A survey is the process of gathering, sampling, analyzing, and interpreting data from a group of people.
The confusion between these terms most likely stems from the fact that questionnaires and data analysis were treated as very separate processes before the Internet became popular. Questionnaires used to be completed on paper, and data analysis occurred later as a separate process. Nowadays, these processes are typically combined since online survey tools allow questionnaire responses to be analyzed and aggregated all in one step.
But questionnaires can still be used for reasons other than data analysis. Job applications and medical history forms are examples of questionnaires that have no intention of being statistically analyzed. The key difference between questionnaires and surveys is that they can exist together or separately.
Below are some of the best free questionnaire templates you can download to gather data that informs your next product or service offering.
What makes a good survey question?
Have a goal in mind, draft clear and distinct answers and questions, ask one question at a time, check for bias and sensitivity, include follow-up questions.
To make a good survey question, you have to choose the right type of questions to use. Include concise, clear, and appropriate questions with answer choices that won’t confuse the respondent and will clearly offer data on their experience.
Good survey questions can give a business good data to examine. Here are some more tips to follow as you draft your survey questions.
To make a good survey, consider what you are trying to learn from it. Understanding why you need to do a survey will help you create clear and concise questions that you need to ask to meet your goal. The more your questions focus on one or two objectives, the better your data will be.
You have a goal in mind for your survey. Now you have to write the questions and answers depending on the form you’re using.
For instance, if you’re using ranks or multiple-choice in your survey, be clear. Here are examples of good and poor multiple-choice answers:
Poor Survey Question and Answer Example
California:
- Contains the tallest mountain in the United States.
- Has an eagle on its state flag.
- Is the second-largest state in terms of area.
- Was the location of the Gold Rush of 1849.
Good Survey Question and Answer Example
What is the main reason so many people moved to California in 1849?
- California's land was fertile, plentiful, and inexpensive.
- The discovery of gold in central California.
- The East was preparing for a civil war.
- They wanted to establish religious settlements.
In the poor example, the question may confuse the respondent because it's not clear what is being asked or how the answers relate to the question. The survey didn’t fully explain the question, and the options are also confusing.
In the good example above, the question and answer choices are clear and easy to understand.
Always make sure answers and questions are clear and distinct to create a good experience for the respondent. This will offer your team the best outcomes from your survey.
It's surprisingly easy to combine multiple questions into one. They even have a name — they’re called "double-barreled" questions. But a good survey asks one question at a time.
For example, a survey question could read, "What is your favorite sneaker and clothing apparel brand?" This is bad because you’re asking two questions at once.
By asking two questions simultaneously, you may confuse your respondents and get unclear answers. Instead, each question should focus on getting specific pieces of information.
For example, ask, "What is your favorite sneaker brand?" then, "What is your favorite clothing apparel brand?" By separating the questions, you allow your respondents to give separate and precise answers.
Biased questions can lead a respondent toward a specific response. They can also be vague or unclear. Sensitive questions such as age, religion, or marital status can be helpful for demographics. These questions can also be uncomfortable for people to answer.
There are a few ways to create a positive experience with your survey questions.
First, think about question placement. Sensitive questions that appear in context with other survey questions can help people understand why you are asking. This can make them feel more comfortable responding.
Next, check your survey for leading questions, assumptions, and double-barreled questions. You want to make sure that your survey is neutral and free of bias.
Asking more than one survey question about an area of interest can make a survey easier to understand and complete. It also helps you collect more in-depth insights from your respondents.
1. Free HubSpot Questionnaire Template
HubSpot offers a variety of free customer surveys and questionnaire templates to analyze and measure customer experience. Choose from five templates: net promoter score, customer satisfaction, customer effort, open-ended questions, and long-form customer surveys.
2. Client Questionnaire Template
It's a good idea to gauge your clients' experiences with your business to uncover opportunities to improve your offerings. That will, in turn, better suit their lifestyles. You don't have to wait for an entire year to pass before polling your customer base about their experience either. A simple client questionnaire, like the one below, can be administered as a micro survey several times throughout the year. These types of quick survey questions work well to retarget your existing customers through social media polls and paid interactive ads.
1. How much time do you spend using [product or service]?
- Less than a minute
- About 1 - 2 minutes
- Between 2 and 5 minutes
- More than 5 minutes
2. In the last month, what has been your biggest pain point?
- Finding enough time for important tasks
- Delegating work
- Having enough to do
3. What's your biggest priority right now?
- Finding a faster way to work
- Problem-solving
- Staff development

3. Website Questionnaire Template
Whether you just launched a brand new website or you're gathering data points to inform a redesign, you'll find customer feedback to be essential in both processes. A website questionnaire template will come in handy to collect this information using an unbiased method.
1. How many times have you visited [website] in the past month?
- More than once
2. What is the primary reason for your visit to [website]?
- To make a purchase
- To find more information before making a purchase in-store
- To contact customer service
3. Are you able to find what you're looking for on the website homepage?
4. Customer Satisfaction Questionnaire Template
If you've never surveyed your customers and are looking for a template to get started, this one includes some basic customer satisfaction questions. These will apply to just about any customer your business serves.
1. How likely are you to recommend us to family, friends, or colleagues?
- Extremely unlikely
- Somewhat unlikely
- Somewhat likely
- Extremely likely
2. How satisfied were you with your experience?
1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10
3. Rank the following items in terms of their priority to your purchasing process.
- Helpful staff
- Quality of product
- Price of product
- Ease of purchase
- Proximity of store
- Online accessibility
- Current need
- Appearance of product
4. Who did you purchase these products for?
- Family member
- On behalf of a business
5. Please rate our staff on the following terms:
- Friendly __ __ __ __ __ Hostile
- Helpful __ __ __ __ __ Useless
- Knowledgeable __ __ __ __ __ Inexperienced
- Professional __ __ __ __ __ Inappropriate
6. Would you purchase from our company again?
7. How can we improve your experience for the future?
________________________________.
5. Customer Effort Score Questionnaire Template
The following template gives an example of a brief customer effort score (CES) questionnaire. This free template works well for new customers to measure their initial reaction to your business.
1. What was the ease of your experience with our company?
- Extremely difficult
- Somewhat difficult
- Somewhat easy
- Extremely easy
2. The company did everything it could to make my process as easy as possible.
- Strongly disagree
- Somewhat disagree
- Somewhat agree
- Strongly agree
3. On a scale of 1 to 10 (1 being "extremely quickly" and 10 being "extremely slowly"), how fast were you able to solve your problem?
4. How much effort did you have to put forth while working with our company?
- Much more than expected
- Somewhat more than expected
- As much as expected
- Somewhat less than expected
- Much less than expected
6. Demographic Questionnaire Template
Here's a template for surveying customers to learn more about their demographic background. You could substantiate the analysis of this questionnaire by corroborating the data with other information from your web analytics, internal customer data, and industry data.
1. How would you describe your employment status?
- Employed full-time
- Employed part-time
- Freelance/contract employee
- Self-employed
2. How many employees work at your company?
3. How would you classify your role?
- Individual Contributor
4. How would you classify your industry?
- Technology/software
- Hospitality/dining
- Entertainment
Below, we have curated a list of questionnaire examples that do a great job of gathering valuable qualitative and quantitative data.
4 Questionnaire Examples
1. customer satisfaction questions.

Learn more about HubSpot's Customer Survey software.
Multiple-Choice
Multiple-choice questions offer respondents several answers to choose from. This is a popular choice of questionnaire format since it's simple for people to fill out and for companies to analyze.
Multiple-choice questions can be in single-answer form (respondents can only choose one response) or multiple-answer form (respondents can choose as many responses as necessary).
Multiple-choice survey question examples : "Which of the following social media platforms do you use most often?"
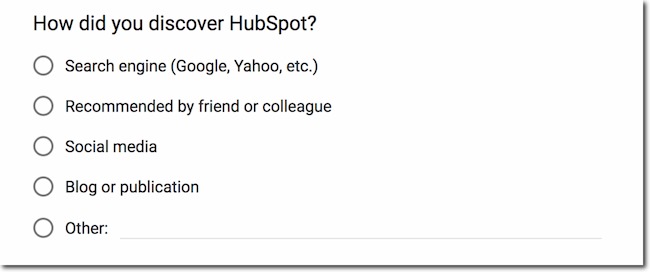
Image Source
Rating Scale
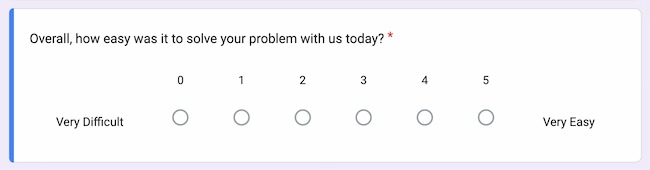
Rating scale questions offer a scale of numbers and ask respondents to rate topics based on the sentiments assigned to that scale. This is effective when assessing customer satisfaction.
Rating scale survey question examples : "Rate your level of satisfaction with the customer service you received today on a scale of 1-10."
Yes or no survey questions are a type of dichotomous question. These are questions that only offer two possible responses. They’re useful because they’re quick to answer and can help with customer segmentation.
Yes or no survey questions example : "Have you ever used HubSpot before?"
Likert Scale
Likert scale questions assess whether a respondent agrees with the statement, as well as the extent to which they agree or disagree.
These questions typically offer five or seven responses, with sentiments ranging from items such as "strongly disagree" to "strongly agree." Check out this post to learn more about the Likert scale .
Likert scale survey question examples : “How satisfied are you with the service from [brand]?”

Open-ended questions ask a broader question or offer a chance to elaborate on a response to a close-ended question. They're accompanied by a text box that leaves room for respondents to write freely. This is particularly important when asking customers to expand on an experience or recommendation.
Open-ended survey question examples : "What are your personal goals for using HubSpot? Please describe."
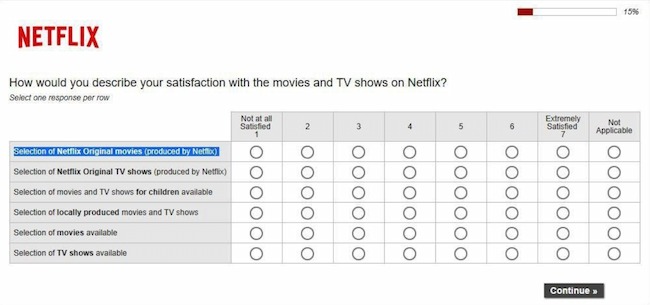
Matrix Table
A matrix table is usually a group of multiple-choice questions grouped in a table. Choices for these survey questions are usually organized in a scale. This makes it easier to understand the relationships between different survey responses.
Matrix table survey question examples : "Rate your level of agreement with the following statements about HubSpot on a scale of 1-5."
Rank Order Scaling
These questions ask respondents to rank a set of terms by order of preference or importance. This is useful for understanding customer priorities.
Rank order scaling examples : "Rank the following factors in order of importance when choosing a new job."
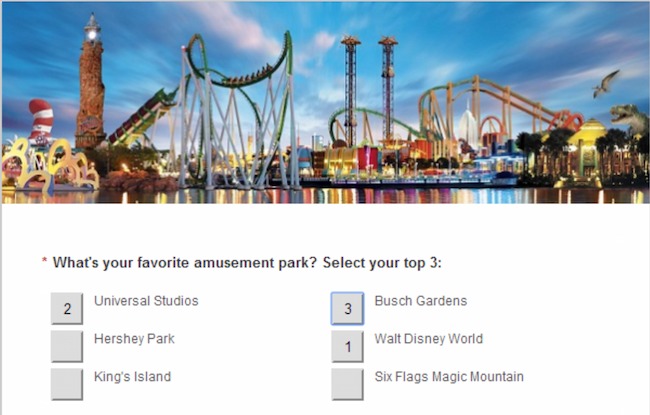
Semantic Differential Scale
This scale features pairs of opposite adjectives that respondents use for rating, usually for a feature or experience. This type of question makes it easier to understand customer attitudes and beliefs.
Semantic differential scale question examples : "Rate your overall impression of this brand as friendly vs. unfriendly, innovative vs. traditional, and boring vs. exciting."
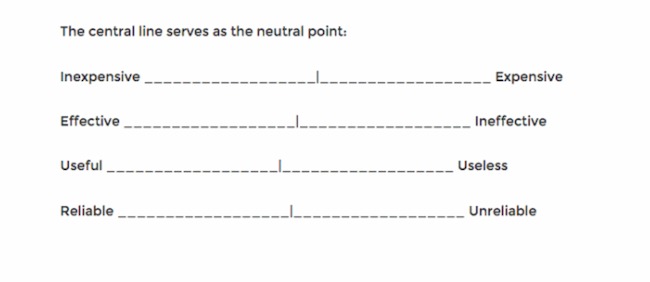
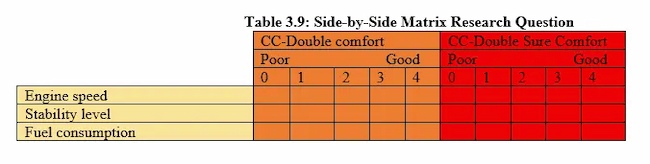
Side-By-Side Matrix
This matrix table format includes two sets of questions horizontally for easy comparison. This format can help with customer gap analysis.
Side-by-side matrix question examples : "Rate your level of satisfaction with HubSpot's customer support compared to its ease of use."
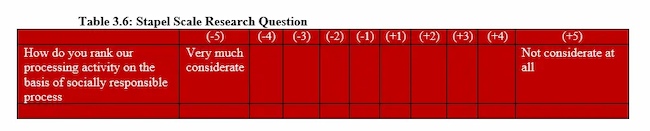
Stapel Scale
The Stapel rating scale offers a single adjective or idea for rating. It uses a numerical scale with a zero point in the middle. This survey question type helps with in-depth analysis.
Stapel scale survey question examples : "Rate your overall experience with this product as +5 (excellent) to -5 (terrible)."
Constant Sum Survey Questions
In this question format, people distribute points to different choices based on the perceived importance of each point. This kind of question is often used in market research and can help your team better understand customer choices .
Constant sum survey question examples : "What is your budget for the following marketing expenses: Paid campaigns, Events, Freelancers, Agencies, Research."
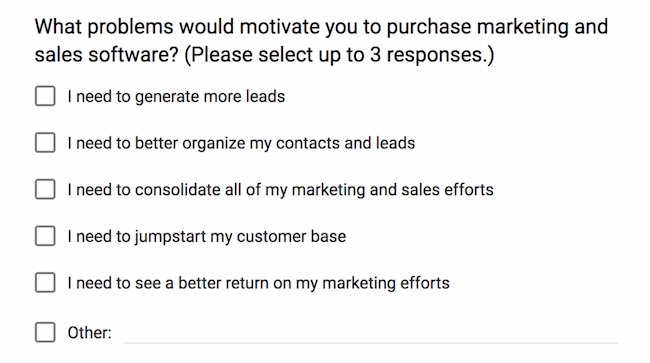
Image Choice
This survey question type shows several images. Then, it asks the respondent to choose the image that best matches their response to the question. These questions are useful for understanding your customers’ design preferences.
Image choice survey questions example : "Which of these three images best represents your brand voice?"

Choice Model
This survey question offers a hypothetical scenario, then the respondent must choose from the presented options. It's a useful type of question when you are refining a product or strategy.
Choice model survey questions example : "Which of these three deals would be most appealing to you?"
Click Map Questions
Click map questions offer an image click on specific areas of the image in response to a question. This question uses data visualization to learn about customer preferences for design and user experience.
Click map question examples : "Click on the section of the website where you would expect to find pricing information."

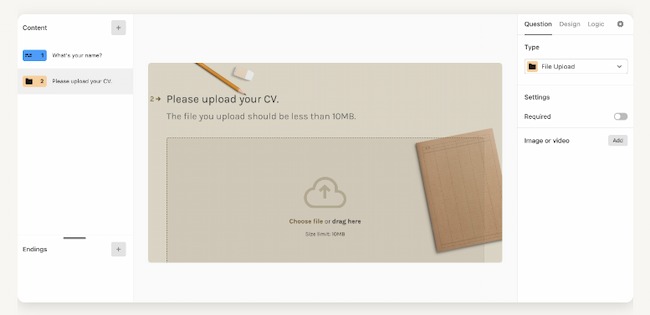
Data Upload
This survey question example asks the respondent to upload a file or document in response to a question. This type of survey question can help your team collect data and context that might be tough to collect otherwise.
Data upload question examples : "Please upload a screenshot of the error you encountered during your purchase."
Benchmarkable Questions
This question type asks a respondent to compare their answers to a group or benchmark. These questions can be useful if you're trying to compare buyer personas or other customer groups.
Benchmarkable survey questions example : "Compare your company's marketing budget to other companies in your industry."
Good Survey Questions
- What is your favorite product?
- Why did you purchase this product?
- How satisfied are you with [product]?
- Would you recommend [product] to a friend?
- Would you recommend [company name] to a friend?
- If you could change one thing about [product], what would it be?
- Which other options were you considering before [product or company name]?
- Did [product] help you accomplish your goal?
- How would you feel if we did not offer this product, feature, or service?
- What would you miss the most if you couldn't use your favorite product from us?
- What is one word that best describes your experience using our product?
- What's the primary reason for canceling your account?
- How satisfied are you with our customer support?
- Did we answer all of your questions and concerns?
- How can we be more helpful?
- What additional features would you like to see in this product?
- Are we meeting your expectations?
- How satisfied are you with your experience?
1. "What is your favorite product?"
This question is a great starter for your survey. Most companies want to know what their most popular products are, and this question cuts right to the point.
It's important to note that this question gives you the customer's perspective, not empirical evidence. You should compare the results to your inventory to see if your customers' answers match your actual sales. You may be surprised to find your customers' "favorite" product isn't the highest-selling one.
2. "Why did you purchase this product?"
Once you know their favorite product, you need to understand why they like it so much. The qualitative data will help your marketing and sales teams attract and engage customers. They'll know which features to advertise most and can seek out new leads similar to your existing customers.
3. "How satisfied are you with [product]?"
When you have a product that isn't selling, you can ask this question to see why customers are unhappy with it. If the reviews are poor, you'll know that the product needs reworking, and you can send it back to product management for improvement. Or, if these results are positive, they may have something to do with your marketing or sales techniques. You can then gather more info during the questionnaire and restrategize your campaigns based on your findings.
4. "Would you recommend [product] to a friend?"
This is a classic survey question used with most NPS® surveys. It asks the customer if they would recommend your product to one of their peers. This is extremely important because most people trust customer referrals more than traditional advertising. So, if your customers are willing to recommend your products, you'll have an easier time acquiring new leads.
5. "Would you recommend [company name] to a friend?"
Similar to the question above, this one asks the customer to consider your business as a whole and not just your product. This gives you insight into your brand's reputation and shows how customers feel about your company's actions. Even if you have an excellent product, your brand's reputation may be the cause of customer churn . Your marketing team should pay close attention to this question to see how they can improve the customer experience .
6. "If you could change one thing about [product], what would it be?"
This is a good question to ask your most loyal customers or ones that have recently churned. For loyal customers, you want to keep adding value to their experience. Asking how your product can improve helps your development team find flaws and increases your chances of retaining a valuable customer segment.
For customers that have recently churned, this question gives insight into how you can retain future users that are unhappy with your product or service. By giving these customers a space to voice their criticisms, you can either reach out and offer solutions or relay feedback for consideration.
7. "Which other options were you considering before [product or company name]?"
If you're operating in a competitive industry, customers will have more than one choice when considering your brand. And if you sell variations of your product or produce new models periodically, customers may prefer one version over another.
For this question, you should offer answers to choose from in a multiple-selection format. This will limit the types of responses you'll receive and help you get the exact information you need.
8. "Did [product] help you accomplish your goal?"
The purpose of any product or service is to help customers reach a goal. So, you should be direct and ask them if your company steered them toward success. After all, customer success is an excellent retention tool. If customers are succeeding with your product, they're more likely to stay loyal to your brand.
9. "How would you feel if we did not offer this product, feature, or service?"
Thinking about discontinuing a product? This question can help you decide whether or not a specific product, service, or feature will be missed if you were to remove it.
Even if you know that a product or service isn't worth offering, it's important to ask this question anyway because there may be a certain aspect of the product that your customers like. They'll be delighted if you can integrate that feature into a new product or service.
10. "If you couldn't use your favorite product from us, what would you miss the most about it?"
This question pairs well with the one above because it frames the customer's favorite product from a different point of view. Instead of describing why they love a particular product, the customer can explain what they'd be missing if they didn't have it at all. This type of question uncovers "fear of loss," which can be a very different motivating factor than "hope for gain."
11. "What word best describes your experience using our product?"
Your marketing team will love this question. A single word or a short phrase can easily sum up your customers’ emotions when they experience your company, product, or brand. Those emotions can be translated into relatable marketing campaigns that use your customers’ exact language.
If the responses reveal negative emotions, it's likely that your entire customer service team can relate to that pain point. Rather than calling it "a bug in the system," you can describe the problem as a "frustrating roadblock" to keep their experience at the forefront of the solution.
12. "What's the primary reason for canceling your account?"
Finding out why customers are unhappy with your product or service is key to decreasing your churn rate . If you don't understand why people leave your brand, it's hard to make effective changes to prevent future turnover. Or worse, you might alter your product or service in a way that increases your churn rate, causing you to lose customers who were once loyal supporters.
13. "How satisfied are you with our customer support?"
It's worth asking customers how happy they are with your support or service team. After all, an excellent product doesn't always guarantee that customers will stay loyal to your brand. Research shows that one in six customers will leave a brand they love after just one poor service experience.
14. "Did we answer all of your questions and concerns?"
This is a good question to ask after a service experience. It shows how thorough your support team is and whether they're prioritizing speed too much over quality. If customers still have questions and concerns after a service interaction, your support team is focusing too much on closing tickets and not enough on meeting customer needs .
15. "How can we be more helpful?"
Sometimes it's easier to be direct and simply ask customers what else you can do to help them. This shows a genuine interest in your buyers' goals which helps your brand foster meaningful relationships with its customer base. The more you can show that you sincerely care about your customers' problems, the more they'll open up to you and be honest about how you can help them.
16. What additional features would you like to see in this product?
With this question, your team can get inspiration for the company's next product launch. Think of the responses as a wish list from your customers. You can discover what features are most valuable to them and whether they already exist within a competitor's product.
Incorporating every feature suggestion is nearly impossible, but it's a convenient way to build a backlog of ideas that can inspire future product releases.
17. "Are we meeting your expectations?"
This is a really important question to ask because customers won't always tell you when they're unhappy with your service. Not every customer will ask to speak with a manager when they're unhappy with your business. In fact, most will quietly move on to a competitor rather than broadcast their unhappiness to your company. To prevent this type of customer churn, you need to be proactive and ask customers if your brand is meeting their expectations.
18. "How satisfied are you with your experience?"
This question asks the customer to summarize their experience with your business. It gives you a snapshot of how the customer is feeling in that moment and their perception of your brand. Asking this question at the right stage in the customer's journey can tell you a lot about what your company is doing well and where you can stand to improve.
Next, let's dig into some tips for creating your own questionnaire.
Start with templates as a foundation. Know your question types. Keep it brief when possible. Choose a simple visual design. Use a clear research process. Create questions with straightforward, unbiased language. Make sure every question is important. Ask one question at a time. Order your questions logically. Consider your target audience. Test your questionnaire.
1. Use questionnaire templates.
Rather than build a questionnaire from scratch, consider using questionnaire templates to get started. HubSpot's collection of customer-facing questionnaire templates can help you quickly build and send a questionnaire to your clients and analyze the results right on Google Drive.
.png?width=375&height=275&name=Image%20Hackathon%20%E2%80%93%20Horizontal%20(24).png)
Download Now
2. Know your question types.
A simple "yes" or "no" doesn't cut it. To get feedback that actually matters, you need to give customers options that go in-depth. There's a method to getting accurate feedback from your questionnaire, and it starts by choosing the appropriate types of questions for the information you want to know.
Vrnda LeValley , customer training manager at HubSpot, recommends starting with an alignment question like, "Does this class meet your expectations?" because it gives more context to any positive or negative scores that follow. She continues, "If it didn't meet expectations, then there will potentially be negative responses across the board (as well as the reverse)."
3. Keep it brief, when possible.
Most questionnaires don't need to be longer than a page. For routine customer satisfaction surveys, it's unnecessary to ask 50 slightly varied questions about a customer's experience when those questions could be combined into 10 solid questions.
The shorter your questionnaire is, the more likely a customer will complete it. Plus a shorter questionnaire means less data for your team to collect and analyze. Based on the feedback, it will be a lot easier for you to get the information you need to make the necessary changes in your organization and products.
4. Choose a simple visual design.
There's no need to make your questionnaire a stunning work of art. As long as it's clear and concise, it will be attractive to customers. When asking questions that are important to furthering your company, it's best to keep things simple. Select a font that’s common and easy to read, like Helvetica or Arial. Use a text size that customers of all abilities can navigate.
A questionnaire is most effective when all the questions are visible on a single screen. The layout is important. If a questionnaire is even remotely difficult to navigate, your response rate could suffer. Make sure that buttons and checkboxes are easy to click and that questions are visible on both computer and mobile screens.
5. Use a clear research process.
Before planning questions for your questionnaire, you'll need to have a definite direction for it. A questionnaire is only effective if the results answer an overarching research question. After all, the research process is an important part of the survey, and a questionnaire is a tool that's used within the process.
In your research process, you should first come up with a research question. What are you trying to find out? What's the point of this questionnaire? Keep this in mind throughout the process.
After coming up with a research question, it's a good idea to have a hypothesis. What do you predict the results will be for your questionnaire? This can be structured in a simple "If … then …" format. A structured experiment — yes, your questionnaire is a type of experiment — will confirm that you're only collecting and analyzing data necessary to answer your research question. Then, you can move forward with your survey .
6. Create questions with straightforward, unbiased language.
When crafting your questions, it's important to structure them to get the point across. You don't want any confusion for your customers because this may influence their answers. Instead, use clear language. Don't use unnecessary jargon, and use simple terms in favor of longer-winded ones.
You may risk the reliability of your data if you try to combine two questions. Rather than asking, "How was your experience shopping with us, and would you recommend us to others?" separate it into two separate questions. Customers will be clear on your question and choose a response most appropriate for each one.
You should always keep the language in your questions unbiased. You never want to sway customers one way or another because this will cause your data to be skewed. Instead of asking, "Some might say that we create the best software products in the world. Would you agree or disagree?" it may be better to ask, "How would you rate our software products on a scale of 1 to 10?" This removes any bias and confirms that all the responses are valid.
7. Ask only the most important questions.
When creating your questionnaire, keep in mind that time is one of the most valuable commodities for customers. Most aren't going to sit through a 50-question survey, especially when they're being asked about products or services they didn't use. Even if they do complete it, most of these will be half-hearted responses from fatigued customers who simply want to be finished with it.
If your questionnaire has five or 55 questions, make sure each has a specific purpose. Individually, they should be aimed at collecting certain pieces of information that reveal new insights into different aspects of your business. If your questions are irrelevant or seem out of place, your customers will be easily derailed by the survey. And, once the customer has lost interest, it'll be difficult to regain their focus.
8. Ask one question at a time.
Since every question has a purpose, ask them one at a time. This lets the customer focus and encourages them to share a thoughtful response. This is particularly important for open-ended questions where customers need to describe an experience or opinion.
By grouping questions together, you risk overwhelming busy customers who don't have time for a long survey. They may think you're asking them too much, or they might see your questionnaire as a daunting task. You want your survey to appear as painless as possible. Keeping your questions separated will make it more user-friendly.
9. Order your questions logically.
A good questionnaire is like a good book. The beginning questions should lay the framework, the middle ones should cut to the core issues, and the final questions should tie up all loose ends. This flow keeps customers engaged throughout the entire survey.
When creating your questionnaire, start with the most basic questions about demographics. You can use this information to segment your customer base and create different buyer personas.
Next, add in your product and services questions. These are the ones that offer insights into common customer roadblocks and where you can improve your business's offerings. Questions like these guide your product development and marketing teams looking for new ways to enhance the customer experience.
Finally, you should conclude your questionnaire with open-ended questions to understand the customer journey. These questions let customers voice their opinions and point out specific experiences they've had with your brand.
10. Consider your target audience.
Whenever you collect customer feedback, you need to keep in mind the goals and needs of your target audience. After all, the participants in this questionnaire are your active customers. Your questions should be geared toward the interests and experiences they've already had with your company.
You can even create multiple surveys that target different buyer personas. For example, if you have a subscription-based pricing model, you can personalize your questionnaire for each type of subscription your company offers.
11. Test your questionnaire.
Once your questionnaire is complete, it's important to test it. If you don't, you may end up asking the wrong questions and collecting irrelevant or inaccurate information. Start by giving your employees the questionnaire to test, then send it to small groups of customers and analyze the results. If you're gathering the data you're looking for, then you should release the questionnaire to all of your customers.
How Questionnaires Can Benefit Your Customer Service Strategy
Whether you have one customer or 1000 customers, their opinions matter when it comes to the success of your business. Their satisfaction with your offerings can reveal how well or how poorly your customer service strategy and business are meeting their needs. A questionnaire is one of the most powerful, cost-effective tools to uncover what your customers think about your business. When analyzed properly, it can inform your product and service launches.
Use the free questionnaire templates, examples, and best practices in this guide to conduct your next customer feedback survey.
Now that you know the slight difference between a survey and a questionnaire, it’s time to put it into practice with your products or services. Remember, a good survey and questionnaire always start with a purpose. But, a great survey and questionnaire give data that you can use to help companies increase the way customers respond to their products or services because of the questions.
Net Promoter, Net Promoter System, Net Promoter Score, NPS, and the NPS-related emoticons are registered trademarks of Bain & Company, Inc., Fred Reichheld, and Satmetrix Systems, Inc.
Editor's note: This post was originally published in July 2018 and has been updated for comprehensiveness.
Don't forget to share this post!
Related articles.

Nonresponse Bias: What to Avoid When Creating Surveys

How to Make a Survey with a QR Code

50 Catchy Referral Slogans & How to Write Your Own
![example of a research survey questionnaire How Automated Phone Surveys Work [+Tips and Examples]](https://www.hubspot.com/hubfs/phone-survey.webp)
How Automated Phone Surveys Work [+Tips and Examples]

Online Panels: What They Are & How to Use Them Effectively

The Complete Guide to Survey Logic (+Expert Tips)

Focus Group vs. Survey: Which One Should You Use?
![example of a research survey questionnaire Leading Questions: What They Are & Why They Matter [+ Examples]](https://www.hubspot.com/hubfs/leading-questions-hero.webp)
Leading Questions: What They Are & Why They Matter [+ Examples]

What are Survey Sample Sizes & How to Find Your Sample Size

24 Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion Survey Questions to Ask Your Employees
5 free templates for learning more about your customers and respondents.
Service Hub provides everything you need to delight and retain customers while supporting the success of your whole front office
Root out friction in every digital experience, super-charge conversion rates, and optimize digital self-service
Uncover insights from any interaction, deliver AI-powered agent coaching, and reduce cost to serve
Increase revenue and loyalty with real-time insights and recommendations delivered to teams on the ground
Know how your people feel and empower managers to improve employee engagement, productivity, and retention
Take action in the moments that matter most along the employee journey and drive bottom line growth
Whatever they’re are saying, wherever they’re saying it, know exactly what’s going on with your people
Get faster, richer insights with qual and quant tools that make powerful market research available to everyone
Run concept tests, pricing studies, prototyping + more with fast, powerful studies designed by UX research experts
Track your brand performance 24/7 and act quickly to respond to opportunities and challenges in your market
Explore the platform powering Experience Management
- Free Account
- Product Demos
- For Digital
- For Customer Care
- For Human Resources
- For Researchers
- Financial Services
- All Industries
Popular Use Cases
- Customer Experience
- Employee Experience
- Net Promoter Score
- Voice of Customer
- Customer Success Hub
- Product Documentation
- Training & Certification
- XM Institute
- Popular Resources
- Customer Stories
- Artificial Intelligence
Market Research
- Partnerships
- Marketplace
The annual gathering of the experience leaders at the world’s iconic brands building breakthrough business results, live in Salt Lake City.
- English/AU & NZ
- Español/Europa
- Español/América Latina
- Português Brasileiro
- REQUEST DEMO

Your ultimate guide to questionnaires and how to design a good one
The written questionnaire is the heart and soul of any survey research project. Whether you conduct your survey using an online questionnaire, in person, by email or over the phone, the way you design your questionnaire plays a critical role in shaping the quality of the data and insights that you’ll get from your target audience. Keep reading to get actionable tips.
What is a questionnaire?
A questionnaire is a research tool consisting of a set of questions or other ‘prompts’ to collect data from a set of respondents.
When used in most research, a questionnaire will consist of a number of types of questions (primarily open-ended and closed) in order to gain both quantitative data that can be analyzed to draw conclusions, and qualitative data to provide longer, more specific explanations.
A research questionnaire is often mistaken for a survey - and many people use the term questionnaire and survey, interchangeably.
But that’s incorrect.
Which is what we talk about next.
Get started with our free survey maker with 50+ templates
Survey vs. questionnaire – what’s the difference?
Before we go too much further, let’s consider the differences between surveys and questionnaires.
These two terms are often used interchangeably, but there is an important difference between them.
Survey definition
A survey is the process of collecting data from a set of respondents and using it to gather insights.
Survey research can be conducted using a questionnaire, but won’t always involve one.
Questionnaire definition
A questionnaire is the list of questions you circulate to your target audience.
In other words, the survey is the task you’re carrying out, and the questionnaire is the instrument you’re using to do it.
By itself, a questionnaire doesn’t achieve much.
It’s when you put it into action as part of a survey that you start to get results.
Advantages vs disadvantages of using a questionnaire
While a questionnaire is a popular method to gather data for market research or other studies, there are a few disadvantages to using this method (although there are plenty of advantages to using a questionnaire too).
Let’s have a look at some of the advantages and disadvantages of using a questionnaire for collecting data.
Advantages of using a questionnaire
1. questionnaires are relatively cheap.
Depending on the complexity of your study, using a questionnaire can be cost effective compared to other methods.
You simply need to write your survey questionnaire, and send it out and then process the responses.
You can set up an online questionnaire relatively easily, or simply carry out market research on the street if that’s the best method.
2. You can get and analyze results quickly
Again depending on the size of your survey you can get results back from a questionnaire quickly, often within 24 hours of putting the questionnaire live.
It also means you can start to analyze responses quickly too.
3. They’re easily scalable
You can easily send an online questionnaire to anyone in the world and with the right software you can quickly identify your target audience and your questionnaire to them.
4. Questionnaires are easy to analyze
If your questionnaire design has been done properly, it’s quick and easy to analyze results from questionnaires once responses start to come back.
This is particularly useful with large scale market research projects.
Because all respondents are answering the same questions, it’s simple to identify trends.
5. You can use the results to make accurate decisions
As a research instrument, a questionnaire is ideal for commercial research because the data you get back is from your target audience (or ideal customers) and the information you get back on their thoughts, preferences or behaviors allows you to make business decisions.
6. A questionnaire can cover any topic
One of the biggest advantages of using questionnaires when conducting research is (because you can adapt them using different types and styles of open ended questions and closed ended questions) they can be used to gather data on almost any topic.
There are many types of questionnaires you can design to gather both quantitative data and qualitative data - so they’re a useful tool for all kinds of data analysis.
Disadvantages of using a questionnaire
1. respondents could lie.
This is by far the biggest risk with a questionnaire, especially when dealing with sensitive topics.
Rather than give their actual opinion, a respondent might feel pressured to give the answer they deem more socially acceptable, which doesn’t give you accurate results.
2. Respondents might not answer every question
There are all kinds of reasons respondents might not answer every question, from questionnaire length, they might not understand what’s being asked, or they simply might not want to answer it.
If you get questionnaires back without complete responses it could negatively affect your research data and provide an inaccurate picture.
3. They might interpret what’s being asked incorrectly
This is a particular problem when running a survey across geographical boundaries and often comes down to the design of the survey questionnaire.
If your questions aren’t written in a very clear way, the respondent might misunderstand what’s being asked and provide an answer that doesn’t reflect what they actually think.
Again this can negatively affect your research data.
4. You could introduce bias
The whole point of producing a questionnaire is to gather accurate data from which decisions can be made or conclusions drawn.
But the data collected can be heavily impacted if the researchers accidentally introduce bias into the questions.
This can be easily done if the researcher is trying to prove a certain hypothesis with their questionnaire, and unwittingly write questions that push people towards giving a certain answer.
In these cases respondents’ answers won’t accurately reflect what is really happening and stop you gathering more accurate data.
5. Respondents could get survey fatigue
One issue you can run into when sending out a questionnaire, particularly if you send them out regularly to the same survey sample, is that your respondents could start to suffer from survey fatigue.
In these circumstances, rather than thinking about the response options in the questionnaire and providing accurate answers, respondents could start to just tick boxes to get through the questionnaire quickly.
Again, this won’t give you an accurate data set.
Questionnaire design: How to do it
It’s essential to carefully craft a questionnaire to reduce survey error and optimize your data . The best way to think about the questionnaire is with the end result in mind.
How do you do that?
Start with questions, like:
- What is my research purpose ?
- What data do I need?
- How am I going to analyze that data?
- What questions are needed to best suit these variables?
Once you have a clear idea of the purpose of your survey, you’ll be in a better position to create an effective questionnaire.
Here are a few steps to help you get into the right mindset.
1. Keep the respondent front and center
A survey is the process of collecting information from people, so it needs to be designed around human beings first and foremost.
In his post about survey design theory, David Vannette, PhD, from the Qualtrics Methodology Lab explains the correlation between the way a survey is designed and the quality of data that is extracted.
“To begin designing an effective survey, take a step back and try to understand what goes on in your respondents’ heads when they are taking your survey.
This step is critical to making sure that your questionnaire makes it as likely as possible that the response process follows that expected path.”
From writing the questions to designing the survey flow, the respondent’s point of view should always be front and center in your mind during a questionnaire design.
2. How to write survey questions
Your questionnaire should only be as long as it needs to be, and every question needs to deliver value.
That means your questions must each have an individual purpose and produce the best possible data for that purpose, all while supporting the overall goal of the survey.
A question must also must be phrased in a way that is easy for all your respondents to understand, and does not produce false results.
To do this, remember the following principles:
Get into the respondent's head
The process for a respondent answering a survey question looks like this:
- The respondent reads the question and determines what information they need to answer it.
- They search their memory for that information.
- They make judgments about that information.
- They translate that judgment into one of the answer options you’ve provided. This is the process of taking the data they have and matching that information with the question that’s asked.
When wording questions, make sure the question means the same thing to all respondents. Words should have one meaning, few syllables, and the sentences should have few words.
Only use the words needed to ask your question and not a word more .
Note that it’s important that the respondent understands the intent behind your question.
If they don’t, they may answer a different question and the data can be skewed.
Some contextual help text, either in the introduction to the questionnaire or before the question itself, can help make sure the respondent understands your goals and the scope of your research.
Use mutually exclusive responses
Be sure to make your response categories mutually exclusive.
Consider the question:
What is your age?
Respondents that are 31 years old have two options, as do respondents that are 40 and 55. As a result, it is impossible to predict which category they will choose.
This can distort results and frustrate respondents. It can be easily avoided by making responses mutually exclusive.
The following question is much better:
This question is clear and will give us better results.
Ask specific questions
Nonspecific questions can confuse respondents and influence results.
Do you like orange juice?
- Like very much
- Neither like nor dislike
- Dislike very much
This question is very unclear. Is it asking about taste, texture, price, or the nutritional content? Different respondents will read this question differently.
A specific question will get more specific answers that are actionable.
How much do you like the current price of orange juice?
This question is more specific and will get better results.
If you need to collect responses about more than one aspect of a subject, you can include multiple questions on it. (Do you like the taste of orange juice? Do you like the nutritional content of orange juice? etc.)
Use a variety of question types
If all of your questionnaire, survey or poll questions are structured the same way (e.g. yes/no or multiple choice) the respondents are likely to become bored and tune out. That could mean they pay less attention to how they’re answering or even give up altogether.
Instead, mix up the question types to keep the experience interesting and varied. It’s a good idea to include questions that yield both qualitative and quantitative data.
For example, an open-ended questionnaire item such as “describe your attitude to life” will provide qualitative data – a form of information that’s rich, unstructured and unpredictable. The respondent will tell you in their own words what they think and feel.
A quantitative / close-ended questionnaire item, such as “Which word describes your attitude to life? a) practical b) philosophical” gives you a much more structured answer, but the answers will be less rich and detailed.
Open-ended questions take more thought and effort to answer, so use them sparingly. They also require a different kind of treatment once your survey is in the analysis stage.
3. Pre-test your questionnaire
Always pre-test a questionnaire before sending it out to respondents. This will help catch any errors you might have missed. You could ask a colleague, friend, or an expert to take the survey and give feedback. If possible, ask a few cognitive questions like, “how did you get to that response?” and “what were you thinking about when you answered that question?” Figure out what was easy for the responder and where there is potential for confusion. You can then re-word where necessary to make the experience as frictionless as possible.
If your resources allow, you could also consider using a focus group to test out your survey. Having multiple respondents road-test the questionnaire will give you a better understanding of its strengths and weaknesses. Match the focus group to your target respondents as closely as possible, for example in terms of age, background, gender, and level of education.
Note: Don't forget to make your survey as accessible as possible for increased response rates.
Questionnaire examples and templates
There are free questionnaire templates and example questions available for all kinds of surveys and market research, many of them online. But they’re not all created equal and you should use critical judgement when selecting one. After all, the questionnaire examples may be free but the time and energy you’ll spend carrying out a survey are not.
If you’re using online questionnaire templates as the basis for your own, make sure it has been developed by professionals and is specific to the type of research you’re doing to ensure higher completion rates. As we’ve explored here, using the wrong kinds of questions can result in skewed or messy data, and could even prompt respondents to abandon the questionnaire without finishing or give thoughtless answers.
You’ll find a full library of downloadable survey templates in the Qualtrics Marketplace , covering many different types of research from employee engagement to post-event feedback . All are fully customizable and have been developed by Qualtrics experts.
Qualtrics // Experience Management
Qualtrics, the leader and creator of the experience management category, is a cloud-native software platform that empowers organizations to deliver exceptional experiences and build deep relationships with their customers and employees.
With insights from Qualtrics, organizations can identify and resolve the greatest friction points in their business, retain and engage top talent, and bring the right products and services to market. Nearly 20,000 organizations around the world use Qualtrics’ advanced AI to listen, understand, and take action. Qualtrics uses its vast universe of experience data to form the largest database of human sentiment in the world. Qualtrics is co-headquartered in Provo, Utah and Seattle.
Related Articles
May 20, 2024
Best strategy & research books to read in 2024
May 13, 2024
Experience Management
X4 2024 Strategy & Research Showcase: Introducing the future of insights generation
November 7, 2023
Brand Experience
The 4 market research trends redefining insights in 2024
June 27, 2023
The fresh insights people: Scaling research at Woolworths Group
June 20, 2023
Bank less, delight more: How Bankwest built an engine room for customer obsession
April 1, 2023
Academic Experience
How to write great survey questions (with examples)
March 21, 2023
Sample size calculator
November 18, 2022
Statistical analysis software: your complete guide to getting started
Stay up to date with the latest xm thought leadership, tips and news., request demo.
Ready to learn more about Qualtrics?
Numbers, Facts and Trends Shaping Your World
Read our research on:
Full Topic List
Regions & Countries
- Publications
- Our Methods
- Short Reads
- Tools & Resources
Read Our Research On:
Writing Survey Questions
Perhaps the most important part of the survey process is the creation of questions that accurately measure the opinions, experiences and behaviors of the public. Accurate random sampling will be wasted if the information gathered is built on a shaky foundation of ambiguous or biased questions. Creating good measures involves both writing good questions and organizing them to form the questionnaire.
Questionnaire design is a multistage process that requires attention to many details at once. Designing the questionnaire is complicated because surveys can ask about topics in varying degrees of detail, questions can be asked in different ways, and questions asked earlier in a survey may influence how people respond to later questions. Researchers are also often interested in measuring change over time and therefore must be attentive to how opinions or behaviors have been measured in prior surveys.
Surveyors may conduct pilot tests or focus groups in the early stages of questionnaire development in order to better understand how people think about an issue or comprehend a question. Pretesting a survey is an essential step in the questionnaire design process to evaluate how people respond to the overall questionnaire and specific questions, especially when questions are being introduced for the first time.
For many years, surveyors approached questionnaire design as an art, but substantial research over the past forty years has demonstrated that there is a lot of science involved in crafting a good survey questionnaire. Here, we discuss the pitfalls and best practices of designing questionnaires.
Question development
There are several steps involved in developing a survey questionnaire. The first is identifying what topics will be covered in the survey. For Pew Research Center surveys, this involves thinking about what is happening in our nation and the world and what will be relevant to the public, policymakers and the media. We also track opinion on a variety of issues over time so we often ensure that we update these trends on a regular basis to better understand whether people’s opinions are changing.
At Pew Research Center, questionnaire development is a collaborative and iterative process where staff meet to discuss drafts of the questionnaire several times over the course of its development. We frequently test new survey questions ahead of time through qualitative research methods such as focus groups , cognitive interviews, pretesting (often using an online, opt-in sample ), or a combination of these approaches. Researchers use insights from this testing to refine questions before they are asked in a production survey, such as on the ATP.
Measuring change over time
Many surveyors want to track changes over time in people’s attitudes, opinions and behaviors. To measure change, questions are asked at two or more points in time. A cross-sectional design surveys different people in the same population at multiple points in time. A panel, such as the ATP, surveys the same people over time. However, it is common for the set of people in survey panels to change over time as new panelists are added and some prior panelists drop out. Many of the questions in Pew Research Center surveys have been asked in prior polls. Asking the same questions at different points in time allows us to report on changes in the overall views of the general public (or a subset of the public, such as registered voters, men or Black Americans), or what we call “trending the data”.
When measuring change over time, it is important to use the same question wording and to be sensitive to where the question is asked in the questionnaire to maintain a similar context as when the question was asked previously (see question wording and question order for further information). All of our survey reports include a topline questionnaire that provides the exact question wording and sequencing, along with results from the current survey and previous surveys in which we asked the question.
The Center’s transition from conducting U.S. surveys by live telephone interviewing to an online panel (around 2014 to 2020) complicated some opinion trends, but not others. Opinion trends that ask about sensitive topics (e.g., personal finances or attending religious services ) or that elicited volunteered answers (e.g., “neither” or “don’t know”) over the phone tended to show larger differences than other trends when shifting from phone polls to the online ATP. The Center adopted several strategies for coping with changes to data trends that may be related to this change in methodology. If there is evidence suggesting that a change in a trend stems from switching from phone to online measurement, Center reports flag that possibility for readers to try to head off confusion or erroneous conclusions.
Open- and closed-ended questions
One of the most significant decisions that can affect how people answer questions is whether the question is posed as an open-ended question, where respondents provide a response in their own words, or a closed-ended question, where they are asked to choose from a list of answer choices.
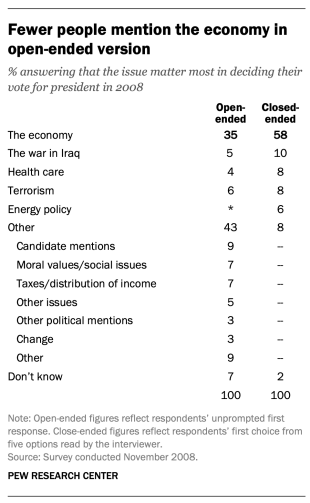
For example, in a poll conducted after the 2008 presidential election, people responded very differently to two versions of the question: “What one issue mattered most to you in deciding how you voted for president?” One was closed-ended and the other open-ended. In the closed-ended version, respondents were provided five options and could volunteer an option not on the list.
When explicitly offered the economy as a response, more than half of respondents (58%) chose this answer; only 35% of those who responded to the open-ended version volunteered the economy. Moreover, among those asked the closed-ended version, fewer than one-in-ten (8%) provided a response other than the five they were read. By contrast, fully 43% of those asked the open-ended version provided a response not listed in the closed-ended version of the question. All of the other issues were chosen at least slightly more often when explicitly offered in the closed-ended version than in the open-ended version. (Also see “High Marks for the Campaign, a High Bar for Obama” for more information.)
Researchers will sometimes conduct a pilot study using open-ended questions to discover which answers are most common. They will then develop closed-ended questions based off that pilot study that include the most common responses as answer choices. In this way, the questions may better reflect what the public is thinking, how they view a particular issue, or bring certain issues to light that the researchers may not have been aware of.
When asking closed-ended questions, the choice of options provided, how each option is described, the number of response options offered, and the order in which options are read can all influence how people respond. One example of the impact of how categories are defined can be found in a Pew Research Center poll conducted in January 2002. When half of the sample was asked whether it was “more important for President Bush to focus on domestic policy or foreign policy,” 52% chose domestic policy while only 34% said foreign policy. When the category “foreign policy” was narrowed to a specific aspect – “the war on terrorism” – far more people chose it; only 33% chose domestic policy while 52% chose the war on terrorism.
In most circumstances, the number of answer choices should be kept to a relatively small number – just four or perhaps five at most – especially in telephone surveys. Psychological research indicates that people have a hard time keeping more than this number of choices in mind at one time. When the question is asking about an objective fact and/or demographics, such as the religious affiliation of the respondent, more categories can be used. In fact, they are encouraged to ensure inclusivity. For example, Pew Research Center’s standard religion questions include more than 12 different categories, beginning with the most common affiliations (Protestant and Catholic). Most respondents have no trouble with this question because they can expect to see their religious group within that list in a self-administered survey.
In addition to the number and choice of response options offered, the order of answer categories can influence how people respond to closed-ended questions. Research suggests that in telephone surveys respondents more frequently choose items heard later in a list (a “recency effect”), and in self-administered surveys, they tend to choose items at the top of the list (a “primacy” effect).
Because of concerns about the effects of category order on responses to closed-ended questions, many sets of response options in Pew Research Center’s surveys are programmed to be randomized to ensure that the options are not asked in the same order for each respondent. Rotating or randomizing means that questions or items in a list are not asked in the same order to each respondent. Answers to questions are sometimes affected by questions that precede them. By presenting questions in a different order to each respondent, we ensure that each question gets asked in the same context as every other question the same number of times (e.g., first, last or any position in between). This does not eliminate the potential impact of previous questions on the current question, but it does ensure that this bias is spread randomly across all of the questions or items in the list. For instance, in the example discussed above about what issue mattered most in people’s vote, the order of the five issues in the closed-ended version of the question was randomized so that no one issue appeared early or late in the list for all respondents. Randomization of response items does not eliminate order effects, but it does ensure that this type of bias is spread randomly.
Questions with ordinal response categories – those with an underlying order (e.g., excellent, good, only fair, poor OR very favorable, mostly favorable, mostly unfavorable, very unfavorable) – are generally not randomized because the order of the categories conveys important information to help respondents answer the question. Generally, these types of scales should be presented in order so respondents can easily place their responses along the continuum, but the order can be reversed for some respondents. For example, in one of Pew Research Center’s questions about abortion, half of the sample is asked whether abortion should be “legal in all cases, legal in most cases, illegal in most cases, illegal in all cases,” while the other half of the sample is asked the same question with the response categories read in reverse order, starting with “illegal in all cases.” Again, reversing the order does not eliminate the recency effect but distributes it randomly across the population.
Question wording
The choice of words and phrases in a question is critical in expressing the meaning and intent of the question to the respondent and ensuring that all respondents interpret the question the same way. Even small wording differences can substantially affect the answers people provide.
[View more Methods 101 Videos ]
An example of a wording difference that had a significant impact on responses comes from a January 2003 Pew Research Center survey. When people were asked whether they would “favor or oppose taking military action in Iraq to end Saddam Hussein’s rule,” 68% said they favored military action while 25% said they opposed military action. However, when asked whether they would “favor or oppose taking military action in Iraq to end Saddam Hussein’s rule even if it meant that U.S. forces might suffer thousands of casualties, ” responses were dramatically different; only 43% said they favored military action, while 48% said they opposed it. The introduction of U.S. casualties altered the context of the question and influenced whether people favored or opposed military action in Iraq.
There has been a substantial amount of research to gauge the impact of different ways of asking questions and how to minimize differences in the way respondents interpret what is being asked. The issues related to question wording are more numerous than can be treated adequately in this short space, but below are a few of the important things to consider:
First, it is important to ask questions that are clear and specific and that each respondent will be able to answer. If a question is open-ended, it should be evident to respondents that they can answer in their own words and what type of response they should provide (an issue or problem, a month, number of days, etc.). Closed-ended questions should include all reasonable responses (i.e., the list of options is exhaustive) and the response categories should not overlap (i.e., response options should be mutually exclusive). Further, it is important to discern when it is best to use forced-choice close-ended questions (often denoted with a radio button in online surveys) versus “select-all-that-apply” lists (or check-all boxes). A 2019 Center study found that forced-choice questions tend to yield more accurate responses, especially for sensitive questions. Based on that research, the Center generally avoids using select-all-that-apply questions.
It is also important to ask only one question at a time. Questions that ask respondents to evaluate more than one concept (known as double-barreled questions) – such as “How much confidence do you have in President Obama to handle domestic and foreign policy?” – are difficult for respondents to answer and often lead to responses that are difficult to interpret. In this example, it would be more effective to ask two separate questions, one about domestic policy and another about foreign policy.
In general, questions that use simple and concrete language are more easily understood by respondents. It is especially important to consider the education level of the survey population when thinking about how easy it will be for respondents to interpret and answer a question. Double negatives (e.g., do you favor or oppose not allowing gays and lesbians to legally marry) or unfamiliar abbreviations or jargon (e.g., ANWR instead of Arctic National Wildlife Refuge) can result in respondent confusion and should be avoided.
Similarly, it is important to consider whether certain words may be viewed as biased or potentially offensive to some respondents, as well as the emotional reaction that some words may provoke. For example, in a 2005 Pew Research Center survey, 51% of respondents said they favored “making it legal for doctors to give terminally ill patients the means to end their lives,” but only 44% said they favored “making it legal for doctors to assist terminally ill patients in committing suicide.” Although both versions of the question are asking about the same thing, the reaction of respondents was different. In another example, respondents have reacted differently to questions using the word “welfare” as opposed to the more generic “assistance to the poor.” Several experiments have shown that there is much greater public support for expanding “assistance to the poor” than for expanding “welfare.”
We often write two versions of a question and ask half of the survey sample one version of the question and the other half the second version. Thus, we say we have two forms of the questionnaire. Respondents are assigned randomly to receive either form, so we can assume that the two groups of respondents are essentially identical. On questions where two versions are used, significant differences in the answers between the two forms tell us that the difference is a result of the way we worded the two versions.

One of the most common formats used in survey questions is the “agree-disagree” format. In this type of question, respondents are asked whether they agree or disagree with a particular statement. Research has shown that, compared with the better educated and better informed, less educated and less informed respondents have a greater tendency to agree with such statements. This is sometimes called an “acquiescence bias” (since some kinds of respondents are more likely to acquiesce to the assertion than are others). This behavior is even more pronounced when there’s an interviewer present, rather than when the survey is self-administered. A better practice is to offer respondents a choice between alternative statements. A Pew Research Center experiment with one of its routinely asked values questions illustrates the difference that question format can make. Not only does the forced choice format yield a very different result overall from the agree-disagree format, but the pattern of answers between respondents with more or less formal education also tends to be very different.
One other challenge in developing questionnaires is what is called “social desirability bias.” People have a natural tendency to want to be accepted and liked, and this may lead people to provide inaccurate answers to questions that deal with sensitive subjects. Research has shown that respondents understate alcohol and drug use, tax evasion and racial bias. They also may overstate church attendance, charitable contributions and the likelihood that they will vote in an election. Researchers attempt to account for this potential bias in crafting questions about these topics. For instance, when Pew Research Center surveys ask about past voting behavior, it is important to note that circumstances may have prevented the respondent from voting: “In the 2012 presidential election between Barack Obama and Mitt Romney, did things come up that kept you from voting, or did you happen to vote?” The choice of response options can also make it easier for people to be honest. For example, a question about church attendance might include three of six response options that indicate infrequent attendance. Research has also shown that social desirability bias can be greater when an interviewer is present (e.g., telephone and face-to-face surveys) than when respondents complete the survey themselves (e.g., paper and web surveys).
Lastly, because slight modifications in question wording can affect responses, identical question wording should be used when the intention is to compare results to those from earlier surveys. Similarly, because question wording and responses can vary based on the mode used to survey respondents, researchers should carefully evaluate the likely effects on trend measurements if a different survey mode will be used to assess change in opinion over time.
Question order
Once the survey questions are developed, particular attention should be paid to how they are ordered in the questionnaire. Surveyors must be attentive to how questions early in a questionnaire may have unintended effects on how respondents answer subsequent questions. Researchers have demonstrated that the order in which questions are asked can influence how people respond; earlier questions can unintentionally provide context for the questions that follow (these effects are called “order effects”).
One kind of order effect can be seen in responses to open-ended questions. Pew Research Center surveys generally ask open-ended questions about national problems, opinions about leaders and similar topics near the beginning of the questionnaire. If closed-ended questions that relate to the topic are placed before the open-ended question, respondents are much more likely to mention concepts or considerations raised in those earlier questions when responding to the open-ended question.
For closed-ended opinion questions, there are two main types of order effects: contrast effects ( where the order results in greater differences in responses), and assimilation effects (where responses are more similar as a result of their order).
An example of a contrast effect can be seen in a Pew Research Center poll conducted in October 2003, a dozen years before same-sex marriage was legalized in the U.S. That poll found that people were more likely to favor allowing gays and lesbians to enter into legal agreements that give them the same rights as married couples when this question was asked after one about whether they favored or opposed allowing gays and lesbians to marry (45% favored legal agreements when asked after the marriage question, but 37% favored legal agreements without the immediate preceding context of a question about same-sex marriage). Responses to the question about same-sex marriage, meanwhile, were not significantly affected by its placement before or after the legal agreements question.
Another experiment embedded in a December 2008 Pew Research Center poll also resulted in a contrast effect. When people were asked “All in all, are you satisfied or dissatisfied with the way things are going in this country today?” immediately after having been asked “Do you approve or disapprove of the way George W. Bush is handling his job as president?”; 88% said they were dissatisfied, compared with only 78% without the context of the prior question.
Responses to presidential approval remained relatively unchanged whether national satisfaction was asked before or after it. A similar finding occurred in December 2004 when both satisfaction and presidential approval were much higher (57% were dissatisfied when Bush approval was asked first vs. 51% when general satisfaction was asked first).
Several studies also have shown that asking a more specific question before a more general question (e.g., asking about happiness with one’s marriage before asking about one’s overall happiness) can result in a contrast effect. Although some exceptions have been found, people tend to avoid redundancy by excluding the more specific question from the general rating.
Assimilation effects occur when responses to two questions are more consistent or closer together because of their placement in the questionnaire. We found an example of an assimilation effect in a Pew Research Center poll conducted in November 2008 when we asked whether Republican leaders should work with Obama or stand up to him on important issues and whether Democratic leaders should work with Republican leaders or stand up to them on important issues. People were more likely to say that Republican leaders should work with Obama when the question was preceded by the one asking what Democratic leaders should do in working with Republican leaders (81% vs. 66%). However, when people were first asked about Republican leaders working with Obama, fewer said that Democratic leaders should work with Republican leaders (71% vs. 82%).
The order questions are asked is of particular importance when tracking trends over time. As a result, care should be taken to ensure that the context is similar each time a question is asked. Modifying the context of the question could call into question any observed changes over time (see measuring change over time for more information).
A questionnaire, like a conversation, should be grouped by topic and unfold in a logical order. It is often helpful to begin the survey with simple questions that respondents will find interesting and engaging. Throughout the survey, an effort should be made to keep the survey interesting and not overburden respondents with several difficult questions right after one another. Demographic questions such as income, education or age should not be asked near the beginning of a survey unless they are needed to determine eligibility for the survey or for routing respondents through particular sections of the questionnaire. Even then, it is best to precede such items with more interesting and engaging questions. One virtue of survey panels like the ATP is that demographic questions usually only need to be asked once a year, not in each survey.
U.S. Surveys
Other research methods.
901 E St. NW, Suite 300 Washington, DC 20004 USA (+1) 202-419-4300 | Main (+1) 202-857-8562 | Fax (+1) 202-419-4372 | Media Inquiries
Research Topics
- Email Newsletters
ABOUT PEW RESEARCH CENTER Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
© 2024 Pew Research Center
- Make a Survey
Opinion Stage » survey » Survey Questions
16 Types of Survey Questions, with 100 Examples
Good survey questions will help your business acquire the right information to drive growth. Surveys can be made up of different types of questions. Each type has a unique approach to gathering data. The questions you choose and the way you use them in your survey will affect its results.
These are the types of survey questions we will cover:
- Open-Ended Questions
- Closed-Ended Questions
- Multiple Choice Questions
- Dichotomous Questions
- Rating Scale Questions
- Likert Scale Questions
- Nominal Questions
- Demographic Questions
- Matrix Table Questions
- Side-by-Side Matrix Questions
- Data Reference Questions
- Choice Model Questions
- Net Promoter Score Questions
- Picture Choice Questions
- Image Rating Questions
- Visual Analog Scale Questions
But before we go into the actual question types, let’s talk a little about how you should use them.
Try this survey
Ready to create your own? Make a survey .
How to Use Survey Questions in Market Research
First, you need to make sure it’s a survey you’re after. In some cases, you may find that it’s actually a questionnaire that you need (read more here to learn the difference: Survey Vs. Questionnaire ), or a research quiz. In any case, though, you will need to use the right type of questions.
To determine the right type of questions for your survey, consider these factors:
- The kind of data you want to gather
- The depth of the information you require
- How long it takes to answer the survey
Regardless of the size of your business, you can use surveys to learn about potential customers, research your product market fit, collect customer feedback or employee feedback, get new registrations, and improve retention.
Surveys can help you gather valuable insights into critical aspects of your business. From brand awareness to customer satisfaction, effective surveys give you the data you need to stay ahead of the competition.
So, how should you use surveys for your market research?
Try this market research survey
Ready to create your own? Make a research survey .
Identify Customer Needs and Expectations
Perhaps the idea of using customer surveys in this advanced era of data analytics seems quaint. But one of the best ways to find out what consumers need and expect is to go directly to the source and ask. That’s why surveys still matter. All companies and online businesses can benefit from using market research surveys to determine the needs of their clients.
Determine Brand Attributes
A market research survey can also help your company identify the attributes that consumers associate with your brand. These could be tangible or intangible features that they think of when they see your brand. By determining your brand attributes, you can identify other brands in the same niche. Additionally, you can gain a clear understanding of what your audience values.
Understand Your Market’s Supply and Demand Chain
Surveying existing and potential customers enables you to understand the language of supply and demand. You can understand the measure of customer satisfaction and identify opportunities for the market to absorb new products. At the same time, you can use the data you collect to build customer-centric products or services. By understanding your target market, you can minimize the risks involved in important business ventures and develop an amazing customer experience.
Acquire Customer Demographic Information
Before any campaign or product launch, every company needs to determine its key demographic. Online surveys make it so much easier for marketers to get to know their audience and build effective user personas. With a market research survey, you can ask demographic survey questions to collect details such as family income, education, professional background, and ethnicity. It’s important to be careful and considerate in this area since questions that seem matter-of-fact to you may be experienced as loaded questions or sensitive questions by your audience.
Strategize for New Product Launches
Businesses of all sizes can use customer surveys to fine-tune products and improve services. Let’s say there’s a product you want to launch. But you’re hesitant to do so without ensuring that it will be well-received by your target audience. Why not send out a survey? With the data you gather from the survey responses, you can identify issues that may have been overlooked in the development process and make the necessary changes to improve your product’s success.
Develop a Strategic Marketing Plan
Surveys can be used in the initial phases of a campaign to help shape your marketing plan. Thanks to in-depth analytics, a quick and easy survey that respondents can finish within minutes can give you a clear idea of what potential consumers need and expect.
Create beautiful online surveys in minutes
Types of Survey Questions
No matter the purpose of your survey, the questions you ask will be crucial to its success. For this reason, it’s best to set the goal of your survey and define the information you want to gather before writing the questions.
Ask yourself: What do I want to know? Why do I want to know this? Can direct questions help me get the information I need? How am I going to use the data I gather?
Once you have a clear goal in mind, you can choose the best questions to elicit the right kind of information. We’ve made a list of the most common types of survey questions to help you get started.
1. Open-Ended Questions
If you prefer to gather qualitative insights from your respondents, the best way to do so is through an open-ended question. That’s because this survey question type gives respondents more opportunity to say what’s on their minds. After all, an open question doesn’t come with pre-set answer choices that respondents can select. Instead, it uses a text box where respondents can leave more detailed responses.
Ideally, you should ask such questions when you’re doing expert interviews or preliminary research. You may also opt to end surveys with this type of question. This is to give respondents a chance to share additional concerns with you. By letting respondents give answers in their own words, even to a single question, you can identify opportunities you might have overlooked. At the same time, it shows that you appreciate their effort to answer all your questions.
Since quantifying written answers isn’t easy to do, opt to use these questions sparingly, especially if you’re dealing with a large population.
Examples of open-ended questions:
- What can you tell us about yourself? (Your age, gender, hobbies, interests, and anything else you’re willing to share)
- How satisfied or dissatisfied are you with our service?
- What has kept you from signing up for our newsletter?
2. Closed-Ended Questions
Consumers want surveys they can answer in a jiffy. Closed-ended questions are ideal for market research for that reason. They come with a limited number of options, often one-word responses such as yes or no, multiple-choice, or a rating scale. Compared to open-ended questions, these drive limited insights because respondents only have to choose from pre-selected choices.
Ask closed-ended questions if you need to gather quantifiable data or to categorize your respondents. Furthermore, you can use such questions to drive higher response rates. Let’s say your audience isn’t particularly interested in the topic you intend to ask them about. You can use closed-ended questions to make it easier for them to complete the survey in minutes.
Close-ended question examples:
- Which of the following are you most likely to read? (a) a series of blog posts (b) a novel (c) the daily news (d) I don’t read on a regular basis
- How would you rate our service on a 5-point scale, with 1 representing bad service, and 5 representing great service?
- How likely are you to recommend us on a scale of 0 to 10?
3. Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple-choice questions are a basic type of closed-ended survey question that give respondents multiple answers to choose from. These questions can be broken down into two main categories:
- Single-answer questions – respondents are directed to choose one, and only one answer from a list of answer options.
- Multiple answer questions – where respondents can select a number of answers in a single question.
When designed correctly they can be very effective survey questions since they’re relatively simple questions to answer, and the data is easy to analyze.
Multiple-choice sample questions:
- It’s exceptional
- Could be better
- It’s terrible
- Whole-grain rice
- Gluten-free noodles
- Suger-free soft drinks
- Lactose-free ice cream
Try this product survey
Ready to create your own? Make a product survey .
4. Dichotomous Questions
Dichotomous questions are a type of close-ended questions with only two answer options that represent the opposite of each other. In other words, yes/no questions, or true/false questions. They’re often used as screening questions to identify potential customers since they’re so quick and easy to answer and require no extra effort.
They’re also good for splitting your audience into two groups, enabling you to direct each group to a different series of questions. This can be done quite easily using skip logic which sends people on different survey paths based on their answers to previous questions.
Examples of questions:
Do you have experience working with Google Analytics? Yes/no Google Analytics is used for tracking user behavior. True/false Google Analytics has a steep learning curve for the average user. Agree/disagree
5. Rating Scale Questions
Also called ordinal questions, these questions help researchers measure customer sentiment in a quantitative way. This type of question comes with a range of response options. It could be from 1 to 5 or 1 to 10.
In a survey, a respondent selects the number that accurately represents their response. Of course, you have to establish the value of the numbers on your scale for it to be effective.
Rating scales can be very effective survey questions, however, the lack of proper survey scaling could lead to bad survey questions that respondents Don’t know how to answer. And even if they think you do, the results won’t be reliable because every respondent could interpret the scale differently. So, it’s important to be clear.
If you want to know how respondents experienced your customer service, you can establish a scale from 1 to 10 to measure customer sentiment. Then, assign the value of 1 and 10. The lowest number on the scale could, for instance, mean “very disappointed” while the highest value could represent “very satisfied”.
Examples of rating scale questions:
- On a scale of 0 to 10, how would you rate your last customer support interaction with us? (0=terrible, 10=amazing)
- How likely are you to recommend our company to a friend or colleague on a scale of 1 to 5? 1=very unlikely, 5=very likely
- How would you rate your shopping experience at our online business on a scale of 1 to 7? 1=bad, 4=ok, 7=amazing
6. Likert Scale Questions
These questions can either be unipolar or bipolar. Unipolar scales center on the presence or absence of quality. Moreover, they don’t have a natural midpoint. For example, a unipolar satisfaction scale may have the following options: extremely satisfied, very satisfied, moderately satisfied, slightly satisfied, and not satisfied.
Bipolar scales, on the other hand, are based on either side of neutrality. That means they have a midpoint. A common bipolar scale, for instance, may have the following options: extremely unsatisfied, very unsatisfied, somewhat unsatisfied, neither satisfied nor dissatisfied, somewhat satisfied, very satisfied, or extremely satisfied.
Likert scale questions can be used for a wide variety of objectives. They are great for collecting initial feedback. They can also help you gauge customer sentiment, among other things.
Likert scale sample questions:
- How important is it that you can access customer support 24/7? (Choices: Very Important, Important, Neutral, Low Importance, and Not Important At All)
- How satisfied are you after using our products? (Choices: Very Satisfied, Moderately Satisfied, Neutral, Slightly Unsatisfied, and Very Unsatisfied)
- How would you rate our customer care representative’s knowledge of our products? (Choices: Not at All Satisfactory, Low Satisfactory, Somewhat Satisfactory, Satisfactory, and Very Satisfactory)
Try this Likert scale survey
Ready to create your own? Make a Likert scale survey .
7. Nominal Questions
Also a type of measurement scale, nominal questions come with tags or labels for identifying or classifying items. For these questions, you can use non-numeric variables. You can also assign numbers to each response option, but they won’t actually have value.
On a nominal scale, you assign each number to a unique label. Especially if the goal is identification, you have to stick to a one-to-one correlation between the numeric value and the label. Much like cars on a race track, numbers are assigned to identify the driver associated with the car. It doesn’t represent the characteristics of the vehicle.
However, when a nominal scale is used for classification, the numerical values assigned to each descriptor serve as a tag. This is for categorizing or arranging the objects in a class. For example, you want to know your respondents’ gender. You can assign the letter M for males and F for females in the survey question.
Examples of nominal questions:
- What is your hair color? (Choices: 1 – Black, 2 – Blonde, 3 – Brown, 4 – Red, 5 – Other)
- How old are you? (Choices: 1 – Under 25, 2 – 25-35, 3 – Over 35)
- How do you commute to work? (Choices: 1- Car, 2 – Bus, 3 – Train, 4 – Walk, 5 – Other)
8. Demographic Questions
As its name suggests, this question type is used for gathering information about a consumer. From their background to income level, these simple questions can provide you with deeper insights into your target market. They’re also used as screening questions since they can help you to identify the population segments you’re targeting.
Demographic questions help you understand your target market. By collecting customer data, you can identify similarities and differences between different demographics. Then, you can make buyer personas and classify them based on who they are or what they do.
Some demographic topics can lead to quite loaded survey questions. When writing your demographic survey, try to identify the loaded questions and ask yourself if someone could find the question, the answer choices, or the lack of a certain answer choice offensive. Do your best to phrase them sensitively and respectfully, and if you can’t consider leaving them out.
With every single question that you write, it’s important to place yourself in the shoes of your respondents. If you want to ask students about their income, your response options should range below $20,000 per year, because most of them are probably not making more than that. But if your respondents are affluent, your choices should have a range higher than $100,000.
Examples of demographic questions:
- How old are you?
- What is your level of education?
- What is your marital status?
- What’s your current employment status?
Try this demographic survey
Ready to create your own? Make a demographic survey .
9. Matrix Table Questions
If you need to ask a series of questions that require the same response options, you can group them together in a matrix table instead of breaking them into separate questions.
While these bundled questions are convenient, you have to use them carefully. Visually, large matrix tables can seem overwhelming. In addition, online survey questions of this sort aren’t always mobile-friendly. Having too many questions or choices may even trigger undesirable survey-taking behavior such as straight-lining. This is when respondents select the same options without carefully considering each one. Sometimes, they do that because the actual experience feels like a complicated matrix and they just want to finish it.
Example of a matrix table:
How satisfied or dissatisfied are you with the following?
Interaction with sales staff
Product selection
Marketing messages
Pricing structure
Then, you can make a brief list of response options. There should be no more than five options.
10. Side-by-Side Matrix Questions
A side-by-side matrix is similar to your regular matrix table in that it allows you to group together questions that require simple response options. However, a matrix table only lets you collect data from a single variable. A side-by-side matrix, on the other hand, enables you to gather data on two or more dimensions.
For example, let’s say you want to ask respondents about the importance of different services and their satisfaction with each. You can group them together in a side-by-side matrix. By organizing questions in tables, your respondents can easily fill out the survey in minutes.
Much like a regular matrix table, you shouldn’t overwhelm consumers. Avoid adding too many variables to your table. Moreover, you should keep the response options short.
Examples of side-by-side matrix questions:
Example of side-by-side matrix:
How would you rate our shopping services?
Identify the variables. They can be customer support, packaging, and punctuality. Next, you should add different dimensions such as importance and satisfaction level. On each table, you should add a similar scale. You can start with 1, which could mean Not Important and Not Satisfied.
11. Data Reference Questions
Use data reference questions to gather validated data against standardized databases. For example, direct respondents to enter their postal code or zip code in a small text box. The value entered will then be cross-referenced with the database. If it is correct, their city or state will be displayed, and they can proceed with the survey. And if it is incorrect, they’ll be asked to enter a valid postal code or zip code.
Examples of data reference questions:
- What is your five-digit zip code?
- What is your postal code?
12. Choice Model Questions
Choice model questions enable you to understand the essential aspects of consumers’ decision-making process. This involves a quantitative method called Conjoint Analysis. It helps you grasp your users’ preferences, the features they like, and the right price range your target market can afford. More importantly, it enables you to understand if your new products will be accepted by your target market.
These questions also involve Maximum Difference Scaling, a method that allows the ranking of up to 30 elements. This can include product features, benefits, opportunities for potential investment, and possible marketing messages for an upcoming product.
Example of a choice model question:
- If you were to buy a sandwich, which ingredient combination would you choose?
Let’s say you want to know about consumers’ bread, filling, and sauce preferences. In your survey, you can give them three sandwich options. You can, for instance, offer three kinds of bread: grain wheat, parmesan oregano, and Italian. As for the sauces, you can make them choose between ranch, blue cheese, and mustard. Finally, you need to suggest three types of filling, for example, chicken, veggies, and meatballs.
Respondents will see unique combinations of these ingredients in your survey. Then, they will have to choose the one that they like best.
13. Net Promoter Score Questions
A net promoter score (NPS) survey question measures brand shareability, as well as customer satisfaction levels. It helps you get reliable customer insights and gauge the likelihood of respondents recommending your company to friends or colleagues (i.e. prospective customers). The scoring model involves a scale of 0 to 10, which is divided into three sections. Respondents who give a 9 to 10 score are considered Promoters. Passives give a 7 to 8 score, while the rest are considered Detractors.
Once you’ve gathered all the data, the responses per section are calculated. Then, the net value of promoters is shown. This type of survey question offers a useful form of initial feedback. It helps you understand why promoters are leaving high ratings so you can work on enhancing those strengths. At the same time, it enables you to determine weaknesses. It illustrates why detractors are leaving such low ratings.
Examples of net promoter score questions:
- On a scale of 0 to 10, how likely are you to recommend our brand to a friend or colleague? (0 = Not at all Likely and 10 = Very Likely)
- Would you encourage friends to work at our company?
- How likely are you to recommend (specific name of the product) to friends?
Try this NPS survey
Ready to create your own? Make an NPS survey .
14. Picture Choice Questions
It’s no secret that people respond to visual content more than plain text. This applies to surveys as well – visual content can boost user experience.
Think of these as alternate questions to multiple-choice questions. Users can pick one or many from a visual list of options. You can use picture choice questions to make your survey more engaging.
Keep in mind, that it’s very easy to unintentionally create a leading question by using images that get a specific reaction from people. For example, if you’re asking about food preferences and one of the images is more attractive than others, people may see it as the perfect answer even if it doesn’t represent their favorite dish because it looks most attractive. So when you’re illustrating a variety of answers with images make sure their quality and attractiveness is similar.
Picture choice examples:
- What is your favorite pizza topping?
- Which color should we choose for our logo?
- What other products would you like to see in our online store?
Opinion Stage has an online survey maker tool that can help you design image-based survey questions in minutes. Choose from hundreds of professionally-designed templates, and tailor them to fit your needs, or design them from scratch.
Try this visual survey
Ready to create your own? Make a visual survey .
15. Image Rating Questions
Another way to incorporate images in questions is through image ratings. Let’s say you want to know how satisfied consumers are with your products. You can display all of the items you want respondents to rate. Under each item, provide a shortlist of options (e.g. very unsatisfied, unsatisfied, neutral, satisfied, very unsatisfied).
You could also use a rank order question to let your respondents rank their favorite products. Simply give them multiple options, and then, ask them for their top three or five favorites. Or you could ask them to organize a series of answers by ranking.
For example, if it’s an employee engagement survey question you could ask your employees to rank a series of office activities from their least favorite to their most favorite. There are many ways to do this visually. Some tools use dropdown menus, and others let you move the answer options around, but the simplest way is to use numbers like in the example below.
Rank order questions should work well on mobile devices. After all, respondents only have to tap on their favorite items to participate.
Example of image rating questions:
- What are your 5 favorite desserts?
16. Visual Analog Scale Questions
Another type of scale you can use in a survey is the visual analog scale, which displays your questions in a more engaging manner. For instance, you can use text sliders or numeric sliders to ask respondents to rate the service they’ve received from your company and let them select an image line that best illustrates their answer.
You can also use pictures to depict each option. Smiley ratings are commonly used in surveys nowadays because they’re simple questions, easy on the eyes, and quite fun. Star ratings are also effective survey questions that require no extra effort.
Examples of visual analog scale questions:
- How would you rate the overall quality of our customer service?
- What do you think of our website’s interface?
- How satisfied are you with the way our service works in offline mode?
Create engaging image-based surveys in minutes
The Fundamentals of Good Survey Questions
There is an art to writing effective questions for your survey. Regardless of the kind of survey you plan to deploy, there are a few practices that you should adhere to.
Use Clear and Simple Language
Always choose clear and simple words when writing your online survey questions. In doing so, you can keep the questions short yet specific.
Complex phrasing, too many words, acronyms, and specialized jargon require extra effort and could cause confusion. Make it easy for your respondents to help you. Keep it simple.
Moreover, avoid double-barreled questions , they will frustrate your respondents and skew your customer insights. Here’s an example of a double-barreled question: “Did you find our new search feature helpful and easy to use? yes/no” Such a question might be simple to understand, but it isn’t easy to answer because it covers two issues. How could someone respond if they found the search feature helpful but difficult to understand? It would make more sense to separate it into two questions, i.e. did you find the new search feature helpful? Was the new search feature easy for you to use?
Focus on the Consumer
Make the survey engaging. Use the second-person (i.e., ‘you’ format) to address your respondents directly, and use the first-person (i.e., ‘we’ format) to refer to your company. This makes the survey more personal and helps respondents recall prior experiences with your company. In turn, it leads to quicker and more accurate answers.
Ask for Feedback
Get initial feedback from external people that fit the profile of your average user before sending your survey out. It’s like a user testing tool, you need someone who isn’t you to take a look and tell you if your survey is clear and friendly.
Require Minimal Effort to Answer
There’s no reason to ask people questions that aren’t essential to you. Ask people questions that really matter to you, and try to keep it down to the minimum number, so as not to waste their time. The more succinct a survey is, the more likely a respondent is to complete it. So, let them know that you value their time by designing a survey they can finish within minutes.
Stay Free From Bias
Survey question mistake #1 is to ask leading or biased questions. Don’t plant opinions in your respondents’ heads before they can formulate their own. Don’t ask people questions like “How good was your in-store experience today?” Phrase it in a neutral way like “On a scale of 1 to 10, how would you rate your in-store experience?”
Keep the Purpose of the Survey Vague
Sometimes, respondents have a tendency to give you the answers you want to hear. One of the simplest ways to prevent that is by keeping the purpose of your survey vague. Instead, you should give a general description of your survey.
Get a personalized survey up and running today
Sample Survey Questions
Below are sample questions for different market research needs. You can use many of them as close-ended questions as well as open questions, depending on your need and preference.
Brand Awareness Questions
- When was the last time you used (a type of product)?
- What brands come to mind as your top choice when you think of buying this product type?
- What factors do you consider when selecting a vendor? (rank by importance)
- Which of the following brands have you heard of? (please select all that apply)
- Where have you seen or heard of our brand in the last three months? (please select all that apply)
- How often have you heard people talking about our brand in the past three months?
- How familiar are you with our company?
- On a scale of 1 to 10, how likely are you to recommend our brand to a friend?
Customer Demographic Questions
- What gender do you identify as?
- Where were you born?
- Are you married?
- What is your annual household income?
- Do you support children under the age of 18?
- How many children under the age of 18 reside in your household?
- What category best describes your employment status?
- Which general geographic area of the state do you reside in?
- What is your current employment status?
- Which of the following languages can you speak fluently?
Brand & Marketing Feedback Questions
- Have you purchased from our company before?
- How long have you been a customer?
- Which best describes your latest experience with our brand? (please select all that apply)
- Which of the following attributes do you associate with our brand? (please select all that apply)
- What kind of feelings do you associate with our brand?
- Which of these marketing messages represents us best in your opinion?
- How would you rate your level of emotional attachment to our brand?
- What five words would you use to describe our brand to a friend or colleague?
- On a scale of 1 to 10, how likely are you to recommend our brand to a friend or colleague? (1 being Not at All Likely at 10 being Extremely Likely)
Product & Package Testing Questions
- What is your first impression of the product?
- How important are the following features to you?
- How would you rate the product’s quality?
- If the product was already available, how likely are you to purchase it?
- How likely are you to replace an old product with this one?
- How likely would you recommend this product to a friend or colleague?
- What did you like best about this product?
- What are the features that you want to see improved?
- Based on the value for money, how would you rate this product compared to the competition?
- What is your first impression of the product packaging?
- How satisfied or dissatisfied are you with the following features? (Visual appeal, Quality, and Price)
- How similar or different is the packaging from the competition?
- Does the packaging have too little or too much information?
- How likely are you to purchase the product based on its packaging?
- What did you like best about the packaging?
- What did you dislike about the packaging?
- How would you like the packaging to be improved?
Pricing Strategy Testing Questions
- How often do you purchase this type of product?
- What brands do you usually purchase? (Please select all that apply).
- On a scale of 1 to 5, how satisfied are you with the pricing of this type of product? (1 being Not at All Satisfied at 5 being Extremely Satisfied)
- What is the ideal price for this type of product?
- What price range would make you consider that the product is too expensive?
- At what price is the product too cheap that its quality is questionable?
- How much does the price for our product compare to other products on the market?
- If the product was available, how likely would you be to purchase it?
Customer Satisfaction Questions
- How would you rate the following products/services at (name of company)?
- Which of the following attributes would you use to describe our product/service? Please select all that apply.
- Would you recommend our company to a friend or colleague? (1 being Very Unlikely and 10 being Very Likely)
- How responsive has our support team been to your questions and concerns?
- How likely are you to purchase from our company again?
- What other comments, concerns, or questions do you have for us?
Brand Performance Questions
- When was the last time you used this type of product?
- When you think of our brand, what words come to mind?
- Which of the following are important to your decision-making process?
- How well do our products perform based on the following categories? (Price, Quality, Design, etc.)
- How well does our product meet your needs?
- What was missing or disappointing about your experience with our brand?
- What did you like most about your experience with our brand?
- How can we improve your experience?
Customer Behavior Questions
- In the household, are you the primary decision maker when it comes to purchasing this type of product?
- When was the last time you purchased this product type?
- How do you find out about brands offering this product type? Please select all that apply.
- When you think of this product type, which of the following are the top three brands that come to mind?
- How much of your purchasing decisions are influenced by social media?
Save time and choose a customizable survey template
How to Improve Survey Response Rates
Every market research survey needs to be designed carefully in order to drive higher response rates. As a result, you can acquire the right data to inform the decision-making process.
Here are a few survey ideas to boost response rates:
Make It Personal
Write a survey as if it’s a conversation between you and your respondents. For example, use first-person pronouns to make your surveys feel more personal and customer-centric. In addition, stick with simple and specific language to better connect with respondents. Simply put, write your questions as you’d use them in a conversation with consumers.
Make It Engaging
Gathering data from consumers is essential to any business, but market research surveys don’t have to be dull. You can engage and connect with respondents on a human level through an interactive survey. As a result, you can obtain thorough responses and maximize the number of respondents that complete the entire survey.
Don’t Waste Their Time
No one wants to answer a survey with 50 questions because it takes too long to complete. Hence, you should narrow down your list to the most important ones. Only ask questions that will lead to actionable insights. As for the rest, you can get rid of them.
Offer Incentives
There are two types of incentives you can offer: monetary or non-monetary. Either way, you need to make sure that the incentive provides value to your target audience. In addition, you must choose between promised or prepaid incentives. In other words, you have to decide if you want to offer everyone or a small group of people some incentives.
Providing respondents with incentives to finish the survey can increase response rates—but not always. Customer satisfaction surveys, for example, won’t always need incentives because it might affect the quality of the results.
Make It Responsive
Perhaps the easiest way to gain respondents is to make your surveys responsive and mobile-optimized. In doing so, it will perform well and look amazing on all devices. It should also enable you to reach consumers during their daily commute or lunch break. Thus, make sure your survey is optimized for different kinds of devices, especially for mobile.
Offer Surveys in Multiple Channels
If a survey is optimized for all device types, it should be easily accessed on social media. So, take advantage of your platforms and share your survey on different social media channels to increase participation rates.
Designing surveys doesn’t have to be challenging. On the contrary, you can easily create interactive surveys with Opinion Stage. Create a survey from scratch, or choose one of our many professionally-made templates to complete it within minutes. Through Opinion Stage, you can drive higher response rates and evaluate results from a powerful analytics dashboard.
It’s important to be familiar with the different types of survey questions and when to use them. Getting to know each survey question type will help you improve your research. Not to mention, you can gain high-quality data when you design a survey with the right types of questions .
In addition, you should leverage the right tool to create engaging surveys in minutes. With an online survey maker like Opinion Stage, you can customize your surveys to fit your brand image. Or, you can choose from professionally-made templates. Either way, it can help boost response rates.
Last but not least, check your survey design before deploying it. Make sure to see what your survey will look like to your respondents. See opportunities for improvement, then apply the necessary changes.
Popular Resources
You can easily do yourself, no need for a developer
Are you an agency specialized in UX, digital marketing, or growth? Join our Partner Program
Learn / Blog / Article
Back to blog
Survey questions 101: 70+ survey question examples, types of surveys, and FAQs
How well do you understand your prospects and customers—who they are, what keeps them awake at night, and what brought them to your business in search of a solution? Asking the right survey questions at the right point in their customer journey is the most effective way to put yourself in your customers’ shoes.
Last updated
Reading time.

This comprehensive intro to survey questions contains over 70 examples of effective questions, an overview of different types of survey questions, and advice on how to word them for maximum effect. Plus, we’ll toss in our pre-built survey templates, expert survey insights, and tips to make the most of AI for Surveys in Hotjar. ✨
Surveying your users is the simplest way to understand their pain points, needs, and motivations. But first, you need to know how to set up surveys that give you the answers you—and your business—truly need. Impactful surveys start here:
❓ The main types of survey questions : most survey questions are classified as open-ended, closed-ended, nominal, Likert scale, rating scale, and yes/no. The best surveys often use a combination of questions.
💡 70+ good survey question examples : our top 70+ survey questions, categorized across ecommerce, SaaS, and publishing, will help you find answers to your business’s most burning questions
✅ What makes a survey question ‘good’ : a good survey question is anything that helps you get clear insights and business-critical information about your customers
❌ The dos and don’ts of writing good survey questions : remember to be concise and polite, use the foot-in-door principle, alternate questions, and test your surveys. But don’t ask leading or loaded questions, overwhelm respondents with too many questions, or neglect other tools that can get you the answers you need.
👍 How to run your surveys the right way : use a versatile survey tool like Hotjar Surveys that allows you to create on-site surveys at specific points in the customer journey or send surveys via a link
🛠️ 10 use cases for good survey questions : use your survey insights to create user personas, understand pain points, measure product-market fit, get valuable testimonials, measure customer satisfaction, and more
Use Hotjar to build your survey and get the customer insight you need to grow your business.
6 main types of survey questions
Let’s dive into our list of survey question examples, starting with a breakdown of the six main categories your questions will fall into:
Open-ended questions
Closed-ended questions
Nominal questions
Likert scale questions
Rating scale questions
'Yes' or 'no' questions
1. Open-ended survey questions
Open-ended questions give your respondents the freedom to answer in their own words , instead of limiting their response to a set of pre-selected choices (such as multiple-choice answers, yes/no answers, 0–10 ratings, etc.).
Examples of open-ended questions:
What other products would you like to see us offer?
If you could change just one thing about our product, what would it be?
When to use open-ended questions in a survey
The majority of example questions included in this post are open-ended, and there are some good reasons for that:
Open-ended questions help you learn about customer needs you didn’t know existed , and they shine a light on areas for improvement that you may not have considered before. If you limit your respondents’ answers, you risk cutting yourself off from key insights.
Open-ended questions are very useful when you first begin surveying your customers and collecting their feedback. If you don't yet have a good amount of insight, answers to open-ended questions will go a long way toward educating you about who your customers are and what they're looking for.
There are, however, a few downsides to open-ended questions:
First, people tend to be less likely to respond to open-ended questions in general because they take comparatively more effort to answer than, say, a yes/no one
Second, but connected: if you ask consecutive open-ended questions during your survey, people will get tired of answering them, and their answers might become less helpful the more you ask
Finally, the data you receive from open-ended questions will take longer to analyze compared to easy 1-5 or yes/no answers—but don’t let that stop you. There are plenty of shortcuts that make it easier than it looks (we explain it all in our post about how to analyze open-ended questions , which includes a free analysis template.)
💡 Pro tip: if you’re using Hotjar Surveys, let our AI for Surveys feature analyze your open-ended survey responses for you. Hotjar AI reviews all your survey responses and provides an automated summary report of key findings, including supporting quotes and actionable recommendations for next steps.
2. Closed-ended survey questions
Closed-end questions limit a user’s response options to a set of pre-selected choices. This broad category of questions includes
‘Yes’ or ‘no’ questions
When to use closed-ended questions
Closed-ended questions work brilliantly in two scenarios:
To open a survey, because they require little time and effort and are therefore easy for people to answer. This is called the foot-in-the-door principle: once someone commits to answering the first question, they may be more likely to answer the open-ended questions that follow.
When you need to create graphs and trends based on people’s answers. Responses to closed-ended questions are easy to measure and use as benchmarks. Rating scale questions, in particular (e.g. where people rate customer service or on a scale of 1-10), allow you to gather customer sentiment and compare your progress over time.
3. Nominal questions
A nominal question is a type of survey question that presents people with multiple answer choices; the answers are non-numerical in nature and don't overlap (unless you include an ‘all of the above’ option).
Example of nominal question:
What are you using [product name] for?
Personal use
Both business and personal use
When to use nominal questions
Nominal questions work well when there is a limited number of categories for a given question (see the example above). They’re easy to create graphs and trends from, but the downside is that you may not be offering enough categories for people to reply.
For example, if you ask people what type of browser they’re using and only give them three options to choose from, you may inadvertently alienate everybody who uses a fourth type and now can’t tell you about it.
That said, you can add an open-ended component to a nominal question with an expandable ’other’ category, where respondents can write in an answer that isn’t on the list. This way, you essentially ask an open-ended question that doesn’t limit them to the options you’ve picked.
4. Likert scale questions
The Likert scale is typically a 5- or 7-point scale that evaluates a respondent’s level of agreement with a statement or the intensity of their reaction toward something.
The scale develops symmetrically: the median number (e.g. a 3 on a 5-point scale) indicates a point of neutrality, the lowest number (always 1) indicates an extreme view, and the highest number (e.g. a 5 on a 5-point scale) indicates the opposite extreme view.
Example of a Likert scale question:
When to use Likert scale questions
Likert-type questions are also known as ordinal questions because the answers are presented in a specific order. Like other multiple-choice questions, Likert scale questions come in handy when you already have some sense of what your customers are thinking. For example, if your open-ended questions uncover a complaint about a recent change to your ordering process, you could use a Likert scale question to determine how the average user felt about the change.
A series of Likert scale questions can also be turned into a matrix question. Since they have identical response options, they are easily combined into a single matrix and break down the pattern of single questions for users.
5. Rating scale questions
Rating scale questions are questions where the answers map onto a numeric scale (such as rating customer support on a scale of 1-5, or likelihood to recommend a product from 0-10).
Examples of rating questions:
How likely are you to recommend us to a friend or colleague on a scale of 0-10?
How would you rate our customer service on a scale of 1-5?
When to use rating questions
Whenever you want to assign a numerical value to your survey or visualize and compare trends , a rating question is the way to go.
A typical rating question is used to determine Net Promoter Score® (NPS®) : the question asks customers to rate their likelihood of recommending products or services to their friends or colleagues, and allows you to look at the results historically and see if you're improving or getting worse. Rating questions are also used for customer satisfaction (CSAT) surveys and product reviews.
When you use a rating question in a survey, be sure to explain what the scale means (e.g. 1 for ‘Poor’, 5 for ‘Amazing’). And consider adding a follow-up open-ended question to understand why the user left that score.
Example of a rating question (NPS):
6. ‘Yes’ or ‘no’ questions
These dichotomous questions are super straightforward, requiring a simple ‘yes’ or ‘no’ reply.
Examples of yes/no questions:
Was this article useful? (Yes/No)
Did you find what you were looking for today? (Yes/No)
When to use ‘yes’ or ‘no’ questions
‘Yes’ and ‘no’ questions are a good way to quickly segment your respondents . For example, say you’re trying to understand what obstacles or objections prevent people from trying your product. You can place a survey on your pricing page asking people if something is stopping them, and follow up with the segment who replied ‘yes’ by asking them to elaborate further.
These questions are also effective for getting your foot in the door: a ‘yes’ or ‘no’ question requires very little effort to answer. Once a user commits to answering the first question, they tend to become more willing to answer the questions that follow, or even leave you their contact information.
70+ more survey question examples
Below is a list of good survey questions, categorized across ecommerce, software as a service (SaaS), and publishing. You don't have to use them word-for-word, but hopefully, this list will spark some extra-good ideas for the surveys you’ll run immediately after reading this article. (Plus, you can create all of them with Hotjar Surveys—stick with us a little longer to find out how. 😉)
📊 9 basic demographic survey questions
Ask these questions when you want context about your respondents and target audience, so you can segment them later. Consider including demographic information questions in your survey when conducting user or market research as well.
But don’t ask demographic questions just for the sake of it—if you're not going to use some of the data points from these sometimes sensitive questions (e.g. if gender is irrelevant to the result of your survey), move on to the ones that are truly useful for you, business-wise.
Take a look at the selection of examples below, and keep in mind that you can convert most of them to multiple choice questions:
What is your name?
What is your age?
What is your gender?
What company do you work for?
What vertical/industry best describes your company?
What best describes your role?
In which department do you work?
What is the total number of employees in your company (including all locations where your employer operates)?
What is your company's annual revenue?
🚀 Get started: gather more info about your users with our product-market fit survey template .
👥 20+ effective customer questions
These questions are particularly recommended for ecommerce companies:
Before purchase
What information is missing or would make your decision to buy easier?
What is your biggest fear or concern about purchasing this item?
Were you able to complete the purpose of your visit today?
If you did not make a purchase today, what stopped you?
After purchase
Was there anything about this checkout process we could improve?
What was your biggest fear or concern about purchasing from us?
What persuaded you to complete the purchase of the item(s) in your cart today?
If you could no longer use [product name], what’s the one thing you would miss the most?
What’s the one thing that nearly stopped you from buying from us?
👉 Check out our 7-step guide to setting up an ecommerce post-purchase survey .
Other useful customer questions
Do you have any questions before you complete your purchase?
What other information would you like to see on this page?
What were the three main things that persuaded you to create an account today?
What nearly stopped you from creating an account today?
Which other options did you consider before choosing [product name]?
What would persuade you to use us more often?
What was your biggest challenge, frustration, or problem in finding the right [product type] online?
Please list the top three things that persuaded you to use us rather than a competitor.
Were you able to find the information you were looking for?
How satisfied are you with our support?
How would you rate our service/support on a scale of 0-10? (0 = terrible, 10 = stellar)
How likely are you to recommend us to a friend or colleague? ( NPS question )
Is there anything preventing you from purchasing at this point?
🚀 Get started: learn how satisfied customers are with our expert-built customer satisfaction and NPS survey templates .
Set up a survey in seconds
Use Hotjar's free survey templates to build virtually any type of survey, and start gathering valuable insights in moments.
🛍 30+ product survey questions
These questions are particularly recommended for SaaS companies:
Questions for new or trial users
What nearly stopped you from signing up today?
How likely are you to recommend us to a friend or colleague on a scale of 0-10? (NPS question)
Is our pricing clear? If not, what would you change?
Questions for paying customers
What convinced you to pay for this service?
What’s the one thing we are missing in [product type]?
What's one feature we can add that would make our product indispensable for you?
If you could no longer use [name of product], what’s the one thing you would miss the most?
🚀 Get started: find out what your buyers really think with our pricing plan feedback survey template .
Questions for former/churned customers
What is the main reason you're canceling your account? Please be blunt and direct.
If you could have changed one thing in [product name], what would it have been?
If you had a magic wand and could change anything in [product name], what would it be?
🚀 Get started: find out why customers churn with our free-to-use churn analysis survey template .
Other useful product questions
What were the three main things that persuaded you to sign up today?
Do you have any questions before starting a free trial?
What persuaded you to start a trial?
Was this help section useful?
Was this article useful?
How would you rate our service/support on a scale of 1-10? (0 = terrible, 10 = stellar)
Is there anything preventing you from upgrading at this point?
Is there anything on this page that doesn't work the way you expected it to?
What could we change to make you want to continue using us?
If you did not upgrade today, what stopped you?
What's the next thing you think we should build?
How would you feel if we discontinued this feature?
What's the next feature or functionality we should build?
🚀 Get started: gather feedback on your product with our free-to-use product feedback survey template .
🖋 20+ effective questions for publishers and bloggers
Questions to help improve content.
If you could change just one thing in [publication name], what would it be?
What other content would you like to see us offer?
How would you rate this article on a scale of 1–10?
If you could change anything on this page, what would you have us do?
If you did not subscribe to [publication name] today, what was it that stopped you?
🚀 Get started: find ways to improve your website copy and messaging with our content feedback survey template .
New subscriptions
What convinced you to subscribe to [publication] today?
What almost stopped you from subscribing?
What were the three main things that persuaded you to join our list today?
Cancellations
What is the main reason you're unsubscribing? Please be specific.
Other useful content-related questions
What’s the one thing we are missing in [publication name]?
What would persuade you to visit us more often?
How likely are you to recommend us to someone with similar interests? (NPS question)
What’s missing on this page?
What topics would you like to see us write about next?
How useful was this article?
What could we do to make this page more useful?
Is there anything on this site that doesn't work the way you expected it to?
What's one thing we can add that would make [publication name] indispensable for you?
If you could no longer read [publication name], what’s the one thing you would miss the most?
💡 Pro tip: do you have a general survey goal in mind, but are struggling to pin down the right questions to ask? Give Hotjar’s AI for Surveys a go and watch as it generates a survey for you in seconds with questions tailored to the exact purpose of the survey you want to run.
What makes a good survey question?
We’ve run through more than 70 of our favorite survey questions—but what is it that makes a good survey question, well, good ? An effective question is anything that helps you get clear insights and business-critical information about your customers , including
Who your target market is
How you should price your products
What’s stopping people from buying from you
Why visitors leave your website
With this information, you can tailor your website, products, landing pages, and messaging to improve the user experience and, ultimately, maximize conversions .
How to write good survey questions: the DOs and DON’Ts
To help you understand the basics and avoid some rookie mistakes, we asked a few experts to give us their thoughts on what makes a good and effective survey question.
Survey question DOs
✅ do focus your questions on the customer.
It may be tempting to focus on your company or products, but it’s usually more effective to put the focus back on the customer. Get to know their needs, drivers, pain points, and barriers to purchase by asking about their experience. That’s what you’re after: you want to know what it’s like inside their heads and how they feel when they use your website and products.
Rather than asking, “Why did you buy our product?” ask, “What was happening in your life that led you to search for this solution?” Instead of asking, “What's the one feature you love about [product],” ask, “If our company were to close tomorrow, what would be the one thing you’d miss the most?” These types of surveys have helped me double and triple my clients.
✅ DO be polite and concise (without skimping on micro-copy)
Put time into your micro-copy—those tiny bits of written content that go into surveys. Explain why you’re asking the questions, and when people reach the end of the survey, remember to thank them for their time. After all, they’re giving you free labor!
✅ DO consider the foot-in-the-door principle
One way to increase your response rate is to ask an easy question upfront, such as a ‘yes’ or ‘no’ question, because once people commit to taking a survey—even just the first question—they’re more likely to finish it.
✅ DO consider asking your questions from the first-person perspective
Disclaimer: we don’t do this here at Hotjar. You’ll notice all our sample questions are listed in second-person (i.e. ‘you’ format), but it’s worth testing to determine which approach gives you better answers. Some experts prefer the first-person approach (i.e. ‘I’ format) because they believe it encourages users to talk about themselves—but only you can decide which approach works best for your business.
I strongly recommend that the questions be worded in the first person. This helps create a more visceral reaction from people and encourages them to tell stories from their actual experiences, rather than making up hypothetical scenarios. For example, here’s a similar question, asked two ways: “What do you think is the hardest thing about creating a UX portfolio?” versus “My biggest problem with creating my UX portfolio is…”
The second version helps get people thinking about their experiences. The best survey responses come from respondents who provide personal accounts of past events that give us specific and real insight into their lives.
✅ DO alternate your questions often
Shake up the questions you ask on a regular basis. Asking a wide variety of questions will help you and your team get a complete view of what your customers are thinking.
✅ DO test your surveys before sending them out
A few years ago, Hotjar created a survey we sent to 2,000 CX professionals via email. Before officially sending it out, we wanted to make sure the questions really worked.
We decided to test them out on internal staff and external people by sending out three rounds of test surveys to 100 respondents each time. Their feedback helped us perfect the questions and clear up any confusing language.
Survey question DON’Ts
❌ don’t ask closed-ended questions if you’ve never done research before.
If you’ve just begun asking questions, make them open-ended questions since you have no idea what your customers think about you at this stage. When you limit their answers, you just reinforce your own assumptions.
There are two exceptions to this rule:
Using a closed-ended question to get your foot in the door at the beginning of a survey
Using rating scale questions to gather customer sentiment (like an NPS survey)
❌ DON’T ask a lot of questions if you’re just getting started
Having to answer too many questions can overwhelm your users. Stick with the most important points and discard the rest.
Try starting off with a single question to see how your audience responds, then move on to two questions once you feel like you know what you’re doing.
How many questions should you ask? There’s really no perfect answer, but we recommend asking as few as you need to ask to get the information you want. In the beginning, focus on the big things:
Who are your users?
What do potential customers want?
How are they using your product?
What would win their loyalty?
❌ DON’T just ask a question when you can combine it with other tools
Don’t just use surveys to answer questions that other tools (such as analytics) can also answer. If you want to learn about whether people find a new website feature helpful, you can also observe how they’re using it through traditional analytics, session recordings , and other user testing tools for a more complete picture.
Don’t use surveys to ask people questions that other tools are better equipped to answer. I’m thinking of questions like “What do you think of the search feature?” with pre-set answer options like ‘Very easy to use,’ ‘Easy to use,’ etc. That’s not a good question to ask.
Why should you care about what people ‘think’ about the search feature? You should find out whether it helps people find what they need and whether it helps drive conversions for you. Analytics, user session recordings, and user testing can tell you whether it does that or not.
❌ DON’T ask leading questions
A leading question is one that prompts a specific answer. Avoid asking leading questions because they’ll give you bad data. For example, asking, “What makes our product better than our competitors’ products?” might boost your self-esteem, but it won’t get you good information. Why? You’re effectively planting the idea that your own product is the best on the market.
❌ DON’T ask loaded questions
A loaded question is similar to a leading question, but it does more than just push a bias—it phrases the question such that it’s impossible to answer without confirming an underlying assumption.
A common (and subtle) form of loaded survey question would be, “What do you find useful about this article?” If we haven’t first asked you whether you found the article useful at all, then we’re asking a loaded question.
❌ DON’T ask about more than one topic at once
For example, “Do you believe our product can help you increase sales and improve cross-collaboration?”
This complex question, also known as a ‘double-barreled question’, requires a very complex answer as it begs the respondent to address two separate questions at once:
Do you believe our product can help you increase sales?
Do you believe our product can help you improve cross-collaboration?
Respondents may very well answer 'yes', but actually mean it for the first part of the question, and not the other. The result? Your survey data is inaccurate, and you’ve missed out on actionable insights.
Instead, ask two specific questions to gather customer feedback on each concept.
How to run your surveys
The format you pick for your survey depends on what you want to achieve and also on how much budget or resources you have. You can
Use an on-site survey tool , like Hotjar Surveys , to set up a website survey that pops up whenever people visit a specific page: this is useful when you want to investigate website- and product-specific topics quickly. This format is relatively inexpensive—with Hotjar’s free forever plan, you can even run up to 3 surveys with unlimited questions for free.
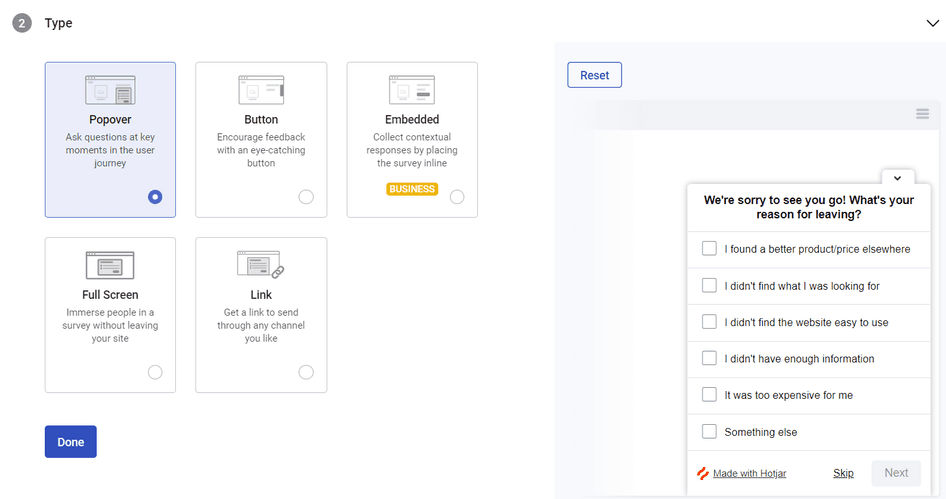
Use Hotjar Surveys to embed a survey as an element directly on a page: this is useful when you want to grab your audience’s attention and connect with customers at relevant moments, without interrupting their browsing. (Scroll to the bottom of this page to see an embedded survey in action!) This format is included on Hotjar’s Business and Scale plans—try it out for 15 days with a free Ask Business trial .
Use a survey builder and create a survey people can access in their own time: this is useful when you want to reach out to your mailing list or a wider audience with an email survey (you just need to share the URL the survey lives at). Sending in-depth questionnaires this way allows for more space for people to elaborate on their answers. This format is also relatively inexpensive, depending on the tool you use.
Place survey kiosks in a physical location where people can give their feedback by pressing a button: this is useful for quick feedback on specific aspects of a customer's experience (there’s usually plenty of these in airports and waiting rooms). This format is relatively expensive to maintain due to the material upkeep.
Run in-person surveys with your existing or prospective customers: in-person questionnaires help you dig deep into your interviewees’ answers. This format is relatively cheap if you do it online with a user interview tool or over the phone, but it’s more expensive and time-consuming if done in a physical location.
💡 Pro tip: looking for an easy, cost-efficient way to connect with your users? Run effortless, automated user interviews with Engage , Hotjar’s user interview tool. Get instant access to a pool of 200,000+ participants (or invite your own), and take notes while Engage records and transcribes your interview.
10 survey use cases: what you can do with good survey questions
Effective survey questions can help improve your business in many different ways. We’ve written in detail about most of these ideas in other blog posts, so we’ve rounded them up for you below.
1. Create user personas
A user persona is a character based on the people who currently use your website or product. A persona combines psychographics and demographics and reflects who they are, what they need, and what may stop them from getting it.
Examples of questions to ask:
Describe yourself in one sentence, e.g. “I am a 30-year-old marketer based in Dublin who enjoys writing articles about user personas.”
What is your main goal for using this website/product?
What, if anything, is preventing you from doing it?
👉 Our post about creating simple and effective user personas in four steps highlights some great survey questions to ask when creating a user persona.
🚀 Get started: use our user persona survey template or AI for Surveys to inform your user persona.
2. Understand why your product is not selling
Few things are more frightening than stagnant sales. When the pressure is mounting, you’ve got to get to the bottom of it, and good survey questions can help you do just that.
What made you buy the product? What challenges are you trying to solve?
What did you like most about the product? What did you dislike the most?
What nearly stopped you from buying?
👉 Here’s a detailed piece about the best survey questions to ask your customers when your product isn’t selling , and why they work so well.
🚀 Get started: our product feedback survey template helps you find out whether your product satisfies your users. Or build your surveys in the blink of an eye with Hotjar AI.
3. Understand why people leave your website
If you want to figure out why people are leaving your website , you’ll have to ask questions.
A good format for that is an exit-intent pop-up survey, which appears when a user clicks to leave the page, giving them the chance to leave website feedback before they go.
Another way is to focus on the people who did convert, but just barely—something Hotjar founder David Darmanin considers essential for taking conversions to the next level. By focusing on customers who bought your product (but almost didn’t), you can learn how to win over another set of users who are similar to them: those who almost bought your products, but backed out in the end.
Example of questions to ask:
Not for you? Tell us why. ( Exit-intent pop-up —ask this when a user leaves without buying.)
What almost stopped you from buying? (Ask this post-conversion .)
👉 Find out how HubSpot Academy increased its conversion rate by adding an exit-intent survey that asked one simple question when users left their website: “Not for you? Tell us why.”
🚀 Get started: place an exit-intent survey on your site. Let Hotjar AI draft the survey questions by telling it what you want to learn.
I spent the better half of my career focusing on the 95% who don’t convert, but it’s better to focus on the 5% who do. Get to know them really well, deliver value to them, and really wow them. That’s how you’re going to take that 5% to 10%.
4. Understand your customers’ fears and concerns
Buying a new product can be scary: nobody wants to make a bad purchase. Your job is to address your prospective customers’ concerns, counter their objections, and calm their fears, which should lead to more conversions.
👉 Take a look at our no-nonsense guide to increasing conversions for a comprehensive write-up about discovering the drivers, barriers, and hooks that lead people to converting on your website.
🚀 Get started: understand why your users are tempted to leave and discover potential barriers with a customer retention survey .
5. Drive your pricing strategy
Are your products overpriced and scaring away potential buyers? Or are you underpricing and leaving money on the table?
Asking the right questions will help you develop a pricing structure that maximizes profit, but you have to be delicate about how you ask. Don’t ask directly about price, or you’ll seem unsure of the value you offer. Instead, ask questions that uncover how your products serve your customers and what would inspire them to buy more.
How do you use our product/service?
What would persuade you to use our product more often?
What’s the one thing our product is missing?
👉 We wrote a series of blog posts about managing the early stage of a SaaS startup, which included a post about developing the right pricing strategy —something businesses in all sectors could benefit from.
🚀 Get started: find the sweet spot in how to price your product or service with a Van Westendorp price sensitivity survey or get feedback on your pricing plan .
6. Measure and understand product-market fit
Product-market fit (PMF) is about understanding demand and creating a product that your customers want, need, and will actually pay money for. A combination of online survey questions and one-on-one interviews can help you figure this out.
What's one thing we can add that would make [product name] indispensable for you?
If you could change just one thing in [product name], what would it be?
👉 In our series of blog posts about managing the early stage of a SaaS startup, we covered a section on product-market fit , which has relevant information for all industries.
🚀 Get started: discover if you’re delivering the best products to your market with our product-market fit survey .
7. Choose effective testimonials
Human beings are social creatures—we’re influenced by people who are similar to us. Testimonials that explain how your product solved a problem for someone are the ultimate form of social proof. The following survey questions can help you get some great testimonials.
What changed for you after you got our product?
How does our product help you get your job done?
How would you feel if you couldn’t use our product anymore?
👉 In our post about positioning and branding your products , we cover the type of questions that help you get effective testimonials.
🚀 Get started: add a question asking respondents whether you can use their answers as testimonials in your surveys, or conduct user interviews to gather quotes from your users.
8. Measure customer satisfaction
It’s important to continually track your overall customer satisfaction so you can address any issues before they start to impact your brand’s reputation. You can do this with rating scale questions.
For example, at Hotjar, we ask for feedback after each customer support interaction (which is one important measure of customer satisfaction). We begin with a simple, foot-in-the-door question to encourage a response, and use the information to improve our customer support, which is strongly tied to overall customer satisfaction.
How would you rate the support you received? (1-5 scale)
If 1-3: How could we improve?
If 4-5: What did you love about the experience?
👉 Our beginner’s guide to website feedback goes into great detail about how to measure customer service, NPS , and other important success metrics.
🚀 Get started: gauge short-term satisfaction level with a CSAT survey .
9. Measure word-of-mouth recommendations
Net Promoter Score is a measure of how likely your customers are to recommend your products or services to their friends or colleagues. NPS is a higher bar than customer satisfaction because customers have to be really impressed with your product to recommend you.
Example of NPS questions (to be asked in the same survey):
How likely are you to recommend this company to a friend or colleague? (0-10 scale)
What’s the main reason for your score?
What should we do to WOW you?
👉 We created an NPS guide with ecommerce companies in mind, but it has plenty of information that will help companies in other industries as well.
🚀 Get started: measure whether your users would refer you to a friend or colleague with an NPS survey . Then, use our free NPS calculator to crunch the numbers.
10. Redefine your messaging
How effective is your messaging? Does it speak to your clients' needs, drives, and fears? Does it speak to your strongest selling points?
Asking the right survey questions can help you figure out what marketing messages work best, so you can double down on them.
What attracted you to [brand or product name]?
Did you have any concerns before buying [product name]?
Since you purchased [product name], what has been the biggest benefit to you?
If you could describe [brand or product name] in one sentence, what would you say?
What is your favorite thing about [brand or product name]?
How likely are you to recommend this product to a friend or colleague? (NPS question)
👉 We talk about positioning and branding your products in a post that’s part of a series written for SaaS startups, but even if you’re not in SaaS (or you’re not a startup), you’ll still find it helpful.
Have a question for your customers? Ask!
Feedback is at the heart of deeper empathy for your customers and a more holistic understanding of their behaviors and motivations. And luckily, people are more than ready to share their thoughts about your business— they're just waiting for you to ask them. Deeper customer insights start right here, with a simple tool like Hotjar Surveys.
Build surveys faster with AI🔥
Use AI in Hotjar Surveys to build your survey, place it on your website or send it via email, and get the customer insight you need to grow your business.
FAQs about survey questions
How many people should i survey/what should my sample size be.
A good rule of thumb is to aim for at least 100 replies that you can work with.
You can use our sample size calculator to get a more precise answer, but understand that collecting feedback is research, not experimentation. Unlike experimentation (such as A/B testing ), all is not lost if you can’t get a statistically significant sample size. In fact, as little as ten replies can give you actionable information about what your users want.
How many questions should my survey have?
There’s no perfect answer to this question, but we recommend asking as few as you need to ask in order to get the information you want. Remember, you’re essentially asking someone to work for free, so be respectful of their time.
Why is it important to ask good survey questions?
A good survey question is asked in a precise way at the right stage in the customer journey to give you insight into your customers’ needs and drives. The qualitative data you get from survey responses can supplement the insight you can capture through other traditional analytics tools (think Google Analytics) and behavior analytics tools (think heatmaps and session recordings , which visualize user behavior on specific pages or across an entire website).
The format you choose for your survey—in-person, email, on-page, etc.—is important, but if the questions themselves are poorly worded you could waste hours trying to fix minimal problems while ignoring major ones a different question could have uncovered.
How do I analyze open-ended survey questions?
A big pile of qualitative data can seem intimidating, but there are some shortcuts that make it much easier to analyze. We put together a guide for analyzing open-ended questions in 5 simple steps , which should answer all your questions.
But the fastest way to analyze open questions is to use the automated summary report with Hotjar AI in Surveys . AI turns the complex survey data into:
Key findings
Actionable insights
Will sending a survey annoy my customers?
Honestly, the real danger is not collecting feedback. Without knowing what users think about your page and why they do what they do, you’ll never create a user experience that maximizes conversions. The truth is, you’re probably already doing something that bugs them more than any survey or feedback button would.
If you’re worried that adding an on-page survey might hurt your conversion rate, start small and survey just 10% of your visitors. You can stop surveying once you have enough replies.
Related articles

User research
5 tips to recruit user research participants that represent the real world
Whether you’re running focus groups for your pricing strategy or conducting usability testing for a new product, user interviews are one of the most effective research methods to get the needle-moving insights you need. But to discover meaningful data that helps you reach your goals, you need to connect with high-quality participants. This article shares five tips to help you optimize your recruiting efforts and find the right people for any type of research study.
Hotjar team

How to instantly transcribe user interviews—and swiftly unlock actionable insights
After the thrill of a successful user interview, the chore of transcribing dialogue can feel like the ultimate anticlimax. Putting spoken words in writing takes several precious hours—time better invested in sharing your findings with your team or boss.
But the fact remains: you need a clear and accurate user interview transcript to analyze and report data effectively. Enter automatic transcription. This process instantly transcribes recorded dialogue in real time without human help. It ensures data integrity (and preserves your sanity), enabling you to unlock valuable insights in your research.

Shadz Loresco

An 8-step guide to conducting empathetic (and insightful) customer interviews in mid-market companies
Customer interviews uncover your ideal users’ challenges and needs in their own words, providing in-depth customer experience insights that inform product development, new features, and decision-making. But to get the most out of your interviews, you need to approach them with empathy. This article explains how to conduct accessible, inclusive, and—above all—insightful interviews to create a smooth (and enjoyable!) process for you and your participants.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Methodology
- Doing Survey Research | A Step-by-Step Guide & Examples
Doing Survey Research | A Step-by-Step Guide & Examples
Published on 6 May 2022 by Shona McCombes . Revised on 10 October 2022.
Survey research means collecting information about a group of people by asking them questions and analysing the results. To conduct an effective survey, follow these six steps:
- Determine who will participate in the survey
- Decide the type of survey (mail, online, or in-person)
- Design the survey questions and layout
- Distribute the survey
- Analyse the responses
- Write up the results
Surveys are a flexible method of data collection that can be used in many different types of research .
Table of contents
What are surveys used for, step 1: define the population and sample, step 2: decide on the type of survey, step 3: design the survey questions, step 4: distribute the survey and collect responses, step 5: analyse the survey results, step 6: write up the survey results, frequently asked questions about surveys.
Surveys are used as a method of gathering data in many different fields. They are a good choice when you want to find out about the characteristics, preferences, opinions, or beliefs of a group of people.
Common uses of survey research include:
- Social research: Investigating the experiences and characteristics of different social groups
- Market research: Finding out what customers think about products, services, and companies
- Health research: Collecting data from patients about symptoms and treatments
- Politics: Measuring public opinion about parties and policies
- Psychology: Researching personality traits, preferences, and behaviours
Surveys can be used in both cross-sectional studies , where you collect data just once, and longitudinal studies , where you survey the same sample several times over an extended period.
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Before you start conducting survey research, you should already have a clear research question that defines what you want to find out. Based on this question, you need to determine exactly who you will target to participate in the survey.
Populations
The target population is the specific group of people that you want to find out about. This group can be very broad or relatively narrow. For example:
- The population of Brazil
- University students in the UK
- Second-generation immigrants in the Netherlands
- Customers of a specific company aged 18 to 24
- British transgender women over the age of 50
Your survey should aim to produce results that can be generalised to the whole population. That means you need to carefully define exactly who you want to draw conclusions about.
It’s rarely possible to survey the entire population of your research – it would be very difficult to get a response from every person in Brazil or every university student in the UK. Instead, you will usually survey a sample from the population.
The sample size depends on how big the population is. You can use an online sample calculator to work out how many responses you need.
There are many sampling methods that allow you to generalise to broad populations. In general, though, the sample should aim to be representative of the population as a whole. The larger and more representative your sample, the more valid your conclusions.
There are two main types of survey:
- A questionnaire , where a list of questions is distributed by post, online, or in person, and respondents fill it out themselves
- An interview , where the researcher asks a set of questions by phone or in person and records the responses
Which type you choose depends on the sample size and location, as well as the focus of the research.
Questionnaires
Sending out a paper survey by post is a common method of gathering demographic information (for example, in a government census of the population).
- You can easily access a large sample.
- You have some control over who is included in the sample (e.g., residents of a specific region).
- The response rate is often low.
Online surveys are a popular choice for students doing dissertation research , due to the low cost and flexibility of this method. There are many online tools available for constructing surveys, such as SurveyMonkey and Google Forms .
- You can quickly access a large sample without constraints on time or location.
- The data is easy to process and analyse.
- The anonymity and accessibility of online surveys mean you have less control over who responds.
If your research focuses on a specific location, you can distribute a written questionnaire to be completed by respondents on the spot. For example, you could approach the customers of a shopping centre or ask all students to complete a questionnaire at the end of a class.
- You can screen respondents to make sure only people in the target population are included in the sample.
- You can collect time- and location-specific data (e.g., the opinions of a shop’s weekday customers).
- The sample size will be smaller, so this method is less suitable for collecting data on broad populations.
Oral interviews are a useful method for smaller sample sizes. They allow you to gather more in-depth information on people’s opinions and preferences. You can conduct interviews by phone or in person.
- You have personal contact with respondents, so you know exactly who will be included in the sample in advance.
- You can clarify questions and ask for follow-up information when necessary.
- The lack of anonymity may cause respondents to answer less honestly, and there is more risk of researcher bias.
Like questionnaires, interviews can be used to collect quantitative data : the researcher records each response as a category or rating and statistically analyses the results. But they are more commonly used to collect qualitative data : the interviewees’ full responses are transcribed and analysed individually to gain a richer understanding of their opinions and feelings.
Next, you need to decide which questions you will ask and how you will ask them. It’s important to consider:
- The type of questions
- The content of the questions
- The phrasing of the questions
- The ordering and layout of the survey
Open-ended vs closed-ended questions
There are two main forms of survey questions: open-ended and closed-ended. Many surveys use a combination of both.
Closed-ended questions give the respondent a predetermined set of answers to choose from. A closed-ended question can include:
- A binary answer (e.g., yes/no or agree/disagree )
- A scale (e.g., a Likert scale with five points ranging from strongly agree to strongly disagree )
- A list of options with a single answer possible (e.g., age categories)
- A list of options with multiple answers possible (e.g., leisure interests)
Closed-ended questions are best for quantitative research . They provide you with numerical data that can be statistically analysed to find patterns, trends, and correlations .
Open-ended questions are best for qualitative research. This type of question has no predetermined answers to choose from. Instead, the respondent answers in their own words.
Open questions are most common in interviews, but you can also use them in questionnaires. They are often useful as follow-up questions to ask for more detailed explanations of responses to the closed questions.
The content of the survey questions
To ensure the validity and reliability of your results, you need to carefully consider each question in the survey. All questions should be narrowly focused with enough context for the respondent to answer accurately. Avoid questions that are not directly relevant to the survey’s purpose.
When constructing closed-ended questions, ensure that the options cover all possibilities. If you include a list of options that isn’t exhaustive, you can add an ‘other’ field.
Phrasing the survey questions
In terms of language, the survey questions should be as clear and precise as possible. Tailor the questions to your target population, keeping in mind their level of knowledge of the topic.
Use language that respondents will easily understand, and avoid words with vague or ambiguous meanings. Make sure your questions are phrased neutrally, with no bias towards one answer or another.
Ordering the survey questions
The questions should be arranged in a logical order. Start with easy, non-sensitive, closed-ended questions that will encourage the respondent to continue.
If the survey covers several different topics or themes, group together related questions. You can divide a questionnaire into sections to help respondents understand what is being asked in each part.
If a question refers back to or depends on the answer to a previous question, they should be placed directly next to one another.
Before you start, create a clear plan for where, when, how, and with whom you will conduct the survey. Determine in advance how many responses you require and how you will gain access to the sample.
When you are satisfied that you have created a strong research design suitable for answering your research questions, you can conduct the survey through your method of choice – by post, online, or in person.
There are many methods of analysing the results of your survey. First you have to process the data, usually with the help of a computer program to sort all the responses. You should also cleanse the data by removing incomplete or incorrectly completed responses.
If you asked open-ended questions, you will have to code the responses by assigning labels to each response and organising them into categories or themes. You can also use more qualitative methods, such as thematic analysis , which is especially suitable for analysing interviews.
Statistical analysis is usually conducted using programs like SPSS or Stata. The same set of survey data can be subject to many analyses.
Finally, when you have collected and analysed all the necessary data, you will write it up as part of your thesis, dissertation , or research paper .
In the methodology section, you describe exactly how you conducted the survey. You should explain the types of questions you used, the sampling method, when and where the survey took place, and the response rate. You can include the full questionnaire as an appendix and refer to it in the text if relevant.
Then introduce the analysis by describing how you prepared the data and the statistical methods you used to analyse it. In the results section, you summarise the key results from your analysis.
A Likert scale is a rating scale that quantitatively assesses opinions, attitudes, or behaviours. It is made up of four or more questions that measure a single attitude or trait when response scores are combined.
To use a Likert scale in a survey , you present participants with Likert-type questions or statements, and a continuum of items, usually with five or seven possible responses, to capture their degree of agreement.
Individual Likert-type questions are generally considered ordinal data , because the items have clear rank order, but don’t have an even distribution.
Overall Likert scale scores are sometimes treated as interval data. These scores are considered to have directionality and even spacing between them.
The type of data determines what statistical tests you should use to analyse your data.
A questionnaire is a data collection tool or instrument, while a survey is an overarching research method that involves collecting and analysing data from people using questionnaires.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. (2022, October 10). Doing Survey Research | A Step-by-Step Guide & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 12 August 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/research-methods/surveys/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, qualitative vs quantitative research | examples & methods, construct validity | definition, types, & examples, what is a likert scale | guide & examples.
Creating a Questionnaire
Create the perfect questionnaire and collect actionable data using our online guide!


Table of Contents
- How to Create
Questionnaire Types
- Collecting Responses
- Analyzing Results
- Getting Started
What is a Questionnaire?
Definition: A questionnaire is a convenient way to collect feedback. A questionnaire can be used to measure customer satisfaction, capture employee feedback, or even conduct product research. Responses can be collected via email, web link, QR code, or using a survey panel.
The term "survey" and "questionnaire" are commonly used interchangeably. A questionnaire refers to the questions used to collect feedback (the form itself). A survey relates to the entire research process, including summarizing and analyzing questionnaire data.
Getting Started + Tips
How to make a questionnaire: Keep questions short and focused on one topic at a time. Use multiple-choice questions to fit answers into a specific category. Use an open-ended question to capture comments. A Likert scale or MaxDiff question can be used for market research. Collect responses for your questionnaire using an email collector, an anonymous link, or even a QR code.
The following 6 tips will help you create the perfect questionnaire:
1) Use 10 Questions or Less
The shorter you keep your survey, the higher your completion rates. Longer questionnaires usually tend to have a high drop-off percentage. Keeping your surveys to 10 questions or fewer forces you to draft a study that only includes important questions; you should remove trivial questions during the draft process.
2) One Idea Per Question
Make sure each question only covers one topic. Try to include only one topic at a time. For example, in an employee survey, you would not want to ask, "Do you feel satisfied with your compensation and career advancement?". Instead, you would like to separate "compensation" and "career advancement" into two questions or use a Likert scale , putting each question on a separate row.
3) Group Similar Questions Together
Suppose the survey is more than ten questions; similar questions should be grouped on separate pages. If you don't want to use more than one page, add extra spacing between groups of the question; extra white space can increase the increase the readability of your questionnaire.
4) Use Skip/Display Logic
If you have questions that only apply to certain people, consider using skip or display logic to show those questions conditionally. This will help reduce the length of your survey and boost response rates.
If you have questions that only apply to certain people, consider using skip or display logic to show those questions conditionally. This will help reduce the length of your survey and boost response rates. For example, if you asked, "Are you currently looking for new employment opportunities?". If the answer were "yes," a follow-up question would ask, "Why?"
5) Use Research Questions Like MaxDiff
Research questions are an excellent tool for customer or product questionnaires. Instead of asking multiple questions on which features are essential or what price is desirable, question types like MaxDiff and Conjoint will provide you with high-quality, actionable data that can be used for feature prioritization and product pricing. In addition, these question types will reduce the length of your questionnaire.
6) Keep the Audience in Mind
An employee questionnaire should use an anonymous link to collect responses; this will help boost trust and increase honest answers. If doing a customer study, consider adding custom data to the weblink to help identify responses. A survey panel and current customers can lend fresh perspectives for general market research.
Questionnaire Templates
Adding customer surveys to your Google review strategy will add additional data points to improve customer satisfaction. In addition, surveys are a valuable tool to identify ways to improve, establish internal benchmarks, and conduct pricing and product research to improve your company's products.
While there are numerous types of questionnaires (or survey types), these are the five most common general categories:
1) Customer Satisfaction
Capturing customer feedback is one of the most common uses of questionnaires. A good customer satisfaction survey will always revolve around a Net Promoter Score question. When the Net Promoter Score question results are tallied, one number from -100 is 100 is displayed. This number is ideal for benchmarks. Net Promoter provides quick and actionable feedback when combined with an open-ended text question.
2) Customer Effort
Measuring how easily customers can complete a purchase or take a specific action is crucial for the customer experience strategy. A customer effort score question is a rating scale from 1 to 7 (disagree to agree). Results for this question are averaged; the higher the score, the easier it is for your customers to complete tasks.
3) Employee Satisfaction & Engagement
Employee satisfaction and engagement are often used interchangeably but measure different things. Both types of surveys often use opinion scales to ask questions.
Employee satisfaction measures how satisfied employees are with their job and work environment. Standard measures of employee satisfaction include salary, benefits, and co-worker relationships.
Employee engagement relates to the emotional commitment employees have to an organization. It goes beyond simple satisfaction. Standard measures of engagement include belief in the company mission, opportunities for career growth, and being inspired to perform at a high level.
4) Employee Exit Interviews
When employees leave for new opportunities, sending a questionnaire is a great way to understand why that employee is leaving. The feedback obtained here can be used to improve the workplace and reduce employee turnover.
5) Product Research
MaxDiff is used to identify what is most important to your audience. For example, if building a new mobile application, asking a group of users what they think is least and most important will help guide product strategy; your team should only focus on the important areas.
For pricing a new product, Van Westendorp will give you a range of prices the market is willing to expect. You could price your product too high or too low without a question like this, reducing your market penetration.
Collecting Responses For Your Questionnaire
There are a few different ways to collect feedback for questionnaires. Depending on your needs, each one could have an advantage.
With email distribution, you would upload a list of email addresses, and the platform would automatically place a link to your questionnaire inside the email body. One advantage is sending email reminders to respondents who still need to complete your survey. In addition, the email links are unique for each respondent, so you can track email open and click rates. As a result, email surveys are ideal for customer research.
A web link is a convenient way to collect feedback at your convenience. You can place a web link on social media, your website, or even inside your CRM email program (instead of an email collector with a unique link to each person). Custom data can be included in the link, such as store location. This custom data can be used to segment and filter results.
Anonymous Link
When you want to protect your respondents' identities, you use an anonymous link . Anonymous inks do not store respondent information, IP address, or email address. Because of this, anonymous survey links are perfect for employee surveys.
QR code Surveys
QR code surveys can be placed on paper receipts, product packaging, or flyers. In addition, QR codes are a great way to collect feedback after or during an event or even during in-person focus groups.
Survey Panels
If you're conducting market research and need access to a customer base, using a survey panel will get you the responses required. A good survey panel will allow you to target specific demographics, job titles, or interest levels (such as car enthusiasts). When using survey panels, you'll want to double-check and clean your data for low-quality responses. People who speed through your survey or mark the first answer for all questions should be removed.
How to Analyze Questionnaire Data
When analyzing the data from a questionnaire, consider a few advanced techniques like the ones below. These techniques will give you better insights than just simple graphs and charts.
Creating a segment or a cross-tabulation is the easiest way to dive deeper into your results. For example, if you conducted an employee satisfaction survey, the overall scores for the company could be high. But that might only tell part of the story. For example, if your company has multiple departments, you should create a cross-tabulation for each department. You might notice that there is one department with low scores. or one department with high scores.
If your company conducted its first Net Promoter Score survey and the results were -10, that score would be your benchmark. Each subsequent customer survey you run should be compared against that initial number to improve it each time.
TURF Analysis
This is an advanced research technique but very valuable. TURF analysis analysis stands for "Total Unduplicated Reach and Frequency" and is used to find the combination of items that would provide the highest reach level. For example, suppose you ask, "Which of the following flavor of ice cream would you buy?" If you run a TURF analysis on the results, you could find the top 3 or 4 combinations of flavors that would result in the highest sales.
Unsure Where to Start?
Creating a questionnaire can be a challenging process. However, these three suggestions can help you with the perfect questionnaire strategy.
1) Talk With Your Team
Some departments might want to conduct pricing research and do simple Net Promoter Score surveys. Having your organization aligned on strategy will simplify the process and eliminate any possibility of re-work. An aligned strategy will also mean a shorter study with fewer overlapping questions.
2) Start with a Template
A pre-made template will show you how to format and word questions. Next, try multiple templates to understand the various question types.
3) Look at Competitor Surveys
You might notice competitors asking specific questions - this would be a sign that those questions provide valuable metrics. If you can incorporate the great things your competition does while making it more efficient for respondents, your questionnaire campaigns will have a greater chance of success.
Get Started Now
We have you covered on anything from customer surveys, employee surveys, to market research. Get started and create your first survey for free.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Methodology
- Survey Research | Definition, Examples & Methods
Survey Research | Definition, Examples & Methods
Published on August 20, 2019 by Shona McCombes . Revised on June 22, 2023.
Survey research means collecting information about a group of people by asking them questions and analyzing the results. To conduct an effective survey, follow these six steps:
- Determine who will participate in the survey
- Decide the type of survey (mail, online, or in-person)
- Design the survey questions and layout
- Distribute the survey
- Analyze the responses
- Write up the results
Surveys are a flexible method of data collection that can be used in many different types of research .
Table of contents
What are surveys used for, step 1: define the population and sample, step 2: decide on the type of survey, step 3: design the survey questions, step 4: distribute the survey and collect responses, step 5: analyze the survey results, step 6: write up the survey results, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about surveys.
Surveys are used as a method of gathering data in many different fields. They are a good choice when you want to find out about the characteristics, preferences, opinions, or beliefs of a group of people.
Common uses of survey research include:
- Social research : investigating the experiences and characteristics of different social groups
- Market research : finding out what customers think about products, services, and companies
- Health research : collecting data from patients about symptoms and treatments
- Politics : measuring public opinion about parties and policies
- Psychology : researching personality traits, preferences and behaviours
Surveys can be used in both cross-sectional studies , where you collect data just once, and in longitudinal studies , where you survey the same sample several times over an extended period.
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
Before you start conducting survey research, you should already have a clear research question that defines what you want to find out. Based on this question, you need to determine exactly who you will target to participate in the survey.
Populations
The target population is the specific group of people that you want to find out about. This group can be very broad or relatively narrow. For example:
- The population of Brazil
- US college students
- Second-generation immigrants in the Netherlands
- Customers of a specific company aged 18-24
- British transgender women over the age of 50
Your survey should aim to produce results that can be generalized to the whole population. That means you need to carefully define exactly who you want to draw conclusions about.
Several common research biases can arise if your survey is not generalizable, particularly sampling bias and selection bias . The presence of these biases have serious repercussions for the validity of your results.
It’s rarely possible to survey the entire population of your research – it would be very difficult to get a response from every person in Brazil or every college student in the US. Instead, you will usually survey a sample from the population.
The sample size depends on how big the population is. You can use an online sample calculator to work out how many responses you need.
There are many sampling methods that allow you to generalize to broad populations. In general, though, the sample should aim to be representative of the population as a whole. The larger and more representative your sample, the more valid your conclusions. Again, beware of various types of sampling bias as you design your sample, particularly self-selection bias , nonresponse bias , undercoverage bias , and survivorship bias .
There are two main types of survey:
- A questionnaire , where a list of questions is distributed by mail, online or in person, and respondents fill it out themselves.
- An interview , where the researcher asks a set of questions by phone or in person and records the responses.
Which type you choose depends on the sample size and location, as well as the focus of the research.
Questionnaires
Sending out a paper survey by mail is a common method of gathering demographic information (for example, in a government census of the population).
- You can easily access a large sample.
- You have some control over who is included in the sample (e.g. residents of a specific region).
- The response rate is often low, and at risk for biases like self-selection bias .
Online surveys are a popular choice for students doing dissertation research , due to the low cost and flexibility of this method. There are many online tools available for constructing surveys, such as SurveyMonkey and Google Forms .
- You can quickly access a large sample without constraints on time or location.
- The data is easy to process and analyze.
- The anonymity and accessibility of online surveys mean you have less control over who responds, which can lead to biases like self-selection bias .
If your research focuses on a specific location, you can distribute a written questionnaire to be completed by respondents on the spot. For example, you could approach the customers of a shopping mall or ask all students to complete a questionnaire at the end of a class.
- You can screen respondents to make sure only people in the target population are included in the sample.
- You can collect time- and location-specific data (e.g. the opinions of a store’s weekday customers).
- The sample size will be smaller, so this method is less suitable for collecting data on broad populations and is at risk for sampling bias .
Oral interviews are a useful method for smaller sample sizes. They allow you to gather more in-depth information on people’s opinions and preferences. You can conduct interviews by phone or in person.
- You have personal contact with respondents, so you know exactly who will be included in the sample in advance.
- You can clarify questions and ask for follow-up information when necessary.
- The lack of anonymity may cause respondents to answer less honestly, and there is more risk of researcher bias.
Like questionnaires, interviews can be used to collect quantitative data: the researcher records each response as a category or rating and statistically analyzes the results. But they are more commonly used to collect qualitative data : the interviewees’ full responses are transcribed and analyzed individually to gain a richer understanding of their opinions and feelings.
Next, you need to decide which questions you will ask and how you will ask them. It’s important to consider:
- The type of questions
- The content of the questions
- The phrasing of the questions
- The ordering and layout of the survey
Open-ended vs closed-ended questions
There are two main forms of survey questions: open-ended and closed-ended. Many surveys use a combination of both.
Closed-ended questions give the respondent a predetermined set of answers to choose from. A closed-ended question can include:
- A binary answer (e.g. yes/no or agree/disagree )
- A scale (e.g. a Likert scale with five points ranging from strongly agree to strongly disagree )
- A list of options with a single answer possible (e.g. age categories)
- A list of options with multiple answers possible (e.g. leisure interests)
Closed-ended questions are best for quantitative research . They provide you with numerical data that can be statistically analyzed to find patterns, trends, and correlations .
Open-ended questions are best for qualitative research. This type of question has no predetermined answers to choose from. Instead, the respondent answers in their own words.
Open questions are most common in interviews, but you can also use them in questionnaires. They are often useful as follow-up questions to ask for more detailed explanations of responses to the closed questions.
The content of the survey questions
To ensure the validity and reliability of your results, you need to carefully consider each question in the survey. All questions should be narrowly focused with enough context for the respondent to answer accurately. Avoid questions that are not directly relevant to the survey’s purpose.
When constructing closed-ended questions, ensure that the options cover all possibilities. If you include a list of options that isn’t exhaustive, you can add an “other” field.
Phrasing the survey questions
In terms of language, the survey questions should be as clear and precise as possible. Tailor the questions to your target population, keeping in mind their level of knowledge of the topic. Avoid jargon or industry-specific terminology.
Survey questions are at risk for biases like social desirability bias , the Hawthorne effect , or demand characteristics . It’s critical to use language that respondents will easily understand, and avoid words with vague or ambiguous meanings. Make sure your questions are phrased neutrally, with no indication that you’d prefer a particular answer or emotion.
Ordering the survey questions
The questions should be arranged in a logical order. Start with easy, non-sensitive, closed-ended questions that will encourage the respondent to continue.
If the survey covers several different topics or themes, group together related questions. You can divide a questionnaire into sections to help respondents understand what is being asked in each part.
If a question refers back to or depends on the answer to a previous question, they should be placed directly next to one another.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
Before you start, create a clear plan for where, when, how, and with whom you will conduct the survey. Determine in advance how many responses you require and how you will gain access to the sample.
When you are satisfied that you have created a strong research design suitable for answering your research questions, you can conduct the survey through your method of choice – by mail, online, or in person.
There are many methods of analyzing the results of your survey. First you have to process the data, usually with the help of a computer program to sort all the responses. You should also clean the data by removing incomplete or incorrectly completed responses.
If you asked open-ended questions, you will have to code the responses by assigning labels to each response and organizing them into categories or themes. You can also use more qualitative methods, such as thematic analysis , which is especially suitable for analyzing interviews.
Statistical analysis is usually conducted using programs like SPSS or Stata. The same set of survey data can be subject to many analyses.
Finally, when you have collected and analyzed all the necessary data, you will write it up as part of your thesis, dissertation , or research paper .
In the methodology section, you describe exactly how you conducted the survey. You should explain the types of questions you used, the sampling method, when and where the survey took place, and the response rate. You can include the full questionnaire as an appendix and refer to it in the text if relevant.
Then introduce the analysis by describing how you prepared the data and the statistical methods you used to analyze it. In the results section, you summarize the key results from your analysis.
In the discussion and conclusion , you give your explanations and interpretations of these results, answer your research question, and reflect on the implications and limitations of the research.
If you want to know more about statistics , methodology , or research bias , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Student’s t -distribution
- Normal distribution
- Null and Alternative Hypotheses
- Chi square tests
- Confidence interval
- Quartiles & Quantiles
- Cluster sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Data cleansing
- Reproducibility vs Replicability
- Peer review
- Prospective cohort study
Research bias
- Implicit bias
- Cognitive bias
- Placebo effect
- Hawthorne effect
- Hindsight bias
- Affect heuristic
- Social desirability bias
A questionnaire is a data collection tool or instrument, while a survey is an overarching research method that involves collecting and analyzing data from people using questionnaires.
A Likert scale is a rating scale that quantitatively assesses opinions, attitudes, or behaviors. It is made up of 4 or more questions that measure a single attitude or trait when response scores are combined.
To use a Likert scale in a survey , you present participants with Likert-type questions or statements, and a continuum of items, usually with 5 or 7 possible responses, to capture their degree of agreement.
Individual Likert-type questions are generally considered ordinal data , because the items have clear rank order, but don’t have an even distribution.
Overall Likert scale scores are sometimes treated as interval data. These scores are considered to have directionality and even spacing between them.
The type of data determines what statistical tests you should use to analyze your data.
The priorities of a research design can vary depending on the field, but you usually have to specify:
- Your research questions and/or hypotheses
- Your overall approach (e.g., qualitative or quantitative )
- The type of design you’re using (e.g., a survey , experiment , or case study )
- Your sampling methods or criteria for selecting subjects
- Your data collection methods (e.g., questionnaires , observations)
- Your data collection procedures (e.g., operationalization , timing and data management)
- Your data analysis methods (e.g., statistical tests or thematic analysis )
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, June 22). Survey Research | Definition, Examples & Methods. Scribbr. Retrieved August 12, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/methodology/survey-research/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, qualitative vs. quantitative research | differences, examples & methods, questionnaire design | methods, question types & examples, what is a likert scale | guide & examples, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”
Research survey examples, templates, and types
Research surveys help base your next important decision on data. With our survey research templates and questions, gather valuable data easily and improve your business.
Get started
What are the benefits of survey research?
Providing data that can be relied on. Whether conducting market research or preparing a new product launch, research surveys supply the precise information needed to succeed. Avoid the confusion of conflicting opinions with data analysis that provides a clear picture of what people think.
At SurveyPlanet, we’re committed to making survey research easy to conduct. With our templates, have access to questions that will deliver the data you need.
The wide variety of research survey templates available is how to get useful data quickly—which makes developing more powerful solutions easier. Survey research can provide data you can rely on.
The wide variety of survey templates available helps develop the correct solution. At SurveyPlanet, we're committed to making research surveys easy to conduct and with our templates, we deliver on that promise.
What are research questionnaires?
They are a tool that returns insight about any topic. Just asking friends, family, and coworkers about a new product is not the best approach. Why? To put it simply, they're not a representative sample and may have biases.
What is needed is the opinions of your target audience. At the end of the day, it is their opinion that matters most. This requires a large enough sample to produce statistically significant data. That's where online surveys can play an important role.
Types of research surveys
Research questionnaires are a great tool to gain insights about all kinds of things (and not just business purposes). These surveys play an important role in extracting valuable insights from diverse populations. When thoughtfully designed, they become powerful instruments for informed decision-making and the advancement of knowledge across various domains.
Let's dive deeper into the types of surveys and where to apply them to get the best results.
Market research survey
Most businesses fail because their management believes their products and services are great—while the market thinks otherwise. To sell anything, the opinions of the people doing the buying need to be understood. Market research surveys offer insights about where a business stands with potential customers—and thus its potential market share—long before resources are dedicated to trying to make a product work in the marketplace.
Learn more about market research surveys.
Media consumption research survey
This type of survey explores how different people consume media content. It provides answers about what they view, how often they do so, and what kind of media they prefer. With a media consumption survey, learn everything about people's viewing and reading habits.
Reading preferences research survey
Ever wondered how, why, and what people enjoy reading? With a reading preferences research survey, such information can be discovered. By further analyzing the data, learn what different groups of people read (and the similarities and differences between different groups).
Product research survey
When launching a new product, understanding its target audience is crucial. This type of survey is a great tool that provides valuable feedback and insight that can be incorporated into a successful product launch.
Learn more about product research surveys.
Brand surveys
These help ascertain how customers feel about a brand. People buy from those they connect with; therefore, ask about their experiences and occasionally check in with them to see if they trust your brand.
Learn more about brand surveys.
Path-to-purchase research surveys
A path-to-purchase research survey investigates the steps consumers take from initial product awareness to final purchase. It typically includes questions about the decision-making process, product research, and factors influencing the ultimate purchasing decision. Such surveys can be conducted through various methods, but the best is via online surveys. The results of path-to-purchase surveys help businesses and marketers understand their target audience and develop effective marketing strategies.
Marketing research surveys
These help a company stand out from competitors and tailor marketing messages that better resonate with a target audience. Market research surveys are another type of research that is crucial when launching a new product or service.
Learn more about marketing research surveys.
Academic research surveys
These surveys are instrumental in improving knowledge about a specific subject. Consolidated results can be used to improve the efficiency of decision-making. Reliability is produced using methodologies and tools like questionnaires, surveys, interviews, and structured online forms.
Learn more about academic surveys.
Types of research methods
The three main types of research methods are exploratory, descriptive, and causal research.
Exploratory research
Exploratory research is conducted when a researcher seeks to explore a new subject or phenomenon with limited or no prior understanding. The primary goal of exploratory research is to gain insights, generate ideas, and form initial hypotheses for more in-depth investigation. This type of research is often the first step in the research process and is particularly useful when the topic is not well-defined or when there is a lack of existing knowledge. Researchers often use open-ended questions and qualitative methods to gather data, allowing them to adapt their approach as they learn more about the topic.
Descriptive research
Descriptive research aims to provide an accurate and detailed portrayal of a specific phenomenon or group. Unlike exploratory research, which seeks to generate insights and hypotheses, descriptive research is focused on describing the characteristics, behaviors, or conditions of a subject without manipulating variables.
Causal research
Causal research, also known as explanatory or experimental research, seeks to establish a cause-and-effect relationship between two or more variables. The primary goal of causal research is to determine whether a change in one variable causes a change in another variable. Unlike descriptive research, which focuses on describing relationships and characteristics, causal research involves manipulating one or more independent variables to observe their impact on dependent variables.
The research survey application
Research methods are designed to produce the best information from a group of research subjects (aka, the focus group). Such methods are used in many types of research and studies. They are methodologies that can be used for research study and data collection.
Depending on the kind of research and research methodology being carried out, different types of research survey questions are used, including multiple choice questions , Likert , scale questions , open-ended questions , demographic questions , and even image choice questions .
There are many survey applications that can collect data from many customers quickly and easily—a great way to get information about products, services, customer experiences, and marketing efforts.
Why you should use research questionnaires
The power of research questionnaires lies in their ease of use and cost-effectiveness. They provide answers to the most vital questions. What are the main benefits of these surveys?
- You don't have to wonder WHO, WHAT, and WHY because this type of analysis provides answers to those—and many other—questions.
- With a complete understanding of what's important in a research project, the best inquiries can be incorporated into survey questions.
- Get an unbiased opinion from a target audience and use it to your advantage.
- Collect data that matters and have it at your fingertips at all times.
Advantages and disadvantages of survey research
People use these surveys because they have many advantages compared to other research tools. What are the main advantages?
- Cost-effective.
- Collect data from many respondents.
- Quantifiable results.
- Convenient.
- The most practical solution for gathering data.
- Fast and reliable.
- Easily comparable results.
- Allows for the exploration of any topic.
While such advantages make it a no-brainer to use research questionnaires, it's always good to know their disadvantages:
- Biased responses.
- Cultural differences in understanding questions.
- Analyzing and understanding responses can be difficult.
- Some people won't read the questions before answering.
- Survey fatigue.
However, when these issues are understood, mitigation strategies can be activated. Every research method has flaws, but we firmly believe their benefits outweigh their disadvantages.
To execute a research campaign, the creation of a survey is one of the first steps. This includes designing questions or using a premade template. Below are some of the best research survey examples, templates, and tips for designing these surveys.
20 research survey examples and templates
Specific survey questions for research depend on your goals. A research questionnaire can be conducted about any topic or interest. Here are some of the best questions and ranking prompts:
- How often do you purchase books without actually reading them?
- What is your favorite foreign language film?
- During an average day, how many times do you check the news?
- Who is your favorite football player of all time? Why?
- Have you ever used any of the following travel websites to plan a vacation?
- Do you currently use a similar or competing product?
- On a scale of 1 to 5, how satisfied are you with the product?
- What is your single favorite feature of our product?
- When our product becomes available, are you likely to use it instead of a similar or competing product?
- What improvements would you suggest for our service?
- Please rank the following features in order of importance.
- How often do you consume fruits and vegetables in a typical week?
- How many days per week do you engage in physical activity?
- Do you prefer traditional classroom learning or online learning?
- How many hours a week do you spend studying for your courses?
- What are your career aspirations upon completing your education?
- Please rate our website's user interface from poor to excellent.
- In what ways can we better support you as a customer?
- Please rank the following factors in order of importance when choosing a new car.
- Order the following smartphone features based on your preference.
Of course, you get demographic information like:
- Employment status
- Marital status
- Household income
No matter the research topic, this demographic information will lead to better data-driven conclusions. Interested in knowing more about demographic survey questions? Check out our blog post explaining the advantages of gathering demographic information and how to do it appropriately.
Sign up for SurveyPlanet for free. Conduct your first survey to explore what people think. And don't worry about questions because we have some amazing templates to get you started.
Sign up now
Free unlimited surveys, questions and responses.
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
- QuestionPro

- Solutions Industries Gaming Automotive Sports and events Education Government Travel & Hospitality Financial Services Healthcare Cannabis Technology Use Case AskWhy Communities Audience Contactless surveys Mobile LivePolls Member Experience GDPR Positive People Science 360 Feedback Surveys
- Resources Blog eBooks Survey Templates Case Studies Training Help center
Home Market Research
Survey Research: Definition, Examples and Methods

Survey Research is a quantitative research method used for collecting data from a set of respondents. It has been perhaps one of the most used methodologies in the industry for several years due to the multiple benefits and advantages that it has when collecting and analyzing data.
LEARN ABOUT: Behavioral Research
In this article, you will learn everything about survey research, such as types, methods, and examples.
Survey Research Definition
Survey Research is defined as the process of conducting research using surveys that researchers send to survey respondents. The data collected from surveys is then statistically analyzed to draw meaningful research conclusions. In the 21st century, every organization’s eager to understand what their customers think about their products or services and make better business decisions. Researchers can conduct research in multiple ways, but surveys are proven to be one of the most effective and trustworthy research methods. An online survey is a method for extracting information about a significant business matter from an individual or a group of individuals. It consists of structured survey questions that motivate the participants to respond. Creditable survey research can give these businesses access to a vast information bank. Organizations in media, other companies, and even governments rely on survey research to obtain accurate data.
The traditional definition of survey research is a quantitative method for collecting information from a pool of respondents by asking multiple survey questions. This research type includes the recruitment of individuals collection, and analysis of data. It’s useful for researchers who aim to communicate new features or trends to their respondents.
LEARN ABOUT: Level of Analysis Generally, it’s the primary step towards obtaining quick information about mainstream topics and conducting more rigorous and detailed quantitative research methods like surveys/polls or qualitative research methods like focus groups/on-call interviews can follow. There are many situations where researchers can conduct research using a blend of both qualitative and quantitative strategies.
LEARN ABOUT: Survey Sampling
Survey Research Methods
Survey research methods can be derived based on two critical factors: Survey research tool and time involved in conducting research. There are three main survey research methods, divided based on the medium of conducting survey research:
- Online/ Email: Online survey research is one of the most popular survey research methods today. The survey cost involved in online survey research is extremely minimal, and the responses gathered are highly accurate.
- Phone: Survey research conducted over the telephone ( CATI survey ) can be useful in collecting data from a more extensive section of the target population. There are chances that the money invested in phone surveys will be higher than other mediums, and the time required will be higher.
- Face-to-face: Researchers conduct face-to-face in-depth interviews in situations where there is a complicated problem to solve. The response rate for this method is the highest, but it can be costly.
Further, based on the time taken, survey research can be classified into two methods:
- Longitudinal survey research: Longitudinal survey research involves conducting survey research over a continuum of time and spread across years and decades. The data collected using this survey research method from one time period to another is qualitative or quantitative. Respondent behavior, preferences, and attitudes are continuously observed over time to analyze reasons for a change in behavior or preferences. For example, suppose a researcher intends to learn about the eating habits of teenagers. In that case, he/she will follow a sample of teenagers over a considerable period to ensure that the collected information is reliable. Often, cross-sectional survey research follows a longitudinal study .
- Cross-sectional survey research: Researchers conduct a cross-sectional survey to collect insights from a target audience at a particular time interval. This survey research method is implemented in various sectors such as retail, education, healthcare, SME businesses, etc. Cross-sectional studies can either be descriptive or analytical. It is quick and helps researchers collect information in a brief period. Researchers rely on the cross-sectional survey research method in situations where descriptive analysis of a subject is required.
Survey research also is bifurcated according to the sampling methods used to form samples for research: Probability and Non-probability sampling. Every individual in a population should be considered equally to be a part of the survey research sample. Probability sampling is a sampling method in which the researcher chooses the elements based on probability theory. The are various probability research methods, such as simple random sampling , systematic sampling, cluster sampling, stratified random sampling, etc. Non-probability sampling is a sampling method where the researcher uses his/her knowledge and experience to form samples.
LEARN ABOUT: Survey Sample Sizes
The various non-probability sampling techniques are :
- Convenience sampling
- Snowball sampling
- Consecutive sampling
- Judgemental sampling
- Quota sampling
Process of implementing survey research methods:
- Decide survey questions: Brainstorm and put together valid survey questions that are grammatically and logically appropriate. Understanding the objective and expected outcomes of the survey helps a lot. There are many surveys where details of responses are not as important as gaining insights about what customers prefer from the provided options. In such situations, a researcher can include multiple-choice questions or closed-ended questions . Whereas, if researchers need to obtain details about specific issues, they can consist of open-ended questions in the questionnaire. Ideally, the surveys should include a smart balance of open-ended and closed-ended questions. Use survey questions like Likert Scale , Semantic Scale, Net Promoter Score question, etc., to avoid fence-sitting.
LEARN ABOUT: System Usability Scale
- Finalize a target audience: Send out relevant surveys as per the target audience and filter out irrelevant questions as per the requirement. The survey research will be instrumental in case the target population decides on a sample. This way, results can be according to the desired market and be generalized to the entire population.
LEARN ABOUT: Testimonial Questions
- Send out surveys via decided mediums: Distribute the surveys to the target audience and patiently wait for the feedback and comments- this is the most crucial step of the survey research. The survey needs to be scheduled, keeping in mind the nature of the target audience and its regions. Surveys can be conducted via email, embedded in a website, shared via social media, etc., to gain maximum responses.
- Analyze survey results: Analyze the feedback in real-time and identify patterns in the responses which might lead to a much-needed breakthrough for your organization. GAP, TURF Analysis , Conjoint analysis, Cross tabulation, and many such survey feedback analysis methods can be used to spot and shed light on respondent behavior. Researchers can use the results to implement corrective measures to improve customer/employee satisfaction.
Reasons to conduct survey research
The most crucial and integral reason for conducting market research using surveys is that you can collect answers regarding specific, essential questions. You can ask these questions in multiple survey formats as per the target audience and the intent of the survey. Before designing a study, every organization must figure out the objective of carrying this out so that the study can be structured, planned, and executed to perfection.
LEARN ABOUT: Research Process Steps
Questions that need to be on your mind while designing a survey are:
- What is the primary aim of conducting the survey?
- How do you plan to utilize the collected survey data?
- What type of decisions do you plan to take based on the points mentioned above?
There are three critical reasons why an organization must conduct survey research.
- Understand respondent behavior to get solutions to your queries: If you’ve carefully curated a survey, the respondents will provide insights about what they like about your organization as well as suggestions for improvement. To motivate them to respond, you must be very vocal about how secure their responses will be and how you will utilize the answers. This will push them to be 100% honest about their feedback, opinions, and comments. Online surveys or mobile surveys have proved their privacy, and due to this, more and more respondents feel free to put forth their feedback through these mediums.
- Present a medium for discussion: A survey can be the perfect platform for respondents to provide criticism or applause for an organization. Important topics like product quality or quality of customer service etc., can be put on the table for discussion. A way you can do it is by including open-ended questions where the respondents can write their thoughts. This will make it easy for you to correlate your survey to what you intend to do with your product or service.
- Strategy for never-ending improvements: An organization can establish the target audience’s attributes from the pilot phase of survey research . Researchers can use the criticism and feedback received from this survey to improve the product/services. Once the company successfully makes the improvements, it can send out another survey to measure the change in feedback keeping the pilot phase the benchmark. By doing this activity, the organization can track what was effectively improved and what still needs improvement.
Survey Research Scales
There are four main scales for the measurement of variables:
- Nominal Scale: A nominal scale associates numbers with variables for mere naming or labeling, and the numbers usually have no other relevance. It is the most basic of the four levels of measurement.
- Ordinal Scale: The ordinal scale has an innate order within the variables along with labels. It establishes the rank between the variables of a scale but not the difference value between the variables.
- Interval Scale: The interval scale is a step ahead in comparison to the other two scales. Along with establishing a rank and name of variables, the scale also makes known the difference between the two variables. The only drawback is that there is no fixed start point of the scale, i.e., the actual zero value is absent.
- Ratio Scale: The ratio scale is the most advanced measurement scale, which has variables that are labeled in order and have a calculated difference between variables. In addition to what interval scale orders, this scale has a fixed starting point, i.e., the actual zero value is present.
Benefits of survey research
In case survey research is used for all the right purposes and is implemented properly, marketers can benefit by gaining useful, trustworthy data that they can use to better the ROI of the organization.
Other benefits of survey research are:
- Minimum investment: Mobile surveys and online surveys have minimal finance invested per respondent. Even with the gifts and other incentives provided to the people who participate in the study, online surveys are extremely economical compared to paper-based surveys.
- Versatile sources for response collection: You can conduct surveys via various mediums like online and mobile surveys. You can further classify them into qualitative mediums like focus groups , and interviews and quantitative mediums like customer-centric surveys. Due to the offline survey response collection option, researchers can conduct surveys in remote areas with limited internet connectivity. This can make data collection and analysis more convenient and extensive.
- Reliable for respondents: Surveys are extremely secure as the respondent details and responses are kept safeguarded. This anonymity makes respondents answer the survey questions candidly and with absolute honesty. An organization seeking to receive explicit responses for its survey research must mention that it will be confidential.
Survey research design
Researchers implement a survey research design in cases where there is a limited cost involved and there is a need to access details easily. This method is often used by small and large organizations to understand and analyze new trends, market demands, and opinions. Collecting information through tactfully designed survey research can be much more effective and productive than a casually conducted survey.
There are five stages of survey research design:
- Decide an aim of the research: There can be multiple reasons for a researcher to conduct a survey, but they need to decide a purpose for the research. This is the primary stage of survey research as it can mold the entire path of a survey, impacting its results.
- Filter the sample from target population: Who to target? is an essential question that a researcher should answer and keep in mind while conducting research. The precision of the results is driven by who the members of a sample are and how useful their opinions are. The quality of respondents in a sample is essential for the results received for research and not the quantity. If a researcher seeks to understand whether a product feature will work well with their target market, he/she can conduct survey research with a group of market experts for that product or technology.
- Zero-in on a survey method: Many qualitative and quantitative research methods can be discussed and decided. Focus groups, online interviews, surveys, polls, questionnaires, etc. can be carried out with a pre-decided sample of individuals.
- Design the questionnaire: What will the content of the survey be? A researcher is required to answer this question to be able to design it effectively. What will the content of the cover letter be? Or what are the survey questions of this questionnaire? Understand the target market thoroughly to create a questionnaire that targets a sample to gain insights about a survey research topic.
- Send out surveys and analyze results: Once the researcher decides on which questions to include in a study, they can send it across to the selected sample . Answers obtained from this survey can be analyzed to make product-related or marketing-related decisions.
Survey examples: 10 tips to design the perfect research survey
Picking the right survey design can be the key to gaining the information you need to make crucial decisions for all your research. It is essential to choose the right topic, choose the right question types, and pick a corresponding design. If this is your first time creating a survey, it can seem like an intimidating task. But with QuestionPro, each step of the process is made simple and easy.
Below are 10 Tips To Design The Perfect Research Survey:
- Set your SMART goals: Before conducting any market research or creating a particular plan, set your SMART Goals . What is that you want to achieve with the survey? How will you measure it promptly, and what are the results you are expecting?
- Choose the right questions: Designing a survey can be a tricky task. Asking the right questions may help you get the answers you are looking for and ease the task of analyzing. So, always choose those specific questions – relevant to your research.
- Begin your survey with a generalized question: Preferably, start your survey with a general question to understand whether the respondent uses the product or not. That also provides an excellent base and intro for your survey.
- Enhance your survey: Choose the best, most relevant, 15-20 questions. Frame each question as a different question type based on the kind of answer you would like to gather from each. Create a survey using different types of questions such as multiple-choice, rating scale, open-ended, etc. Look at more survey examples and four measurement scales every researcher should remember.
- Prepare yes/no questions: You may also want to use yes/no questions to separate people or branch them into groups of those who “have purchased” and those who “have not yet purchased” your products or services. Once you separate them, you can ask them different questions.
- Test all electronic devices: It becomes effortless to distribute your surveys if respondents can answer them on different electronic devices like mobiles, tablets, etc. Once you have created your survey, it’s time to TEST. You can also make any corrections if needed at this stage.
- Distribute your survey: Once your survey is ready, it is time to share and distribute it to the right audience. You can share handouts and share them via email, social media, and other industry-related offline/online communities.
- Collect and analyze responses: After distributing your survey, it is time to gather all responses. Make sure you store your results in a particular document or an Excel sheet with all the necessary categories mentioned so that you don’t lose your data. Remember, this is the most crucial stage. Segregate your responses based on demographics, psychographics, and behavior. This is because, as a researcher, you must know where your responses are coming from. It will help you to analyze, predict decisions, and help write the summary report.
- Prepare your summary report: Now is the time to share your analysis. At this stage, you should mention all the responses gathered from a survey in a fixed format. Also, the reader/customer must get clarity about your goal, which you were trying to gain from the study. Questions such as – whether the product or service has been used/preferred or not. Do respondents prefer some other product to another? Any recommendations?
Having a tool that helps you carry out all the necessary steps to carry out this type of study is a vital part of any project. At QuestionPro, we have helped more than 10,000 clients around the world to carry out data collection in a simple and effective way, in addition to offering a wide range of solutions to take advantage of this data in the best possible way.
From dashboards, advanced analysis tools, automation, and dedicated functions, in QuestionPro, you will find everything you need to execute your research projects effectively. Uncover insights that matter the most!
MORE LIKE THIS

Life@QuestionPro: Thomas Maiwald-Immer’s Experience
Aug 9, 2024

Top 13 Reporting Tools to Transform Your Data Insights & More
Aug 8, 2024

Employee Satisfaction: How to Boost Your Workplace Happiness?
Aug 7, 2024

Jotform vs Formstack: Which Form Builder Should You Choose?
Other categories.
- Academic Research
- Artificial Intelligence
- Assessments
- Brand Awareness
- Case Studies
- Communities
- Consumer Insights
- Customer effort score
- Customer Engagement
- Customer Experience
- Customer Loyalty
- Customer Research
- Customer Satisfaction
- Employee Benefits
- Employee Engagement
- Employee Retention
- Friday Five
- General Data Protection Regulation
- Insights Hub
- Life@QuestionPro
- Market Research
- Mobile diaries
- Mobile Surveys
- New Features
- Online Communities
- Question Types
- Questionnaire
- QuestionPro Products
- Release Notes
- Research Tools and Apps
- Revenue at Risk
- Survey Templates
- Training Tips
- Tuesday CX Thoughts (TCXT)
- Uncategorized
- What’s Coming Up
- Workforce Intelligence
20+ SAMPLE Research Questionnaires Templates in PDF | MS Word | Google Docs | Apple Pages
Research questionnaires templates | ms word | google docs | apple pages, 20+ sample research questionnaires templates, what is a research questionnaire, types of research questionnaires, how to make an effective research questionnaire, research questionnaire vs. research survey, the dos and don’ts of a research questionnaire.
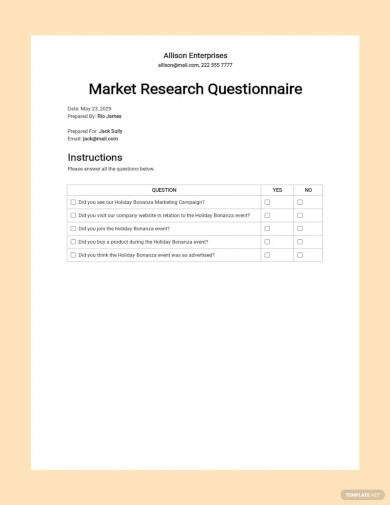
Market Research Questionnaire Template

Veterans Health Care Survey Questionnaire

Basic Market Survey Questionnaire
Market Research Questionnaires Format

Research Protocol Survey

Clinical Study PI Questionnaire

Human Study Questionnaire

Research Interest Questionnaire

Research Financial Disclosure Questionnaire
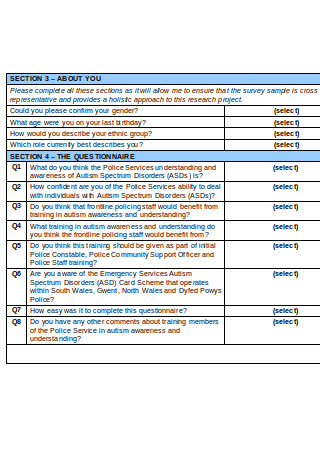
Research Project Questionnaire

Questionnaire for Legal Practitioners

Sample Research Questionnaire

Research Survey Questionnaires
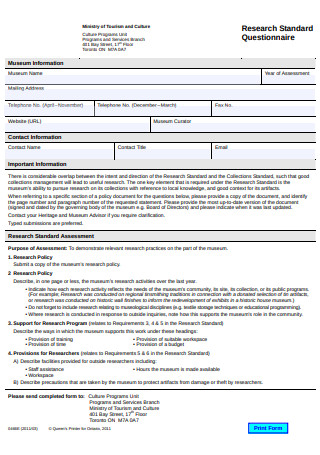
Research Standard Questionnaires

Auto Compensation Research Questionnaire

Orientation Research Questionnaire
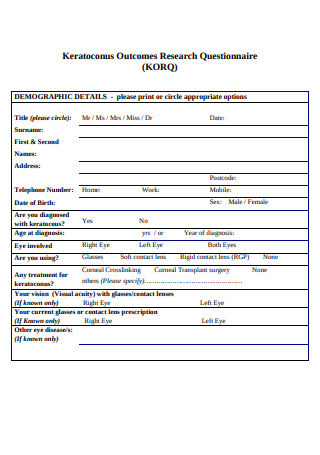
Research Questionnaire Format
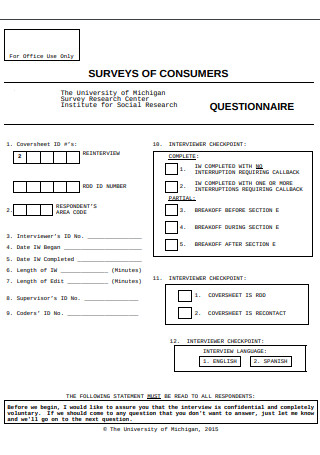
Social Research Questionnaire

Social Survey Questionnaire

Research into Questionnaire Design
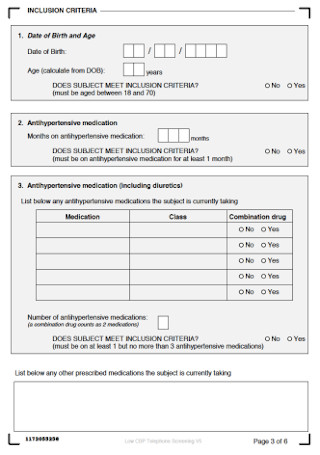
Questionnaires in Clinical Research
1. open-ended questionnaires, 2. closed-ended questionnaires, 3. mixed questionnaires, 4. pictorial questionnaires, step 1: identify the goals of your research questionnaire , step 2: define your target respondents, step 3: create questions , step 4: choose an appropriate question type , step 5: design the sequence and layout of the questions.
- The instrument used for data collection
- Is a tool that is distributed
- May contain open- or closed-ended questions
- Collects information on a topic
- Process of gathering and analyzing data
- Is an activity that is conducted
- Mainly comprised of closed-ended questions
- Aims to draw data for statistical analysis
Dont’s
Share this post on your network, you may also like these articles, research questionnaire.

Research questionnaires are vital tools for gathering data and insights in various fields. This comprehensive guide explores how to design and use them effectively. Whether you are working on…
51+ SAMPLE Food Questionnaire Templates in PDF | MS Word | Google Docs | Apple Pages

A food questionnaire can be used for a lot of purposes by a variety of businesses in the food service, hospitality, catering, and restaurant industry. Developing a food questionnaire is…
browse by categories
- Questionnaire
- Description
- Reconciliation
- Certificate
- Spreadsheet
Information
- privacy policy
- Terms & Conditions
- Privacy Policy

Home » Survey Research – Types, Methods, Examples
Survey Research – Types, Methods, Examples
Table of Contents

Survey Research
Definition:
Survey Research is a quantitative research method that involves collecting standardized data from a sample of individuals or groups through the use of structured questionnaires or interviews. The data collected is then analyzed statistically to identify patterns and relationships between variables, and to draw conclusions about the population being studied.
Survey research can be used to answer a variety of questions, including:
- What are people’s opinions about a certain topic?
- What are people’s experiences with a certain product or service?
- What are people’s beliefs about a certain issue?
Survey Research Methods
Survey Research Methods are as follows:
- Telephone surveys: A survey research method where questions are administered to respondents over the phone, often used in market research or political polling.
- Face-to-face surveys: A survey research method where questions are administered to respondents in person, often used in social or health research.
- Mail surveys: A survey research method where questionnaires are sent to respondents through mail, often used in customer satisfaction or opinion surveys.
- Online surveys: A survey research method where questions are administered to respondents through online platforms, often used in market research or customer feedback.
- Email surveys: A survey research method where questionnaires are sent to respondents through email, often used in customer satisfaction or opinion surveys.
- Mixed-mode surveys: A survey research method that combines two or more survey modes, often used to increase response rates or reach diverse populations.
- Computer-assisted surveys: A survey research method that uses computer technology to administer or collect survey data, often used in large-scale surveys or data collection.
- Interactive voice response surveys: A survey research method where respondents answer questions through a touch-tone telephone system, often used in automated customer satisfaction or opinion surveys.
- Mobile surveys: A survey research method where questions are administered to respondents through mobile devices, often used in market research or customer feedback.
- Group-administered surveys: A survey research method where questions are administered to a group of respondents simultaneously, often used in education or training evaluation.
- Web-intercept surveys: A survey research method where questions are administered to website visitors, often used in website or user experience research.
- In-app surveys: A survey research method where questions are administered to users of a mobile application, often used in mobile app or user experience research.
- Social media surveys: A survey research method where questions are administered to respondents through social media platforms, often used in social media or brand awareness research.
- SMS surveys: A survey research method where questions are administered to respondents through text messaging, often used in customer feedback or opinion surveys.
- IVR surveys: A survey research method where questions are administered to respondents through an interactive voice response system, often used in automated customer feedback or opinion surveys.
- Mixed-method surveys: A survey research method that combines both qualitative and quantitative data collection methods, often used in exploratory or mixed-method research.
- Drop-off surveys: A survey research method where respondents are provided with a survey questionnaire and asked to return it at a later time or through a designated drop-off location.
- Intercept surveys: A survey research method where respondents are approached in public places and asked to participate in a survey, often used in market research or customer feedback.
- Hybrid surveys: A survey research method that combines two or more survey modes, data sources, or research methods, often used in complex or multi-dimensional research questions.
Types of Survey Research
There are several types of survey research that can be used to collect data from a sample of individuals or groups. following are Types of Survey Research:
- Cross-sectional survey: A type of survey research that gathers data from a sample of individuals at a specific point in time, providing a snapshot of the population being studied.
- Longitudinal survey: A type of survey research that gathers data from the same sample of individuals over an extended period of time, allowing researchers to track changes or trends in the population being studied.
- Panel survey: A type of longitudinal survey research that tracks the same sample of individuals over time, typically collecting data at multiple points in time.
- Epidemiological survey: A type of survey research that studies the distribution and determinants of health and disease in a population, often used to identify risk factors and inform public health interventions.
- Observational survey: A type of survey research that collects data through direct observation of individuals or groups, often used in behavioral or social research.
- Correlational survey: A type of survey research that measures the degree of association or relationship between two or more variables, often used to identify patterns or trends in data.
- Experimental survey: A type of survey research that involves manipulating one or more variables to observe the effect on an outcome, often used to test causal hypotheses.
- Descriptive survey: A type of survey research that describes the characteristics or attributes of a population or phenomenon, often used in exploratory research or to summarize existing data.
- Diagnostic survey: A type of survey research that assesses the current state or condition of an individual or system, often used in health or organizational research.
- Explanatory survey: A type of survey research that seeks to explain or understand the causes or mechanisms behind a phenomenon, often used in social or psychological research.
- Process evaluation survey: A type of survey research that measures the implementation and outcomes of a program or intervention, often used in program evaluation or quality improvement.
- Impact evaluation survey: A type of survey research that assesses the effectiveness or impact of a program or intervention, often used to inform policy or decision-making.
- Customer satisfaction survey: A type of survey research that measures the satisfaction or dissatisfaction of customers with a product, service, or experience, often used in marketing or customer service research.
- Market research survey: A type of survey research that collects data on consumer preferences, behaviors, or attitudes, often used in market research or product development.
- Public opinion survey: A type of survey research that measures the attitudes, beliefs, or opinions of a population on a specific issue or topic, often used in political or social research.
- Behavioral survey: A type of survey research that measures actual behavior or actions of individuals, often used in health or social research.
- Attitude survey: A type of survey research that measures the attitudes, beliefs, or opinions of individuals, often used in social or psychological research.
- Opinion poll: A type of survey research that measures the opinions or preferences of a population on a specific issue or topic, often used in political or media research.
- Ad hoc survey: A type of survey research that is conducted for a specific purpose or research question, often used in exploratory research or to answer a specific research question.
Types Based on Methodology
Based on Methodology Survey are divided into two Types:
Quantitative Survey Research
Qualitative survey research.
Quantitative survey research is a method of collecting numerical data from a sample of participants through the use of standardized surveys or questionnaires. The purpose of quantitative survey research is to gather empirical evidence that can be analyzed statistically to draw conclusions about a particular population or phenomenon.
In quantitative survey research, the questions are structured and pre-determined, often utilizing closed-ended questions, where participants are given a limited set of response options to choose from. This approach allows for efficient data collection and analysis, as well as the ability to generalize the findings to a larger population.
Quantitative survey research is often used in market research, social sciences, public health, and other fields where numerical data is needed to make informed decisions and recommendations.
Qualitative survey research is a method of collecting non-numerical data from a sample of participants through the use of open-ended questions or semi-structured interviews. The purpose of qualitative survey research is to gain a deeper understanding of the experiences, perceptions, and attitudes of participants towards a particular phenomenon or topic.
In qualitative survey research, the questions are open-ended, allowing participants to share their thoughts and experiences in their own words. This approach allows for a rich and nuanced understanding of the topic being studied, and can provide insights that are difficult to capture through quantitative methods alone.
Qualitative survey research is often used in social sciences, education, psychology, and other fields where a deeper understanding of human experiences and perceptions is needed to inform policy, practice, or theory.
Data Analysis Methods
There are several Survey Research Data Analysis Methods that researchers may use, including:
- Descriptive statistics: This method is used to summarize and describe the basic features of the survey data, such as the mean, median, mode, and standard deviation. These statistics can help researchers understand the distribution of responses and identify any trends or patterns.
- Inferential statistics: This method is used to make inferences about the larger population based on the data collected in the survey. Common inferential statistical methods include hypothesis testing, regression analysis, and correlation analysis.
- Factor analysis: This method is used to identify underlying factors or dimensions in the survey data. This can help researchers simplify the data and identify patterns and relationships that may not be immediately apparent.
- Cluster analysis: This method is used to group similar respondents together based on their survey responses. This can help researchers identify subgroups within the larger population and understand how different groups may differ in their attitudes, behaviors, or preferences.
- Structural equation modeling: This method is used to test complex relationships between variables in the survey data. It can help researchers understand how different variables may be related to one another and how they may influence one another.
- Content analysis: This method is used to analyze open-ended responses in the survey data. Researchers may use software to identify themes or categories in the responses, or they may manually review and code the responses.
- Text mining: This method is used to analyze text-based survey data, such as responses to open-ended questions. Researchers may use software to identify patterns and themes in the text, or they may manually review and code the text.
Applications of Survey Research
Here are some common applications of survey research:
- Market Research: Companies use survey research to gather insights about customer needs, preferences, and behavior. These insights are used to create marketing strategies and develop new products.
- Public Opinion Research: Governments and political parties use survey research to understand public opinion on various issues. This information is used to develop policies and make decisions.
- Social Research: Survey research is used in social research to study social trends, attitudes, and behavior. Researchers use survey data to explore topics such as education, health, and social inequality.
- Academic Research: Survey research is used in academic research to study various phenomena. Researchers use survey data to test theories, explore relationships between variables, and draw conclusions.
- Customer Satisfaction Research: Companies use survey research to gather information about customer satisfaction with their products and services. This information is used to improve customer experience and retention.
- Employee Surveys: Employers use survey research to gather feedback from employees about their job satisfaction, working conditions, and organizational culture. This information is used to improve employee retention and productivity.
- Health Research: Survey research is used in health research to study topics such as disease prevalence, health behaviors, and healthcare access. Researchers use survey data to develop interventions and improve healthcare outcomes.
Examples of Survey Research
Here are some real-time examples of survey research:
- COVID-19 Pandemic Surveys: Since the outbreak of the COVID-19 pandemic, surveys have been conducted to gather information about public attitudes, behaviors, and perceptions related to the pandemic. Governments and healthcare organizations have used this data to develop public health strategies and messaging.
- Political Polls During Elections: During election seasons, surveys are used to measure public opinion on political candidates, policies, and issues in real-time. This information is used by political parties to develop campaign strategies and make decisions.
- Customer Feedback Surveys: Companies often use real-time customer feedback surveys to gather insights about customer experience and satisfaction. This information is used to improve products and services quickly.
- Event Surveys: Organizers of events such as conferences and trade shows often use surveys to gather feedback from attendees in real-time. This information can be used to improve future events and make adjustments during the current event.
- Website and App Surveys: Website and app owners use surveys to gather real-time feedback from users about the functionality, user experience, and overall satisfaction with their platforms. This feedback can be used to improve the user experience and retain customers.
- Employee Pulse Surveys: Employers use real-time pulse surveys to gather feedback from employees about their work experience and overall job satisfaction. This feedback is used to make changes in real-time to improve employee retention and productivity.
Survey Sample
Purpose of survey research.
The purpose of survey research is to gather data and insights from a representative sample of individuals. Survey research allows researchers to collect data quickly and efficiently from a large number of people, making it a valuable tool for understanding attitudes, behaviors, and preferences.
Here are some common purposes of survey research:
- Descriptive Research: Survey research is often used to describe characteristics of a population or a phenomenon. For example, a survey could be used to describe the characteristics of a particular demographic group, such as age, gender, or income.
- Exploratory Research: Survey research can be used to explore new topics or areas of research. Exploratory surveys are often used to generate hypotheses or identify potential relationships between variables.
- Explanatory Research: Survey research can be used to explain relationships between variables. For example, a survey could be used to determine whether there is a relationship between educational attainment and income.
- Evaluation Research: Survey research can be used to evaluate the effectiveness of a program or intervention. For example, a survey could be used to evaluate the impact of a health education program on behavior change.
- Monitoring Research: Survey research can be used to monitor trends or changes over time. For example, a survey could be used to monitor changes in attitudes towards climate change or political candidates over time.
When to use Survey Research
there are certain circumstances where survey research is particularly appropriate. Here are some situations where survey research may be useful:
- When the research question involves attitudes, beliefs, or opinions: Survey research is particularly useful for understanding attitudes, beliefs, and opinions on a particular topic. For example, a survey could be used to understand public opinion on a political issue.
- When the research question involves behaviors or experiences: Survey research can also be useful for understanding behaviors and experiences. For example, a survey could be used to understand the prevalence of a particular health behavior.
- When a large sample size is needed: Survey research allows researchers to collect data from a large number of people quickly and efficiently. This makes it a useful method when a large sample size is needed to ensure statistical validity.
- When the research question is time-sensitive: Survey research can be conducted quickly, which makes it a useful method when the research question is time-sensitive. For example, a survey could be used to understand public opinion on a breaking news story.
- When the research question involves a geographically dispersed population: Survey research can be conducted online, which makes it a useful method when the population of interest is geographically dispersed.
How to Conduct Survey Research
Conducting survey research involves several steps that need to be carefully planned and executed. Here is a general overview of the process:
- Define the research question: The first step in conducting survey research is to clearly define the research question. The research question should be specific, measurable, and relevant to the population of interest.
- Develop a survey instrument : The next step is to develop a survey instrument. This can be done using various methods, such as online survey tools or paper surveys. The survey instrument should be designed to elicit the information needed to answer the research question, and should be pre-tested with a small sample of individuals.
- Select a sample : The sample is the group of individuals who will be invited to participate in the survey. The sample should be representative of the population of interest, and the size of the sample should be sufficient to ensure statistical validity.
- Administer the survey: The survey can be administered in various ways, such as online, by mail, or in person. The method of administration should be chosen based on the population of interest and the research question.
- Analyze the data: Once the survey data is collected, it needs to be analyzed. This involves summarizing the data using statistical methods, such as frequency distributions or regression analysis.
- Draw conclusions: The final step is to draw conclusions based on the data analysis. This involves interpreting the results and answering the research question.
Advantages of Survey Research
There are several advantages to using survey research, including:
- Efficient data collection: Survey research allows researchers to collect data quickly and efficiently from a large number of people. This makes it a useful method for gathering information on a wide range of topics.
- Standardized data collection: Surveys are typically standardized, which means that all participants receive the same questions in the same order. This ensures that the data collected is consistent and reliable.
- Cost-effective: Surveys can be conducted online, by mail, or in person, which makes them a cost-effective method of data collection.
- Anonymity: Participants can remain anonymous when responding to a survey. This can encourage participants to be more honest and open in their responses.
- Easy comparison: Surveys allow for easy comparison of data between different groups or over time. This makes it possible to identify trends and patterns in the data.
- Versatility: Surveys can be used to collect data on a wide range of topics, including attitudes, beliefs, behaviors, and preferences.
Limitations of Survey Research
Here are some of the main limitations of survey research:
- Limited depth: Surveys are typically designed to collect quantitative data, which means that they do not provide much depth or detail about people’s experiences or opinions. This can limit the insights that can be gained from the data.
- Potential for bias: Surveys can be affected by various biases, including selection bias, response bias, and social desirability bias. These biases can distort the results and make them less accurate.
- L imited validity: Surveys are only as valid as the questions they ask. If the questions are poorly designed or ambiguous, the results may not accurately reflect the respondents’ attitudes or behaviors.
- Limited generalizability : Survey results are only generalizable to the population from which the sample was drawn. If the sample is not representative of the population, the results may not be generalizable to the larger population.
- Limited ability to capture context: Surveys typically do not capture the context in which attitudes or behaviors occur. This can make it difficult to understand the reasons behind the responses.
- Limited ability to capture complex phenomena: Surveys are not well-suited to capture complex phenomena, such as emotions or the dynamics of interpersonal relationships.
Following is an example of a Survey Sample:
Welcome to our Survey Research Page! We value your opinions and appreciate your participation in this survey. Please answer the questions below as honestly and thoroughly as possible.
1. What is your age?
- A) Under 18
- G) 65 or older
2. What is your highest level of education completed?
- A) Less than high school
- B) High school or equivalent
- C) Some college or technical school
- D) Bachelor’s degree
- E) Graduate or professional degree
3. What is your current employment status?
- A) Employed full-time
- B) Employed part-time
- C) Self-employed
- D) Unemployed
4. How often do you use the internet per day?
- A) Less than 1 hour
- B) 1-3 hours
- C) 3-5 hours
- D) 5-7 hours
- E) More than 7 hours
5. How often do you engage in social media per day?
6. Have you ever participated in a survey research study before?
7. If you have participated in a survey research study before, how was your experience?
- A) Excellent
- E) Very poor
8. What are some of the topics that you would be interested in participating in a survey research study about?
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
9. How often would you be willing to participate in survey research studies?
- A) Once a week
- B) Once a month
- C) Once every 6 months
- D) Once a year
10. Any additional comments or suggestions?
Thank you for taking the time to complete this survey. Your feedback is important to us and will help us improve our survey research efforts.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Textual Analysis – Types, Examples and Guide

Observational Research – Methods and Guide

Phenomenology – Methods, Examples and Guide

Quantitative Research – Methods, Types and...

Correlational Research – Methods, Types and...

Focus Groups – Steps, Examples and Guide
- TemplateLab
Questionnaire Templates
30+ questionnaire templates (word).
If you’re looking to gain insights on your audience or customers, a questionnaire or social survey is a reliable method used to collect standardized data from large numbers of people. (All of the information is collected in the exact same way. Questionnaires are often used by the government to find out more information about geographic areas, the lifestyles of its citizens, and assess which programs get funded . Many government entities rely on questionnaires to run programs or fund certain initiatives. This is because surveys are a favorite way to collect data in a statistical form.
Table of Contents
- 1 Questionnaire Templates
- 2.1 What Kinds of Surveys Work Best?
- 3.1 Choosing Your Template By The Questions Your Survey Asks
- 3.2 Choosing Your Questions Carefully
- 4.1 Getting the Answers and Responses You Need For Your Research
- 4.2 Why Are Questionnaires Better than Focus Groups?
- 4.3 What Factors Affect The Response Rate of Your Questionnaires?
- 4.4 Get the Most Out Of Your Questionnaire and Survey Templates
A questionnaire is a powerful tool that provides the important function of eliciting the feelings, beliefs, perceptions, or attitudes of a group of individuals. In other words, to collect valuable and previously unknown data.
The questionnaire is most frequently a very concise, preplanned set of questions designed to yield specific information to meet a particular need for research information about a pertinent topic. The research information is attained from respondents normally from a related interest area. The dictionary definition gives a clearer definition: A questionnaire is a written or printed form used in gathering information on some subject or subjects consisting of a list of questions to be submitted to one or more persons.

How Do Businesses Use Questionnaires and Surveys?
Using a questionnaire to find out more about your customers or other stakeholders, as a business or organization, is essential to adequate audience research. You can use this information to get to know your audience better, plan communication with them, and even orchestrate campaigns tailored to the ideas you’ve surveyed them about.
How do you put this into practice, anyway? Well, let’s say, for example, Ted is a small business owner that sells upscale, designed umbrellas on his website. He has a few colorful designs, but he want to raise he prices in order to carry more choices of designer umbrellas. He also wants to sell a raincoat line and Tom wonders if his target customers will think it’s all too fancy.
In order to put his “feelers” out, Tom decides to incentivize a survey on his website asking questions from people who have previously purchased from him. All of the survey respondents will be entered into a raffle worth $100 on his website. Because of this, he gets over 200 responses. He’s able to ask the questions he needs about the potential product line he wants to add. When the response is overwhelmingly positive, he knows that the quantitative data he acquires is worth the wait.
Are you ready to get started? We have several Excel questionnaire templates available for download on this page as well as questionnaire templates for Word. They’re free to help you get started.
Or, alternatively, keep reading to learn more about how to put these templates to best use.
What Kinds of Surveys Work Best?
If you want to gather unique and powerful information about an audience, a survey can help you tailor your questions and gauge their reactions accordingly. The kind of information you are seeking will help you determine the type of surveys you want to put into motion.
Basically, there are three types of surveys that are used for research purposes. There are factual surveys, which are used to collect descriptive information, such as demographic information that is used by the government to collect data. Attitude surveys, often called opinion polls, attempt to collect and measure people’s attitudes and opinions. Explanatory surveys go a step further in seeking out opinions. They’re designed to test theories and hypothesis as well as form new theories.
Essentially, the type of survey or questionnaire you choose will be tailored to your project. If you’re looking to capture the attitudes of young voters across America, then you may want to offer multiple-choice questions to allow them to explain their levels of interest and involvement in certain issues.
Researchers usually use questionnaires to make data-driven generalizations about attitudes, opinions, and behaviors. Because of this, you must be very careful when choosing whom you will be surveying, such as your customers or donors. These carefully selected samples should reflect the diversity of your base in order to be as accurate as possible. In fact, most often, a survey therefore, the surveys are usually based on carefully selected samples.
There are also many types of questionnaire templates for Excel and Word that may fit your purposes. We have several templates available for free download on this page.
Questionnaire Examples

Choosing Your Template By The Questions Your Survey Asks
If you’re getting ready to design a questionnaire, you will want to know some of the basics about survey design. The type of questions you will be asking your participants will decide the design of your survey and questionnaires, in part. Keep in mind that a neat, clean document design is also important for practical purposes; after all, a disorganized survey can be a pain for both the participants as well as the researcher.
There are basically two kinds of questionnaires that are used by researchers. Closed or restricted form surveys, which simply ask “yes” or “no” answers, or multiple choice-type questions, are known for being fairly easy to interpret and summarize. The second type of questionnaire, called an open or unrestricted survey, allows respondents to answer freely as they see fit. While these types of surveys are great for learning in-depth about the users and their thoughts, they can also be difficult to interpret and summarize.
Restricted surveys will work great with our Excel Questionnaire templates, while you may choose a Microsoft Word questionnaire template to ask users open-ended questions.
Choosing Your Questions Carefully
A questionnaire template is only as good as the questions you are asking. Sometimes a survey will include what is essentially a “loaded question”, meant to skew the results one way or another. This is often used by biased news sources or politicians who want to portray a public opinion that aligns with their views. This is great for propaganda purposes, but for actual, scientifically sound research on opinions, you’ll want to use questions that can be answered in a way that will truly reflect the views of your respondents.
When writing out the questions you will ask, keep the following questions in mind for yourself:
- Is each question you’re asking truly necessary?
- How will the answers to the questions be used?
- How will the answers to your questionnaire be analyzed, and interpreted?
- How many questions are truly needed? (Anything over 10 may have a high drop-out rate)
- Do questionnaire respondents have the information/experience necessary to answer your questions?
- Is the question written in a clear way, with no bias or emotional overtones?
- Will the survey respondents feel comfortable answering the question honestly?
- Could the wording of the question possibly offend or put-off respondents?
- Are you going to ask direct or indirect questions?
- If a checklist is used , do you have a wide range of answers to choose from? Or are you forcing opinions on somebody?
- Is the answer to any of your questions likely to be influenced by prior questions you’ve asked? (If so, you may want to change the order up to keep participants from drawing conclusion.)
Your questionnaires should all be exactly alike, unless you’re testing the survey itself to see which one gets the most responses. Questionnaires used on a template should consist of the same set of questions, asked in the same order every time.
Questionnaire Samples
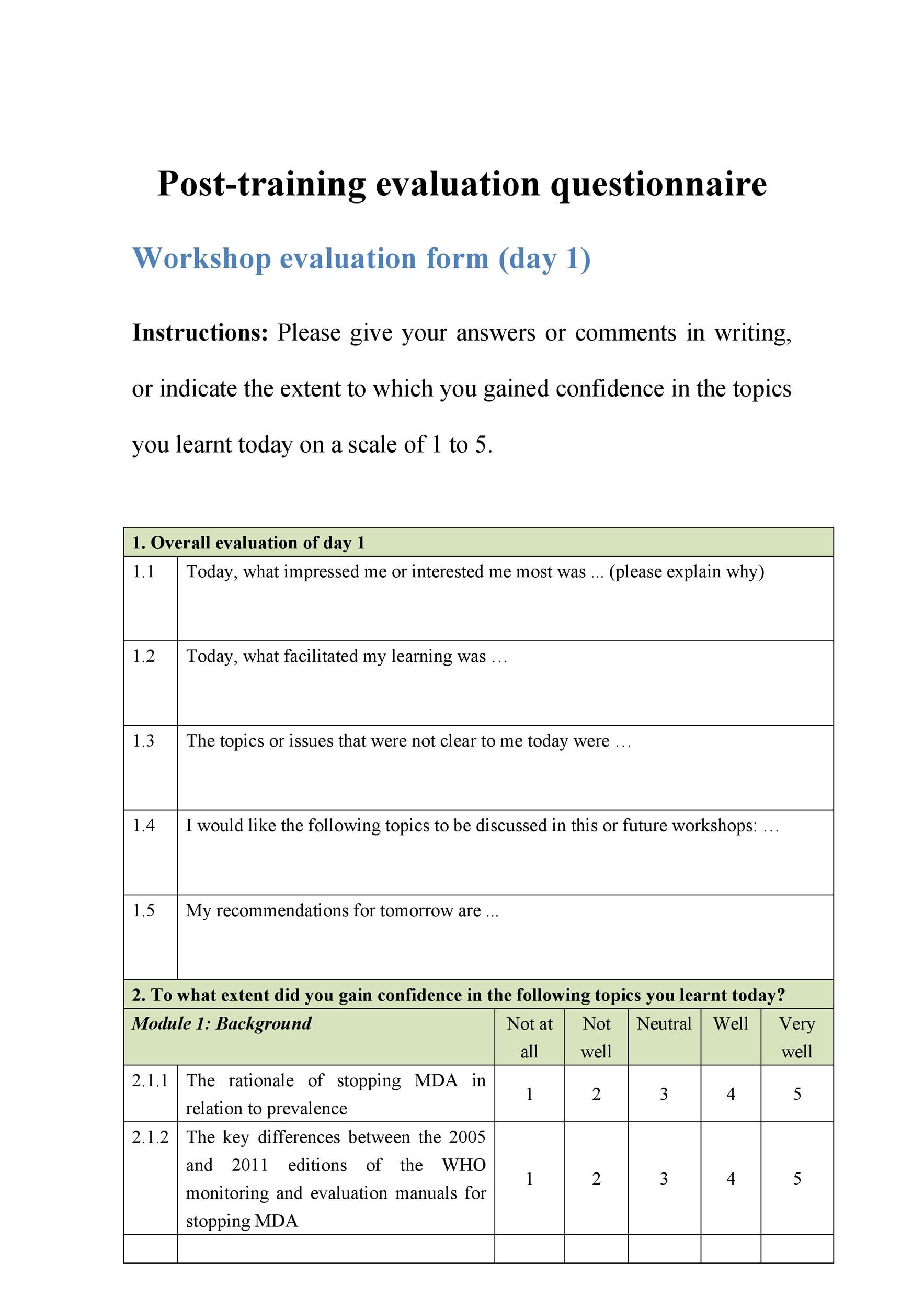
Getting the Answers and Responses You Need For Your Research
When conducting research, you can either have the participants fill out the surveys themselves, or you can have researchers interview participants over the phone or face-to-face.
If you’re having your respondents fill out the questionnaire, you may want to incentivize filling it out and returning it. Consider giving a coupon reward or holding a raffle for a gift certificate . Each person who returns their form by a certain date will get a chance at these rewards. Also consider which mode of deliver you find most useful.
Postal questionnaires can be used, but you’ll want to make sure you can count on the group returning their answers and to the researcher by a specified time and date. Telephone questionnaires can be set up to robocall, but most people find them annoying so they tend to be ineffective. You could also use your printed questionnaire to administer the questions to a group. For example, you may want to survey members of a certain club or organization. If you choose this option, be aware that groups tend to hold a bias when they fill out questionnaires in the same room together and tend to also have trouble concentrating on the task at hand when in the presence of their social circle.
Some forms of surveys will be done on the Internet with a link emailed to the questions. This is a very simple way to do our research. You can keep this data tabulated in a structured way by using an Excel questionnaire template, or you can choose to use a plain old pen and paper to tabulate your responses.
Another way to conduct surveys and questionnaires is to have the questions asked in a structured and formal way by an interviewer in a setting where each participant is interviewed one at a time. The greatest advantage of this type of research is that the interviewer can clarify any ambiguous-sounding questions and help if the respondent is confused in any way.
Why Are Questionnaires Better than Focus Groups?
Many marketers will use questionnaires and surveys to get vital information about their customer to use in their future marketing campaigns. Questionnaires are a great way to make audience segmentation easier; as long as you know which questions you need answer. They’re also much cheaper in comparison to other data-gathering methods.
Questionnaires and surveys are more economical than training interviewers and holding focus groups. Most focus groups will require some sort of compensation and there is always a chance of interview bias involved in them. Sometimes these groups can veer off-topic as well. For this reason, having respondents fill out their own surveys gives you, as a researcher, more control over the results and guaranteed answers to your question.
When you design your questionnaire in Word, you’ll want to pay attention to the uniformity of the questions. Through this, questionnaires may give you more data than most in=person meetings or interviews. You can still guide the readers toward an answer if you are not careful, but at least make sure that the questionnaires are uniform, asking the same questions, in the same order, in the same way. If the questions are highly structured, and you provide multiple choice answers, then the survey you are working with is standardize and therefore more likely to answer the deeper questions surrounding the research h you are doing.
Please keep in mind, when designing your surveys and using Word or Excel templates, that a random sampling is the best way to distribute a survey. By asking a random group of customers or people in a certain demographic or geographic area, you will be able to rule out biased samples. If you are using incentives to entice people to respond to your survey, then you should realize that some people might only be participating in your survey to get the “prize”. Because of this, your survey may fall short and have biased respondents who may not even be totally honest about their opinions.
What Factors Affect The Response Rate of Your Questionnaires?
There are several factors to keep in mind as you begin to fill out your survey or questionnaire templates. There are a few things that can affect the outcome of a mailing or other campaign asking a sampling of people to respond. Ask yourself the following questions before doing any mailing, postal or email :
- What is the length of the questionnaire? Is it too long and consuming for most people to answer? Keep it to one page or less than ten questions to optimize responses.
- What is the reputation of the business or organization sending out the survey? If you’re a political organization known for a right or left-leaning ideology, you will likely have people who oppose your ideology that may ignore your survey or skew it on purpose.
- Are the questions too complex or have you simplified them to eliminate any ambiguities?
- Are the questions on a subject that the respondent may find important? Can you change the wording to reflect more urgency? When a respondent feels that their opinion is truly needed and important, they are more likely to answer your questions.
- What time of year are you sending your surveys out? Think about the timing of your mailing in relation to national and religious holidays. Don’t send a survey out to parents in the middle of summer vacation. It will sit unopened if they are out of town.
- Are you asking questions that only your sampling group can answer? Don’t overlap with publicly available information such as demographic data that can be easily found in free government sources such as the census.
Get the Most Out Of Your Questionnaire and Survey Templates
A good questionnaire deals with a topic that the recipient will feel is important and has opinions on. Each survey you send out should have an accompanying letter that explains why it’s important to spend time completing it. For example, if you’re a nonprofit surveying the community to decide where you will allocate funds this year within the community, you should explain how the answers would shape new programs that will provide vital services. The importance of the answers should be stated clearly and the cover letter should make a compelling introduction to the needs you have for the information.
Are you ready to get started with your own survey or questionnaire? We have free Word and Excel templates ready for you to download and start customizing today.

More Templates
Mind Map Templates
Likert Scale Templates

Secret Santa Questionnaires
Behavior Charts

Ecomap Templates

Army Counseling Forms

Research Questionnaire
Questionnaire generator.

When a researcher creates a research paper using the scientific method they will need to use a gathering method that is adjacent to the research topic. This means that the researcher will use a quantitative research method for a quantitive topic and a qualitative method for a qualitative one. The research questionnaire is one of the quantitative data-gathering methods a researcher can use in their research paper.
1. Market Research Questionnaire Template Example
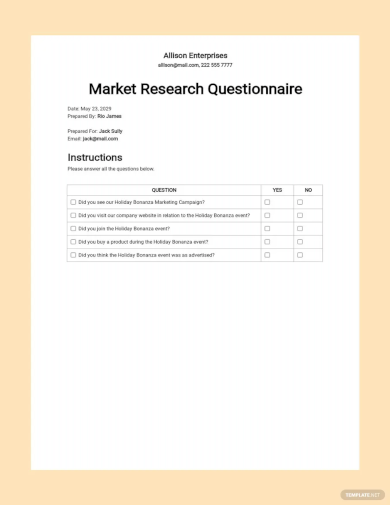
- Google Docs
- Apple Pages
Size: 38 KB
2. Market Research Questionnaire Example

Size: 94 KB
3. Research Questionnaire Example

4. Sample Market Research Questionnaire
Size: 35 KB
5. Research Survey Questionnaire

Size: 42 KB
6. Research Survey Questionnaire Construction

Size: 80 KB
7. Research Questionnaire Survey of Consumers

Size: 39 KB
8. Guide to the Design of Research Questionnaires

Size: 77 KB
9. Planning Survey Research Questionnaires

Size: 85 KB
10. Climate Change Survey Questionnaires
Size: 41 KB
11. Survey Questionnaire Design

Size: 96 KB
12. Developing Questionnaires for Educational Research

Size: 81 KB
13. Graudate Research Student Questionnaires

14. Sample Research Survey Questionnaires

Size: 46 KB
15. Market Research Questionnaire Example

16. Research Survey Questionnaire Example
17. Product X Research Study Questionnaire Example

What Is a Research Questionnaire?
A research questionnaire is a physical or digital questionnaire that researchers use to obtain quantitative data. The research questionnaire is a more in-depth version of a survey as its questions often delve deeper than survey questions .
How to Write a Research Questionnaire
A well-made research questionnaire can effectively and efficiently gather data from the population. Creating a good research questionnaire does not require that many writing skills , soft skills , or hard skills , it just requires the person to properly understand the data set they are looking for.
Step 1: Select a Topic or Theme for the Research Questionnaire
Begin by choosing a topic or theme for the research questionnaire as this will provide much-needed context for the research questionnaire. Not only that but the topic will also dictate the tone of the questions in the questionnaire.
Step 2: Obtain or Use a Research Questionnaire Outline
You may opt to use a research questionnaire outline or outline format for your research questionnaire. This outline will provide you with a structure you can use to easily make your research questionnaire.
Step 3: Create your Research Questionnaire
Start by creating questions that will help provide you with the necessary data to prove or disprove your research question. You may conduct brainstorming sessions to formulate the questions for your research questionnaire.
Step 4: Edit and Have Someone Proofread the Questionnaire
After you have created and completed the research questionnaire, you must edit the contents of the questionnaire. Not only that but it is wise to have someone proofread the contents of your questionnaire before deploying the questionnaire.
How does a research questionnaire help businesses?
A successful business or company utilizes research questionnaires to not only obtain data from their customers but also to gather data about the performance and quality of the employees in the business. The research questionnaire provides the business or company with actionable data, which they can use to improve the product, service, or commodity to obtain more customers.
Do I need to provide a consent form when I ask someone to answer the research questionnaire?
Yes, consent is very important as without this the data you have gathered from your questionnaires or surveys are useless. Therefore it is important to provide a consent form with your research questionnaire when you are asking a participant to answer the document.
What type of answers are allowed in the research questionnaire?
Research questionnaires can host a multitude of types of questions each with its specific way of answering. A questionnaire can use multiple-choice questions, open-ended questions, and closed questions. Just be sure to properly pace the questions as having too many different types of answering styles can demotivate or distract the target audience, which might lead to errors.
A research questionnaire is a data-gathering document people can use to obtain information and data from a specific group of people. Well-made and crafted research questionnaires will provide much-needed information one can use to answer a specific research question.
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
Create a fun quiz to find out which historical figure you're most like in your study habits
Design a survey to discover students' favorite school subjects and why they love them.
- A/B (or Split) Testing
- Affiliate Marketing
- Cart Abandonment
- Click Through Rate
- Compliance & Regulation
- Conversion Rate Optimization
- Customer Data Platform
- Customer Engagement
- Customer Experience
- Data Security & Privacy
- Grow Traffic and Subscribers
- Landing Page Optimization
- Mobile App Insights
- Mobile App Testing
- Multivariate Testing
- Partner Ecosystem
- Personalization
- Segmentation & Targeting
- Server-Side Testing
- Usability Testing
- Visitor Behavior Analytics
- Web Insights
- Web Testing
- Website Analysis
- Website Optimization
- Website Redesign
- Product Updates

Uncover hidden visitor insights to improve their website journey
Understand the obstacles visitors encounter, pinpoint their most engaging touch points, and analyze their actions on your website to identify areas for improvement, resulting in enhanced experiences and increased conversions.

Follow us and stay on top of everything CRO
Customer satisfaction survey examples covering top questions.

Next time you see negative feedback in your customer satisfaction survey, be grateful.
Let me explain why.
Bill Gates once said, ‘Your most unhappy customers are your greatest source of learning.’
In other words, customer feedback (both good and bad) helps shape your business’s path forward — you understand what to improve and what to keep doing more of.
And one of the best ways to capture customer feedback is through surveys where you proactively seek feedback to adapt to their preferences and needs.
But what exactly should these surveys include? Which questions should you ask to make the most of it? How should it look? It can be fairly tough to get everything right.
In this blog, we explore the dos and don’ts of setting up a survey and provide 50+ customer satisfaction survey questions you can ask.
I’m sure you’ll have all your doubts resolved.
So, let’s begin.

What are customer satisfaction surveys?
Customer satisfaction surveys are a qualitative tool that helps you understand how satisfied your customers are with your services, products, or websites. Based on the feedback, companies can assess what they are doing right and what they could do better.
Importance of customer satisfaction surveys
There are several advantages to customer satisfaction surveys that businesses might not see unless they have looked into it.
Competitive edge
Listening to your customer allows you to be more agile, responding with the necessary improvement faster than a competitor can. A conversation with your customers provides you with a constant barrage of feedback about what they like and dislike. In turn, it ensures that you are always tuned into what it is your customer wants.
Identify trends
Keeping an eye on consumer behavior changing faster than your competitors can help you spot trends. This gives you time to innovate ahead of the curve and create new services and products to meet customers’ unspoken needs.
Spot negative feedback
Gathering client feedback can let you address complaints before they damage your brand reputation publicly. It’s an early intervention to keep your reputation pure and come across as reliable and trustworthy among your customer base.
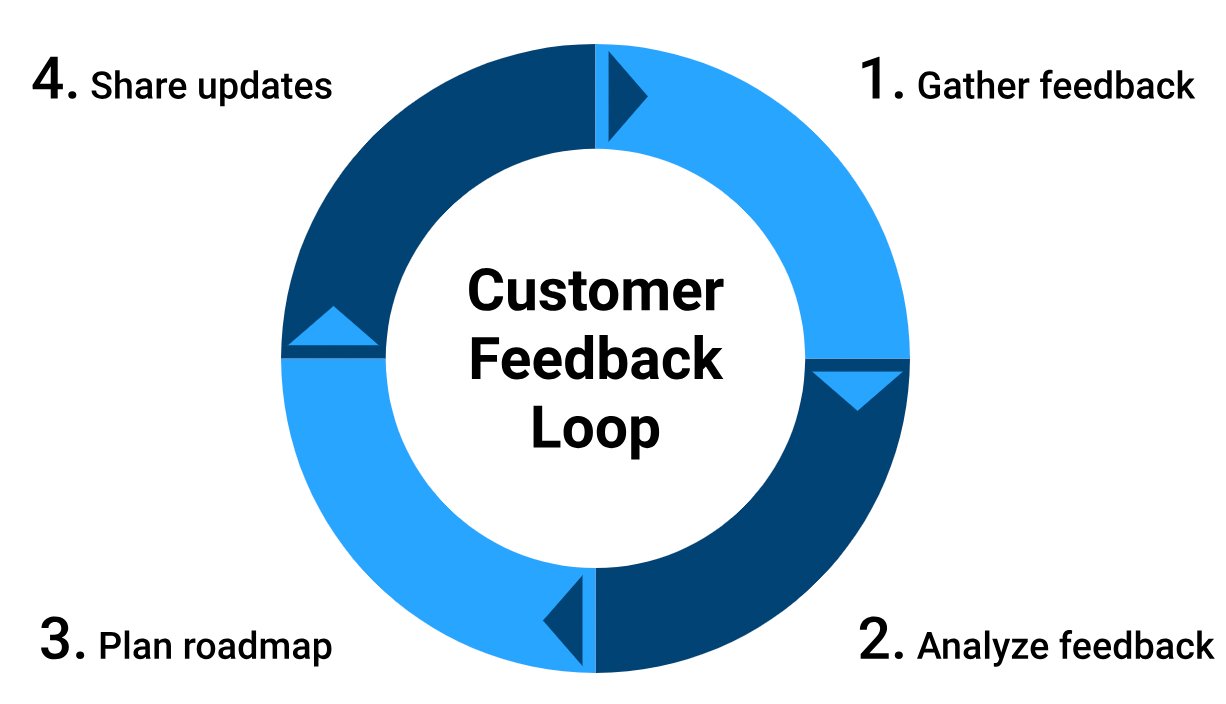
Gauge loyalty
Feedback showing appreciation can be extremely satisfying, beyond what numbers can measure. Legitimate expressions of loyalty and appreciation can highlight successes, and can also be leveraged as testimonials.
Shape business decisions
With feedback collected through surveys, you can identify what your customers want and inform your strategic decisions. It ensures that you put your resources into viable ideas and projects to develop usable products and services.
Feedback showing appreciation can be extremely satisfying, beyond what numbers can measure.
How to build customer satisfaction surveys
Want to achieve the benefits we described with your website surveys? There are some best practices you must follow. Check them out:
Option to skip questions
Start with asking questions that matter – ‘To what degree are you satisfied with our product?’ and ‘How likely are you to suggest our product to others?’ Give your customers the option to skip the less important ones – ‘Which age group do you belong to?’ ‘How did you get to know us?’
A good mix of open-ended and close-ended questions
Close-ended questions are easy to answer but provide limited insights.
For instance, translating all those ratings into evaluative comments might leave you wondering what, specifically, you need to change. This is where asking open-ended questions that allow your customers to share their thoughts can help uncover what they liked or didn’t like.
Ask open-ended questions to allow your customers to elaborate on what they liked or disliked most about their experience on your website. This way, you can capture information that scale ratings might miss.
However, asking too many open-ended survey questions wastes time and can frustrate your customers. Therefore, balance your survey with both open-ended and closed survey questions to get more insights without overwhelming your respondents.
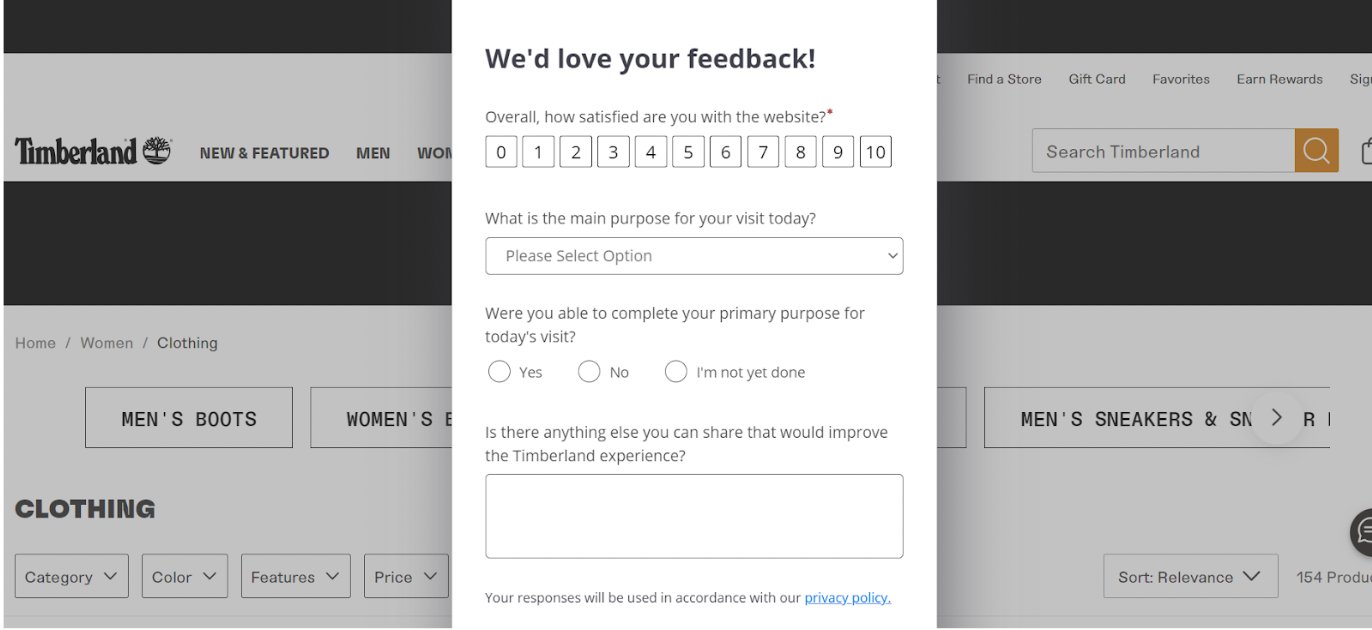
Minimum number of questions
An overlooked mistake is asking customers too many questions.
Customers are often willing to give feedback on your product or services. But don’t spoil their experience by pushing for more information. Survey fatigue kicks in here.
Remember that data quality drops after 10 minutes of fill time, so ensure your surveys can be completed within that time frame.
Simple questions
Your customers are busy. Do them a favor by making your surveys easy to comprehend. If they are faced with a question that they have to think hard about, they will most likely give up midway through a survey.
Look at the options below –

We’re sure you liked the second one.
Avoid asking conditional questions
Avoid asking hypothetical questions, as this approach can make you seem less confident in your business.
For example, a question like ‘If we improve our website navigation, will you engage better and buy from our website?’ comes across as a blatant need for validation.
Additionally, it’s difficult for customers to predict their behavior in a hypothetical situation. Instead, you can ask: “How can we improve our website navigation to make your experience better?”
In this question, the tone focuses on helping customers navigate better and avoids leaving respondents wondering what to answer.
Select the goal of your survey
Yes, customer satisfaction surveys help you assess the satisfaction of your customers, but in which area of your business do you want to assess their satisfaction?
Is it about customer support? Is it about a recent feature you rolled out and want feedback on? Or is it about their overall experience on your website? Your survey should focus on a particular area of your business to ask precise questions and get concrete feedback. This is why you need to make your survey goal specific.
With VWO Surveys of VWO Insights – Web , you can receive AI-generated survey questions tailored to your goals. It doesn’t stop there. You can keep refining them until you’re fully satisfied with their quality. Watch the video below, or if you want to try it yourself, take a free trial today .
Make your surveys goal-specific with the help of VWO Surveys to focus on a particular area of your business. This way, you can ask precise questions and get actionable feedback.
Align it with your brand theme
Once you have decided what questions to ask, it’s time to decide on the appearance of your on-page survey .
While basic survey-building tools can help you create a standard survey, if you want your survey to be taken seriously, it should reflect your brand identity and have a professional appearance.
Tools like VWO Surveys enable you to create branded surveys. Not only can you customize the appearance of your survey, but you can also save the new custom theme you’ve created for future use. Need to create a survey in a language other than English for your website in a foreign language? That is also possible with VWO Surveys, as they offer internationalization support. Check out more benefits of our survey feature in this blog.
Examples of customer survey questions
You can’t simply pick general survey questions and expect them to work for every website. Every website is different, the problems each business solves are different, and as we’ve already discussed, the goal of every survey is different.

So, here is a pool of questions from which you can select the most appropriate questions to ask based on your industry, page on your website, and customer experience. Hopefully, this will kick off your journey.
Create surveys aligned with your brand theme using VWO Surveys, enabling you to customize your survey’s appearance. This ensures your surveys are consistent with your brand identity, making them more engaging and professional.
1. How satisfied were you with your most recent order on our website? (Scale: 1-5)
2. What specific feature did you find most helpful during your recent purchase?
3. How likely are you to recommend our website to someone you know?
4. Is there anything we could improve to enhance your future shopping experience?
5. Did you encounter any difficulties during the checkout process? (Yes/No)
6. How would you rate the service you received? (Scale: Very satisfied to Very dissatisfied)
7. Can you share an instance where our service exceeded your expectations?
8. Were our service experts helpful and knowledgeable? (Yes/No)
9. What improvements do you suggest to enhance our service quality?
10. How likely are you to continue using our services in the future? (Scale: Likely, Unlikely, Unsure)
11. How easy to use do you find our software? (Scale: Excellent to Very poor)
12. What features do you find most valuable in our software?
13. Did our software meet your expectations? (Yes/No)
14. Is there any functionality you would like to see added to our platform?
15. How responsive is our customer support to your queries or issues? (Scale: Very responsive to Not responsive)
Travel & hospitality
16. Overall, how satisfied were you with your most recent visit/experience? (Scale: Very satisfied to Very dissatisfied)
17. What aspects of your stay/experience exceeded your expectations?
18. Would you consider booking with us again in the future? (Yes/No/Maybe)
19. Is there anything we could improve to make your next stay/experience better?
20. Did you find our staff friendly and helpful during your visit? (Yes/No)
21. Would you be interested in taking additional online courses from us?
22. Which course topic did you find most valuable and why?
23. Did our platform meet your learning needs? (Yes/No)
24. What additional features or resources would enhance your learning experience?
25. How likely are you to recommend our eLearning platform to others? (Likely, Unlikely, Unsure)
When should you show surveys to avoid disrupting the customer journey? Here are some triggers to help you decide the best time to display your survey and increase submissions.
26. On a scale of 0-10, how satisfied are you with our agency? (0 = not at all, 10 = extremely satisfied)
27. Can you share a specific project where our agency exceeded your expectations?
28. Did our team communicate effectively and respond promptly to your inquiries? (Yes/No)
29. What improvements do you suggest for us to better meet your business needs?
30. How likely is it that you will continue to work with our agency on future projects?
31. Can you share a positive experience you’ve had engaging our financial services?
32. Were our financial advisors helpful in addressing your financial goals? (Yes/No)
33. Where do you think we can improve in making your finances feel better?
34. How likely is it that you will allow us to handle your financial affairs over the next 12 months? (Likely, Unlikely, Unsure)
35. Is there any additional feedback you would like to provide?
36. On a scale of 1 to 10, how likely are you to keep investigating after spending five minutes on our home page?
37. What specific information or features caught your attention first when you visited our homepage?
38. Is our homepage a good reflection of our values and brand personality? (Yes, Definitely/Yes, Likely/No, Somewhat unlikely)
Product/Service pages
39. Did you find the product/service descriptions comprehensive and informative? (Yes/No)
40. What additional features would solve the current problem you’re facing?
41. How certain are you that these pages provide adequate information about the quality of our products/services? (Very certain, Quite certain, Not too certain, Not certain at all)
Contact/Support page
42. Was the information you needed, or the support you were looking for, easy to find? (Yes/No)
43. Was there anything on this page that you couldn’t find or understand?
44. How likely are you to contact our support team if you are experiencing discomfort on this page? (Very likely, Likely, Neutral, Unlikely, Very unlikely)
Checkout page
45. Did you encounter any issues or obstacles during the checkout process? (Yes/No)
46. What could we do to make the checkout process smoother and more convenient for you?
47. How satisfied are you with the transparency and clarity of the payment process? (Very satisfied, Satisfied, Neutral, Dissatisfied, Very dissatisfied)
See below the checkout page survey on OnePlus’s online store:
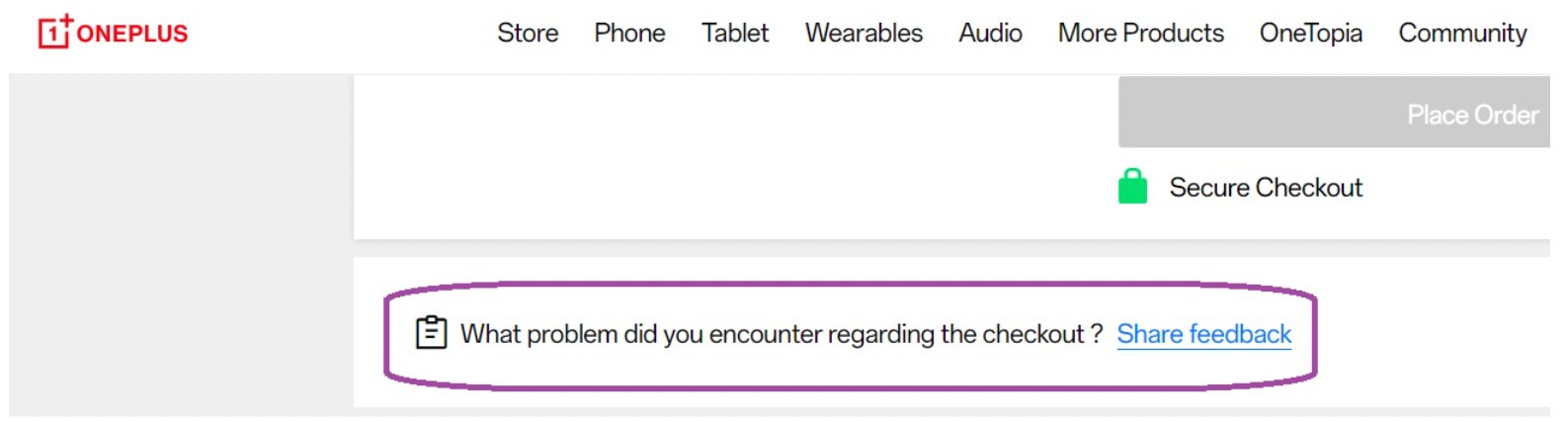
Product feedback
48. Can you share feedback on a specific product or feature you recently used?
49. How satisfied are you with our product’s performance and reliability? (Options: Very satisfied, Satisfied, Neutral, Dissatisfied, Very dissatisfied)
50. What aspect of our products do you find most beneficial or frustrating?
51. How likely are you to purchase our products again in the future? (Options: Very likely, Likely, Neutral, Unlikely, Very unlikely)
52. What improvements or enhancements would you suggest for our product lineup?
Shopclues, an eCommerce brand, aimed to boost visit-to-order conversions on its website. Before taking action, they conducted in-depth visitor behavior research. Using on-page surveys, they gathered feedback on product filters from visitors on their product category page. Implementing changes based on this feedback, they streamlined the search process. As a result, they achieved a 48% increase in visit-to-order conversions from the category page .
Customer sentiment
53. How would you describe your feelings towards our brand/company? (Options: Positive, Neutral, Negative)
54. Can you share a recent experience with our brand/company that left you particularly satisfied or dissatisfied?
55. How well do you think our company understands and addresses your needs and preferences? (Options: Very well, Somewhat well, Not very well, Not at all)
56. What emotions come to mind when you think about our brand/company?
57. How likely are you to continue doing business with our company in the future? (Options: Very likely, Likely, Neutral, Unlikely, Very unlikely)
Market research
58. What factors influenced your decision to choose our company over competitors?
59. How aware are you of our company’s competitors in the market? (Options: Very aware, Somewhat aware, Not very aware, Not at all aware)
60. Can you provide insights into industry trends or changes that could impact our business?
61. How satisfied are you with the variety and selection of products/services offered by our company compared to competitors? (Options: Very satisfied, Satisfied, Neutral, Dissatisfied, Very dissatisfied)
62. What do you see as our company’s unique strengths or advantages compared to others in the market?

Customer experience
63. Can you describe a recent experience you had with our company that exceeded your expectations?
64. On a scale of 1 to 10, how likely are you to recommend our company to a friend or colleague based on your overall experience?
65. What specific improvements could we make to enhance your future interactions with our company?
66. How satisfied are you with the navigation of our website/mobile app? (Very satisfied, Satisfied, Neutral, Dissatisfied, Very dissatisfied)
67. Is there a particular feature or service you wish our company offered to better meet your needs?
Customer support
68. Were you satisfied with the responsiveness of our customer support team to your inquiries or issues? (Yes/No)
69. How would you rate the effectiveness of our customer support in resolving your concerns? (Highly effective, Somewhat effective, Neutral, Not very effective, Not at all effective)
70. What suggestions do you have for improving the quality of our customer support services?
Customer satisfaction survey response analysis made simple with VWO
What is the right way to analyze the responses from the customer satisfaction survey? You must wonder, ‘Is there no magic wand or the best practice to tackle this?’
Well, the AI feature in VWO Surveys is back to help you again.
Gone are the days of the tedious task of sifting through hundreds of survey responses, because the VWO Surveys would summarize survey responses for you.
It will contain the key insights from the survey, any suggestions your customers may have sent your way, and even what action you can take to satisfy them.
You will now be able to take the next step on the insights you uncover. Watch how it works in the video below.
Further, you can slide and dice reports to see responses for a specific segment. Get more details about advanced filtering in this article.
Conclusion
We’ve given you the what and the how. Now all that’s left for you to do is to start making surveys. The ball is in your court. You know what to do. Take a free trial of VWO , play around a little, and see how it works. If you like what you see, you can move over to a paid plan and explore more advanced features. Either way, no pressure. But get started with your surveys. The sooner you unlock these insights, the faster you’ll start winning. All the best!
Hitting that sweet spot by asking just enough questions without taking up too much of customers’ time is crucial. According to a study, a survey that runs between 10-14 minutes with 7-10 questions should be sufficient to gather insights without overwhelming respondents.
Research has found that sending surveys in the mid-day or mid-week results in greater engagement from respondents. If you want to decide precisely when to trigger your survey on your website, you can choose from various options on VWO. Whether it’s based on the time spent on a page exceeding a certain threshold or when a visitor attempts to close the page, there are many options to choose from.
Categories:
Related content.
Success Story
More from VWO

Exploring Generative AI-based Surveys: The Future of Feedback
In the bustling office of a rapidly expanding tech company, Kim is a product manager…

Ketan Pande

Requirements for Running Serious Experimentation Programs
Haley is the founder of Chirpy and specializes in user research-based experimentation. Running experimentation programs…

Haley Carpenter

No, that won’t work
Last week I interviewed Ian Harris, a professor of surgery, for my podcast. His research…
Paras Chopra
Scale your A/B testing and experimentation with VWO.
Opt for higher roi on your optimization efforts.
Take a 30 -day, all-inclusive free trial with VWO.

Hi, I am Pratyusha from the VWO Research Desk.
Join our community of 10,000+ Marketing, Product & UX Folks today & never miss the latest from the world of experience optimization.
Check your inbox for the confirmation mail
Talk to a sales representative
Get in touch
Thank you for writing to us.
One of our representatives will get in touch with you shortly.
Signup for a full-featured trial
Free for 30 days. No credit card required
Set up your password to get started
Awesome! Your meeting is confirmed for at
Thank you, for sharing your details.
Hi 👋 Let's schedule your demo
To begin, tell us a bit about yourself
While we will deliver a demo that covers the entire VWO platform, please share a few details for us to personalize the demo for you.
Select the capabilities that you would like us to emphasise on during the demo., which of these sounds like you, please share the use cases, goals or needs that you are trying to solve., please share the url of your website..
We will come prepared with a demo environment for this specific website.
I can't wait to meet you on at
, thank you for sharing the details. Your dedicated VWO representative, will be in touch shortly to set up a time for this demo.
We're satisfied and glad we picked VWO. We're getting the ROI from our experiments. Christoffer Kjellberg CRO Manager
VWO has been so helpful in our optimization efforts. Testing opportunities are endless and it has allowed us to easily identify, set up, and run multiple tests at a time. Elizabeth Levitan Digital Optimization Specialist
As the project manager for our experimentation process, I love how the functionality of VWO allows us to get up and going quickly but also gives us the flexibility to be more complex with our testing. Tara Rowe Marketing Technology Manager
You don't need a website development background to make VWO work for you. The VWO support team is amazing Elizabeth Romanski Consumer Marketing & Analytics Manager
Trusted by thousands of leading brands

Share on Mastodon
A complete guide to customer satisfaction research
Last updated
10 August 2024
Reviewed by
Miroslav Damyanov
If you’re not in business to create happy customers, you won’t be in business for very long.
Customer satisfaction research is the best way to determine how happy your customers are with your product or service. It also enables you to ensure their happiness becomes long-term satisfaction. When you understand customer feedback, you can improve your products and services, increase customer loyalty, and drive long-term success.
In this article, we’ll take a detailed look at what this type of research is and how you can conduct it.
- What is customer satisfaction research?
Happy customers are repeat customers. They are likely to tell their friends and colleagues about the products and services they enjoy, potentially sending new customers your way.
Unsatisfied customers are the opposite. They won’t return, and they will possibly warn their friends, family members, and colleagues to stay away too. It stands to reason that building a successful brand means creating far more happy customers than unhappy ones.
Customer satisfaction research is the process of collecting and analyzing feedback from customers to understand how well you are meeting their expectations and needs. This vital research can help your business improve its products and services, ensuring happier and more loyal customers.
Through customer satisfaction research, you can learn which steps your company should take to create more happy customers.
- Why do customer satisfaction research?
Getting more happy customers and fewer unhappy customers is important as a general aim, but it’s quite broad. Customer satisfaction research has several concrete goals that it provides insights into. Some companies begin their journey into customer satisfaction research specifically because they have one or more of these goals in mind:
Improving product/service quality
Enhancing customer loyalty and retention
Gaining a competitive advantage
Identifying areas for improvement
Measuring the impact of business initiatives
- What are the objectives of customer satisfaction research?
To provide you with actionable insights, customer satisfaction research needs to be comprehensive. It isn’t enough to know whether a customer is happy with your brand or not; you need to understand the specifics of what makes them happy or unhappy.
Here are some objectives:
Measure overall customer satisfaction levels
Understand the drivers of satisfaction
Identify strengths and weaknesses
Track changes in satisfaction over time
Benchmark against industry standards
Gather feedback for product/service development
Understanding how your company measures up in these areas will enable you to determine whether you have a problem with customer satisfaction. It will also provide an important guide for how to address those issues and improve how customers view your brand.
When you know the true reasons your satisfied customers keep coming back, you can incorporate that into your value proposition. This will make your marketing efforts more effective, helping you retain customers who might not have considered that positive aspect of your offering before.
This information also tells you which of your features are worth developing further, which need work to live up to your expectations of them, and which you can abandon entirely.
- Examples of customer satisfaction research topics
All the questions above can be applied to a number of customer satisfaction questions. Trying to answer them all at once will result in unfocused and possibly unhelpful research. Instead, it’s best to focus your research on one or two areas. Some common areas for customer satisfaction research are listed below:
Product/service quality
Customer support and service
Pricing and value perception
Ease of doing business
Brand reputation and loyalty
Post-purchase experience
Comparison to competitor offerings
You might not know which of these you should start with. By gathering some initial customer feedback, you can narrow down which of these topics are strengths and which are weaknesses, allowing you to drill down deeper in your next round of research.
- Levels of customer satisfaction research
We can also take a different view of granularity when doing customer satisfaction research. Customers interact with your brand on several levels. Their opinions of the brand at each of these levels may vary.
Transactional (single interaction)
This level of customer satisfaction deals with a single interaction. While a customer could generally be very happy with your brand, an individual transaction could annoy them in some way. Eliminating these sources of annoyance could be the tipping point that pushes less satisfied customers toward brand loyalty and away from dissatisfaction.
Here are some examples of transactional customer satisfaction research:
Post-purchase surveys
Service desk satisfaction surveys
Website/app feedback surveys
Point-of-sale customer satisfaction ratings
Event feedback forms
Relational (ongoing relationship)
This deals with the customer’s overall perception of your brand independent of any single interaction.
Just as it’s possible for a generally happy customer to have a negative single experience, customers can develop a negative view of your brand even if they have one or two great transactions.
By looking at customer satisfaction from a broader perspective and focusing on the customer’s view of your brand itself, you can unlock deeper insights into what makes customers leave or stay.
Examples of relational customer satisfaction research include the following:
Customer satisfaction and loyalty survey programs
Churn/retention analysis
Net promoter score (NPS) surveys
Long-term, in-depth customer interviews
Quarterly customer surveys
Brand perception studies
Holistic (overall experience)
This level of customer satisfaction research involves combining the previous two. Instead of focusing solely on single interactions or the brand’s overall perception, holistic customer satisfaction research examines the entire picture.
So, why is this helpful? In customer satisfaction, the whole is often more than the sum of its parts. By looking at how everything fits together, you can get a broader sense of which areas need adjustment.
Examples of holistic customer satisfaction research include the following:
Customer journey mapping
Customer lifecycle analysis
Omnichannel experience surveys
Ethnographic studies and observational research
Comprehensive customer feedback programs
- How to carry out customer satisfaction research
Although the specifics will depend on your business and the type of customer research you’re interested in, the seven steps below provide a solid roadmap for successfully carrying out customer satisfaction research.
Step 1: define research objectives
The first step is defining your objectives. Before you can research something, you need to know what you’re researching.
Your research objectives might include, for example, retaining customers, improving marketing and sales efforts, elevating long-term product use, and more.
Next, identify the key performance indicators (KPIs) you’ll be measuring. These can include retention rate, monthly active users, repeat purchase rate, net promoter score, customer satisfaction (CSAT) scores , churn rate, and various customer support metrics, among other things. Include these or any others that are specific to your goals.
As you’re deciding what your objectives are and which KPIs to use, ensure that your choices align with your business objectives.
Step 2: select a research methodology
The next step is to determine which research methodology you’ll use to gather your data. Quantitative methods, such as surveys and rating scales, can provide concrete numbers that are easy to track over time. Qualitative methods, such as interviews and focus groups, can provide more in-depth information about what customers do and don’t like about your product or service.
In practice, you’ll likely want to use a mixture of these two methods. A hybrid approach will provide you with data you can use to compare your results with industry standards or past results from your own research. It will also give you more actionable insights to drive those numbers in the direction you want.
Step 3: develop customer satisfaction surveys
If surveys will be a part of your methodology, you need to decide what those surveys will entail.
Remember, focus is key. There are many questions you can ask customers, but you should limit yourself to those that directly address the current research topic. This will make the data easier to sort through and help you use your resources more effectively.
When crafting your surveys, consider your customers. If you want to get a sufficient number of well-thought-out responses, you’ll need to make sure the surveys are easy and convenient to complete. Overly lengthy surveys or those that use challenging technologies can limit the number and quality of responses you get.
The customer satisfaction score (CSAT) is the simplest and most straightforward method for measuring customer satisfaction. It typically involves asking customers to rate their satisfaction with a specific interaction or transaction on a scale, such as 1–5.
Step 4: choose a sampling strategy
Next, decide who you’ll be conducting research on. Do you have a specific customer segment that you’d like to better understand? If your company makes heavy use of customer personas, it can be helpful to survey each of them independently to better understand how to appeal to them.
Here are some sampling methods you can consider:
Random sampling: randomly pick participants from your full customer base to ensure each customer has an equal chance of being included.
Stratified sampling: divide your customer base into distinct subgroups and sample equally from each to ensure complete representation across key segments.
Systematic sampling: choose every nth customer from a list to ensure an even spread of participants.
Convenience sampling: select participants who are easiest to reach or most readily available, which is quicker but may not be as representative.
Step 5: data collection and analysis
Now we come to the meat and potatoes of customer satisfaction research—the collection and analysis of the data. If you’re conducting surveys, this could mean online forms, phone calls, or in-person questioning. Whatever your method, collect all the data and store it in a convenient place.
Tools like Dovetail make it easy to do the following:
Collect disparate data types and create a single source of truth around customer insights
Sort through the data and glean actionable insights from what you have collected
Analyze both quantitative and qualitative results, identify trends and patterns, and determine what the next steps should be
Step 6: implement changes
Once you have analyzed the data, it’s time to put what you have learned into action.
First, identify all the areas that need improvement and prioritize them. The insights provided by customers can provide a great metric for prioritization, but be sure to also factor in the resources available to you and your business goals.
Once you have decided which areas to work on, develop an action plan to make the necessary changes. To stay organized, assign responsibility for overseeing these changes to someone who is capable and reliable. You might have several people handle larger changes, each with their own specific area of the plan.
Step 7: implement a feedback loop
Customer satisfaction research isn’t a one-and-done thing. You’ll want to revisit the research regularly to ensure that changing customer preferences and market dynamics haven’t altered how your customers view you. Quantitative measurements that can be tracked over time can be a big help.
If you’re making improvements but the rate of improvement is leveling off compared to previous results, it could indicate that a change is underway, shifting customer desires. It could also mean that you’re nearing peak customer satisfaction. The best way to know for sure is to set up more customer satisfaction research to understand your numbers.
The important thing is that you don’t let your customer satisfaction efforts become stagnant. Customer needs and preferences change all the time, and if you’re not making an effort to meet those evolving needs, a competitor will happily step in and do it for you.
Should you be using a customer insights hub?
Do you want to discover previous research faster?
Do you share your research findings with others?
Do you analyze research data?
Start for free today, add your research, and get to key insights faster
Editor’s picks
Last updated: 3 April 2024
Last updated: 30 April 2024
Last updated: 13 May 2024
Last updated: 22 July 2023
Last updated: 26 July 2024
Last updated: 23 July 2024
Latest articles
Related topics, .css-je19u9{-webkit-align-items:flex-end;-webkit-box-align:flex-end;-ms-flex-align:flex-end;align-items:flex-end;display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-flex-direction:row;-ms-flex-direction:row;flex-direction:row;-webkit-box-flex-wrap:wrap;-webkit-flex-wrap:wrap;-ms-flex-wrap:wrap;flex-wrap:wrap;-webkit-box-pack:center;-ms-flex-pack:center;-webkit-justify-content:center;justify-content:center;row-gap:0;text-align:center;max-width:671px;}@media (max-width: 1079px){.css-je19u9{max-width:400px;}.css-je19u9>span{white-space:pre;}}@media (max-width: 799px){.css-je19u9{max-width:400px;}.css-je19u9>span{white-space:pre;}} decide what to .css-1kiodld{max-height:56px;display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;}@media (max-width: 1079px){.css-1kiodld{display:none;}} build next, decide what to build next, log in or sign up.
Get started for free
- Open access
- Published: 12 August 2024
Precision assessment of a hypertension prevalence survey
- Reinaldo José Gianini ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-7046-7306 1 ,
- Natália Ferreira Caneto ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-2535-7455 1 ,
- Natália Murate Junqueira ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-9743-6246 1 ,
- Leticia Gouvea Rodrigues ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-1692-0691 1 ,
- Beatriz Zurma Parri ORCID: orcid.org/0009-0002-2194-9867 1 &
- Cibele Isaac Saad Rodrigues ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-9490-7997 1
BMC Public Health volume 24 , Article number: 2188 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
Metrics details
Population surveys are crucial for public policy planning and provide valuable representative data. In the health sector studies to identify and assess the prevalence of Arterial Hypertension (AH), a chronic non-communicable disease (NCD), along with its associated risk factors have been conducted.
This study aims to assess the effectiveness of a population health survey in estimating the prevalence of arterial hypertension (AH) in the Sorocaba municipality between August 2021 and June 2023. Methods: The analyzed performance indicator is the precision (design effect - deff) of AH prevalence in adults (≥ 18 years) and their exposure to primary risk factors. The total sample included 1,080 individuals from the urban area, deemed sufficient to estimate a deff of 1.5. This cluster-based study utilized census sectors as clusters, with data collected through household interviews, standardized questionnaires, and measurements of blood pressure and biometric parameters. The deff calculation formula used was weighted variance / raw variance. The Research Ethics Committee approved this study, with registration CAAE 30538520-1-0000-5373.
The deff values ranged from 0.44 for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease to 1.63 for asthma, with a deff of 1.00 for AH prevalence. Conclusion: The study demonstrated good precision in its results, with high receptivity and cooperation from participants. The cost-effectiveness of the research deemed appropriate. The technique of selecting households within clusters (census sectors) based on detailed mapping and demographic data from the Instituto Brasileiro de Geografia e Estatística (IBGE) proved to be practical and efficient, suitable for replication in other municipalities and for studying other NCDs.
Peer Review reports
Population health surveys are epidemiological tools used to construct reliable health information and are carried out with probabilistic and representative samples. These surveys may be international, national, regional or local [ 1 ]. When primary data are obtained, the methodology is defined by the researcher, who has control over the data collection and application of the instrument, usually through a questionnaire. On the other hand, when secondary data are collected, the information databases are public and were originally created for administrative, financial or epidemiological purposes [ 2 ]. In healthcare, these surveys deal with the description and analysis of the prevalence of diseases and their risk factors, including reported or diagnosed morbidity. They assess, through questionnaires, the functioning of healthcare from the user’s point of view, knowledge about morbidity and lifestyles, reliable estimates about the prevalence of a given event, risk and protective factors, conditions of health, the development of health systems, the surveillance of various chronic diseases, and their determinants [ 3 , 4 ].
The need for health surveys arises from the limitations of the available recorded health data, which may be continuous, as yearly report, or with defined periodicity. These data can be classified as timely, partial, incomplete, unsatisfactory, fragmented, outdated or those that not allows disaggregation [ 5 , 6 ].
The National Health Survey (PNS), one of the main Brazilian population surveys, uses a probabilistic cluster sample. It is obtained in 3 selection stages: primary units – census tracts; secondary units – households; and tertiary units – individuals aged 18 or over. In 2013, the PNS included 6,081 census sectors, 81,767 households and 62,986 individuals [ 7 ].
These surveys can be performed via telephone, mail, the internet, home visits or interviews. Regarding diagnosed morbidity, these methods of surveys include subsamples with clinical examinations and biological specimen collections [ 8 ].
In developed countries, population-based surveys have been conducted since the 1960s. In the case of Brazil, the Ministry of Health has made substantial investments in this area since the 1990s, such as financing the National Research Health Supplement by Household Sample (PNAD) since 1967, which became continuous, repeated every three months, since 2012 [ 9 ].
Other important surveys in Brazil were the National Cancer Institute (INCA) [ 10 ], the Municipality of São Paulo Survey [ 11 ], the ISA SP CAPITAL [ 12 ], and the VIGITEL which is conducted annually since 2006 [ 13 ].
At the international level, the following surveys have been conducted: the National Health Interview Survey (USA) [ 14 ], the European Health Interview [ 15 ], the General Health Survey for England [ 16 ], the National Population Health Survey [ 17 ] (Canada), and the World Health Survey [ 18 ].
Regarding the prevalence of arterial hypertension (AH) in adults ≥ 18 years old, the 2013 PNS reported a prevalence of 21.4% (95% CI 20.8–22.0) using self-reported criteria, 22.8% (95% CI 22.1–23.4) for measured AH, and 32.3% (95% CI 31.7–33.0) for measured hypertension and/or reported medication use. The prevalence for adults ≥ 75 years old was 55% [ 19 ].
For complex samples like the PNS, the method involves cluster sampling with multiple selection stages, each with unequal draw probabilities. Estimating the design effect (deff) on the collected sample data is recommended. Deff is an important indicator in both planning the sample size and evaluating the precision of survey results. The formula to calculate the design effect is typically: \(\:DEFF=\frac{{Var}_{clustersampledesign}}{{Var}_{simplerandomsample}}\) [ 20 ]. A deff lower than 2 is recommended [ 21 ].
Studying the prevalence of chronic non-communicable diseases in Brazilian populations, such as AH, has epidemiological value, as long as the statistical criteria established for defining the prevalence and associated risk factors are valid. To this end, calculating the deff helps in assessing the performance of the methodology used.
To assess the performance of a population health survey carried out in the municipality of Sorocaba from 2021 to 2023, which aimed to estimate the prevalence of AH. The performance indicator used is the precision (deff) of the AH and its main risk factors in adults.
This survey aimed to analyze the urban resident population of the municipality of Sorocaba, aged 18 years and older, estimated at 535,843 individuals in 2022. The total population of Sorocaba in the same year was estimated at 723,682 individuals [ 22 ]. The survey was performed using a stratified cluster sampling method Sampling was performed in clusters composed of 6 strata represented by the regionalized division of the Municipal Health Department of Sorocaba: Center South, East, Center North, North, Northwest and Southwest Regions. In each census sector, data were collected from 18 individuals divided into 6 domains: 6 individuals over 60 years of age (3 men and 3 women), 6 individuals aged 40 to 59 years (3 of each sex), and 6 individuals aged 18 to 39 years (3 of each sex). In each stratum, 10 census sectors were selected. The total sample included 1,080 individuals, satisfying the following parameters: expected prevalence of arterial hypertension = 33.7% with an estimated error of 3.65%; significance level of 0.05 considering a two-sided test with Z = 1.96; design effect (deff) = 1.5; and loss of information (non response) = 10%. The selection of 60 census sectors was conducted according to the following procedure: listing all sectors belonging to a given region in descending order according to the size of the population of each sector, calculating the interval to be used in systematic random sampling (total sectors of the region/10), drawing the sector from the first interval and systematically repeating the interval to select the 9 remaining sectors in that region.
The selection of households was carried out using the following procedure: mapping the residential streets of the census sector, defining the route, calculating the interval between households to be selected (total households/18), drawing a random number between 1 and 18 to select the first household to be included and systematically repeating the interval for the selection of the remaining 17 individuals. To ensure data collection, the recruitment of individuals followed the order of the rarest domain to the most frequent, namely, elderly males, elderly females, young males, young females, adult males and adult females. Collection was extended on holidays, Saturdays and Sundays to ensure the inclusion of workers.
As this is a survey sample, considering each domain, the weight of the sampling unit is the inverse of sampling fractions, and was composed of the following: a . Individual weight = total of individuals in the census sector divided by 3; b . Sector weight = region population divided by sampled sector population, multiplied by 10; c . Weight of the region = total population divided by population of the region, multiplied by 6. The final weight of each sample unit = ( a × b × c ) [ 20 ].
For data collection, a standardized form containing sociodemographic data and risk factors for AH was used as an instrument. In addition to the measurements of blood pressure (BP), age and sex of the individuals selected for the sample, additional information was collected, such as skin color/race/ethnicity, marital status, education, occupation/type of work, religion, family income in Reais, number of people in the family, family morbidity history, use of health services, chronic diseases and comorbidities, medical treatment, practice of physical activity, ingestion of alcoholic beverages, and smoking. Every human participant gave its informed consent after reading the Free and Informed Consent Form, which is attached in a supplementary file.
Data were collected from August 2021 to June 2023 during household visits. Interviews were conducted using a standardized questionnaire with open-ended and multiple-choice questions. In addition, blood pressure was measured in accordance with the recommendations of the Brazilian AH Guidelines 2020. Participants who had an average systolic blood pressure ≥ 140 mmHg and/or diastolic blood pressure ≥ 90 mmHg were considered to have AH or who had a BP below these limits and were receiving regular treatment with anti-hypertensive medications [ 23 , 24 , 25 ].
The STATA 16.0 program and its survey command were used for the analyses. The calculation of the deff was carried out using the stat effects command with the deff option after svy mean command for continuous quantitative variables, or svy ,
proportion for qualitative variables [ 26 ]. The deff is the ratio between the weighted variance, which considers both inter-cluster and intra-cluster variance, and the raw variance, which can be thought of as intra-cluster variance assuming the entire sample is one cluster. [ 20 ].
This project was submitted and approved by the Research Ethics Committee (CEP) of the Faculty of Medical and Health Sciences (FCMS) of the Pontifical Catholic University of São Paulo (PUC-SP), registered as CAAE 30538520-1-0000-5373.
Between the second half of 2021 and the first half of 2023, data were collected from 1,080 individuals in 60 sectors as planned. The intracluster weights assigned to the individuals interviewed ranged from 1.7 to 161. All sectors planned for collection were included. The sector weights ranged from 1.93 to 159.1. The region weights ranged from 0.14 to 3.35. The greatest data loss was for family income (34%); however, for the other variables, the losses did not exceed 0.4%. The interviewers, always in pairs, strictly followed the collection protocol, trying to cover the entire area of the census sector. Vertical or horizontal condominiums were included, applying the same proportionality rule (draw) for choosing the residential unit. Non-regular situations, such as collective housing or clusters of precarious housing, were registered, analyzed and included, and the same sample selection rule was applied. The interviewers, students of the Scientific Initiation Program of Medicine, supervised by professors, followed the construction of the database in STATA, based on data collected in an EXCEL spreadsheet, and they participated in the first analyses.
Table 1 shows that for the global deff according to social and demographic variables, exception to Ethnicity/Brown, they were less than 1.5, which was the value estimated in the sample planning, indicating better precision of the results. The Family monthly income and Occupation have the lowest deff (1.03), indicating good accuracy in information. As the sampling was planned for representing the global prevalence of AH among people from 18 or more years old, it can be observed that the deff by sex and age categories show more variability, with higher values for 18–39 years and lower values for 60 years or more; this trend is similar for both genders.
Table 2 shows that the global highest deff, defined according to variables related to lifestyle, was for Quantity of physical activity (1.61); deff values lower than 1 were observed for time of smoking (0.60) and time as an ex-smoker (0.67). Ex-smokers and ex-alcoholics have deff values close to 1. Again, it is verified the same trend by sexo and age, higher deff for 18–39 years. Use of depressant drugs and Use of stimulant drugs show non-calculable deff because had not enough sample number.
Table 3 shows that according to the variables related to family and personal morbidity history, the global deff varied from 0.44 for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) to 1.63 for asthma. Those values were equal to or close to 1 for dyslipidemia, and hyperthyroidism. Family member with some morbidity has deff lower than 1 for all domains.
Table 4 shows that according to variables related to the clinical examination, the global deff varied from 0.88 for arm circumference to 1.28 for stress, and the deff was very satisfactory for HA, at 1.00. Height, and metabolic syndrome factors presented deff values close to 1. The same pattern is verified according to domains: higher deff for youngers.
As shown in Table 5 , according to variables related to the drug treatment of AH the global deff varied from 0.86 for the Use of calcium channel blockers, to 1.41 for the use of sympatholytics.
This research can be considered a successful study representing the urban population of Sorocaba. It required significant effort but minimal resources. The strategy of implementing it as a scientific initiation program with students supervised by medical teachers utilizing available software at the institution was effective. In terms of urban population aged 18 and above, it can be inferred that the selection bias was minimal, evident from both data analysis and comparison with other surveys [ 20 , 26 , 27 , 28 , 29 ].
In terms of precision, the research demonstrated high satisfatory levels, with a global deff of less than 1.64 for all variables analyzed. Specifically for arterial hypertension, the deff was 1.00 in our study, indicating high precision. For example, in the study by Alves [ 20 ], it was 1.37 for the group of teenagers and 1.52 for the group of elderly people. From the data, it can be inferred that one of the axes of precision was objective information, subject to verification, notably variables related to clinical examination, as opposed to subjective information such as variables related to lifestyle. The other axis of precision refers to the frequency of the event in the population and its intra-cluster and inter-cluster variance. If the clusters are more similar than expected for a random distribution of a given variable, the deff may be less than 1. Furthermore, if the variable is widely distributed in the population, there is a small cluster effect, and the prevalence of the event studied differs significantly inside strata, so it is likely that the deff is less than 1 [ 27 ]. It can occur in both, very frequent and rare events, which explains the deff of osteoporosis (0.58) and of COPD (0.44), respectively.
Concerning the study limitations, it is important to note that information on family income was highly unreliable, that information on drug use was probably influenced by modesty or fear, and that information on seeking health services was compromised by the respondents’ memories [ 30 , 31 , 32 ].
As for the domains, the tendency for higher deff for younger people indicates the need to increase this subsample, while deff below one for older people indicates a smaller amount needed for this subsample, and this occurs in both men and women. This is because there is a sample planned for satisfying a maximum global deff of 1.5 for AH, and not planned for each domain. Furthermore, some very specific conditions demonstrate that different sample calculations would be necessary if there were interest.
As suggestions for future studies, the comorbidities of the interviewees could have been diagnosed in some situations. For example, in patients with diabetes, asthma and COPD, capillary blood glucose tests and spirometry could be employed. Furthermore, considering that it is a resident population and that the bond established in the first contact was of high quality, it would be possible to schedule new visits to obtain more information, including various clinical protocols, such as adherence to treatment.
A survey was conducted with the urban population of Sorocaba between 2021 and 2023 for measuring the prevalence of AH in adults. The results showed good precision, with a global deff of 1.00 for this variable. There was good receptivity and collaboration from interviewees, and the research had an adequate cost‒benefit ratio. The technique used for selecting households in the respective clusters (census sectors), based on detailed mapping and demographic information from the IBGE, proved to be practical and efficient.
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are not openly available due to reasons of sensitivity and are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Silva VSTM, Pinto LF. Nationwide population-based household surveys in health: a narrative review. Ciênc saúde Coletiva. 2021;26(09):4045–58. https://doi.org/10.1590/1413-81232021269.28792020 .
Article Google Scholar
Kindratt TB. Big Data for Epidemiology: Applied Data Analysis Using National Health Surveys, 2022.
Malta DC, Leal MC, Costa MFL. Inquéritos Nacionais De Saúde: experiência acumulada e proposta para o inquérito de saúde brasileiro. Rev bras Epidemiol. 2008;11(supl1):159–67. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1415-790X2008000500017 .
http://doi.org: 10.1136/jech.2008.077172.
Mota E. Integrating population surveys to the National Health Information System. Ciênc saúdecoletiva. 2006;11(4):870–86. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1413-81232006000400010 .
Andrade FRe, Narval PC. Population surveys as management tools and health care models rev. Saúde Pública. 2013;47(Suppl3):154–60. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0034-8910.2013047004447 .
Instituto Brasileiro de Geografia e Estatística - IBGE. Pesquisa Nacional De Saúde [National Health Survey] – 2013. https://www.ibge.gov.br › estatisticas › sociais › saude.
Monteiro CA, Florindo AA, Claro RM, Moura EC. Validity of indicators of physical activity and sedentariness obtained by telephone survey. Rev Saude Publica. 2008;42(4):575–81. https://doi.org/10.1590/s0034-89102008000400001 .
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Pesquisa. Nacional por Amostra de Domicílios – PNAD [National Household Sample Survey] – 2008. www.datasus.gov.br/informações de saúde/inquéritos e pesquisas/suplemento saúde.
Instituto Nacional do Câncer INCA. Inquérito Domiciliar [Household Survey]. 2004 http://www.inca.gov.br/inquerito/
Inquérito de Saúde [Health Survey] do Municipio de São Paulo ISA-SP-Capital. 2008. http://extranet.saude.prefeitura.sp.gov.br/areas/ceinfo/inquerito-de-saude-isa-capital
Zaitune MPA, Barros MBA, César CLC, Carandina L, Goldbaum M, Alves MCGP. Factors associated with global and leisure-time physical activity in elderly individuals: a health survey in São Paulo (ISA-SP), Brazil. Cad Saude Publica. 2010;26(8):1606–18. https://doi.org/10.1590/s0102-311x2010000800014 .
Vigilância de fatores. de risco e proteção para doenças crônicas por inquérito telefônico VIGITEL – 2008. www.datasus.gov.br/informações de saúde/inquéritos e pesquisas.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention – National Center for Health Statistics. Natl Health Interview Surv. 2019. https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/nhis/about_nhis.htm
Kuulasmaa K, Tolonen H (Prepared), editors. What is EHES and why it is needed? National Institute for Health and Welfare, 2013. Discussion Paper 2013_007. URN:ISBN: 978-952-245-844-5, URL: http://urn.fi/URN:ISBN:978-952-245-844-5
National Health Services. Narional Health Survey for England 2019 (NS). http://healthsurvey.hscic.gov.uk/support-guidance/public-health/health-survey-for-england-2019.aspx
Canadian Research Data Centre Network. National Population Health Survey, 1994–2011. https://crdcn.ca/data/national-population-health-survey/
World Health Organization – WHO. World Health Surveys 2024.WHO.Int. https://apps.who.int/healthinfo/systems/surveydata/index.php/collections/whs
Andrade SSA, Stopa SR, Brito AS, Chueri PS, Szwarcwald CL, Malta DC. Self-reported hypertension prevalence in the Brazilian population: analysis of the National Health Survey, 2013. Epidemiol Serv Saúde. 2015;24(2):297–304. https://doi.org/10.5123/S1679-49742015000200012 .
Alves MCGP, Escuder MML, Goldbaum M, Barros MBA, Fisberg RM, Cesar CLG. Sampling plan in health surveys, city of São Paulo, Brazil, 2015. Rev Saúde Pública. 2018;52. https://doi.org/10.11606/S1518-8787.2018052000471 .
Barata RB, Moraes JC, Antonio PRA, Dominguez M, World Health Organization. Rev Panam Salud Publica. Immunization coverage survey: empirical assessment of the cluster sampling method proposed by the. 2005;17(3):184 – 90. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1020-49892005000300006 22. Instituto Brasilerio de Geografia e Estatistica. Censo 2022. IBGE. https://www.ibge.gov.br/estatisticas/sociais/trabalho/22827-censo-demografico-2022.html
Instituto Brasilerio de Geografia e Estatistica. Censo 2022. IBGE. https://www.ibge.gov.br/estatisticas/sociais/trabalho/22827-censo-demografico-2022.html
Barroso WKS, Rodrigues CIS, Bortolotto LA, Mota-Gomes MA, Brandão AA, Feitosa ADM, et al. Diretrizes Brasileiras De Hipertensão arterial – 2020. Arq Bras Cardiol. 2021;116(3):516–658. https://doi.org/10.36660/abc.20201238 .
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Rodrigues CIS. (coord) – Diretrizes brasileiras de hipertensão VI. Diagnósticoeclassificação.Braz.J.Nephrol2010;32(suppl1). https://doi.org/10.1590/S0101-28002010000500004
Malachias MVB, Souza WKSB, Plavnik FL, Rodrigues CIS, Brandão AA, Neves MFT, et al. 7ª Diretriz Brasileira De. Hipertensão Arterial Arq Bras Cardiol. 2016;107(3 Suppl 3):1–103.
Google Scholar
STATA 16.0 (R). Copyright 1985–2019 StataCorp LLC. Statistics/Data Analysis. Texas USA.
Thomson DR, Rhoda DA, Tatem AJ, Castro MC. Gridded population survey sampling: a systematic scoping review of the field and strategic research agenda. Int J Health Geogr. 2020;19:34. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12942-020-00230-4 .
USAID. Sampling and household listing manual. Demographic and health survey methodology. Calverton, USA: ICF International; 2012.
Grais RF, et al. Don’t spin the pen: two alternatives methods for second-stage sampling in urban cluster surveys. Emerg Themes Epidemiol. 2007;4(8). https://doi.org/10.1186/1742-7622-4-8 .
Silva NNe, Roncalli AG. Sampling plan, weighting process and design effects of the Brazilian oral Health Survey. Rev Saude Publica 2013:47(supl.3):3–11. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0034-8910.2013047004362
Galobardes B, Lynch J, Smith GD. Measuring socioeconomic position in health research. Br Med Bull. 2007;81–2. https://doi.org/10.1093/bmb/ldm001 .
Rothman KJ, Greenlan S, Lash TL. Modern epidemiology. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2008.
Download references
Acknowledgements
Thanks for support from Sorocaba City Hall.
This research received funding from Pontifícia Universidade Católica de São Paulo, with grant numbers 17807 and 15504.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Faculdade de Ciências Médicas e da Saúde, Pontifícia Universidade Católica de São Paulo, Sorocaba, Brazil
Reinaldo José Gianini, Natália Ferreira Caneto, Natália Murate Junqueira, Leticia Gouvea Rodrigues, Beatriz Zurma Parri & Cibele Isaac Saad Rodrigues
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
Reinaldo José Gianini (RJG)planned, supervised, analyzed and interpreted data, and wrote this article. Natália Ferreira Caneto planned, analyzed and interpreted data Natália Murate Junqueira (NMF) planned, analyzed and interpreted data Leticia Gouvea Rodrigues (LGR) planned, analyzed and interpreted data Beatriz Zurma Parri (BZP) planned, analyzed and interpreted data Cibele Isaac Saad Rodrigues (CISR) planned, supervised, analyzed and interpreted data, and wrote this article.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Reinaldo José Gianini .
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval.
This project was submitted and approved by the Research Ethics Committee (Comitê de Ética em Pesquisa) of the Faculdade de Ciências Médicas e da Saúde of the Pontifícia Universidade Católica de São Paulo, registered as CAAE 30538520-1-0000-5373.
Consent to participate
Every human participant has given their consent to participate.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Material 1
Supplementary material 2, rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it.The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder.To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Gianini, R.J., Caneto, N.F., Junqueira, N.M. et al. Precision assessment of a hypertension prevalence survey. BMC Public Health 24 , 2188 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-024-19626-z
Download citation
Received : 16 April 2024
Accepted : 29 July 2024
Published : 12 August 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-024-19626-z
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Hypertension
- Cluster sampling
- Health surveys
- Data accuracy
- Epidemiology
BMC Public Health
ISSN: 1471-2458
- General enquiries: [email protected]
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Open access
- Published: 12 August 2024
Attitudes of European psychiatrists on psychedelics: a cross-sectional survey study
- Marija Franka Žuljević ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-9805-7491 1 , 2 ,
- Darko Hren 3 ,
- Dawid Storman 4 ,
- Mariano Kaliterna 2 , 5 &
- Darko Duplančić 1 , 2
Scientific Reports volume 14 , Article number: 18716 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
Metrics details
- Health policy
- Human behaviour
- Medical ethics
Research and public interest in psychedelic-assisted psychotherapy (PAP) are growing. This study investigated attitudes toward psychedelics among a diverse and multinational sample of psychiatrists currently working in Europe. We conducted an anonymous, web-based survey consisting of demographic information, a test of basic knowledge on psychedelics, and the previously validated 20-item Attitudes on Psychedelics Questionnaire (APQ), which was validated for the first time in English within this sample. We included N = 419 participants from 33 countries in the study. One-third of participants (34%) reported past use of psychedelics. The APQ sub-scale with the highest score was Openness to Psychedelics , while Risk Assessment of Psychedelics was rated lowest. Regression modelling, explaining 31.3% of variance in APQ scores, showed that younger male psychiatrists who identified as spiritual, were better at recognizing and classifying substances as psychedelics and had previously used psychedelics had more positive attitudes on psychedelics. No professional variables besides self-reported previous experience with PAP or psychedelic research predicted APQ scores. European psychiatrists, therefore, show a general openness to psychedelics and PAP, but are concerned by the potential risks associated with them. Our findings overall suggest that psychedelics are a subject where it is difficult to remain impartial. Protocol registration: The study was pre-registered at the Open Science Framework (available online at https://osf.io/upkv3 ).
Introduction
Psychedelics are a group of psychoactive substances that have seen a recent resurgence of research interest regarding their potential in treating mental illness within psychedelic-assisted psychotherapy (PAP), but have also been subject to controversy 1 , 2 . The current wave of research has seen rapidly increasing interest and the loosening of regulatory barriers to psychedelic research imply the disappearance of some of the historic stigma on these substances 3 . At present, we are seeing a mismatch between the level of interest and enthusiasm surrounding psychedelics as tools for treatment and their prohibited legal status in many countries around the world 4 . Since this enthusiasm may lead to bias, it is important that high ethical and practice standards are enforced within psychedelic research, in proportion to their novelty and wide spectrum of possible effects 5 . Australia was the first to down-schedule psilocybin and 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA) in 2023, allowing them to be prescribed under strict legislation. However, a commissioned independent report criticized this decision as premature in light of the low quality of evidence presented in clinical trials involving these substances, in most part due to methodological issues with randomization, blinding, and attrition 6 . In early 2024, the European Union announced that it is allocating €6.5M for research on psilocybin for treating psychological distress in people with progressive incurable illnesses requiring palliative care 7 . This new development signals an upcoming intensification of the discussion around PAP and its future in Europe, as well; mental health professionals such as psychiatrists are likely to be involved in various decision-making processes and discussions around this topic.
There have been efforts to explore what mental health professionals, as potential PAP providers, feel about psychedelics. Generally, psychiatrists and psychologists showed a baseline openness to psychedelics in the context of medical use 8 , 9 , 10 , 11 , 12 , 13 . Some of their main concerns, however, were related to possible side effects of psychedelics, especially in relation to cognition 8 , 9 . They also claimed to have insufficient knowledge on psychedelics and PAP and that they require more education on this topic before its implementation in practice 11 , 14 . Overall, negative attitudes on psychedelics and PAP could potentially impact the likelihood of referring patients to PAP trials, the willingness to implement PAP in practice, or the quality of delivery of PAP 15 . A 2024 systematic review on this topic reported that the majority of surveys on attitudes on psychedelics among mental health professionals were conducted in the United States, Canada, and the United Kingdom; attitudes in other European countries are still unexplored 15 . Surveys in these studies used unvalidated instruments and heterogeneous methodological approaches and survey questions which makes comparison between different findings difficult. In a previous publication, we developed and validated the Attitudes on Psychedelics Questionnaire (APQ) to assess attitudes on psychedelics on a large sample of laypersons 16 . Such a scale allows for the quantification of an overall score that can be used as an objective summary measure in quantitative analyses, possibly also allowing future meta-analyses to be conducted. The APQ also has four different sub-scales which measure different aspects of this attitude, including to an individual’s views on the legal uses and effects of psychedelics, their risk assessment of psychedelics, and their general openness to psychedelics and PAP.
Therefore, our aim in this study was to survey a large, geographically and culturally diverse sample of psychiatrists currently based in Europe and apply the APQ, along with a basic knowledge test on psychedelics, considering the previously self-reported knowledge gap in this population. We aimed to explore both personal and professional characteristics of our target population and how they relate to positive or negative attitudes as measured by the APQ and its sub-scales.
Demographic information and response rate
A total of 680 surveys were recorded. The response rate was 61.6%, leaving 419 for inclusion into the study. The majority of excluded surveys (n = 186, 71.3%) were not completed, participants were not psychiatrists (n = 68, 26.1%), or were not based in Europe (n = 7, 2.7%).
The data came from 33 European countries, mostly from: Poland (n = 55, 13.1%), United Kingdom (n = 35, 8.4%), Italy (n = 33, 7.9%), Croatia (n = 30, 7.2%), Germany (n = 24, 5.7%), the Netherlands (n = 22, 5.3%), Sweden (n = 19, 4.5%), Slovenia (n = 17, 4.1%), Czech Republic and Estonia (n = 17, 4.1% each), as well as Bosnia and Herzegovina, North Macedonia, and Romania (n = 16, 3.7% each) (Supplementary Table S1 in the Supplementary Files).
There were 55.4% male respondents and the median age was 38 years (IQR = 31.0–47.8). They were predominantly psychiatry specialists (65.6%), working primarily in a hospital setting (67.3%), and who used an equally biological and psychotherapeutic treatment approach (57.8%). A smaller subset of participants reported having previous experience with PAP or psychedelic research (19.6%). Almost two-thirds of participants identified themselves as an atheist (32.2%) or agnostic (27.4%). Self-assessed knowledge on psychedelics was moderate (Md = 52.0 on a scale 0–100, IQR = 30.0–70.0), and the median number of scientific publications was Md = 2 (IQR = 0.0–15.0) Past lifetime use of a psychedelic was reported by 34.4% (n = 144) participants, most commonly involving psilocybin (24.3%), followed by MDMA (20%), while 58.9% of participants tried cannabis. A detailed overview of demographic data is provided in Table 1 .
Attitudes on psychedelics scores
The four-factor 20-item model of the APQ in English was applied in this study for the first time, showing satisfactory psychometric characteristics (reported in the Supplementary Files), congruent with its initial validation in Croatian 16 . The median total score on the APQ scale (theoretical range 20–100) was Md = 66.0 (IQR = 56.5–75.0). The Openness to Psychedelics sub-scale had the highest median attitude scores (Md = 20.0, IQR = 17.0–22.0), followed by Legal use of Psychedelics (Md = 18.0, IQR = 15.0–20.0), Effects of Psychedelics (Md = 14.0, IQR = 12.0–18.0), and Risk Assessment of Psychedelics (Md = 14.0, IQR = 12.0–17.0), where all sub-scales had theoretical score ranges of 5–25. When looking at the frequencies of response options for individual APQ items, the Openness to Psychedelics sub-scale showed a visible trend towards higher agreement with its items, while participants tended to show the highest degree of uncertainty in terms of agreement or disagreement with items on the Effects of Psychedelics and Risk Assessment of Psychedelics sub-scales. A full overview of response frequencies for each item on the APQ is shown in Fig. 1 .

Visual representation showing frequencies of response options marking participants’ degree of agreement or disagreement with different items on the APQ. Note: the results of reversely worded questions are shown in their unreversed form to ease readers' comprehension.
Basic knowledge on psychedelics scores
The median score on the knowledge on psychedelics test (theoretical range 0–100) was Md = 86.0 (IQR = 82.0–91.0). The three most commonly correctly identified psychedelics were psilocybin (n = 411, 98.1%), LSD (n = 409, 97.6%), and mescaline (n = 385, 91.9%). Three non-psychedelics most commonly named as psychedelics were ketamine (n = 264, 63.0%), methamphetamine (n = 107, 25.5%), and gamma-hydroxybutyric acid (GHB) (n = 109, 26.0%). Responses for each substance are shown in Supplementary Table S2 in the Supplementary Files.
Additional analyses
All additional analyses are fully described and presented in the Supplementary Files. A regression model, explaining 31.3% of variance in APQ scores, showed that previous lifetime use of a psychedelic, higher basic knowledge on psychedelics test scores, younger age, considering oneself as spiritual, having previous experience with PAP or psychedelic research, and male gender were associated with more positive attitudes on psychedelics. The same predictors were significant when all the sub-scale scores of the APQ were the criterion variable, respectively, with the exception of the following: male gender was only associated with the Legal Use of Psychedelics and Risk Assessment of Psychedelics sub-scales, considering oneself as spiritual was associated with all sub-scales except for Legal Use of Psychedelics , and having previous experience with PAP and with psychedelic research was associated with all sub-scales except Openness to Psychedelics (Supplementary Table S3 in the Supplementary Files).
In comparison to those without previous experience, psychiatrists who reported previous experience with PAP or experience with psychedelic research published more scientific papers, assessed their knowledge on psychedelics as higher, were more often male, had a higher frequency of working in a private hospital institution, identified as spiritual more often, and were more likely to have used cannabis, LSD, psilocybin, ayahuasca, DMT, mescaline or MDMA in the past (Supplementary Table S4 in the Supplementary Files).
When we analysed the possibility of attrition bias, we found that psychiatrists who did not complete the survey but still provided their demographic information were less overall likely to have ever tried cannabis or psychedelics in general (Supplementary Table S5 in the Supplementary Files).
Additionally, we compared participants of male and female gender by all variables which were predictive of APQ scores in the regression model in order to identify possible reasons for gender differences in attitudes on psychedelics (non-significant comparisons not shown). We found that males in our sample had a higher median age (Md = 40.0, IQR = 32.0–52.0 for males vs. Md = 36.0, IQR = 30.0–44.0 for women, p < 0.001), higher median basic knowledge test scores (Md = 91.0, IQR = 82.0–95.0 for males vs. Md = 86.0, IQR = 77.0–91.0 for women, p < 0.001), and assessed their knowledge on psychedelics higher than women (Md = 60.0, IQR = 31.8–72.0 for males vs. Md = 50.0, IQR = 25.0–65.0 for women). Males also reported having experience with PAP and psychedelic research more often (n = 57, 24.6% for males vs. n = 25, 13.7% in women, p = 0.006). Participants who did not want to disclose their gender (n = 2, 15%) and those who marked their gender as “Other” (n = 3, 0.7%) were not included in this analysis because they were too few in number.
Deviations from the protocol
One of the authors (IB) withdrew from the study due to time constraints. One question in the survey was reformulated. All changes from the pre-registered protocol are fully described in the Supplementary Files.
European psychiatrists in our survey showed moderate overall attitudes on psychedelics and were successful in identifying psychedelics among a group of psychoactive substances, especially LSD, psilocybin, and mescaline. Younger male psychiatrists who identified as spiritual, showed better capability at recognizing and classifying substances as psychedelics, and had previously used psychedelics had more positive attitudes, in particular. No professional variables besides self-reported previous experience with PAP or psychedelic research were associated with attitudes on psychedelics. We also observed a significant positive association between both self-assessed knowledge on psychedelics and objectively tested basic knowledge on psychedelics with APQ scores, respectively.
These findings should be interpreted in light of a possible response and sampling bias. A high proportion of our participants tried cannabis and psychedelics; past use of these substances was also associated with more positive attitudes, it may be that participants with more positive attitudes were more likely to complete the survey. Although the attrition analysis was performed only with a smaller subset of participants who dropped out, those who dropped out but filled out the demographic information part of the survey had less experience with cannabis and psychedelics. Therefore, although we cannot account for all of the individuals who dropped out, it is likely that we may have lost participants who would have skewed findings towards more negative APQ scores. Our actual response rate is most likely very low (< 3%), considering a large number of organizations initially contacted with an invite to disseminate the survey and the small number who agreed to do so, and we cannot account for individuals who chose not to answer the survey. For this reason, we do not claim full representation of all European psychiatrists. Other web-based surveys of PAP, however, had similar response rates 10 , 15 and our large sample size constitutes one of the study strengths. A final limitation is the question on the self-reported previous experience with PAP and psychedelic research. We initially intended to ask “Are you a psychedelic researcher?” but opted instead for a wider category that also allows people who may not have conducted clinical research but have intensely followed the scientific publications on this topic. We cannot delineate between these two, which partially limits the interpretation. However, both activities imply expertise in the subject and a deeper understanding of the issues related to the topic. Additionally, the classification of psychedelics in the knowledge test given to participants is somewhat limited in light of the lack of consensus on whether substances like MDMA and ketamine are considered to belong to the psychedelics group. Future uses of this test may either exclude these substances or choose to evaluate them differently.
Median APQ scores among psychiatrists were comparable to scores in the general population assessed in a previous study, both situated toward the middle of the APQ scale 16 . The sub-scale with the highest score was Openness to Psychedelics , and the lowest score was found for Risk Assessment of Psychedelics , quantifying the previous findings of mental health experts showing baseline openness to psychedelics and PAP, but also a significant degree of uncertainty and caution in regards to possible risks and side effects of psychedelic use 9 , 10 , 15 . Our previous survey of the general population found no difference between knowledge among healthcare workers of all specialties and laypersons 16 . However, the present sample of psychiatrists showed higher basic knowledge on psychedelics compared to these two groups. Methamphetamine and GHB were most often mistaken as psychedelics, which was a less concerning result than our survey of the Croatian general population, where participants, apart from methamphetamine, often considered substances such as heroin, methamphetamine, and opium to be psychedelics 16 . Overall, the findings related to knowledge align with what is expected based on psychiatrists' basic expertise in psychopharmacology 11 . Ketamine was the most polarized substance in terms of classification, where half of the participants classified it as a psychedelic. This finding points to a need of reaching a clear consensus about psychedelics' classification that will be widely used and accepted.
Our study is the first to demonstrate that past psychedelic use and personal experience with PAP and psychedelic research were both strongly associated with more positive attitudes on psychedelics, regardless of one's background and training in psychiatry. This is congruent with the well-established postulate that previous behaviour is the strongest predictive factor for attitudes 17 . However, this reinforces the previously described risks of bias and enthusiasm of treatment providers who have previously personally used psychedelics 5 . It also carries implications for previously recommended educational interventions on psychedelics 10 , 15 , 16 , where it may be difficult to determine what is balanced and bias-free information. The association between higher knowledge and more positive attitudes on psychedelics raises into question whether individuals creating and providing such interventions can remain neutral. Similarly, considering the stigma and historical controversies associated with psychedelics, significant bias could also be present among individuals who are poorly informed on psychedelics and PAP. Overall, negative bias towards psychedelics and PAP within the psychiatric profession could potentially reduce PAP uptake in practice, make practitioners less likely to recommend it to patients, and provide a point of resistance that may not be supported by real-world evidence. The association of male gender and younger age with more positive attitudes on psychedelics is also consistent with previous surveys 9 , 13 , 16 . However, our study saw that male gender was only associated with higher scores on the Risk Assessment of Psychedelics and Legal Use of Psychedelics sub-scales of the APQ, indicating that men may be less risk-averse towards psychedelics than females, which is consistent with previous findings in psychology 18 and also supported by the higher proportion of men in our sample who previously used psychedelics. Men also reported experience with PAP and psychedelic research more frequently, implying that they may engage more with resources and information related to psychedelics. Lower APQ among older participants could potentially be explained due to the effect of “war-on-drugs” propaganda from the 60s onwards, which had a negative focus on the side effects and dangers of psychedelics 19 , 20 . Additionally, the association of both spirituality and past use of psychedelics to more positive attitudes can be interpreted through what is known about psychedelic use changing one's beliefs to be more geared towards panpsychism, belief in reincarnation and the afterlife, and attributing consciousness to living and non-living entities 21 , 22 , 23 .
Overall, this is the first validation of the APQ in English and in the psychiatrist population. Its metric characteristics are consistent with our initial validation study, which is encouraging for further application in this group 16 . These findings can serve as a reference point for all further surveys of psychiatrists with the APQ, which can explore culture- or nation-specific differences. The APQ can also be used in clinical trials of PAP to explore whether patients with higher APQ scores have better treatment outcomes. This could possibly quantify the expectancy bias known to be present among patients in such trials 24 . Considering the relatively high prevalence of previous psychedelic use we found among psychiatrists, future studies can explore the context in which it took place and whether some of it had the purpose of self-experimentation or self-treatment 25 , 26 . It would be useful to develop and validate a standardized knowledge test for psychedelics that goes beyond the recognition and classification of substances, since we found that median self-assessed knowledge on psychedelics was lower than the median score on a basic recognition-based test (56.0 vs. 86.0, both on a scale 0–100). When designing future educational interventions on psychedelics, it may be worthwhile to consider artificial intelligence-assisted education to avoid impartiality and bias. We also suggest a further exploration of gender differences in the perception of psychedelics, specifically in terms of how they engage with information on psychedelics or psychedelic research.
Study design and setting
This cross-sectional study used a web-based survey on the SurveyMonkey data collection platform (SurveyMonkey Inc., San Mateo, CA, USA). The study protocol was pre-registered on the Open Science Framework on April 5, 2022 ( https://osf.io/upkv3 ).
Participants and data collection
Inclusion criteria for participation included being a psychiatry resident/specialist or psychiatry trainee and currently working in Europe. There were no specific exclusion criteria. A complete list of eligible countries is provided in the supplementary material. Participants were recruited by contacting psychiatrist organizations (all member organizations within the European Federation of Psychiatry Trainees and the European Psychiatric Associations), psychotherapeutic organizations, hospitals, and individual e-mails. Detailed information on sampling is available in the Supplementary Files. The data collection lasted from April 13, 2022 to March 5, 2023.
The survey was anonymous, in English, and consisted of three parts: demographic information, a basic knowledge on psychedelics test, and the 20-item APQ. Items of the knowledge test and the APQ were presented to the participants in a randomized order. The full survey is available in the Supplementary Files. The validation of the 20-item APQ and its properties were described in detail in a previous publication 16 . This paper also described a rationale for including and developing the test of basic knowledge on psychedelics, along with all information related to scoring 16 .
Sample size
According to the information available at Eurostat, we estimated the number of psychiatrists in Europe to be 100000 27 . With a population of that size, a 5% margin of error, and a confidence level of 95%, we determined that we needed at least 383 participants to complete the survey. We aimed to collect at least 100 responses above the targeted sample size to safeguard against incomplete or invalid surveys. The sample size calculation was performed using the SurveyMonkey Sample Size Calculator 28 .
Ethical aspects
The Ethics Committee of the University of Split School of Medicine in Croatia reviewed and approved the study protocol (document No. 2181-198-03-04-22-0019), as did the Jagiellonian University in Kraków, Poland (document No. 1072.6120.261.2022). The basic information about the study was provided at the entry screen, and the participants gave their informed consent by checking a box before moving to the survey. All responses were anonymous, and the survey in SurveyMonkey was set not to collect the IP addresses of participants. All methods were carried out in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki.
Statistical analysis
The normality of data distribution for continuous variables was assessed using the Shapiro-Wilk test and the observation of Q-Q plots. Categorical variables were expressed as frequencies and percentages. Continuous variables were expressed using mean or median ± 95% confidence interval and standard deviation or interquartile range, depending on the data distribution. The response rate for the survey was defined as the number of participants who completed the survey divided by the total number of participants who accessed the survey. A web-based survey setting and our snowballing sampling technique did not allow insight into who received the link to the survey. We excluded all incomplete participant survey responses but not outliers, as these values may represent extremes in knowledge or attitudes within the sample population.
Since this was the first use of the APQ in this population and its first use in English, we validated the four-factor 20-item structure of the questionnaire in this sample using confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) and assessing the instrument's reliability. The CFA was performed using the diagonally weighted least squares (DWLS) estimation method with a polychoric correlation matrix. We used model fit index cut-offs to assess adequate model fit as defined by Hu and Bentler 29 . Root Mean Square Error of Approximation (RMSEA) was expressed using a 95% confidence interval (CI). We used McDonald's ω and a 95% CI to assess the reliability of the APQ (overall and for each sub-scale), where scores >0.70 were considered satisfactory.
We also estimated the correlation between APQ scores and scores on the basic knowledge test using Spearman's rho (ρ). We performed a stepwise linear regression analysis to assess the multiple associations between all collected demographic variables as predictors and the total APQ score and the score on each of its sub-scales as criterion variables, respectively. Results were expressed as standardized regression coefficients (β), P values, and adjusted coefficients of determination (R 2 ). Demographic data were compared between psychiatrists with no experience with psychedelic research or therapy and psychiatrists who self-reported previous experience with psychedelic research or therapy using the Mann–Whitney (continuous variables) and chi-square tests (categorical variables). To address attrition bias, we compared the demographic data of participants who completed the survey vs. those with incomplete surveys who provided their demographic information before dropping out.
Data availability
The dataset from this study and its corresponding data dictionary are freely available at the Open Science Framework, https://doi.org/ https://doi.org/10.17605/OSF.IO/S52RV .
Carhart-Harris, R. L. & Goodwin, G. M. The Therapeutic potential of psychedelic drugs: Past, present, and future. Neuropsychopharmacology 42 , 2105–2113. https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2017.84 (2017).
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Sessa, B. Turn on and tune in to evidence-based psychedelic research. Lancet Psychiatry 2 , 10–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2215-0366(14)00120-5 (2015).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Schlag, A. K., Aday, J., Salam, I., Neill, J. C. & Nutt, D. J. Adverse effects of psychedelics: From anecdotes and misinformation to systematic science. J. Psychopharmacol. 36 , 258–272. https://doi.org/10.1177/02698811211069100 (2022).
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Pilecki, B., Luoma, J. B., Bathje, G. J., Rhea, J. & Narloch, V. F. Ethical and legal issues in psychedelic harm reduction and integration therapy. Harm Reduct. J. 18 , 40. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12954-021-00489-1 (2021).
Anderson, B. T., Danforth, A. L. & Grob, C. S. Psychedelic medicine: Safety and ethical concerns. Lancet Psychiatry 7 , 829–830. https://doi.org/10.1016/s2215-0366(20)30146-2 (2020).
Kisely, S. The down-scheduling of MDMA and psilocybin(e): Too fast and too soon. Aust. N. Z. J. Psychiatry 57 , 933–934. https://doi.org/10.1177/00048674231174171 (2023).
European Psychiatric Association. European union funds groundbreaking research into psychedelic therapy. https://www.europsy.net/european-union-funds-groundbreaking-research-into-psychedelic-therapy/ (2024).
Barnett, B. S., Siu, W. O. & Pope, H. G. Jr. A survey of american psychiatrists’ attitudes toward classic hallucinogens. J. Nerv. Ment. Dis. 206 , 476–480. https://doi.org/10.1097/NMD.0000000000000828 (2018).
Davis, A. K., Agin-Liebes, G., Espana, M., Pilecki, B. & Luoma, J. Attitudes and beliefs about the therapeutic use of psychedelic drugs among psychologists in the United States. J. Psychoact. Drugs 54 , 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1080/02791072.2021.1971343 (2021).
Article Google Scholar
Ginati, Y. D. et al. A nationwide study comparing mental health professionals’ willingness to try hallucinogenic drugs in basic research or clinical practice. J. Psychoact. Drugs 54 , 177–187. https://doi.org/10.1080/02791072.2021.1941444 (2022).
Barnett, B. S., Beaussant, Y., King, F. T. & Doblin, R. Psychedelic knowledge and opinions in psychiatrists at two professional conferences: An exploratory survey. J. Psychoact. Drugs 54 , 269–277. https://doi.org/10.1080/02791072.2021.1957183 (2022).
Hearn, B. G., Brubaker, M. D. & Richardson, G. Counselors’ attitudes toward psychedelics and their use in therapy. J. Couns. Dev. 100 , 364–373. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcad.12429 (2022).
Schmidt, C., Wolff, M., Grunder, G. & Jungaberle, H. Attitudes of mental health experts towards psilocybin. Fortschr. Neurol. Psychiatr. 91 , 80–87. https://doi.org/10.1055/a-1846-1161 (2023).
Page, L. A., Rehman, A., Syed, H., Forcer, K. & Campbell, G. The readiness of psychiatrists to implement psychedelic-assisted psychotherapy. Front. Psychiatry 12 , 743599. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2021.743599 (2021).
Wells, A., Fernandes, M. & Reynolds, L. Perceptions and attitudes towards psychedelic-assisted psychotherapy among health professionals, patients, and the public: A systematic review. J. Psychedelic Stud. 8 (1), 43–62. https://doi.org/10.1556/2054.2023.00294 (2024).
Žuljević, M. F. et al. Validation of a new instrument for assessing attitudes on psychedelics in the general population. Sci. Rep. 12 , 18225. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-23056-5 (2022).
Article ADS CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Fazio, R. H. & Zanna, M. P. Direct experience and attitude-behavior consistency. Adv. Exp. Soc. Psychol. 14 , 161–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0065-2601(08)60372-X (1981).
Byrnes, J. P., Miller, D. C. & Schafer, W. D. Gender differences in risk taking: A meta-analysis. Psychol. Bull. 125 , 367–383. https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-2909.125.3.367 (1999).
Hartogsohn, I. American Trip: Set, Setting, and the Psychedelic Experience in the Twentieth Century (The MIT Press, Cambridge, 2020).
Book Google Scholar
Stevens, J. Storming Heaven: LSD and the American Dream (Grove Press, New York, 1998).
Google Scholar
Timmermann, C. et al. Psychedelics alter metaphysical beliefs. Sci. Rep. 11 , 22166. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-01209-2 (2021).
Nayak, S. M., Singh, M., Yaden, D. B. & Griffiths, R. R. Belief changes associated with psychedelic use. J. Psychopharmacol. 37 , 80–92. https://doi.org/10.1177/02698811221131989 (2023).
Nayak, S. M. & Griffiths, R. R. A single belief-changing psychedelic experience is associated with increased attribution of consciousness to living and non-living entities. Front. Psychol. 13 , 852248. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2022.852248 (2022).
Romeo, B., Hermand, M., Petillion, A., Karila, L. & Benyamina, A. Clinical and biological predictors of psychedelic response in the treatment of psychiatric and addictive disorders: A systematic review. J. Psychiatr. Res. 137 , 273–282. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpsychires.2021.03.002 (2021).
Kopra, E. I. et al. Investigation of self-treatment with lysergic acid diethylamide and psilocybin mushrooms: Findings from the global drug survey 2020. J. Psychopharmacol. 37 , 2698811231158245. https://doi.org/10.1177/02698811231158245 (2023).
Passie, T. & Brandt, S. D. Self-experiments with psychoactive substances: A historical perspective. In New Psychoactive Substances: Pharmacology Clinical, Forensic and Analytical Toxicology (eds Maurer, H. H. & Brandt, S. D.) 69–103 (Springer, Cham, 2018).
Chapter Google Scholar
Eurostat. Mental health: How many psychiatrists in the EU? https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/web/products-eurostat-news/-/edn-20171010-1 (2023).
SurveyMonkey. Sample size calculator. https://www.surveymonkey.com/mp/sample-size-calculator/ (2023).
Hu, L. T. & Bentler, P. M. Cutoff criteria for fit indexes in covariance structure analysis: Conventional criteria versus new alternatives. Struct. Equ. Model. A Multidiscip. J. 6 , 1–55. https://doi.org/10.1080/10705519909540118 (1999).
Download references
Acknowledgements
We are deeply grateful to Prof. Malgorzata Bala for her help with finding additional contacts for survey dissemination and for assisting with obtaining the ethical approval in Poland. Likewise, we thank Ass. Prof. Ivan Buljan for his help with developing the protocol of the study. We are grateful to Paweł Jemioło for his help with scraping individual e-mails of psychiatrists from online documents. We also thank Antonija Mijatović, MPhys, PhD for her help with using her expertise in programming to format and finalize the e-mail list which we used to contact some of our survey participants.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Centre for Evidence-Based Medicine, University of Split School of Medicine, Šoltanska 2a, 21000, Split, Croatia
Marija Franka Žuljević & Darko Duplančić
Department of Medical Humanities, University of Split School of Medicine, Šoltanska 2a, 21000, Split, Croatia
Marija Franka Žuljević, Mariano Kaliterna & Darko Duplančić
Department of Psychology, Faculty of Humanities and Social Sciences, Poljička cesta 35, 21000, Split, Croatia
Chair of Epidemiology and Preventive Medicine, Department of Hygiene and Dietetics, Jagiellonian University Medical College, Świętej Anny 12, 31-008, Kraków, Poland
Dawid Storman
Department of Psychiatry, Clinical Hospital Centre Split, Spinčićeva ulica 1, 21000, Split, Croatia
Mariano Kaliterna
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
MFŽ, DH and DD conceptualized the idea for the study and the methodological design. MFŽ, DH, DS, MK, and DD participated in the data collection. MFŽ analysed the data and then interpreted the findings together with DH. DH created the figures. MFŽ drafted the first version of the manuscript and all authors critically reviewed and revised the work. All authors agree to be accountable for all aspects of the study and its manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Marija Franka Žuljević .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Supplementary information., rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Žuljević, M.F., Hren, D., Storman, D. et al. Attitudes of European psychiatrists on psychedelics: a cross-sectional survey study. Sci Rep 14 , 18716 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-69688-7
Download citation
Received : 03 October 2023
Accepted : 06 August 2024
Published : 12 August 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-69688-7
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines . If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Questionnaires vs. surveys. A survey is a research method where you collect and analyze data from a group of people. A questionnaire is a specific tool or instrument for collecting the data.. Designing a questionnaire means creating valid and reliable questions that address your research objectives, placing them in a useful order, and selecting an appropriate method for administration.
A questionnaire is a research tool used to conduct surveys. It includes specific questions with the goal to understand a topic from the respondents' point of view. Questionnaires typically have closed-ended, open-ended, short-form, and long-form questions. ... Benchmarkable survey questions example: "Compare your company's marketing budget to ...
A questionnaire is defined a market research instrument that consists of questions or prompts to elicit and collect responses from a sample of respondents. This article enlists 21 questionnaire templates along with samples and examples. It also describes the different types of questionnaires and the question types that are used in these questionnaires.
When used in most research, a questionnaire will consist of a number of types of questions (primarily open-ended and closed) in order to gain both quantitative data that can be analyzed to draw conclusions, and qualitative data to provide longer, more specific explanations. A research questionnaire is often mistaken for a survey - and many ...
Writing Survey Questions. Perhaps the most important part of the survey process is the creation of questions that accurately measure the opinions, experiences and behaviors of the public. Accurate random sampling will be wasted if the information gathered is built on a shaky foundation of ambiguous or biased questions.
The questions you choose and the way you use them in your survey will affect its results. These are the types of survey questions we will cover: Open-Ended Questions. Closed-Ended Questions. Multiple Choice Questions. Dichotomous Questions. Rating Scale Questions. Likert Scale Questions. Nominal Questions.
29 min. Share. This comprehensive intro to survey questions contains over 70 examples of effective questions, an overview of different types of survey questions, and advice on how to word them for maximum effect. Plus, we'll toss in our pre-built survey templates, expert survey insights, and tips to make the most of AI for Surveys in Hotjar. .
Survey research means collecting information about a group of people by asking them questions and analysing the results. To conduct an effective survey, follow these six steps: Determine who will participate in the survey. Decide the type of survey (mail, online, or in-person) Design the survey questions and layout. Distribute the survey.
Getting Started + Tips. How to make a questionnaire: Keep questions short and focused on one topic at a time. Use multiple-choice questions to fit answers into a specific category. Use an open-ended question to capture comments. A Likert scale or MaxDiff question can be used for market research. Collect responses for your questionnaire using an ...
Survey research means collecting information about a group of people by asking them questions and analyzing the results. To conduct an effective survey, follow these six steps: Determine who will participate in the survey. Decide the type of survey (mail, online, or in-person) Design the survey questions and layout.
This includes designing questions or using a premade template. Below are some of the best research survey examples, templates, and tips for designing these surveys. 20 research survey examples and templates. Specific survey questions for research depend on your goals. A research questionnaire can be conducted about any topic or interest.
Our list of sample survey questionnaires: 360 Degree Feedback. Make-up Products Feedback. Airline Passenger Feedback. Management Performance. Before They Were Famous Survey. Market Research - Product Feedback. Brand Awareness Survey.
1. Early questions should be easy and pleasant to answer, and should build rapport between the respondent and the researcher. 2. Questions at the very beginning of a questionnaire should explicitly address the topic of the survey, as it was described to the respondent prior to the interview. 3. Questions on the same topic should be grouped ...
Survey Research Definition. Survey Research is defined as the process of conducting research using surveys that researchers send to survey respondents. The data collected from surveys is then statistically analyzed to draw meaningful research conclusions. In the 21st century, every organization's eager to understand what their customers think ...
Choose a template below to preview sample questions. Most templates are available in English only: Customer satisfaction. Employee satisfaction template. Customer service template. Market research template. Public school survey. 360 degree employee evaluation. K-12 parent survey (in collaboration with Harvard)
A Questionnaire is a research tool or survey instrument that consists of a set of questions or prompts designed to gather information from individuals or groups of people. ... For example, a questionnaire can be used to gather information on people's opinions about a particular political issue. To collect demographic information ...
The questions included in the survey questionnaire can be both qualitative and quantitative in nature, depending on the researcher's objectives. For instance, a consumer questionnaire may help researchers gain market feedback on the company's products and services for further development.
Survey Research. Definition: Survey Research is a quantitative research method that involves collecting standardized data from a sample of individuals or groups through the use of structured questionnaires or interviews. The data collected is then analyzed statistically to identify patterns and relationships between variables, and to draw conclusions about the population being studied.
Abstract. Survey methodologies, usually using questionnaires, are among the most popular in. the social sciences, but they are also among the most mis-used. The ir popularity in. small-scale ...
30+ Questionnaire Templates (Word) If you're looking to gain insights on your audience or customers, a questionnaire or social survey is a reliable method used to collect standardized data from large numbers of people. (All of the information is collected in the exact same way. Questionnaires are often used by the government to find out more ...
The research questionnaire is one of the quantitative data-gathering methods a researcher can use in their research paper. 1. Market Research Questionnaire Template Example. Details. File Format. Size: 38 KB. Download. 2. Market Research Questionnaire Example.
Examples of customer survey questions ... Before taking action, they conducted in-depth visitor behavior research. Using on-page surveys, they gathered feedback on product filters from visitors on their product category page. Implementing changes based on this feedback, they streamlined the search process. ...
Here are some examples of transactional customer satisfaction research: Post-purchase surveys. Service desk satisfaction surveys. Website/app feedback surveys. Point-of-sale customer satisfaction ratings. Event feedback forms. Relational (ongoing relationship)
Population surveys are crucial for public policy planning and provide valuable representative data. In the health sector studies to identify and assess the prevalence of Arterial Hypertension (AH), a chronic non-communicable disease (NCD), along with its associated risk factors have been conducted. This study aims to assess the effectiveness of a population health survey in estimating the ...
Research and public interest in psychedelic-assisted psychotherapy (PAP) are growing. This study investigated attitudes toward psychedelics among a diverse and multinational sample of ...